- 1AgroBioSciences Program, College of Agriculture and Environmental Science, Mohammed VI Polytechnic University, Ben Guerir, Morocco
- 2Laboratory of Entomology and Phytopathology, International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA), Rabat, Morocco
- 3Plant and Microbial Biotechnology Center, Moroccan Foundation for Advanced Science, Innovation and Research (MaScIR), Mohammed VI Polytechnic University, Ben Guerir, Morocco
Pulse crops such as faba beans, chickpea and lentils are an important contributor to the necessary food thanks to their richness of proteins and low-fat content, in addition to the presence of fibers and bioactive components. However, like all crops, pulse crops face many biotic and abiotic challenges that lead to a reduction in productivity and quality. Managing key biotic stresses, such as insect pests and diseases in pulse crops, primarily involves a combination of multiple strategies including cultural practices, biological control, host plant resistance, and synthetic pesticides. One of the promising cultural control approaches to address insect pest challenges is adopting intercropping as a sustainable agricultural practice. When implemented effectively, intercropping can significantly mitigate the pressure of insect pests attacking pulse crops. In addition to intercropping, semiochemicals such as pheromones and kairomones have started as a component of biorational pest management in modern agriculture. This review provides a comprehensive guide on the multifunctional roles of intercropping in the management of insect pests in pulse crops, with a focus on the role of volatile organic compounds associated with in the intercropping system.
1 Introduction
Throughout history, human reliance on the land for shelter and food has led to the development of agricultural practices aimed at ensuring an adequate yield. These practices have evolved from simple rainfed monocropping systems, dependent solely on natural conditions, to advanced approaches such as precision agriculture, smart irrigation, Conservation cropping and chemical based agriculture. Agriculture serves as a crucial pillar for many countries, offering economic prosperity and a pathway toward sustainable development. However, agricultural endeavors encounter numerous obstacles, some stemming from Anthropogenic activities climate and framing system changes, while others arise from nature’s attempts to maintain balance. Pulse crops are a vital source of nutrition for humans, offering high levels of plant proteins with low fat content, and significant sources of fiber and bioactive components (Pauline and Rimm, 2003; Houasli et al., 2020). Beyond their nutritional value, pulse crops perform several roles in agricultural systems. They contribute to soil fertility and serve various purposes, including use as food crops (consumed as grain, green pods, leaves, cash crops, and fodder crops). Additionally, many pulse crops play a key role in a rotation system with cereals to improve soil health and reduce pests and weeds (Mantri et al., 2013). Major pulse crops include common beans, peas, lentils, cowpeas, dry beans, chickpeas, pigeon peas, lentils, and faba beans. However, only a few locations grow minor pulse crops like green gram, black gram, moth bean, rice bean, and grass pea. Unfortunately, the productivity of pulses is still lower than the global average in many regions including mostly the Central and West Asia, and North Africa (CWANA) region (Bhat et al., 2022; El Bouhssini et al., 2021). This underperformance is mostly attributable to abiotic limiting factors, including terminal drought stress and different biotic pressures like insect pests, diseases, and weeds that have a detrimental effect on crop productivity and production (Houasli et al., 2020; Brahmi et al., 2021). Among biotic stresses, several insect pests have been associated with harming pulse crops, leading to substantial economic losses. Different parts of the world have described thrips, leaf miners, whiteflies, leafhoppers, aphids, pod borers, stem flies, and others as major pests posing the greatest threat to pulse crops production. Some of the insect pests are vectors of devastating viruses’ diseases of different pulse crops and agroecosystems. For instance, more than 250 insect pests reportedly impact pulses in India (Sabraoui et al., 2019; Yadav et al., 2020). Among these reported insect pests, some are known to harm pulse crops significantly, resulting in economic losses for both production and quality.
The need for pest-control measures has recently grown due to the high costs of pulses and increasing awareness. The chemical control aspect of IPM has received a lot of attention compared to other pest management techniques, such as cultural practices, genetic resistance, and biological control agents (Sabraoui et al., 2019). Even with the late start of host plant resistance as the foundation of integrated pest management, research in North Africa, West Asia, and Central Asia (CWANA) is considered at least 30 years behind compared to other countries in North America and Europe. Relatively important progress has been made in developing germplasm holding resistance to key pests in chickpeas (for example, El Bouhssini et al., 2021). However, this is not the case for the chickpea pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).
In normal monocropping systems, pulse crops have a high yield potential, but they require a lot of energy, resources, and chemicals. However, the use of chemical insecticides, while effective, carries substantial negative environmental implications (pollution in both soil and air) and entails high costs, contributing to pest resistance and affecting human and animal health as well as affecting pollinators (Devonshire et al., 1998; Foster et al., 2002; Harris and Dent, 2000; Yano, 2006).
As a result, there is a growing need to adopt biorational pest management where cropping system plays key roles. Intercropping emerges as a key strategy in sustainable agriculture due to its capacity to restore diversity, manage ecosystems through ecological balance, and optimize the use of spatial resources. Implementing intercropping systems unquestionably enhances soil fertility, facilitates pest and disease management, and ultimately improves both the quantity and quality of crop yields (Nandhini and Somasundaram, 2020). Companion plants in intercropped systems emerge as a promising approach, offering regulation of insect pest populations and reducing their damage by providing natural enemies. Numerous studies have found that several companion plants, such as coriander, mustard, tomato, safflower, and lentil, can effectively manage H. armigera in chickpea crops (Paul et al., 2015; Patil et al., 2018). Furthermore, previous studies (Fernández-Aparicio et al., 2010; Schoeny et al., 2010) demonstrated that intercropping pea with faba bean, barley, oat, triticale, or wheat reduced the severity of pea Ascochyta blight. Furthermore, the incidence and severity of Ascochyta blight decreased when chickpeas and flax were intercropped (Zhou et al., 2023).
This review aims to shed light on different types of intercropping systems as a sustainable strategy towards insect pest management in pulse crops, explaining (when available) the mechanism behind it and examining their agronomic benefits. It reviews various types of companion plants, highlighting the effects of planting configurations and the mechanisms through which these plants efficiently control a wide range of insect pests with or without adding semiochemicals.
1.1 Methodology
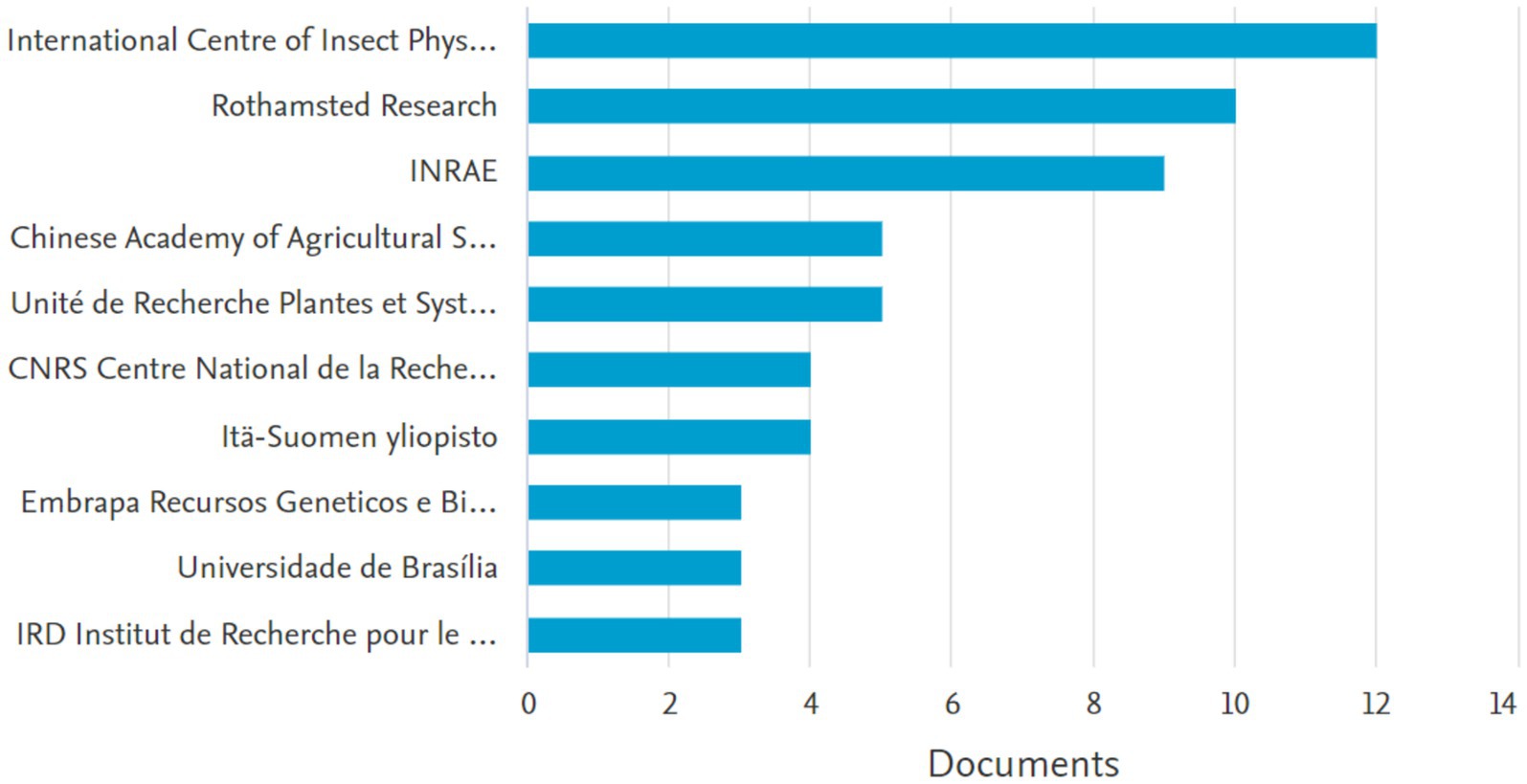
In this comprehensive bibliometric analysis, we examined the scholarly landscape surrounding the interplay of key thematic elements in agricultural research, specifically “Crops” OR “grain legumes “OR “Legumes” OR “Pulses” AND “Intercropping” OR “mixed cropping” OR “Companion Plants” OR “companion planting “OR “cover crops” AND “Insect Pest” OR “insects “OR “pests “AND “volatile organic compounds “OR “VOCS “OR “semiochemicals “OR “plant pheromones” OR “pheromones.” Leveraging VOSviewer and Scopus, our study reveals a notable emphasis on this subject matter, with the Kenya International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology in Nairobi with 12 documents, followed by Rothamsted Research in the United Kingdom with 10 documents. Additionally, the significant involvement of the INRAE (National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food, and Environment) with 9 documents, China and the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences emerging as major contributors with 5 documents (as illustrated in Figure 1).
