- 1School of Pharmacy, Monash University, Subang Jaya, Malaysia
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Quaid i Azam University Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan
- 3National AIDs Control Program, Prime Minister Health Complex, Islamabad, Pakistan
- 4University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab, Allama Iqbal, Lahore, Pakistan
- 5Department of Pharmacy, The University of Lahore, Islamabad, Pakistan
Introduction: Anxiety and depression in people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) can lead to non-adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART), morbidity, and mortality. Therefore, assessing the stigma, social support, and other determinants of anxiety and depression in PLWHA are important for developing further interventions.
Methods: An institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted in 505 PLWHA, approached through systematic sampling, who paid routine visits to the ART center, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences (PIMS), Islamabad. Data was collected by pretested validated hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS). Version 26 of the SPSS was used to apply Logistic regression analysis to identify determinants, and the 95% confidence interval (CI) adjusted odds ratio (AOR) was calculated to assess the magnitude of the relationships.
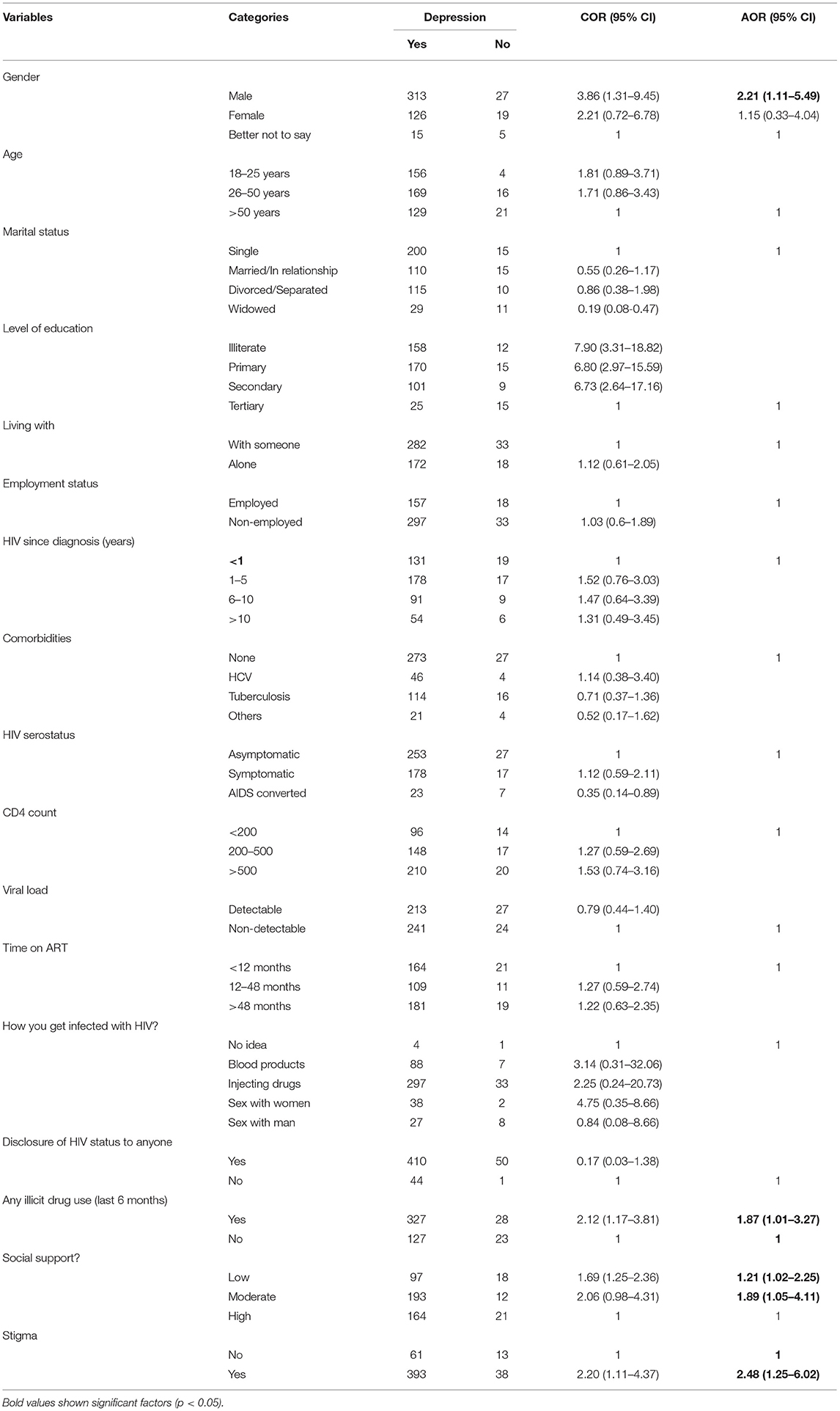
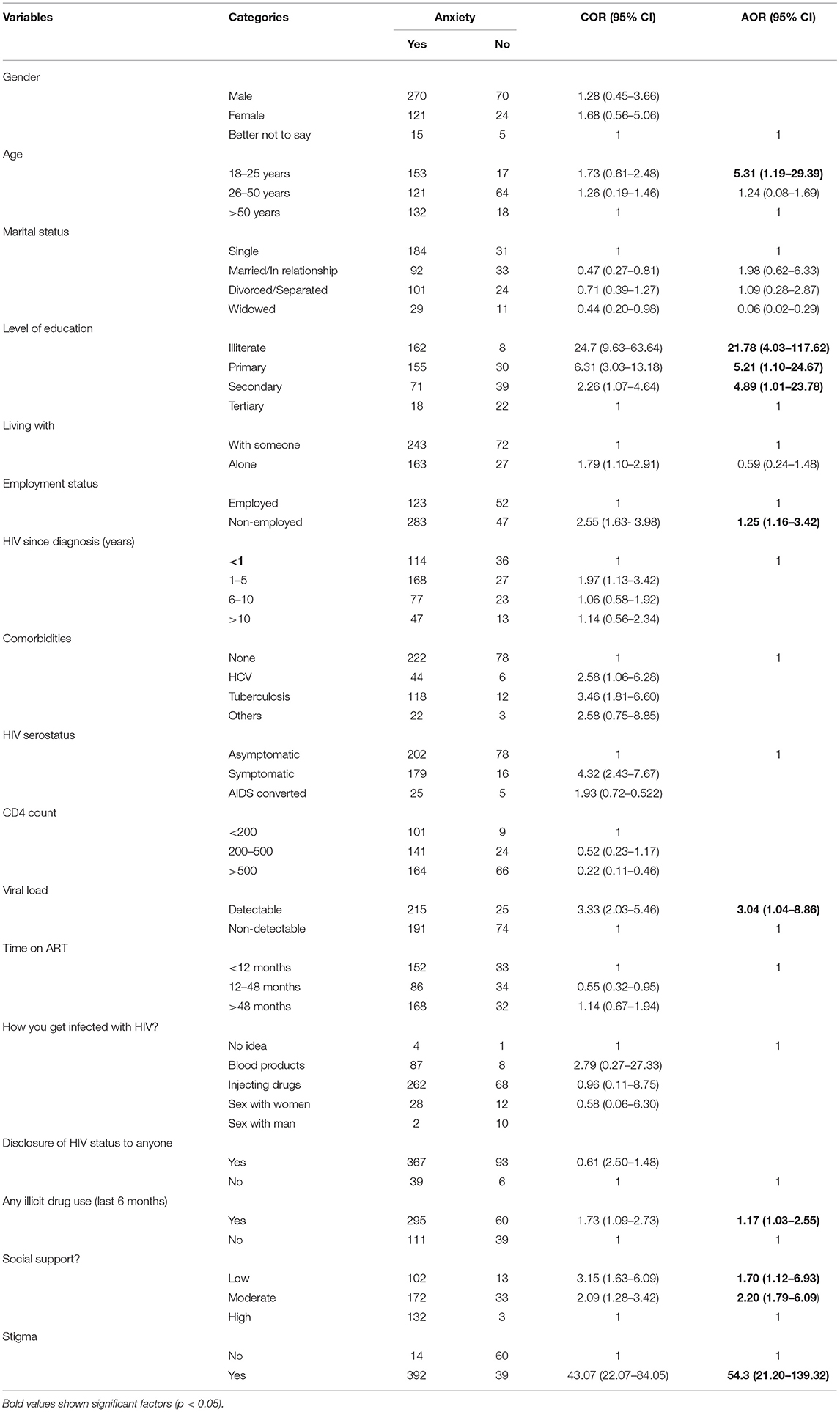
Results: In PLWHA, the prevalence of co-morbid depression and anxiety was 80%. Separately, 89.9% had depression, and 80.3% had anxiety. Use of illicit drugs [AOR = 1.87, 95% CI (1.01, 3.27)], low social support [AOR = 1.21, 95% CI (1.02, 2.25)], being male [AOR = 2.21, 95% CI (1.11, 5.49)], and HIV related stigma [AOR = 2.48, 95% CI (1.25, 6.02)] were significant predictors of depression. Having detectable viral load [AOR = 3.04, 95% CI (1.04, 8.86)], young age [AOR = 5.31, 95% CI (1.19, 29.39)], no formal education [AOR = 21.78, 95% CI (4.03, 117.62)], low [AOR = 1.70, 95% CI (1.12, 6.93)] or moderate [AOR = 2.20, 95% CI (1.79, 6.09)] social support, illicit drugs addiction [AOR = 1.17, 95% CI (1.03, 2.55)], and HIV stigma [AOR = 54.3, 95% CI (21.20, 139.32)] had a remarkable association with anxiety.
Conclusions: Given the high prevalence of anxiety and depression among PLWHA, the Pakistan Ministry of Health should focus more on monitoring mental health, expanding mental health services, and developing interventions based on identified factors to treat depression and anxiety among PLWHA.
