Due to a production error, there was a mistake in Figures 3–9 as published. The images were inserted in the incorrect order and did not match the respective captions. The corrected Figures 3–9 appear below.
FIGURE 3

FEM simulation of the stress distribution of LISPER with a pressure range from 10 kPa to 65 kPA. Note: The c-shaped brace is hidden on the image for clear demonstration.
FIGURE 4

(A, D) Comparison between modelings and experimental bending angle for LISPER and SCASPER, respectively. (B, E) Comparison between analytical model-based prediction, FEA, and experiment on Pressure vs. Force and Pressure vs. Torque of LISPER and SCASPER under different fixed angles. (C, F) Comparison between the PID model-free controller and the model-based position controller applied to the elbow and shoulder, respectively.
FIGURE 5
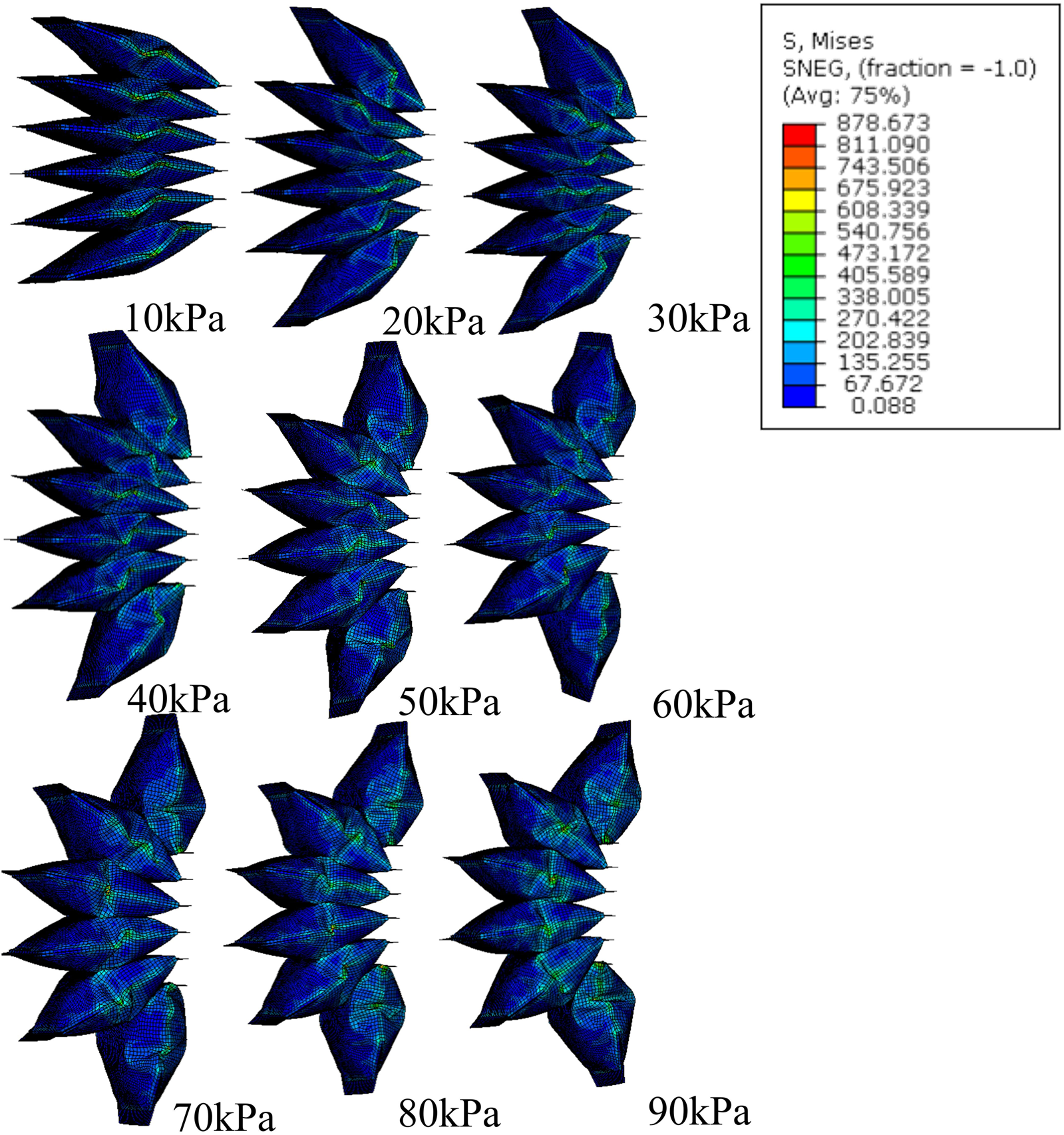
FEM simulation of stress distribution of SCASPER with pressure range from 10 kPa to 90 kPa.
FIGURE 6
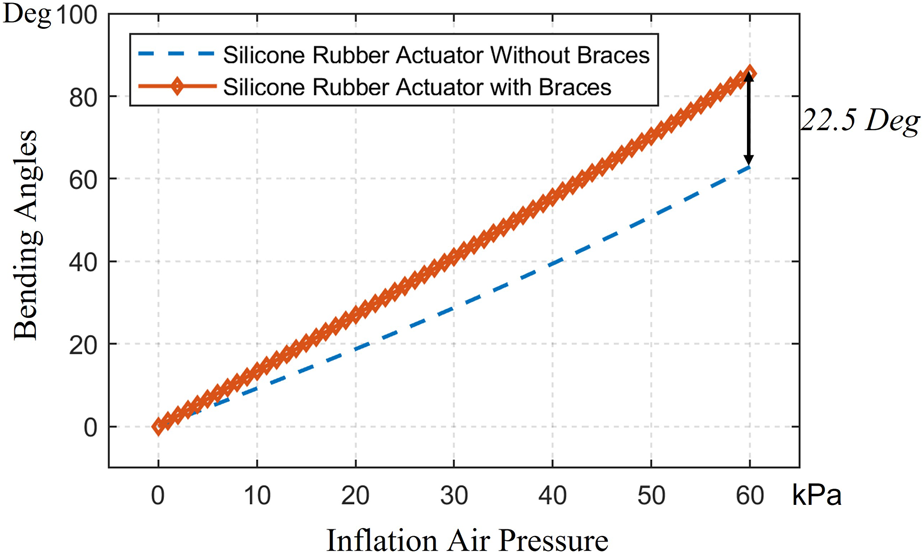
The comparison in the simulation of LISPER with and without c-shaped braces.
FIGURE 7

