- 1School of Economics and Management, Jiangxi Agricultural University, Nanchang, China
- 2Jiangxi Institute of Scientific and Technological Information, Nanchang, China
Introduction: The problem of agricultural non-point source pollution in China seriously affects the sustainability of grain production and poses a great threat to food security. The key to solving the problem of agricultural non-point source pollution is to change farmers’ past agricultural production methods at the source of production and make them adopt pro-environmental agricultural production behaviors. Policy-based agricultural insurance can incentivize farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors by reducing their production risks and protecting their agricultural income.
Methods: Based on the theory of farmers’ behavior and the theory of planned behavior, this paper empirically analyzes the influence mechanism of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors in Jiangxi Province, China, through the establishment of the OLS model and the Ordered-Logit model. In addition, this paper also explores the mediating roles of planting scale, planting structure and risk attitude through the mediating effect model and Bootstrap method.
Results: The main findings of this paper are as follows: (1) Policy-based agricultural insurance can effectively enhance farmers’ adoption willingness to adopt pro-environmental production willingness. (2) Policy-based agricultural insurance can enhance farmers’ pro-environmental production willingness by incentivizing them to expand the scale of planting. (3) Policy-based agricultural insurance can increase farmers’ pro-environmental production willingness by changing their risk attitudes and increasing their risk preferences.
Discussion: Based on the results of the study, this paper suggests that the government should continue to optimize the policy-based agricultural insurance products, expand the coverage, improve the payout process, increase the payout capacity, and enhance its stimulating effect on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors.
1 Introduction
Food security is an important foundation for national security and a major strategic issue of global significance that has a bearing on the country’s livelihood, social stability and national self-reliance (Ding et al., 2011). Food security is usually measured by such indicators as food production, per capita food possession, and the area sown with food. These indicators, in turn, usually affect the national standard of living, determine the degree of acceptance of the government’s level of governance, and have a very important impact on national security (Gao et al., 2012). Chinese agriculture has made great progress and development over the past four decades, and one of its most important achievements is that we have achieved basic self-sufficiency in food (Niu et al., 2022). However, along with the continuous population growth, rapid economic development, and the continuous advancement of urbanization and industrialization, the factor constraints on food production are tightening, and soil and water pollution are intensifying, and other problems are becoming more and more prominent (Gao et al., 2012). With 7% of the world’s land, China produces 20% of the world’s food, and uses 35% of the chemical fertilizers and nearly 50% of the pesticides (Gao et al., 2012). Excessive use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers, as well as heavy metals and other harmful substances, spread through field runoff, drainage and underground infiltration, resulting in increased agricultural surface pollution (Niu et al., 2022). It is imperative to promote the transformation of the grain production methods of the farmers.
Jiangxi Province, as one of the main rice-producing areas in China, with a grain sown area of 3,774,300 hectares and an output of 21,985,000 tons in 2023, is also facing a serious problem of agricultural nonpoint source pollution. Rice is one of the most important food crops in China. Some studies have shown that rice has been one of the more serious crops in China in terms of indiscriminate use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides (Wei et al., 2021). At present, the prevention and control of agricultural non-point source pollution is the key to promote the sustainable development of grain production in Jiangxi Province (Zhang et al., 2022). At the same time, agricultural non-point source pollution formed in the process of grain production cannot be dealt with in a similar way to the end-of-pipe treatment of industrial pollution, and it is the fundamental way to deal with agricultural surface source pollution in grain production to motivate farmers to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors by grasping from the source of agricultural production (Mao et al., 2023). Farmers’ pro-environmental behavior refers to the agricultural business model in which farmers consciously carry out reduction, reuse and low pollution in the agricultural production process (Salazar and Rand, 2016), which has obvious positive externality characteristics. However, in recent years, the relatively low returns from grain production and the frequent occurrence of extreme weather have led to a low level of willingness of rice farmers to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors in Jiangxi Province (Jensen, 2002).
Agricultural insurance is an important means of dispersing the risks of agricultural production and operation, and has become one of the most effective agricultural risk protection tools for Chinese agricultural growers. In 2020, China’s agricultural insurance premium income will be as high as 81.493 billion yuan, which will be the largest premium income in the world (Guo et al., 2014). According to the latest data from China’s National Ministry of Finance, China’s agricultural insurance premium income will be about 150 billion yuan in 2024, making China the world’s largest agricultural insurance market (Xuguang and Zhihui, 2024). Specifically, in Jiangxi Province, according to the National Financial Supervisory Authority (NFSA), the scale of agricultural insurance in Jiangxi Province ranked No. 1 in the country in 2023, of which the coverage rate of rice insurance reached 90 per cent, with an area of 313,619,193 hectares insured by rice insurance, and the scale of premiums reached RMB 2.076 billion. Agricultural insurance in Jiangxi Province is mostly policy-based agricultural insurance. Policy-based agricultural insurance is a kind of direct physical cost insurance provided to crops affected by natural disasters, and the government will pay 70% of the premium, with rice being the main insured crop (Ding et al., 2011; Niu et al., 2022; Mao et al., 2023). This type of insurance is called policy-based agricultural insurance because it is established by a partnership between the government and insurance and the government subsidizes the premiums. Policy-based agricultural insurance can share farmers’ planting risks, provide farmers with income protection, increase farmers’ risk preferences, and thus enhance their willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors (Kollmuss and Agyeman, 2002; Atanu et al., 1994). Agricultural insurance in this paper refers to policy-based agricultural insurance.
Based on the survey data from the College of Economics and Management of Jiangxi Agricultural University from June to July 2023 on grain farmers in Jiangxi Province, and with the help of Stata17 software, this paper empirically analyzes the influence mechanism of the impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on the willingness of adoption of pro-environmental production behaviors of grain farmers in Jiangxi Province. The purpose of this study is to explore the stimulating effect of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors and its influencing mechanism, so as to put forward reasonable suggestions for optimizing the policy-based agricultural insurance, enhancing the farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors, and reducing the agricultural non-point source pollution in Jiangxi Province. This study provides theoretical references and reasonable suggestions for improving policy-based agricultural insurance and enhancing farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors in Jiangxi Province, and it has positive practical significance for reducing agricultural non-point source pollution and promoting the sustainable development of grain production in Jiangxi Province.
The rest of this study is structured as follows: Section 2 is the literature review, combing the current literature on agricultural insurance and pro-environmental production behavior. Section 3 is the theoretical analysis and research hypothesis, which analyzes the mechanism of the influence of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors and puts forward the research hypothesis of this paper. Section 4 is research methodology and design, which introduces the research methodology of this paper, the specific empirical research design, and the preliminary test. Section 5 is the empirical analysis of the impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior, including tests of the mediating roles of planting scale, planting structure, and risk attitudes. Section 6 is the discussion, including the discussion of the results, innovations and limitations. Section 7 contains conclusions and implications.
2 Literature review
At present, there are a large number of studies which focused on the change of farmers’ production behavior (Butler, 2000). Farmers’ implementation of pro-environmental behaviors in food production, such as the adoption of environmentally friendly technologies or the use of environmentally friendly production materials and products, and the production of environmentally friendly products, have attracted much attention because they can curb agricultural pollution at the source and achieve sustainable development (Barham et al., 2015). Existing studies have found that organizational incentives, social capital, land size, policy support, and risk preference have a certain effect on farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior (Zheng and Zhao, 2025; Bhuiyan et al., 2022), of which the low implementation rate of farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior due to risk is worth focusing on. Risk management can share farmers’ agricultural risks and protect farmers’ agricultural income, which is an effective way to improve farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior (Zheng and Zhao, 2025).
Based on a study of plantation family farms in Shandong Province, China, some researchers have found that agricultural insurance can significantly promote the adoption of green agricultural technologies by family farms by changing income expectations and thus influencing factor allocation (Zhang et al., 2020). Green production techniques usually refer to environmentally friendly agricultural production methods, often including the application of organic fertilizers, reduced application of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and the resourceful reuse of straw, etc., and the production practices that incorporate these techniques are often referred to as pro-environmental production practices (Kollmuss and Agyeman, 2002; Atanu et al., 1994). Based on the above studies, it is clear that the role of agricultural insurance in promoting the adoption of pro-environmental production behavior by farmers is a question worth studying.
Current researchers’ studies focus on the direct impact of agricultural insurance on farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior or explore the impact of agricultural insurance on farmers’ adoption of specific green production technologies in different production segments (Zheng and Zhao, 2025; Bhuiyan et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2020; Akinrinola and Okunola, 2014). Some researchers have analyzed the role of agricultural insurance in promoting the adoption of green and low-carbon technologies, and found that agricultural insurance promotes the adoption of green technologies by reducing the risk of technology adoption and changing farmers’ expected income (Zhang et al., 2020). Some researchers have also argued that crop insurance can spread risks, protect farmers’ income, and promote the adoption of green technologies in agriculture by using crop insurance as collateral to obtain production financing and increase investment in equipment (Ahmed et al., 2022; Hou and Wang, 2022). Participation in agricultural insurance can increase the likelihood that agriculture will adopt pro-environmental production behaviors by ensuring stable incomes and effectively changing farmers’ attitudes toward risk in unfavorable situations (Li et al., 2025; Cai et al., 2025; Ejeta and Bai, 2025).
Although a large number of studies have focused on the impact of agricultural insurance on farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior, fewer studies have delved into the mechanisms of agricultural insurance’s impact on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behavior and the possible mediating variables. Moreover, agricultural insurance in existing studies usually does not focus on a specific type of insurance, but only uses the term “agricultural insurance” in general, and is unable to explore the impact of specific agricultural insurance products on farmers’ production behavior (Chen et al., 2017). In addition, few studies have examined the effects of agricultural insurance on pro-environmental production behavior at different stages of production. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to explore the mechanism of the influence of policy-based agricultural insurance on the willingness of farmers’ pro-environmental production behaviors in the context of serious agricultural non-point source pollution.
This study explores the influence mechanism of the impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors, and comparatively analyzes the differential impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors in different production segments. This paper fills the research gap between agricultural insurance and farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior, verifies the incentive role of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behavior and the mediating role of planting scale and risk attitude, and has certain theoretical significance.
3 Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
3.1 Analysis of the impact of agricultural insurance on farmers’ production behavior
Policy-based agricultural insurance can effectively share farmers’ production risks, improve farmers’ production confidence, motivate them to optimize factor allocation, change their production behaviors, enable them to shift from traditional chemical production methods to green production methods, and promote farmers to implement pro-environmental production behaviors (Breckner et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2023; Jiang et al., 2023). Some researchers have found that agricultural insurance has a stimulating effect on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors through empirical studies of Chinese farmers (Wei et al., 2021; Hou and Wang, 2022).
In addition, the implementation of the ‘insurance + subsidy’ policy by the government has effectively increased the motivation of farmers to implement pro-environmental production behavior (Hungerford and O’Donoghue, 2016). The effect of agricultural insurance on farmers’ pro-environmental production behaviors is influenced by government support (Sherrick et al., 2004), so policy-based agricultural insurance is more likely to motivate farmers to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors.
Based on the research of the above researchers, this paper proposes the following hypotheses:
H1: Policy agricultural insurance can stimulate farmers’ adoption willingness of pro-environmental production behaviors.
3.2 Analysis of the mediating effect of planting scales
Agricultural insurance will incentivize farmers’ factor inputs, which in turn will expand their planting scale (Fang et al., 2021); and the expansion of planting scale will reduce farmers’ field management costs, creating economies of scale, and will make it easier for farmers to make medium- and long-term production plans (Tan et al., 2022). The implementation of pro-environmental production behaviors can not only alleviate the pollution of arable land and ensure the sustainable use of land, but also reduce the production costs of farmers, as the expected benefits of implementing pro-environmental production behaviors continue to increase (Goodwin and Rejesus, 2008), the willingness of farmers to implement pro-environmental production behaviors as ‘rational economic actors’ will also grow, which will ultimately lead to the implementation of pro-environmental production behaviors. This will ultimately lead to the implementation of pro-environmental production behaviors (Babcock and Hennessy, 1996). In other words, there may be a mediating effect of planting scale in the process of agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior (Brick and Visser, 2015).
Based on the research of the above researchers, this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
H2: There is a mediating effect of planting scale in the process of policy agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior adoption intention.
3.3 Analysis of the mediating effects of planting structure
Agricultural insurance has an impact on the cropping structure of farmers (Fahad et al., 2018). On the one hand, since the crop varieties covered by current policy-based agricultural insurance are mainly related to food security (Li et al., 2022), the role of agricultural insurance development in promoting crop structure adjustment is mainly reflected in incentivizing agricultural operators to plant more food crops (Goodwin et al., 2004). On the other hand, as diversified planting increases time cost, management cost and labor cost, while agricultural insurance can effectively alleviate the Self-Insurance behavior of farmers’ diversified planting, and significantly enhance the tendency of farmers to specialize in planting (Dube et al., 2016). The ‘grain-tendency’ of farmers’ planting structure will reduce the cost of implementing pro-environmental production behaviors, increase the willingness of farmers to implement pro-environmental production behaviors, and motivate them to implement pro-environmental production behaviors (Pratiwi and Budiasa, 2022). That is, the planting structure may play a significant role in the process of agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ pro-environmental production behaviors. Environmental production behavior (Wu et al., 2024).
Based on the research of the above researchers, this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
H3: There is a mediating effect of planting structure in the process of policy-based agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors.
3.4 Analysis of the mediating effect of risk attitude
Agricultural technology inputs are risky and irreversible, and agriculture itself has the characteristic of ‘living off the land’, so the risk characteristics of agricultural technology and implementation of new production behaviors of farmers are more prominent than in other industries, and therefore risk attitude is one of the most important factors influencing the production behaviors of farmers (Babcock and Hennessy, 1996). And the individual risk attitude determines the individual risk decision-making behavior to a certain extent (Gao et al., 2019).
And agricultural insurance affects growers’ risk attitude and then changes their production behavior (Lu et al., 2024); agricultural insurance can smooth natural risks, reduce farmers’ risk aversion, and motivate their pro-environmental production behaviors (Ahsan et al., 1982). Some researchers have proved that agricultural insurance can change farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior by changing their risk attitudes and then changing their pro-environmental production behavior (Yu et al., 2019). That is, in the process of agricultural insurance affecting farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior, there may be a mediating effect of risk attitude (Liu et al., 2023).
Based on the research of the above researchers, this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
H4: There is a mediating effect of risk attitude in the process of policy agricultural insurance affecting farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior adoption intention.
