- 1Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China
- 2Department of Family Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China
- 3Guangfu People’s Hospital, Suzhou, China
Background: Numerous studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between osteoporosis and nutritional status and inflammation, while albumin and globulin are important references for nutritional status and inflammation, respectively. The albumin to globulin ratio (AGR), which combines the levels of albumin (ALB) and globulin (GLB), is a new comprehensive index that offers a more precise reflection of the inflammatory state of the body and its nutritional status. However, the connection between AGR and thoracic spine bone mineral density (BMD) remains poorly understood. The purpose of this research was to examine the link between the AGR and thoracic spine BMD in adolescents.
Methods: This study used the most recent data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2011 to 2016, and used weighted multivariate linear regression modeling to examine the correlation between AGR and thoracic spine BMD in adolescents. Threshold effects and non-linear relationships were assessed using a smoothed curve-fitting algorithm alongside threshold effects analysis. Furthermore, subgroup analyses and interaction tests were performed.
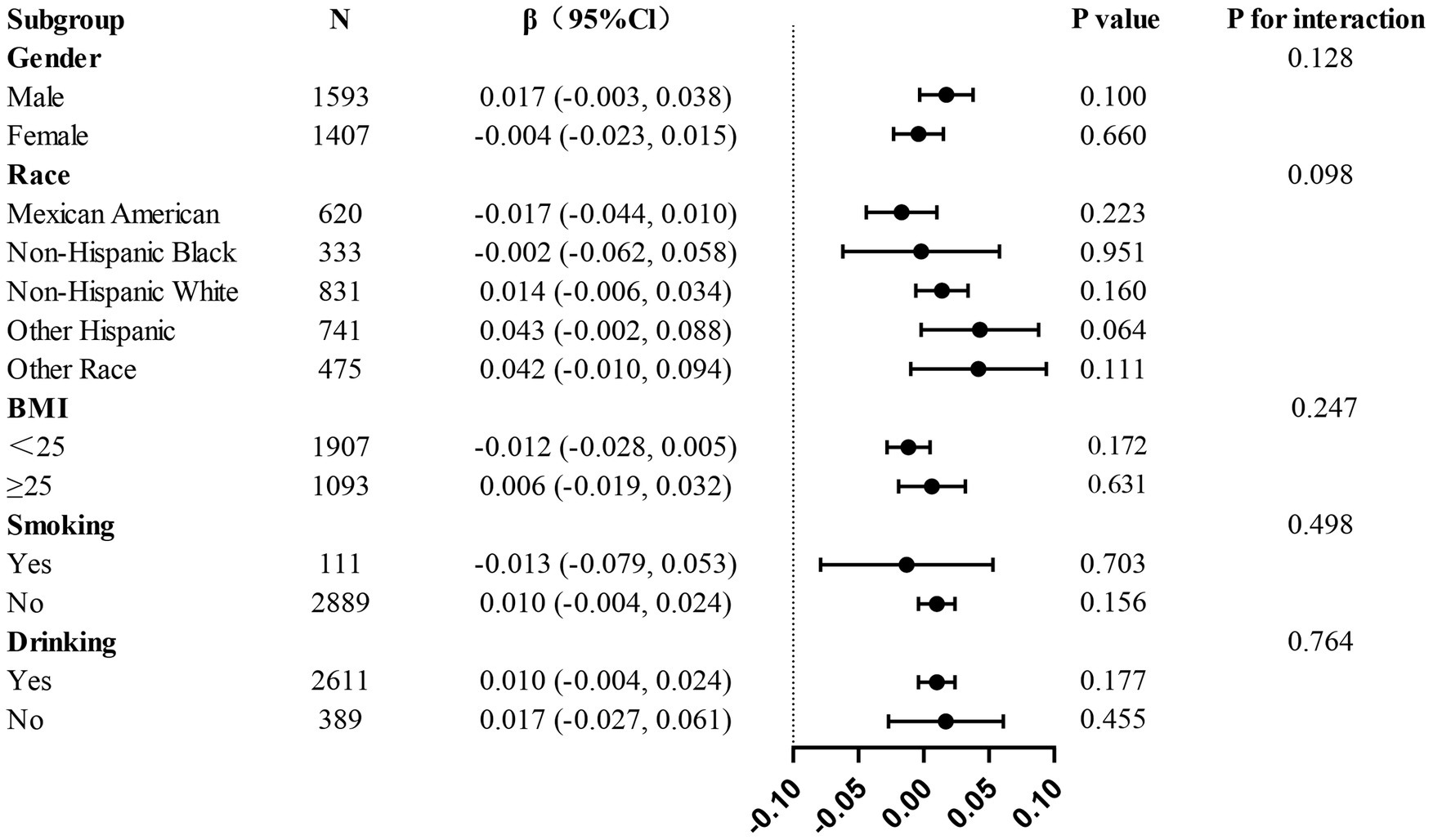
Results: The study comprised a total of 3,000 participants who were all aged 20 years or younger. Based on weighted multivariate linear regression analysis, in the fully adjusted model, a significantly higher thoracic spine BMD was found in the highest AGR quartile compared to the lowest AGR quartile (p < 0.05). After adjusting for variables, subgroup analyses showed no significant interaction effects. The study of threshold effects and the fitting of smooth curves identified a specific threshold effect for AGR and thoracic BMD with an inflection point of 1.237, after which AGR was significantly positively correlated with thoracic spine BMD.
Conclusion: The study identified a notable positive correlation between AGR and adolescent thoracic spine BMD. This finding indicates a potential correlation between higher AGR and higher thoracic spine BMD, which may be indicative of a reduced risk of developing Osteoporosis (OP). This emphasizes the importance of considering nutritional and inflammatory status in the prevention of OP, thereby validating the utilization of AGR as a pivotal marker for the development of early intervention methodologies.
Introduction
Osteoporosis (OP) is a systemic skeletal disorder distinguished by diminished bone mass and the breakdown of bone tissue microarchitecture. As a consequence, bone fragility is exacerbated, leading to a higher fracture risk (1, 2). Under the criteria established by the WHO (World Health Organization), osteoporosis affects an estimated 19.7% of the global population (3). Adolescence represents a pivotal period for the accrual of bone mineral, with substantial contributions to the attainment of peak bone mass. In osteological research, the loss of bone mass during adolescence is known to increase the risk of fractures in later life (4, 5). In conclusion, bone metabolism in adolescence exerts a significant influence on the development of osteoporosis in later life (6).
