- 1School of Intelligent Manufacturing, Chengdu Technological University, Chengdu, China
- 2Institute of Exploration Technology, CGS, Chengdu, China
- 3School of Information Science, Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Nomi, Japan
Landslide deformation prediction is a crucial task in geotechnical engineering and disaster prevention. Developing an accurate and reliable landslide displacement prediction model is vital for effective landslide warning systems. This paper proposes a TCN-Multihead-Attention prediction model for landslide deformation based on temporal convolutional networks (TCNs). We collected 8 years of monitoring data from the Huangniba Dengkan landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, including surface deformation (horizontal displacement and elevation), rainfall, and reservoir levels. A comprehensive analysis was conducted to assess the effects of rainfall, reservoir levels, and elevation on landslide horizontal displacement. Utilizing the multi-input and single-output characteristics of the long-period time series dataset, we developed the TCN-Multihead-Attention prediction model of landslide deformation. Model evaluation demonstrated that the coefficient of determination (R2) for the test set reached 0.995, with MAPE and RMSE at only 0.482 and 7.180, respectively, indicating high accuracy. Additionally, we developed other prediction models based on single TCN, Attention-based Transformer, RNN-based LSTM, and the hybrid CNN-BiLSTM for comparison. Compared with existing models, the TCN-Multihead-Attention model integrates dilated causal convolutions from TCN with multi-head attention to effectively fuse nonlinear interactions of multi-source environmental factors, capture long-term evolutionary trends, and accurately identify local mutation patterns, demonstrating superior reliability for landslide deformation forecasting in reservoir regions.
1 Introduction
Landslides, collapses and debris flows are the main exogenous geological phenomena in the Three Gorges Reservoir area and the main types of geological disasters. In the Three Gorges Reservoir, under the combined effects of rainfall and reservoir level, the cumulative displacement of landslides usually shows a “step-like” feature, accelerating in the rainy season and remaining almost stable in the dry season (Zhou et al., 2016). Therefore, how to predict the changing trend of landslide displacement has become a focus of scholars at this stage. For landslide monitoring and early warning work, studying a stable and reliable early identification risk warning system is a reasonable way to reduce landslide risks.
For landslide monitoring and early warning, studying a stable and reliable early risk identification and warning system is a reasonable way to reduce landslide risks. Since Saito (1965) proposed the empirical formula for landslide prediction, many landslide prediction models have been developed. Classic landslide prediction models can be divided into two categories: physical models and data-driven models (Huang et al., 2017). Physical models mainly use physical parameters from general creep theory, large-scale indoor simulation experiments, and field monitoring to predict landslide events (Xu et al., 2009; Mufundirwa et al., 2010). These models can provide clear physical explanations of landslides, but implementation of sufficiently accurate models can be complex, time-consuming, and expensive (Thiebers, 2014). Compared with physical models, data-driven models are usually more popular because of their advantages of simple process, accurate prediction, and lower cost (Corominas et al., 2005).
In recent years, among data-driven models, machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms have been widely used in landslide displacement prediction and have achieved good performance (Kayacan et al., 2010; Reichenbach et al., 2018; Du et al., 2013) decomposed cumulative displacement into trend components and periodic components, who used a backpropagation neural network (BPNN) to predict periodic displacement and conducted case studies on two typical colluvial landslides: the Baishui River landslide and the Bazimen landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Lian et al. (2015) proposed a multiple ANN switching prediction method for landslide displacement prediction to reduce the risk associated with the types of influencing factors and the selection of artificial neural networks (ANNs). This method was applied to three typical landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, demonstrating better model generalization capability compared to individual ANN predictors. Zhou et al. (2016) and Miao et al. (2018) developed landslide displacement prediction models based on time series analysis and support vector machine (SVM) models, achieving high-accuracy results. To overcome some limitations of classical machine learning methods, Li et al. (2018) proposed a novel data-driven framework incorporating an ensemble-based ELM and Copula model. The effectiveness and practicality of this model were validated through back-analysis of landslide displacement predictions in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of multi-physics coupling in geohazard prediction. Ye et al. (2024) investigates the spatiotemporal evolution of the Outang landslide in China’s Three Gorges Reservoir area through a multidisciplinary approach, introducing weighted displacement parameters to delineate subzone-specific kinematics, and reveals a critical shift from reservoir water-level dominance to rainfall-triggered deformation under climate extremes, while proposing a transition toward compound failure modes, offering insights for dynamic risk management of reservoir landslides through integrated multi-source monitoring data analysis. Xie and Huang (2024) proposes a hybrid SSA-VMD-LSTM model for landslide displacement prediction, which optimizes variational mode decomposition via sparrow search algorithm to disentangle trend-periodic-random components, integrates rainfall-reservoir hydrological drivers through LSTM-based subitem fitting, and demonstrates superior accuracy over conventional methods in Shuping landslide case analysis, offering an interpretable machine learning framework for dynamic early warning of reservoir bank landslides.
Most of the aforementioned prediction models are static models, treating landslide deformation prediction as a static regression problem. However, landslide evolution is a complex nonlinear dynamic process where the influencing factors and deformation conditions at one moment affect the deformation and stability conditions at the next moment (Qin et al., 2002; Reichenbach et al., 2018). Therefore, establishing dynamic models is more suitable for landslide deformation prediction. Currently, dynamic modeling research primarily focuses on recurrent neural networks (RNNs), which can remember historical information and apply it to the current output, thereby achieving state feedback within the network (Medsker and Jain, 2001). Since traditional RNNs cannot capture long-term dependencies in input sequences, an improved version, the long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network, was developed (Hochreite and Schmidhuber, 1997). LSTM is better suited for handling and predicting important events with long intervals in time series. The LSTM model was earlier applied to predict displacement in the Baijiabao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area and achieved better performance than BPNN and SVM models (Xu and Niu, 2018). Yang et al. (2019) employed an LSTM dynamic model for time series analysis to predict landslide displacement, decomposing cumulative displacement into trend and periodic components and analyzing the interplay between landslide deformation, rainfall, and water level, achieving more reliable predictions than SVM.
In summary, the data-driven landslide prediction model has evolved from static to dynamic modeling, through RNN, LSTM, and various combined models, with a focus on model establishment, optimization, and analysis. While traditional methods such as physical models, ARIMA, and SVM have been widely used, they face significant limitations in capturing complex spatiotemporal couplings and nonlinear interactions. For instance, physical models often rely on simplified assumptions and struggle with multi-scale dependencies, while statistical models like ARIMA and SVM are constrained by their inability to handle long-term dependencies and dynamic feature weighting. In contrast, AI algorithms, particularly those combining Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCNs) with Multihead-Attention, excel in addressing these challenges. TCNs leverage dilated convolutions to effectively model long-term dependencies, while attention mechanisms dynamically adjust feature importance, enabling the model to focus on critical spatiotemporal interactions such as rainfall infiltration softening sliding zones and reservoir drawdown-induced stress redistribution. This paper focuses on long time series data to thoroughly analyze the impact of factors like rainfall and reservoir water levels on landslide deformation. By selecting an appropriate deep learning model tailored to the dataset’s characteristics, this study aims to enhance the predictive accuracy of landslide deformation models, providing effective means and methods for predicting reservoir landslide deformation in the Three Gorges Reservoir area.
2 Characteristics of the Huangniba Dengkan landslide
2.1 Landslide overview
The Huangniba Dengkan landslide is situated on the left bank of the Zhu River, a tributary of the Yangtze River, in the Lianhua community, Group 8, Renhe Street, Yunyang County. Its geographic coordinates are approximately longitude 108°37′52″ and latitude 30°57′55″, with a straight-line distance of about 7 km from Yunyang County. The landslide area belongs to the erosion and denudation low hills and hilly terrain, with an overall east-high and west-low topography. The front edge is bordered by the Zhuxi River, while the rear portion consists of steep slopes, resulting in significant terrain undulation. The landslide is situated on a slope, exhibiting a longitudinal platform-slope terrain. The terrain slope angle in the rear platform gentle slope area ranges from 2° to 10°, while in the front slope area, it averages 16–23°, with an average of 18°. The slope mainly consists of cultivated land, forest land, and wasteland. The lowest point in the area is approximately 155 m at the bottom of the western slope, while the highest point is around 290 m at the top of the eastern slope, with an elevation difference of 135 m.
