- 1Taishan Vocational College of Nursing, Taian, Shandong, China
- 2Center for Toxicology and Health Risk, Faculty of Health Sciences, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- 3Center for Healthy Ageing and Wellness, Faculty of Health Sciences, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- 4Centre for Community Health Studies, Faculty of Health Sciences, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- 5College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, China
Background: Sleep disturbances are a widespread public health concern among nursing and healthcare students globally, with consequences for academic performance, mental health, and long-term professional competence. Despite evidence linking multiple lifestyle factors, such as physical activity, diet, stress management, and relaxation techniques, to sleep quality, comprehensive interventions integrating these elements remain limited in nursing education. We plan to conduct a pre-registered 4-week pre–post effectiveness pilot and will report effect sizes (Cohen’s d, 95% CI).
Methods: This study applied the Sidek Module Development Model (SMDM) to design and validate a multi-component lifestyle intervention module aimed at improving sleep quality among vocational nursing students in China. The module integrated five evidence-based components: physical activity, psychoeducation, music therapy, meditation, and nutrition. Content validity and educational quality were assessed by six independent experts using the Content Validity Index (CVI) and the Template for Evaluating Patient Education Documents (TEMPtED). Reliability and acceptability were further evaluated among 47 nursing students through a Likert-scale questionnaire, with Cronbach’s alpha computed for internal consistency.
Results: The module demonstrated strong psychometric properties. The overall scale-level content validity index (S-CVI/Ave) was 0.985, exceeding the recommended threshold and confirming excellent content validity. All five sub-modules were rated as “Excellent” in educational quality based on the TEMPtED evaluation. Student feedback yielded a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.980, reflecting high internal consistency and suggesting that the module’s structure and materials were coherent and well-received. These results indicate strong preliminary evidence supporting the module’s validity and reliability during the development and validation phase.
Conclusion: This study developed and validated a scientifically robust, educationally feasible, and culturally responsive lifestyle module designed to promote sleep health among nursing students. While the findings demonstrate strong content validity, educational quality, and internal consistency, they represent an initial validation stage rather than evidence of intervention effectiveness. The validated framework provides a solid foundation for future implementation, cross-cultural adaptation, and evaluation studies aimed at examining its impact and long-term sustainability across diverse educational contexts.
1 Introduction
For Sleep quality has become a critical public health concern, particularly among university and vocational students in health-related fields. Nursing students are especially vulnerable due to their heavy academic workload, irregular class and clinical schedules, and the psychological demands of caring for patients in training environments. Numerous studies have demonstrated that insufficient or poor-quality sleep negatively affects cognitive performance, attention span, memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and overall mental health (1–3). In the context of nursing education, these impairments may directly compromise professional learning outcomes, reduce clinical competence, and ultimately impact the quality of patient care (4, 5).
Emerging evidence further indicates that lifestyle-related factors play a substantial role in the prevalence of sleep disturbances among young adults. Behaviors such as insufficient or irregular physical activity, poor dietary habits, maladaptive stress management, prolonged screen time, and lack of effective relaxation techniques are strongly correlated with sleep disorders (6–8). Consequently, interventions focusing on a single factor, such as exercise or diet alone, often yield limited improvements. In contrast, multi-component lifestyle interventions that integrate diverse elements such as physical exercise, mindfulness or meditation, music therapy, nutrition education, and psychoeducation have been shown to produce more robust and sustainable effects on sleep quality (9–14).
Despite the growing body of international research, structured intervention programs tailored to the needs of Chinese vocational nursing students remain scarce. Existing sleep health initiatives are often fragmented, overly generalized, or lack systematic guidance and measurable outcomes (15, 16). In contrast, module-based interventions provide unique advantages. The delivery of structured learning materials, step-by-step activities, explicit objectives, and evaluation criteria provides a systematic and replicable framework that can be readily adopted by educators and students alike. Furthermore, the modular design allows for flexibility in adaptation to different educational settings, enhancing scalability and sustainability (17–19).
The Sidek Module Development Model (SMDM) has been widely acknowledged as a rigorous framework for the systematic design, development, and validation of educational modules. Its two-phase structure, which comprises module drafting through expert consultation followed by testing and validation with the target audience, ensures that the final product is theoretically grounded, content-valid, and reliable in real-world applications (20). SMDM has been successfully applied across a range of educational and health-related contexts, further supporting its utility for developing interventions addressing sleep health among nursing students.
Therefore, the present study sought to develop and validate a multi-component lifestyle intervention module intended to enhance sleep quality among vocational nursing students. The specific objectives were: (1) to design and refine the intervention module through an iterative process of expert consultation, (2) to evaluate its content validity and educational quality using expert assessments with the Content Validity Index (CVI) and the Template for Evaluating Patient Education Documents (TEMPtED) instrument, and (3) to assess its internal consistency and acceptability through a structured Likert-scale questionnaire administered to nursing students.