Recent research has increasingly emphasized the significant role of albumin (ALB) and globulin (GLB) in various clinical diseases. Albumin, the primary plasma protein produced by the liver, plays a critical role in regulating osmotic pressure, maintaining fluid balance, and transporting various substances such as hormones, drugs, and fatty acids. Additionally, it is commonly used as a biomarker to evaluate the body’s nutritional status (7). In contrast, globulin is closely associated with the inflammatory response, which is an important trigger for osteoporosis and disorders of bone metabolism (8, 9). In order to assess an individual’s nutritional and inflammatory status more comprehensively, the albumin-globulin ratio (AGR) was developed. This ratio offers a more precise assessment of the body’s inflammatory status and nutritional condition by simultaneously considering changes in both albumin and globulin levels (10). In recent years, AGR has gained widespread use in the study of various clinical diseases, including malignant tumors, acute ischaemic stroke and chronic heart failure (11–17). These studies suggest that changes in AGR may be closely linked to disease prognosis, clinical manifestations, and the overall health of the patient.
Drawing on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), this study sought to evaluate the correlation between AGR and thoracic spine bone mineral density (BMD) in adolescents aged 12–20 years in the United States.
Methods
Study population
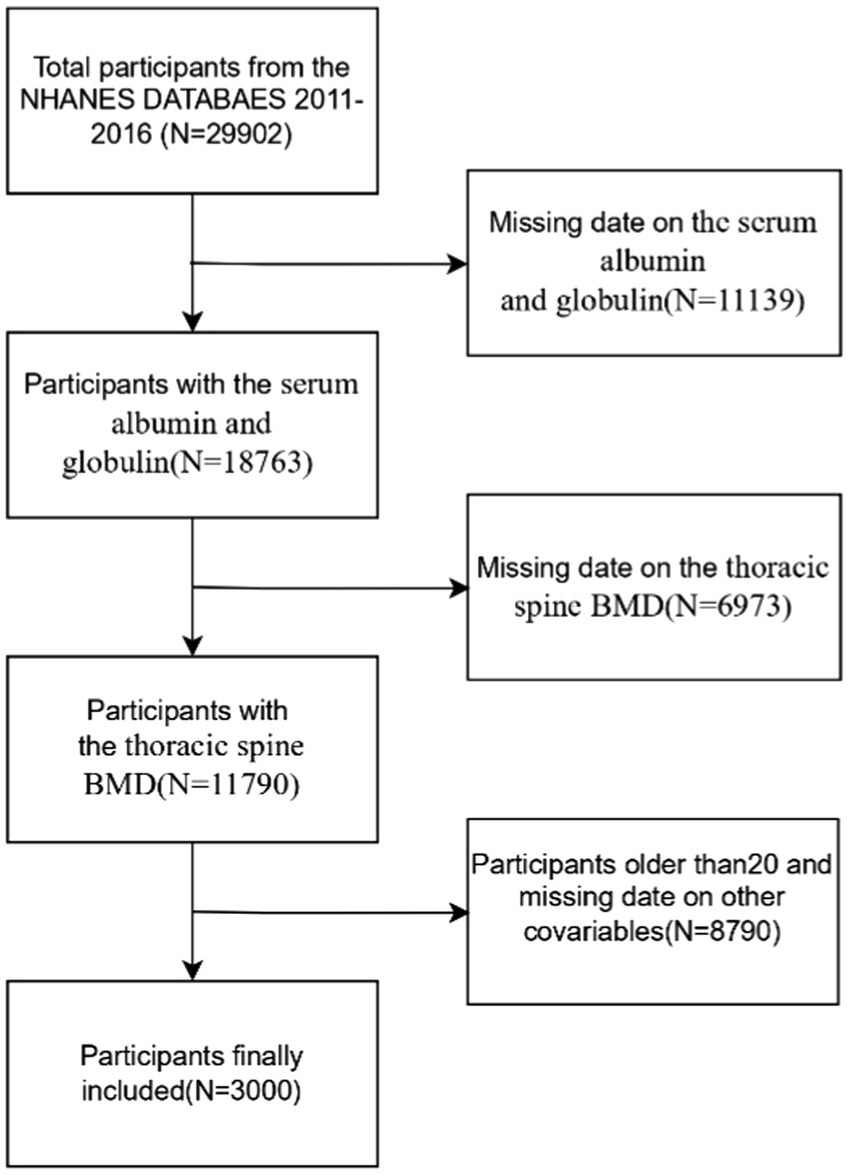
The data used in this study come from NHANES, an ongoing program, which is a national survey that measures the health and nutrition of U. S. population. The survey integrates interviews, clinical assessments, and laboratory analyses to provide comprehensive and reliable health-related data and is a valuable resource for population-based research. The NHANES employs complex sampling design weights to ensure national representativeness. Weights were calculated as the inverse of selection probabilities (base weights), adjusted for non-response, and calibrated via post-stratification to U. S. Census Bureau population benchmarks. For merged multi-cycle data, weights were adjusted proportionally (18). Further details can be found on the official website at https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm. This study uses data from surveys conducted between 2011 and 2016, involving a total of 29,902 participants, and intends to assess the nutritional and health conditions of the U. S. population. Exclusion criteria were applied to remove participants with missing data on albumin and globulin (n = 11,139), thoracic spine BMD (n = 6,973), those older than 20 years (n = 8,466), and individuals with incomplete data on other relevant covariates, including BMI (n = 5), PIR (poverty-to-income ratio) (n = 283), total calcium (n = 13), hypertension (n = 1), diabetes (n = 21), and triglycerides (n = 1). For missing data, we imputed continuous variables using medians or means based on the data distribution and categorical variables using modes. After applying the exclusion criteria, the final sample consisted of 3,000 participants (Figure 1).
Exposure variable
In the present study, AGR was designed as the exposure variable, which is the calculated ratio of serum albumin to serum globulin. The AGR is a comprehensive metric that evaluates both albumin and globulin levels and provides a more precise assessment of the body’s nutritional and inflammatory conditions.
Outcome variable
The primary outcome indicator in this study was thoracic spine bone mineral density. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) has been clinically validated for its safety and is suitable for use in all age groups (including children and the geriatric population). The young and healthy population demonstrate optimal accuracy (coefficient of variation ≤1%) in the measurement of spine and whole-body bone mass (19, 20). Consequently, DXA was utilized to assess bone mineral density in this study.
