- 1Institute of Food and Strategic Reverse, Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, Nanjing, China
- 2School of Economics and Management, Huizhou University, Huizhou, China
- 3College of Economics, Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, Nanjing, China
Diet serves as the primary source of nutrition, and dietary quality determines individuals’ nutritional status. Poor dietary quality may result in malnutrition such as undernutrition and overnutrition. This study examines the association between women’s educational attainment and rural household dietary quality and the heterogeneity in this association when accounting for the employment status of male and female household heads. We use dietary intake data for 2,069 households from the first round of China Rural Revitalization Survey (2020) and conceptualize dietary quality using the Diet Balance Index (DBI). Multiple linear regression indicates that a one-standard-deviation increase in women’s years of education reduces dietary imbalance by 3.65%, overconsumption by 6.51%, and underconsumption by 2.09%. Specifically, higher education attainment is associated with less inadequate consumption of milk and fish and more balanced meat intake in rural households. Heterogeneity analysis shows that the positive effect of women’s education on dietary quality is stronger when women engage in on-farm employment, while it is more pronounced in households where men are employed in off-farm work. The findings of this research provide theoretical support for improving the nutritional status of rural residents in China and other developing regions by allocating more educational resources and enhancing access to education for rural women.
1 Introduction
Over the past 4 decades since major economic and social reforms, the dietary quality of rural residents in China has continuously improved (1, 2). However, rural residents still face the dilemma of low dietary quality stemming from an irrational dietary structure. First, rural residents have insufficient dietary diversity. Data from 2,069 households in the 2020 China Rural Revitalization Survey (CRRS) show that a large proportion of rural households did not consume milk (60%), beef and mutton (73%), fish (49%), soybeans (48%), and chicken (34%). Second, compared with urban residents, there are still significant urban–rural differences in dietary quality. Rural residents have higher levels of both insufficient and excessive dietary intake. For example, their intake of vegetables, fish and shrimp, milk, and soybeans remains low, while cereal intake is excessive (3). Third, compared with the recommended dietary pattern outlined in the Chinese Dietary Guidelines 2016 (CDG 2016) (a guideline for a healthy diet released by the National Health Commission of China), most rural residents in China consume more animal meat and less aquatic products and milk. For example, in 2020, the per capita intake of livestock and poultry meat among rural residents was 124 g/day, exceeding the recommended amount of 40–75 g/day, whereas the per capita milk intake was 23 g/day, falling below the recommended 300–500 g/day. Overall, the diversity, moderation, and balance of dietary quality among rural residents in China are inadequate.
Dietary quality, a key determinant of individual nutritional intake, is directly related to their nutritional and health status. Poor dietary quality increases the likelihood of malnutrition—including micronutrient deficiencies and overnutrition associated with overweight and obesity—thereby posing risks to health and wellbeing. For instance, low dietary quality increases the risk of dietary-related chronic diseases (4, 5). Thus, implementing effective measures to improve dietary quality is not only critical for enhancing the nutritional status of rural residents but also contributes to reducing household health maintenance costs in rural China.
Studies in the literature have found that dietary quality in China and other developing countries is directly linked to increases in household income (6, 7), food consumption habits of rural residents (8, 9), agricultural production diversification and rural food market development (10–12), as well as government intervention policies such as government transfer payment policies (13). Among these, education is one factor that appears to have a fundamental influence on dietary quality of households (14–20). Because members of higher educational attainment tend to know more about food nutrition (21, 22), they are also more inclined to healthy dietary habits (23).
Other studies have examined the role of information processing channels (24), the adoption of health-promoting behaviors (25), and perceived control (17) in the relationship between educational attainment and dietary quality. People of higher educational attainment would adopt healthy behaviors such as conscious control of salt, sugar, and oil incorporation to improve dietary quality. In addition to income and the price of goods, consumer decisions are influenced by social class. Social epidemiologists have argued that education levels enable people to rise up the social class hierarchy, which in turn gives them more conviction and a higher degree of self-control in their lives. This feeling of control is reflected in the higher quality of their diets.
Nevertheless, these studies have not adequately addressed whether educational attainment helps narrow the gap between actual dietary pattern and recommended balanced diets in China Food Pagoda 2016 (CFP 2016). Different food varies in nutrient composition and beneficial components. Insufficient intake of specific food groups may affect health by reducing the intake of essential micronutrients, whereas excessive consumption often leads to caloric surpluses, increasing the risk of health issues such as obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, only a balanced diet can optimally meet the body’s energy and nutrient requirements. Thus, to accurately reflect the nutritional and health status of rural Chinese residents, this study employs the Chinese Dietary Balance Index (DBI_16) to comprehensively evaluate the dietary quality.
On the other hand, the moderating effect of employment status (i.e., non-farm employment vs. on-farm employment) on the relationship between educational attainment and dietary quality has been rarely discussed. Within traditional household labor division framework, women mainly play the role of caring for family members in rural China. They tend to take more responsibility for food selection and cooking compared to men. However, when rural women engage in non-farm work, the time available for household care tends to decrease. Therefore, it is essential to account for women’s employment status when examining the relationship between educational attainment and dietary quality.
In this study, we use dietary intake data for 2,069 households from the first round of China Rural Revitalization Survey (2020) and measure dietary quality using the Diet Balance Index (DBI), to estimate the association between women’s educational attainment and dietary quality. The study has three goals: first, to apply the adjusted Chinese Dietary Balance Index-16 (DBI_16) to assess the dietary quality of rural households in China in 2020; second, to examine whether an increase in women’s educational attainment contributes to the enhancement of dietary quality; third, to estimate the heterogeneous impact of women’s educational attainment on dietary quality among women and men with diverse employment statuses within the same household. It is meaningful to discuss the relationship between women’s educational attainment and household dietary quality. Unlike other established demographic traits, education is more influenced by later policy intervention.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Study setting: the rural China context
China’s agricultural production is undergoing a transformation from traditional fragmented operations toward large-scale, specialized production systems. The number of specialized rice/wheat farms and commercial fruit–vegetable cooperatives has grown rapidly. According to the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China, the number of farmers engaged in large-scale operations (i.e., individual operation areas exceeding 8 acres) exceeds 3 million, with their total cultivated land area surpassing 66 million acres in 2022.
By 2023, the proportion of large-scale pig farms (≥500 head) reached 68%, commercial layer and broiler farms (≥20,000 birds) accounted for over 80%, and large-scale dairy farms (≥100 cows) represented 76% of total operations.
