- 1Department of Biotechnology, University Institute of Biotechnology, Chandigarh University, Mohali, Punjab, India
- 2University Centre for Research and Development, Chandigarh University, Mohali, Punjab, India
As the global population expands and protein demand also rises, the environmental and ethical issues around traditional animal-based proteins become more important. Conventional proteins are associated with several issues, such as greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and extensive use of water and land. However, alternative proteins (APs) originating from plants, microbes, insects, and cultured cells have the potential to overcome such problems. Such proteins not only provide a solution to the growing population but also a sustainable alternative to conventional protein sources. This review focuses on the various sources of alternative proteins, such as plant-based (oil seeds, soybeans, peas), insects (mealworms and crickets), microbial (algae and fungi), and lab-grown proteins. It investigates the extraction and production processes, such as wet and dry fractionation, enzymatic hydrolysis, fermentation, and cell culture, with a focus on efficiency, scalability, and sustainability. Furthermore, the review discusses current consumption trends and commercial acceptance of alternative proteins, taking into account taste, texture, price, and cultural preferences. Despite their potential, alternative proteins are limited by high production costs, regulatory hurdles, and market acceptance issues. The analysis continues by exploring future potential for boosting protein quality, advancing processing technology, and broadening uses in the food and industrial sectors. Overall, AP may play an important role in developing a sustainable food system, providing nutritional safety, and mitigating the environmental effects of conventional protein production.
1 Introduction
As a sustainable and moral solution to the world’s expanding protein needs, alternative proteins (APs) have gained popularity in recent years. Traditionally, animal-based proteins like beef, poultry, and pork have taken center stage in our diet as the primary source of protein (Caminiti et al., 2023). However, these proteins need a lot of resources and effort for their production. Also, their production and consumption are connected to many environmental and health problems. APs are a new source of solutions that can solve the world’s expanding food needs in an era when people are becoming more environmentally conscious and population expansion, as well as diverse dietary requirements, necessitate the urgent search for alternative solutions. Moreover, APs are efficient and sustainable sources that can tackle the issues of the environment and provide a solution to food security. The main examples of APs include single-cell protein, plant-based meat, insect protein, and cultured meat (Munialo et al., 2022). Each type contributes to a change in food systems and has its advantages and limitations.
These proteins originate from a variety of sources, including plant-based materials, such as soybeans, lentils and peas (Bryant et al., 2021), microbial proteins, such as fungi and algae (Munialo et al., 2022), insect-based proteins (Kouřimská and Adámková, 2016), and cultured or lab-grown meats.
Raw materials are important for developing a desired protein using an efficient processing method. Different processing methods are employed to convert these raw materials into food-grade products. Plant-based proteins undergo extrusion and fermentation to improve their texture and digestion. To make microbial and insect proteins more digestible, they are dried, milled, and fermented (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021). Alternatively, cultured meat employs processes in tissue engineering and cell culture methods to build muscle-like structures.
Alternative proteins are becoming increasingly popular, particularly in the United States, Europe, and parts of Asia, due to environmental concerns and dietary preferences, such as vegetarianism and veganism (Sexton et al., 2022). However, there are several problems associated with APs, including regulatory hurdles, high manufacturing costs, customer acceptance issues, and technological limitations in scaling up production (Alcorta et al., 2021). It is necessary to address these issues to incorporate APs into the global diet (Cedeno et al., 2025). The current review deals with the sources, extraction, processing, and production of APs. It also discusses the market, consumption status, and regulatory aspects of APs.
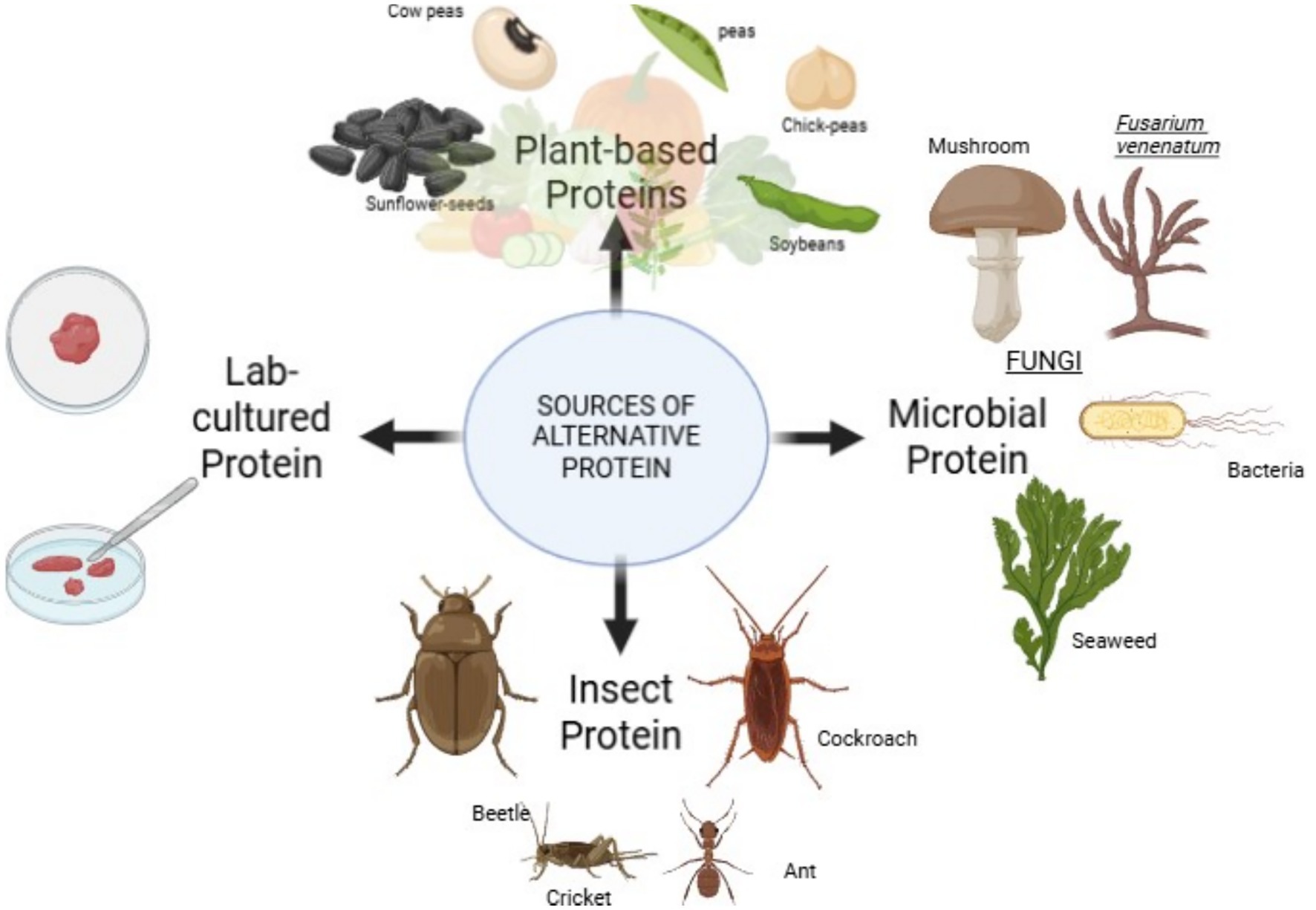
2 Sources of alternative proteins
APs can come from various sources, including plants, insects, and cell-based meat. Plant-based proteins, like soy, peas, and chickpeas, have been around for a long time and are the most commonly consumed alternative protein (Figure 1). Additionally, insects including crickets and mealworms, are becoming popular as a sustainable protein source due to their reduced water, land, and nutritional requirements in comparison to traditional livestock (Yadav et al., 2025). Cell-based meat, referred as lab-grown meat, is a more recent development where meat is produced in a laboratory without animals (Yadav et al., 2025). This eliminates the need for animal slaughter and reduces the environmental impact of meat production.
2.1 Plant-based protein
Plant-based proteins are probably the most well-known and widely available alternative to traditional animal proteins. It includes legumes such as beans, lentils, and peas as well as whole grains, nuts and seeds. With the rise of veganism and plant-based diets, these protein sources have gained even more popularity. Besides being a more sustainable option, plant-based proteins are also rich in fibers, vitamins, and minerals, making them a healthier choice for many individuals (Bryant et al., 2021).
2.1.1 Legume protein
Legumes are defined as edible seeds from leguminous plants such as beans and pulses. They are an essential part of human nutrition as they are rich in protein content, minerals, vitamins and caloric content. Legumes are commonly known as “poor man’s meat” as they are known for their high protein content at affordable prices (Mistry et al., 2022). It consists of some of the pulses like but not limited to beans, peas, pigeon peas, chickpeas, fava beans, soybeans, lentils, cowpeas, black gram, etc. (Chib et al., 2024).
2.1.2 Soy protein
Soybeans are the legume crop grown primarily for edible oil. Soybean has higher protein content in comparison with other grains and legumes, which amount to nearly 34–37%, including dietary fibers as well as carbohydrates. Additional processing of the soy is able to produce safe food for humans, such as soya milk, soy flour, soy concentrate, tofu, and soy isolates (Mistry et al., 2022). Proteins isolated from soy contain storage proteins like glycinin and β-conglycinin. The proteins lack some of the essential amino acids, such as cysteine and methionine, but possess all the remaining essential amino acids (Yuliarti et al., 2023). Other compounds, such as lipoxygenase, lectins, and other minor proteins, are also removed since they have a role in reducing the nutritional quality of the proteins and also influencing their flavor (Mistry et al., 2022).
