- Business School of Liaocheng University, Liaocheng, China
Introduction: Promoting the coupled and coordinated development of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization is a key link and an inevitable choice to achieve the goal of “double carbon” and sustainable rural development.
Methods: This study takes 31 provinces (cities) in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan) from 2010 to 2022 as the research object, and adopts the entropy value method, the coupling coordination degree model, the Gini coefficient and its decomposition, and the convergence degree model, etc., to analyze the level of coupling coordination between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in terms of spatial and temporal development characteristics, regional differences and convergence.
Results and discussion: The study found that: (1) the coupling and coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization at the national level and in the four major regions continues to improve, and the type of coupled coordination in the provinces is dominated by “primary coordination” in 2022; (2) inter-regional differences are the main source of differences in the coupling and coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in China; (3) There is no σ-convergence in the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization at the national level, but there are significant absolute β-convergence and conditional β-convergence, and there are some differences in the regional convergence characteristics, and there is obvious regional heterogeneity in the development of external factors on the coupled coordination level in different regions. The results of the study provide strong empirical support and important practical guidance for an in-depth understanding of the current situation and trend of the coupled and coordinated development of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization, in order to explore effective ways to promote the synergistic progress of the two.
1 Introduction
Rural revitalization is an important strategy to realize the modernization of agriculture and rural areas, and a key initiative to promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas and the promotion of common prosperity.2025, the “Central Document No. 1” once again emphasized the importance of rural revitalization, pointing out that it is necessary to comprehensively promote the revitalization of the rural industry, human resources, culture, ecology, and organization, and accelerate the modernization of agriculture and rural areas. The process of modernization of agriculture and rural areas has been accelerated. In recent years, China’s rural revitalization has achieved remarkable results, with rural infrastructure constantly improving, farmers’ incomes continuing to grow, and the level of rural governance steadily improving. However, in the process of rural revitalization, the large-scale and intensive development of agricultural production has also brought about rapid growth in agricultural carbon emissions. According to the data of “2023 China Agricultural and Rural Low Carbon Development Report,” the total agricultural carbon emission in China has reached 828 million tons in 2023 (Mei et al., 2024). Agricultural carbon emission not only exacerbates global climate change, but also poses a serious challenge to rural ecological environment and sustainable development, and becomes an important obstacle to comprehensively promote rural revitalization. In this context, how to achieve the agricultural carbon emission reduction target and realize the green and low-carbon transformation of agriculture while implementing the rural revitalization strategy has become an important issue to be urgently solved.
2 Literature review
With regard to the research on agricultural carbon emission reduction, the academic community mainly focuses on the following three dimensions: first, research on the measurement of agricultural carbon emissions. Scholars have mostly used the carbon emission factor method to calculate the total agricultural carbon emissions based on their corresponding carbon emission coefficients from a single perspective such as agricultural material inputs, energy consumption, crop cultivation, livestock and poultry breeding and straw burning, or from a comprehensive perspective covering multiple carbon sources (Tian and Hao, 2022; Lu et al., 2025). The second is the research on the factors affecting carbon emission reduction in agriculture. Existing studies have found through empirical analysis that the digitization of agriculture (Shi, 2025), the transfer of rural labor force (Huang et al., 2025), the level of awareness of low-carbon technologies among farmers (Yao et al., 2023), the removal of pollutants (Sulaiman et al., 2025), and Circular and integrated farming in agriculture & farming (Poddar, 2024) contribute significantly to agricultural carbon emission reduction. Third, research on the potential of agricultural carbon emission reduction. Some scholars have assessed and analyzed the level of agricultural carbon emission reduction potential in various provinces and regions based on the dual perspective of equity and efficiency, and found that there is a large difference in the cost of carbon emission reduction between regions, and that the level of agricultural carbon emission reduction potential in a region is not only affected by its own economic and industrial conditions, but also closely related to the environment it is located in and the development of the neighboring regions (Wu et al., 2015). At the national level, the agricultural production sector is capable of realizing the expected carbon emission reduction targets committed by the government (Tian and Zhang, 2019).
On the study of rural revitalization, academics mainly focus on the following three dimensions: first, the theoretical study of rural revitalization. On the basis of the analysis of the background of the proposed rural revitalization strategy (Zhang et al., 2018), scholars mostly interpret the main meaning, implementation dilemma and realization path of the rural revitalization strategy from the “twenty-word guideline” (Ye, 2018; Xinwen and Guolei, 2018), and believe that the theory of high-quality development, Chinese-style modernization theory, common wealth theory, etc. provide theoretical support for the construction of the theoretical system of rural revitalization (Huang, 2025). Second, the research on the measurement of the level of rural revitalization. In terms of measurement indexes, academics generally take the “Twenty-word Guidelines” as the basis for the design of the first-level indexes (Xu and Wang, 2022; Sun et al., 2023). However, in terms of the selection of second- and third-level indicators, different scholars have constructed distinctive evaluation systems, such as “six-ization, four-rate, three-wind, three-rule, and three-dimensional” according to the differences in research focus (Chen et al., 2018; Jia et al., 2018). In terms of measurement methods, scholars have used different methods such as hierarchical analysis, Delphi method, principal component analysis, entropy value method, etc. to measure the development level of rural revitalization in different regions (Xu and Wang, 2021; Shen et al., 2020; Zheng, 2019; Zhoufu and Fangwei, 2019; Liu and Zhang, 2024). Thirdly, research on the influencing factors of rural revitalization. Through empirical analysis, scholars have found that the level of financial inclusion (Guo et al., 2025), the level of economic development, and industrial agglomeration (Liu and Wang, 2022) are important factors that affect the level of development of rural revitalization.
Research on combining agricultural carbon emission reduction with rural revitalization is slightly insufficient, with academics focusing on incorporating a specific point in the process of rural revitalization, such as agricultural modernization, food security, agricultural economic growth, digital village construction, and ecological environment, into the same framework for coupled and coordinated analyses of agricultural carbon emissions (Xia et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2024a; Sun et al., 2024b; Wang et al., 2024a, 2024b; Chen et al., 2020), and relatively few studies have directly measured the level of coupled coordination between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization (Qi et al., 2023; Guo et al., 2024), which provides ideas for in-depth exploration in this study. In view of this, the possible marginal contributions of this study are the following three points: firstly, incorporating agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization into the same framework, measuring the level of coupling and coordination between the two, and analyzing the spatial and temporal evolution of the two, so as to provide new research perspectives and practices for the subsequent studies; secondly, using the Gini coefficient and its decomposition method to quantify the regional differences in the level of coupling and coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization, and the sources Second, the Gini coefficient and its decomposition method are used to quantify the regional differences and sources of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization, so as to provide empirical support for the formulation of more targeted regional development policies and the realization of inter-regional synergistic development. Third, based on the σ-convergence, absolute β-convergence and conditional β-convergence models, we systematically test the convergence characteristics of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in the “East-Central-West-Northeast-North-East” region, and explore the key factors that promote the convergence of the coupled coordination level of the two, so as to provide policy references for the optimization of regional development paths and the acceleration of the green transformation of agriculture.
3 Coupled coordination mechanisms
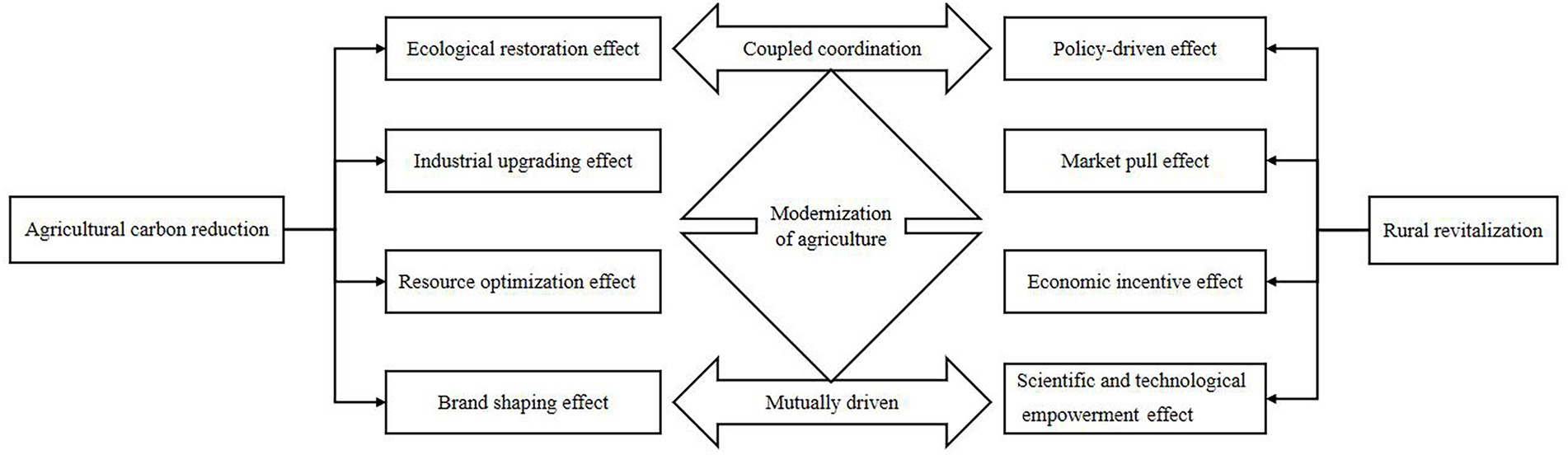
Agricultural carbon emission reduction, as a pivotal component of the process of promoting agricultural and rural modernization, can facilitate the comprehensive implementation of the rural revitalization strategy by promoting industrial upgrading and optimizing resource allocation. The comprehensive promotion of the rural revitalization strategy has engendered more favorable conditions and broader development space for agricultural carbon emission reduction, and the two promote each other and develop together in practice, exhibiting an inherent logic of coordination and mutual promotion. The coupled coordination mechanism of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization is illustrated in Figure 1.
3.1 Carbon emission reduction in agriculture is an important tool for the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy
The role of agricultural carbon emission reduction on rural revitalization is mainly reflected in the following four aspects:
First, the ecological restoration effect: agricultural carbon emission reduction measures can take advantage of the “pollution control-environmental improvement-ecological premium” conduction mechanism to effectively reduce agricultural surface pollution and optimize the rural habitat while enhancing the value of ecological products. This process not only promotes the development of rural tourism, but also feeds back through tourism revenue, so that rural areas have more funds for ecological environmental protection and construction, forming a virtuous cycle of ecology and economic mutual promotion.
Second, the industrial upgrading effect: the implementation of agricultural carbon emission reduction strategy not only drives the flourishing development of green agriculture and extends the agricultural industry chain, but also promotes the development of rural tourism, leisure agriculture and other industries in rural areas. In addition, agricultural carbon emission reduction has led traditional agriculture to move towards resource-saving and environment-friendly modern agriculture, improved agricultural production efficiency, and injected new kinetic energy into the high-quality development of rural industries.
Third, the resource optimization effect: on the one hand, actively promoting energy-saving and low-consumption agricultural machinery and equipment can effectively reduce carbon emissions in the process of agricultural production, and promote the transformation of agriculture in the direction of green and low-carbon. On the other hand, the combination of planting and raising, agriculture and animal husbandry cycle and other circular agricultural models, promote the transformation of the economic value of agricultural waste, and open up new growth points for the rural economy. The synergistic force of the two has injected new vitality into the green development of the rural economy.
Fourth, the branding effect: in today’s consumer trend of focusing on environmental protection and health, the carbon emission reduction-oriented production mode helps shape a unique brand image, meets consumer demand for healthy, green food, and enhances consumer trust and recognition of agricultural products. This trust and recognition directly promotes the return of consumption, improves the competitiveness of agricultural products, and provides sustainable economic security and a development engine for rural revitalization.
