- 1School of Ocean and Civil Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 2School of Mechanical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Industrial terminal assembly tasks are often repetitive and involve handling components with tight tolerances that are susceptible to damage. Learning an effective terminal assembly policy in real-world is challenging, as collisions between parts and the environment can lead to slippage or part breakage. In this paper, we propose a safe reinforcement learning approach to develop a visuo-tactile assembly policy that is robust to variations in grasp poses. Our method minimizes collisions between the terminal head and terminal base by decomposing the assembly task into three distinct phases. In the first grasp phase,a vision-guided model is trained to pick the terminal head from an initial bin. In the second align phase, a tactile-based grasp pose estimation model is employed to align the terminal head with the terminal base. In the final assembly phase, a visuo-tactile policy is learned to precisely insert the terminal head into the terminal base. To ensure safe training, the robot leverages human demonstrations and interventions. Experimental results on PLC terminal assembly demonstrate that the proposed method achieves 100% successful insertions across 100 different initial end-effector and grasp poses, while imitation learning and online-RL policy yield only 9% and 0%.
1 Introduction
Terminal assembly (McKee et al., 1985) is a precision manipulation task that involves part-to-part contact. Its four key sub-tasks—part feeding, object reorientation, peg insertion, and terminal buckling—have been widely investigated (McKee et al., 1985; Goldberg, 1993; Lozano-Pérez, 1986; Lozano-Perez et al., 1984; Natarajan, 1989). Early research primarily focused on mechanical design aspects (Lozano-Pérez, 1986; Natarajan, 1989) and motion planning strategies (Goldberg, 1993; Lozano-Perez et al., 1984; Qiao et al., 1995). With the aid of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), the assembly sequence can be pre-defined in simulation using accurate pose information (De Mello and Sanderson, 1989), enabling robots to plan the required actions for executing the assembly (Koga et al., 2022). Recently, reinforcement learning (RL)-based approaches have demonstrated potential in handling assembly tasks involving parts with complex geometries (Wen et al., 2022; Lian et al., 2021). However, RL remains challenging due to the requirement for frequent human inputs during learning (Luo et al., 2021) or high-precision sensors for collecting training data (Wen et al., 2022). Meanwhile, because the terminal head has the characteristics of irregular shape, easy damage, there is also a need for a safe training and data collection method for learning assembly tasks.
Another challenge in terminal assembly tasks is that the precise initial pose of the terminal is often unknown. Since the grasped object is frequently visually occluded by the gripper, tactile sensing provides a more effective means for grasp pose estimation (Okumura et al., 2022; Dang et al., 2023). Although recent advances have demonstrated improved simulation accuracy for industrial insertion tasks (Narang et al., 2022), and successful Sim2Real transfer has been achieved for tactile-based insertion tasks (Kelestemur et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022), simulating soft contacts between tactile sensors and objects with complex geometries remains an open challenge (Wang et al., 2021). This issue often hinders real-world transfer, as accurate object models are rarely publicly available. Additionally, a major obstacle in applying reinforcement learning (RL) to real-world terminal assembly tasks involving tactile feedback is the frequent slippage of parts caused by environmental collisions and the inherently smooth surface of the tactile sensor’s gel pad. Such slippage makes it difficult for RL methods to succeed without human intervention or the use of a dedicated pose estimation algorithm to detect and correct misalignments.
In this work, we present a novel method to safely learn visuo-tactile feedback policies in real for terminal assembly tasks under grasp pose uncertainties, with inexpensive off-the-shelf sensors. Our approach draws on tactile and visual feedback to deal with the uncertainty of grasp pose and a safe RL training procedure, minimizing damage during the training phase. We use Sample-Efficient Robotic reinforcement Learning (SERL) (Luo et al., 2024), a software suite that provides a well-designed foundation for robotic RL, to develop a data collection and training pipeline that minimizes collision between the part and its environment.
The whole pipeline can be divided into three steps: First, Training Reward Classifier: Labeling visual and tactile images from human instruction instances to train a reward classifier to decide when to give policy rewards throughout the RL training process. Second, Recording Demonstrations: To accelerate training, record a predetermined number of human-operated robot demonstrations to finish terminal assembly. This will serve as a demo buffer for RL. Third, Policy Training: Using the trained reward classifier and recorded demonstrations to complete the task training (during training, human interventions can be added to avoid collisions and speed up the training).
The main contributions of this paper are as follows: the development of a policy for complex terminal assembly in real-world scenarios, which leverages visual and tactile information through reinforcement learning and can be acquired in less than 60 min; the introduction of a safe exploratory strategy for reinforcement learning, accompanied by a secure data collection methodology grounded in a designated manual remote operation technique; and the presentation of experimental findings that indicate the policy attains a success rate of 100 out of 100 in Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) terminal assembly, thereby surpassing two baseline approaches that recorded success rates of 0 out of 100 and nine out of 100, respectively.
2 Related work
For many years, terminal assembly has been an essential part of robotics. The parts’ fragility, the moderate force during terminal buckling, the occlusions caused by the robot gripper, the grasp uncertainty from the acquisition process and its collision with the environment, and the precision required to control the robot for insertion render the task challenging. Early work approached this problem using CAD information to infer desired assembly sequences (De Mello and Sanderson, 1989) and generating designs of part feeders based on object geometry (Natarajan, 1989). Other work approached the problem from an algorithmic design perspective, with a focus on developing motion planning strategies for peg insertion (Lozano-Pérez, 1986; Qiao et al., 1995).
