- 1Food Technology Department, Faculty Engineering, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
- 2Laboratory of Postharvest Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
Fruit losses during postharvest handling remain a major global challenge. Edible coatings, particularly those stabilized by cellulose nanomaterials (CNM), offer a sustainable solution to enhance fruit preservation. This review aims to explore the role of CNM-stabilized Pickering emulsions in improving coating stability, antimicrobial activity, and barrier properties. The findings indicate that CNM possess a high aspect ratio, enabling them to create a compact and efficient interfacial layer at the oil-water interface. Incorporating CNM as a stabilizer enhances the barrier properties of emulsion-based coatings, effectively delaying fruit ripening by slowing the respiration rate through mechanisms such as improved inhibition of gas exchange, reduced oxygen availability, and suppression of ethylene production. The effectiveness in reducing microbial growth is attributed to the sustained-release capability of the active components by CNM in the Pickering emulsion coating. Its antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, yeast, and fungi at appropriate concentrations. The optimization of CNM-based Pickering emulsions should be tailored to the specific requirements of the intended application, particularly considering the potential of CNM to serve as a growth medium for microbes. Future work should focus on formulation optimization for industrial application and on sensory evaluations to ensure consumer acceptance, paving the way for CNM as a viable strategy in sustainable fruit preservation.
1 Introduction
Fruit losses occur at various stages, from production through postharvest handling, storage, and transportation, significantly reducing the amount of food available for human consumption. According to the FAO (2019), ~14% of global food is lost between harvest and retail. These substantial losses are primarily attributed to mishandling, ineffective transportation methods, and contamination by fungi and bacteria (Udayanga et al., 2013). The application of edible films or coatings, particularly for highly perishable products such as fruits, has been reported as an alternative strategy to preserve food quality and protect against undesirable mechanical, physical, chemical, and microbiological damage (Falguera et al., 2011; Jung et al., 2020; Wardana et al., 2021). Those are typically fabricated from renewable polymers, including polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, or their mixtures, which serve as the primary matrix for forming a thin protective layer (Lin et al., 2017). However, due to the inherent limitations of these biopolymer matrices, ongoing research efforts are focused on enhancing their functional properties.
Emulsification, a technique involving the mixing of two or more immiscible phases, has received considerable attention for its ability to improve the functional properties of edible films and coatings. However, emulsion-based systems often face challenges such as phase separation and long-term instability, which can adversely affect coating functionality (Taherian et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2013). Moreover, excessive use of synthetic surfactants may trigger allergic reactions and pose potential carcinogenic risks (Jiang et al., 2020; Shah et al., 2021). The Pickering emulsion technique represents a promising approach to improving the performance of emulsion-based biomaterials, particularly with respect to stability, safety, barrier properties, and antimicrobial activity (Ma et al., 2019; Nkede et al., 2023). Solid particles adsorbed at the oil–water (o/w) interface, along with interactions among particles and between particles and droplets, contribute to enhanced system stability, often outperforming conventional surfactants (Monégier du Sorbier et al., 2015; Jiang et al., 2025). The use of cellulose-based stabilizers in the development of emulsified biomaterials is gaining momentum, with 1,091 studies reported on the subject (Figure 1). In addition to being renewable and sustainable, cellulose nanomaterials (CNM) can be readily modified through chemical functionalization to tailor their properties for specific applications, making them a versatile component for a wide range of Pickering emulsion systems (Lu et al., 2021; Seo et al., 2021). This review focuses on CNM as stabilizers in Pickering emulsions and their application in the preservation of fresh fruit.