3.2 The implementation of the rural revitalization strategy has given strong impetus to the development of carbon emission reduction in agriculture
Rural revitalization plays a major role in agricultural carbon emission reduction in the following four aspects:
First, the policy-driven effect: during the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy, the government has increased the financial investment in rural areas, which can be used to give tax incentives to agricultural production main bodies that take carbon emission reduction measures, in order to reduce the economic threshold of agricultural carbon emission reduction. In addition, in the process of rural revitalization, the government in order to achieve sustainable development of agriculture, will be through the formulation of agricultural carbon emission standards and other policies and regulations to strengthen the supervision of the main body of agricultural production, to promote the standardization of agricultural carbon emission reduction work, institutionalization.
Second, the market pull effect: the in-depth implementation of the rural revitalization strategy has promoted the development of agricultural e-commerce and other emerging industries, expanding the sales channels of low-carbon agricultural products. In order to meet the market demand for low-carbon agricultural products, farmers have to rely on professional organizations to provide carbon emission monitoring and other services in the agricultural production process, which not only promotes the large-scale production of low-carbon agricultural products, but also promotes the flourishing of the carbon emission reduction service market.
Third, the Economic incentive effect: rural revitalization improves farmers’ income by expanding employment channels, etc. The increase in income motivates farmers to actively adopt low-carbon technologies and management modes, thus effectively reducing carbon emissions in the process of agricultural production. Moreover, rural revitalization has attracted a large amount of social capital to low-carbon agriculture, and this social capital has promoted the market-oriented operation of agricultural carbon emission reduction.
Forth, the Scientific and technological empowerment effect: rural revitalization has prompted more scientific research resources to converge on the countryside, driving the popularization of agricultural research results in the field (Yang, 2023), and new agricultural low-carbon technologies have been rapidly applied to agricultural production practices, effectively enhancing the carbon emission reduction efficiency in the agricultural production process. In addition, the construction of digital countryside in the process of rural revitalization provides a new opportunity for agricultural carbon emission reduction. With the help of big data and other information technology, the input status of agricultural production factors can be precisely regulated, realizing the intelligent and refined management of agricultural carbon emission reduction.
4 Methodology
4.1 Description of variables
4.1.1 Construction of the rural revitalization indicator system
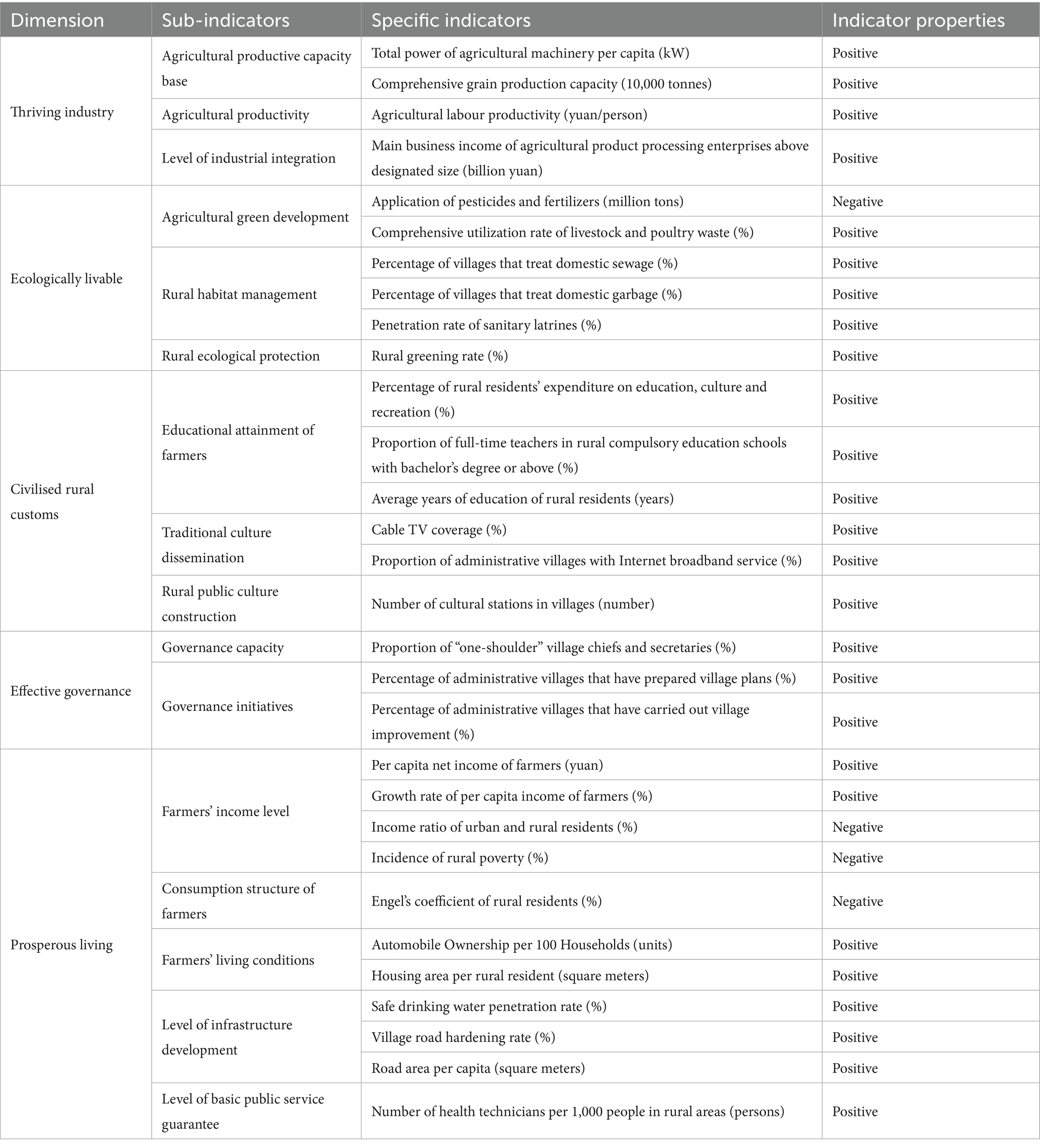
A substantial corpus of research on rural revitalization has emerged in academic circles. The majority of scholars in this field employ the “twenty-word policy” as a metric for evaluating and analyzing the indicators of rural revitalization. This study aligns with the research of Xu Xue, Zhao Jincai, and other scholars (Xu and Wang, 2022; Zhao et al., 2024), and employs a selection of 29 indicators from the five dimensions of industrial prosperity, ecological livability, civilized countryside, effective governance, and affluent life to construct an evaluation index system of rural revitalization, as illustrated in Table 1.
4.1.2 Measurement of carbon emission reductions in agriculture
There are four main categories of agricultural carbon emission sources: first, agricultural input substances, mainly including carbon emissions directly or indirectly caused by diesel fuel, fertilizers, pesticides, agricultural films, irrigation and tilling in the process of agricultural production; second, crop cultivation, mainly considering the N2O gas generated by six crops, namely, corn, soybeans, vegetables, rice, winter wheat and spring wheat, through soil respiration in the process of production, as well as the rice production process CH4 gas due to root anaerobicity; three is livestock and poultry farming, mainly examining the CH4 and N2O gas generated through enteric fermentation and manure management of the four major livestock species of cattle, sheep, hogs, and poultry in the process of farming, with its average annual feeding volume adjusted according to the amount of each species out of the pen, the average life cycle, and end-of-the-year stocking; and four is straw incineration, and as of 2023, China’s straw comprehensive utilization rate More than 88%,1 straw burning has been effectively banned and transformed into a highly utilized resource, so on the basis of reference to existing studies, considering the actual characteristics of China and data availability, this study mainly examin.es the carbon emissions directly or indirectly caused by the three aspects of agricultural input materials, crop cultivation and livestock and poultry breeding, and uses the relevant carbon emission coefficients to measure the agricultural carbon emissions. Agricultural carbon emission reduction is calculated by taking the negative value of agricultural carbon emission. The specific formula for calculating agricultural carbon emission reduction is shown in Equations 1–3:
In this study, CE denotes the total amount of agricultural carbon emissions, CEi denotes carbon emissions from the ith source of agricultural carbon, Ti denotes the input of the ith carbon source, εi denotes the carbon emission coefficient of the ith source, CI denotes the agricultural carbon emissions, and CA denotes the agricultural carbon emission reduction. Combined with the assessment report released by IPCC in 2013, this study evaluates China’s agricultural carbon emissions by converting all types of greenhouse gases into standard CO2 according to the conversion relationship of 1 t(CH4) = 25 t(CO2) and 1 t(N2O) = 298 t(CO2).
4.2 Data sources
The present study is predicated on panel data from 31 provinces (municipalities) in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan) from 2010 to 2022. The data were obtained from the China Rural Statistical Yearbook and the China Agricultural Products Processing Industry. Yearbook, China Urban and Rural Construction Statistical Yearbook, China Education Statistical Yearbook, China Social Statistical Yearbook, China Tertiary Industry Statistical Yearbook, China Civil Affairs Statistical Yearbook, China Population and Employment Statistical Yearbook, and statistical yearbooks of provinces, Wind Database, China Knowledge Patent Database, and so on. Employment Statistics Yearbook” and provincial statistical yearbooks, China’s economic and social big data research platform, Wind database, China Knowledge Network patent database, etc. For individual missing data, the interpolation method was used to fill in the blanks.
4.3 Research methods
4.3.1 Entropy value method
Considering that the entropy value method has the advantages of high precision and objectivity (Xu and Wang, 2021), this study applies the entropy value method to measure the proportion of agricultural carbon emissions and rural revitalization in the rural revitalization index system and the coupled coordination model. The specific calculation steps as shown in Equations 4–10:
Step 1: Indicator standardization and non-negative leveling, where i = 1…n; j = 1…m.
Step 2: Calculate the weights of the indicators.
4.3.2 Coupling coordination degree model
In order to objectively reflect the coordinated development status of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization, the coupling coordination degree model is introduced for measurement. The larger the degree of coupling coordination (D), the better the development of the coupling coordination between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization. The calculation formula is as shown in Equations 11–13:
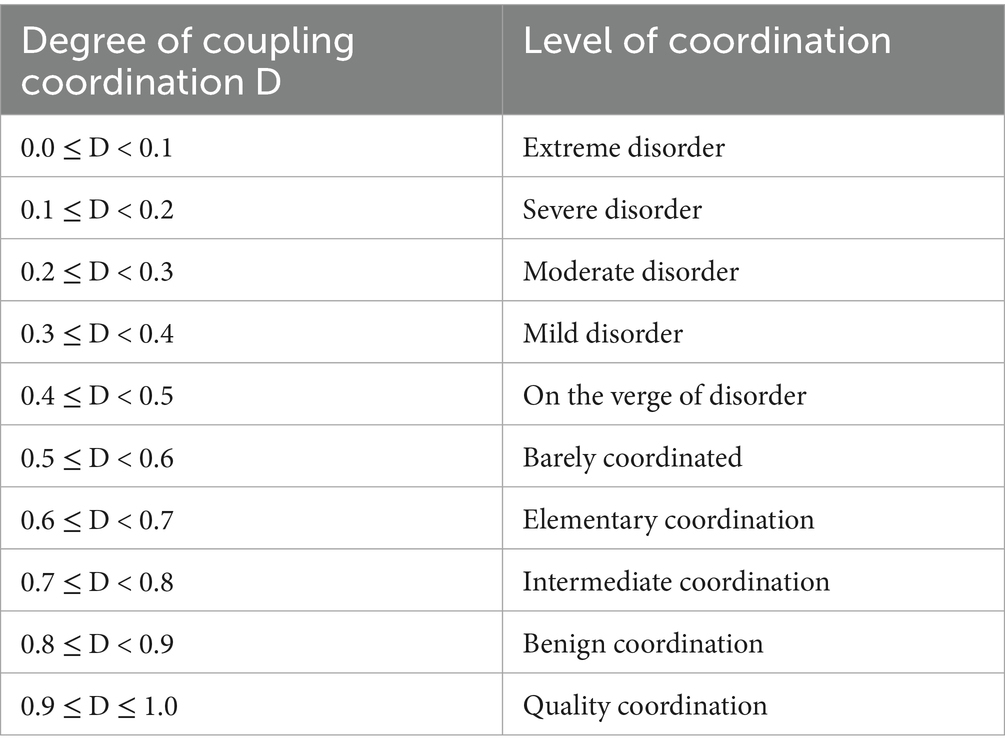
The following variables are of particular relevance in this study: C (U1, U2) denotes the coupling degree, U1 represents the rural revitalization index, and U2 signifies the agricultural carbon emission reduction. T is the comprehensive coordination index, while D is the coupling coordination degree. It is imperative to note that “α” and “β” are the contributions of the two subsystems to the overall level of development. In order to avoid the arbitrariness of the subjective empowerment, this study is carried out with the help of the entropy method for the determination of the value of α and β. After calculation, α and β are taken as the value of 0.954 and 0.046, respectively. To more intuitively reflect the coupling coordination status of each region, drawing on the practice of existing studies (Zhao and Zhang, 2022), the coupling coordination degree type is divided into levels, as shown in Table 2.