While the study is grounded in the context of Chinese vocational nursing education, its implications extend far beyond national boundaries. Sleep disturbances among nursing and healthcare students are a global challenge, affecting academic performance, clinical competence, and long-term professional well-being. By integrating physical activity, psychoeducation, music therapy, meditation, and nutrition into a structured and culturally sensitive framework, this study provides not only a locally relevant solution but also a potentially adaptable model for nursing and health education programs worldwide. In doing so, it contributes to the broader international effort to improve student health, enhance the quality of professional training, and strengthen the resilience of the future healthcare workforce.
2 Methodology
2.1 Research design
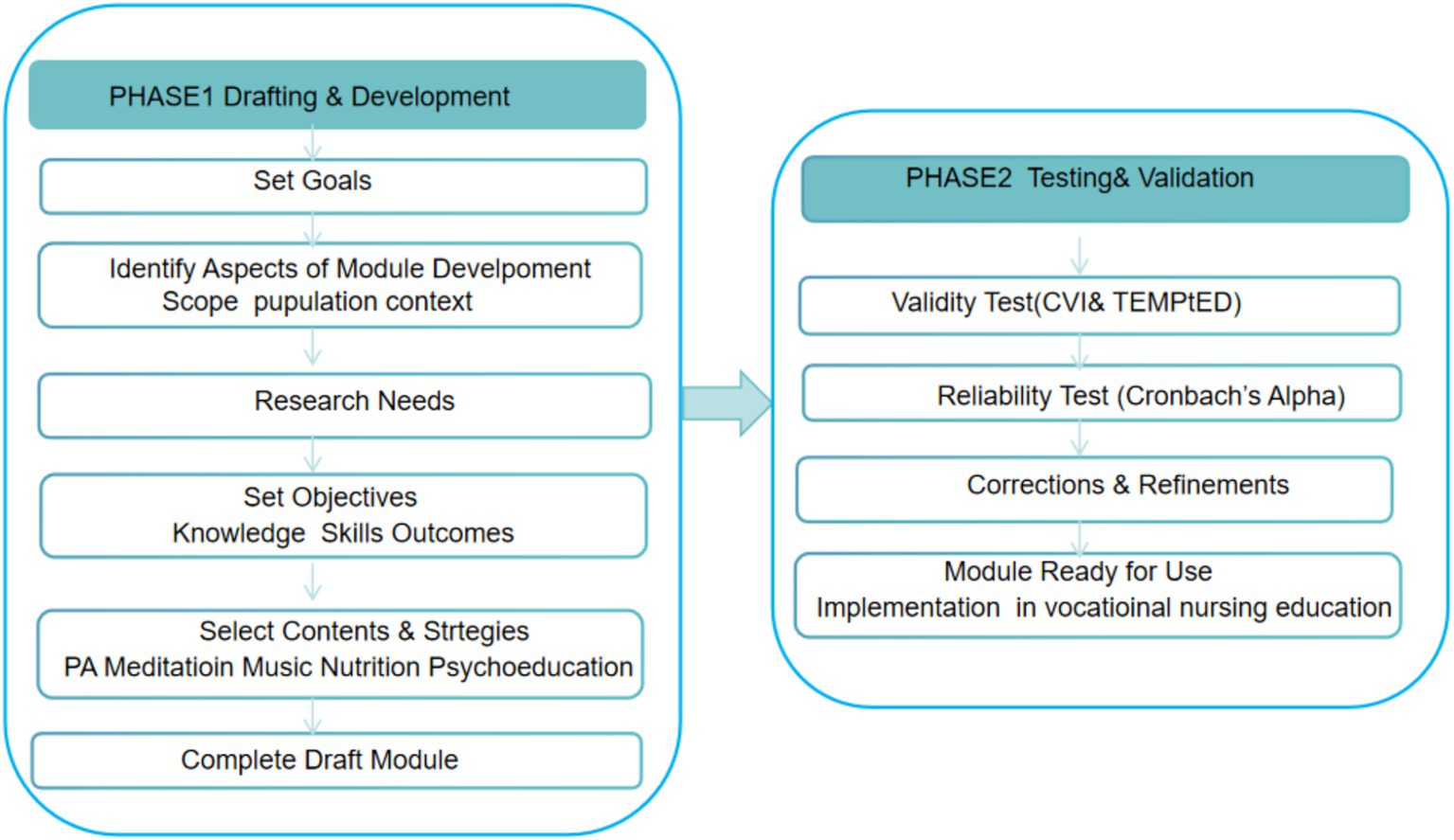
This study was conducted based on the Sidek Module Development Model (SMDM), which emphasizes a systematic two-phase approach: module development followed by validation. The first phase involved drafting the module by generating preliminary content through a comprehensive literature review and initial expert input, after which the draft underwent multiple rounds of consultation and refinement until consensus was reached. The second phase focused on testing and validation, which comprised two components: expert assessments of content validity and educational quality, and student-based evaluations of reliability and acceptability. This structured design ensured that the developed module was both theoretically grounded and practically feasible for implementation in vocational nursing education. Figure 1 illustrates the overall research process following the SMDM framework.
