- 1School of Architecture and Urban Planning, Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan, China
- 2School of Art and Design, Shandong Jiaotong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 3Institute of Urban and Sustainable Development, City University of Macau, Taipa, Macau, China
- 4Faculty of Humanities and Arts, Macau University of Science and Technology, Taipa, Macau, China
- 5School of Humanities, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Gelugor, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
- 6Faculty of Creative Arts, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Settlement heritage refers to the remains of human settlements with historical, cultural, and scientific value. It represents the social and architectural remains left by humans at a specific time and place. It can also refer to a settlement, the formation and characteristics of which are inherently valuable for research. Settlement heritage is the result of the interaction between human activities and the natural environment in historical periods. Extracting their rich historical and cultural information is of positive significance as it contributes to the development of modern industries. This study, using Shandong Province as an example, examines the distribution pattern and driving factors of settlement heritage in coastal peninsulas. We first screened 580 settlement heritages information points by collecting Chinese settlement heritage lists and verifying them through field surveys. GIS geographic information analysis technology and field survey data collection quantitative research methods were used. The research results show that: 1. The spatial distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province shows significant clustering characteristics, and the high-density distribution areas have obvious multicentricity. The central Shandong region, the Jiaodong Peninsula, the southern Shandong region, and the northern Shandong region are the main concentrations of the traditional high-density areas. 2. The number of settlement heritages in Weifang City and Yantai City are 110 and 95, respectively, which accounts for the highest proportion in the province and has a high geographical concentration. They are the core areas of the distribution of settlement heritage in the province. 3. The distribution of the 580 settlements heritage in Shandong Province is generally dominated by the topography of the natural environment. Cultural landscape sites and historical heritage spaces have a greater impact on the distribution of settlements. Cultural and folk areas, along with slopes, significantly influence the distribution of settlements.
1 Introduction
Rural settlements are the outcome of interactions between humans and their geographical environment (Xiao et al., 2022). Settlement heritage refers to the tangible and intangible elements that possess historical, cultural, and social value, preserved and passed down during the formation and development of rural settlements. These include spatial layouts, traditional architectural styles, local customs, and traditional craftsmanship (Tang et al., 2025). As a living form of cultural heritage, settlement heritage carries unique local cultural memory and embodies indigenous spatial construction wisdom (Cai et al., 2025). Protecting such heritage helps strengthen residents’ sense of cultural identity, promotes intergenerational cultural transmission and emotional connection, and reinforces local identity. However, with the accelerating process of globalization, the cross-regional flow of culture has become increasingly frequent. In this process, the traditional lifestyles, folk customs, and local histories of rural villages are being challenged, potentially weakening the uniqueness of settlement heritage (Tang et al., 2025). In addition, under the rapid urbanization in China, large-scale rural out-migration has led to the continuous loss of the social and cultural carriers that sustain the vitality of settlement heritage, further accelerating the decline of traditional architectural forms and other heritage elements (Guo and Qiao, 2020). Simultaneously, the strong influence of urban culture has brought about significant changes in the ideological concepts, cultural awareness, housing concepts, production and living patterns of villagers, which is leading to the disappearance of many villages’ traditional forms (Jaszczak et al., 2018). Shandong, as one of the important birthplaces of China’s agricultural civilization. In recent years, in order to comprehensively promote the protection of Shandong’s settlement heritage, strengthen the awareness of settlement heritage protection, and enhance the vitality of traditional culture, both at the national level and at all levels of Shandong provincial governments, academic groups in colleges and universities, and relevant social groups have paid extensive attention to the protection and development of Shandong’s settlement heritage (Liu L. et al., 2023). Therefore, it is urgently necessary to conduct systematic spatial analysis and mechanism exploration of settlement heritage in Shandong Province.
In the 20th century, Chinese scholars began to use methods such as space syntax, GIS spatial analysis, Moran’s I index, standard deviation ellipse, nearest neighbor index, GWR model, etc., combining qualitative description with quantitative models, to conduct in-depth analysis on the spatial distribution of settlement heritage, village landscape knowledge maps, the relationship between settlements and regional culture, development and utilization, the impact of tourism development, and problems and countermeasures in the urbanization process (Li et al., 2024). Some scholars have explored the distribution of all settlement heritage in Chinese mainland and found that four major traditional village clusters have been formed at the junction of Hebei, Shandong and Henan provinces, at the junction of Guizhou, Guangxi and Hunan, and at the junction of Anhui, Zhejiang and Jiangxi (Bian et al., 2022). In addition, there are also some research results and progress at the provincial administrative level (Li et al., 2024; Bian et al., 2022; Duan et al., 2025; Zhang et al., 2025; Li et al., 2025; Jiang et al., 2025; Zhang et al., 2023a; Ma et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023b; Yang et al., 2023; Yang Z. et al., 2022; Liao and Zhang, 2022; Wang et al., 2022; Yihong et al., 2022). For example, Fujian Province, Henan Province, Hubei Province, Jinlin Province, Guizhou Province and Guangdong Province in China (Table 1).
At the same time, many scholars have taken the river basin area as a perspective and further explored the distribution relationship with intangible cultural heritage based on traditional villages (Xue and Huang, 2025; Huang et al., 2025). At present, some scholars have also conducted research on the distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province. They focused on the evolution of the cultural landscape of agricultural villages, the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and accessibility of traditional villages, the evaluation of tourism development potential, the spatial distribution pattern and influencing factors, and the topics of hollow villages and rural reconstruction (Fang and Liu, 2008; Li et al., 2024; Ma et al., 2022; Ma and Fang, 2021). However, previous research has revealed imbalances and insufficient sample coverage, especially regarding geographical scope. The distribution of national-level traditional villages is highly concentrated in central and eastern Shandong, while many counties in the northwest and southwest remain unrated.
Existing studies in Shandong Province mainly focus on a limited number of national-level traditional villages, resulting in insufficient sample size and the absence of many counties in the northwest and southwest regions. More importantly, such restricted samples lead to fragmented spatial coverage and prevent scholars from conducting continuous and systematic spatial analysis at the provincial scale. In addition, current research tends to emphasize descriptive discussions of settlement patterns, with relatively few studies integrating spatial pattern identification, spatial inequality measurement, and mechanism exploration into a unified analytical framework. These limitations restrict our understanding of the comprehensive spatial characteristics and driving mechanisms of settlement heritage in Shandong.
Therefore, to address these issues, this study expands the dataset beyond national-level traditional villages. We include provincial-level traditional villages, national and provincial historical and cultural villages, and other officially recognized settlement heritage resources. Through extensive field verification and multiple rounds of confirmation, a comprehensive dataset of 580 settlement heritage sites in Shandong Province was constructed.
Shandong Province, as a typical coastal peninsula region with diverse landforms—including mountains, hills, and plains—provides an ideal setting for examining how geographical environments shape settlement distribution. The complexity of natural conditions and the long-standing agricultural civilization make Shandong a highly representative case for exploring spatial differentiation and driving mechanisms of settlement heritage in coastal peninsula regions. This study takes 580 rural settlements in Shandong Province as research samples, aiming to reveal the spatial distribution characteristics and primary driving mechanisms of settlement heritage in the region. First, the nearest-neighbor index and kernel density analysis are employed to identify the overall spatial morphology, clustering characteristics, and multicore structures of settlement heritage, thereby clarifying its spatial patterns and distributional regularities across Shandong Province. Second, the coefficient of variation, geographic concentration index, imbalance index, and Lorenz curve are used to quantitatively assess spatial disparities and degrees of concentration at both provincial and municipal scales, identifying the spatial characteristics and regional differences of uneven distribution. Finally, overlay analysis and the geographical detector are applied to systematically examine the explanatory power and interaction enhancement effects of natural, socio-economic, and historical-cultural factors on the spatial distribution of settlement heritage, thus revealing its underlying formation mechanisms. The findings provide a data foundation and theoretical support for the scientific formulation of protection planning and policy development for traditional settlement heritage. To achieve these research objectives, this study employs a comprehensive combination of spatial analytical methods. The nearest-neighbor index and kernel density estimation are effective tools for identifying the spatial pattern, clustering structure, and dispersion characteristics of settlement heritage. The coefficient of variation, geographic concentration index, imbalance index, and Lorenz curve enable quantitative evaluation of spatial inequality at both provincial and municipal scales. Furthermore, overlay analysis and the geographical detector are widely adopted in settlement geography and landscape research because they allow not only the assessment of the explanatory power of natural, socio-economic, and cultural factors, but also the detection of interaction effects among multiple variables. Together, these methods provide a systematic analytical framework that integrates spatial pattern identification, spatial inequality measurement, and mechanism exploration, ensuring a robust and multidimensional interpretation of settlement heritage distribution.
The structure of this study is arranged as follows. The Section 2 “Research Area and Methods” introduces the study area of Shandong Province, describes the construction and field verification of the settlement heritage dataset, and elaborates on the application of spatial analytical methods such as nearest-neighbor analysis, kernel density estimation, the geographic concentration index, the imbalance index, and the Lorenz curve. It also explains the use of the geographical detector in identifying influencing factors. The “Results” section presents the main empirical findings of the study, including the spatial distribution patterns of settlement heritage, the degree of spatial inequality among different regions, and the interaction mechanisms of natural, socio-economic, and cultural factors affecting settlement distribution. The Section 4 “Discussion: Influencing Factors and Social Changes” further interprets the results from the perspectives of regional development, heritage conservation, and human–environment relationships, highlighting their theoretical and practical implications for the sustainable preservation of settlement heritage. The final section, “Conclusions,” summarizes the main findings of this research and proposes policy recommendations to promote the conservation and sustainable development of settlement heritage in Shandong Province.
2 Research area and methods
2.1 Research area: Shandong Province
Shandong Province is in the northern part of East China (Figure 1). The southern inland borders Hebei Province, Henan Province, Anhui Province, and Jiangsu Province, and the peninsula is adjacent to the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea (Guo, 2013). The land area is about 155,800 km2. Mountains and hills dominate the terrain of Shandong, with plains and basins surrounding them. The North China Plain in the west is low and flat; the mountains in the middle are undulating, and the hills in the east are undulating. The highest point on land is Mount Tai in Tai’an City in the central part, with the main peak at an altitude of 1,532.7 m. The lowest point is in the Yellow River Delta in Dongying City, with an altitude of about 2–10 m. The northwest and southwest of Shandong primarily contain the Shandong plains, making up 65.56% of the province’s land area; the eastern coastal areas and southwestern Shandong primarily host hills, making up 15.39% of the province’s land area; central Shandong and southwestern Shandong primarily host mountains, making up 14.59% of the province’s land area; and the eastern coastal areas primarily host plateaus, making up 4.46% of the province’s land area. The central and southern Shandong mountainous areas and the Jiaodong hilly areas contain the main mountain ranges in the region.