Covariable
Based on previous studies, other relevant potential confounders were included, including demographic, questionnaire, screening, and laboratory data. The demographic data set includes variables such as age, gender, race, and the poverty-to-income ratio (PIR); questionnaires included diabetes (yes/no), hypertension (yes/no), smoking (yes/no), drinking (yes/no) and Physical activity (yes/no)(whether they met the American Physical activity guideline (at moderate intensity should be done for 150 min a week or, at vigorous intensity, should be performed 75 min/week for adults); screening data included body mass index (BMI) and thoracic spine BMD; and laboratory data included alkaline phosphatase (ALP), serum calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), Alanine transaminase (ALT), Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), albumin (ALB), globulin (GLB), total protein, total protein and triglycerides (TG). Details of how these variables are calculated can be found on the NHANES website.
Statistical analysis
For continuous variables, the mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD) was used, while categorical variables are reported as percentages. In order to facilitate meaningful comparisons, the continuous variables were analyzed using weighted t-tests, while the categorical variables were analyzed using chi-square tests. The results obtained from this analysis are presented as counts (n) and percentages (%). The correlation between AGR and thoracic spine BMD was examined using weighted multiple linear regression analysis across three different models, with the lower quartile serving as the reference group. Model 1 served as the baseline, with no adjustments for any variables; Model 2 adjusted for age, gender, and race; and Model 3 incorporated a broader range of factors, including gender, age, race, PIR, ALP, Ca, P, ALT, AST, BUN, total protein, TG, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, drinking, and BMI. Subsequently, an assessment was conducted to determine the existence of a non-linear relationship between AGR and thoracic spine BMD. This assessment employed a smoothed curve-fitting technique in conjunction with a threshold effects assessment. Subsequent to this, subgroup analyses were performed in the ultimate stage of data analysis. EmpowerStats was employed for the statistical analysis in this study (accessible at http://www.empowerstats.com). Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
Results
Study population features
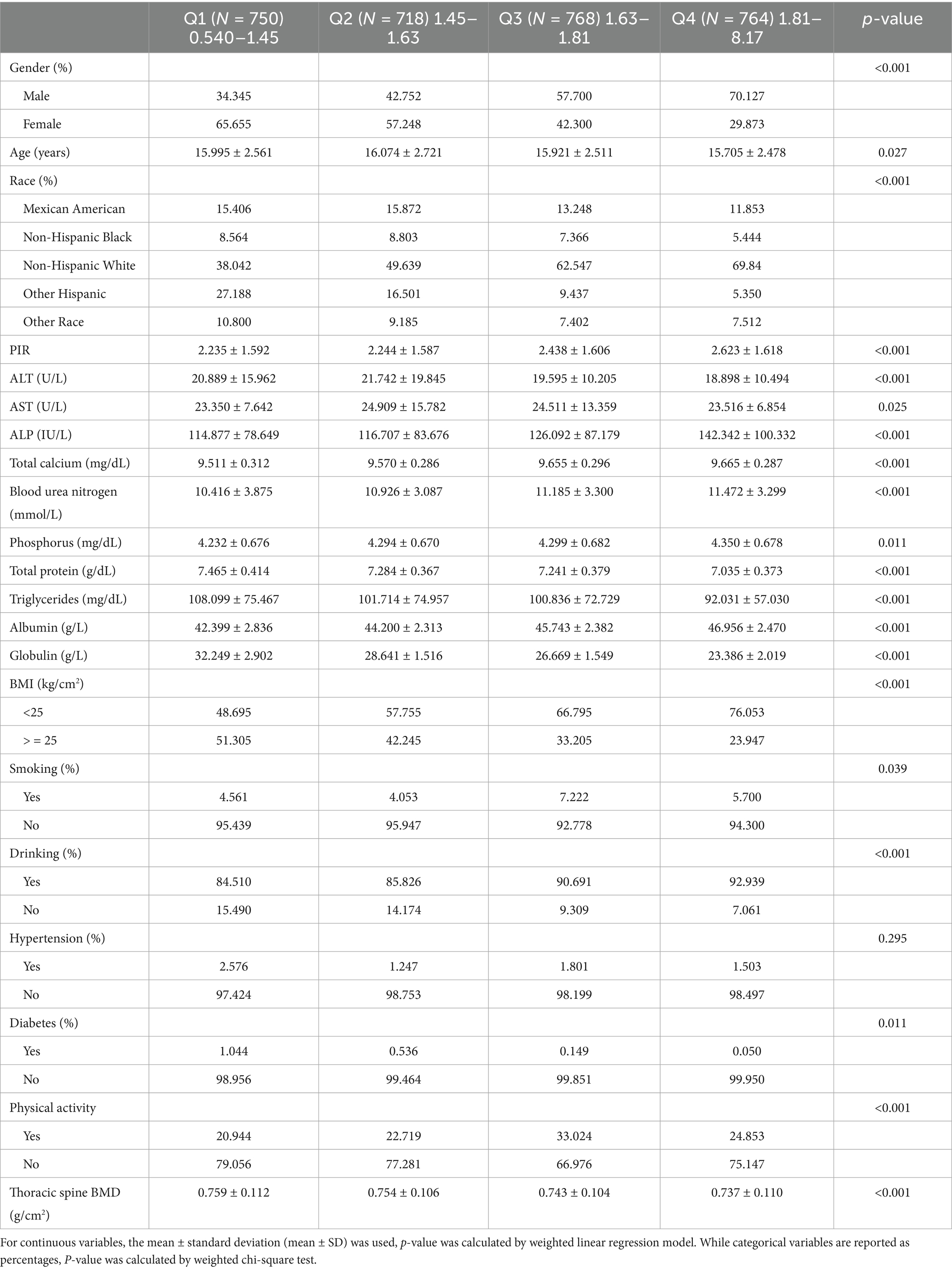
The study included 3,000 participants, with a mean age of 15.69 ± 2.45 years. Of the cohort, 46.9% were female and 53.1% were male, with an average AGR of 1.65 ± 0.30. Among the different groups AGR (quartiles, Q1–Q4), all covariates were statistically significant (p < 0.05), except for hypertension status, which did not achieve statistical significance (p > 0.05) (Table 1).
