- 1School of Public Health, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 3Health Department, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Background: Private caregivers are common in developing countries as supplements to healthcare human resources. However, the effects of private caregivers on inpatient conditions remain unclear. This study explored the effect of private caregivers on nutritional risk and anxiety in patients with dysphagia after ischemic stroke.
Methods: This observational study included patients with dysphagia after ischemic stroke between 2022 and 2024 in central China. Participants were divided into non-caregiver and private caregiver groups. A single-factor analysis was used to explore the differences between the baseline assessments of the two groups. We then used propensity score matching (PSM) to balance significant baseline variables, including anxiety at admission, and demographic and clinical characteristics. In the matched sample, we used the average treatment effect on the treated (ATT) to uncover the influence of the patient groups on nutritional risks and anxiety on day 10.
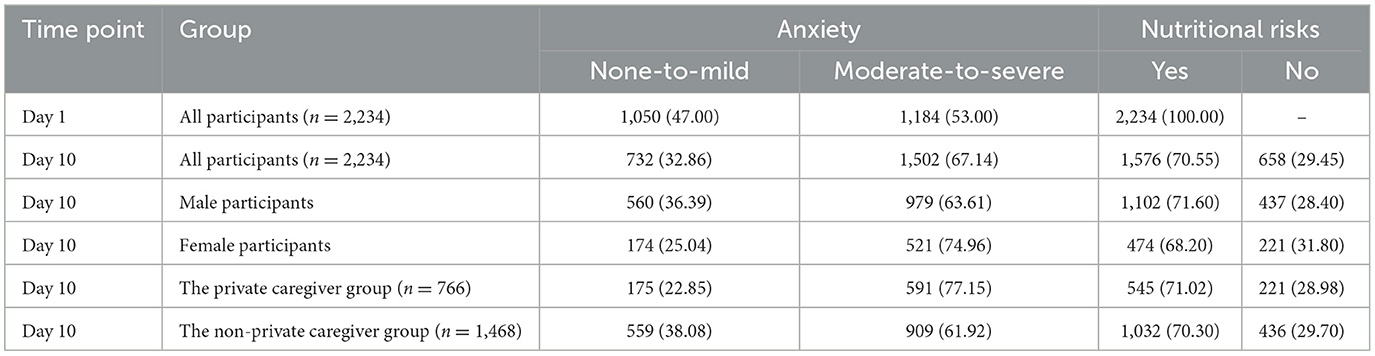
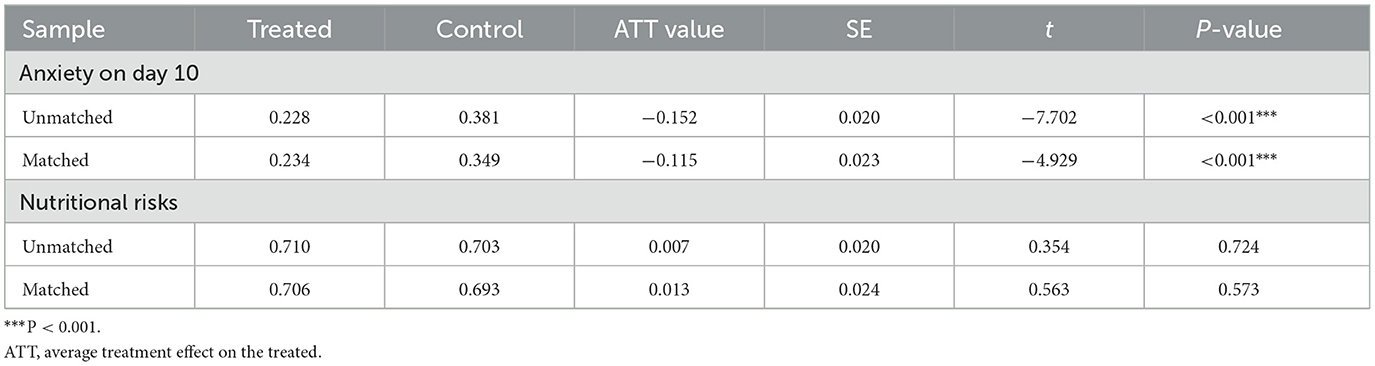
Results: A total of 2,234 patients were included, and there were 766 cases in the private caregiver group. Before PSM, there were significant reductions in anxiety (47.00 vs. 32.86%, P < 0.001) and nutritional risks (100.00 vs. 70.55%, P < 0.001) from days 1 to 10. After PSM, there were no significant differences in any baseline assessments, and 766 pairs of cases were successfully captured. The ATT analysis showed that before and after PSM, there was no significant correlation between groups and nutritional risks (30.75 vs. 29.41%, P = 0.573), but there was a significant correlation between groups and anxiety on day 10 (34.89 vs. 23.40%, ATT = 0.234 after matching, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Private caregivers can effectively reduce anxiety in hospitalized patients with dysphagia following ischemic stroke, but they do not have a significant impact on nutritional risks.
1 Introduction
Ischemic stroke typically causes functional impairment to various degrees and types, with dysphagia being one of them (1). Swallowing disorders can lead to malnutrition, pneumonia, choking, and decreased quality of life (2). According to previous studies, almost half of the patients experience swallowing issues during the acute and subacute phases of stroke (3). Additionally, stroke increases the risk of psychological problems (4). It has been reported that ~30% of stroke survivors suffer from generalized anxiety (5). Therefore, the care of stroke patients requires dual attention to both physiological and psychological aspects (6).
