- School of Nursing and Midwifery, Monash University, Clayton, VIC, Australia
The need to improve career development and training for residential aged care workers in Australia to achieve required essential competencies, including infection prevention and control competencies, has been repeatedly highlighted. In Australia long-term care settings for older adults are known as residential aged care facilities (RACFs). The COVID-19 pandemic has brought to light the lack of preparedness of the aged care sector to respond to emergencies, and the urgent need to improve the infection prevention and control training in residential aged care facilities. The government in the Australian State of Victoria allocated funds to support older Australians in RACFs, including funds toward infection prevention and control training of RACF staff. The School of Nursing and Midwifery at Monash University addressed some of these challenges in delivering an education program on effective infection prevention and control practices to the RACF workforce in Victoria, Australia. This was the largest state-funded program delivered to RACF workers to date in the State of Victoria. The aim of this paper is to provide a community case study, where we share our experience of program planning and implementation during early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic and lessons learned.
Introduction
In Australia long-term care settings for older adults are known as residential aged care facilities (RACFs). Globally, studies indicate that even before the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, RACFs were the most vulnerable institutions in terms of high incidence of infectious disease and suboptimal infection prevention and control (IPC) procedures (1). Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers reported numerous coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection outbreaks occurring in RACFs worldwide that affected both residents and staff (2, 3). SARS-CoV-2 can spread rapidly through RACFs if not managed appropriately (4, 5). The underlying factors for this transmission include: (1) the characteristics of the coronavirus pathogen (transmissibility, high replication and mutation rates), (2) the condition of hosts (residents’ older age, frailty and co-morbid conditions), and (3) transmission factors, including the ability to practice preventive behaviors (suboptimal IPC training of the RACF workforce, cognitive impairment of some RACF residents, personal protective equipment (PPE) availability, close-contact personal care) and built environment (close-contact living, shared communal areas and equipment) (4, 6–8). In addition, evidence from a rapid systematic review indicated that a larger facility size (number of beds), greater number of employees, staff availability, RACF staff operating between multiple facilities, and for-profit status of RACFs also contribute to the number and size of COVID-19 outbreaks in this setting (9). A systematic review of the causes of transmission and control measures of any pathogen outbreaks in RACFs indicated that the violation of basic IPC could play a major role in introducing and facilitating the spread of infectious diseases in RACFs (10).
IPC expertise in Australian RACFs is limited; and the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted significant gaps in IPC practices in facilities (7). A recent review reported that out of 134 RACFs, 44% of staff responsible for IPC had no specific IPC qualifications (11). Two independent reports into COVID-19 outbreaks in New South Wales and Victoria, Australia recommended improved continuing IPC training for staff in RACFs outside of outbreak situations, to be overseen by an appropriately trained member of the nursing staff (12, 13).
In Australia, The Royal Commission into Aged Care Quality and Safety (The Royal Commission) special report into COVID-19 in aged care (14) highlighted that the aged care workforce must be provided with regular IPC training, with the responsibility for this training resting with aged care providers. The Royal Commission called on the federal government to establish a national aged care plan for COVID-19 and deployment of infection control experts into RACFs as a condition of accreditation (15). In December 2020, the Australian Commonwealth Department of Health instructed all RACFs to appoint a nurse with appropriate accredited IPC training to lead IPC in their facility (16).
Staff training is important for effective IPC practices in RACFs (17). Infection prevention and control guidelines and training programs are often based on evidence collected in acute healthcare settings and not always relevant for the RACF context (18). Although IPC is the most commonly reported specialist skill among direct care workers in RACFs (19), little is known about the quality, relevance and frequency of training, or the undertaking of competency assessments (20). There are challenges implementing education programs in RACFs due to the diverse workforce with varied knowledge and educational experience, time to participate in education, and relevance, accessibility and sustainability of education programs (19, 21). Factors that may increase the efficacy of staff education in RACFs include a high-quality program using an interactive experiential learning format, that is relevant for staff and includes positive reinforcement and promoting sustainability (22).
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the lack of preparedness of the aged care sector in Australia to respond to emergencies and the urgent need to improve IPC training in RACFs among other challenges (23). The Victorian Government allocated funds to support people living in RACFs, including support for training the workforce in IPC practices (24). The School of Nursing and Midwifery at Monash University addressed some of these challenges through design and delivery of an education program on effective IPC practices to the RACF workforce in Victoria, Australia. This program was co-designed with nurses and direct care workers specifically for the RACF workforce and implemented an innovative education strategy, and evaluated its effectiveness to optimize IPC practice and protect people from healthcare-associated infections in RACFs. To date, this was the largest state-funded program delivered to the residential aged care workforce in the State of Victoria. The aim of this paper is to provide a community case study, where we share our experience of the program planning and implementation from the early emergency stages of the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia and the lessons learned.
Context
Setting and population
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 outbreak in Australia, residents in RACFs were considered at a high risk of COVID-19, leading to illness and loss of life (4, 5, 7). During the ‘second wave’ of COVID-19 from July to September 2020, there were over 2000 COVID-19 cases occurred within RACFs in the state of Victoria, which lead to almost 700 deaths (25). Older people in general (26, 27), and particularly those with co-existing illnesses, are at increased risk of severe infection, serious complications and increased case-mortality rates if they contract COVID-19 (28–33).
Based on the 2020 National Aged Care Workforce Census (19), 70% of the aged care workforce are Personal Care Attendants (PCAs), 23% are nurses and 7% are allied health professionals. The proportion of PCAs from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds (CALD) comprised over 62% (19). The majority (70%) of the PCA workforce were both migrant and spoke a language other than English; and almost three quarters (71%) of PCAs hold a Certificate III or higher qualification in a direct care field (19). The broad and diverse aged care workforce also includes auxiliary workers who may not have substantial infection control training; and as the outbreak progressed, there were surge workforce staff who may have been new to aged care. The delivery of care in RACFs is 24 h, 7 days a week and many workers concurrently worked in two or more RACFs (34).
Program funders
The Victorian Government is committed to providing infection control training for the aged care workforce to help them adapt to the risky and changing environment posed by COVID-19. The Coronavirus (COVID-19) Plan for the Victorian Aged Care Sector for Victoria developed by the Department of Health and Human Services Victoria (DHHS) (23) provides guidelines to assist RACFs to support their workers, residents, families and visitors to prepare for prevention and management of COVID-19 individual cases and facility outbreaks. This project was funded by the Victorian Government through the DHHS.
Program owners
Monash University, the owner of the program, is Australia’s largest university; and the School of Nursing and Midwifery is ranked 5th in the Academic Ranking of World Universities by Shanghai Ranking in 20221. Monash Nursing and Midwifery is one of the largest educators of nurses and midwives in Australia, and has delivered nursing and midwifery educational courses for over 30 years, and graduated over 13,000 students.
Key programmatic elements
Program goal and objectives
The overall aim of this practical education program was to improve RACF staff IPC knowledge and practice, specifically related to appropriate donning and doffing of PPE to prevent transmission of COVID-19.
Program components
This program incorporates three components: (1) practical face-to-face education on IPC knowledge and practices, including the application of PPE; (2) a train-the trainer model to facilitate sustainability of the program via facility champions; (3) and a virtual reality simulation, designed specifically for the aged care sector and used to consolidate knowledge.
Due to the nature of the evolving coronavirus pandemic, the education program was iteratively reviewed and updated to ensure alignment with both Australian and Victorian State Government guidelines and advice.