2.1.3 Lentils
Legumes, a family of the Leguminosae family, lentils are characterized by the resemblance of their shape to a lens; that is why they are called “lentils.” There are several varieties of lentils available that can be consumed. The most frequently used are green gram beans, red lentils, yellow pigeon peas, green and white peas, Bengal gram and black gram (Mistry et al., 2022; Yuliarti et al., 2023). Lentils also carry essential amino acids like leucine, phenylalanine, threonine, and lysine, yet they lack more sulfur-containing amino acids like cysteine and methionine. Lentils also carry minerals such as iron, potassium, phosphorus, and zinc (Chib et al., 2024). They are also rich in vitamin B. Since they complement cereals in order to form complete protein, individuals tend to consume lentils along with cereals (Mistry et al., 2022).
2.1.4 Oilseed protein
A significant amount of protein, which has enormous potential for usage in the human diet, is present in many plants that produce oil. Sunflower seeds, cotton seeds, rapeseeds, soybeans, and peanuts, which account for 68, 12, 7, 4, and 2% of global protein meal production, respectively, are the most abundant sources of protein., Some oilseed proteins do not have amino acids that contain sulfur like animal proteins do; however, this can be easily fixed by adding a cereal (Surya Ulhas et al., 2023).
2.1.5 Peas
Peas are the other popular plant-based protein source that has attracted considerable attention recently. They are packed with protein, fibers, and antioxidants. Pea protein has a neutral flavor and is easily digested (Shanthakumar et al., 2022).
2.2 Microbial protein
There are various types of microorganisms that serve as protein sources algae, bacteria, fungi.
2.2.1 Fungi
A separate kingdom from plants and animals is inhabited by fungi, which include sporocarps of edible mushrooms and protein ray of micro fungi species like yeast and molds (Cardoso Alves et al., 2023) recent research have focus on the production and characterization of vegetative mycelial cells with protein contents between 9and 45%, which are frequently processed into meat replacements for human consumption (Schweiggert-Weisz et al., 2020). Products such as tempeh and Quora, a meat substitute, which has about a protein content of 45% are made from Fusarium venenatum mycelium (Schweiggert-Weisz et al., 2020). Additionally, mycoprotein has a high ribonucleic acid (RNA) content, which is characteristic of cells that divide quickly. Overindulging in meals high in RNA might result in health issues like gout; therefore, it is vital to reduce the RNA content by, for instance, heat treatment. Centrifugation is used to recover mycelia when the RNA level is lowered, yielding a paste that contains 75% water. The mycoprotein is in this paste. The diameter and length of F.venenatum’s hyphae enable them to give items a meat-like feel (Câmara et al., 2024). The mixture is further processed after adding a binder (usually egg white), flavorings, and other ingredients to obtain the required organoleptic and physical qualities. Fungal protein contains 56% total protein content and 44% other nutrients (Munialo et al., 2022).
Edible Mushrooms have a protein concentration of approximately 8.5–36.9%, which is much higher than that of many cereals and vegetables (Câmara et al., 2024). The edible mushrooms that have the highest protein content present in Trichloma are about 36.9% and the lowest in Tremella is about 8.5% (Yu et al., 2020).
2.2.2 Algae
Another amazing source of protein is algae. However, because marine algae are not widely consumed, there is less in vivo research on the optimal digestion of algae. This makes it difficult to evaluate the quality of algal protein (Uma et al., 2023). Essential amino acids like tryptophan and lysine, leucine, and isoleucine, methionine, cysteine, and lysine are frequently found in algae species, which sometimes lack in plant-based proteins (Pipliya et al., 2025). Many seaweed species normally contain trace amounts of cysteine, which is frequently undetectable (Bleakley and Hayes, 2017). Compared to plant-based sources, Microalgae and seaweed contain higher protein content. Microalgae can produce up to 70% of proteins in cells, while soybeans only yield 30–40% (Kurek et al., 2022). Some examples of sources of algal protein are Spirulina (Arthospira platensis) and Chlorella (Chlorella vulgaris, Chlorella protothecoides). Bleakley and Hayes (2017) categorize the methods of extraction for algal protein into conventional, such as physical, chemical, enzymatic and current.
2.3 Insect protein
Edible Insects have a high amount of protein, lipids, energy, and other micronutrients, which help to improve dietary health in many regions of the globe (Kouřimská and Adámková, 2016). Some uncooked edible insects, such as Sphenarium purpurascens, have a substantially greater protein content than fish, hogs, poultry, cattle and many plant-based proteins (Munialo et al., 2022). The most commonly consumed insects for protein are Coleoptera Beetles, Lepidoptera Caterpillars, and Hymenoptera, wasps, bees, and ants (Kurek et al., 2022). Diet, developmental stage, and environment all have a significant impact on the species protein quantity and quality (Kurek et al., 2022). The incorporation of non-protein nitrogen in insects can lead to an underestimation of their protein content (Kurek et al., 2022).
Edible Insects contain nutritionally valuable amino acids like lysine, tryptophan, tyrosine, phenylalanine, and threonine as plant-based proteins do not have these amino acids (Rumpold and Schlüter, 2013).
2.4 Lab cultured meat (clean meat)
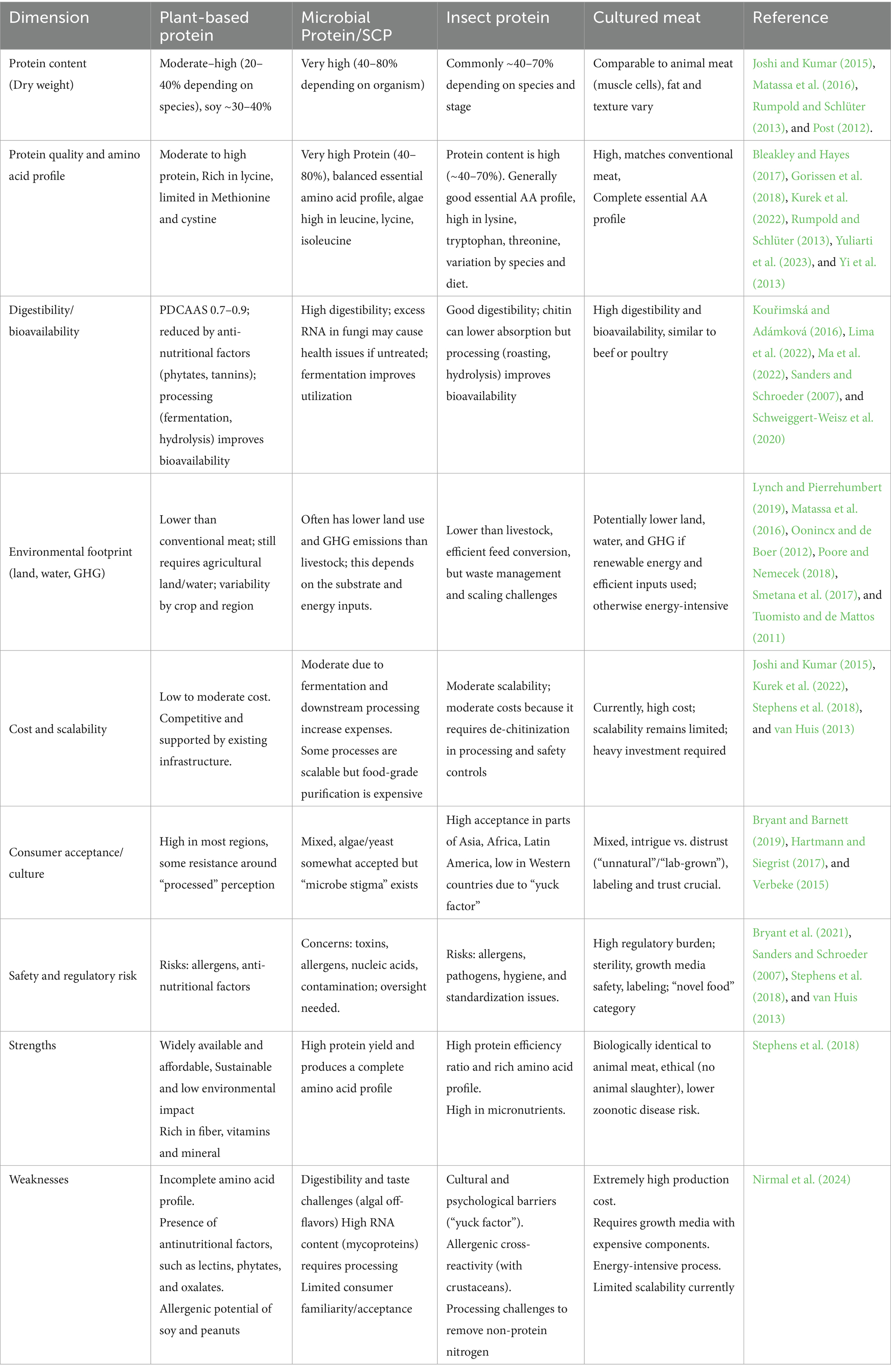
Cell-based or cultured meat is the other name for lab-cultured Meat (Yuksel and Mohr, 2023). By this groundbreaking method of making animal protein, the animals are not nurtured and killed (Bryant et al., 2021). These animal cells are carefully cultured to create meat that is biologically identical to conventional meat. A very small number of animal cells, usually stem or satellite cells, are extracted at the start of the procedure and put in a cultured medium that is rich in nutrients (Lima et al., 2022). The nutrition, growth factors, and environmental conditions required for the cell to proliferate, divide, and differentiate into muscle and fat tissue (Post, 2012). Unlike traditional meat production, this method avoids the need to raise and slaughter animals, offering significant potential to address ethical concerns, reduce environmental impacts, and mitigate risks associated with zoonotic diseases (Roy et al., 2021). Therefore, it is important to note the protein content, its quality and bioavailability along with the environmental footprint of APs. Also, the scalable cost, consumer acceptability and regulatory checks (Table 1).