Connection of AGR with thoracic spine BMD
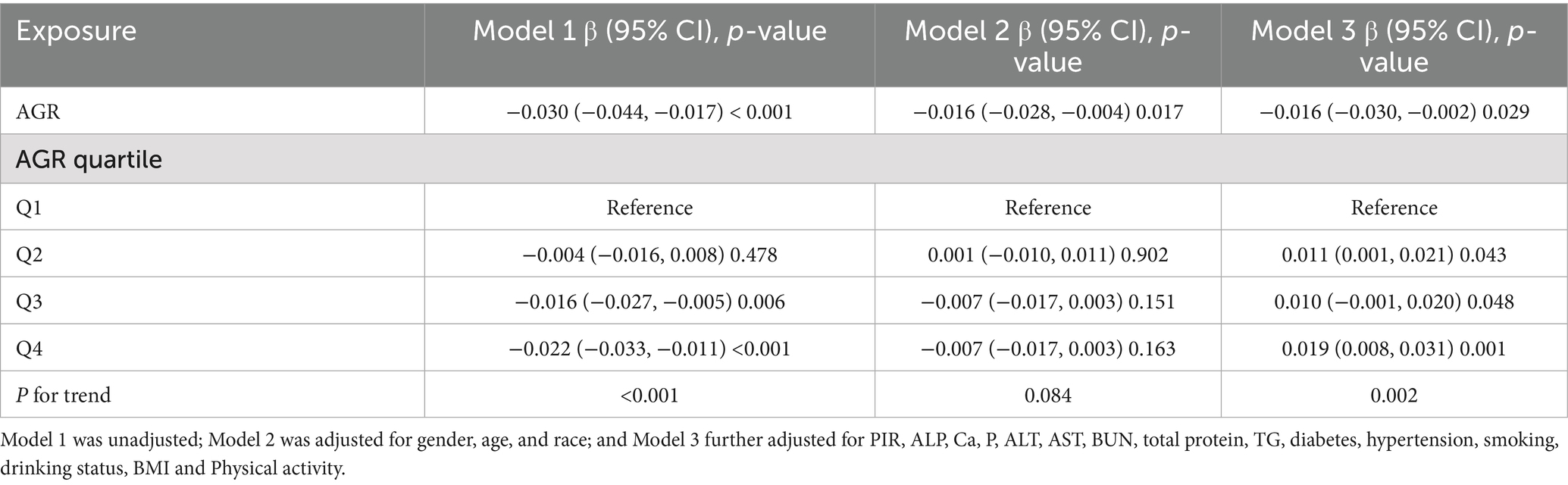
To examine the correlation between AGR and thoracic spine BMD, a weighted multivariate linear regression model was used in this study (Table 2). In Model 1, without adjustment for any confounders, a significant negative correlation was observed between AGR and thoracic spine BMD (β = −0.002, 95%CI: −0.033, −0.011, P < 0.001). In model 2, after adjustment for age, gender, and race, there was no significant correlation between AGR and thoracic spine BMD (β = −0.007, 95% CI: −0.017, 0.003, p = 0.084). In Model 3, after adjustment for all potential confounders, a significant positive correlation was found between AGR and thoracic spine BMD (β = 0.019, 95%CI: 0.007, 0.030, p = 0.002). Specifically, in Model 3, thoracic spine BMD was 0.019 g/cm2 higher in the highest quartile compared to the lowest quartile.
Non-linear relationship between AGR and thoracic spine BMD
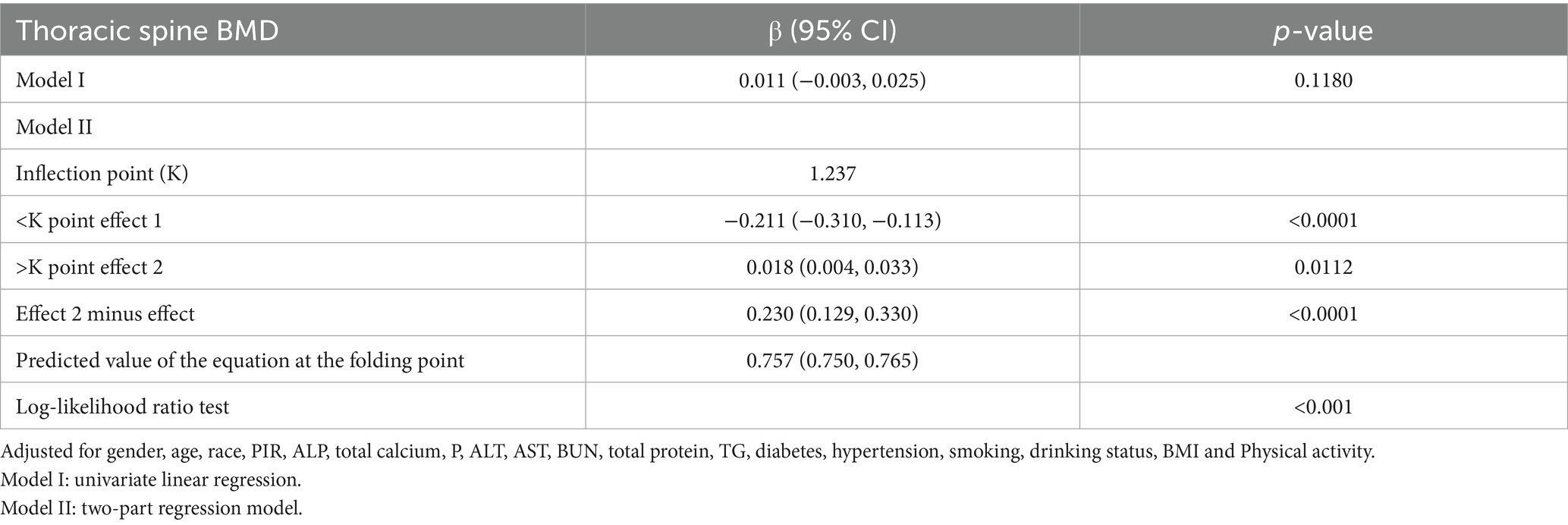
In this study, we used a smoothed curve-fitting technique to further investigate the correlation between AGR and thoracic spine BMD. Figure 2 shows a complex, non-linear U-shaped association between AGR and thoracic spine BMD. To explore this correlation further, a threshold effect analysis was performed using a weighted two-segment linear regression model, with all confounding factors fully adjusted for. An inflection point of 1.237 for AGR was identified in this analysis, with the likelihood ratio test showing a statistically significant p-value of <0.001. Below the AGR threshold of 1.237, each 1-unit increase in AGR was associated with a decrease in thoracic spine BMD of 0.213 g/cm2 (β = −0.213, 95%CI: −0.311, −0.114). Above this threshold, a one-unit increase in AGR was linked to a 0.018 g/cm2 rise in thoracic spine BMD (β = 0.018, 95% CI: 0.004, 0.032) (Table 3).
