- Beijing Key Laboratory of Pediatric Respiratory Infectious Diseases, Key Laboratory of Major Diseases in Children, Ministry of Education, National Clinical Research Center for Respiratory Diseases, National Key Discipline of Pediatrics (Capital Medical University), Beijing Pediatric Research Institute, Beijing Children's Hospital, Capital Medical University, National Center for Children's Health, Beijing, China
Epstein-Barr virus-positive T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative disorders (EBV+ T/NK LPD) encompass a heterogeneous group of disorders, including chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection (CAEBV), Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (EBV-HLH), systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoma of childhood and hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder (HVLPD) and so on, predominantly affecting children and young adults with high mortality. Patients with EBV+ T/NK LPD have overlapping clinical symptoms as well as histologic and immunophenotypic features. In this review, we summarized the clinical features of EBV+ T/NK LPD in Chinese patients from the published articles.
Introduction
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive T/natural killer (NK)-cell lymphoproliferative disorder (EBV+ T/NK LPD) encompasses a heterogeneous group of disorders, including chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection (CAEBV), Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (EBV-HLH), systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoma of childhood and hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder (HVLPD) and so on. EBV+ T/NK LPD are rare, predominantly affect children and young adults, and associated with high mortality. To date, only hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been shown to be promising for EBV+ T/NK LPD patients, including those not yet having progressed to lymphoma (1). In this review, we summarized the clinical features of EBV+ T/NK LPD in Chinese patients including CAEBV, EBV-HLH, systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoma of childhood and HVLPD.
Chronic Active Epstein–Barr Virus Infection (CAEBV)
CAEBV has been defined as a systemic EBV-positive lymphoproliferative disease (EBV+ LPD) characterized by fever, lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly developing after EBV infection in patients without known immunodeficiency. CAEBV is more common in children than in adults.
In China, there were only two retrospective studies on the clinical features of CAEBV systematically, one is about pediatric patients and the other is about adult cases (2, 3). In total, eighty one CAEBV patients were reported, including 53 children with a mean age of 6.3 years (ranging from 6 months to 15 years) and 28 adults with a median age of 45 years (ranging from 20 to 81 years). The male to female ratios were 2.12 and 0.75 in children and adults, respectively.
The clinical features and complications of CAEBV in Chinese patients are summarized in Table S1. The most frequent signs and symptoms of CAEBV were fever, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly and lymphadenopathy. Life-threatening complications mainly included hemophagocytic syndrome, hepatic failure, and interstitial pneumonia. The peripheral blood count depletions are common in CAEBV patients. In China, one study about pediatric CAEBV patients showed that there was an imbalance in lymphocyte subsets and disturbance in cellular immunity. The number of lymphocytes, NK cell, B cell, total T cell, CD4+ T cell, and CD8+ T cell in CAEBV were lower than that in acute EBV infection (4). In adult onset CAEBV patients, the B cell, NK cell, CD4+ T cell and CD8+ T cell counts were also decreased (3).
The clinical characteristics of pediatric CAEBV cases were different from that of adult patients in China. The prevalence of hemophagocytic syndrome was lower in pediatric patients than in adult patients. Unlike pediatric cases reported, the manifestations of cardiovascular diseases in adult patients included pulmonary arterial hypertension, decreased cardiac function and aorta vasculitis. A comparison with Japanese CAEBV (5) was also made in Table S1. The incidences of lymphadenopathy and interstitial pneumonitis were comparatively higher and the prevalence of hypersensitivity to mosquito bites was comparatively lower in Chinese patients than in Japanese patients.
CAEBV can be classified into the T-cell, NK-cell and B-cell types, depending on which lymphocyte subset is mainly infected with EBV. However, in Chinese CAEBV patients, EBV infected cell types were analyzed in only small fraction of patients. In a study, in seven out of 10 CAEBV patients the virus infected cell type was detected, with six cases in T cells, and one in NK cells (6).
