- 1Colleges of Human and Osteopathic Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
- 2Department of Medicine, College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
- 3College of Osteopathic Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
- 4Department of Family Practice, College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
- 5Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, College of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
- 6Department of Physiology, College of Natural Sciences, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
- 7Department of Nutritional Sciences, Harold Hamm Diabetes Center, College of Allied Health, University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, OK, United States
- 8College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
Aggressive primary brain tumors (APBT) glioblastoma multiforme and grade IV astrocytoma are treated with multimodality treatments that include surgery to remove as much tumor as possible without sacrificing neurological function followed by radiation therapy and chemotherapy usually temozolomide. Survivals in adults are in the range of 8–16 months. The addition of a ketogenic diet (KD) to rodents with transplanted brain tumors increased survival in nine of 11 animals to over 299 days compared to survival in untreated controls of 33 days and radiation only controls of 38 days. We treated humans with APBT with standard of care neurosurgery immediately followed by 6 weeks of an adjuvant ketogenic diet concurrent with radiation therapy and temozolomide. Twice daily measurements of blood ketones and glucose were recorded and the patients' diet was modified toward the goal of maintaining blood ketone levels approaching 3 mM. Of the nine patients who completed the protocol three younger patients age 32, 28, and 22 at enrollment are alive and employed with clinically stable disease and brain images 74, 58, and 52 months since diagnosis. All the six older patients mean age 55 have died with disease progression detected on average 8 months after Dx. In conclusion: 1. It is possible to implement and maintain dietary induced ketosis in patients with APBT; 2. The longer survivals observed in younger patients treated with KD need to be confirmed in larger studies that should be focused on younger patients possibly under age 40.
Introduction
While treatments for many malignancies have advanced to more targeted therapies, systemic treatments for aggressive primary brain malignancies (glioblastoma multiforme, GBM, also known as WHO grade IV astrocytoma) continue to rely on alkylating agents that can cross the blood brain barrier (usually temozolomide, TMZ) (1). Current therapy includes surgical resection of as much of the tumor as possible without impairing vital brain functions, followed by radiation therapy and TMZ (2). The addition of TMZ prolongs survival on average 2.5 months (3). Bevacizumab (Avastin®) does not increase survival in patients with newly diagnosed GBM, but is helpful in the treatment of relapsed patients (4). Wearing an “electric hat” for alternating electric field therapy is reported to prolong survival on average by 2.7 months (5). These therapies prolong life incrementally with median survivals in adult patients in the range of 8–16 months (6).
Studies including rodent models suggest that adding a ketogenic diet (KD) to some of the standard treatments used in humans may prolong survival. The addition of KD to radiation therapy markedly prolonged the life of nine of 11 rodents. Histological evaluation 299 days post GBM implantation showed that nine of 11 animals were free of disease. This compared with survival of 33 days in untreated controls, and 38 days in animals treated with just radiation (7). Reports from other investigators also demonstrate increased survival in animals treated with KD, with retarded growth of their brain malignancy (8–11).
We report long term follow up of nine adult patients with aggressive primary brain tumors who, following their initial neurosurgery, were treated with 6 weeks of an adjuvant KD combined with standard of care radiation therapy and chemotherapy with TMZ. The patients' blood ketones were measured twice daily and the results were used to make adjustments in their diets to assure that ketosis was maintained during the entire 6 weeks of the study period.