The comparison of LISPER actuator with or without braces at 65 kPa pressure input. Figure (A) is LISPER without braces and Figure (B) is with braces.
FIGURE 8

Geometric diagram of LISPER. (A) The sectional view of the silicone rubber body. The outer ring section is constrained by PLA rings, the inner ring is the smallest contour of each bellow segment. (A1) The zoomed-in view of three pieces of bellow segments. (B) The labeling of three sections of small ring, arc, wall, and base. (C) Dimension labeling of the inner ring before inflation. (D) Dimension labeling of the inner ring after inflation. (F) Equivalent center of gravity and equivalent moment of arm. (G) Side view of the base section when it is bent.
FIGURE 9
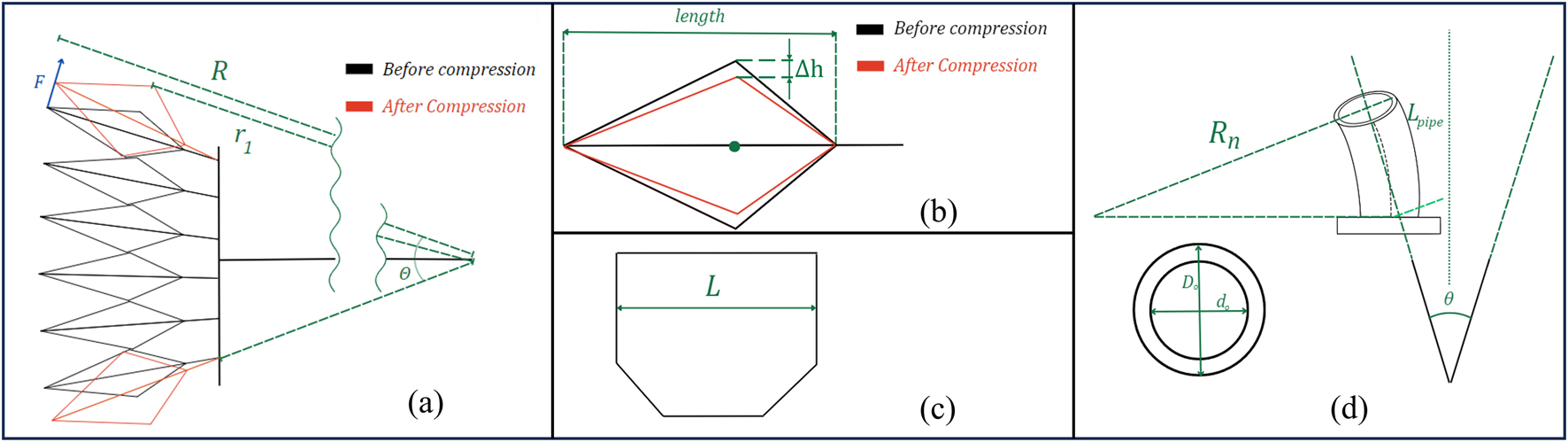
Geometric diagram of SCASPER. (A) The geometric labeling of SCASPER before and after compressed. F is the force output r1 is the moment of the arm from the contact point between the airbags to the center of rotation. (B) The sectional view of one airbag before and after compression from the environment. (C) The width of each airbag from the top view. (D) The geometric labeling of the PU pipe when they are bent.
The publisher apologizes for this mistake. The original version of this article has been updated.
Summary
Keywords
index terms-pneumatic soft actuators, bio-inspired design, analytical modeling, wearable devices, exoskeleton
Citation
Frontiers Production Office (2024) Erratum: Novel bio-inspired soft actuators for upper-limb exoskeletons: design, fabrication and feasibility study. Front. Robot. AI 11:1517037. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1517037
Received
25 October 2024
Accepted
25 October 2024
Published
13 November 2024
Approved by
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, Switzerland
Volume
11 - 2024
Updates
Copyright
© 2024 Frontiers Production Office.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Frontiers Production Office, production.office@frontiersin.org
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.