- 1Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Biomedical Sciences, Kampala International University, Ishaka, Uganda
- 2Department of Publication and Extension, Kampala International University, Ishaka, Uganda
- 3Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Kampala International University, Ishaka, Uganda
- 4Department of Electrical, Telecommunication and Computer Engineering, Kampala International University, Ishaka, Uganda
- 5Department of Microbiology and Parasitology, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, University of Rwanda, Butare, Rwanda
- 6Department of Physiology, Equator University of Science and Technology, Masaka, Uganda
- 7Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Biomedical Sciences, Kampala International University, Kampala, Uganda
Biosecurity threats, which include natural outbreaks, laboratory accidents, and intentional bioterrorism, are a major issue for global health security. The impact of poor preparedness on the health, social, and economic effects of the 1918 influenza pandemic, the 2001 anthrax attacks, and the COVID-19 crisis is devastating. Standard methods, such as quarantine and serology, as well as traditional inoculations, offered basic defences but were often reactive, slow, and unfair. The recent scientific and technological progress has altered the concept of biosecurity preparedness by providing new instruments of early detection, quick reaction, and fair health solutions. Artificial intelligence-based epidemic prediction, next-generation sequencing, CRISPR-based diagnostics, and digital epidemiology are emerging technologies that enable near-real-time surveillance. New therapeutic agents and vaccines, such as mRNA and DNA platforms, monoclonal antibodies, and nanobody therapies, have enhanced response capabilities. Containment measures based on robotics, biosensors, nanotechnology-based PPE, and portable biocontainment units have simultaneously improved frontline safety. Sensitive health information and enhanced coordination are today secured with the help of digital and cyber-biosecurity tools. Nonetheless, the innovations have ethical, legal, and equity issues, which point to the need to govern responsibly and make them accessible to all. This review brings forth the incorporation of emerging technologies with international cooperation, fair systems, and responsive policies as the keys to developing resilient and future-orientated systems that could help alleviate natural, accidental, and intentional biosecurity threats.
1 Introduction
Biosecurity threats pose one of the most time-sensitive issues of the contemporary world, as a broad range of biological threats can undermine the health security of the world population (1). They can be divided into broad categories, namely natural events, including pandemics due to new or re-emerging infectious diseases; accidental events, including laboratory malfunctions, mishandling of research, or unintentional release of pathogens; and deliberate events, including bioterrorism, or the intention to abuse biotechnology (2). Both categories are potentially associated with extensive morbidity, mortality, and disruption of society, whose impacts are not limited to the health systems but also extend to the economic stability, political trust, and international security (2). The increased globalisation of societies and the high rate of travelling make localised cases of biosecurity outbreaks even more dangerous, as they could turn into worldwide crises (1).
Traditionally, biosecurity threats have proven themselves many times in terms of their ability to disrupt society and overwhelm the public health systems (3). The influenza pandemic of 1918 claimed millions of lives, which still impacts the infrastructure in the field of health (4). The 2001 anthrax attacks in the United States in the 21st century demonstrated the risks of bioterrorism, as well as revealed weaknesses in preparedness (5). The recent COVID-19 pandemic has given a startling insight into how fast new pathogens can cross national borders, with disastrous health, economic, and social impacts (6). On the same note, the 2014–2016 Ebola outbreak in West Africa demonstrated major flaws in health systems, the international response, and the capacity to respond at the global level (7). Even laboratory-related accidents, despite their rarity, have underscored the risks associated with inadequate biosafety and biosecurity protocols. The following historical examples also stress the magnitude of the effect of biosecurity threats on the whole world and the necessity of active preparedness.
Global health preparedness is essential because it can enhance resilience to foreseen and unforeseen biosecurity incidents (1). Preparedness refers to the ability to avert, identify, and address biological threats by having strong surveillance, communication networks, quick diagnostic tools, and strong healthcare systems (8). Strong health systems can reduce the immediate impact of outbreaks, as well as safeguard against the long-term impact of undermining trust, stability, and development (9). Additionally, preparedness also needs to be beyond national borders since a biological threat is by definition transnational and requires a combination of international efforts (8). The inequalities experienced in crises in the past, especially those that are resource-constrained, underscore the necessity of fair access to tools and innovations that can further improve global preparedness. The purpose of this review is to determine how new technologies and innovative solutions can revolutionise global health preparedness and responses to biosecurity threats. This study evaluates the ability of technological innovation to solve long-standing preparedness challenges by analysing progress in diagnosis, surveillance, vaccine development, and digital health tools. Additionally, the review compares these innovations to traditional methods, highlighting their contrasting advantages, constraints, and implications for global equity. However, eventually, the analysis is expected to prove that the incorporation of the latest technologies, backed by effective governance and global collaboration, could be instrumental in improving resilience to natural, accidental, and intentional biological incidents and securing a safer and more secure global health future.
2 Global landscape of biosecurity threats
Biosecurity threats refer to a broad spectrum of biological hazards that are challenging to human, animal, and environmental health. These threats are complex and occur due to the natural processes, human activity, or intentional incorrect use of biological agents. Knowing how they are classified, trend amplification, real-life realisations, and the international structures that are geared towards curbing them are vital in the development of robust global health systems (see Table 1). We can categorise biosecurity risks as four broad categories: infectious diseases, synthetic biology threats, bioterrorism, and antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
2.1 Infectious diseases
The most common and most impactful biosecurity risks are naturally occurring outbreaks. An infectious disease may be defined as a disease caused by a pathogen or its toxin, which occurs when an infected individual, an infected animal, or an inanimate object contaminated with the pathogen transmits the disease to a vulnerable host (10). The global burden of disease caused by infectious diseases has been of unimaginable weight to the global health systems and economies, and its negative effect is disproportionately experienced by vulnerable populations (10). The determinants of this infectious disease are the exposure of a potential host to an infectious agent; the result of the exposure is determined by the dynamic relationship between determinants of infectiveness, pathogenicity, virulence of the agent, and determinants of susceptibility to infection and disease of the intrinsic host. Extrinsic determinants that increase the host’s vulnerability to exposure include environmental factors, which consist of both physical and social behavioural elements (11). There are pathogens, including influenza, coronaviruses, and haemorrhagic fever viruses, that can infect a large number of people quickly and overload the health fields (11). New threats are a significant percentage of emerging infectious diseases, which are often of zoonotic origin (12). Infectious diseases have to be properly diagnosed to treat patients and conduct prevention and control surveillance (11). Sensitivity and specificity are two crucial attributes that any diagnostic test used should have (11). Sensitivity is the test’s ability to detect those infected (positive for disease). A very sensitive test will be more likely to identify those with the disease (and maybe those without the disease); a very sensitive test will have few false negatives (10). Specificity: This aspect is the capacity of the test to correctly recognise people who are not infected by a given agent (a healthy negative); high specificity means that there is a low number of false positives. Commonly, screening tests are highly sensitive (to detect any potential cases), and confirmatory tests are more specific (to rule out false-positive screening tests).
In general, the laboratory diagnosis of infectious diseases is founded on the tests that either directly detect an infectious agent or are indicative of infection that has occurred and show evidence of agent-specific immunity in the host (10). Diagnosis of an infecting agent may be done by direct testing of host samples (e.g., blood, tissue, urine) or environmental samples or by testing after agent culture and isolation of host samples. The principal types of analyses applied in identifying pathogens can be divided into phenotypic, which reveal the properties of an intact agent; nucleic acid-based, which identify the characteristics and composition of an agent’s nucleic acid (DNA or RNA); and immunologic, which identify the presence of an immune response to an agent (11).
2.2 Synthetic biology risks
Genetic engineering and synthetic biology made remarkable breakthroughs in medicine and biotechnology and brought about biosecurity issues (13). Synthetic viral genomes, pathogen virulence, and the design of resistant organisms bring dangers of unintended and intentional abuse. Examples of various emerging risks identified in synthetic biology include artificial intelligence misuse and biological dataset targeting, hacking of insecure internet-of-medical-things, genetic blackmail, and bio-discrimination (14). These risks highlight the dual-use nature of synthetic biology, where powerful tools for innovation can also be weaponized or exploited. Dual-use research of concern (DURC) is a constructive example of the ethical and security dilemmas of the advanced life sciences. There has been some progress with the synthetic biology tools used to design and optimise biological systems. Examples of transcriptional tools include synthetic promoters or RNA-based transcriptional regulation and are commonly used in the very specific control of gene expression (15). These modifications can be done through the extension of flanking sequences upstream and downstream of core promoters and by increasing the number of copies of promoters so that the desired transcription efficiency is obtained (16). It has been demonstrated by numerous studies that the translation initiation site of mRNA, including a ribosome-binding site (RBS) and the 5′ structural region (5′), makes significant contributions to the establishment of the translation efficiency of a certain mRNA (15). A research study by Hewett et al. (17) suggests 44 risks in synthetic biology, and they can be divided into four risk categories concerning human health and environmental pollution. Allergies, antibiotic resistance, carcinogens, and pathogenicity or toxicity are the problems in human-health-related risks, and environmental risks include changes in the environment or depletion, horizontal gene transfer, and pathogenicity or toxicity (17). In addition, CRISPR/Cas9, the new technology of genome editing, has had immense impacts on the sphere of synthetic biology. This technology not only enhances the accuracy and efficiency of editing of pathogens, animals, plants, and human genomes, but also produces traceless modification of genomes within a short time. Hence, the technology can increase the pathogenicity, virulence, or transfer of toxins or bacteria, or interfere with the key genes in humans, animals, and plants (18). Moreover, some research states that CRISPR/Cas9 has off-target effects, which may lead to unspecified health effects (19, 20). Additionally, facilitated and low-cost operations enhance the risks of deliberate abuse. The CRISPR/Cas9 genome-editing technology was mentioned in a report by the U. S. Intelligence Agency submitted to the U. S. Senate in 2016 as a possible weapon of mass destruction (21).