4.3.3 Gini coefficient and its decomposition
The Gini coefficient and its decomposition method, as proposed by Dagum, are the foundation for measuring regional differences in the level of coupled coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in China. The calculation formula is shown in Equation 14:
In this study, Dij and Dvr are used to denote the coupling coordination level of province j in region i and province r in region v, respectively. The term “D” is used to denote the mean value of the coupling coordination level of each province. The number of provinces is denoted by “n,” the number of dividing districts by “k,” and the number of provinces contained within regions i and v by “ni” and “nv,” respectively.
4.3.4 Convergence degree model
4.3.4.1 Σ convergence
This study aligns with prevailing literature by employing the coefficient of variation to ascertain whether the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization exhibits a σ-convergence characteristic. That is, it determines whether the discrete degree of the coupled coordination level among provinces demonstrates a decreasing trend over time. The calculation formula is shown in Equation 15:
In this study, the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization of the jth province in region i is denoted by Dij, the mean value of the coupled coordination level of each province in region i is denoted by Di, and the number of provinces in region i is denoted by ni.
4.3.4.2 Absolute β-convergence
This econometric approach is employed to ascertain whether there is a tendency for the temporarily lagging regions to catch up with the temporarily leading regions in the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization, and whether the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization of each province can be converged with the passage of time (Qin et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2024a, 2024b). The calculation formula is shown in Equation 16:
In this study, we explore the annual growth rate of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in the ith region from t to t + 1, denoted by ln(Di,t + 1/Dit). We also examine the significance level test, which indicates the existence of absolute β convergence and vice versa, as well as the area effect, denoted by μi, the time effect, denoted by ηt, and the random disturbance term, denoted by εit. This disturbance term obeys the assumption of independent homogeneous distribution. The significance level test indicates the existence of absolute β convergence, and vice versa, there is absolute β dispersion. ui is the area effect, ηt denotes the time effect, and εit is the random disturbance term obeying the assumption of independent homogeneous distribution.
4.3.4.3 Conditional β-convergence
Conditional β-convergence signifies that subsequent to the incorporation of a series of control variables, the level of coupled coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in each region ultimately converges to the respective steady-state level. The calculation formula is shown in Equation 17:
In this study, the parameter to be estimated for each control variable is denoted by λ. The term “Control” refers to a series of control variables, “j” denotes the jth control variable, and “n” indicates the total number of control variables. The control variables selected for analysis include the land transfer rate (Land), the level of financial support for agriculture (Fin), the structure of the agricultural industry (Ais), the strength of environmental regulation (EI), and the amount of patent authorization (Pat). The land transfer rate (Land) is expressed as the ratio of the area of family-contracted arable land transferred to the area of family-contracted arable land. The level of financial support for agriculture (Fin) is expressed in terms of provincial expenditures on agriculture, forestry and water affairs. The structure of the agricultural industry (Ais) is expressed as the ratio of the plantation output value to the total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery. The environmental regulation (EI) is expressed as the ratio of the word frequency of the word “environmental protection” in the annual government work report of each province to the total word frequency of the text (Chen and Chen, 2018). The amount of patent authorization (Pat) is expressed as the number of agricultural science and technology patents authorized in logarithmic form.
5 Analysis of the temporal and spatial evolution of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization
5.1 Time-series changes in the level of coupled coordination between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization
The present study measured the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in 31 provinces (cities) in China from 2010 to 2022. The average value of each region was calculated, and the results are shown in Figure 2, the eastern region exhibits the highest level of coordination, and the overall coordination level of the entire country exhibits a steady growth trend,the coupling coordination level in the central region is close to the overall national level; and the coordination level in the western region and the northeastern region is still lower than the average coordination level of the whole country, although the level of the western region and the northeastern region has improved. During the study period, the fastest growth rate in the level of coupling coordination was observed in the eastern region, at 30.41%. This development trend may be attributed to the combined effect of the following three key factors: first, favorable geographical conditions provide natural convenience for the development of modern agriculture and the promotion of low-carbon technologies; second, a perfect infrastructure system not only reduces the implementation cost of clean agricultural production, but also promotes the development of new industries such as rural tourism by improving transportation conditions; third, a mature industrial structure effectively promotes the green agricultural Third, the mature industrial structure effectively promotes the green transformation of agriculture and the integrated development of rural industries. With these advantages, the eastern region has always maintained a leading position in the coordinated development of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
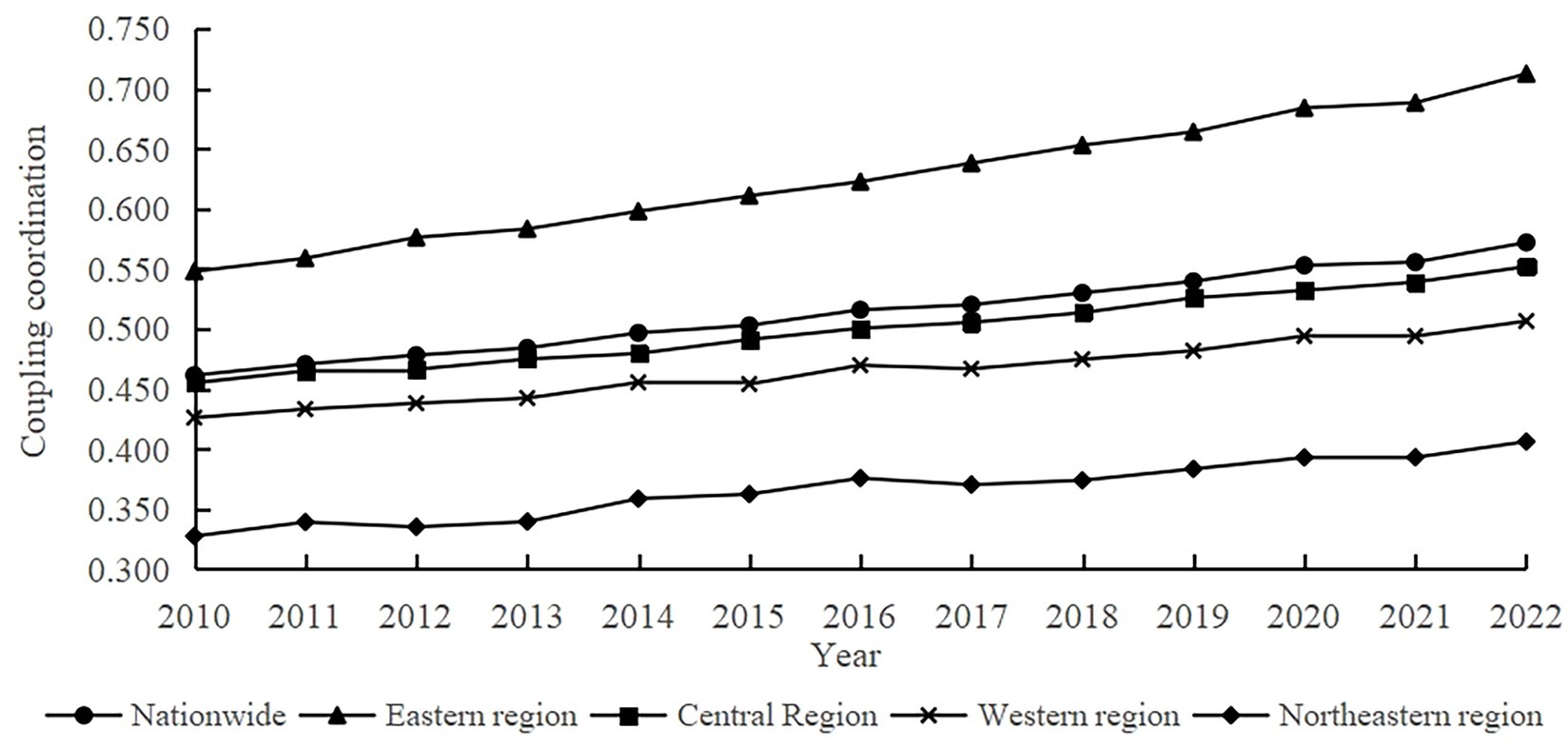
Figure 2. Evolution trend of the coupling and coordination level of rural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
5.2 Spatial pattern of coupled coordination types of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization
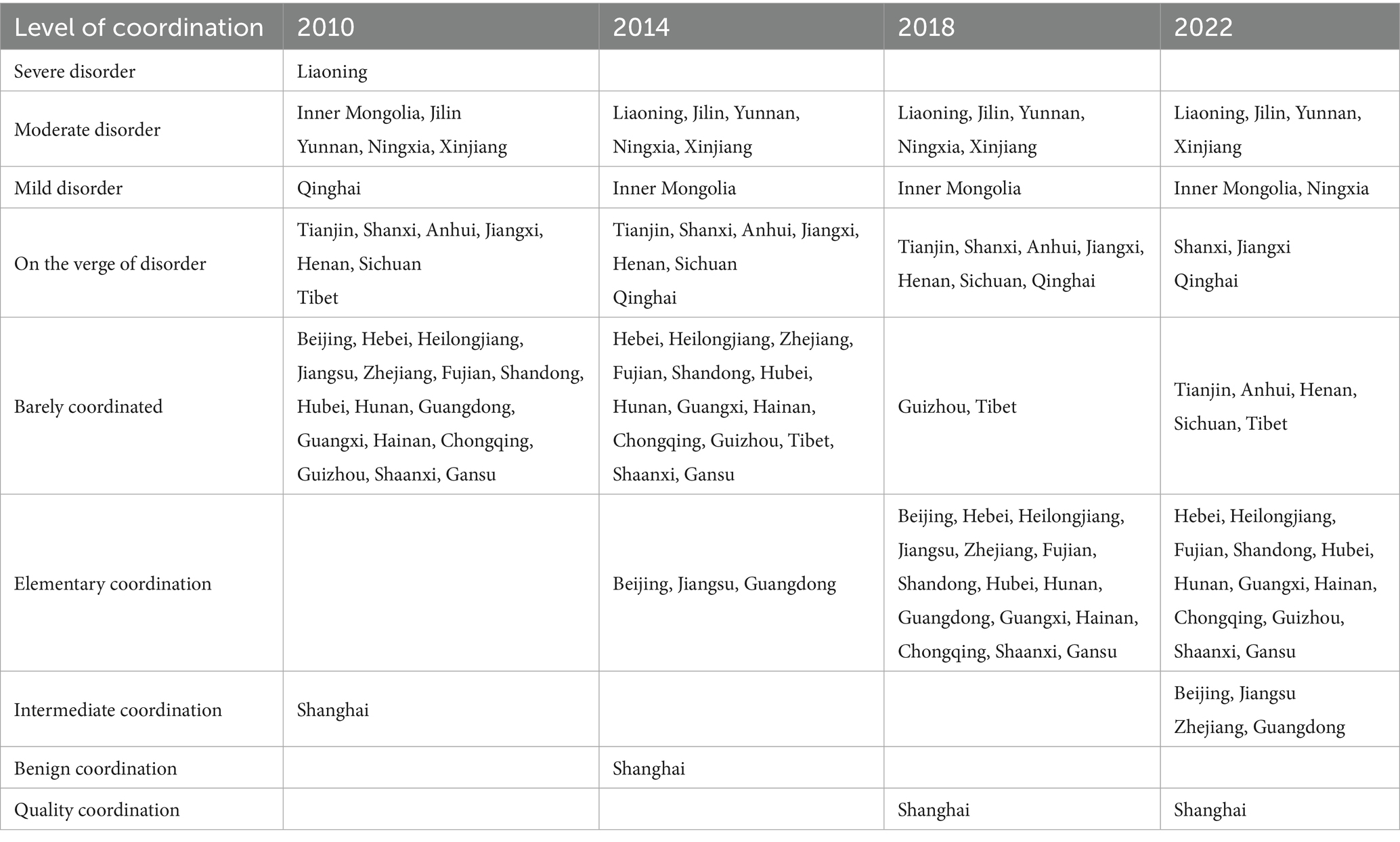
In this study, with reference to the classification criteria of the coupling coordination level in Table 2, the study interval was expanded with a 4-year interval, mainly examining the spatial evolution pattern of the coupling coordination type of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in 31 provinces (cities) in China in the years of 2010, 2014, 2018 and 2022, and the results are shown in Table 3.
