- Department of Disaster Risk Management and Sustainable Development, Institute of Disaster Risk Management and Food Security Studies, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia
Introduction: Climate change is currently one of the three major challenges facing the global population. Developing countries like Ethiopia are disproportionately affected by the negative impacts of climate change. Food security is highly jeopardized by climate-induced shocks such as drought and flood. This review aims to critically examine the interlinkages between climate change and food security in Ethiopia, highlighting key challenges, impacts, and potential policy responses.
Methods: This study adopts a systematic review of peer-reviewed literature on climate change and food security in Ethiopia, employing a realistic review approach. Before commencing the systematic review, databases were thoroughly searched for existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses to prevent duplication.
Result: A total of 11 peer-reviewed articles were identified to investigate the relationship between climate change and food security in Ethiopia, revealing that climate change is a major factor aggravating food insecurity. Agriculture, the primary source of livelihood for the majority of the population is highly susceptible to climate change. This vulnerability directly affects the four components of household food security. The review also highlighted persistent forecasts of reduced crop production, land degradation, volatile market prices, and deteriorating livelihoods due to climate change, all contributing to food insecurity. Generally, climate change in Ethiopia is a setback to food security and is linked to broader development issues. Identified adaptation mechanisms include practicing climate-smart agriculture, implementing irrigation, managing soil and water resources, providing short-season seeds, planting drought-tolerant crops, altering planting dates, diversifying livelihoods, improving farmers’ awareness, and increasing the participation of female-led households in income-generating activities. The review recommends that Ethiopia, as a developing country, adopt locally suitable climate change adaptation strategies to enhance food security.
1 Introduction
Currently, climate change is one of the three major challenges facing the global population (Perry et al., 2022). Its impact is particularly severe in developing regions such as Africa (Thompson et al., 2010). Africa is often described as extremely vulnerable to climate change, especially sub-Saharan countries (Kotir, 2011; Serdeczny et al., 2017). Among these, Ethiopia is notably at high risk (Bedeke et al., 2020; Shukla et al., 2021). The majority of Ethiopia’s population (around 80%) lives in rural areas (Dube et al., 2019), with agriculture being their primary source of livelihood (Deressa et al., 2008; Dube et al., 2019). This sector employs 85% of the workforce, contributes 50% of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP), and generates more than 90% of foreign exchange earnings (Abebe, 2024; Ayele and Tarekegn, 2020). Additionally, the growth of other sectors is highly dependent on agriculture (Economic Commission for Africa, 2016; Welteji, 2018). However, agriculture in Ethiopia is highly vulnerable to climate change (Abeje et al., 2019; Teshome, 2016).
Hence, the rural poor are severely affected by the impact of climate change (Perry et al., 2022). This is because climate change is a major cause of soil erosion (Barungi and Maonga, 2011), environmental degradation (Wei et al., 2011; Yu et al., 2019), loss of agricultural production (Dendir and Simane, 2019), and increased poverty (Bangalore et al., 2019; Hallegatte et al., 2018). These cumulative effects have also led to food price inflation (Iliyasu et al., 2023) and food insecurity (Alemu and Mengistu, 2019; Molotoks et al., 2021), ultimately resulting in loss of life (Teshome, 2016). Ethiopia has experienced successive droughts and famines in the years 1952, 1959, 1965, 1972, 1973, 1978, 1984, 1991, 1994, 1999, 2002 (Hailu and Amare, 2022), and 2015 (Kasie et al., 2020). Given these recurring issues, the projected climate change in Ethiopia is expected to increase the inconsistency of rainfall (Getahun et al., 2020). According to Dendir and Simane (2019) and the National Meteorological Agency (2007), temperatures are also projected to rise by 1.1–3.1°C by 2060 and 1.5–5.1°C by 2090.
This will increase the frequency and intensity of extreme events such as droughts and floods (Abeje et al., 2019; Deressa et al., 2008). These conditions will adversely affect household livelihoods (Abeje et al., 2019; Maru et al., 2021), and household food security (Sileshi et al., 2019), exacerbating vulnerability to food insecurity (Ibok et al., 2019). Food security occurs when “all people at all times have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life” (Ben Hassen and El Bilali, 2022; FAO, 1996). Food insecurity, the inability to meet this definition, has become a predominant issue for Ethiopian households (Abebe, 2024; Awoke et al., 2022). This issue may be caused by natural catastrophic phenomena such as climate change (Abeje et al., 2019). Therefore, when examining the topic of food security concerning climate change, it is vital to understand what constitutes food security and where it is most affected.
Hence, as can be understood from the definition, food security depends on the availability of food, households’ ability to access food (which depends on household income and food prices), and the effective utilization of food over a consistent period (Abebe, 2024; Cohen and Garrett, 2010). Therefore, to fully understand the concept, it is important to examine the relationship between climate change and all components of food security. Authors such as Mekonnen et al. (2021), Kassaye et al. (2021), and Hagos et al. (2014), have explored the relationship between climate change and household food security in Ethiopia. However, these studies have not fully addressed the impact of climate change on all components of food security. They place a strong emphasis on the impact of climate change on a single aspect of food security: food availability. Furthermore, there is a lack of comprehensive scientific evidence verified at the national level.
This study systematically reviews the peer-reviewed literature concerning climate change and food security in Ethiopia to inform and synthesize the authors’ understanding of the issues and to identify priorities for future research. Specifically, the study aims to answer two key questions: (1) how will climate change affect food security in terms of availability, access, utilization, and stability? (2) What existing climate change adaptation strategies help to improve household food security?
2 Method
2.1 Search strategy, keywords, and criteria selection
This study conducted a systematic review of peer-reviewed literature on climate change and food security in Ethiopia, employing a realistic review approach. This approach is rooted in the principles of Cochrane systematic reviews, emphasizing explanation over empirical evidence (Pawson et al., 2005). Realistic review methods typically involve stricter inclusion criteria and a narrower selection of documents compared to other review methods, focusing on in-depth rather than extensive analysis and predominantly qualitative critical assessments (Thompson et al., 2010). Before commencing the systematic review, databases were thoroughly searched for existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses to prevent duplication. Initially, the DARE database1 was consulted to identify any ongoing projects or existing systematic reviews related to the topic.
The search was conducted on December 16, 2023, confirming that no review or meta-analysis had been published in peer-reviewed or science-indexed articles on the topic. Subsequently, the study followed a framework developed by Koutsos et al. (2019) for conducting a systematic review of the available literature. To ensure scientific rigor and transparency, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement protocol (Moher et al., 2010) was adopted. This study included articles that were peer-reviewed and published in science-indexed journals.
A questionnaire was developed to facilitate the review of documents, guided by a realistic review strategy and focusing on four key research questions. These questions aimed to identify and distinguish: (1) the main message conveyed by the authors; (2) the impact of climate change on the four components of food security (availability, accessibility, utilization, and stability); (3) recommended climate change adaptation strategies to achieve food security; and (4) the insights or outcomes of the article for overall development. The questionnaire was utilized to direct the document review process. Once completed, the questionnaires were organized and analyzed using thematic analysis. This analytical approach involves identifying patterns within the data, with emerging features categorized to facilitate analysis (Fereday and Muir-Cochrane, 2006).
The major databases such as PubMed/MEDLINE, WHOLIS, Cochrane Library, Embase, PsycINFO, Scopus, Web of Science, and reference lists were used to identify published articles. A keyword search was performed using the keywords (in all fields): (nutrition*) OR (food) AND (security) OR (diet)* OR (food) AND (insecurity) AND (climat*) AND (change) OR (global) AND (warming) AND (Ethiopia)) AND PUBYEAR > 2013 AND PUBYEAR < 2024 AND (LIMIT-TO (AFFILCOUNTRY, “Ethiopia”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, “English”)).
2.2 Eligibility criteria
2.2.1 Inclusion criteria
Articles published in English and at the national level (Ethiopia) or elsewhere in Ethiopia were included in this review. Only articles and reviews published in science-indexed journals were considered. The review focused on articles examining the relationship between climate change and food security, crop productivity, alternative food sources in the context of climate change, and potential adaptation mechanisms to achieve food security. Additionally, articles addressing the impacts of climate change on land productivity, soil fertility, desertification, and their implications for food security were also included.
2.2.2 Exclusion criteria
Articles that were not published in English and out of Ethiopia were excluded from consideration. Additionally, articles focusing on human evolution or historic climate change, the impact of climate change on non-food sources, vector-borne infectious diseases, and chronic diseases (non-nutritional in origin) were not included. Technical analyses of climate change projections, theoretical models, and simulations were also excluded. Furthermore, articles categorized as predatory or gray literature were not part of this review.