In some developing countries, such as China and India, the lack of nursing staff has forced patients' families to take on some caregiving responsibilities (7). However, most family members do not receive relevant training and lack nursing experience, which can result in suboptimal outcomes. In this context, a role has emerged between professional caregivers and family members known as private caregivers or professional escorts (8). These practitioners can be regarded as supplements and compromises to healthcare human resources (9). The terminology and scope of work for private caregivers can vary across regions. In China, they are referred to as accompanying caregivers. Most of these service providers do not have a medical background, but are trained to offer assistance in daily living, exercises, procedures, toileting, and personal hygiene for patients during hospitalization (10). In China, the costs of private caregiving are primarily paid by patients and are excluded from most medical insurance coverage. Therefore, private caregiving may increase the financial burden on patients to some extent, while alleviating the pressure on public health insurance (11). On this basis, self-funded private care might indicate higher socioeconomic status.
Due to the professional experience and training, private caregivers may be able to improve treatment outcomes (12). Some studies have reported that caregivers can positively influence the success rate of tracheostomy tube removal in patients with persistent vegetative state (13). For conscious patients, private caregivers can provide companionship and communication, offering comfort and encouragement during treatment (10). This may help to improve patients' psychological conditions.
Malnutrition is a risk factor for rehabilitation outcomes in stroke survivors with dysphagia (14). To address this issue, enteral nutritional support is clinically practiced (15). This nutritional method deprives patients of their eating experience and can lead to poor compliance and low appetite (16). A study has suggested that patients' emotional state and willingness to eat are associated with the effectiveness of tube feeding (17). Private caregivers are expected to improve the nutritional status of patients through psychological support and daytime care. However, relevant reports are lacking. By accurately understanding the effect of private caregivers on nutrition and mental health, we can optimize their use, explore ways to provide support in these areas, assess whether they have a positive impact, and add care value. This can help reduce the burden on patients' families and minimize the waste of healthcare resources. Therefore, this observational study aimed to explore the impact of private caregivers on nutritional risk and anxiety in patients with dysphagia after ischemic stroke.
2 Methods
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (2022-KY-0094-002), and all participants signed informed consent forms.
2.1 Study design
This observational study was conducted at five hospitals in central China. We invited ischemic stroke survivors with dysphagia who sought treatment in the Department of Rehabilitation and conducted assessments on the first and tenth day of hospitalization. Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to balance confounding factors, including demographic and clinical characteristics (18). The net effect of private caregivers on nutritional risk and anxiety was analyzed in the matched sample.
2.2 Participants
The inclusion criteria were: (1) age >18 years. (2) Ischemic stroke (19). (3) Nutritional risk screening-2002 (NRS-2002) ≥3, (20) indicating the need of nutritional supports (4). Based on the patient's worst swallowing performance in modified barium swallow studies, the penetration-aspiration scale (PAS) ≥3 on the videofluoroscopy (21). (5) Duration from onset to admission <15 days. (6) Stable conditions and good consciousness, able to cooperate with treatment and questionnaires. (7) Hospital stays at least 10 days. (8) First stroke.
The exclusion criteria were: (1) other brain diseases, cancers, or severe systemic diseases. (2) Malnutrition or psychiatric disorders before this stroke, based on medical records or evidence from family reports (e.g., pictures or documents). (3) Tracheostomized patients. Participants were retrospectively excluded if they (1) experienced stroke recurrence, (2) used parental nutrition during the study, or (3) had severe deterioration in condition. Participants had the right to quit the study halfway and the dropout cases were excluded from the final analysis.
Before entering the study, the research staff introduced private caregivers in a uniform and unbiased manner. The aims were (1) to minimize the influence of non-research-related factors on the decisions made by patients' families, (2) to ensure the informed consent rights of patients and their families, and (3) ethical considerations. Whether to hire a private caregiver entirely depended on patients and their family and was independent of this study. In this study, all private caregivers were provided by a third party, independent of the hospital and this study. To ensure the homogeneity of private caregiving services, we requested that the private caregivers: (1) were trained by the company for at least 3 months before work, (2) had worked in caregiving for 5–10 years, and (3) did not have a medical background. Patients who hired private caregivers for at least 6 days during the study were included in the caregiver group; otherwise, they were placed in the non-caregiver group. The decision to hire a private caregiver did not affect the duties of doctors and nurses. Due to their lack of medical background, private caregivers did not participate in clinical nursing work.