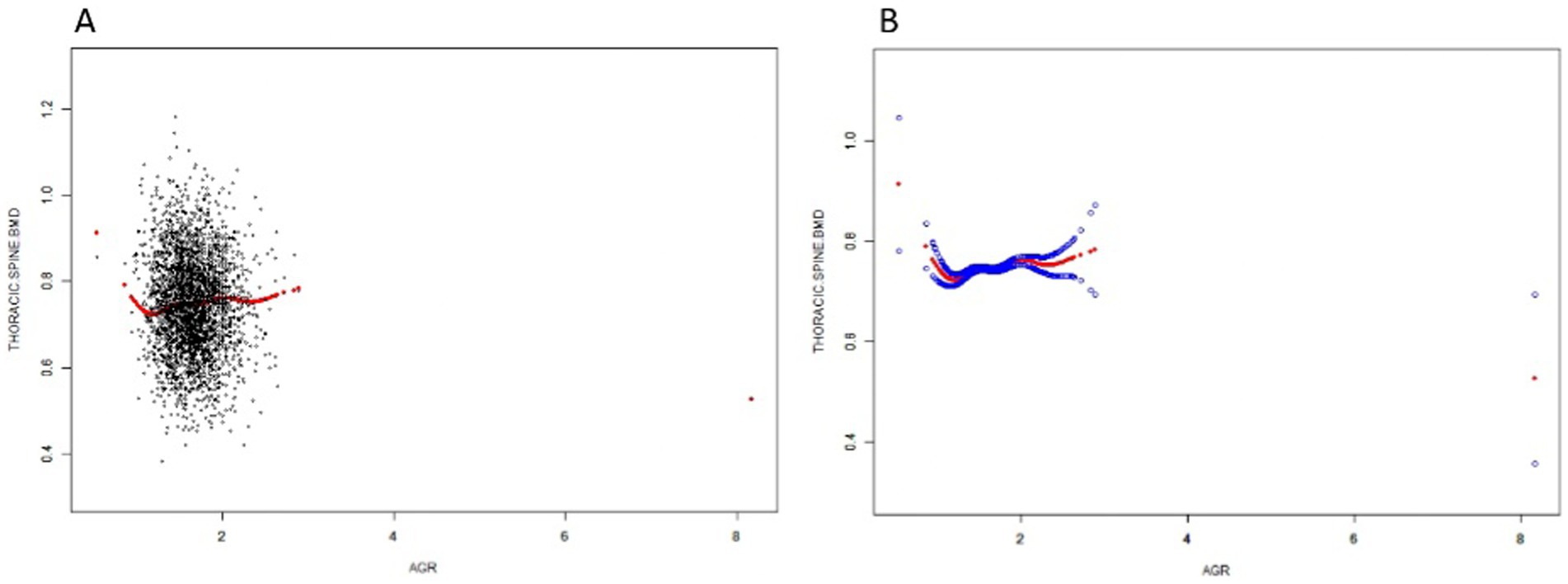
Figure 2. The Relationship between AGR and Thoracic spine BMD. (A) Each black dot on the graph denotes a single sample and the red line represents the fitted line for all participants. (B) The figure shows a smooth curve fit between the variables indicated by the red line. The blue line shows the 95% confidence interval of the fit.
Subgroup analysis
The present study conducted a subgroup analysis in order to examine the relationship between AGR and thoracic spine BMD across various populations. When participants were grouped by age, gender, race, smoking, drinking, hypertension, and diabetes status, no statistically significant interactions were detected across any of the subgroups (Figure 3), further validating the consistency of the role of AGR in adolescents aged 12–20 years.
Discussion
The study sought to evaluate the relationship between AGR and thoracic spine BMD in a sample of adolescents aged 12–20 years residing in the U. S. A cross-sectional study involving 3,000 participants demonstrated a positive correlation between AGR and thoracic spine BMD in a fully adjusted model of weighted multiple linear regression. Curve fitting and threshold effect analyses revealed a non-linear relationship with an inflection point of 1.237. When AGR ≤ 1.237, thoracic spine BMD decreased with increasing AGR. When AGR ≥ 1.237, thoracic spine BMD increased with increasing AGR. Subgroup analyses and interactions showed no significant interactions between the different subgroups.
Earlier research has concentrated on the impact of albumin or globulin on BMD, and this research is the first to explore the connection between the AGR and thoracic spine BMD, establishing it as a pioneering study in the field. This approach integrates nutritional and inflammatory biomarkers to provide a more nuanced understanding of bone health. As demonstrated in numerous preceding studies, albumin plays a pivotal role in maintaining optimal bone health, functioning as an indicator of nutritional status. A large-scale U. S. study demonstrated a notable correlation between lower serum albumin levels and reduced BMD, with the duration of hypoalbuminemia strongly correlating with the severity of BMD deterioration (21). Another study similarly demonstrated that individuals with hypoalbuminemia faced a notably increased risk of developing osteoporosis in comparison with individuals with normal albumin levels (22, 23). In addition, several studies have indicated that low albumin levels may elevate the risk of fracture (22, 24). In contrast, another study found no association between serum albumin and osteoporosis (25). Serum globulin contains a variety of proteins involved in the inflammatory response, such as complement, immunoglobulins, and acute-phase reactive proteins, and have been recognized as reliable indicators of inflammatory status (26, 27). Specifically, serum globulin include: immunoglobulins, proteins of the complement system, and acute phase response proteins [e.g., C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin, and α1-antitrypsin]. A number of studies have indicated that immunoglobulins and complement proteins can exacerbate the onset and progression of osteoporosis by contributing to the inflammatory response and promoting oxidative stress. These factors can subsequently accelerate the onset and progression of osteoporosis through multiple mechanisms, including the promotion of osteoclast activation, the inhibition of osteoclast function, and the alteration of the skeletal microenvironment (28). Several studies have shown that elevated levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) are linked to a reduction in BMD (29, 30); and some studies have found that elevated serum ferritin levels may indicate an increased risk of bone loss (31–33). In contrast to single indicators, AGR takes into account the combined effects of albumin and globulin on BMD, which may reflect not only changes in nutritional status but also inflammatory status in the mid-to long-term (12, 34).