Figure 1. Study area: (a) the location of Shandong Province in China; (b) the distribution location of each city in Shandong Province.
As of December 2020, Shandong Province has 16 prefecture-level cities, including two sub-provincial cities, Jinan and Qingdao; 136 county-level administrative regions, including 58 municipal districts, 26 county-level cities, and 52 counties; and 1,824 township-level administrative regions, including 664 sub-districts, 1,092 towns, and 68 townships. The geographical scope of this study is settlement heritages of all levels within the administrative area of Shandong Province today, including 168 national-level traditional villages in 6 batches, 511 provincial-level traditional villages in 5 batches, 11 national-level historical and cultural villages in 7 batches, and 70 provincial-level historical and cultural villages in Shandong Province. These are all important reference lists of settlement heritage in Shandong Province.
2.2 Research methods
This study focused on analyzing the distribution pattern of settlement heritage in Shandong Province and its influencing factors. Through the collection of the Chinese traditional village list and field survey verification, 580 traditional settlement information points were screened (Figure 2), and the settlement coordinate data (mainly the points of each village committee) was crawled through the Baidu Map API, and the point data was corrected through satellite images (Deng et al., 2024). This study used geographical information systems (GIS) analysis and field survey data collection to explore the spatial distribution pattern of settlement heritage in Shandong Province and its influencing mechanism. The study primarily focuses on three topics: 1. Spatial pattern distribution research explores the spatial distribution law of settlements through methods such as nearest neighbor analysis, kernel density analysis, and coefficient variation analysis (Yanbo et al., 2018). 2. The imbalance relationship of settlement distribution, quantifying the data results of geographic space through geographic concentration coefficient analysis, imbalance index analysis, and Lorenz curve analysis, revealing spatial differences (Wang et al., 2018). 3. Factors affecting settlement distribution: The spatial relationship between traditional settlements and the natural environment, socio-economic, historical, and cultural factors are examined through overlay analysis (Qu et al., 2021), and the weight of each influencing factor and the intensity of interaction are analyzed using geographic detectors (Tan et al., 2021).

Figure 2. From February to September 2022, the research team conducted field surveys in Shuangru Village, Fangyu Village, and Zhujiayu Village in Jinan City, Shandong Province. Figure contains images of the author(s) only.
To better connect these methods and clarify how they jointly fulfill the research aim, a structured analytical workflow is adopted (see Figure 3). The methodology progresses through three consecutive modules—spatial pattern identification, spatial imbalance evaluation, and driving-factor detection—corresponding respectively to describing where settlement heritage is distributed, measuring how unevenly it is distributed, and explaining why such patterns occur. This workflow also reflects the different geographical environments in Shandong Province, including mountainous inland regions, hilly transitional zones, plains, and coastal peninsulas, enabling a systematic examination of environmental heterogeneity.
2.2.1 Nearest neighbor index
As the first step of spatial pattern identification, the Nearest Neighbor Index (NNI) measures the difference between the actual nearest neighbor distance in a point-like traditional settlement distribution and the theoretical distance of a random distribution. This tells us if the pattern of settlements is clustered, random, or discrete (Mauro et al., 2017). In the study of how traditional settlements are spread out in space, NNI can show how settlements are spread out and how they are connected to the natural environment and socio-economic factors. This gives scientists a way to find places where settlements are grouped or where there are empty spaces. NNI thus establishes the baseline spatial structure that subsequent density and imbalance analyses build upon. At the same time, it lays the foundation for the subsequent in-depth analysis of settlement density distribution, equilibrium characteristics, and driving mechanisms. For specific formulas and interpretations, please refer to Liu W. et al. (2023).
2.2.2 Kernel density estimation
Following NNI, Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) deepens spatial pattern identification by creating a continuous density map of settlement distribution through smoothing spatial data points. This makes it easy to see where there are a lot of settlements and where there are not many in the study area (Ma et al., 2013). In traditional settlement research, KDE can analyze the spatial distribution pattern of traditional settlements in Shandong Province and help identify the core areas with concentrated settlements and the sparsely distributed edge areas. It helps visualize spatial clustering in different geographical environments such as mountainous, plain, or coastal areas. For specific formulas and interpretations, please refer to Li et al. (2024).
2.2.3 Coefficient of variation analysis
Using the coefficient of variation analysis, which measures the degree of dispersion of spatial distribution attributes like scale and density, Yang et al. (2019) can figure out how balanced traditional settlements are Yang et al. (2019). In the study, this method generates patch areas of different scales through Thiessen polygons to reveal the differences and imbalances in the distribution of settlements in different regions of Shandong Province. This indicator acts as a bridging step between spatial pattern identification (NNI, KDE) and spatial imbalance evaluation (GCI, Lorenz curve), because it quantifies the extent of regional variability and helps determine whether further inequality analysis is necessary. For specific formulas and interpretations, please refer to Zhang et al. (2024).
2.2.4 Geographic concentration coefficient analysis
The Geographic Concentration Coefficient Analysis, as described by Zhong and Dong (2024), quantitatively reveals the spatial distribution characteristics of traditional settlements in the study area by measuring the concentration of settlements within spatial units. This method can pinpoint the concentration of settlements in specific geographical areas like rivers, mountains, or transportation hubs, and delve into the natural, social, and historical factors that shaped their formation. Assuming G is the average geographic concentration coefficient, if G is greater than G, the settlement heritage is clustered; if G is equal to G0, the settlements are evenly distributed. As the first method in the spatial imbalance module, the geographic concentration coefficient transforms earlier descriptive pattern results into a quantitative measure of how strongly settlements are concentrated in particular regions, laying the foundation for subsequent inequality analysis. If G is less than G, the settlements are dispersed. For specific formulas and interpretations, please refer to Bi et al. (2024).
2.2.5 Imbalance index analysis and lorenz curve analysis
By quantifying and visualizing the balance of the spatial distribution of traditional settlements, the distribution differences between core areas and peripheral areas are revealed (Qi et al., 2022). The imbalance index provides a quantitative indicator of distribution balance, while the Lorenz curve intuitively shows the imbalanced degree of settlement distribution and its concentration characteristics (Zhang et al., 2023b). This study uses it to evaluate the balanced distribution of settlement heritage in different cities in Shandong Province. Lorenz curve analysis is a graph that uses cumulative frequency numbers to characterize concentration or dispersion. The imbalance index is calculated by applying the concentration index formula in Lorenz curve analysis. Together with the geographic concentration coefficient, these indicators complete the spatial imbalance evaluation module by measuring not only how concentrated settlements are, but also how unequal the distribution is across administrative units. This is crucial for identifying whether spatial differences reflect natural geographic constraints, historical processes, or socio-economic disparities. For specific formulas and interpretations, please refer to Dong et al. (2023).
2.2.6 GeoDetector analysis
The Geodetector is a statistical analysis tool that reveals the spatial differentiation of geographical phenomena and their driving mechanisms. By finding the explanatory power (q value) of each factor on the spatial distribution of the target variable (Chen et al., 2023), it gives a quantitative look at how single factors and interactions between multiple factors affect the geographical pattern. This study conducted a Geodetector analysis on traditional settlements in Shandong Province. To effectively identify the key driving factors affecting the spatial distribution of settlements and their interactive effects, we selected three influencing factors: nature, economy, and culture. These factors correspond to nine influencing factors, including elevation, water system distance, slope, and transportation network (Chen et al., 2022; Shen et al., 2024; Wu et al., 2014). We then conducted a relationship analysis of the influencing mechanism of settlement distribution (see Table 2) and analyzed the interactive influence relationship between the factors. GeoDetector constitutes the core of the mechanism-analysis module, transforming observed spatial imbalance into interpretable causal relationships. By quantifying both single-factor effects and factor interactions, it allows the study to differentiate the influence of various geographical environments—mountainous, coastal, urban–rural, and cultural regions—thus directly responding to the aim of understanding how different geographical environments shape settlement heritage distribution. For specific formulas and interpretations, please refer to Cui and Wei (2024).
Among them, the single influencing factor detection method evaluates the independent influence of each factor on the spatial differentiation of the target variable by calculating the explanatory power (q value) of each factor. This method is used to identify the key factors that play a dominant role in settlement distribution and reveal the driving role of a single environmental factor (He and Liu, 2024). The interactive influencing factor detection scrutinizes the interplay among various factors to ascertain if their combined influence on the target variable intensifies, diminishes, or remains independent. By exploring the impact of the joint action of multiple factors on the spatial distribution of settlements, complex geographical mechanisms can be revealed (Liu M. et al., 2023).
2.2.7 Analysis of influencing factors superposition
This study used the geographic detector to analyze the impact of a single variable on the distribution of settlements according to nine different influencing factors. It then processed the data for each factor index using the kernel density method and stratified the bandwidth using the GIS natural breakpoint method (Xu et al., 2020). In addition to the river impact factor, to more scientifically express the spatial relationship, the buffer zone is selected for overlay analysis. The distribution of settlements under a single factor was specifically explored. This research method enhanced the specific analysis and discussion of the single factor’s impact on settlement distribution, based on the original geographic detection. It also revealed the impact correlation at the micro level and transformed the influencing factor research from a quantitative to a qualitative analysis of physical space (Bevan and Wilson, 2013).
Furthermore, this superposition analysis functions as the final step of the mechanism-analysis module, directly linking quantitative detection results with spatial visualization. By overlaying settlement points with classified natural, socio-economic, and cultural layers, the method illustrates how different geographical environments shape settlement distribution in an intuitive spatial form. This step also complements GeoDetector by verifying whether statistically significant factors (e.g., elevation, proximity to rivers, transportation accessibility, cultural heritage density) have clear spatial correspondence in actual geographic space. Through this integration, the study bridges statistical interpretation and spatial interpretation, thereby strengthening the explanatory power of the entire methodological framework.
2.3 Data source
The data sources for this study mainly include four types: 1. Collection of digital point data of rural settlements. The Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of China, in collaboration with other institutions, selected settlement points within Shandong Province from the first to sixth batches of the Chinese Traditional Villages List from 2012 to 2023 (http://main.dmctv.com.cn/index.aspx, accessed on 31 December 2024). 2. Administrative district data collection. We collected the administrative boundaries of Shandong Province and its counties, cities, and towns in 2023 using the Baidu Map API interface (https://lbsyun.baidu.com/, accessed on 31 December 2024), and drew the research area accordingly. 3. Influencing factor data collection. Data statistics on natural, economic, and cultural influencing factors such as elevation, water system, slope, transportation network, and scenic area distribution related to settlement distribution were retrieved (Table 3). 4. Field investigation and sample verification. We further confirmed the correctness of the geographical location, the integrity of the spatial structure, and the unity of the research value through field investigation of 580 settlements in the Chinese Traditional Villages List, thereby ensuring the validity of the source of the research data.
2.4 Preliminary processing of data samples
During the data preprocessing stage, the primary objective is to identify the settlement heritage samples and carry out the subsequent analysis of the spatial distribution characteristics of these settlements. Firstly, to ensure comprehensive coverage and rich samples, we add the rated national and provincial historical and cultural settlements in Shandong Province to the national and provincial traditional settlements in Shandong Province. This fills in the gaps and creates a more comprehensive settlement heritage research sample. Secondly, the aim is to demonstrate the spatial distribution characteristics of traditional settlements in the region, investigate the interrelationships and distinctions among these settlements from a geographical standpoint, and establish a robust research foundation for the regionalization of traditional settlements local cultural landscapes. Finally, by constructing a substantial amount of sample data and integrating it with the natural geographical environment, we culturally segmented the local landscape based on factors like dialects and folk customs. This approach systematically showcased the diversity of the local cultural landscape in this region, scrutinized its shared and unique characteristics, and established the groundwork for future research on the preservation of the Qilu local cultural landscape.
According to the definition of the research object, the researchers’ research samples are divided into two major categories: the rated national and provincial traditional settlements in Shandong Province, and the national and provincial historical and cultural settlements in Shandong Province (Tables 4–7). Among them, there are 168 national traditional settlements in Shandong Province in 6 batches, 511 provincial traditional settlements in 5 batches, 11 national historical and cultural settlements in Shandong Province in 7 batches, and 70 provincial historical and cultural settlements. After removing duplicate traditional settlements, a sample data of 580 traditional settlements was formed (Table 8). Statistics show that the sample encompassed all 16 prefecture-level cities in the province and 84 out of the 136 counties in the province. Numerous factors, including urbanization, have influenced the sample, ensuring that no traditional settlement objects fail to meet the criteria outlined in this article. The average number of samples in each county is 6.5, which basically covers the different types of traditional settlements in the province and objectively reflects the local geographical, climate, environmental, human, and historical characteristics. Finally, we entered the sample data of traditional settlements (including settlement heritage type, spatial location, and other information) into the ArcGIS platform (https://www.esri.com/en-us/arcgis/geospatial-platform/overview) (Figure 4). We used the ArcGIS platform to mark the geographical distribution of 580 traditional settlements at various levels in the province on the Shandong topographic map. This process resulted in the creation of a map that intuitively reflects the characteristics of traditional settlements in their geographical distribution.
3 Results
3.1 Distribution pattern of settlement heritage
3.1.1 Distribution randomness analysis
Based on the Nearest Neighbor Index (NNI) analysis, the spatial distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province shows significant clustering characteristics. The information in Table 9 shows that the average distance between settlement heritage is 5156.0270 m, which is much closer than the average distance that would be expected if the settlements were spread out randomly, which is 8336.7840 m. The nearest neighbor ratio (NNR) is 0.618467, which makes it clear that settlement heritages are grouped together in space. Further statistical test results show that the z-score is −17.578298, and the p-value is 0. Statistics demonstrate the high significance of settlement heritage distribution clustering, ruling out the possibility of random distribution.
3.1.2 Concentrated distribution area analysis
According to official data, Shandong Province has a total land area of 157,900 km2, and the average spatial distribution density of traditional settlement heritage is about 0.00376/km2. Based on the results of kernel density analysis, the locations of traditional villages in Shandong Province show strong clustering patterns, and the areas with a lot of villages are clearly polycentric. Figure 5 reveals that the central Shandong region, the Jiaodong Peninsula, the southern Shandong region, and the northern Shandong region are the main locations of high-density villages. The central Shandong region (Mount Tai and its surrounding areas) shows the highest level of kernel density value and is the core concentration area of the distribution of settlement heritage in the province. The coastal areas of the Jiaodong Peninsula (Yantai, Weihai, and Qingdao) show higher density values, especially in the northwest and east, and the distribution of settlement heritage has a certain continuity. The southern Shandong region (such as Linyi and its surrounding areas) has also formed an obvious clustering center, and the kernel density value is second only to the central Shandong and Jiaodong regions. Although the density values in some areas of northern Shandong are relatively low, local clustering phenomena can still be observed.