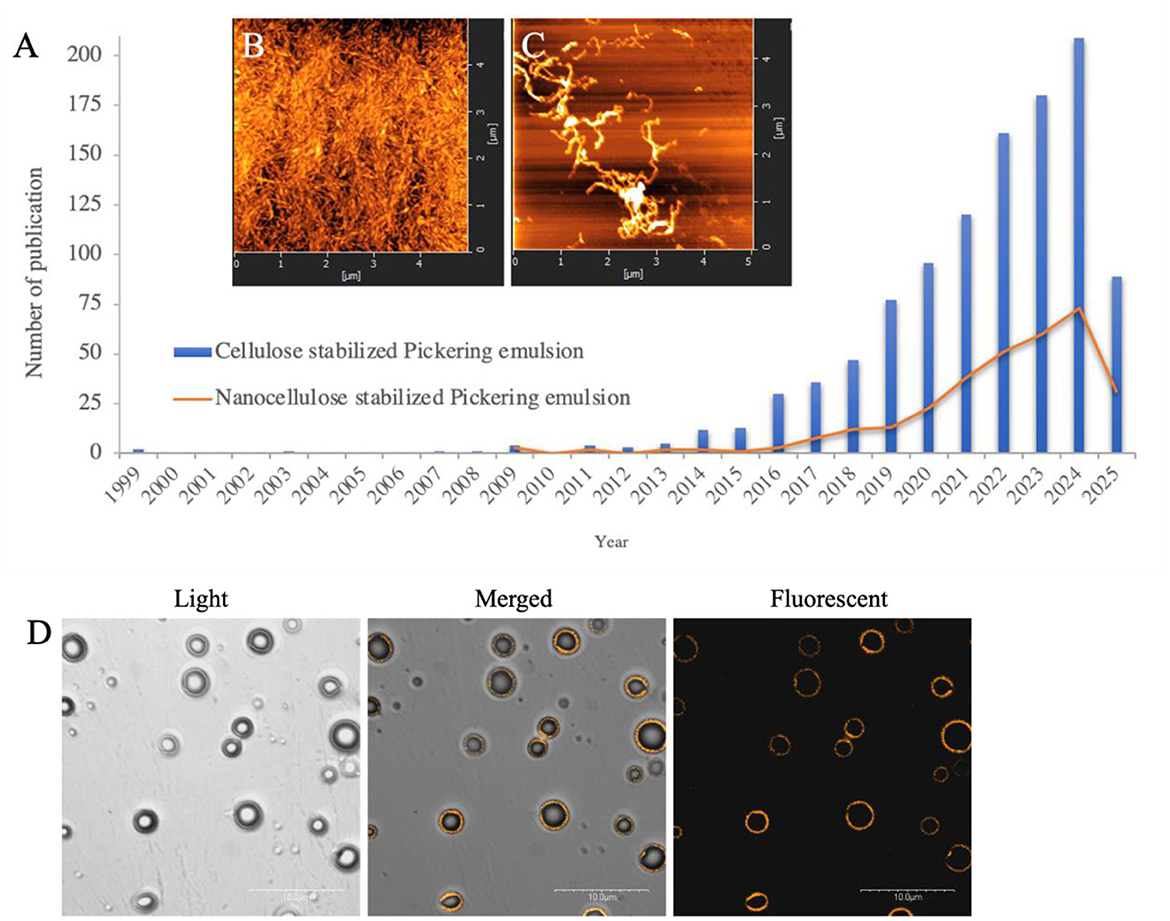
Figure 1. (A) Number of annual reports and documents by subject area by search keywords “cellulose Pickering emulsion” and “nanocellulose Pickering emulsion” over the past 26 years. Indexed by Scopus, update-March 2025; (B) Atomic force microscopy photograph of CNC and (C) CNF; (D) Pickering emulsion system stabilized with Cellulose Nano Materials (CNM) observed with Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM). The CNM was stained with fluorescence dye, acridine orange.
2 Potency of CNM for Pickering emulsion coating
Pickering emulsions are stabilized by solid colloidal particles instead of traditional emulsifiers like surfactants, proteins, or phospholipids (Tan et al., 2022). First introduced by Ramsden (1903) and Pickering (1907), they offered an enhanced stability, eco-friendly stabilizers, and lower health risks (Albert et al., 2019). Applications include edible films and coatings with functional lipids (Deng et al., 2018; Jung et al., 2020). Two theories explain their stabilization: the solid particle interface film theory, where particles form a rigid layer at the oil–water interface preventing coalescence (Aveyard et al., 2003); and the three-dimensional viscoelastic particle network theory, where particle networks increase viscosity and inhibit droplet merging (Lagaly et al., 1999; Chen et al., 2020). Stability is influenced by particle wettability, concentration, electrolytes, temperature, pressure, and pH (Chen et al., 2020).
The CNM have gained significant attention in recent years as potential stabilizers. They are tiny, natural, hydrophilic particles, but their crystalline form reveals amphiphilic properties, derived from cellulose, the earth's most abundant organic polymer. According to Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry (TAPPI) WI 3021, CNM is defined as materials with nanoscale external dimensions or internal structures (Teo et al., 2022). They are often produced from cellulose extracted from various plant sources, such as softwood, hardwood, cotton, agricultural resides/wastes, grasses, or other fibrous materials (Figure 1) (Hassan et al., 2018). The CNM includes nanostructured materials and nanofibers. Cellulose microcrystals and microfibrils fall under nanostructures, while cellulose nanocrystals (CNC), cellulose nanofibrils (CNF), and bacterial cellulose (BC) are nanofibers (Trache et al., 2020). Though chemically similar, these nanofibers differ in morphology, crystallinity, and flexibility due to varying sources and extraction methods (Phanthong et al., 2018).