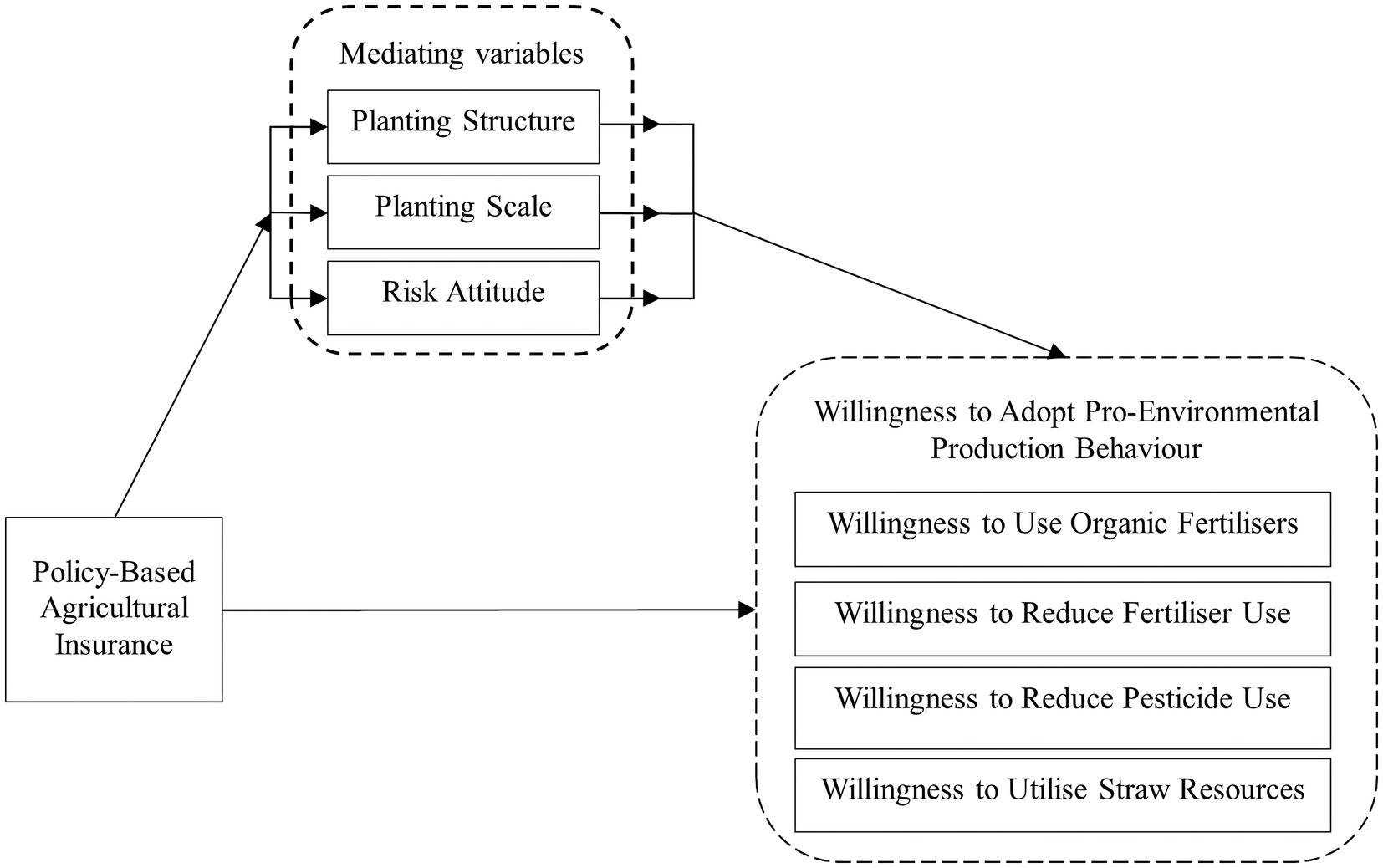
In order to answer the key question of the mechanism of the influence of policy agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to pro-environmental production behavior, this paper, based on the relevant studies of existing researchers, combines the theory of farmer behavior and the theory of planned behavior to explore in depth the mechanism of the influence of policy agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to pro-environmental production behavior by affecting farmers’ planting scale, planting structure and risk attitude (Grabowski et al., 2016; Chai and Zhang, 2023), this paper finally constructed the theoretical framework of ‘policy agricultural insurance - planting scale, planting structure, risk attitude - pro-environmental production behavior and willingness’, as shown in Figure 1.
4 Materials and methods
4.1 Research methodology
4.1.1 Theoretical analysis method
Based on the 2023 summer ‘Double Hundred and Double Thousand’ research data from the School of Economics and Management of Jiangxi Agricultural University, this paper explores the influence mechanism of policy-based agricultural insurance on the willingness of pro-environmental production behaviors of farmers based on the theory of farmers’ behaviors (Zheng and Zhao, 2025), the theory of planned behaviors (Zhang et al., 2020), and the assumption of “rational small farmers” (Li et al., 2025). Eventually, this paper constructs the theoretical framework of ‘agricultural insurance - individual and production characteristics - pro-environmental production behavior willingness’, which provides a theoretical basis for the empirical research of this paper.
4.1.2 Literature analysis method
Firstly, this study combed the research history of domestic and foreign researchers on policy-based agricultural insurance and farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior, and elaborated the different insights of researchers on the impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior, which provided a rich theoretical foundation for the study of this paper. Second, this paper points out through the literature review that fewer current studies have explored the influence mechanism of policy-based agricultural insurance affecting farmers’ pro-environmental production willingness from a micro perspective, which affirms the research value and marginal contribution of this paper.
4.1.3 Questionnaire survey method
The data for the empirical analysis of this study came from the ‘Two Hundred and Two Thousand’ rural revitalization research conducted by the School of Ecological Economics and Management of Jiangxi Agricultural University in the summer of 2023. The ‘Double Hundred and Double Thousand’ research adopts a combination of stratified sampling and random sampling, and a total of 2,160 samples of farmers covering 216 administrative villages in 24 counties of 11 prefectural-level cities in Jiangxi Province were taken, and 1,440 effective samples of farmers engaging in rice cultivation were retained as the total samples for this paper, which provide the data basis for the empirical analysis of this paper. The total sample of this paper provides a data base for the empirical analysis of this paper to be carried out, and also provides a realistic basis for this paper to study the current situation and problems in the implementation of agricultural insurance and pro-environmental production behaviors of rice growers in Jiangxi Province.
4.1.4 Empirical analysis method
Based on the existing studies on farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior, this paper chooses the OLS and the ordered logit models, respectively, to explore the impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on the willingness of pro-environmental production behaviors of rice farmers in Jiangxi Province (Zhang et al., 2020; Ahmed et al., 2022; Hou and Wang, 2022). OLS model and ordered logit model can fully reflect the influence coefficient and significance of independent variables on dependent variables (Li et al., 2025), so this paper selected them to explore the effect of policy-based agricultural insurance on the intention of rice farmers to pro-environment production behavior in Jiangxi Province. However, these two models have limitations (Cai et al., 2025), both of them have requirements for the data types of in-dependent variables, and this point is fully considered in the subsequent model establishment in this paper. In addition, this paper examines the mediating effects of planting scale, planting structure, and risk attitude in the process of policy agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors with the help of the mediating effects testing process provided by Wen ZL (Chen et al., 2017).
4.2 Model building
4.2.1 OLS model
In this paper, the dependent variable ‘farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors’ is a continuous numerical variable that is a composite score calculated using the entropy method on farmers’ willingness to adopt the four pro-environmental production behaviors. Therefore, this paper chooses OLS model to regression analysis of farmers’ willingness to participate in agricultural insurance and participation decision-making (Babcock and Hennessy, 1996; Goodwin et al., 2004), and the expression of the model is as follows:
In Equation 1-1, X1, X2…Xm represent the m influencing factors of farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior willingness, which includes core explanatory variables, mediating variables and control variables. Willingm represents the explanatory variable (the mth farmer’s willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors), F(−) represents the probability density function of the cumulative normal distribution, β0 represents the constant term, Xm represents the factors influencing the specific growers’ agricultural insurance participation behaviors, βm is the estimation parameter, and μ is the random perturbation term.
4.2.2 Ordered-logit model
In this paper, the dependent variable ‘farmers’ willingness to the four pro-environmental production behaviors’ is an ordered multicategorical discrete variable with progressive order, taking the value of 1–5. Therefore, this paper chooses the ordered logit model to investigate the impact of policy agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to the four pro-environmental production behaviors (Zhang et al., 2023; Fang et al., 2021), and the expression of the model is as follows:
In Equation 2-1, Xn* represents all the factors that may have an impact on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors, n represents individual farmers, β0 represents a constant term, θ represents a random disturbance term obeying a normal distribution, βn represents the unknown impact coefficient to be estimated, and y* is the explanatory variable (willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors including the willingness to apply organic fertilizers, the willingness to reduce the use of fertilizers, the willingness to reduce the use of pesticides, and the willingness to treat straw resources). As y* is an unobservable latent variable, it is represented by the observable alternative variable ym. The Equation (2-2) represents the relationship between the unobservable latent variable y* and its alternative variable ym, where φ1, φ2, φ3, φ4, and φ5 are the positional split points of the dependent variable, and satisfy φ1 < φ2 < φ3 < φ4 < φ5.
4.2.3 Mediation effects model
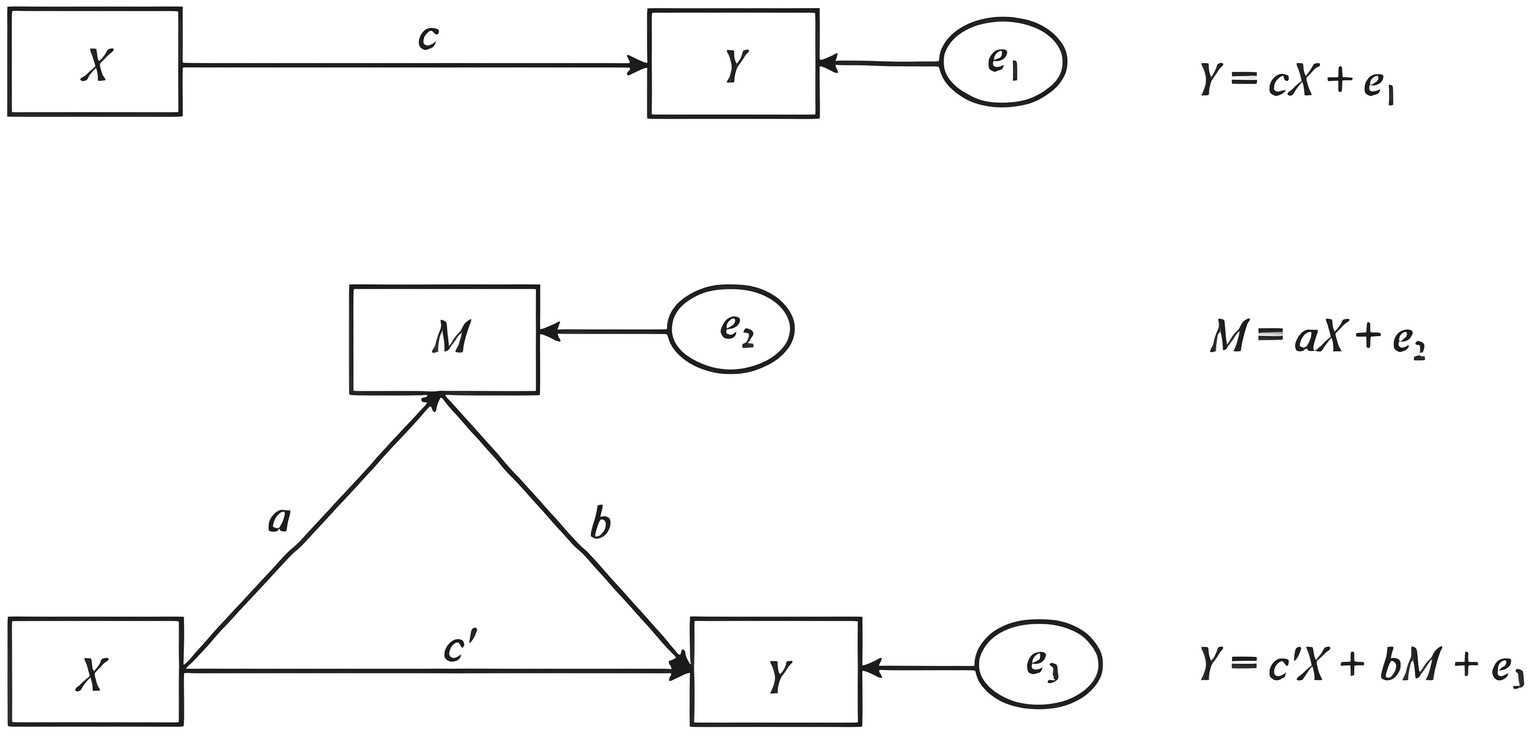
At present, mediation effect analysis has been widely applied in the research of farmers’ behavior analysis, which is used to explore the mechanism of the role of some mediating variables between the independent variables and the dependent variables. Since the comprehensive willingness of farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior is a discrete numerical variable, in order to explore the mediating effect of planting scale, planting structure, and risk attitude in the process of agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ willingness to pro-environmental production behavior, this paper refers to the mediating effect testing process provided by Wen ZL (Chen et al., 2017), and establishes the mediating effect model based on the OLS model as follows:
In Equations 3-1–3-3, Willingg denotes the willingness of pro-environmental production behavior of the sample farmers, where α0, β0, γ0 are constants, Xg is the policy agricultural insurance participation, e1, e2, e3 are the residuals of the model regression, Mg denotes the mediator variables, i.e., cultivation scale, cultivation structure and risk attitude, and Kg denotes the control variables. α1, β1, γ1 are the core explanatory variables, i.e., regression coefficients of policy agricultural insurance participation, which denote the overall effect of policy agricultural insurance participation affecting the willingness of pro-environmental production behaviors of the gth farm household, the effect of policy agricultural insurance participation on the mediator variable of the gth farm household, the direct effect of the mediator variable on the willingness of pro-environmental production behaviors of the gth farm household, respectively, whereas α2, β2, and γ3 are regression coefficients of the control variables, and γ2 denotes the regression coefficient of mediator variable on the willingness of pro-environmental production behaviors of the gth farmer’s willingness to pro-environmental production behavior direct effect. Substituting Equation 2-1 into Equation 2-2, the mediating effect of policy agricultural insurance participation β1γ2 can be obtained, i.e., the indirect effect of policy agricultural insurance participation on the willingness of pro-environmental production behavior of farmers by influencing their mediating variables (planting scale, planting structure and risk attitude).
Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of the mediation model of this study. In Figure 2, X is the policy-based agricultural insurance participation, M is the mediating variables (planting scale, planting structure and risk attitude), Y is the willingness to pro-environmental production behaviors, c is the main effect of the policy agricultural insurance participation on the willingness to pro-environmental production behaviors of farmers, including the direct and indirect effects of the policy agricultural insurance participation on the willingness to pro-environmental production behaviors of farmers, where a is the direct effect of the policy agricultural insurance participation on the mediator variable, b is the direct effect of the mediator variable on farmers’ willingness to pro-environmental production behavior, c’ is the direct effect of policy agricultural insurance participation on farmers’ willingness to pro-environmental production behavior, and e1, e2 and e3 are all disturbance terms.