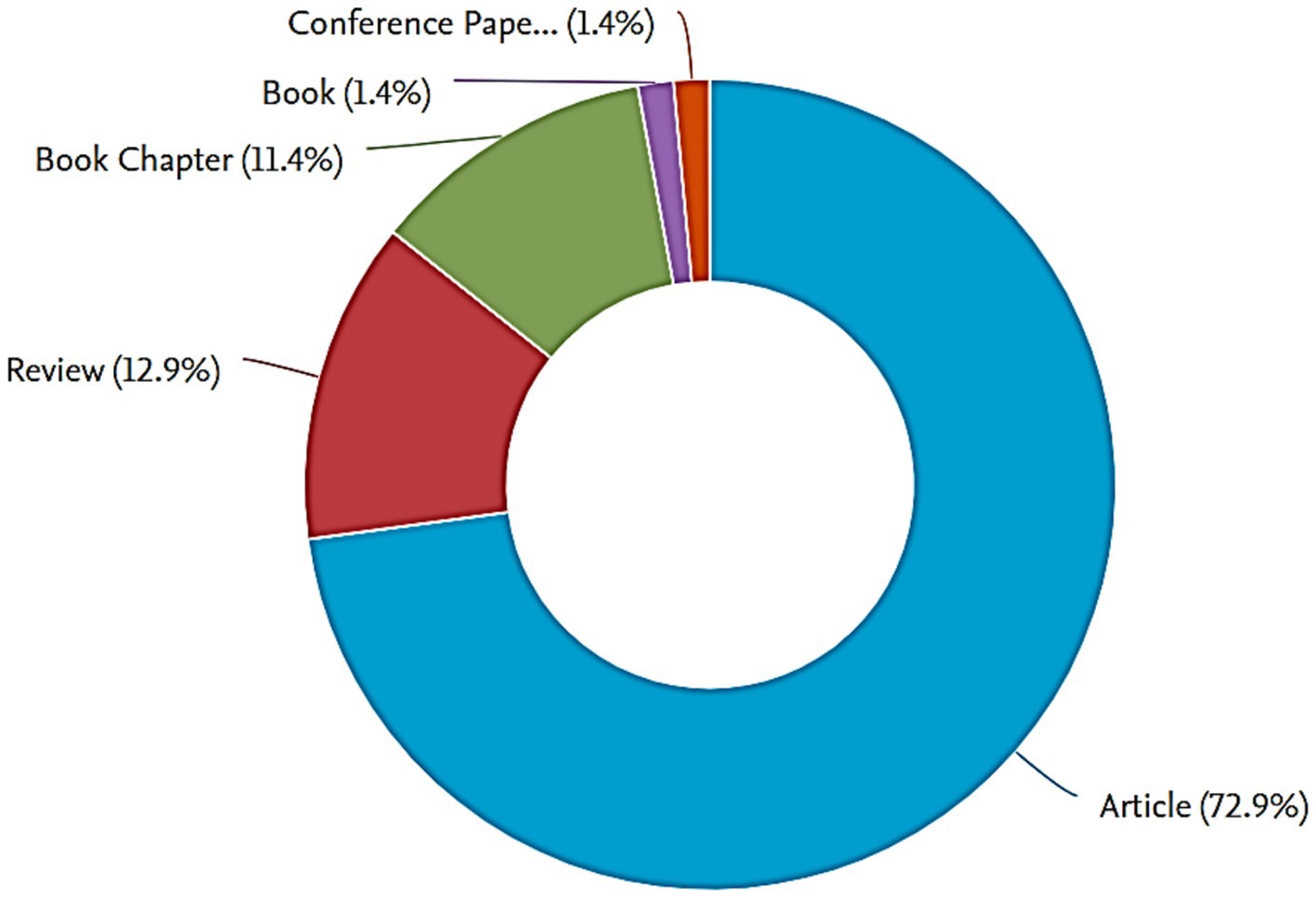
Our findings underscore a predominant publication format, with 72.9% of the publications comprising articles, followed by 12.9% for reviews, 11.4% for book chapters, and 1.4% for conference papers and books. Noteworthy authors in this domain include Zeyaur Rahman Khan from Kenya, holding a prominent position, and John Anthony Pickett, whose contributions merit further exploration (as illustrated in Figure 2).
This bibliometric synthesis provides a structured overview of scientific discourse, revealing key contributors, prevalent publication types, influential authors, and pivotal journals, thereby contributing to the advancement of knowledge in agricultural entomology and sustainable crop management (Figure 3).
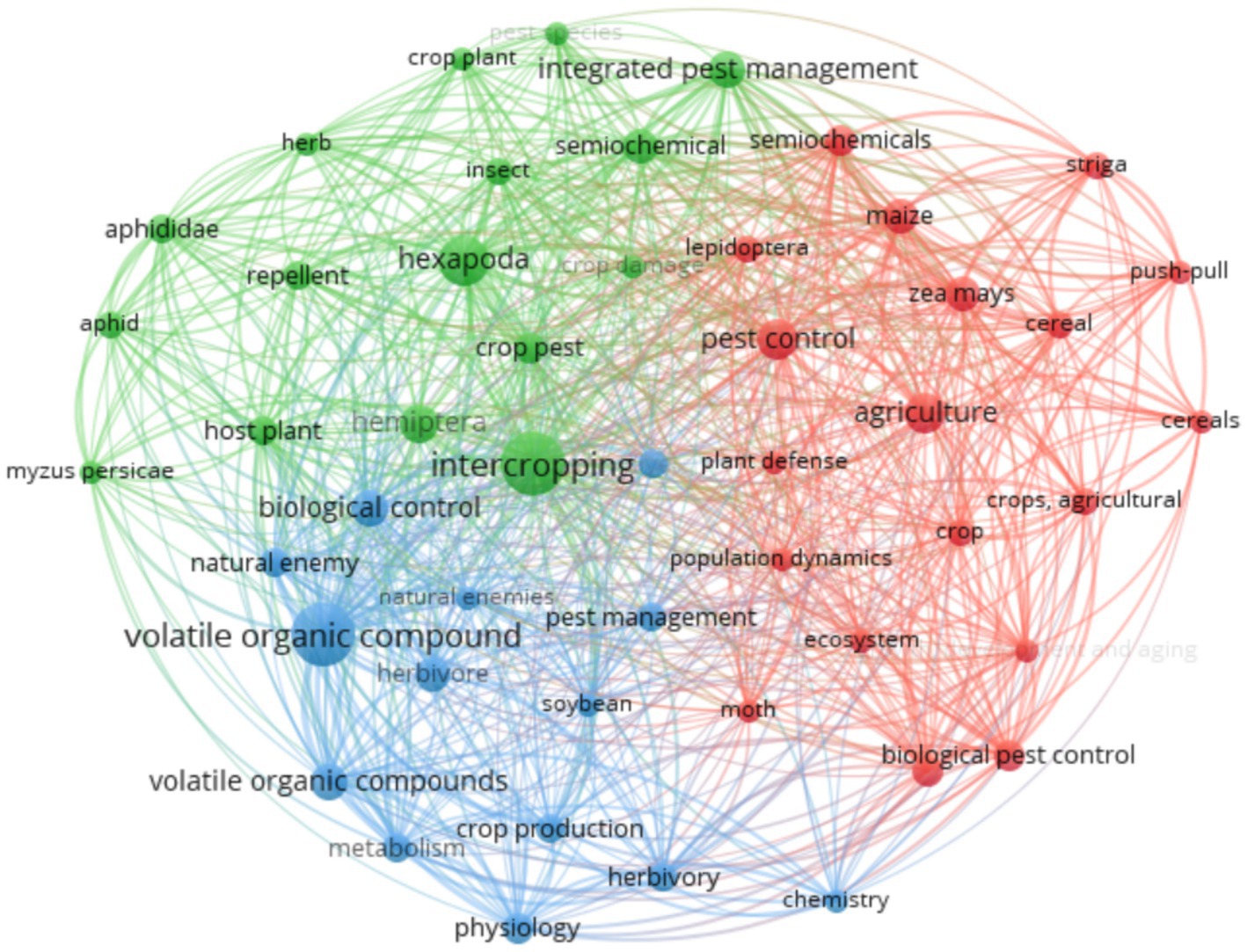
Figure 3. Visualization of intercropping with pulse crops research topics using overlay visualization.
1.1.1 Criteria for inclusion and exclusion
This comprehensive study analyzed only full-text research publications from the referenced databases that evaluated the impact of intercropping and companion planting, together with their volatile organic compounds (VOCs), on insect damage in food legume crops up to the beginning of 2025. Studies were declined if they did not evaluate infestation levels, were books, unpublished articles, doctorate theses, comments, conference abstracts, or case reports, were not written in English or French, or were not quantitative in nature.
1.2 Intercropping systems
Intercropping is the cultural practice that involves growing two or more crops at the same time on the same piece of land during a particular period of their growth (Figure 4). This approach aims to benefit more efficiently from the available resources by taking advantage of the complementarity between the different crops, leading to an increase in production and enhancing the quality of the yield due to the reduction of the biotic and abiotic stressors that this approach offers. It has multifunctional roles, of which we mention the creation of a physical barrier that conceal the host crop from the pests, or by the volatile organic compounds emission that could repel the pests or attract the natural enemies, the interference with the pest’s ovulation caused by the presence of non-host plants nearby, and the immigration forced on the pests away from the host crops (Yousefi et al., 2024).
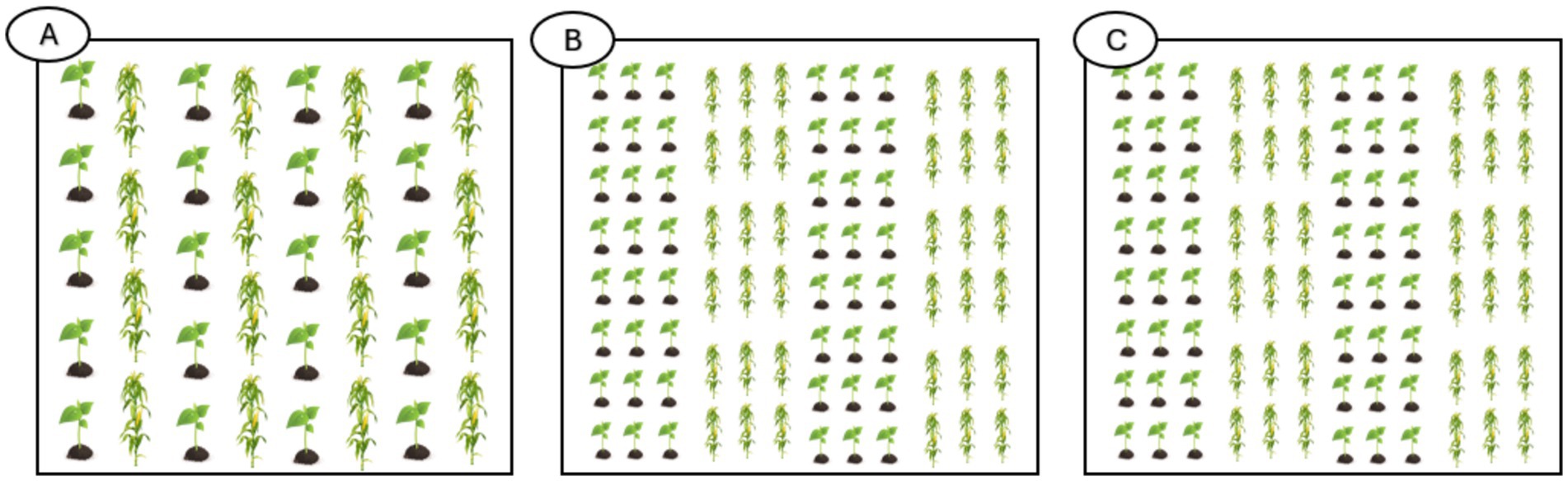
Figure 4. (A) Row intercropping (crops are sowed in alternate rows). (B) Relay intercropping (one crop is sowed ahead in time of the other). (C) Strip intercropping (both crops are sowed at the same time in strips).
In an agroecological approach, companion planting serves as a valuable agronomic strategy to diversify crop rotations, reduce the use of inputs and their negative impacts on the environment, as well as boost resilience to risks (Bedoussac et al., 2015).