The present study observed a U-shaped relationship between AGR and thoracic spine BMD, which began to decrease as AGR increased and then decreased after reaching the inflection point of AGR 1.237 levels, which reflect nutritional status, decrease during inflammation, while globulin levels increase (35). Total serum protein is predominantly constituted of albumin (approximately 50%) and globulin (approximately 48%). Albumin, a pivotal nutritional assessment index and a negative acute time-phase response protein, exhibits changes in its concentration. These changes can synchronize the nutritional and metabolic status of the body and the degree of inflammatory response. Abnormally low levels of this protein have been observed in a range of clinical conditions, including malnutrition syndromes, hepatic and renal dysfunction, and systemic inflammatory diseases (36). Globulin fractions are primarily constituted of immunoglobulin family and acute phase response proteins, and their biosynthesis is modulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α. In the context of chronic inflammatory pathologies, these proteins exhibit a characteristic increase in concentration, and their dynamic changes can provide a valuable reference point for the clinical assessment of infectious diseases and chronic inflammatory states (37). In cases where the AGR is low, this may be indicative of malnutrition or chronic disease, as lower albumin levels are commonly associated with a poorer nutritional status or inadequate protein synthesis. It has been hypothesized that low albumin levels may result in bone loss. This is due to the fact that inadequate protein synthesis may interfere with the formation of bone matrix. Furthermore, lower AGR has been associated with pathologies such as chronic inflammation and abnormal liver function, which themselves can negatively affect bone metabolism and lead to decreased bone density. As the AGR increases, it is indicative of a gradual improvement in the albumin to globulin ratio, which may reflect improved nutritional status or reduced levels of chronic inflammation. In conclusion, the compensatory increase of globulin, stimulated by inflammatory factors (IL-6, TNF-α, etc.) and the consumptive decrease of albumin, as a negative acute time-phase reactive protein form, establish a dynamic equilibrium. This characteristic inverse fluctuation pattern significantly enhances the specificity of the AGR for the identification of inflammatory versus infectious states. An increase in AGR value is suggestive of the body’s gradual realization of homeostatic reconstruction of inflammation regulation and nutrient metabolism. The restoration of this physiological balance has the capacity to promote the maintenance of a normal bone metabolism microenvironment and the homeostasis of bone density. It is evident that the AGR is of significant clinical value in the evaluation of inflammation-related diseases.
The relationship between albumin levels and BMD and osteoporosis can be explained in several ways. Firstly, albumin has antioxidant capacity (38), and low albumin levels reduce its antioxidant effect, leading to enhanced oxidative stress, which in turn triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage (39, 40), contributes to bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell senescence (41, 42), affects osteogenesis, and increases the risk of osteoporosis; second, low albumin levels may promote osteoclasts through activation of NF-κB pathway differentiation and survival (43, 44), leading to osteolysis and further exacerbating osteoporosis. Finally, low albumin levels may affect the metabolism of bone formation-related proteins and reduce the formation of calcium phosphate apatite crystals, thereby decreasing BMD and increasing fracture risk (45). Globulin, on the other hand, act more through inflammatory states. In chronic inflammatory states, globulin levels rise, and the production of inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) is heightened. TNF-α stimulates osteoclast differentiation, promotes the expression of RANK in osteoclast precursors, and facilitates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis (46–48). IL-6 activates the JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway, which enhances the production of RANKL by stromal cells and osteoblasts. This increase in RANKL stimulates osteoclastogenesis, promoting osteoclast activation (49–51). All of these ultimately promote osteoclast activation, leading to increased bone resorption and decreased BMD.
Limitation and strengths
Several limitations should be considered in this study. Firstly, the cross-sectional design restricts the ability to determine a causal correlation between AGR and thoracic spine BMD. In order to corroborate these findings and elucidate the underlying mechanisms, it is imperative that longitudinal studies are conducted. Second, the study focused only on individuals aged ≤20 years, limiting the applicability of the results to other populations, such as the elderly, who may exhibit different AGR-BMD dynamics. Third, although full adjustment was made for known confounders, it was not possible to exclude the potential influence of unmeasured variables such as genetic factors, physical activity levels, or specific dietary patterns. Fourth, direct indicators of pubertal development (e.g., Tanner staging or bone age) were not systematically recorded in the NHANES data, although we performed sensitivity analyses stratified by age and sex, and these alternative methods may not fully capture individual differences in biological maturity. Finally, as an observational study, it did not explore the biological mechanisms between AGR and BMD, emphasizing the need for experimental studies to better understand these pathways. Despite these limitations, this study has significant strengths. It benefited from a large, diverse, and well-characterized sample, increasing the reliability and robustness of the findings. The analysis included rigorous adjustment for numerous potential confounders to ensure the validity of the observed correlations. Non-linear relationships and saturation effects between AGR and BMD were identified using advanced statistical methods like Smooth curve fitting and threshold effects analysis, offering a more detailed understanding of their connection. In addition, the novel focus of this study on AGR as a combined biomarker of nutritional and inflammatory status provides new insights into the factors that influence bone health. Importantly, these findings highlight the potential of AGR as an early marker for identifying individuals at risk of impaired bone health, especially during adolescence, a critical period for bone development and osteoporosis prevention.
Conclusion
The present study demonstrated a notable positive correlation between AGR and thoracic spine BMD in adolescents, thereby identifying a complex non-linear association between the two. Notably, when AGR is lower than 1.237, thoracic spine BMD decreased with increasing AGR. This study provides a new perspective on the clinical use of AGR as a predictor of BMD, especially in adolescent and young individuals, where lower AGR may indicate potential bone health risks. Changes in AGR may signal trends in BMD changes. Consequently, monitoring AGR in a clinical context may facilitate the early detection of bone quality issues and intervention.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number (s) can be found: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
HY: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YD: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YL: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. PZ: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. LL: Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Discipline Construction of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (XKTJ-XK202404-3).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Correction note
This article has been corrected with minor changes. These changes do not impact the scientific content of the article.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AGR, albumin to globulin ratio; ALB, albumin; GLB, globulin; BMD, bone mineral density; NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; OP, Osteoporosis; WHO, World Health Organization; DXA, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; ALT, Alanine transaminase; ALP, Alkaline phosphatase; AST, Aspartate aminotransferase; P, phosphorus; Ca, serum calcium; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; TG, triglycerides; BMI, body mass index; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor; IL-6, interleukin-6; CRP, C-reactive protein.