The scope of the private caregivers' work included the following aspects: (1) morning routine: (a) assisting with personal hygiene: help the patient with brushing teeth, washing face, and other morning hygiene activities. (b) Getting dressed: assist the patient in getting dressed, ensuring they are comfortable and appropriately clothed for the day. (c) Mobility assistance: help the patient get out of bed, move to a wheelchair or chair, and ensure they are positioned safely and comfortably. (2) Meal assistance: (a) monitoring nutrition: keep track of the patient's food and fluid intake, encouraging and help patients to meet their nutritional needs. (3) Medication management: (a) Administering medications: assist the patient in taking prescribed medications at the correct times, ensuring they follow the doctor's instructions. (b) Monitoring side effects: observe the patient for any adverse reactions to medications and report any concerns to the medical staff. (4) Therapy and exercises: (a) rehabilitation exercises: assist the patient with prescribed physical therapy exercises, helping them perform movements correctly and safely. (b) Speech therapy support: encourage and assist the patient with speech therapy exercises, especially if they have difficulty swallowing or speaking. (5) Emotional and psychological support: (a) companionship: spend time talking with the patient, providing emotional support, and engaging in activities that the patient enjoys. (b) Encouragement: motivate the patient to stay positive and adhere to their treatment and rehabilitation plans. (6) Daily living activities: (a) toileting assistance: help the patient with using the toilet, ensuring they maintain dignity and hygiene. (b) Bathing: assist with bathing or showering, ensuring the patient is clean and comfortable. (7) Monitoring health status: (a) observing symptoms: continuously monitor the patient's condition, noting any changes in symptoms or behavior. (b) Reporting to medical staff: communicate any significant observations or concerns to the healthcare team promptly. (8) Evening routine: (a) preparing for bed: assist the patient with their evening routine, including changing into nightwear and settling into bed. (b) Ensuring comfort: make sure the patient is comfortable, adjusting pillows and blankets as needed. (9) Additional responsibilities: (a) transportation: accompany the patient to medical appointments or therapy sessions if needed. (b) Housekeeping: perform light housekeeping tasks to ensure the patient's environment is clean and safe. (c) Emergency preparedness: be prepared to handle emergencies, such as sudden health deteriorations, and know the protocols for contacting medical help. (d) Keeping records: maintain a log of the patient's daily activities, food intake, medication administration, and any notable incidents or changes in condition.
2.3 Assessment
2.3.1 Anxiety
The 7-item generalized anxiety disorder (GAD-7) was used to evaluate anxiety on days 1 and 10. This scale has been validated for Chinese inpatients (22). In this study, patients were divided into non-to-mild anxiety (GAD-7 ≤ 9 points) and moderate-to-severe anxiety (GAD-7 > 9 points) groups. For patients with limited comprehension abilities or mild aphasia, researchers were allowed to provide non-leading explanations of the items.
2.3.2 Nutritional risks
The NRS-2002 was used to evaluate nutritional risks on days 1 and 10. It was initially designed for severely ill patients or those with increased nutritional needs or undernutrition, and its adaptability makes it suitable for our study population (23–25). This nutritional risk screening tool is suitable for use over a period of more than 1 week. The assessment included nutritional status and disease severity. The NRS-2002 has been widely validated in stroke survivors in the Chinese context (26). A total score of ≥3 indicated nutritional risk (20).
2.3.3 Covariates
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were used as covariates for matching, to ensure comparability. The details and assignments of the covariates are provided in Supplementary Appendix S1. Due to the need for enteral feeding, the feeding type has been included as a covariate. We provided two common types of enteral nutrition support in China: intermittent oro-esophageal tubes (IOE) and nasogastric tubes (NGT). For IOE, the tube was intermittently inserted orally into the upper esophagus (27), whereas for NGT, the tube was placed persistently through the nostril into the stomach (28). The feeding types were selected through negotiation among patients and doctors, independent of this study. According to the relevant guidelines, the nutritional standards were the same, with a daily intake of 25–35 kcal/kg and protein intake of 0.8–1.2 g/kg (29). Independent clinical nutritionists arranged individualized feeding contents for the patients. The patients' actual intake fluctuated around the nutritional standards and was influenced by factors such as compliance, adverse events, and willingness to eat. However, all the staff members made every effort to prevent malnutrition. All feedings were administered by healthcare professionals instead of patients' family members or private caregivers. Secondary prevention with appropriate medication, health education guidance, and rehabilitation interventions were provided individually for all patients.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Categorical data, normal continuous data, and skewed continuous data were expressed using counts and percentages (n, %), means and standard deviations (x ± s), and medians and interquartile ranges [M (Q25, Q75)], respectively. For single-factor analysis, we used chi-square, t or rank-sum tests to explore any differences in covariates between the non- and private caregiver groups. The significant items were included in a set of covariates for subsequent PSM. The anxiety on day 1 was included in the PSM to balance baseline situations. In the PSM, the patient groups were set as independent variables, and the GAD-7 and NRS-2002 on day 10 were set as outcomes variables. The average treatment effect on the treated (ATT) values were used to report the associations between independent and outcome variables before and after matching. Propensity scores were used for matching, which were based on logistic regression. We matched the sample 1:1 without replacement (caliper = 0.1). A P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant, and SPSS 21.0 was used for statistical analysis.
3 Results
3.1 Basic information
In total, we invited 2,819 potential participants who met the inclusion criteria. Among them, 332 patients met the exclusion criteria upon admission, 75 patients were retrospectively excluded, and another 178 patients quit the study voluntarily. Finally, 2,234 cases were included in the final analysis. There were 766 patients who hired private caregivers. Before PSM, there were significant differences in anxiety (47.00 vs. 32.86%, P < 0.001) and nutritional risks (100.00 vs. 70.55%, P < 0.001) on days 1 and 10. Additionally, the male participants showed a significantly higher prevalence of moderate-to-severe anxiety than female participants on day 10 (36.39 vs. 25.04%, P < 0.001). There were no significant sex differences in nutritional risk on day 10 (P = 0.102). The details are shown in Table 1.