The CNM have a high aspect ratio, allowing them to form a dense and effective interfacial layer at the oil-water interface (Napso et al., 2018; Dominguez et al., 2024). This dense packing of particles helps in stabilizing the emulsion by preventing coalescence and Ostwald ripening (Liu et al., 2019). However, due to the abundance of hydroxyl groups on its surface, nanocellulose tends to aggregate in non-polar solvents, restricting its applications and usage (Trache et al., 2020). The surface chemistry of CNM can be modified to enhance their compatibility with different oil and water phases such as esterification, etherification, silylation, grafting and others (Abitbol et al., 2016; Afrin and Karim, 2017; Kamel et al., 2020). Functionalization of CNM can improve their ability to stabilize Pickering emulsions in a wider range of systems. Furthermore, CNM provide emulsions with good mechanical and thermal stability, which is important in various industrial applications, including food products (Gong et al., 2017). Therefore, the formulation and optimization of CNM-based Pickering emulsions should be tailored to the specific requirements of the intended application.
3 Effect of CNM-stabilized Pickering emulsions on antimicrobial activity
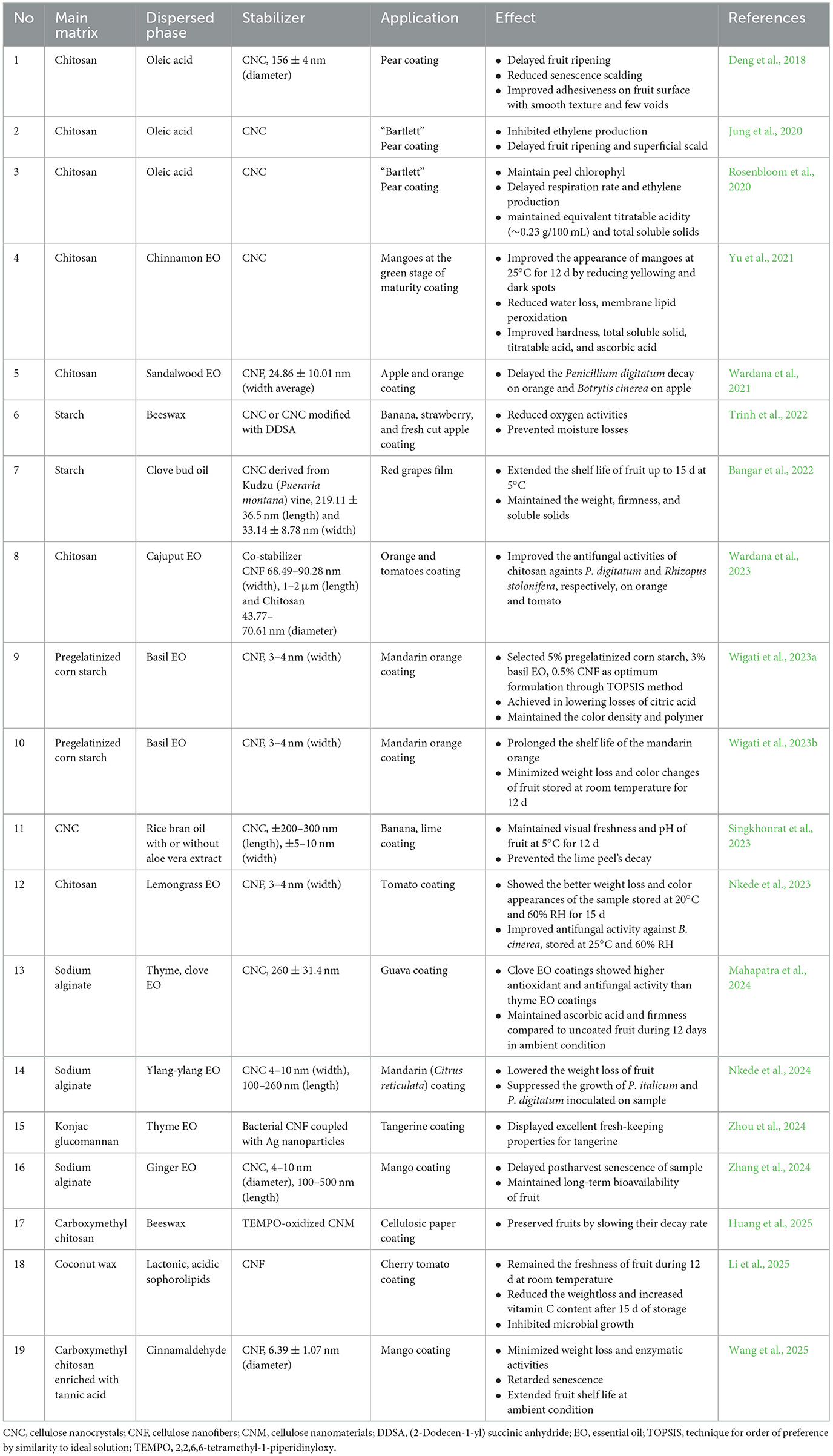
The antimicrobial activity is important parameter of biomaterial especially for food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetics application. In recent years, several studies have evaluated the potentials of CNM as Pickering emulsion stabilizer in various biomatrices in the terms of antimicrobial action improvement (Wardana et al., 2021; Bangar et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2024). The main discoveries of those of related works, describing antimicrobial activity against bacteria (G+ and G−), yeast, and fungi, are summarized in Table 1. However, naturally, cellulose can be used by microbes as a growth medium, hence the appropriate of the concentration is essential.