Figure 5. The results of the Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) analysis of settlement heritage (or traditional villages) in Shandong Province are presented.
In general, the low-density areas around the high-density areas form a gradient transition, indicating that the distribution of settlement heritage gradually spread from the center to the periphery. At the same time, the kernel density value of the distribution boundary area is low, indicating that the distribution of settlement heritage in these areas is relatively sparse. The distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province is not uniform but has obvious spatial aggregation characteristics. The specific kernel density distribution reflects the concentrated area range of settlement heritage and their gradient changes.
3.2 Balanced distribution of settlement heritage
3.2.1 Analysis of coefficient of variation results
The spatial distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province is characterized by both concentrated high-density areas and low-density sparse distribution areas, with the overall distribution displaying significant spatial differences. This study established Thiessen polygons for each village and used the standard deviation and mean of the area of each Thiessen polygon to calculate the coefficient of variation. The standard deviation of the data is about twice the mean, and the variability of the data is relatively high. The high standard deviation and a coefficient of variation of 1.985 indicate strong spatial heterogeneity in the distribution of settlement heritage. Table 10’s results reveal a standard deviation of 559694699.6 m2 for the area of Thiessen polygons, a mean area of 281896094.5 m2, and a corresponding coefficient of variation of 1.985. When the coefficient of variation is greater than 1, it indicates that the spatial distribution of settlement heritage has high heterogeneity; that is, there are significant differences in the spatial distance between different villages and the control range around the settlement heritage. Figure 6 reveals that some areas, like central Shandong and Jiaodong, exhibit small Thiessen polygons and densely distributed settlements, whereas other areas, like northern Shandong and parts of southwestern Shandong, display large polygons and sparse distribution.

Figure 6. The results of the coefficient of variation analysis of settlement heritage (or traditional villages) in Shandong Province are presented.
3.2.2 Geographic concentration index results
The cumulative distribution analysis of the calculation results reveals a degree of spatial imbalance in the distribution of settlements, with some areas exhibiting high concentration. According to the calculation results of the geographic concentration index, the distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province shows obvious spatial concentration characteristics. Table 11 shows that the calculated G value is 36.25, and the G0 value is 32.9865032. The results show that G>G0, indicating that Shandong’s settlements are in a clustered state in terms of administrative regional distribution.
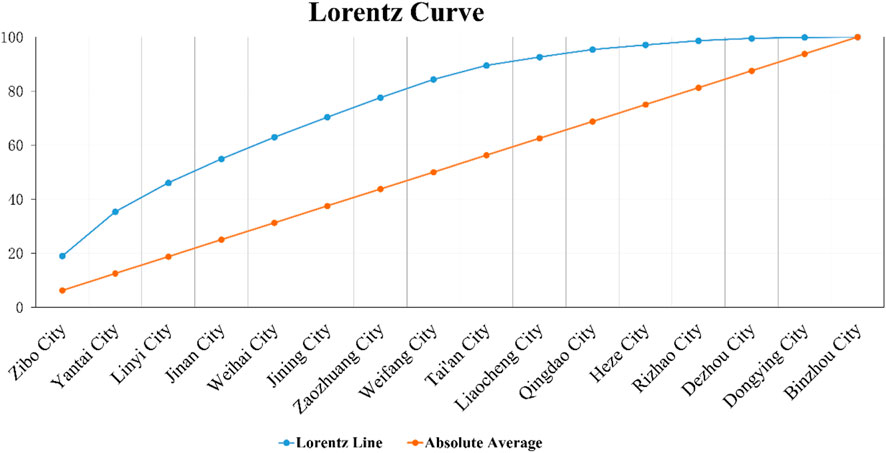
Based on specific data from various prefecture-level cities, Zibo City and Yantai City have the highest proportion of settlement heritage in the Shandong, with 110 and 95, respectively, representing the highest geographical concentration. They are the core areas of the distribution of settlement heritage. The number of settlement heritage in Linyi City, Jining City, and Weihai City is at a medium level, with a certain degree of geographical concentration. Relatively speaking, the number of settlement heritages in Liaocheng, Qingdao City, Binzhou City, Rizhao City, and other places is relatively small, with a low geographical concentration and a sparse distribution.
3.2.3 Imbalance index analysis and lorenz curve analysis
The spatial distribution of settlements in Shandong Province has a certain degree of concentration and imbalance. First, the imbalance index calculation result is 0.497, close to 0.5, indicating that the distribution of settlement heritage deviates from the completely balanced state and has a moderate degree of imbalance. This value shows that the number of settlement heritage in some prefecture-level cities (such as Zibo City, Yantai City, and Linyi City) accounts for a large proportion of the province, while other regions (such as Dezhou City, Dongying City, and Binzhou City) are relatively sparse.
The Lorenz curve reveals a significant deviation between the blue line in Figure 7, which represents the actual distribution curve, and the orange complete equilibrium line. Specifically, the number of settlements in Zibo City, Yantai City, and Linyi City accounts for a large proportion of the cumulative distribution, and the curve rises steeply, while the number of villages in Qingdao City, Rizhao City, Dezhou City, and Binzhou City is small, and the contribution to the total distribution is low, and the curve tends to be flat. The cumulative percentage data further confirms this distribution imbalance. In Table 12, the number of traditional villages in Zibo City accounts for 18.97% of the province, while Binzhou City accounts for only 0.17%, reflecting the significant distribution differences between different prefecture-level cities. The gradient change of the Lorenz curve intuitively reflects this imbalance, highlighting the significant regional differences in the distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province.
3.3 Factors affecting the distribution of settlement heritage
This study created a GIS grid fishing net for the research area of Shandong Province, with a grid size of 1,500 m × 1,500 m, generating a total of 25,787 points, evenly distributed in Shandong Province. Secondly, this study conducted a geographic detector and superimposed influencing factor analysis on the 9 influencing factor distribution data points determined and 580 settlement heritage points and obtained the following results.
3.3.1 Analysis of influencing factors
Natural, economic, and cultural factors jointly influence the distribution of settlement heritages in Shandong Province. The influence of the three major factors on the distribution of villages is balanced, with no clear dominant factor orientation. According to Table 13, the p-values of the detection results of the 9 influencing factors are all 0, indicating that the data are significant. In the geographic detector analysis, the q-value ranking of the influencing factors is cultural factors (0.392698) > natural factors (0.379577) > economic factors (0.037801), among which cultural factors are the higher factor influence among the three major factors. Specifically, the ranking results of the nine influencing factors are as follows: elevation factor X1 (0.292533) > scenic area factor X7 (0.196796) > cultural heritage factor X8 (0.132069) > slope factor X2 (0.0793) > cultural custom factor X9 (0.063812) > cultivated land area factor X6 (0.019765) > GDP factor X5 (0.014079) > river factor X3 (0.007744) > transportation factor X4 (0.003957).
Figure 8 shows the differences in the effects of the nine influencing factors. Elevation, scenic areas, cultural heritage, slope, and folk culture are the more significant influencing factors. The topography of the natural environment generally dominates the distribution of 580 settlements in Shandong Province. Cultural landscape places and historical heritage spaces have a greater impact on the distribution of settlement heritage. Cultural folk areas and slopes significantly influence the distribution of settlement heritage.
3.3.2 Analysis of the relationship between factors and settlement heritage
This study uses geographic detectors to numerically analyze and rank the importance of nine influencing factors in affecting the distribution of settlement heritage. Next, the specific impact and mechanism issues will be analyzed through the specific spatial overlay data of each factor. This approach allows for a deeper exploration of the coupling correlation system between each factor and the settlement heritage.
1. Elevation Factor in Settlements
Medium- and high-altitude areas host a large number of settlement heritage, while plain villages are less prevalent. The village distribution in Shandong Province shows a significant negative correlation with the elevation factor (Table 14). The topographic distribution map of Shandong Province is superimposed with the traditional village points to obtain the topography and traditional village distribution map of Shandong Province. Figure 9 reveals that the majority of Shandong’s settlements are in the mountainous and hilly regions of central and southern Shandong, as well as the hilly areas of the Jiaodong Peninsula. The number of villages distributed in the plain areas of southwestern and northwestern Shandong and the Jiaolai plain area is relatively small. In central and southern Shandong, settlement heritage primarily reside in the mountainous hinterland, whereas in the Jiaodong Peninsula, they spread out on a coastal belt along the coastline.
2. Slope Factor in Settlements