3.2 Single-factor analysis
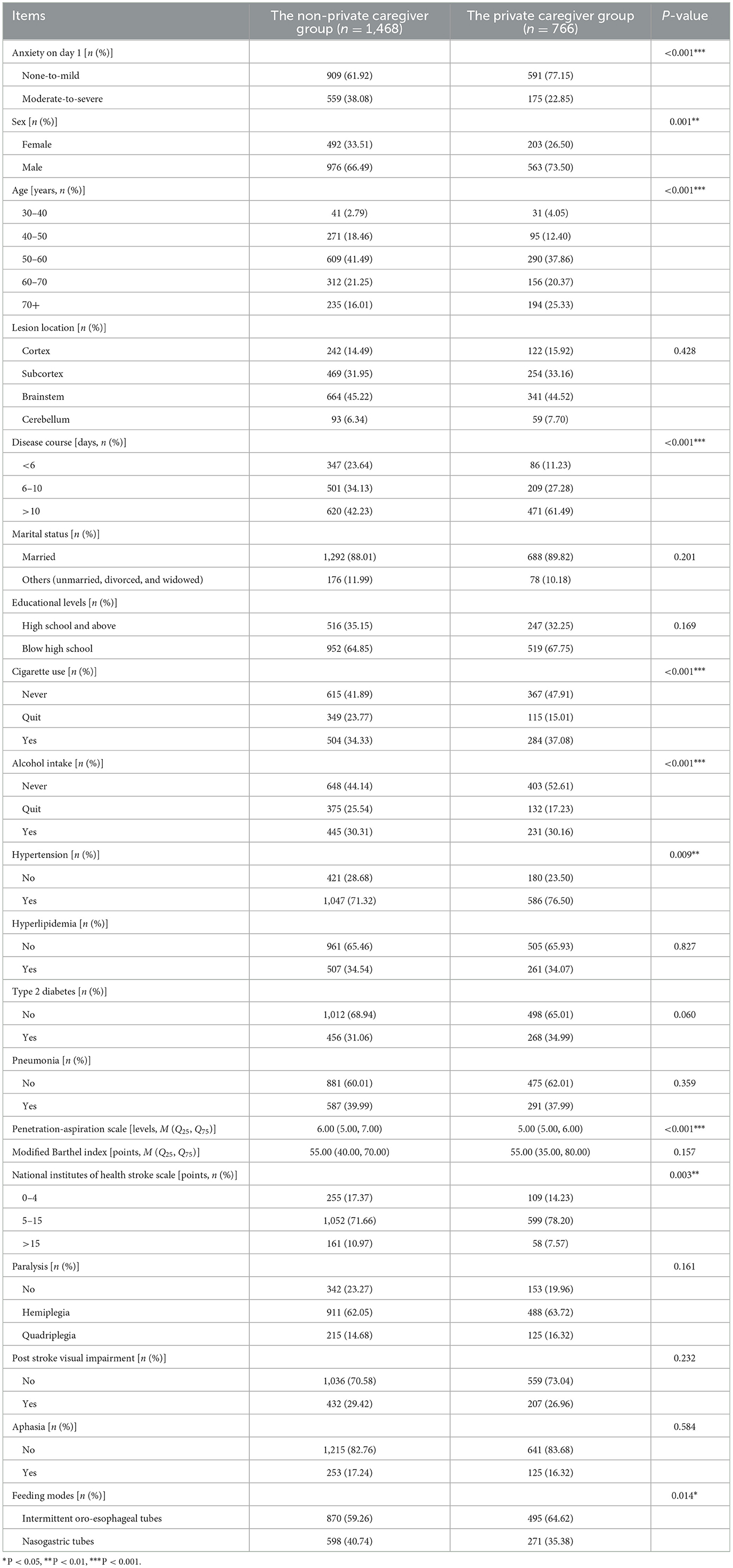
Significant differences were found between the groups in the following items (P < 0.05): anxiety on day 1, sex, age, disease course, cigarette use, alcohol intake, hypertension, the PAS, neurological impairment, and feeding modes, as shown in Table 2. These variables were included in the set of covariates for the subsequent PSM.
3.3 Propensity score matching
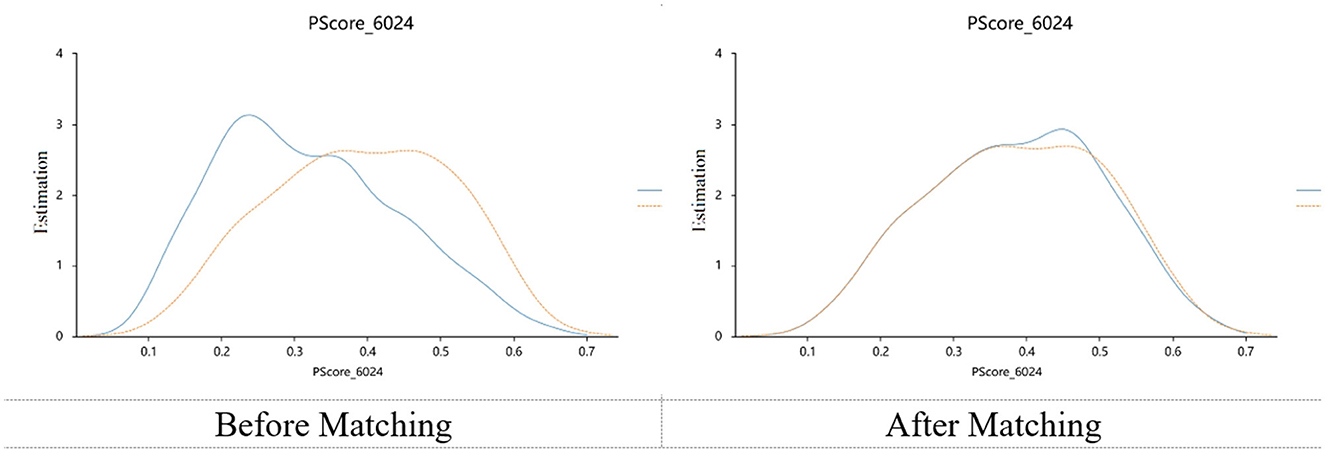
A total of 766 pairs were successfully captured using PSM. There were no significant differences in the matched samples for all covariates, and the absolute values of the standardized bias were all <0.1. This indicated that in the matched sample, the relationship between the independent and dependent variables was not affected by the covariates in the statistical analysis. The PSM balance test is shown in Table 3, and the kernel density plots are shown in Figure 1. The ATT analysis showed that before and after PSM, there was no significant correlation between groups and nutritional risks (30.75 vs. 29.41%, P = 0.573), but there was a significant correlation between groups and anxiety on day 10 (34.89 vs. 23.40%, ATT = 0.234 after matching, P < 0.001), as shown in Table 4.