2.2 Participants
The participants in this study comprised both experts and nursing students. For the development phase, six experts were purposively selected to represent a multidisciplinary perspective encompassing sleep medicine, psychology, physical activity, nutrition, music therapy, and meditation. The use of 5–10 experts is recommended in module development and validation studies to balance diversity and manageability (21). A total of six was deemed sufficient to ensure comprehensive evaluation across relevant domains. In the event of disagreement (e.g., a 50:50 split in expert ratings), the item was retained and discussed until a consensus (at least 80% agreement) was achieved through iterative consultation, consistent with the content validation procedures outlined by Grant and Davis Grant and Davis (22).
For the validation phase, another six experts, distinct from those involved in development, were engaged to evaluate the module’s content validity and educational quality. The use of separate panels for development and validation has been recommended to minimize confirmation bias and to enhance the credibility of content validation results (22). The six validation experts included one specialist each in (1) sleep medicine, (2) psychology, (3) nursing education, (4) physical activity, (5) music therapy, and (6) nutrition. All held doctoral or senior professional qualifications and had more than ten years of experience in their respective fields.
To test internal consistency reliability (Cronbach’s α) of the module acceptance scale, a sample size was calculated using the single population proportion formula with a margin of error (δ) of 0.15, appropriate for reliability pilot studies (27):
Accounting for 10% attrition, the final recommended sample was 47 students. This number satisfies minimum thresholds for preliminary scale validation and reliability analysis using Cronbach’s alpha (28).
Three instruments were utilized to evaluate the developed module.
First, the Content Validity Questionnaire was distributed to the six validation experts. Each module item was rated on a five-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (not relevant) to 5 (highly relevant). From these ratings, both the Item-level Content Validity Index (I-CVI) and the Scale-level CVI (S-CVI/Ave) were calculated. Items with I-CVI values above 0.80 were considered acceptable, and an S-CVI/Ave value of 0.90 or above was interpreted as strong evidence of overall content validity.
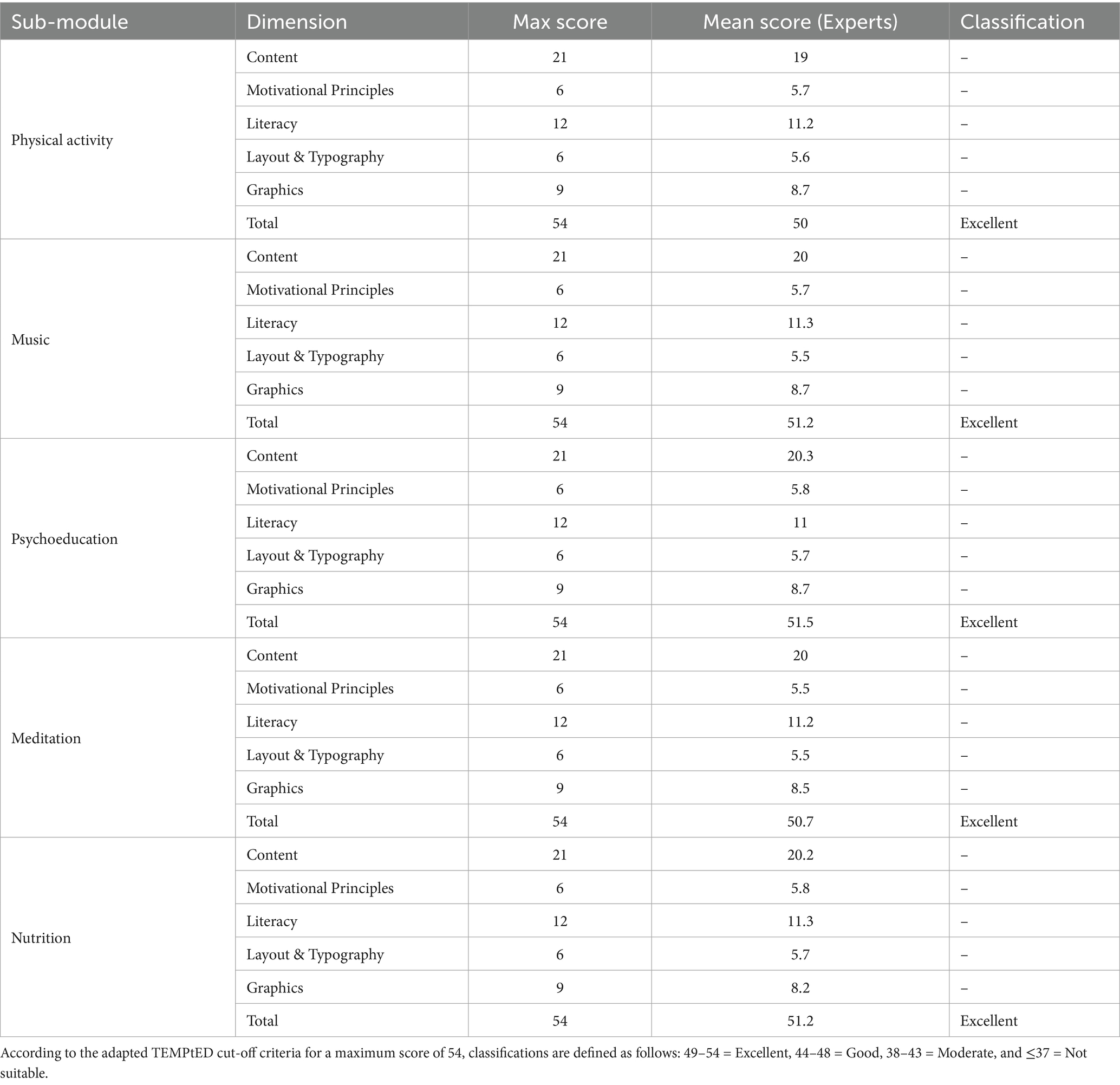
Second, the TEMPtED instrument (Template for Evaluating Patient Education Documents) was used to assess the educational quality of the module. This tool comprises five dimensions, namely Content, Motivational Principles, Literacy, Layout and Typography, and Graphics. Each item within these dimensions was scored on a four-point scale from 0 (not met) to 3 (fully met). Dimension scores were summed to produce an overall total score, which was then classified according to established thresholds: 49–54 (Excellent), 44–48 (Good), 38–43 (Moderate), and ≤37 (Not suitable).