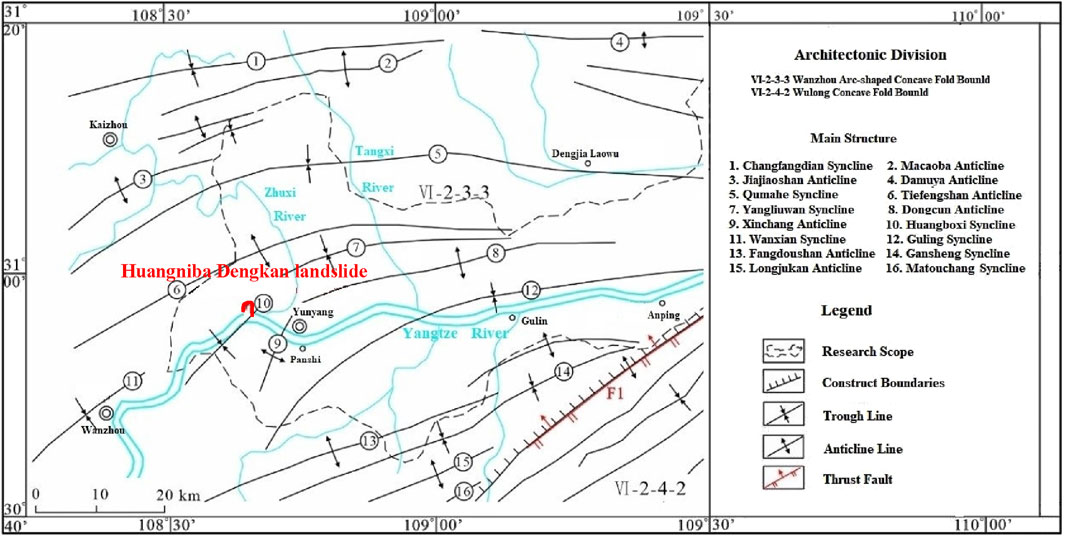
As shown in Figure 1, the landslide area is located on the northern wing of the Huangboxi syncline, and no fault or shear zone pass through the area. According to field investigations, the dip of the rock strata in the area is gentle, ranging from 170° to 190° with a dip angle of 8–18°. Two sets of fractures are mainly developed:
(1) LX1, trending at 236° with a dip angle of 76°, has a fracture opening of 0.5∼2 mm, unfilled, with a smooth and straight fracture surface, extending for 1∼3 m with a spacing of 0.3∼1.0 m.
(2) LX2, trending at 321° with a dip angle of 71°, has a fracture opening of 0.3–0.5 mm, a smooth and straight fracture surface, extending for 1∼4 m with a spacing of 0.3∼0.8 m.
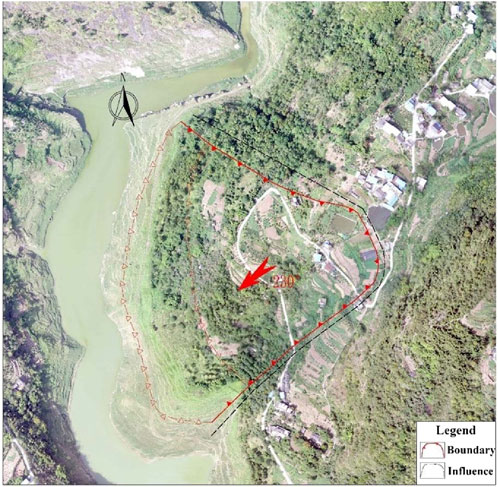
The landslide has a length of 270 m, a width of 345 m, and a slide thickness of 12 m. It covers an area of approximately 9.32 × 104 m2 with a volume of about 1.118 × 106 m3. The main sliding direction is 250°, and the landslide has a “fan-shaped” plan, classifying it as a large mid-layer soil landslide. Its orthophoto is shown in Figure 2.
2.2 Sliding mode and its characteristics
As shown in Figure 3, the drilling revealed that the sliding zone is 0.2–0.4 m thick and developed near the rock-soil interface. The material composition is mostly silty clay intercalated with sandstone breccia and rock debris. The Huangniba Dengkan landslide has the characteristics of graded sliding. It is mainly Q4col+dl containing crushed stone silty clay and broken stone soil. The soil body is hollow, with a large porosity and good permeability, which is conducive to rainfall infiltration and generates seepage pressure. The slope area on the east side of the landslide is large, the catchment area is large, and there are many and wide weirs and ponds in the landslide area, which become a good water storage space. The area near the rock-soil interface in the landslide area contains crushed stone silty clay and crushed stone soil, and the shear strength index is low. Therefore, the short-term rise of the groundwater level in the landslide area may generate seepage pressure, and the low shear strength of the sliding zone soil causes creep-crack sliding deformation of the soil body along the slope.
3 Monitoring plan design
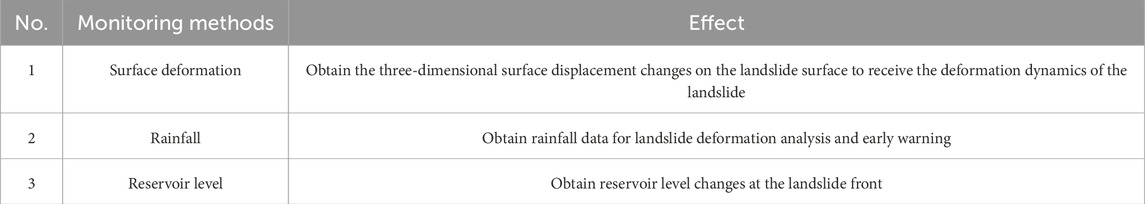
Based on the analysis of the deformation characteristics and formation mechanisms of the Huangniba Dengkan landslide, combined with field surveys, the primary components of professional monitoring and early warning systems include surface deformation monitoring, rainfall monitoring, and reservoir level monitoring, as outlined in Table 1.
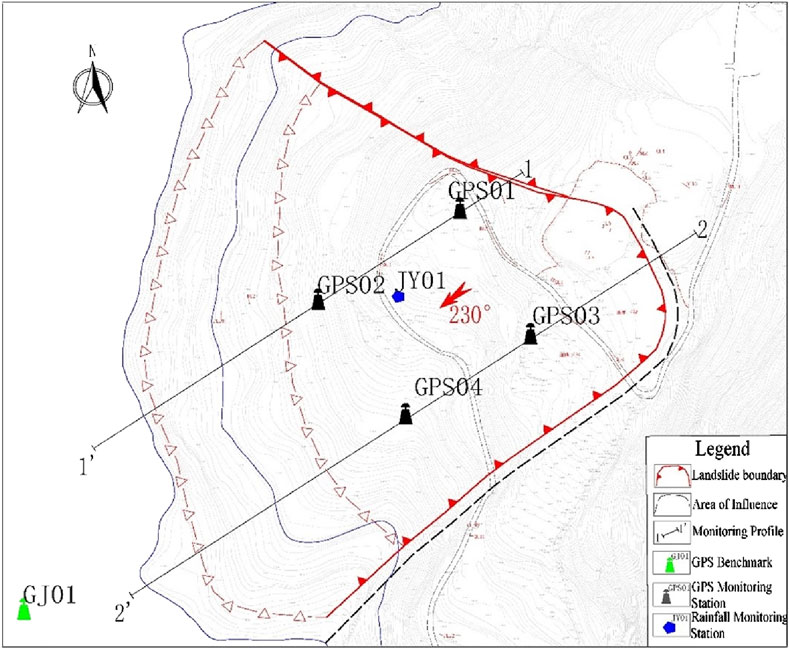
The specific layout plan for monitoring is shown in Figure 4.