4 Discussion
This observational study aimed to explore the effect of private caregivers on nutritional risk and anxiety among stroke survivors with dysphagia. The primary findings revealed that private caregivers significantly reduced anxiety levels in patients during the 10-day hospitalization but had no significant effect on nutritional risk. This indicated that, while private caregivers can alleviate psychological distress, their influence on nutritional outcomes might be limited, particularly in settings where nutritional support is managed by hospital staff. In addition, this study showed sex differences in the prevalence of post-stroke anxiety. Previous studies have reported that the prevalence of post-stroke psychological disorders is higher in males than in females, which is consistent with our results (30). The study highlighted the potential of private caregivers to complement healthcare resources, particularly in addressing the psychological needs of stroke survivors. However, further research is needed to optimize their role in managing nutritional risks.
The unmatched sample showed that approximately half of the participants experienced anxiety upon admission. After the 10-day rehabilitation intervention, this rate decreased to ~30%, consistent with the findings of previous studies (31). A longitudinal study has indicated that the psychological status of tube-fed patients improved during the rehabilitation period, which is consistent with the current study (32). Dysphagia has been associated with psychological problems (33), and feeding tubes can pose an additional burden on patients (34). The overall nutritional risk ratio of the patients decreased by ~30%, which is consistent with a previous study (35). Dysphagia patients typically receive various interventions in the rehabilitation department, such as nerve block therapy (36), behavioral training (28), and acupuncture (37). Although these therapies are not directly related to nutritional status, they can influence nutritional intake by improving neurological function, mood, and swallowing ability (38, 39). This factors can ultimately contribute to a reduction in nutritional risk.
Population aging has increased the prevalence of stroke and the demand for medical resources (40). The shortage of nursing staff is particularly severe in developing countries. As a compromise, private caregivers in these regions could partially alleviate the burden of care for nurses and family members (41). Their roles are similar to those of the family caregivers (42). However, research on private caregivers is limited. In developed regions, private caregivers typically refer to full-time employment of professional nursing staff (43). This situation has not yet been widely realized in areas such as China and India. Moreover, the scope of work in this profession may vary across different regions (7). In China, the social security system has not yet extended its coverage to private care. In recent years, the challenges posed by an aging society have been gradually acknowledged. Therefore, some organizations and regions have provided subsidies or support for private caregiving, such as caregiver training and public welfare caregiving. However, cost-benefit analyses of caregiving still require further research to assist families and policymakers in understanding the long-term economic benefits of investing in private care (44). This study found that hiring private caregivers can significantly improve anxiety levels in patients with post-stroke dysphagia. Private caregivers are expected to understand the needs and habits of their patients and provide attentive and customized services (45). They can offer round-the-clock care and provide emotional support and companionship to patients, which helps to alleviate anxiety (46). Additionally, private caregivers can assist patients with activities of daily living, reduce their burden, and closely monitor changes in their condition (47). This allows for timely identification of and response to anxiety, thereby providing better care for patients. One study has suggested that family caregiving can increase the psychological burden on patients (48), while having a private caregiver who is not a family member may help reduce anxiety.
Nutrition is fundamental to rehabilitation and dysphagia is closely associated with malnutrition (49). One study indicated that stroke patients with dysphagia had a significantly higher risk of malnutrition than those with normal swallowing function (50). In China, tube feeding is the most common method for enteral nutrition support. The two tube-feeding methods provided in this study are widely applied for dysphagia caused by various diseases (13, 27, 51, 52). We incorporated this variable into the matching process to reduce potential influences caused by the feeding methods, which is one of the innovations of this research. The matched samples were well-balanced across all covariates, and the kernel density plots indicated good matching effectiveness. While some studies have suggested that private caregiving can improve rehabilitation outcomes (13, 41, 53), we did not observe a correlation between private caregivers and malnutrition risk in the matched samples. The focus of private caregivers is typically on providing daily living assistance, rather than specifically managing nutrition (46). Moreover, all tube-feeding operations in this study were carried out by hospital nursing staff, which limited the role of private caregivers. Although we speculated that private caregivers could improve patients' nutritional intake by encouraging them, enhancing compliance, and supporting psychological aspects, this effect remains insignificant. We hypothesized that one of the reasons might be that tube feeding deprived them of their eating experience. The patients could not taste, chew, or actively swallow the food (50). This reduced patients' proactive engagement in nutritional intake. Furthermore, during rehabilitation, patients' nutritional standards were prescribed uniformly. Nursing staff have typically made every effort to help patients achieve the nutritional goals set by dietitians, which may diminish the contributions of private caregivers. It should be noted that in some clinical practices, some private caregivers are authorized to perform tube-feeding procedures. This situation may have a more significant influence on the patients' nutritional status (54). Under this circumstances, nutritional outcomes may be further affected by factors such as the professional experience of caregivers and the relationship between private caregivers and patients.
