Abstract
The inversion of elastic and fracture parameters from azimuthal seismic data plays a critical role in charactering naturally fractured reservoirs. We propose a Fourier coefficients-based stepwise Bayesian inversion method to estimate these reservoir parameters with improved accuracy. Utilizing the relationship between the azimuthal PP-wave reflection coefficient and Fourier series expansion, we first derive the Fourier coefficient equation for horizontally transverse isotropic (HTI) media. We then conduct a sensitivity analysis of azimuthal Fourier coefficients with respect to P- and S-wave velocities, density, and fracture weaknesses. The results indicate that the zeroth-order Fourier coefficient exhibits greater sensitivity to P- and S-wave velocities and density compared to normal and tangential fracture weaknesses, whereas the second-order Fourier coefficient is more responsive to fracture weaknesses than the fourth-order Fourier coefficient. Based on these sensitivity observations, we develop a stepwise Bayesian inversion approach that involves (1) computing the cosine and sine components of the Fourier coefficients for the azimuthal seismic data, (2) estimating normal and tangential fracture weaknesses using use the second-order Fourier coefficient within a Bayesian framework, and (3) recovering background P- and S-wave velocities and density using the zeroth-order Fourier coefficient along with the previously estimated fracture weaknesses. Both synthetic and field data applications confirm the robustness and effectiveness of the proposed Fourier coefficients-based stepwise Bayesian inversion method for estimating elastic and fracture parameters in naturally fractured reservoirs.
Introduction
Natural fractures, prevalent geological features within subsurface rock formations, play a crucial role in controlling reservoir permeability and influencing fluid migration pathways during hydrocarbon production (Sayers and Dean, 2001; den Boer and Sayers, 2018; Pan et al., 2021; Pan and Liu, 2024; Cao et al., 2025). In this context, amplitude variation with offset and azimuth (AVOAz) inversion has emerged as a key technique for quantitatively predicting fracture parameters due to its superior vertical resolution. AVOAz inversion establishes a mapping relationship between seismic data acquired at varying azimuths and the anisotropic medium’s response, enabling the extraction of essential fracture parameters such as fracture density, normal weakness, and tangential weakness—critical for effective reservoir characterization (Mallick et al., 1988; Bachrach et al., 2009; Pan et al., 2020; Ma et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023; Xie et al., 2024; Li et al., 2025).
Fracture development induces seismic anisotropy, which significantly alters wave propagation characteristics (Schoenberg, 1980; Hudson, 1981; Pan et al., 2017). Traditional isotropic reflection coefficient equations fail to accurately model wavefield response in anisotropic media, prompting the development of various anisotropic AVOAz inversion frameworks. Pšenčik and Martins (2001) formulated a linearized AVOAz relationship for complex anisotropic media, though its inherent nonlinearity poses challenges in practical applications. Shaw and Sen (2006) introduced a joint AVOAz inversion approach, simultaneously estimating fracture weakness parameters and fluid indicators, offering new insights into multiparameter coupled inversion. Bachrach (2015) addressed the uncertainties and non-uniqueness issues in orthorhombic AVOAz inversion, laying the foundation for subsequent regularization techniques. Narhari et al. (2015) successfully predicted fracture density in deep carbonate reservoirs using pre-stack orthorhombic anisotropic AVOAz inversion. Pan et al. (2018) proposed a Bayesian AVOAz inversion framework incorporating prior constraints, significantly improving the estimation accuracy of fracture weakness. Luo et al. (2019) demonstrated the applicability of orthorhombic anisotropic parameter inversion in the Longmaxi Formation shale reservoir, though the process remains unstable due to the high number of parameters involved Isotropic elastic parameters contribute more significantly to reflection coefficients than fracture weakness parameters, and strong nonlinear interactions between anisotropic and elastic parameters lead to substantial parameter coupling effects, complicating the inversion process (Downton and Gray, 2006; Bachrach, 2015; Li et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020).