4.3 Variable selection and definition
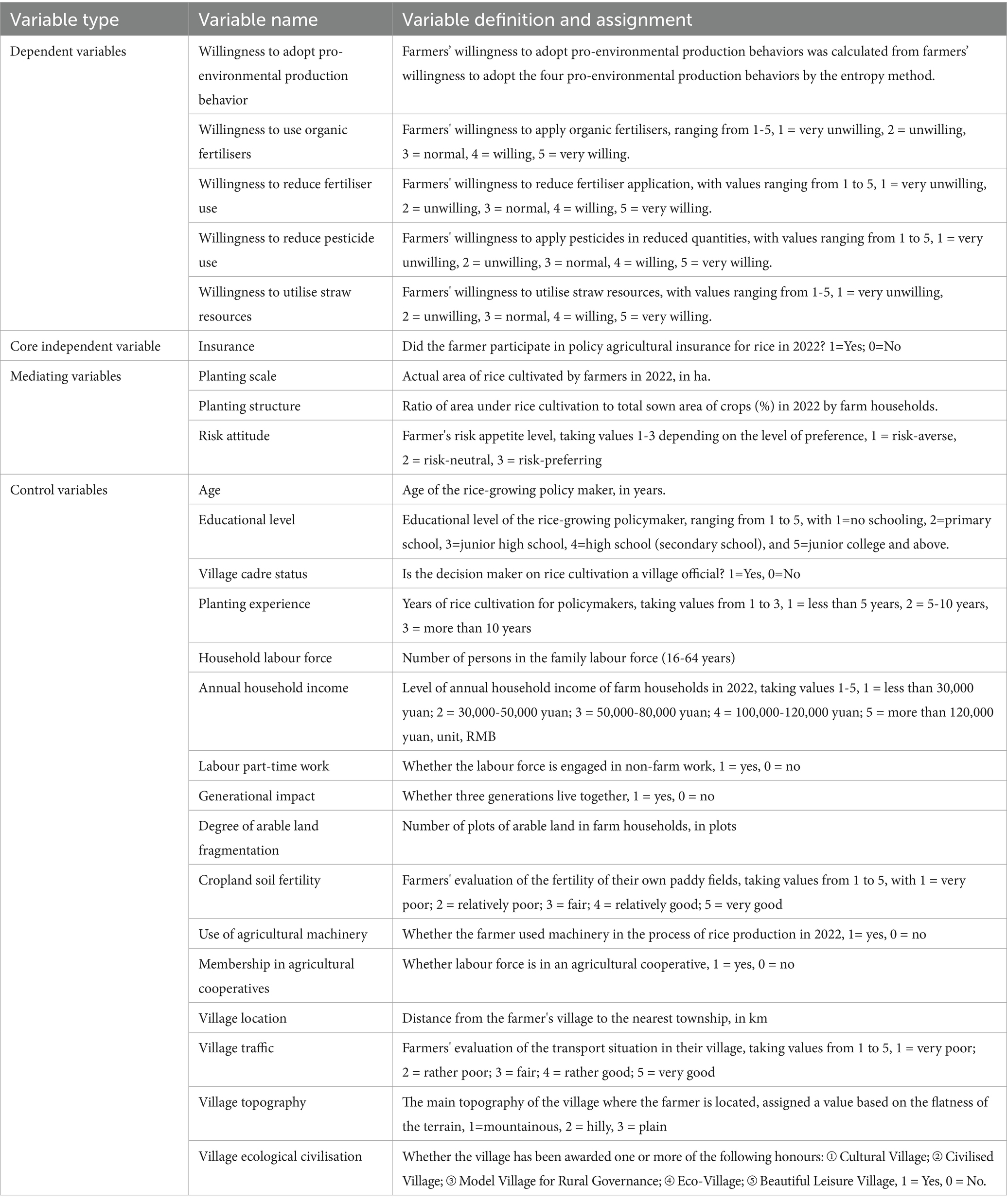
Dependent variable. Including farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior comprehensive adoption willingness and the adoption willingness of the four types of pro-environmental production behavior (Ejeta and Bai, 2025). The pro-environmental production behaviors of farmers studied in this paper include four types of organic fertilizer application behaviors, chemical fertilizer reduction application behaviors, pesticide reduction application behaviors and straw resource treatment behaviors (Babcock and Hennessy, 1996). In this paper, the responses of farmers to the question “Are you willing to implement the four types of pro-environmental production behaviors?” were taken as their willingness to adopt the four specific types of pro-environmental production behaviors (Brick and Visser, 2015), and assigned values using a Likert scale, which ranges from 1 to 5, with the values from low to high representing “very unwilling,” “relatively unwilling,” “average,” “more willing” and “very willing.” Finally, this paper uses the entropy method to calculate the weight and comprehensive score of farmers’ willingness to adopt four kinds of pro-environment production behaviors, and take the comprehensive score value as farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environment production behaviors (comprehensive willingness) (Ajzen and Madden, 1986).
Entropy method is a kind of multi-criteria method which combines the information value provided by entropy to determine the weight. The higher the entropy, the more chaotic the data, the less information it carries, the smaller the utility value, and thus the smaller the weight (Goodwin et al., 2004). According to the definition of “farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environment production behaviors,” this paper adopts entropy method to standardize the values of farmers’ willingness to adopt four kinds of environment-friendly production behaviors and calculate the weights (Liu et al., 2023). Finally, the comprehensive score is obtained as the value of the explained variable “farmers’ willingness to adopt environment-friendly production behaviors.” The specific construction method is as follows (Gao et al., 2019):
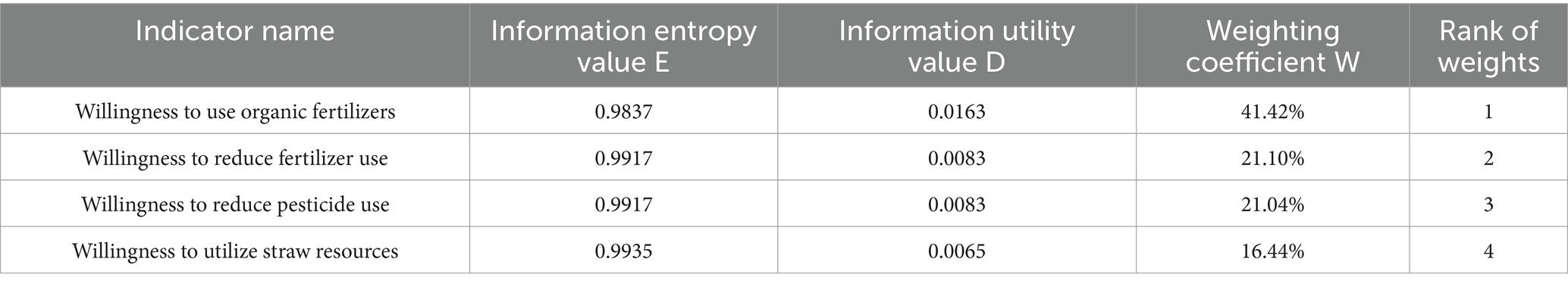
Firstly, the base matrix is constructed. Let S = (sij), sij is the standardized form of the observed value of the jth indicator of the ith farmer’s willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors. Secondly, use matrix S to generate a new matrix P = (pij), and the correspondence between matrix S and P is shown in Equation 4-1. It should be noted here that since the farmers’ willingness to adopt the four pro-environmental production behaviors are all positive variables and have the same units, there is no need to quantify the data (Goodwin et al., 2004). The entropy Ej of the jth indicator is found and the formula is shown in Equation 4-2. Where the value of n is equal to the total number of farmers in the sample since the sample data are cross-sectional. Then, the indicator weights Wj and the comprehensive evaluation value Vi are calculated, and the formula is shown in Equation 4-3. Finally, according to the indicator weights and comprehensive scores derived from the entropy value method, the weights of the farmers’ willingness to adopt the four pro-environmental production behaviors and the value of the comprehensive willingness are obtained (Chambers, 1989). The results of the weights of farmers’ willingness to adopt the four pro-environmental production behaviors calculated by the entropy value method in this paper are in Table 1.
Table 1 shows that the indicator ‘Willingness to Use Organic Fertilizers’ has the lowest entropy value, the highest utility value and the highest weight. This paper ranked the farmers’ willingness to adopt the four pro-environmental production behaviors according to their weights, and concluded that: Willingness to Use Organic Fertilizers > Willingness to Reduce Fertilizer Use > Willingness to Reduce Pesticide Use > Willingness to Utilize Straw Resources.
Core independent variable. Referring to related studies (Wang et al., 2022), this paper selects farmers’ policy agricultural insurance participation behavior as the core ex-explanatory variable of this paper, i.e., ‘Did farmers purchase rice planting insurance in 2022?’, taking values of 0 and 1, representing not purchased and purchased, respectively.
Mediating variables. Referring to the relevant studies, this paper selected planting scale, planting structure and risk attitude as the mediating variables of policy agricultural insurance affecting the process of pro-environmental production behaviors of farmers (Grabowski et al., 2016; Chai and Zhang, 2023), and tested the transmission mechanism of the three kinds of mediating effects respectively, and then compared and analyzed the size of the mediating effects.
Among them, the scale of cultivation refers to the area of land actually cultivated by farmers, i.e., ‘the area of land actually cultivated by farmers in 2022’, in hectares (Lu et al., 2024); the planting structure refers to the proportion of rice among the crops grown by farmers, i.e., ‘the proportion of rice planted area to the total sown area of crops by farmers in 2022’ in per cent (Li et al., 2022); risk attitude refers to the degree of risk preference of the farmer and is assigned a value according to the degree, risk aversion = 1, risk neutrality = 2, and risk preference = 3 (Atanu et al., 1994; Butler, 2000; Babcock and Hennessy, 1996).
Control variables. The control variables include individual farmer characteristics, family characteristics, production and operation characteristics, and village characteristics. Among them, the individual farm household characteristics variables were selected as age, education level, whether they were village cadres, and planting experience (Chambers, 1989); the household characteristics variables were selected as household labor force, annual household income, whether the labor force was part-time, and whether they were living together for three generations (Norton et al., 2014); production and operation characteristic variables were selected as the degree of fine fragmentation of arable land, soil fertility of arable land, whether to use machinery, and whether to join an agricultural co-operative (Hazell, 1982); and village characteristic variables were selected as the location of the village, village traffic condition, main topography of the village, and ecological civilization of the village (Dai and Cheng, 2022).
In this paper, a table of classification and definition of all variables was shown in Table 2.
4.4 Data sources
The research data in this paper comes from the “Double Hundred and Double Thousand” Farmer Questionnaire Survey on Rural Revitalization conducted in Jiangxi Province by the School of Economics and Management of Jiangxi Agricultural University in June–July 2023. The survey was called the ‘Double Hundred and Double Thousand’ survey because it covered more than 2,000 farmers in over 200 villages in Jiangxi Province. The questionnaire survey of “Double Hundred and Double Thousand” includes the investigation of farmers’ individual characteristics, family characteristics, agricultural production and operation characteristics, and environmental characteristics. The survey was conducted through face-to-face interviews, and the data were recorded anonymously, without involving any farmers’ private information. In addition, the survey obtained the consent of all the interviewed farmers, and the farmers were informed that the collected data would only be used for academic research.
The ‘Double Hundred Double Thousand’ survey used a combination of stratified and random sampling methods: first, the 100 counties in Jiangxi Province were divided into three levels according to the level of economic development, rural population and other indicators, and 8 counties were randomly selected from each level; then, all the administrative villages in each county were divided into three levels according to the level of economic development and rural population and other indicators, and 3 villages were randomly selected from each level; finally, 10 farmers were randomly selected from each administrative village. The survey finally included a sample of 2,160 farmers from 216 administrative villages in 24 counties in Jiangxi Province. Figure 3 shows the coverage area of farmers interviewed in the “Two Hundred, Two Thousand” survey. The orange areas in Figure 3 are the counties in Jiangxi Province covered by the survey. As can be seen from Figure 3, the coverage of the “Two Hundred and Two Thousand” survey is extensive and relatively evenly distributed, with no geographic preference for omission.
Figure 3. Sample Regional Map of ‘Double Hundred and Double Thousand’ Survey in Jiangxi Province, China, 2023.
Finally, this paper handles the survey data according to the needs of the study as follows: first, data integration, matching and merging the data of each part according to the corresponding questionnaire number; second, data screening, eliminating missing data and contradictory values of important information. In addition, since the research object of this paper is rice farmers in Jiangxi Province, this paper screened the samples based on whether the sample farmers planted rice in 2022 or not. In addition, since the research object of this paper is rice farmers in Jiangxi Province, this paper screened the samples based on whether the sample farmers planted rice in 2022 or not. This paper deleted the sample of farmers who did not plant rice in 2022, and finally retained 1,440 valid samples of rice-growing farmers as the total sample of this paper. This paper will explore the mechanism of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ pro-environmental production willingness based on the data of the screened 1,440 samples of rice farmers in Jiangxi Province.
4.5 Descriptive statistics for variables
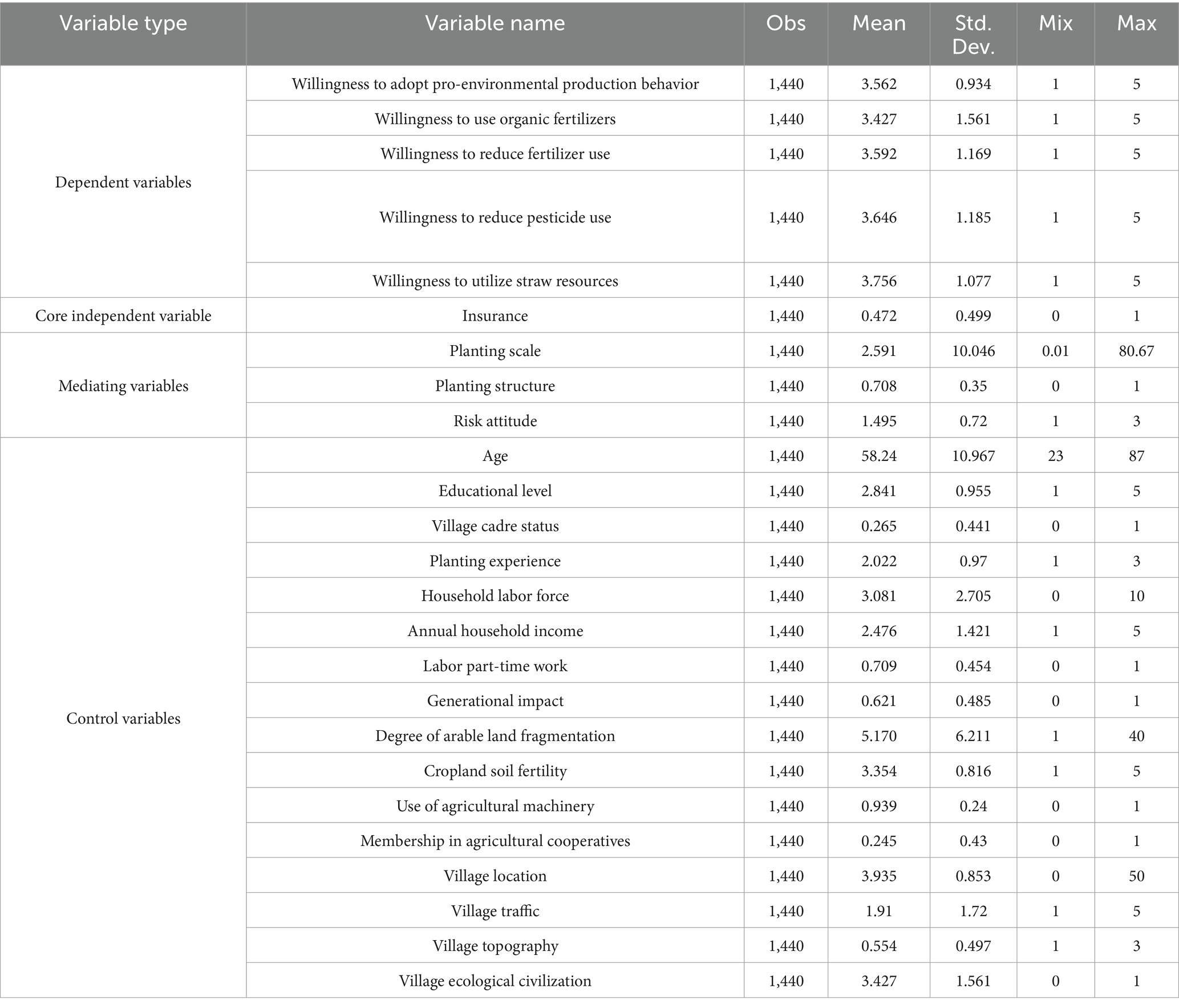
Descriptive statistics of the sample data can reflect the characteristics and patterns of the sample, and it is also helpful in analyzing some status quo problems. Therefore, this paper carried out descriptive statistics on the samples, resulting in Table 3.