Zhou et al. (2024) investigated the antibacterial properties of Pickering emulsion coatings made from konjac glucomannan-loaded bacterial cellulose nanofibers (BCN), silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), and thyme EO against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Their findings showed that the Pickering emulsion films produced larger zones of inhibition compared to other treatments, indicating superior antibacterial activity. Specifically, the inhibition zones measured 1.12 cm for S. aureus and 1.07 cm for E. coli. This effectiveness was attributed to the sustained-release capability of the active components in the Pickering emulsion films. Similarly, Bangar et al. (2022) incorporated clove bud oil (CBO)/CNC-based PE into pearl millet starch (PMS) films to combat S. aureus ATCC 29213 and E. coli ATCC 25922. While PMS and PMS/CNC films showed no antibacterial activity, the addition of CNC/CBO-PE significantly enhanced antimicrobial performance. Clear zones formed around the film disks indicated inhibition, with S. aureus exhibiting a larger inhibition diameter (21.5 mm) compared to E. coli (16.6 mm). This suggests that the active films were more effective against Gram-positive bacteria, likely due to the extra protective outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria, which hinders the penetration of antimicrobial compounds. The strong antibacterial effect of the CNC/CBO-PE films was credited to the phenolic compounds in CBO, which disrupt bacterial cell membranes, damage cell walls, inhibit respiration, and ultimately lead to cell death.
Nkede et al. (2023) developed active coatings using chitosan (CH), CNF, and lemongrass oil (LGO) in a Pickering emulsiom system to preserve tomatoes. The formulations included CH, CH/1% LGO PE, and CH/2% LGO PE. Antifungal activity was tested against fruit fungal pathogen, Botrytis cinerea, on inoculated tomatoes. Results showed that tomatoes coated with LGO-PE films had significantly smaller lesion diameters compared to uncoated or CH-coated tomatoes. After 9 d of storage, the CH/2% LGO PE treatment achieved the smallest lesion diameter (10.64 mm), corresponding to a 57.44% inhibition rate, indicating effective suppression of B. cinerea. This was attributed to citral and neral, active compounds in LGO that penetrate fungal cell walls, disrupt metabolic processes, and lead to fungal death. In another study, Wardana et al. (2023) explored the antifungal potential of alginate/LGO/CNF PE coatings against Penicillium italicum and Penicillium digitatum. Various in vitro assays revealed that 0.75% LGO PE significantly enhanced antifungal activity. Spore germination was inhibited by 88.28% for P. digitatum and 91.94% for P. italicum; germ tube elongation was reduced by 89.28 and 90.13%, respectively; and membrane integrity was disrupted by 41.67% (P. digitatum) and 63% (P. italicum). The antifungal effect was attributed to geranial and neral in LGO, which compromise fungal cell membrane integrity, ultimately leading to cell death.
4 Effect of CNM-stabilized Pickering emulsions on barrier properties
Fruit ripening is one of the most important indicators of fruit quality, with its effect determining the fruit's edibility and quality. The biggest factor contributing to fruit ripening, especially in climacteric fruits, is the respiration process due to ethylene production. The production of ethylene mainly results in growth and physiological processes in plants, with the ripening process being one of the crucial parts. Therefore, controlling ethylene concentrations by reducing ethylene production and inhibiting ethylene receptors becomes the key interest in delaying fruits from ripening (Ebrahimi et al., 2022). Although commercial ethylene scavengers and synthetic coating have been developed throughout the year to combat the problem, CNM has been researched as an alternative for controlling ethylene levels, with recent research showing similar or even better results compared to commercial coating (Deng et al., 2018; Jung et al., 2020; Rosenbloom et al., 2020; Trinh et al., 2022). CNM mainly contributes on delaying the respiration rate through mechanisms such as inhibiting gas exchange and reducing oxygen activities during respiration (Chen et al., 2020; Yan et al., 2017). These mechanisms inhibited fruit ripening by indirectly reducing the ethylene content inside the coated fruits with controlling the circulation of O2 and CO2 content being its main mechanism (Rosenbloom et al., 2020). Studies from Deng et al. (2018) and Jung et al. (2020) show the usage of coating using CNC as the stabilizer with the Pickering emulsion technique for Bartlett pears delay the ripening process by increased hydrophobicity, which resulted in maintained fruit structure firmness and retained chlorophyll content. As Pickering emulsion was more stabilized, the coating improved its hydrophobic properties, which results in a stable and less permeable gas barrier. This phenomenon resulted in much less oxygen entering the system and remaining inside for ethylene biosynthesis to produce ethylene in larger quantities (Riaño et al., 2022).
