Featured news
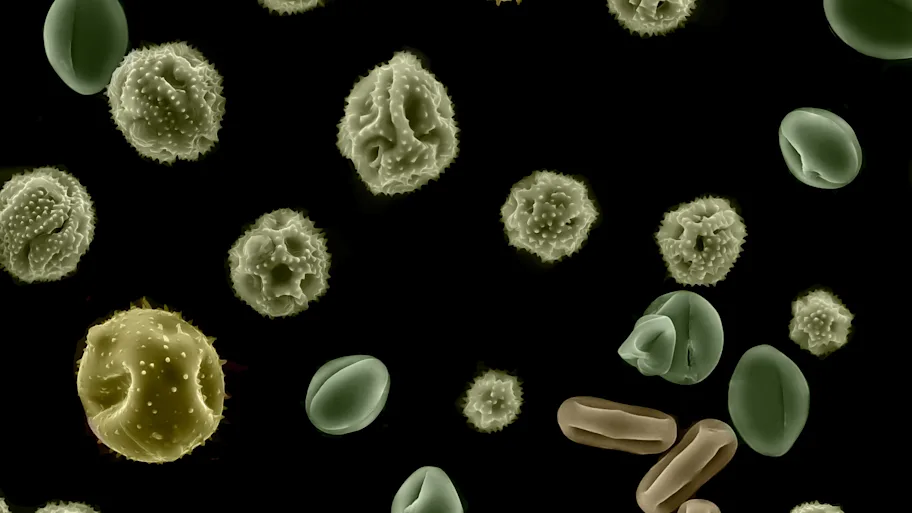
Natural antimicrobial drugs found in pollen could help us protect bee colonies from infection
Pollen gathered by honeybees contains antimicrobial-producing bacteria that protect the hive against disease


Featured news
Pollen gathered by honeybees contains antimicrobial-producing bacteria that protect the hive against disease

Health
Measles infections are on the rise, due partly to falling vaccination rates — and because of their work, healthcare workers and those around them are particularly vulnerable. In a new Frontiers in Public Health article, Nikki Heinze and her colleagues talk to healthcare workers in a London hospital to understand the factors that encourage or discourage measles vaccination. In this editorial, Heinze explores those factors, and calls for action to improve immunity screening, raise awareness, and support healthcare workers who want to be vaccinated.

Featured news
Intravenous lactate is enough to trigger release of brain-rejuvenating hormone, also without physical exercise

Featured news
Scientists date dinosaur eggs that had laid buried in rock for millions of years for the first time, using new, ‘atomic clock for fossils’ method



Health
Reducing industrial animal use can help to shrink our carbon footprint and boost health—but doing so means we need nutritious meat alternatives that are also tasty and affordable.

Health
Measles infections are on the rise, due partly to falling vaccination rates — and because of their work, healthcare workers and those around them are particularly vulnerable. In a new Frontiers in Public Health article, Nikki Heinze and her colleagues talk to healthcare workers in a London hospital to understand the factors that encourage or discourage measles vaccination. In this editorial, Heinze explores those factors, and calls for action to improve immunity screening, raise awareness, and support healthcare workers who want to be vaccinated.

Health
Scientists studying people taking GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic found that those who experienced emotional eating were less likely to lose clinically significant weight.

Health
Labelling expressed breast milk could be a way to ensure babies receive important cues at the right time, helping busy mothers support the development of their baby

Neuroscience
Listening to joyful music helped study participants with motion sickness recover better than other participants — while sad music helped less than doing nothing.

Neuroscience
In well-designed gardens, our gaze shifts quicker and more often. Researchers believe this could be key to understanding the relaxing effects gardens can have on viewers.

Neuroscience
A new model of brain metabolism – the most complex ever generated –shows how altering key chemicals could restore aged cells to their youthful activity and resilience.

Neuroscience
The auricular muscles, which helped our distant ancestors move their ears to improve hearing quality, activated when people were trying to listen to competing sounds.

Environment
Scientists studying the devastating Lāhainā, Maui fires of August 2023 found that deaths were two-thirds higher than expected that month — and 367% higher during the most intense week of the blaze.

Environment
Stable isotope analysis can tell apart ivory from mammoths dug up from the permafrost and modern elephants, closing a loophole for selling elephant ivory

Environment
Scientists studying the impact of solar power on local neighborhoods find that most people living close to large-scale solar plants wouldn’t mind if a new plant was built nearby.

Environment
First video footage shows impacts of anchor and chain damage caused by cruise, research, fishing, and private vessels on Antarctic sea floor and animals, highlighting critically understudied conservation issue.

Psychology
Scientists find that people mostly avoid social media ads when they see them, but many ads blend in seamlessly.

Psychology
Physiological rhythms could explain why Italian university students were more likely to fail exams early or late in the day.

Psychology
Study participants asked to choose whether to empathize with or describe people preferred to empathize with groups, despite finding it difficult and distressing.

Psychology
A researcher put physical distance between people and their phones and found that our devices may not be the cause of our distraction – it’s what we do with them.

Space sciences and astronomy
Guest editorial by Prof Heidi Newberg, an astrophysicist at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and author of a new Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences article

Space sciences and astronomy
Scientists successfully identify microbe fossils in terrestrial rocks like those found on Mars, opening up the possibility of searching for fossils on the Red Planet.
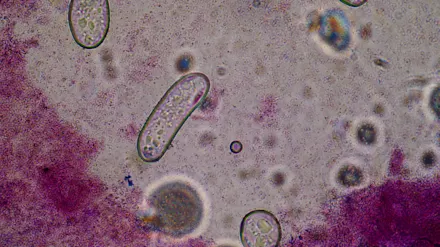
Space sciences and astronomy
Scientists explored microbial movement as a possible biosignature to detect life on Mars and beyond, cheaper and faster than ever before.

Space sciences and astronomy
Space belongs to no-one, yet many nations and private entities now plan to lay their claim on its resources. In a recent Frontiers in Space Technologies article, Nishith Mishra, Martina Elia Vitoloni and Dr Joseph Pelton shared their thoughts about how plans to exploit the ocean floors could impact the way resources from space are used and managed.
Get the latest research updates, subscribe to our newsletter