(1) GPS monitoring points arrangement plan: two monitoring profiles, 1–1′ and 2–2′, are established on the landslide. On profile 1–1′, two GPS are set up at elevations of 237 m and 200 m, denoted as GPS1 and GPS2, respectively. On profile 2–2′, two GPS are established at elevations of 241 m and 200 m, denoted as GPS3 and GPS4, respectively. One GPS benchmark point is placed at the stable bedrock outside the landslide, denoted as GJ01 in the lower left corner of the Figure 4.
Therefore, five GPS monitoring points are arranged (including 1 benchmark point).
(2) Rainfall monitoring point arrangement plan: a rainfall monitoring point, denoted as JY01, is established near the middle of the landslide.
(3) Reservoir level acquisition: reservoir level data is obtained from the official website of the Yangtze River Maritime Safety Administration, with a frequency of once per day.
4 Monitoring data analysis
4.1 Data display
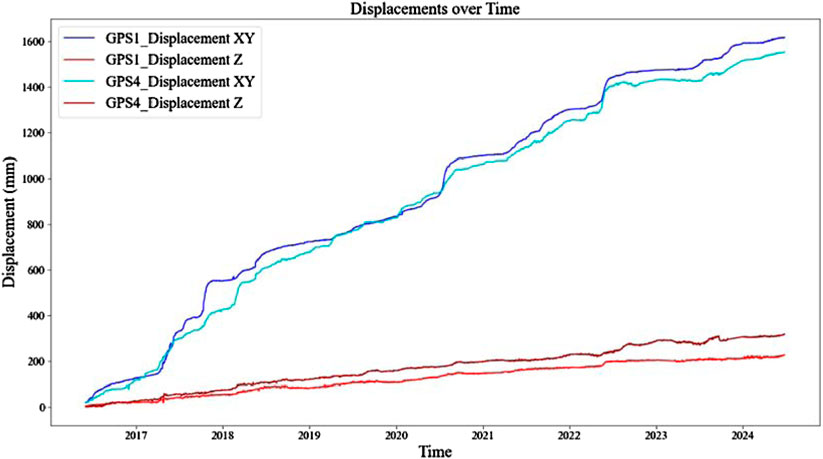
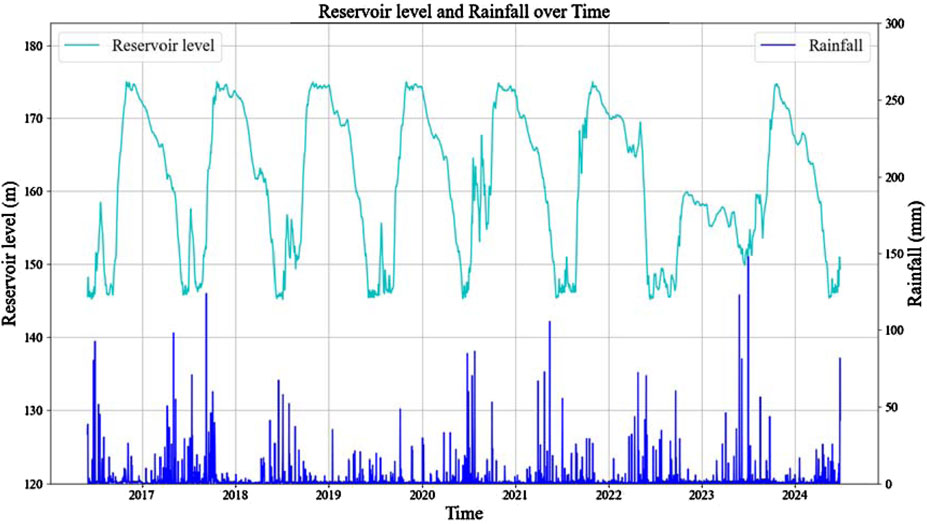
This paper collected monitoring data of the Huangniba Dengkan Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area over the past 8 years (June 2016 to June 2024), mainly including various parameters such as rainfall, reservoir level, and surface deformation (horizontal displacement and elevation). The monitoring dataset is constructed by selecting the horizontal displacement and elevation of GPS1 and GPS4 with significant deformation, daily cumulative rainfall, and daily reservoir level. The monitoring curves are shown in Figures 5, 6, where GPS_Displacement XY represents horizontal displacement, GPS_Displacement Z represents elevation.
4.2 Data analysis
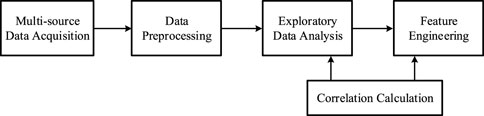
Figure 7 shows the steps involved in data processing and analysis. Firstly, a multi-parameter time series dataset is constructed by acquiring multi-source data. Then, exploratory data analysis (EDA) is performed to understand the data characteristics, and feature engineering is guided by correlation calculation to obtain the effects of rainfall and reservoir level on the horizontal displacement of the landslide.
Scatter plots is a data visualization tool used to show the relationship between different variables in a data set. Figure 8 provides a more comprehensive understanding of the structure and characteristics of the data, thereby providing support for subsequent correlation analysis and model building.
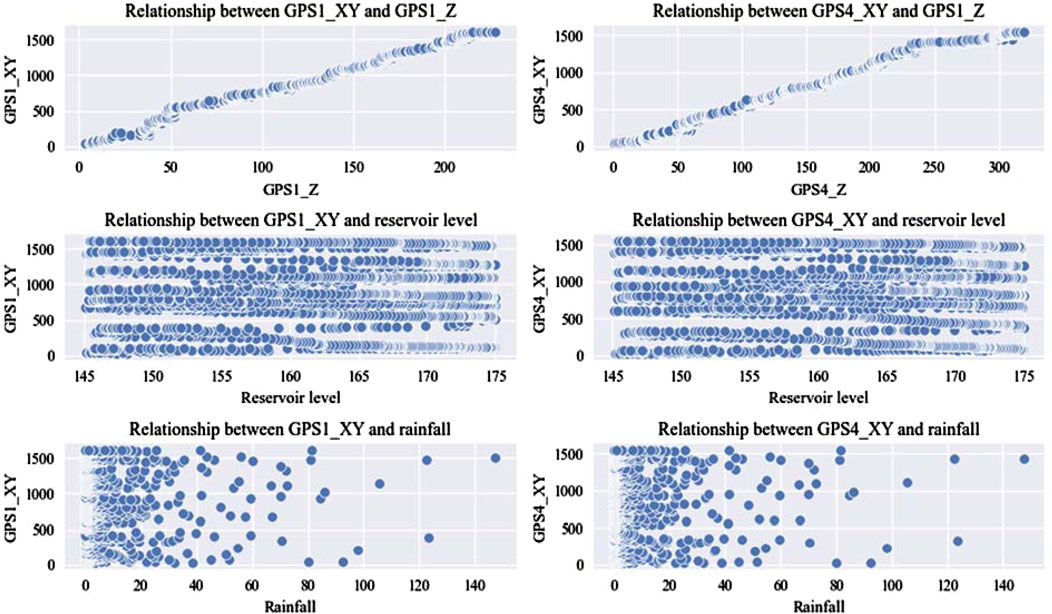
Figure 8. Scatter plots of the relationship between horizontal displacement and multiple parameters (rainfall and reservoir level).