Recently, learning-based methods have shown success on this task. This includes learning assembly policies with a physical robot via Sim2Real transfer (Johannink et al., 2019), online adaptation with meta-learning (Schoettler et al., 2020b; Zhao et al., 2022), reinforcement learning (Luo et al., 2021; Schoettler et al., 2020a), self-supervised data collection with impedance control (Spector and Di Castro, 2021), accurate state estimation (Wen et al., 2022), or decomposing the assembly algorithm into a residual policy that relies on conventional feedback control (Johannink et al., 2019). These approaches assume that the parts are grasped with a fixed pose. To overcome this assumption, Wen et al. (Wen et al., 2022) perform accurate pose estimation and motion tracking with a high-precision depth camera and use a behavioral cloning algorithm to insert the part. Spector et al. (Spector and Di Castro, 2021; Spector et al., 2022) proposed Insertionnet for industrial assembly, which requires contact between the part and the environment to occur during data collection, a process that is expensive and often impractical for fragile parts. Ozalp et al. (2024) made advancements in deep RL and inverse RL for robotic manipulation. In comparison, we use inexpensive tactile sensors and a safe human-guided data collection and RL procedure that does not require such contact.
In systems using only visual perception, grasped parts are often visually occluded by the gripper, and changes in environment light can affect the accuracy of visual recognition. However, tactile perception is not affected by these factors: the camera of the tactile sensor is placed inside the body, so the collected tactile images will not be blocked by itself or environmental objects; the light source for tactile images is a built-in LED strip, so the image brightness, color, etc. are also not affected by environment light. Meanwhile, tactile images contain rich physical information such as object geometric features, contact force, contact deformation, and displacement. Based on this information, the system can achieve more precise contact control. Therefore, tactile feedback can be an alternative sensing modality for grasp pose estimation. Recent work uses tactile images from vision-based tactile sensors such as GelSight (Yuan et al., 2017), DIGIT (Lambeta et al., 2020) and GelSlim3.0 (Taylor et al., 2022) to estimate the relative pose and 3D motion field between grasped objects and tactile grippers. Meanwhile, many new types of tactile fingers (DexiTac (Lu et al., 2024)) and tactile sensors (Evetac (Funk et al., 2024)) are being applied in robotic operations. Li et al. (Li et al., 2014) use Gelsight sensors, BRISK features and RANSAC to estimate grasp pose. Gelsight produces high-quality 3D tactile images and can determine depth imprint, which improves feature detection by isolating the object from the background. DIGIT, a more affordable tactile sensor, provides a 2D RGB image but not the light incident direction (to generate the depth image). Liu et al. (2024) develops a method to reconstruct 3-D tactile motion field in real-time, that can provide rich tactile information (such as contact force) and serve as the foundation for many downstream tasks. Kelestemur et al. (2022) generates tactile image data in simulation for pose estimation of bottle caps but simulating contact and physical interaction between tactile sensors and objects with more intricate geometry is still challenging (Wang et al., 2021). In this work, we combine tactile images from a real-world PLC terminal with reinforcement learning process as part of observation. By means of contact tactile information analysis, these images enable the policy to precisely locate the terminal base and so try to minimize the contact force needed for terminal buckling.
Most prior work on tight tolerance assembly tasks (Wen et al., 2022; Li et al., 2014; Fan et al., 2019; Florence et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2025; Lin et al., 2024) leverages a single modality, such as vision, tactile, or force-torque, limiting the accuracy of the system due to occlusion, perspective effect, and sensory inaccuracy. Multi-modal systems have been explored to improve the robustness of automated insertion. Spector and Di Castro (2021), Spector et al. (2022) use RGB cameras and a force-torque sensor for learning contact and impedance control. Chaudhury et al. (2022) couple vision and tactile data to perform localization and pose estimation, and demonstrate that vision helps with disambiguating tactile signals for objects without distinctive features. Ichiwara et al. (2022) leverage tactile and vision for deformable bag manipulation by performing auto-regressive prediction. Hansen et al. (Hansen et al., 2022) use a contact-gated tactile, vision and proprioceptive observation to train reinforcement learning policies. Okumura et al. (2022) also tackle the problem of grasp pose uncertainty for insertion by using Newtonian Variational Autoencoders to combine camera observations and tactile images. Hao et al. (2025), Zhao et al. (2024) and Zhang et al. (2025) combined tactile information with large language models, achieving robotic arm manipulation of articulated objects and preference learning for insertion manipulation, respectively. They demonstrate results for USB insertion accounting for grasp pose uncertainty in one translation direction. In this work, we address terminal grasping, path planning, and terminal buckling as the whole reinforcement learning task. As the observation for the RL policy, combine two wrist camera images, one side camera image, and two tactile gripper images into visual-tactile multi-modal information. Concurrent with this was an artificial intervention program designed to guarantee a safe exploration for the policy. Our policy is able to handle both grasp pose rotation and translation uncertainty for the PLC terminal’s assembly.
3 Problem statement and preliminaries
Overview: We sort out a terminal assembly task for a 7-DoF robot with a parallel-jaw gripper and tactile sensors on both jaws. The end-effector has two wrist-mounted RGBD cameras, and one RGB side-camera is configured to capture the entire assembly scenario. The objective is to learn a policy that can robustly insert the terminal head into the terminal base with an unknown part’s pose within the gripper, while minimizing head-base collisions by human guidance during training. Figure 1A shows the experiment setup.