Research conducted on the physical mechanism of cellulose films and coatings showed that blends of CNM with other biopolymers, such as chitosan, could effectively block UV radiation. For instance, films containing cellulose and chitosan exhibit reduced transmittance of UV light, thereby offering protection against oxidative reactions that could compromise product integrity (Cazón et al., 2019; Davoodi et al., 2020). The interaction between CNM and other polymers enhances the mechanical strength and water barrier properties while effectively limiting moisture transfer through the packaging (Cazón et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2021). Such compositions enabled the production of edible films and coatings, which are vital for sustainable applications in food and material sciences. Furthermore, recent studies indicate that CNC and CNF can significantly enhance the water vapor barrier properties of films due to their high surface area and hydrophilic nature, which creates robust biofilms capable of controlling moisture transmission (Fotie et al., 2017; Rampazzo et al., 2017). By forming hydrogen bonds in the biofilm, these cellulose structures minimized voids where water molecules can permeate, thus improving the overall barrier efficiency (Zhao et al., 2021). The functionality of these cellulose-based biofilms is particularly beneficial in food packaging, where maintaining product freshness and extending shelf life are critical.
Finally, the use of CNM-stabilized Pickering emulsions has emerged as a promising strategy to enhance the postharvest quality and longevity of fresh fruits and vegetables. By integrating CNM such as CNC and CNF into edible coatings, often in combination with biopolymer matrices like chitosan, starch, or alginate and natural essential oils, these emulsions form protective features that significantly delay ripening, reduce microbial spoilage, and preserve visual and nutritional quality. The coatings have demonstrated a broad range of benefits, including maintaining firmness, color, chlorophyll content, and ascorbic acid levels, while minimizing weight loss and oxidative degradation. Moreover, the antifungal and antioxidant properties delivered through essential oil incorporation further enhance the preservation effects. Collectively, these findings highlight the considerable potential of CNM-based emulsions as a sustainable, functional, and effective solution for prolonging shelf life and ensuring the safety and appeal of fresh produce during storage and distribution.
5 Future prospects
The Pickering emulsion technique, using CNM as a stabilizer, shows promise for food preservation. CNM coatings enhance structural stability, add functional properties, and extend shelf life, as confirmed by studies on fruits and vegetables. These positive results suggest CNM's potential for industrial-scale application. Further research should optimize formulations for upscaling and explore the compatibility between dispers phases and stabilizers to improve emulsion coherence. Additionally, sensory evaluations are crucial to assess consumer acceptance, an area still underexplored in recent studies.
Data availability statement
All data are available within this article and no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Author contributions
AAW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Validation, Methodology, Conceptualization. VM: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Data curation. LPW: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Conceptualization. FNN: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. FuminT: Resources, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. FumihT: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Research and Technology Transfer Office – Bina Nusantara University.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical, resource, and financial support from Bina Nusantara University, Indonesia and Kyushu University, Japan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abitbol, T., Rivkin, A., Cao, Y., Nevo, Y., Abraham, E., Ben-Shalom, T., et al. (2016). Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 39, 76–88. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2016.01.002
Afrin, S., and Karim, Z. (2017). Isolation and surface modification of nanocellulose: necessity of enzymes over chemicals. ChemBioEng Rev. 4, 289–303. doi: 10.1002/cben.201600001
Albert, C., Beladjine, M., Tsapis, N., Fattal, E., Agnely, F., and Huang, N. (2019). Pickering emulsions: preparation processes, key parameters governing their properties and potential for pharmaceutical applications. J. Control. Release 309, 302–332. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.07.003
Aveyard, R., Binks, B. P., and Clint, J. H. (2003). Emulsions stabilised solely by colloidal particles. Adv. Coll. Interf. Sci. 100, 503–546. doi: 10.1016/S0001-8686(02)00069-6
Bangar, S. P., Whiteside, W. S., Ozogul, F., Dunno, K. D., Cavender, G. A., and Dawson, P. (2022). Development of starch-based films reinforced with cellulosic nanocrystals and essential oil to extend the shelf life of red grapes. Food Biosci. 47:101621. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101621
Cazón, P., Vázquez, M., and Velázquez, G. (2019). Composite films with UV-barrier properties based on bacterial cellulose combined with chitosan and poly(vinyl alcohol): study of puncture and water interaction properties. Biomacromolecules 20, 2084–2095. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.9b00317
Cazón, P., Vázquez, M., and Velázquez, G. (2020). Regenerated cellulose films with chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol: effect of the moisture content on the barrier, mechanical and optical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 236:116031. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116031
Chen, L., Ao, F., Ge, X., and Shen, W. (2020). Food-grade Pickering emulsions: preparation, stabilization and applications. Molecules 25:3202. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143202
Davoodi, S., Davachi, S. M., Ghorbani Golkhajeh, A., Shekarabi, A. S., and Abbaspourrad, A. (2020). Development and characterization of salvia macrosiphon/chitosan edible films. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 8, 1487–1496. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05894
Deng, Z., Jung, J., Simonsen, J., and Zhao, Y. (2018). Cellulose nanocrystals Pickering emulsion incorporated chitosan coatings for improving storability of postharvest Bartlett pears (Pyrus communis) during long-term cold storage. Food Hydrocoll. 84, 229–237. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.06.012
Dominguez, R. C. V., Wagner, J. R., and Porfiri, M. C. (2024). Nanofibers from soybean hull insoluble polysaccharides as Pickering stabilizers in oil-in-water emulsions formulated under acidic conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 104, 125–133. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12897
Ebrahimi, A., Zabihzadeh Khajavi, M., Ahmadi, S., Mortazavian, A., Abdolshahi, A., Rafiee, S., et al. (2022). Novel strategies to control ethylene in fruit and vegetables for extending their shelf life: a review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 4599–4610. doi: 10.1007/s13762-021-03485-x
Falguera, V., Quintero, J. P., Jiménez, A., Muñoz, J. A., and Ibarz, A. (2011). Edible films and coatings: structures, active functions and trends in their use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 22, 292–303. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2011.02.004
FAO (2019). Redução de perdas e desperdícios alimentares é essencial para alcançar metas globais. Available online at: http://www.fao.org/brasil/noticias/detail-events/pt/c/1199506/ (accessed March 14, 2025).