By year: in 2010, China’s agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization coupling coordination rank was mainly barely coordinated (16 provinces) and on the verge of becoming dysfunctional (7 provinces-2022), the Quality Rural Initiative and other policies are implemented and optimized, a large number of provinces at the barely coordinated level are transformed into the primary coordination level. In 2022, most of the provinces in China are at the primary coordination level and above, and China’s agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization coupling coordination level evolves to be dominated by primary coordination (12 provinces), barely coordinated (5 provinces).
In terms of sub-provinces, Shanghai is the only city in China where the coupled coordination grade of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization has reached high-quality coordination,largely due to its unique economic advantages and sustainable development strategy. First, Shanghai, as the largest economic center in China, has strong economic strength and scientific and technological innovation capacity, which provides a solid material foundation and technical support for low-carbon transformation and rural revitalization in rural areas; second, Shanghai pays attention to the construction of rural ecological networks, and enhances the carbon sink function of the countryside through the construction of rural eco-rivers and lakes, eco-corridors, and public welfare eco-forests and other key projects, and these ecological networks are capable of absorbing and storing large amounts of carbon dioxide, effectively reducing agricultural carbon emissions while promoting the construction of Shanghai’s eco-livable environment, thus promoting the coordinated development of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
6 Spatial differences in the level of coupled coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization
6.1 Overall and intra-regional differences
In order to further explore the regional differences in the degree of coordination between the coupling of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization and their sources, this study examines the development process of the level of coordination between the two couplings and the gaps between the two couplings in four major regions, namely, the East, the Middle East, the West, and the Northeast, and the results are shown in Table 4. Table 4 shows that the Gini coefficient of the coupling and coordination level of the two increased from 0.147 to 0.162 during the sample period, indicating that the spatial differences in the coupling and coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in each province (city) in China are expanding. Among the four regions, the Gini coefficients of the coupling and coordination levels of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in the three regions of the East, Middle East and West all show a fluctuating upward trend, with the annual average value of the Gini coefficient of the Central Region being the lowest among the four regions, at 0.070. The Gini coefficients of the coupling and coordination levels of the two in the Northeast Region show a fluctuating downward trend, but the average value of the Gini coefficients is still higher than the overall Gini coefficient average, which shows that although the development gap between the coupling and coordination levels of provinces in the Northeast Region is gradually decreasing, the intra-regional differences are still higher than the overall differences.
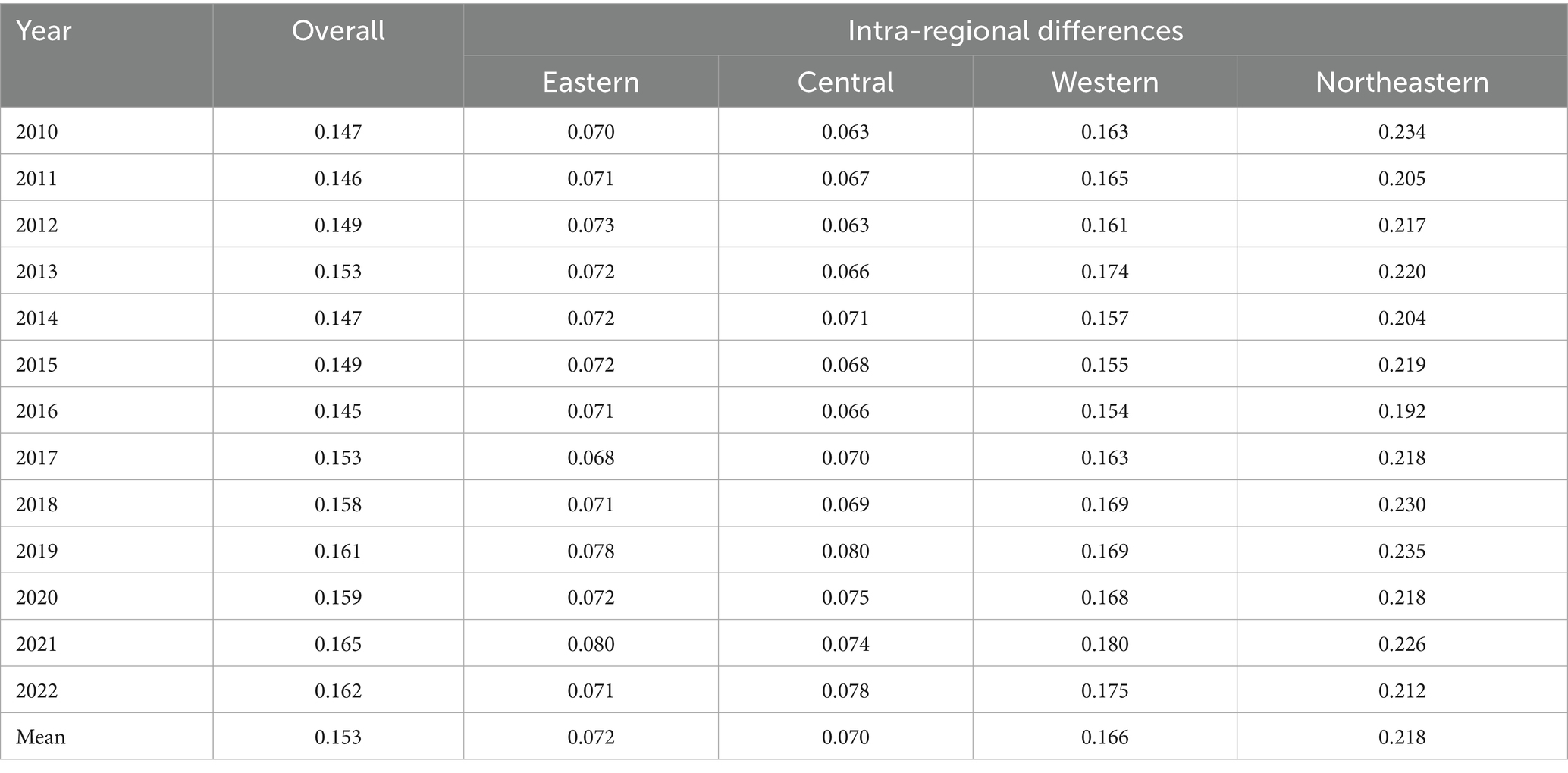
Table 4. Overall and intra-regional Gini coefficient results for China’s four major regions, 2010–2022.
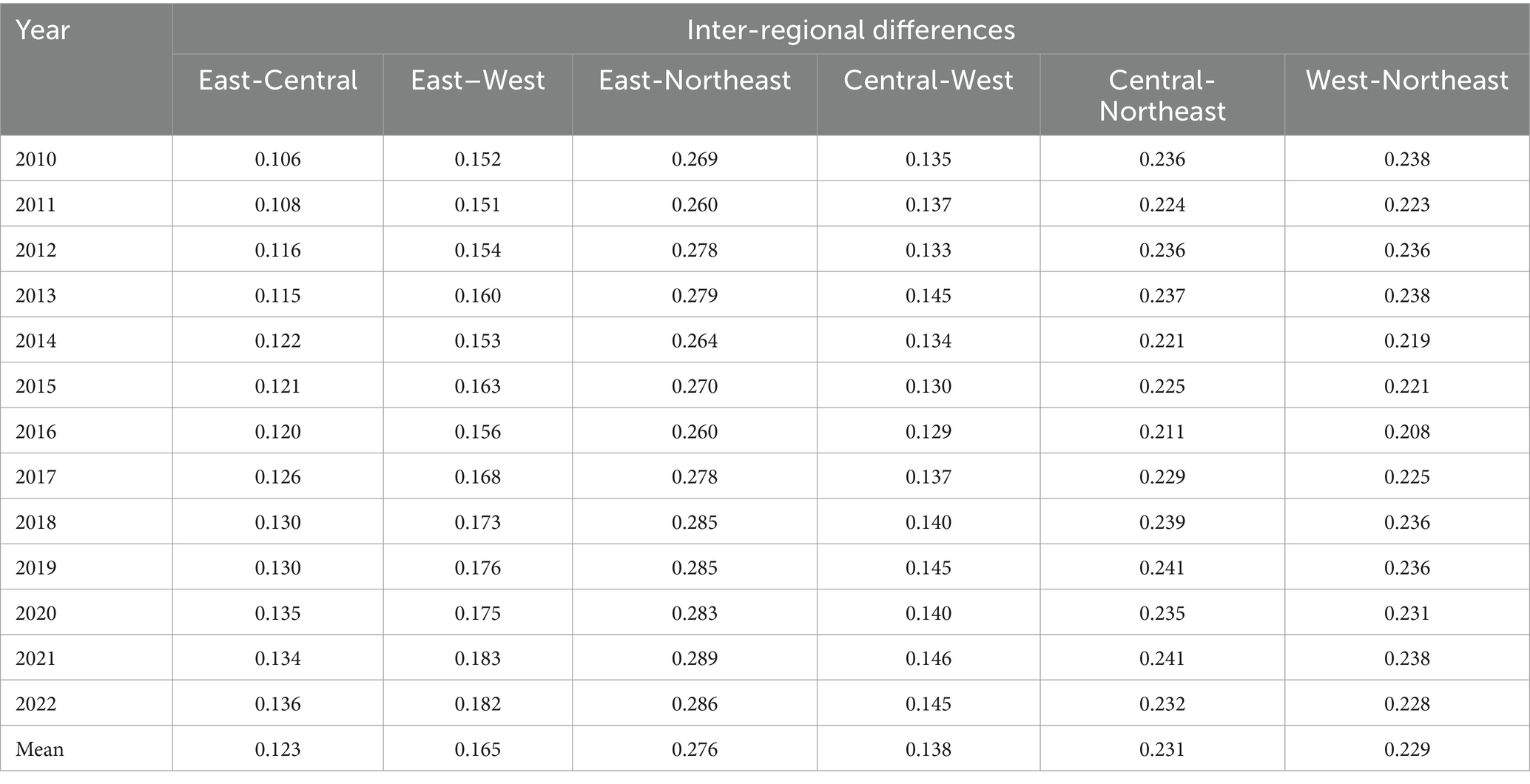
6.2 Inter-regional differences
Using the decomposition method of the Gini coefficient, we explored the differences in the level of coordination of the coupling of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization among the four major regions of “East-Central-West-Northeast,” and the results of the decomposition are shown in Table 5. As shown in Table 5, the average value of Gini coefficient between regions is in descending order: East-Northeast (0.276) > Central-Northeast (0.231) > West-Northeast (0.229) > East–West (0.165) > Central-West (0.138) > East-Central (0.123). This result shows that the difference in the level of coupled and coordinated development between the Northeast and other regions is more pronounced compared to the difference between non-Northeast regions. Among them, the imbalance between the East and the Northeast is particularly prominent (Zhao and Zuo, 2023), and it is important to focus on solving the problem of imbalance between the Northeast and other regions in the future.