Although CAEBV occurred in individuals without apparent immunodeficiency, primary HLH associated immune gene mutations were detected in some CAEBV patients in China, such as heterozygous mutations in PRF1, UNC13D, and STXBP2 (7). Furthermore, a pediatric patient with atypical primary immunodeficiency (PID) was reported with CAEBV as the initial symptom (8). Thus, genetic background may play a role in this disease.
There were few studies on the treatment of CAEBV in China. Retrospective studies showed that the prognosis of CAEBV is poor. Without HSCT, only 12.0% patients (5/42) experienced remission for 1 to 3 years after the onset of the disease and 26.2% (11/42) patients died 7 months to 3 years after onset because of the life-threatening complications, such as hemophagocytic syndrome, malignant lymphoma and hepatic failure and so on (2).
Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (EBV-HLH)
HLH is an immune disorder characterized by uncontrolled T lymphocyte and macrophage activation and an excessive production of inflammatory cytokines. EBV-HLH is the most frequent subtype of secondary HLH triggered by infections. Eligibility criteria for EBV-HLH were as follows: (1) meeting HLH-2004 diagnostic criteria (9), (2) high level of EBV viral load in the peripheral blood or tissues or number of cells containing EBV-encoded small RNA (EBER) in the peripheral blood or tissues.
In China, most of the studies on EBV-HLH were retrospective (10–12). There was no exact number of EBV-HLH cases in China because the overlap among different studies conducted in the same hospital. EBV-HLH was more common in pediatric patients than in adults, with the age of onset from 2 months to 78 years (12, 13). Over all, male was more likely to develop EBV-HLH than female.
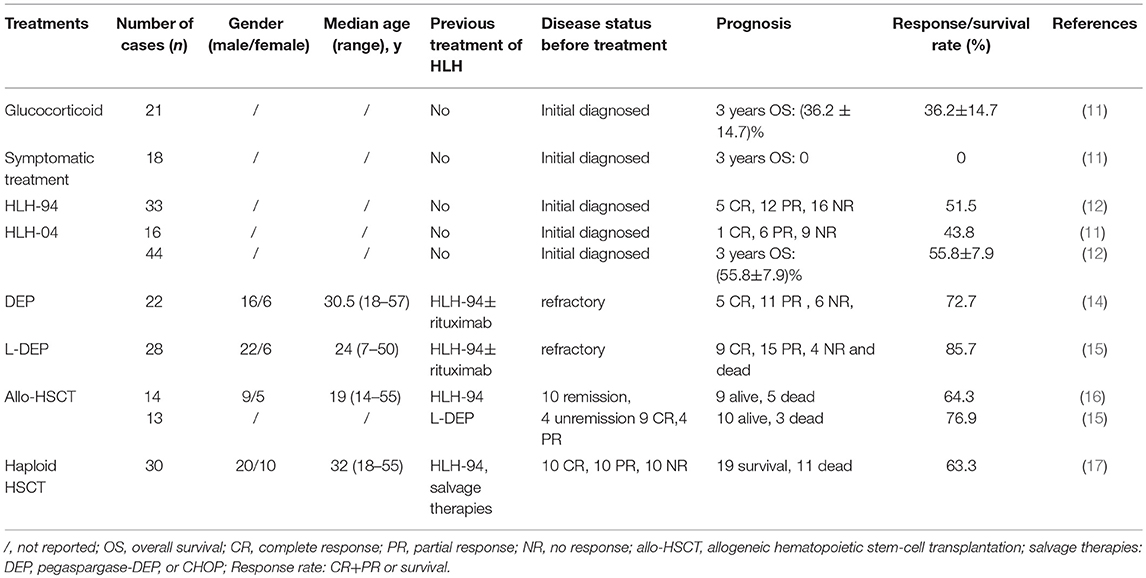
Active EBV-HLH develops rapidly with a high mortality rate if reasonable and effective interventions are not undertaken. The initial therapies of EBV-HLH used in China included antiviral therapy, glucocorticosteroid, symptomatic therapy, HLH-94, and HLH-04 regimen. Antiviral therapy was also used in some EBV-HLH patients in China (10, 12, 13), but the exact benefit of antiviral therapy was not shown in these studies. The treatments of EBV-HLH in China are shown in Table 1. The response rate showed that HLH-94 and HLH-04 regimens were more effective. Without chemotherapy, the prognosis of EBV-HLH was very poor.