2.3 Bioterrorism
The intended release of pathogens or toxins, whether political, ideological, or military, is one of the gravest biosecurity threats (22). Bioterrorism incidents are not as frequent as natural outbreaks, but they may cause disproportionate fear and social destabilisation. A systematic review conducted by Elgabry et al. (23), underscores bioterrorism as a significant future threat enabled by synthetic biology, particularly through the misuse of genome editing tools like CRISPR and the increasing accessibility of biological data and technologies. It highlights how synthetic biology could facilitate the creation of more virulent pathogens or covert biological attacks, such as engineered viruses that mimic natural deaths, making detection and attribution difficult. Thirty-three terrorist attacks involving biological agents were recorded between 1970 through 2019 (24). Despite numerous possible pathogens that can be utilised in a bioterrorist attack, the most alarming agents to national security and the health of the population reported include anthrax, smallpox, plague, tularaemia, botulism, and the viral haemorrhagic fevers, in decreasing order of probability, as presented in Table 2 (22). Although the 1997 outbreak of Shigella dysenteriae type 2 among laboratory workers also listed in Table 2, was not officially classified as a national security threat, it underscored the potential risks posed by insider threats and intentional misuse of biological agents within controlled environments (25). The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) classify these pathogens as Category A (26). Thus, one of the possible preventive or severity-minimising measures is vaccine prophylaxis, which is only relevant when applied before the onset of the symptom, preferably within 4 days of exposure (26).
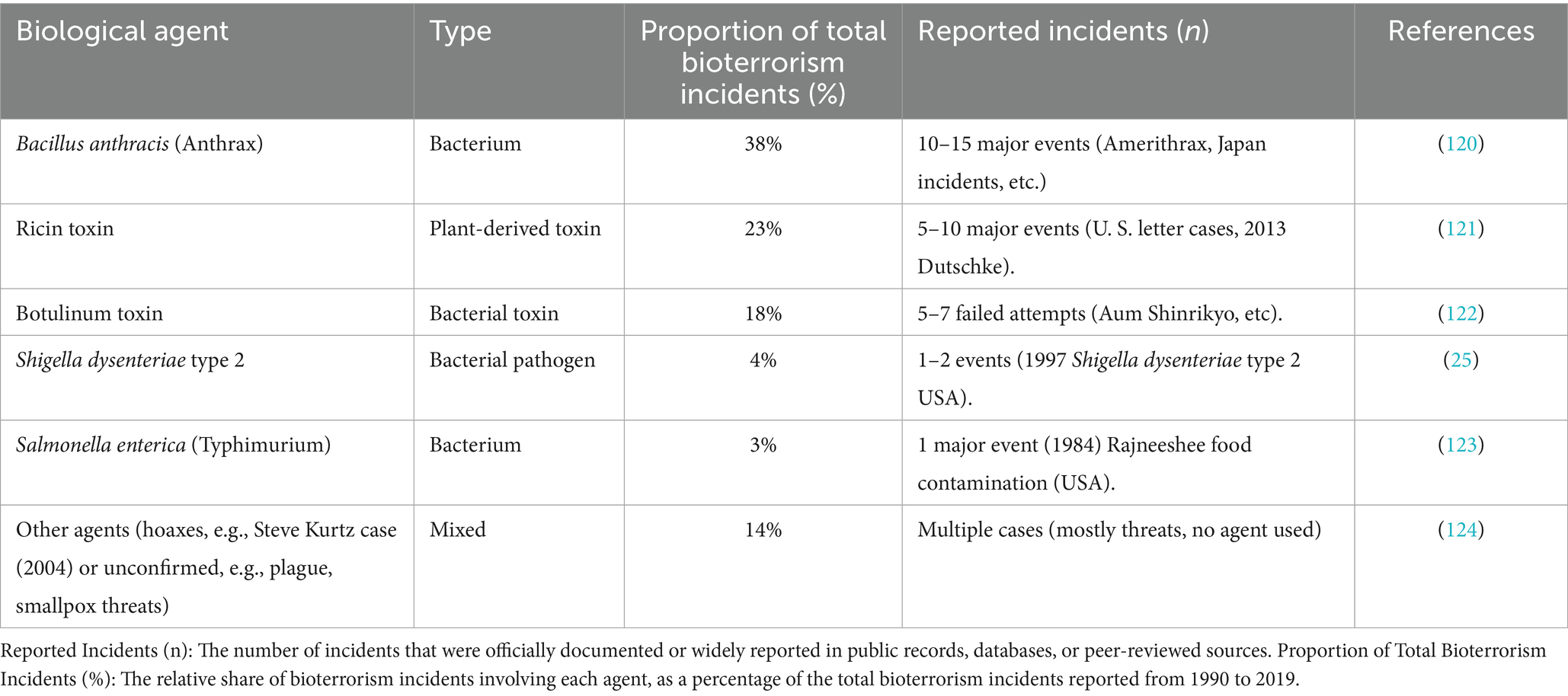
Table 2. Showing proportional distribution of the main biological agents based on documented modern-era cases.
2.4 Antimicrobial resistance (AMR)
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a serious worldwide biosecurity issue that has created significant problems in the health of people, economic prosperity, and efficacy of contemporary medicine (27). AMR poses a threat to the efforts made to fight infectious diseases by characterising it as the capacity of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, to develop mechanisms that diminish the effectiveness of antimicrobial treatments (28). AMR is among the top 10 global public health threats identified by the World Health Organisation (WHO) (27). In 2019, AMR was directly responsible for 1.27 million deaths and contributed to an additional 3.68 million deaths globally (29). The AMR rates have also been a cause of alarm in 2020, as WHO published data on the surveillance of 78 countries (30). The seriousness of the situation is supported by the fact that the World Bank assessment estimates that the failure to curb AMR may result in the world witnessing a 1.1 per cent to 3.8 per cent decrease in global domestic product (GDP) by the year 2050 (31).
A historical approach to major outbreaks worldwide can help offer important insights into how biosecurity policies and preparedness approaches evolved (Figure 1). The timeline outlines major events from previous pandemics, such as SARS, flu outbreaks, and Ebola, up to the recent COVID-19 crisis, and shows how each outbreak led to innovations in surveillance, diagnostics, containment, and governance (32–37). Analysing these milestones reveals how the lessons learnt from past crises have shaped current frameworks and led to the development of new technologies for anticipating and addressing future biosecurity threats.

Figure 1. Timeline of major global outbreaks and innovation milestones in biosecurity preparedness (1918–2019).
3 Conventional and traditional approaches
Before the emergence of high-tech biotechnological and digital solutions, the preparedness for biosecurity threats in the world depended on traditional approaches to these problems (38, 39). These methodologies, despite their fundamental nature, were often reactive and restricted. Reactive outbreak management characterised much of the 20th century (40). The mobilisation of resources by the public health systems was usually done only after it was confirmed that an outbreak had occurred, in most cases through the clinical identification of clusters of unusual illnesses. The use of quarantine, isolation, and restrictions on borders was common, including during historic cholera outbreaks and the 1918 influenza pandemic (41). Although these measures occasionally impeded the spread of the disease, they hardly prevented any large-scale spread because of the delay in detection and lack of predictive capability. Laboratory confirmation was based on conventional investigations, including culture-based techniques and serological tests (42). Culture methods enabled the cultivation and determination of the pathogens, which revealed useful information on antimicrobial susceptibility (42). The immune responses were discovered with the help of serology, which is often applied retrospectively to verify the exposure (43). Such approaches, however, demanded the services of skilled staff, special infrastructure, and quite a considerable period of time, which could be days, weeks, or months before one could see a result. These delays were harmful in the case of fast-spreading outbreaks. Standard vaccines and antibiotics were pivotal in prevention and treatment, with notable achievements of traditional vaccines, developed from inactivated or attenuated pathogens, particularly evident in the global eradication of smallpox and polio, marking significant milestones in public health. The mid-20th century saw the introduction of antibiotics, which revolutionised the treatment of bacterial infections and significantly reduced mortality (28). However, antibiotics had long development cycles, were expensive to produce, and were only effective against known pathogens. Though traditional methods laid the groundwork for infectious disease control, their inefficiency became more evident when new and complicated biosecurity challenges came into the limelight. Lagging in detection and response was a recurrent weakness. Culture and serological diagnostics used long processing times, and in most cases, outbreaks were confirmed late. Interventions were already established in the form of transmission chains, as observed during the initial stages of the HIV/AIDS crisis and SARS outbreaks (44). The most recent and advanced method now is the integration of culturomics, which is a high-end microbiological approach that integrates high-throughput culturing with genomic sequencing to address the shortcomings of the conventional biosecurity approach, including the use of culture-based diagnostics (45, 46). In contrast to traditional methods, where the diversity of microbes, including those that are difficult to grow in culture or impossible to grow in culture, is usually greatly underestimated, culturomics maximizes the diversity of microbes by employing diverse culture conditions and incorporates molecular profiling by means of sequencing, which facilitates the detection of hitherto unidentified pathogens. It is an all-encompassing strategy that benefits biosecurity through better surveillance, outbreak surveillance and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) surveillance. Despite its capability to detect pathogens more easily and precisely, culturomics has to overcome such drawbacks as high price, infrastructure demands and complexity of data management, though its implementation into biosecurity systems becomes a strong tool in response and detection of new biological threats (45).