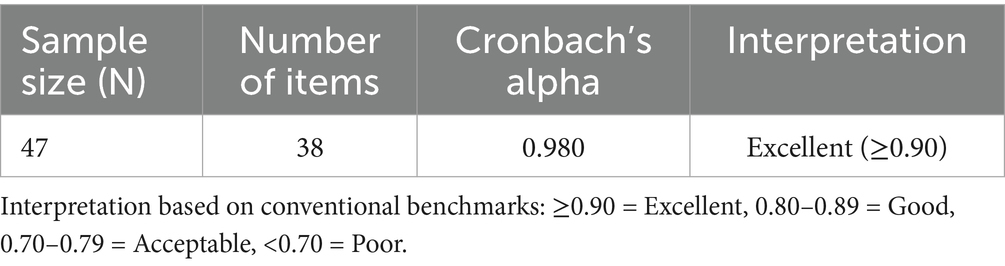
Third, a Student Acceptability Questionnaire was administered to the 47 nursing students. The questionnaire used a five-point Likert scale to evaluate the clarity, relevance, and feasibility of the module. Responses were used to compute Cronbach’s alpha, a measure of internal consistency reliability.
2.3 Procedure
The module development process followed a structured sequence. Based on findings from Phase I and relevant literature, five sub-modules were drafted:
1. Physical activity, addressing exercise type, frequency, and duration.
2. Psychoeducation, focusing on stress and anxiety management and responsible smartphone use.
3. Music therapy, guiding students in selecting and applying therapeutic music.
4. Meditation, providing step-by-step techniques for mindfulness practices.
5. Nutrition, emphasizing dietary balance, caffeine regulation, and practical implementation.
Detailed descriptions of the intervention design and implementation are provided in Supplementary Table S1. Drafts of these sub-modules were presented in workshops involving the six development experts, who reviewed the materials and suggested revisions. Iterative modifications were made until consensus was achieved. In Phase 2, the finalized module was distributed to the validation experts, who assessed content validity and educational quality using the CVI and TEMPtED instruments. Simultaneously, 47 nursing students completed the acceptability questionnaire, which generated data for reliability analysis.
2.4 Data analysis
Data analysis followed a multi-step process. I-CVI was defined as the proportion of experts rating an item ≥3 on a five-point scale. Items with I-CVI between 0.78 and 0.89 were discussed, revised for clarity, and retained after consensus was reached. S-CVI/Ave was computed as the mean of all I-CVI values. Discrepancies were resolved when at least 80% agreement was achieved. TEMPtED scores were averaged across six independent raters. For the Content Validity Index, I-CVI was calculated as the proportion of experts rating each item with a score of 3 or higher, while S-CVI/Ave was computed as the average of all I-CVI values across items. For the TEMPtED evaluation, individual dimension scores and total scores were calculated and interpreted according to the classification thresholds described earlier. For the student acceptability data, Cronbach’s alpha was computed to assess internal consistency reliability. Following conventional benchmarks, values ≥0.90 were interpreted as excellent, 0.80–0.89 as good, 0.70–0.79 as acceptable, and values below 0.70 as poor.