Practical face-to-face education session
With a focus on practical application of PPE, the face-to-face component of the program addressed the following key concepts related to infection prevention: COVID-19 transmission routes, current COVID-19 pandemic concerns specific to the aged care sector, and the role of health workers in prevention of COVID-19 transmission. The use of standard infection prevention precautions, including hand hygiene, face masks and physical distancing, and their effectiveness in preventing COVID-19 transmission were also covered. Further to this, the use of transmission-based infection prevention precautions, including different levels of PPE required and situations when it is used were a focus. Finally, the correct sequencing for donning and doffing PPE to avoid contamination of self, residents, or the RACF environment were also included in this program component.
This practical education session was conducted using contemporary education practices, including guided group discussion, active learning activities, and role play simulation. Pre- and post-session knowledge quizzes and observation of donning and doffing PPE using a structured checklist to assess each participant’s PPE application were used as assessments for learning. The education session was underpinned by a detailed lesson plan, which was used by all educators to promote quality and consistency in program delivery.
Train-the trainer model – Facility Champions
Following the practical component of the education program, additional education was provided to key RACF staff, nominated as IPC Facility Champions. This train-the trainer model was adopted as an effective strategy to equip the appointed Facility Champions with the ability to educate others in their organization. The core advantage of a train-the-trainer model is its cost and time effectiveness when providing education to large numbers, and a greater acceptance of content delivered by internal trainers enabling the facility to have an up to date content expert to assist with day to day challenges.
The train-the-trainer education session focused on the organization of the training sessions in RACFs, education practices during the training session, and accessing follow up support. Facility Champions were also able to further clarify IPC knowledge and practice if required. All education resources used during the face-to-face session, such as lesson plan, PowerPoint presentation, and handout materia were provided to the Facility Champions. Facility Champions were asked to upload a list of RACF staff they conducted training with to Monash University at the end of each session.
The Monash University education program coordinator contacted Facility Champions following their face-to-face session to provide support with ongoing training for their RACF staff. Facility Champions were able to contact the University training team via email for ongoing support as required; and all requests were attended within two business days.
Virtual reality simulation
To consolidate knowledge and build on sustainability of the education program, an online competency-based virtual reality simulation (VRS) was developed. The Monash University team worked closely with a commercial company with expertise in immersive technology and together a custom-built program of practice simulations was created. The VRS leveraged an advanced conversation engine allowing learners to have conversations with characters using artificial intelligence (AI). Mimicking real scenarios that aged care workers would face during healthcare delivery, the VRS facilitated consolidation of learning and complemented the face-to-face education. Designed purposefully and specifically for the aged care workforce, the VRS was accessible through a Windows-based personal computer PC or MAC. Enabling unscripted conversations between participants and AI characters that speak, listen, interact and are designed to replicate aged care staff, the VRS aimed to further support competency development and continued learning. On entering the VRS, participants were introduced to a simulated RACF environment and presented with a series of realistic clinical scenarios along with three different AI characters, a registered nurse, a PCA and an auxiliary staff member. The scenarios posed cases that required participants to make decisions related to prevention of infection, e.g., which level of PPE is required and the sequence of their use. Each AI character required instruction in the selection of appropriate PPE (transmission-based or standard precautions), and in the safe donning and doffing of PPE.
The VRS provided RACF staff with unlimited opportunities to practice instructions in donning and doffing of PPE, in a safe, low-risk setting, and to receive real-time feedback on the accuracy of their instruction, confirming information when it was provided correctly, and correcting inaccuracies. The VRS continues to be a sustainable source of relevant information, requiring fewer human resources while ensuring the quality of training delivery and enabling a depth of understanding. Staff are able to access the platform at any time of the day or night, including weekends. The VRS has been purposefully designed to be engaging for people of all language backgrounds and literacy levels, with cases tailored to ensure they reflect the diversity of the RACFs workforce. As such, the platform provided an inclusive and sustainable risk management strategy.
This education paradigm was chosen by the project team because it is engaging for users, consolidates learning, and assesses decision-making. This paradigm also has the added advantage of creating the basis for potential transformation of ongoing professional development for the aged care workforce, including via potential rapid delivery of new modules during times of crisis.
Program planning, design and evaluation strategies
Needs assessment
The education program was developed in response to discussions with the Victorian Government to help support Victoria’s RACFs during the second wave of COVID-19. A targeted IPC program that specifically focused on application of PPE in the setting of an ever changing COVID-19 infection landscape. The DHHS had already identified the need for this education in RACFs.
Pilot
Prior to implementation of the education program, a pilot of the face-to-face education session was held with staff at a RACF in Melbourne, Victoria. Eight RACF staff attended: a mix of the facility care manager (a registered nurse), registered nurses (RNs), enrolled nurses (ENs) and PCAs. The aim of the pilot was to ensure the content of the education session was appropriate, engaging and useful for RACF staff, as well ensuring timing and sequencing was appropriate for the setting and intended audience. Participants most highly valued the opportunity to practice donning and doffing PPE. They also highly valued the ability to discuss IPC and PPE, and the challenges faced in the aged care sector, raising potential and actual challenges in relation to the prevention of COVID-19, with discussion related to what they would do if they had a confirmed case. The feedback provided from the pilot session was very positive. The participants valued the opportunity to identify the difficulties and develop possible solutions if a positive case of COVID-19 was detected in their RACF. Following the pilot, the face-to-face education session was refined and reduced to 90 min, with an additional 30 min allocated to the train-the-trainer session.