3 Extraction and processing methods of alternative protein
3.1 Extraction methods of alternative proteins
Alternative proteins extracted from fungi, plants, algae, insects, and microbial sources offer a viable solution to challenges such as a growing population, reducing environmental impacts, and meeting evolving consumer demands for ethical and sustainable products. The extraction of these proteins is a critical step in their transformation into consumable forms. The extraction methods are divided mainly into two categories: conventional and innovative methods (Table 2).
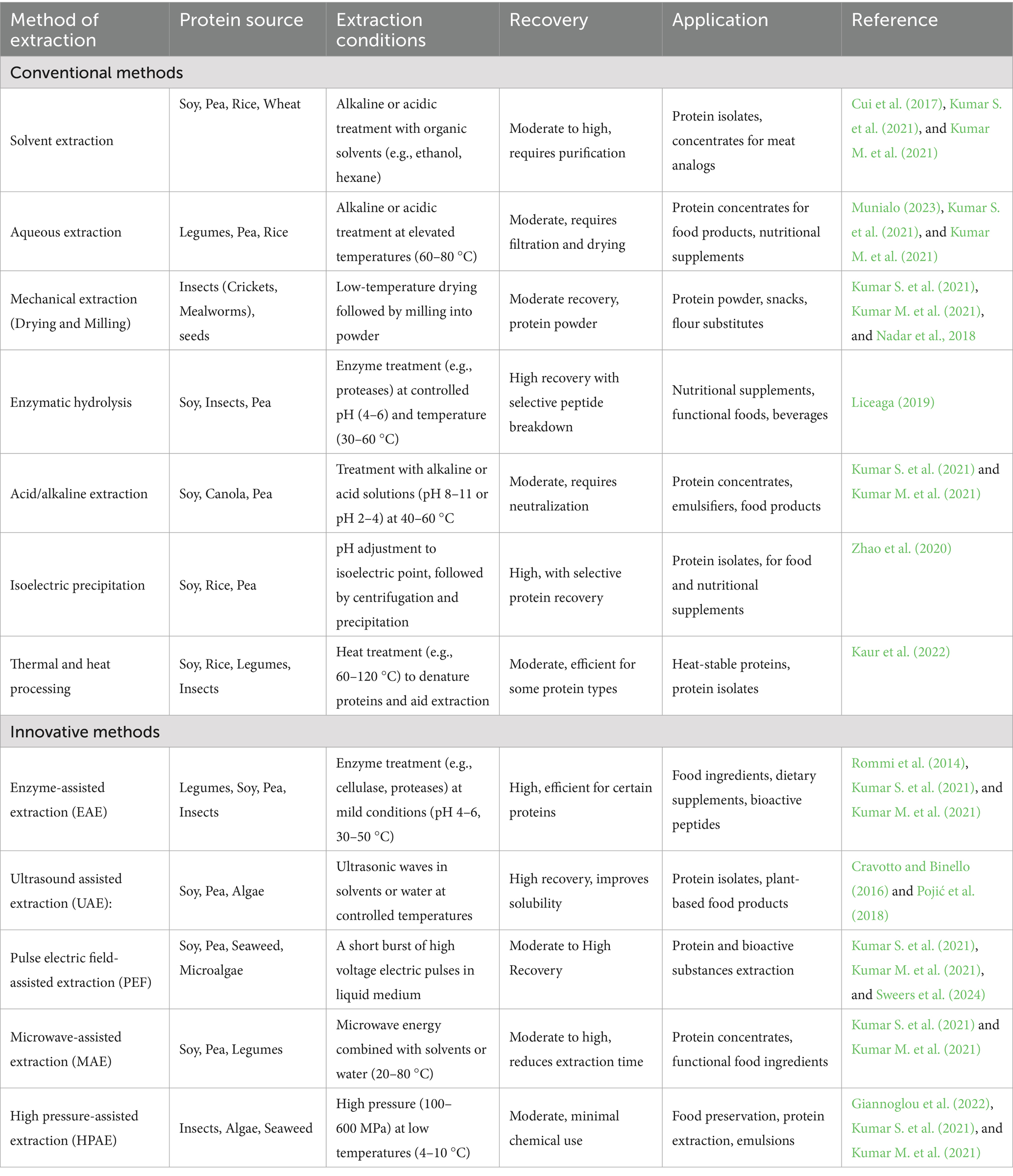
Table 2. Extraction methods of alternative proteins from various sources: conventional vs. innovative methods.
3.2 Conventional extraction techniques
It involves isolation of protein from various non-traditional sources. Some of the methods are as follows:
1. Solvent extraction: This process uses chemical solvents such as hexane, ethanol, or acetone to separate protein from the source material (Cui et al., 2017). This extraction process is mainly used for plant-based proteins such as oilseeds (soy, sunflower) (Munialo, 2023). This technique involves mixing the raw material, ground into fine powder with the help of chemical solvents. These solvents dissolve the proteins and other components, separating them from solid residues. The protein rich solution is then processed to precipitate protein. The solvent used in the process is usually evaporated or recovered for reuse (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021). Solvent Extraction is valued for its high protein yield and scalability. It has limitation, including use of volatile organic solvent residues in final product, risk of protein denaturation under harsh conditions.
2. Aqueous extraction: In this method, proteins are extracted using water or buffered solution (alkali and acids) at specific pH levels. It is widely used for plant-based protein extraction mainly rice and peas (Munialo, 2023). It involves soaking or homogenizing the raw material, such as plants, algae, or pulses, in water under controlled conditions. The process often includes adjusting the pH to enhance protein solubility and separation from other components like fibers or lipids (Munialo, 2023). After extraction the protein is recovered by various processing methods. It is environment friendly, safe, simple, and avoid use of any harmful chemicals. Its efficiency is less compared to solvent extraction (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021).
3. Mechanical extraction: It is a chemical-free method of isolating protein, including physical processes to separate protein from raw materials such as seeds, nuts, or insects. This method involves grinding or milling the raw material to break it into smaller particles, followed by pressing or centrifugation to separate the protein-rich fractions from oils, water, or solid residue (Nadar et al., 2018). Mechanical Extraction is used for oilseeds and insects. Mechanical treatment combined with enzyme-assisted extraction improves the yield and quality of protein extracts (Nadar et al., 2018; Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021).
4. Isoelectric precipitation: It involves adjustment of pH of solution to isoelectric point, causing protein to precipitate. It exploits the principle of protein solubility at different pH levels. Proteins are least soluble at their isoelectric point (Specific pH at which their net electric charge is zero). The pH of the solution is then adjusted to match the isoelectric point of the target proteins, causing them to aggregate and precipitate out of the solution (Ma et al., 2022). Once precipitated, the proteins are separated by centrifugation or filtration, washed, and dried to produce a concentrate or isolate. It is commonly used for extraction of protein from plant and microbes (Zhao et al., 2020). Isoelectric Precipitation is favored for its ability to yield proteins with high purity and functionality. However, it requires precise pH control, and the acidic and alkaline conditions used may denature some proteins, potentially affecting their nutritional and functional properties (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021).
5. Heat or thermal processing: Heat or thermal processing is a method in which raw materials are heated to increase protein production, functionality, or digestibility. The process entails heating protein sources such as insects, plant seeds, or microbial biomass to regulated temperatures, which are frequently combined with other extraction methods. Heat can denature proteins, breaking down their complex structure and making them more soluble or easier to separate from other components like fats, carbohydrates, or cell walls. Thermal processing is used to deactivate antinutritional components, such as trypsin inhibitors in legumes, or enhance the sensory quality and texture of protein-based items. However, excessive heating can have negative consequences, such as protein denaturation or the loss of key amino acids, lowering nutritional quality.
Conventional extraction processes are time-consuming, energy-intensive, and environmentally unfriendly, since they require organic solvents, alkalis, and acids, lesser yield for some sources and produce large amount of waste and by-products (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021).
3.3 Innovative extraction techniques
To overcome the drawbacks of traditional protein extraction methods, several innovative approaches have emerged that focuses on improving extraction efficiency, ensuring environmental sustainability and maintaining protein quality while lowering energy consumption. There are various innovative extraction techniques that are as follows:
1 Enzyme assisted extraction (EAE): It is a technique that uses specific enzymes to improve protein recovery from biological sources. This method involves treating raw materials such as plants, algae, or insects with enzymes like cellulases, proteases, or pectinases (Rommi et al., 2014)., are employed to break down complex structures like cell walls, protein complexes, or polysaccharides, thereby increasing protein accessibility and solubility (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021).