References
1. Consensus development conference: diagnosis, prophylaxis, and treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med. (1993) 94:646–50. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90218-e
2. Clynes, MA, Harvey, NC, Curtis, EM, Fuggle, NR, Dennison, EM, and Cooper, C. The epidemiology of osteoporosis. Br Med Bull. (2020) 133:105–17. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldaa005
3. Xiao, PL, Cui, AY, Hsu, CJ, Peng, R, Jiang, N, Xu, XH, et al. Global, regional prevalence, and risk factors of osteoporosis according to the World Health Organization diagnostic criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. (2022) 33:2137–53. doi: 10.1007/s00198-022-06454-3
4. Weaver, CM, Gordon, CM, Janz, KF, Kalkwarf, HJ, Lappe, JM, Lewis, R, et al. The National Osteoporosis Foundation’s position statement on peak bone mass development and lifestyle factors: a systematic review and implementation recommendations. Osteoporos Int. (2016) 27:1281–386. doi: 10.1007/s00198-015-3440-3
5. Zhu, X, and Zheng, H. Factors influencing peak bone mass gain. Front Med. (2021) 15:53–69. doi: 10.1007/s11684-020-0748-y
6. Bonjour, JP, Theintz, G, Law, F, Slosman, D, and Rizzoli, R. Peak bone mass. Osteoporos Int. (1994) 4:S7–S13. doi: 10.1007/BF01623429
7. Abedi, F, Zarei, B, and Elyasi, S. Albumin: a comprehensive review and practical guideline for clinical use. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (2024) 80:1151–69. doi: 10.1007/s00228-024-03664-y
8. Zha, X, Hu, Y, Pang, X-N, Zhu, J-H, Chang, G-L, Li, L, et al. Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) as an independent determinant of bone mineral density (BMD) among Chinese middle-aged and elderly men. Endocrine. (2014) 47:590–7. doi: 10.1007/s12020-013-0155-0
9. Xu, K, Fu, Y, Cao, B, and Zhao, M. Association of sex Hormones and sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Levels with Bone Mineral Density in adolescents aged 12-19 years. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:891217. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.891217
10. Li, J, Zhu, N, Wang, C, You, LP, Guo, WL, Yuan, ZH, et al. Preoperative albumin-to-globulin ratio and prognostic nutritional index predict the prognosis of colorectal cancer: a retrospective study. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:17272. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43391-5
11. Li, J, Wang, Y, Wu, Y, Li, J, and Che, G. Prognostic value of pretreatment albumin to globulin ratio in lung Cancer: a meta-analysis. Nutr Cancer. (2021) 73:75–82. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2020.1737155
12. Xie, H, Zhang, Q, Ruan, G-T, Ge, Y-Z, Hu, C-L, Song, M-M, et al. Evaluation and validation of the prognostic value of serum albumin to globulin ratio in patients with cancer cachexia: results from a large multicenter collaboration. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:707705. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.707705
13. Salciccia, S, Frisenda, M, Bevilacqua, G, Viscuso, P, Casale, P, de Berardinis, E, et al. Prognostic value of albumin to globulin ratio in non-metastatic and metastatic prostate Cancer patients: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1501. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911501
14. Wang, A, Zhang, Y, Xia, G, Tian, X, Zuo, Y, Chen, P, et al. Association of serum albumin to globulin ratio with outcomes in acute ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29:1357–67. doi: 10.1111/cns.14108
15. Niedziela, JT, Hudzik, B, Szygula-Jurkiewicz, B, Nowak, JU, Polonski, L, Gasior, M, et al. Albumin-to-globulin ratio as an independent predictor of mortality in chronic heart failure. Biomark Med. (2018) 12:749–57. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2017-0378
16. Azab, B, Bibawy, J, Harris, K, Khoueiry, G, Akerman, M, Selim, J, et al. Value of albumin-globulin ratio as a predictor of all-cause mortality after non-ST elevation myocardial infarction. Angiology. (2013) 64:137–45. doi: 10.1177/0003319712436577
17. Zeng, M, Liu, Y, Liu, F, Peng, Y, Sun, L, and Xiao, L. Association between albumin-to-globulin ratio and long-term mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease: a cohort study. Int Urol Nephrol. (2020) 52:1103–15. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02453-7
18. Johnson, CL, Dohrmann, SM, Burt, VL, and Mohadjer, LK. National health and nutrition examination survey: sample design, 2011-2014. Vital Health Stat 2. (2014):1–33.
19. Laskey, MA. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and body composition. Nutrition. (1996) 12:45–51. doi: 10.1016/0899-9007(95)00017-8
20. Shepherd, JA, Ng, BK, Sommer, MJ, and Heymsfield, SB. Body composition by DXA. Bone. (2017) 104:101–5. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.06.010
21. Afshinnia, F, Wong, KK, Sundaram, B, Ackermann, RJ, and Pennathur, S. Hypoalbuminemia and osteoporosis: reappraisal of a controversy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 101:167–75. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3212
22. Afshinnia, F, and Pennathur, S. Association of Hypoalbuminemia with Osteoporosis: analysis of the National Health and nutrition examination survey. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 101:2468–74. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-1099
23. Wang, H, Jiang, Q, Yan, J, Yang, J, Sun, J, Wang, Y, et al. Gastrointestinal health and serum proteins are associated with BMD in postmenopausal women: a cross-sectional study. Nutr Metab. (2024) 21:86. doi: 10.1186/s12986-024-00865-1
24. Li, Q, Zhu, M, Liu, X, Tian, C, Li, D, Wang, H, et al. Abnormally low serum albumin levels are associated with abnormal bone mineral density and osteoporotic fractures: a retrospective studies. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2024) 25:888. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08021-9
25. Lunde, AV, Barrett-Connor, E, and Morton, DJ. Serum albumin and bone mineral density in healthy older men and women: the rancho Bernardo study. Osteoporos Int. (1998) 8:547–51. doi: 10.1007/s001980050097
26. Zhou, T, Yu, ST, Chen, WZ, Xie, R, and Yu, JC. Pretreatment albumin globulin ratio has a superior prognostic value in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma patients: a comparison study. J Cancer. (2019) 10:594–601. doi: 10.7150/jca.28817
27. Tani, S, Imatake, K, Suzuki, Y, Yagi, T, and Takahashi, A. Association of aerobic exercise habits with higher albumin-globulin ratio and lower cellular immune-inflammatory markers: implication of the preventive effect of aerobic exercise on atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Heart Vessel. (2025) 40:509–522. doi: 10.1007/s00380-024-02490-7