In refractory EBV-HLH after the therapy of HLH-94, a salvage therapy DEP regimen (including liposomal doxorubicin, etoposide, and high-dose methylprednisolone) was used and achieved better efficacy with overall response rates (complete and partial response) of 72.7% (14). However, the duration of response after DEP regimen is relatively short and there is a significant risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. A modified PEG-aspargase and DEP regimen combination therapy (L-DEP) was used in refractory EBV-HLH as the salvage therapy (15). The overall response rate of L-DEP regimen was 85.7%. It seems that L-DEP is a safe and effective salvage therapy prior to allo-HSCT (allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation) for refractory EBV-HLH and increases the possibility of such patients receiving allo-HSCT. A prospective multicenter large-scale clinical trial that aims to validate the L-DEP regimen for refractory EBV-HLH is currently underway (ClinicalTrails.gov Identifier: NCT02631109) (15).
For refractory EBV-HLH, allo-HSCT should be used as early as possible. In China, the survival rates of allo-HSCT were 64.3 and 76.9% after the HLH-94 and L-DEP regimen, respectively (15, 16). Haploidentical HSCT was also used in Chinese adult EBV-HLH patients. The 3-year overall survival rate of haploidentical HSCT was 63.3% (17).
Systemic EBV+ T-cell Lymphoma of Childhood
Systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoma of childhood is a life-threatening illness in children and young adults, and is characterized by the clonal proliferation of EBV infected T cells with an activated cytotoxic phenotype. Its name used to be systemic EBV+ T-cell LPD of childhood in the 2008 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of lymphomas (18) and changed to systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoma of childhood in 2016 WHO Classification of lymphoid neoplasms (19).
In China, 3 pediatric cases with systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoma were reported (20, 21) (Table S2). The common clinical features of this disease were fever and hepatosplenomegaly. A special patient manifested as gastrointestinal disorders and skin lesion progressed from CAEBV (T-cell type) to systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoma of childhood was reported (21).
The prognosis of systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoma is poor. Among the 3 cases reported in China, 2 of them died. One patient experienced rapid progression and died within 5 months of onset (20). The other one died of intestinal hemorrhea (21).
Hydroa Vacciniforme-Like Lymphoproliferative Disorder (HVLPD)
HVLPD is a rare type of EBV+ lymphoproliferative disorder of cytotoxic T-cell or NK-cell origin that mainly affect children, characterized by a vesicopapular skin eruption that clinically resemble hydroa vacciniforme (HV). The disease is reported to more frequently affect Asians and Latin Americans. Its name used to be hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoma in 2008 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of lymphomas (18) and changed to HVLPD in 2016 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms (19).
In China, 31 patients with HVLPD were reported and their clinical features were summarized in Table 2 (22–31). Among them, 20 patients were children with the age ranging from 3 to 15 years old, and 11 patients were adult with the age ranging from 18 to 74 years old.