At the same time, with the advancement of marketization, rural residents in China have largely overcome the constraints of agricultural production on food consumption, gradually shifting from a self-sufficiency-based consumption pattern to a market-oriented pattern. Data from CRRS (2020) show that only 20% of rural households consume self-grown rice, with 80% relying on market purchases; 13% consume self-grown wheat, while the remaining 87% obtain wheat exclusively through markets. The commercialization rate is notably higher for meat products, with 91% of pork consumption sourced from markets, compared to 55% for vegetables. Notably, 45% of rural households still maintain the traditional practice of cultivating vegetables in their backyard for self-consumption.
The dietary pattern in most regions of China is dominated by plant food, supplemented by animal products. Staple food remains the primary source of dietary energy for rural residents in China, but the consumption has been declining annually. As income increases, rural residents tend to consume more animal products, particularly meat.
In general, with the transformation of China’s agriculture from self-sufficiency to marketization and the continuous improvement of rural residents’ income, the food sources of rural residents have become increasingly dependent on the market. The development of the rural food market has enriched rural residents’ food consumption choices and improved their dietary diversity. However, it is weakly associated with dietary quality, i.e., nutrient adequacy. One reason is that the consumption of different food groups may deviate from the recommended dietary pattern in CFP 2016. When such deviations are significant, dietary diversity may weaken the potential association with micronutrient adequacy. In other words, “food accessibility” does not necessarily equate to “buying appropriately.”
2.2 Research hypothesis
“Food accessibility” does not necessarily equate to “buying appropriately.” Conversely, education serves to enhance dietary quality by improving cognitive capabilities and income levels. Previous studies have demonstrated that individuals with higher educational attainment are more likely to acquire knowledge about food nutrition (21, 22) and are more prone to adopting healthy eating habits (13). Education empowers individuals to ascend the social class hierarchy, which in turn promotes greater self-confidence and self-control in life (16). For instance, women with higher education exhibit a higher dietary quality compared to those with lower education levels due to their ability to regulate food choices for themselves and their families (17).
In traditional Chinese families, women typically take on the primary responsibility for food selection and preparation, acting as the crucial decision-makers in household food procurement and cooking. Consequently, women have a more direct impact on household dietary quality. Based on the empirical evidence presented above, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H1: An increase in women’s educational attainment contributes to the improvement of rural household dietary quality.
The correlation between women’s educational attainment and dietary quality varies by the employment statuses of male and female household heads. Notably, within households where men engage in off-farm work, the impact of women’s educational attainment on household dietary quality is more significant. This may be attributed to the fact that men’s off-farm or part-time employment increases off-farm income, thereby expanding families’ available food choices (26). In addition, men working away from home enhance women’s empowerment (27), endowing them greater decision-making authority over household food consumption (28–30).
Conversely, within households where women engage in on-farm work, the influence of women’s educational attainment on household dietary balance is more pronounced. This may be attributed to the fact that rural women, as primary caregivers, engaging in off-farm or part-time farming employment away from home will reduce the time available for family care (31). Under such circumstances, female heads of household who work away from home find it difficult to improve household dietary quality (32–34). It is evident that women engaged in on-farm work strengthen the impact of women’s educational attainment on household dietary quality. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H2: The positive effect of women’s education on dietary quality is more pronounced when women engage in on-farm employment, whereas this effect is stronger in households where men are employed in off-farm work.
2.3 CRRS dataset
The China Rural Revitalization Survey (CRRS) is an ongoing national survey on agriculture, rural areas, and rural residents, implemented by the Rural Development Institute Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. The survey was conducted every 2 years starting from 2020. The data cover 300 villages and 3,833 rural households across 10 provinces of China (i.e., Guangdong, Zhejiang, Shandong, Anhui, Henan, Heilongjiang, Guizhou, Sichuan, Shaanxi, and Ningxia). These provinces include the eastern, central, western, and northeastern regions, and the well-developed region and the poor region. The currently released data are from the 2020 survey round.
The survey provides sufficient data for our study. We focus on the total amount of food consumed by the permanent household population through all channels (i.e., purchasing, granting, and self-planting), as well as data related to the basic information of household members (gender, age, educational attainment and employment status, etc.), net income of the rural household, health behaviors, and the basic conditions of the village.
Since family members include the elderly, children and adults, people of different ages, genders and activity levels have different food requirements. It is therefore customary in international studies to express the number of persons in a population in terms of its equivalent in adult males (or “consumption units”) (35). Many different systems are used in effecting this conversion. In this study, an adult man engaged in light physical activity (whose energy requirement is usually set as a standard value, e.g., 2,250 kcal/day) is taken as the reference standard, and the food consumption of other family members is converted into the consumption equivalent to that of this standard adult man, and this converted amount is called adult equivalent (36). Then, dividing the total household consumption by the number of adult equivalent is called the per capita food consumption of each family.
In this study, samples with daily caloric intake below 800 kcal or above 10,000 kcal were excluded, along with those containing missing data. Following these exclusions, data from 2,069 rural households were retained for analysis.
2.4 Empirical model
The impact of women’s educational attainment on dietary quality can be modeled as follows:
where refers to dietary balance index indices of household i in year 2020, including three indicators of diet quality distance (DQD), high bound score (HBS), and low bound score (LBS); refers to educational attainment of women head of household i; refers to all other variables, including individual and household characteristics (e.g., women’s occupation, men’s occupation, per capita net income, household size, and ratio of elderly and children) and village characteristics (level of village distribution, distance between the village committee and the county government, and the terrain of the village).
In addition, we investigate the heterogeneous effects of women’s education attainment on household dietary quality across subgroups: households where female heads engage in on-farm work at home, and households where male heads are employed in off-farm work.
2.5 Measurement of key variables
2.5.1 Dietary quality
We employed the Revised Dietary Balance Index-16 [DBI_16, (3)] to evaluate dietary quality by quantifying the deviation between residents’ dietary patterns and the recommended patterns according to Chinese Dietary Guidelines 2016 (CDG 2016) and China Food Pagoda 2016 (CFP 2016). The DBI_16 indicator evaluates the balance degree of diet through the consumption of foods such as cereals (grains, potatoes, and beans), vegetables, meat (pork, chicken, beef, and mutton), eggs, dairy, and fish. Specifically, each food item receives score “0” if the real consumption is within the recommended consumption interval, and it shows that the intake of this food group is reasonable. The sore is positive if the real consumption is higher than the recommended consumption, and the score increased “1” when real consumption increased a certain number of grams. The sore is negative if the real consumption is lower than the recommended consumption, and the score decreased “1” when real consumption decreased a certain number of grams. Then, the positive scores are summed up as the High Bound Score (HBS), which reflect the degree of dietary overconsumption. The absolute values of negative scores are summed up as the Low Bound Score (LBS), which reflected the degree of dietary underconsumption. Finally, the positive scores and the absolute values of negative scores of six food groups are summed up as Diet Quality Distance (DQD), with a score of “0” indicating a balanced diet and a higher score indicating a greater degree of dietary imbalance.