To address these challenges, recent research has focused on differential seismic feature extraction. Downton and Russell (2011) introduced an azimuthal P-wave reflection coefficient reconstruction method based on Fourier decomposition, enabling fracture orientation identification by isolating anisotropic gradient features. Downton and Roure (2015) interpreting the azimuthal Fourier coefficients for anisotropic and fracture parameters in HTI and orthorhombic anisotropic media. Barone and Sen (2018) applied a Fourier-based azimuthal amplitude variation model to the joint inversion of fracture density and orientation in the Haynesville shale reservoir. Building on these advancements, this study integrates the Fourier-form P-wave reflection coefficient equation proposed by Downton and Russell (2011) with the HTI medium P-wave reflection coefficient equation developed by Pan et al. (2018). This integration leads to a fracture weakness inversion method based on reflection amplitude Fourier coefficients, improving the accuracy and robustness of parameter estimation by separately inverting isotropic and fracture weakness parameters.
Our findings demonstrate that combining Fourier decomposition with AVOAz inversion enables high-resolution estimation of normal and tangential fracture weaknesses—key parameters for reservoir characterization and resource management. The proposed method enhances understanding of fracture behavior in subsurface formations and provides a practical tool for optimizing exploration and production strategies in fractured reservoirs. Validation with synthetic and field data confirms the method’s effectiveness and feasibility, paving the way for broader applications across diverse geological settings.
Theory and method
Azimuthal Fourier coefficients characterized by fracture weaknesses in HTI media
For a single set of vertical, parallel fractures embedded in an isotropic background rock, the fractured medium exhibits horizontally transverse isotropic (HTI) symmetry, with the horizontal axis of symmetry perpendicular to the fracture orientation (Bakulin et al., 2000). The linear-slip model (Schoenberg and Sayers, 1995) is commonly used to describe the fracture-induced anisotropy, where the fracture properties are characterized by the dimensionless normal and tangential fracture weaknesses:where and are the first and second Lamé constants of the isotropic background rock, and denote the normal and tangential compliances induced by the fractures, while and denote the normal and tangential fracture weaknesses. These fracture weaknesses range between 0 and 1, reflecting the impact of fractures on seismic wave propagation (Schoenberg and Douma, 1988). According to Hudson’s aligned penny-shaped crack model (Hudson, 1981), the normal and tangential fracture weaknesses can be further expressed as:where represents the ratio of the square of S-to-P wave velocity for the host rocks, represents the aspect ratio of fractures, in which a and b are the semimajor and semiminor axis of the penny-shaped cracks with the form of oblate spheroid, respectively, and represents the fracture density, in which and are the number of fractures per unit volume and the volume averaging, respectively (Hudson, 1980).
Characterized by the fracture weaknesses, the PP-wave reflection coefficient in an HTI medium can be expressed as (Pan et al., 2018):whereand , , , , and . Here and denote the angle of incidence and the azimuth angle between the observed azimuth and the azimuth of fracture symmetry axis , respectively; and represents the differences of normal and tangential fracture weaknesses between the upper and lower layers, respectively.