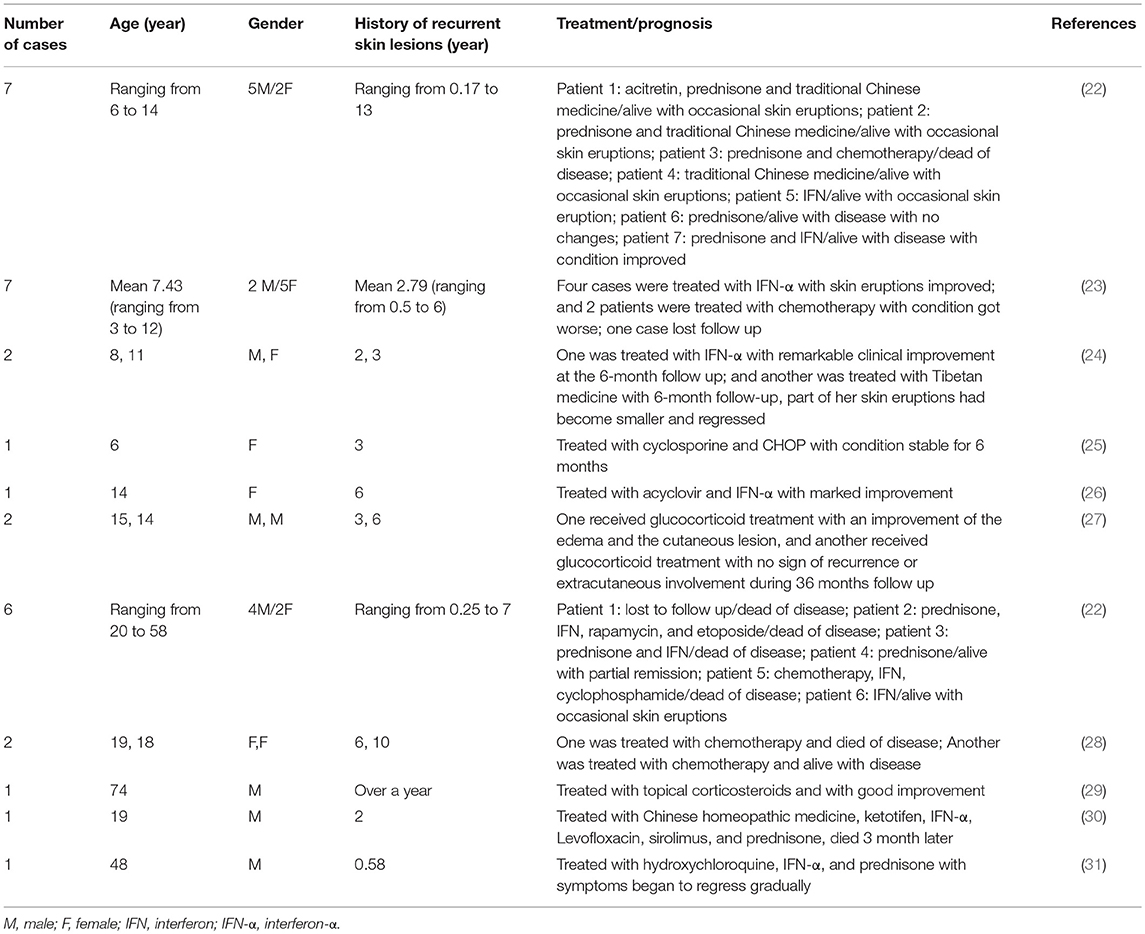
Table 2. Clinical features of hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder (HVLPD) reported in China.
HVLPD patients often had a long history of recurrent skin lesions before systemic manifestations. In Chinese HVLPD patients, the history of recurrent skin lesions ranged from 2 months to 13 years (22). Many therapies have been applied for the treatment of HVLPD, including interferon (IFN), traditional Chinese medicine, acitretin, acyclovir, prednisone, prednisolone, and chemotherapy. IFN and glucocorticoid were used more commonly and always made an improvement of the disease (22–24, 26). Chemotherapy is uncommonly used because the temporary improvement of disease and the worsened condition of patients after the use of it (22, 23, 25). The prognosis of HVLPD was not well. In all patients reported in China, 20 cases (64.5%) had condition improved after therapy, 6 cases (19.4%) died, 3 cases (9.7%) got worse after therapy, 1 case (3.2%) had no change after therapy and 1 case (3.2%) lost follow up.