Program evaluation strategies
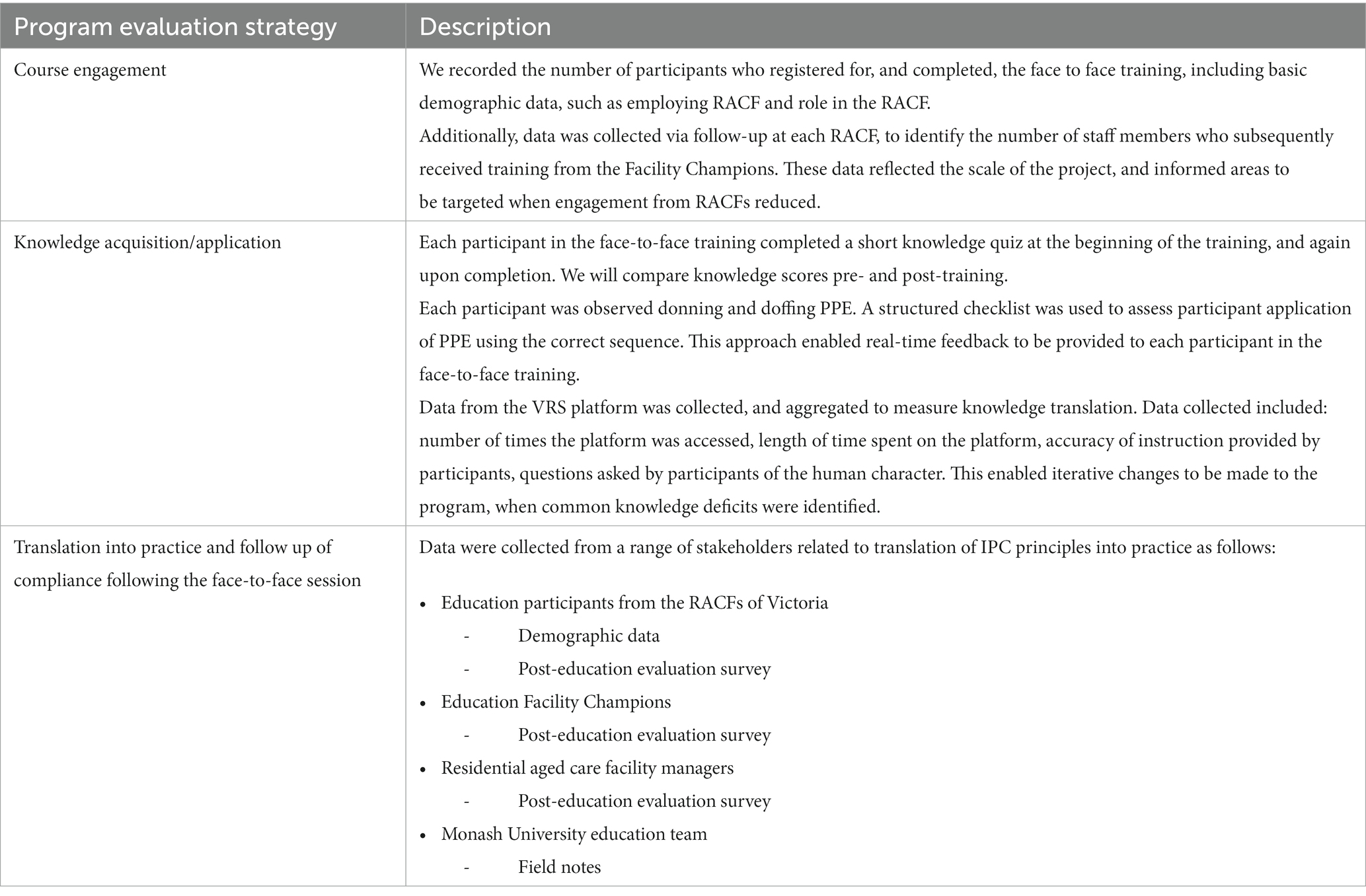
The program operated under an education research design to ensure program quality and demonstrate outcomes. Data were collected concurrently with program delivery to inform iterative changes required to program delivery. We used a concurrent triangulation mixed methods design (35), and employed the following methods of data collection: course engagement, knowledge acquisition and application and translation to practice (Table 1).
Risk mitigation plan
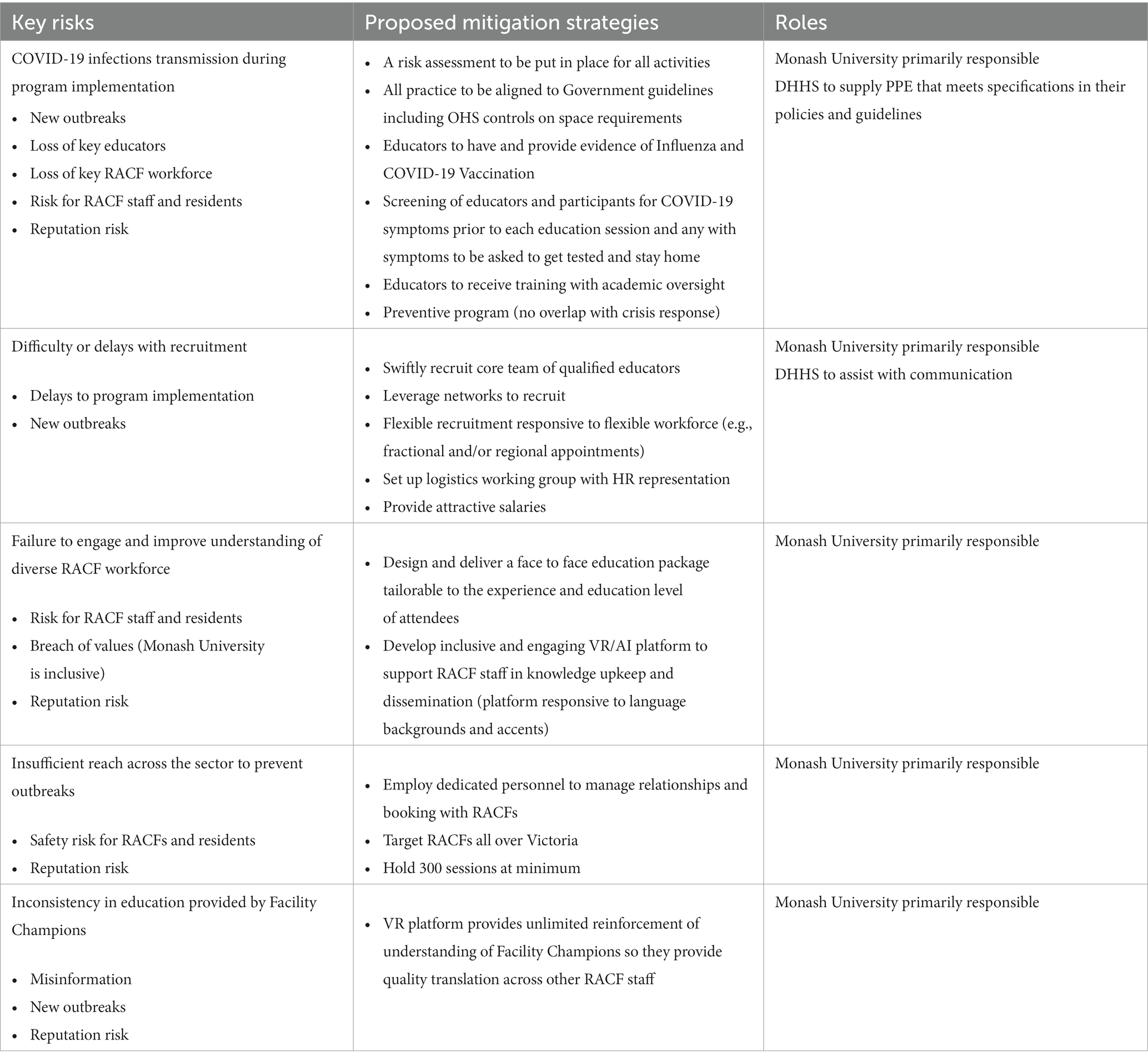
The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted the conduct of education provision, research and evidence synthesis of pandemic-related research projects that were launched at high speed in large numbers (36). Risk management at a University and project level became a key aspect of the project team’s approach to quality assurance (37). Monash University has a specialized Risk and Compliance Unit which facilitates risk management programs across the University. The University actions its risk management programs through a number of guidelines, policies and procedures including, risk assessment guidelines for major ventures and projects, fiscal misconduct policy, legal compliance policy and the risk management policy and procedures. Monash University recognized the significant safety and reputation risks associated with the delivery of the program. Five key risks were identified: (1) COVID-19 infection transmission during training; (2) difficulty or delays with educator recruitment; (3) failure to engage and improve understanding of the diverse residential aged care workforce; (4) insufficient reach across the sector to prevent outbreaks; and (5) inconsistency in education provided by Facility Champions. A risk mitigation plan was developed for all risks identified (Table 2).