3 Results
3.1 Module development outcomes
The final intervention module was structured around five interrelated sub-modules: physical activity, psychoeducation, music therapy, meditation, and nutrition. Each sub-module incorporated objectives, theoretical justification, recommended strategies, and implementation guidelines. For example, the physical activity module emphasized moderate-intensity aerobic exercise and muscle-strengthening routines, while the nutrition module highlighted balanced dietary intake and caffeine management. The psychoeducation sub-module focused on stress management and smartphone use, the music therapy sub-module guided students in selecting and applying therapeutic music, and the meditation sub-module introduced mindfulness practices with step-by-step exercises.
The module drafting process required several iterative rounds of expert review. Six validation experts were selected based on doctoral or senior clinical qualifications and at least 10 years of experience in sleep medicine, psychology, nursing education, physical activity, or nutrition. These experts were not affiliated with the authors’ institution and had no involvement in module development to ensure independence. The development and validation panels were distinct to reduce confirmation bias. Experts highlighted the importance of aligning the content with the daily schedules of nursing students, who often face irregular sleep–wake patterns due to clinical training. Revisions were made to ensure feasibility, such as recommending 20–30 min of physical activity per day instead of longer sessions. Experts also emphasized cultural appropriateness, for example by suggesting familiar forms of meditation and music genres more acceptable to Chinese students. The final consensus confirmed that the module not only reflected scientific evidence but also met the needs of the specific target population.
This systematic development process aligns with prior research emphasizing that health education modules are most effective when co-designed with multidisciplinary input and tailored to the lived experiences of the intended learners. Thus, the present module represents a significant advancement in bridging theory and practice for sleep health promotion among nursing students.
3.2 Content validity (CVI analysis)
The content validity of the module was rigorously evaluated by six independent experts who were not involved in the development stage. Each expert rated the relevance of the module items using a five-point Likert scale. The item-level CVI (I-CVI) values ranged from 0.833 to 1.000, indicating that almost all items were consistently judged as relevant or highly relevant by the majority of experts. The scale-level CVI (S-CVI/Ave) reached 0.985, which is substantially higher than the recommended threshold of 0.80 and suggests excellent overall content validity.
As shown in Table 1, the detailed results highlight the breadth and appropriateness of the module content. The consistently high I-CVI and S-CVI values demonstrate that the expert panel considered the module to be conceptually clear, comprehensive, and reflective of the essential domains required for effective sleep quality interventions.
These results align with prior studies in health education, where S-CVI values above 0.90 are generally regarded as strong evidence of content validity. Comparable findings have been reported in module development research related to stress management, physical activity, and nutrition education, further supporting the robustness of the present results. The high content validity established in this study provides confidence that the module’s learning materials and activities are well aligned with its intended objectives and are directly relevant to improving sleep quality among nursing students.
3.3 Educational quality (TEMPtED evaluation)
The quality of the developed module was further evaluated through the application of the Template for Evaluating Patient Education Documents (TEMPtED) instrument. This tool measures five key dimensions, namely content, motivational principles, literacy, layout and typography, and graphics. Each dimension is composed of multiple items that were rated on a four-point scale, producing a maximum total score of 54 points for each sub-module. A total of 6 experts independently completed the evaluation, and their scores were averaged to generate the results for each dimension and sub-module.
The evaluation outcomes, as summarized in Table 2, demonstrate that all 5 sub-modules of the intervention achieved mean total scores ranging from 50.0 to 51.5. According to TEMPtED classification thresholds, scores between 49 and 54 indicate excellence, thereby placing every sub-module within the “Excellent” category. The content dimension consistently achieved the highest scores, ranging from 19.0 to 20.3 out of 21, which indicates that experts considered the instructional material to be accurate, comprehensive, and highly relevant to the target population. Motivational principles also received high ratings, with averages between 5.5 and 5.8 out of 6, reflecting that the module successfully incorporated strategies such as goal setting and reinforcement to stimulate student engagement. The literacy dimension was scored between 11.0 and 11.3 out of 12, confirming that the materials were presented using accessible language and appropriate terminology for vocational nursing students. Layout and typography obtained scores of 5.5 to 5.7 out of 6, showing that the overall structure was clear and logically organized, although experts suggested minor adjustments to font size consistency to further enhance readability. The graphics dimension received slightly lower averages, between 8.2 and 8.7 out of 9, with experts recommending the inclusion of more culturally tailored images to strengthen relevance.
Despite these minor recommendations, the consistently high ratings across all dimensions confirmed that the module is both scientifically robust and practically applicable. The results provide strong evidence that the educational materials are not only accurate and complete but also user-friendly, visually appealing, and motivational in nature. Achieving “Excellent” scores in TEMPtED across all 5 sub-modules is particularly meaningful because it affirms that the intervention meets the highest standards of educational material design. Prior research in health education has shown that materials classified as excellent in TEMPtED evaluations are more likely to be adopted effectively in educational and clinical environments. Therefore, the current findings strengthen confidence in the feasibility and potential impact of this lifestyle intervention module for improving sleep quality among vocational nursing students.