Downton and Russell (2011) formulated the azimuthal PP-wave reflection coefficient in terms of a Fourier series expansion so Equation 5 can be rewritten aswhere represents Fourier coefficients varying with the angle of incidence, including the magnitude and the phase . Therefore, the azimuthal reflectivity at a specified incidence angle can be expressed as a linear superposition of sinusoidal components, and Each nth order component is characterized by three defining parameters: amplitude modulation governed by coefficient , spatial periodicity scaled by integer index , and phase retardation controlled by term . Only the n = 0, 2, and 4 magnitude weighting terms are nonzero (Downton and Roure, 2015), and Equation 11 can be thus simplified towith magnitudeswhere
To calculate the Fourier coefficients in Equation 12, the form of a Fourier series can be written as the sum of trigonometric functions, i.e.,with coefficientsand the coefficients and in front of the cosine and sine functions with K-samples azimuthal seismic data are defined as follows:
The above parameters can be transformed to magnitude and phase as
We then analyze the sensitivity of azimuthal Fourier coefficients to variations in P- and S-wave velocities, density, and fracture weaknesses. Figure 1 illustrates the effect of P- and S-wave velocities, density, and fracture weaknesses on the zeroth-order Fourier coefficient, while Figures 2, 3 depict the effects of normal and tangential fracture weaknesses on the second- and fourth-order Fourier coefficients, respectively. The sensitivity analysis is conducted by varying five key parameters , , , , and within the range of −0.3 to 0.3 in increments of 0.1. Results demonstrate that the zeroth-order Fourier coefficient exhibits higher sensitivity to P- and S-wave velocities and density than to normal and tangential fracture weaknesses. Conversely, the second-order Fourier coefficient demonstrates greater sensitivity to fracture weaknesses compared to the fourth-order coefficient. These findings suggest that the zeroth-order Fourier coefficient is primarily useful for estimating P-wave and S-wave velocities and density, while both the second- and fourth-order Fourier coefficients provide valuable information for characterizing normal and tangential fracture weaknesses. Of course, the second-order Fourier coefficient is more effective than the fourth-order coefficient for inverting fracture weaknesses.
FIGURE 1

Sensitivity analysis of zeroth-order Fourier coefficients, where (a) only changes , (b) only changes , (c) only changes , (d) only changes and (e) only changes .
FIGURE 2

Sensitivity analysis of second-order Fourier coefficients, where (a) only changes and (b) only changes .
FIGURE 3

Sensitivity analysis of fourth-order Fourier coefficients, where (a) only changes and (b) only changes .
Stepwise Bayesian inversion for elastic and fracture parameters using azimuthal seismic data
From the sensitivity analysis of azimuthal Fourier coefficients, we propose a stepwise Bayesian inversion for elastic and fracture parameters using the azimuthal seismic data.
Firstly, we calculate the cosine and sine components of the Fourier coefficients for the azimuthal seismic data. The azimuthal seismic data vector can be obtained via the convolution model (Pan and Zhang, 2019) and the estimated seismic wavelets aswhere represents the azimuthal seismic wavelet matrix. For seismic data with five azimuths and three angles of incidence, the cosine and sine components of the Fourier coefficients of each order including the influence of the wavelet can be obtained according to the discrete Fourier transform:where and represent the cosine and sine components of the Fourier coefficients for the kth-azimuth seismic data .
Next, we use the second-order Fourier coefficient to estimate the normal and tangential fracture weaknesses in a Bayesian framework.
Due to the sensitivity of second-order Fourier coefficient to the fracture weaknesses characterized by Equation 14, the coefficients and in front of the cosine and sine functions are also sensitive to the fracture weaknesses expressed by Equations 24 and 25. Incorporating Equations 33 and 34, the forward modeling can be expressed in the matrix form aswhereandin which M represents the number of samples for the azimuthal seismic data, and the symbol T represents the transposition of matrix.
We use the Bayesian theory to estimate the normal and tangential fracture weaknesses, in which the posterior probability distribution function (PDF) of the fracture weaknesses can be written as a joint PDF of the prior PDF and the likelihood function :where represents the PDF. Following Pan et al. (2018), the Cauchy PDF can be used as the prior PDF (Alemie and Sacchi, 2011), and the Gaussian PDF used as the likelihood function, thus the posterior PDF can be also expressed aswhere and represent the variances of seismic data and model parameters, respectively, and the symbol represents the square of the 2-norm.
Combining the smoothing-model regularization (Pan and Zhang, 2018), the maximum posterior solution can be derived by maximizing the posterior PDF aswhere represents the regularization coefficients of normal and tangential fracture weaknesses, represents the integral operator, and , in which represents the initial smoothing model of fracture weaknesses.