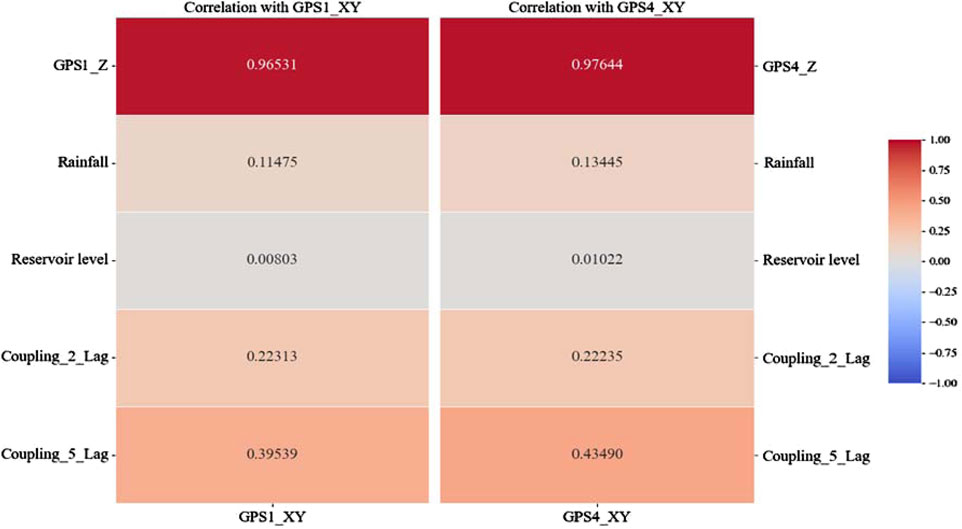
According to the scatter plots in Figure 8, the Correlation Heatmap is obtained in Figure 9. This Figure 9 illustrates the relationships between various factors and the horizontal displacements of GPS1 and GPS4. GPS1_XY and GPS4_XY represent the horizontal displacements of GPS1 and GPS4, respectively. GPS1_Z and GPS4_Z denote the elevations of GPS1 and GPS4. Coupling_2_Lag is the coupling effect of rainfall and reservoir level on horizontal displacement (the displacement variation after 2 days), and correspondingly, Coupling_5_Lag is the coupling effect after 5 days. The heatmap shows strong correlation between horizontal displacement and elevation, and weaker correlation with rainfall and reservoir level. Coupling_2_Lag and Coupling_5_Lag have a certain correlation with horizontal displacement, which may be due to the lag effect of the coupling effect of rainfall and water level on horizontal displacement changes.
From the correlation data of variables in Figure 9, it is evident that the deformation of the landslide is closely related to changes in rainfall and reservoir levels. These fluctuations are the primary factors contributing to reservoir landslide deformation. Therefore, in designing a prediction model of landslide deformation, it is crucial to focus on analyzing and predicting the impact of rainfall and reservoir level changes on landslide deformation.
5 Prediction model of landslides deformation
5.1 Structure of the prediction model
Temporal convolutional networks (TCNs) are a deep learning model specifically designed for processing time series data. Unlike traditional recurrent neural networks (RNNs), TCNs capture long-term and short-term dependencies in time series through one-dimensional convolution operations, which has the advantages of strong parallel computing capabilities and high training efficiency (Razavian and Sontag, 2015). At the same time, since the self-attention mechanism (Attention) is different from RNN and CNN in the way of processing sequence data, the self-attention mechanism captures global context information by calculating the correlation between different positions. Therefore, the self-attention mechanism has the advantages of capturing long-distance dependencies, parallel computing, flexible adaptation, and interpretability (Povey et al., 2018).
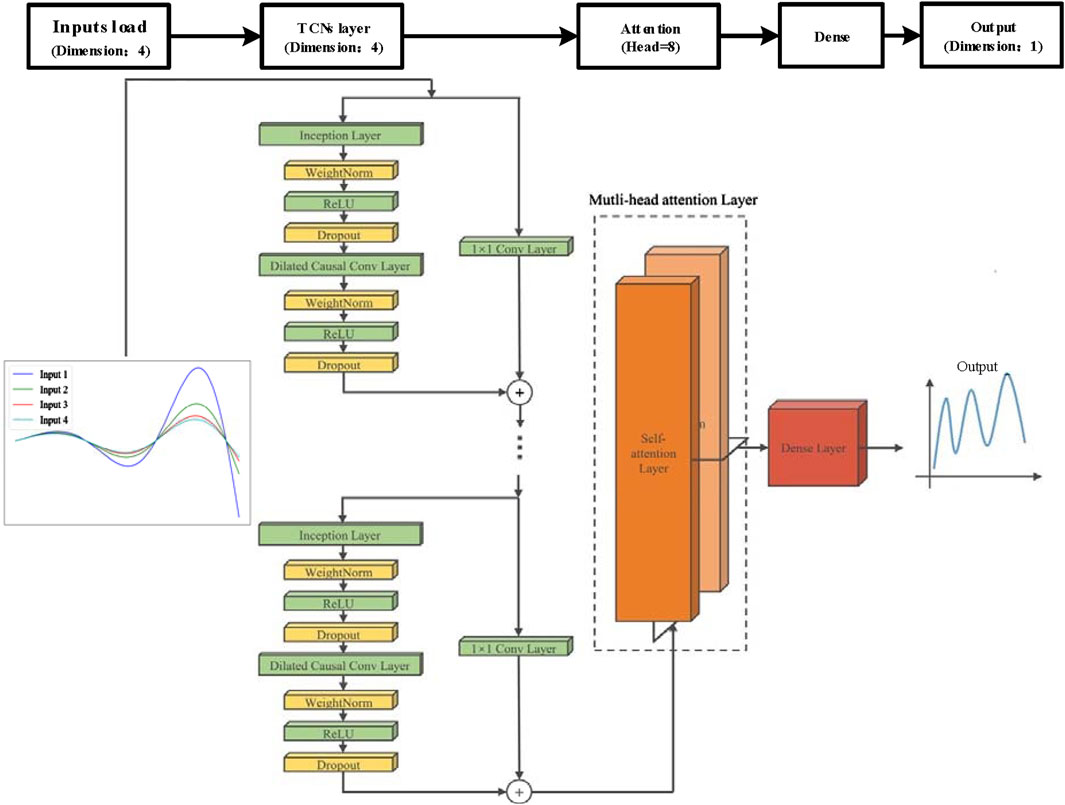
The monitoring data of landslide deformation constitutes a typical time series dataset, characterized by continuous changes throughout the long-term monitoring process. This section employs a temporal convolutional network (TCN) as the primary framework, enhanced with a multi-head self-attention mechanism layer, to construct the TCN-Multihead-Attention model for predicting synthetic horizontal displacement. The model inputs consist of a multi-parameter time series dataset. Based on the monitoring data analysis in Figure 4, the horizontal displacement values of GPS1 and GPS4 points are designated as input 1, while elevation, reservoir level, and rainfall are designated as inputs 2, 3, and 4, respectively. The output is the predicted horizontal displacement. The structural diagram of the model is depicted in Figure 10.
The TCN-Multihead-Attention model fully combines the advantages of TCN and self-attention mechanisms through a multi-level structure. The TCN layer is responsible for extracting short-term and long-term dependency features in the time series, the ReLU layer introduces nonlinearity, the Dropout layer prevents overfitting, the self-attention layer dynamically allocates feature weights, and the fully connected layer integrates the features of multi-head attention and finally outputs the prediction results. This design not only improves the model’s ability to process complex time series data, but also enhances its ability to capture long-distance dependencies. As shown in Figure 10, The structure of this model can be divided into the following main parts: inputs layer, temporal convolutional networks (TCNs), attention mechanism layer, dense layer and output layer.