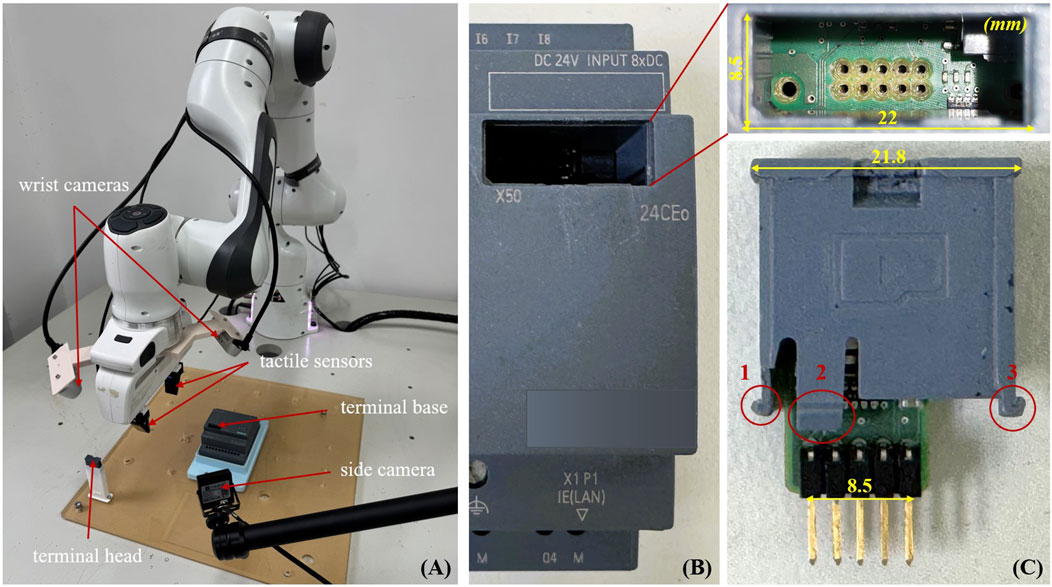
Figure 1. (A) An overview of the terminal assembly task is shown in the figure. The goal is to grasp the terminal head from the placement tray and guide the robot to the terminal base. Two RGBD cameras on the wrist and one RGB side camera are used to observe the environment. The final step is to insert the terminal head clamped by the tactile sensors onto the terminal base using visual-tactile feedback. (B,C) Exhibition of the components and specifics of each segment of the terminal.
Details of the assembled terminal: As seen in Figures 1B,C, our work accomplished the PLC terminal assembly. The terminal base and the terminal head are the two components that make up the hardware. Three barbed elastic latches and ten parallel-positioned pins make up the major mating components of the terminal head. The terminal base mating area is partially enlarged in the upper right corner, where the base’s inner wall has three guide grooves that match the three spring clips, and the base’s bottom has insertion holes that match the pins. The main challenge of this work is correctly inserting the pins into the holes and snapping the three spring clips into their respective guiding grooves without causing any damage to the pins, such as bending or breaking them. Therefore, we use tactile sensing and manual intervention to minimize collision forces during the assembly process to ensure the safety of the terminal hardware.
Robotic Reinforcement Learning: Robotic reinforcement learning tasks can be defined via an Markov Decision Process (MDP)
While the specification of the RL task is concise and simple, turning real-world robotic learning problems into RL problems requires care. First, the sample efficiency of the algorithm for learning
4 Methods
In this section, we introduce our visuo-tactile feedback policies with the assistance of human intervention to address the terminal assembly problem. The overview of our method is shown in Figure 2.
