- 1College of Food and Bioengineering, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Health Care Food Science and Technology, Hezhou University, Hezhou, Guangxi, China
- 2College of Mechanical and Control Engineering, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin, Guangxi, China
Introduction: Vacuum-microwave drying (VMD) can lead to undesirable effects in persimmons, such as browning, charring, surface wrinkling, and structural collapse, all of which significantly reduce product quality.
Methods: This study proposed and evaluated a freezing pretreatment at an optimized temperature of −80°C prior to VMD. Persimmon slices with and without pretreatment were assessed in terms of appearance, physical properties, processing and quality indicators, sensory texture characteristics, and pore structure.
Results: The freezing pretreatment improved color uniformity by 64.5% and reduced the browning index growth rate by 21.4%. It also increased expansion rate and rehydration capacity by 15.7% and 21.5%, respectively. In terms of texture, hardness and chewiness decreased by 84.4% and 91.6%, while crispness improved by 40.4%.
Discussion: Integrating freezing pretreatment with VMD effectively mitigates browning and texture degradation in persimmons. These results demonstrate a promising approach for producing high-quality persimmon crisps. Future studies should explore the optimal freezing duration and temperature, and assess the applicability of this method to other fruits and vegetables.
1 Introduction
Persimmon is widely popular due to its attractive color and appearance, sweet taste, and unique chewiness. It is a kind of health-promoting food (Hu Y. et al., 2022), but a seasonal fruit with a short harvesting period (Karaman et al., 2014). Characterized by relatively high water content and a brief harvesting window, they are highly susceptible to microbial decay during storage, resulting in low post-harvest stability and a short shelf life (Zhao et al., 2021). Processed dried fruits offer various advantages, such as extending the storage period, preventing quality changes due to reduced enzyme and microbial activity, and adding value through the acquisition of distinct flavors and textures (Sehrawat et al., 2018).
Drying is one of the most effective methods to extend the shelf life of persimmon products by reducing moisture content and water activity (EL-Mesery et al., 2022), thereby inhibiting microbial growth, enzymatic activity, and other deteriorative reactions (An et al., 2022). Drying is a complex, unsteady heat and mass transfer process occurring both at the surface and within the material (Hu Z. et al., 2022). And, it can also cause structural damage that degrades product quality and reduces commercial value (Bhattacharjee et al., 2024). For example, issues such as local charring, browning, shrinkage, and pore collapse are commonly observed. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the effects of drying processes on the quality attributes of the end product.
Vacuum-microwave drying (VMD) is an efficient volumetric drying method characterized by a high drying rate, good energy efficiency, and an excellent rehydration ratio (Zhang et al., 2024). However, challenges in process control arise due to the rapid and non-uniform heating behavior of microwaves, which often leads to thermal runaway and localized scorching (Tang et al., 2024). These issues are primarily attributed to the unstable distribution of microwave energy, resulting in undesirable browning and compromised color quality in persimmon products (Wu et al., 2023). In contrast, hot air drying (HD) is widely used in the food industry due to its low cost and operational simplicity (El-Mesery et al., 2024a). However, it is less effective in preserving nutritional and sensory qualities, often resulting in excessive browning, structural shrinkage, reduced rehydration capacity, and the degradation of heat-sensitive nutrients due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures and oxidative conditions (Zhao et al., 2021). Freeze-drying (FD), on the other hand, is widely regarded as one of the most advanced methods for producing high-quality dried products. It effectively preserves heat-sensitive nutrients (Boateng, 2024), reduces shrinkage and hardness, and results in a crispier texture (Zhang et al., 2022), but requires high costs and an immense amount of drying time (Sedmak et al., 2023).
Various drying techniques have been employed for the preservation of persimmon. Numerous studies have explored methods such as freeze-drying (Sedmak et al., 2023), vacuum oven drying (Yang et al., 2022), hot air drying (Zhao et al., 2021), infrared drying (Polat et al., 2024), combined hot air–microwave drying (Dash and Bhagya Raj, 2023), microwave drying (Qin et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2023), and sun drying. Although several advanced drying technologies, including hybrid microwave-based methods, have been developed to enhance drying efficiency and product quality (Dash and Bhagya Raj, 2023; Yosefiyan et al., 2024), no previous research has specifically addressed the use of freezing pretreatment combined with vacuum–microwave drying for persimmon processing. Therefore, the primary objective of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of combining freezing pretreatment with vacuum–microwave drying in mitigating browning and improving the texture of persimmon crisps. This approach is compared against conventional VMD, with a comprehensive analysis of rehydration capacity, color changes, physical properties, processing and quality parameters, sensory texture attributes, and microstructural (pore structure) characteristics.
2 Materials and methods
Figure 1 depicts the experimental procedure. This study investigated a process in which freezing pretreatment was employed to mitigate local charring, browning, and shrinkage during VMD of persimmon slices.
2.1 Experimental materials and reagents
Gongcheng persimmons were from Guangxi province. N-Hexane (Analytical Grade), provided by Guangdong Guanghua Technology Co., Ltd. Nitrogen Gas (Purity 99.99%), supplied by Guangzhou Yuejia Gas Co., Ltd.
2.2 Experimental instruments
Physical property tester (TA.XT PLUS, Stable MicroSystems Ltd., UK); colorimeter (CR-400, Konica Minolta Corporation, Japan); intelligent static VMD machine (WZB-10, Guiyang Newqi Microwave Industry Co., Ltd.); ultra-low temperature freezer (DW-HL398, Zhongke Meiling Cryogenics Technology Co., Ltd.); medical low-temperature incubator (DW-YL450, Zhongke Meiling Cryogenics Technology Co., Ltd.); capacitive refrigerator (BCD-220RC2NEC, Hisense Kelon Electrical Holdings Co., Ltd.); analytical balance (BSA124S, Sartorius AG, Germany); electric constant temperature water bath (DK-98-IIA, Tianjin Taist Instrument Co., Ltd.); moisture analyzer (MX-50, Guangzhou A and E Instrument Co., Ltd.); transmission scanning electron microscope (EVO 10, Zeiss, Germany); and specific surface area and pore size analyzer (JW-BK200A, Beijing JWGB Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd.).