Minimizing the objective function of Equation 47 yieldswherewhere represents the Cauchy sparse matrix (Sacchi and Ulrych, 1995).
We solve Equation 48 by using the iteratively re-weighted least-square (IRLS) algorithm (Sacchi and Ulrych, 1995; Pan et al., 2018) obtain the normal and tangential fracture weaknesses via the second-order Fourier coefficient. We then integrate the reflectivities of normal and tangential fracture weaknesses to recover the fracture parameters based on the smoothing-model data as follows:
We finally estimate the background P- and S-wave velocities and density using the zeroth-order Fourier coefficient and the estimated fracture weaknesses in a Bayesian framework.
Due to the sensitivity of zeroth-order Fourier coefficient to the P- and S-wave velocities and density characterized by Equations 13 and 23, we use Equation 23 to express the forward modeling in the matrix form aswhereand
We then use the Bayesian theory to estimate the P- and S-wave velocities and density using the estimated normal and tangential fracture weaknesses, and details about the Bayesian inversion for P- and S-wave velocities and density are the same as the inversion method of normal and tangential fracture weaknesses mentioned above. The final estimated P- and S-wave velocities and density can be expressed as
Results
Synthetic examples
The feasibility of the proposed method was validated through numerical experiments using well log data from a single borehole, incorporating P-wave velocity, S-wave velocity, density, normal and tangential fracture weakness parameters derived from rock physics modeling. Synthetic seismic records were generated for five azimuths (10°, 50°, 90°,130°, and 170°) using a 35 Hz Ricker wavelet and Equation 22, as shown in Figure 4. To evaluate the method’s robustness in realistic noise conditions, Gaussian noise with signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) of 10 and 5 was introduced to the seismic records, as demonstrated in Figures 5, 6. The inversion results for noise-free, SNR = 10, and SNR = 5 cases are illustrated in Figures 7–9, respectively. Comparative analysis indicates strong consistency between the inversion results of the noisy and noise-free cases. As summarized in Table 1, the correlation coefficients for P- and S-wave velocity inversion results remain stable across different noise levels. Although the correlation of density and normal/tangential fracture weaknesses slightly decreases under SNR = 10 and SNR = 5 conditions, it still maintains a good agreement with the reference, demonstrating the noise robustness and algorithmic stability of the proposed inversion approach. Figure 10 demonstrates the noise susceptibility of inverted normal weakness (upper panel) and tangential weakness (lower panel) through box-and-whisker plots comparing error distributions at SNR = 10 and SNR = 5. For the normal weakness parameter, median errors increase by 66.7% (1.5→2.5 × 10−5) with SNR reduction, accompanied by interquartile range expansion from 0.8 × 10−5 to 1.6 × 10−5, indicating doubled dispersion. The tangential weakness parameter exhibits more pronounced sensitivity: median errors escalate 150% (2→5 × 10−5) while interquartile range triples (1→3 × 10−5), revealing non-linear instability growth. The error growth rates quantify parameter-specific noise amplification, establishing the tangential weakness parameter as the critical constraint for system robustness. This differential response necessitates SNR-dependent weighting strategies in joint inversion frameworks, particularly below the identified reliability thresholds.
FIGURE 4

Synthetic seismic record without noise, where (a) azimuth angle is 10°, (b) azimuth angle is 50°, (c) azimuth angle is 90°, (d) azimuth angle is 130°, and (e) azimuth angle is 170°.