2.5.2 Women’s educational attainment
The primary explanatory variable of women’s educational attainment is measured by years of schooling completed. 0 represents no schooling. 6 represents graduation from primary school. 9 represents graduation from junior high school. 12 indicates graduation from high school, secondary school, and vocational school. 15 indicates graduation from junior college. 16 represents the education level is undergraduate degree. In the sample, female household heads have an average of 6 years of schooling (primary school level) and a maximum of 16 years (undergraduate degree).
2.5.3 Employment status of men and women
The employment status of men and women is measured as three categories: full-time farming, off-farm employment, and concurrent employment (concurrent employment refers to farmers returning to their rural hometowns for agricultural production during busy farming seasons and seeking non-agricultural employment during slack agricultural periods). We assign a value of 1 to denote off-farm employment or concurrent employment and 0 for full-time farming.
2.5.4 Other covariates
We measure the healthy eating behaviors with the questions of the questionnaire: “whether consciously learning health or health knowledge,” “whether consciously controlling sugar intake,” “whether consciously controlling salt intake,” “whether consciously controlling the intake of edible oil,” and “whether consuming health products.” The score for health behavior is the sum of the number of the above health behaviors. If there is one health behavior, the score is 1, and so on.
The variable of information access via online platforms is scored according to the question in the survey questionnaire: “If you have daily needs, can you obtain relevant information through your mobile phone or network at any time by yourself?” If the answer is “Completely,” the score is 1; if it is “Sometimes,” the score is 0.5; and if it is “Rather difficult,” the score is 0.
The per capita net income of rural households is the net income of rural household divided by the total household size in 2019. The income includes planting, livestock, forestry and fruit farming, fishing, non-agricultural operating, wage, property, and transfer. We also control individual characteristics, household characteristics, and village characteristics. We also control the provincial dummy variables. Table 1 provides a brief summary and definition of all variables.
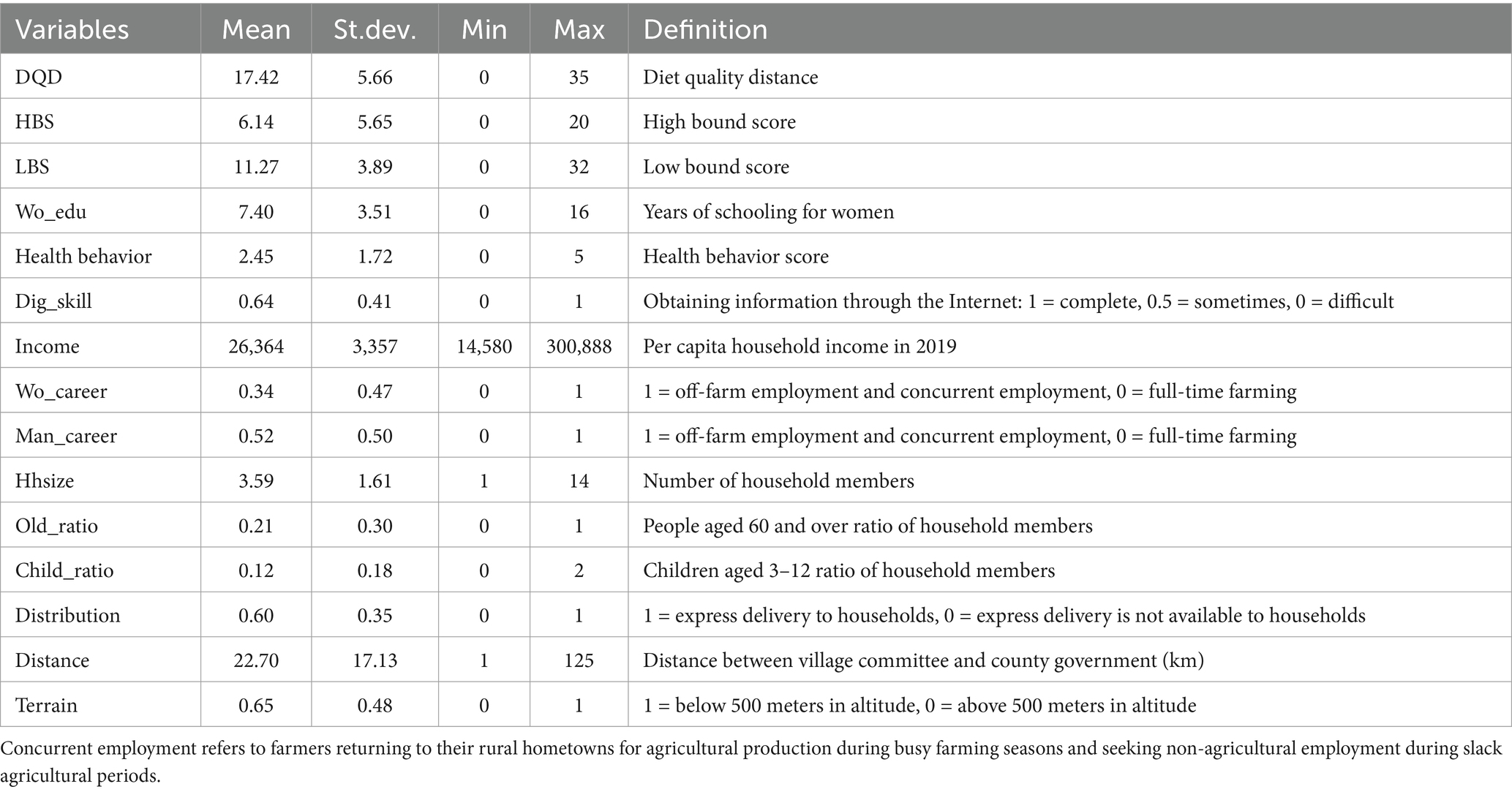
Table 1. Descriptive statistics and variable definitions (N = 2,067 households; Data source: CRRS 2020).
3 Results
3.1 Dietary quality of Chinese rural households
We first present the DBI_16 scores of different food groups of Chinese rural households in 2020, which reflected the balance degree of various food intakes. The results are presented in Figure 1. Our data reveal that Chinese rural households have an overconsumption of cereals and meats and a severe deficient intake of dairy products and fish. Overall, cereals, dairy products, and fish present a moderate dietary imbalance, while meat and eggs exhibit a low-level dietary imbalance. The intake of vegetables is relatively appropriate.