3 Results
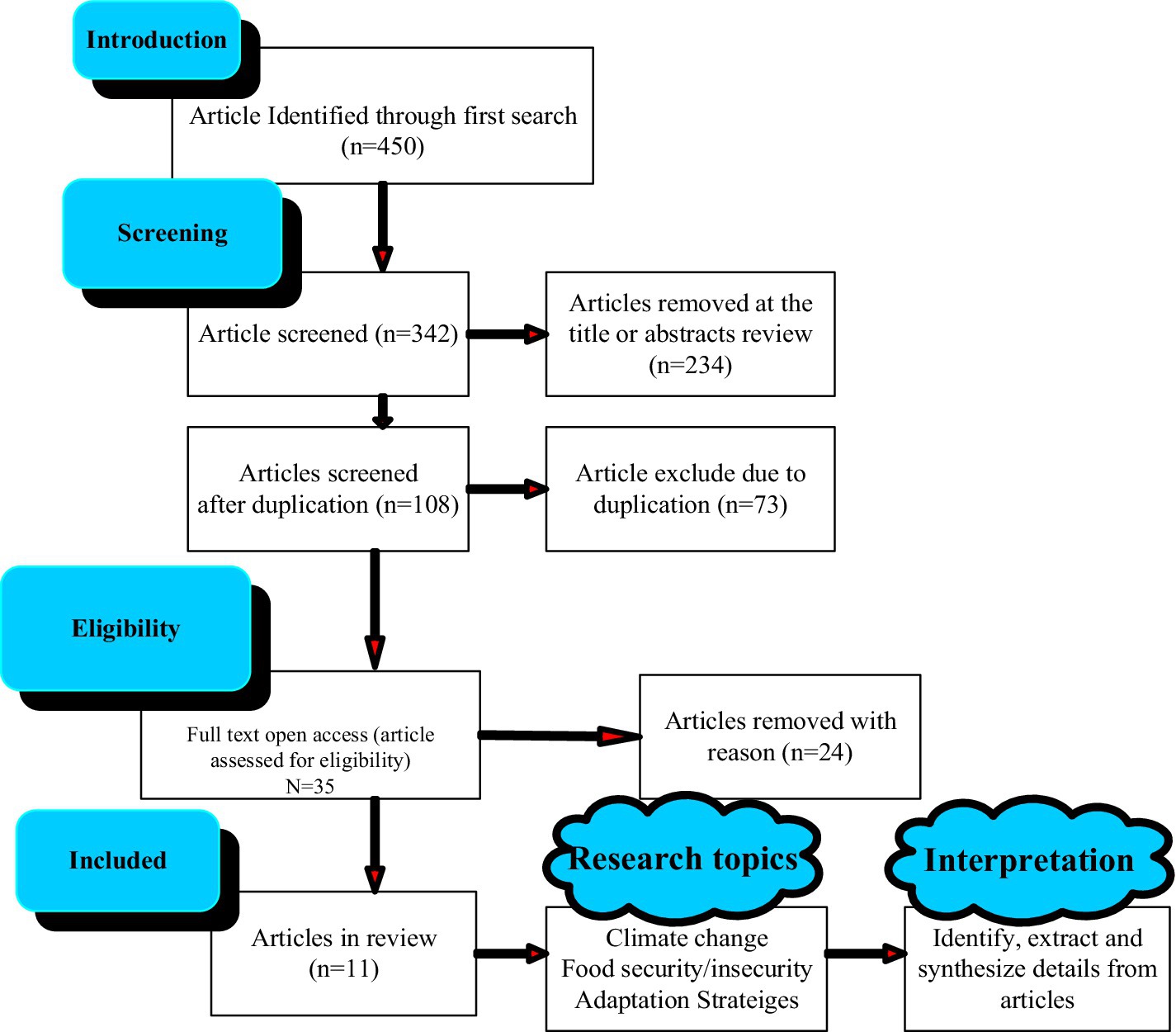
In the initial search, a total of 450 documents were identified across all databases. After removing duplicates, 298 unique articles were kept on. Upon careful examination of titles and abstracts, only 35 articles were deemed suitable for full-text review. Subsequently, these 35 full-text articles were accessed and evaluated against the eligibility criteria. Following critical appraisal, only 11 articles met the pre-defined criteria and were included in the final analysis. These articles are as follows: Amare and Simane (2017), Ayinu et al. (2022), Baylie and Fogarassy (2021), Di Falco et al. (2011), Hagos et al. (2014), Hilemelekot et al. (2021), Kassaye et al. (2021), Lemessa et al. (2019), Lewis (2017), Mekonnen et al. (2021), and Muluneh et al. (2017) (Figure 1).
3.1 Characteristics and limitations of the selected studies
3.1.1 Characteristics of the selected studies
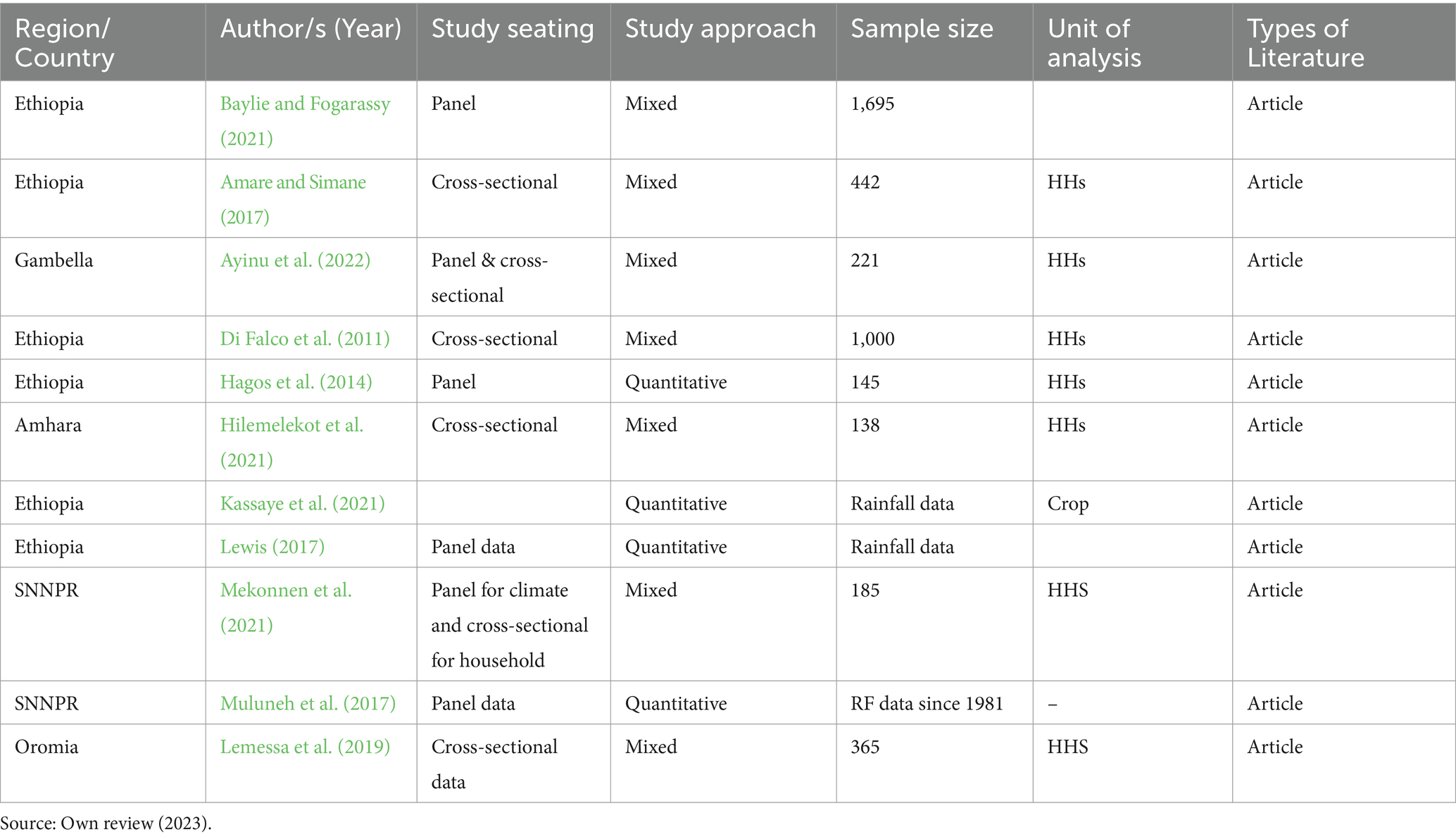
The characteristics of the 11 studies included in the systematic review are summarized in Table 1. Regarding the location where the studies were conducted, six studies such as (Amare and Simane, 2017; Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021; Di Falco et al., 2011; Hagos et al., 2014; Kassaye et al., 2021; Lewis, 2017) were done at the broader scale or national level, two in the Southern Nations Nationalities and Peoples’ Region (SNNPR) (Mekonnen et al., 2021; Muluneh et al., 2017), one in the Gambela region (Ayinu et al., 2022), one in Oromia (Lemessa et al., 2019), and one in the Amhara region (Hilemelekot et al., 2021). The studies included sample households ranging from 138 (Hilemelekot et al., 2021) to 1,695 (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021). Some articles such as Kassaye et al. (2021), Lewis (2017), and Muluneh et al. (2017) utilized rainfall data to demonstrate the link between climate change and food security instead of using households as a unit of analysis.