Introduction
Currently, 37.6 million people are living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA), and the rate of new infections has decreased from 2.1 million in 2010 to 1.5 million per year worldwide in 2020 (1). However, in low middle-income countries (LMICs) like Pakistan, new HIV infections have increased from 14,000 to 25,000 per year for the same duration (2). Since the introduction of safe combination antiretroviral therapy (ART), HIV/AIDS has progressed from an acute to a manageable chronic condition, and PLWHA's life expectancy has increased as ordinary people, with significant improvements in their quality of life (3–5). Nonetheless, PLWHA is vulnerable to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression due to stigma, prejudice, ART side effects, and neurophysiological changes (6–8).
Depression and anxiety are potentially dangerous conditions that may affect not only personal well-being, relationships, employment, and compliance with medical treatment but are also likely to affect survival (9, 10). Due to limited education of health professionals about determinants of mental health in HIV patients, poor understanding among HIV patients, and lack of advice on clinical issues in HIV clinics, the impact of mental health concerns on HIV patients has sometimes been overlooked in resource-constrained settings (11, 12). As a result, PLWHA are more likely to exhibit anxious and depressive symptoms, affecting illness-related stigma, reducing personal satisfaction, increasing mortality, reducing drug adherence, and impairing their ability to resist illness (13, 14).
Research findings indicate that the prevalence of mental illnesses in PLWHA is two to four times greater than in the general population (15, 16). It was associated with higher viral HIV loads, lower CD4 T lymphocyte counts, and affected adherence that predicts disease progression and mortality (16–18). A recent Ethiopian study reported 32% depression and 34% anxiety in 2019 (16), a Spanish study reported 35.4% depression in 2012 (19), Indian study reported 58.1% depression in 2014 (20). In 2017, Cameron, Brazilian, and Chinese studies reported 28.5, 59, and 80%, respectively, depression in PLWHA (21–23). A recent meta-analysis of 51,143 PLWHA found a global prevalence of depression of about 31%, with the highest prevalence in South America, i.e., 44%, and the lowest prevalence of about 22% in Europe (24). The meta-analysis also reported a lack of data from Pakistan, and the results of some other countries can not be generalized in Pakistani setting (24).