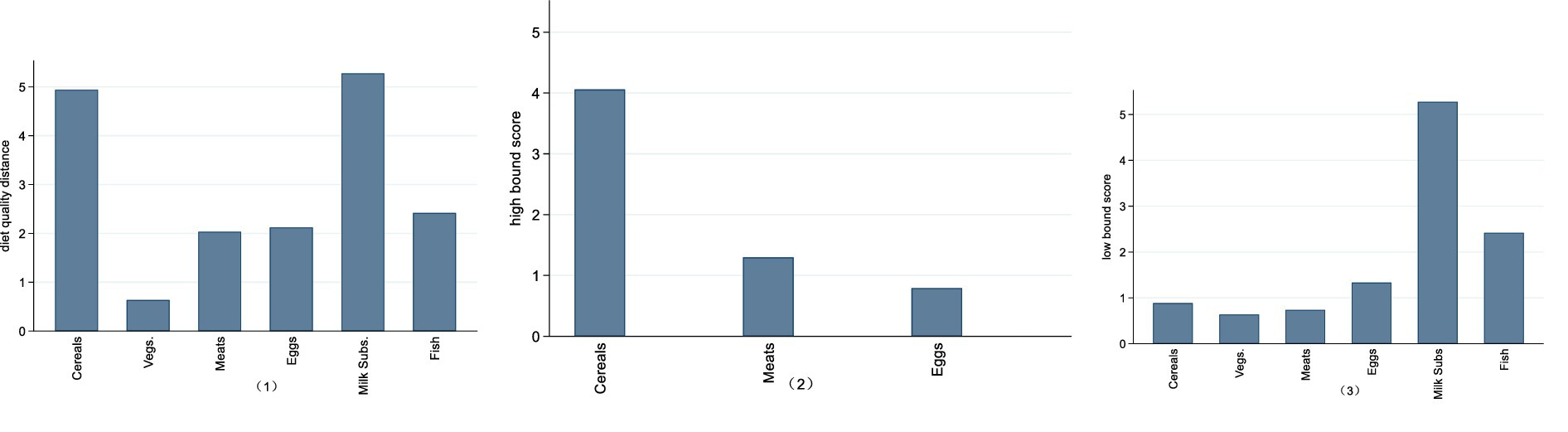
Figure 1. DBI_16 scores of different food groups of Chinese rural households in 2020. (1) The horizontal axis represents different food groups, and the vertical axis represents the DBI_16 score. The Diet Quality Distance comprehensively reflects issues in dietary patterns. The High Bound Score indicates the degree of dietary overconsumption, while the Low Bound Score reflects the degree of dietary underconsumption. All three indicators are derived from China Food Pagoda (CFP 2016). A higher score signifies a greater degree of dietary imbalance and lower dietary quality. (2) In this figure (2), there are no high bound scores for vegetables, dairy products and fish.
3.2 Impact of women’s educational attainment on the dietary quality of Chinese rural households
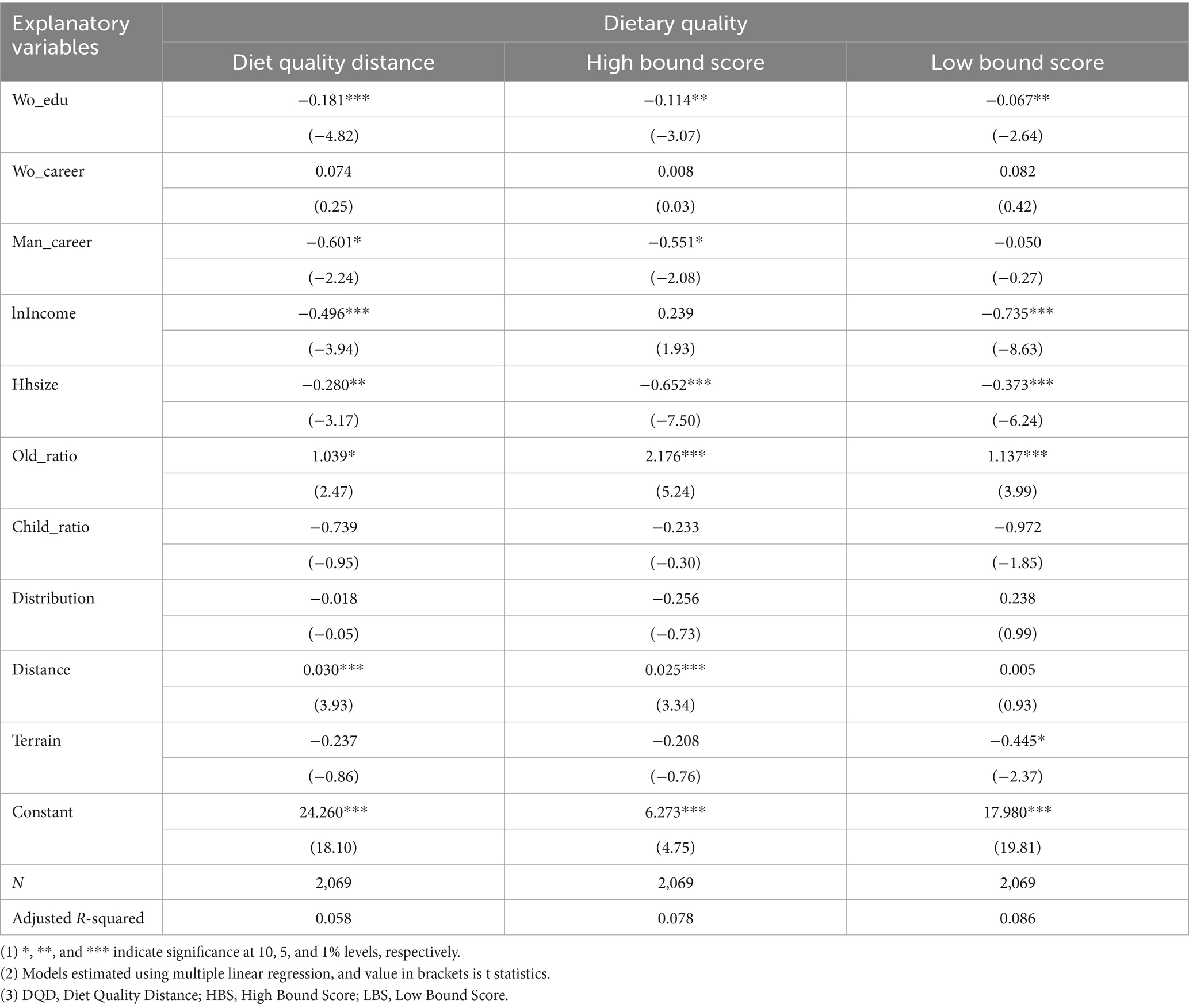
Table 2 presents the test results regarding the impact of women’s educational attainment on the dietary quality of households. With the inclusion of all controls in the model, we find that a one-standard-deviation increase in women’s years of education reduces dietary imbalance by 3.65%, overconsumption by 6.51%, and underconsumption by 2.09%. The research outcomes indicate that women’s educational attainment promotes the dietary quality of rural households in China.