28. Iantomasi, T, Romagnoli, C, Palmini, G, Donati, S, Falsetti, I, Miglietta, F, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoporosis: molecular mechanisms involved and the relationship with microRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3772. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043772
29. Greendale, GA, Jackson, NJ, Han, W, Huang, MH, Cauley, JA, Karvonen-Gutierrez, C, et al. Increase in C-reactive protein predicts increase in rate of bone mineral density loss: the study of women’s health across the nation. JBMR Plus. (2021) 5:e10480. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10480
30. Berglundh, S, Malmgren, L, Luthman, H, McGuigan, F, and Åkesson, K. C-reactive protein, bone loss, fracture, and mortality in elderly women: a longitudinal study in the OPRA cohort. Osteoporos Int. (2015) 26:727–35. doi: 10.1007/s00198-014-2951-7
31. Peng, P, Xiao, F, Gao, S, Fang, W, Lin, T, He, W, et al. Association between serum ferritin and bone mineral density in US adults. J Orthop Surg Res. (2022) 17:494. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03357-1
32. Babaei, M, Bijani, A, Heidari, P, Hosseini, SR, and Heidari, B. Serum ferritin levels and bone mineral density in the elderly. Caspian J Intern Med. (2018) 9:232–8. doi: 10.22088/cjim.9.3.232
33. Lu, M, Liu, Y, Shao, M, Tesfaye, GC, and Yang, S. Associations of Iron intake, serum Iron and serum ferritin with bone mineral density in women: the National Health and nutrition examination survey, 2005-2010. Calcif Tissue Int. (2020) 106:232–8. doi: 10.1007/s00223-019-00627-9
34. Maeda, S, Takeya, Y, Oguro, R, Akasaka, H, Ryuno, H, Kabayama, M, et al. Serum albumin/globulin ratio is associated with cognitive function in community-dwelling older people: the septuagenarians, octogenarians, nonagenarians investigation with centenarians study. Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2019) 19:967–71. doi: 10.1111/ggi.13751
35. Vincent, J, Dubois, M-J, Navickis, RJ, and Wilkes, MM. Hypoalbuminemia in acute illness: is there a rationale for intervention? A meta-analysis of cohort studies and controlled trials. Ann Surg. (2003) 237:319–34. doi: 10.1097/01.SLA.0000055547.93484.87
36. Soeters, PB, Wolfe, RR, and Shenkin, A. Hypoalbuminemia: pathogenesis and clinical significance. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2019) 43:181–93. doi: 10.1002/jpen.1451
37. Gabay, C, and Kushner, I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med. (1999) 340:448–54. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199902113400607
38. Sastre-Oliva, T, Corbacho-Alonso, N, Rodriguez-Sanchez, E, Mercado-García, E, Perales-Sanchez, I, Hernandez-Fernandez, G, et al. Albumin redox modifications promote cell calcification reflecting the impact of oxidative status on aortic valve disease and atherosclerosis. Antioxidants. (2024) 13:108. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010108
39. Barzilai, A, and Yamamoto, K. DNA damage responses to oxidative stress. DNA Repair (Amst). (2004) 3:1109–15. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.03.002
40. Passos, JF, Saretzki, G, and von Zglinicki, T. DNA damage in telomeres and mitochondria during cellular senescence: is there a connection? Nucleic Acids Res. (2007) 35:7505–13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm893
41. Bourdon, E, Loreau, N, Lagrost, L, and Blache, D. Differential effects of cysteine and methionine residues in the antioxidant activity of human serum albumin. Free Radic Res. (2005) 39:15–20. doi: 10.1080/10715760400024935
42. Mijiritsky, E, Gardin, C, Ferroni, L, Lacza, Z, and Zavan, B. Albumin-impregnated bone granules modulate the interactions between mesenchymal stem cells and monocytes under in vitro inflammatory conditions. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. (2020) 110:110678. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110678
43. Morgan, MJ, and Liu, Z. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Res. (2011) 21:103–15. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.178
44. Abu-Amer, Y. NF-kappaB signaling and bone resorption. Osteoporos Int. (2013) 24:2377–86. doi: 10.1007/s00198-013-2313-x
45. Fisher, A, Srikusalanukul, W, Fisher, L, and Smith, PN. Lower serum P1NP/betaCTX ratio and hypoalbuminemia are independently associated with osteoporotic nonvertebral fractures in older adults. Clin Interv Aging. (2017) 12:1131–40. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S141097
46. Kitaura, H, Zhou, P, Kim, HJ, Novack, DV, Ross, FP, and Teitelbaum, SL. M-CSF mediates TNF-induced inflammatory osteolysis. J Clin Invest. (2005) 115:3418–27. doi: 10.1172/JCI26132
47. Kitaura, H, Kimura, K, Ishida, M, Kohara, H, Yoshimatsu, M, Takano-Yamamoto, T, et al. Immunological reaction in TNF-alpha-mediated osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo. Clin Dev Immunol. (2013) 2013:181849. doi: 10.1155/2013/181849
48. Weitzmann, MN, Cenci, S, Rifas, L, Brown, C, and Pacifici, R. Interleukin-7 stimulates osteoclast formation by up-regulating the T-cell production of soluble osteoclastogenic cytokines. Blood. (2000) 96:1873–8. doi: 10.1182/blood.V96.5.1873
49. Girasole, G, Passeri, G, Jilka, RL, and Manolagas, SC. Interleukin-11: a new cytokine critical for osteoclast development. J Clin Invest. (1994) 93:1516–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI117130
50. Yoshitake, F, Itoh, S, Narita, H, Ishihara, K, and Ebisu, S. Interleukin-6 directly inhibits osteoclast differentiation by suppressing receptor activator of NF-kappaB signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:11535–40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607999200
51. Palmqvist, P, Persson, E, Conaway, HH, and Lerner, UH. IL-6, leukemia inhibitory factor, and oncostatin M stimulate bone resorption and regulate the expression of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand, osteoprotegerin, and receptor activator of NF-kappa B in mouse calvariae. J Immunol. (2002) 169:3353–62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.6.3353
Keywords: albumin to globulin ratio (AGR), bone mineral density (BMD), osteoporosis, NHANES, adolescent
Citation: Yan H, Yang J, Dai Y, Li Y, Zhang P and Li L (2025) The association between the albumin to globulin ratio and thoracic spine bone mineral density in adolescents: NHANES 2011–2016. Front. Nutr. 12:1560013. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1560013
Edited by:
Owen Kelly, Sam Houston State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Tsutomu Nakashima, Nagoya University, JapanHiroya Ohta, Hokkaido University of Science, Japan
Xuchang Zhou, Beijing Sport University, China
Louisa Bechohra, University of Science and Technology Houari Boumediene, Algeria
Copyright © 2025 Yan, Yang, Dai, Li, Zhang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liuyan Li, MTI0Mjg3NjgzQHFxLmNvbQ==; Peng Zhang, emhhbmdwZW5nODIwMzEwQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
 Haoyu Yan
Haoyu Yan Jie Yang2†
Jie Yang2†