Figure 9. The relationship between elevation and settlement heritage (or traditional villages) distribution.
The slope in Shandong Province strongly correlates with the distribution of settlement heritage. The slope reflects the inclination of the terrain, which directly affects the suitability of land development, agricultural production conditions, and sustainable village development. Slope is typically a crucial criterion for assessing the features of a particular terrain, and it serves as a crucial reference point for individuals selecting a village site. The land slope is divided into five slope levels: ≤2°, 2°–6°, 6°–15°, 15°–25°, and >25°. The slope level codes are I, II, III, IV, and V. Based on the above classification, this study conducted a statistical analysis of the number of villages distributed in different cells through the ArcGIS (Table 15). The main distribution areas of settlement heritage in Shandong, accounting for up to 74.65%, are the foothills where mountains and hills with a slope range of 2°–6° meet the plains and the hinterland of mountains and hills with a slope range of 6°–15°. The plain areas with a slope of ≤2° account for 18.10%, and the traditional villages with a slope of more than 15° account for only 7.24%. Figure 10 demonstrates a significant relationship between the slope value and the distribution of traditional villages. Most settlement heritage (74.65%) are located in areas with slopes between 2° and 15°, while no traditional settlements are found on slopes steeper than 25° (Table 15), indicating a clear preference for low–medium slope environments. Low-slope foothill zones where mountains and hills meet the plains, and the hinterlands of hilly areas, therefore constitute the main distribution areas of settlement heritage in Shandong Province, whereas high-slope zones show very sparse or no settlement presence.
3. Water System Factor in Settlements

Figure 10. The relationship between slope and settlement heritage (or traditional villages) distribution.
The water system factor has no significant impact on the spatial distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province (Figure 11). In the central Shandong region, a significant number of settlements lie within the medium and high-level water system distance range, with only the Jiaodong Peninsula exhibiting a certain spatial correlation with the river near the coast. In certain arid or water-scarce areas of Shandong Province, such as some mountainous areas in the northwest and southern Shandong, the distribution of settlement heritage is relatively sparse.
4. Transportation Factor in Settlements

Figure 11. The relationship between water system and settlement heritage (or traditional villages) distribution.
In Shandong Province, the transportation network generally correlates with the spatial distribution of settlement heritage. Areas with convenient transportation usually have dense villages, while settlement heritage in areas with inconvenient transportation are more dispersed. As an important factor in promoting population mobility, resource allocation, and economic development, transportation plays a key role in the formation and development of settlements. High-density areas of traditional villages are mainly concentrated along transportation hubs and major transportation corridors, especially in important cities such as Jinan City, Qingdao City, and Yantai City and their surrounding areas (Figure 12).
5. Cultivated Land Area Factor in Settlements

Figure 12. The relationship between transportation and settlement heritage (or traditional villages) distribution.
The distribution of settlement heritage shows a clear correspondence with areas of abundant cultivated land. High-density settlement clusters occur in regions with extensive cropland, particularly in central and southern Shandong and parts of the Yellow River Basin (Figure 13). In contrast, mountainous and coastal zones with limited cultivated land show sparse and scattered settlement distributions. This pattern indicates that traditional settlements are more concentrated in areas with larger cultivated land resources.
6. GDP Economic Income Factor in Settlements

Figure 13. The relationship between cultivated land area and settlement heritage (or traditional villages) distribution.
The spatial distribution of settlement heritage corresponds to areas with higher economic levels. High-density clusters are mainly distributed around economically developed cities such as Jinan, Qingdao and Yantai (Figure 14). In contrast, the inland areas of northwest and southern Shandong with lower GDP levels show sparse and dispersed settlement patterns. The results indicate that settlement density is generally higher in regions with stronger economic performance.
7.Scenic Spot Factor in Settlements

Figure 14. The relationship between GDP economic income and settlement heritage (or traditional villages) distribution.
Settlement heritage exhibits clear clustering around major scenic areas, particularly Mount Tai, Qufu and coastal Qingdao (Figure 15). Areas lacking significant scenic resources show sparse settlement distributions. This indicates a spatial association between settlement density and the presence of scenic or heritage landscape resources.
8. Cultural Heritage Factor in Settlements

Figure 15. The relationship between scenic spot and settlement heritage (or traditional villages) distribution.
Settlement heritage shows strong spatial correspondence with the distribution of cultural heritage resources. High-density settlement clusters appear in Tai’an, Jining and Linyi, as well as Zibo and Binzhou (Figure 16), all of which contain concentrated cultural heritage sites. Eastern coastal and western remote areas—where cultural heritage resources are relatively scarce, show low settlement density.
9. Folk Culture Area Factor in Settlements

Figure 16. The relationship between cultural heritage and settlement heritage (or traditional villages) distribution.
The spatial distribution of settlement heritage differs significantly across folk culture zones. High-density clusters occur in the Confucius–Mencius cultural area and the Qi culture area, whereas the island–marine cultural zone and diversified cultural zone show sparse distributions (Figure 17). This indicates that settlement density varies across cultural landscape regions.

Figure 17. The relationship between folk culture area and settlement heritage (or traditional villages) distribution.
3.3.3 Interaction detection factor analysis
The interaction of multiple factors jointly shapes the distribution pattern of traditional settlements in Shandong Province. The interaction between different factors not only strengthens the agglomeration of settlements in certain areas but also restricts their expansion in other areas. As shown in Figure 18, the four factors—elevation, scenic area, cultural heritage, and cultural folk customs—have high interactions with other factors. Among them, the elevation factor (X1) has the strongest interactive correlation with other factors, and it has a strong impact on scenic areas, cultural heritage, and cultural folk customs in the distribution of villages. Secondly, the scenic area factor (X7) also has a strong interaction with the elevation, transportation, and water system factors. Therefore, different factors intertwine and jointly shape the spatial pattern of traditional villages in Shandong Province.