We further estimate the impact of women’s educational attainment on the DBI for each food group separately, with the results presented in Table 3. We observe that women with a higher level of education tend to reduce cereal consumption, and the degree of insufficient intake increases. This suggests that better-educated women prioritize family members’ weight management and are concerned that consuming staple foods such as rice and noodles may contribute to obesity. Conversely, highly educated women are more likely to choose a more diverse set of foods, incorporating more meat, dairy products, and fish, thereby decreasing reliance on traditional staple foods.
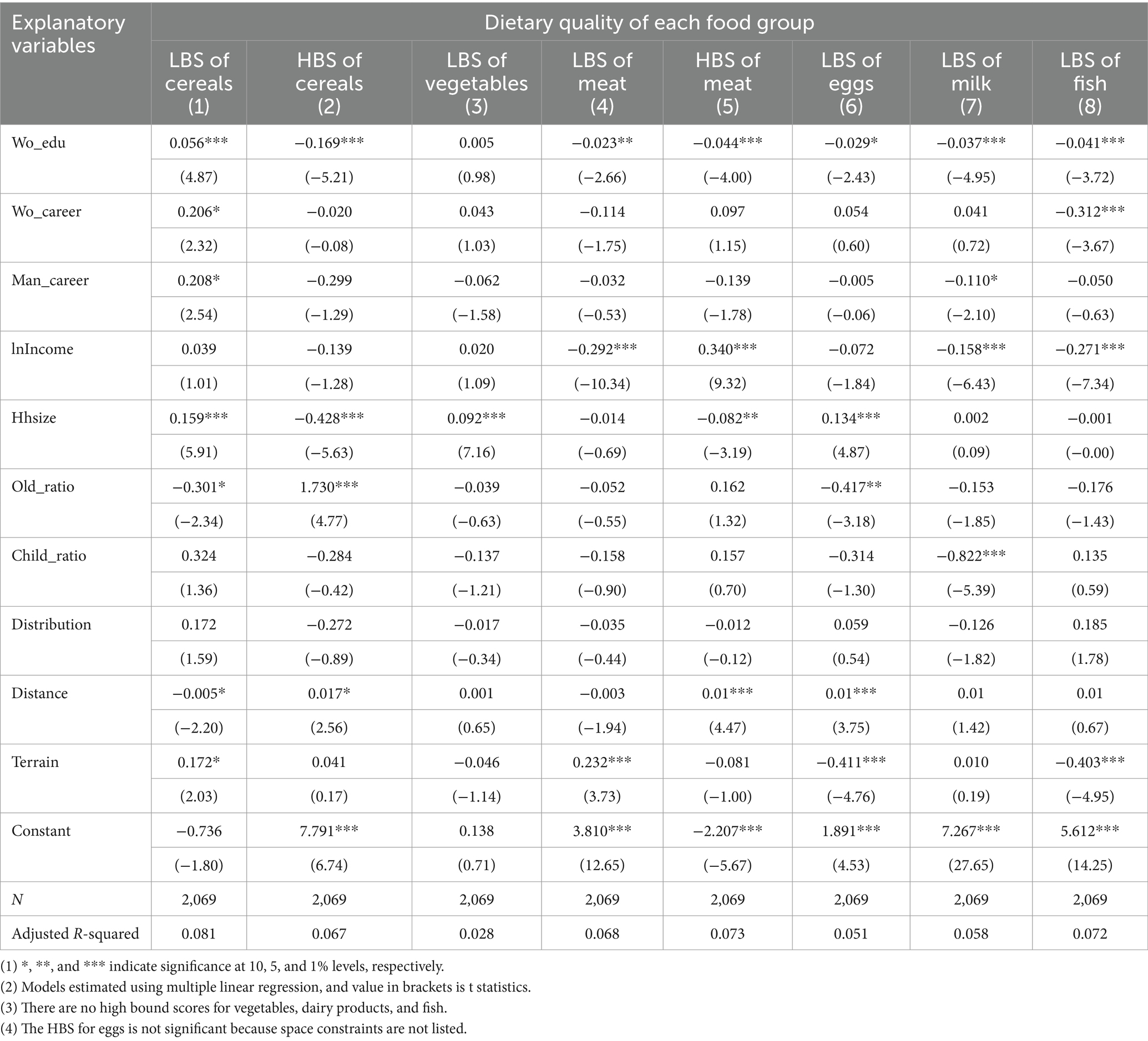
Table 3. Impact of women’s educational attainment on the dietary quality of each food group separately.
However, improvement in women’s educational attainment can effectively reduce the severity of insufficient intake of dairy products and fish in rural households. Specifically, a one-standard-deviation increase in women’s educational attainment is associated with a 2.46% decrease in dairy insufficiency and a 5.96% decrease in fish insufficiency, relative to the sample mean. Regarding balanced meat consumption, the same increase in educational attainment leads to a 10.98% reduction in under-consumption and an 11.92% reduction in over-consumption of meat.
3.3 Heterogeneous effects
We further conduct grouped regression analyses based on the employment status of male and female household heads, aiming to examine the heterogeneous effects of women’s educational attainment on dietary quality.
3.3.1 By the employment status of men
First, we divide the total sample into two subgroups based on male household heads’ employment status: off-farm employment (including part-time farming) and full-time farming. The results are presented in Table 4. We find that the effect of women’s educational attainment on dietary quality is more significant in households where male heads engage in off-farm work.