3.1.2 Limitations of the selected studies
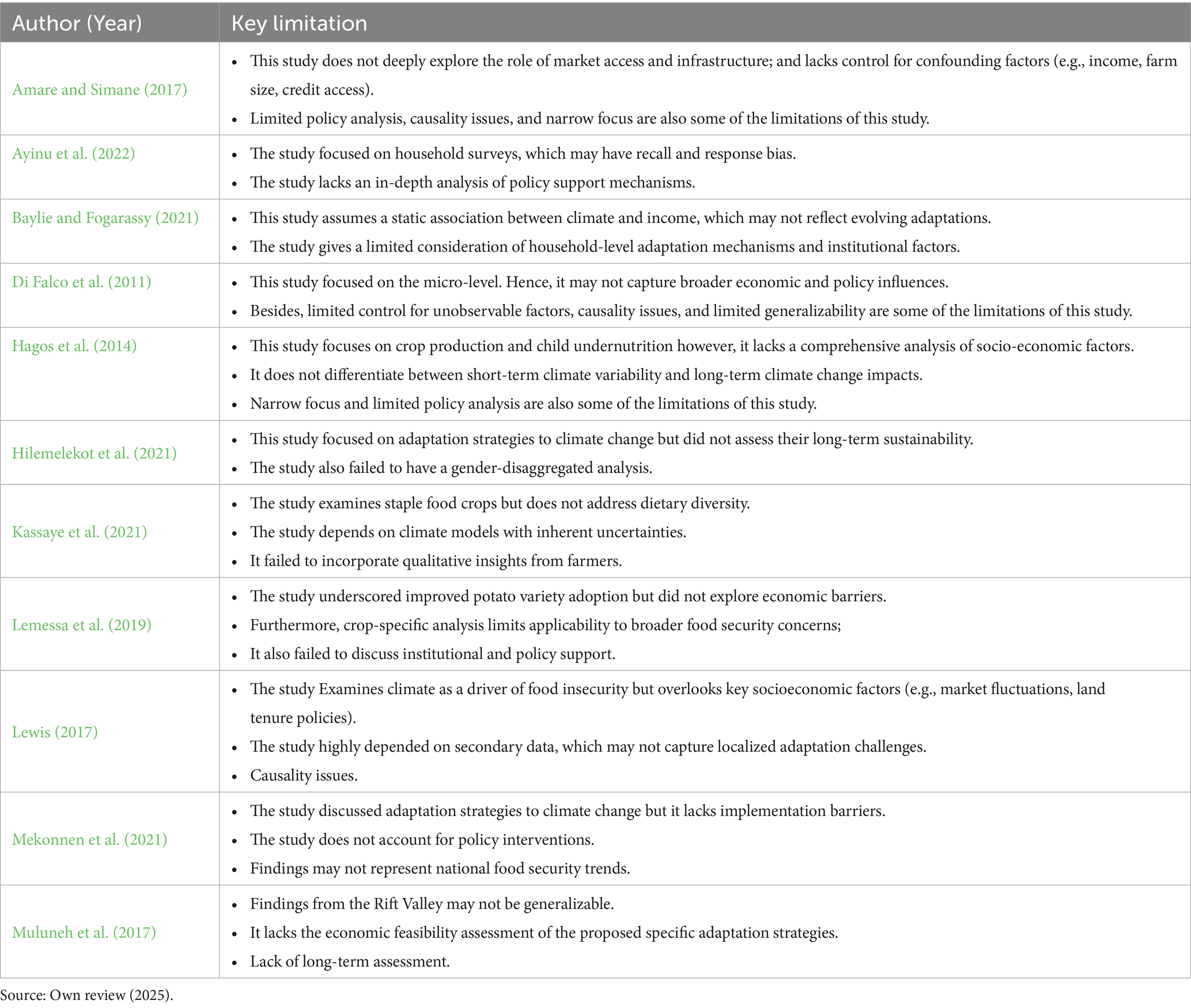
The studies included in this systematic review had their own limitation. Some of the shared limitations of all these studies are limited generalizability, casual issues, data bias, narrow focus, lack of long-term assessment, and limited policy analysis. Table 2 discusses the detailed limitations of each study. All these limitations may impact the ability of this review to draw definitive conclusions.
3.2 The impact of climate change on food security
Today, food security receives special attention, particularly amidst the imminent threats of climate change and variability (Amare and Simane, 2017). In Ethiopia, this issue poses a significant threat to the lives of millions (Mekonnen et al., 2021). Climate change impacts food security in the country through a complex interplay of environmental, economic, and social factors. Rural households grapple with both acute and chronic food insecurity exacerbated by the impact of climate change (Lewis, 2017). Recurrent droughts and unpredictable rainfall directly reduce crop yields and livestock productivity, these climatic stressors also exacerbate existing vulnerabilities, such as poverty, weak infrastructure, and limited access to adaptive technologies. Given that Ethiopia’s economy heavily relies on climate-sensitive livelihoods, such as agriculture (Ayinu et al., 2022; Kassaye et al., 2021; Mekonnen et al., 2021). There exists limited potential to adapt to these climate variability and change (Amare and Simane, 2017; Di Falco et al., 2011; Muluneh et al., 2017). Several factors contribute to the vulnerability of Ethiopian household food security in the face of climate change: (1) approximately 85% of the population depends primarily on rain-fed agriculture (Di Falco et al., 2011; Kassaye et al., 2021); (2) Ethiopia’s status as a low-income country further complicates the situation (Mekonnen et al., 2021); (3) the country’s diverse geographical locations experience varying degrees of climate impacts (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021; Mekonnen et al., 2021); and (4) high exposure to both natural and anthropogenic catastrophes (Amare and Simane, 2017).
Furthermore, extensive regions of Ethiopia face food insecurity (Di Falco et al., 2011). Moreover, the country has consistently endured the repercussions of severe El Niño events throughout its documented history. These events have resulted in agricultural production failures, livelihood disruptions, and exacerbated food insecurity (Amare and Simane, 2017).
On the contrary, Ethiopia’s population is projected to fly to 209 million by 2050, driven by a high birth rate (Tesfaye et al., 2018). Meeting the nutritional needs of this escalating population in the challenges posed by climate change is a pressing concern. Climate change impacts all components of food security, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of how and when these effects manifest across various dimensions. This understanding is crucial for identifying appropriate adaptation strategies to mitigate these impacts effectively. Furthermore, climate change also impacts sectors beyond agriculture, including livestock herding (Di Falco et al., 2011). These multifaceted challenges significantly affect each component of food security.
3.2.1 Impact of climate change on food availability
For most rural households, the primary sources of food are production and purchase (Mekonnen et al., 2021). Climate change directly affects the availability (production) component of food security by diminishing crop yields (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021; Mekonnen et al., 2021). It’s evident that smallholders in Ethiopia heavily rely on rain-fed agriculture (Ayinu et al., 2022; Kassaye et al., 2021), compounded by the agricultural sector’s low production capacity (Di Falco et al., 2011). Food crops in Ethiopia are particularly sensitive to climate change (Kassaye et al., 2021), with rural farming systems characterized by traditional methods such as plowing and animal draught power (Di Falco et al., 2011) and limited technological input (Lewis, 2017). Consequently, they are highly susceptible to the adverse impacts of climate change (Mekonnen et al., 2021), exacerbated by constraints in crop production due to inadequate rainfall and rising temperatures (Ayinu et al., 2022; Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021; Mekonnen et al., 2021). Additionally, Lewis (2017), highlights that rainfall variability significantly contributes to food insecurity nationwide.
Moreover, climate change exacerbates the prevalence of crop pests and diseases (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021), which significantly diminishes crop yield and productivity (Mekonnen et al., 2021). Rain-fed agriculture, the predominant crop production method in Ethiopia, covering 90–95% of crops, is highly vulnerable to climate change impacts (Kassaye et al., 2021). However, this method faces considerable challenges such as severe erosion and flooding (Mekonnen et al., 2021), which result in soil fertility depletion and consequently, low crop productivity (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021; Hagos et al., 2014). Additionally, the land’s productive capacity is compromised, further reducing estimated mean crop productivity across various regions of the country (Kassaye et al., 2021).
Furthermore, variations in temperature and rainfall are anticipated to have detrimental effects on crop productivity by constraining crop growth and duration (Mekonnen et al., 2021; Muluneh et al., 2017). Studies like Kassaye et al. (2021), have indicated that by the end of the twenty-first century, major crops in Ethiopia such as sorghum and wheat may experience yield reductions of 18.1 and 13.2%, respectively. Nearly 60% of the average daily caloric intake for Ethiopian households is derived from cereals such as sorghum (a local grain indigenous to Ethiopia), and wheat. Hence, the loss of these major crops due to climate change significantly exacerbates food insecurity (Kassaye et al., 2021; Mekonnen et al., 2021).