Results
Implementation of the face-to face and train-the-trainer components
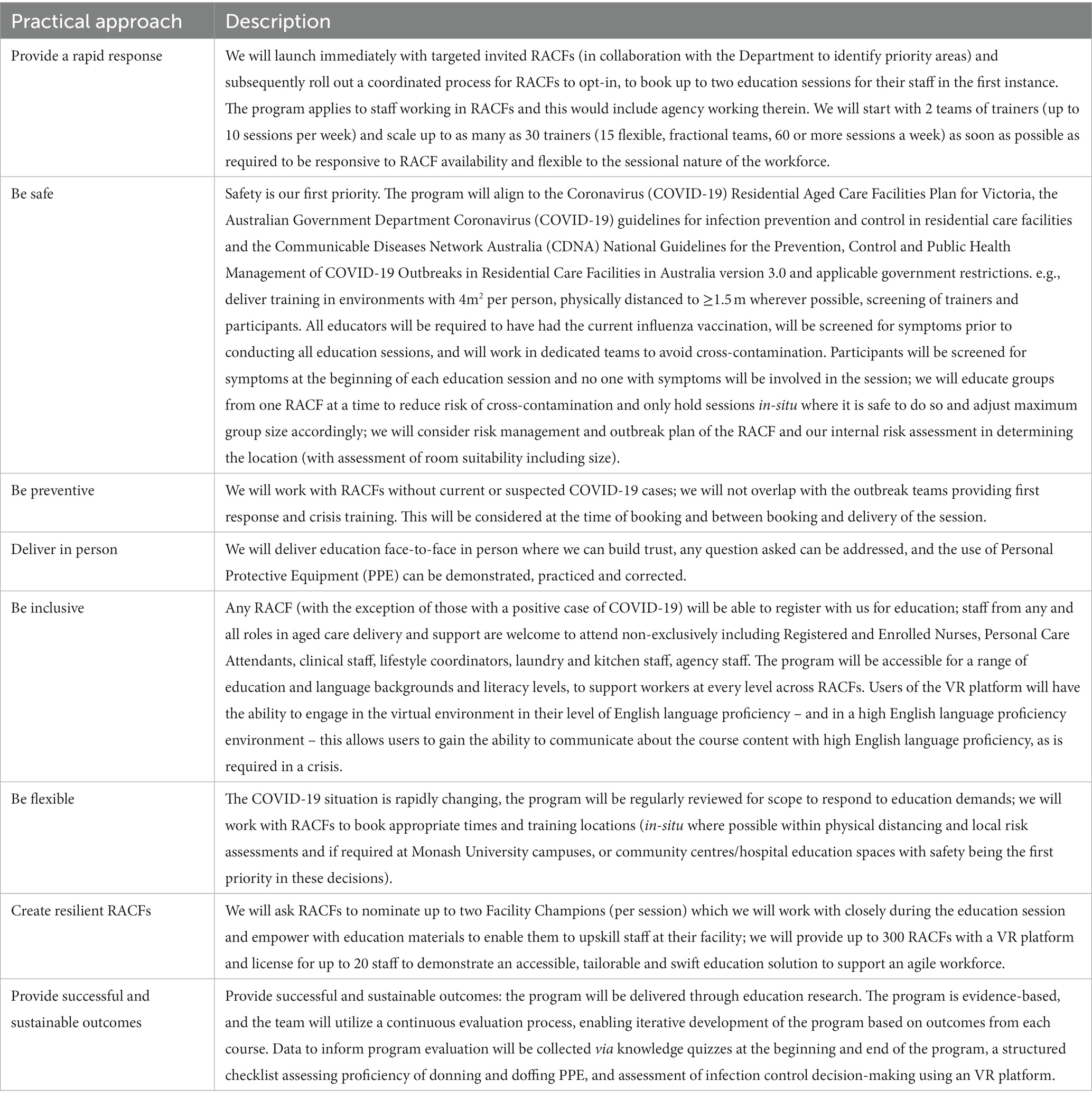
To facilitate smooth implementation of the education program, the following framework guided the approach: (1) provide a rapid response; (2) be safe; (3) be preventive; (4) deliver in person; (5) be inclusive; (6) be flexible; (7) create resilient RACFs; and (8) provide successful and sustainable outcomes (Table 3).
A team of nurse academics from Monash University, with expertise and leadership in IPC, aged care, education evaluation research, clinical training development, and delivery, operations and logistics, worked together to rapidly co-design and implement this large-scale education program designed specifically for RACF staff across Victoria. The importance and urgency of rapid training of RACF staff in IPC and the evidence-based PPE use became heightened with the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic in Australia (7, 17). Prior to this, all available education and training in PPE application for the residential aged care workforce were primarily available online, based on evidence from acute healthcare and not fully adapted to the RACF setting and had low uptake and completion rates by workers.
The program was offered to all Victorian RACFs via an opt-in model and was promoted by the DHHS via newsletters and direct correspondence. A dedicated Monash University website2 was launched, enabling RACFs to directly register for the education program.
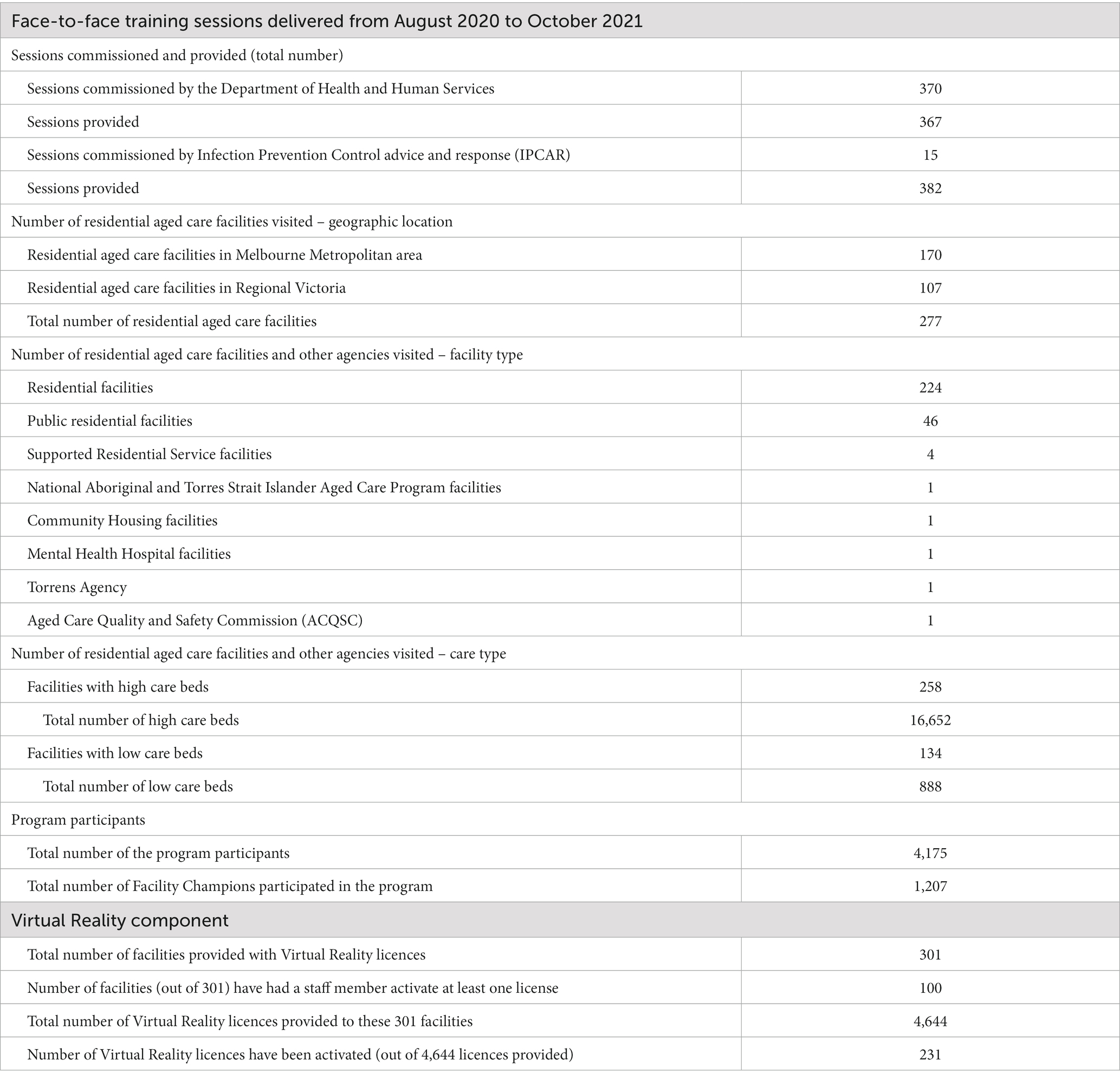
A team of educators worked in pairs to co-deliver each education session to a maximum of 20 participants per session. Within 3 months of commencement 309 face-to-face education sessions and train the trainer sessions were provided across 226 individual RACFs, including 159 RACFs located in Melbourne metropolitan area and 67 in regional Victoria. In total, 377 face-to-face education sessions were provided across 277 individual RACFs, including 170 RACFs located in Melbourne Metropolitan area and 107 in Regional Victoria. As part of this program, 4,219 RACF staff, including 1,207 Facility Champions completed the education (Table 4).