As can be seen from Table 3, the total insurance coverage rate of the sample farmers is 47.2 per cent, which is nearly half. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that most of the sample farmers have less than 2 hectares of rice cultivation (about 84.65 per cent) and are small-scale farmers (Chambers, 1989), whose production decisions change frequently, resulting in a lower percentage of purchasing agricultural insurance; on the other hand, it is because some sample farmers did not purchase agricultural insurance in 2022 because the frequency of natural disasters in their localities is low, and they believe that purchasing agricultural insurance is not necessary and will increase production costs.
From the perspective of farmers’ willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors, the mean value of farmers’ willingness to engage in the four pro-environmental production behaviors is above 3, of which the mean value of the willingness to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers, the willingness to reduce the use of pesticides, the willingness to treat straw resources are all above 3.5, and the mean value of the comprehensive willingness is 3.562. It can be seen that the farmers’ willingness to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers, reduce the use of pesticides, reduce the use of straw resource treatment, and their combined willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors are all inclined to be “more willing,” while their willingness to apply organic fertilizers is inclined to be “average.” This phenomenon may be explained by the fact that the application of organic fertilizers increases the cost of cultivation compared to the other three pro-environmental production practices (Breckner et al., 2016). For farmers, the benefits of performing this behavior are characterized by “uncertainty” (Sherrick et al., 2004), so the willingness to perform this behavior is slightly lower than the other three, but the overall level is still higher than the “average” level.
In order to more visually reflect the intensity of farmers’ willingness to adopt the four pro-environmental production behaviors and the comprehensive willingness, this paper draws a bar chart of the mean values of farmers’ willingness, as shown in Figure 4. In Figure 4, the vertical axis represents the different willingness variables, and the horizontal axis represents the mean values of these willingness. It can be seen from Figure 4 that the sample farmers had the highest willingness to adopt straw resource utilization and the lowest willingness to adopt organic fertilizer.
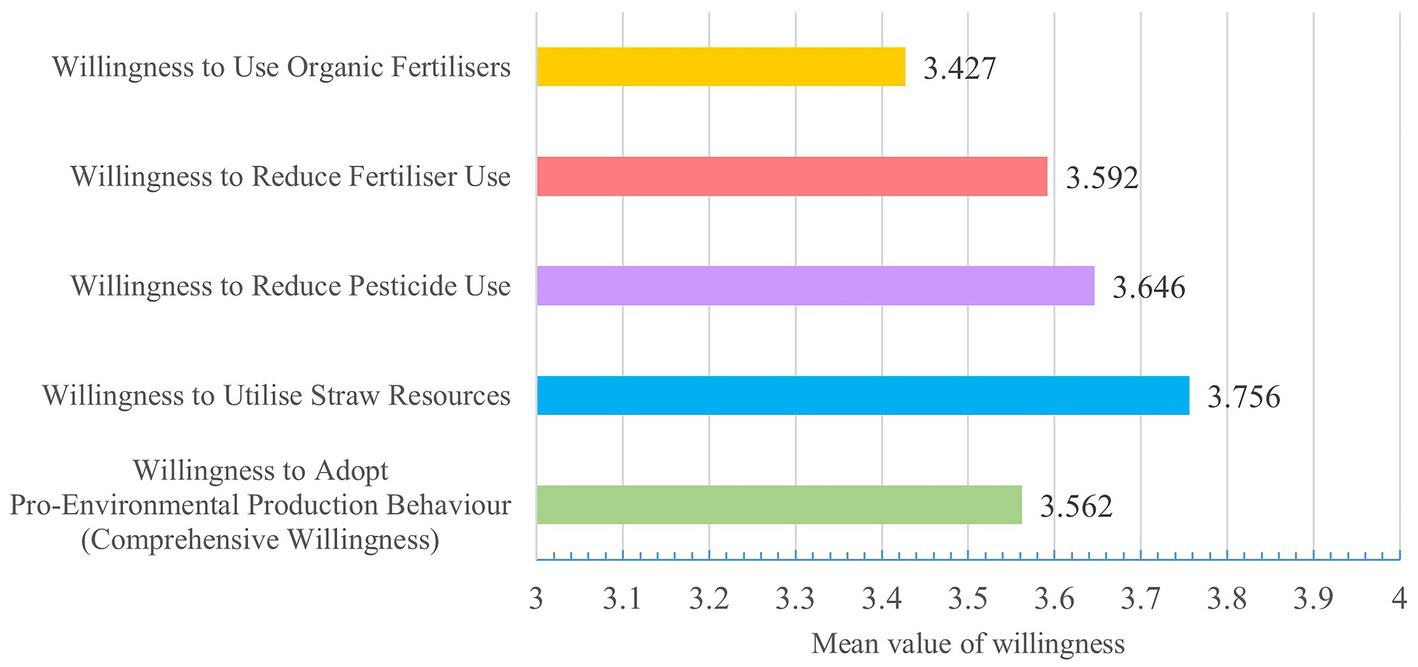
Figure 4. Bar chart of willingness of sample farmers to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors.
4.6 Multicollinearity test
In the empirical analysis of real economic problems, the selected explanatory variables often have a certain correlation between them, and because the explanatory variables do not have complete multicollinearity between them (Niu et al., 2022), this problem is often also known as the problem of incomplete multicollinearity between the explanatory variables. If the selected explanatory variables have multicollinearity among them, it may lead to inaccurate results of the coefficients estimated by the model and cannot better explore the individual influencing effects of each explanatory variable on the explained variables (Butler, 2000).
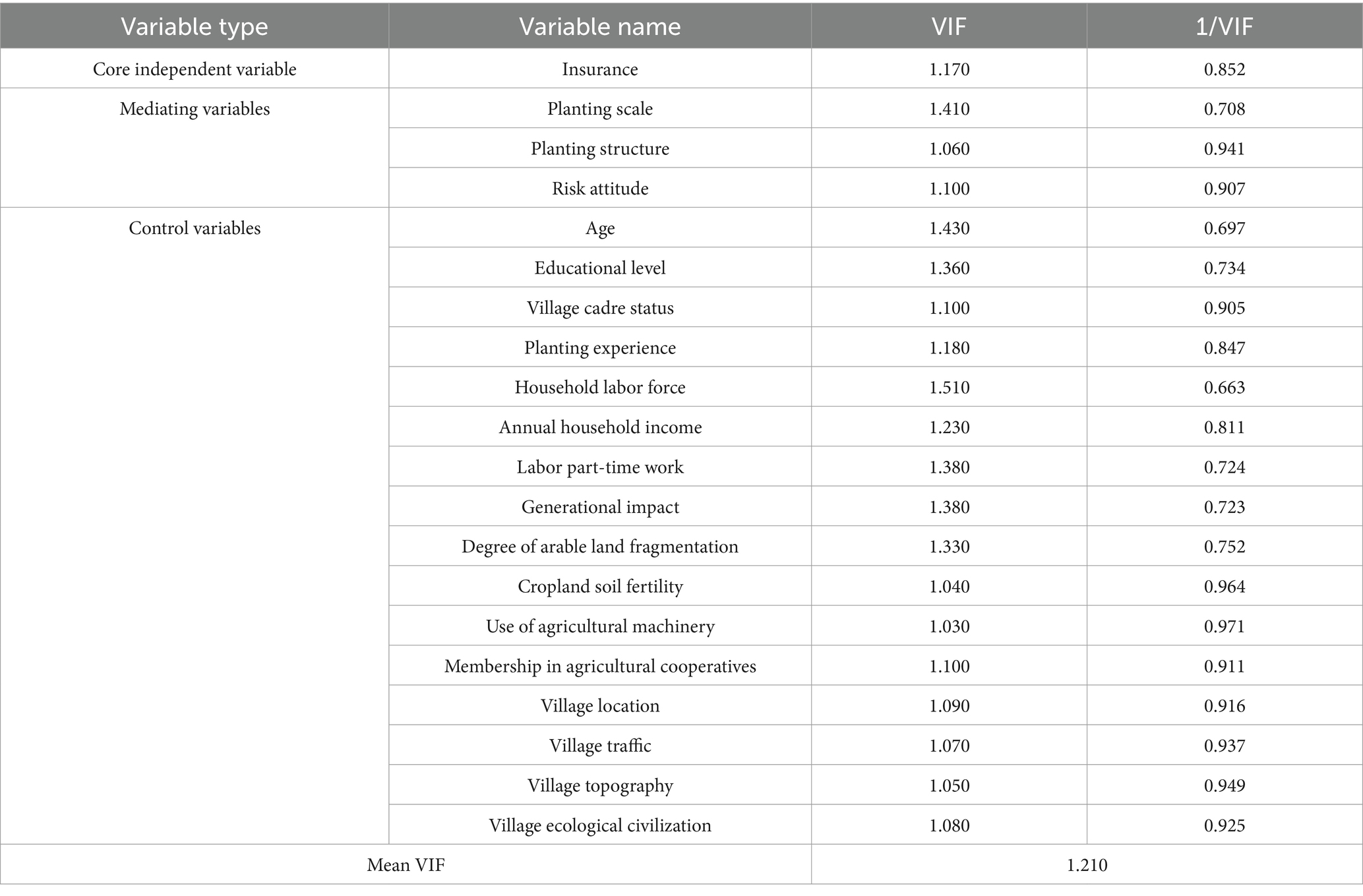
In this paper, there are more explanatory variables selected for model regression, which may have the problem of multicollinearity among each other, which will affect the accuracy of the model estimation results. Therefore, in order to ensure the accuracy of the model estimation results in this paper, the core explanatory variables and control variables selected in this paper are now tested for multicollinearity using Stata17 software, and the results are shown in Table 4.
As can be seen from Table 4, the Tolerance values of all the explanatory variables selected in this paper are between 0.663 and 0.971, and all of them are greater than 0.1, and the values of VIF (Variance Inflation Factor) are between 1.03 and 1.51, and all of them are less than 10, therefore, there is no serious problem of multicollinearity between the explanatory variables selected in this paper (Butler, 2000), and the regression model constructed in this paper is stable.
5 Results
5.1 Results of the OLS model regression
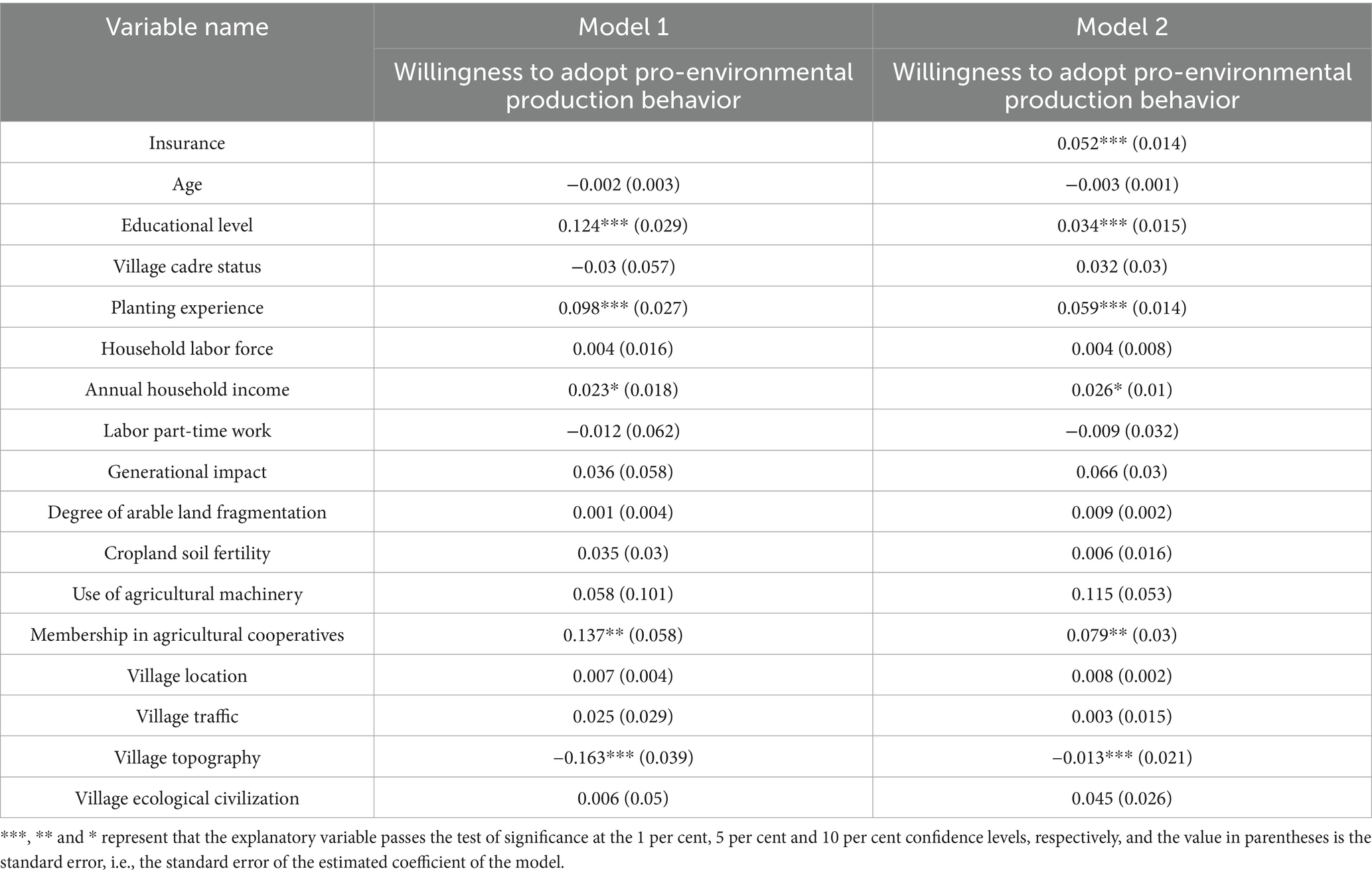
First, to explore the effect of policy-based agricultural insurance and control variables on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors, this paper reports the results of the OLS model regression, as shown in Table 5.