2.3 Experimental methods
2.3.1 Pre-treatment and drying
Initially, damaged and rotten persimmons were removed, and fresh fruits with uniform size and approximately 70% ripeness were selected for the experiments. The selection criteria followed the national standard of the People's Republic of China, GB/T 20453-2022: Quality Grades of Products for Persimmon (SAMR and SAC, 2023). The chosen persimmons were flat and round in shape, with an average weight of 170 g per fruit, a soluble solids content of around 21%, and flesh hardness exceeding 6 kg/cm2. All selected fruits exhibited orange-yellow flesh and were free from mechanical damage. Subsequently, the persimmons were thoroughly cleaned and peeled. Using a transverse cutting method, the persimmons were sliced into 3 mm, with each portion weighing 500 g. Then, the persimmon slices were individually placed into freezing environments at –24°C (slow freezing, using a standard freeze), –80°C (rapid freezing, using an ultra-low freezer), and –196°C (rapid freezing, using liquid nitrogen). After the freezing process completed, the samples were left at room temperature for thawing. The surface moisture of the persimmon slices was absorbed using test paper, and finally, the persimmon slices were arranged on plates and subjected to VMD in the equipment. Additionally, the control group undergoes VMD after being refrigerated at 4°C for 12 hours.
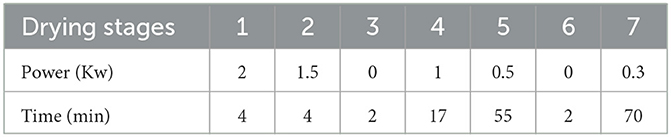
In an environment with a vacuum pressure of 0.095 MPa, persimmon slices undergo a seven-stage microwave drying process. The specific parameters for microwave drying were detailed in Table 1. The drying process concludes when the sample moisture content reaches ≥5%. At this point, the samples were removed and cooled. Finally, the dried samples were packaged and stored.
2.3.2 Color measurement
The color of persimmon slices was measured using a colorimeter, with ΔE values indicating the total color change. An increased ΔE indicates a greater color deviation from the standard fresh material. ΔE and browning index (BI) were calculated according to Equation 1 (El-Mesery et al., 2024c), Equations 2, 3 (Wu et al., 2021):
2.3.3 Volume measurement
Volume determination was performed using the displacement method. A 100 mL graduated cylinder was used as the container, with 50 mL of fine quartz sand as filler. Persimmon crisps were placed into the graduated cylinder, and the volume of persimmon crisps was calculated as the total volume minus the filler volume. The calculation was done according to equation (Tabtiang et al., 2022):
2.3.4 Puffing rate
In the experiment, quartz sand was used as the displacement medium to measure the change in material volume and determined the volume of persimmon crisps before and after drying. The following equation is used to calculate the puffing rate (P) of persimmon crisps (Xu et al., 2021):
2.3.5 Apparent density measurement
Apparent density (ρm) is the mass per unit volume in its natural state, used to characterize the degree of surface shrinkage and structural looseness of the product. It is determined through the filling method (Feng et al., 2023).
2.3.6 Rehydration ratio
A certain number of persimmon crisps are weighed and placed in a 250 mL beaker. Subsequently, 200 mL of distilled water is added to the beaker, and it is heated in a water bath at 50°C for 1 h. Then, the surface water is wiped dry, and the beaker is reweighed. The rehydration ratio is calculated using the following equation (Wang et al., 2023).
2.3.7 Hardness, brittleness, and chewiness
The TA-Xtplus Texture Analyzer is used to perform TPA (Texture Profile Analysis) on the samples to measure hardness, brittleness, and chewiness. The probe used is a P/2 cylindrical probe. The probe's pre-test speed is set to 1.0 mm/s, the test speed is 2.0 mm/s, and the post-test speed is 10.0 mm/s. The trigger force is set at 20.0 g. In the testing process, the hardness of the sample is represented by the maximum pressure peak value on the coordinate graph, with a larger peak indicating higher hardness. Brittleness is represented by the first significant pressure peak value on the coordinate graph when the probe first approaches the sample during compression. A smaller peak indicates greater brittleness.
2.3.8 Pore distribution and characteristics analysis
The differential method is employed for measurement. 1.0 g of the sample is placed in the sample tube, and the sample is heated at 60 °C. After 60 min of heating, the sample is pre-treated under vacuum for 1 h. Following the pre-treatment, the sample is subjected to N2 adsorption using physical adsorption to determine the specific surface area and pore size of the sample.
Total porosity measurement. The porosity of the sample is determined using the pycnometer method. The dried sample is crushed to below 0.2 mm (passed through an 80-mesh sieve), and then the sample is placed in a pycnometer filled with N-Hexane, and kept at 20°C for 30 min. The equations for calculating density ρn and porosity ε are as follows (Li et al., 2022):
The opening pore porosity (εa) is determined by the impregnation method. The sample is placed in a 100 mL beaker and immersed in n-hexane for 2 hours. Afterwards, it is removed, and any free n-hexane on the sample surface is wiped off before being weighed using an analytical balance. The equation for opening pore porosity is Li et al. (2022):
Closed-pore porosity (εb) can be calculated using the following equation (Li et al., 2022):
2.3.9 Microstructure
The German Zeiss EVO 10 high-resolution transmission electron microscope is used to scan the persimmon crisps. The accelerating voltage (EHT) is set to 10.00 KV, with a resolution of 2.5 nm.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Color properties
Color is a key indicator of the quality and consumer acceptance of dried fruit and vegetable products. Figure 2a shows fresh persimmon slices prior to drying, while Figure 2b presents samples subjected to VMD following refrigeration, referred to as the control group. Figures 2c–e display samples that underwent various freezing temperature pre-treatments before VMD, referred to as the experimental group. As illustrated, the fresh samples exhibit a light yellow color with central chambers clearly visible. In contrast, both the control and experimental groups show noticeable color changes after drying. The control group displays poor color uniformity, with apparent browning and localized charring. Although the chamber structures remain relatively intact, the surface lacks fluffiness. In the experimental group, however, samples exhibit a brighter and more uniform color, with significantly reduced browning and charring. This improvement can be attributed to the freezing pre-treatment, which likely optimized the microstructure of the persimmon slices. The modified microstructure may have promoted more uniform microwave energy distribution during drying, thereby effectively minimizing thermal degradation such as browning and charring (Nowak and Jakubczyk, 2022). Furthermore, compared to the fresh and control group samples, the chamber structures in the experimental group show noticeable volume expansion, with some even disappearing–indicating superior puffing performance in frozen-pre-treated persimmon crisps. Visual analysis confirms that freezing pretreatment effectively reduces localized browning and charring during VMD while contributing to a fluffier texture, consistent with findings from a previous study (Chu et al., 2023).