6.3 Sources and contributions of regional differences
The Gini coefficient decomposition method is employed to ascertain the sources of variation in the coupled coordination level of China’s agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization. The results are presented in Table 6. As illustrated in Table 6, the disparities in the coupling and coordination levels between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in China primarily stem from the inter-regional gap (Gb), with a mean value of 0.088, accounting for 57.615%. This is followed by The intra-regional gap (Gw), with a mean value of 0.036, accounting for 22.561%; and hypervariable density (Gt), with a mean value of 0.029, accounting for 19.155%. The decomposition results show that the inter-regional disparity is the main reason affecting the differences in the level of coupled coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in China, and in the future, to reduce the regional differences in the level of coupled coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization, we should focus on reducing the inter-regional disparity, and then achieve the coordinated development of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization on the national level.
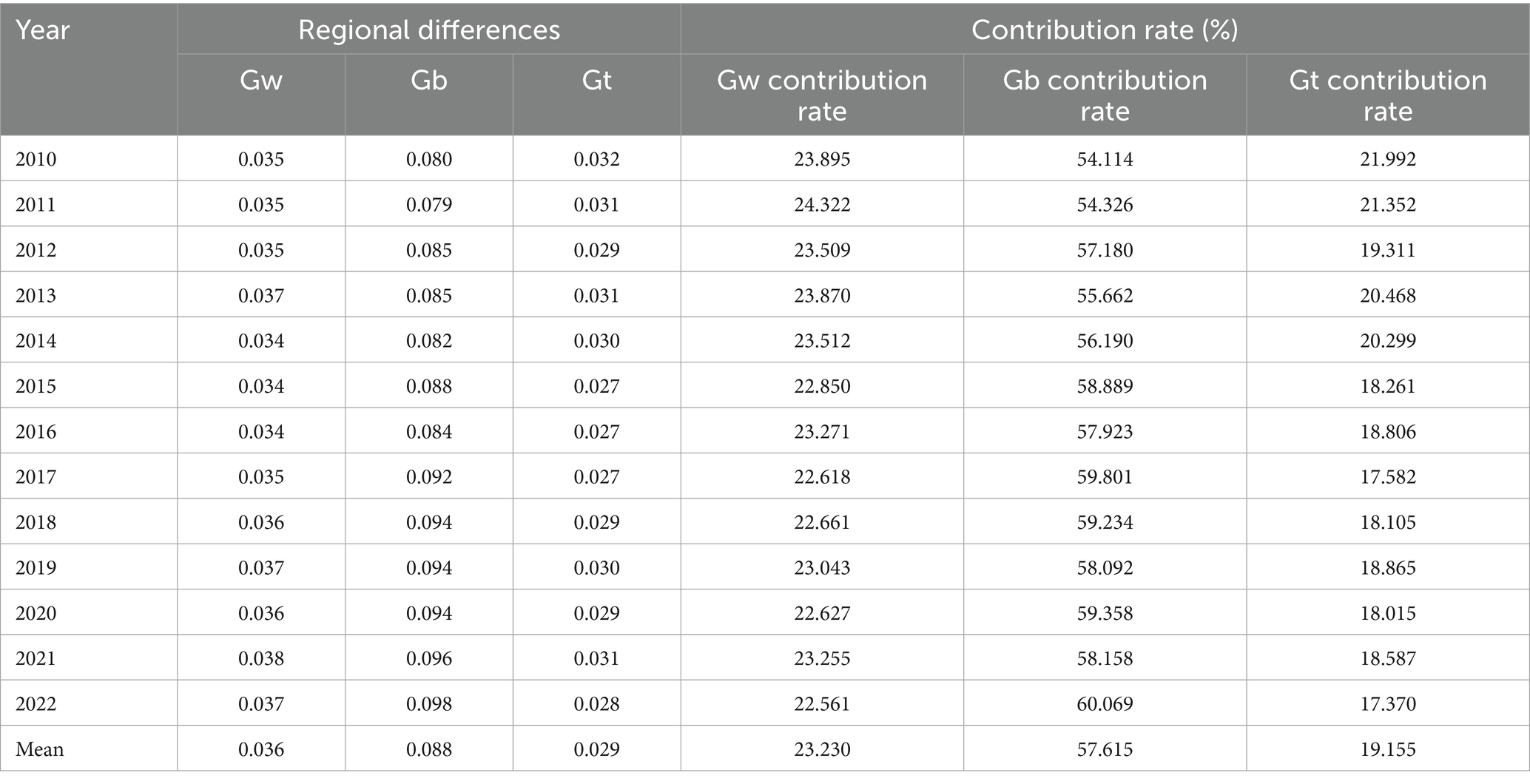
Table 6. Decomposition of differences in the level of coupled coordination among China’s four major regions, 2010–2022.
7 Convergence analysis of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization
7.1 Σ-convergence
In this study, the coefficient of variation method was used to conduct a σ convergence test for the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization from 2010 to 2022 for the whole country and the four major regions, and if the end value of the coefficient of variation during the sample period is smaller than the beginning value, there is a σ convergence; conversely, there is a σ divergence. The results are shown in Figure 3. During the sample period, the coefficient of variation at the national level shows a trend of “horizontal fluctuation - gentle increase,” with an increase of 9.35%, and there is no σ convergence, that is, the gap between the level of coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization coupling in various provinces (cities) of China has been widening (Xu et al., 2023a). Specifically, the coefficient of variation in the eastern region shows a small decrease, with a decrease of only 0.62%; the coefficient of variation in the central region and the eastern region shows a spatial distribution of “central region < eastern region” before 2019, and basically flat from 2019 onwards, with an increase of 23.70% in the coefficient of variation in the central region; the coefficient of variation in the western region increases by 23.70%; the coefficient of variation of the western region has a similar trajectory to the overall coefficient of variation of the whole country, with a small fluctuation of 7.52% during the observation period; the coefficient of variation of the northeastern region has the largest fluctuation, with a decrease of 3.87%, and there is a significant σ-convergence, that is, the gap between the level of coordination of the coupling between the agricultural carbon emission reduction and the revitalization of the countryside within the region is narrowing. The results of the analysis of σ-convergence are consistent with the results of the previous Dagum Gini coefficient analysis.
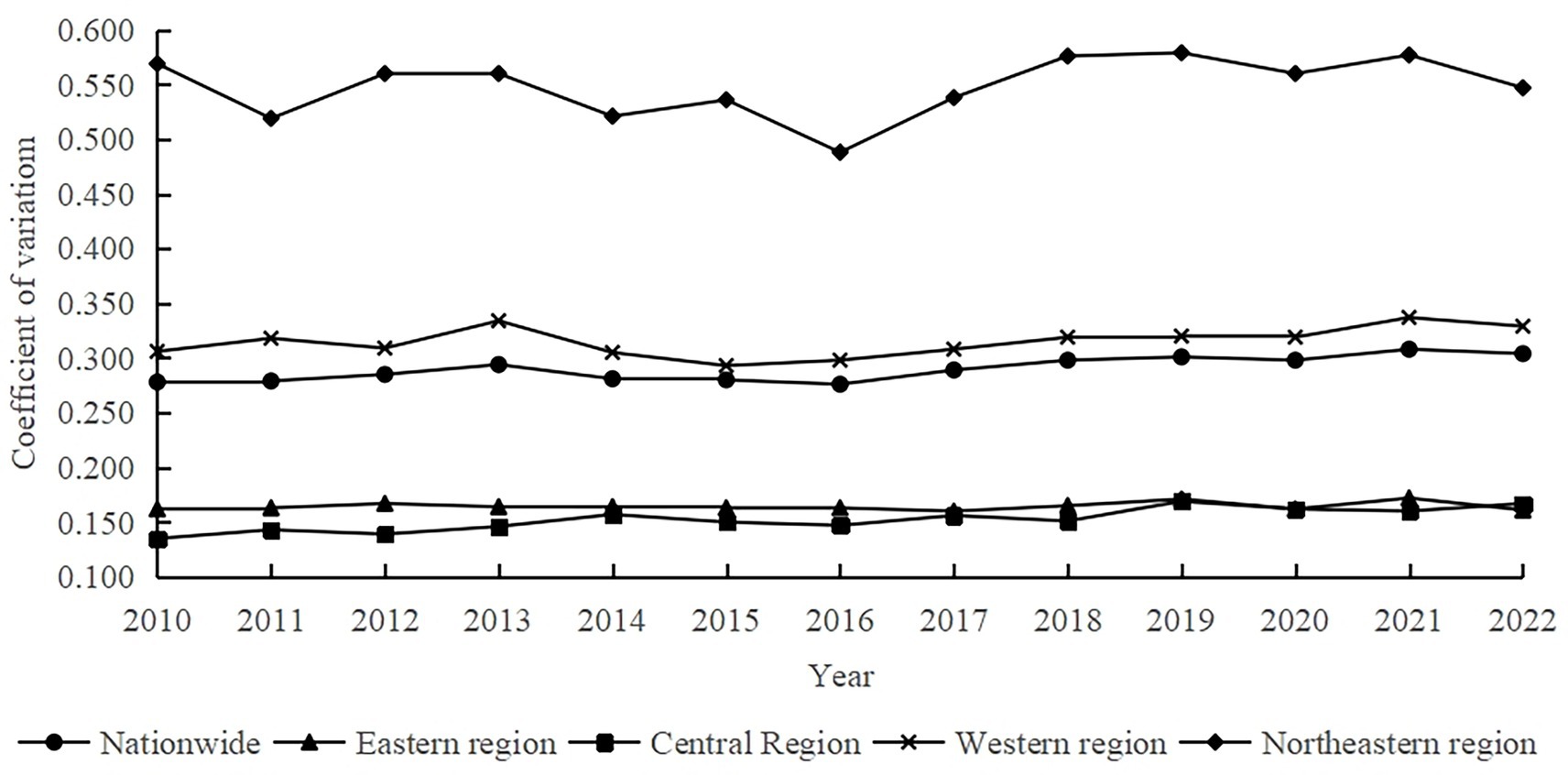
Figure 3. The trend of coupling and coordination level σ convergence of rural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
7.2 β-convergence
7.2.1 Spatial correlation analysis
Prior to the assessment of β convergence, an examination of the spatial correlation of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization is conducted, and the global Moran’s I index of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in China from 2010 to 2022 is measured using Stata software. The results are presented in Table 7. During the study period, the Moran’s I indexes of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization all passed the 10 and 5% significance test, indicating that there is a significant positive spatial correlation between the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in China, which manifests itself as a strong spatial clustering phenomenon (Xie et al., 2024). From the trend of change, the Moran’s I index of the level of coordination of the two couplings shows a fluctuating upward trend, indicating that the spatial correlation of the degree of coordination of the two couplings has been strengthened, and the inter-regional differences are gradually expanding (Gao et al., 2024).