Factors such as age, low income, unemployment, being female, living alone, marital status, substance abuse including intravenous drug use, non-adherence to drugs, stigma, lack of social support, low educational status, and being in symptomatic stage contribute to anxiety and depression among PLWHA (25–28). Compared to other LMICs in which anxiety and depression have been more carefully studied (e.g., countries in Europe and sub-Saharan Africa), Pakistan has a significantly different sociocultural background and a strongly clustered epidemic amongst deported migrants and intravenous drug users (29–31). As such, it cannot be concluded that the reports of anxiety and depression from other LMICs relate to Pakistani conditions. Therefore, we aim to fill the knowledge gap on the stigma, social support, and other determinants of anxiety and depression in PLWHA in Pakistan.
Methods
Ethical Considerations
The Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences (PIMS) ethical review board (ERB) and the National AIDS Control Program of Pakistan (NACP) (Approval Number: 1827) provided the ethical permissions to carry out this project. The study's procedures and objectives were explained verbally and in writing to all PLWHA. Informed consent was obtained from PLWHA members who agreed to participate in research. People living with HIV/AIDS were advised that their involvement would be optional and could be withdrawn at any point. Only those patients who agreed to participate in this study were given booklets, and no one requested to withdraw at any stage of study. The data collected has been saved confidentially and is only available to the research team. All research procedures have been adopted following the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and subsequent amendments (32).
Study Setting and Design
The cross-sectional research was conducted at the ART center of PIMS institute, a tertiary care hospital having 947 beds situated in Islamabad Capital Territory of Pakistan. Antiretroviral therapy Center PIMS is Pakistan's largest HIV referral center, with more than 3,600 registered PLWHA receiving free HIV treatment (5). Every day, 15–20 PLWHA visit the ART center to meet their medical needs. This center was chosen because of its geographical location, allowing patients from various cultural backgrounds and places in Pakistan to access ART (31, 33).
Study Population and Sampling Technique
Adult PLWHA (>18 years of age) with a confirmed HIV diagnosis and a disease duration of more than 6 months, with recent viral load and CD-4 lymphocyte count tests (no more than 2 months old at the time of data collection), on ART therapy, and scheduled for regular follow-up at the ART center were invited to participate in the study. Participants who were terminally ill, visually impaired, deaf, cognitively challenged, or unable to understand and converse in Urdu (Pakistan's national language) were excluded from the study.
The sample size was calculated with the Raosoft calculator using a single population proportion formula with a 5% margin of error and an HIV prevalence of 180,000 (34). Assuming that 20% of the total were non-responsive, a sample size of 505 was required. The sampling period was calculated by dividing the research population by 7 weeks of follow-up during the data collection period. The sample was taken as a whole, and the starting point was chosen at random.
Research Instrument
The data collection instrument consisted of sociodemographic (gender, age, marital status, level of education, and employment) and clinical parameters (viral load, CD4 T lymphocytes counts, comorbidities, HIV serostatus, time since on ART) assessing questions. HIV-related stigma was evaluated by a six-item instrument, Internalized AIDS-Related Stigma Scale (IARSS) (35). The internalized stigma is a significant predictor of health outcomes (14, 36). IARSS is an internationally validated tool and has been translated into many other languages and is a brief tool compared to other community tools, such as the Berger stigma scale (37, 38). IARSS measure responses as a binary scale (yes/no) with a cumulative score range (0–6) without any clear prevalence information being interrupted (39). A score of 1–4 indicates no stigma, while a score of 5–6 indicates stigma. Social support for PLWHA has been assessed by using the 12-item Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support (MSPSS) (40). MSPSS is a validated tool in Pakistan that measures the responses on a scale of seven points, ranging from very strongly disagree to very strongly agree (40, 41). The instrument has a score range of 1–7 with three general rankings: poor support 1–2.9, moderate support 3–5, and strong support 5.1–7 (42). Besides, a 14 item hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS) was used to assess anxiety and depression symptoms (43). HADS contains seven items for each anxiety and depression measurement, with a score ≥8 being considered as an indicator of anxiety and depression (44). HADS is psychometrically valid, reliable, and has been extensively used in Pakistan for anxiety and depression evaluation in different health conditions (45–48).
Data Collection Process
The principal investigator (AA) approached each PLWHA attending the ART center and asked them to participate by providing them with study details. AA assessed each consented PLWHA against pre-defined inclusion/exclusion criteria. Those who qualified for the inclusion criteria were provided with a questionnaire booklet and asked to fill it completely and independently. Each respondent completed their questionnaire booklet in 15–20 min, after which it was checked for completeness. AA assisted illiterate and less educated participants by asking them questions verbally and documented their responses. If any missing items were discovered, the respondents were asked to complete them. Participants were not provided with any gifts or monetary benefits due to a lack of funds. Instead, patients' clinical parameters were retrieved from their clinical records at the ART center.
Data Analysis
Data were checked, cleaned, and inserted for analysis in SPSS Version 26 (49). Bivariate analysis was performed to evaluate the association between each independent variable and the dependent variable. Those variables with p < 0.2 in bivariate analysis were managed to enter into the multivariable logistic regression model to confound off any bias from these covariates. To determine associations, the adjusted odds ratio (AOR) that did not include the value 1 in the 95% confidence interval (CI) and p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Finally, the findings were presented in tables in the form of frequency, percentages, and AOR.