Conventional means could not always cope with the demands of new health threats. The development of vaccines with traditional platforms might require years, which will make them useless in the case of rapidly spreading pandemics (47). Discovery of antibiotics slowed dramatically at the end of the 20th century, and abuse and overuse contributed to antimicrobial resistance (AMR) (28). The limited laboratory facilities, human resources, and supply chains in resource-restricted areas further limit the usefulness of such methods. Traditionally, national organisations dominated the control of infectious diseases, with minimal data exchange and international cooperation (48). This piecemeal response compromised the world’s ability to respond promptly, as it took place during the initial transmission of Ebola in West Africa (2014–2016) and highlighted the poor coordination of influenza surveillance before the establishment of the WHO Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS).
4 Emerging technologies in biosecurity preparedness
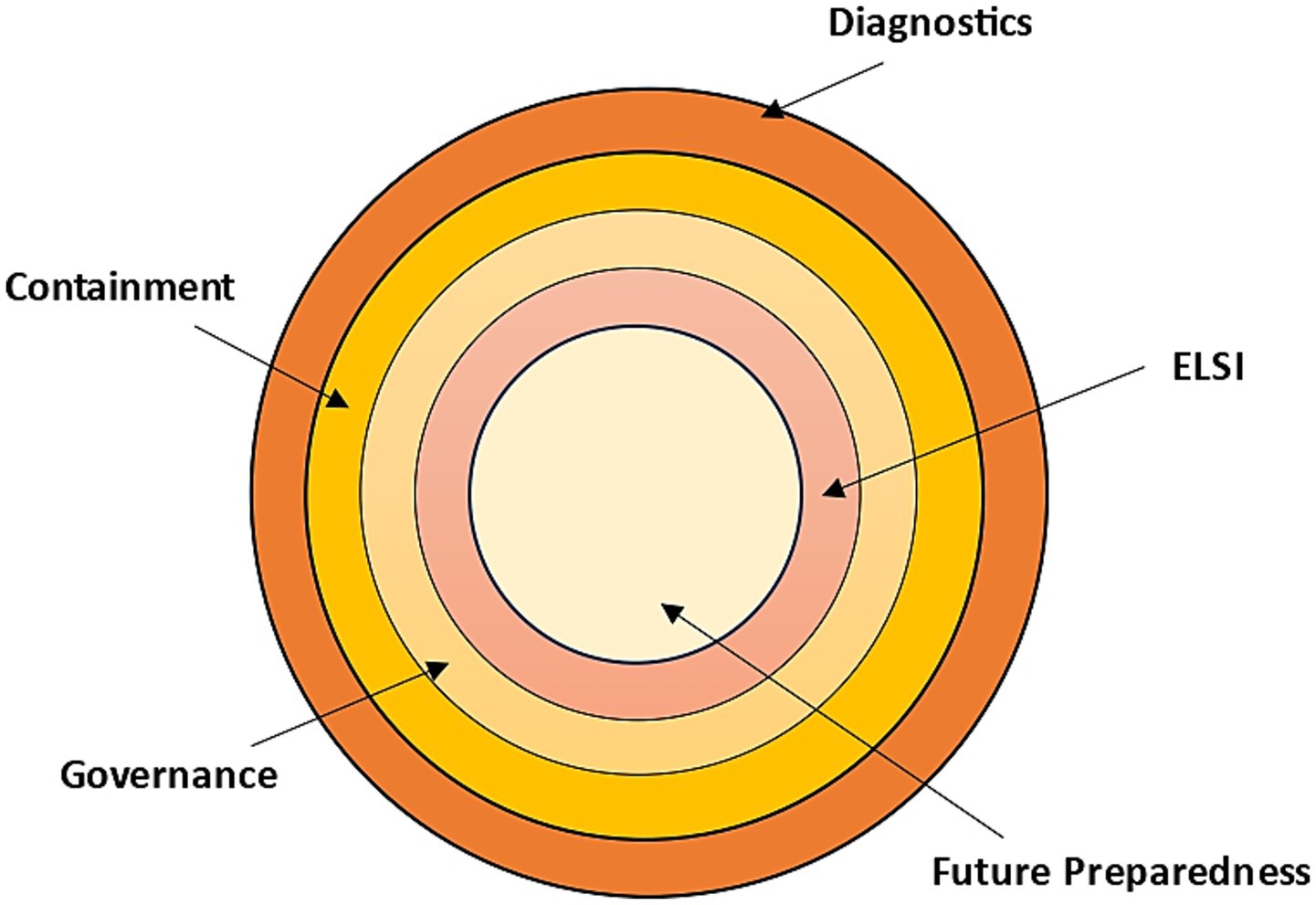
Recent developments in science and technology are transforming the way the global community prepares, detects, and responds to biosecurity threats. Epidemic forecasting based on artificial intelligence, next-generation sequencing, CRISPR-based rapid assays, and digital epidemiology platforms are some of the tools used in diagnostics and surveillance to detect outbreaks faster and more accurately (49, 50). In the therapeutic and vaccine sector, new technologies, such as mRNA or DNA vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, AI-assisted drug discovery, and designs made possible by synthetic biology, are hastening the creation of countermeasures to known and emerging pathogens (19, 51, 52). Containment and response technologies, i.e., biosensors, wearable health monitoring, robotics in outbreak areas, and advanced protective materials, are equally important for increasing the safety of the frontline and minimising human risk (53, 54). Simultaneously, digital and cyber-biosecurity tools, such as blockchain to exchange health data safely (55), BAKE to identify criminally-exploitable vulnerabilities in electronic devices, especially medical products (56), the Internet-of-Medical-Things (IoMT), which is transforming healthcare through the introduction of internet-connected medical-grade devices that are integrated to wider-scale health networks to improve patients’ health (57), cloud-networked emergency strategies (58), and more robust cybersecurity systems to protect sensitive health data, are increasingly important to protect sensitive health information and avert the misuse of technology. Furthermore, adequate biosecurity preparedness requires the consolidation and sequential fortification of science, systems, ethics, and foresight, as shown in Figure 2. Together, these innovations have never been used to offer such opportunities to enhance global health preparedness, but they come with the challenge of equity, safety, and governance (59), that should be handled with caution.
4.1 Diagnostics and surveillance
Proper diagnostics and surveillance are central to the national and world biosecurity preparedness, which allows detecting new pathogens early, describing their features, and implementing evidence-based measures to reduce the spread. Recent technological developments, especially the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to forecast threats, genomics and next-generation sequencing (NGS), CRISPR-based rapid diagnostics, and digital epidemiology based on extensive behavioural and mobility data, have revolutionised the ability to detect threats almost in real time and react to them (60). Integrating these modalities into interoperable surveillance systems is essential for transforming the traditional practice of public health into a proactive risk mitigation approach.
Now, AI-based modelling and forecasting integrate machine learning with mechanistic epidemiological models to enhance accuracy, interpretability, and strength in changing epidemic conditions (61). Modern methods integrate data-centric ML (time-series forecasting, ensemble models, deep learning) with mechanistic epidemiological models (SEIR-type compartmental frameworks) to enhance interpretability and strength in nonstationary epidemic contexts (60). These hybrid architectures minimise the error in forecasting by investigating prior mechanistic knowledge but learn complex, data-driven trends (seasonality, change of behaviour, variants) (61). Findings from a recent series of reviews and applied studies indicate that there is an enhanced lead time for resource allocation and the prediction of hotspots when AI-augmented systems are operationalised within public health pipelines (62). Significant weaknesses include data quality and representativeness, early epidemic curve overfitting, explainability of models, and cross-population predictive performance equity, which have to be overcome to achieve operational credibility (61). Some of the considerations that are applicable in practice involve transparent model validation (hindcast/real-time evaluation), ensemble forecasting to reflect epistemic uncertainty, the use of nontraditional covariates (mobility, wastewater signals, and weather), and continuous calibration as the dynamics of pathogens and human behaviour change. The regulatory and governance frameworks of AI in the field of public health must require the documentation of the model, the evaluation of bias, and the system to update the model quickly based on the new phenotypes of pathogens (63).
The further development of genomics and next-generation sequencing (NGS) also restructured the concept of pathogen surveillance by providing the capability to characterise pathogens on a genome scale, identify pathogens, perform phylogeny, and identify mutations that are linked to transmission advantage or resistance to multiple drugs (44). Large-scale use throughout the COVID-19 pandemic revealed the strength of genomic epidemiology in the detection of variants, the reconstruction of the process of their transmission, and the provision of information regarding vaccines and treatment. Mobile sequencing platforms and simplified bioinformatics pipelines have increased genomic surveillance in the field and low-resource environments, but disparities in sequencing capacity across the world remain. Genomic data can be enhanced with epidemiological metadata (timing, location, clinical severity), which enhances the investigation of outbreaks and assists in decision-making to contain and provide clinical care (64). Among the issues are turnaround times in clinical facilities, metadata standardisation, the governance of data sharing, and long-term funding for regular genomic surveillance (44). Genomic surveillance operational best practices are focused on representative sampling methods, faster sequencing-to-report pipelines (to produce actionable information within days), and interoperable data standards to facilitate interjurisdictional aggregation. To eliminate the observed capacity gaps in the lower-resource regions, it is essential to invest in workforce training and the local sequencing infrastructure (64).
CRISPR-based diagnostics (CRISPRdx) is a technology that uses programmable Cas enzymes (e.g., Cas12, Cas13) to detect nucleic acids in a sensitive and specific manner with fast readouts that can be used in point-of-care (POC) settings (50). Examples of platform exemplars include SHERLOCK and DETECTR, which are viable in viral detection during recent outbreaks and can be adapted to lateral-flow and fluorescence readouts to be used in the field (65). The benefits of CRISPRdx are high analytical sensitivity (when used with isothermal pre-amplification), short time-to-result, adaptability to retarget guides to novel pathogens or variants, and possible inexpensive production (66). Current development is aimed at enhancing single-nucleotide specificity (to differentiate point mutations), multiplexing, simple sample preparation, and non-laboratory readouts (smartphone-based imaging, handheld readers). Strong clinical-validation research and regulatory measures are hastening the bench-to-business POC test translations (50). Field applications Limitations for field applications are that a pre-amplification step is required with very low copy targets (which can complicate matters), a cold chain or reagent stability factor, and quality control and standardised performance measurements across manufacturers. The development of amplification-free CRISPR assays, lyophilised reaction chemistries, and integrated sample-to-answer cartridges can overcome these barriers (67).