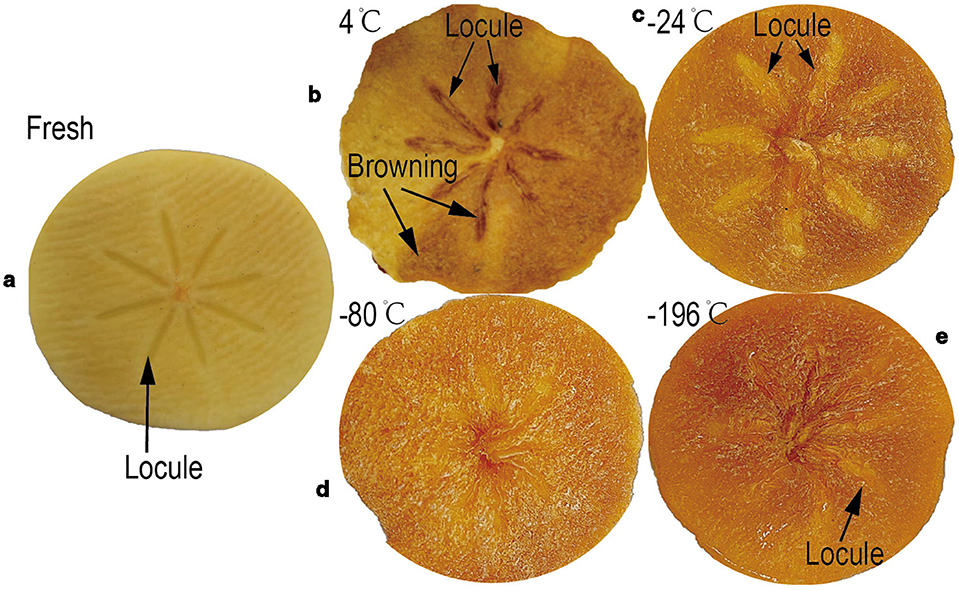
Figure 2. The persimmon slices before and after drying (a) fresh, (b) –4°C, (c) –24°C, (d) –80°C, (e) –196°C.
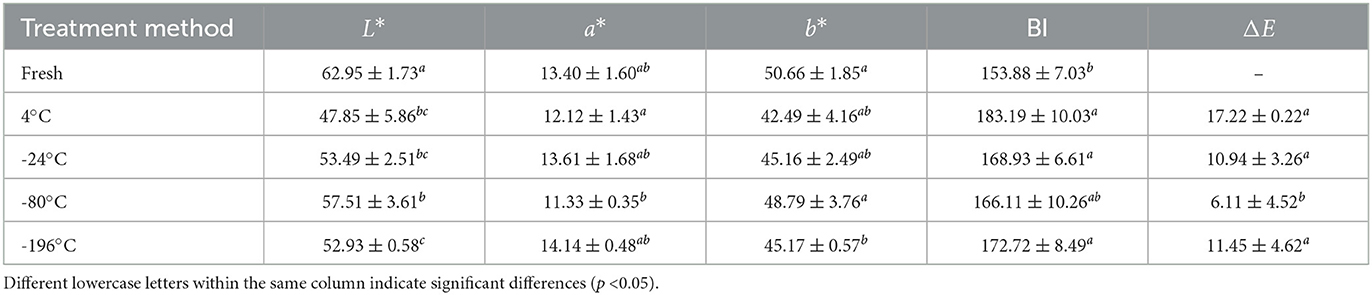
To quantitatively assess the color changes in persimmon crisps before and after drying, ΔE and BI were calculated using Equations 1, 2, with the results summarized in Table 2. The data show that, compared to fresh slices, both the control and experimental groups exhibited decreases in the L*, a*, and b* color parameters. The calculated color difference for the control group was 17.22. In contrast, the experimental group showed a trend of decreasing and then increasing ΔE with decreasing freezing temperature. The lowest color difference in the experimental group was 6.11, representing a 33.8% to 64.5% reduction compared to the control group. This indicates that freezing pretreatment significantly improves color retention. Compared to microwave drying alone, the color difference was also significantly reduced (Wu et al., 2023). Drying led to a marked increase in BI, primarily due to moisture loss and the corresponding concentration of browning-prone compounds such as sugars and amino acids (Wu et al., 2023). Additionally, oxidation of phenolic compounds likely contributed to the increase in BI. Specifically, the control group reached a BI of 183.19, nearly 30 units higher than fresh samples. The experimental group, following freezing pretreatment, exhibited a similar trend of initial decline and then increase in BI with decreasing freezing temperature, but overall maintained lower BI values than the control group. Notably, the BI at –80°C dropped to a minimum of 166.11, suggesting that ultra-low temperature freezing effectively suppresses browning. This suppression may result from structural damage to cell membranes and walls during freezing, which reduces the release and interaction of phenolic compounds with oxidative enzymes such as polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase (Ando and Watanabe, 2023). Taken together, the visual assessment, ΔE, and BI results demonstrate that freezing pretreatment significantly mitigates undesirable browning and charring during the VMD process of persimmon crisps.