This study had several limitations. First, we only collected data from patients with dysphagia, which limited the representativeness of the sample. Second, as an observational study, we were unable to standardize the interventions received by different groups. For ethical reasons, we did not restrict the involvement of family members in daily care, which might have introduced potential bias. Third, although we discussed potential mechanisms, we did not collect the mediating variables for statistical analysis. Furthermore, although socioeconomic status has been hypothesized to be associated with private care, income level and social status are often underreported. We did not receive support from the relevant authorities to access such data directly. Consequently, socioeconomic status was not included as a covariate in the PSM. Additionally, due to the confidentiality of patient data and the difficulty in achieving cross-regional collaboration, we have only collected data from several hospitals in central China. This affected the representativeness of the results and feasibility of cross-cultural comparisons. Also, we did not explore long-term effects. The primary reason was that the average length of hospital stays for patients in the study hospital did not exceed 14 days. As the observation period increased, the sample size decreased significantly. Moreover, patients no longer needed private caregivers after discharge. This raised concerns that uncontrolled variables in their post-discharge lives might introduce greater bias. A large-scale long-term cohort study should be designed to address these issues. Finally, although we used PSM to reduce confounding factors. The observational design cannot fully establish causality unless a randomized controlled study is conducted. Therefore, this study only revealed the predictive relationships between the variables. Stronger evidence is necessary to establish causality.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (2022-KY-0094-002). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
WZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SC: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the NHC Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Cerebrovascular Disease. The funders were not involved in the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation, or manuscript writing.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate all participants for their cooperation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1513609/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Shiraishi R, Kato S, Shiraishi N, Ogawa T. Association between improved dysphagia and increased trunk muscle mass in older patients with stroke undergoing convalescent rehabilitation. Nutrition. (2025) 130:112609. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2024.112609
2. Zeng H, Zhao W, Wang R, Wei S, Wang X, Luo S, et al. Effect of simple swallowing training program on early oropharyngeal dysphagia in community-dwelling older adults: a randomized controlled study. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2024) 25:105297. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2024.105297
3. Banda KJ, Chu H, Kang XL, Liu D, Pien LC, Jen HJ, et al. Prevalence of dysphagia and risk of pneumonia and mortality in acute stroke patients: a meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. (2022) 22:420. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-02960-5
4. Khazaal W, Taliani M, Boutros C, Abou-Abbas L, Hosseini H, Salameh P, et al. Psychological complications at 3 months following stroke: prevalence and correlates among stroke survivors in Lebanon. Front Psychol. (2021) 12:663267. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.663267
5. Knapp P, Dunn-Roberts A, Sahib N, Cook L, Astin F, Kontou E, et al. Frequency of anxiety after stroke: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int J Stroke. (2020) 15:244–55. doi: 10.1177/1747493019896958
6. Lawrence M, Booth J, Mercer S, Crawford E. A systematic review of the benefits of mindfulness-based interventions following transient ischemic attack and stroke. Int J Stroke. (2013) 8:465–74. doi: 10.1111/ijs.12135
7. Wang W, Zhang X, Kong D, Zhou W, Jin L, Wei M, et al. The management for caregivers of inpatients in a general hospital during the coronavirus disease 2019 epidemic. Chin J Nurs. (2020) 55:827–31. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2020.06.005
8. Wu B. The construction and application of an intensive care inpatient companion intelligent management system. Chin Nurs Manage. (2020) 20:23–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2020.z1.011
9. Yan Y, Chen X, Kang Y, Zhang Y. Inpatients' needs on medical nursing assistants: a qualitative user Persona study. Chin J Pract Nurs. (2025) 41:367–73. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn211501-20240513-01190
10. Dong E, Wang X, Tang H. Mutual impacts of factors of stroke inpatients and their caregivers on their life satisfaction: a cross-sectional analysis. China J Pub Health. (2020) 36:1590–4. doi: 10.11847/zgggws1119885
11. Chen S, Li L, Yang J, Jiao L, Golden T, Wang Z, et al. The impact of long-term care insurance in China on beneficiaries and caregivers: a systematic review. J Glob Health Econ Policy. (2021) 1:e2021014. doi: 10.52872/001c.29559
12. Wang X, He W, Yan T, Huang W. Development and application of inpatient companions management program based on hospital information platforms. J Nurs Sci. (2022) 37:94–7.