Figure 18. Heat map of geodetector interaction results. The horizontal and vertical axes represent the following: Elevation (X1), Water system distance (X2), Slope (X3), Traffic network (X4), Agricultural land (X5), Economic development level (X6), Scenic area distribution (X7), Cultural heritage sites (X8), and Cultural area distribution (X9), respectively.
As shown by the geographic detector’s interaction results (Table 16), the relationships between DEM and slope, DEM and scenery, slope and scenery, and scenery and heritage are all dual-factor enhancements. The other relationships are linear enhancements. Specifically, DEM ∩ Slope (0.299874291) shows that the combination of terrain elevation and slope enhances the explanatory power of village distribution, especially in high-slope areas, where terrain restricts village development, while low-slope areas are conducive to village concentration. Slope ∩ Scenery (slope and scenic area interaction) (0.272186134) shows that the slope and landscape value work together to create special natural landscapes and tourism resources and promote population agglomeration and village distribution. Scenery ∩ Heritage (scenic area and cultural heritage interaction) (0.291479556) shows that the combination of scenic area and cultural heritage enhances the formation of villages, especially in areas rich in cultural and natural resources, promoting the concentration of villages and the development of tourism. It can be seen that the interaction of factors such as DEM, slope, scenic area, and cultural heritage is more complex and has an enhancement effect, especially the relationship of double factor enhancement. The joint action of these factors will significantly affect the formation and distribution of villages, as demonstrated by the interaction of double factor enhancement. The interaction effect of these factors reveals the complex interaction between natural geographical factors, cultural factors, and economic development, which plays a significant role in guiding heritage protection, land planning, and regional development. Conversely, other interactions that demonstrate “nonlinear enhancement” primarily display nonlinear enhancement effects. Nonlinear enhancement usually means that the effect of factor interaction shows complex changes under different conditions, rather than the result of linear superposition. This means that the impact of such interactions on village distribution is relatively complex and superimposed, and there is often no more regular and double-factor-related econometric model to demonstrate their relationship.
4 Discussion: influencing factors and social changes
4.1 Population migration and social development
The migration of culture and population, as well as the evolution of social development, have profoundly influenced the distribution and evolution of settlements. With the historical changes in social economy, population mobility, and the inheritance of cultural traditions, the formation and expansion of settlements present a complex spatial and temporal pattern. Throughout history, specific cultural groups have frequently accompanied population migration. Multiple factors, including land cultivation, war, policy migration, and natural disasters, often affect population mobility in China’s agricultural society. Migrants bring new culture, economic activities, and social structures, which have a profound impact on the development of settlements. In Shandong Province, cultural and population migration has occurred in different historical periods, especially due to factors such as war and immigration policies. Many traditional settlements have not only migrated geographically but also presented different cultural features. For example, immigration and reclamation promoted the expansion of rural areas in Shandong during the Ming and Qing dynasties, and many emerging settlements gradually formed and integrated into local agricultural and cultural traditions (Pan et al., 2024). As these immigrants arrive, they often build emerging settlements on the foundation of pre-existing cultural and social structures, creating distinct settlement types with distinct customs, economic models, and social ties.
In addition, changes in social development, especially economic development, have promoted the expansion of settlement space. The development of the agricultural economy has promoted the improvement of productivity, and the development and utilization of land have changed the form of traditional settlements. Especially in modern times, with the advancement of industrialization and urbanization, many traditional rural settlements have begun to gather in cities. Factors such as the transportation revolution, the industrialization process, and policy promotion have gradually incorporated the originally isolated villages into a larger economic circle and even transformed them into part of towns or cities. For example, the opening of the Jiaoji Railway in Shandong Province has enabled many traditional settlements originally located inland to gradually establish connections with the outside world, promoting the development of the local economy and population migration. The original agricultural foundation no longer limits the spatial distribution of settlements, as the development of transportation and industry connects rural areas to cities, forming new towns and industrial clusters. Cultural population migration intertwines with social development and settlements. Population migration is not just a simple physical migration but also includes the intersection and integration of cultural, social, and economic activities. In Shandong Province, historical immigration waves and population mobility have promoted the spatial distribution and morphological changes of settlements. With the development of the social economy and the influence of cultural background, traditional settlements have continued to develop and evolve, forming a variety of settlement types.
There is a correlation between the distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province and the level of economic income. Economically developed areas usually have higher settlement density, while economically backward areas show a trend of scattered settlement distribution and low density. Economically developed areas, particularly the surrounding areas of cities like Jinan City, Qingdao City, and Yantai City, primarily concentrate on the high-density areas of traditional settlements (Figure 14). Higher economic incomes, more resources, and concentrated infrastructure in these areas encourage the dense distribution and development of settlements. Specifically, Jinan City and Qingdao City, as the economic centers of Shandong Province, have a dense distribution of traditional settlements around them. The high-density areas in Figure 14 are located around these two cities, indicating that areas with higher economic development levels can attract more villages to concentrate, especially in the context of rural revitalization and accelerated urbanization. Traditional settlements often rely on the resources and policy support provided by economic growth to expand and prosper. In contrast, some inland and relatively economically backward areas of Shandong Province, such as northwest Shandong and southern Shandong, have a relatively scattered distribution of traditional settlements and low density. The economic development of these areas is relatively lagging, the GDP income level is low, and there is a lack of sufficient resource input and policy support, which has restricted the development of settlements and shown the characteristics of dispersion and low density.
4.2 Weak correlation between settlement heritage and water system factors
It is worth affirming that Chinese scholars (Li et al., 2024) believe that the key factors affecting the accessibility of traditional villages in Shandong are mainly altitude, slope, and road network density, among which altitude and slope are negatively correlated with accessibility (Li et al., 2024). Based on the research foundation of settlement distribution and accessibility, this study further explores the relationship between settlement distribution and water system classification. The study found that due to the navigation restrictions of the Yellow River and surrounding canals and the large runoff problems of the first and second-level river networks, settlements in Shandong Province tend to be distributed in low-level rivers to avoid disaster risks, which deeply reveals the relationship of the influencing mechanism of geo-space.
There are many water systems in Shandong, with more than 5,000 rivers over 5 km in length. According to the width of each water system, the water system can be divided into four levels: the river width ≥ 100 m is the first-level water system, which has wide rivers and is convenient for navigation but is more likely to cause flooding problems. The river width of 50–100 m is a second-level water system. The river at this level is wide, and the water flow is fast. It is the main river for water transportation. Flood problems occasionally arise in rivers of this level; a river width of 10–50 m represents the third-level water system. The water flow is relatively slow, and the water level is shallow. Large ships cannot pass through it, and only small ships can use it for transportation. The possibility of floods in the third-level water system is relatively small; the river width is less than or equal to 10 m in the fourth-level water system. The river at this level is narrow, the flow is slow, and there is no river transportation function. The river is only capable of meeting the production and living water needs of its residents. The likelihood of floods in the fourth-level water system is extremely low, posing virtually no threat.
The investigation and statistics of the traditional villages’ surrounding water system environment reveal that the Yellow River Basin, a first-level water system, has fewer traditional villages nearby. Historically, the Yellow River has repeatedly burst its banks, causing floods that have destroyed most villages. Most of the villages that have endured to this day are located in Liaocheng and the area where the Yellow River and the canal intersect. The Yellow River Basin more densely distributes traditional villages adjacent to the second- and third-level water systems. The Beijing-Hangzhou Canal is where most of the villages are located, primarily due to the canal’s ease of navigation, which has boosted their economic prosperity. In contrast, due to the limited shipping potential of the Yi River and the Mu River, there are relatively few villages around them. In other water systems of the same level, frequent floods lead to a relatively sparse distribution of nearby villages. Therefore, in the overall results, traditional villages and water systems show a weak correlation.
4.3 The high impact of cultural factors
In this study, cultural factors, particularly those related to cultural and folk areas, significantly influenced the distribution of settlements. Different from previous studies on settlement distribution in Shandong Province, the cultural factors in this study are no longer conventional cultural indicators. Instead, the influencing factors of different dimensions, such as folk culture areas (geopolitical), scenic areas (landscape), and cultural heritage (individual memory), are added to deeply consider the connection between settlements and local culture, and the coupling relationship between culture and settlements is further explored by combining field and anthropological methods.
This result suggests that culture and folk traditions play a vital role in the formation and evolution of settlements. The formation of culture is the result of people’s continuous adaptation to the geographical environment and its continuous development. The geographical environment serves as the foundation for people to engage in social production and material activities, and it significantly influences village site selection, house construction, economic production, people’s lives, and cultural exchanges and dissemination. After thousands of years of historical events on the land, villages gradually emerged through the original development and accumulation of the land by the indigenous people. In addition, the migration of people and the mutual exchange of cultures of various ethnic groups have also given new vitality and connotation to the local culture, laying a geographical and cultural foundation for the formation of the diverse characteristics of the local culture of traditional villages. As one of the cultural birthplaces of China, Shandong Province has a profound historical and cultural heritage, especially in Confucianism, traditional festivals, religious beliefs, and other aspects. Shandong has produced many talents in history. Since the Spring and Autumn Period, there have been a series of historical and cultural celebrities such as Confucius, Meng Qi, Yan Hui, Zeng Shen, and Lu Ban.
4.3.1 Cultural and folk areas
Cultural and folk areas are usually the core areas of settlement development, because these areas are not only the center of religious activities and cultural exchanges, but also important nodes of social and economic activities. For instance, Shandong Province boasts five “tourism business cards”: “Qilu Land”, “Hometown of Confucius and Mencius”, “Hai Dai Shengjing”, “Red Holy Land”, and “Hospitable Shandong”. Shandong Province boasts stone tools, jades, pottery, and primitive writing from the Dawenkou and Longshan cultures, which date back four or five thousand years. It also boasts numerous scenic spots and historical sites, the hometowns of historical sages like Confucius and Mencius, and natural scenery such as Mount Tai, the Yellow River, and the seaside. Furthermore, Shandong is the birthplace of the Yimeng spirit, and there are revolutionary relics from the war years. The Eastern Holy Land, the Fairyland Coast, the Peaceful Mount Tai, the Spring City Jinan, the Former Capital of Qi, the Lufeng Canal, the Hometown of Shuihu, the Yellow River Entering the Sea, the Family Yimeng, and the Ion City Longcheng are the top ten cultural tourism destination brands in Shandong Province. Cultural symbols, historical relics, and social customs often play a crucial role in the formation of settlements, transforming them into hubs for population and cultural activities. These motivations further enhance the influence of cultural factors.
4.3.2 Cultural diversity based on natural geography and locational environment
Shandong is located in the eastern coastal area of China. Its terrain is complex and diverse, with typical mountainous, hilly, plain, and ocean features. People adapt to the influence of different geographical conditions, resulting in a variety of economic production and living styles such as agriculture, forestry, and fishery. Shandong boasts numerous rivers that run alongside alluvial plains and plateaus. The land is fertile. Simultaneously, the temperate monsoon climate influences it, making it ideal for cultivating crops like wheat, cotton, and soybeans. From the perspective of location, Shandong is more suitable for agricultural development. However, Shandong’s proximity to the Yellow Sea and its exposure to a temperate monsoon climate make it vulnerable to drought and flood disasters, which significantly impact the agricultural and economic development of the region. Not only do they occur frequently and affect a wide range of areas, but they also often appear alternately, greatly affecting agricultural production and people’s lives.
The plains in southwestern and northwestern Shandong have fertile soil, abundant water resources, and excellent agricultural cultivation conditions. They are more suitable for growing various food crops and cash crops and can also develop forestry, animal husbandry, and other economic methods. Therefore, these areas often become the preferred choice for village site selection and thus become areas where village sites are relatively concentrated, providing a basic guarantee for the scale development of villages. The different location conditions and natural geographical environments in various regions of Shandong have formed a variety of economic production methods, derived different residential and village forms, enriched the regional local culture, and laid the foundation for the birth of multiculturalism (Figures 19, 20).
4.3.3 Cultural diversity based on agricultural economy and marine economy
Shandong primarily distributed its agricultural areas in the Neolithic Age in the foothills around the Luzhong Mountains, including the Taiyi Mountains, the Jiaolai Plain, and the flood-alluvial plains in front of the mountains. The common characteristics of these areas are high and cool terrain, gentle slopes, abundant water supply, and excellent drainage. The proximity to the mountains and forests is conducive to the gathering and hunting economy, and there is flat land suitable for farming. The aborigines of Shandong began to grow grain crops in the pre-Qin period. The fourth river control during the reign of Emperor Ming of the Eastern Han Dynasty promoted the development of Shandong’s water conservancy and irrigation. During the Sui and Tang Dynasties, the ruling class built a large number of water conservancy projects in Shandong, and Shandong’s agricultural development was prosperous. The Ming Dynasty, through immigration and other means, reclaimed a large amount of wasteland. By the 26th year of Hongwu, Shandong had reclaimed more than 724,000 mu of mature arable land, and during the Wanli year, the arable land area exceeded 1.16 million mu.
In addition to the land that is directly used for farming, it also contributes to related scenery, such as landscapes, agricultural production ecosystems, engineering, villages, crops and vegetables, forests and fruits, animals, and heritage. Higher-level spiritual elements, such as folklore, technology, literature, and classics, are also present. The related scenery derived from the land, for example, engineering agricultural cultural heritage, includes the canal dug in the Yuan Dynasty—Huitong River (now the section from Dongping to Linqing), Xiajin Daicun Dam, Ningyang Qicheng Dam, Wucheng Si Nu Temple Hub, and other important water conservancy, irrigation, and other engineering heritage. Coexisting with the heritage is the village agricultural cultural heritage (Figure 21). The traditional villages of Qi and Lu contain Confucian ethical ideas such as filial piety, respect, benevolence, harmony, righteousness, and courtesy; architectural concepts that adapt to local conditions; embrace the yin and the yang; and the harmony between man and nature; vivid historical and cultural values; and the family cultural style of Confucianism, Qi family, and poetry and books governing the world. It has a profound cultural heritage and extremely high cultural value.