FIGURE 5
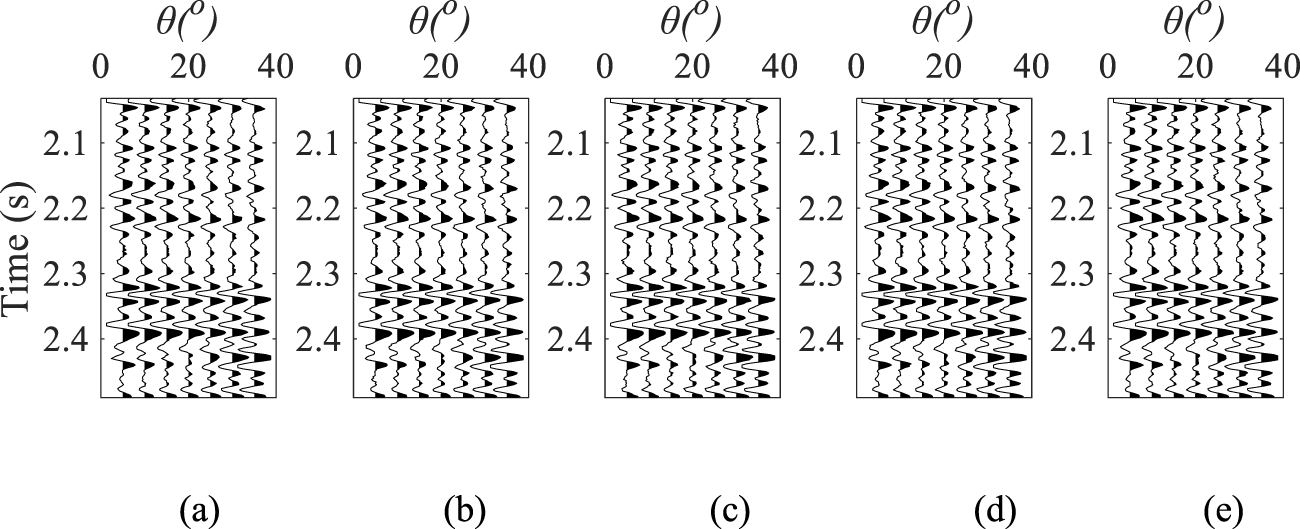
Synthetic seismic record with SNR of 10, where (a) azimuth angle is 10°, (b) azimuth angle is 50°, (c) azimuth angle is 90°, (d) azimuth angle is 130°, and (e) azimuth angle is 170°.
FIGURE 6

Synthetic seismic record with SNR of 5, where (a) azimuth angle is 10°, (b) azimuth angle is 50°, (c) azimuth angle is 90°, (d) azimuth angle is 130°, and (e) azimuth angle is 170°.
FIGURE 7

Inversion results without noise, where (a) shows the inverted P- and S-wave velocities and density, (b) shows the inverted normal and tangential fracture weaknesses.
FIGURE 8

Inversion results with SNR of 10, where (a) shows the inverted P- and S-wave velocities and density, (b) shows the inverted normal and tangential fracture weaknesses.
FIGURE 9

Inversion results with SNR of 5, where (a) shows the inverted P- and S-wave velocities and density, (b) shows the inverted normal and tangential fracture weaknesses.
TABLE 1
| Correlation coefficients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noise free | 97.56% | 98.27% | 95.11% | 97.85% | 97.93% |
| SNR = 10 | 97.47% | 98.13% | 83.64% | 84.88% | 85.17% |
| SNR = 5 | 97.13% | 96.86% | 81.12% | 73.71% | 74.16% |
Correlation coefficients of inversion results under different noise conditions.
FIGURE 10

Error analysis for inversion results of normal and tangential fracture weaknesses in different SNRs.
Field data example
To further validate the feasibility of the proposed method, we applied it to actual data from a research area in southwestern China. This study area is characterized by deep gas reservoirs, high formation pressures, and fractures primarily associated with fault zones, making it suitable for modeling as an HTI medium. Initially, we conducted denoising and amplitude-preserving processing on the prestack seismic data. The processed data were then stacked by angle, resulting in seismic profiles for azimuth angles of 10°, 50°, 90°, 130°, and 170°, with three incident angles of 18°, 22°, and 26°. This produced a total of 15 azimuth-specific seismic profiles, with the corresponding shear-wave velocity logs included in Figure 11. We then extracted the zeroth- and second-order Fourier coefficients (both cosine and sine components) from the processed seismic data. The second-order Fourier coefficients were used to estimate the normal and tangential fracture weaknesses. Using the zeroth-order Fourier coefficients, we further inverted for the normal and tangential fracture weaknesses, as well as the P- and S-wave velocities and density. The inversion results are shown in Figures 12, 13, where the profiles for P-wave and S-wave velocities, density, and normal and tangential fracture intensities demonstrate good continuity and alignment with the logging curves. This strong correlation between the inversion results and well log data confirms the feasibility and stability of the proposed method in real-world applications.