3.2 Volume, puffing rate, apparent density, and rehydration ratio
Through the analysis of the appearance shown in Figure 2, it is clear that the surface of the samples after freezing pretreatment exhibits significant fluffy structural characteristics. To quantify this effect more precisely and intuitively, we conducted an in-depth study on the direct impact of freezing pretreatment on the volume change and expansion effect of persimmon crisps. This aims to reflect the positive role of freezing pretreatment in improving the texture and structure of persimmon crisps through specific data and indicators. The volumes and expansion rates of the control group and experimental group samples were calculated by Equations 4, 5, as shown in Figure 3a. The results in Figure 3a indicate that when the freezing temperature is relatively high (–24°C), there is no significant change in the volume of the samples. However, when the freezing temperature reaches –80°C, the volume of the samples increases; conversely, when the temperature drops to –196°C, the volume decreases again. Additionally, the expansion rates of the experimental group samples all increased, with the samples at -80°C showing the highest expansion rate, which is 15.17% higher than that of the control group.
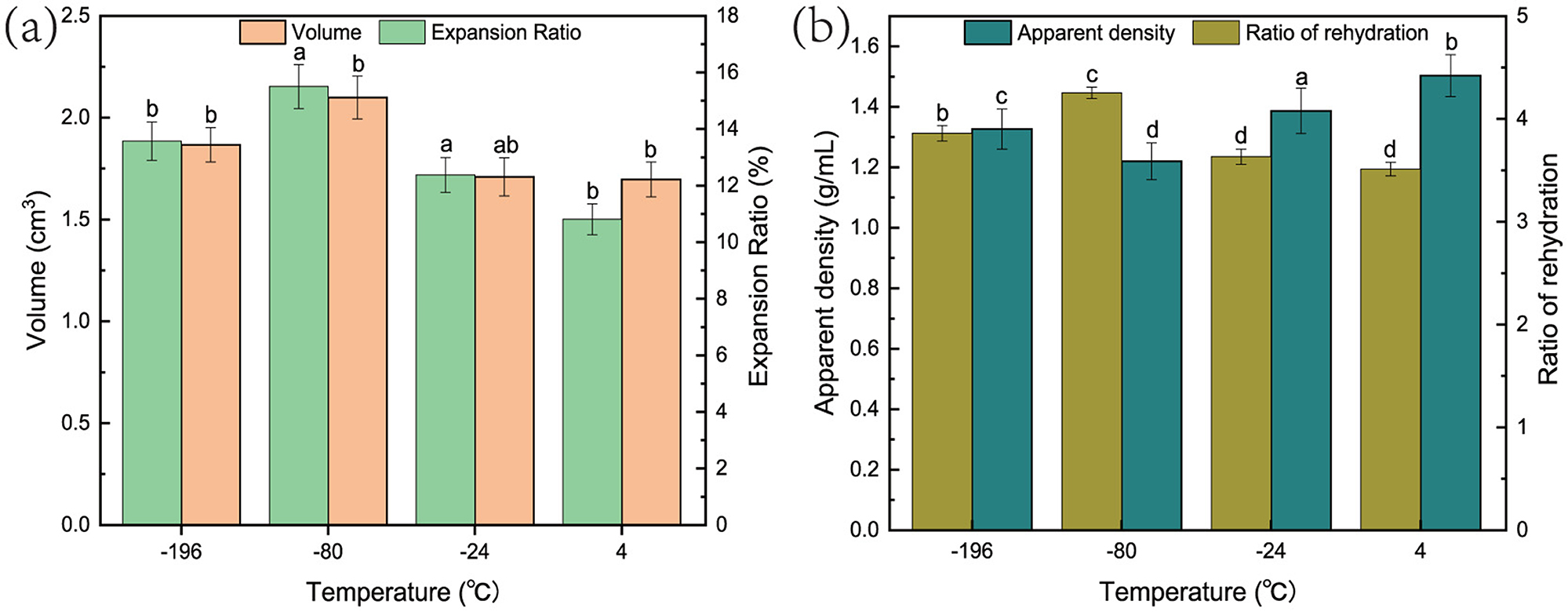
Figure 3. The impact of freezing treatment on (a) volume and expansion rate, and (b) apparent density of vacuum microwave persimmon crisps. Freezing pretreatment increases the volume and expansion rate of persimmon crisps, reduces their apparent density, and enhances their rehydration capacity. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between groups (P < 0.05).
The observed results can be attributed to the absence of ultra-low temperature freezing pretreatment, during which the internal moisture in persimmon slices does not freeze, thereby failing to preserve the original structural integrity of the tissue (Qiu et al., 2022). During drying, the loss of moisture leads to cellular shrinkage and pore collapse. In contrast, when freezing pretreatment, especially at ultra-low temperatures, is applied, intracellular water freezes and forms ice crystals, which can partially disrupt cellular and tissue structures (Mokhova et al., 2023). However, these ice crystals also help maintain structural integrity by acting as a scaffold, leading to more uniform moisture evaporation during VMD. Moreover, freezing pretreatment facilitates the formation of ice crystals from free water within the cells, thereby accelerating the drying process. As the freezing temperature decreases, water within the persimmon cells gradually solidifies and migrates to extracellular spaces, forming larger ice crystals. Rapid freezing, on the other hand, produces smaller ice crystals that minimize cellular damage, retain more moisture, and better preserve the texture of the crisps (Feng et al., 2023). In addition, the sublimation of ice during the freezing process, which involves a direct transition from the solid to the vapor phase, further helps preserve the cellular microstructure.
By measuring the apparent density of the processed samples, we can determine the extent of their volume change. Under the same mass conditions, a lower density indicates a larger volume, which suggests better expansion effects and improved pore structure. Figure 3b shows the apparent density values calculated using the filling method based on Equation 6 The results indicate that the apparent density of the control group samples is 1.50 g/mL, while the experimental group samples at –80°C have the lowest apparent density of 1.22 g/mL, representing an 18.7% reduction compared to the control group.