Methods
Clinical Protocol
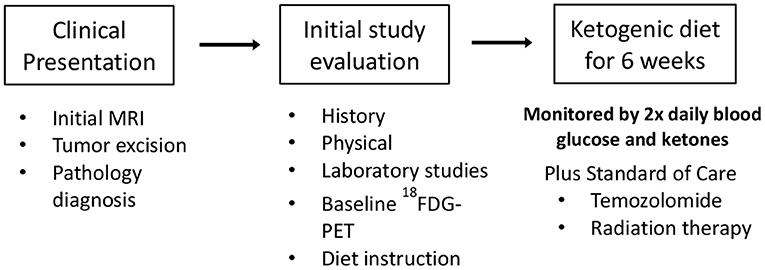
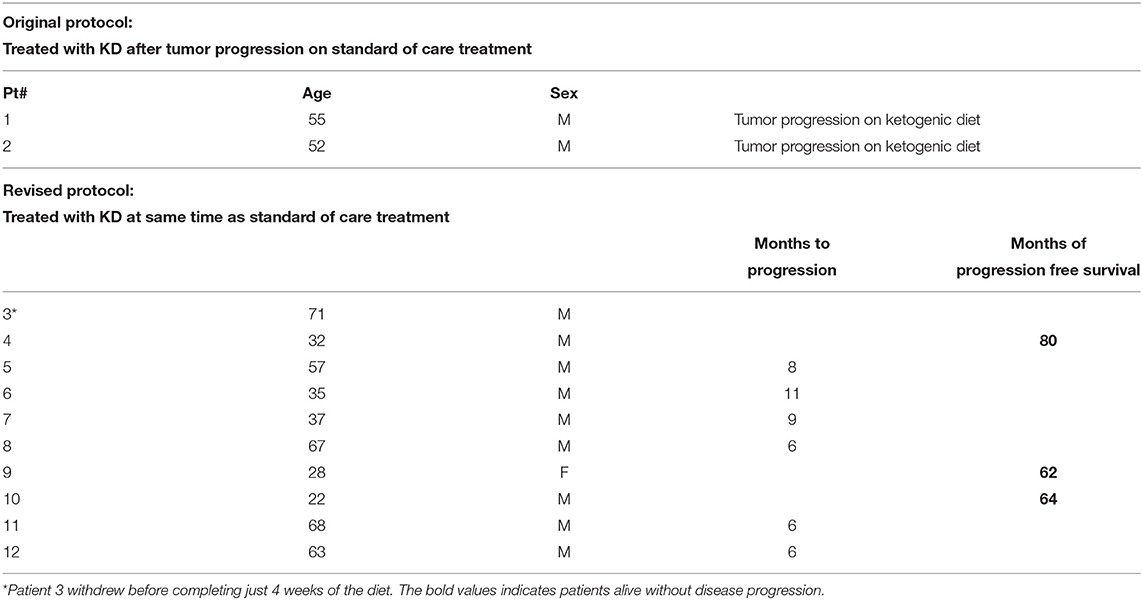
After signing informed consent 12 patients were enrolled in our clinical trial protocol that was IRB approved (11-452s). Two patients (#1 and #2, Tables 1, 2) were studied with the original protocol that stipulated starting the KD after they failed conventional treatments, and 10 were treated with the revised protocol that started the KD at the same time as the initial radiation and chemotherapy treatments, and continued KD for 6 weeks. This protocol had the primary objectives of investigating side effects attributable to the KD, as well as noting tumor response and time to progression. Patient #3 withdrew before completing just 4 weeks of the diet because he had to return to work as a long haul truck driver and could not complete the protocol after the fourth week. Nine patients completed the revised protocol.
The inclusion criteria were participants must be over 16 years of age, had histologically confirmed diagnosis of GBM, had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of ≤ 2, a life expectancy of >3 months, could tolerate a high-fat diet, and had the ability to give informed consent. The exclusion criteria were participants may not have diabetes mellitus, may not have had a cholecystectomy within a year prior to entering the study, did not have any malignancy other than the brain cancer, had not participated in another investigational study within 2 weeks prior to this study's entrance, did not have brain metastasis from a non-brain primary tumor, did not have any major comorbidity such as liver, kidney, or heart failure, and were not pregnant.