Figure 21. China’s Important Agricultural Cultural Heritage - Shandong Zhangqiu Scallion Cultivation System.
Shandong’s offshore fishing culture was already highly developed during the Neolithic Age. Hundreds of villages dotted the highlands and river estuaries in the coastal areas of the Jiaodong Peninsula more than 7,000 years ago. It was the region with the largest population and the most concentrated number of villages in the East during this period. During the Shang Dynasty, the Yellow River Delta and the coast of Laizhou Bay became the salt production center of the Shang Dynasty at that time. The total number of large-scale salt industry sites in the Shang Dynasty reached more than 500. Coastal villagers have dedicated thousands of years to enhancing production efficiency, consistently innovating and refining the methods of boiling, frying, and drying salt. These efforts have not only made sea salt production more sophisticated but also injected rich connotations into marine culture (Figure 22). In addition to the marine salt economy, Jiaodong was the first place where “immortal thought” and “Penglai Fairyland” appeared. Qin Shihuang once sent Xu Fu and others to the sea to seek elixirs, and Emperor Wu of Han also “toured the sea to the east and worshipped the eight gods”. This kind of immortality played a significant role in the formation of Taoism in China. The ocean has always been a Feng Shui treasured land for the spread and cultivation of Taoism and has nurtured many Taoist elites.
The agricultural and marine economies have become two of the most important economic production modes in Shandong. People’s production and lifestyles have also changed with the continuous development of agriculture. At the same time, it has promoted the development of economic production modes such as handicrafts and commerce, forming the most fundamental production and life characteristics of the people on the land of Qilu and enriching the unique Qilu local culture.
4.4 Enlightenment from the protection planning of settlement heritage
Through an in-depth analysis of the distribution of traditional settlements in Shandong Province and their influencing factors, this paper provides important inspiration for the protection of traditional settlements in Shandong Province and other provinces along the coastal peninsula. These inspirations can not only guide the theoretical framework and methods of settlement protection but also provide practical directions for regional development planning, cultural heritage protection, and sustainable development. However, when promoting and applying across provinces, adjustments need to be made based on the specific cultural, geographical, and social conditions of the place to ensure the effectiveness and adaptability of protection measures.
These revelations include: 1. Prioritize the protection of cultural factors. Shandong Province’s cultural heritage and folk customs have a profound impact on traditional settlements, especially in Confucian culture, local religions, and traditional festivals. Cultural factors are not only the core of settlement form and function but also support the local social structure. Therefore, when protecting traditional settlements, we should focus on maintaining their cultural characteristics and historical values and avoid blind modernization. 2. Pay attention to the harmonious coexistence of natural and cultural environments. The spatial layout of settlements closely relates to the natural environment, particularly factors like water systems and topography. The protection of settlements’ natural landscapes and cultural heritage should be carried out in coordination. For example, by combining the protection of scenic spots and cultural heritage, we can combine natural protection with the utilization of cultural resources to achieve the sustainable development of traditional settlements. 3. Pay attention to the role of socio-economic factors. With the improvement of transportation and economic development levels, some traditional settlements may face the problem of population loss or loss of function. In light of this, it is crucial to rationally guide economic development and promote a rural revitalization strategy that aligns with the characteristics of traditional settlements. By introducing industries such as cultural tourism and characteristic agriculture, we can promote local economic revitalization and avoid the phenomenon of the “hollowing out” of settlements.
4.4.1 Implications for the ecological environment
From the perspective of the ecological environment, when people choose to build a settlement, the lower the slope, the better. Although flat terrain is conducive to the construction of settlement buildings, Shandong Province has a lot of rain in summer, and the flat terrain is prone to accumulated rain due to the slope problem, leading to flood disasters. Terrain with a certain slope is more advantageous than flat terrain in terms of drainage and can eliminate or reduce flood problems in the village to a certain extent. A slope greater than 25° will significantly complicate the villagers’ daily lives. The steep terrain is not conducive to house construction or agricultural cultivation and does not have the natural conditions for the formation of a village. Due to the limitations of topographic conditions, there are relatively few flat areas in the mountains and hills. As the size of settlements continues to expand and the number of settlement populations increases, the scope of buildings and cultivated land has further extended to areas with better natural conditions but slightly steeper slopes. From a social and economic perspective, plain areas with relatively flat terrain have more convenient transportation, are more conducive to economic development, and often have more advantageous social and economic conditions than hilly and mountainous areas. Therefore, during the rapid urbanization stage, settlements in flat areas are often easily annexed by cities, while settlements in hilly and mountainous areas are more likely to be preserved because they develop more slowly and are farther away from cities.
First, there is a dense distribution of settlements in low-slope areas. Shandong Province primarily concentrates traditional villages in plain areas with low slopes, particularly in the Yellow River Basin, Huaihe River Basin, and coastal areas. The relatively flat terrain in these low-slope areas is ideal for agricultural production and infrastructure construction, particularly due to the excellent irrigation conditions that promote grain production and the growth of the agricultural economy. Therefore, settlements often choose to settle in these low-slope areas where land development is easier. The settlement density in these areas is relatively high, forming a relatively dense village distribution pattern. Secondly, the distribution of villages in high-slope areas is relatively scattered. Compared with low-slope areas, the distribution of traditional settlements in high-slope areas in Shandong Province, such as some mountainous and hilly areas, appears to be sparser and lower in density. The terrain in these high-slope areas is undulating, making land development difficult and restricting agricultural production, especially in hilly and mountainous areas where the agricultural land is small and the slope is steep, resulting in a more scattered distribution of settlements.
Numerous studies have pointed out that steep slopes are generally unsuitable for the formation of traditional rural settlements because of constraints on building stability, arable land development and transport accessibility (Xiao et al., 2018; Yang Z. et al., 2022). Consistent with these findings, our results show that no settlement heritage in Shandong Province is located on slopes steeper than 25° (Table 15). In steep mountainous areas, limited flat land and fragmented cultivated plots make it difficult to support stable village development, whereas low–medium slope foothill zones provide both drainage advantages and sufficient land for construction and agriculture (Zhou et al., 2018; Anderson et al., 2007).
4.4.2 Implications for transportation
Specifically, as the provincial capital and transportation center, Jinan has a high density of traditional settlements around it. The data in Figure 12 show that the railways, highways, and other transportation facilities around Jinan have facilitated the development of settlements in the region and promoted the flow of urban and rural populations and the agglomeration of resources. Jinan’s transportation advantages have not only promoted economic development but also driven the expansion and agglomeration of villages in surrounding areas. Similarly, as an important coastal port city, Qingdao’s transportation network has also promoted the distribution of traditional settlements. Qingdao’s traditional settlements primarily cluster around transportation arteries and ports, mirroring the influence of shipping, logistics, and coastal trade on settlement morphology. Qingdao’s port traffic attracted a large number of commercial activities and population migration, which promoted the development of surrounding settlements. In contrast, in some inland mountainous areas or areas with inconvenient transportation in Shandong Province, such as parts of northern and western Shandong, the density of traditional settlements is low, and the distribution is more scattered. The transportation network in these areas is relatively weak, and there is a lack of convenient transportation channels, which restricts the intensive development of personnel flow and economic activities, resulting in the scattered distribution of settlements.
4.4.3 Implications for land use
There is a certain correlation between the distribution of settlement heritage in Shandong Province and the area of cultivated land. The densely populated areas of traditional settlements are primarily found in areas with large, cultivated land areas, particularly in agriculturally developed areas like the Yellow River Basin, southern Shandong, and central Shandong (Figure 12). These areas have rich, cultivated land resources and good agricultural production conditions, which have promoted the formation and agglomeration of settlement heritage. Specifically, the extensive cultivated land area in central and southern Shandong closely correlates with the high density of traditional villages in these areas. These areas have fertile land and excellent irrigation conditions. These areas have fully developed traditional agricultural activities, resulting in a settlement structure where agriculture dominates. The increase in cultivated land has provided stable economic support for these areas and promoted population agglomeration and village expansion. In addition, some typical large agricultural counties in Shandong Province, such as Linyi City and Heze City, have large, cultivated land areas and a high density of traditional settlements. The data in Figure 13 show that the abundance of cultivated land resources in these areas directly promotes the prosperity of local villages. Agricultural production not only supports the livelihoods of residents but also encourages the agglomeration of rural populations, thereby promoting the formation of traditional settlements. However, in certain areas with limited cultivated land or poor agricultural production conditions, such as some mountainous and coastal areas in northern Shandong, the distribution of traditional settlements is relatively scattered. These areas have limited cultivated land, relatively poor agricultural production conditions, a small population, and a low density of traditional settlements. These areas lack sufficient cultivated land resources, resulting in a low village density and a more scattered distribution.