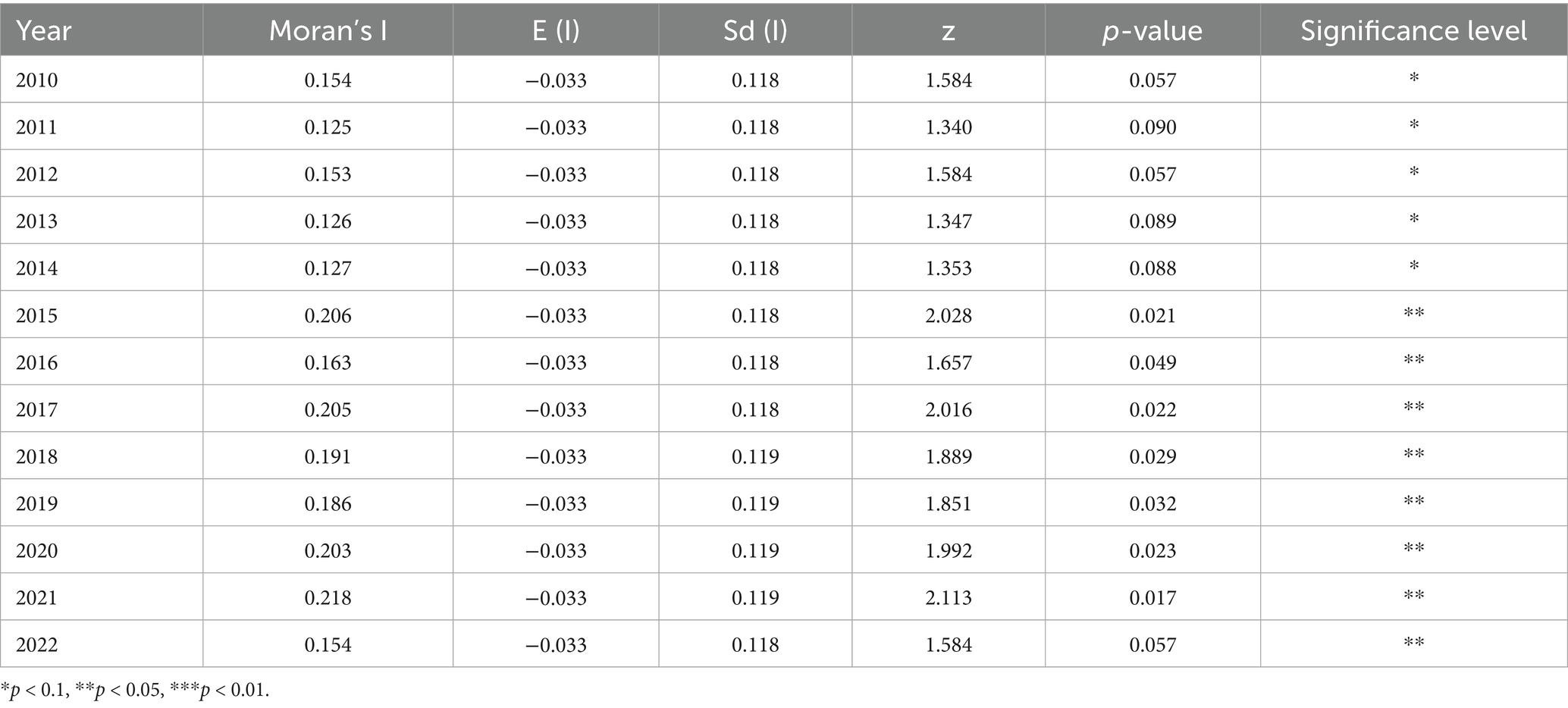
Table 7. Moran’s index of coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission and rural revitalization.
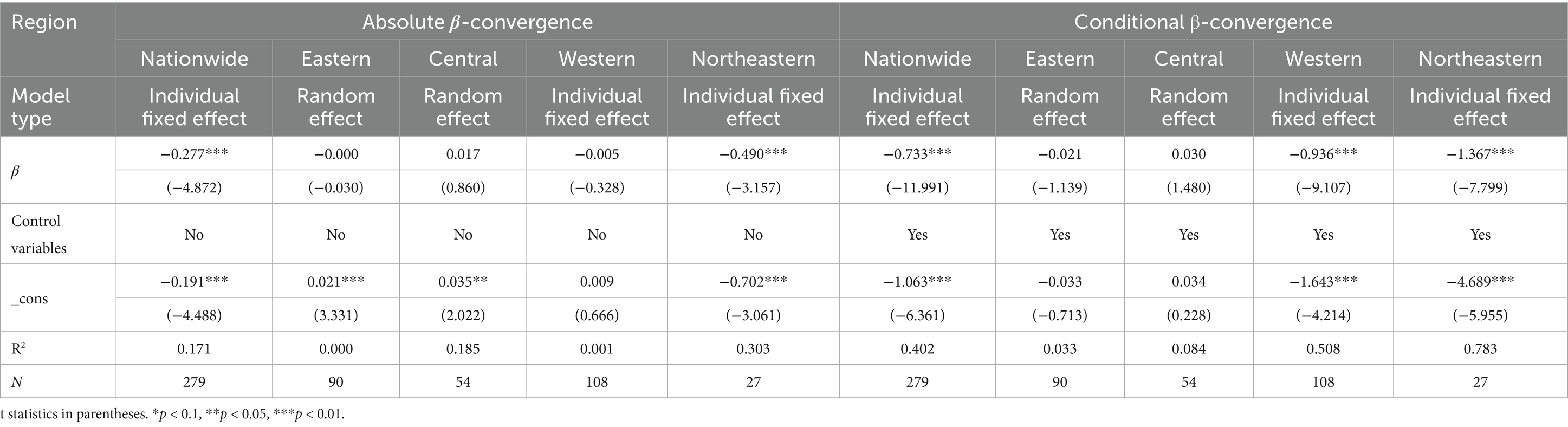
7.2.2 Absolute β-convergence
This study utilizes Elhorst’s methodology to conduct a model selection test for absolute β-convergence at the level of coordination of the two couplings (Elhorst, 2014), and the results are presented in Table 8. The findings indicate that, first, after the LM and Hausman tests, when conducting the absolute β convergence regression, the national, western and northeastern regions choose individual fixed effects models, and the eastern and central regions choose random effects models. Second, from the regression results, the absolute β coefficients of the national and northeastern regions are significantly negative when control variables are not taken into account, indicating that the coupling coordination levels of the national and northeastern regions possess the tendency to gradually converge to their respective steady state levels with the development of time, which embodies the typical characteristics of absolute β convergence. Third, the β coefficients for the eastern and western regions are negative but not significant, probably because the differences in the level of coupling coordination within the regions are large, resulting in an insignificant convergence trend; the convergence coefficient for the central region is positive but not significant, probably because there are significant differences in the level of coupling coordination among the provinces in the central region, which are difficult to eliminate with the evolution of time.
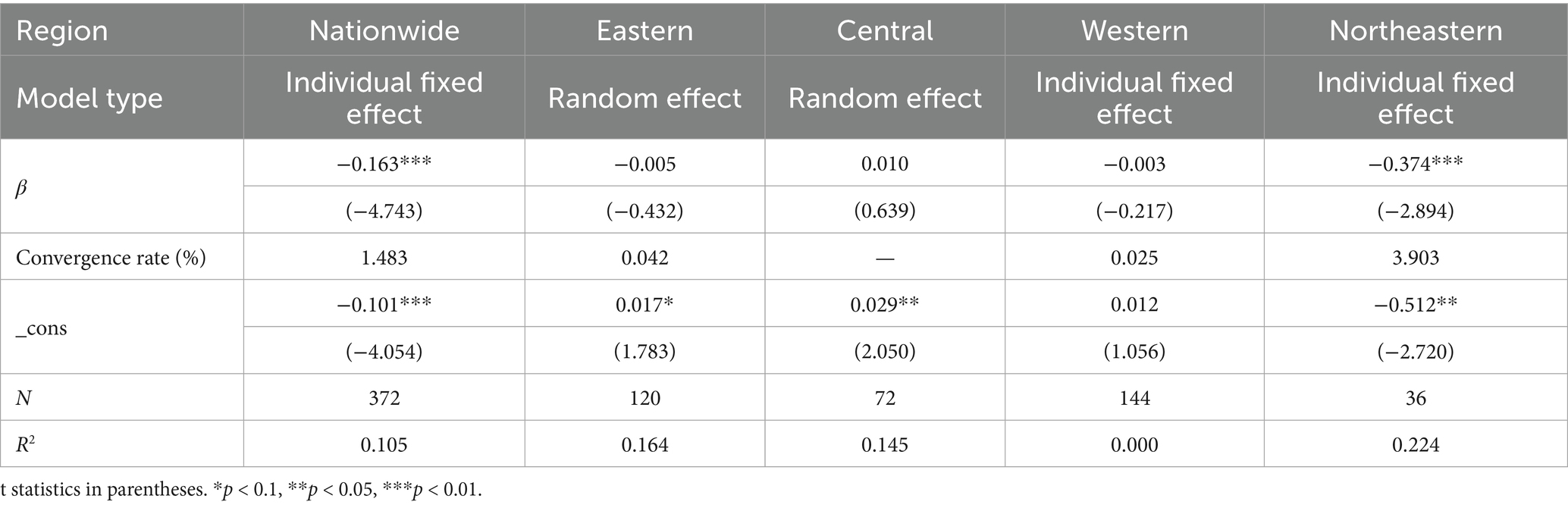
Table 8. Absolute β-convergence of coupled coordination levels of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
From the point of view of the speed of convergence, except for the central region, where there is no convergence feature, a comparison of the speed of convergence between the country as a whole and the eastern, western and northeastern regions reveals that the northeastern region has the fastest speed of convergence. The reason may be: the Northeast region is rich in arable land resources and is an important commodity grain base in China, and large-scale grain production is conducive to promoting energy-saving and emission reduction technologies and realizing economies of scale. At the same time, stable food supply facilitates the development of large-scale and modern agricultural product processing industry in Northeast China, which in turn creates a complete industrial chain, and optimizes energy use through industrial synergy while promoting rural economic growth, enabling the level of coordination between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization coupling to rapidly increase and converge to a steady state.
7.2.3 Conditional β-convergence
Given the absence of an examination of external factors in the absolute β convergence model, the estimation results may not accurately reflect reality. To address this limitation, this study re-conducted the model selection test, incorporating external control variables. The results are presented in Table 9. The results indicate that: first, the conditional β-convergence coefficients of the coupled coordination levels of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in the national, western and northeastern regions are negative and have passed the 1% significance level test, indicating that the coupled coordination levels of agricultural carbon emission and rural revitalization in these regions will ultimately converge to their respective steady-state levels after fully considering the potential impacts brought about by a series of control variables, i.e., there exists the conditional β-convergence. Second, after the introduction of control variables, the speed of convergence increases in all regions except for the central region which still does not have convergence characteristics, indicating that factors such as the land transfer rate and the level of financial support for agriculture can accelerate the speed of convergence of the level of coordination of the two couplings. Third, the regression coefficients and significance levels of the control variables across the entire country and the four regions are marked by substantial heterogeneity (Pan et al., 2023).