Fotie, G., Rampazzo, R., Ortenzi, M. A., Checchia, S., Fessas, D., and Piergiovanni, L. (2017). The effect of moisture on cellulose nanocrystals intended as a high gas barrier coating on flexible packaging materials. Polymers 9:415. doi: 10.3390/polym9090415
Gong, X., Wang, Y., and Chen, L. (2017). Enhanced emulsifying properties of wood-based cellulose nanocrystals as Pickering emulsion stabilizer. Carbohydr. Polym. 169, 295–303. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.04.024
Hassan, S. S., Williams, G. A., and Jaiswal, A. K. (2018). Emerging technologies for the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 262, 310–318. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.099
Huang, S., Lv, J., Liu, X., Yuan, H., Wang, Y., Huan, S., et al. (2025). Sustainable and green design of beeswax-based Pickering emulsion coating for food packaging. J. Clean. Prod. 495:145096. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2025.145096
Jiang, W., Lei, X., Rao, Z., Zhao, J., Zeng, K., and Ming, J. (2025). Stable Pickering emulsions of cinnamaldehyde formulated using tannic acid-assisted cellulose nanofibers and applied for mango preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 290:139135. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.139135
Jiang, Y., Zhu, Y., Li, F., Du, J., Huang, Q., Sun-Waterhouse, D., et al. (2020). Antioxidative pectin from hawthorn wine pomace stabilizes and protects Pickering emulsions via forming zein-pectin gel-like shell structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 151, 193–203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.164
Jung, J., Deng, Z., and Zhao, Y. (2020). Mechanisms and performance of cellulose nanocrystals Pickering emulsion chitosan coatings for reducing ethylene production and physiological disorders in postharvest ‘Bartlett' pears (Pyrus communis L.) during cold storage. Food Chem. 309:125693. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125693
Kamel, R., El-Wakil, N. A., Dufresne, A., and Elkasabgy, N. A. (2020). Nanocellulose: from an agricultural waste to a valuable pharmaceutical ingredient. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 163, 1579–1590. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.242
Lagaly, G., Reese, M., and Abend, S. (1999). Smectites as colloidal stabilizers of emulsions. Appl. Clay Sci. 14, 83–103. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1317(98)00051-9
Li, G., Wang, T., Wei, Q., Jin, Z., Han, H., Zhu, H., et al. (2025). Effects of sophorolipids and coconut wax incorporation on the physical, structural, and antibacterial properties of cellulose nanofibers-based Pickering emulsion for cherry tomato preservation. Food Chem. 475:143345. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143345
Lin, M. G., Lasekan, O., Saari, N., and Khairunniza-Bejo, S. (2017). The effect of the application of edible coatings on or before ultraviolet treatment on postharvested longan fruits. J. Food Qual. 2017, 1–11. doi: 10.1155/2017/5454263
Liu, B., Zhu, Y., Tian, J., Guan, T., Li, D., Bao, C., et al. (2019). Inhibition of oil digestion in Pickering emulsions stabilized by oxidized cellulose nanofibrils for low-calorie food design. RSC Adv. 9, 14966–14973. doi: 10.1039/C9RA02417D
Lu, Y., Li, J., Ge, L., Xie, W., and Wu, D. (2021). Pickering emulsion stabilized with fibrous nanocelluloses: insight into fiber flexibility-emulsifying capacity relations. Carbohydr. Polym. 255:117483. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117483
Ma, W., Wang, J., Xu, X., Qin, L., Wu, C., and Du, M. (2019). Ultrasound treatment improved the physicochemical characteristics of cod protein and enhanced the stability of oil-in-water emulsion. Food Res. Int. 121, 247–256. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.03.024
Mahapatra, A., Dhakane-Lad, J., Patil, S., et al. (2024). Amelioration of sodium alginate-CNC edible coating with thyme and/or clove essential oil for post-harvest quality of guava. Food Meas. 18, 5281–5296. doi: 10.1007/s11694-024-02565-z
Monégier du Sorbier, Q., Aimable, A., and Pagnoux, C. (2015). Influence of the electrostatic interactions in a Pickering emulsion polymerization for the synthesis of silica-polystyrene hybrid nanoparticles. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 448, 306–314. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.02.017
Napso, S., Rein, D. M., Fu, Z., Radulescu, A., and Cohen, Y. (2018). Structural analysis of cellulose-coated oil-in-water emulsions fabricated from molecular solution. Langmuir 34, 8857–8865. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01325