In conclusion, EBV-positive T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative disorders encompass a heterogeneous group of disorders which have a common feature with excessive lymphoid proliferation of mainly T cells and/or NK cells. They often have overlapping clinical symptoms as well as histologic and immunophenotypic features because both T and NK lymphoid cell types derive from a common precursor.
Limitation of the Mini Review
There were some limitations in this mini review. First, in China EBV infected lymphocyte lineages were only characterized in small part of CAEBV patients, not characterized in EBV-HLH and HVLPD patients. It has been shown that clinical feature of CAEBV are different between T-cell type and NK-cell type. So it is difficult to compare the clinical features of Chinese CAEBV with Japanese CAEBV without considering EBV infected cell types. Second, the treatment and outcome of some CAEBV cases were not fully described in references.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (01-071-31) and Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (Z181100001718061).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2018.00289/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
DEP, doxorubicin-etoposide-methylprednisolone, L-DEP, DEP regimen in combination with PEG-aspargase.
References
1. Okano M. Recent concise viewpoints of chronic active epstein-barr virus infection. Curr Pediatr Rev. (2015) 11:5–9. doi: 10.2174/1573396311666150501002809
2. Lu G, Xie ZD, Zhao SY, Ye LJ, Wu RH, Liu CY, et al. Clinical analysis and follow-up study of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection in 53 pediatric cases. Chin Med J. (2009) 122:262–6.
3. Luo L, Wang H, Fan H, Xie J, Qiu Z, Li T. The clinical characteristics and the features of immunophenotype of peripheral lymphocytes of adult onset chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Beijing. Medicine (2018) 97:e9854. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009854
4. Xing Y, Song HM, Li TS, Qiu ZF, Wu XY, Wang W, et al. [Characteristics of peripheral blood lymphocyte immune subsets in patients with chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi (2009) 47:441–5.
5. Kimura H, Cohen JI. Chronic active epstein-barr virus disease. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:1867. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01867
6. Xing Y, Song HM, Wu XY, Wang W, Wei M. [Significance of detecting the EBV-DNA level in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the EBV-infected cell type in patients with chronic active EBV infection]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi (2011) 49:495–500.
7. Tong CR, Liu HX, Xie JJ, Wang F, Cai P, Wang H, et al. [The study of gene mutations in unknown refractory viral infection and primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi (2011) 50:280–3.
8. Zhong L, Wang W, Ma M, Gou L, Tang X, Song H. Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection as the initial symptom in a Janus kinase 3 deficiency child: Case report and literature review. Medicine (2017) 96:e7989. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007989
9. Henter JI, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer (2007) 48:124–31. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21039
10. Jin YK, Xie ZD, Yang S, Lu G, Shen KL. Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective study of 78 pediatric cases in mainland of China. Chin Med J. (2010) 123:1426–30.
11. Xiao L, Xian Y, Dai BT, Su YC, Xiao JW, Zheng QC, et al. [Clinical features and outcome analysis of 83 childhood Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with HLH-2004 protocol]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi (2011) 32:668–72.
12. Zeng X, Wei N, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhang J, Wu L, et al. [Treatment outcomes and prognostic analysis of 61 Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi (2015) 36:507–10. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2015.06.013
13. Lu G, Xie ZD, Shen KL, Wu RH, Jin YK, Yang S, et al. [Clinical analysis and follow-up study of Epstein-Barr virus associated-hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in childhood]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi (2010) 48:121–6.