Non-traditional, big-scale sources of data, such as social media activity, web search trends, call detail records, aggregated mobility metrics, and participatory symptom reporting, are also exploited by digital epidemiology to complement the traditional surveillance systems (68). These data can give earlier indications of behavioural shifts, new clusters, or even local increases in symptomatic reporting, which are the antecedents of clinical case reporting. In the COVID-19 context, several digital indicators were given early warning about the spread and monitored: the mood of the population, misinformation, and compliance with nonpharmaceutical measures (69). Digital streams, in conjunction with AI, have the potential to improve situational awareness and streamline the prioritisation of laboratory testing and targeted interventions (70). Significant ethical, legal, and technical issues include privacy, sampling bias (access to the digital divide), signal-to-noise ratio, and the reflectiveness of social media groups. Strong privacy-preserving analytics (aggregation, differential privacy), signal validation against clinical ground truth, and explicit equity evaluations are requirements for responsible adoption. In combination with both genomic and clinical information, digital epidemiology is a component of a multi-layered surveillance architecture that can identify and respond to outbreaks at an early stage (71).
The combination of AI forecasting, high-resolution genomics, rapid diagnostics using CRISPR, and digital epidemiology can act as a strong and multifaceted surveillance system with the ability to build lead time, enhance situational granularity, and target interventions (50). The implementation of this synergy would necessitate interoperable data architecture, metadata standardisation, ongoing funding for laboratory and computational capabilities (including in resource-poor environments), human resource training, and data sharing and accountability policies for AI. Pilot programmes where genomic sequencing hubs are co-located with digital signal surveillance and AI-driven early-warning systems can provide convenient avenues to assess changes in outcome measures of the response to the outbreak (time-to-detection, size of the outbreak, efficacy of the interventions). These connections will be important in enhancing the biosecurity preparedness of both naturally occurring pathogens and deliberate biological weapons (44).
Besides technological advances in biosecurity preparedness, government biosurveillance systems are also very important in identifying, tracking, and acting on biosecurity threats. The water surveillance and microbial surveillance are some of the programs needed to detect infectious diseases early and reduce their spread. An example is that the United States has several programs, such as the National Biosurveillance Integration Center (NBIC), that combine federal information streams to monitor the extent of transmission of pathogens and environmental hazards (72). Wastewater surveillance is a surveillance method used in this program to identify the existence of infectious agents in communities, which is crucial in the monitoring of pandemics, as in the example of the COVID-19 pandemic. Also, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) conduct microbial surveillance in different sectors to track antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and the development of new pathogens (73). The UK has a well-developed system of monitoring microbial threats through wastewater and air surveillance by the National Health Service (NHS) and UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) (74). Digital epidemiology is also used in the UK, which combines both traditional and digital surveillance to evaluate the risk to biosecurity quickly (75). Such program integration contributes to the prompt detection of any possible outbreak, as was the case in the UK response to E. coli outbreaks and avian influenza.
4.2 Therapeutics and vaccines
The therapeutic and vaccine technologies have also improved biosecurity preparedness around the world tremendously. Recent advancements in mRNA and DNA vaccine technologies, monoclonal antibodies, nanobody therapies, AI-aided drug repurposing, and synthetic biology for vaccine design have been critical.
The development of mRNA vaccines has revolutionised the vaccinology sphere with their fast developmental paths and solid immune responses. The effectiveness of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 has prompted interest in using such technology against other infectious diseases. Recent research has also shown the effectiveness of mRNA vaccines in preclinical disease models of diseases such as the Zika virus and cytomegalovirus and that the technology also has potential beyond respiratory pathogens (76). The development of lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems has enhanced the stability and immunogenicity of mRNA vaccines, thereby making mRNA vaccines usable across various populations and contexts (77). DNA vaccines, although not the leading counterparts of their mRNA colleagues, have some benefits regarding stability and portability, especially in low-resource environments. Recent trends aim to enhance the immunogenicity of DNA vaccines through the use of improved adjuvants and improved delivery systems, such as electroporation. DNA vaccines against such diseases as West Nile virus and malaria have demonstrated positive outcomes in clinical trials, meaning that they can be used as a complement to mRNA vaccines (78).
The monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have also emerged as a new pillar in the treatment of a wide variety of diseases, including cancers and infectious diseases. The latest innovations resulted in the creation of bispecific antibodies, which are able to bind two antigens at the same time and increase the therapeutic effect. Clinical uses have also been extended to treat diseases like HIV, where mAbs are used to neutralise the viruses and inhibit their transmission (79). Nanobodies are the tiniest functional fragments of antibodies found in camelid species; they have been recognised as a new therapeutic modality. Their distinctive characteristics, such as small size, stability, and easy production, qualify them as viable candidates for attacking intracellular pathogens and cancer cells. Nanobodies have recently been proven effective at neutralising SARS-CoV-2 and suppressing tumour growth in preclinical models. They are in clinical trials to determine their human safety and effectiveness (80).
Artificial intelligence (AI) has also advanced drug discovery by enabling the analysis of large volumes of data to identify potential therapeutic agents. AI-driven drug repurposing has accelerated the identification of available compounds for the treatment of novel diseases. As an example, machine learning models have been utilised to forecast the effectiveness of FDA-approved drugs against SARS-CoV-2, which resulted in the quick discovery of promising drug candidates to be used in clinical trials (81). In addition, AI has been used to design new therapeutics through the structure–activity relationship between compounds and the optimization of drug properties. Recent developments in generative models have allowed the design of small molecules with targeted biological activities that simplify the drug development process. Such AI-based solutions can lower the cost and time to develop new therapies and introduce them to patients faster (49).
Similar to other approaches, synthetic biology has offered novel paradigms in vaccine development because it has made it possible to design novel antigens and delivery systems. These have found recent uses such as engineering live attenuated vaccines with better safety profiles and developing self-amplifying RNA vaccines capable of generating stronger immune responses with lower doses (52). Protein engineering and glycan engineering have also advanced and made it easy to design vaccine antigens, which are more stable and immunogenic. The innovations have resulted in the production of vaccines with a more extended coverage of the different strains of pathogens to overcome the challenges of antigenic variation (82). These innovations provide additional opportunities for preventing and treating infectious diseases, as well as increasing biosecurity preparedness on a global level.
4.3 Containment and response
Response and containment strategies are essential aspects of biosecurity preparedness, as they make it possible to deal with infectious threats as quickly as possible and reduce transmission. Innovations in biosensors, wearable health monitoring, robotics, nanotechnology-enabled PPE, and portable biocontainment systems have revolutionised the ability to detect, isolate, and control infectious agents at the clinical and field levels (83). The combination of these technologies promotes interventions in time, safeguards the frontline responders, and improves the efficiency of operations in case of outbreaks.
The wearable biosensors have become the key players of real-time health monitoring, providing continuous and non-invasive measurements of physiological parameters. Recent progress has resulted in the creation of miniaturised and flexible sensors that can be used to detect the presence of biomarkers of infectious diseases, including volatile organic compounds, in exhaled breath (53). By identifying the disease onset early, these machines enable us to implement timely interventions and enhance the response to the outbreak. Furthermore, biosensor data have been enhanced by incorporating machine learning algorithms, which have helped to better predict and improve the accuracy of these systems to personalise health monitoring and early warning systems (84). The clinical and community environments can transform the current methods of surveillance and health response by implementing wearable biosensors. Robotic systems have also been incorporated in the control of infectious disease outbreaks, especially under circumstances where human beings are restricted by the risks of contamination. Automated robots with artificial intelligence (AI) have performed tasks such as wastewater monitoring, pathogen detection, and environmental disinfection (85). Medical supply transportation, patient care, and facility decontamination also utilise robotics. Such autonomous systems lower the human contact with infectious agents, improve the efficiency of operations, and promote the preservation of the necessary services in case of an outbreak (54).
Designing superior PPE with the use of nanotechnology has greatly enhanced the safety of healthcare workers and responders in the case of an outbreak of an infectious disease. Antimicrobial properties include nanomaterials (like silver nanoparticles and graphene oxide) that are effective in supplementing the protective garments, masks, and gloves (86). New technologies, such as the introduction of sensors into PPE to track environmental conditions and find violations in real time, offer dynamic protection and minimise the risk of infection (87). These innovations are also used in the evolution of intelligent PPE that can react to the different levels of threat.
Portable biocontainment units (PBCUs) have been created to transport patients with high-consequence infectious diseases (HCID) long distances safely (88). These are self-contained systems with negative pressure, which employ HEPA filtration and are compatible with different means of transport, such as ground and air transportation. Simultaneously, portable decontamination systems based on the technologies of multi-spectral ultraviolet (UV) light, plasma, and others have been proposed to neutralise pathogens in contaminated regions within a short period of time (89). These systems are very effective in the deactivation of a wide range of microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and thus, improve the containment and the response capacity to outbreaks.
4.4 Digital and cyber-biosecurity tools
Increased healthcare and biotechnology digitisation has brought about opportunities, as well as vulnerabilities in biosecurity. Digital and cyber-biosecurity solutions, including blockchain for secure data sharing, robust cybersecurity measures to support bioinformatics and synthetic biology, and cloud-based health emergency platforms, enable the real-time and safe management of sensitive health information. Such tools increase coordination, mitigate the abuse of biological data, and improve the resilience of cyber threats in the public health and outbreak management systems.