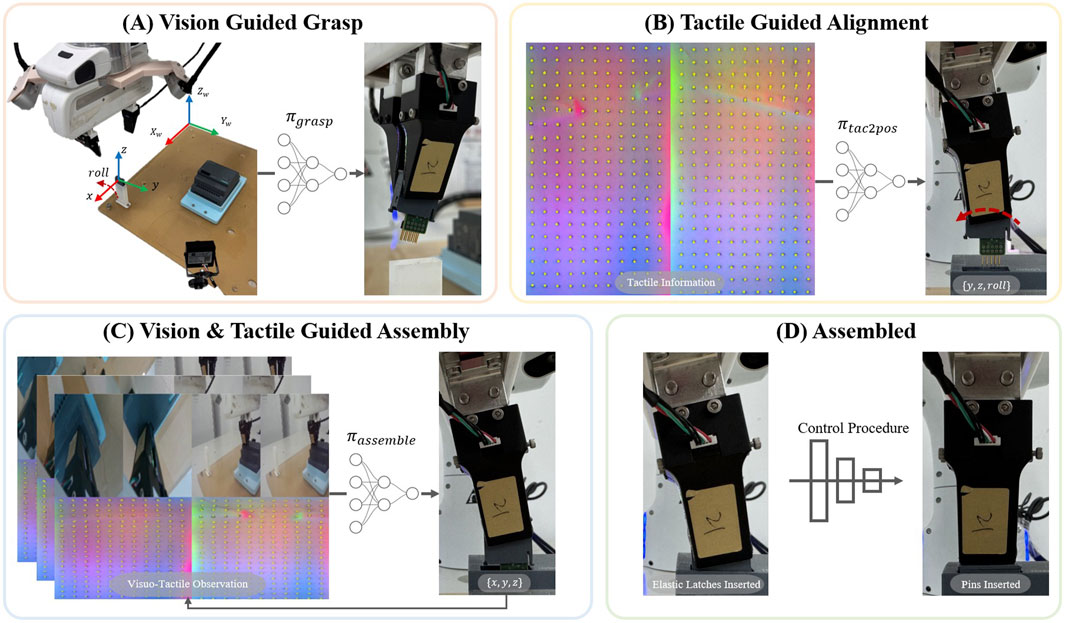
Figure 2. Overview of the learned three-phase assembly policy: (A) The vision guided policy
4.1 Real-world RL for terminal grasp and assembly
4.1.1 Fundamental RL algorithm
For the reinforcement learning method to be used in terminal assembly, there are two requirements: It must be (1) effective and capable of making several gradient adjustments in a time step, and (2) readily integrate prior data and then get improved with further training. In pursuit of this objective, we expand upon the recently proposed RLPD algorithm (Ball et al., 2023), which has demonstrated remarkable outcomes in sample-efficient robotic learning. The off-policy actor-critic reinforcement learning algorithm, known as RLPD, relies on the success of temporal difference algorithms with soft-actor critic (Haarnoja et al., 2018), it undergoes some significant changes to satisfy the requirements above. Three main improvements are made by RLPD: (i) high update-to-data ratio training (UTD); (ii) symmetric sampling between on-policy and prior data, where half of each batch comes from the online replay buffer and half from prior data; and (iii) layer-norm regularization during training. In order to accelerate learning, this technique can either start from scratch or leverage prior data (e.g., demonstrations). Each step of the algorithm updates the parameters of a parametric Q-function
where
In this work,
4.1.2 Classifier-based reward specification
Reward functions are difficult to specify by hand when learning with image observations, as the robot typically requires some sort of perception system just to determine if the task was performed successfully. While some tasks can accommodate hand-specified rewards based on the location of the end effector (under the assumption that the object is held rigidly in the gripper), most tasks require rewards to be deduced from images. In this case, the reward function can be provided by a binary classifier that takes in the state observation
This classifier can be trained either using hand specified positive and negative examples, or via an adversarial method called VICE (Fu et al., 2018). The latter addresses a reward exploitation problem that can arise when learning with classifier based rewards, and removes the need for negative examples in the classifier training set: when the RL algorithm optimizes the reward
4.1.3 Actor and learner nodes
In order to decouple inferring actions and updating policies, this work incorporates alternatives for training and acting in tandem, as seen in Figure 3. In sample-efficient real-world learning tasks with large UTD ratios, we discovered that this was advantageous. Our policy reduces the overall wall-clock time spent training in the real world while maintaining the control frequency at a fixed rate, which is essential for tasks requiring instant feedback and reactions, like deformable objects and contact-rich manipulations (e.g., terminal assembly). This is achieved by separating the actor and learner on two separate threads.
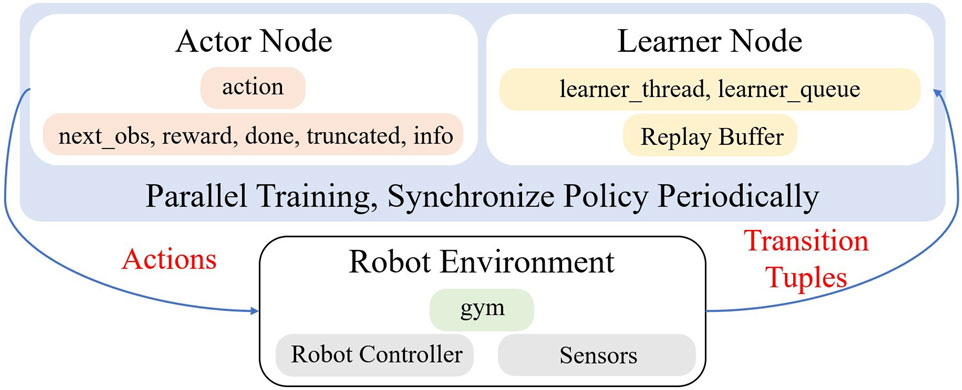
Figure 3. Policy training and real-world robot architecture. Three parallel processes, consisting of the actor, which chooses actions, and the learner node, which actually runs the training code, and the robot environment, which executes the actions from the actor and contributes data back to the learner.
4.2 Supervised learning for tactile guided alignment
Data Collection: The terminal head fixed in the initial bin throughout data collection. We explore grasp pose variations in 3-DoF (
Alignment Policy: We adopted RegNet 3.2 GF (Radosavovic et al., 2020) as the backbone of the policy network and replaced its last layer with a linear layer producing 3 outputs. Using the aforementioned data—comprising pairs of tactile images (Figure 2B,
4.3 Impedance controller for terminal assembly
During the experiment, we found that the choice of controllers can heavily affect the final performance. This is more pronounced for contact-rich manipulation. In this work (Figures 2C,D), an overly stiff controller might bend the fragile pins and make insertion difficult, while an overly compliant controller might struggle to move the object into position quickly.