Model 1 in Table 5 reports the effect of control variables on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors without adding the core explanatory variable “policy-based agricultural insurance,” while Model 2 shows the regression results of the model with the addition of “policy-based agricultural insurance.”
From the regression results of model 2 in Table 5, it can be seen that policy-based agricultural insurance participation significantly and positively affects farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors at the 1% confidence level, which also verifies this paper’s hypothesis H1.
In addition, the educational level, planting experience, membership in agricultural cooperatives and annual household income positively and significantly affect farmers’ willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors at the 1, 1, 5, and 10% confidence levels, respectively. It should be noted that the topography of the village significantly and negatively affects farmers’ willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behavior at the 1% confidence level. The possible reason is that farmers located in mountainous and hilly areas pay more attention to the protection of land ecology because of the smaller area of arable land, while farmers in flat areas may take a chance on land pollution, which has a higher possibility of generating moral hazards, and thus have a lower willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors.
5.2 Results of the ordered-logit model regression
The willingness of farmers to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors in this paper is calculated from the willingness of farmers to adopt the four specific pro-environmental production behaviors by the entropy method. Therefore, to explore the effects of policy-based agricultural insurance and control variables on farmers’ willingness to adopt four specific pro-environmental production behaviors in more detail, this paper reports the Ordered-Logit model regression results, as shown in Table 6.
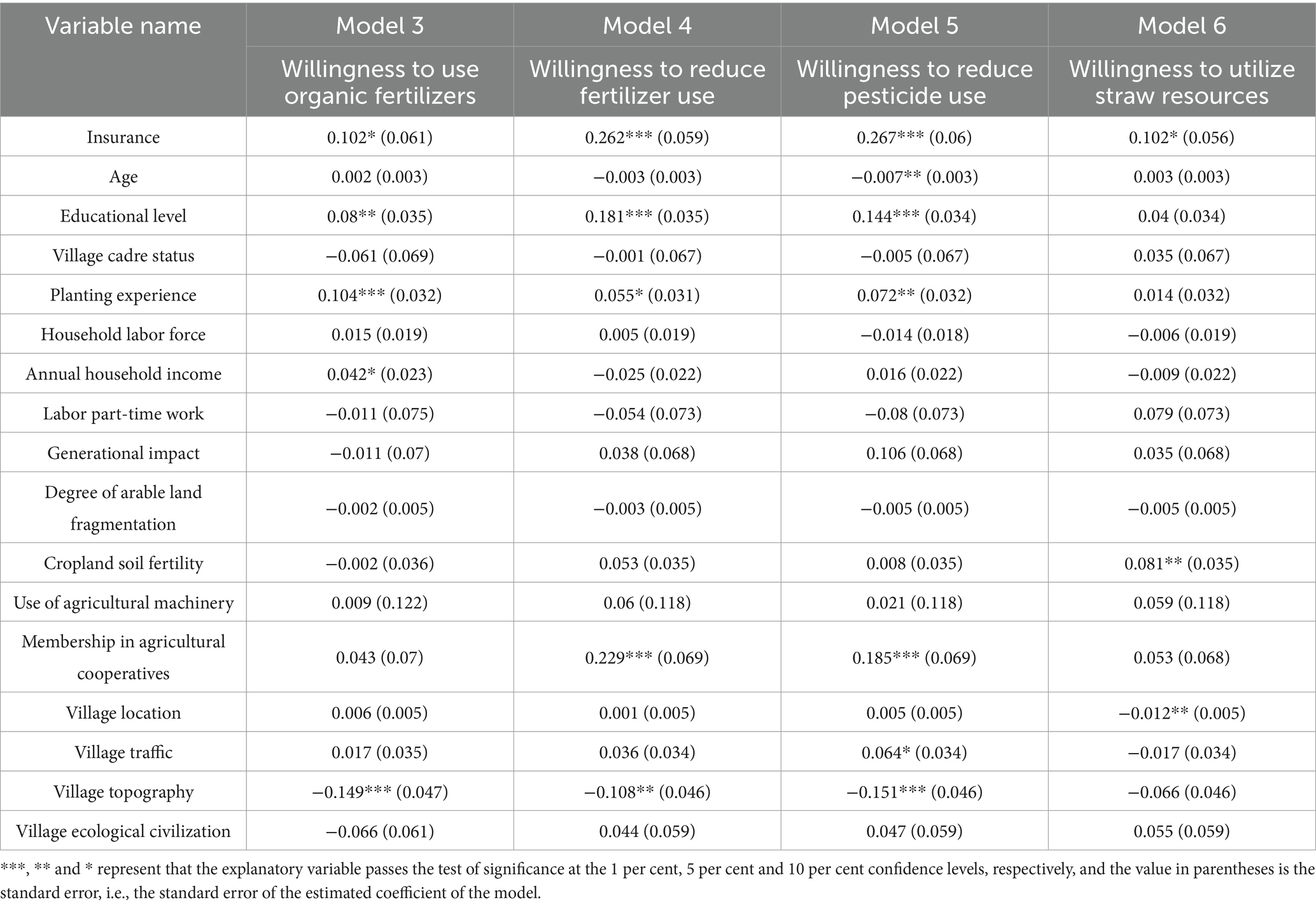
Table 6. Results of the regression of willingness to adopt four specific pro-environmental production behaviors.
From the regression results of model 3 in Table 6, it can be seen that policy-based agricultural insurance participation significantly and positively affects farmers’ willingness to apply organic fertilizer at the 10% confidence level, which again verifies hypothesis H1. In addition, planting experience, educational level, and annual household income significantly and positively affect farmers’ willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors at the 1, 5, and 10% confidence levels, respectively, while the main topography of the village significantly and negatively affects farmers’ willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors at the 1% confidence level. It should be noted that the annual household income only has a significant positive effect on farmers’ willingness to apply organic fertilizer. The possible reason is that applying organic fertilizer can improve the quality of the crop although it will increase the cost of production. Farmers with higher annual household incomes have higher willingness to use organic fertilizers because they demand higher food quality and are more receptive to the increased costs of organic fertilizer application.
From the regression results of model 4 in Table 6, it can be seen that the policy-based agricultural insurance participation significantly and positively affects the willingness of farmers to reduce the use of fertilizer at the 1% confidence level, which again verifies hypothesis H1. In addition, the educational level and whether to join a cooperative significantly and positively affects the willingness of farmers to pro-environmental production behaviors at the 1, 1, and 10% confidence levels, respectively. And the main topography of the village significantly and negatively influences the willingness to reduce the use of fertilizer at the 1% confidence level. It should be noted that the regression coefficient for planting experience is still positive but no longer significant. This shows that the number of years farmers have been engaged in agricultural production has no effect on their willingness to adopt reduced fertilizer application. The possible reason for this is due to the fact that most of the sample farmers are professional farmers who are too deeply influenced by traditional farming practices and are too dependent on chemical fertilizers. Although they are aware that adopting pro-environmental production practices can reduce pollution and promote sustainable use of arable land, they are still reluctant to reduce fertilizer application in pursuit of high crop yields.
From the regression results of model 5 in Table 6, it can be seen that policy-based agricultural insurance significantly and positively affects the willingness of farmers to reduce pesticide application at the 1% confidence level, which verifies the hypothesis H1. The education level, cultivation experience, intergenerational influences, and whether to participate in agricultural cooperatives significantly and positively affect the willingness of farmers to reduce the application of pesticides at the 1, 5, 10, and 1% confidence levels, respectively. In addition, age and major topography of the village and age significantly and negatively influenced farmers’ willingness to reduce pesticide application at 5 and 1% confidence level, respectively. It is important to note that intergenerational influence significantly contributes to farmers’ willingness to reduce pesticide application. The reason may be that farmers with three generations living together pay more attention to the greenness and healthiness of the food than the yield. In order to ensure the dietary safety of the elderly and children, they are willing to reduce pesticide application to obtain greener and healthier food. In addition, age has a significant negative effect on pesticide application reduction. The reason is that older farmers have a deeper impression of the impacts of pests and diseases on their grain in earlier years, so they are less willing to reduce pesticide application.
From the regression results of model 6 in Table 6, it can be seen that policy-based agricultural insurance participation significantly and positively affects farmers’ willingness to utilize straw resources at the 10% confidence level, which again verifies hypothesis H1. The cropland soil fertility significantly and positively affect farmers’ willingness to utilize straw resources at the 5% confidence level. It should be pointed out that the distance from the farmer’s village to the nearest township significantly and negatively affects farmers’ willingness to utilize straw resources. On the one hand, the distance from villages to towns affects the convenience of farmers in obtaining social communication, social resources and information, and villages that are farther away from towns are less likely to obtain information and incentives for straw resource disposal. On the other hand, centralized straw resource disposal stations are usually set up closer to towns, and the further the villages are from towns means that the cost of transporting straw will be higher.
As can be seen from Table 6, the magnitude and significance of the impact coefficients of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ four pro-environmental production willingness differ from each other. Compared with the willingness to apply organic fertilizer and the willingness to treat straw resources, the coefficients of influence of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to reduce the amount of fertilizer application and the willingness to reduce the amount of pesticide application is larger and more significant. Among them, policy-based agricultural insurance has the most significant effect on farmers’ willingness to reduce pesticide application.
5.3 Robustness tests
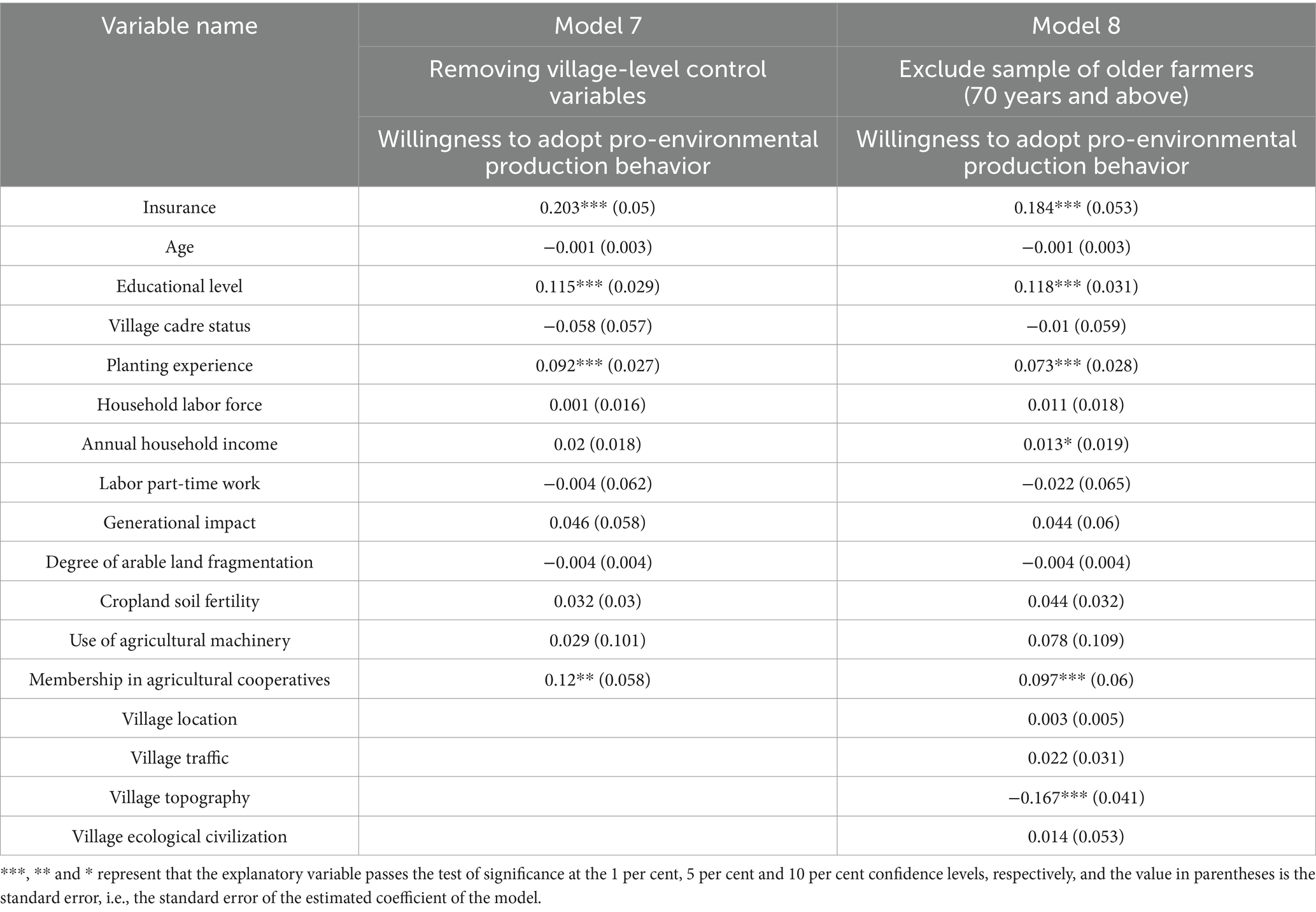
Then, this paper employs both replacement models (or changing the model settings) and excluding some samples (70 years and above) to conduct sensitivity analyses of the OLS model and Ordered-Logit model to test the robustness of their regression results (Cai et al., 2025; Ejeta and Bai, 2025; Chen et al., 2017; Breckner et al., 2016).
5.3.1 Robustness tests for the OLS model
Table 7 reports the results of the robustness tests of the OLS model. First, the paper tests the sensitivity of the model setting of the OLS model. In Table 7, Model 7 reports the regression results based on Model 2 with all village-level control variables removed. Next, the paper examines the sensitivity of the OLS model to sample size. And Model 8 reports the OLS regression results based on Model 2 with some of the older farmers (70 years and above) removed from the sample. The reason for excluding the older sample farmers is to reduce the impact of differences in cognitive level and information acquisition on the regression results due to the large age difference in the sample. Comparing the regression results in Tables 5, 7, it can be found that the directions and significance levels of the regression coefficients of the core variables are basically the same, proving that the regression results of the OLS model are robust.