The protocol KD was caloric balanced, based on the patient's starting weight and was constructed using the KetoDietCalculator software program so that the ratio in grams of fat to combined grams of protein and carbohydrates was 3:1. The calculation ranges used for all subjects in the original protocol was 20–25 kilocalories (kcal)/kilogram (kg) of body weight, considered a mild restriction. The protein was low at 20 kcal/kg body weight so 25 kcal/kg was used to provide minimum of 0.6 gram (g) protein (pro)/kg. Actual meals plan for all subjects started as a range of 23–25 kcal/kg. In that range, with a 3:1 ratio, a 0.6–0.7 g pro/kg was provided. Calculations for an 1,800 kcal daily intake yields the following range of macronutrients: 1,566 fat kilocalories (174 grams of fat) 234 protein and carbohydrate kilocalories (58.5 grams). Protein grams for the meal plan are based on the subject's weight to achieve at least 0.6 gm pro/kg and the remaining kcal from carbohydrates. A gram food scale was given to each participant to ensure the correct measurements of each food item as calculated by the KetoDietCalculator. Other studies have used 1,600 kcal and higher fat ratio of 4:1 but those provide even lower protein so are not sustainable for muscle maintenance.
Before starting and after completing the KD protocol, the patients had a history and physical exam along with complete blood counts, chemistries, lipids, and uric acid. During the 6 weeks of KD, the patients recorded their daily weights, and twice daily measurements of blood glucose and ketones obtained upon waking prior to eating and evenings 2 h after eating. Each patient was given an Omron Model HBF-400 Scale for their daily weights, an Abbot Precision Xtra Meter with test strips to measure their blood ketones and glucose twice daily, a log to record their results and a food scale. Participants received dietary instruction by a registered dietitian who developed a meal plan and menus for each subject. In addition, a dietitian called or visited the patients regularly (at least once a week) to review results of the patients' glucose and ketone measurements as they related to the food logs which were kept by the patients throughout their time on the KD. Follow up examination and imaging were at the discretion of the referring physician.
Protocol Revision, Tolerability, and Side Effects
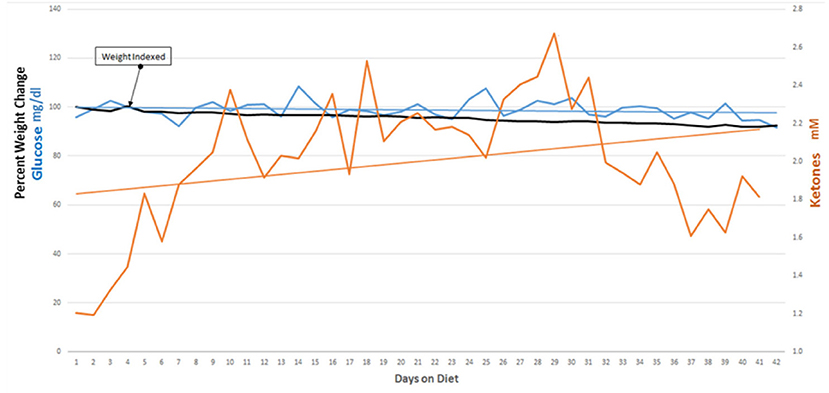
Our initial protocol stipulated starting of the KD after tumor growth was demonstrated following the patients' initial treatment with surgery, radiation and temozolomide. We revised our protocol based on a report, in a rodent model, that nine of 11 mice with a transplanted primary brain tumor that were treated with a KD simultaneously with radiation therapy survived, whereas all of the control mice and mice treated with only radiation therapy or only KD died (7). The success of this simultaneous dual treatment in animals prompted a revision of our protocol so that patients' initial post-surgery treatment included a KD begun at the same time as radiation therapy and chemotherapy. The enrolled patients maintained ketosis for 6 weeks with support from their family and/or caregivers and our dieticians (MN, and MMN). Participants maintained blood glucoses under 100 mg/dl and blood ketones around 1–2 mM. All participants lost weight, averaging about 5 lbs. Combining the KD with standard-of-care radiation and chemotherapies did not add any significant side effects to the patients' therapy.