In this process, the raw material is immersed in an aqueous solution after which enzymes are added and mixture is then incubated under controlled conditions such as optimal temperature and pH to allow enzymatic activity. After the completion of reaction, the extracted protein is separated by filtration or centrifugation. This method is used in food and pharmaceuticals industry as it is highly effective in producing high-quality proteins with minimal structural damage. EAE is valuable in industries particularly food and pharmaceutical because it yields high quality protein with minimal damage to their structure (Pojić et al., 2018). However, the method does have some limitations such as high cost of enzymes, longer processing times and need to precise control over reaction conditions to maintain efficiency (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021).
2 Ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE): UAE is a modern method that uses high frequency sound waves to boost protein extraction from various biological sources (Tiwari, 2015). In this method, the material is placed in a liquid medium and exposed to ultrasonic waves frequency of around 20 kHz (Pojić et al., 2018). These waves cause rapid pressure changes, leading to the formation and collapse of microscopic bubbles in a process known as cavitation (Tiwari, 2015). The energy released during cavitation helps break down cell walls and protein complexes, which improves the mass transfer, and releases proteins into the surrounding liquid (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021).
One of the main advantages of the UAE is efficiency. It often requires shorter processing time and operates at lower temperatures compared to conventional methods, which helps preserve the structure of sensitive proteins. This process is also eco-friendly, as it reduces the need for strong chemicals and excessive energy. UAE is flexible and can be used with a variety of protein sources such as soybeans, pulses, microalgae, and even insects (Cravotto and Binello, 2016). However, there are some challenges as high-intensity ultrasound potentially damages proteins and scaling up the process for industrial use can be difficult. The extraction efficiency depends on several variables such as frequency, amplitude and duration of ultrasound exposure, which must be carefully optimized for each material type. Despite these limitations, it is a promising technology for a sustainable and high-yield protein extraction method (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021).
3 Pulse electric field assisted extraction (PEF): PEF is an innovative extraction method that disrupts cell membranes with a short burst of high voltage electric pulses, enhancing the release of intracellular protein and useful substances (Sweers et al., 2024). In this process, raw materials like microalgae, plant cells, or microbial biomass are exposed to an electric field in a liquid medium (Faizah et al., 2024). These electric pulses create pores in the cell membranes, a phenomenon known as electroporation, allowing proteins to diffuse out into the surrounding solution. PEF is a non-thermal technique, which means it preserves the functional and nutritional integrity of sensitive proteins (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021). It is highly energy-efficient and eco-friendly. The process is particularly effective for sources with tough walls, such as microalgae and some plants, where traditional methods struggle to achieve high protein yields. However, PEF has some limitations, including high initial equipment costs, the need for specialized systems to handle large-scale applications, and variability in efficiency depending on type and structure of the material being processed.
4 Microwave assisted extraction (MAE): MAE uses microwave energy to enhance the extraction of proteins and other bioactive compounds from raw materials like plants, algae or insects. Microwaves generate heat by causing water molecules in the material to vibrate rapidly, leading to localized heating. This disrupts cell walls, loosens protein complexes, and facilitates the release of proteins into the extraction medium, typically water or a buffered solution (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021).
MAE has various advantages, including shorter extraction times, less solvent consumption, and more energy efficiency. It is especially useful for materials with a high-water content or those that require mild heating to maintain protein functioning and nutritional quality. The regulated application of microwave energy reduces the risk of protein denaturation, making it ideal for delicate applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries. However, MAE has limitations; it may be less effective for low-moisture materials or for removing proteins firmly rooted in thick structures
5 High pressure-assisted extraction (HPAE): HPAE is a novel technique that uses hydrostatic pressure to increase protein recovery from a variety of biological materials, including plants, algae, and microbial biomass. This approach involves subjecting raw materials to pressures ranging from 100 to 600 MPa (megapascals) in a liquid medium (Kumar S. et al., 2021; Kumar M. et al., 2021). The high-pressure damages cell walls and membranes, increases permeability, and encourages the release of intracellular proteins into the surrounding fluid.
The advantages of EAE include increased protein yield, less use of harsh chemicals, and lowered energy use. However, it has drawbacks, such as the high cost of enzymes, more prolonged processing periods, and the necessity for careful control over reaction conditions to ensure efficiency.
3.4 Processing methods
Various processing processes have been employed to fabricate plant-based analog meat. Sha and Xiong (2020) use these approaches to replicate the texture of meat products, namely, producing fibrils comparable to those seen in muscle. There are two techniques for including fibrils in the product structure (Dekkers et al., 2018). Dekkers et al. (2018) describe two approaches to texture creation:
1. bottom-up, which involves forming individual fibrils from a protein source and assembling them into a structure, and
2. top-down, which involves applying force to elongate specific constituents in the formulation.
The protein fractions have to be isolated from their sources, such as plants, fungi, algae, insects, and microorganisms. The processing of alternative protein involves concentrating or isolating the protein to enhance its purity and functionality. It can be done by techniques such as Centrifugation and Filtration (non-protein part is separated from protein part), isoelectric Precipitation (precipitation of protein by bringing the pH to its isoelectric point) (Mondor and Hernández-Álvarez, 2022), Membrane Filtration (includes Ultrafiltration and diafiltrations -separation based on molecular weight), and Dry Filtration. These techniques provide isolates with a protein level of above 90% and protein concentrates with a protein content of 60–80% (Munialo, 2023).
Texturization of protein transforms protein into structures resembling meat to enhance their appearance and functionality. A number of techniques have been used to produce a texture of the same kind as meat.
3.4.1 Extrusion
Extrusion is the most used processing technique (Ozturk and Hamaker, 2023). It is a high-temperature and high-pressure process in which a protein-based material is pushed through a narrow opening using a screw mechanism inside an extruder (Ek et al., 2020). Extraction processing is of two types: high moisture and low moisture. Texturized vegetable proteins (TVP) with low moisture content and somewhat enlarged structures are produced using low-moisture extrusion (Sha and Xiong, 2020). These TVPs are often rehydrated and processed into plant-based nuggets, chunks, or strips (Sha and Xiong, 2020). High-moisture extrusion yields soft products with meat-like fibrous structure, texture, and sensory properties (Ozturk and Hamaker, 2023). Extrusion is a highly flexible method that combines several unit activities into a single system. Shear, which is produced by the action of the screws and material particles rubbing against one another, causes the food material to undergo compaction, shearing, particle size reduction, phase transition, and molecular breakdown throughout the extrusion process (Sha and Xiong, 2020).
3.4.2 Cell shearing
It is a comparatively new method of texturization. In this technology, the upper cone remains motionless while the lower cone rotates at a predetermined speed. After the cell is sealed, the product is subjected to shear force and high temperatures (95–140 °C) in the space between the cones to reduce water evaporation (Ozturk and Hamaker, 2023). Typically, the sample is treated for 15 to 20 min in these circumstances, then cooled and allowed to rest for 1 h at room temperature (Schreuders et al., 2019).
In contrast to other high shear technologies like extrusion, shear flow is well-defined due to its straightforward geometry and the fewer parameters of the shear cell (Ozturk and Hamaker, 2023). This allows easy control over the system and product properties, including fibril formation (Dekkers et al., 2018).
3.4.3 3-D printing
Ozturk and Hamaker (2023) explain 3-D Printing as a paste-like substance composed of protein powder, other chemicals, and water is applied layer by layer to create a structure. Inkjet printing and hot-melt extrusion printing are two popular 3D printing techniques for foods (McClements and Grossmann, 2021). However, this method works well with liquid materials since it is optimized for thermoplastic polymers with few constituents. When new components are added, the system must be reoptimized to identify important factors such as printing viscosity, rheology, and cooking qualities. Depending on the requirements of the product, other materials, such as crosslinkers, may be added to the paste mixtures (McClements and Grossmann, 2021). A whole-cut beef analog product may take many hours to process due to the technology’s poor printing pace.
3.4.4 Electrospinning
Ozturk and Hamaker (2023) describe Electrospinning as a technique that uses an electric force to fabricate micro and nanoscale fibers. Although this technique is mostly employed in food delivery systems, researchers have also been interested in meat analog applications. Because of their intricate secondary and tertiary structures, proteins especially those derived from plants are challenging to electro-spin. Nonetheless, plant-based product compositions that resemble chicken strips can make use of electrospun zein fibers. The electrospinning process creates the well-formed fibrous structures needed in plant-based formulations, even if mechanical elongation is better at creating fibrous networks (Ozturk and Hamaker, 2023). However, for the majority of plant proteins to spin well, a synthetic biopolymer could be needed.
4 Market and consumption status
Alternative protein has increased at a rapid pace since 2020 and is likely to continue growing until 2028, with increasing consumer demand for sustainable and health (Bashi et al., 2019). The global alternative market was valued at approximately $53.1 billion USD in 2021 and is likely to reach $160.3 billion USD by 2028 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.6% from 2022 to 2028 (Zion Market Research, 2025).