5.3.2 Robustness tests for the ordered-logit model
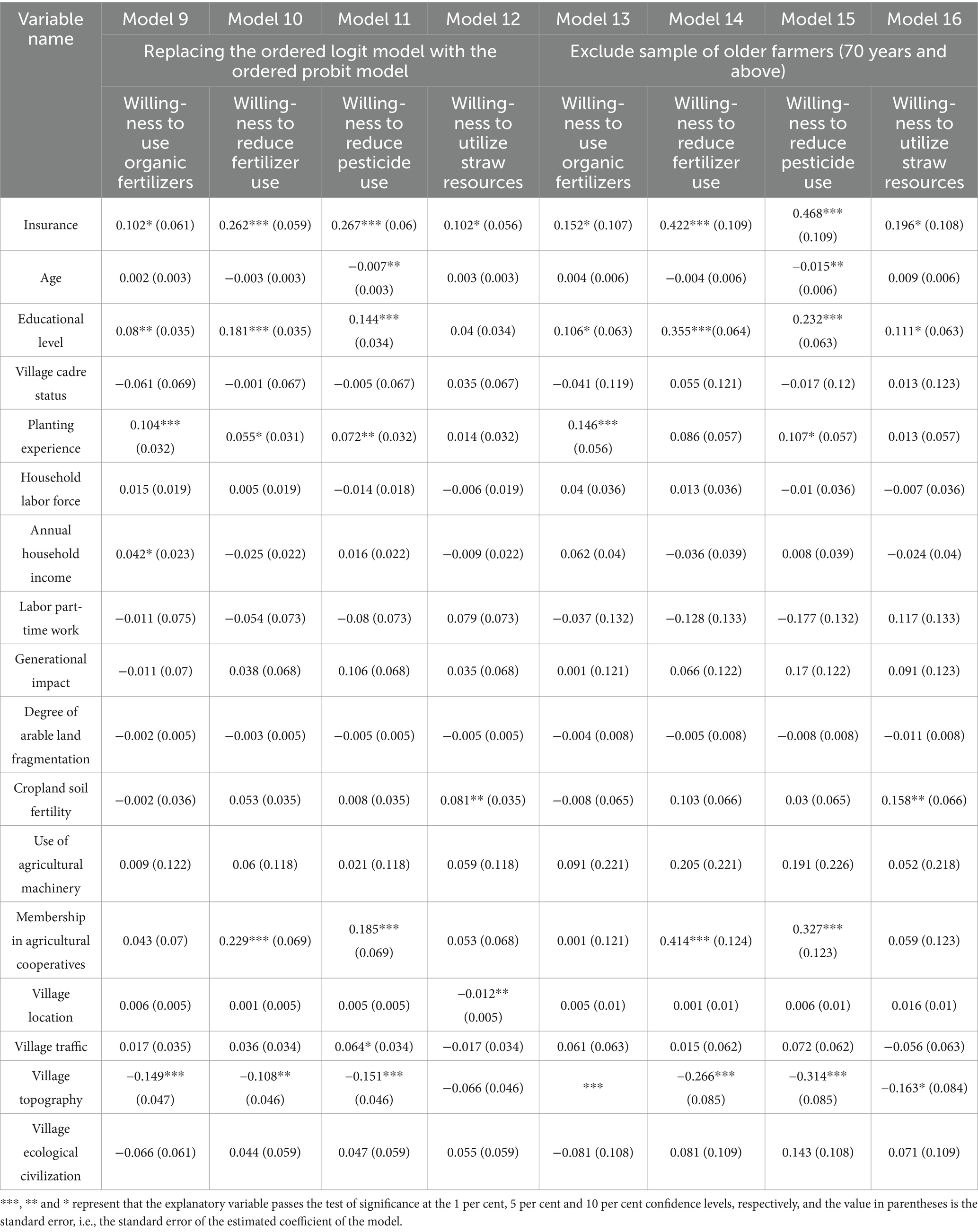
Table 8 reports the results of the robustness tests for the ordered logit model. In Table 8, Models 9–12 report the regression results of replacing the ordered logit model with the ordered probit model on the basis of Models 3–6, respectively. And Models 13–16 report the ordered logit results of deleting part of the sample of elderly farmers (over 70 years old) on the basis of Models 3–6. Comparing the regression results in Tables 6, 8, it can be found that the directions and significance levels of the regression coefficients of the core variables are basically the same, proving that the regression results of the ordered logit model are robust.
5.4 Post-diagnostic tests
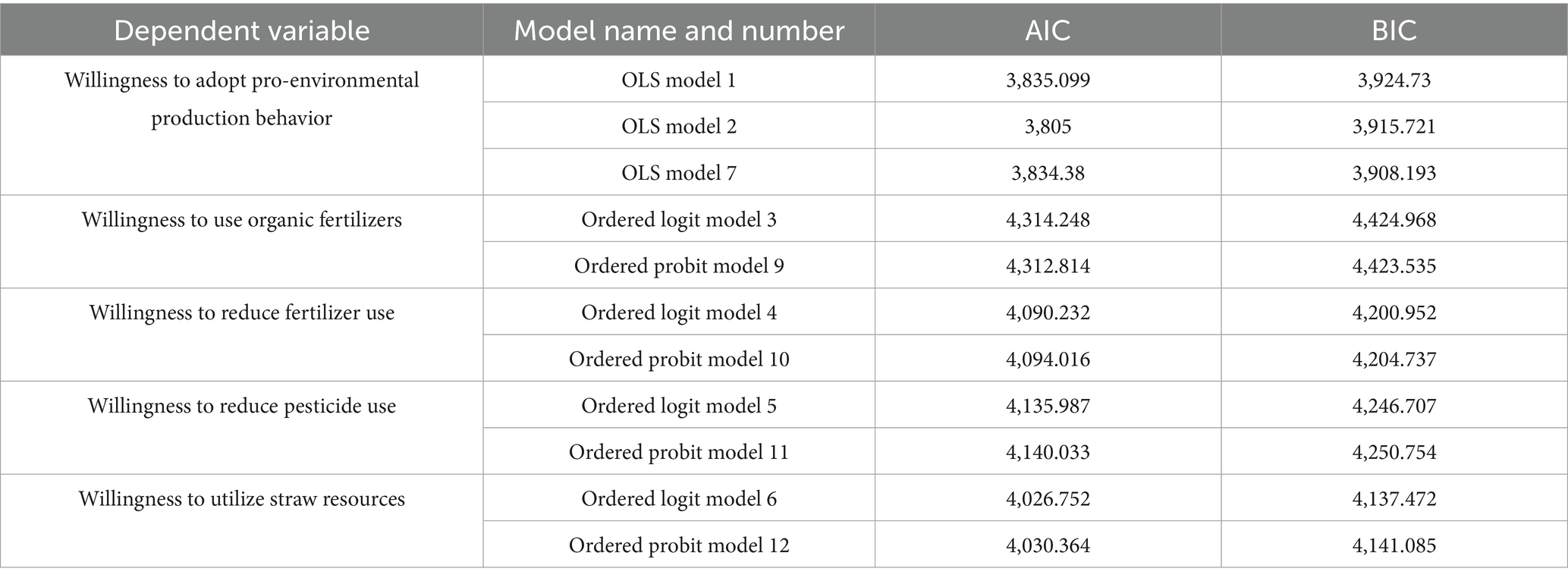
In order to test whether the model design and model selection are reasonable, this paper conducts post-diagnostic tests on OLS model and ordered logit model, respectively. The AIC and BIC values are usually used to compare the goodness-of-fit of the models (Zhang et al., 2023; Li et al., 2022). In general, the smaller the AIC and BIC values are, the better the model’s goodness-of-fit is (Goodwin et al., 2004; Dube et al., 2016). Therefore, in this paper, the values of AIC and BIC are used as indicators of the rationality of variable selection and design.
First, in order to test the rationality of the OLS model design, this paper conducted post-diagnostic tests for OLS models 1, 2, and 7 with different model settings (different combinations of independent variables) (Sherrick et al., 2004; Fang et al., 2021). Table 9 lists the AIC and BIC values for the three models. From Table 9, it can be seen that the AIC and BIC values of Model 2 are smaller than other models, indicating that Model 2 has the best fit. Model 2 is the regression of the dependent variable on the core independent variables and all control variables. This shows that the OLS model design in this paper is reasonable.
Second, to test the rationality of the selection of the ordered logit model to explore the impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to adopt the four pro-environmental production behaviors, this paper conducted the post-diagnostic tests on the ordered logit models (Models 3–6) and the ordered probit models (Models 9–12). Table 9 has reported the AIC and BIC values of these models, respectively. From Table 9, it can be seen that in the regression models of willingness to reduce fertilizer use, willingness to reduce pesticide use and willingness to utilize straw resources, the AIC and BIC values of the ordered logit model (Models 4–6) are smaller than those of the ordered probit model (Models 10–12). Only in the regression of the willingness to use organic fertilizer, the AIC and BIC values of the ordered logit model (Model 3) are larger than those of the ordered probit model (Model 9) and the difference value is less than 2, which proves that there is no essential difference in the goodness-of-fit of these two models (Pratiwi and Budiasa, 2022; Wu et al., 2024). In summary, the overall goodness-of-fit of the ordered logit model is greater than that of the ordered probit model. Therefore, the choice of the logit model ordered in this paper is reasonable.
5.5 Mediating effects tests
Finally, the paper tests the mediating effects of the three mediating variables. Although the previous paper has analyzed the direct impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behavior, the specific transmission mechanism of this impact has not been explored in depth. Therefore, this paper will test the mediating effect of planting scale, planting structure, and risk preference in the process of policy agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ willingness to pro-environmental production behavior through the mediating effect testing process provided by Wen ZL (Chen et al., 2017).
It is known from the baseline regression results that policy-based agricultural insurance participation will have a significant promotion effect on farmers’ willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors, i.e., the main effect exists significantly, and step-by-step regression is carried out next:
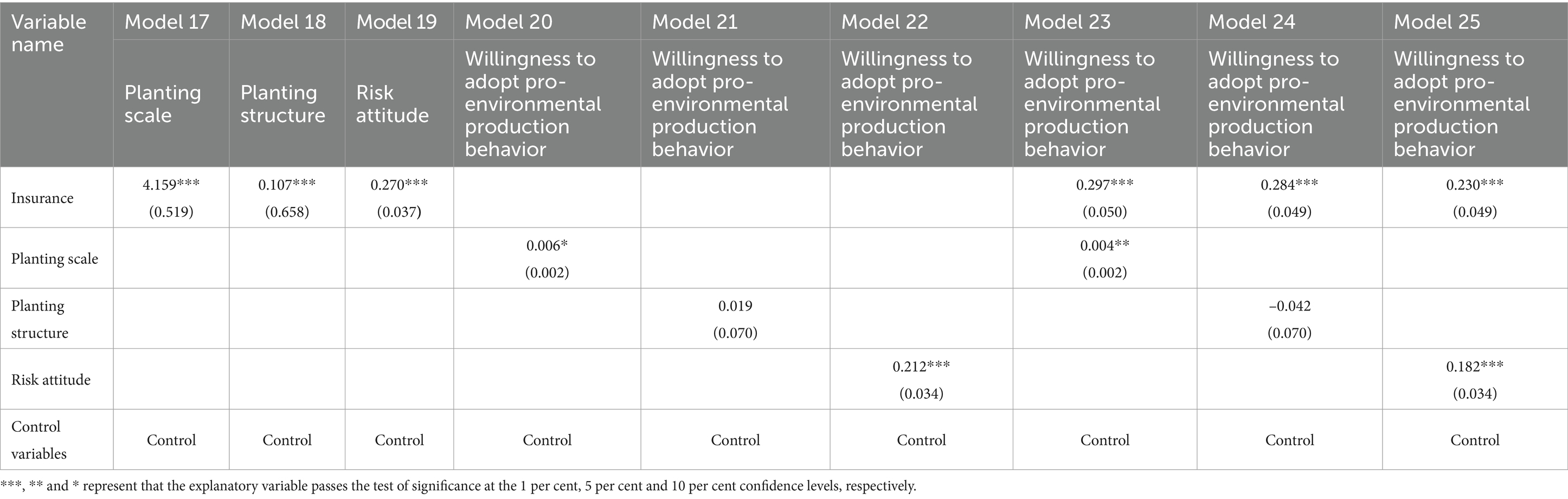
Firstly, the three mediating variables (planting scale, planting structure and risk attitude) are substituted into Equation 3-1 for regression to obtain the regression results of Models 17–19, i.e., the regression results of the three mediating variables on the policy agricultural insurance participation variable.
Secondly, the three mediating variables (planting scale, planting structure and risk attitude) are substituted into Equation 3-2 for regression to obtain the regression results of Models 20–22, i.e., the regression results of pro-environmental production behavioral willingness on the three mediating variables.
Finally, the three mediating variables (planting scale, planting structure, and risk attitude) are substituted into Equation 3-3 and regressed with the core explanatory variables to obtain regression results of Models 23–25, i.e., the results of the regression of pro-environmental production behavioral intentions on policy-based agricultural insurance participation and the three mediating variables.
Referring to the mediation effect test process provided by Wen ZL (Chen et al., 2017), combined with the schematic diagram of the mediation model in Figure 2 of this paper, this paper tested the mediation effect of planting scale, planting structure, and risk attitude respectively, and the results are shown in Models 17–25 in Table 10. In Table 10, Models 17–19 are regressions of the three mediating variables on policy agricultural insurance, Models 20–22 are regressions of farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors on the three mediating variables, and Models 23–25 are regressions of farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors on policy agricultural insurance and the three mediating variables.
First, planting scale has a mediating role in the process of policy-based agricultural insurance affecting farmers’ pro-environmental production willingness to adopt production behaviors, and it is a partial mediating role, which verifies the hypothesis H2 of this paper. From this, it can be seen that policy-based agricultural insurance can enhance farmers’ pro-environmental production willingness by incentivizing them to expand the scale of planting of rice, and then enhance their pro-environmental production willingness.
Second, the mediating role of planting structure in the process of policy-based agricultural insurance affecting farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior adoption willingness is not significant, and the mediating role does not exist, which negates this paper’s hypothesis H3. Although policy-based agricultural insurance promotes farmers to streamline the planting structure and expand the proportion of rice in all crops, the streamlining of planting structure does not further promote farmers’ pro-environmental production willingness.
Finally, risk attitude has a mediating effect in the process of policy-based agricultural insurance affecting farmers’ pro-environmental production willingness, and it is a partial mediating effect, which verifies the hypothesis H4 of this paper. Policy-based agricultural insurance can change farmers’ risk attitude, increase their risk appetite, and then enhance their pro-environmental production willingness.