A typical setup for robotic RL employs a two-layered control hierarchy, where an RL policy produces setpoint actions at a much lower frequency than the downstream real-time controller. The RL controller can set targets for the low-level controller, but such targets may lead to physically undesirable consequences—especially in contact-rich manipulation tasks—if not regulated by a robust low-level control mechanism. To this end, the impedance controller is integrated into this hierarchy as a core component, with its framework encompassing a spring-damper-based force objective and a critical error-bounding safety constraint. A typical impedance control objective for this controller (Equation 3) is
where
5 Experiments
In this section, we introduce the experimental setup of the assembly task and the evaluation of the proposed methods.
5.1 Experiment setup
We consider a terminal assembly task using a Franka Emika Panda Robot (7-DoF), equipped with a parallel-jaw gripper with XENSE G1-WS vision-based tactile sensors (used in AgiBot World Colosseo (Bu et al., 2025)) mounted on both jaws. The G1-WS sensor, independently developed by our laboratory, captures RGB tactile images with a fixed resolution of 700
The end effector is equipped with two wrist-mounted Intel RealSense Depth Camera D435i RGBD cameras, selected for their high-quality 1,280
The D435i′s compact form factor minimizes interference with the gripper and assembly components, while its robust SDK (compatible with ROS and Python) facilitates seamless integration into our custom control pipeline. It also delivers reliable performance under varying lighting conditions, including low-light environments, ensuring stable data quality throughout experiments. Additionally, a jieruiweitong DF100 RGB side-camera is configured to capture the entire assembly scene (Figure 1), chosen for its 1,280
At the beginning of each training and evaluation episode, the initial end effector pose is sampled uniformly
5.2 Experimental procedure
At the beginning of each test experiment, the end effector is set to the initial pose sampled from
Then the robot activates the align policy
After the alignment, the vision-tactile guided assembly policy
During the policy training and testing process, human intervention was triggered by a hybrid mechanism combining manual visual observation and automatic force sensing, with clearly defined termination conditions: (i) Successful termination: The robot successfully grasps the terminal head
5.3 Comparison and ablation studies
Examine the function and significance of the RLPD algorithm: As outlined in Section 4.1.1, the most distinctive characteristic of the RLPD algorithm lies in its integration of human prior demonstrations to guide the learning process, which effectively reduces both training time and sample complexity. To assess the necessity of these demonstrations, we compare our approach with the Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (TD3), an off-policy Actor-Critic algorithm derived from DDPG. TD3 belongs to the class of online reinforcement learning algorithms that require continuous interaction with the environment and rely solely on trial-and-error learning to discover optimal policies, without incorporating human demonstrations. The comparison is conducted under identical environmental settings: (1) Exploration noise: Gaussian noise with standard deviation = 0.1 (applied to end-effector pose commands); (2) Learning rate: 1e-3 for actor/critic networks (Adam optimizer); (3) Training epochs: 200 epochs (1,000 steps per epoch); (4) Network architecture: Same 3-layer actor/critic structure (consistent with RLPD’s base design).
Furthermore, to demonstrate that expert demonstrations alone are insufficient for task completion, we also evaluate a behavioral cloning (BC) baseline trained on 150 high-quality expert teleoperated demonstrations. This dataset size approximately matches the total amount of data stored in the RLPD replay buffer at convergence. To ensure fair comparison: (1) Network architecture: BC used the same RegNet 3.2 GF backbone as RLPD’s alignment policy
We report the results in Table 1, and show example executions in Figure 4. Training the TD3 policy in the physical environment resulted in divergence across all conducted training trials. In each case, the terminal head collided with the terminal base during the training of
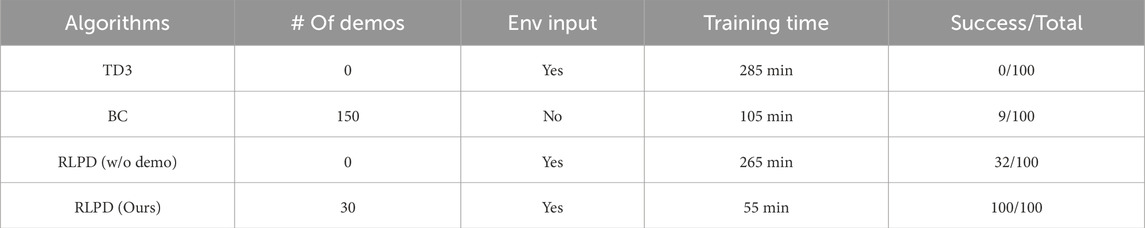
Table 1. Results suggest that (1) frequent slippage and rotations of the terminal head caused by collisions with the terminal base lead to failure in training TD3, (2) the BC trained solely on 150 human demonstrations is insufficient for training an accurate assembly model and (3) the human demonstrations play an important role in improving training efficiency and policy success rate. Our approach outperforms both baseline policies.
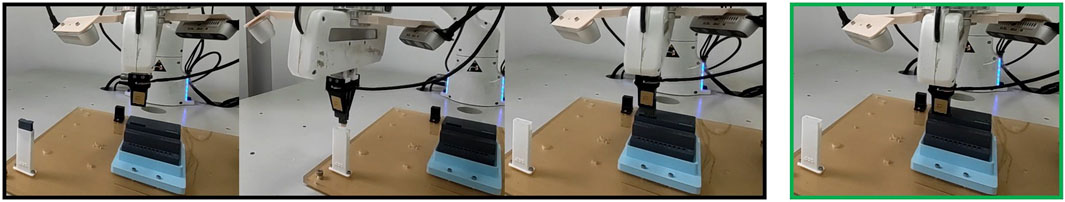
Figure 4. Illustration of the robot performing terminal assembly with our method. The green box indicates a state where the robot receives classifier reward for completing the task.