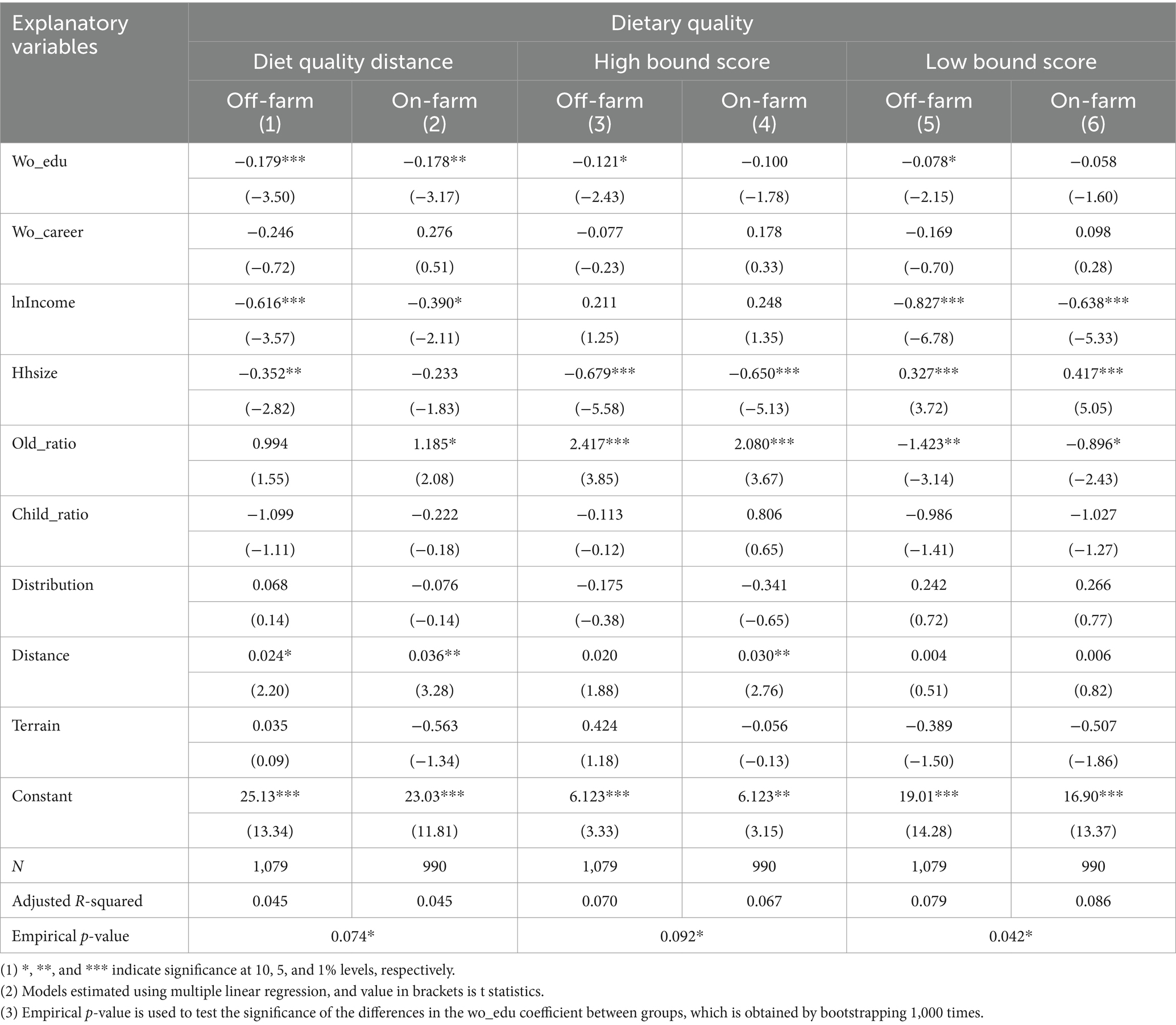
Table 4. Heterogeneous impact of women’s educational attainment on dietary quality at different employment statuses of men.
3.3.2 By the employment status of women
We further divide the total sample into two subgroups based on female household heads’ employment status: off-farm employment (including part-time farming) and full-time farming. The results are presented in Table 5. We find that the influence of women’s educational attainment on household dietary balance is more pronounced among households where women engage in full-time farming.
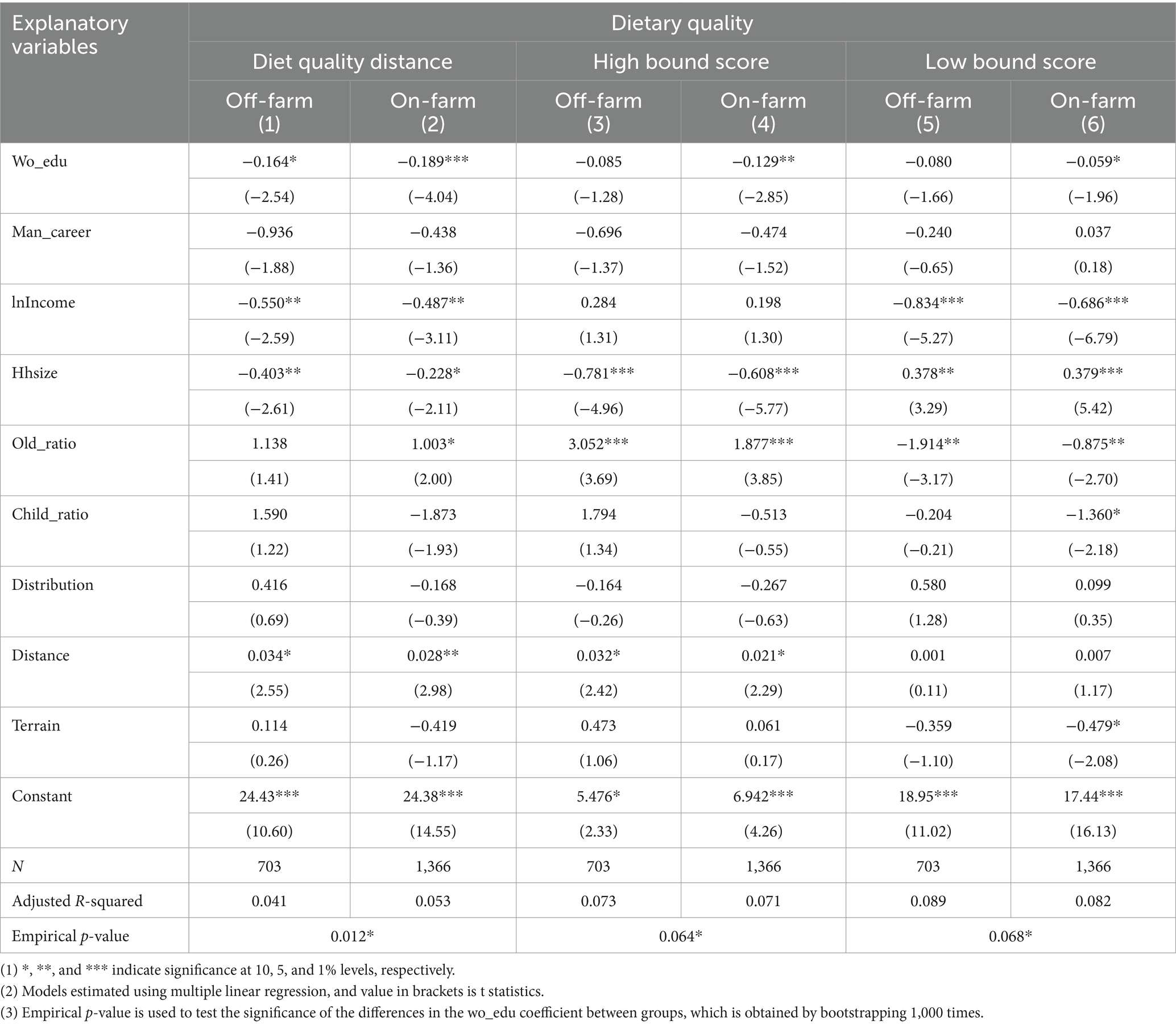
Table 5. Heterogeneous impact of women’s educational attainment on dietary quality at different employment statuses of women.