(1) Inputs Layer: it consists of four input nodes, which represent the inputs of different characteristic variables (horizontal displacement, elevation, rainfall and reservoir level) of landslide time series data. The inputs are four different time series signals (Equation 1):
where each
(2) TCNs Layer: the TCN model mainly consists of dilated convolution layers and residual blocks. The convolutional layers are used to extract local features in the sequence, while the residual blocks help capture long-term dependencies in the sequence. The dilated convolution expands the receptive field by inserting zero elements between the kernel elements, its mathematical expression is Equation 2:
where y[t] is the output of the convolution operation, w[k] is the weight of the convolution kernel, x[t−d⋅k] is the element of the input sequence, and d is the dilation rate. A residual block consists of two convolutional layers and a residual connection. The calculation process of the residual block is as follows: the input x passes through a dilated convolutional layer and the output y is obtained. Add y to the input x to get the output of the residual block. By stacking multiple residual blocks, the Rbolckoutput is passed to the next layer (Equation 3):
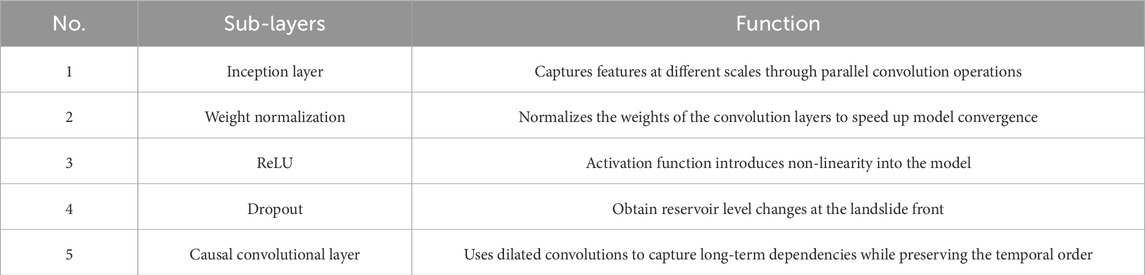
The structure of the TCNs layer comprises several parallel inception modules, each consisting of the following sub-layers, is shown in Table 2.
(3) Multi-head self-attention layer: it includes a Multi-head Attention Layer, which captures dependencies between different time steps in the sequence through a self-attention mechanism, which can capture different levels of abstraction of the input and improve the expressiveness of the model. Here’s a concise breakdown (Equations 4, 5):
where Qi, Ki, Vi are the query, key, and value matrices for the i-th head.
(4) Dense Layer: the features processed by the attention mechanism are further transformed and extracted by a dense layer. The attention output is then passed through a dense layer to produce the final output (Equation 6):
(5) Output layer: it from these parallel inception modules is merged through a 1x1 convolutional layer to form the final feature representation, the final output is a time series prediction, to give the prediction result of the horizontal displacement.
5.2 Model parameter settings
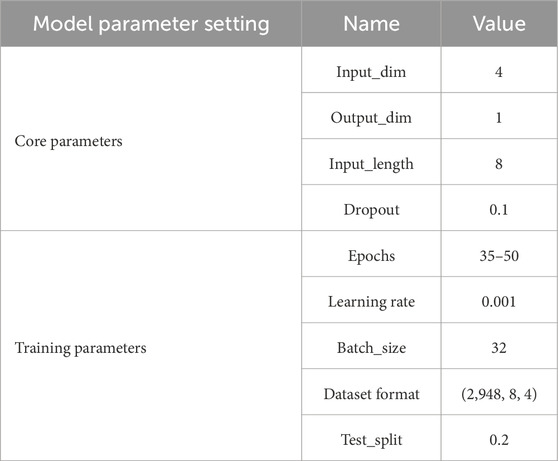
The core and training parameters of the TCN-Multihead-Attention model are configured before introducing the training set for model training. The core parameters include input dimension (input_dim), output dimension (output_dim), input sequence length (input_length), and dropout rate (dropout). The training parameters encompass the number of iterations (epochs), learning rate (learning_rate), batch size (batch_size), and test set ratio (test_split). The values for these core parameters are presented in Table 3.
In the core parameter settings, given the four input parameters—horizontal displacement, elevation, rainfall, and water level—the input dimension (input_dim) is set to 4. The output dimension (output_dim) is set to 1, representing the predicted value of the horizontal displacement. The input sequence length (input_length) is set to 8, based on the dataset size (approximately 3,000 groups) and the need to balance computational efficiency with capturing temporal dependencies. This choice was validated through systematic experimentation with varying window sizes, ensuring optimal prediction accuracy while avoiding overfitting or excessive computational complexity. The dropout rate, which employs regularization to discard neural network units based on a set probability, is set to 0.1 to ensure model generalization and prevent overfitting. Early stopping is utilized during training to further mitigate overfitting.
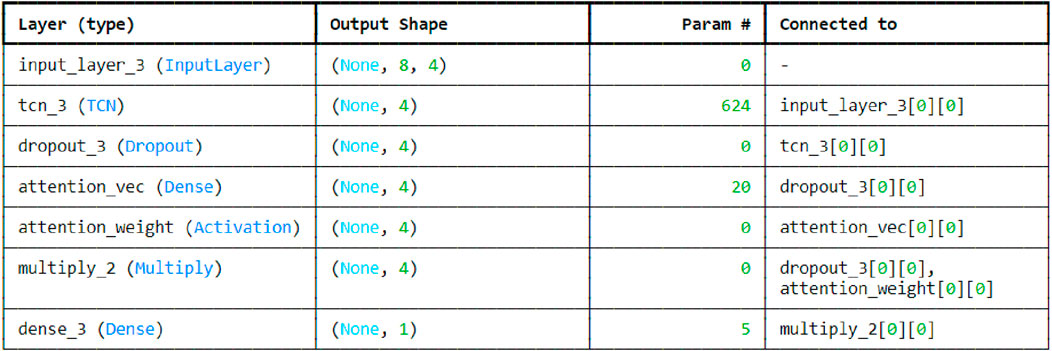
For the training parameters, the optimal configuration is determined through multiple experiments and fine-tuning, considering the model structure and training set characteristics. The number of iterations (epochs) is set to 35–50 to provide sufficient training time for the model. The Adam optimizer (Adaptive Moment Estimation) is used, with a learning rate set to 0.001. The batch size (batch_size) is set to 32, balancing memory usage and computational efficiency while enhancing the model’s generalization ability. The test set ratio (test_split) is set to 0.2, providing a sufficiently large independent sample for evaluation, avoiding overfitting, and aligns with time series data characteristics by evaluating on future data for temporal generalization, ensuring a reasonable division of training and test data for effective model performance evaluation. The full-link structural diagram of the TCN-Multihead-Attention model is depicted in Figure 11.
5.3 Model performance
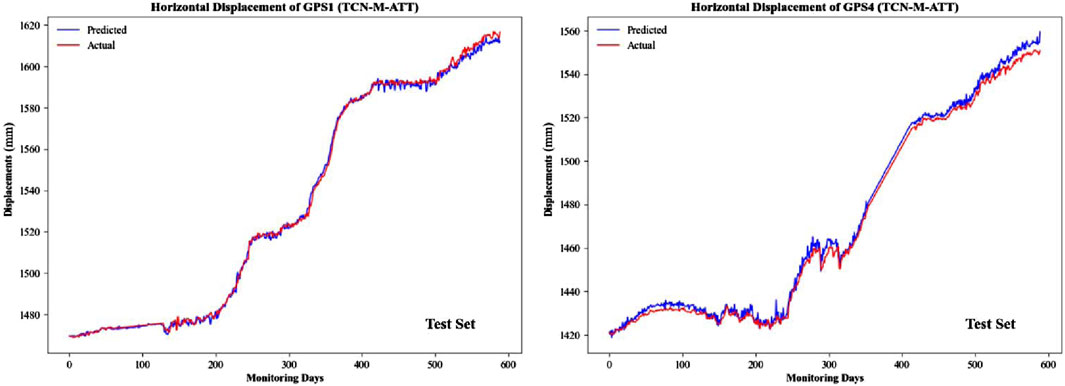
Based on the established model and its parameter settings, the segmented training set is used for model training to learn the patterns and features in the data, enabling more accurate predictions. Figure 12 illustrates the predicted versus actual landslide horizontal composite displacement at GPS1 and GPS4, where the red curve represents the monitoring data (actual horizontal displacement) and the blue curve represents the model’s predictions (predicted horizontal displacement).