Indeed, the high vulnerability of smallholders to climate change, coupled with their limited capacity to cope with its effects, exacerbates the situation (Ayinu et al., 2022). The collective consequences of these challenges significantly affect household food availability in the country (Muluneh et al., 2017). Therefore, in light of climate change’s detrimental impact on food productivity, it is imperative to focus on strategies aimed at mitigating these effects and enhancing food production.
3.2.2 Impact of climate change on food accessibility
As mentioned in the availability section, purchasing is a significant source of food for rural households (Muluneh et al., 2017). Household purchasing power is directly linked to household income, which in turn affects food accessibility and affordability (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021). Given that a majority of the Ethiopian population relies on subsistence agriculture (Kassaye et al., 2021; Muluneh et al., 2017), markets play a crucial role as a secondary source of food (Amare and Simane, 2017). Research, such as that conducted by Hilemelekot et al. (2021) has shown that many farmers face shortages in production from July to September and rely on purchasing food from the market during this period. However, climate change impacts rural households’ ability to purchase food by driving up food prices during the wet season (Di Falco et al., 2011). This indicates climate variability intensifies food price volatility, limiting affordability for low-income households and heightening malnutrition risk. Additionally, it diminishes livestock production and market value, further exacerbating food insecurity (Hilemelekot et al., 2021).
Climate-related shocks not only impact productivity but also hinder economic growth and exacerbate existing social and economic challenges (Mekonnen et al., 2021). Consequently, rural household food accessibility depends upon both food production shortfalls and the capacity to procure food (Di Falco et al., 2011). As a result, households often confront food deficits and experience hunger when crop yields fail to meet demands, necessitating reliance on food purchases from markets (Hilemelekot et al., 2021). This reliance on market purchases stems from the fact that agricultural production remains the primary source of income for the majority of rural households (Muluneh et al., 2017).
Moreover, in Ethiopia, climate change-induced droughts have had a profound impact on household livelihoods. Due to climate change and other factors, residents have been unable to fulfill their food needs by purchasing food from other regions (Lewis, 2017). Studies, such as that by Di Falco et al. (2011), indicate that catastrophic hydrological events like droughts and floods have reduced Ethiopia’s economic growth by more than a third. This underscores the reality that as long as Ethiopian populations rely on rainfall for both food availability and access, they will continue to face regular acute food insecurity (Lewis, 2017). On the flip side, limited access to credit may hinder households’ ability to invest in climate change adaptation strategies, exacerbating issues of food inaccessibility (Lewis, 2017).
As history reveals, the consumption of purchased food tends to flow during drought years (Lewis, 2017). However, during such periods, household income is also impacted by the drought, given its dependence on rain-fed agriculture. Even though some rural households may rely on non-agricultural livelihoods, these livelihoods are directly or indirectly linked to natural resources. Consequently, those whose livelihoods pivot on natural resources will experience heightened food insecurity due to reduced crop yields, limiting both personal consumption and the availability of food as a source of capital (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021). Consequently, they are constrained in their ability to purchase and consume food as desired.
Climate change significantly exacerbates food price inflation. For example, Mekonnen et al. (2021) found that the total monetary loss due to a 1°C increase in temperature during the study period amounted to approximately 976.80 Ethiopian Birr (ETB) (equivalent to 35.9 US$). This constrains households’ purchasing power, particularly during periods of food deficits, which are often observed in July and August. The lack of assets is identified as a major hindrance to poor farmers’ ability to adapt, rendering them highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021). Additionally, climate change-induced flooding poses a significant threat to the farming community (Hilemelekot et al., 2021). In years when certain regions receive insufficient rainfall, even if national food production remains unaffected, those regions may struggle to access food through markets, leading to food insecurity (Lewis, 2017).
3.2.3 Impact of climate change on food utilization
Another crucial dimension of food security is the utilization of proper, healthy, and nutritious food for our bodies (Abebe, 2024). Health is essential for engaging in livelihood activities, contributing to society, and enhancing personal quality of life (Thompson et al., 2010). However, if food availability and accessibility are compromised by climate change, there is no guarantee that food utilization will not be affected. Climate change has a profound impact on the quality of food produced (Mekonnen et al., 2021). In Ethiopia, crops like teff, maize, wheat, barley, and beans cover approximately 65% of cultivated land and constitute the major components of the local diet (Di Falco et al., 2011). However, the production of these diverse foods is compromised due to climate change, affecting the dietary variety of households (Hilemelekot et al., 2021). Additionally, this review confirms that households producing a variety of crops, including cereals, pulses, and vegetables, are more food secure than those producing a limited variety of crops. Low crop and livestock productivity due to climate change exert pressure on households to consume less diverse and less nutritionally rich foods (Mekonnen et al., 2021).
The study by Di Falco et al. (2011) revealed that out of 95% of the country’s agricultural products, 75% are consumed by farm households. However, when climate change leads to crop pests and diseases, the quality of food becomes jeopardized (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021). Besides, climate change exacerbates hidden hunger and micronutrient deficiencies by reducing the availability and nutritional quality of staple crops, disrupting food systems, and increasing the frequency of climate-related shocks that limit access to diverse and nutrient-rich foods. Additionally, climate change contributes to the proliferation of biological hazards Ayinu et al. (2022), further compromising food safety. Furthermore, climate change affects the infrastructure, basic services, and facilities of households (Ayinu et al., 2022). These non-food items (such as hygiene and sanitation, cooking conditions and facilities, health services, and poor housing and living conditions), play a crucial role in facilitating the proper utilization of food. This suggests that if these basic services are affected by climate change, food utilization will be indirectly compromised.
3.2.4 Impact of climate change on food stability
Climate change also impacts food stability. If the first three dimensions of food security are disrupted by climate change-induced shocks, the state of food stability will be compromised. Climate change alters the cropping calendar (Ayinu et al., 2022; Hilemelekot et al., 2021), potentially leading to unstable productivity. Additionally, shifts in the suitability of farmlands for crop production due to climate change can further undermine consistency in food production and access (Hilemelekot et al., 2021). Moreover, since the livelihoods of rural households in Ethiopia rely on rain-fed agriculture (Kassaye et al., 2021; Muluneh et al., 2017), food production is not consistent throughout the year. During the harvesting season (months such as November–January), food may appear abundant, whereas during the wet season (months like July to September), food shortages may occur (Hilemelekot et al., 2021).
Climate change-induced shocks, such as drought, result in a remarkable decrease in pasture and fodder availability, consequently impacting livestock production and productivity (Hilemelekot et al., 2021). These circumstances suggest that food insecurity in rural Ethiopia follows a seasonal pattern closely tied to rainfall patterns. Following the wet season, hunger trends see a significant reduction, and vice versa (Mekonnen et al., 2021). These observations highlight the inconsistency of the food security situation throughout the year. When food security lacks consistency, the stability components of food security are compromised. Therefore, creating an environment where food is sustainably produced, marketed, and consumed without distortion plays a key role in ensuring food security.
3.2.5 Climate change impact on food sovereignty
Almost all studies included in this review did not directly evaluate the impact of climate change on food sovereignty. However, this review indirectly examines the impact of climate change on food sovereignty using the selected articles. To effectively discuss food sovereignty, it is essential to first understand its key concepts. Food sovereignty is the right of people to control their own food systems, prioritizing local production, farmers’ rights, and sustainable practices (Wittman, 2011). Hence, it might be affected by the situations of smallholder land tenure rights, power dynamics in agricultural policy, local knowledge, and agroecology. Some studies such as Ayinu et al. (2022), state that situations of land governance affect levels of household food security. Besides, Lemessa et al. (2019), state that the size of the land owned by the smallholders can affect their food security. On the other hand, Ayinu et al. (2022), acknowledge that indigenous knowledge needs to be recognized for effective climate change adaptation. However, in Ethiopia, state-owned land, bureaucratic land management, neglect of indigenous knowledge, and accelerating climate change pose significant challenges to food sovereignty. Therefore, addressing these issues is essential to achieving food sovereignty.
In general, while the reviewed studies have contributed valuable insights into production-related (food availability) challenges of climate change, they have paid limited attention to equity and nutrition. Particularly, there is a notable gap in examining power dynamics within food systems such as who controls resources, decision-making, and access, and how these affect vulnerability and adaptive capacity. Future research should explore how climate shocks differentially impact marginalized groups and influence nutrition outcomes.
3.3 Adaptation strategies and potential implementation barriers
3.3.1 Adaptation strategies
Climate change is an unavoidable reality (Mekonnen et al., 2021), underscoring the urgent need to find solutions to coexist with and take advantage of its effects. Adaptation strategies emerge as vital avenues to address climate change (Ayinu et al., 2022; Hilemelekot et al., 2021; Lewis, 2017; Mekonnen et al., 2021; Muluneh et al., 2017). As highlighted by Hilemelekot et al. (2021), smallholder farmers in Ethiopia commonly employ two types of climate change adaptation strategies to safeguard their food security: biophysical adjustments and livelihood adjustments.