FIGURE 11

Seismic records for different azimuth angles, where (a) shows the azimuth angle of 10°, (b) shows the azimuth angle of 50°, (c) shows the azimuth angle of 90°, (d) shows the azimuth angle of 130°, and (e) shows the azimuth angle of 170° (the black curve represents the P-wave velocity log).
FIGURE 12

Inversion results of parameter profiles, where (a) shows the inverted P-wave velocity profile, (b) shows the inverted S-wave velocity profile, and (c) shows the inverted density profile (the red curves represent the corresponding logging curves).
FIGURE 13

Inversion results of parameter profiles, where (a) shows the inverted normal fracture weakness profile, and (b) shows the inverted tangential fracture weakness profile (the red curves represent the corresponding logging curves).
Conclusion
This study introduced a Fourier coefficients-based stepwise Bayesian inversion method for estimating elastic and fracture parameters in fractured reservoirs using azimuthal seismic data. By analyzing the sensitivity of Fourier coefficients to key subsurface properties, we established that the zeroth-order Fourier coefficient is predominantly sensitive to P- and S-wave velocities and density, while the second-order Fourier coefficient is more responsive to fracture weaknesses. Building upon this sensitivity analysis, we developed a stepwise Bayesian inversion approach, where fracture weaknesses are first estimated using the second-order Fourier coefficient, followed by the estimation of background elastic parameters using the zeroth-order Fourier coefficient. Synthetic experiments demonstrated the robustness of the proposed method, with inversion results maintaining strong consistency with noise-free reference data, even under SNR of 10 and 5. Furthermore, application to field data from a research area in southwestern China confirmed the method’s practical feasibility. The inversion results for P-wave and S-wave velocities, density, and fracture intensities exhibited excellent continuity and alignment with well log data, highlighting the effectiveness and stability of the approach in fractured reservoir characterization.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
JS: Project administration, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Investigation. HX: Data curation, Software, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. SC: Project administration, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – review and editing. XZ: Investigation, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Project administration. XP: Software, Methodology, Visualization, Resources, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. We would like to express our gratitude to the sponsorship of the program of China National Petroleum Corporation (2023ZZ05-05 and 2023ZZ14YJ05), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42474172), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2025JJ20036) for their fundings in this research. The authors declare that this study received funding from China National Petroleum Corporation. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Acknowledgments
We also thank the reviewers for their constructive suggestions.