Results
Sociodemographic and Clinical Characteristics of PLWHA
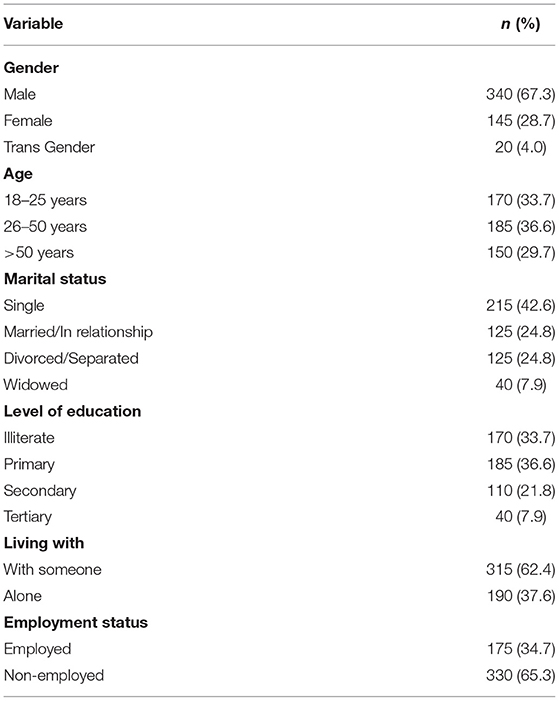
Of the 505 PLWHA included in the study, 340 (67.3%) were males, 185 (36.6%) were of age group 26–50 years, and 170 (33.7%) were illiterate. Among the participants, 315 (62.4%) were living with someone, and 330 (65.3%) were unemployed (Table 1).
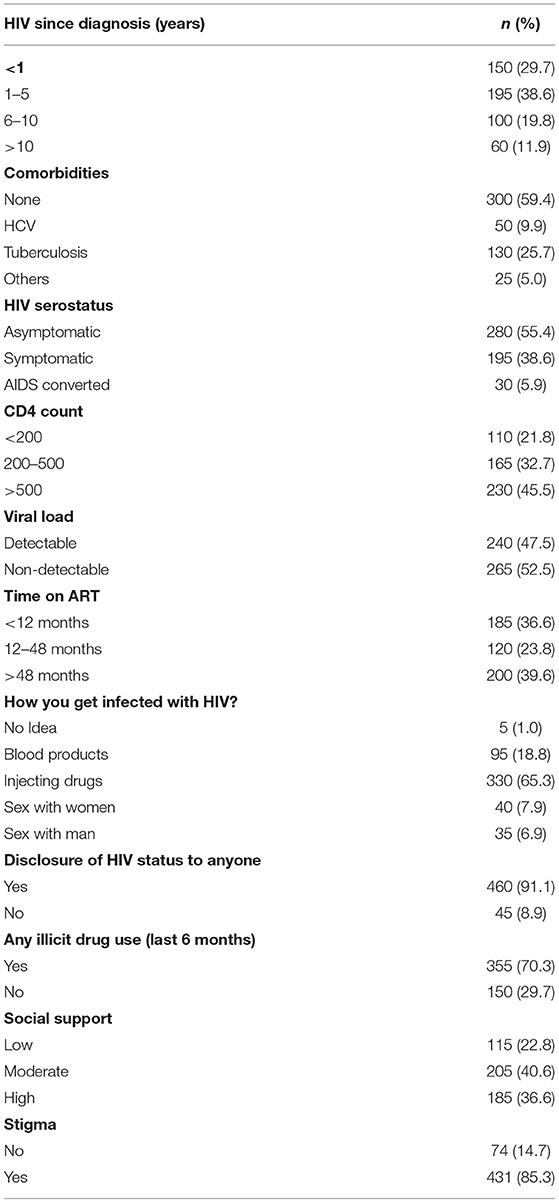
Regarding clinical characteristics of study population, 195 (38.6%) participants had HIV from 1 to 5 years, 300 (59.4%) were without comorbid conditions, 200 (39.6%) were on ART for >48 months, 230 (45.5%) were having >500 CD-4 T lymphocytes cells/mm3, and 265 (52.5%) had undetectable viral load. Regarding social characteristics, 205 (40.6%) participants had moderate social supports, 431 (85.3%) had a stigma, and 355 (70.3%) were illicit drug users (Table 2).
Factors Associated With Depression and Anxiety
The study found that 80% of PLWHA had co-occurring anxiety and depression. Separately, 80.3% (406) reported anxiety, and 89.9% (454) reported depression.
Multivariable binary logistic regression analysis revealed that illicit drug use was significantly associated with depression in contrast to non-drug users [AOR: 1.87, 95% CI (1.01–3.27)]. Similarly, those with HIV perceived stigma were 2.48 times more likely to be associated with depression than those without stigma [AOR: 2.48, 95% CI (1.25–6.02)]. People living with HIV/AIDS having low [AOR = 1.21, 95% CI (1.02–2.25)] and moderate social support [AOR: 1.89, 95% CI (1.05–4.11)] were more likely to be associated with depression than those who had good social support (Table 3).
Multivariable binary logistic regression demonstrated that some patient subgroups had significantly increased odds of having anxiety. PLWHA aged 18–25 years [AOR: 5.31, 95% CI (1.19–29.39)], had higher associated odds of experiencing anxiety than individuals of age 26–50 and >50 years. Anxiety was highest among illiterate PLWHA [AOR: 21.78, 95% CI (4.03–117.62)], followed by primary and secondary education participants. Similarly, patients with detectable viral load had 3.04 times [AOR: 3.04, 95% CI (1.04–8.86)] associated anxiety than individuals with non-detectable viral load. Unemployed PLWHA were experiencing 1.25 times more anxiety than the employed PLWHA. Patients with low [AOR: 1.70, 95% CI (1.12–6.93)] and moderate [AOR: 2.20, 95% CI (1.79–6.09)] social support were more likely to experience anxiety than those with high social support. Anxiety was associated with patients who used illicit drugs [AOR = 1.17, 95% CI (1.03, 2.55)]. Individuals with HIV-related stigma were 54 times more prone to have anxiety [AOR: 54.3, 95% CI (21.20–139.32)] (Table 4).