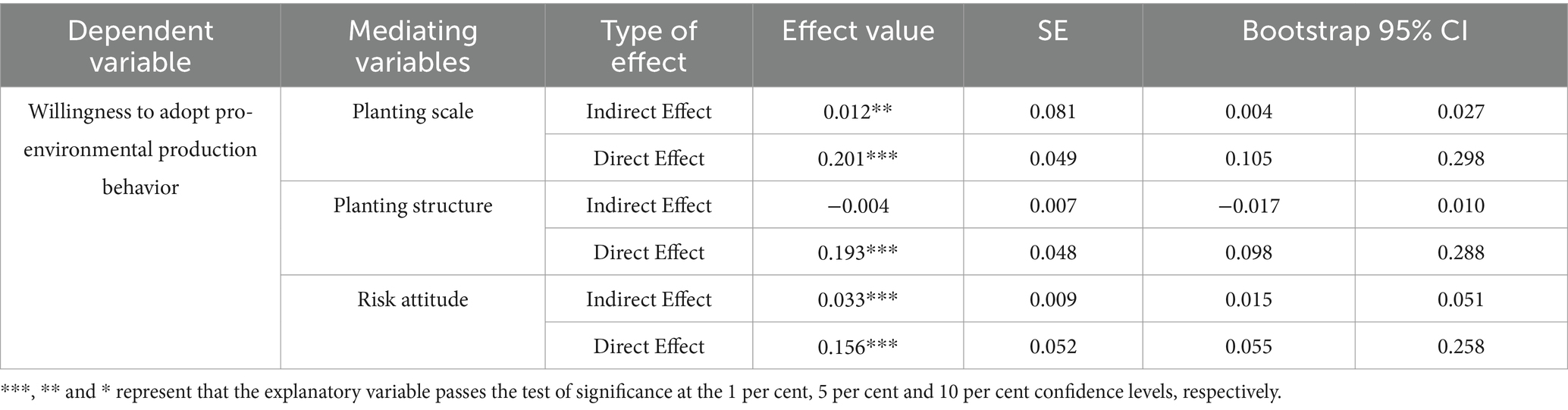
In order to further test the robustness of the mediation effect, this paper uses the Bootstrap method to further test the mediation effect and sets the number of repeated samples to 1,000, and the results are shown in Table 11. As can be seen from Table 11, the confidence intervals of the indirect and direct effects of planting size do not include 0, and their mediating effects are significant, the hypothesis H2 was tested again; the confidence intervals of the indirect and direct effects of risk attitude also do not include 0, and their mediating effects are significant, the hypothesis H4 was tested again; the confidence intervals of the indirect effect of planting structure include 0, and the confidence intervals of the direct effect do not include 0, which indicates that the mediating effect of planting structure is not significant, the Hypothesis H3 was rejected again. It can be seen that the Bootstrap method is consistent with the results of the three-step test and that the mediating effects of planting scale and risk attitude are robust and both of them are partially mediated.
Based on the above results of the mediation effect test on the three mediating variables, it can be seen that the mediation effect of planting structure is not significant. Specifically, while policy-based agricultural insurance has promoted farmers to streamline their cropping structure and increase the proportion of rice among all the crops they grow, the change in cropping structure failed to effectively motivate farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors. This may be due to the fact that a greater proportion of rice cultivation reduces the time required for agricultural production, allowing farmers to devote more time to more profitable off-farm work, and therefore unwilling to adopt more time-consuming and costly pro-environmental production behaviors (Chambers, 1989). The underlying reason for this thought is that farmers do not have a full understanding of the economic and ecological benefits of pro-environmental production practices (Hazell, 1982). In the view of the farmers, the task of agricultural production has become simpler after a larger proportion of insured rice is grown, and there is no need to invest more effort in agricultural production (Dai and Cheng, 2022). Moreover, the economic benefits of adopting pro-environmental production behaviors are uncertain (Fang et al., 2019). Therefore, farmers’ willingness to adopt is not incentivized. In this regard, farmers’ governments and insurance institutions should increase their efforts to publicize the economic and ecological benefits of pro-environmental production practices. Only if more farmers are willing to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors, can the problem of agricultural surface pollution be solved from the root cause, which is conducive to the sustainable development of the plantation industry.
6 Discussion
6.1 Research findings and discussion
First of all, policy-based agricultural insurance can effectively stimulate farmers’ willingness to engage in environmentally friendly production behavior. This result is consistent with the findings of the existing literatures (Kollmuss and Agyeman, 2002). Policy-based agricultural insurance can not only protect farmers’ grain cultivation income, but also promote their willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors, which is conducive to the sustainable development of grain production (Atanu et al., 1994). Specifically for the pro-environmental production behaviors in different production segments, policy-based agricultural insurance has a significant incentive effect on farmers’ willingness to apply organic fertilizer, reduce the amount of chemical fertilizer application, reduce the amount of pesticide application, and the adoption of straw resource utilization (Zheng and Zhao, 2025; Bhuiyan et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2020; Akinrinola and Okunola, 2014). In addition, compared with the willingness to apply organic fertilizer and the willingness to adopt straw resource treatment, policy-based agricultural insurance has a greater and more significant role in promoting farmers’ willingness to reduce the amount of pesticide application and the willingness to reduce the amount of chemical fertilizer application. Among them, the enhancement effect of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to reduce the amount of pesticide application is the most significant. Policy-based agricultural insurance can promote the green and sustainable transformation of farmers’ grain production methods, which is important for reducing agricultural surface pollution and promoting the sustainable development of the grain industry (Chen et al., 2022; Yamoah et al., 2021).
Second, planting scale has a mediating role in the process of policy-based agricultural insurance affecting farmers’ willingness to pro-environmental production behavior. This result validates the opinions of the existing literatures (Brick and Visser, 2015). Agricultural insurance protects farmers’ income (Breckner et al., 2016), enhances farmers’ confidence in production (Zhang et al., 2023), and incentivizes farmers’ factor input behavior for grain production (Jiang et al., 2023). Expanding the scale of cultivation is the most common way for farmers to increase factor inputs to grain production (Akter et al., 2016; Zhu and Chen, 2022). Farmers in the policy-based agricultural insurance incentives, spontaneous expansion of the scale of grain production thereby generating scale effects, reducing the cost of farmers to take the pro-environmental production behaviors (Aheibam et al., 2017), and ultimately enhance the willingness of farmers to adopt the pro-environmental production behavior.
Third, planting structure policy-based agricultural insurance does not have a mediating role in the process of influencing the willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behavior. Policy-based agricultural insurance has a significant positive effect on farmers’ planting structure streamlining behavior, which is consistent with the findings of the current study (Fahad et al., 2018). However, unlike the findings of the current study (Wu et al., 2024), cropping structure streamlining did not enhance farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors. This may be due to the fact that the streamlining of cropping structure has increased the degree of part-time employment of farmers (Horowitz and Lichtenberg, 1993; Alotaibi et al., 2021). Single and simple crop cultivation allows farmers to spend more time on non-farm work, and they do not want to spend too much time and energy on food cultivation and arable land protection (Sargani et al., 2023). The green technologies and production knowledge contained in pro-environmental production behaviors, on the other hand, require farmers to spend a lot of time to learn and practice (Mao et al., 2022; Zhong et al., 2007). Therefore, the streamlining of cropping structure did not enhance the willingness of farmers to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors in Jiangxi Province.
Finally, risk attitude has a mediating effect in the process of policy-based agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors. This finding reaffirms the conclusions of existing studies (Ahsan et al., 1982; Yu et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2023). Policy-based agricultural insurance can change farmers’ risk attitude by protecting their income (Hu and Allen, 2017). While green production technologies included in pro-environmental production behaviors contribute to the protection of the environment and the sustainability of arable land, they increase the uncertainty of farmers’ expected income (Sun et al., 2024). Policy-based agricultural insurance can change farmers’ risk attitudes and increase their risk preferences by sharing their rice cultivation risks and protecting their expected income (Tang and Luo, 2021). The increase in the degree of risk preference enhances farmers’ intention to adopt new technologies and their psychological tolerance for risk, which ultimately enhances their pro-environmental production willingness (Zheng and Zhao, 2025).
6.2 Possible innovations of this study
First of all, this paper starts from the perspective of farmers, and based on the research results of existing researchers, it takes the theory of farmers’ behavior and the theory of planned behavior as theoretical basis, and probes deeply into the mechanism of the influence of policy agricultural insurance on the willingness of farmers to implement pro-environmental production behaviors. In addition, this paper also considers the mediating effects of planting scale, planting structure, and risk attitude, and constructs the research framework of ‘policy agricultural insurance - individual and production characteristics - willingness and implementation of pro-environmental production behaviors’, which is somewhat theoretically innovative. This study provides some theoretical references for subsequent research on the factors influencing farmers’ environmentally friendly production behavior.
Many researchers have studied the influencing factors of farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors, but there is little literature on the systematic study of the influencing mechanism of policy-based agricultural insurance affecting farmers’ pro-environmental production behaviors. Based on the existing research results of researchers, this paper verifies the incentive effect of policy-based agricultural insurance on the adoption willingness and comprehensive willingness of four kinds of pro-environmental production behaviors of farm households through the method of empirical research, and at the same time verifies the mediating effect of planting scale and risk attitude in the process of this influence. Finally, this study establishes the systematic mechanism of policy agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors, which provides a certain practical basis and theoretical foundation for subsequent studies.
6.3 Research limitations
Although the authors have tried their best to make this study complete and rigorous, it is inevitable that this study also has some limitations. First, there are limitations in the regional focus of this paper. Since the research object of this paper is rice farmers in Jiangxi Province, it can only reflect the willingness of rice farmers in this province to be influenced by policy-based agricultural insurance on their pro-environmental production behavior. Therefore, the conclusions and countermeasure suggestions in this paper have limited relevance to other regions in China. The sampling method for the sample is relatively robust, but it does not consider the factor of resident population density in selecting specific counties and villages. Finally, this paper also has limitations in terms of the content of the study. The paper only measures farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors, but not whether and to what extent they adopt them. In addition, the pro-environmental production behaviors examined in this paper are only the four most common ones, and there may be many more pro-environmental production behaviors stimulated by policy-based agricultural insurance.
The authors will endeavor to address the above research limitations in future studies. The survey team will endeavor to expand the coverage and sample capacity of the samples, adopt tracking surveys to obtain data, and increase the breadth and depth of the study in order to expand the application of the findings. In addition, the authors will consider introducing new mediating variables such as political trust and government regulation to enrich the research on the mechanism of policy-based agricultural insurance’s influence on farmers’ pro-environmental production behavior. With the support of more sample data, the authors expect to make more contributions to the field of research on the mechanism of agricultural insurance influencing farmers’ behavior.
7 Conclusions and implications
7.1 Conclusion
Based on the field survey data of 1,440 rice farmers in Jiangxi Province, this paper empirically analyzes the impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on the willingness of pro-environmental production behavior of rice farmers in Jiangxi Province with the help of stata17 software. In addition, this paper also explores the mediating role of planting scale, planting structure and risk attitude.
Policy-based agricultural insurance can effectively incentivize farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors. The empirical results of this paper show that policy-based agricultural insurance has a significant promotion effect on farmers’ willingness to apply organic fertilizer, reduce chemical fertilizer application, reduce pesticide application and straw resource utilization. Compared with the willingness to apply organic fertilizer and the willingness to resource straw, policy-based agricultural insurance has a greater and more significant role in promoting farmers’ willingness to reduce the amount of pesticide application and the willingness to reduce the amount of chemical fertilizer application. Among them, policy-based agricultural insurance has the most significant effect on farmers’ willingness to reduce pesticide application. Therefore, it is necessary to continue to develop and improve policy-based agricultural insurance in order to continue to tap its potential in promoting farmers to adopt environmentally friendly production behaviors, reducing agricultural surface pollution and ensuring food security.
Policy-based agricultural insurance can motivate farmers to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors by encouraging them to expand the scale of cultivation. Policy-based agricultural insurance can encourage farmers to expand the scale of cultivation by providing them with income security. Expanding the scale of planting can produce a scale effect and reduce the cost of adopting pro-environmental production behaviors.
Policy-based agricultural insurance can motivate farmers to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors by changing their attitudes toward risk. Policy-based agricultural insurance can share the risk of grain production for farmers, enhance their confidence in production, and increase their risk appetite. The increase in risk preference reduces farmers’ concern about expected income and motivates their willingness to adopt pro-environmental production behaviors.
This paper provides a theoretical reference for the field of research on the mechanism of agricultural insurance affecting farmers’ behavior, and also provides a certain realistic basis for the management of agricultural surface pollution in Jiangxi Province. Future research should continue to enrich the measurement method of pro-environmental production behavior, focusing on whether farmers adopt pro-environmental behaviors and the consistency between willingness and behavior. In addition, with the abundance of policy-based agricultural insurance, different types of insurance may have different effects on farmers’ willingness to engage in pro-environmental production behaviors.
7.2 Policy implications
Firstly, optimize insurance products and expand the insurance group. The government and insurance institutions should continue to improve policy-based agricultural insurance products, increase the policy-based agricultural insurance publicity, expand its coverage, so that more farmers enjoy the policy-based agricultural insurance services. Besides, the government should provide differentiated insurance options and support measures for farmers with different land endowments, and set up incentive mechanisms to motivate farmers in mountainous or hilly areas to adopt pro-environmental production behavior.
Secondly, improve the payout process and increase the payout power. Relevant departments and institutions should continue to improve the policy-based agricultural insurance payout process, appropriately increase the payout efforts, and do a good job of payout supervision. Insurance companies should give more policy concessions to large-scale farmers, provide more comprehensive risk-sharing services for farmers, so as to stimulate the environmental protection production behavior of farmers participating in policy-based agricultural insurance. And the Government should encourage small-scale farmers to operate cooperatively, consolidate their land management and form a scale effect to reduce the cost of adopting pro-environmental production behaviors.
Thirdly, increase the scope of insurance and pay attention to the supervision of compensation. Insurance institutions should gradually increase the coverage of policy-based agricultural insurance to cope with the risks faced by grain under different circumstances. Relevant government departments should also do a good job of supervising and maintaining close contact with farmers and insurance institutions to ensure the timeliness and reasonableness of policy-based agricultural insurance payouts. In addition, agricultural administrations should pay attention to the differences in the impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ production willingness in different pro-environmental situations. Agricultural management departments should expand financial support for farmers’ organic fertilizer application behavior and straw resource treatment behavior, such as including the cost of organic fertilizer application in insurance coverage, establishing an incentive system for farmers’ straw resource treatment, and providing organic fertilizer subsidies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Jiangxi Agricultural University Science and Technology Ethics Committee. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YL: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation. KH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HW: Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. WL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the 2024 Jiangxi Young Marxists’ Theoretical Research and Innovation Project of the Jiangxi Federation of Social Science Circles (grant number 24ZXQM104), the Jiangxi Social Science Planning Key Project of the Jiangxi Federation of Social Science Circles (grant number 22SQ06), and the 2024 Management Science Project of Science and Technology Department of Jiangxi Province (grant number 20244BAA10026).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the editors and reviewers for their helpful comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2025.1556958/full#supplementary-material
References
Aheibam, M., Singh, R., Feroze, S. M., Singh, N. U., Singh, R. J., and Singh, A. K. (2017). Identifying the determinants and extent of crop diversification at household level: an evidence from Ukhrul District, Manipur. Econ. Aff. 62, 89–95. doi: 10.5958/0976-4666.2017.00031.6
Ahmed, N., Hamid, Z., Mahboob, F., Rehman, K. U., Ali, M. S. E., Senkus, P., et al. (2022). Causal linkage among agricultural insurance, air pollution, and agricultural green total factor productivity in United States: pairwise granger causality approach. Agriculture 12:1320. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12091320
Ahsan, S. M., Ali, A. A. G., and John Kurian, N. (1982). Toward a theory of agricultural insurance. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 64, 510–529. doi: 10.2307/1240644
Ajzen, I., and Madden, T. J. (1986). Prediction of goal-directed behavior: attitudes, intentions, and perceived behavioral control. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 22, 453–474. doi: 10.1016/0022-1031(86)90045-4
Akinrinola, Olumide Oyewole, and Okunola, Akinbode Michael. (2014). Effects of agricultural insurance scheme on agricultural production in ondo state. Available online at: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/id/eprint/74558 (Accessed on January 1, 2025).