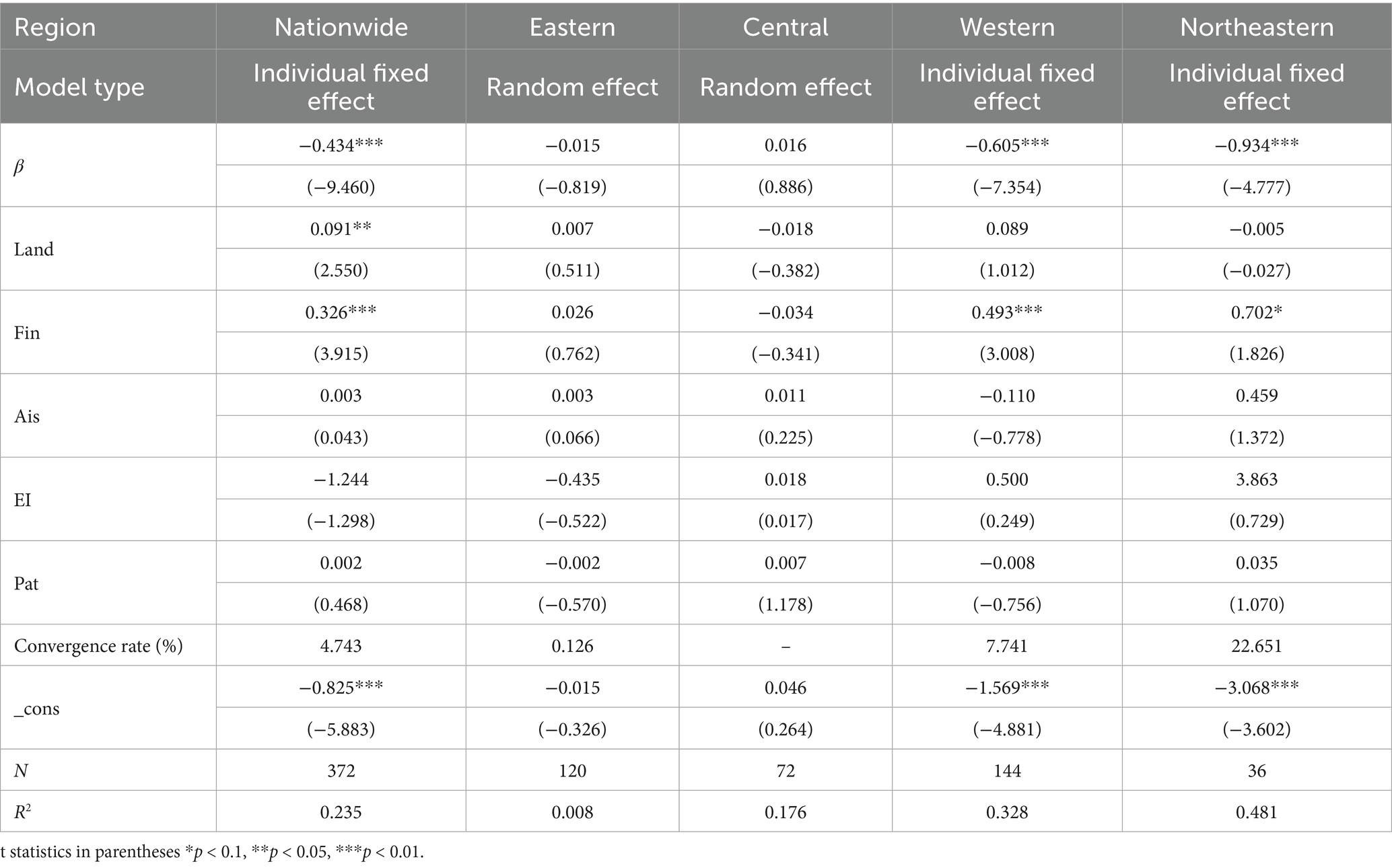
Table 9. Conditional β-convergence of coupled coordination levels of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
Land transfer rates contribute significantly to the level of coupled harmonization at the national level. This is due to the fact that land transfer consolidates the land management right into the hands of a few new agricultural management main bodies operating on a large scale (Li et al., 2025). This consolidation is conducive to the This phenomenon fosters the establishment of large-scale operations, thereby reducing the cost of and the difficulty in obtaining factors of production that are low in carbon, toxicity, and pollution. Consequently, farmers’ dependence on traditional chemicals is reduced, which in turn promotes an increase in the level of coupled coordination (Kuang and Zhang, 2024).
The level of financial support for agriculture (Fin) has an inhibitory effect on the level of coupling coordination only in the central region, a phenomenon that may stem from the deep mismatch between the characteristics of the regional industrial structure and the investment of funds. Specifically, the central region is dominated by traditional planting industry, agricultural scale and mechanization is low, the main body of agricultural business is mostly dispersed small farmers, technology absorption and market docking capacity is limited. However, the current financial support for agriculture in the choice of investment, excessive tendency to high value-added agricultural projects (such as facilities agriculture, agricultural product processing) or green technology promotion, traditional planting transformation and upgrading of key links (such as soil improvement, water-saving irrigation, pest and disease green prevention and control, etc.) but due to the lack of capital investment and slow progress. This disconnect between funding and actual demand not only weakens the marginal benefits of financial policies to support agriculture, but also may trigger structural imbalances in regional agricultural development due to misplaced resources, further inhibiting the improvement of the level of coupled coordination.
Agricultural industrial structure (Ais) only has an inhibitory effect on the level of coupling and coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in the western region, which may be due to the fact that the western region is facing the limitation of natural conditions such as water shortage, poor soil, etc., and in order to maintain the production, farmers tend to adopt the crude production mode with high input, high emission and low efficiency. This not only increases production costs and leads to higher carbon emissions, but also restricts the value-added space of the agricultural industry and the income channels of farmers due to inefficient production methods, which is not conducive to the realization of industrial prosperity and affluent living in the goal of rural revitalization, thus inhibiting the improvement of the level of coordination between the coupling of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
The greater contribution of environmental regulation intensity (EI) to the level of coupled coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in the Northeast region may stem from the following two factors: first, the Northeast region, as an old industrial base, possesses a relatively complete industrial system and strong technological research and development capabilities. Driven by environmental regulations, the energy-saving and emission reduction technologies and environmental protection equipment manufacturing experience accumulated in the industrial field can be rapidly migrated to the agricultural field, effectively reducing agricultural carbon emissions. Secondly, the degree of large-scale operation of agriculture in Northeast China is high, and large-scale agricultural production is more likely to adopt advanced green production technology and management mode, improve agricultural production efficiency and resource utilization efficiency, reduce the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and other inputs, and promote farmers’ income increase by improving the quality and added value of agricultural products while reducing agricultural surface pollution. The coordinated efforts of the two have promoted the synergistic promotion of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
Patent authorization (Pat) only has an inhibitory effect on the level of coupled coordination in the eastern region, which may be due to the fact that while rural patent authorization promotes energy-saving technological innovation in the eastern region and reduces the cost of energy use, energy consumption increases with economic growth, which produces a rebound effect on the agricultural carbon emissions in the eastern region, restricting the innovation-driven carbon emission reduction effect (Xu et al., 2023b), which in turn inhibits the improvement of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
7.3 Robustness test for β-convergence
Considering the negative impacts on agricultural economic activities and rural social life during the COVID 19 epidemic, there may be large fluctuations in various data, and in order to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the study, this study deletes the data in 2020, 2021, and 2022 to re-examine the model selection and econometric tests, and the results are shown in Table 10. The positive and negative and significance levels of the absolute beta convergence coefficients and conditional beta convergence coefficients for the whole country and the four major regions have not changed fundamentally. Therefore, it is reasonable to believe that the absolute β-convergence and conditional β-convergence results of the coupled coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization for the whole country and the four major regions are still robust after excluding the potential impact of COVID 19 prevalence.
8 Conclusions and policy implications
8.1 Conclusion
This study analyzes the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics, regional differences, and convergence of the coupling and coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization. The analysis is based on panel data from 31 provinces (municipalities) in China from 2010 to 2022. The entropy method, coupling coordination degree model, Gini coefficient and its decomposition, and convergence degree model were applied in the study. The results show that:
First, from the viewpoint of spatial and temporal evolution characteristics, during the study period, the coupling and coordination level of China’s agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization has shown a development pattern of “eastern region > national > central region > western region > northeastern region,” and the type of coupling and coordination has evolved from a spatial pattern of barely coordinated and on the verge of being out of order to a spatial pattern of primary coordination and barely coordinated. Coordination is supplemented by the spatial pattern.
Second, from the perspective of spatial differences, the overall spatial differences in the level of coupled coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in the whole country are expanding, and the differences mainly come from inter-regional differences, especially between the northeast and other regions.
Third, from the perspective of convergence characteristics, the level of coupled coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in the east and northeast regions during the sample period has a σ-convergence characteristic, and the whole country and the northeast region have an absolute β-convergence characteristic. Northeast regions have absolute β convergence characteristics, the national, western and Northeast regions have conditional β convergence characteristics, and the influence of external factors on the level of coupled coordination in different regions has significant regional heterogeneity.
8.2 Policy implications
In light of the aforementioned findings, the following recommendations are proposed:
First, it is imperative to objectively comprehend and meticulously examine the spatial distribution characteristics of the coupling and coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in China, which exhibit a pronounced gradient from east to west. Local governments must thoroughly analyze their local resource endowments, industrial characteristics, and development potential, and proactively link governments at all levels, agricultural cooperatives, and leading enterprises to formulate differentiated development strategies to promote coordinated regional development. For instance, the eastern region should further leverage its economic, technological, and policy advantages to promote low-carbon agricultural technologies and successful experiences in rural revitalization, thereby providing demonstrations and leadership for other regions. Conversely, the western region stands to benefit from its substantial wind and solar energy resources, along with other clean energy sources, to drive the green transformation of the agricultural energy structure. This can be achieved by establishing clean energy agricultural demonstration zones, thereby fostering a symbiotic relationship between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization.
Second, in order to address the significant disparity in the degree of coupled coordination between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization among various regions, the primary focus should be on narrowing the gap between the northeastern region and other regions. Firstly, the government should assume a leading role in comprehensively evaluating and assessing the current status of agricultural carbon emissions and the progress of rural revitalization in the Northeast, while also identifying its developmental shortcomings and advantages. The establishment of a scientific assessment system will facilitate the identification of key issues in the green transformation of agriculture and rural revitalization in the Northeast. Secondly, a dynamic monitoring and assessment mechanism will be implemented to regularly track the development progress of the coupled and coordinated level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in the Northeast region. This mechanism will enable the government to make timely adjustments to policies and measures, thereby promoting synergistic development between the Northeast region will collaborate with the eastern, central, and western regions to facilitate the exchange of technology, capital, and human resources, thereby reducing disparities among regions and promoting balanced development nationwide through the optimization of resources and the leveraging of complementary strengths.
Third, it is imperative to leverage the positive impact of external factors on the coupling coordination level of each region. This will accelerate the convergence of the coupling coordination level of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization to the steady state. For the central region where convergence characteristics do not exist, the enhancement of the land transfer market, the optimization of financial fund utilization, and the augmentation of the proportion of eco-agriculture can be employed to enhance the level of coupling and coordination of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization, and to promote the in-depth integration of the green transformation of agriculture and the rural economic development. Consequently, this will provide strong support for the realization of balanced regional development and sustainable growth.
8.3 Shortcomings and future prospects
Firstly, this study launched the analysis based on panel data from 31 provinces (cities) in China, but due to the obvious spatial heterogeneity within provinces in terms of economic structure, social development level, climatic conditions, and agricultural production characteristics, it may be difficult to adequately capture the intra-regional differentiation characteristics by using data at the provincial level only, which limits the precision of the study’s conclusions and the relevance of the policy guidance to a certain extent. Future research can further integrate city- and county-level data, and through the construction of a multilevel analytical framework, identify more accurately the key influencing factors for the synergistic development of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in different regions, so as to provide a more scientific and effective decision-making basis for the formulation of differentiated regional coordination policies.