Discussion
To the authors' best knowledge, this is the first study to measure the prevalence and associations of anxiety and depression in PLWHA in resource-limited settings in Pakistan. The prevalence of co-occurring anxiety and depression in PLWHA is 80%, higher than the 34% mean depression and anxiety in Pakistan's general population (50). In addition, the prevalence of 89.9% depression in this study is greater than the prevalence reported by Ethiopian, Spanish, Indian, Cameron, Brazilian, Conakry (capital of Guinea), USA, Denmark, Albania, China studies in which prevalence were reported to be 32, 35.4, 58.1, 28.5, 59, 16.9, 43.9, 38, 58.75, and 73.1% respectively (16, 19–22, 26, 51). Likewise, the prevalence of anxiety reported in this research is 80.3%, which is higher than reported by Ethiopian, USA, Canada, China, Thailand, Brazil, Western Europe, South African studies in which prevalence were reported to be 32.4, 33, 33.4, 49, 16.3, 12.6, 33.3, and 30.6% respectively (26, 52, 53). These alterations in the prevalence of depression and anxiety might be due to several factors comprised of methodological variations, such as the selection of target population, sample size, different data collection locations, and using different types of instruments to measure anxiety and depression.
Our study's higher rate of anxiety and depression in PLWHA could be attributed to sociodemographic and sociocultural differences. Like in Pakistan, most PLWHA are deported migrants or intravenous drug users (29, 30). People avoid PLWHA because they believe these individuals have been punished for their bad behaviors. As a result, greater self-reported passive coping and lower active coping were significantly associated with greater depression and anxiety symptoms. In our study, the most common risk factor associated with depression and anxiety was the stigma. This finding was consistent with studies conducted in the USA, Botswana, and Ethiopia (16, 26, 54, 55). In Pakistan, the general public believes HIV is associated with deviant behavior from social norms, and people try to avoid PLWHA out of fear of contracting the disease. This is primarily due to the general public's lack of disease knowledge.
Furthermore, people believe that it is the punishment for their sins. Thus, stigma raises the level of discomfort, fear of disclosure and develops a feeling of lack of value (26). Internalized HIV stigma can also cause people to postpone HIV testing, limit the use of preventative programs, and impede the adoption of preventive behaviors (56). Moreover, discrimination behavior toward PLWHA is a dynamic sociocultural phenomenon that is an outcome of viewing people with HIV/AIDS as “less than human.”
Low social support was more likely to develop depression and anxiety than those with good social support, which was comparable to studies conducted in Ethiopia, Ghana, Nigeria, and India (16, 20, 26, 57). This may be due to how social isolation diminishes social care, adversely affecting emotional and physical well-being. Similarly, these people prefer to refrain from seeking the help of others and from opening themselves up to their well-being because of the social stigma that builds their loneliness and depression (16).
The current study showed that the use of addictive drugs is 1.87 times more likely to develop depression than without the use of drugs. These results are consistent with the Chinese study (53). Alcohol use contributes to loss of adherence, poor health outcomes of PLWHA, and worsening of disease progression (58). Having a detectable viral load was more likely to develop 3.04 times anxiety as compared to having an undetectable viral load. This result was also supported by a study conducted in the USA (59). A possible explanation for this is that mental health changes as the disease progresses.
In this study, younger patients were 5.3 times more likely to experience anxiety than elderly patients (>50 years). Another study conducted in Conakry by Camara et al. also identified younger age as a determinant for psychological problems (51). Another critical determinant of anxiety was found to be education, and results of this study suggested that illiterate patients were likely to experience higher odds, 21.78 times, of anxiety than the HIV patients having university-level education. These results corroborate the findings of a Kenyan study (60). According to the findings of this study, depression in men is 2.21 times higher than in women, which is consistent with meta-analysis findings that depression in men is 8% higher (24). This could be explained in part by the prevalence of unemployment and job-related stress in males.
Although resources have been stepped up in Pakistan for the last 5 years in response to HIV, little policy attention has been paid to the needs of PLWHA in mental health (61, 62). A challenge for this resource-restricted nation is to create structures, skilled staff, and resources to enhance mental health services in general and, in particular, to meet the needs of people living with HIV (63, 64). Our findings support the need for more research into HIV-psychological manifestations and identify those who are most vulnerable and develop interventions to reduce the individual and social factors that exacerbate vulnerability to depression and anxiety. Access to antiretroviral treatment is growing in Pakistan (5); however, consideration should be given to the potential impacts of high anxiety and depression on access to and compliance with HIV treatment.
The world health organization (WHO) recommended that PLWHA, their families, and friends seek psychological and social assistance (65). A meta-analysis of 62 randomized controlled trials concluded that psychosocial therapies (Relaxation techniques, Cognitive-behavioral, Motivational interviewing, Stress-management, Mental health primary focus intervention, Theory-driven intervention, Treatment duration) inclusion in HIV care could result in significant improvement of mental health (66). Such psychosocial assistance will lead to increased health and treatment outcomes for PLWHA.
Strengths and Limitations
This is the first study to use HADS to determine the prevalence and risk factors for anxiety and depression in Pakistani PLWHA, and we also used a large enough sample size. However, the study has several limitations, such as we collected data from only one ART center, although it was the largest center; hence we cannot generalize the results to the whole PLWHA in Pakistan. Secondly, a cross-sectional study is not adequate for finding the direction of cause-and-effect associations.
Conclusions
This study has identified a high prevalence of depression and anxiety in PLWHA in Pakistan. Using illicit drugs, low social support, being male, and perceived high HIV-related stigma were significant predictors of depression. Having detectable viral load, young age, no formal education, low or moderate social support, illicit drug addiction, and perceived high HIV stigma are significantly associated with anxiety. National AIDS Control Program of Pakistan should develop methods to screen the mental health issues and develop relevant interventions to improve these health outcomes of PLWHA in Pakistan. In addition, NACP should integrate mental health services into the national HIV treatment program to mitigate the adverse effects of depression and anxiety on PLWHA in Pakistan. Further studies should be conducted to check the impact of locally tailored interventions on mental health improvement.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics Statement
The Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences (PIMS) Ethical Review Board (ERB) and the National AIDS Control Program of Pakistan (NACP) (Approval Number: 1827) provided the ethical permissions to carry out this project.