The results of the rehydration capacity of the samples, calculated by Equation 7, are presented in Figure 3b. The findings demonstrate that the rehydration capacity of the experimental group samples is improved compared to the control group and is related to the freezing pretreatment temperature. Specifically, the rehydration capacity of the experimental group samples increased from an original value of 3.53 to a range of 3.87 to 4.29. Compared to hot air drying, the rehydration ratio (3.06) is significantly improved (Yang et al., 2022). The improvement in rehydration capacity is attributed to the fact that during the drying process, the pores in the control group samples are prone to collapse or shrink, reducing the spatial volume of the samples. In contrast, during freezing pretreatment, free water inside the pores of the experimental group samples forms ice crystals, which help support the pore structure. As a result, during subsequent drying, even with moisture evaporation, the pores in the experimental group samples can maintain their original shape as much as possible, thereby enhancing rehydration capacity.
There are differences in the rehydration capacities of the samples obtained after drying under different freezing pretreatment temperatures, primarily due to the varying speeds and forms of ice crystal formation. When the freezing temperature is relatively high (e.g., –24°C), the longer freezing time leads to the formation of larger ice crystals. These large ice crystals may cause collapse and rupture of the cellular structure during thawing, resulting in significant loss of tissue fluid and reduced rehydration performance (Yan et al., 2025). At an optimal freezing temperature (e.g., –80°C), moisture in the samples freezes rapidly, forming smaller ice crystals that minimize cell wall damage during thawing. This helps preserve the pore structure and enhances rehydration capacity, likely due to the increased specific surface area of the crisps, which facilitates greater water absorption, consistent with findings from a previous study (El-Mesery et al., 2024b).
3.3 Hardness, crispiness, and chewiness
To evaluate the texture and mouthfeel of persimmon crisps, the hardness, crispness, and chewiness of the samples were analyzed, with results summarized in Table 3. Compared to the control group, experimental samples exhibited significantly reduced hardness and chewiness. Specifically, hardness decreased from 2,005.22 g to a range of 312.35–768.50g, representing a maximum reduction of 84.4%, while chewiness dropped from 508.58 J to 42.96–164.33 J, with a maximum reduction of 91.6%. In contrast, crispness improved markedly, increasing from 1,719.54 g to 2,019.36–2,413.84 g, with a maximum increase of 40.4%.
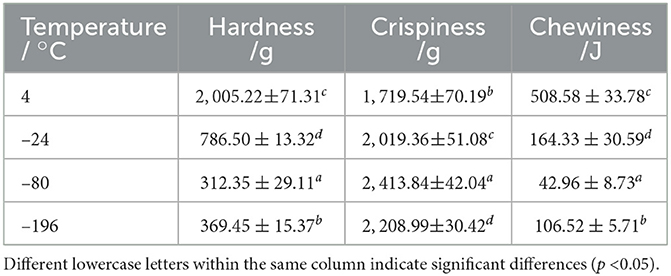
Table 3. The effect of freezing pretreatment on the hardness, crispiness, and chewiness of the persimmon crisps.
These improvements in texture are likely due to optimized pore structures resulting from freezing pretreatment, which helped prevent localized charring and pore collapse during VMD, leading to a fluffier product structure (Li et al., 2024). Freezing temperature had a significant effect on these properties; notably, samples frozen at –80°C showed the lowest hardness and chewiness and the highest crispness. These differences are primarily attributed to the influence of freezing temperature on the rate, size, and morphology of ice crystal formation, which ultimately determines the microstructure of the final product (Ma et al., 2024). Thus, tuning the freezing temperature enables the production of persimmon crisps with superior textural quality.
3.4 Pore distribution and characteristics
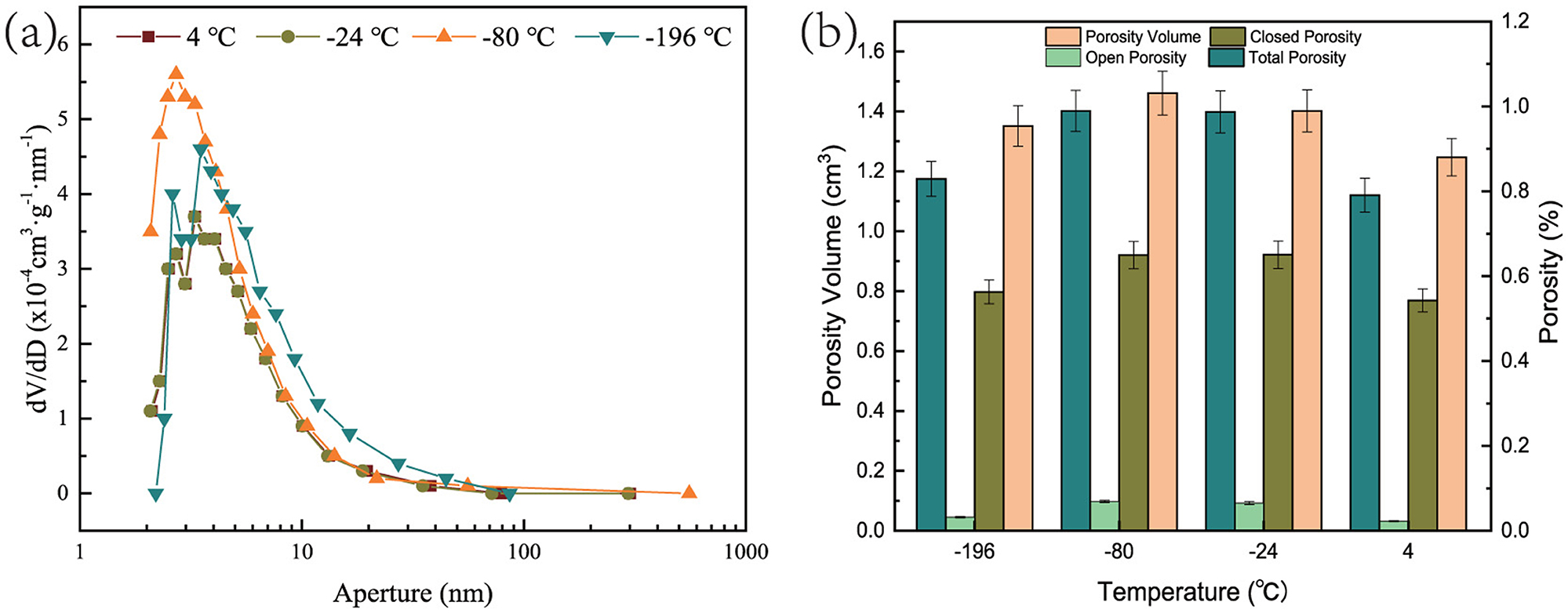