3.4 Reliability analysis (student acceptability)
Reliability testing was conducted with 47 nursing students who evaluated the clarity, relevance, and feasibility of the module through a structured 38-item questionnaire based on a five-point Likert scale. The internal consistency analysis yielded a Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of 0.980, which exceeds the conventional threshold of 0.90 and indicates excellent reliability (Table 3). This result demonstrates that the questionnaire items consistently measured a coherent construct and that student responses were highly internally consistent.
The very high alpha coefficient suggests that the instrument was well-structured and that the items were strongly correlated with each other, reflecting a unified perception of the module’s clarity, relevance, and feasibility. Future module iterations will streamline items to reduce redundancy while maintaining adequate construct coverage and content comprehensiveness. This finding provides strong support for the reliability of the student acceptability questionnaire and reinforces the robustness of the evaluation process. It further indicates that the module was perceived by students as a cohesive and feasible intervention, thereby affirming the consistency of the measurement tool and the stability of the responses.
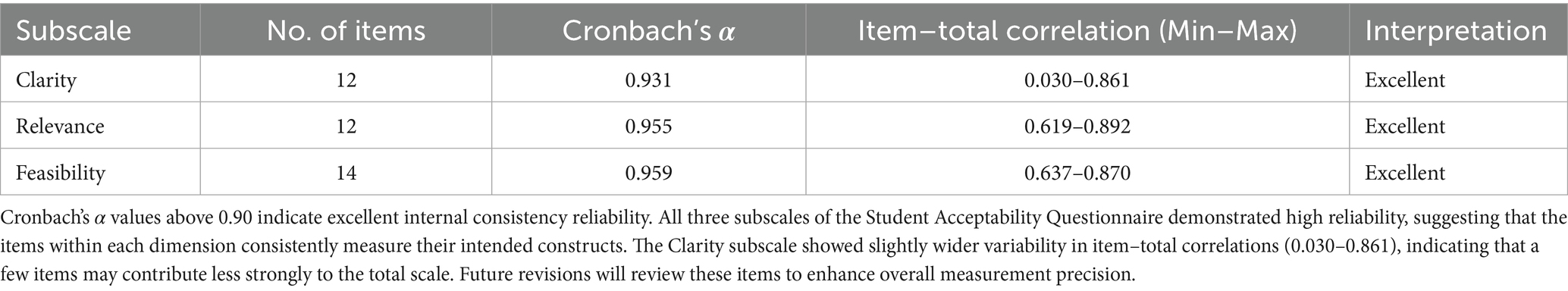
To further evaluate internal consistency, reliability coefficients were computed for each subscale of the Student Acceptability Questionnaire. Cronbach’s alpha values across subscales ranged from 0.931 to 0.959, demonstrating excellent and consistent internal reliability. Item–total correlations ranged from 0.030 to 0.892, with most items showing moderate to strong positive relationships with the total score. These results confirm the coherence of each subscale and the strong homogeneity of most items, while suggesting that a few items within the Clarity subscale may require refinement in future revisions (Table 4).
4 Discussion
Taken together, the findings indicate that the developed module demonstrates strong psychometric properties across multiple dimensions, including content validity, educational quality, and reliability. The high I-CVI and S-CVI/Ave values confirmed that the content was judged by experts as accurate, comprehensive, and directly relevant to the needs of vocational nursing students (21). Similarly, the TEMPtED evaluation results placed all five sub-modules within the “Excellent” category, confirming that the educational materials met rigorous standards for accuracy, usability, motivation, and visual design (23). These outcomes underscore the importance of combining multidisciplinary expertise and structured evaluation frameworks in developing effective health education modules. We plan to conduct a pre-registered 4-week pre–post effectiveness pilot and will report effect sizes (Cohen’s d, 95% CI).
Importantly, this study contributes to the scarce body of literature on sleep health promotion in nursing education. Most prior interventions have focused on single factors, such as physical activity or stress management, with relatively modest outcomes. By contrast, the present study adopted a multi-component approach, integrating physical activity, psychoeducation, music therapy, meditation, and nutrition into a single structured framework. This holistic perspective reflects international best practices in health promotion and highlights the value of addressing sleep health through comprehensive lifestyle interventions (24).
Another important contribution lies in the use of the Sidek Module Development Model (SMDM), which provided a systematic framework to ensure that the module is theoretically grounded, culturally relevant, and educationally feasible. The rigorous validation process enhances its transferability, not only within Chinese vocational colleges but also to other nursing education contexts globally, where students face similar challenges such as heavy workloads, irregular schedules, and poor sleep hygiene (25, 26). By tailoring the intervention to a culturally specific population while ensuring methodological rigor, this study offers a model that can be adapted and scaled across diverse educational and healthcare systems.