1.2.1 Row intercropping
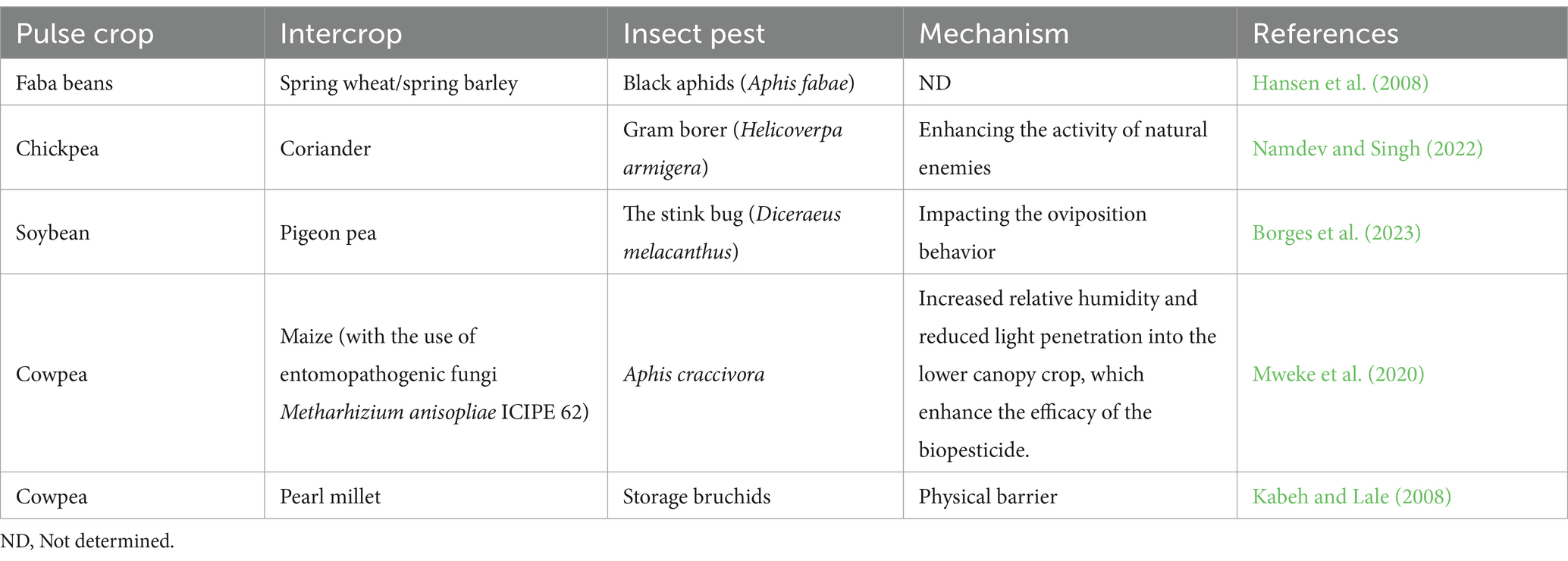
Row intercropping is when two or more crops are planted next to each other in alternate rows, to maximize the interaction between the different crops, which leads to a maximum benefit in terms of management of insect pests. It works in different ways, such as disrupting the natural behavior of the insect pest when it finds itself in a non-host plant, and by the combined emission of volatile organic compounds from different crops. For example, Mweke et al. (2020) thanks to the increase in relative humidity and reduced UV light penetration in the lower canopy which enhanced the effectiveness of the fungal-based pesticide, successfully used row intercropping of cowpea and maize, combined with a fungal-based pesticide, that biologically infects and kills Aphis craccivora (Hemiptera: Aphididae), reducing their population.
1.2.2 Strip intercropping
Strip intercropping is when two or more crops are planted close to each other in strips, to profit from the intercropping benefits and facilitate the harvest process. One of the parameters that could have a significant impact on the outcome of strip intercropping is the width of the strips, as confirmed by Mahallati et al. (2015). The strip intercropping included maize with beans, where the optimal width of the strips was two rows per crop, and three strips per crop. Although the biological yield was lower in the intercropping design compared to monocropping, the total land productivity increased by a greater land equivalent ratio. This experiment showed that 39 and 37% more land was required for the monocropping to produce similar yields in both years 2009 and 2010.
1.2.3 Relay intercropping
Relay-intercropping remains one of the most successful intercropping designs used, in particular cereals with legumes. This method involves planting different crops in the same field but at staggered times, where one crop must be planted either way before and after the planting of the other one with a well calculated time gap between the two dates. Relay intercropping is suitable mostly for short period crops, can lead to good results in terms of overall economic profitability, and suppression of weeds and insect pests. As demonstrated by Raza et al. (2019), relay intercropping soybean with maize in addition to the removal of the topmost six leaves of maize for a better sunlight exposition, where the relay intercropped soybean produced 78% of sole soy-bean seed yield.
1.2.4 Mixed intercropping
Crops are planted together without a particular row design; it is very suitable for the combined cultivation of grasses and legumes in pastures. This type exhibits a rich biodiversity and enhances below-soil interactions. It is considered to be very effective in small-scale farming systems where manual harvesting is more practical (Toker et al., 2024).
1.2.5 Alternate intercropping
Alternative intercropping can be referred to as transposition. Intercropping is a strategy that demands the sowing of different crops in alternating positions annually; it is a combination of both intercropping and rotation, which offers gains beyond those obtained by each method individually. It boosts plant interactions, improves soil health, and disrupts the cycle of pests and diseases (Toker et al., 2024).
1.3 Intercropping with pulses for the management of insect pests
The management of significant biotic stresses, including insect pests and diseases in food legumes primarily involves a combination of several strategies such as cultural practices, biological control, host resistance, and chemical pesticides. Plants emit a wide range of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in response to biotic stimuli, such as pests or pathogens, as a natural defense mechanism (Maffei et al., 2007). Chemical signals in plants have several functions, such as protecting against pests and diseases, and attracting pollinators. There is an increasing emphasis on reducing chemical pesticides use by implementing different farming practices and integrating biopesticides for more efficient pest and disease management. Service plants VOCs used in the intercropping system with pulses can affect the foraging behavior, reproduction, olfactory perception, and hosts selection of insect pests because of their attractive or repellent action. Consequently, they can be employed as pest traps to regulate the dynamics of insect populations. Comprehending and understanding the chemical ecology of insects may provide opportunities to improve eco-friendly strategies for combating bio-aggressors. This encompasses the use of repellent or disruptive VOCs to repel insect pests, as well as the application of attractive compounds for pest trapping (Makhlouf et al., 2024a,b; Santos et al., 2015; Singh et al., 2021). The concept of intercropping offers several benefits, including the diversification of habitat, the establishment of physical barriers, the reduction of pest resistance, and the improvement of soil health. These factors can enhance soil biodiversity and fertility, indirectly influencing pest populations by promoting healthier pulse plants (Hauggaard-Nielsen et al., 2008; Makhlouf et al., 2024a,b). The role of intercropping and the functions of VOCs in insect pest management of pulses are described (Table 1).
1.3.1 Aphis fabae
The black bean aphid, A. fabae Scopoli (Hemiptera: Aphididae), is commonly acknowledged as a significant pest affecting spring-sown field beans in northern Europe. Empirical field studies have demonstrated that infestations by the black bean aphid can result in yield losses surpassing 50% in this agricultural context (Skovgård and Stoddard, 2023). Beside the direct effect of black aphids on multiple crops, they are famous for their capability of being virus and disease vectors that could be intensively destructive to pulse crops such as mosaic disease affecting common beans (Muute et al., 2021).
To manage black aphids A. fabae, an intercropping strategy was applied, where field beans were mixed cropped with spring wheat, and mixed cropped with spring barley, and the control was sole field beans. This study showed that mixed cropping of the susceptible variety ‘Colombo’ with spring wheat significantly reduced the number of aphids compared to monocropping of field beans. Furthermore, compared to field beans cultivated as monocropping, field beans mixed cropping with spring barley produced a significant benefit, demonstrating a successful decrease in black bean aphid infestation. Field beans mixed cropping in 2002 (67% field bean and 33% barley), produced a 70% higher profit compared to field bean monocropping. The profit from the intercropping design was 433 euros per hectare, compared to 271 euros per hectare for the sole cropping of faba beans. The value of organic grown field beans is 18.7 euro/dt and 18 eur/dt for spring barley. This approach also reduced the number of aphids per plant from 53 in sole faba beans to 43 in the intercropping design. Additionally, the percentage of infested plants decreased from 68% in sole faba beans to 48% in the intercropping design. These findings, reported by Hansen et al. (2008), highlight the effectiveness of intercropping as a sustainable strategy to mitigate black bean aphid infestations.
1.3.2 Helicoverpa armigera
Helicoverpa armigera Hübner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) is a widespread and cosmopolitan pest that significantly reduces chickpea production around the world. Managing this insect is crucial for achieving sustainable chickpea yields (Mahmood et al., 2021). Intercropping has emerged as an effective strategy for managing H. armigera. Among the four tested intercrop combinations, chickpea intercropped with coriander harbored the lowest population of H. armigera larvae (2.38 larvae per meter row) and caused the least amount of damage, demonstrating the effectiveness of intercropping for the management of the pod borer larvae, followed by Chickpea + Mustard intercropping (2.40 larvae per meter). In contrast, the sole chickpea crop had the highest population (6.43 larvae per meter row) (Namdev and Singh, 2022).
1.3.3 Diceraeus melacanthus
The stink bug, D. melacanthus (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), is a major insect pest pigeon pea that attacks maize, wheat, and soybean crops in South America. This species has been favored by no-till farming systems and by intensive sequential multiple cropping systems, which offer host plants throughout the year (Borges et al., 2023).
Intercropping pigeon peas with maize or soybean plants could be an effective strategy for controlling D. melacanthus. Researchers found a significant difference in the oviposition behavior of D. melacanthus between cotton bolls and pigeon pea pods. The stink bugs preferred to lay their eggs on cotton bolls rather than on C. cajan pods. This finding suggests that pigeon peas could be used as a trap crop to lure D. melacanthus away from the main crop. Furthermore, intercropping maize or soybean with pigeon peas reduced the number of D. melacanthus eggs laid on the main crop by up to 80%. This highlights the potential of intercropping with pigeon peas as a viable alternative to chemical insecticides for managing D. melacanthus populations in maize and soybean crops (Borges et al., 2023).
1.3.4 Aphis craccivora, Callosobruchids maculatus
Aphis craccivora Koch (Hemiptera: Aphididae), also known as cowpea aphid, is a polyphagous pest that poses a significant threat to cowpea crops by feeding on all plant parts, leading to significant yield losses. Its feeding damage includes sucking and removing plant sap, which reduces the amount of nutrients and water available to the crop and causes plant viruses to spread. Aphid feeding induces symptoms such as chlorosis and stunting, which delay the onset of flowering and even plant death, especially when infestations are high, at the seedling stage (Sayed et al., 2020).
Intercropping cowpea with cereal creates a physical barrier against aphids, which reduces their survival and damage. In intercropped systems, pests are visually disturbed and tend to stay on the hosts for shorter periods of time due to the disruptive effect of landing on non-host plants. Mweke et al. (2020) found that a cowpea-maize intercropping combined with the application of Metarhizium anisopliae ICIPE 62 provided better control of A. craccivora compared to other treatments, specifically, the number of aphids per plant in monocrop cowpea was 15.3 aphids per plant, while intercropped cowpea maize treated with M. anisopliae ICIPE 62 had only 5.9 aphids per plant. The superior performance of this combination could be attributed to the synergistical potential in terms of increasing relative humidity and reducing light penetration into the lower canopy crop, which enhances the efficacy of the biopesticide.
In a different study, four susceptible types of cowpeas were grown with pearl millet and other crops. These included landraces Borno brown and Kanannado, as well as improved varieties that were grown as sole crops or mixed with crops. The intercropping system involved a meticulous intra-row pattern of two cowpea stands to one stand of millet, with appropriate spacing and timely thinning of millet seedlings. The results revealed that in both cropping seasons, the intercrop demonstrated significant potential in reducing field infestation of cowpeas by storage bruchids. Notably, the intercropping approach led to a lower proportion of adult bruchids that developed, as well as a decrease in the number of eggs laid on pods (13.7) in monocrop compared to intercrop (0.7) (Kabeh and Lale, 2008).