To evaluate the education program, participants were asked to complete a feedback survey 1–5 weeks after completion of their education session. Questions asked related to the usefulness of the session, changes made to IPC practice following the session and general feedback. Overwhelmingly, the feedback was positive with RACF workers reporting more understanding of IPC practices and their application within the facility. A snapshot of the participants’ responses to the process evaluation survey is presented in Table 5. Participants’ questions and educators’ concerns were regularly assessed by the project team; and the session content modified according with the raised needs (Table 5). Outcomes and impact evaluation of this program be presented in a subsequent publication.
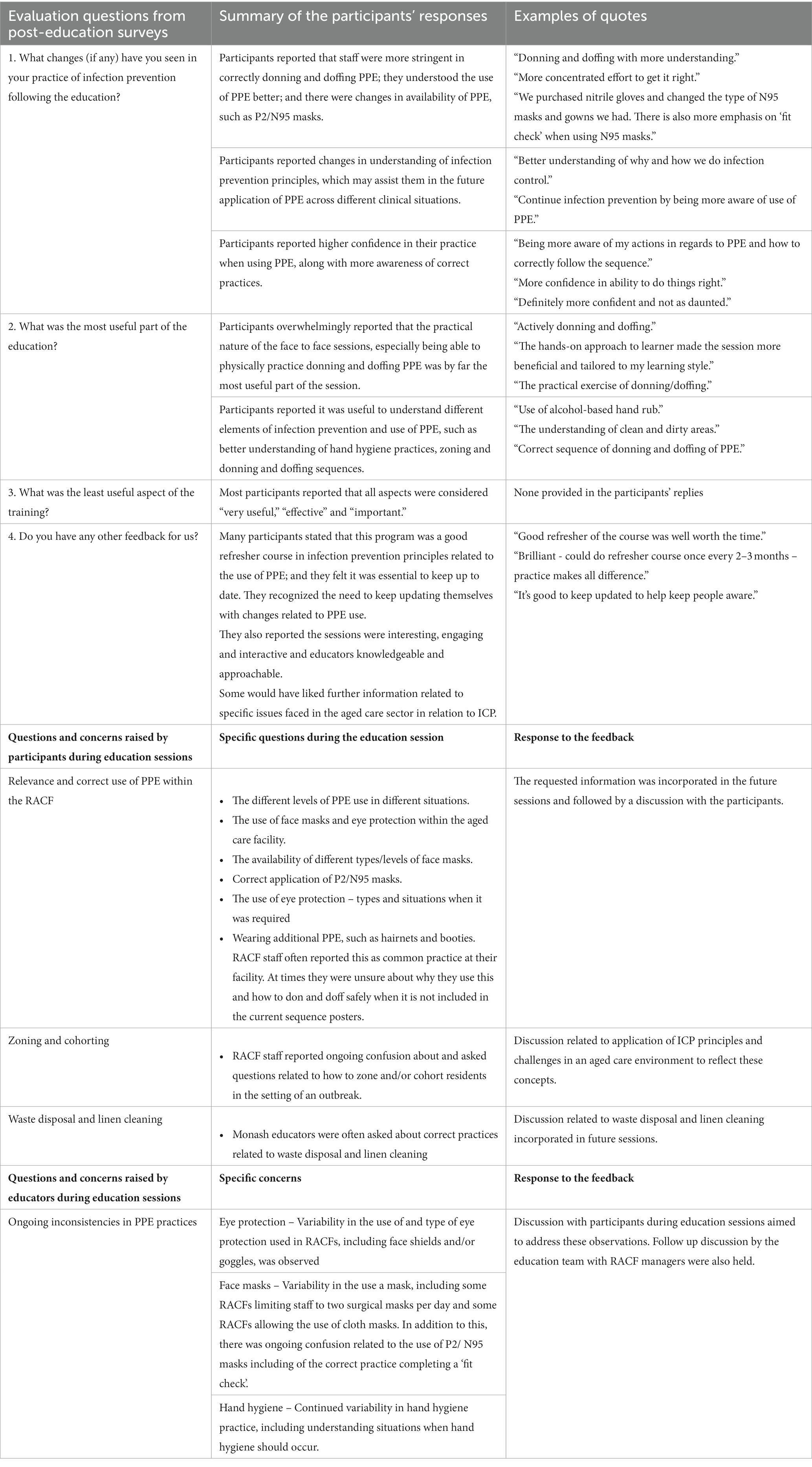
Table 5. A snapshot from the process evaluation survey and feedback from the participants and educators.
Implementation of the VRS component
Monash University commenced a targeted and intensive roll out of the VRS component in November 2020 to all RACF workers that had attended the face-to-face education session. Access to the VRS was via an individual coded license which gave workers unlimited access to the VRS software program.
A longer than anticipated time for testing and updating the VRS to align with emerging IPC knowledge and practice related to COVID-19 precautions meant there were some delays with the roll out of the VR component to RACF’s. In an effort to overcome these delays, the education team worked closely with RACF IPC leads and management in the roll out phase to facilitate license provision and VRS access for individual RACF’s. A staggered approach to RACF access allowed for follow up phone and video calls and face-to-face VR support sessions with RACF IPC leads and management. To incentivize RACF workers to engage with the VRS a $500 gift voucher was offered to the top four facilities with the most VR license activations.
Discussion and conclusion
Lessons learned
There have been a few lessons learned from this program design and implementation, which are important to document, analyze and share to improve further educational projects delivered to RACF staff. In the field of health program implementation, the discussion of the lessons learned traditionally consists of reflection on the three key questions what went right, what went wrong, and how it could be improved (38).