These findings are consistent with previous module validation studies emphasizing multidisciplinary collaboration for health education interventions (17, 20, 23). Similar validation frameworks have demonstrated the importance of combining expert consensus and pilot reliability testing in nursing education (21, 24).
From a public health perspective, improving sleep health among nursing students holds significant long-term importance. Nursing students represent the future healthcare workforce, and inadequate sleep is closely associated with diminished academic performance, increased burnout, and reduced clinical competence. Addressing sleep-related issues early in professional education may therefore contribute to improved well-being, enhanced learning outcomes, and ultimately safer patient care.
This study focused on the development and validation of a multi-component lifestyle intervention module designed to promote sleep health among vocational nursing students in China. Guided by the Sidek Module Development Model, the module demonstrated strong content validity, high educational quality, and excellent internal consistency, providing evidence of its scientific soundness and practical feasibility. These findings represent an essential preliminary step toward establishing a structured and culturally responsive framework for sleep health education in nursing programs.
While the study was conducted within a specific national context, the validated framework may serve as a reference for adaptation in other cultural and educational environments. Given that sleep problems among healthcare and university students are a global public health issue, this module offers a potentially adaptable foundation for future implementation and evaluation. Its modular and low-cost structure allows flexible integration into existing nursing curricula and digital learning platforms, supporting future multi-institutional and cross-cultural research on its effectiveness and sustainability.
This pilot was limited to 47 participants from a single vocational nursing college. Findings should therefore be interpreted as preliminary and context-specific. The module framework, while promising, requires replication across multiple institutions, disciplines, and cultural settings to establish generalizability and ensure applicability to broader nursing education contexts.
In conclusion, the present study developed and validated a multi-component lifestyle intervention module designed to promote sleep health among vocational nursing students in China. By establishing strong evidence of content validity, educational quality, and internal consistency, this research provides a solid methodological foundation for subsequent implementation and effectiveness studies. Rather than claiming proven impact, the findings should be viewed as preliminary validation results that demonstrate the feasibility of the module. Future research should focus on multi-institutional pilots, cross-cultural adaptations, and longitudinal evaluations to confirm its effectiveness and sustainability across diverse educational contexts.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of University Kebangsaan Malaysia (Approval number: JEP-2024-914) and Taishan Vocational College of Nursing (Approval number: TSVCN20240105). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JW: Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Conceptualization, Visualization. II: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Validation. FM: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Methodology. CS: Writing – review & editing, Software, Validation. FX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. AM: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Project administration, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the participating students and faculty for their time and support. We are grateful to the expert panel for conducting the CVI and TEMPtED evaluations, and to the administrative staff of [Taishan Vocational College of Nursing, Taishan City, Shandong Province, China] for facilitating logistics and classroom access. Any remaining errors are our own.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1698558/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Almarzouki, AF, Mandili, RL, Salloom, J, Kamal, LK, Alharthi, O, Alharthi, S, et al. The impact of sleep and mental health on working memory and academic performance: a longitudinal study. Brain Sci. (2022) 12:1525. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12111525
3. Hyndych, A, El-Abassi, R, and Mader, EC Jr. The role of sleep and the effects of sleep loss on cognitive, affective, and behavioral processes. Cureus. (2025) 17:232. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84232
4. Ren, W, Li, W, Ji, C, Kong, F, Chao, L, Yang, Q, et al. The association between sleep and burnout in psychiatric nurses: a survey from China. BMC Nurs. (2025) 24:639. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03238-y
5. Vahedi, S, and Davoudi, B. The relationship between death anxiety and sleep quality among nurses working in the intensive care unit. Eurasian J Chem Med Pet Res. (2024) 3:129–39.
6. Darku, ED, and Diyaolu, CO. The role of stress, sleep, and mental health in obesity and weight gain. Int Res J Mod Educ Technol Soc. (2025) 6:3216–35. doi: 10.56726/IRJMETS62817
7. Sharma, I, Marwale, AV, Sidana, R, and Gupta, ID. Lifestyle modification for mental health and well-being. Indian J Psychiatry. (2024) 66:219–34. doi: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_39_24
8. Sun, Z, Gao, X, and Ren, P. The relationship between time anxiety and college students’ sleep quality: the mediating role of irrational procrastination and the moderating effect of physical activity. Front Psychol. (2024) 15:1410746. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1410746
9. Alnawwar, MA, Alraddadi, MI, Algethmi, RA, Salem, GA, Salem, MA, and Alharbi, AA. The effect of physical activity on sleep quality and sleep disorder: a systematic review. Cureus. (2023) 15:595. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43595
10. Aydın Özkan, S, Başoğul, C, and Karaca, T. The effect of psychoeducation-based intervention on sleep quality and anxiety level in third trimester pregnant women: a randomized controlled trial. Curr Psychol. (2024) 43:33170–9. doi: 10.1007/s12144-024-06846-0
11. Kabalı, S, Çelik, MN, and Öner, N. Associations of nutrition education with diet quality indexes and chronotype: a cross-sectional study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2025) 35:2015–27. doi: 10.1080/09603123.2024.2421830
12. Li, Y, Tang, J, and Chen, G. The effect of meditation-based mind-body interventions on older adults with poor sleep quality: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Behav Sleep Med. (2025) 23:341–59. doi: 10.1080/15402002.2025.2475911
13. Morin, CM, and Benca, R. Chronic insomnia. Lancet. (2012) 379:1129–41. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60750-2
14. Wang, X, Feng, T, Liu, S, and Ruan, J. Application of music therapy in improving the sleep quality and mental health of nurses with circadian rhythm sleep disorders caused by work shifts. Noise Health. (2024) 26:294–9. doi: 10.4103/nah.nah_32_24
15. Harvey, AG, Belanger, L, Talbot, L, Edelmann, K, Bastien, C, Morin, CM, et al. Evidence-based psychological treatments for insomnia. Lancet Psychiatry. (2018) 5:975–84.