2 Semiochemicals combined with intercropping for insect pests’ control in pulses
Intercropping has been proven to reduce insect pests’ populations in most cases; however, it does not always lead to an increase in the presence of natural enemies (Xu et al., 2018). Similarly, the application of semiochemicals in pure stands may not always enhance the presence of natural enemies and in the case of low pest density it may even negatively affect the presence of natural enemies (Table 2) (Wang et al., 2011).
To overcome the negative effects of using intercropping or semiochemicals separately, the combination of both approaches can be very effective in terms of reducing the population of pests and enhancing the presence of their natural enemies (Xu et al., 2018).
2.1 Case study 1: (cluster bean/cowpea/black gram – okra) with acetone extract of Cyamous tetragocalobe flowers
Baskaran and Parthiban (2017) carried out a field experiment to manage lepidopteran pests of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) using non-host kairomones and an intercropping system. The study targeted pests such as Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), Earias vittella (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), and Helicoverpa armigera. In addition to the use of non-host kairomone, an acetone extract of C. tetragocalobe flowers that exhibited an increase in the parasitism percentage on the eggs of both pests S. litura, E. vittella, and H. armigera by 51.25 and 57.21%, respectively, compared to the control levels of 12.56 and 12.87%. In addition, cluster bean (C. tetragocalobe) showcased the highest results in terms of reducing fruit damage from 28.56 to 16.51%.
2.2 Case study 2: (pea-wheat) with the (E-B-farnesene and methyl salicylate)
Pea aphids Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera: Aphididae) is a major pest of leguminous crops, including peas, lentils, and alfalfa. These aphids damage plants by feeding on their sap, which can lead to stunted growth, reduced yield, and even plant death. Pea aphids also secrete honeydew, a sugary substance that can attract other pests and promote the growth of sooty mold, which can further reduce the plant’s ability to photosynthesize. In addition, pea aphids can transmit plant viruses, which can cause significant economic losses to affected crops. Therefore, finding effective and sustainable ways to control pea aphids is crucial for maintaining crop productivity and quality (Wale et al., 2000).
As a solution to several aphids including pea aphid A. pisum, a study by Xu et al. (2018) examined the intercropping arrangement including a wheat-pea strip, while utilizing E-B-farnesene (EBF) and methyl salicylate (MeSA). The incidence counting of several natural enemies including the lady beetle (Coccinella septempunctata) and lacewing (Chrysopa sinica and Chrysopa septempunctata), and the incidence counting of several aphid mummies including the pea aphid were conducted to evaluate the success of the suggested solution. The average number of aphids on pea plants in the control (pea-wheat intercropping) was estimated to be between 150 and 200; thus, the mean aphid population decreased to about 150 and 100 when intercropping was coupled with the emission of methyl salicylate and E-B-farnesene, respectively (Xu et al., 2018). Regarding the mean number of natural enemies, such as lady beetles and lacewings, the intercropping system alone supported a population slightly over 20 individuals. This number increased significantly when E-B-farnesene and methyl salicylate were introduced, reaching an estimated range of 30–40 and 40–60 respectively (Xu et al., 2018). These semiochemicals act as key informative molecules in plant-insect interactions, with the potential to repel pests and attract natural enemies, thus creating a push-pull strategy for pest management.
2.3 Case study 3: (chickpea-mustard) with unnamed semiochemicals
Several measures have been utilized to manage the chickpea pod borer H. armigera, with varying degrees of success in years of research. Certain tactics have been effective, while the use of host plant resistance has shown many limitations. Among the more successful approaches, were intercropping chickpea with mustard and monitoring adults using sex pheromone traps, which showed significant promise. The practice of intercropping chickpea with mustard (at a ratio of 6:2) led to the maximum yield of chickpea equivalent grain. Furthermore, the use of pheromone traps has shown efficacy in monitoring the adult population of H. armigera and allowing the detection of the initial flight. Also, the damage caused by H. armigera larvae decreased from 68.1% in a sole crop of chickpea to 44.2% for the chickpea-mustard intercropping (Singh et al., 2010).
3 Semiochemicals for the management of insect pests in pulses
Semiochemicals, (sex and aggregation pheromones) specific to each species, are employed as behavior-altering substances to lure, eliminate, or confuse pests; hence impeding their ability to locate mates and/or host plants. Therefore, the use of semiochemicals solely in very small amounts is seen as an eco-friendly method of plant protection. Even though the combination of semiochemicals with intercropping does lead to positive results as mentioned (Table 3), it is undeniable that there are several cases where the use of semiochemicals solely led to positive results as well. The main methods in pest management that use effectively the semiochemicals for detection, monitoring, and control are described in few available examples in pulses in combination with kairomones, or those that showed potential despite existing limitations. Studies have shown that the chemicals released by plants during herbivores feed can function as signals to attract beneficial insects. These beneficial insects then use other chemical and visual signals to effectively search for various life stages of the plant pests (Makhlouf et al., 2024a,b; Annaz et al., 2023). The integration of pheromones with kairomones derived from host plants has been proven to be an effective tool for biological control of some key insect pests of pulses (Table 2).
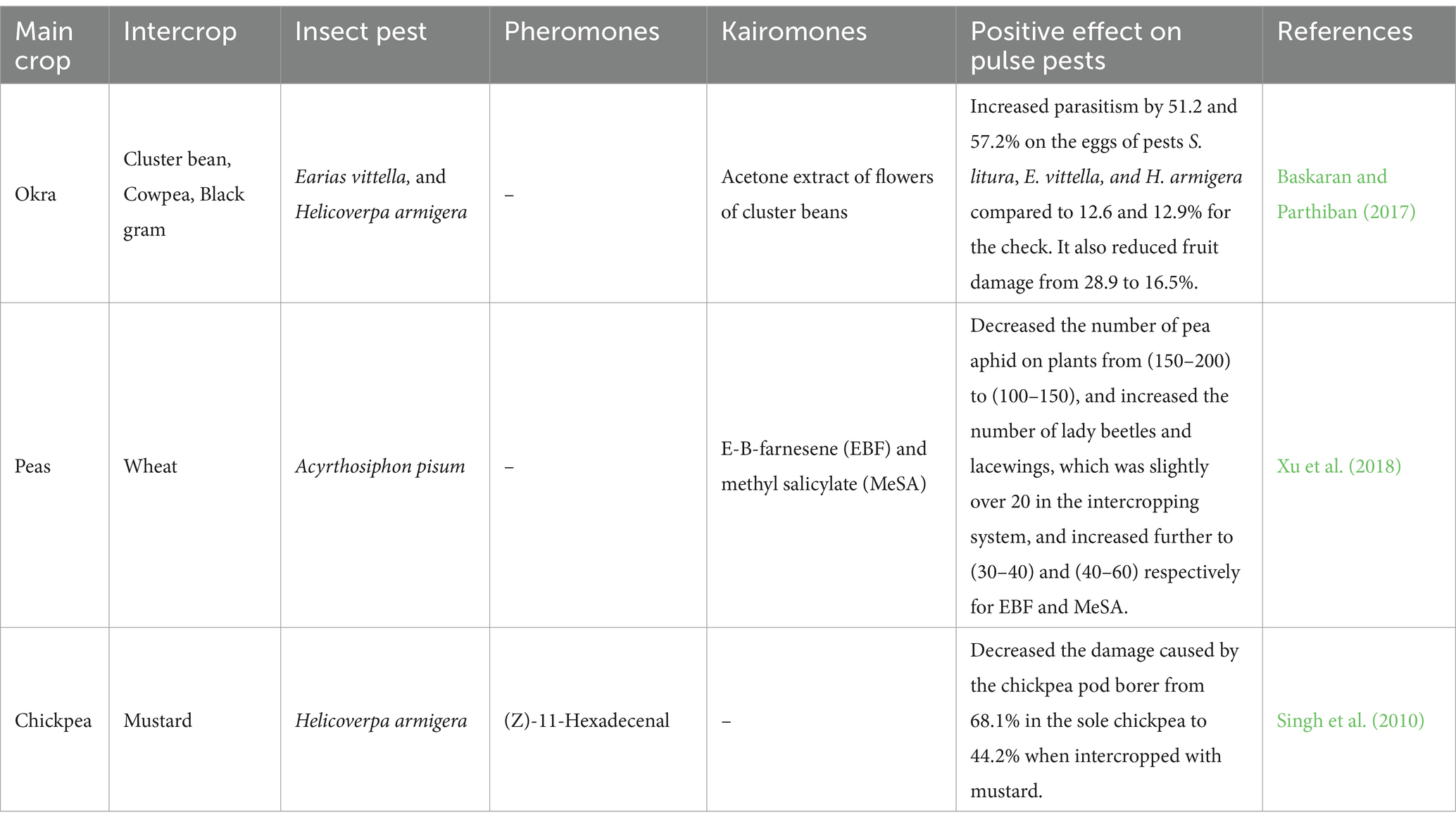
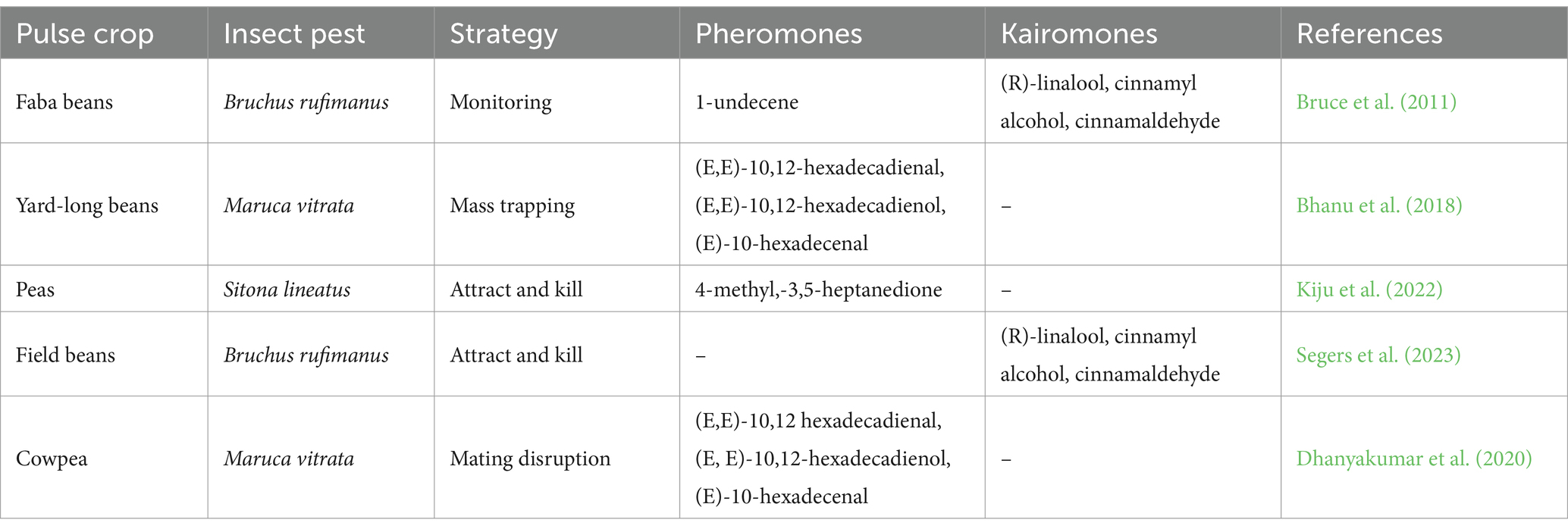
Table 3. Intercropping combined with the release of semiochemicals for the management of pulse crops’ insect pests.