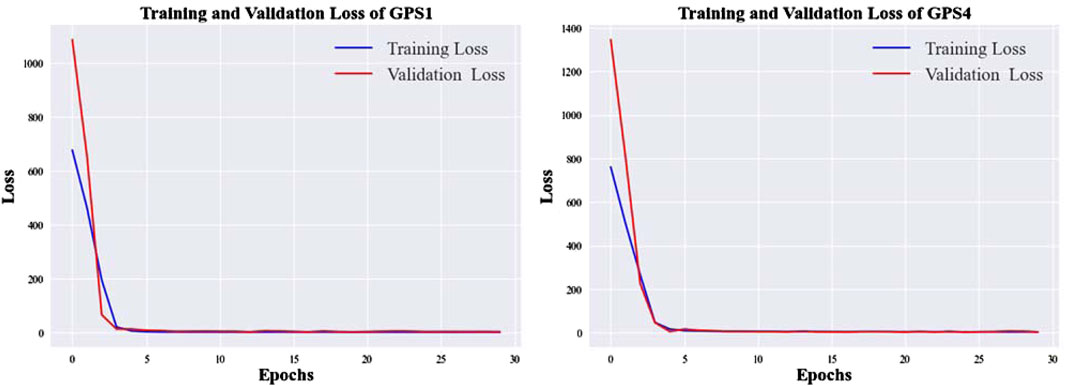
The loss function curve is a crucial tool in deep learning, primarily used to illustrate how the model’s loss changes over time, typically with the number of training iterations or epochs (Neil et al., 2016). Figure 13 displays the loss function curves for the GPS1 and GPS4 points during model training, where the loss value curves for both the training set and validation set continuously decrease and tend to stabilize. This trend indicates that the model gradually approaches the optimal solution during training and incrementally identifies the optimal parameters. Additionally, the concurrent decrease and stabilization of the training and validation loss values suggest that the model is performing well, without signs of underfitting or overfitting, thereby demonstrating convergence during the training process.
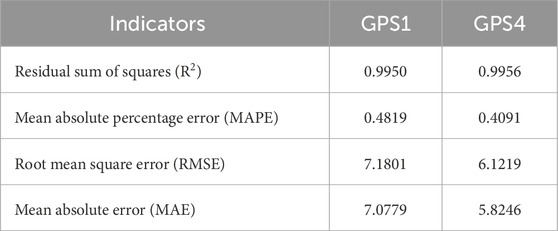
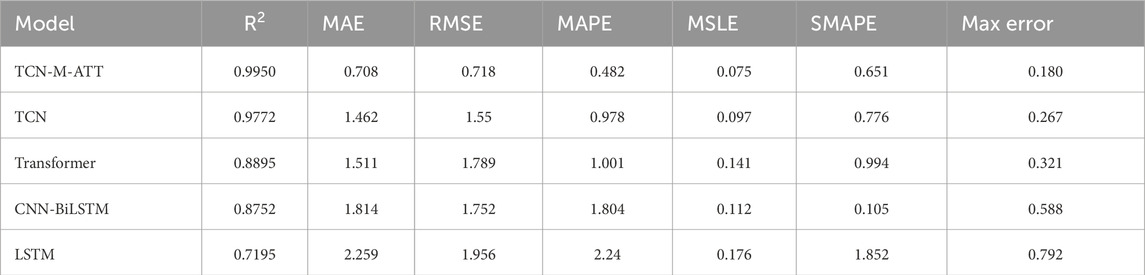
Then, the model is evaluated, and the error is calculated on the validation set. Common metrics include mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), and the coefficient of determination (R2) to measure goodness of fit. The R2value closer to 1 indicates a more accurate model. MAPE, RMSE, and MAE are typical indicators of regression models, used to show the extent of errors in model predictions; thus, smaller values indicate better model performance.
Table 4 shows that the R2 coefficient of determination for this predictive model is 0.995, which is close to the ideal value. The MAPE, RMSE, and MAE values are 0.4819, 7.1801, and 7.0779, respectively, indicating that the predictive model has a high goodness of fit and small errors. This demonstrates that the model accurately explains the dynamic changes in long-term time series data. The predicted values from this model closely approximate the actual observations, exhibiting good accuracy.
6 Discussion
6.1 Model performance comparison
Deep learning has significantly advanced time series forecasting by capturing complex temporal dependencies and patterns. Prominent models in this domain include Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) such as LSTM and GRU, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), autoregressive models like the Transformer, hybrid models combining CNN-LSTM and attention mechanisms, and Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCNs).
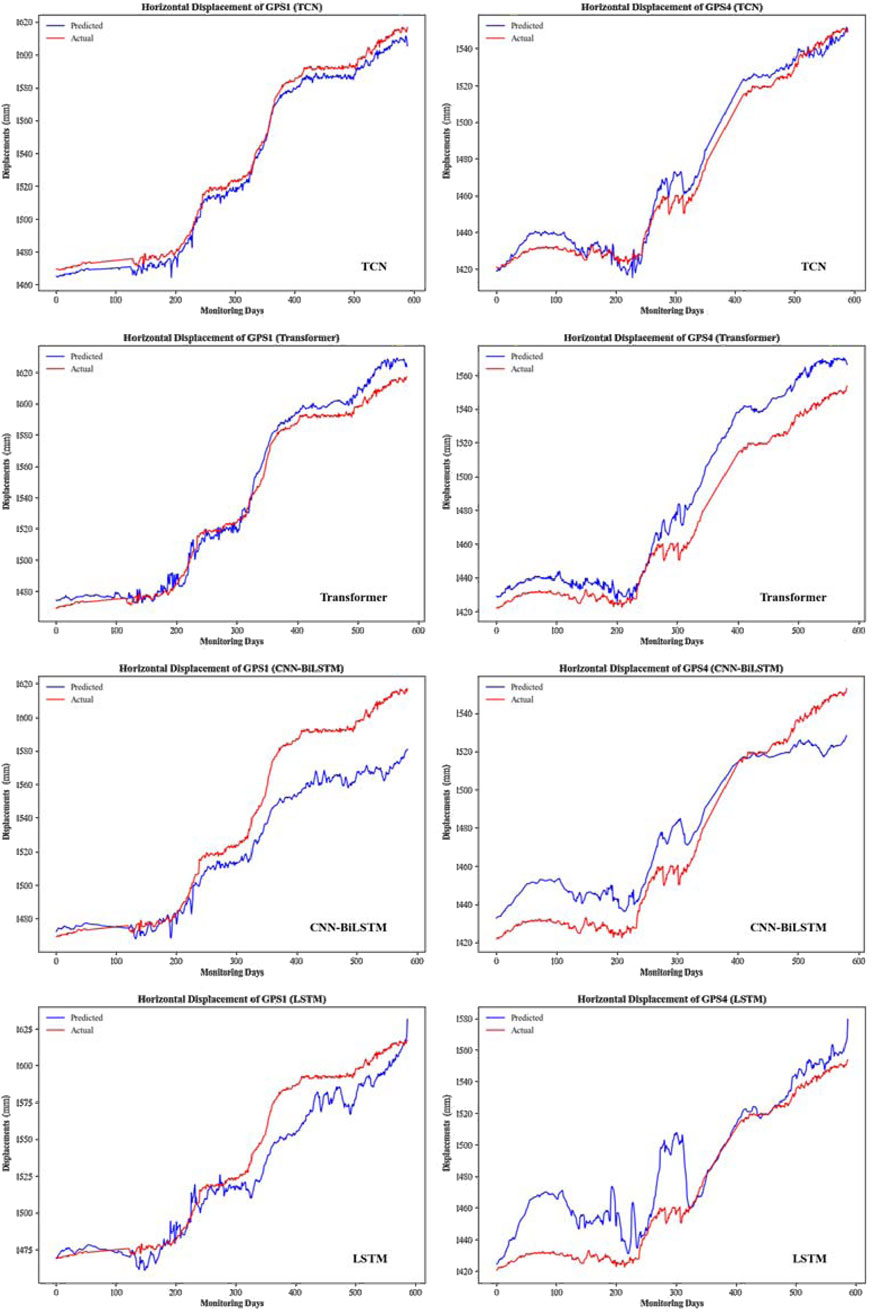
In this section, several deep learning models were developed and trained using the same dataset, including RNN-based LSTM, Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN), Attention-based Transformer, and a hybrid model CNN-BiLSTM. These models were compared with the TCN-Multihead-Attention model described in Chapter 4. Figure 14 shows the prediction curves of the test sets for GPS1 and GPS4 obtained from these models.