Results
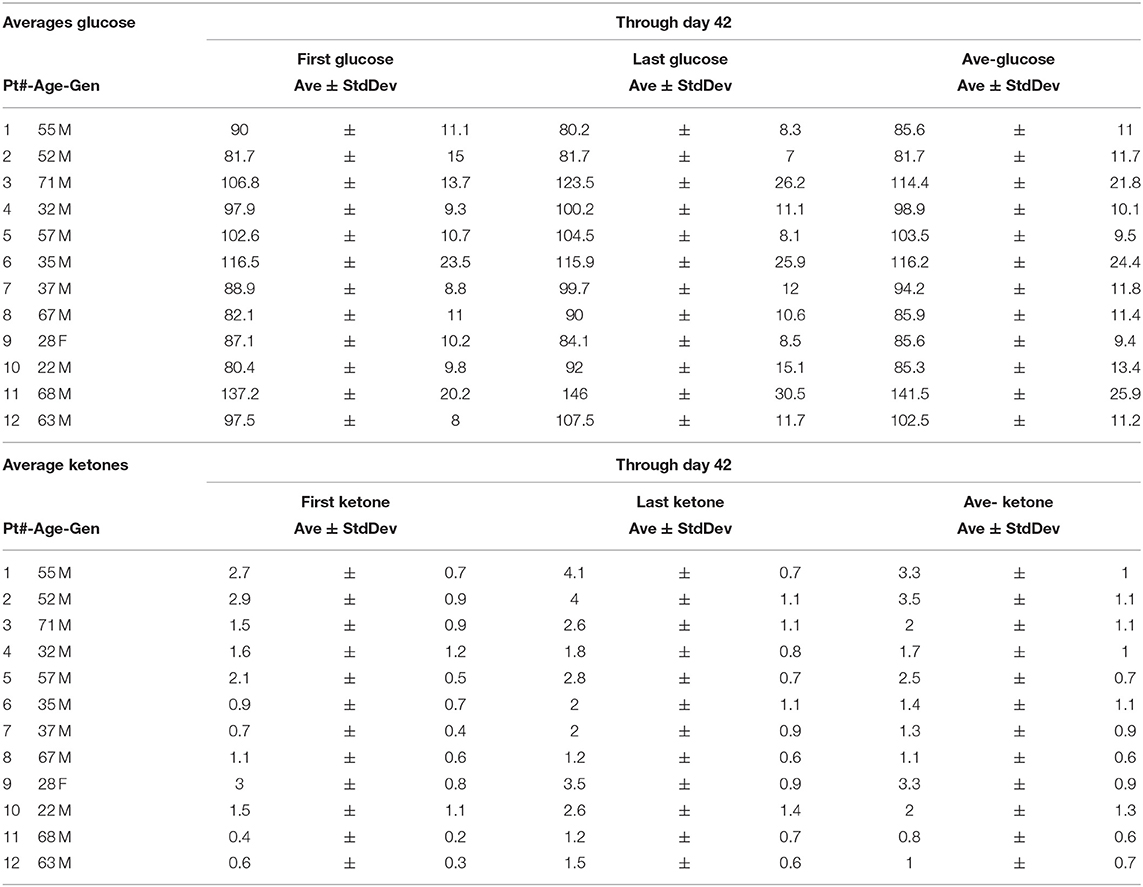
Nine of 10 patients completed the revised protocol (Figure 1) with KD therapy initiated at the same time that they started their treatments with radiation therapy and TMZ. Patient #3 had to return to work as a long haul truck driver and could not complete the protocol after the fourth week. Blood glucose and ketone concentrations were measured twice daily, fasting in the morning when the patients first awoke and in the evening before they went to bed. Table 1 shows the means and standard deviations for each patient's ketone and glucose measurements on days 1 and 14 and averages throughout the study. Aggregate averages for all the patients and lines of linear best fit are depicted in Figure 2 for the patients' twice daily blood glucose and ketone measurements as well as their daily weights.