The adoption of blockchain technology has continued to ensure the safety of health data exchange with regard to data integrity, privacy, and interoperability. Blockchain can guarantee a secure and unaltered registry of health data because it offers a decentralised system that cannot be modified by a third party (55). The most recent applications involve hybrid blockchain systems that integrate both public and private chains to trade off transparency and confidentiality and enable a safe exchange of data across healthcare systems and increase trust in stakeholders (90).
Synthetic biology has been met with artificial intelligence (AI), with new biosecurity issues, such as the possible misuse of bioinformatics tools and the development of novel pathogens. Cybersecurity is necessary to protect against unauthorised access to genetic data, the malicious design of harmful biological agents, and the responsible use of biotechnology (91). The measures to address risks include the adoption of effective cybersecurity measures, the creation of safe bioinformatics solutions, and the creation of management systems to control the use of synthetic biology in an ethical manner (92).
Cloud computing has also revolutionised medical emergency management by offering scalable and flexible platforms for data storage, analysis, and sharing. Cloud-based needs allow the real-time tracking of health indicators, the synchronisation of responses, and the sharing of information in case of outbreaks (58). The latest developments are the implementation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with cloud infrastructure to enable continuous health monitoring and the application of edge computing to localise data processing to minimise latency and improve the responsiveness of health emergency platforms (93).
It is also notable that the development of global health preparedness represents a gradual process of transitioning between the use of traditional tools and the reactive approaches to the innovations aimed at speed, flexibility, and integration. Although each of the two methods helps to learn valuable lessons, the comparative analysis of the two approaches indicates that there are essential insights to be made regarding the future of biosecurity preparedness as presented in Table 3.
5 Global collaborative frameworks
Biosecurity preparedness is based on global collaboration, which allows countries and organisations to coordinate their efforts, exchange important information, and share resources during health emergencies. The WHO, UN agencies, and regional health networks are institutions that have major roles in streamlining the efforts and implementing international health regulations, as well as establishing public-private partnerships that enhance the speed of biotechnology innovations and enhance global governance.
Global health security has its coordinating centre at the World Health Organisation (WHO), which leads the global health response to disasters and establishes global health standards (94). The United Nations (UN) facilitates the work of WHO by assisting in the efforts of the former through different special agencies that focus on the more comprehensive determinants of health, such as socioeconomic factors and environmental conditions (95). Regional health networks, including the WHO Regional Health Alliance (RHA), are a solution that enables countries that are neighbours to jointly tackle any health-related issues that cross countries, to share resources and knowledge and respond to health crises (96). Instead, the International Health Regulations (2005) (IHR) are legally binding rules that establish the rights and responsibilities of countries in managing public health events and emergencies that may have international consequences (97). Although the IHR is expected to increase global health security, problems remain with its practical implementation, such as poor reporting, insufficient surveillance, and resource mobilisation in low-income nations (97). These loopholes support the necessity of more powerful compliance systems and the assistance the countries need to fulfil their duties in accordance with the IHR.
Public-privacy partnerships (PPP) in the context of biosecurity refer to collaborations between government agencies (public sector) and private companies or organizations to enhance public health preparedness in promoting biotechnology innovation, especially in the design of diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccines. The collaborative efforts include public institutions, private industry, and academia in research and development in areas of unmet needs in public health (98). Such collaborations complement the capabilities of both sectors to hasten the process of turning scientific breakthroughs into practical health solutions to increase global readiness for new infectious disease outbreaks. Example of this PPP is the Biosecurity Leadership Council (BLC) which is now renamed as the Engineering Biology Responsible Innovation Advisory Panel (RIAP) (Engineering Biology Responsible Innovation Advisory Panel - GOV.UK) plays a pivotal role in fostering public-private partnerships (PPPs) to enhance the UK’s biosecurity preparedness, GAVI, which help to increase access to immunization in low-income countries by facilitating the procurement and distribution of vaccines (99), and Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations CEPI’s whose aim is to accelerate the development of vaccines for emerging infectious diseases (100).
Global biosecurity heavily depends on the effective data sharing that will allow the timely identification of health threats and informed decisions. Privacy issues, national security, and various regulatory standards frequently constrain information exchange (101). International agreements and governance are being developed to address these challenges, ensuring that data-sharing practices are harmonised to facilitate responsible and ethical data sharing while protecting individual rights and national interests.
6 Case studies
COVID-19 demonstrated both the potential and limitations of global preparedness for health emergencies. Another strength was the record-breaking vaccine development, especially the use of mRNA platforms in the year of the outbreak (102). International organisations like COVAX tried to make vaccine distribution equitable, but still, there were inequities, and low-income countries got their vaccines much later (103). Among the weaknesses were delays in the global reporting, lack of coordination among the countries, and lack of necessary protective gear, which indicated that more resilient supply chains and greater adherence to the International Health Regulations (IHR) were required (104).
CRISPR-based diagnostics, like SHERLOCK and DETECTR, have become quick, portable, and very sensitive to detect SARS-CoV-2 and its variants (105). These technologies enabled decentralised testing, particularly in low-resource environments where traditional PCR testing facilities were scarce. Their low cost, scalability, and the ability to respond to a variety of pathogens proved their usefulness in pandemic preparedness, but there are still problems related to regulatory approval, manufacturing capacity, and field validation (50).
Predicting Ebola epidemics through the use of epidemiological, mobility, and ecological information has seen more extensive use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models (106). Table 4 summarises these predictive systems, enabling early detection of high-risk areas for resource allocation and preparedness ahead. Nevertheless, challenges include issues such as the lack of data, the need for correct mobility tracking, and the necessity of integrating predictive tools into national public health systems (107). The mRNA vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) have been successful, which is a milestone in biotechnology. Several decades of previous research, synthetic biology, and international public-private collaborations allowed them to grow fast (51). The innovation established new standards of speed in clinical trials and international regulatory collaboration. Significantly, mRNA manufacturing can be scaled, which will provide future vaccines against emerging pathogens, such as influenza, RSV, and possible pandemic threats (47).
7 Ethical, legal, and social considerations (ELSI)
New developments in synthetic biology and gain-of-function studies pose two-sided dilemmas of dual-use research, in which a study aimed at benefiting society can be used maliciously to harm individuals (108). Ethical systems focus on openness, safety of biology, and control systems, yet the management of risky studies is not balanced worldwide (108). The problem is to arrive at a compromise between the freedom of science and the prevention of bioterrorism threats. The COVID-19 pandemic revealed the existence of severe disparities in terms of access to vaccines. Even though the high-income nations gained access to early supplies, in the majority of the low-income areas, both the purchase and introduction of vaccines were delayed (109). There were efforts like the COVAX that aimed to reduce inequities, but structural barriers remained. To achieve equity, it is necessary to have decentralised vaccine manufacturing centres in Africa, Asia, and Latin America (110). Biotechnology is rapidly developing, and regulatory regimes do not keep pace. Although the experience of COVID-19 and fast-tracked approvals of vaccines showed the advantages of adaptive regulation, there are still concerns about the long-term safety and proper oversight (111). Regulatory organisations need to come up with strong, adaptable policies that embrace innovation without compromising safety or ethics. The problem of misinformation and disinformation during COVID-19 had a devastating impact on the vaccination campaigns and the people’s adherence to health measures (112). Open communication about risks, community involvement, and collaboration with trusted local leaders is necessary to address this. We should regard the establishment of trust among people as the foundation of biosecurity preparedness (113).
8 Future directions and policy recommendations
The key to the further development of global biosecurity and the preparedness for new threats is strategic foresight and consistent policy action. The future of the issues is based on strengthening international governance structures, investing in resilient and fair health systems, responsible biotechnology development, and education and civic involvement (1). Particularly the education and civic engagement are central to enhancing biosecurity and preparedness on a global scale, as well as making communities informed and engaged that can respond efficiently to the threat of a biological attack. Educational programs especially those with a focus on biosecurity and disaster preparedness increase the knowledge of people and help to encourage risk-reducing behaviors. As an example, the studies have shown that disaster preparedness education has a considerable positive impact on the resilience of the community, providing individuals with the knowledge and skills required to effectively respond to emergencies (114). Besides, civic engagement practices, including community-based disaster preparedness interventions, have been reported to increase social cohesion and collective efficacy, which are key to effective biosecurity responses (115). Moreover, the incorporation of civic education in curricula has been linked with the rise in the number of people participating in civic health programs and an enhanced responsibility to the community, which enhances the biosecurity response at the community level. All of these educational and civic engagement measures will help to create resilient societies that could effectively prevent, detect, and respond to biological threats. Effective coordination and response to any health emergencies can be achieved by reinforcing international agreements, especially the International Health Regulations, and improving compliance mechanisms. Simultaneously, to ensure early identification and efficient control of biological risks, it is critical to develop strong health systems by investing in infrastructure, developing a workforce, and building capacity. The capacity to ensure fair access to health services and technologies is key to the reduction of disparities and universal health coverage and, consequently, increases the resilience of different populations.
New biotechnologies, such as gene editing and synthetic biology, have transformative potential in the field of diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccines, but their development should be informed by strict safety measures and ethics to reduce the chances of misuse or undesirable side effects (116). It is also significant to develop a skilled and competent workforce via education and training and to develop public participation to create trust, transparency, and active participation of people in biosecurity activities (117). Collectively, these measures can help not only to make biosecurity preparedness scientifically sound but also ethically sound and socially inclusive and, therefore, to create a more resilient and secure global health environment.