Akter, S., Krupnik, T. J., Rossi, F., and Khanam, F. (2016). The influence of gender and product design on farmers’ preferences for weather-indexed crop insurance. Glob. Environ. Chang. 38, 217–229. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.03.010
Alotaibi, B. A., Abbas, A., Ullah, R., Nayak, R. K., Azeem, M. I., and Kassem, H. S. (2021). Climate change concerns of Saudi Arabian farmers: the drivers and their role in perceived capacity building needs for adaptation. Sustain. For. 13:12677. doi: 10.3390/su132212677
Atanu, S., Alan Love, H., and Schwart, R. (1994). Adoption of emerging technologies under output uncertainty. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 76, 836–846. doi: 10.2307/1243745
Babcock, B. A., and Hennessy, D. A. (1996). Input demand under yield and revenue insurance. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 78, 416–427. doi: 10.2307/1243713
Barham, B. L., Chavas, J.-P., Fitz, D., Ríos-Salas, V., and Schechter, L. (2015). Risk, learning, and technology adoption. Agric. Econ. 46, 11–24. doi: 10.1111/agec.12123
Bhuiyan, M. A., Davit, M., XinBin, Z., and Zurong, Z. (2022). The impact of agricultural insurance on farmers’ income: Guangdong Province (China) as an example. PLoS One 17:e0274047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274047
Breckner, M., Englmaier, F., Stowasser, T., and Sunde, U. (2016). Resilience to natural disasters—insurance penetration, institutions, and disaster types. Econ. Lett. 148, 106–110. doi: 10.1016/j.econlet.2016.09.023
Brick, K., and Visser, M. (2015). Risk preferences, technology adoption and insurance uptake: a framed experiment. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 118, 383–396. doi: 10.1016/j.jebo.2015.02.010
Butler, D. J. (2000). Do non-expected utility choice patterns spring from hazy preferences? An experimental study of choice ‘errors’. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 41, 277–297. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2681(99)00077-3
Cai, J., Chen, J., Wu, R., Omar, R., and Ning, B. (2025). How do intermediary organizations affect cultivated land conservation in China: the mediating role of land tenure stability. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1485376. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1485376
Chai, Z., and Zhang, X. (2023). The impact of agricultural insurance on planting structure adjustment—an empirical study from Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Agriculture 14:41. doi: 10.3390/agriculture14010041
Chambers, R. G. (1989). Insurability and moral hazard in agricultural insurance markets. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 71, 604–616. doi: 10.2307/1242016
Chen, Y., Han, X., Lv, S., Song, B., Zhang, X., and Li, H. (2022). The influencing factors of pro-environmental behaviors of farmer households participating in understory economy: evidence from China. Sustain. For. 15:688. doi: 10.3390/su15010688
Chen, Q., Wen, Z., Kong, Y., Niu, J., and Hau, K. T. (2017). Influence of leaders’ psychological capital on their followers: Multilevel mediation effect of organizational identification. Front. Psychol. 8:1776. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01776
Dai, Q., and Cheng, K. (2022). What drives the adoption of agricultural green production technologies? An extension of TAM in agriculture. Sustain. For. 14:14457. doi: 10.3390/su142114457
Ding, S., Meriluoto, L., Reed, W. R., Tao, D., and Wu, H. (2011). The impact of agricultural technology adoption on income inequality in rural China: evidence from southern Yunnan Province. China Econ. Rev. 22, 344–356. doi: 10.1016/j.chieco.2011.04.003
Dube, L., Numbwa, R., and Guveya, E. (2016). Determinants of crop diversification amongst agricultural co-operators in Dundwa agricultural camp, Choma district, Zambia. Asian J. Agric. Rural Dev. 6, 1–13. doi: 10.22004/ag.econ.338760
Ejeta, T. T., and Bai, X. (2025). The effect of sustainable agricultural practices on crop productivity in Ethiopia: insights from a meta-analysis. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1499412. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1499412
Fahad, S., Wang, J., Hu, G., Wang, H., Yang, X., Shah, A. A., et al. (2018). Empirical analysis of factors influencing farmers crop insurance decisions in Pakistan: evidence from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province. Land Use Policy 75, 459–467. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.04.016
Fang, L., Hu, R., Mao, H., and Chen, S. (2021). How crop insurance influences agricultural green total factor productivity: evidence from Chinese farmers. J. Clean. Prod. 321:128977. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128977
Fang, J., Wen, Z., and Hau, K.-T. (2019). Mediation effects in 2-1-1 multilevel model: evaluation of alternative estimation methods. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 26, 591–606. doi: 10.1080/10705511.2018.1547967
Gao, L., Huang, J., and Rozelle, S. (2012). Rental markets for cultivated land and agricultural investments in China. Agric. Econ. 43, 391–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-0862.2012.00591.x
Gao, Y., Zhao, D., Yu, L., and Yang, H. (2019). Duration analysis on the adoption behavior of green control techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 6319–6327. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-04088-9
Goodwin, B. K., and Rejesus, R. M. (2008). Safety nets or trampolines? Federal crop insurance, disaster assistance, and the farm bill. J. Agric. Appl. Econ. 40, 415–429. doi: 10.1017/S1074070800023713
Goodwin, B. K., Vandeveer, M. L., and Deal, J. L. (2004). An empirical analysis of acreage effects of participation in the federal crop insurance program. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 86, 1058–1077. doi: 10.1111/j.0002-9092.2004.00653.x
Grabowski, P. P., Kerr, J. M., Haggblade, S., and Kabwe, S. (2016). Determinants of adoption and disadoption of minimum tillage by cotton farmers in eastern Zambia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 231, 54–67. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2016.06.027
Guo, S., Liu, S., Peng, L., and Wang, H. (2014). The impact of severe natural disasters on the livelihoods of farmers in mountainous areas: a case study of Qingping township, Mianzhu City. Nat. Hazards 73, 1679–1696. doi: 10.1007/s11069-014-1165-9
Hazell, P. B. R. (1982). Application of risk preference estimates in firm-household and agricultural sector models. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 64, 384–390. doi: 10.2307/1241153
Horowitz, J. K., and Lichtenberg, E. (1993). Insurance, moral hazard, and chemical use in agriculture. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 75, 926–935. doi: 10.2307/1243980
Hou, D., and Wang, X. (2022). Inhibition or promotion?–the effect of agricultural insurance on agricultural green development. Front. Public Health 10:910534. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.910534
Hu, K., and Allen, D. (2017). Firm size, ownership, industry characteristic and enterprises’ R&D behavior-based on survey to the agricultural leading enterprises of Jiangxi Province. Int. J. Res. Innov. Commercial. 1, 112–123. doi: 10.1504/IJRIC.2017.082302
Hungerford, A., and O’Donoghue, E. (2016). Federal crop insurance options for upland cotton farmers and their revenue effects. ERR-218, U.S. department of agriculture, economic research service. doi: 10.22004/ag.econ.249774
Jensen, B. B. (2002). Knowledge, action and pro-environmental behavior. Environ. Educ. Res. 8, 325–334. doi: 10.1080/13504620220145474
Jiang, S.-j., Wang, L., and Xiang, F. (2023). The effect of agriculture insurance on agricultural carbon emissions in China: the mediation role of low-carbon technology innovation. Sustain. For. 15:4431. doi: 10.3390/su15054431
Kollmuss, A., and Agyeman, J. (2002). Mind the gap: why do people act environmentally and what are the barriers to pro-environmental behavior? Environ. Educ. Res. 8, 239–260. doi: 10.1080/13504620220145401
Li, Z., Kai, H., and Shi, Q. (2025). The influence of digital village construction on agricultural green development-based on the mediate role of industrial structure upgrading. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1538845. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1538845
Li, H., Tang, M., Cao, A., and Guo, L. (2022). Assessing the relationship between air pollution, agricultural insurance, and agricultural green total factor productivity: evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 78381–78395. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-21287-7
Liu, R., Yue, Z., Ijaz, A., Lutfi, A., and Mao, J. (2023). Sustainable business performance: examining the role of green HRM practices, green innovation and responsible leadership through the lens of pro-environmental behavior. Sustain. For. 15:7317. doi: 10.3390/su15097317
Lu, F., Wang, W., Liu, M., Liu, M., and Qi, D. (2024). The non-linear effect of agricultural insurance on agricultural green competitiveness. Tech. Anal. Strat. Manag. 36, 1414–1429. doi: 10.1080/09537325.2022.2098102
Mao, H., Hu, R., Zhou, L., and Sun, J. (2022). Crop insurance and the farmers’ adoption of GreenTechnology: empirical analysis based on cotton farmers. J. Agrotech. Econ. 11, 95–111. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2022.11.004 (in Chinese).
Mao, H., Chen, S., Ying, R., and Fu, Y. (2023). How crop insurance influences agrochemical input use: evidence from cotton farmers in China. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 67, 224–244. doi: 10.1111/1467-8489.12507
Niu, Z., Yi, F., and Chen, C. (2022). Agricultural insurance and agricultural fertilizer non-point source pollution: evidence from China’s policy-based agricultural insurance pilot. Sustain. For. 14:2800. doi: 10.3390/su14052800
Norton, T. A., Zacher, H., and Ashkanasy, N. M. (2014). Organisational sustainability policies and employee green behavior: the mediating role of work climate perceptions. J. Environ. Psychol. 38, 49–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvp.2013.12.008
Pratiwi, L. P. K., and Budiasa, M. (2022). Effectiveness of agricultural insurance program as a sustainable agricultural development effort. SEAS (Sustain. Environ. Agric. Sci.) 6, 134–143. doi: 10.22225/seas.6.2.5856.134-143
Salazar, C., and Rand, J. (2016). Production risk and adoption of irrigation technology: evidence from small-scale farmers in Chile. Latin Am. Econ. Rev. 25, 1–37. doi: 10.1007/s40503-016-0032-3
Sargani, G. R., Jiang, Y., Joyo, M. A., Liu, Y., Shen, Y., and Chandio, A. A. (2023). No farmer no food, assessing farmers climate change mitigation, and adaptation behaviors in farm production. J. Rural. Stud. 100:103035. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2023.103035
Sherrick, B. J., Barry, P. J., Ellinger, P. N., and Schnitkey, G. D. (2004). Factors influencing farmers’ crop insurance decisions. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 86, 103–114. doi: 10.1111/j.0092-5853.2004.00565.x
Tan, C., Tao, J., Yi, L., He, J., and Huang, Q. (2022). Dynamic relationship between agricultural technology progress, agricultural insurance and farmers’ income. Agriculture 12:1331. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12091331
Wang, H., Liu, H., and Wang, D. (2022). Agricultural insurance, climate change, and food security: evidence from Chinese farmers. Sustain. For. 14:9493. doi: 10.3390/su14159493
Wei, T., Liu, Y., Wang, K., and Zhang, Q. (2021). Can crop insurance encourage farmers to adopt environmentally friendly agricultural technology—the evidence from Shandong Province in China. Sustain. For. 13:13843. doi: 10.3390/su132413843
Wu, Y., Duan, X., Liu, R., Ma, H., and Zhang, Y. (2024). How does full-cost insurance for wheat affect pesticide use? From the perspective of the differentiation of farmers’ production scale. Environ. Res. 242:117766. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117766
Xuguang, Z., and Zhihui, C. (2024). A research on the impacts of policy-based agricultural insurance on green production of farmers-based on survey data of wheat growers in four provinces of China. Insurance Stud. 6, 70–80. doi: 10.13497/j.cnki.is.2024.06.006 (in Chinese)
Yamoah, F. A., Kaba, J. S., Botchie, D., and Amankwah-Amoah, J. (2021). Working towards sustainable innovation for green waste benefits: the role of awareness of consequences in the adoption of shaded cocoa agroforestry in Ghana. Sustain. For. 13:1453. doi: 10.3390/su13031453
Yu, T.-K., Chang, Y.-J., Chang, I.-C., and Yu, T.-Y. (2019). A pro-environmental behavior model for investigating the roles of social norm, risk perception, and place attachment on adaptation strategies of climate change. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 25178–25189. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05806-7
Zhang, Z., Haodong, X., Shan, S., Liu, Q., and Yuqi, L. (2022). Whether the agricultural insurance policy achieves green income growth—evidence from the implementation of China’s total cost insurance pilot program. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:852. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19020852
Zhang, W., Khan, A., Luo, Y., Qi, T., and Zhao, M. (2023). How do risk preferences influence forage planting behaviors among farmers in the agro-pastoral ecotone of China? Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1252626. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1252626
Zhang, H., Zhang, Y., Wu, S., and Cai, R. (2020). The effect of labor migration on farmers’ cultivated land quality protection. Sustain. For. 12:2953. doi: 10.3390/su12072953
Zheng, T., and Zhao, G. (2025). The impact of policy-oriented agricultural insurance on China’s grain production resilience. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1510953. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1510953
Zhong, F., Ning, M., Xing, L., and Miao, Q. (2007). A study on the relationship between CropInsurance and agrochemical uses-an empirical analysis of the Manas watershed, Xinjiang, China. China Econ. Quart. 1, 291–308. doi: 10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2007.01.021 (in Chinese)
Zhu, Y., and Chen, J. (2022). Small-scale farmers’ preference heterogeneity for green agriculture policy incentives identified by choice experiment. Sustain. For. 14:5770. doi: 10.3390/su14105770
Sun, J., Zhan, J., and Chen, Z. (2024). Agricultural Insurance and Selection of Soil Testing and Formula Fertilization Technology—An Empirical Study Based on the Main Rice-Producing Areas in China[J]. Sustainability 16:9222. doi: 10.3390/su16219222
Tang, L., and Luo, X. (2021). Can agricultural insurance encourage farmers to apply biological pesticides? Evidence from rural China[J]. Food Policy. 105:102174. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2021.102174
Keywords: agricultural non-point source pollution, policy-based agricultural insurance, pro-environmental production behavior, influence mechanism, sustainability of food production
Citation: Li Y, Hu K, Wu H, Luo W and Li Z (2025) A study of the impact of policy-based agricultural insurance on farmers’ willingness to adopt pro-environmentally production behaviors: evidence from Jiangxi Province in China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1556958. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1556958
Edited by:
Abdullah Mohammad Ghazi Al Khatib, Damascus University, SyriaReviewed by:
Md. Emran Hossain, Bangladesh Agricultural University, BangladeshMengling Zhang, Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Hu, Wu, Luo and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kai Hu, Y2FybC1odUAxNjMuY29t
 Yanzhe Li
Yanzhe Li Kai Hu1*
Kai Hu1* Zhaoguang Li
Zhaoguang Li