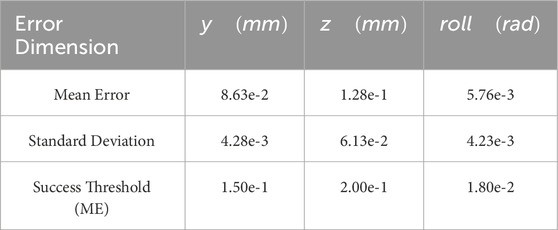
Table 2. Mean and standard deviation of the error in estimating the relative grasp pose
Exploring Utility of Tactile and Vision Information: We perform study the relative benefits of using tactile and vision for assembly term
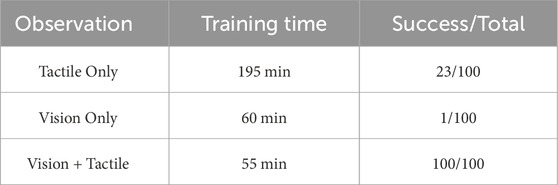
Table 3. Ablation study with comparing single modal Tactile Only, Vision Only, and a Combined two-modal approach leveraging tactile and visual information.
The Tactile Only model achieved successful assembly 23/100 times. However, its training time exceeded 3 times that of the other two models. This is because, across much of the exploration range, no contact occurred between the terminal head and terminal base, resulting in static tactile sensor images. Consequently, a significant portion of the training process involved the policy exploring for the position of the terminal base. These findings suggest that visual observation is essential for estimating the approximate location of the terminal base, enabling the policy to actively reduce the exploration space and accelerate learning. In contrast, the Vision Only model exhibited faster convergence during training but performed poorly in completing the assembly task, achieving only one success in 100 attempts. This limitation stems from the absence of fine-grained tactile feedback regarding contact events, highlighting the necessity of tactile sensing for millimeter-level positional estimation in contact-rich tasks. The multi-modal model, which integrates both tactile and visual inputs, outperforms either modal approach by combining tactile-based terminal head position prediction with vision-based implicit estimation of environmental states. This synergy demonstrates that the integration of tactile and visual observations effectively reduces uncertainties inherent in assembly tasks.
6 Discussion
In conclusion, we propose an effective and safe methodology for acquiring a visuo-tactile insertion policy within real-world reinforcement learning (RL) environments characterized by unknown component positions and grasping configurations. This is achieved by leveraging human demonstrations to accelerate the training process while maintaining the safety of the components, alongside the implementation of a structured three-phase assembly framework that delineates the task into distinct stages—grasping, alignment, and insertion—facilitated by integrated tactile and visual feedback.
6.1 Limitations
Although our results are promising, several limitations of the proposed approach remain. First, the generalizability of our method has yet to be validated across various assembly tasks, particularly those involving objects with more intricate geometric properties (e.g., non-prismatic components with curved mating surfaces) or scenarios where the physical dimensions significantly deviate from the scale of the tactile sensor (e.g., micro-assembly tasks with parts
6.2 Future work
To address these limitations, future research should focus on three main directions. First, generalizing the proposed methodology to encompass assembly tasks involving objects with diverse shapes, materials, and dimensions: this will involve developing few-shot tactile pose estimation models that adapt to new parts with minimal retraining data, as well as integrating material property estimation (e.g., friction coefficient) from tactile images to handle slippage—directly addressing the need for multi-material terminal adaptation in industrial scenarios. Specifically, we aim to extend the current PLC terminal-focused framework to metallic, Teflon-coated, and composite-material terminals, where varying surface properties (e.g., friction coefficients ranging from 0.2 to 0.6) require adaptive tactile signal interpretation and grasp force adjustment. Second, the development of an automated reset learning framework tailored specifically for terminal insertion and extraction processes: this framework could leverage the existing
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
YL: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Validation, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. ZJ: Writing – review and editing, Data curation. JL: Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Software. DM: Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Grant No. 12272220), Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited (CATL) and SIEMENS AG. The funders were not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ball, P. J., Smith, L., Kostrikov, I., and Levine, S. (2023). “Efficient online reinforcement learning with offline data,” in International conference on machine learning (PMLR), 1577–1594.
Bu, Q., Cai, J., Chen, L., Cui, X., Ding, Y., Feng, S., et al. (2025). Agibot world colosseo: a large-scale manipulation platform for scalable and intelligent embodied systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.06669
Chaudhury, A. N., Man, T., Yuan, W., and Atkeson, C. G. (2022). Using collocated vision and tactile sensors for visual servoing and localization. IEEE Robotics Automation Lett. 7, 3427–3434. doi:10.1109/LRA.2022.3146565
Dang, R., Hou, Z., Yang, W., Chen, R., and Xu, J. (2023). “Fusing vision and force: a framework of reinforcement learning for elastic peg-in-hole assembly,” in 2023 WRC symposium on advanced robotics and automation (WRC SARA) (IEEE), 1–6.
De Mello, L. H., and Sanderson, A. C. (1989). “A correct and complete algorithm for the generation of mechanical assembly sequences,” in 1989 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (IEEE Computer Society), 56–57.