Acknowledging the contextual factors, this program was designed to address new reality of IPC and the use of PPE which COVID-19 brought to RACFs. This reality was evolving and changing in line with the SARS-CoV-2 adaptation, the stage of the pandemic, and new rapidly-attained evidence on COVID-19 infection control and prevention (39). These contextual factors impacted project planning and implementation. The importance of rapid training of RACF staff in IPC and the accurate use of PPE became heightened with the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic in Australia (7, 17); and the project team had limited time for planning the project. Nevertheless, effective leadership and the project team’s previous experience in delivering healthcare related education, including state-level projects allowed for successful planning, including the design of the multi-component training program, the development of the risk-mitigation plan, and adoption of the practical implementation approaches. A KPMG report (40) on program management in COVID-19 reality emphasized the importance of clarity of the project scope and delivery structures and the role of the project leadership. Other key lessons emphasized in this report (40), and also observed by us during the implementation process, were the need for stakeholder engagement, effective use of resources and successful management of the project phases, ensuring flexibility in altering schedules to accommodate changing needs. Well established research-RACF community collaborations between Monash University and RACF management and stakeholders’ direct interest in improved IPC skills of RACF staff were the main factors that facilitated successful implementation of the Program. The direct responsibility of the RACF management for IPC training of their staff (14) enabled the project team to run training sessions during the most challenging time when many staff were either sick or quarantined and the need for direct care was prioritized over training as the remaining staff were overworked (17).
The program design, specifically intended for the RACF setting, and particularly the multi-component program structure, contributed to successful program implementation despite the fact that some components were not engaged with as much as others by the RACF management and staff. The face-to-face training component, and particularly physical practice donning and doffing PPE, were acknowledged by the participants as the most useful parts of the program. The train-the trainer component was adopted as an effective strategy to equip the RACF Facility Champions with the ability to educate others in their organization and ensure program sustainability. The core advantage of a train-the trainer model is its cost and time effectiveness when providing education to large numbers, a greater acceptance of content delivered by internal trainers; and certainty the facility has an up to date content expert to assist with day to day challenges (41–43). Despite effective implementation of face-to-face, and train-the-trainer components, the VRS component was not well accepted. As already discussed, the unanticipated challenges included the lower than expected level of computer literacy among participants and issues with access to computers. Although the project team decided to incentivize the use of the VR component, this approach did not work given that the barriers to its implementation were not financial.
VR is an effective teaching/learning strategy, which is well established and is increasingly used in health professions education to improve procedural skills, technical knowledge and proficiency, and psychomotor skills (44–48). Acceptability and perceived usefulness of VR programs may vary and depend on the ability of the VR program to meet the users’ needs and complexity of the VR platform. In Australia, VR-based education on empathy and understanding of the physical environment for dementia care workers reported that VR may differentially assist the participants of different age and English-speaking background (49).
Program limitations
This education program was designed and implemented as an emergency response to the evolving impact of COVID 19 in RACFs rather than regular planned professional development. An education program that is purposefully planned for specific learners allows for development of deeper understanding and knowledge that can be applied in the workplace to improve patient care (50). The rapid nature of the development and implementation of this education program limited the impact of the use of the VRS as a sustainable education strategy, with implications for future program implementation.
During the roll-out of the VRS, a number of unanticipated challenges were encountered in engaging RACF staff; and current activation sits at 19% of RACFs. These challenges included lower than expected level of computer literacy among RACF workers and reported limited access to computers both during work time and outside of work. Compounding this, is the lack of dedicated professional development time for RACF workers, an issue highlighted in The Royal Commission (14). Large changes in staffing in RACFs during and following the COVID-19 pandemic has seen many RACF workers that completed the face-to-face education, no longer working in the sector. Finally, the introduction of a trained IPC lead nurse at all RACFs within the aged care sector [following the impact of COVID 19 in some RACFs and the COVID-19 Special report by The Royal Commission (14)], who have been focusing more on the requirements for their new roles and responsibilities including ensuring their IPC education qualifications are met and have not yet established program implementation/staff training in their RACF.
Practical implications
The need to improve career development and training the RACF workforce in Australia to improve the required essential competencies has been repeatedly highlighted (51), including their IPC competencies (7, 17). Effective IPC training is essential for protection of residents and staff in RACFs not only during a pandemic, but also for routine care; however, it is often neglected (52). Improved IPC practices will help to reduce RACF financial costs related to the need to replace quarantined staff with agency staff, and employ additional staff to address the extra workload due to the increased acuity of care (52).
Education and training in the aged care sector are often based on evidence collected in acute healthcare settings and adapted for their use in RACFs, where the needs of patients and educational level of staff are significantly different to that of RACFs. These programs are not always relevant for the RACF context (18), making it difficult for staff to translate knowledge and understanding gained from the education to care of residents in RACFs. Therefore, well planned education programs specifically designed for RACF workers would be meaningful and beneficial for future education practice.
Adding to this, the RACF workforce development in Australia is a complex issue, as RACF staff do not have time away from care tasks to attend training and access educational resources (53). Previous studies also discussed the RACF staff diversity and highlighted the need for equitable access to educational resources for staff from non-English speaking backgrounds (53). The lack of clear pathways for RACF workers to develop their knowledge and skills and advance within the sector has also been acknowledged (54). In addition to attracting and retaining, RACF staff, education and training in Australia becomes an increasingly important area of concern (54).
This program was implemented in the beginning of COVID-19 outbreak when a State of Emergency was declared in Victoria. At that time, knowledge of the impact of the pathogen and its transmission routes were limited. It is important to note that, in addition to common worries about their own and their family’s health and life, RACF workers were anxious about transmitting COVID-19 infection to residents (14). This situation was the main driver of the program uptake by RACFs, potentially reducing motivation for ongoing education related to IPC practices after the State of Emergency was lifted.
We shared this community case study to demonstrate that educational sector-aged care sector partnership enhanced the collaborative capacity of our project for the design, development and implementation of an education program specifically for the IPC training of RACF workers. Careful project planning and program co-design, strong leadership, effective communication with the project stakeholders and their engagement in the project, as well as process evaluation and program adaptation to reflect the participants’ needs and address the educators’ concerns, were the critical success factors that facilitated smooth implementation. The program provided direct feedback and support to industry partners, and optimized potentially life-saving procedures during a traumatizing time for the sector.
In regards to the programmatic elements, we aimed to highlight the RACF workers’ and managers’ preference for the traditional face-to-face and the train-the trainer components of the IPC training rather than VR component. In emergency situations, such as the COVID-19 outbreak, we suggest that developers of educational projects intended to upskill RACF staff use these traditional educational methods. However, the use of technology, such as VR, for education purposes in RACFs warrants further exploration.
Ethical issues
An online survey using a secure web-based platform was used to collect pre-and post-quiz knowledge data. Completion of the quiz was anonymous and contained no identifying features. Participants used a QR code at the face-to-face session to access and complete the pre-quiz and were emailed the link to the post-quiz 3–6 weeks following completion of face-to-face education. Participant email addresses were provided to the Monash University PPE Project Administrator upon registration in the program.
VRS data was collected when participants accessed and interacted with the virtual reality platform using an individual access code emailed to each participant with the link to the post-quiz survey. Prior to entering the VRS, participants were required to complete a privacy statement regarding the collection and use of data for this activity. Data collected were de-identified, aggregated and analyzed to evaluate the PPE education program outcomes.