4.5 Limitations
However, this study is not without its limitations. The samples for the study were selected from the national traditional villages in Shandong Province, provincial traditional villages in Shandong Province, national historical and cultural villages in Shandong Province, and provincial historical and cultural villages in Shandong Province announced by the government. First, as one of the important origins of Chinese civilization, Shandong Province has a long history and culture and a large number of villages. Many areas do not feature in the traditional village list, yet these villages hold significant scientific research value due to their material form and local cultural characteristics. This limitation stems from two objective factors: First, the identification of settlement heritage in official lists is based on rigorous academic and administrative evaluation criteria, which ensures the reliability of the core research objects but inevitably excludes some potential heritage sites with less recognized status. Second, due to data accessibility and research scope constraints, it is challenging to comprehensively collect information on all unlisted settlements within the study period. Therefore, in future research, it is necessary to conduct field surveys on these atypical villages and study the characteristics and constructions of their local cultural landscapes. Secondly, Shandong Province is home to a significant number of ethnic minority communities. After investigating, it was found that Shandong Province contains some traditional villages that exhibit ethnic characteristics. However, this study primarily focuses on traditional villages dominated by the Han nationality, with minimal attention given to minority villages. In the thousands of years of development, the ethnic culture of these minority villages has developed and blended with the Han culture and merged into a national culture with the characteristics of Shandong local culture. Therefore, to address the shortcomings of this study, future research on these traditional minority villages must be conducted in-depth and in a systematic manner.
5 Conclusion
Shandong, China, has a complex and diverse terrain, with plains, hills, mountains, and other landforms. Settlement heritages are the product of man and nature’s adaptation. To guarantee the steady growth of settlement heritage, traditional villages in various regions primarily adjust to their surrounding environment during the selection and construction process, mirroring the site selection features that fluctuate with the environment and exhibit robust adaptability. From the perspective of “synchronicity” distribution characteristics, these settlement heritages exhibit a close connection with the natural environment and clearly display “agglomeration” characteristics. The number of traditional villages in the southern mountainous areas of central Shandong and the coastal areas of the Jiaodong Peninsula is relatively dense, but the scale of the settlement heritage is relatively small; the number of traditional villages in the northwest, southwest, and Jiaolai Plain areas of central Shandong is relatively small and scattered, and the scale of the villages is relatively large. From the perspective of “historical” evolution, traditional villages show a “diffusion” feature, with the village core shifting southward and extending from the center to the outer circles. Affected by the terrain, the spatial layout of traditional villages in different areas shows obvious regional differences. The northwest area of Shandong primarily consists of plains with fertile land, through which the Yellow River, canals, and numerous tributaries flow. Therefore, the traditional villages in this area are large in scale. Most villages in the plains cluster together, while those along the rivers take on a strip-shaped form. The terrain of the southwest area of Shandong is mainly plains, bordering the mountains of central Shandong in the east. The plains and gentle slopes of the mountains host a cluster of villages. The terrain of the southern part of central Shandong is diverse, mainly mountainous, with basin-plain landforms. The area’s villages cluster on hillsides, valleys, and gentle slopes in front of the mountains, exhibiting a variety of layout forms such as clusters and belts. The Jiaolai area of central Shandong is a transitional area between the mountainous area of central Shandong and the hilly area of Jiaodong. The terrain is mainly plains. The number of traditional villages in the area is relatively small, and their layout primarily consists of clusters. The Jiaodong Peninsula area primarily features hilly and plain terrain. The settlement heritage primarily cluster in the hilly valleys of the plain area, exhibiting a comb-shaped layout.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
QL: Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. ZP: Writing – original draft, Project administration, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Funding acquisition. YH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Methodology. LZ: Writing – review and editing. JF: Validation, Writing – review and editing, Visualization. YQ: Writing – review and editing, Validation. YZ: Writing – review and editing, Validation. LK: Writing – review and editing, Validation. YC: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
AcknowledgementsZhao Pan sincerely thanks his supervisor, Professor Chun Zhu from Macau University of Science and Technology, for his important guidance in the thesis research. Meanwhile, ZP extends his special gratitude to his student team, under the leadership of Master Yuanrui Qin from the University of Malaya, for their diligent efforts in combing through a vast amount of literature, conducting textual research, conducting investigations, compiling data statistics, identifying audio recordings, and classifying images. Master Yuanhao Pan from the Xinjiang Academy of Arts helped to sort out a large amount of literature; Master Wenjie Hu from the Macau University of Science and Technology; and Bachelor Rusong Zhu and Hua Zhang from Shandong Jiaotong University contributed to the collection and arrangement of basic data in this study. At the same time, we would like to thank the village leaders and villagers for their help during the field investigation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Anderson, M. G., Holcombe, L., and Renaud, J. P. (2007). Assessing slope stability in unplanned settlements in developing countries. J. Environmental Management 85 (1), 101–111. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.08.005
Bevan, A., and Wilson, A. (2013). Models of settlement hierarchy based on partial evidence. J. Archaeol. Sci. 40 (5), 2415–2427. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2012.12.025
Bi, S., Du, J., Tian, Z., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Investigating the spatial distribution mechanisms of traditional villages from the human geography region: a case study of jiangnan, China. Ecol. Inf. 81, 102649. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2024.102649
Bian, J., Chen, W., and Zeng, J. (2022). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19, 4627. doi:10.3390/ijerph19084627
Cai, X., Chen, X., Zhou, W., Liu, R., Yin, T., and He, X. (2025). Assessment and protection of heritage value of traditional villages from the perspective of historic urban landscape: a case study of huaqiu village. Sustainability 17 (20), 8981. doi:10.3390/su17208981
Chen, Z., Liu, Y., Feng, W., Li, Y., and Li, L. (2022). Study on spatial tropism distribution of rural settlements in the loess hilly and gully region based on natural factors and traffic accessibility. J. Rural Stud. 93, 441–448. doi:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2019.02.014
Chen, W., Yang, L., Wu, J., Wu, J., Wang, G., Bian, J., et al. (2023). Spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages in the yangtze river basin: a geodetector model. Herit. Sci. 11 (1), 111. doi:10.1186/s40494-023-00948-x
Cui, W., and Wei, Y. (2024). Spatio-temporal evolution and the driving factors of municipal solid waste in Chinese different geographical regions between 2002 and 2020. Environ. Res. 240, 117456. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.117456
Deng, W., Xu, W., Huang, Y., and Li, X. (2024). A large-scale multipurpose benchmark dataset and real-time interpretation platform based on Chinese rural buildings. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 17, 10914–10928. doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3386830
Dong, Q., Lu, H., Luo, X., He, P., Li, D., Wu, L., et al. (2023). Evaluation and optimization of green space fairness in urban Built-Up areas based on an improved supply and demand model: a case study of chengdu, China. Sustainability 15, 15014. doi:10.3390/su152015014
Duan, Y., Chen, M., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., and Zhang, L. (2025). Research on the cultural landscape features and regional variations of traditional villages and dwellings in multicultural blending areas: a case study of the Jiangxi-Anhui junction region. Appl. Sci. 15, 2185. doi:10.3390/app15042185
Fang, Y., and Liu, J. (2008). Cultural landscape evolution of traditional agricultural villages in north china—case of qianzhai village in Shandong Province. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 18, 308–315. doi:10.1007/s11769-008-0308-x
Guo, R. (2013). Shandong regional China: a business and economic handbook. London: Palgrave Macmillan UK, 250–261.
Guo, Y., and Qiao, W. (2020). Rural migration and urbanization in China: historical evolution and coupling pattern. Sustainability 12 (18), 7307. doi:10.3390/su12187307
He, X., and Liu, W. (2024). Analysis of spatial patterns and influencing factors of farmland transfer in China based on ESDA-GeoDetector. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 12485. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-62931-1
Huang, Y., Huang, Y., Chen, Y., and Yang, S. (2025). Spatial evolution of traditional waterside settlements south of the yangtze river and the distribution of settlement heritage: evidence from the nanxi river basin. Npj Herit. Sci. 13 (1), 62. doi:10.1038/s40494-025-01649-3
Jaszczak, A., Kristianova, K., Vaznonienė, G., and Žukovskis, J. (2018). Phenomenon of abandoned villages and its impact on transformation of rural landscapes. Manag. Theory Stud. Rural Bus. Infrastructure Dev. 40 (4), 467–480. doi:10.15544/mts.2018.43