3.4 Robustness check
3.4.1 Instrumental variable method
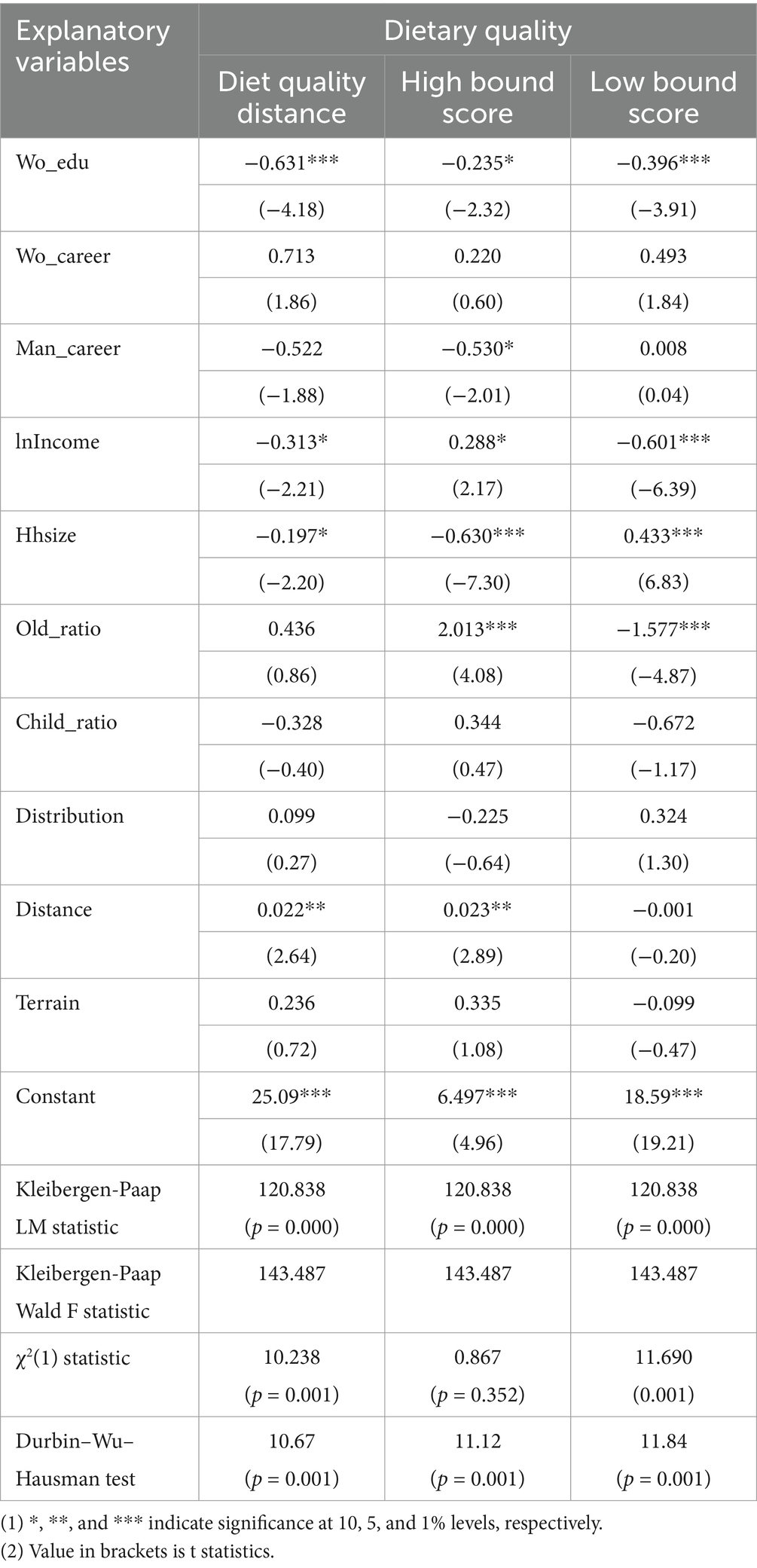
The regression results mentioned above might suffer from endogeneity issues due to omitted variables. In light of this, we proceed to introduce instrumental variables based on the benchmark model. By leveraging the two-stage least squares (2SLS) methodology, we aim to address the potential endogeneity issues and enhance the robustness and reliability of our analytical findings.
Drawing on previous research, we choose to use the average educational attainment of women in other townships within the same county as an instrumental variable. Table 6 reports the estimation results. The findings show that the educational attainment of women still significantly improves the dietary quality of rural households even after instrumental variables are used to address the potential endogeneity biases. In comparison with the OLS regression results presented in Table 2, we find that the estimated magnitude of the impact of women’s educational attainment on the household dietary quality increases when the instrumental variable method is employed. This suggests that overlooking endogeneity concerns would lead to an underestimation of the impact. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the results obtained from the OLS test still have a certain degree of validity within the overall analysis.