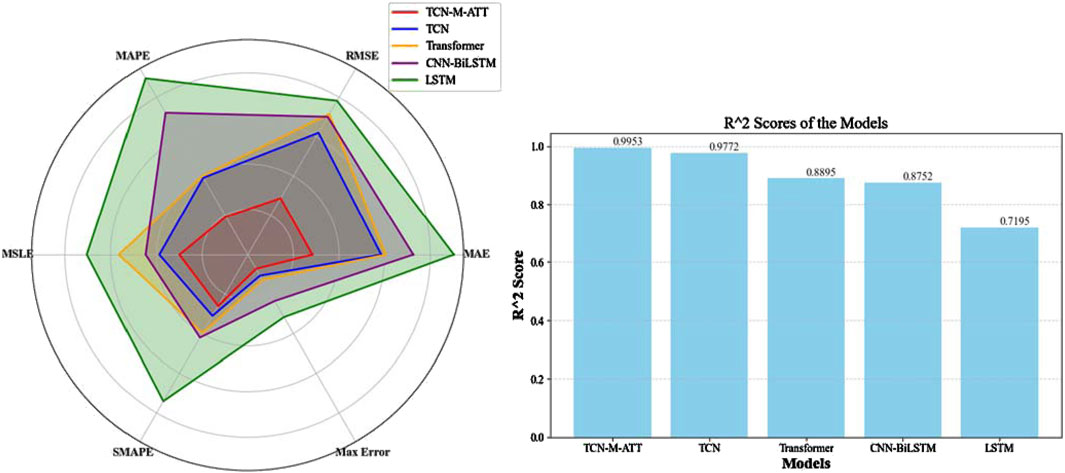
Evaluate the performance of the aforementioned models by calculating indicators such as Goodness of Fit(R2), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), mean squared log error (MSLE), symmetric mean absolute percentage error (SMAPE), and maximum error (Max Error). Table 5 presents these evaluation indicators, while Figure 15 uses a radar chart to visually display their predictive performance (all indicators are normalized for intuitive representation).
The evaluation indicators displayed in the radar chart in Figure 15 are all reverse indicators reflecting the errors of the prediction models, while the right-hand figure shows the R2 indicators for each prediction model. Figure 15 demonstrates that the TCN-Multihead-Attention model established in this paper has the smallest prediction error and the closest fit to 1, indicating that the correlation between the model’s predicted values and the actual values is the strongest. This proves that the model based on TCN and Multihead-Attention effectively captures the long-range dependencies and critical time points of multiple inputs and single outputs, making it highly suitable for predicting landslide displacement influenced by rainfall and reservoir level. The main reasons for this are as follows:
(1) Complementary Strengths: TCNs provide a strong foundation for capturing temporal patterns and long-range dependencies, while attention mechanisms enhance the model’s ability to focus on the most important inputs dynamically.
(2) Handling Non-Stationarity: Landslide displacement data influenced by rainfall and reservoir levels can be non-stationary. The TCN can model the underlying temporal dependencies, and the attention mechanism can adaptively weigh the influence of different inputs, making the combined approach robust to such non-stationarities.
(3) Efficiency and Performance: TCNs’ ability to process sequences in parallel and the attention mechanism’s selective focus result in a model that is both efficient to train and highly performant in making accurate predictions.
6.2 The coupling effect of rainfall and reservoir water
Rainfall and reservoir level fluctuations are two primary factors contributing to reservoir landslides. In the Three Gorges Reservoir area, significant reservoir water level fluctuations often coincide with periods of abundant rainfall, making it challenging to distinguish which factor predominantly influences landslide deformation. The interaction between rainfall and reservoir level fluctuations creates complex triggering mechanisms for landslide deformation in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Our multi-parameter correlation analysis (Section 4.2; Figure 9) aligns with previous studies (Ling and Rui-Qing, 2011; Zhao et al., 2017) while providing some insights into factor coupling and hysteresis effects:
(1) Factor Decoupling Challenge: The low individual correlations (0.01–0.1) confirm that neither rainfall nor reservoir level alone sufficiently explains deformation mechanisms. This echoes Ling and Rui-Qing, 2011 finding that displacement velocity depends on the synchronized intensity of rainfall and drawdown rates. Our TCN-Multihead-Attention model addresses this through dynamic weight allocation–its attention layers automatically amplify critical factor combinations (e.g., high rainfall + rapid drawdown) while suppressing noise from isolated events.
(2) Coupled Hydro-Mechanical Effects: The moderate coupled correlation (0.1–0.2) reflects the synergistic process described by Zhao et al. (2017): rainfall-induced pore pressure reduces shear strength, while reservoir fluctuations generate hydraulic gradients. The model’s dilated TCN convolutions capture these interactions across temporal scales – shallow layers detect immediate infiltration responses, while deeper layers model slow pore pressure propagation through slip zones.
(3) Hysteresis Dynamics: The 2–5 days lagged correlations (0.4–0.44) reveal two-phase deformation controls: Short-term (2-day): Matches surface runoff saturation and initial groundwater recharge processes in silty clay layers; Mid-term (5-day): Corresponds to stress redistribution from reservoir drawdown and sliding zone softening (Figure 9). The model’s hierarchical architecture mimics this physical progression: lower TCN layers process immediate rainfall signals, while upper layers with expanded receptive fields track reservoir level impacts over 30+ days. The correlation heatmaps further show increasing weight on reservoir features beyond 15-day lags, consistent with consolidation theory.
The discussion results indicate that changes in rainfall and reservoir water levels significantly influence reservoir landslide deformation. When atmospheric rainfall occurs, part of the rainwater flows into the Zhuxi River as surface runoff, while another part infiltrates into depressions. This increases the gravitational force on the landslide, enhancing downslope forces. During the flood season, the rising water level combined with rainfall recharges groundwater, soaking and softening the silty clay in the sliding zone. This process decreases the anti-slip force, leading to landslide instability.
6.3 Deformation and failure mechanism of the Huangniba Dengkan landslide
The stability of the landslide is primarily influenced by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Intrinsic factors include topographical conditions, the properties of the rock and soil mass, and geological structures. Extrinsic factors encompass rainfall, reservoir level changes, earthquakes, and human engineering activities. Among these, intrinsic factors control the overall stability of the landslide, while extrinsic factors often increase the driving force of the slide, reduce the strength of the rock and soil mass, and weaken the resisting force, thereby promoting the occurrence and development of landslide deformation and failure.
(1) Impact of rainfall: The intense short-term rainfall will significantly affect the stability of the landslide. After continuous rainfall, the groundwater level within the slope rapidly rises, altering the original stress state. Under the effect of rainwater immersion, the pore water stress of the soil increases rapidly, while the effective stress decreases rapidly, causing the shear strength of the slope to decrease, thus rapidly deteriorating the stability of the landslide and causing deformation. Additionally, concentrated rainfall will penetrate into the slope and sliding surface. The surface soil contains broken stones, gravel, etc., so it has good permeability. However, the permeability of the top surface of the bedrock is relatively weak. The groundwater mainly migrates along the top surface of the bedrock and discharges into the Zhuxi River at the foot of the slope, thereby softening the sliding surface and causing local stress concentration.
(2) Impact of reservoir level changes: The long-term cyclical changes in reservoir level cause continuous erosion of the front slope of the landslide by the Zhu River, affecting the stability of landslide bodies and reservoir banks within the Three Gorges Reservoir. This exacerbates bank collapse and improves the free face conditions of the landslide’s front edge, reducing its stability. Additionally, the upward pressure within the more permeable sections of the landslide during rising waterlevel, and the dynamic water pressure within the less permeable sections during falling waterlevel, provide intrinsic forces that drive the segmented and layered movement of the landslide.