Jiang, B., Huang, Y., Chen, Y., Lu, J., and Yang, T. (2025). The distribution pattern and spatial morphological characteristics of military settlements along the ming great wall in the hexi corridor region. Buildings 15, 1136. doi:10.3390/buildings15071136
Jie, Y., and Xin, H. (2024). The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1985 to 2023 [Dataset]. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 13 (1), 3907–3925. doi:10.5281/zenodo.12779975
Li, B., Lu, Y., Li, Y., Zuo, H., and Ding, Z. (2024). Research on the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and accessibility of traditional villages based on geographic information systems—A case study of Shandong Province, China. Land 13, 1049. doi:10.3390/land13071049
Li, J., Xiao, Y., Yan, J., Liang, C., and Zhong, H. (2025). Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and causative analysis of toponymic cultural landscapes in traditional villages in northern Guangdong, China. Sustainability 17, 271. doi:10.3390/su17010271
Liao, Z., and Zhang, L. (2022). Spatial distribution characteristics and accessibility analysis of characteristic towns in Guangdong province based on Ripley’s K function. J. Math. 2022 (1), 2873707. doi:10.1155/2022/2873707
Liu, L., Li, F., Liu, Y., Wang, T., and Liu, Y. (2023). The strategy of the revitalization of Shandong rural culture by the agricultural cultural heritage. Art Soc. 2 (4), 6–8. doi:10.56397/as.2023.08.02
Liu, M., Ma, M., Liu, J., Lu, X., Dong, Z., and Li, J. (2023). Quantifying impacts of natural and anthropogenic factors on urban ecological quality changes: a multiscale survey in Xi’an, China. Ecol. Indic. 153, 110463. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110463
Liu, W., Xue, Y., and Shang, C. (2023). Spatial distribution analysis and driving factors of traditional villages in Henan Province: a comprehensive approach via geospatial techniques and statistical models. Herit. Sci. 11 (1), 185. doi:10.1186/s40494-023-01038-8
Ma, S., and Fang, X. (2021). Research on traditional villages tourism resources analysis based on GIS: a case study on zichuan district, zibo city, Shandong Province, China. Asia-pacific J. Convergent Res. Interchange 7, 1–10. doi:10.47116/apjcri.2021.01.01
Ma, X., Qiu, F., Li, Q., Shan, Y., and Cao, Y. (2013). Spatial pattern and regional types of rural settlements in xuzhou city, Jiangsu Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 23, 482–491. doi:10.1007/s11769-013-0615-8
Ma, X., Yang, X., and Fan, Y. (2022). Study on spatial distribution pattern and influencing factors of traditional villages in Shandong Province based on GIS. 2nd Int. Conf. Internet Things Smart City (IoTSC 2022) 12249, 132–735. doi:10.1117/12.2637045
Ma, Y., Zhang, Q., and Huang, L. (2023). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages in Fujian province, China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 10 (1), 883. doi:10.1057/s41599-023-02407-1
Mauro, F., Haxtema, Z., and Temesgen, H. (2017). Comparison of sampling methods for estimation of nearest-neighbor index values. Can. J. For. Res. 47 (6), 703–715. doi:10.1139/cjfr-2016-0239
Pan, Z., Chen, Y., Huang, Y., and Zheng, L. (2024). The vernacular cultural landscape in traditional villages: global hotspots, emerging trends, and a case study of China’s qilu cultural district. Front. Earth Sci. 12, 1511292. doi:10.3389/feart.2024.1511292
Qi, J., Lu, Y., Han, F., Ma, X., and Yang, Z. (2022). Spatial distribution characteristics of the rural tourism villages in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its influencing factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19, 9330. doi:10.3390/ijerph19159330
Qu, Y., Zhan, L., Jiang, G., Ma, W., and Dong, X. (2021). How to address “Population Decline and Land Expansion (PDLE)” of rural residential areas in the process of urbanization: a comparative regional analysis of human-land interaction in Shandong Province. Habitat Int. 117, 102441. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2021.102441
Shen, W., Chen, Y., Cao, W., Yu, R., Rong, P., and Cheng, J. (2024). Spatial pattern and its influencing factors of national-level cultural heritage in China. Herit. Sci. 12 (1), 384. doi:10.1186/s40494-024-01508-7
Tan, X., Yu, H., An, Y., Wang, Z., Jiang, L., and Ren, H. (2021). Spatial differentiation and influencing factors of poverty alleviation performance under the background of sustainable development: a case study of contiguous destitute areas in Hunan Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 31, 1029–1044. doi:10.1007/s11769-021-1242-4
Tang, C., Qiu, T., and Li, Y. (2025). Heritage perspectives on cultural memory and spatial identity in yuan river basin, Hunan, China. Npj Herit. Sci. 13 (1), 261. doi:10.1038/s40494-025-01841-5
Wang, F., Mao, W., Dong, Y., and Zhu, X. (2018). Implications for cultural landscape in a Chinese context: geo-analysis of spatial distribution of historic sites. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 28, 167–182. doi:10.1007/s11769-017-0915-5
Wang, Q., Bing, H., Wang, S., and Xu, Q. (2022). Study on the spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of famous historical and cultural towns or villages in Hubei Province, China. Sustainability 14, 13735. doi:10.3390/su142113735
Wu, C.-F., Lin, Y.-P., Chiang, L.-C., and Huang, T. (2014). Assessing highway's impacts on landscape patterns and ecosystem services: a case study in puli township, Taiwan. Landsc. Urban Plan. 128, 60–71. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2014.04.020
Xiao, C. W., Feng, Z. M., Li, P., You, Z., and Teng, J. K. (2018). Evaluating the suitability of different terrains for sustaining human settlements according to the local elevation range in China using the ASTER GDEM. J. Mt. Sci. 15 (12), 2741–2751. doi:10.1007/s11629-018-5058-3
Xiao, X., Tang, C., and Liang, W. (2022). Spatial distribution and cultural features of traditional villages in beijing and influencing factors. J. Resour. Ecol. 13 (6), 1074–1086. doi:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2022.06.012
Xu, L., Zhao, S., Chen, S. S., Yu, C., and Lei, B. (2020). Analysis of arable land distribution around human settlements in the riparian area of Lake Tanganyika in Africa. Appl. Geogr. 125, 102344. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102344
Xue, Q., and Huang, Y. (2025). The spatial relationship and influence mechanism of traditional villages and intangible cultural heritage: a case study of the upper reaches of the yellow river basin. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 12 (1), 142. doi:10.1057/s41599-025-04447-1
Yanbo, Q., Guanghui, J., Yuting, Y., Qiuyue, Z., Yuling, L., and Wenqiu, M. (2018). Multi-scale analysis on spatial morphology differentiation and formation mechanism of rural residential land: a case study in Shandong Province, China. Habitat Int. 71, 135–146. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.11.011
Yang, R., Xu, Q., Xu, X., and Chen, Y. (2019). Rural settlement spatial patterns and effects: road traffic accessibility and geographic factors in Guangdong province, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 29, 213–230. doi:10.1007/s11442-019-1593-2
Yang, Z., Wang, S., Hao, F., Ma, L., Chang, X., and Long, W. (2023). Spatial distribution of different types of villages for the rural revitalization strategy and their influencing factors: a case of Jilin Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 33 (5), 880–897. doi:10.1007/s11769-023-1359-8
Yang, R., Zhang, X., and Xu, Q. (2022). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural specialized villages in Guangdong province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 32 (6), 1013–1034. doi:10.1007/s11769-022-1317-x
Yang, Z., Yang, D., Geng, J., and Tian, F. (2022). Evaluation of suitability and spatial distribution of rural settlements in the karst mountainous area of China. Land 11 (11), 2101. doi:10.3390/land11112101
Yihong, Z. H. A. N. G., Tingdong, M., Bin, B. A. I., and Qing, Y. A. N. G. (2022). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages in Guizhou province. J. Landscape Research 14 (1). doi:10.16785/j.issn1943-989x.2022.1.008
Zhang, X., Yu, L., and Xu, X. (2023a). Study on the spatial distribution characteristics and poverty inducements of poverty-stricken villages in Henan Province. Land 12, 957. doi:10.3390/land12050957
Zhang, X., Huang, X., and Li, J. (2023b). The evolution of green development, spatial differentiation pattern and its influencing factors in characteristic Chinese towns. Sustainability 15, 5079. doi:10.3390/su15065079
Zhang, W., Ma, L., Li, H., and Wang, X. (2024). Trends in the future evolution of rural settlements in oasis-desert areas under water use simulation scenarios: take the hexi corridor region of China as an example. Landsc. Urban Plan. 248, 105110. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2024.105110
Zhang, X., Yang, H., and An, Y. (2025). Spatial morphology and geographic adaptability of traditional villages in the hehuang region, China. Buildings 15, 244. doi:10.3390/buildings15020244
Zhang, Y., Zheng, Q., Ye, S., Zhang, K., and Lin, W. (2023). Spatial distribution characteristics and analysis of influencing factors on different manufacturing types in Shandong Province. Plos One 18 (9), e0291691. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0291691
Zhong, Q., and Dong, T. (2024). Exploring the spatiotemporal trends and influencing factors of human settlement suitability in Hunan Province traditional villages. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 25319. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-76746-7
Keywords: settlement heritage, driving factors, distribution characteristics, coastal peninsula, geographic information systems (GIS)
Citation: Liang Q, Pan Z, Huang Y, Zheng L, Fang J, Qin Y, Zhu Y, Kang L and Chen Y (2025) Distribution and driving factors of settlement heritage of coastal peninsulas via GIS: evidence from Shandong, China. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1735907. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1735907
Received: 30 October 2025; Accepted: 18 November 2025;
Published: 18 December 2025.
Edited by:
Karoly Nemeth, Institute of Earth Physics and Space Science (EPSS), HungaryReviewed by:
Wael Salah Fahmi, Helwan University, EgyptVladyslav Zakharovskyi, Massey University, New Zealand
Copyright © 2025 Liang, Pan, Huang, Zheng, Fang, Qin, Zhu, Kang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuhao Huang, VTI0MDkyMTIwMTc2QGNpdHl1LmVkdS5tbw==; Yile Chen, Y2hlbnlpbGVAbXVzdC5lZHUubW8=
†ORCID: Zhao Pan, orcid.org/0009-0003-2927-1154; Yuhao Huang, orcid.org/0009-0004-8445-5666; Liang Zheng, orcid.org/0000-0003-3142-7704; Jiaying Fang, orcid.org//0000-0001-8091-626X; Yufei Zhu, orcid.org/0009-0002-8076-7406; Lulong Kang, orcid.org/0009-0001-1720-3555; Yile Chen, orcid.org/0000-0002-8424-8059
 Qibai Liang
Qibai Liang Zhao Pan
Zhao Pan Yuhao Huang
Yuhao Huang Liang Zheng
Liang Zheng Jiaying Fang
Jiaying Fang Yuanrui Qin6
Yuanrui Qin6 Yile Chen
Yile Chen