Conflict of interest
Authors JS, SC, and XZ were employed by PetroChina.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Alemie W. Sacchi M. D. (2011). High-resolution three-term AVO inversion by means of a Trivariate Cauchy probability distribution. Geophysics76, R43–R55. 10.1190/1.3554627
2
Bachrach R. (2015). Uncertainty and nonuniqueness in linearized AVAZ for orthorhombic media. Lead. Edge34, 1048–1056. 10.1190/tle34091048.1
3
Bachrach R. Sengupta M. Salama A. Miller P. (2009). Reconstruction of the layer anisotropic elastic parameters and high‐resolution fracture characterization from P‐wave data: a case study using seismic inversion and Bayesian rock physics parameter estimation. Geophys. Prospect.57, 253–262. 10.1111/j.1365-2478.2008.00768.x
4
Bakulin A. Grechka V. Tsvankin I. (2000). Estimation of fracture parameters from reflection seismic data—part I: HTI model due to a single fracture set. Geophysics65, 1788–1802. 10.1190/1.1444863
5
Barone A. Sen M. K. (2018). A new Fourier azimuthal amplitude variation fracture characterization method: case study in the Haynesville Shale. Geophysics83, WA101–WA120. 10.1190/geo2017-0030.1
6
Cao Z. Zhang S. Xue Y. Wang Z. Du F. Li Z. et al (2025). Disaster-causing mechanism of spalling rock burst based on folding catastrophe model in coal mine. Rock Mech. Rock Eng.10.1007/s00603-025-04497-6
7
den Boer L. D. Sayers C. M. (2018). Constructing a discrete fracture network constrained by seismic inversion data. Geophys. Prospect.66, 124–140. 10.1111/1365-2478.12527
8
Downton J. Russell H. (2011). Azimuthal fourier coefficients: a simple method to estimate fracture parameters. CSEG Rec.Houston, TX: SEG.
9
Downton J. E. Gray D. (2006). AVAZ parameter uncertainty estimation. Houston, TX: SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts.
10
Downton J. E. Roure B. (2015). Interpreting azimuthal Fourier coefficients for anisotropic and fracture parameters. Interpretation3, ST9–ST27. 10.1190/int-2014-0235.1
11
Hudson J. A. (1980). Overall properties of a cracked solid. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc.88, 371–384. 10.1017/s0305004100057674
12
Hudson J. A. (1981). Wave speeds and attenuation of elastic waves in material containing cracks. Geophys. J. Int.64, 133–150. 10.1111/j.1365-246x.1981.tb02662.x
13
Li L. Zhang G. Wang Y. Hu G. (2025). Bayesian Fourier coefficient inversion for gravity-induced stress parameters in tilted transversely isotropic gas-bearing reservoirs. Geophysics90, M59–M73. 10.1190/geo2024-0355.1
14
Li L. Zhang J. Pan X. Zhang G. (2020). Azimuthal elastic impedance-based Fourier coefficient variation with angle inversion for fracture weakness. Petro. Sci.17, 86–104. 10.1007/s12182-019-00405-0
15
Liu X. Zhou H. Guo K. Li C. Zu S. Wu L. (2023). Quantitative characterization of shale gas reservoir properties based on BiLSTM with attention mechanism. Geosci. Front.14, 101567. 10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101567
16
Luo T. Feng X. Guo Z. Liu C. Liu X. (2019). Seismic AVAZ inversion for orthorhombic shale reservoirs in the Longmaxi area, Sichuan. Appl. Geophys.16, 185–198. 10.1007/s11770-019-0759-0
17
Ma Z. Yin X. Li K. Tan Y. (2022). Fourier coefficients variation with angle for fracture detection and fluid discrimination in tilted transversely isotropic media. Surv. Geophys.43, 775–813. 10.1007/s10712-022-09704-5
18
Mallick S. Craft K. L. Meister L. J. Chambers R. E. (1998). Determination of the principal directions of azimuthal anisotropy from P-wave seismic data. Geophysics63, 692–706. 10.1190/1.1444369
19
Narhari S. R. Al-Qadeeri B. Dashti J. Sliva J. Dasgupta S. Hannan A. et al (2015). Application of prestack orthotropic AVAz inversion for fracture characterization of a deep carbonate reservoir in northern Kuwait. Lead. Edge34, 1488–1493. 10.1190/tle34121488.1
20