Market size in the United States was around $ 1.1 billion USD in 2020 and will be $ 10.1 billion USD by 2027, with a CAGR of 9.7% (Medeiros et al., 2024; Vegconomist, 2021). North America leads the market, an indicator of high adoption and investment in food innovation. North America led the alternative protein market in 2023. North American consumers have seen explosive demand for alternative protein products because of trends such as flexitarianism, veganism, vegetarianism, and healthy eating.
The European plant protein market will reach $7 billion USD by 2028 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.0% from 2021 to 2028. The plant protein market is growing in the Middle East and Africa as well, where it will reach 1.1 billion USD by 2028 and at a CAGR of 10.3% (Talwar et al., 2024).
Indian alternative protein market was worth $795.9 million USD in 2023 and is anticipated to be worth $1467.7 million by 2030 with a CAGR of 9.1% between 2024 and 2030. Plant protein is still the biggest segment following conventional vegetarian culture and growing awareness of health and insect protein is most profitable and fastest-growing market, indicating a change in direction toward novel protein sources (Grand View Research, 2024).
The alternative protein industry in 2025 is one of expansion with more consumer take-up, technological innovation, and sustainability-driven demand. Precedence Research Report on Alternative Protein Market Size, Share, and Trends 2025 to 2034 has estimated the 2024 size of the alternative protein market at $16.65 billion with an estimated CAGR of 8.23%. The industry is expected to grow up to $36.37 billion by the year 2030 (Precedence Research, 2025).
As alternatives to traditional animal-based products, customers in this segment are proactively seeking out plant-based, insect-based, and cell-based protein sources. Increasing consumer knowledge about sustainability and health has compelled the creation of alternative protein sources such as plant-based, insect-based, and cell-based proteins. Innovation is centered on taste, texture, and nutritional clarity to attract health-oriented consumers. Consumers are now more interested in health benefits and sustainability in the environment through food consumption, leading to a plant-based protein boom.
5 Relation of alternative protein with veganism
Alternative proteins have emerged as a cornerstone of veganism, tackling nutritional, ethical, and environmental issues by offering non-animal sources of protein. A vegan diet rich in mycoprotein can promote muscle protein synthesis similarly to an omnivorous diet, based on research published in the British Journal of Nutrition.
Moreover, there has been a recent increase in plant-derived protein and fermented meats, providing vegans with a wide variety of options. These products allow for replacing meat with eco-friendly methods that strive to replicate meat-like taste and texture. Consumers view farmed meat for various health and environmental motivations; nonetheless, certain initiatives faced criticism for being excessively processed (Grafenauer et al., 2021).
Worries about animal welfare and ecological sustainability are fuelling veganism and substitute proteins. The organization’s transition from animal-derived to plant-derived sources is a consequence of the “protein revolution” (Koole, 2022). Advancements in alternative proteins frequently face hurdles in attaining high nutritional quality, gaining consumer acceptance, and ensuring sustainable product creation. The rise of veganism has spurred greater investment in alternative protein studies, influencing non-profit initiatives and market growth. Advocacy organizations greatly influence public perceptions of these matters (Abrell, 2024).
Research in public health indicates that alternative proteins are generally beneficial, but some vegan products contain lower protein levels compared to conventional foods (Surya Ulhas et al., 2023). The plant-based protein trend is a part of a global drive to rethink the world food system in a more sustainable and equitable way (Sexton et al., 2022).
In a vegetarian diet, substitute proteins are needed as they fulfill nutritional needs but also consider cultural and environmental aspects. Evidence supports its viability as an animal protein source, despite obstacles including consumer awareness, production expenses, and attaining sustainability (Surya Ulhas et al., 2023).
6 Regulatory aspects of alternative proteins
The regulatory framework is a crucial aspect of food safety to ensure wholesome consumption and global trading of APs. APs, such as insect proteins, cultured meat, algal protein, etc., fall under novel food category. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the apex food regulatory body in Europe that ensures the safety, hygienic processing, and trading of food products. The most recent EC novel food legislation Regulation (EC) 2015/2283, which was implemented in 2018, governs the approval of foods made from ingredients or production methods that were not followed in the European Union before May 15, 1997 (Turck et al., 2016). According to the Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, alternative proteins may also be subject to regulation, including potential evaluation for generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status in the US (FDA, 2018). The United States Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) Food Safety and Inspection Services (USDA-FSIS) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) collaborated in 2019 to work together to regulate cultured meat (FDA, 2023). As per the agreement, USDA-FSIS will manage postharvest procedures, such as the manufacturing and labeling of the final cultured food items (USDA, 2019), while FDA will supervise cell collection, cell banks, cell growth, and cell differentiation. Additionally, the Poultry Product Inspection Act and the Federal Meat Inspection Act have been suggested as supplementary laws (Post et al., 2020). In Europe, if GM cells (i.e., iPSC) are utilized, regulations (EC) 1829/2003 and 1830/2003 may apply to cultured meat (European Commission, 2003). Likewise, the new food law Regulation (EC) 2015/2283 applies to proteins from bacteria and insects. Under this regulation, the EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods, and Food Allergens declared Tenebrio molitor (mealworm) safe for human consumption in 2021 (Turck et al., 2021). Belluco, Halloran and Ricci summarized other supporting EC regulations relevant to edible insects. Microalgal products must obtain GRAS status in the USA. A report also summarized supporting EC regulations related to edible insects (Belluco et al., 2017). In the USA, several microalgal products, such as extract from Haematococcus pluvialis, oil from Ulkenia sp. SAM2179, DHA-rich single-cell oil from Crypthecodinium cohni, and dried biomass from A. platensis are granted GRAS status. Such microalgal products are found to have astaxanthin esters. The conventional food safety standard Regulation (EC) 178/2002 permits the approval of microalgal products, i.e., A. platensis, in Europe. All other products are subject to the new food regulation (Enzing et al., 2014). However, since GM soybeans are approved by the FDA and EFSA, plant-based meats are regulated similarly to other non-animal foods (Rubio et al., 2020). While different states may have different regulations regarding soy leghemoglobin in plant-based meats, some plant-based foods that contain this protein may be subject to novel food regulations in Europe (European Commission, 2021). However, soy leghemoglobin has been designated as GRAS in the United States (Fraser et al., 2018).
7 Alternative proteins in global food policy and sustainable food system
The transformation of global food systems not only requires technology breakthroughs but also the combination of policy architectures for sustainability, equity and resilience. Alternative Proteins (APs) could serve as potential key component of sustainable diets. However, their potential could only be achieved when worked within complete and comprehensive governance architectures. In consonance with the 2030 Agenda, the FAO Sustainable Food Systems Program recognizes centrality of food systems delivering food security and nutrition for all people as well as sustainability of the economy, social sustainability as well as sustainability of the environment (FAO, 2018). Also, APs could meet diverse targets for SDG2 (Zero Hunger) including hunger and malnutrition eradication, increased productivity value addition for small producers, as well as promoting resilient production systems responsive to climates (FAO, 2018). Modern architectures such as the Food Systems Countdown to 2030 also stressed the requirement of monitoring the evolution of the global food systems through inequity indices of nutrition as well as by way of providing an important vantage point for the measurement of the spread of the APs (Schneider et al., 2023).
In spite of their promise, the equitable dissemination of agricultural practices still poses an important barrier. Current production methodologies are heavily reliant on capital and predominantly situated in affluent areas which heightens the likelihood that advantages may primarily benefit wealthy consumers, consequently perpetuating prevailing disparities in global nutrition. In the food-insecure areas of the Global South, prices for products being too high, supply chain infrastructure being inadequate and research and development capacity being limited are important barriers for adoption. To help alleviate these barriers, an array of interventions should be considered. Public procurement programs, for example, the integration of APs for school feeding programs and social protection programs, could boost affordability and cater more widely. Introduction of tiered prices and cross-subsidies could reduce consumer costs in impoverished market areas, while expansion of localized production infrastructure and decentralized processing facilities may boost localized strength and reduce import dependency. In addition, capacity development as well as technology transfers remain crucial for the development of self-sufficiency in the production of APs for the areas of the Global South, thereby avoiding market dependency. According to Nirmal et al. (2024), those innovations should go hand-in-hand with proactive measures ensuring food equity, inclusiveness, as well as sustainable transformations.
Institutional and governance aspects are equally critical. Issues of regulation, safety, labeling, intellectual property rights and trade policy will significantly influence the accessibility as well as the legitimacy of APs in diverse settings. Regulatory regimes must reconcile consumer safety and innovation encouragement without monopolistic concentration of supply chains. Inclusive governance must also occur so smallholder farmers, women and the underserved may become both producers and consumers of the new APs in the emerging market. This corresponds with recent literature focusing on the point that sustainability transformations of the food system not only require new ideas for technology but institutional transformations too for the broad democratization of access to resources as well as technologies (von Braun et al., 2023; Govindan, 2024).
Considered together, these points out that the extension of APs into sustainable food system transformations relies as much on the basis of governance and equity as on technical possibility. Integrating APs into international policy modalities like the FAO Sustainable Food Systems Programme and SDG 2 at the same time as facilitating affordability and access in areas of food insecurity and can assist in making their diffusion transformational and equitable instead of exclusive and disjointed. In incorporating thinking toward food equity, governance and sustainability transformations, APs may break free of niche innovation to become the foundation of just and resilient food systems.