To enhance the model’s generalization performance and enable cross-landslide transfer prediction, leveraging long-term monitoring data to capture common hydro-mechanical coupling patterns in reservoir landslides, particularly the synergistic triggering mechanism of “reservoir drawdown rate - rainfall intensity” revealed by correlation analysis. This universal pattern provides a physical basis for model generalization. Building upon this foundation, proposing a transfer learning framework tailored for reservoir landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, advancing a regional landslide prediction paradigm that integrates “physics-informed guidance with data-driven enhancement.”
7 Conclusion
This paper focuses on the Huangniba Dengkan landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, using its monitoring data to construct a prediction model for horizontal displacement based on a Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) and a multi-head attention mechanism. Through the establishment of a long-period time series dataset, correlation analysis, feature engineering, model construction, parameter setting, training, and performance evaluation, the study demonstrates the remarkable effectiveness of the TCN-Multihead-Attention predicting model in landslide deformation. TCN-Multihead-Attention model integrates dilated causal convolutions from TCN with multi-head attention to effectively fuse nonlinear interactions of multi-source environmental factors, capture long-term evolutionary trends, and accurately identify local mutation patterns, demonstrating superior reliability for landslide deformation forecasting in reservoir regions. The main conclusions are as follows:
(1) Analysis of landslide deformation and failure mode with the monitoring data.
The deformation and failure mechanism, sliding mode, and long-period time series dataset of the Huangniba Dengkan landslide were analyzed in detail. Using scatter plots and correlation heatmaps of multiple influencing factors, the coupling and hysteresis effects were examined. It was determined that rainfall and reservoir level changes are the primary factors affecting landslide deformation. Consequently, the model was designed to use rainfall, reservoir level, elevation, and horizontal displacement as input values, with horizontal displacement as the output.
(2) Establishment and evaluation of the TCN-Multihead-Attention model.
By integrating TCN’s dilated causal convolution with multi-head attention mechanisms, the TCN-Multihead-Attention model achieves dynamic weight allocation for multiple factors, long-term temporal dependency modeling, and sensitive detection of local mutations, significantly enhancing the accuracy and reliability of landslide deformation forecasting in reservoir regions. The model’s evaluation indicators showed the R2 determination coefficient of 0.995, with MAPE and RMSE values of only 0.482 and 7.180, respectively. Compared to other deep learning models discussed, the TCN-Multihead-Attention model demonstrated significantly improved prediction performance.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HC: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YxL: Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. YmL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Author HC was employed by CGS.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feart.2025.1587623/full#supplementary-material
References
Corominas, J., Moya, J., Ledesma, A., Lloret, A., and Gili, J. A. (2005). Prediction of ground displacements and velocities from groundwater level changes at the Vallcebre landslide (Eastern Pyrenees, Spain). Landslides 2 (2), 83–96. doi:10.1007/s10346-005-0049-1
Du, J., Yin, K., and Lacasse, S. (2013). Displacement prediction in colluvial landslides, three Gorges reservoir, China. Landslides 10 (2), 203–218. doi:10.1007/s10346-012-0326-8
Hochreite, S., and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9 (8), 1735–1780. doi:10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Huang, F., Huang, J., Jiang, S., and Zhou, C. (2017). Landslide displacement prediction based on multivariate chaotic model and extreme learning machine. Eng. Geol. 218, 173–186. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.01.016
Kayacan, E., Ulutas, B., and Kaynak, O. (2010). Grey system theory-based models in time series prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 37 (2), 1784–1789. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2009.07.064
Li, H., Xu, Q., He, Y., and Deng, J. (2018). Prediction of landslide displacement with an ensemble based extreme learning machine and copula models. Landslides 15, 2047–2059. doi:10.1007/s10346-018-1020-2
Lian, C., Zeng, Z., Yao, W., and Tang, H. (2015). Multiple neural networks switched prediction for landslide displacement. Eng. Geol. 186, 91–99. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.014
Ling, P., and Rui-Qing, N. (2011). Analysis on deformation characteristics and influential factors of Baijiabao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control. doi:10.1007/s12250-011-3157-6
Miao, F., Wu, Y., Xie, Y., and Li, Y. (2018). Prediction of landslide displacement with step-like behavior based on multialgorithm optimization and a support vector regression model. Landslides 15 (3), 475–488. doi:10.1007/s10346-017-0883-y
Mufundirwa, A., Fujii, Y., and Kodama, J. (2010). A new practical method for prediction of geomechanical failure-time. Int. J. Rock Mech. And Min. Sci. 47 (7), 1079–1090. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.07.001
Neil, D., Pfeiffer, M., and Liu, S. C. (2016). Phased LSTM: accelerating recurrent network training for long or event-based sequences. NIPS’16: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Pain, December 5–10, 2016, 3889–3897.
Povey, D., Hadian, H., Ghahremani, P., Li, K., and Khudanpur, S. (2018). A time-restricted self-attention layer for ASR. in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada (IEEE), 5874–5878. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8462497
Qin, S., Jiao, J., and Wang, S. (2002). A nonlinear dynamical model of landslide evolution. Geomorphology 43(1–2):77–85. doi:10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00122-2
Razavian, N., and Sontag, D. (2015). Temporal convolutional neural networks for diagnosis from lab tests. arXiv doi:10.48550/arXiv.1511.07938
Reichenbach, P., Rossi, M., Malamud, B., Mihir, M., and Guzzetti, F. (2018). A review of statistically based landslide susceptibility models. Earth-Science Rev. 180, 60–91. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.03.001
Saito, M. (1965). “Forecasting the time of occurrence of a slope failure,” in Proceedings of the 6th international mechanics and Foundation Engineering, 537–541.
Thiebers, H., Bell, R., Glade, T., Jäger, S., Mayer, J., Anderson, M., et al. (2014). Integration of a limit-equilibrium model into a landslide early warning system. Landslides 11 (5), 859–875. doi:10.1007/s10346-013-0416-2
Xie, X., and Huang, Y. (2024). Displacement prediction method for bank landslide based on SSA-VMD and LSTM model. Mathematics 12 (7), 1001–1015. doi:10.3390/math12071001
Xu, Q., Chen, J. J., Feng, W. K., Xiao, R. H., and Zuo, Y. Y. (2009). Study of the seismic response of slopes by physical modeling. J. Sichuan Univ. Eng. Sci. Ed. 41 (3), 266–272. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-85168-4_52
Xu, S., and Niu, R. (2018). Displacement prediction of Baijiabao landslide based on empirical mode decomposition and long short-term memory neural network in Three Gorges area, China. Comput. Geosciences. 111, 87–96. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2017.10.013
Yang, B., Yin, K., Lacasse, S., and Liu, Z. (2019). Time series analysis and long short-term memory neural network to predict landslide displacement. Landslides 16, 677–694. doi:10.1007/s10346-018-01127-x
Ye, X., Zhu, H. H., Chang, F. N., Xie, T. C., Tian, F., Zhang, W., et al. (2024). Revisiting spatiotemporal evolution process and mechanism of a giant reservoir landslide during weather extremes. Eng. Geol. 332, 107480–107515. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2024.107480
Zhao, N., Hu, B., Yi, Q., Yao, W., and Chong, M. (2017). The coupling effect of rainfall and reservoir water level decline on the Baijiabao landslide in the three Gorges reservoir area, China. Geofluids 2017, 1–12. doi:10.1155/2017/3724867
Keywords: landslide deformation prediction, TCN-Multihead-Attention model, deep learning, the three gorges reservoir area, environmental factors
Citation: Chen H, Li Y and Liu Y (2025) Research and analysis of the TCN-Multihead-Attention prediction model of landslide deformation in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1587623. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1587623
Received: 04 March 2025; Accepted: 29 April 2025;
Published: 03 June 2025.
Edited by:
Hong-Hu Zhu, Nanjing University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Chen, Li and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yimin Liu, bHltaW5AY2R0dS5lZHUuY24=
 Huan Chen1,2
Huan Chen1,2 Yimin Liu
Yimin Liu