14. Wang Y, Huang W, Hu L, Cen X, Li L, Wang J, et al. Multicenter study of combination DEP regimen as a salvage therapy for adult refractory hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood (2015) 126:2186–92. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-05-644914
15. Wang J, Wang Y, Wu L, Zhang J, Lai W, Wang Z. PEG-aspargase and DEP regimen combination therapy for refractory Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Hematol Oncol. (2016) 9:84. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0317-7
16. Fu L, Wang J, Wei N, Wu L, Wang Y, Huang W, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for adult and adolescent hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a single center analysis. Int J Hematol. (2016) 104:628–35. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2062-7
17. Li Z, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhang J, Wang Z. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult patients with Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Leuk Lymphoma (2018) 59:77–84. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1330467
18. Jaffe ES. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphomas: implications for clinical practice and translational research. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program (2009) 523–31. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2009.1.523
19. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, Harris NL, Stein H, Siebert R, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood (2016) 127:2375–90. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569
20. Huang W, Lv N, Ying J, Qiu T, Feng X. Clinicopathological characteristics of four cases of EBV positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders of childhood in China. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2014) 7:4991–9.
21. Xiao HJ, Li J, Song HM, Li ZH, Dong M, Zhou XG. Epstein-barr virus-positive T/NK-Cell lymphoproliferative disorders manifested as gastrointestinal perforations and skin lesions: a case report. Medicine (2016) 95:e2676. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002676
22. Wen PF, Zhang M, Wang TT, Liu HJ, Zhang WY, Liu WP, et al. Comparative study of the clinical pathology, immunophenotype, epstein-barr virus infection status, and gene rearrangements in adult and children patients with hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder. Am J Dermatopathol. (2018). doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000001229. [Epub ahead of print].
23. Xu Z, Lian S. Epstein-Barr virus-associated hydroa vacciniforme-like cutaneous lymphoma in seven Chinese children. Pediatr Dermatol. (2010) 27:463–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01094.x
24. Zhang X, Wang T, Wang L. Hydroa Vacciniforme-Like Lymphoma in Tibetan Children: 2 Cases and a Literature Review. Am J Dermatopathol. (2018) 40:358–61. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000880
25. Li J, Zan Y, Liu H, Liu H, Chen L. Hydroa vacciniforme-like cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in a child: a case report. Medicine (2018) 97:e0319. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010319
26. Shi JQ, Chen QX, Li SF, Li W. Hydroa vacciniforme-like cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Indian J Dermatol. (2014) 59:91–3. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.123516
27. Li Y, Chen XH, Tian XY, Li B, Li Z. Primary cutaneous hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoma with indolent clinical course: report of two cases and review of literature. Int J Surg Pathol. (2013) 21:161–8. doi: 10.1177/1066896912453200
28. Yang YQ, Fan L, Wang L, Xu J, Zhang R, Ge Z, et al. Systemic lymphoma arising from hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoma: report of two cases with review of literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2014) 7:6403–8.
29. Long V, Liang MW, Tan SH. Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder in an elderly Chinese patient and a literature review of adult cases. Int J Dermatol. (2018). doi: 10.1111/ijd.14050. [Epub ahead of print].
30. Wang M, Wang S, Yang QP, Liu YM, Gao LM, Sun H, et al. Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoma of an adult: a case report with review of the literature. Diagn Pathol. (2013) 8:72. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-72
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus, T/natural killer cell, lymphoproliferative disorder, clinical feature, China
Citation: Ai J and Xie Z (2018) Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive T/NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Diseases in Chinese Mainland. Front. Pediatr. 6:289. doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00289
Received: 27 July 2018; Accepted: 19 September 2018;
Published: 09 October 2018.
Edited by:
Shigeyoshi Fujiwara, National Center for Child Health and Development (NCCHD), JapanReviewed by:
Suoqin Tang, PLA General Hospital, ChinaJun-ichi Kawada, Nagoya University Hospital, Japan
Akihisa Sawada, Osaka Medical Center and Research Institute for Maternal and Child Health, Japan
Copyright © 2018 Ai and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhengde Xie, eGllemhlbmdkZUBiY2guY29tLmNu
 Junhong Ai
Junhong Ai Zhengde Xie
Zhengde Xie