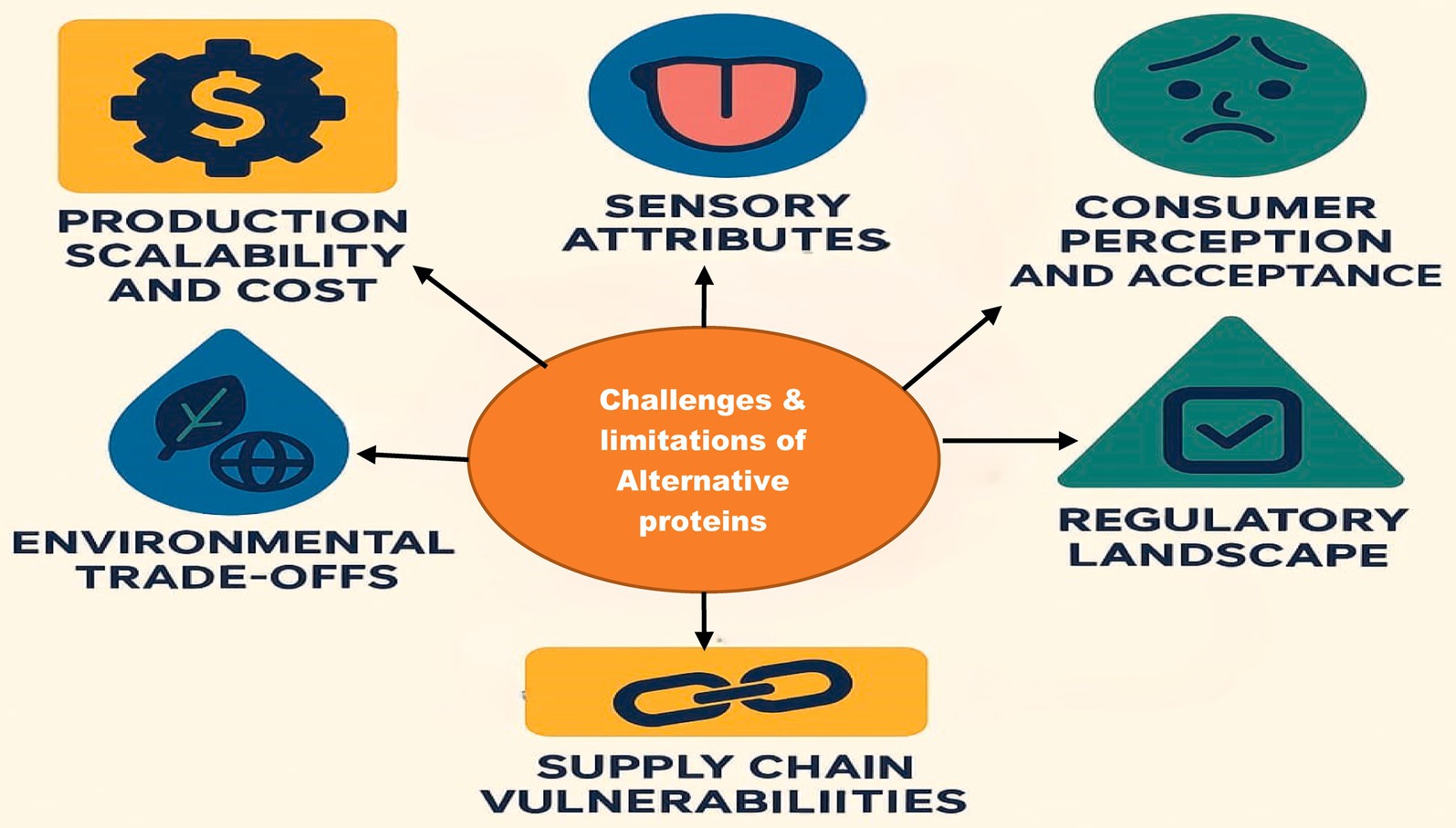
8 Challenges and limitations
The adoption of alternative proteins, such as plant-based, microbial, and lab-cultured options, faces numerous challenges and limitations despite their potential to revolutionize food systems. One significant obstacle is production scalability and cost, particularly for lab-cultured meat, which involves complex technologies like cell cultures and bioreactors, driving up expenses compared to conventional protein sources (Ahmad et al., 2022). Sensory attributes, including taste, texture, and mouthfeel, remain difficult to replicate, which can deter cofthat they were an editorial board member of Frontiersnsumers accustomed to traditional animal proteins (Figure 2). Nutritional gaps are another concern, as some alternatives lack critical nutrients like heme iron or vitamin B12, requiring supplementation or fortification to match the benefits of meat (Alcorta et al., 2021). Consumer perception and acceptance also pose hurdles; many individuals perceive these products as overly processed or unnatural, which can inhibit market adoption (Alcorta et al., 2021). Additionally, environmental trade-offs arise, particularly in plant-based proteins, where reliance on monoculture crops like soy and pea contributes to land degradation, water use, and biodiversity loss. The regulatory landscape is equally challenging, with uneven global standards and approval processes slowing innovation and market entry. Furthermore, supply chain vulnerabilities tied to raw material availability and geopolitical factors can restrict consistent production. Addressing these challenges requires advancing production efficiency, enhancing sensory and nutritional profiles, fostering consumer trust, and implementing clear regulatory frameworks to ensure the sustainable growth of alternative proteins (Post et al., 2020).
9 Conclusion and future scope
Growing global protein demand, along with growing environmental and ethical concerns, require scalable and sustainable food solutions today. New protein sources like plant-based, microbial, insect-based, and cultured meat provide a potential solution to the problem. Even though these new protein sources provide significant environmental, nutritional and ethical benefits, widespread adoption must overcome challenges like cost, consumer acceptance and regulatory ones.
Demand for sustainable, high-quality, and low-cost sources of food has driven to alternative proteins. To achieve the world goal of 10 billion people by 2050, conventional sources of protein like beef and milk will be stretched while maintaining ethics, resource management, and sustainability in the environment. Thus, alternative protein maybe from plants, insects, algae, fungus, or cultured meat are the solution. Protein production has been transformed with advancements in the area of biotechnology in the form of tissue engineering, fermentation, and precision fermentation. These technologies have produced proteins indistinguishable from conventional alternatives in flavor, texture, and nutrition.
Trending trends indicate howl new food products such as plant-based meat alternatives, insect protein bars, and protein-enriched dairy substitutes are integrating alternative proteins into mainstream diets.
To finance such business, the corporate sector, as well as governments, are putting more resources into infrastructure, research, and policy frameworks. The demand for protein alternatives will also rise due to growing concern for environmental as well as health issues. The alternative proteins will be 3D-printed protein-rich food, bioengineered foods that are more functional, or could be customized according to each and every individual person’s unique nutrition needs. Alternative proteins will serve to drive the world’s food system in a grand shift to a sustainable direction, with broad implications for global climate change, as well as food security.
Author contributions
SK: Data curation, Writing – original draft. NS: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. NR: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abrell, E. L. (2024). Reinventing the meal: A genealogy of plant-based alternative proteins. Agric. Human Values 41, 509–523. doi: 10.1007/s10460-023-10496-6
Ahmad, M., Qureshi, S., Akbar, M. H., Siddiqui, S. A., Gani, A., Mushtaq, M., et al. (2022). Plant-based meat alternatives: Compositional analysis, current development and challenges. Appl. Food Res. 2:100154. doi: 10.1016/j.afres.2022.100154
Alcorta, A., Porta, A., Tárrega, A., Alvarez, M. D., and Vaquero, M. P. (2021). Foods for plant-based diets: Challenges and innovations. Foods 10:293. doi: 10.3390/foods10020293
Bashi, Z., McCullough, R., Ong, L., and Ramirez, M. (2019). Alternative proteins: The race for market share is on. Available online at: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/agriculture/our-insights/alternative-proteins-the-race-for-market-share-is-on (Accessed August 16, 2019).
Belluco, S., Halloran, A., and Ricci, A. (2017). New protein sources and food legislation: The case of edible insects and EU law. Food Secur. 9, 803–814. doi: 10.1007/s12571-017-0704-0
Bleakley, S., and Hayes, M. (2017). Algal proteins: Extraction, application, and challenges concerning production. Foods 6:33. doi: 10.3390/foods6050033
Bryant, C., and Barnett, J. (2019). Consumer acceptance of cultured meat: A systematic review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 3:11. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2019.00011
Bryant, C., van Nek, L., and Rolland, N. C. (2021). European markets for cultivated meat: A comparison of consumer attitudes and willingness to pay in the UK and the Netherlands. Foods 9:1297. doi: 10.3390/foods9091152
Câmara, A. K. F., Ozaki, M. M., de Souza, P. C., dos Santos, M., and Pollonio, M. A. R. (2024). “Hybrid meat products: Using plant, fungi, and insect sources for flexitarian diets—technological, nutritional and sensory insights” in Food Analogues: Emerging Methods and Challenges. eds. Ö. P. Can, M. G. Saraç, and D. A. Türkler (Switzerland: Springer Nature), 245–289.
Caminiti, J., Badiger, A., Amoafo, O., and Serventi, L. (2023). “Understanding new foods: Alternative protein sources” in Sustainable Food Innovation. ed. L. Serventi (Berlin: Springer International Publishing), 135–146.