The pore distribution and characteristics of the samples significantly influence their hardness, crispiness, and chewiness. Figure 4a illustrates the pore diameter distribution of both the control and experimental group samples. It is evident from the figure that the samples pretreated at a lower freezing temperature (–80°C) exhibit higher peak values in the mesopore range (2–50 nm), indicating a more concentrated distribution of pore quantities at this size. This phenomenon indirectly verifies that freezing pretreatment can optimize the pore structure of the samples, increasing porosity and expanding pore diameters. Furthermore, it confirms that freezing pretreatment can effectively mitigate potential shrinkage and pore collapse during the drying process, thereby enhancing the overall quality of the samples (Zhao et al., 2021). Figure 4b presents the measured pore volume and porosity of the samples, which were calculated by Equations 8–11. The results show that, compared to the control group samples, the experimental group samples exhibited a significant increase in both pore volume and porosity. This is primarily manifested in the experimental group having a larger porosity, with a greater number of open and closed pores. The marked improvement can be attributed to the slow freezing of moisture within the persimmon pores during the freezing process, which leads to the formation of larger ice crystals. These ice crystals cause a certain degree of damage to cell walls and structures during subsequent thawing and drying, resulting in the creation of more pores (Mao et al., 2024; Ando and Nei, 2024). Therefore, the analysis of the pore volume and porosity test results confirms that freezing pretreatment indeed helps improve the wrinkling and pore collapse phenomena observed on the surface of samples during VMD.
3.5 Microstructure
Porosity analysis highlights the critical role of freezing pretreatment in enhancing the void structure of persimmon crisps at both macroscopic and mesoscopic levels. To provide more direct visual evidence of how freezing pretreatment mitigates surface wrinkling and pore collapse, SEM images are presented in Figure 5. As shown in Figure 5a, the control group samples display pronounced wrinkling and pore collapse. This deformation is likely caused by the inability of cell structures to retain their original shape following moisture loss during vacuum drying, leading to structural shrinkage. Such shrinkage increases local sample thickness, reduces heat distribution uniformity, and can promote charring and increased hardness. In contrast, the experimental group samples shown in Figures 5b–d exhibit more expanded and well-preserved pore morphologies. This structural improvement suggests that freezing pretreatment not only helps retain the integrity of the pore architecture but also contributes to its expansion. This effect is likely driven by the formation and recrystallization of intracellular ice crystals during the freezing process, which induce mechanical damage to cell walls and membranes. These disruptions weaken the structural elasticity of the cells, limiting their ability to revert to their original state and thereby facilitating the development of a more porous structure during drying (Li et al., 2024). Furthermore, the observed differences in microstructures across various freezing temperatures can be primarily attributed to the varying rates of ice crystal nucleation and growth (Impe et al., 2022). The SEM analysis clearly illustrates that freezing pretreatment, particularly at ultra-low temperatures, significantly enhances the pore structure of the final product. These structural modifications promote more efficient moisture removal during vacuum–microwave drying, ultimately improving the texture and mouthfeel of the persimmon crisps.
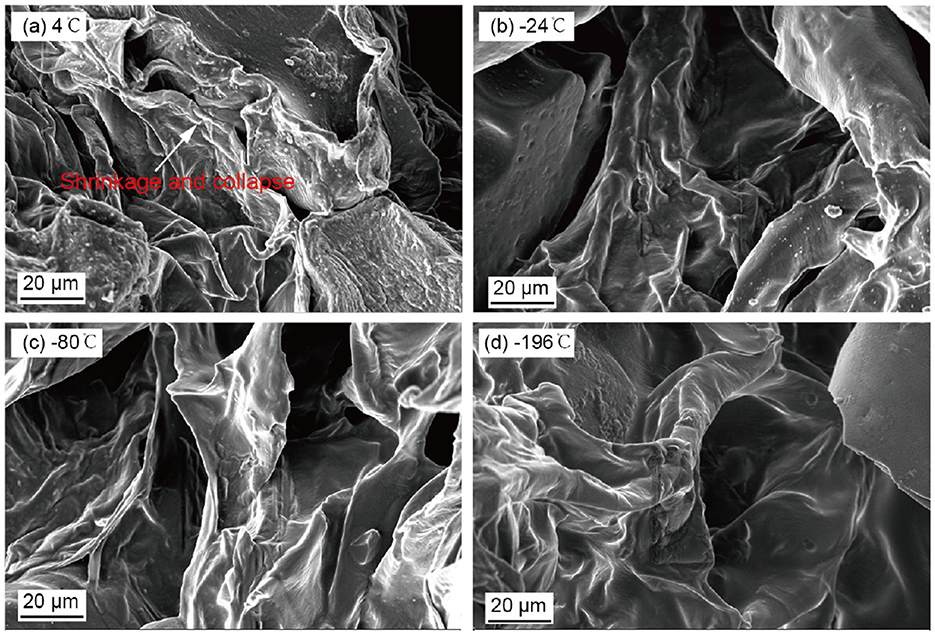
Figure 5. SEM images of persimmon crisps treated with different freezing temperatures: (a) −4°C, (b) −24°C, (c) −80°C, (d) −196°C.