Author Contributions
AA: conceptualize the research, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, project administration, writing—original draft, review, and editing. MS: formal analysis and results writing. MU: collected the data and supervised. FKH: reviewed the data and analyzed data. HS: edited the paper and supervised. MA: data analysis and data collection. AQB: reviewed the final paper and supervised. JAD: supervised and reviewed the paper. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all participants for their voluntary participation. We also thank ART center PIMS Islamabad staff for helping us in data collection.
Abbreviations
PLWHA, people living with HIV/AIDS; HIV/AIDS, human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; LMIC, low middle-income countries; ART, anti-retroviral therapy; PIMS, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences; NACP, National AIDS Control Program of Pakistan; IARSS, internalized AIDS-related stigma scale; MSPSS, multidimensional scale of perceived social support; HADS, hospital anxiety and depression scale; CI, confidence interval; AOR, adjusted odds ratios.
References
3. Taiwo B, Barcena L, Tressler R. Understanding and controlling chronic immune activation in the HIV-infected patients suppressed on combination antiretroviral therapy. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. (2013) 10:21–32. doi: 10.1007/s11904-012-0147-3
4. Fang X, Vincent W, Calabrese SK, Heckman TG, Sikkema KJ, Humphries DL, et al. Resilience, stress, and life quality in older adults living with HIV/AIDS. Aging Ment Health. (2015) 19:1015–21. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2014.1003287
5. Ahmed A, Saqlain M, Bashir N, Dujaili J, Hashmi F, Mazhar F, et al. Health-related quality of life and its predictors among adults living with HIV/AIDS and receiving antiretroviral therapy in Pakistan. Qual Life Res. (2021) 30:1653–64. doi: 10.1007/s11136-021-02771-y
6. Grov C, Golub SA, Parsons JT, Brennan M, Karpiak SE. Loneliness and HIV-related stigma explain depression among older HIV-positive adults. AIDS Care. (2010) 22:630–9. doi: 10.1080/09540120903280901
7. Schuster R, Bornovalova M, Hunt E. The influence of depression on the progression of HIV: direct and indirect effects. Behav Modif. (2012) 36:123–45. doi: 10.1177/0145445511425231
8. Ahmed A, Dujaili J, Hashmi FK, Awaisu A, Chaiyakunapruk N, Hasan SS. The economic impact of pharmacist care for people living with HIV/AIDS: a systematic review. Explor Res Clin Soc Pharmacy. (2021) 2021:100066. doi: 10.1016/j.rcsop.2021.100066
9. Mayston R, Kinyanda E, Chishinga N, Prince M, Patel V. Mental disorder and the outcome of HIV/AIDS in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Aids. (2012) 26:S117–35. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32835bde0f
10. Charlson FJ, Baxter AJ, Cheng HG, Shidhaye R, Whiteford HA. The burden of mental, neurological, and substance use disorders in China and India: a systematic analysis of community representative epidemiological studies. Lancet. (2016) 388:376–89. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30590-6
11. Ian E, Gwen CL, Soo CT, Melissa C, Chun-Kai H, Eosu K, et al. The burden of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND) in the Asia-Pacific region and recommendations for screening. Asian J Psychiatr. (2016) 22:182–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2015.10.009
12. Vreeman RC, Mccoy BM, Lee S. Mental health challenges among adolescents living with HIV. J Int AIDS Soc. (2017) 20:21497. doi: 10.7448/IAS.20.4.21497
13. Aguocha CM, Uwakwe RU, Duru CB, Diwe KC, Aguocha JK, Enwere OO, et al. Prevalence and socio-demographic determinants of depression among patients attending HIV/AIDS clinic in a teaching hospital in Imo State, Nigeria. Amer J Med Sci Med. (2015) 3:106–12. doi: 10.12691/ajmsm-3-6-4
14. Chan BT, Pradeep A, Prasad L, Murugesan V, Chandrasekaran E, Kumarasamy N, et al. Association between internalized stigma and depression among HIV-positive persons entering into care in Southern India. J Glob Health. (2017) 7:020403. doi: 10.7189/jogh.07.020403
15. Wang W, Xiao C, Yao X, Yang Y, Yan H, Li S. Psychosocial health and suicidal ideation among people living with HIV/AIDS: a cross-sectional study in Nanjing, China. PLoS ONE. (2018) 13:e0192940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192940
16. Duko B, Toma A, Asnake S, Abraham Y. Depression and anxiety and its correlates among patients with HIV in South Ethiopia, cross-sectional study. Front Psychiatry. (2019) 10:290. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00290
17. Uthman OA, Magidson JF, Safren SA, Nachega JB. Depression and adherence to antiretroviral therapy in low-, middle-and high-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. (2014) 11:291–307. doi: 10.1007/s11904-014-0220-1
18. Ahmed A, Abdulelah Dujaili J, Rehman IU, Lay Hong AC, Hashmi FK, Awaisu A, et al. Effect of pharmacist care on clinical outcomes among people living with HIV/AIDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Res Social Adm Pharm. (2021). doi: 10.1016/j.sapharm.2021.07.020. [Epub ahead of print].