3.1 Monitoring
The bean seed beetle, Bruchus rufimanus (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), is a serious pest of field beans. According to Bruce et al. (2011), volatile compounds from Vicia faba were attractive to B. rufimanus and were formulated into lures for traps. A three-component floral volatile blend, consisting of (R)-linalool, cinnamyl alcohol, and cinnamaldehyde a ratio of 44:1:2, respectively, was found to be particularly effective (Table 3). The researchers also identified a male-produced volatile, 1-undecene, which was attractive to B. rufimanus female and considered a putative pheromone. The traps were baited with a ten-component semiochemical blend comprising the nine floral volatiles found in the three-component blend and the putative sex pheromone 1-undecene, which was released at a rate of 1.5 mg/day. The results showed that the traps baited with the semiochemical blends caught significantly more of both sexes of B. rufimanus than unbaited control traps. The mean catch of both sexes was 3.75 with the unbaited trap, 34.75 with the simple floral lure, 57.75 with the more complex floral lure, and 64.75 with the complex floral lure combined with the putative pheromone (Bruce et al., 2011).
3.2 Mass trapping
The Legume Pod Borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyraloidea: Crambidae), is a major pest of legume crops in tropical Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. Sex pheromones have been identified as an important component in integrated pest management (IPM) programs, especially for monitoring, mass-trapping, and/or mating disruption. The major compound of the M. vitrata pheromone is (E,E)-10,12-hexadecadienal, while the minor components are (E,E)-10,12-hexadecadienol and (E)-10-hexadecenal (Table 3).
The isomers of M. vitrata’s primary and minor pheromone components were assessed in a study by Bhanu et al. (2018). An improved antennal response was observed when the isomer (Z, E)-10,12-hexadecadienal was mixed with the minor components (E,E)-10,12-hexadecadienol and (E)-10-hexadecenol in a ratio of 100:10:5 (Table 3). In field tests conducted in India, it was found that this formulation was the most successful in attracting male moths, capturing a significantly higher number of male moths than other mixes examined. In addition, there was a notable 24.49% increase in yield in the pheromone-treated plots compared to the untreated plots (Bhanu et al., 2018).
3.3 Attract and kill
Pea leaf weevil (PLW), Sitona lineatus L. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), is considered as significant pest of pea, and faba bean in many parts of the world. In the field experiment, the PLW aggregation pheromone (4-methyl-3,5-heptanedione) and a granular contact insecticide based on 0.1% deltamethrin were utilized to evaluate the effectiveness of an attract-and-kill strategy for lowering PLW populations. According to Kiju et al. (2022), the effective treatment, which included deltamethrin and pheromone rubber septum, resulted in a significant increase in the yield of field peas by 20% compared to the control (Kiju et al., 2022).
Broad bean weevil Bruchus rufimanus Boheman (1833) (coleoptera: chrysomelidae) is a serious pest that causes decent damage to field bean seeds in terms of quantity and quality, the insect induce a loss that can go up to 9.4%, a decrease in the germination rate, and a fall in the nutritional and the flavour properties, due to the accumulation of waste by the feeding larvae, which makes these seeds a suitable host to phytopathogenic fungi (Segers et al., 2021). Recent studies have identified different kairomones particularly emitted by the flowers of faba beans, such as (R)-limonene, (E)-ocimene, (R)-linalool, 4-allylanisole (i.e., estragol), cinnamyl alcohol, cinnamaldehyde, αand β-caryophyllene for the development of a semiochemical-based trap as a management method for this pest (Segers et al., 2023).
In a study conducted by Segers et al. (2023), two field trials were conducted to test the efficacy of three different semiochemicals lures combined with two different trap types in two different periods (early and late flowering field bean crops), the authors reported that the most effective combination was white pan traps baited with floral kairomones emitted by faba beans flowers and pods, specifically (R)-linalool, cinnamyl alcohol, and cinnamaldehyde. This setup successfully trapped 1,380 broad bean weevils, significantly outperforming manual catching which yielded only 236 insects. This blend was successful in attracting a broad range of beneficial insects, with a total count of 1,424.
3.4 Mating disruption
To develop more environmentally friendly pest management strategies for the control of legume pod borer M. vitrata, Dhanyakumar et al. (2020) were conducted a study focused on the efficacy of synthetic pheromone lures for mating disruption of this devastating insect pest. The pheromone blend used in the study consisted of three components: (E, E)-10,12-hexadecadienal (major), (E, E)-10,12-hexadecadienol (minor), and (E)-10-hexadecenal (minor). The results revealed that the complete pheromone blend with a ratio of 1:1:1 effectively disrupted mating behavior, leading to a reduction of 71% in fecundity and an 85% decrease in egg hatch/eclosion. Furthermore, the small-scale field study demonstrated that the same pheromone blend in a 1:1:1 ratio significantly disrupted normal mating, resulting in lower flower and pod damage and a 44.9% increase in mung bean yield (Dhanyakumar et al., 2020).
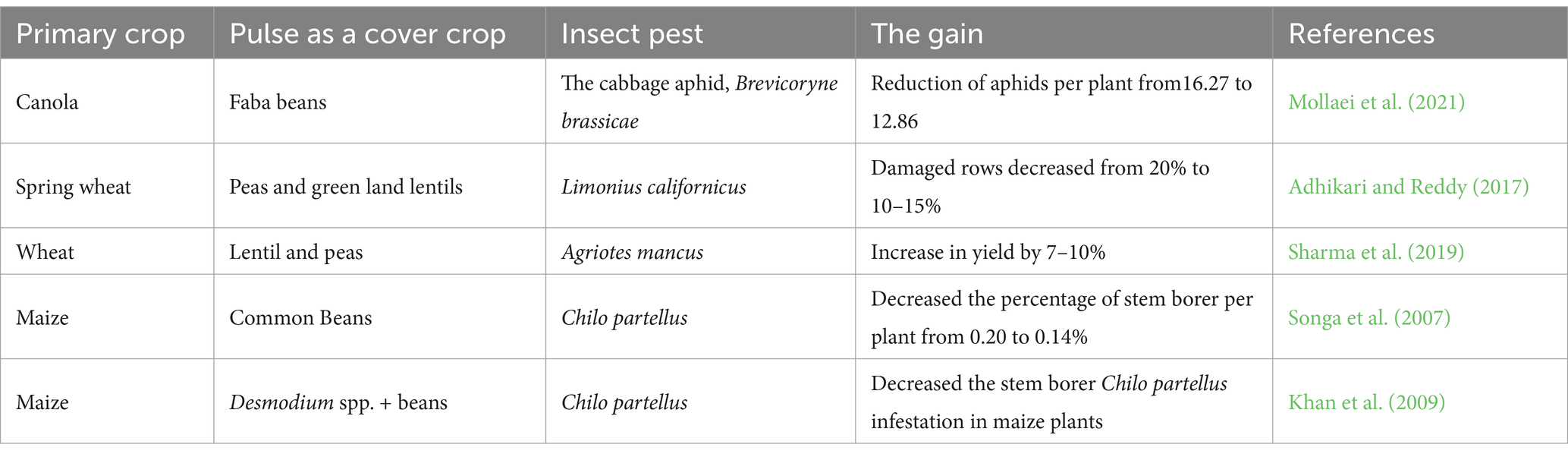
4 Pulse crops as cover crops for the management of insect pests
Pulse legumes, in addition to their high economic and nutrient value, possess the potential of being excellent cover crops. They play a crucial role in sustainable agro-ecosystems by contributing to the stability of production and profitability, carbon sequestration, nitrogen fixation, soil stabilization, and insect pest management (Sankaranarayanan et al., 2010).
Although pulse legumes suffer from a large scale of insect pests, which exhibit varying levels of host specificity, some pests are monophagous, targeting one particular pulse crop, such as Lixus algirus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) commonly known as the faba bean stem borer that attacks faba beans (Ait Taadaouit et al., 2021a,b). Conversely, others are polyphagous, such as chickpea pod borer H. armigera, which attacks chickpea, lentils, faba beans, and many other pulse legumes (El Fakhouri et al., 2022). Despite these challenges, they can be used as cover crops for the management of other primary crops, and the examples are listed below in Table 4.
4.1 Canola, Brevicoryne brassicae
The cabbage aphid, B. brassicae (Homoptera:Aphididae), is a major insect pest that attacks canola (Brassica napus) and other members of the Brassicaceae family, such as cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower. This insect feeds on plants by sucking sap, causing stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and reduced yields. In addition to direct damage, cabbage aphids can also transmit viruses that further harm the plant. The effects of intercropping canola with garlic, faba beans, or field peas on the control of cabbage aphids were examined in recent research by Mollaei et al. (2021). The study revealed that intercropping canola with faba beans notably reduced aphid populations compared to monoculture canola. In a 2019 field trial, the mean number of aphids per plant in the sole canola was 16.27, and in the intercropping plots was 12.86, this was likely due to the presence of natural enemies, such as Coccinellidae, Chrysopidae, and Syrphidae species which were more abundant in the intercropped plots. Moreover, compared to monoculture, intercropping did not adversely affect canola yield, and, in certain situations, this cropping system can significantly enhance yield (Mollaei et al., 2021).
4.2 Spring wheat, Limonius californicus
One of the main pest groups affecting spring wheat in the northwest of the United States is wireworm, which are the soil-dwelling larvae of many species of click beetles (Coleoptera: Elateridae). According to Adhikari and Reddy (2017), wireworms can cause damage to both crop production and the general health of plants by feeding on plant roots and underground parts of plants.
To mitigate the impact of wireworm L. californicus (Coleoptera: Elateridae), seven crops were evaluated for their potential as trap crops when intercropped with wheat. Among them, Montech peas and green land lentils were the crops that exhibited a strong trap crop potential. Field trials conducted in two different regions (Valier and Ledger) over 2 years (2015 and 2016) revealed promising results. For example, in the region of Valier in 2015, the estimated damage to wheat rows was reduced to 10% when intercropped with peas and 15% with lentils, compared to 20% in the sole wheat.
In addition a counting of wireworm’s populations was done daily for 10 days in the wheat and the trap crops rows, and it was observed that there were between 60–70 in the pea rows and between 25–30 in the wheat rows, respectively. As for the lentils and wheat rows, they contained between 35–40 and 40–50, respectively (Adhikari and Reddy, 2017).
4.3 Wheat, Agriotes mancus
In order to control A. mancus (Coleoptera: Elateridae), Sharma et al. (2019) explored the effects of intercropping wheat with pulse crops, particularly lentils and pea, using different seeding densities. The results revealed that at standard seeding rates of 8 seeds/sq. ft. for peas and 12 seeds/sq. ft. for lentils, both trap crops were effective in protecting wheat. Intercropping at these seeding rates led to a higher yield (7–10%) of the associated spring wheat plant stands compared to sole cropping. Wheat intercropped with pea showed an increase in yield from 2,237 kg/ha to 4,018 kg/ha, while wheat intercropped with lentil increased yields from 6,446 kg/ha to 7,382 kg/ha, representing a significant improvement in yield.
4.4 Maize, Chilo partellus
In sub-Saharan Africa, one of the main biotic stresses that cause significant damage to the maize crops is a complex of the lepidopteran stem borer, resulting in a loss that varies from 10 to 60%. Intercropping system has been suggested as a sustainable pest management strategy. In Kenya, Songa et al. (2007) found that intercropping systems of maize intercropped with non-host beans were more effective at reducing pest populations than intercropping maize with millet or sorghum alone. In their study, the percentage of stem borer infestation per plant in sole maize was recorded 0.20%. This was reduced to 0.14% when maize was intercropped with beans and 0.15% in a mixed intercropping system involving maize, beans, millet, and sorghum.