16. Lim, DC, Najafi, A, Afifi, L, Bassetti, CL, Buysse, DJ, Han, F, et al. The need to promote sleep health in public health agendas across the globe. Lancet Public Health. (2023) 8:e820–6. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(23)00182-2
17. Capezuti, E, Zadeh, RS, Brigham, MA, Dias, BA, Kim, BC, Lengetti, E, et al. Development and palliative care staff reactions to a sleep regulation educational intervention. BMC Palliat Care. (2022) 21:12. doi: 10.1186/s12904-022-00902-x
18. Irish, LA, Kline, CE, Gunn, HE, Buysse, DJ, and Hall, MH. Behavioral and psychosocial treatments for insomnia in adults: an update of the 2006 review. Sleep. (2015) 38:217–26.
19. Roberts, K, Beckenkamp, P, Comachio, J, Castrillon, CM, Silveira, AMC, Ho, E, et al. The design process and development of MySleepSolutions-A sleep module for a lifestyle self-management app for low back pain. Health Informatics J. (2025) 31:14604582251340548. doi: 10.1177/14604582251340548
20. Othman, MH, Johari, KSK, and Amat, S. Sidek’s module development model in the Adler marital therapy module. Int J Acad Res Bus Soc Sci. (2023) 13:2023–37. doi: 10.6007/IJARBSS/v13-i10/19102
21. Polit, DF, and Beck, CT. The content validity index: are you sure you know what's being reported? Critique and recommendations. Res Nurs Health. (2006) 29:489–97. doi: 10.1002/nur.20147
22. Grant, JS, and Davis, LL. Selection and use of content experts for instrument development. Res Nurs Health. (1997) 20:269–74. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-240X(199706)20:3<>3.0.CO;2-G
23. Clayton, LH. TemptEd: development and psychometric properties of a tool to evaluate material used in patient education. J Adv Nurs. (2009) 65:2229–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2009.05049.x
24. Holmbeck, GN, and Devine, KA. An author's checklist for measure development and validation manuscripts. Oxford: Oxford University Press (2009).
25. Brooks, SK, and Greenberg, N. Mental health and psychological wellbeing of maritime personnel: a systematic review. BMC Psychol. (2022) 10:139. doi: 10.1186/s40359-022-00850-4
26. Leger, D, Ferini-Strambi, L, Han, F, Poyares, D, Uchiyama, M, and Zee, PC. Novel perspective of ‘poor sleep’in public health: a narrative review. BMJ Public Health. (2024) 2:952. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2024-000952
27. Hertzog, MA. Considerations in determining sample size for pilot studies. Research in Nursing & Health. (2008) 31:180–91. doi: 10.1002/nur.20247
Keywords: sleep health, nursing education, lifestyle intervention, module validation, public health
Citation: Wang J, Ishak I, Mazri FH, Siau CS, Xin FX and Mat Ludin AF (2025) Promoting sleep health in future healthcare professionals: development and validation of a multi-component lifestyle intervention module for nursing students. Front. Public Health. 13:1698558. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1698558
Edited by:
Carlos Alberto De Oliveira Magalhães Júnior, State University of Maringá, BrazilReviewed by:
Dursun Alper Yilmaz, Ağrı İbrahim Çeçen University, TürkiyeSyahruramdhani Syahruramdhani, Muhammadiyah University of Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Ishak, Mazri, Siau, Xin and Mat Ludin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ismarulyusda Ishak, aXNtYXJ1bEB1a20uZWR1Lm15
 Jing Wang
Jing Wang Ismarulyusda Ishak
Ismarulyusda Ishak Fatin Hanani Mazri
Fatin Hanani Mazri Ching Sin Siau
Ching Sin Siau Fengxue Xin
Fengxue Xin Arimi Fitri Mat Ludin
Arimi Fitri Mat Ludin