Various papers in different contexts within Ethiopia recommend diverse strategies to adapt to the adverse impacts of climate change. Among these, implementing biophysical soil and water conservation measures such as stone bunds, trenches, mulching, area closure, strip cropping, contour plowing, check dams, and crop rotation emerges as one of the most common climate change adaptation strategies in the country (Baylie and Fogarassy, 2021; Hilemelekot et al., 2021). Additionally, locally tailored climate-smart agriculture (Kassaye et al., 2021), irrigation (Amare and Simane, 2017; Hilemelekot et al., 2021), soil and water management (Di Falco et al., 2011), provision of short-season seeds and cultivation of drought-tolerant crops (Amare and Simane, 2017; Hilemelekot et al., 2021), access to credit (Di Falco et al., 2011), adjusting planting date, diversification of household income sources (Ayinu et al., 2022; Hilemelekot et al., 2021), improving awareness about climate change (Ayinu et al., 2022; Di Falco et al., 2011), enhancing the involvement of female-headed households in income-generating activities (Mekonnen et al., 2021), changing crop varieties (Di Falco et al., 2011), improving access to basic infrastructure services and facilities (Ayinu et al., 2022), and adopting new agricultural technologies (Kassaye et al., 2021) stand out as major climate change adaptation strategies with positive impacts on the enhancements of household food security.
Implementing afforestation measures is another effective strategy to mitigate the adverse effects of temperature rise (Amare and Simane, 2017). Furthermore, recognizing the value of indigenous knowledge (Ayinu et al., 2022), promoting water harvesting technologies (Di Falco et al., 2011), and embracing agroforestry practices (Hilemelekot et al., 2021) also contribute to climate change adaptation efforts. Moreover, investing in sustainable land management practices helps reduce vulnerability to climate change and enhances the adaptive capacity of smallholder farmers to its adverse effects (Amare and Simane, 2017).
3.3.1.1 Climate-smart agriculture (CSA)
Climate-smart agriculture techniques, including conservation agriculture, drought-resistant crop varieties, and agroforestry, have shown promise in improving agricultural productivity under changing climate conditions. However, their scalability remains limited due to high initial investment costs, limited access to extension services, and knowledge gaps among smallholder farmers. The subsection below provides details on selected CSA practices, explaining how they work and their effectiveness in the face of climate change.
3.3.1.2 Soil and water conservation practices
Soil and water conservation practices help the agricultural community adapt to the adverse impacts of climate change and variability. For instance, Hilemelekot et al. (2021), revealed that soil and water conservation measures help to reduce the creation and growth of gullies, landslides, crop damages by flood, flooding of grazing lands, soil erosion, and runoff and thus improve soil moisture in the cultivated lands and communal grazing lands. Besides, Amare and Simane (2017), and Mekonnen et al. (2021), indicate that, in terms of food security, a significant statistical difference exists between households that implemented soil and water conservation measures and those that did not. The land is a fundamental resource for agricultural activities in Ethiopia. However, it is damaged from time to time and needs constant care. Therefore, soil and water conservation is an effective land management practice that enhances land productivity while preserving biodiversity. This is because soil and water conservation measures are evident in the improved fertility of their farmlands, soil moisture, and agricultural production. Even focus group discussants in Hilemelekot et al. (2021) expressed a preference for increased support in soil and water conservation over food aid, highlighting their recognition of its greater role in ensuring long-term stability. On the other hand, the local community’s long-standing indigenous knowledge in soil and moisture management must also be properly taken into account.
3.3.1.3 Small-scale irrigation expansion
Small-scale irrigation can be essential for adapting to unpredictable rainfall patterns and recurring droughts, thereby contributing to household food security (Lemessa et al., 2019). For instance, a study conducted by Hilemelekot et al. (2021), showed that the food consumption score of the irrigation adopter households in Basona Worena district is better than non-adopter. Likewise, Amare and Simane (2017), showed that households that have implemented small-scale irrigation on their farms are more likely to be food secure than those that have not. All these indicate that households that use small-scale irrigation are able to produce more food for both household consumption and sale, even during climate change-related hardships, and are more likely to be food secure compared to those who do not practice irrigation on their farmland. While irrigation is a crucial strategy for stabilizing agricultural output amid erratic rainfall patterns, only a small of Ethiopia’s cultivated land is irrigated due to infrastructure limitations (Ayinu et al., 2022). Besides, Moreover, water governance challenges and conflicts over resource allocation further restrict large-scale irrigation development.
3.3.1.4 Livelihood diversification
Diversifying livelihoods, especially in ways that enhance climate resilience and alleviate pressure on natural resources, can help mitigate climate-related risks. For instance, Hilemelekot et al. (2021), revealed that households that engage in various income-generating activities (such as on-farm, off-farm, and non-farm activities) are more food secure compared to those that rely on a single income source. Furthermore, Ayinu et al. (2022), showed that off-farm income-generating activities are increasingly recognized as climate change adaptation strategies in Godere district and those who are involved in off-farm activities are relatively food secure than others. Besides, Mekonnen et al. (2021), also explained that diversifying income sources are a potential solution to tackle climate change challenges and address food insecurity issues. All this shows that even if climate change completely destroys one source of income, households can still support themselves with another source of income. Therefore, it shows that a favorable environment should be created for households to engage in diversified livelihood activities.
3.3.1.5 Adopting and practicing agroforestry
Agroforestry offers a dual advantage by reducing soil and water degradation, enhancing land management, and improving environmental sustainability on one hand, while ensuring household food security on the other. As depicted in Hilemelekot et al. (2021), those who adopted and practiced agroforestry are relatively food secure than non-adopters. In doing so, it is good to consider the community’s indigenous knowledge and long-term experience when selecting tree species and seedlings that are suitable for the area.
3.3.1.6 Cultivating diversified crops
Crop diversification also plays a key role in spreading risk in coping with climate change. Planting different crops has two benefits: one is to reduce the potential for the total loss of a single crop when the climate changes and the second is to provide a balanced diet by producing a variety of crops. In connection with this Hilemelekot et al. (2021), showed that households that cultivate a diverse range of food crops are more food secure than those that produce a limited number of crops. Furthermore, Mekonnen et al. (2021), showed that farmers who have begun to adapt to selected crops have shown that they are more drought-resistant than others and, as a result, are less likely to face food insecurity due to climate change. Therefore, to enable communities to adapt to diverse crops, research institutions should develop improved varieties, extension agents must demonstrate optimal planting and care techniques, and policymakers should create supportive policy frameworks that encourage the cultivation of selected and diversified crops.
3.3.1.7 Drought-tolerant crops and improved variety of seeds
Temperatures and droughts are increasing over time. At the same time, the human population is also growing. On the other hand, this growing population needs food. As Sustainable Development Goal 2 states, no one should go to bed hungry. Therefore, we must adapt by cultivating drought-resistant crops that can withstand the rising temperatures and drought conditions. To strengthen this Amare and Simane (2017), state that households that produce more drought-tolerant crops are highly resilient to withstand drought. Likewise, Lemessa et al. (2019), also state that Adopting early-maturing, drought-tolerant, and pest-and disease-resistant crop varieties can help mitigate or prevent the negative impacts of climate change. Therefore, farmers must recognize that climate change is inevitable and adapt to the harsh conditions in order to survive and thrive in those difficult situation. They must immediately develop crops that can withstand drought, pests, and other problems that may arise as a result of climate change. To achieve this, development agents, practitioners, researchers, and policymakers must collaborate effectively.
3.3.1.8 The role of adopting agricultural technologies in climate change adaptation
The world is becoming increasingly technologically advanced (Dosi and Nelson, 2018; Wolff, 2021). This situation has also contributed to unprecedented technologies in the agricultural sector (Karunathilake et al., 2023; Shafi et al., 2019). The use of various technologies can help to adapt to climate change and increase productivity. For example, if we look at early warning technology, collects data on various rainfall and temperature conditions, makes predictions, and delivers accurate information to the farmer. If the farmer knows the nature and conditions of the future, they can take preventive/mitigation measures either to prevent the disaster from occurring or mitigate the impact of disasters (Di Falco et al., 2011). However, there are limitations to doing so in Ethiopia. According to Ayinu et al. (2022), one reason for this is that infrastructure has not developed as expected. This study emphasized that to bring the required level of agricultural technology, we must first focus on infrastructural development. After the infrastructure is conducive, agricultural technologies such as precision agriculture, mobile-based early warning systems, weather-based index insurance, and farmer-led innovation networks might be effective in addressing long-term climate issues and in turn, satisfying the short-term demands of food. All these are the untapped potential of the Ethiopia.