Fan, Y., Luo, J., and Tomizuka, M. (2019). “A learning framework for high precision industrial assembly,” in 2019 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (IEEE), 811–817.
Florence, P., Lynch, C., Zeng, A., Ramirez, O. A., Wahid, A., Downs, L., et al. (2022). “Implicit behavioral cloning,” in Conference on robot learning (PMLR), 158–168.
Fu, J., Singh, A., Ghosh, D., Yang, L., and Levine, S. (2018). Variational inverse control with events: a general framework for data-driven reward definition. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 31. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1805.11686
Fujimoto, S., Hoof, H., and Meger, D. (2018). “Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods,” in International conference on machine learning (Cambridge, MA: PMLR), 1587–1596.
Funk, N., Helmut, E., Chalvatzaki, G., Calandra, R., and Peters, J. (2024). Evetac: an event-based optical tactile sensor for robotic manipulation. IEEE Trans. Robotics 40, 3812–3832. doi:10.1109/tro.2024.3428430
Goldberg, K. Y. (1993). Orienting polygonal parts without sensors. Algorithmica 10, 201–225. doi:10.1007/bf01891840
Haarnoja, T., Zhou, A., Abbeel, P., and Levine, S. (2018). “Soft actor-critic: off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor,” in International conference on machine learning (Cambridge, MA: Pmlr), 1861–1870.
Hansen, J., Hogan, F., Rivkin, D., Meger, D., Jenkin, M., and Dudek, G. (2022). “Visuotactile-rl: learning multimodal manipulation policies with deep reinforcement learning,” in 2022 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (IEEE), 8298–8304.
Hao, P., Zhang, C., Li, D., Cao, X., Hao, X., Cui, S., et al. (2025). Tla: tactile-language-action model for contact-rich manipulation. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:2503.08548. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2503.08548
Ichiwara, H., Ito, H., Yamamoto, K., Mori, H., and Ogata, T. (2022). “Contact-rich manipulation of a flexible object based on deep predictive learning using vision and tactility,” in 2022 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), 5375–5381. doi:10.1109/ICRA46639.2022.9811940
Johannink, T., Bahl, S., Nair, A., Luo, J., Kumar, A., Loskyll, M., et al. (2019). “Residual reinforcement learning for robot control,” in 2019 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (IEEE), 6023–6029.
Kelestemur, T., Platt, R., and Padir, T. (2022). Tactile pose estimation and policy learning for unknown object manipulation. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:2203, 10685. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2203.10685
Koga, Y., Kerrick, H., and Chitta, S. (2022). “On cad informed adaptive robotic assembly,” in 2022 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS) (IEEE), 10207–10214.
Konda, V., and Tsitsiklis, J. (1999). Actor-critic algorithms. Adv. neural Inf. Process. Syst. 12. doi:10.1137/S0363012901385691
Lambeta, M., Chou, P.-W., Tian, S., Yang, B., Maloon, B., Most, V. R., et al. (2020). Digit: a novel design for a low-cost compact high-resolution tactile sensor with application to in-hand manipulation. IEEE Robotics Automation Lett. 5, 3838–3845. doi:10.1109/lra.2020.2977257
Li, R., Platt, R., Yuan, W., Ten Pas, A., Roscup, N., Srinivasan, M. A., et al. (2014). “Localization and manipulation of small parts using gelsight tactile sensing,” in 2014 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IEEE), 3988–3993.
Lian, W., Kelch, T., Holz, D., Norton, A., and Schaal, S. (2021). “Benchmarking off-the-shelf solutions to robotic assembly tasks,” in 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (IEEE), 1046–1053.
Lin, H., Corcodel, R., and Zhao, D. (2024). “Generalize by touching: tactile ensemble skill transfer for robotic furniture assembly,” in 2024 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (IEEE), 9227–9233.
Liu, J., Yu, H., Zhao, C., Liu, W., Ma, D., and Wang, W. (2024). Real-time reconstruction of 3d tactile motion field via multi-task learning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 73, 1–13. doi:10.1109/tim.2024.3398136
Lozano-Pérez, T. (1986). “Motion planning and the design of orienting devices for vibratory part feeders,” in IEEE journal of robotics and automation (MIT AI Laboratory).
Lozano-Perez, T., Mason, M. T., and Taylor, R. H. (1984). Automatic synthesis of fine-motion strategies for robots. Int. J. Robotics Res. 3, 3–24. doi:10.1177/027836498400300101
Lu, C., Tang, K., Yang, M., Yue, T., Li, H., and Lepora, N. F. (2024). Dexitac: soft dexterous tactile gripping. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 30, 333–344. doi:10.1109/tmech.2024.3384432
Luo, J., Sushkov, O., Pevceviciute, R., Lian, W., Su, C., Vecerik, M., et al. (2021). Robust multi-modal policies for industrial assembly via reinforcement learning and demonstrations: a large-scale study. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.11512
Luo, J., Hu, Z., Xu, C., Tan, Y. L., Berg, J., Sharma, A., et al. (2024). “Serl: a software suite for sample-efficient robotic reinforcement learning,” in 2024 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (IEEE), 16961–16969.