9 Conclusion
The international response to the threats posed by biosecurity should no longer be a reactive response but a proactive strategy. The new technologies, including the use of AI in forecasting, diagnostics using CRISPR, and mRNA, provide prompt detection and reaction, but their usefulness requires equal access, ethical control, and powerful governance. We must strengthen health systems in resource-constrained areas and globally to promote resilience and equity. The population’s trust, open communication, and community interaction further enhance preparedness. The world can create inclusive systems that will reduce natural, accidental, and intentional biological threats and ensure a safer global health future by using scientific innovation, equity, and global cooperation.
Author contributions
MO: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – original draft. OPU: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CNU: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. FO: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DS: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CA: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. VE: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JU: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SA: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. RM: Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. EA: Formal analysis, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Miley, K. Global health biosecurity in a vulnerable world–an evaluation of emerging threats and current disaster preparedness strategies for the future In: AJ Masys, R Izurieta, and MR Ortiz, editors. Global Health security: Recognizing vulnerabilities, creating opportunities. Cham: Springer (2020). 79–102.
2. Sasani, MS. The importance of biosecurity in emerging biotechnologies and synthetic biology. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. (2024) 16:223–32. doi: 10.18502/ajmb.v16i4.16738
3. Albert, C, Baez, A, and Rutland, J. Human security as biosecurity: reconceptualizing national security threats in the time of COVID-19. Politics Life Sci. (2021) 40:83–105. doi: 10.1017/pls.2021.1
4. Beach, B, Clay, K, and Saavedra, M. The 1918 influenza pandemic and its lessons for COVID-19. J Econ Lit. (2022) 60:41–84. doi: 10.1257/jel.20201641
5. Sabra, DM, Krin, A, Romeral, AB, Frieß, JL, and Jeremias, G. Anthrax revisited: how assessing the unpredictable can improve biosecurity. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2023) 11:1215773. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1215773
6. Mayer, JD, and Lewis, ND. An inevitable pandemic: geographic insights into the COVID-19 global health emergency. Eurasian Geogr Econ. (2020) 61:404–22. doi: 10.1080/15387216.2020.1786425
7. Ostergard, RL. The West Africa Ebola outbreak (2014–2016): a health intelligence failure? In: F Lentzos, MS Goodman, and JM Wilson, editors. Health security intelligence. London: Routledge (2021). 13–28.
8. Bedi, JS, Vijay, D, Dhaka, P, Gill, JPS, and Barbuddhe, SB. Emergency preparedness for public health threats, surveillance, modelling & forecasting. Indian J Med Res. (2021) 153:287–98. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_653_21
9. Haldane, V, De Foo, C, Abdalla, SM, Jung, A-S, Tan, M, Wu, S, et al. Health systems resilience in managing the COVID-19 pandemic: lessons from 28 countries. Nat Med. (2021) 27:964–80. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01381-y
10. Nayak, J., Soni, M., Anjaria, P., and Brahmbhatt, M. N. (2025). Principles of general disease prevention and control measures. Epidemiology and environmental hygiene in veterinary public health, United Kingdom: Cham Springer 569–580.
11. Collett, SR, Smith, JA, Boulianne, M, Owen, RL, Gingerich, E, Singer, RS, et al. Principles of disease prevention, diagnosis, and control. Dis poultry. (2020) 22:1–78.
12. Contini, C, Di Nuzzo, M, Barp, N, Bonazza, A, De Giorgio, R, Tognon, M, et al. The novel zoonotic COVID-19 pandemic: an expected global health concern. J. Inf. Dev. Countries. (2020) 14:254–64. doi: 10.3855/jidc.12671
13. Wang, F, and Zhang, W. Synthetic biology: recent progress, biosafety and biosecurity concerns, and possible solutions. J Biosafety Biosecur. (2019) 1:22–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jobb.2018.12.003
14. Elgabry, M, and Johnson, S. Cyber-biological convergence: a systematic review and future outlook. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2024) 12:1456354. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1456354
15. de Smit, MH, and van Duin, J. Secondary structure of the ribosome binding site determines translational efficiency: a quantitative analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (1990) 87:7668–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7668
16. Ajikumar, PK, Xiao, W-H, Tyo, KEJ, Wang, Y, Simeon, F, Leonard, E, et al. Isoprenoid pathway optimization for Taxol precursor overproduction in Escherichia coli. Science. (2010) 330:70–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1191652
17. Hewett, JP, Wolfe, AK, Bergmann, RA, Stelling, SC, and Davis, KL. Human health and environmental risks posed by synthetic biology R&D for energy applications: a literature analysis. Applied Biosafety. (2016) 21:177–84. doi: 10.1177/1535676016672377
18. El-Mounadi, K, Morales-Floriano, ML, and Garcia-Ruiz, H. Principles, applications, and biosafety of plant genome editing using CRISPR-Cas9. Front Plant Sci. (2020) 11:56. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00056
19. Yin, H, Song, C-Q, Suresh, S, Kwan, S-Y, Wu, Q, Walsh, S, et al. Partial DNA-guided Cas9 enables genome editing with reduced off-target activity. Nat Chem Biol. (2018) 14:311–6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2559
20. Zhang, Q, Xing, H-L, Wang, Z-P, Zhang, H-Y, Yang, F, Wang, X-C, et al. Potential high-frequency off-target mutagenesis induced by CRISPR/Cas9 in Arabidopsis and its prevention. Plant Mol Biol. (2018) 96:445–56. doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0709-x
21. Regalado, A. 2016. Top US intelligence official calls gene editing a WMD threat. US: MIT technology review.
23. Elgabry, M, Nesbeth, D, and Johnson, SD. A systematic review of the criminogenic potential of synthetic biology and routes to future crime prevention. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2020) 8:571672. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.571672
24. Tin, D, Sabeti, P, and Ciottone, GR. Bioterrorism: an analysis of biological agents used in terrorist events. Am J Emerg Med. (2022) 54:117–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2022.01.056
25. Kolavic, SA, Kimura, A, Simons, SL, Slutsker, L, Barth, S, and Haley, CE. An outbreak of Shigella dysenteriae type 2 among laboratory workers due to intentional food contamination. JAMA. (1997) 278:396–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.1997.03550050058034
26. Janik, E, Ceremuga, M, Saluk-Bijak, J, and Bijak, M. Biological toxins as the potential tools for bioterrorism. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1181. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051181
27. Walsh, TR, Gales, AC, Laxminarayan, R, and Dodd, PC. Antimicrobial resistance: addressing a global threat to humanity. PLoS Med. (2023) 20:e1004264. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004264
28. Ferraz, MP. Antimicrobial resistance: the impact from and on society according to one health approach. Soc Sci. (2024) 14:187. doi: 10.3390/soc14090187
29. WHO. Global report on infection prevention and control 2024. Geneva: World Health Organization (2024).
30. WHO. Global antimicrobial resistance and use surveillance system (GLASS) report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization (2022).
31. Aslam, B, Asghar, R, Muzammil, S, Shafique, M, Siddique, AB, Khurshid, M, et al. AMR and sustainable development goals: at a crossroads. Glob Health. (2024) 20:73. doi: 10.1186/s12992-024-01046-8
32. Ciotti, M, Angeletti, S, Minieri, M, Giovannetti, M, Benvenuto, D, Pascarella, S, et al. COVID-19 outbreak: an overview. Chemotherapy. (2020) 64:215–23. doi: 10.1159/000507423
33. Fakhriansyah, M, and Kurniawati, K. Asian flu pandemic in Indonesia, 1957: government and public response. Indonesian Historical Stu. (2024) 8:128–43. doi: 10.14710/ihis.v8i2.15045
34. Gavrilova, NS, and Gavrilov, LA. Patterns of mortality during pandemic: an example of Spanish flu pandemic of 1918. Population Econ. (2020) 4:56–64. doi: 10.3897/popecon.4.e53492
35. Kamorudeen, RT, Adedokun, KA, and Olarinmoye, AO. Ebola outbreak in West Africa, 2014–2016: epidemic timeline, differential diagnoses, determining factors, and lessons for future response. J Infect Public Health. (2020) 13:956–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.03.014
36. Quinn, TC. Forty years of AIDS: a retrospective and the way forward. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:196. doi: 10.1172/JCI154196
37. Wu, Z, Harrich, D, Li, Z, Hu, D, and Li, D. The unique features of SARS-CoV-2 transmission: comparison with SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza virus. Rev Med Virol. (2021) 31:e2171. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2171
38. Othman, R, Elabd, H, Pratiwy, FM, Barzkar, N, Lim, L-S, and Rodrigues, KF. Biosecurity in aquaculture: nurturing health and ensuring sustainability In: NM Faudzi, MD Shah, N Mazlan, and SRM Shaleh, editors. Essentials of aquaculture practices. Cham: Springer (2024). 139–82.
39. Tang, Q, Yan, F, Yuan, L, Tang, Y, Chen, H, Sun, Y, et al. Enhancing laboratory biosafety management: a comprehensive strategy from theory to practice. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1439051. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1439051
40. Niang, M, Dupéré, S, Alami, H, and Gagnon, M-P. Why is repositioning public health innovation towards a social paradigm necessary? A reflection on the field of public health through the examples of Ebola and Covid-19. Glob Health. (2021) 17:46. doi: 10.1186/s12992-021-00695-3
41. Piret, J, and Boivin, G. Pandemics throughout history. Front Microbiol. (2021) 11:631736. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.631736
42. Altheide, ST. Biochemical and culture-based approaches to identification in the diagnostic microbiology laboratory. Am Soc Clin Lab Sci. (2019) 32:166–75. doi: 10.29074/ascls.2019001875
43. Peeling, RW, Wedderburn, CJ, Garcia, PJ, Boeras, D, Fongwen, N, Nkengasong, J, et al. Serology testing in the COVID-19 pandemic response. Lancet Infect Dis. (2020) 20:e245–9. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30517-X
44. Tosta, S, Moreno, K, Schuab, G, Fonseca, V, Segovia, FMC, Kashima, S, et al. Global SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance: what we have learned (so far). Infect Genet Evol. (2023) 108:105405. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2023.105405
45. Kambouris, ME. Culturomics: the alternative from the past In: CS Parello, editor. Microbiomics. New York, NY: Elsevier (2020). 155–73.