Cardoso Alves, S., Díaz-Ruiz, E., Lisboa, B., Sharma, M., Mussatto, S. I., Thakur, V. K., et al. (2023). Microbial meat: A sustainable vegan protein source produced from agri-waste to feed the world. Food Res. Int. 166:112596. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112596
Cedeno, F. R. P., Olubiyo, O. J., and Ferreira, S. (2025). From microbial proteins to cultivated meat for alternative meat-like products: A review on sustainable fermentation approaches. J. Biol. Eng. 19:44. doi: 10.1186/s13036-025-00509-9
Chib, A., Gupta, N., Singh, J., Rishi, M., Verma, S., Langeh, A., et al. (2024). The plant advantage: Unlocking the secrets of plant-based proteins. Plant. Arch. 24:75. doi: 10.51470/PLANTARCHIVES.2024.v24.no.1.075
Cravotto, G., and Binello, A. (2016). “Low-frequency, high-power ultrasound-assisted food component extraction” in Innovative Food Processing Technologies (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 3–29.
Cui, Q., Ni, X., Zeng, L., Tu, Z., Li, J., Sun, K., et al. (2017). Optimization of protein extraction and decoloration conditions for tea residues. Hortic. Plant J. 3, 172–176. doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2017.06.003
Dekkers, B. L., Boom, R. M., and van der Goot, A. J. (2018). Structuring processes for meat analogues. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 81, 25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.08.011
Ek, P., Baner, J. M., and Ganjyal, G. M. (2020). “Extrusion processing of cereal grains, tubers, and seeds” in Extrusion Cooking. ed. G. M. Ganjyal (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 225–263.
Enzing, C., Ploeg, M., Barbosa, M., and Sijtsma, L. (2014). Microalgae-based products for the food and feed sector: An outlook for Europe. JRC Sci Policy Rep 1, 19–37. doi: 10.2791/3339
European Commission. (2003). Regulation (EC) No. 1829/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2003 on genetically modified food and feed. Available online at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2003/1829/oj/eng (Accessed May 30, 2025).
European Commission. (2021). The Commission authorises eight genetically modified crops for use as food and feed. Available online at: https://www.isaaa.org/kc/cropbiotechupdate/article/default.asp?ID=18561 (Accessed May 29, 2025).
Faizah, N., Widiyastuti, W., Setyawan, H., and Nurtono, T. (2024). Extraction of antioxidant and antibacterial agents from avocado (Persea americana) seed using pulsed electric field method. Ind. Crop. Prod. 222:119803. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.119803
FDA. (2018). Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act). Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/laws-enforced-fda/federal-food-drug-and-cosmetic-act-fdc-act (Accessed May 29, 2025).
FDA. (2023). Generally recognized as safe (GRAS). Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-ingredients-packaging/generally-recognized-safe-gras (Accessed May 29, 2025).
Fraser, R. Z., Shitut, M., Agrawal, P., Mendes, O., and Klapholz, S. (2018). Safety evaluation of soy leghemoglobin protein preparation derived from Pichia pastoris, intended for use as a flavor catalyst in plant-based meat. Int. J. Toxicol. 37, 241–262. doi: 10.1177/1091581818766318
Giannoglou, M., Andreou, V., Thanou, I., Markou, G., and Katsaros, G. (2022). High pressure assisted extraction of proteins from wet biomass of Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) – a kinetic approach. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 81:103138. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2022.103138
Gorissen, S. H., Crombag, J. J., Senden, J. M., Waterval, W. A., Bierau, J., and van Loon, L. J. (2018). Protein content and amino acid composition of commercially available plant-based protein isolates. Amino Acids 50, 1685–1695. doi: 10.1007/s00726-018-2640-5
Govindan, K. (2024). Theoretical perspectives on sustainable supply chains: Past, present and future. J. Clean. Prod. 439:140657. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.140657
Grafenauer, S., Estell, M., and Hughes, J. (2021). Plant protein and plant-based meat alternatives: Consumer and nutrition professional attitudes and perceptions. Sustainability 13:1478. doi: 10.3390/su13031478
Grand View Research. (2024). India alternative protein market size & outlook, 2023–2030. Available online at: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/horizon/outlook/alternative-protein-market/india (Accessed May 30, 2025).
Hartmann, C., and Siegrist, M. (2017). Consumer perception and behaviour regarding sustainable protein consumption: A systematic review. Appetite 112, 227–234. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2017.02.004
Joshi, V. K., and Kumar, S. (2015). Meat analogues: Plant-based alternatives to meat products—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 55, 1241–1245. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.689381
Kaur, L., Mao, B., Beniwal, A. S., Abhilasha, K. R., Chian, F. M., and Singh, J. (2022). Alternative proteins vs animal proteins: The influence of structure and processing on their gastro-small intestinal digestion. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 122, 275–286. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.02.021
Koole, B. (2022). Veganism and plant-based protein crops: Contentious visioning almost obstructing a transition. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 42, 88–98. doi: 10.1016/j.eist.2021.12.003
Kouřimská, L., and Adámková, A. (2016). Nutritional and sensory quality of edible insects. NFS J. 4, 22–26. doi: 10.1016/j.nfs.2016.07.001
Kumar, S., Ghosh, P., and Agrawal, D. (2021). Single-cell protein: Production and process. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 15:100728. doi: 10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100728
Kumar, M., Tomar, M., Potkule, J., Verma, R., Punia, S., Mahapatra, A., et al. (2021). Advances in the plant protein extraction: Mechanism and recommendations. Food Hydrocoll. 115:106595. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106595
Kurek, M. A., Onopiuk, A., Pogorzelska-Nowicka, E., Szpicer, A., Zalewska, M., and Półtorak, A. (2022). Novel protein sources for applications in meat-alternative products—Insight and challenges. Foods 11:957. doi: 10.3390/foods11070957
Liceaga, A. M. (2019). Approaches for utilizing insect protein for human consumption: Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on protein quality and functionality. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 112, 529–532. doi: 10.1093/aesa/saz010
Lima, M., Costa, R., Rodrigues, I., Lameiras, J., and Botelho, G. (2022). A narrative review of alternative protein sources: Highlights on meat, fish, egg and dairy analogues. Foods 11:2053. doi: 10.3390/foods11142053
Lynch, J., and Pierrehumbert, R. (2019). Climate impacts of cultured meat and beef cattle. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 3:5. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2019.00005
Ma, K. K., Greis, M., Lu, J., Nolden, A. A., McClements, D. J., and Kinchla, A. J. (2022). Functional performance of plant proteins. Foods 11:594. doi: 10.3390/foods11040594
Matassa, S., Boon, N., Pikaar, I., and Verstraete, W. (2016). Microbial protein: Future sustainable food supply route with low environmental footprint. Microb. Biotechnol. 9, 568–575. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12369
McClements, D. J., and Grossmann, L. (2021). A brief review of the science behind the design of healthy and sustainable plant-based foods. NPJ Sci. Food 5:17. doi: 10.1038/s41538-021-00099-y
Medeiros, F., Aleman, R. S., Gabríny, L., You, S. W., Hoskin, R. T., and Moncada, M. (2024). Current status and economic prospects of alternative protein sources for the food industry. Appl. Sci. (Switz) 14:3733. doi: 10.3390/app14093733
Mistry, K., Sardar, S. D., Alim, H., Patel, N., Thakur, M., Jabbarova, D., et al. (2022). Plant-based proteins: Sustainable alternatives. Plant Sci. Today 2022:1652. doi: 10.14719/pst.1652
Mondor, M., and Hernández-Álvarez, A. J. (2022). “Processing technologies to produce plant protein concentrates and isolates” in Plant Protein Foods. eds. A. Manickavasagan, L. T. Lim, and A. Ali (Berlin: Springer International Publishing), 61–108.
Munialo, C. D. (2023). A review of alternative plant protein sources, their extraction, functional characterisation, application, nutritional value and pinch points to being the solution to sustainable food production. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 59, 462–472. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.16467
Munialo, C. D., Stewart, D., Campbell, L., and Euston, S. R. (2022). Extraction, characterisation and functional applications of sustainable alternative protein sources for future foods: A review. Future Foods 6:100152. doi: 10.1016/j.fufo.2022.100152
Nadar, S. S., Rao, P., and Rathod, V. K. (2018). Enzyme assisted extraction of biomolecules as an approach to novel extraction technology: A review. Food Res. Int. 108, 309–330. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.03.006
Nirmal, R., Anyimadu, C. F., Khanashyam, A. C., Bekhit, A. E., and Dhar, B. K. (2024). Alternative protein sources: Addressing global food security and environmental sustainability. Sustain. Dev. 33, 3958–3969. doi: 10.1002/sd.3338
Oonincx, D. G. A. B., and de Boer, I. J. M. (2012). Environmental impact of the production of mealworms as a protein source for humans—A life cycle assessment. PLoS One 7:e51145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051145
Ozturk, O. K., and Hamaker, B. R. (2023). Texturization of plant protein-based meat alternatives: Processing, base proteins, and other constructional ingredients. Future Foods 8:100248. doi: 10.1016/j.fufo.2023.100248
Pipliya, S., Kumar, S., Gupta, R. K., Das, R. S., Meena, D., Srivastav, P. P., et al. (2025). The future of algal proteins: Innovations in extraction and modifications, functional properties, and sustainable food applications. Future Foods 11:100549. doi: 10.1016/j.fufo.2025.100549
Pojić, M., Mišan, A., and Tiwari, B. K. (2018). Eco-innovative technologies for extraction of proteins for human consumption from renewable protein sources of plant origin. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 75, 93–104. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.03.010
Poore, J., and Nemecek, T. (2018). Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science 360, 987–992. doi: 10.1126/science.aaq0216
Post, M. J. (2012). Cultured meat from stem cells: Challenges and prospects. Meat Sci. 92, 297–301. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.04.008
Post, M. J., Levenberg, S., Kaplan, D. L., Genovese, N., Fu, J., Bryant, C. J., et al. (2020). Scientific, sustainability and regulatory challenges of cultured meat. Nat. Food 1, 403–415. doi: 10.1038/s43016-020-0112-z
Precedence Research. (2025). Alternative protein market size and forecast 2025 to 2034. Available online at: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/alternative-protein-market (Accessed May 30, 2025).