McKee, K. E. (1985). Automatic assembly by G. Boothroyd, C. poli and L.E. murch, marcel dekker, New York, 378 pp., 1982 ($45.00), Robotica, Marcel Dekker, new york, 3, 195–196. doi:10.1017/S0263574700009255
Nair, A., Dalal, M., Gupta, A., and Levine, S. (2020). Accelerating online reinforcement learning with offline datasets. arxiv 2020. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:2006, 09359. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2006.09359
Narang, Y., Storey, K., Akinola, I., Macklin, M., Reist, P., Wawrzyniak, L., et al. (2022). Factory: fast contact for robotic assembly. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.03532
Natarajan, B. K. (1989). Some paradigms for the automated design of parts feeders. Int. J. Robotics Res. 8, 98–109. doi:10.1177/027836498900800607
Okumura, R., Nishio, N., and Taniguchi, T. (2022). “Tactile-sensitive newtonianvae for high-accuracy industrial connector insertion,” in 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (IEEE), 4625–4631.
Ozalp, R., Ucar, A., and Guzelis, C. (2024). Advancements in deep reinforcement learning and inverse reinforcement learning for robotic manipulation: toward trustworthy, interpretable, and explainable artificial intelligence. IEEE Access 12, 51840–51858. doi:10.1109/access.2024.3385426
Qiao, H., Dalay, B., and Parkin, R. (1995). Fine motion strategies for robotic peg-hole insertion. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 209, 429–448. doi:10.1243/pime_proc_1995_209_173_02
Radosavovic, I., Kosaraju, R. P., Girshick, R., He, K., and Dollár, P. (2020). “Designing network design spaces,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 10428–10436.
Rajeswaran, A., Kumar, V., Gupta, A., Vezzani, G., Schulman, J., Todorov, E., et al. (2017). Learning complex dexterous manipulation with deep reinforcement learning and demonstrations. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1709, 10087. doi:10.15607/RSS.2018.XIV.049
Schoettler, G., Nair, A., Luo, J., Bahl, S., Ojea, J. A., Solowjow, E., et al. (2020a). “Deep reinforcement learning for industrial insertion tasks with visual inputs and natural rewards,” in 2020 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS) (IEEE), 5548–5555.
Schoettler, G., Nair, A., Ojea, J. A., Levine, S., and Solowjow, E. (2020b). “Meta-reinforcement learning for robotic industrial insertion tasks,” in 2020 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS) (IEEE), 9728–9735.
Spector, O., and Di Castro, D. (2021). Insertionnet-a scalable solution for insertion. IEEE Robotics Automation Lett. 6, 5509–5516. doi:10.1109/lra.2021.3076971
Spector, O., Tchuiev, V., and Di Castro, D. (2022). “Insertionnet 2.0: minimal contact multi-step insertion using multimodal multiview sensory input,” in 2022 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (IEEE), 6330–6336.
Taylor, I. H., Dong, S., and Rodriguez, A. (2022). “Gelslim 3.0: high-Resolution measurement of shape, force and slip in a compact tactile-sensing finger,” in 2022 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (IEEE), 10781–10787.
Wang, Y., Huang, W., Fang, B., Sun, F., and Li, C. (2021). “Elastic tactile simulation towards tactile-visual perception,” in Proceedings of the 29th ACM international conference on multimedia, 2690–2698.
Wang, S., Lambeta, M., Chou, P.-W., and Calandra, R. (2022). Tacto: a fast, flexible, and open-source simulator for high-resolution vision-based tactile sensors. IEEE Robotics Automation Lett. 7, 3930–3937. doi:10.1109/lra.2022.3146945
Wen, B., Lian, W., Bekris, K., and Schaal, S. (2022). You only demonstrate once: category-level manipulation from single visual demonstration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.12716
Wu, Y., Chen, Z., Wu, F., Chen, L., Zhang, L., Bing, Z., et al. (2025). “Tacdiffusion: force-domain diffusion policy for precise tactile manipulation,” in 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (IEEE), 11831–11837.
Yuan, W., Dong, S., and Adelson, E. H. (2017). Gelsight: high-resolution robot tactile sensors for estimating geometry and force. Sensors 17, 2762. doi:10.3390/s17122762
Zhang, C., Hao, P., Cao, X., Hao, X., Cui, S., and Wang, S. (2025). Vtla: vision-tactile-language-action model with preference learning for insertion manipulation. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:2505.09577. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2505.09577
Zhao, T. Z., Luo, J., Sushkov, O., Pevceviciute, R., Heess, N., Scholz, J., et al. (2022). “Offline meta-reinforcement learning for industrial insertion,” in 2022 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (IEEE), 6386–6393.
Keywords: visual perception, tactile sensing, multi-modal fusion, terminal assembly, reinforcement learning
Citation: Li Y, Jin Z, Liu J and Ma D (2025) Visuo-tactile feedback policies for terminal assembly facilitated by reinforcement learning. Front. Robot. AI 12:1660244. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2025.1660244
Received: 05 July 2025; Accepted: 07 October 2025;
Published: 22 October 2025.
Edited by:
Rajkumar Muthusamy, Dubai Future Foundation, United Arab EmiratesReviewed by:
Chuanfei Hu, Southeast University, ChinaZhongpan Zhu, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Jin, Liu and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Daolin Ma, ZGFvbGlubWFAc2p0dS5lZHUuY24=
 Yuchao Li
Yuchao Li Ziqi Jin
Ziqi Jin Jin Liu
Jin Liu Daolin Ma
Daolin Ma