46. Wang, H, Ceylan Koydemir, H, Qiu, Y, Bai, B, Zhang, Y, Jin, Y, et al. Early detection and classification of live bacteria using time-lapse coherent imaging and deep learning. Light Sci Appl. (2020) 9:118. doi: 10.1038/s41377-020-00358-9
47. Li, M, Wang, H, Tian, L, Pang, Z, Yang, Q, Huang, T, et al. COVID-19 vaccine development: milestones, lessons and prospects. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:146. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00996-y
48. Bloom, DE, and Cadarette, D. Infectious disease threats in the twenty-first century: strengthening the global response. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:549. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00549
49. Ferreira, FJN, and Carneiro, AS. AI-driven drug discovery: a comprehensive review. ACS Omega. (2025) 10:23889–903. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00549
50. Kaminski, MM, Abudayyeh, OO, Gootenberg, JS, Zhang, F, and Collins, JJ. CRISPR-based diagnostics. Nat Biomed Eng. (2021) 5:643–56. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00760-7
51. Chandra, S, Wilson, JC, Good, D, and Wei, MQ. mRNA vaccines: a new era in vaccine development. Oncol Res. (2024) 32:1543–64. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.043987
52. Zhang, Q, Cheng, J, Hou, J, Su, Y, Li, L, Tong, L, et al. Synthetic biology-inspired development of live attenuated influenza vaccines. NPJ Vaccines. (2025) 10:204. doi: 10.1038/s41541-025-01255-1
53. Song, K, Ji, H, Lee, J, Jang, G, and Yoon, Y. Engineered Ttg R-based whole-cell biosensors for quantitative and selective monitoring of bioactive compounds. Biosensors. (2025) 15:554. doi: 10.3390/bios15080554
54. Zhao, Z, Ma, Y, Mushtaq, A, Rajper, AMA, Shehab, M, Heybourne, A, et al. Applications of robotics, artificial intelligence, and digital technologies during COVID-19: a review. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. (2022) 16:1634–44. doi: 10.1017/dmp.2021.9
55. Adeniyi, JK, Ajagbe, SA, Adeniyi, AE, Adeyanju, KI, Afolorunso, AA, Adigun, MO, et al. A blockchain-based smart healthcare system for data protection. IScience. (2025) 28:112109. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112109
56. Elgabry, M, Nesbeth, D, Ekblom, P, and Johnson, S. BAKE: a novel framework for iterative security design for identifying criminally-exploitable vulnerabilities in biotechnology products. Crime Sci. (2025) 14:16. doi: 10.1186/s40163-025-00256-8
57. Elgabry, M. Towards cyber-biosecurity by design: an experimental approach to internet-of-medical-things design and development. Crime Sci. (2023b) 12:1–5. doi: 10.1186/s40163-023-00181-8
58. Harnal, S, Sharma, G, Malik, S, Kaur, G, Simaiya, S, Khurana, S, et al. Current and future trends of cloud-based solutions for healthcare. IBCFHA. (2023) 22:115–36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-22959-6_7
59. Elgabry, M. Biocrime, the internet-of-ingestible-things and cyber-biosecurity In: D Greenbaum, editor. Cyberbiosecurity: A new field to Deal with emerging threats. Cham: Springer (2023a). 135–46.
60. Kraemer, MUG, Tsui, JL-H, Chang, SY, Lytras, S, Khurana, MP, Vanderslott, S, et al. Artificial intelligence for modelling infectious disease epidemics. Nature. (2025) 638:623–35. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08564-w
61. Ye, Y, Pandey, A, Bawden, C, Sumsuzzman, DM, Rajput, R, Shoukat, A, et al. Integrating artificial intelligence with mechanistic epidemiological modeling: a scoping review of opportunities and challenges. Nat Commun. (2025) 16:581. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55461-x
62. Adegboye, O., Arowosegbe, O. B., and Prosper, O. (2024). AI optimized supply chain mapping for green energy storage systems: predictive risk Modeling under geopolitical and climate shocks. International Journal of Advance Research Publication and Reviews. (2024) 1:63–86.
63. El Morr, C, Ozdemir, D, Asdaah, Y, Saab, A, El-Lahib, Y, and Sokhn, ES. AI-based epidemic and pandemic early warning systems: a systematic scoping review. Health Informatics J. (2024) 30:14604582241275844. doi: 10.1177/14604582241275844
64. Oude Munnink, BB, Worp, N, Nieuwenhuijse, DF, Sikkema, RS, Haagmans, B, Fouchier, RAM, et al. The next phase of SARS-CoV-2 surveillance: real-time molecular epidemiology. Nat Med. (2021) 27:1518–24. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01472-w
65. Zahra, A, Shahid, A, Shamim, A, Khan, SH, and Arshad, MI. The SHERLOCK platform: an insight into advances in viral disease diagnosis. Mol Biotechnol. (2023) 65:699–714. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00625-7
66. Ghouneimy, A, Mahas, A, Marsic, T, Aman, R, and Mahfouz, M. CRISPR-based diagnostics: challenges and potential solutions toward point-of-care applications. ACS Synth Biol. (2022) 12:1–16. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.2c00496
67. Hassan, YM, Mohamed, AS, Hassan, YM, and El-Sayed, WM. Recent developments and future directions in point-of-care next-generation CRISPR-based rapid diagnosis. Clin Exp Med. (2025) 25:33. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01540-8
68. Fallatah, DI, and Adekola, HA. Digital epidemiology: harnessing big data for early detection and monitoring of viral outbreaks. Inf Prev Prac. (2024) 6:100382. doi: 10.1016/j.infpip.2024.100382
69. Zang, S, Zhang, X, Xing, Y, Chen, J, Lin, L, and Hou, Z. Applications of social media and digital technologies in COVID-19 vaccination: scoping review. J Med Internet Res. (2023) 25:e40057. doi: 10.2196/40057
70. Pillay, TS. Increasing the impact and value of laboratory medicine through effective and AI-assisted communication. EJIFCC. (2025) 36:12
71. Litchfield, I, Shukla, D, and Greenfield, S. Impact of COVID-19 on the digital divide: a rapid review. BMJ Open. (2021) 11:e053440. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053440
72. Lesperance, W. The National Biosurveillance Integration Center (NBIC) In: SN Romaniuk, MS Catino, and CA Martin, editors. The handbook of homeland security. London: CRC Press (2023). 147–51.
73. Kadri, SS. Key takeaways from the US CDC’S 2019 antibiotic resistance threats report for frontline providers. Crit Care Med. (2020) 48:939–45. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004371
74. Shi, T., Gu, X., Meza-Torres, B., Agrawal, U., Anand, S., and Ordonez-Mena, J. (2024). A public health response to pathogen X: safeguarding communities through frameworks for emerging epidemics and pandemics. UK Health Security Agency. University of Oxford Repository. Avaliable online at: https://ora.ox.ac.uk/objects/uuid:df160b32-4ac2-4277-975a-9ba2c263fcf5/files/sd217qr37t
75. Eckmanns, T, Füller, H, and Roberts, SL. Digital epidemiology and global health security; an interdisciplinary conversation. Life Sci. Soc. Policy. (2019) 15:2. doi: 10.1186/s40504-019-0091-8
76. Rzymski, P, Szuster-Ciesielska, A, Dzieciątkowski, T, Gwenzi, W, and Fal, A. mRNA vaccines: the future of prevention of viral infections? J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e28572. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28572
77. Leong, KY, Tham, SK, and Poh, CL. Revolutionizing immunization: a comprehensive review of mRNA vaccine technology and applications. Virol J. (2025) 22:71. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02645-6
78. Invenção, MCV, Macêdo, LS, Moura, IA, Santos, LAB d O, Espinoza, BCF, Pinho, SS, et al. Design and immune profile of multi-epitope synthetic antigen vaccine against SARS-coV-2: an in silico and in vivo approach. Vaccine. (2025) 13:149. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13020149
79. Justiz-Vaillant, A, Pandit, BR, Unakal, C, Vuma, S, and Akpaka, PE. A comprehensive review about the use of monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Antibodies. (2025) 14:35. doi: 10.3390/antib14020035
80. Mohammed, A, and Muustafa, MI. Nanobodies: a new frontier in antiviral therapies. SLAS Discovery. (2025) 35:100251. doi: 10.1016/J.SLASD.2025.100251
81. Wan, Z, Sun, X, Li, Y, Chu, T, Hao, X, Cao, Y, et al. Applications of artificial intelligence in drug repurposing. Advanced Sci. (2025) 12:e2411325. doi: 10.1002/advs.202411325
82. Kearns, M, Li, M, and Williams, AJ. Protein–glycan engineering in vaccine design: merging immune mechanisms with biotechnological innovation. Trends Biotechnol. (2025). doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2025.06.022
83. Hemdan, M, Ali, MA, Doghish, AS, Mageed, SSA, Elazab, IM, Khalil, MM, et al. Innovations in biosensor technologies for healthcare diagnostics and therapeutic drug monitoring: applications, recent progress, and future research challenges. Sensors. (2024) 24:5143. doi: 10.3390/s24165143
84. Yu, X, Li, H, Wang, J, Zhang, X, Jiao, R, Ren, Y, et al. Recent advances and future prospects of wearable sensors based on nanomaterial sensing mechanisms for biosafety monitoring. Chem Eng J. (2025) 512:162695. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2025.162695
85. Ou, G, Tang, Y, Liu, J, Hao, Y, Chen, Z, Huang, T, et al. Automated robot and artificial intelligence-powered wastewater surveillance for proactive mpox outbreak prediction. Biosafety Health. (2024) 6:225–34. doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2024.07.002
86. De Luca, PB, Nagy, J, and Macario, A. Nanomaterials used in the preparation of personal protective equipment (PPE) in the fight against SARS-CoV-2. Inorganics. (2023) 11:294. doi: 10.3390/inorganics11070294
87. Varma, P, Senapati, JN, Sharma, V, and Choudhary, AS. Technological advancements in personal protective equipment: a future perspective. Health Leadership Quality of Life. (2022) 1:52. doi: 10.56294/hl2022136
88. Levine, C., and Marshall, K. (2024). Planning for the next infectious disease threat: Considerations to ensure every facility is prepared Institute for Homeland Security
89. Beć, KB, Grabska, J, Bonn, GK, Popp, M, and Huck, CW. Principles and applications of vibrational spectroscopic imaging in plant science: a review. Front Plant Sci. (2020) 11:1226. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01226
90. Hasan, K, Chowdhury, MJM, Biswas, K, Ahmed, K, Islam, MS, and Usman, M. A blockchain-based secure data-sharing framework for software defined wireless body area networks. Comput Netw. (2022) 211:109004. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2022.109004
91. Hynek, N. Synthetic biology/AI convergence (SynBioAI): security threats in frontier science and regulatory challenges. AI & Soc. (2025) 22:1–18. doi: 10.1007/s00146-025-02576-4
92. Vindman, C, Trump, B, Cummings, C, Smith, M, Titus, AJ, and Oye, K. The convergence of AI and synthetic biology: the looming deluge. npj Biomed. Innov. (2025) 2:20. doi: 10.1038/s44385-025-00021-1
93. Orro, A, Geminiani, GA, Sicurello, F, Modica, M, Pegreffi, F, Neri, L, et al. A cloud infrastructure for health monitoring in emergency response scenarios. Sensors. (2024) 24:6992. doi: 10.3390/s24216992
95. Saleem, H, Jiandong, W, Aldakhil, AM, Nassani, AA, Abro, MMQ, Zaman, K, et al. Socio-economic and environmental factors influenced the United Nations healthcare sustainable agenda: evidence from a panel of selected Asian and African countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. (2019) 26:14435–60. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04692-3
96. Aginam, O. Regional cooperation for health In: P De Lombaerde, editor. Handbook of regional cooperation and integration. New York, NY: Edward Elgar Publishing (2024). 311–25.