Rommi, K., Hakala, T. K., Holopainen, U., Nordlund, E., Poutanen, K., and Lantto, R. (2014). Effect of enzyme-aided cell wall disintegration on protein extractability from intact and dehulled rapeseed (Brassica rapa L. and Brassica napus L.) press cakes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 7989–7997. doi: 10.1021/jf501802e
Roy, B., Hagappa, A., Ramalingam, Y. D., Mahalingam, N., and Shaik, A. B. (2021). A review on lab-grown meat: Advantages and disadvantages. Quest Int. J. Med. Health Sci. 4, 19–24. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.5201528
Rubio, N. R., Xiang, N., and Kaplan, D. L. (2020). Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production. Nat. Commun. 11:6276. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20061-y
Rumpold, B. A., and Schlüter, O. K. (2013). Nutritional composition and safety aspects of edible insects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 57, 802–823. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201200735
Sanders, T. A. B., and Schroeder, N. (2007). Anti-nutrients in plant foods. Br. J. Nutr. 97, S5–S7. doi: 10.1017/S000711450783792X
Schneider, K. R., Fanzo, J., Haddad, L., Herrero, M., Moncayo, J. R., Herforth, A., et al. (2023). The state of food systems worldwide in the countdown to 2030. Nat. Food 4, 1090–1110. doi: 10.1038/s43016-023-00885-9
Schreuders, F. K. G., Dekkers, B. L., Bodnár, I., Erni, P., Boom, R. M., and van der Goot, A. J. (2019). Comparing structuring potential of pea and soy protein with gluten for meat analogue preparation. J. Food Eng. 261, 32–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2019.04.022
Schweiggert-Weisz, U., Eisner, P., Bader-Mittermaier, S., and Osen, R. (2020). Food proteins from plants and fungi. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 32, 156–162. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2020.08.003
Sexton, A. E., Garnett, T., and Lorimer, J. (2022). Vegan food geographies and the rise of Big Veganism. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 46, 605–628. doi: 10.1177/03091325211051021
Sha, L., and Xiong, Y. L. (2020). Plant protein-based alternatives of reconstructed meat: Science, technology, and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 102, 51–61. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.05.022
Shanthakumar, P., Klepacka, J., Bains, A., Chawla, P., Dhull, S. B., and Najda, A. (2022). The current situation of pea protein and its application in the food industry. Molecules 27:5354. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165354
Smetana, S., Mathys, A., Knoch, A., and Heinz, V. (2017). Meat alternatives: Life cycle assessment of most known meat substitutes. J. Clean. Prod. 142, 3789–3797. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.084
Stephens, N., Di Silvio, L., Dunsford, I., Ellis, M., Glencross, A., and Sexton, A. (2018). Bringing cultured meat to market: Technical, socio-political, and regulatory challenges in cellular agriculture. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 78, 155–166. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.04.010
Surya Ulhas, R., Ravindran, R., Malaviya, A., Priyadarshini, A., Tiwari, B. K., and Rajauria, G. (2023). A review of alternative proteins for vegan diets: Sources, physico-chemical properties, nutritional equivalency, and consumer acceptance. Food Res. Int. 173:113479. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113479
Sweers, L. J. H., Mishyna, M., Ahrné, L. M., Boom, R. M., Fogliano, V., Patra, T., et al. (2024). Pulsed electric field processing of edible insect slurries induces thermally-assisted microbial inactivation. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 10:100940. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100940
Talwar, R., Freymond, M., Beesabathuni, K., and Lingala, S. (2024). Current and future market opportunities for alternative proteins in low- and middle-income countries. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 8:102035. doi: 10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.102035
Tiwari, B. K. (2015). Ultrasound: A clean, green extraction technology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 71, 100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2015.04.013
Tuomisto, H. L., and de Mattos, M. J. T. (2011). Environmental impacts of cultured meat production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 6117–6123. doi: 10.1021/es200130u
Turck, D., Bohn, T., Castenmiller, J., and Knutsen, H. K. (2021). Safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food pursuant to regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 19:e06779. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6779
Turck, D., Bresson, J. L., Burlingame, B., Dean, T., Fairweather-Tait, S., and van Loveren, H. (2016). Guidance on the preparation and presentation of an application for authorisation of a novel food in the context of regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 14:e04594. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2016.4594
Uma, G., Jeraldine Nisha, S., Rameshbabu, D., Citarasu, T., and Immanuel, G. (2023). “Algal polymers, proteins, and pigments for industrial applications” in Haematococcus: Biochemistry. eds. R. Raja, S. Hemaiswarya, M. Narayanan, S. Kandasamy, and K. R. Jayappriyan (Berlin, Springer Nature: Biotechnology and Biomedical Applications), 247–271.
USDA. (2019). USDA and FDA announce a formal agreement to regulate cell-cultured food products from cell lines of livestock and poultry. Available online at: https://www.fsis.usda.gov/news-events/news-press-releases/usda-and-fda-announce-a-formal-agreement-regulate-cell-cultured (Accessed May 29, 2025).
Van Huis, A. (2013). Potential of insects as food and feed in assuring food security. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 58, 563–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-120811-153704
Vegconomist. (2021). Global alternative proteins to reach US$4.8 billion by 2027: China and mycoprotein as key drivers. Available online at: https://vegconomist.com/studies-and-numbers/global-alternative-proteins-to-reach-us4-8-bn-by-2027-china-mycoprotein-as-key-drivers/ (Accessed Dec 2, 2023).
Verbeke, W. (2015). Profiling consumers who are ready to adopt insects as a meat substitute in a Western society. Food Qual. Prefer. 39, 147–155. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2014.07.008
Von Braun, J., Afsana, K., Fresco, L. O., and Hassan, M. (2023). Science and innovations for food systems transformation. Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
Yadav, S., Kambhampati, V., and Mishra, S. (2025). “Future trends in food and dairy process engineering and business: A comprehensive exploration” in Engineering Solutions for Sustainable Food and Dairy Production: Innovations and Techniques in Food Processing and Dairy Engineering. eds. S. C. Deka, C. Nickhil, and A. K. Haghi (Berlin: Springer Nature Switzerland), 515–534.
Yi, L., Lakemond, C. M., Sagis, L. M., Eisner-Schadler, V., van Huis, A., and van Boekel, M. A. (2013). Extraction and characterisation of protein fractions from five insect species. Food Chem. 141, 3341–3348. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.05.115
Yu, Q., Guo, M., Zhang, B., Wu, H., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, L. (2020). Analysis of nutritional composition in 23 kinds of edible fungi. J. Food Qual. 2020:8821315.
Yuksel, S., and Mohr, J. J. (2023). Disrupting the plate: Cultured meat technology. Available online at: https://cmr.berkeley.edu/2023/07/disrupting-the-plate-cultured-meat-technology/ (Accessed Jul 31, 2023).
Yuliarti, O., Muhd, B., Abdullah, F., Tan, M. F., and Tay, J. K. K. (2023). “Plant-based meat analogue” in Engineering Plant-Based Food Systems. eds. S. Prakash, B. R. Bhandari, and C. Gaiani (Cambridge, MA: Academic Press), 169–183.
Zhao, H., Shen, C., Wu, Z., Zhang, Z., and Xu, C. (2020). Comparison of wheat, soybean, rice, and pea protein properties for effective applications in food products. Journal of food biochemistry. 44:e13157.
Zion Market Research. (2025). Alternative protein market size, share, value and forecast 2030. Available online at: https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/report/alternative-protein-market (Accessed May 25, 2025).
Keywords: alternative protein, extraction methods, market possibility, processing methods, veganism
Citation: Kaur SP, Sagar NA and Rani N (2025) Alternative proteins: innovations in sources, processing, and consumption. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1641712. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1641712
Edited by:
Debabandya Mohapatra, Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), IndiaReviewed by:
Carolina Ramírez-López, National Polytechnic Institute (IPN), MexicoBablu Kumar Dhar, Mahidol University, Thailand
Copyright © 2025 Kaur, Sagar and Rani. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Narashans Alok Sagar, bmFyYXNoYW5zLmFsb2tAZ21haWwuY29t
 Simar Preet Kaur1
Simar Preet Kaur1 Narashans Alok Sagar
Narashans Alok Sagar Nitu Rani
Nitu Rani