4.5 Maize, Chilo partellus
By combining stimuli that make the protected resource unappealing or unsuitable for the pests (push) and attracting them to an alluring source (pull) from which the pests are later removed, push-pull strategies manipulate the behavior of insect pests and their natural enemies (Cook et al., 2007). In an attempt to manage maize stem borer Chilo partellus, Khan et al. (2009) were successful in evaluating the effectiveness of the push and pull strategy in managing this pest, where the intercropping system included maize (host plant), Desmodium spp. (push crop) known for its repelling effect on the stem borers, and edible beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). This combination of crops was successful in reducing both the weed Striga hermonthica and the stem borer Chilo partellus and increasing the yield of maize. The damaged maize per plot in the short rains of 2007 in the sole maize was approximately 11 plants out of 63 plants in total per plot, whereas in the maize-desmodium-beans, when the beans and maize were planted in different holes were 0 damaged plants per plot. This result was confirmed by the same trial in the long rains season in 2008, where the number of damaged maize plants per plot in the sole maize was approximately 17, compared to just 2 at max when the maize was intercropped with desmodium and beans (beans and maize in different holes).
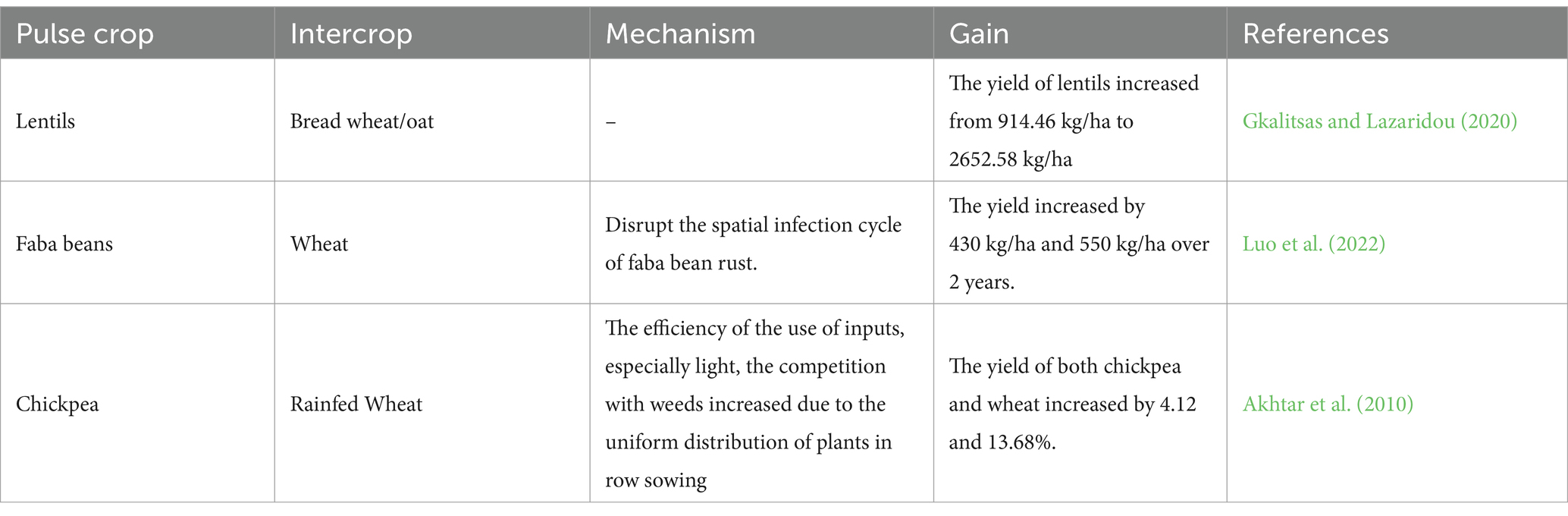
5 Agronomic performance of pulse-based intercropping systems
Intercropping is one of the key approaches for better land use, and higher profitability if the right candidates for the intercropping system are used. The most common intercropping system used is cereal-legumes intercropping, it has proven to be an insurance against crop failure in monocropping systems. Since cereals are an exhausting nutrient absorber from the upper layer of soil, the legumes by having the ability to absorb nutrients from deeper layers in the soil and fixing N for the cereals to take advantage of it makes the cereal-legume a compatible intercropping system that increases the profit and production such as the examples listed in Table 5 (Layek et al., 2018).
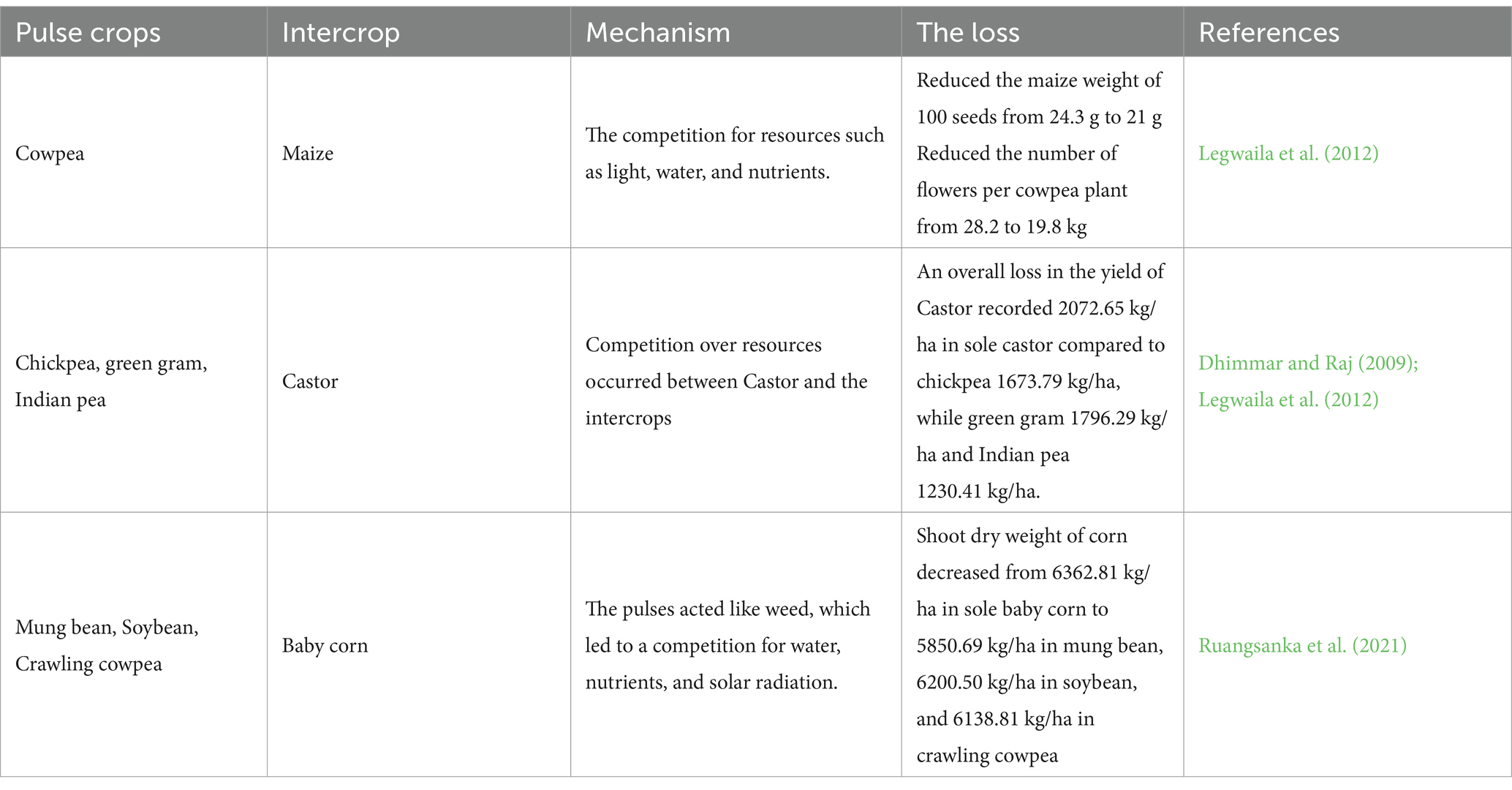
Although the fact that Intercropping sounds like a good solution for better land resource use, pest management, and higher production, it does not always provide positive results, the idea of planting two different crops next to each other comes with the risk of a reduction in the yield if the two different crops enter in a competition rather than a compatibility like the cases described below in Table 6.
5.1 Successful pulses-based intercropping systems
5.1.1 Lentil-bread wheat/oat
A study conducted by Gkalitsas and Lazaridou (2020) at the University of Western Macedonia in Florina, Greece, examined the potential of intercropping grain legumes with cereals for food production. The experiment involved growing two varieties of lentils, two varieties of bread wheat, and one variety of oat, which were grown individually as well as intercropped with each other in mixed rows at a sowing ratio of 50:50. The findings showed that intercropping had a significant positive impact on grain yields for bread wheat, oats, and lentils, with notable differences observed between the genotypes examined. According to Gkalitsas and Lazaridou (2020), the yield of lentils increased from 914.46 kg/ha to 2652.58 kg/ha when interplanted with bread wheat.
5.1.2 Faba bean-wheat
Faba bean production faces several challenges, including susceptibility to diseases such as faba bean rust. This disease can lead to significant yield losses, impacting the economic viability of faba bean cultivation. Additionally, excessive nitrogen fertilizer application can exacerbate the severity of faba bean rust, further compromising yield and quality.
Luo et al. (2022) investigated the intercropping design by planting faba bean and wheat in a specific ratio within the same field. The planting pattern consisted of two rows of faba bean and six rows of wheat, with three wheat planting belts and two faba bean planting belts in the intercropping plot. The design aimed to establish a diversified cropping system that could disrupt the spatial infection cycle of faba bean rust, thereby minimizing the disease’s damage. The results of this study demonstrated that intercropping effectively reduced the severity of faba bean rust and increased the yield of faba bean grains by 430 kg/ha and 550 kg/ha over 2 years. Furthermore, the study found that intercropping, when combined with suitable nitrogen application, significantly enhanced disease control efficacy and contributed to overall yield advantage, providing a practical and sustainable approach for faba bean production. These positive outcomes underscore the potential of intercropping as a valuable strategy for disease management and yield improvement in faba bean cultivation.
5.1.3 Chickpea-wheat
The study by Akhtar et al. (2010), which aimed to investigate the role of intercropping design, included growing four wheat cultivars with chickpeas to assess their yield, nutrient absorption, compatibility, and profitability.
Before the experiment, the soil was enriched through green manuring of legume-cereal biomass for 2 years to enhance organic matter and nutrient content, thereby reducing the reliance on mineral fertilizer. The results revealed a significant improvement in yield and nutrient uptake in the intercropping system compared to monoculture farming, where the grain yield of chickpea and wheat was increased by 4.12 and 13.68%, respectively. Furthermore, the associated crops accumulated significantly higher nitrogen and phosphorus in their biomass, indicating enhanced nutrient utilization in the intercropping system.
5.2 Unsuccessful pulses-based intercropping systems
5.2.1 Cowpeas-maize
Legwaila et al. (2012) conducted a field experiment at Botswana College of Agriculture, which found that intercropping cowpeas and maize had an adverse effect on the yield of both crops. The study found that intercropping with cowpeas significantly reduced the dry matter weight of maize seeds (21 g of 100 seeds weight) compared to sole cropping (24.33 g of 100 seeds weight). This reduction in dry matter weight indicates a potential decrease in overall maize yield. The competition for resources such as light, water, and nutrients between the maize and cowpea plants in the intercropping system contributed to these negative outcomes. Furthermore, the reduced number of cowpea flowers per plant went from 28.25 to 19.75 flowers per plant, and the impact on seed production underscores the challenges posed by this intercropping approach.