Patient outcomes for the 12 patients initiating the KD protocols are presented in Table 2. The two patients (Patients # 1 and 2) who were treated with KD after they had progression of their disease following initial standard of care had died as a result of their GBM. Patient #3 failed to complete the required 6 weeks of the protocol. Nine patients (#4 thru 12) completed the protocol and were treated with the KD simultaneously with standard of care radiation and chemotherapies administered following their neurosurgery. Three of these nine patients are progression-free 80, 64, and 62 months since diagnosis. These three long term survivors were younger: 32, 28, and 22 years old at the time of diagnosis. The other six patients were older, mean age 55 at diagnosis, and had progression of their disease 8, 11, 9, 6, 6, and 6 months after their diagnosis. The two patients who are alive 80 and 62 months without progression had GBM that were positive for the isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 R132H mutation (IDH1-R132H). The tumor of the third long-term progression-free patient was grade III astrocytoma (IDH mutation status undetermined).
Discussion
Younger patients with GBM are reported to have a better prognosis (12–17). A recent report documents long term survival in a 26 year old male treated for GBM with only a KD who is alive 80 months post diagnosis with just slow growth of this tumor documented by serial imaging studies (18). Our present study showed three of nine patients treated with an adjuvant ketogenic diet along with standard treatments of surgery and radiation are still alive 80, 62, and 64 months from diagnosis with no evidence of disease advancement. These long-term survivors were all younger (age 32, 28, and 22) when diagnosed as compared to those who died with progression of disease (mean age 55 at diagnosis).
Longer survival in younger patients suggests that aggressive primary brain cancers in these patients may have a biological propensity for slower growth and/or a greater sensitivity to treatment with a ketogenic diet along with radiation and chemotherapy (2, 19). Tumors of two of our patients tested positive for the IDH 131/132 polymorphism associated with longer survival (20). These features at diagnosis suggested that these patients may have had a favorable prognosis. Methylation of the MGMT promoter (21) was not evaluated in our study. The six older patients treated in our study, mean age 55, did not live longer than expected and probably did not benefit from the addition of the ketogenic diet to their therapy. Our results align with previous reports showing that age is a critical factor for survival (22, 23). We suggest that future studies evaluating the addition of a ketogenic diet to GBM therapy should be targeted toward younger patients perhaps 40 years of age or younger (24).
After their initial neurosurgery, radiation, chemotherapy and adjuvant ketogenic diet treatments, all of our patients reported some decrease in mental capacity. One of the surviving patients prior to his GBM diagnosis worked as an investment counselor. After his initial surgeries, radiation and chemotherapy, he could not perform the executive functions quick enough to continue working in that capacity. However, he is able to work in a position that does not require such a high level of executive function. All three of the surviving patients have returned to full employment.
The cooperation of the patients, their families and caregivers was essential for preparation of the foods in the ketogenic diet and twice-a-day monitoring and recording of blood glucose and ketone levels. Following neurosurgery, patients may require assistance to check their blood ketones and implement changes in their diet based on their ketone concentrations. It is critical that the patients' ketotic state be verified with twice daily checks of the level of ketones in their blood. Ongoing reinforcement of the protocol was provided by dietitians (MMN or MN) who helped to maintain the patients' ketotic state throughout the 6 weeks study. If needed, dietary modifications were made by the dietitian (MN) to keep the twice daily blood ketone levels approaching 3 mM. Patients and their families agreed that 6 weeks was about as long as they could adhere to the dietary specifications and restrictions stipulated by the ketogenic diet.
It was hypothesized that aggressive primary brain tumors may not be able to metabolize ketones like normal brain tissues depriving the tumor tissue of nutrients required for survival and growth and this was the rationale used to initiate this study (25). However, ketone metabolism in human brain tumors does not differ from metabolism in neighboring normal brain, suggesting that selective ketone metabolic differences between normal and malignant brain cells may not be a plausible mechanism for the proposed antineoplastic effects of dietary induced ketosis (26). β-hydroxybutyrate is the main ketone produced with a ketogenic diet and is known to function as a histone deacetylase inhibitor which affects translation of DNA and this may be part of the mechanism responsible for the significant anti-tumor effects observed in controlled studies using animal models of aggressive primary brain cancers treated with a ketogenic diet (8, 9, 26–29).