All survey and VRS data were stored securely in LabArchives, and were accessible only to the research team.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Monash University Human Research Ethics Committee (Project ID: 26516). Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SD, JM, HR, PR, and DG secured the grant. SD and VT conducted the literature search and drafted the manuscript with support and guidance from JM, HR, PR, and DG. All the authors critically reviewed and contributed to the individual parts of the manuscript, approved the final version, and agreed to be accountable for the content of this work.
Funding
This project was funded by the Victorian Government through the Department of Health and Human Services Victoria (HHSD/20/350937).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the contributions of the program administration officer, Penny Walker who managed all the RACF bookings and information management, including government reports. In addition, the nurse education team that drove across the state to deliver the education program during a time of uncertainty due to the pandemic. Finally, we acknowledge the participating residential aged care facilities and staff for completing the education program in an effort to keep those they care for safe. Some information included in this article was included in the unpublished program progress report to DHHS.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1. Thompson, D-C, Barbu, M-G, Beiu, C, Popa, LG, Mihai, MM, Berteanu, M, et al. The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on long-term care facilities worldwide: an overview on international issues. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:8870249. doi: 10.1155/2020/8870249
2. Comas-Herrera, A, Patel, J, Arling, G, Mossong, J, and Schmidt, A. International data on deaths attributed to COVID-19 among people living in care homes. Available at https://ltccovid.org/2022/02/22/international-data-on-deaths-attributed-to-covid-19-among-people-living-in-care-homes/
3. Salcher-Konrad, M, Jhass, A, Naci, H, Tan, M, El-Tawil, Y, and Comas-Herrera, A. COVID-19 related mortality and spread of disease in long-term care: a living systematic review of emerging evidence. MedRxiv. (2020). doi: 10.1101/2020.06.09.20125237
4. Quigley, A, Stone, H, Nguyen, PY, Chughtai, AA, and MacIntyre, CR. COVID-19 outbreaks in aged-care facilities in Australia. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. (2022) 16:429–37. doi: 10.1111/irv.12942
5. Viray, P, Low, Z, Sinnappu, R, Harvey, PA, and Brown, S. Residential aged care facility COVID-19 outbreaks and magnitude of spread among residents: observations from a Victorian residential in-reach service. Intern Med J. (2021) 51:99–101. doi: 10.1111/imj.15143
6. Team VManderson, L. How COVID-19 reveals structures of vulnerability. Med Anthropol. (2020) 39:671–4. doi: 10.1080/01459740.2020.1830281
7. Ibrahim, JE, Li, Y, McKee, G, Eren, H, Brown, C, Aitken, G, et al. Characteristics of nursing homes associated with COVID-19 outbreaks and mortality among residents in Victoria, Australia. Australas J Ageing. (2021) 40:283–92. doi: 10.1111/ajag.12982
8. Ibrahim, JE. An equation to predict deaths of nursing home residents during a pandemic. Nat Aging. (2021) 1:571–3. doi: 10.1038/s43587-021-00083-x
9. Frazer, K, Mitchell, L, Stokes, D, Lacey, E, Crowley, E, and Kelleher, CC. A rapid systematic review of measures to protect older people in long-term care facilities from COVID-19. BMJ Open. (2021) 11:e047012. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047012
10. Lee, MH, Lee, GA, Lee, SH, and Park, Y-H. A systematic review on the causes of the transmission and control measures of outbreaks in long-term care facilities: back to basics of infection control. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0229911. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229911
11. Mitchell, BG, Shaban, RZ, MacBeth, D, Wood, CJ, and Russo, PL. The burden of healthcare-associated infection in Australian hospitals: a systematic review of the literature. Infect Dis Health. (2017) 22:117–28. doi: 10.1016/j.idh.2017.07.001
12. Gilbert, L. (2020). Independent review: Newmarch house. COVID-19 outbreak. at St Basil’s Home for the Aged in Fawkner, Victoria and Heritage Care Epping Gardens in Epping, Victoria. Available at: https://www.health.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/2020/12/coronavirus-covid-19-independent-review-of-covid-19-outbreaks-at-st-basil-s-and-epping-gardens-aged-care-facilities.pdf
13. Gilbert, L, and Lilly, A. (2020). Independent review of COVID-19 outbreaks at St Basil’s home for the aged in Fawkner, Victoria and heritage care Epping gardens in Epping, Victoria. : https://www.health.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/2020/12/coronavirus-covid-19-independent-review-of-covid-19-outbreaks-at-st-basil-s-and-epping-gardens-aged-care-facilities.pdf ().
14. Commonwealth of Australia. (2020). Royal Commission into aged care quality and safety. Aged care and COVID-19: a special report. Available at: https://agedcare.royalcommission.gov.au/sites/default/files/2020-12/aged-care-and-covid-19-a-special-report.pdf
15. Cousins, S. Experts criticise Australia's aged care failings over COVID-19. Lancet. (2020) 396:1322–3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32206-6
16. Australian Government. (2020). Infection prevention and control leads. Available at: https://www.health.gov.au/initiatives-and-programs/infection-prevention-and-control-leads
17. Aitken, GE, Holmes, AL, and Ibrahim, JE. COVID-19 and residential aged care: priorities for optimising preparation and management of outbreaks. Med J Aust. (2021) 214:6–8.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50892
18. Cohen, CC, Pogorzelska-Maziarz, M, Herzig, CT, Carter, EJ, Bjarnadottir, R, Semeraro, P, et al. Infection prevention and control in nursing homes: a qualitative study of decision-making regarding isolation-based practices. BMJ Qual Saf. (2015) 24:630–6. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2015-003952
19. Australian Government Department of Health. (2020). Aged care workforce census report. Available at: https://www.health.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/2021/10/2020-aged-care-workforce-census.pdf
20. Shaban, RZ, Sotomayor-Castillo, C, Macbeth, D, Russo, PL, and Mitchell, BG. Scope of practice and educational needs of infection prevention and control professionals in Australian residential aged care facilities. Infect Dis Healt. (2020) 25:286–93. doi: 10.1016/j.idh.2020.06.001
21. Mavromaras, K, Knight, G, Isherwood, L, Crettenden, A, Flavel, J, Karmel, T, et al. The aged care workforce, 2016. Canberra: Australian Government Department of Health (2017).
22. Moyle, W, Hsu, MC, Lieff, S, and Vernooij-Dassen, M. Recommendations for staff education and training for older people with mental illness in long-term aged care. Int Psychogeriatr. (2010) 22:1097–106. doi: 10.1017/S1041610210001754
23. Department of Health and Human Services. Coronavirus (COVID-19). (2020). Plan for the Victorian aged care sector. Version 5. Available at: https://www.health.vic.gov.au/covid-19/aged-care-sector-covid-19 (Accessed November 6, 2020).
24. Schismenos, S, Buhler, C, Gurung, S, Wali, N, Ball, C, Gannon, S, et al. Side by Side’for COVID recovery: De-Stigmatising ageing and re-integrating elders as valued contributors to society. Royal Commission into Aged Care Quality and Safety (2021). Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348862848_’Side_by_Side’_for_COVID_recovery_De-Stigmatising_ageing_and_re-integrating_elders_as_valued_contributors_to_society
25. Commonwealth of Australia, Australian Government Department of Health. (2020). COVID-19 outbreaks in Australian residential aged care facilities. Available at: https://www.health.gov.au/resources/publications/covid-19-outbreaks-in-australian-residential-aged-care-facilities-6-november-2020 (Accessed November 6, 2020).