Nkede, F. N., Wardak, M. H., Wardana, A. A., Fanze, M., Yan, X., Jothi, J. S., et al. (2024). Preparation and characterization of edible coating and film composed of sodium alginate/ylang-ylang oil/cellulose nanocrystals Pickering emulsion and its application to post-harvest control of mandarin (Citrus reticulata). Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 691:133859. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2024.133859
Nkede, F. N., Wardana, A. A., Phuong, N. T. H., et al. (2023). Preparation and characterization of chitosan/lemongrass oil/cellulose nanofiber Pickering emulsions active packaging and its application on tomato preservation. J. Polym. Environ. 31, 4930–4945. doi: 10.1007/s10924-023-02885-z
Phanthong, P., Reubroycharoen, P., Hao, X., Xu, G., Abudula, A., and Guan, G. (2018). Nanocellulose: extraction and application. Carbon Resour. Convers. 1, 32–43. doi: 10.1016/j.crcon.2018.05.004
Rampazzo, R., Alkan, D., Gazzotti, S., Ortenzi, M. A., Piva, G., and Piergiovanni, L. (2017). Cellulose nanocrystals from lignocellulosic raw materials, for oxygen barrier coatings on food packaging films. Packag. Technol. Sci. 30, 645–661. doi: 10.1002/pts.2308
Ramsden, W. (1903). Separation of solids in the surface-layers of solutions and suspensions (observations on surface-membranes, bubbles, emulsions, and mechanical coagulation). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 72, 156–164. doi: 10.1098/rspl.1903.0034
Riaño, C., Ribba, T., Marchant, J. I., 'Brien, J. A., Contreras, C., and Zoffoli, J. P. (2022). Ultra-low oxygen and preconditioning storage regulate ethylene synthesis to prevent corky disorders in ‘Fuji' apple. Front. Plant Sci. 13:910139. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.910139
Rosenbloom, R. A., Wang, W., and Zhao, Y. (2020). Delaying ripening of ‘Bartlett' pears (Pyrus communis) during long-term simulated industrial cold storage: mechanisms and validation of chitosan coatings with cellulose nanocrystals Pickering emulsions. LWT 122:109053. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109053
Seo, S.-M., Lee, J. W., Shin, J., Tak, J. H., Hyun, J., and Park, K. (2021). Development of cellulose nanocrystal-stabilized Pickering emulsions of massoia and nutmeg essential oils for the control of Aedes albopictus. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91442-6
Shah, B. R., Dvorák, P., Velíšek, J., and Mráz, J. (2021). Opening a new gateway towards the applications of chitosan nanoparticles stabilized Pickering emulsion in the realm of aquaculture. Carbohydr. Polym. 265:118096. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118096
Singkhonrat, J., Ovatlarnporn, C., Khan, K. R., Basit, A., Suksuwan, A., Nalinbenjapun, S., et al. (2023). Fabrication of different nanocrystal (CNC)-based coatings for the enhancement of shelf life and quality of minimally processed fruits. Cellulose 30, 11521–11536. doi: 10.1007/s10570-023-05583-0
Taherian, A. R., Britten, M., Sabik, H., and Fustier, P. (2011). Ability of whey protein isolate and/or fish gelatin to inhibit physical separation and lipid oxidation in fish oil-in-water beverage emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 25, 868–878. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.08.007
Tan, H., Zhang, R., Han, L., Zhang, T., and Ngai, T. (2022). Pickering emulsions stabilized by aminated gelatin nanoparticles: are gelatin nanoparticles acting as genuine Pickering stabilizers or structuring agents? Food Hydrocoll. 123:107151. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107151
Teo, S. H., Chee, C. Y., Fahmi, M. Z., Sakti, S. C., and Lee, H. V. (2022). Review of functional aspects of nanocellulose-based Pickering emulsifier for non-toxic application and its colloid stabilization mechanism. Molecules 27:7170. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217170
Trache, D., Tarchoun, A. F., Derradji, M., Hamidon, T. S., Masruchin, N., Brosse, N., et al. (2020). Nanocellulose: from fundamentals to advanced applications. Front. Chem. 8:392. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00392
Trinh, B. M., Smith, M., and Mekonnen, T. H. (2022). A nanomaterial-stabilized starch-beeswax Pickering emulsion coating to extend produce shelf-life. Chem. Eng. J. 431:133905. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133905