3.3.2 Potential implementation barriers
Even though the aforementioned adaptation strategies offer promising opportunities to adapt to climate change while ensuring food security, there may be several barriers to implementing these strategies in Ethiopia. Among many, the major factors that are frequently mentioned in the selected articles are limited awareness, infrastructural factors, financial constraints, institutional barriers, and socio-cultural and technological factors. It is crucial to note that illiterate household heads may exhibit less willingness to adopt new technologies and may struggle to grasp climate information essential for combating climate change (Mekonnen et al., 2021). However, the successful implementation of these strategies hinges upon awareness and access to information (Ayinu et al., 2022; Di Falco et al., 2011). Therefore, prioritizing awareness and education among farmers is paramount for the efficient and effective adoption of other climate change adaptation strategies. This is because, for farmers to consider adopting these technologies, they must first have access to information about farming practices (Di Falco et al., 2011).
Besides, farmers need infrastructure and other basic services to build skills, access markets, and adopt new technologies (Ayinu et al., 2022). In this regard, extension services play a crucial role in disseminating relevant climate and technology-related information to smallholder farmers (Hilemelekot et al., 2021). Nonetheless, the decision to adopt climate change adaptation strategies is voluntary and may depend on individual self-selection (Di Falco et al., 2011). With sufficient knowledge of climate adaptation methods, farmers are more likely to adopt other innovative technologies. For instance, Lemessa et al. (2019), highlight that education and extension services can improve farmers’ analytical capacity to evaluate the available strategies for the selection of feasible strategies. Therefore, it is essential to raise awareness through various methods to empower smallholders to make informed decisions and adopt these strategies to combat climate change and capitalize on its potential benefits.
Additionally, CSA adoption is hindered by institutional factors such as land tenure insecurity, as many farmers are reluctant to invest in long-term soil conservation practices without guaranteed land rights (Kassaye et al., 2021). Therefore, land must be sustainably managed while ensuring secure ownership and usage rights for farmers. The other broader and more pressing issue is limited access to credit. This may hinder farmers from implementing their preferred climate change adaptation strategies. In connection with this, Lemessa et al. (2019), showed that access to credit has negative effects on farmers’ irrigation usage and other farm inputs to maximize crop yields. This is because limited access to credit and investment capital restricts the ability of smallholder farmers to implement adaptation measures (Lewis, 2017). However, improved access to credit markets enables farmers to adopt new technologies and obtain seeds of climate-resilient crops (Di Falco et al., 2011). This indicates the need for an integrated approach that links access to credit with innovation, policy support, and community resilience to address climate change impacts on food security.
A policy framework is necessary to address these aforementioned problems to adopt and practice climate change adaptation strategies. Public policies play a crucial role in supporting farm households’ adaptation efforts (Di Falco et al., 2011). Therefore, the government should implement policies that enhance agriculture, provide timely climate information, diversify incomes, and promote improved crops to reduce food security risks amid climate change (Mekonnen et al., 2021).
3.4 Future climate scenario and the fate of food security in Ethiopia
Climate change and food insecurity have long been persistent challenges in Ethiopia (Lewis, 2017). It is not just the only problem; nonetheless, by the late 21st century, Ethiopia is projected to face higher temperatures, reduced rainfall, and increased droughts, threatening agriculture and food security (Kassaye et al., 2021). In connection with this, the National Meteorological Agency (2007), and Dendir and Simane (2019), confirm that Ethiopian temperatures are expected to rise by 1.1–3.1°C by 2060 and by 1.5–5.1°C by 2090. All this evidence shows us climate change is unavoidable (Lemessa et al., 2019). In addition, another headache is the rapid increase in the country’s population. According to Tesfaye et al. (2018), Ethiopia’s population is projected to rise to 209 million, nearly doubling the current number by 2050. This further exacerbates the potential problems posed by climate change.
However, this temperature increment and rainfall reduction pose two distinct situations for ensuring or not ensuring household food security. One is that some crop varieties are unable to withstand the heat and lack of rainfall, resulting in reduced yields. As a result, common food crops might disappear. Among the common crops that will reduce their productivity are sorghum and wheat. For instance, Kassaye et al. (2021), indicate that an increase in temperature and reductions in rainfall will lead to an 18.1% decline in sorghum yield and a 13.2% decrease in wheat yield by the late 21st century. On the other hand, some crops will adapt well to rising temperatures and reduced rainfall, leading to increased yields. For instance, Kassaye et al. (2021), also showed that the yields of teff and maize are expected to increase by 20.2 and 17.9%, respectively. This shows that climate change is not only a challenge but also an opportunity to achieve food security. Therefore, humanity’s role is to learn from the challenges prepare itself, and seize the opportunities. On the other hand, growing and consuming nutrient-rich crops as substitutes for declining food grains will help ensure adequate nutrition.
3.5 Comparing climate change and food security in Ethiopia and other developing nations
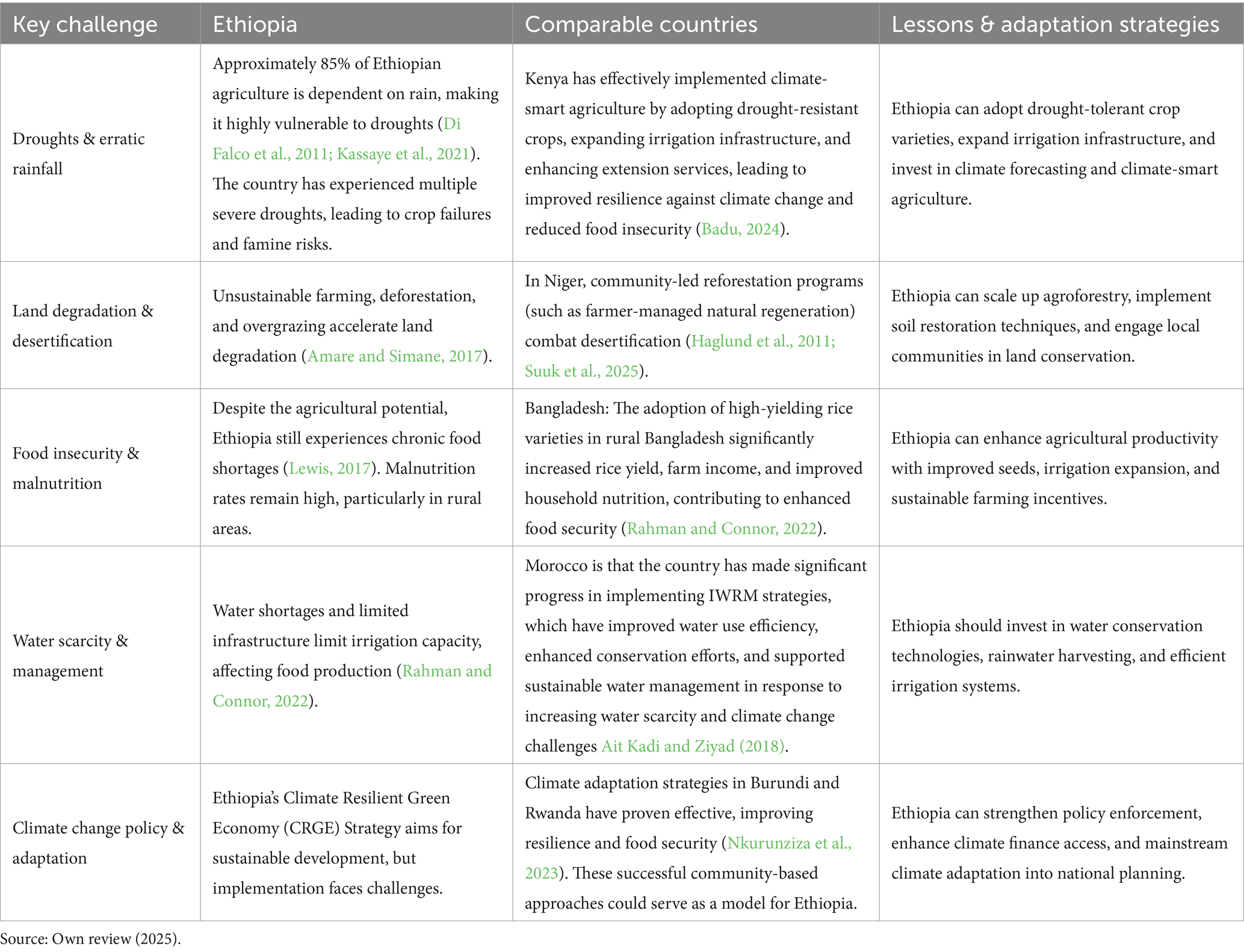
Some developing countries around the globe face similar challenges to Ethiopia such as climate change and food security. However, some have attempted to overcome these challenges by implementing various mitigation and climate change adaptation measures. Table 3 summarizes the key challenges faced by developing countries like Ethiopia, the effective measures they have adopted, and recommended solutions for Ethiopia.
4 Summary and policy implication
4.1 Summary
Climate change remains a significant global challenge, impacting household food security in both developed and developing nations. Ethiopia, as a developing country, is particularly vulnerable to climate change-induced food insecurity. While the link between climate change and food security is evident, it has not been uniformly explored. Climate change affects all components of food security availability, accessibility, utilization, stability, and food sovereignty. However, much of the academic research in Ethiopia has primarily focused on the impact of climate change on food availability. Climate change contributes to temperature and rainfall variability, soil fertility reductions, and environmental degradation. Additionally, it exacerbates crop pests and animal diseases. These cumulative effects ultimately diminish production and productivity, crucial components of food security.