26. Phua, J, Weng, L, Ling, L, Egi, M, Lim, CM, Divatia, JV, et al. Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): challenges and recommendations. Lancet Respir Med. (2020) 8:506–17. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30161-2
27. Mueller, AL, McNamara, MS, and Sinclair, DA. Why does COVID-19 disproportionately affect older people? Aging. (2020) 12:9959–81. doi: 10.18632/aging.103344
28. Chen, T, Wu, D, Chen, H, Yan, W, Yang, D, Chen, G, et al. Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study. BMJ. (2020) 368:m1091. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1091
29. Shang, L, Shao, M, Guo, Q, Shi, J, Zhao, Y, Xiaokereti, J, et al. Diabetes mellitus is associated with severe infection and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Med Res. (2020) 51:700–9. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.07.005
30. Chavez-MacGregor, M, Lei, X, Zhao, H, Scheet, P, and Giordano, SH. Evaluation of COVID-19 mortality and adverse outcomes in US patients with or without cancer. JAMA Oncol. (2022) 8:69–78. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.5148
31. Nadkarni, AR, Vijayakumaran, SC, Gupta, S, and Divatia, JV. Mortality in Cancer patients with COVID-19 who are admitted to an ICU or who have severe COVID-19: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. JCO Glob Oncol. (2021) 7:1286–305. doi: 10.1200/GO.21.00072
32. Mubarik, S, Liu, X, Eshak, ES, Liu, K, Liu, Q, Wang, F, et al. The Association of Hypertension with the severity of and mortality from the COVID-19 in the early stage of the epidemic in Wuhan, China: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Front Med. (2021) 8:623608. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.623608
33. Andrikopoulos, S, and Johnson, G. The Australian response to the COVID-19 pandemic and diabetes - lessons learned. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2020) 165:108246. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108246
34. Jepsen, DM, and Barker, RT. Single-site employment (multiple jobholding) in residential aged care: a response to COVID-19 with wider workforce lessons. Australas J Ageing. (2022) 41:e298–304. doi: 10.1111/ajag.13072
35. Creswell, JW, and Plano Clark, VL. Designing and conducting mixed methods research. 3d ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE (2018).
36. Seidler, AL, Aberoumand, M, Williams, JG, Tan, A, Hunter, KE, and Webster, A. The landscape of COVID-19 trials in Australia. Med J Aust. (2021) 215:58–61.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51148
37. Universities Australia. Principles and protocols for reducing the potential risk of COVID-19 transmission at universities. Canberra: Universities Australia (2020).
38. Issel, LM, and Wells, R. Health program planning and evaluation. A practical systematic approach to community health. 5th ed. Burlington: Jones & Bartlett Learning (2021).
39. Escandón, K, Rasmussen, AL, Bogoch, II, Murray, EJ, Escandón, K, Popescu, SV, et al. COVID-19 false dichotomies and a comprehensive review of the evidence regarding public health, COVID-19 symptomatology, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, mask wearing, and reinfection. BMC Infect Dis. (2021) 21:710. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06357-4
40. KPMG. (2020). COVID-19: the new reality for project and program management. Addressing the new reality of project and program delivery in Australia, post COVID-19. Available at https://home.kpmg/au/en/home/insights/2020/05/coronavirus-covid-19-project-program-management-new-reality.html (Accessed May 29, 2020).
41. Mayrhofer, A, Goodman, C, Smeeton, N, Handley, M, Amador, S, and Davies, S. The feasibility of a train-the-trainer approach to end of life care training in care homes: an evaluation. BMC Palliat Care. (2016) 15:11. doi: 10.1186/s12904-016-0081-z
42. Clifton, A, De Vries, K, Juttla, K, Welyczko, N, Carroll, R, and O’Keeffe, G. Evaluating a train-the-trainer educational intervention to raise standards of care, within the nursing home sector in the United Kingdom. Health Edu Care. (2018) 3:1–5. doi: 10.15761/HEC.1000143
43. Anderson, CR, and Taira, BR. The train the trainer model for the propagation of resuscitation knowledge in limited resource settings: a systematic review. Resuscitation. (2018) 127:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2018.03.009
44. Plotzky, C, Lindwedel, U, Sorber, M, Loessl, B, König, P, Kunze, C, et al. Virtual reality simulations in nurse education: a systematic mapping review. Nurse Educ Today. (2021) 101:104868. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104868
45. Kyaw, BM, Saxena, N, Posadzki, P, Vseteckova, J, Nikolaou, CK, George, PP, et al. Virtual reality for health professions education: systematic review and Meta-analysis by the digital health education collaboration. J Med Internet Res. (2019) 21:e12959. doi: 10.2196/12959
46. Zhao, J, Xu, X, Jiang, H, and Ding, Y. The effectiveness of virtual reality-based technology on anatomy teaching: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. BMC Med Educ. (2020) 20:127. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-1994-z
47. Rourke, S. How does virtual reality simulation compare to simulated practice in the acquisition of clinical psychomotor skills for pre-registration student nurses? A systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. (2020) 102:103466. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2019.103466
48. Jallad, ST, and Işık, B. The effectiveness of virtual reality simulation as learning strategy in the acquisition of medical skills in nursing education: a systematic review. Ir J Med Sci. (1971 -). 2022) 191:1407–26. doi: 10.1007/s11845-021-02695-z
49. Stargatt, J, Bhar, S, Petrovich, T, Bhowmik, J, Sykes, D, and Burns, K. The effects of virtual reality-based education on empathy and understanding of the physical environment for dementia care workers in Australia: a controlled study. J Alzheimers Dis. (2021) 84:1247–57. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210723
50. Ramasubramaniam, S, and Angeline, G. Curriculum development in nursing education. Where is the pathway. J Nurs Health Sci. (2015) 4:76–81. doi: 10.9790/1959-04537681
51. Lee, HY, Short, S, Lee, M-J, Jeon, Y-H, Park, E, and Chin, Y-R. Improving the quality of long-term care services in workforce dimension: expert views from Australia and South Korea. Arch Public Health. (2022) 80:112. doi: 10.1186/s13690-022-00872-9
52. Gilbert, GL. COVID-19 in a Sydney nursing home: a case study and lessons learnt. Med J Aust. (2020) 213:393–396.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50817
53. Watson, K, Hatcher, D, and Good, A. Influencing factors that support and build aged care research capacity: staff perspectives. Collegian. (2020) 27:34–9. doi: 10.1016/j.colegn.2019.04.006
Keywords: COVID-19, education, health care professionals (HCP), infection control, personal protective equipment (PPE) compliance, program delivery, long-term care, workplace safety
Citation: Dix S, Rawson H, Russo P, Team V, Griffiths D and Morphet J (2023) Practical infection control training for Victoria’s aged care workforce at the time of COVID-19 pandemic: a community case study. Front. Public Health 11:1155980. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1155980
Edited by:
Madhan Balasubramanian, Flinders University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Ying-Chun Li, National Sun Yat-sen University, TaiwanZhichao Hao, Southwest University, China
Copyright © 2023 Dix, Rawson, Russo, Team, Griffiths and Morphet. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Samantha Dix, c2FtYW50aGEuZGl4QG1vbmFzaC5lZHU=
 Samantha Dix
Samantha Dix Helen Rawson
Helen Rawson Philip Russo
Philip Russo Victoria Team
Victoria Team