Long term survival with aggressive primary brain cancer is possible (30–33). The three younger patients reported here are alive and working with stable brain images and clinical exams following treatment with standard of care neurosurgery followed by radiation, temozolomide and an adjuvant ketogenic diet. The diet was implemented and adjusted over time by registered dieticians experienced with using the ketogenic diet for patients with intractable seizures (34). Following neurosurgery our patients needed help from family members for executive functions and this included assistance with food preparation and adjustments to their diets based on the results of twice a day measurements of blood glucose and ketones.
Previous studies demonstrated that it is possible to prescribe a ketogenic diet in patients with primary aggressive brain malignancies (35–38). Our study extends these reports by enlisting the cooperation of family members and dietitians to help insure maintenance of the ketotic state. Whether the diet contributed to the longevity in our three surviving patients is a question that can only be answered by larger studies. Since 12 older patients with verified diet induced ketosis, six in our study and six reported by van der Leuw (24) did not appear to benefit from an adjuvant ketogenic diet, we suggest that future evaluations of the ketogenic diet in patients with aggressive primary brain cancer be restricted to younger patients, possibly under 40 years of age.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Board (IRB), Michigan State University. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Funding
We remain grateful for initial funding through a grant from Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, and a grant from the VFWRN031117(15SCH) and a grant from The American Institute for Cancer Research #207193.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank (posthumously) Charles Sweeley Ph.D., whose vision, leadership and determination made this research possible. We also thank Donald and Rebecca McMahon, and Dianne Schwartz for helping with data management and graphical design; and Mr. Ira Ginsburg, Vice President Sparrow Hospital (Lansing MI), who facilitated initiation of this research.
References
1. Alexander BM, Cloughesy TF. Adult Glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. (2017) 35:2402–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.0119
2. Nabors LB, Portnow J, Ahluwalia M, Baehring J, Brem H, Brem S, et al. Central nervous system cancers, version 3.2020, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2020) 18:1537–70. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0052
3. Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. (2005) 352:987–96. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043330
4. Gilbert MR, Dignam JJ, Armstrong TS, Wefel JS, Blumenthal DT, Vogelbaum MA, et al. A Randomized Trial of Bevacizumab for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. New England Journal of Medicine. (2014) 370:699–708. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1308573
5. Stupp R, Taillibert S, Kanner A, Read W, Steinberg D, Lhermitte B, et al. Effect of tumor-treating fields plus maintenance temozolomide vs maintenance temozolomide alone on survival in patients with glioblastoma: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2017) 318:2306–16. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.18718
6. Ostrom QT, Patil N, Cioffi G, Waite K, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro Oncol. (2020) 22:iv1–96. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa200
7. Abdelwahab M, Fenton K, Preul M, Rho J, Lynch A, Stafford P, et al. The ketogenic diet is an effective adjuvant to radiation therapy for the treatment of malignant glioma. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e36197. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036197
8. Zhou W, Mukherjee P, Kiebish MA, Markis WT, Mantis JG, Seyfried TN. The calorically restricted ketogenic diet, an effective alternative therapy for malignant brain cancer. Nutr Metab. (2007) 4:5. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-4-5