There is a scarcity of academic research that directly explores the relationship between climate change and the other dimensions of food security, namely accessibility, utilization, stability, and food sovereignty. Nonetheless, this review indirectly examines the impact of climate change on these aspects of food security. It reveals that climate change in Ethiopia diminishes food accessibility by decreasing household income or purchasing power. Additionally, climate change contributes to the proliferation of crop diseases, pests, and other biological hazards, consequently reducing crop variety. This indirectly affects food quality, safety, and dietary diversity, jeopardizing proper nutrition and health. Moreover, when the first three components of food security are compromised, households struggle to maintain food sustainability and food sovereignty.
With Ethiopia’s population projected to reach 209 million by 2050, coupled with the challenges posed by climate change, there will be an increased demand for environmental resources. This will put pressure on already scarce resources, especially in the agricultural sector. To mitigate the negative impacts of climate change and meet the growing demand for food, smallholders are encouraged to implement locally tailored adaptation strategies. Among the various adaptation strategies identified in this review, adopting climate-smart agriculture such as implementing irrigation techniques, diversifying livelihoods, and cultivating drought, disease, and pest-resistant crops are essential. Additionally, raising awareness and providing education on climate change adaptation, as well as implementing soil and water conservation measures such as stone bunds, trenching, mulching, and crop rotation, are crucial steps toward ensuring food security and maximizing productivity in the face of climate change. In all efforts of climate change adaptation, the indigenous knowledge of the community must be taken into account.
4.2 Policy implication
The following are some policy recommendations based on this review.
• The government should have to strengthen climate-resilient agricultural policies. These policies need to be in the context of climate-smart agricultural techniques such as drought-resistant crops, agroforestry, and soil conservation.
• It is also better if the government and other private sectors introduce and expand climate financing such as weather index-based crop insurance to protect farmers from climate-induced losses.
• Addressing land tenure and ownership issues encourages farmers to manage their farmland sustainably.
• Develop climate-resilient irrigation infrastructure to reduce dependence on rain-fed agriculture, prioritizing smallholder farmers in drought-prone areas.
• Improve watershed management programs to enhance water availability and prevent land degradation.
• Improve rural infrastructure (e.g., roads, storage facilities, and market access) to strengthen food distribution networks.
• Enhance financial support mechanisms such as microfinance and credit access for smallholder farmers to invest in adaptive agricultural technologies.
• Establish multi-stakeholder platforms to bridge gaps between researchers, policymakers, farmers, and civil society in shaping climate and food security policies.
• Develop gender-responsive adaptation strategies that empower women farmers and address gender disparities in access to land, credit, and extension services.
• Improve climate and food security data systems to enable evidence-based decision-making and localized adaptation strategies.
• It would be better if future research focused on food sovereignty as a component of food security.
• The main gap in the existing research is the lack of localized, integrated research data that captures micro-level climate impacts and socio-economic factors such as gender and policy gaps affecting food security in the country. Hence, future research should prioritize localized, community-based studies that integrate socio-economic, gender, and policy dimensions to better understand and address the complex and uneven impacts of climate change on food security in Ethiopia.
• The other gap in the existing literature is paying limited attention to the impacts of climate change on children, the elderly, and other marginalized groups. Hence, future research should prioritize the impacts of climate change on children, the elderly, and other marginalized groups to ensure inclusive and equitable adaptation strategies.
• Future research should adopt a holistic approach that incorporates equity, nutrition, and governance aspects of food systems, focusing on who controls resources and who is most vulnerable to climate shocks, to ensure more sustainable and inclusive climate adaptation strategies.
Finally, this review acknowledges that the review, based on 11 peer-reviewed articles selected through strict systematic review criteria, may not fully capture the diversity of Ethiopia’s agroecological zones or the temporal evolution of climate change impacts due to the exclusion of gray literature and regional reports.
Data availability statement
All data supporting the findings of this study are fully included in the article.
Author contributions
MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZA: Formal analysis, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
Abebe, M. G. (2024). Impacts of urbanization on food security in Ethiopia. A review with empirical evidence. J. Agric. Food Res. 15:100997. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2024.100997
Abeje, M. T., Tsunekawa, A., Haregeweyn, N., Nigussie, Z., Adgo, E., Ayalew, Z., et al. (2019). Communities’ livelihood vulnerability to climate variability in Ethiopia. Sustain. For. 11:6302. doi: 10.3390/su11226302
Ait Kadi, M., and Ziyad, A. (2018). “Integrated water resources management in Morocco” in Global water security: lessons learnt and long-term implications, 143–163.
Alemu, T., and Mengistu, A. (2019). “Impacts of climate change on food security in Ethiopia” in Adaptation and mitigation options: a review climate change management (Cham, Switzerland: Springer), 397–412.
Amare, A., and Simane, B. (2017). Assessment of household food security in the face of climate change and variability in the upper Blue-Nile of Ethiopia. J. Agric. Sci. 7, 285–300. doi: 10.17265/2161-6264/2017.04.006
Awoke, W., Eniyew, K., Agitew, G., and Meseret, B. (2022). Determinants of food security status of household in central and North Gondar zone, Ethiopia. Cogent Soc. Sci. 8:2040138. doi: 10.1080/23311886.2022.2040138
Ayele, A., and Tarekegn, K. (2020). The impact of urbanization expansion on agricultural land in Ethiopia: a review. Environ. Socio-econ. Stud. 8, 73–80. doi: 10.2478/environ-2020-0024
Ayinu, Y. T., Ayal, D. Y., Zeleke, T. T., and Beketie, K. T. (2022). Impact of climate variability on household food security in Godere District, Gambella region, Ethiopia. Climate Serv. 27:100307. doi: 10.1016/j.cliser.2022.100307
Badu, K. (2024). Agricultural innovations and climate change adaptation in sub-Saharan Africa. Well Test. J. 33, 265–274.
Bangalore, M., Smith, A., and Veldkamp, T. (2019). Exposure to floods, climate change, and poverty in Vietnam. Econ. Disasters Climate Change 3, 79–99. doi: 10.1007/s41885-018-0035-4
Barungi, M., and Maonga, B. B. (2011). Adoption of soil management technologies by smallholder farmers in central and southern Malawi. J. Sustain. Dev. Africa 13, 28–38.
Baylie, M. M., and Fogarassy, C. (2021). Examining the economic impacts of climate change on net crop income in the Ethiopian Nile basin: a Ricardian fixed effect approach. Sustain. For. 13:7243. doi: 10.3390/su13137243
Bedeke, S. B., Vanhove, W., Wordofa, M. G., Natarajan, K., and Van Damme, P. (2020). Vulnerability to climate change among maize-dependent smallholders in three districts of Ethiopia. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 22, 693–718. doi: 10.1007/s10668-018-0215-y
Ben Hassen, T., and El Bilali, H. (2022). Impacts of the Russia-Ukraine war on global food security: towards more sustainable and resilient food systems. Food Secur. 11:2301. doi: 10.3390/foods11152301
Cohen, M. J., and Garrett, J. L. (2010). The food price crisis and urban food (in) security. Environ. Urban. 22, 467–482. doi: 10.1177/0956247810380375
Dendir, Z., and Simane, B. (2019). Livelihood vulnerability to climate variability and change in different agroecological zones of Gurage administrative zone, Ethiopia. Prog. Disaster Sci. 3:100035. doi: 10.1016/j.pdisas.2019.100035
Deressa, T., Hassan, R. M., and Ringler, C. (2008). Measuring Ethiopian farmers’ vulnerability to climate change across regional states : Intl Food Policy Res Inst.
Di Falco, S., Veronesi, M., and Yesuf, M. (2011). Does adaptation to climate change provide food security? A micro-perspective from Ethiopia. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 93, 829–846. doi: 10.1093/ajae/aar006
Dosi, G., and Nelson, R. R. (2018). “Technological advance as an evolutionary process” in Modern evolutionary economics: an overview, 35–84.
Dube, A. K., Fawole, W. O., Govindasamy, R., and Özkan, B. (2019). Agricultural development led industrialization in Ethiopia: structural break analysis. Int. J. Agric. Forest. Life Sci. 3, 193–201.
Economic Commission for Africa (2016). The demographic profile of African countries. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Economic Commission for Africa.
FAO (1996). Rome declaration on world food security and world food summit plan of action Rome declaration on world food security. FAO: Rome, Italy.