13. Zeng H, Zeng X, Liu N, Ding Y, Wu J, Zhang F, et al. Development and validation of a nomogram for tracheotomy decannulation in individuals in a persistent vegetative state: a multicentre study. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. (2024) 67:101849. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2024.101849
14. Shimizu A, Maeda K, Koyanagi Y, Kayashita J, Fujishima I, Mori N. The global leadership initiative on malnutrition-defined malnutrition predicts prognosis in persons with stroke-related dysphagia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2019) 20:1628–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.07.008
15. Shimazu S, Yoshimura Y, Kudo M, Nagano F, Bise T, Shiraishi A, et al. Frequent and personalized nutritional support leads to improved nutritional status, activities of daily living, and dysphagia after stroke. Nutrition. (2021) 83:111091. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.111091
16. Zeng H, Cai A, Zhao W, Wu J, Ding Y, Zeng X. Factors and predictive model for malnutrition in poststroke disabled patients: a multicenter cross-sectional study. Nutrition. (2024) 123:112423. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2024.112423
17. Zeng H, Zeng J, Zhao W, Qin Y, Wen C, Zeng X. The mediating role of perceived social isolation in feeding methods and depression among patients with dysphagia after ischemic stroke: a multicenter study. Nutrition. (2025) 135:112769. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2025.112769
18. Zhao QY, Luo JC, Su Y, Zhang YJ, Tu GW, Luo Z. Propensity score matching with R: conventional methods and new features. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9:812. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3998
19. Chinese SON, Chinese SS. Chinese guideline for the secondary prevention of ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack 2022. Chin J Neurol. (2022) 55:1071–110. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113694-20220714-00548
20. Foletto E, Bernardes S, Milanez D, Razzera EL, Silva FM. Complementarity of nutrition screening with global leadership initiative on malnutrition criteria for diagnosing malnutrition in critically ill patients: a comparison study of nutritional risk screening 2002 and modified nutrition risk in the critically ill score. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2024) 48:440–8. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2629
21. Borders JC, Brates D. Use of the penetration-aspiration scale in dysphagia research: a systematic review. Dysphagia. (2020) 35:583–97. doi: 10.1007/s00455-019-10064-3
22. Wang Y, Chen R, Zhang L. A study on the reliability and validity of the generalized anxiety disorder-7 scale (GAD-7) in hospitalized patients in comprehensive hospitals in China. J Clin Psychiatry. (2018) 28:168–71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3220.2018.03.007
23. Kondrup J, Rasmussen HH, Hamberg O, Stanga Z. Nutritional risk screening (NRS 2002): a new method based on an analysis of controlled clinical trials. Clin Nutr. (2003) 22:321–36. doi: 10.1016/S0261-5614(02)00214-5
24. Rabito EI, Marcadenti A, Da Silva Fink J, Figueira L, Silva FM. Nutritional risk screening 2002, short nutritional assessment questionnaire, malnutrition screening tool, and malnutrition universal screening tool are good predictors of nutrition risk in an emergency service. Nutr Clin Pract. (2017) 32:526–32. doi: 10.1177/0884533617692527
25. Di Vincenzo O, Luisi ML, Alicante P, Ballarin G, Biffi B, Gheri CF, et al. The assessment of the risk of malnutrition (undernutrition) in stroke patients. Nutrients. (2023) 15:683. doi: 10.3390/nu15030683
26. Liu L, Wang Y, Xia Y. The correlation between NRS2002 nutritional risk screening and nutritional assessment indicators in stroke patients. J Med Theory Pract. (2018) 31:3270–2. doi: 10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2018.21.058
27. Zeng H, Zhao W, Wu J, Wei J, Li H, Wang L, et al. Effect of intermittent oro-esophageal tube feeding in bulbar palsy after ischemic stroke: a randomized controlled study. Stroke. (2024) 55:1142–50. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.123.046122
28. Labeit B, Michou E, Trapl-Grundschober M, Suntrup-Krueger S, Muhle P, Bath PM, et al. Dysphagia after stroke: research advances in treatment interventions. Lancet Neurol. (2024) 23:418–28. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00053-X
29. Chinese ECG. Chinese expert consensus on food and nutrition management for dysphagia (2019 version). Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2020) 29:434–44. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.202007_29(2).0026
30. Almhdawi KA, Alazrai A, Kanaan S, Shyyab AA, Oteir AO, Mansour ZM, et al. Post-stroke depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms and their associated factors: a cross-sectional study. Neuropsychol Rehabil. (2021) 31:1091–104. doi: 10.1080/09602011.2020.1760893
31. Ruthmann F, Lo JW, Mendyk-Bordet AM, Allart E, Köhler S, Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A, et al. Prevalence of poststroke anxiety and its associations with global cognitive impairment: an individual participant data analysis. J Affect Disord. (2025) 369:1136–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.10.099
32. Zeng H, Zhao W, Zeng J, Wang R, Luo H, Wen C, et al. How tube feeding modes influence anxiety in patients with dysphagia after ischemic stroke: a propensity score matched, longitudinal study. Int J Stroke. (2024) 1099039012. doi: 10.1177/17474930241306916
33. Zeng H, Zhao W, Wang R, Li H, Wang L, Zeng X. Association between swallowing function and depressive symptoms among community-dwelling older adults: a cross-sectional study in central China. J Affect Disord. (2025) 380:78–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2025.03.113