9. Martuscello RT, Vedam-Mai V, McCarthy DJ, Schmoll ME, Jundi MA, Louviere CD, et al. A supplemented high-fat low-carbohydrate diet for the treatment of glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 22:2482–95. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0916
10. Maeyama M, Tanaka K, Nishihara M, Irino Y, Shinohara M, Nagashima H, et al. Metabolic changes and anti-tumor effects of a ketogenic diet combined with anti-angiogenic therapy in a glioblastoma mouse model. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:79. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79465-x
11. Mukherjee P, Augur ZM, Li M, Hill C, Greenwood B, Domin MA, et al. Therapeutic benefit of combining calorie-restricted ketogenic diet and glutamine targeting in late-stage experimental glioblastoma. Commun Biol. (2019) 2:200. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0455-x
12. Lacroix M, Abi-Said D, Fourney DR, Gokaslan ZL, Shi W, DeMonte F, et al. A multivariate analysis of 416 patients with glioblastoma multiforme: prognosis, extent of resection, and survival. J Neurosurg. (2001) 95:190–8. doi: 10.3171/jns.2001.95.2.0190
13. Gorlia T, van den Bent MJ, Hegi ME, Mirimanoff RO, Weller M, Cairncross JG, et al. Nomograms for predicting survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: prognostic factor analysis of EORTC and NCIC trial 26981-22981/CE.3. Lancet Oncol. (2008) 9:29–38. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70384-4
14. Bozdag S, Li A, Riddick G, Kotliarov Y, Baysan M, Iwamoto FM, et al. Age-specific signatures of glioblastoma at the genomic, genetic, and epigenetic levels. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e62982. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062982
15. Chang CH, Horton J, Schoenfeld D, Salazer O, Perez-Tamayo R, Kramer S, et al. Comparison of postoperative radiotherapy and combined postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy in the multidisciplinary management of malignant gliomas. A joint radiation therapy oncology group and eastern cooperative oncology group study. Cancer. (1983)52:997–1007.
16. Tsao-Wei DD, Hu J, Groshen SG, Chamberlain MC. Conditional survival of high-grade glioma in Los Angeles County during the year 1990–2000. J Neurooncol. (2012) 110:145–52. doi: 10.1007/s11060-012-0949-6
17. Mineo JF, Bordron A, Baroncini M, Ramirez C, Maurage CA, Blond S, et al. Prognosis factors of survival time in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: a multivariate analysis of 340 patients. Acta Neurochir. (2007) 149:245–52. doi: 10.1007/s00701-006-1092-y
18. Seyfried TN, Shivane AG, Kalamian M, Maroon JC, Mukherjee P, Zuccoli G. Ketogenic metabolic therapy, without chemo or radiation, for the long-term management of IDH1-mutant glioblastoma: an 80-month follow-up case report. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:682243. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.682243
19. Lee Y, Scheck AC, Cloughesy TF, Lai A, Dong J, Farooqi HK, et al. Gene expression analysis of glioblastomas identifies the major molecular basis for the prognostic benefit of younger age. BMC Med Genomics. (2008) 1:52. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-1-52
20. Yan H, Parsons DW, Jin G, McLendon R, Rasheed BA, Yuan W, et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. N Engl J Med. (2009) 360:765–73. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808710
21. Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N, Weller M, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. (2005) 352:997–1003. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043331
22. Winger MJ, Macdonald DR, Cairncross JG. Supratentorial anaplastic gliomas in adults. The prognostic importance of extent of resection and prior low-grade glioma. J Neurosurg. (1989) 71:487–93. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.71.4.0487
23. Keles GE, Anderson B, Berger MS. The effect of extent of resection on time to tumor progression and survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme of the cerebral hemisphere. Surg Neurol. (1999) 52:371–9. doi: 10.1016/S0090-3019(99)00103-2
24. van der Louw E, Olieman JF, van den Bemt P, Bromberg JEC, Oomen-de Hoop E, Neuteboom RF, et al. Ketogenic diet treatment as adjuvant to standard treatment of glioblastoma multiforme: a feasibility and safety study. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2019) 11:1758835919853958. doi: 10.1177/1758835919853958