4 Conclusions
This study proposes a novel strategy by coupling freezing pretreatment with VMD to effectively mitigate local charring, browning, shrinkage, and pore collapse on the surface of persimmon chips. This dual-method approach not only reduces the detrimental effects associated with conventional drying processes but also preserves the microstructural integrity of persimmon crisps. A comprehensive evaluation of physical properties—including color, browning index, volume, apparent density, expansion rate, and rehydration capacity—as well as sensory attributes such as texture, hardness, crispness, and chewiness, confirmed that freezing pretreatment significantly enhances product quality. Specifically, at a freezing temperature of –80°C, the samples exhibited optimal quality indicators, demonstrating substantial improvements compared to untreated samples. These results confirm that the combination of VMD with freezing pretreatment can effectively inhibit browning and charring phenomena in persimmon crisps while significantly enhancing their microstructure. However, since the experiments were conducted using a limited range of freezing temperatures and drying conditions, the generalizability of the results to other fruit types or large-scale applications may be limited. Nevertheless, these findings offer valuable insights for producing high-quality fruit and vegetable chips, and future research should focus on further optimizing freezing parameters and exploring the applicability of this technique to a broader range of perishable produce.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft. MZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AR: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. ZD: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YL: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZX: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2022GXNSFBA035605 and 2025GXNSFAA069983), the Guilin University of Technology (GUTQDJJ2024018), and the Opening Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Health Care Food Science and Technology.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
An, N.-N., Sun, W.-H., Li, B.-Z., Wang, Y., Shang, N., Lv, W.-Q., et al. (2022). Effect of different drying techniques on drying kinetics, nutritional components, antioxidant capacity, physical properties and microstructure of edamame. Food Chem. 373:131412. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131412
Ando, Y., and Nei, D. (2024). Effects of different pre-freezing methods and pressure levels on the pore structure and mechanical properties of microwave-vacuum dried apple. J. Food Eng. 369:111944. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2024.111944
Ando, Y., and Watanabe, T. (2023). Mechanical properties of dehydrofrozen carrots as a function of cell membrane damage, ice crystal development, and rehydration. J. Food Eng. 357:111643. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2023.111643
Bhattacharjee, S., Mohanty, P., Sahu, J. K., and Sahu, J. N. (2024). A critical review on drying of food materials: recent progress and key challenges. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 158:111643. doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2024.107863
Boateng, I. D. (2024). Recent processing of fruits and vegetables using emerging thermal and non-thermal technologies. A critical review of their potentialities and limitations on bioactives, structure, and drying performance. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 4240–4274. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2140121
Chu, Q., Li, L., Duan, X., Zhao, M., Wang, Z., Wang, Z., et al. (2023). Effect mechanism of different drying methods on the quality and browning for daylily. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 182:114862. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.114862
Dash, K. K., and Bhagya Raj, G. V. S. (2023). Ultrasound assisted microwave vacuum drying of persimmon fruit: modeling by artificial neural network and optimization by genetic algorithm. J. Food Process Eng. 46:14315. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.14315
El-Mesery, H. S., Ali, M., Qenawy, M., and Adelusi, O. A. (2024a). Application of artificial intelligence to predict energy consumption and thermal efficiency of hybrid convection-radiation dryer for garlic slices. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 138:109338. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2024.109338
El-Mesery, H. S., Hu, Z., Ashiagbor, K., and Rostom, M. (2024b). A study into how thickness, infrared intensity, and airflow affect drying kinetics, modeling, activation energy, and quality attributes of apple slices using infrared dryer. J. Food Sci. 89, 2895–2908. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.17064
El-Mesery, H. S., Huang, H., Hu, Z., Kaveh, M., and Qenawy, M. (2024c). Experimental performance analysis of an infrared heating system for continuous applications of drying. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 59:104522. doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2024.104522
EL-Mesery, H. S., Sarpong, F., Xu, W., and Elabd, M. A. (2022). Design of low-energy consumption hybrid dryer: a case study of garlic (Allium sativum) drying process. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 33:101929. doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2022.101929
Feng, S., Yi, J., Wu, X., Ma, Y., and Bi, J. (2023). Effects of cell morphology on the textural attributes of fruit cubes in freeze-drying: apples, strawberries, and mangoes as examples. J. Texture Stud. 54, 775–786. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12779
Hu, Y., Yan, H., Yin, Y., Li, X., Li, H., et al. (2022). Effect of microwave-assisted hydrothermal extraction on the bioactive compounds and antioxidant activities of dateplum persimmon juice and vinegar. LWT 154:112642. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112642
Hu, Z., Li, Y., El-Mesery, H. S., Yin, D., Qin, H., and Ge, F. (2022). Design of new heat pump dryer system: a case study in drying characteristics of kelp knots. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 32:101912. doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2022.101912
Impe, D., Ballesteros, D., and Nagel, M. (2022). Impact of drying and cooling rate on the survival of the desiccation-sensitive wheat pollen. Plant Cell Rep. 41, 447–461. doi: 10.1007/s00299-021-02819-w
Karaman, S., Toker, O. S., Çam, M., Hayta, M., Doğan, M., and Kayacier, A. (2014). Bioactive and physicochemical properties of persimmon as affected by drying methods. Drying Technol. 32, 258–267. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2013.821480
Li, G., Li, L., Liu, W., Cao, W., Chen, J., Ren, G., et al. (2024). Effects of multiphase microwave drying on the microstructure of chinese yam: a study based on x-ray micro-computed tomography technology. LWT 203:116327. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2024.116327
Li, L., Ren, X., Chen, J., Cao, W., Ren, G., Bhandari, B., et al. (2022). Changes and relationships of viscoelastic and physical properties of chinese yam during a novel multiphase microwave drying process. LWT 168:113969. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113969
Ma, Y., Bi, J., Wu, Z., Feng, S., and Yi, J. (2024). Tailoring microstructure and mechanical properties of pectin cryogels by modulate intensity of ionic interconnection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 262:130028. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130028
Mao, C., Chen, Y., Liu, T., Ye, P., Wang, Y., Chen, X., et al. (2024). Freezing pre-treatment improves radio frequency explosion puffing (RFEP) quality by altering the cellular structure of purple sweet potato [Ipomoea batatas (l) lam.]. Food Res. Int. 184:114265. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114265
Mokhova, E., Gordienko, M., Menshutina, N., Gurskiy, I., and Tvorogova, A. (2023). Ultrasonic freezing of polymers of various compositions before freeze drying: Effect of ultrasound on freezing kinetics and ice crystal size. Drying Technol. 41, 1663–1685. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2023.2173226
Nowak, D., and Jakubczyk, E. (2022). Effect of pulsed electric field pre-treatment and the freezing methods on the kinetics of the freeze-drying process of apple and its selected physical properties. Foods 11:2407. doi: 10.3390/foods11162407
Polat, A., Taskin, O., and Izli, N. (2024). Assessment of freeze, continuous, and intermittent infrared drying methods for sliced persimmon. J. Food Sci. 89, 2332–2346. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16994
Qin, Y., Duan, Z., Zhou, S., and Wei, Z. (2022). Effect of intermittent microwave drying on nutritional quality and drying characteristics of persimmon slices. Food Sci. Technol. 42:37422. doi: 10.1590/fst.37422
Qiu, Y., Bi, J., Jin, X., Wu, X., Hu, L., and Chen, L. (2022). Investigation on the rehydration mechanism of freeze-dried and hot-air dried shiitake mushrooms from pores and cell wall fibrous material. Food Chem. 383:132360. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132360
SAMR and SAC (2023). Quality Grades of Products for Persimmon: Gb/t 20453–2022. Beijing: China Standards Press.