Pan X. Du X. Zhao X. Ge Z. Li L. Zhang D. et al (2021). Seismic characterization of decoupled orthorhombic fractures based on observed surface azimuthal amplitude data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.60, 1–12. 10.1109/tgrs.2021.3105724
21
Pan X. Liu J. (2024). Stress-dependent PP-wave reflection coefficient for fourier-coefficients-based seismic inversion in horizontally stressed vertical transversely isotropic media. Surv. Geophys.45, 1143–1176. 10.1007/s10712-024-09841-z
22
Pan X. Zhang G. (2018). Model parameterization and PP-wave Amplitude versus Angle and Azimuth (AVAZ) direct inversion for fracture quasi-weaknesses in weakly anisotropic elastic media. Surv. Geophys.39, 937–964. 10.1007/s10712-018-9481-3
23
Pan X. Zhang G. (2019). Fracture detection and fluid identification based on anisotropic Gassmann equation and linear-slip model. Geophysics84 (1), R85–R98. 10.1190/geo2018-0255.1
24
Pan X. Zhang G. Cui Y. (2020). Matrix-fluid-fracture decoupled-based elastic impedance variation with angle and azimuth inversion for fluid modulus and fracture weaknesses. J.Petro. Sci. Eng.189, 106974. 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.106974
25
Pan X. Zhang G. Yin X. (2017). Azimuthally anisotropic elastic impedance inversion for fluid indicator driven by rock physics. Geophysics82, C211–C227. 10.1190/geo2017-0191.1
26
Pan X. Zhang G. Yin X. (2018). Azimuthal seismic amplitude variation with offset and azimuth inversion in weakly anisotropic media with orthorhombic symmetry. Surv. Geophys.39, 99–123. 10.1007/s10712-017-9434-2
27
Pšenčik I. Martins J. L. (2001). Properties of weak contrast PP reflection/transmission coefficients for weakly anisotropic elastic media. Stud. Geophys. Geod.45, 176–199. 10.1023/A:1021868328668
28
Sacchi M. D. Ulrych T. J. (1995). High-resolution velocity gathers and offset space reconstruction. Geophysics60, 1169–1177. 10.1190/1.1443845
29
Sayers C. M. Dean S. (2001). Azimuth‐dependent AVO in reservoirs containing non‐orthogonal fracture sets. Geophys. Prospect.49, 100–106. 10.1046/j.1365-2478.2001.00236.x
30
Schoenberg M. (1980). Elastic wave behavior across linear slip interfaces. J. Acoust. Soc. Am.68, 1516–1521. 10.1121/1.385077
31
Schoenberg M. Douma J. (1988). Elastic wave propagation in media with parallel fractures and aligned cracks. Geophys. Prospect.36, 571–590. 10.1111/j.1365-2478.1988.tb02181.x
32
Schoenberg M. Sayers C. M. (1995). Seismic anisotropy of fractured rock. Geophysics60, 204–211. 10.1190/1.1443748
33
Shaw R. K. Sen M. K. (2006). Use of AVOA data to estimate fluid indicator in a vertically fractured medium. Geophysics71, C15–C24. 10.1190/1.2194896
34
Xie L. Huang L. Wang W. Lin L. Pan X. (2024). Fourier-coefficients-based multiscale seismic inversion for elastic and fracture parameters in frequency domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.62, 1–7. 10.1109/tgrs.2024.3361654
35
Zhang G. Li L. Pan X. Li H. Liu J. Han L. (2020). Azimuthal Fourier coefficient inversion for horizontal and vertical fracture characterization in weakly orthorhombic media. Geophysics85, C199–C214. 10.1190/geo2019-0797.1
Summary
Keywords
naturally fractured reservoirs, Fourier coefficient, stepwise Bayesian inversion, fracture weaknesses, azimuthal seismic data
Citation
Sui J, Xu H, Chen S, Zheng X and Pan X (2025) Fourier coefficients-based stepwise Bayesian inversion for elastic and fracture parameters using azimuthal seismic data. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1596402. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1596402
Received
19 March 2025
Accepted
12 May 2025
Published
02 June 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Qingchun Li, Chang’an University, China
Reviewed by
Zhengzheng Cao, Henan Polytechnic University, China
Zhanyuan Liang, Qilu University of Technology, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Sui, Xu, Chen, Zheng and Pan.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xinpeng Pan, panxinpeng1990@gmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.