19. Bayón C, Ribera E, Cabrero E, Griffa L, Burgos Á. Prevalence of depressive and other central nervous system symptoms in HIV-infected patients treated with HAART in Spain. J Int Assoc Physicians AIDS Care. (2012) 11:321–8. doi: 10.1177/1545109712448217
20. Bhatia M, Munjal S. Prevalence of depression in people living with HIV/AIDS undergoing ART and factors associated with it. J Clin Diagnos Res. (2014) 8:WC01. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/7725.4927
21. Betancur MN, Lins L, Oliveira IRD, Brites C. Quality of life, anxiety and depression in patients with HIV/AIDS who present poor adherence to antiretroviral therapy: a cross-sectional study in Salvador, Brazil. Brazil J Infect Dis. (2017) 21:507–14. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2017.04.004
22. Kanmogne GD, Qiu F, Ntone FE, Fonsah JY, Njamnshi DM, Kuate CT, et al. Depressive symptoms in HIV-infected and seronegative control subjects in Cameroon: effect of age, education and gender. PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e171956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171956
23. Rong H, Nianhua X, Jun X, Lianguo R, Si W, Sheng W, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for depressive symptoms among people living with HIV/AIDS receiving antiretroviral treatment in Wuhan, China: a short report. AIDS Care. (2017) 29:1524–8. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2017.1327649
24. Rezaei S, Ahmadi S, Rahmati J, Hosseinifard H, Dehnad A, Aryankhesal A, et al. Global prevalence of depression in HIV/AIDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Support Palliat Care. (2019) 9:404–12. doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2019-001952
25. Pappin M, Wouters E, Booysen FL. Anxiety and depression amongst patients enrolled in a public sector antiretroviral treatment programme in South Africa: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. (2012) 12:244. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-244
26. Tesfaw G, Ayano G, Awoke T, Assefa D, Birhanu Z, Miheretie G, et al. Prevalence and correlates of depression and anxiety among patients with HIV on-follow up at Alert Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Psychiatry. (2016) 16:368. doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-1037-9
27. Amare T, Getinet W, Shumet S, Asrat B. Prevalence and associated factors of depression among PLHIV in Ethiopia: systematic review and meta-analysis, 2017. AIDS Res Treat. (2018) 2018:5462959. doi: 10.1155/2018/5462959
28. Thai TT, Jones MK, Harris LM, Heard RC, Hills NK, Lindan CP. Symptoms of depression in people living with HIV in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam: prevalence and associated factors. AIDS Behav. (2018) 22:76–84. doi: 10.1007/s10461-017-1946-8
29. Ahmed A, Hashmi FK, Khan GM. HIV outbreaks in Pakistan. The Lancet HIV. (2019) 6:e418. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(19)30179-1
30. Ahmed A, Dujaili J, Sandhu AK, Hashmi FK. Concerns of HIV-positive migrant workers in COVID-19 pandemic: a call for action. J Glob Health. (2020) 10:020342. doi: 10.7189/jogh.10.020342
31. Ahmed A, Saqlain M, Akhtar N, Hashmi F, Blebil A, Dujaili J, et al. Translation and cross-cultural adaptation of WHOQOL-HIV Bref among people living with HIV/AIDS in Pakistan. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2021) 19:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12955-021-01693-0
32. Williams JR. The Declaration of Helsinki and public health. Bull World Health Organ. (2008) 86:650–2. doi: 10.2471/BLT.08.050955
33. Ahmed A, Saqlain M, Tanveer M, Tahir AH, Ud-Din F, Shinwari MI, et al. Knowledge, attitude and perceptions about Crimean Congo Haemorrhagic Fever (CCHF) among occupationally high-risk healthcare professionals of Pakistan. BMC Infect Dis. (2021) 21:35. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05714-z
34. Raosoft I. Sample Size Calculator. (2004). Available online at: http://www.raosoft.com/samplesize.html (accessed July 16, 2019).
35. Kalichman SC, Simbayi LC, Cloete A, Mthembu PP, Mkhonta RN, Ginindza T. Measuring AIDS stigmas in people living with HIV/AIDS: the Internalized AIDS-Related Stigma Scale. AIDS Care. (2008) 21:87–93. doi: 10.1037/t62107-000
36. Earnshaw VA, Chaudoir SR. From conceptualizing to measuring HIV stigma: a review of HIV stigma mechanism measures. AIDS Behav. (2009) 13:1160. doi: 10.1007/s10461-009-9593-3
37. Tsai AC, Weiser SD, Steward WT, Mukiibi NF, Kawuma A, Kembabazi A, et al. Evidence for the reliability and validity of the internalized AIDS-related stigma scale in rural Uganda. AIDS Behav. (2013) 17:427–33. doi: 10.1007/s10461-012-0281-3
38. Pantelic M, Shenderovich Y, Cluver L, Boyes M. Predictors of internalised HIV-related stigma: a systematic review of studies in sub-Saharan Africa. Health Psychol Rev. (2015) 9:469–90. doi: 10.1080/17437199.2014.996243
39. Overstreet NM, Earnshaw VA, Kalichman SC, Quinn DM. Internalized stigma and HIV status disclosure among HIV-positive black men who have sex with men. AIDS Care. (2013) 25:466–71. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2012.720362
40. Zimet GD, Dahlem NW, Zimet SG, Farley GK. The multidimensional scale of perceived social support. J Pers Assess. (1988) 52:30–41. doi: 10.1207/s15327752jpa5201_2
41. Rizwan M, Aftab S. Psychometric properties of the multidimensional scale of perceived social support in Pakistani young adults. Pak J Psychol. (2009) 40:51–65.