34. Gözceylan G, Findik I. Comparison of anxiety and depression levels in caregivers of patients with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy for home enteral tube feeding against other enteral nutrition methods. BMC Palliat Care. (2024) 23:20. doi: 10.1186/s12904-024-01360-3
35. Diendéré J, Millogo A, Preux PM, Jésus P, Desport JC. Changes in nutritional state and dysphagia in stroke patients monitored during a 14-d period in a Burkina Faso hospital setting. Nutrition. (2018) 48:55–60. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2017.10.022
36. Zeng H, Zhao W, Fang L, Pan H, Huang S, Zeng X. Effect of stellate ganglion block on dysphagia and cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease: a randomized controlled study. J Speech Lang Hear Res. (2024) 67:3660–72. doi: 10.1044/2024_JSLHR-24-00145
37. Zeng H, Zhao W, Luo P, Zhang X, Luo S, Li Y, et al. Acupuncture therapy on dysphagia in patients with Parkinson's disease: a randomized controlled study. Chin J Integr Med. (2025) 31:261–9. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3668-x
38. Cai A, Li Y, Xi X, Wang QM, Yang JF, Wang LG, et al. Analysis of risk factors and development of predictive model for malnutrition in patients with traumatic brain injury. Nutr Neurosci. (2024) 27:1439–49. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2024.2342152
39. Zeng H, Liu L, Cai A, Zhao W, Liu Y, Wang L, et al. Prevalence and influencing factors of malnutrition in stroke patients with bulbar paralysis: a cross-sectional study in China. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1392217. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1392217
40. Zeng H, Miao C, Wang R, Zhao W, Wang W, Liu Y, et al. Influence of comorbidity of chronic diseases on basic activities of daily living among older adults in China: a propensity score-matched study. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1292289. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1292289
41. Amiresmaili M, Emrani Z. Informal caregivers in hospitals: opportunities and threats. Int J Health Plann Manage. (2018) 33:880–9. doi: 10.1002/hpm.2543
42. Karlsen L, Mjølstad BP, Løfaldli BB, Helvik A. Family caregiver involvement and role in hospital at home for adults: the patients' and family caregivers' perspective - a Norwegian qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. (2023) 23:499. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-09531-3
43. Lucas MR. A private caregiver ListServ: maximum benefit for minimum cost. J Psychosoc Oncol. (2011) 29:168–74. doi: 10.1080/07347332.2010.548442
44. Song Z, Xie X, Shi J, Liu S, He Q, Fan G, et al. Management and application effect of inpatients escorts based on intelligent escort platform. Shenzhen J Integr Trad Chin West Med. (2024) 34:114–7. doi: 10.16458/j.cnki.1007-0893.2024.03.033
45. Li F, Ding Y, Du J. Investigation on the current situation of the use and management of medical nursing assistants in 44 tertiary hospitals. Chin J Nurs. (2022) 57:2629–34. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2022.21.011
46. Lin Q, Zhu L. Evaluation system of the service quality of hospital professional escort. Nurs J Chin PLA. (2019) 36:78–80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9993.2019.05.021
47. Li LZ, Yang PL, Singer SJ, Pfeffer J, Mathur MB, Shanafelt T. Nurse burnout and patient safety, satisfaction, and quality of care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7:e2443059. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.43059
48. Li LZ, Bian JY, Wang S. Moving beyond family: unequal burden across mental health patients' social networks. Qual Life Res. (2021) 30:1873–9. doi: 10.1007/s11136-021-02782-9
49. Zeng H, Zeng J, Zhao W, Luo S, Luo P, Wang Z, et al. Reliability and validity of the Chinese mandarin version of the dysphagia handicap index. Dysphagia. (2025) 40:419–30. doi: 10.1007/s00455-024-10744-9
50. Zeng H, Zeng X, Xiong N, Wang L, Yang Y, Wang L, et al. How stroke-related dysphagia relates to quality of life: the mediating role of nutritional status and psychological disorders, and the moderating effect of enteral nutrition mode. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1339694. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1339694
51. Zeng H, Zhao W, Zhang X, Wang XA, Luo P, Li H, et al. How enteral nutrition modes influence nasopharyngeal carcinoma survivors with late dysphagia after radiotherapy: a randomized controlled study. Support Care Cancer. (2024) 32:702. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08912-6
52. Zeng H, Yang J, Zhao W, Tian Q, Luo P, Li H, et al. Intermittent oro-esophageal tube feeding for cerebral small vessel disease patients with dysphagia: a randomized controlled study. Nutrition. (2025) 131:112673. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2024.112673
53. Hogan U, Bingley A, Morbey H, Walshe C. The experience of informal caregivers in providing patient care in hospitals in low- and middle-income countries: a qualitative meta-synthesis. J Health Serv Res Policy. (2022) 27:321–9. doi: 10.1177/13558196221101968
Keywords: accompanying persons, accompany nursing staff, professional escorts, patient escorts, rehabilitation
Citation: Zhao W, Zeng J, Li S and Chen S (2025) Effects of private caregivers on nutritional risk and anxiety in stroke survivors with dysphagia: an observational study. Front. Nutr. 12:1513609. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1513609
Received: 25 October 2024; Accepted: 07 May 2025;
Published: 30 May 2025.
Edited by:
Teresa Balboa-Castillo, University of La Frontera, ChileReviewed by:
Lambert Zixin Li, National University of Singapore, SingaporeAmy Yee Liu, Auckland District Health Board, New Zealand
Shuangxi Chen, University of South China, China
Abiodun Idowu, Einstein Healthcare Network, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Zeng, Li and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sheju Chen, Y3NqbmFtZUAxMjYuY29t
 Weijia Zhao
Weijia Zhao Jing Zeng2
Jing Zeng2