Fereday, J., and Muir-Cochrane, E. (2006). Demonstrating rigor using thematic analysis: a hybrid approach of inductive and deductive coding and theme development Int. J. Qual. Methods 5, 80–92. doi: 10.1177/160940690600500107
Getahun, Y. S., Li, M. H., and Chen, P. Y. (2020). Assessing impact of climate change on hydrology of Melka Kuntrie subbasin, Ethiopia with Ar4 and Ar5 projections. Water (Switzerland) 12:1308. doi: 10.3390/W12051308
Haglund, E., Ndjeunga, J., Snook, L., and Pasternak, D. (2011). Dry land tree management for improved household livelihoods: farmer managed natural regeneration in Niger. J. Environ. Manag. 92, 1696–1705. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.01.027
Hagos, S., Lunde, T., Mariam, D. H., Woldehanna, T., and Lindtjørn, B. (2014). Climate change, crop production and child under nutrition in Ethiopia; a longitudinal panel study. BMC Public Health 14:884. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-884
Hailu, A. G., and Amare, Z. Y. (2022). Impact of productive safety net program on food security of beneficiary households in western Ethiopia: a matching estimator approach. PLoS One 17:e0260817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260817
Hallegatte, S., Fay, M., and Barbier, E. B. (2018). Poverty and climate change: introduction. Environ. Dev. Econ. 23, 217–233. doi: 10.1017/S1355770X18000141
Hilemelekot, F., Ayal, D. Y., Ture, K., and Zeleke, T. T. (2021). Climate change and variability adaptation strategies and their implications for household food security: the case of Basona Worena District, north Shewa zone, Ethiopia. Climate Serv. 24:100269. doi: 10.1016/j.cliser.2021.100269
Ibok, O. W., Osbahr, H., and Srinivasan, C. (2019). Advancing a new index for measuring household vulnerability to food insecurity. Food Policy 84, 10–20. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2019.01.011
Iliyasu, J., Mamman, S. O., and Ahmed, U. A. (2023). Impact of climate change on output and inflation in Africa’s largest economies. Clim. Dev. 15, 864–875. doi: 10.1080/17565529.2023.2172315
Karunathilake, E., Le, A. T., Heo, S., Chung, Y. S., and Mansoor, S. (2023). The path to smart farming: innovations and opportunities in precision agriculture. Agriculture 13:1593. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13081593
Kasie, T. A., Demissie, B. S., Bahry, M. J., Gessesse, G. M., and Wale, L. E. (2020). The impact of the 2015 El Niño-induced drought on household consumption: evidence from rural Ethiopia. Clim. Dev. 12, 854–863. doi: 10.1080/17565529.2019.1701400
Kassaye, A. Y., Shao, G., Wang, X., Shifaw, E., and Wu, S. (2021). Impact of climate change on the staple food crops yield in Ethiopia: implications for food security. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 145, 327–343. doi: 10.1007/s00704-021-03635-8
Kotir, J. H. (2011). Climate change and variability in sub-Saharan Africa: a review of current and future trends and impacts on agriculture and food security. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 13, 587–605. doi: 10.1007/s10668-010-9278-0
Koutsos, T. M., Menexes, G. C., and Dordas, C. A. (2019). An efficient framework for conducting systematic literature reviews in agricultural sciences. Sci. Total Environ. 682, 106–117. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.354
Lemessa, S. D., Watebaji, M. D., and Yismaw, M. A. (2019). Climate change adaptation strategies in response to food insecurity: the paradox of improved potato varieties adoption in eastern Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 5:1640835. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2019.1640835
Lewis, K. (2017). Understanding climate as a driver of food insecurity in Ethiopia. Clim. Chang. 144, 317–328. doi: 10.1007/s10584-017-2036-7
Maru, H., Haileslassie, A., Zeleke, T., and Esayas, B. (2021). Analysis of smallholders’ livelihood vulnerability to drought across agroecology and farm typology in the upper awash sub-basin, Ethiopia. Sustainability 13:9764. doi: 10.3390/su13179764
Mekonnen, A., Tessema, A., Ganewo, Z., and Haile, A. (2021). Climate change impacts on household food security and adaptation strategies in southern Ethiopia. Food Energy Secur. 10, 1–14. doi: 10.1002/fes3.266
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., and Group, P. (2010). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 8, 336–341. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007
Molotoks, A., Smith, P., and Dawson, T. P. (2021). Impacts of land use, population, and climate change on global food security. Food Energy Secur. 10:e261. doi: 10.1002/fes3.261
Muluneh, A., Stroosnijder, L., Keesstra, S., and Biazin, B. (2017). Adapting to climate change for food security in the Rift Valley dry lands of Ethiopia: supplemental irrigation, plant density and sowing date. J. Agric. Sci. 155, 703–724. doi: 10.1017/S0021859616000897
National Meteorological Agency (2007). Climate change national adapation program of action (NAPA) of Ethiopia. Addis Ababa: NMA.
Nkurunziza, A., Intwarinkase Mutaganzwa, D., Ndayitwayeko, W. M., Nkengurutse, J., Kaplin, B. A., Teixidor Toneu, I., et al. (2023). Local observations of climate change and adaptation responses: a case study in the mountain region of Burundi-Rwanda. Land 12:329. doi: 10.3390/land12020329
Pawson, R., Greenhalgh, T., Harvey, G., and Walshe, K. (2005). Realist review-a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. J. Health Serv. Res. Policy 10, 21–34. doi: 10.1258/1355819054308530
Perry, G., Gebresenbet, F., DaPra, M., Branco, P., Whibesilassie, W., Jelacic, M., et al. (2022). Why urban ecology matters in Ethiopia. Front. Ecol. Evol. 10:203. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.843698
Rahman, M. M., and Connor, J. D. (2022). The effect of high-yielding variety on rice yield, farm income and household nutrition: evidence from rural Bangladesh. Agric. Food Secur. 11:35. doi: 10.1186/s40066-022-00365-6
Serdeczny, O., Adams, S., Baarsch, F., Coumou, D., Robinson, A., Hare, W., et al. (2017). Climate change impacts in sub-Saharan Africa: from physical changes to their social repercussions. Reg. Environ. Chang. 17, 1585–1600. doi: 10.1007/s10113-015-0910-2
Shafi, U., Mumtaz, R., García-Nieto, J., Hassan, S. A., Zaidi, S. A. R., and Iqbal, N. (2019). Precision agriculture techniques and practices: from considerations to applications. Sensors 19:3796. doi: 10.3390/s19173796
Shukla, R., Gleixner, S., Yalew, A. W., Schauberger, B., Sietz, D., and Gornott, C. (2021). Dynamic vulnerability of smallholder agricultural systems in the face of climate change for Ethiopia. Environ. Res. Lett. 16:044007. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/abdb5c
Sileshi, M., Kadigi, R., Mutabazi, K., and Sieber, S. (2019). Analysis of households’ vulnerability to food insecurity and its influencing factors in East Hararghe, Ethiopia. J. Econ. Struct. 8, 1–17. doi: 10.1186/s40008-019-0174-y
Suuk, S. S., Laube, W., Seyni, A. A., and Cantrell, R. A. (2025). The adoption of farmer-managed natural regeneration in Dogonkiria, Niger. Hum. Ecol. 53, 127–136. doi: 10.1007/s10745-025-00568-y
Tesfaye, K., Ittersum, M. K. V, Wiebe, K. D., Boogaard, H. L., Radeny, M. A., and Solomon, D. (2018). Can Ethiopia feed itself by 2050? Estimating cereal self-sufficiency to 2050. Wageningen, The Netherlands: CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS).
Teshome, M. (2016). Rural households’ agricultural land vulnerability to climate change in Dembia woreda, Northwest Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 5, 1–18. doi: 10.1186/s40068-016-0064-3
Thompson, H. E., Berrang-Ford, L., and Ford, J. D. (2010). Climate change and food security in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic literature review. Sustain. For. 2, 2719–2733. doi: 10.3390/su2082719
Wei, Z., Jin, H., Zhang, J., Yu, S., Han, X., Ji, Y., et al. (2011). Prediction of permafrost changes in northeastern China under a changing climate. Sci. China Earth Sci. 54, 924–935. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4109-6
Welteji, D. (2018). A critical review of rural development policy of Ethiopia: access, utilization and coverage agriculture &. Food Secur. 7:55. doi: 10.1186/s40066-018-0208-y
Wittman, H. (2011). Food sovereignty: a new rights framework for food and nature? Environ. Soc. 2, 87–105. doi: 10.3167/ares.2011.020106
Wolff, J. (2021). How is technology changing the world, and how should the world change technology? Global Perspect. 2, 1–5. doi: 10.1525/gp.2021.27353
Keywords: adaptation strategy, climate variability, food insecurity, realist review, stability
Citation: Abebe MG and Amare ZY (2025) Climate change and food security nexus in Ethiopia: challenges to food sustainability—a systematic literature review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1563379. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1563379
Edited by:
Niaz Ali, Hazara University, PakistanReviewed by:
Omarsherif Mohammed Jemal, Arsi University, EthiopiaMuhammad Shahbaz Farooq, National Agricultural Research Center, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Abebe and Amare. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mekonen Getachew Abebe, bWVrdWdldG9AZ21haWwuY29t
 Mekonen Getachew Abebe
Mekonen Getachew Abebe Zerihun Yohannes Amare
Zerihun Yohannes Amare