25. Seyfried TN, Kiebish MA, Marsh J, Shelton LM, Huysentruyt LC, Mukherjee P. Metabolic management of brain cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2011) 1807:577–94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.08.009
26. Sperry J, Condro MC, Guo L, Braas D, Vanderveer-Harris N, Kim KKO, et al. Glioblastoma utilizes fatty acids and ketone bodies for growth allowing progression during ketogenic diet therapy. iScience. (2020) 23:101453. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101453
27. Maurer GD, Brucker DP, Bähr O, Harter PN, Hattingen E, Walenta S, et al. Differential utilization of ketone bodies by neurons and glioma cell lines: a rationale for ketogenic diet as experimental glioma therapy. BMC Cancer. (2011) 11:315. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-315
28. Shimazu T, Hirschey MD, Newman J, He W, Shirakawa K, Le Moan N, et al. Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science. (2013) 339:211–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1227166
29. Vertosick FT Jr, Selker RG. Long-term survival after the diagnosis of malignant glioma: a series of 22 patients surviving more than 4 years after diagnosis. Surg Neurol. (1992) 38:359–63. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(92)90022-F
30. Krex D, Klink B, Hartmann C, von Deimling A, Pietsch T, Simon M, et al. Long-term survival with glioblastoma multiforme. Brain. (2007) 130:2596–606. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm204
31. Rutz HP, de Tribolet N, Calmes JM, Chapuis G. Long-time survival of a patient with glioblastoma and Turcot's syndrome. Case report J Neurosurg. (1991) 74:813–5. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.74.5.0813
32. Imperato JP, Paleologos NA, Vick NA. Effects of treatment on long-term survivors with malignant astrocytomas. Ann Neurol. (1990) 28:818–22. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280614
33. Elvidge AR, Barone BM. Long-term postoperative survival in two cases of glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurosurg. (1965) 22:382–6. doi: 10.3171/jns.1965.22.4.0382
34. Zarnowska IM. therapeutic use of the ketogenic diet in refractory epilepsy: what we know and what still needs to be learned. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2616. doi: 10.3390/nu12092616
35. Porper K, Shpatz Y, Plotkin L, Pechthold RG, Talianski A, Champ CE, et al. A phase I clinical trial of dose-escalated metabolic therapy combined with concomitant radiation therapy in high-grade glioma. J Neurooncol. (2021) 153:487–96. doi: 10.1007/s11060-021-03786-8
36. Martin-McGill KJ, Marson AG, Tudur Smith C, Young B, Mills SJ, Cherry MG, et al. Ketogenic diets as an adjuvant therapy for glioblastoma (KEATING): a randomized, mixed methods, feasibility study. J Neurooncol. (2020) 147:213–27. doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03417-8
37. Martin-McGill KJ, Marson AG, Tudur Smith C, Jenkinson MD. The modified ketogenic diet in adults with glioblastoma: an evaluation of feasibility and deliverability within the national health service. Nutr Cancer. (2018) 70:643–9. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2018.1460677
Keywords: glioblastoma multiforme, ketogenic diet, diet therapy, long term survival, verified ketosis
Citation: Schwartz KA, Noel M, Nikolai M, Olson LK, Hord NG, Zakem M, Clark J, Elnabtity M, Figueroa B and Chang HT (2022) Long Term Survivals in Aggressive Primary Brain Malignancies Treated With an Adjuvant Ketogenic Diet. Front. Nutr. 9:770796. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.770796
Received: 04 September 2021; Accepted: 23 February 2022;
Published: 03 May 2022.
Edited by:
Paula Ravasco, Santa Maria Hospital, PortugalReviewed by:
Purna Mukherjee, Boston College, United StatesDavid Ruskin, Trinity College, United States
Copyright © 2022 Schwartz, Noel, Nikolai, Olson, Hord, Zakem, Clark, Elnabtity, Figueroa and Chang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kenneth A. Schwartz, c2Nod2FydDdAbXN1LmVkdQ==
 Kenneth A. Schwartz
Kenneth A. Schwartz Mary Noel
Mary Noel Michele Nikolai
Michele Nikolai Lawrence K. Olson
Lawrence K. Olson Norman G. Hord
Norman G. Hord Micheal Zakem
Micheal Zakem Justin Clark8
Justin Clark8 Howard T. Chang
Howard T. Chang