5.2.2 Chickpea, green gram and Indian pea-castor
Dhimmar and Raj (2009) evaluated three pulse intercrop varieties, namely chickpea, green gram, and Indian bean, under normal and paired row planting patterns to enhance the productivity of castor-based intercropping systems. However, the results revealed that the intercropping of pulses led to a reduction in castor growth and yield, with a more pronounced decrease observed under the paired row planting pattern. Indian bean intercropping caused severe reductions in the yield attributes and overall yield of the castor, where the sole castor provided 2072.65 kg/ha compared to the castor intercropped with Indian bean which was 1230.41 kg/ha. Chickpea intercropped with castor caused reduction loss of nearly 399 kg/ha, and with green gram, it caused a loss of nearly 276 kg/ha. These findings suggest that while intercropping holds the potential for enhancing agricultural productivity, the specific combinations of pulses and planting patterns evaluated in this study resulted in negative outcomes for castor cultivation. As a result, in similar limited resource conditions, it is advisable to exercise caution and potentially avoid intercropping with the specific pulse varieties studied, particularly under the paired row planting pattern.
5.2.3 Baby corn-pulse legumes (mung bean, soybean, crawling cowpea)
Ruangsanka et al. (2021) examined four intercropping systems: baby corn alone, baby corn with mung bean, baby corn with soybean, and baby corn with crawling cowpea. The results revealed that all intercropping systems reduced baby corn growth and yield. The authors found that pulse legumes acted as weeds, competing with baby corn for water, nutrients, and solar radiation, ultimately diminishing the productivity of the corn in all treatment combinations, where the sole corn provided 6362.81 kg/ha compared to 5850.69, 6200.50, and 6138.81 kg/ha for the intercropping with mung bean, soybean and crawling cowpea, respectively. Despite the initial assumption that pulse legumes might provide additional income to reimburse crop loss from competition, the income from the legumes could not compensate for the reduction in baby corn yield. As a result, the study concluded that intercropping baby corn with pulse legumes did not increase income for baby corn growers, particularly because baby corn had the highest market price (1.150 kg/USD), and pulse legumes reduced its yield. Therefore, based on the negative outcomes observed in this study, it is advisable to avoid these intercropping examples and consider alternative means for intercropping to enhance profitability.
6 Conclusion
The pulse legumes-based intercropping system is certainly one of the most promising agricultural methods for enhancing production and profitability. It accomplishes this by supplying an optimal nutrient medium (e.g., nitrogen fixation) facilitated by legumes for the benefit of cereals, diminishing pests by disrupting their natural behavior in monoculture crops, enhancing natural enemies’ and prolonging their lifespan to increase their predation on pests, and augmenting pollinator populations by fostering biodiversity that is highly advantageous to these beneficial organisms.
In often cases, intercropping as an agricultural approach is used to enhance the agronomical performance, regardless of the mechanism that led to that positive outcome. Despite the many advantages of intercropping, it is a risky approach if it is implemented without any theoretical or scientific foundation. The objective is to achieve compatibility between the intercrops in terms of sunlight, soil nutrients, and water resources rather than a competition where one or both crops will suffer in order to thrive in such systems.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) play a crucial role in the success of these systems below and above ground, where they serve in repelling pests and/or attracting their natural enemies. In addition to intercropping, as shown in this review, understanding or implementing volatile organic compounds regardless of their source (kairomones/pheromones) in intercropping systems serves positively in the management of several insect pests.
Although it shows in the limited available number of published articles that when adding semiochemicals to intercropping systems, the benefit increases compared to using intercropping or semiochemicals solely. In general, there is a huge lack of understanding of the role of volatile organic compounds that are emitted by the intercrops or applied in addition to intercropping.
This review serves as a systematic guide for optimizing the use of pulse legumes in intercropping systems, and sheds light on the lack of studies related to the understanding of the mechanisms involved in pulses-based intercropping systems, and the use of semiochemicals combined with pulses-based intercropping systems for effective pest management.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
RL: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Methodology. KE: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Supervision. RB: Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Validation. SK: Investigation, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AO: Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. CR: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Investigation, Methodology. IM: Validation, Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. ME: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This review is part of the “SpectraVOCS” project, which is funded by the APRD Program and sponsored by the OCP Foundation, Mohammed VI Polytechnic University, the National Center of Scientific and Technical Research (CNRST), and the Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research, and Innovation of Morocco.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank OCP Foundation, UM6P, CNRST and DESRS for their financial support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Generative AI was used (https://quillbot.com/).
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adhikari, A., and Reddy, G. V. (2017). Evaluation of trap crops for the management of wireworms in spring wheat in Montana. Arthropod Plant Interact. 11, 755–766. doi: 10.1007/s11829-017-9533-5
Ait Taadaouit, N., El Fakhouri, K., Sabraoui, A., Maalouf, F., Rohi, L., and El Bouhssini, M. (2021a). First sources of resistance in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) to the stem borer weevil, Lixus algirus L. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Phytoparasitica 49, 349–356. doi: 10.1007/s12600-021-00885-0
Ait Taadaouit, N., El Fakhouri, K., Sabraoui, A., Rohi, L., and El Bouhssini, M. (2021b). Lixus algirus L. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): biology, population fluctuation, infestation as affected by varieties, location, and planting dates in Morocco. J. Entomol. Acarol. Res 53:9324. doi: 10.4081/jear.2021.9324
Akhtar, M., Yaqub, M., Iqbal, Z., Ashraf, M. Y., Akhter, J., and Hussain, F. (2010). Improvement in yield and nutrient uptake by co-cropping of wheat and chickpea. Pak. J. Bot. 42, 4043–4049.
Annaz, H., El Fakhouri, K., Ben Bakrim, W., Mahdi, I., El Bouhssini, M., and Sobeh, M. (2023). Bergamotenes: a comprehensive compile of their natural occurrence, biosynthesis, toxicity, therapeutic merits and agricultural applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 7343–7362. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2184766
Baskaran, R. M., and Parthiban, P. (2017). Non-host plant derived kairomone to enhance activity of natural enemies of lepidopteran pests of Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench. J. Entomol. Zool 5, 414–421.
Bedoussac, L., Journet, E. P., Hauggaard-Nielsen, H., Naudin, C., Corre-Hellou, G., Jensen, E. S., et al. (2015). Ecological principles underlying the increase of productivity achieved by cereal-grain legume intercrops in organic farming. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 35, 911–935. doi: 10.1007/s13593-014-0277-7
Bhanu, K. R. M., Gowda, G. B., Ramasamy, S., Divya, T. N., Ramchandra, V. A., Chakravarthy, A. K., et al. (2018). The sex pheromone of legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) revisited. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 15, 163–182.
Bhat, S., Aditya, K. S., Kumari, B., Acharya, K. K., and Sendhil, R. (2022). “Pulses production, trade and policy imperatives: a global perspective” in Advances in legumes for sustainable intensification. eds. R. S. Meena and S. Kumar (New York: Academic Press), 639–656.
Boheman, C. H. (1833). Bruchus rufimanus. In: Genera et species curculionidum, cum synonymia hujus familiae, specie novae aut hactenus minus cognitae, descriptionibus a dom. Leonardo Gyllenhal, C. H. Boheman; et entomologis aliis illustratae. (ed.) C. J. Schönherr, Vol. 1, Part 2. (Paris: Roret), p. 383–681.
Borges, M., Michereff, M. F. F., Laumann, R. A., Santana, G. T., Castro, B. S., Silva, C. C., et al. (2023). Influence of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) on oviposition behaviour of Diceraeus melacanthus stink bug, an important pest of soybean and maize crops in South America. Arthropod Plant Interact. 17, 77–89. doi: 10.1007/s11829-022-09932-x
Brahmi, H., Lazraq, A., Boulamtat, R., El Fakhouri, K., Bassi, F. M., and El Bouhssini, M. (2021). Effect of temperature on the expression of resistance to Hessian fly (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in durum wheat cultivars. Phytoparasitica 49, 357–362. doi: 10.1007/s12600-020-00877-6
Bruce, T. J., Martin, J. L., Smart, L. E., and Pickett, J. A. (2011). Development of semiochemical attractants for monitoring bean seed beetle, Bruchus rufimanus. Pest Manage. Sci. 67, 1303–1308. doi: 10.1002/ps.2186
Cook, S. M., Khan, Z. R., and Pickett, J. A. (2007). The use of push-pull strategies in integrated pest management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 52, 375–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.52.110405.091407
Devonshire, A. L., Field, L. M., Foster, S. P., Moores, G. D., Williamson, M. S., and Blackman, R. L. (1998). The evolution of insecticide resistance in the peach–potato aphid, Myzus persicae. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 353, 1677–1684. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1998.0318
Dhanyakumar, O., Srinivasan, R., Mohan, M., Venkatesan, T., Murali Mohan, K., Nagesha, N., et al. (2020). Effect of pheromone-mediated mating disruption on pest population density of Maruca vitrata (Fabricius)(Crambidae: Lepidoptera). Insects 11:558. doi: 10.3390/insects11090558
Dhimmar, S. K., and Raj, V. C. (2009). Effect on growth and yield of rabi castor in pulses intercropping under varying planting geometry. Am.-Eurasian J. Sustain. Agric. 3, 448–451.
El Bouhssini, M., Amri, A., and Lhaloui, S. (2021). Plant resistance to cereal and food legume insect pests in North Africa, west and Central Asia: challenges and achievements. Curr. Opini. Insect Sci. 45, 35–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2020.11.009
El Fakhouri, K., Boulamtat, R., Sabraoui, A., and El Bouhssini, M. (2022). The chickpea pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner): yield loss estimation and biorational insecticide assessment in Morocco. Agronomy 12:3017. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12123017
Fernández-Aparicio, M., Amri, M., Kharrat, M., and Rubiales, D. (2010). Intercropping reduces Mycosphaerella pinodes severity and delays upward progress on the pea plant. Crop Prot. 29, 744–750. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2010.02.013
Foster, S. P., Harrington, R., Dewar, A. M., Denholm, I., and Devonshire, A. L. (2002). Temporal and spatial dynamics of insecticide resistance in Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Pest Manag. Sci. 58, 895–907. doi: 10.1002/ps.553
Gkalitsas, Τ., and Lazaridou, T. B. (2020). Yield of grain legumes intercropping with cereals in the florina area in Greece. AGROFOR 5:102. doi: 10.7251/AGRENG2003100G
Hansen, L. M., Lorentsen, L., and Boelt, B. (2008). How to reduce the incidence of black bean aphids (Aphis fabae Scop.) attacking organic growing field beans (Vicia faba L.) by growing partially resistant bean varieties and by intercropping field beans with cereals. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 58, 359–364. doi: 10.1080/09064710701788844
Harris, J., and Dent, D. R. (eds.). (2000). “Priorities in biopesticide research and development in developing countries: biopesticides series no. 2” in Priorities in biopesticide research and development in developing countries (Wallingford UK: CABI), 1–3.
Hauggaard-Nielsen, H., Jørnsgaard, B., Kinane, J., and Jensen, E. S. (2008). Grain legume–cereal intercropping: the practical application of diversity, competition and facilitation in arable and organic cropping systems. Renewable Agric. Food Syst. 23, 3–12. doi: 10.1017/S1742170507002025
Houasli, C., Idrissi, O., and Nsarellah, N. (2020). Chickpea genetic improvement in Morocco: state of the art, progress and prospects. Moroc. J. Agric. Sci. 1, 5–8.
Kabeh, J. D., and Lale, N. E. S. (2008). Role of host plant resistance and intercropping in reducing field infestation of cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata (l.) Walp.) by bruchids in the Nigerian Sudan savanna. Acad. J. Entomol. 1, 12–18.