Sedmak, I., Moze, M., Kambic, G., and Golobic, I. (2023). Heat flux analysis and assessment of drying kinetics during lyophilization of fruits in a pilot-scale freeze dryer. Foods 12:3399. doi: 10.3390/foods12183399
Sehrawat, R., Nema, P. K., and Kaur, B. P. (2018). Quality evaluation and drying characteristics of mango cubes dried using low-pressure superheated steam, vacuum and hot air drying methods. LWT 92, 548–555. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.03.012
Tabtiang, S., Umroong, P., and Soponronnarit, S. (2022). Comparative study of the effects of thermal blanching pretreatments and puffing temperature levels on the microstructure and qualities of crisp banana slices. J. Food Process Eng. 45:e13931. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.13931
Tang, X., Xian, Z., Liu, Y., Ren, A., Tan, H., Pan, Y., et al. (2024). Optimization of variable-temperature pressure-difference puffing drying process for persimmon chips using response surface methodology. Foods 13:3830. doi: 10.3390/foods13233830
Wang, M., Gao, Y., Hu, B., Wang, J., Si, X., Zhu, B., et al. (2023). Freeze-thaw pretreatment improves the vacuum freeze-drying efficiency and storage stability of goji berry (Lycium barbarum L.). LWT 189:115439. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.115439
Wu, B., Guo, X., Guo, Y., Ma, H., and Zhou, C. (2021). Enhancing jackfruit infrared drying by combining ultrasound treatments: effect on drying characteristics, quality properties and microstructure. Food Chem. 358:129845. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129845
Wu, T., Duan, Z., and Wang, C. (2023). Effects of microwave drying on color change, phenolic substance content and phenolase activity of different parts of persimmon slices. J. Food Measur. Character. 18, 357–369. doi: 10.1007/s11694-023-02162-6
Xu, X., Zhang, L., Feng, Y., Zhou, C., Yagoub, A. E. A., Wahia, H., et al. (2021). Ultrasound freeze-thawing style pretreatment to improve the efficiency of the vacuum freeze-drying of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) moench) and the quality characteristics of the dried product. Ultrason. Sonochem. 70:105300. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105300
Yan, X., Li, H., Yi, J., Sun, C., Yu, Q., and Wen, R. (2025). Unravelling the effects of drying techniques on porphyra yezoensis: Morphology, rehydration properties, metabolomic profile, and taste formation. Food Chem. 464:141562. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141562
Yang, K.-W., Wang, D., Vidyarthi, S. K., Li, S.-B., Liu, Z.-L., Wang, H., et al. (2022). Pulsed vacuum drying of persimmon slices: drying kinetics, physicochemical properties, microstructure and antioxidant capacity. Plants-Basel 11:2500. doi: 10.3390/plants11192500
Yosefiyan, M., Mahdian, E., Kordjazi, A., and Hesarinejad, M. A. (2024). Freeze-dried persimmon peel: a potential ingredient for functional ice cream. Heliyon 10:e25488. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25488
Zhang, L., Yu, X., Mujudar Arun, S., and Zhou, C. (2022). Effect of freeze-thaw pretreatment combined with variable temperature on infrared and convection drying of lotus root. LWT 154:112804. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112804
Zhang, M., Wu, C., Zhang, H., Yang, N., Wang, C., Jike, X., et al. (2024). Comparison of different drying technologies for kiwifruit pomace: changes in physical characteristics, nutritional properties and antioxidant capacities. Food Chem. 451:139497. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.139497
Zhao, C.-C., Ameer, K., and Eun, J.-B. (2021). Effects of various drying conditions and methods on drying kinetics and retention of bioactive compounds in sliced persimmon. LWT 143:111149. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111149
Nomenclature
Keywords: freezing pretreatment, persimmon crisps, vacuum-microwave drying, browning, texture, physicochemical properties
Citation: Tang X, Zhao M, Ren A, Duan Z, Liu Y and Xian Z (2025) Mitigating browning and improving texture issues in persimmons: the impact of freezing pretreatment on vacuum microwave drying. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1523548. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1523548
Received: 06 November 2024; Accepted: 28 April 2025;
Published: 30 May 2025.
Edited by:
Poonam Rani, Teagasc Food Research Centre, IrelandReviewed by:
Hany El-Mesery, Jiangsu University, ChinaXu Duan, Henan University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Tang, Zhao, Ren, Duan, Liu and Xian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhaokun Xian, emhhb2t1bnhpYW5Ac3QuZ3h1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Xiaoxian Tang1
Xiaoxian Tang1 Aiqing Ren
Aiqing Ren Yan Liu
Yan Liu Zhaokun Xian
Zhaokun Xian