Udayanga, D., Manamgoda, D. S., Liu, X., Chukeatirote, E., and Hyde, K. D. (2013). What are the common anthracnose pathogens of tropical fruits? Fungal Divers. 61, 165–179. doi: 10.1007/s13225-013-0257-2
Wang, J., Qin, M., Wang, W., Xia, Y., Wu, G., Deng, H., et al. (2025). Konjac glucomannan/carboxylated cellulose nanofiber-based edible coating with tannic acid maintains quality and prolongs shelf-life of mango fruit. Food Chem. 478:143750. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143750
Wang, L. J., Yin, Y. C., Yin, S. W., Yang, X. Q., Shi, W. J., Tang, C. H., et al. (2013). Development of novel zein-sodium caseinate nanoparticle (ZP)-stabilized emulsion films for improved water barrier properties via emulsion/solvent evaporation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61, 11089–11097. doi: 10.1021/jf4029943
Wardana, A. A., Koga, A., Tanaka, F., et al. (2021). Antifungal features and properties of chitosan/sandalwood oil Pickering emulsion coating stabilized by appropriate cellulose nanofiber dosage for fresh fruit application. Sci. Rep. 11:18412. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98074-w
Wardana, A. A., Wigati, L. P., Van, T. T., Tanaka, F., and Tanaka, F. (2023). Antifungal features and properties of Pickering emulsion coating from alginate/lemongrass oil/cellulose nanofibers. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 58, 966–978. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.16192
Wigati, L. P., Wardana, A. A., Jothi, J. S., Leonard, S., Van, T. T., Yan, X., et al. (2023a). Preserving mandarin quality during ambient storage using edible coatings of pregelatinized corn starch Pickering emulsions and essential oil. Food Biosci. 53, 102710. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102710
Wigati, L. P., Wardana, A. A., Tanaka, F., and Tanaka, F. (2023b). Application of pregelatinized corn starch and basil essential oil edible coating with cellulose nanofiber as Pickering emulsion agent to prevent quality-quantity loss of mandarin orange. Food Packag. Shelf Life 35:101010. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2022.101010
Yan, H., Chen, X., Song, H., Li, J., Feng, Y., Shi, Z., et al. (2017). Synthesis of bacterial cellulose and bacterial cellulose nanocrystals for their applications in the stabilization of olive oil pickering emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 72, 127–135. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.05.044
Yu, K., Xu, J., Zhou, L., Zou, L., and Liu, W. (2021). Effect of chitosan coatings with cinnamon essential oil on postharvest quality of mangoes. Foods 10:3003. doi: 10.3390/foods10123003
Zhang, Y., Pu, Y., Jiang, H., Chen, L., Shen, C., Zhang, W., et al. (2024). Improved sustained-release properties of ginger essential oil in a Pickering emulsion system incorporated in sodium alginate film and delayed postharvest senescence of mango fruits. Food Chem. 435:137534. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137534
Zhao, N., Mou, H., Zhou, Y., Ju, X., Yang, S., Liu, S., et al. (2021). Upgrading solid digestate from anaerobic digestion of agricultural waste as performance enhancer for starch-based mulching biofilm. Molecules 26:832. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040832
Zhou, S., Peng, H., Zhao, A., Yang, X., Lin, D., and Tanaka, F. (2024). Konjac glucomannan-based highly antibacterial active films loaded with thyme essential oil through bacterial cellulose nanofibers/Ag nanoparticles stabilized Pickering emulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 269:131875. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131875
Keywords: nanocomposite, food, lipid, quality, shelf life, packaging, postharvest
Citation: Wardana AA, Marcellino V, Wigati LP, Nkede FN, Tanaka F and Tanaka F (2025) Stabilization of emulsified edible coating using cellulose nanomaterials for fruit preservation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1618714. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1618714
Received: 26 April 2025; Accepted: 28 May 2025;
Published: 07 July 2025.
Edited by:
Norma E. Marcovich, Universidad Nacional de Mar del Plata, ArgentinaReviewed by:
Shahzad Zafar Iqbal, Government College University, Faisalabad, PakistanCopyright © 2025 Wardana, Marcellino, Wigati, Nkede, Tanaka and Tanaka. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ata Aditya Wardana, YXRhLndhcmRhbmFAYmludXMuYWMuaWQ=
 Ata Aditya Wardana
Ata Aditya Wardana Vincensius Marcellino1
Vincensius Marcellino1 Francis Ngwane Nkede
Francis Ngwane Nkede