42. Dambi JM, Corten L, Chiwaridzo M, Jack H, Mlambo T, Jelsma J. A systematic review of the psychometric properties of the cross-cultural translations and adaptations of the Multidimensional Perceived Social Support Scale (MSPSS). Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2018) 16:80. doi: 10.1186/s12955-018-0912-0
43. Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. (1983) 67:361–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x
44. Waqas A, Aedma KK, Tariq M, Meraj H, Naveed S. Validity and reliability of the Urdu version of the hospital anxiety and depression scale for assessing antenatal anxiety and depression in Pakistan. Asian J Psychiatr. (2019) 45:20–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2019.08.008
45. Husain MO, Dearman SP, Chaudhry IB, Rizvi N, Waheed W. The relationship between anxiety, depression and illness perception in tberculosis patients in Pakistan. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. (2008) 4:4. doi: 10.1186/1745-0179-4-4
46. Waqas A, Raza N, Lodhi HW, Muhammad Z, Jamal M, Rehman A. Psychosocial factors of antenatal anxiety and depression in Pakistan: is social support a mediator? PLoS ONE. (2015) 10:e0116510. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116510
47. Rahman A, Hamdani SU, Awan NR, Bryant RA, Dawson KS, Khan MF, et al. Effect of a multicomponent behavioral intervention in adults impaired by psychological distress in a conflict-affected area of Pakistan: a randomized clinical trial. Jama. (2016) 316:2609–17. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.17165
48. Rahman A, Khan MN, Hamdani SU, Chiumento A, Akhtar P, Nazir H, et al. Effectiveness of a brief group psychological intervention for women in a post-conflict setting in Pakistan: a single-blind, cluster, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2019) 393:1733–44. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32343-2
49. Pallant J. SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS. London: Routledge (2020). doi: 10.4324/9781003117445
50. Mirza I, Jenkins R. Risk factors, prevalence, and treatment of anxiety and depressive disorders in Pakistan: systematic review. Bmj. (2004) 328:794. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7443.794
51. Camara A, Sow M, Touré A, Sako F, Camara I, Soumaoro K, et al. Anxiety and depression among HIV patients of the infectious disease department of Conakry University Hospital in 2018. Epidemiol Infect. (2020). 148 e8. doi: 10.1017/S095026881900222X
52. Liu L, Pang R, Sun W, Wu M, Qu P, Lu C, et al. Functional social support, psychological capital, and depressive and anxiety symptoms among people living with HIV/AIDS employed full-time. BMC Psychiatry. (2013) 13:324. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-324
53. Sun W, Wu M, Qu P, Lu C, Wang L. Psychological well-being of people living with HIV/AIDS under the new epidemic characteristics in China and the risk factors: a population-based study. Int J Infect Dis. (2014) 28:147–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.07.010
54. Gupta R, Dandu M, Packel L, Rutherford G, Leiter K, Phaladze N, et al. Depression and HIV in Botswana: a population-based study on gender-specific socioeconomic and behavioral correlates. PLoS ONE. (2010) 5:e14252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014252
55. Rao D, Feldman BJ, Fredericksen RJ, Crane PK, Simoni JM, Kitahata MM, et al. A structural equation model of HIV-related stigma, depressive symptoms, and medication adherence. AIDS Behav. (2012) 16:711–6. doi: 10.1007/s10461-011-9915-0
56. Raza A, Ullah I, Tahir MJ, Jabbar A, Ahmed A. COVID-19 is a health-care dilemma for HIV-positive individuals in Pakistan. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. (2021) 1–6. doi: 10.1017/ice.2021.376
57. Shittu R, Issa B, Olanrewaju G, Mahmoud A, Odeigah L, Salami A, et al. Prevalence and correlates of depressive disorders among people living with HIV/AIDS. North Central Nigeria J AIDS Clin Res. (2013) 4:251. doi: 10.4172/2155-6113.1000251
58. Nakimuli-Mpungu E, Bass JK, Alexandre P, Mills EJ, Musisi S, Ram M, et al. Depression, alcohol use and adherence to antiretroviral therapy in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. AIDS Behav. (2012) 16:2101–18. doi: 10.1007/s10461-011-0087-8
59. Kalichman SC, Difonzo K, Austin J, Luke W, Rompa D. Prospective study of emotional reactions to changes in HIV viral load. AIDS Patient Care STDS. (2002) 16:113–20. doi: 10.1089/108729102317330454
60. Nyongesa MK, Mwangala PN, Mwangi P, Kombe M, Newton CR, Abubakar AA. Neurocognitive and mental health outcomes and association with quality of life among adults living with HIV: a cross-sectional focus on a low-literacy population from coastal Kenya. BMJ Open. (2018) 8:e023914. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023914
61. Akram B, Ilyas M. Coping strategies, mental health and HIV status: predictors of suicidal behaviour among PWIDs. JPMA. (2017) 67:568–72.
62. Rabold EM, Ali H, Fernandez D, Knuth M, Schenkel K, Asghar RJ, et al. Systematic review of reported HIV outbreaks, Pakistan, 2000–2019. Emerg Infect Dis. (2021) 27:1039. doi: 10.3201/eid2704.204205
63. Abdullah MA, Shaikh BT, Ghazanfar H. Curing or causing? HIV/AIDS in health care system of Punjab, Pakistan. PLoS ONE. (2021) 16:e0254476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254476
64. Ahmed A, Saqlain M, Tanveer M, Blebil AQ, Dujaili JA, Hasan SS. The impact of clinical pharmacist services on patient health outcomes in Pakistan: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. (2021) 21:859. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06897-0
65. World Health Organization. Consolidated Guidelines on the Use of Antiretroviral Drugs for Treating and Preventing HIV Infection: Recommendations for a Public Health Approach (2016).
Keywords: Pakistan, lower-middle-income country, anxiety, depression, predictors, risk factors, HIV, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
Citation: Ahmed A, Saqlain M, Umair MM, Hashmi FK, Saeed H, Amer M, Blebil AQ and Dujaili JA (2021) Stigma, Social Support, Illicit Drug Use, and Other Predictors of Anxiety and Depression Among HIV/AIDS Patients in Pakistan: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Public Health 9:745545. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.745545
Received: 22 July 2021; Accepted: 31 August 2021;
Published: 30 September 2021.
Edited by:
Yuka Kotozaki, Iwate Medical University, JapanReviewed by:
Qi Wang, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, SAR ChinaSi-Tong Chen, Victoria University, Australia
Copyright © 2021 Ahmed, Saqlain, Umair, Hashmi, Saeed, Amer, Blebil and Dujaili. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ali Ahmed, YWxpLmFobWVkQG1vbmFzaC5lZHU=; Juman Abdulelah Dujaili, SnVtYW4uRHVqYWlsaUBtb25hc2guZWR1
 Ali Ahmed
Ali Ahmed Muhammad Saqlain2
Muhammad Saqlain2 Furqan Khurshid Hashmi
Furqan Khurshid Hashmi Hamid Saeed
Hamid Saeed Ali Qais Blebil
Ali Qais Blebil Juman Abdulelah Dujaili
Juman Abdulelah Dujaili