Khan, Z. R., Midega, C. A., Wanyama, J. M., Amudavi, D. M., Hassanali, A., Pittchar, J., et al. (2009). Integration of edible beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) into the push–pull technology developed for stemborer and Striga control in maize-based cropping systems. Crop Prot. 28, 997–1006. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2009.05.014
Kiju, P., Wanner, K. W., and Reddy, G. V. P. (2022). Field efficacy of pea leaf weevil aggregation pheromone combined with contact insecticide as an attract-and-kill method, 2020. Arthropod Manage. Tests 47:tsac053. doi: 10.1093/amt/tsac053
Layek, J., Das, A., Mitran, T., Nath, C., Meena, R. S., Yadav, G. S., et al. (2018). “Cereal+ legume intercropping: an option for improving productivity and sustaining soil health” in Legumes for soil health and sustainable management. eds. R. S. Meena, A. Das, G. S. Yadav, and R. Lal, 347–386.
Legwaila, G. M., Marokane, T. K., and Mojeremane, W. (2012). Effects of intercropping on the performance of maize and cowpeas in Botswana. Int. J. Agric. For. 2, 307–310. doi: 10.5923/j.ijaf.20120206.07
Luo, C., Lv, J., Guo, Z., and Dong, Y. (2022). Intercropping of faba bean with wheat under different nitrogen levels reduces faba bean rust and consequent yield loss. Plant Dis. 106, 2370–2379. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-11-21-2451-RE
Maffei, M. E., Mithöfer, A., and Boland, W. (2007). Insects feeding on plants: rapid signals and responses preceding the induction of phytochemical release. Phytochemistry 68, 2946–2959. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.07.016
Mahallati, M. N., Koocheki, A., Mondani, F., Feizi, H., and Amirmoradi, S. (2015). Determination of optimal strip width in strip intercropping of maize (Zea mays L.) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Northeast Iran. J. Clean. Prod. 106, 343–350. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.10.099
Mahmood, M. T., Akhtar, M., Ahmad, M., Saleem, M., Aziz, A., Rasool, I., et al. (2021). An update on biology, extent of damage and effective management strategies of chickpea pod borer (Helicoverpa armigera). Pak. J. Agric. Res. 34, 91–101. doi: 10.17582/journal.pjar/2021/34.1.91.101
Makhlouf, L., El Fakhouri, K., Kemal, S. A., Aasfar, A., Meftah Kadmiri, I., and El Bouhssini, M. (2024a). Advances in analytical techniques for assessing volatile organic compounds in pulse crops: a comprehensive review. Front. Hortic. 3:1394041. doi: 10.3389/fhort.2024.1394041
Makhlouf, L., El Fakhouri, K., Kemal, S. A., Maafa, I., Meftah Kadmiri, I., and El Bouhssini, M. (2024b). Potential of volatile organic compounds in the management of insect pests and diseases of food legumes: a comprehensive review. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1430863. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1430863
Mantri, N., Basker, N., Ford, R., Pang, E., and Pardeshi, V. (2013). The role of micro-ribonucleic acids in legumes with a focus on abioticstress response. Plant Genome 6, 1–14. doi: 10.3835/plantgenome2013.05.0013
Mollaei, M., Fathi, S. A. A., Nouri-Ganbalani, G., Hassanpour, M., and Golizadeh, A. (2021). Effects of strip intercropping of canola with faba bean, field pea, garlic, or wheat on control of cabbage aphid and crop yield. Plant Prot. Sci. 57, 59–65. doi: 10.17221/132/2019-PPS
Muute, N. A., Muli, B., and Orek, C. (2021). Evaluation of bean common mosaic disease and associated aphid vector, Aphis fabae L., on common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) production in lower eastern Kenya. Int. J. Pathogen Res. 8, 1–18. doi: 10.9734/ijpr/2021/v8i330203
Mweke, A., Akutse, K. S., Ulrichs, C., Fiaboe, K. K. M., Maniania, N. K., and Ekesi, S. (2020). Integrated management of Aphis craccivora in cowpea using intercropping and entomopathogenic fungi under field conditions. J. Fungi 6:60. doi: 10.3390/jof6020060
Namdev, H. P., and Singh, R. S. (2022). Influence of intercropping on crop losses by chickpea pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Hub.) in chickpea.
Nandhini, U., and Somasundaram, E. (2020). Intercropping—a substantial component in sustainable organic agriculture. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 8, 133–143. doi: 10.18782/2582-2845.8007
Patil, A. A., Thakur, S., Navale, J. S., Narode, M. K., and Kolhe, P. S. (2018). Influence of intercropping on incidence of gram pod borer (Helicoverpa armigera) in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 6, 12–15.
Paul, S. K., Mazumder, S., Mujahidi, T. A., Roy, S. K., and Kundu, S. (2015). Intercropping coriander with chickpea for pod borer insect suppression. World J. Agric. Sci. 11, 307–310.
Pauline, K.-B., and Rimm, E. B. (2003). Whole grain consumption and weight gain: a review of the epidemiological evidence, potential mechanisms and opportunities for future research. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 62, 25–29. doi: 10.1079/PNS2002232
Raza, M. A., Feng, L. Y., Iqbal, N., Ahmed, M., Chen, Y. K., Khalid, M. H. B., et al. (2019). Growth and development of soybean under changing light environments in relay intercropping system. J. Life Environ. Sci. 7:e7262. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7262
Ruangsanka, S., Sanfan, S., and Chaiwong, U. (2021). Does intercropping of baby corn (Zea mays L.) with pulse legumes improve soil fertility, crop productivity and profitability? J. Agric. Sci. (Sri Lanka) 16:22. doi: 10.4038/jas.v16i1.9366
Sabraoui, A., Lhaloui, S., Bouchelta, A., El Fakhouri, K., and El Bouhssini, M. (2019). Grain yield losses due to leaf miner (Liriomyza cicerina R.) in winter-and spring-planted chickpea in Morocco. Crop Prot. 117, 115–120. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2018.11.021
Sankaranarayanan, K., Praharaj, C. S., Nalayini, P., Bandyopadhyay, K. K., and Gopalakrishnan, N. (2010). Legume as companion crop for cotton. J. Cotton Res. 24, 115–126.
Santos, D. R. C., Peñaflor, M. F. G. V., Sanches, P. A., Nardi, C., and Bento, J. M. S. (2015). The effects of Gibberella zeae, barley yellow dwarf virus, and co-infection on Rhopalosiphum padi olfactory preference and performance. Phytoparasitica 44, 47–54. doi: 10.1007/s12600-015-0493-y
Sayed, S. M., Alotaibi, S. S., Gaber, N., and Elarrnaouty, S. A. (2020). Evaluation of five medicinal plant extracts on Aphis craccivora (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and its predator, Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) under laboratory conditions. Insects 11:398. doi: 10.3390/insects11060398
Schoeny, A., Jumel, S., Rouault, F., Lemarchand, E., and Tivoli, B. (2010). Effect and underlying mechanisms of pea-cereal intercropping on the epidemic development of Ascochyta blight. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 126, 317–331. doi: 10.1007/s10658-009-9548-6
Segers, A., Megido, R. C., Lognay, G., and Francis, F. (2021). Overview of Bruchus rufimanus Boheman 1833 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae): Biology, chemical ecology and semiochemical opportunities in integrated pest management programs. Crop Prot. 140:105411.
Segers, A., Noël, G., Delanglez, L., Caparros Megido, R., and Francis, F. (2023). Impacts of semiochemical traps designed for Bruchus rufimanus Boheman 1833 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on nontarget beneficial Entomofauna in Field bean crops. Insects 14:153. doi: 10.3390/insects14020153
Sharma, A., Sandhi, R. K., Briar, S. S., Miller, J. H., and Reddy, G. V. (2019). Assessing the performance of pea and lentil at different seeding densities as trap crops for the management of wireworms in spring wheat. J. Appl. Entomol. 143, 460–469. doi: 10.1111/jen.12601
Singh, K. D., Mobolade, A. J., and Bharali, R. (2021). Main plant volatiles as stored grain pest management approach: a review. J. Agric. Food Res. 4:100127. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2021.100127
Singh, S. K., Sinha, B. K., and Jamwal, B. S. (2010). Management of gram pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) by intercropping and monitoring through pheromone traps in chickpea. Karnataka J. Agric. Sci. 22, 524–526.
Skovgård, H., and Stoddard, F. L. (2023). Reproductive potential of the black bean aphid (Aphis fabae Scop.) on a range of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) accessions. Legume Sci. 5:e199. doi: 10.1002/leg3.199
Songa, J. M., Jiang, N., Schulthess, F., and Omwega, C. (2007). The role of intercropping different cereal species in controlling lepidopteran stemborers on maize in Kenya. J. Appl. Entomol. 131, 40–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0418.2006.01116.x
Toker, P., Canci, H., Turhan, I., Isci, A., Scherzinger, M., Kordrostami, M., et al. (2024). The advantages of intercropping to improve productivity in food and forage production–a review. Plant Prod. Sci. 27, 155–169. doi: 10.1080/1343943X.2024.2372878
Wale, M., Jembere, B., and Seyoum, E. (2000). Biology of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris)(Homoptera: Aphididae) on cool-season legumes. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 20, 171–180. doi: 10.1017/S1742758400019603
Wang, G., Cui, L. L., Dong, J., Francis, F., Liu, Y., and Tooker, J. (2011). Combining intercropping with semiochemical releases: optimization of alternative control of Sitobion avenae in wheat crops in China. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 140, 189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1570-7458.2011.01150.x
Xu, Q., Hatt, S., Lopes, T., Zhang, Y., Bodson, B., Chen, J., et al. (2018). A push–pull strategy to control aphids combines intercropping with semiochemical releases. J. Pest. Sci. 91, 93–103. doi: 10.1007/s10340-017-0888-2
Yadav, S. K., Patel, S., and Hasan, W. (2020). “Insect pest of pulse crop and their management” in Integrated pest management – a holistic approach for pest risk management. eds. C. P. Wajid Hasan, K. C. Signh, and S. Joginder (New Delhi: BIOTECH BOOKS®), 217–230.
Yano, E. (2006). Ecological considerations for biological control of aphids in protected culture. Popul. Ecol. 48, 333–339. doi: 10.1007/s10144-006-0008-2
Yousefi, M., Marja, R., Barmettler, E., Six, J., Dray, A., and Ghazoul, J. (2024). The effectiveness of intercropping and agri-environmental schemes on ecosystem service of biological pest control: a meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 44:15. doi: 10.1007/s13593-024-00947-7
Keywords: multifunction, legumes, cropping system, volatile organic compounds, biorational pest managed, agronomic performance
Citation: Lamzira R, El Fakhouri K, Boulamtat R, Kemal SA, Oubayoucef A, Ramdani C, Meftah Kadmiri I and El Bouhssini M (2025) Multifunctional roles of intercropping in the management of insect pests affecting pulse crops: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1599254. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1599254
Edited by:
Liming Ye, Ghent University, BelgiumReviewed by:
Huseyin Canci, Akdeniz University, TürkiyeReuben Chumba, Masinde Muliro University of Science and Technology, Kenya
Vitalis Ogemah, Masinde Muliro University of Science and Technology, Kenya
Copyright © 2025 Lamzira, El Fakhouri, Boulamtat, Kemal, Oubayoucef, Ramdani, Meftah Kadmiri and El Bouhssini. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Karim El Fakhouri, a2FyaW0uZWxmYWtob3VyaUB1bTZwLm1h
 Rachid Lamzira
Rachid Lamzira Karim El Fakhouri
Karim El Fakhouri Rachid Boulamtat
Rachid Boulamtat Seid Ahmed Kemal
Seid Ahmed Kemal Ali Oubayoucef1
Ali Oubayoucef1 Chaimae Ramdani
Chaimae Ramdani