Secondly, this study adopts the traditional method of dividing the four major regions of East, Central, West and Northeast in the analysis of regional differences. Although this method facilitates macro comparison, the division is mainly considered at the macro level of the level of economic development and geographic location, and fails to take into full consideration of the intrinsic characteristics of the degree of coordination of the coupling of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization, and is unable to reflect the actual regional differences in the degree of coordination of the coupling of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization accurately. Future research should be based on subregional agricultural development, regional division from the perspectives of climatic conditions, resource endowment, and the level of agricultural economic development, etc., and build a more scientific regional division framework to more accurately identify the coordinated relationship between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in different regions, and to provide a more reliable basis for the formulation of differentiated policies.
Finally, although the policy recommendations based on empirical analysis in this study are supported by data, the implementation effects of these recommendations have not yet been fully verified by practice. In the future, policy experimental bases can be set up in typical regions such as the Northeast, and causal inference methods such as double difference method (DID) and regression of discontinuity (RDD) can be used to accurately assess the net effect of policy implementation. At the same time, the feedback mechanism between policy variables can be simulated through system dynamics and other methods to predict the long-term evolution trend of regional coordinated development under different policy scenarios, so as to provide a powerful guideline for promoting the coupled and coordinated development of agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in a more efficient and sustainable way.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HY: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. KF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Shandong Provincial Social Science Planning and Research Key Project “Research on the Development and Growth Path of New Rural Collective Economy in Shandong Province under the Background of Rural Revitalization Strategy “(23BJJJ04).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the editor and the anonymous referees for their helpful comments and suggestions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2025.1627247/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
1. ^The comprehensive utilization rate of straw in China exceeds 88%, https://www.gov.cn/yaowen/liebiao/202309/content_6905985.htm.
References
Chen, S., and Chen, D. (2018). Haze pollution, government governance and high quality economic development. Econ. Res. 53, 20–34.
Chen, Y., Huang, X., and Wang, L. (2018). Rural revitalization and evaluation in China from the perspective of multifunctional theory. Chin. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 39, 201–209.
Chen, J., Li, Z., Dong, Y., Song, M., Shahbaz, M., and Xie, Q. (2020). Coupling coordination between carbon emissions and the eco-environment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 276:123848. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123848
Elhorst, J. P. (2014). Matlab software for spatial panels. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 37, 389–405. doi: 10.1177/0160017612452429
Gao, Y., Xing, T., and Ma, Y. (2024). Spatio-temporal evolution of tourism resilience and analysis of driving factors in the Yellow River Basin. J. Northwest Univ. Philos. Soc. Sci. 54, 124–136. doi: 10.16152/j.cnki.xdxbsk.2024-06-011
Guo, W., Tan, Q., and Lei, M. (2024). Analysis of the synergistic development of rural carbon emission intensity and rural revitalization in China. Sci. Technol. Manage. Res. 44, 217–226.
Guo, P., Yin, Z., Sha, Y., and Gou, K. (2025). Digital finance empowers rural revitalization: evidence from the survey of urban and rural community governance in China. Econ. Theory Econ. Manage. 45, 37–54.
Huang, C. (2025). The basic problems in the construction of the theoretical system of rural revitalization in China. Soc. Sci. 1, 17–24.
Huang, J., Chang, H., Tian, Y., and Wang, W. (2025). Mechanism of labor transfer on agricultural carbon emission and analysis of emission reduction potential. Chin. Agric. Resour. Zoning 12, 1–15.
Jia, J., Li, X., and Shen, Y. (2018). Construction and empirical analysis of index system of rural revitalization strategy. Finance Econ. 11, 70–82.
Kuang, Y., and Zhang, H. (2024). Does agricultural land transfer enhance green total factor productivity in agriculture? World Agric. 2, 59–71. doi: 10.13856/j.cn11-1097/s.2024.02.006
Li, Q., Yuting, J., and Ming, C. (2025). Land transfer and agricultural carbon emissions: theoretical mechanisms and empirical tests. East China Econ. Manage. 22, 1–12.
Liu, Y., and Wang, Q. (2022). Spatiotemporal pattern and influencing factors of rural revitalization in China. Expl. Econ. Issues 9, 12–25.
Liu, X., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Does green finance help improve the level of common prosperity? Modern Econ. Discussion 8, 27–43. doi: 10.13891/j.cnki.mer.2024.08.005
Lu, Y., Yin, Y., Tian, Y., and Huang, J. (2025). Nonlinear impact mechanism of rural industrial integration on agricultural carbon emissions. East China Econ. Manage. 39, 48–59. doi: 10.19629/j.cnki.34-1014/f.240528021
Mei, Y., Dai, L., and Wu, M. (2024). Research on the coupling and coordination of agricultural carbon emission efficiency and food security in Anhui Province. J. Saf. Environ. 24, 4506–4517. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2024.0864
Pan, Z., Ma, L., Tian, P., and Zhu, C. (2023). Spatio-temporal evolution of urban-rural integration and development in the three northeastern provinces with regional differences and its convergence. J. Nat. Resour. 38, 3093–3115.
Poddar, S. (2024). “Sustainable integrated farming in agriculture” in Water-Soil-Plant-Animal Nexus in the Era of Climate Change. ed. A. Karmaoui (Hershey, PA: IGI Global Scientific Publishing), 329–343.
Qi, P., Du, G., and Zhu, R. (2023). Institutional embeddedness of the coupled development of “double carbon” goal realization and rural revitalization. Jiangsu Soc. Sci. 6, 72–81. doi: 10.13858/j.cnki.cn32-1312/c.20231127.013
Qin, Z., Wang, X., Yu, W., and Jing, G. (2025). Measurement of factor allocation efficiency and convergence analysis of rice cultivation in China. China Agric. Resour. Zoning 22, 1–18.
Shen, J., Wang, Y., Zhu, M., and Wang, K. (2020). Construction and empirical evidence of the evaluation index system of rural revitalization level. Trans. CSAE 36, 236–243.
Shi, C. (2025). Carbon emission reduction effect of agricultural digitization: theoretical analysis and empirical evidence. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 22, 1–13.
Sulaiman, A., Almuslamawy, H., Hashim, A., and Al-Abodi, E. (2025). Efficiency of eco-friendly surface in removing organic and inorganic pollutants from wastewater. Int. J. Adv. Life Sci. Res. 8, 143–151. doi: 10.31632/ijalsr.2025.v08i02.011
Sun, C., Xia, E., Huang, J., and Tong, H. (2024a). Coupling and coordination of food security and agricultural carbon emission efficiency: changing trends, influencing factors, and different government priority scenarios. J. Environ. Manag. 370:122533. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122533
Sun, J., Yu, M., Zhen, F., Zhou, L., and Miao, L. (2023). Evaluation of the coordinated development of new urbanization and rural revitalization: a case study of Zhejiang Province. Econ. Geogr. 43, 115–123. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2023.02.012
Sun, C., Zeng, N., Yan, G., and Yang, Y. (2024b). Research on the coordinated development of agricultural carbon emission-ecological environment-agricultural economy coupling in Southwest China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/195352
Tian, Y., and Hao, Y. Y. (2022). Remeasurement of agricultural carbon emissions in China: basic status quo, dynamic evolution and spatial spillover effects. China Rural Econ. 3, 104–127.
Tian, Y., and Zhang, Y. (2019). Research on the effectiveness evaluation, target reconstruction and path emission reduction optimization of agricultural carbon emissions in China. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 33, 1–7. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2019.338
Wang, Y., Gao, X., and Wang, Z. (2024b). Analysis of digitalization level measurement and spatial and temporal evolution of rural industries in China. East China Econ. Manage. 38, 97–107. doi: 10.19629/j.cnki.34-1014/f.231211008
Wang, K.-L., Peng, J.-H., and Miao, Z. (2024a). Coupling coordination between digital village construction and agricultural carbon emissions in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 53100–53120. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-34742-4
Wu, X., Zhang, J., Tian, Y., and Xue, F. (2015). Analysis of China's agricultural carbon emission reduction potential from the dual perspectives of fairness and efficiency. J. Nat. Resour. 30, 1172–1182.
Xia, M., Zeng, D., Qi, H., and Chen, J. (2022). Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal dynamic evolution between agricultural carbon emissions and agricultural modernization in China 2010–2020. Agriculture 12:1809. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12111809
Xie, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Zheng, B., Xiang, J., and Gao, M. (2024). Spatial and temporal variability of non-food cultivated land in hilly mountainous areas of Chongqing and the division of driving types. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 41, 15–26. doi: 10.13254/j.jare.2023.0008
Xinwen, Z., and Guolei, Z. (2018). The transformation of the main social contradictions, the transformation of rural governance and rural revitalization. J. Northwest A&F Univ. 18, 63–71. doi: 10.13968/j.cnki.1009-9107.2018.03.09
Xu, Y., Cheng, Y., and Wang, J. (2023b). Spatial and temporal evolution of carbon emission efficiency and the impact of green technology innovation in Chinese resource cities. Geogr. Res. 42, 878–894.
Xu, M., Li, J., Liu, T., Zhang, C., and Wang, C. (2023a). Regional differences, dynamic evolution and convergence of China's environmental governance performance: a comparative analysis based on the watershed perspective. Econ. Geogr. 43, 1–12. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2023.10.001
Xu, X., and Wang, Y. (2021). Measurement of rural revitalization level and influencing factors of western development in the new era. J. Southwest Univ. Nation. 42, 129–137.
Xu, X., and Wang, Y. (2022). Measurement of rural revitalization level in China, decomposition of regional differences and dynamic evolution. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 39, 64–83. doi: 10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2022.05.009
Yang, H. (2023). Research on consolidating and perfecting the basic rural management system. Beijing: Economic Science Press.
Yao, J. Y., Liu, L., Fan, X. X., Jia, Q., and Yang, X. (2023). A study on the influence of technology awareness and promotion on farmers' low-carbon agricultural technology adoption behavior. Arid Zone Res. Environ. 37, 21–30. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2023.275
Ye, X. (2018). Outline of China's rural revitalization strategy in the new era. Reformation 1, 65–73.
Zhang, H., Gao, L., and Yan, K. (2018). The theoretical origin, main innovation and realization path of the strategic thought of rural revitalization. China Rural Econ. 11, 2–16. doi: 10.20077/j.cnki.11-1262/f.2018.11.001
Zhao, J., Du, Y., Ren, S., Duan, F., and Ren, Y. (2024). Study on the spatial spillover and threshold effect of rural revitalization on agricultural carbon emissions in the Yellow River Basin. Chinese J. Ecol. Agric. 32, 1766–1779.
Zhao, W., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Study on the dynamics, spatial differences and convergence of the distribution of the degree of coordination of the coupled double-cycle economy in China. Res. Q. Tech. Econ. 39, 23–42. doi: 10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2022.02.009
Zhao, L., and Zuo, Y. (2023). Coupled and coordinated development of rural revitalization and common wealth: a study on distribution dynamics, spatial differences and convergence. J. Southwest Univ. 45, 98–113. doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2023.09.010
Zheng, X. (2019). Research on the evaluation index system of rural revitalization potential based on classification promotion: survey data from 6 villages in 3 counties and cities in Fujian Province. Soc. Sci. 6, 36–47. doi: 10.13644/j.cnki.cn31-1112.2019.06.004
Keywords: agricultural carbon emission reduction, rural revitalization, synergistic development, spatial variability, convergence speed
Citation: Yang H and Feng K (2025) Spatial variability and convergence of the coupled relationship between agricultural carbon emission reduction and rural revitalization in China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1627247. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1627247
Edited by:
Juan Lu, Nanjing Agricultural University, ChinaReviewed by:
Qiao Chen, Hubei University of Economics, ChinaSandeep Poddar, Lincoln University College, Malaysia
Fang Fang, Xinjiang University, China
Copyright © 2025 Yang and Feng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongli Yang, eWhsbGN1QDE2My5jb20=
 Hongli Yang
Hongli Yang Kai Feng
Kai Feng