97. Burci, GL. The legal response to pandemics: the strengths and weaknesses of the international health regulations. J Int Humanit Leg Stud. (2020) 11:204–17. doi: 10.1163/18781527-01102003
98. Vaudano, E. The innovative health initiative public–private partnership: a catalyst for big data-driven health research and innovation. Front Med. (2025) 12:1554948. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1554948
99. Dadari, I, Higgins-Steele, A, Sharkey, A, Charlet, D, Shahabuddin, A, Nandy, R, et al. Pro-equity immunization and health systems strengthening strategies in select Gavi-supported countries. Vaccine. (2021) 39:2434–44. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.03.044
100. Halabi, S, Gostin, LO, Aneja, K, Nardi, F, Gottschalk, K, and Monahan, J. The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) and the partnerships of equitable vaccine access. J Law Med Ethics. (2023) 51:234–46. doi: 10.1017/jme.2023.85
101. Rehm, HL, Page, AJH, Smith, L, Adams, JB, Alterovitz, G, Babb, LJ, et al. GA4GH: international policies and standards for data sharing across genomic research and healthcare. Cell Genom. (2021) 1:100029. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2021.100029
102. Verbeke, R, Cheng, MHY, and Cullis, PR. A historical overview on mRNA vaccine development In: J Fischer, C Klein, and WE Childers, editors. Trends in MRNA vaccine research. London: John Wiley & Sons (2025). 1–27.
103. Mathieu, E, Ritchie, H, Ortiz-Ospina, E, Roser, M, Hasell, J, Appel, C, et al. A global database of COVID-19 vaccinations. Nat Hum Behav. (2021) 5:947–53. doi: 10.1038/s41562-021-01122-8
104. Manish, J. Beyond Borders: rethinking Global Health governance in a post-pandemic world In: SK Singh, editor. Intersecting realities of health resilience and governance in India: Emerging domestic and global perspectives. Cham: Springer (2025). 35–54.
105. Ackerman, CM, Myhrvold, C, Thakku, SG, Freije, CA, Metsky, HC, Yang, DK, et al. Massively multiplexed nucleic acid detection with Cas13. Nature. (2020) 582:277–82. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2279-8
106. Soni, U, and Gupta, N. An artificial intelligence approach for forecasting Ebola disease. J Phys Conf Ser. (2021) 1950:012038. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1950/1/012038
107. Sarumi, O. A. (2020). “Machine learning-based big data analytics framework for ebola outbreak surveillance,” in International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, 580–589.
108. Magdalena Guraiib, M, Ross, AL, Frewer, A, Sprumont, D, Shamsi Gooshki, E, Dzenowagis, J, et al. Oversight of dual-use research: what role for ethics committees? Health Security. (2024) 22:281–93. doi: 10.1089/hs.2023.0095
109. de Bengy Puyvallée, A, and Storeng, KT. COVAX, vaccine donations and the politics of global vaccine inequity. Glob Health. (2022) 18:26. doi: 10.1186/s12992-022-00801-z
110. Thompson, LJR, Grubo, M, Veller, M, Badenhorst, RH, Nott, J, Debruyne, L, et al. Building global vaccine manufacturing capacity: spotlight on Africa. Vaccine. (2023) 41:4050–6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.05.009
111. Beretta, G, and Marelli, L. Fast-tracking development and regulatory approval of COVID-19 vaccines in the EU: a review of ethical implications. Bioethics. (2023) 37:498–507. doi: 10.1111/bioe.13151
112. Caceres, MMF, Sosa, JP, Lawrence, JA, Sestacovschi, C, Tidd-Johnson, A, Rasool, MHUI, et al. The impact of misinformation on the COVID-19 pandemic. AIMS Public Health. (2022) 9:262. doi: 10.3934/publichealth.2022018
113. Vergara, RJD, Sarmiento, PJD, and Lagman, JDN. Building public trust: a response to COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy predicament. J Public Health. (2021) 43:e291–2. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdaa282
114. Guo, L, Fang, M, Liu, L, Chong, H, Zeng, W, and Hu, X. The development of disaster preparedness education for public: a scoping review. BMC Public Health. (2025) 25:1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21664-0
115. Whittaker, S, Khalfan, MMA, and UlHaq, I. Developing community disaster resilience through preparedness. Int J Crit Infrastruct. (2020) 16:53–76. doi: 10.1504/IJCIS.2020.105411
116. Lee, HL, and Vavitsas, K. Driving innovation in biotechnology with private-public partnerships: a Singapore perspective. Biotechnol. Notes. (2021) 2:59–62. doi: 10.1016/j.biotno.2021.10.001
117. Elgabry, M. What is the art of biosecurity? Res Directions Biotechnol Design. (2023c) 1:e11. doi: 10.1017/btd.2023.6
118. Blendon, RJ, DesRoches, CM, Benson, JM, Herrmann, MJ, Taylor-Clark, K, and Weldon, KJ. The public and the smallpox threat. N Engl J Med. (2003) 348:426–32. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa023184
119. Nelson, C, Kugeler, K, Petersen, J, and Mead, P. Tularemia—United States, 2001–2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2013) 62:963.
120. Flora, SJS. Biological warfare agents: history and modern-day relevance In: SJS Flora and V Pachauri, editors. Handbook on biological warfare preparedness. New York, NY: Elsevier (2020). 1–11.
121. Zajaczkowski, W, Bojarska, E, Furtak, E, Bijak, M, Szelenberger, R, Niemcewicz, M, et al. Ricin and abrin in biosecurity: detection technologies and strategic responses. Toxins. (2025) 17:494. doi: 10.3390/toxins17100494
122. Drambarean, L. Searching for a purpose in post-war Japan: Aum Shinrikyo’s ideological and cultural origins. Columbus, OH: Ohio State University (2023).
123. Turner, MD, Marinconz, K, and Shimp, G. The 1984 Rajneeshee bioterrorism attack: an example of biological warfare by violent non-state actors. Cureus. (2025) 17:88514. doi: 10.7759/cureus.88514
Keywords: biosecurity threats, global health preparedness, antimicrobial resistance, digital health, surveillance systems, global collaboration
Citation: Okon MB, Ugwu OP, Ugwu CN, Ogenyi FC, Swase DT, Anyanwu CN, Eze VHU, Ugwu JN, Akinola SA, Mujinya R and Anyanwu EG (2025) From pandemics to preparedness: harnessing AI, CRISPR, and synthetic biology to counter biosecurity threats. Front. Public Health. 13:1711344. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1711344
Edited by:
Oluwafemi Balogun, Massachusetts General Hospital, United StatesReviewed by:
Mariam Elgabry, Bronic Ltd, United KingdomKripa Nand, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, United States
Copyright © 2025 Okon, Ugwu, Ugwu, Ogenyi, Swase, Anyanwu, Eze, Ugwu, Akinola, Mujinya and Anyanwu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Michael Ben Okon, YmVuLm9rb25Aa2l1LmFjLnVn
 Michael Ben Okon
Michael Ben Okon Okechukwu Paul-Chima Ugwu2
Okechukwu Paul-Chima Ugwu2 Chinyere Nneoma Ugwu
Chinyere Nneoma Ugwu Dominic Terkimbi Swase
Dominic Terkimbi Swase Saheed Adekunle Akinola
Saheed Adekunle Akinola Regan Mujinya
Regan Mujinya