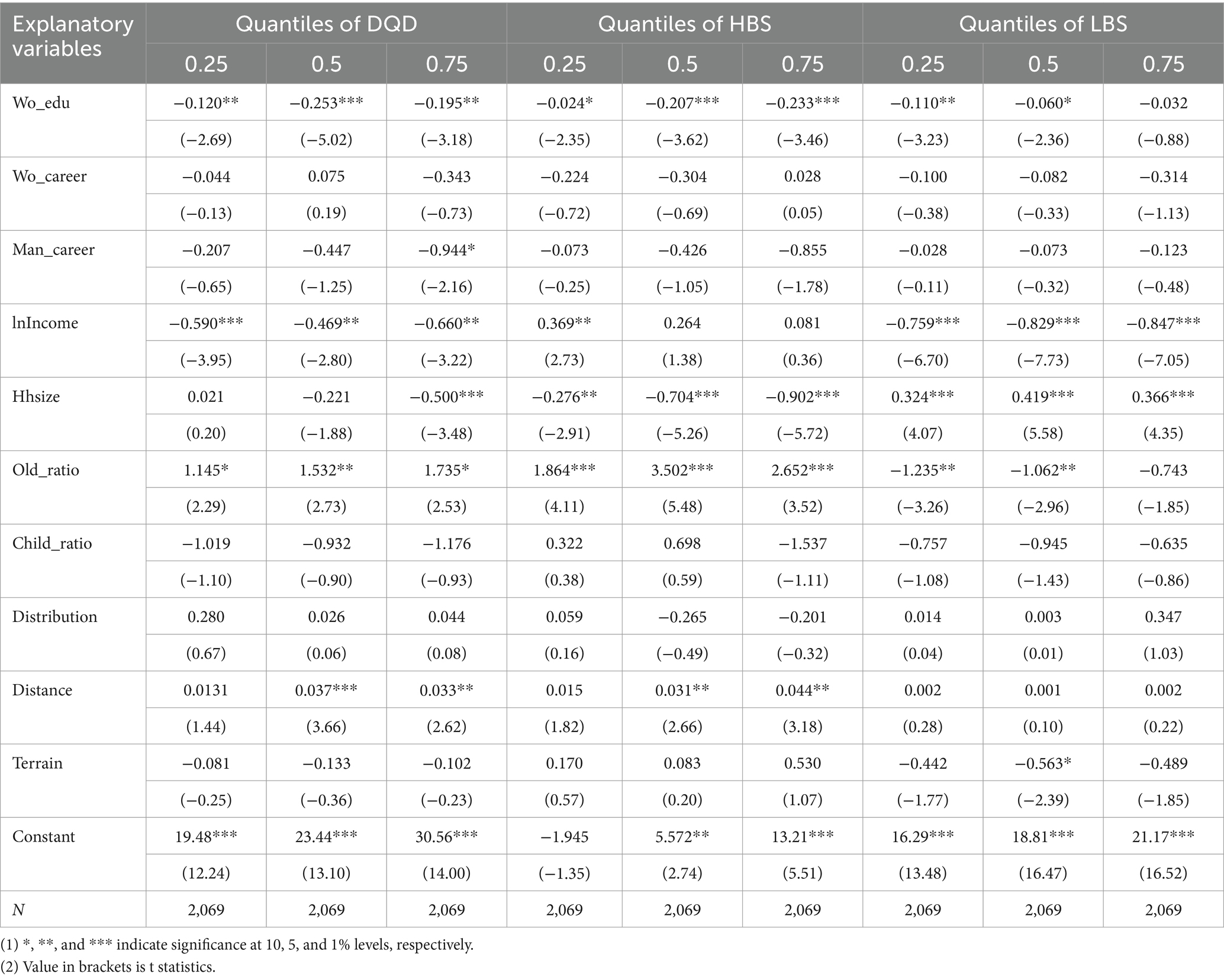
3.4.2 Quantile regression
We select three quantiles (1/4, 1/2, and 3/4) to assess the robustness of the “mean regression” results in Table 2, which are obtained using the ordinary least squares (OLS) method. The findings, presented in Table 7, suggest that across different quantiles, women’s educational attainment significantly impacts household dietary quality. Moreover, the signs of the quantile regression coefficients exactly match those of the OLS regression results in Table 2. This correspondence indicates that the OLS model estimates in Table 2 are reliable and robust, validating the initial analysis and strengthening the confidence in the observed variable relationships.
The robustness test results indicate that neither the instrumental variable (IV) approach nor quantile regression alters the conclusion regarding the impact of women’s educational attainment on household dietary quality, thereby confirming the validity of the earlier OLS estimates in Table 2.
4 Discussion
This study investigates the impact of women’s educational attainment on the dietary quality of rural households in China, with a specific focus on the moderating effect of different employment statuses of household heads. The CRRS data (2020) are adopted, and the dietary quality is assessed with Dietary Balance Index. In general, the main findings can be summarized as follows:
First, the findings indicate that a one-standard-deviation increase in women’s years of education is associated with a 3.65% reduction in dietary imbalance, a 6.51% decrease in dietary overconsumption, and a 2.09% decline in dietary underconsumption. Specifically, higher educational attainment is linked to less inadequate intake of milk and fish and more balanced meat consumption in rural households. These associations can be attributed to several underlying mechanisms. For example, education empowers women with enhanced cognitive abilities and self-learning skills, enabling them to acquire dietary and nutritional knowledge beyond formal education and interpret nutritional information, such as food ingredient labels and dietary recommendations. In addition, education strengthens women’s capacity to access online information. More educated women can efficiently identify reliable dietary resources, such as government dietary guidelines and online platforms (e.g., dietary guideline apps), and leverage these tools to inform food choices.
Second, heterogeneity analysis reveals that the association between women’s educational attainment and dietary quality varies by the employment status of male and female household heads. This variation can be attributed to three key mechanisms: (1) Off-farm income earned by male migrant workers significantly expands household food budgets, thereby laying an economic foundation for improving dietary quality. (2) When men engage in off-farm work, women often assume primary responsibility for household food procurement. Compared with less-educated women, those with higher education demonstrate distinct advantages in developing science-based procurement strategies, which directly enhance the nutritional value of household diet. (3) Women engaged in on-farm work can prepare daily meals for their families after field labor, ensuring regular dietary supply. By contrast, if they migrate for off-farm employment, the workplace is typically far from home, and they usually return home only once every year. This reduction in time available for attending to household dietary needs can consequently affect dietary quality.
4.1 Study limitations
The main limitation of this study is that cross-sectional data do not capture the dynamic interplay between education, occupation, and dietary quality over time. In addition, we do not examine how women’s educational attainment improves child dietary quality as household dietary quality may differ at the individual level. Future research can build on this body of work by analyzing how the education–occupation–dietary quality relationship evolves over time across diverse subnational regions, exploring the pathways through which women’s educational attainment impacts dietary quality using quantitative methods, and examining how maternal education affects children’s dietary quality. Researchers may anticipate the release of the second and third rounds of China Rural Revitalization Survey (CRRS) data, which could provide more nuanced metrics at the individual level.
4.2 Policy implications
These findings highlight the critical role of women’s education in promoting healthier dietary patterns among rural residents in developing countries other than China. This study demonstrates that investing in rural women’s education can effectively address the coexistence of undernutrition and overnutrition stemming from poor dietary quality by promoting balanced consumption of food. Therefore, policymakers should prioritize allocating more educational resources and opportunities for rural women. Second, encouraging male household heads to engage in off-farm work not only increases household income but also empowers women to assume greater decision-making authority over dietary choices, leveraging their improved education to prioritize nutritious options. Third, health education should be strengthened to correct misconceptions such as “staple foods equal carbohydrates” or “staple foods cause obesity.” Cereal-based staples, while rich in starch, are also vital sources of micronutrients and dietary fiber. Moderate intake of these foods is essential for maintaining health.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: China Rural Revitalization Survey: http://rdi.cass.cn/dcsj/202306/t20230607_5643271.shtml.
Author contributions
RL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LY: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JH: Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China funded research project “Research on the changes in the nature of rural poverty in China in the new era and anti-poverty policies after 2020” (Project Code: 19ZDA116).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Gao, Y, Zheng, ZH, and Zhang, ZX. Changes of diet quality across different income groups of rural residents: 1997-2018. J Agrotech Econ. (2023) 11:19–37. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2023.11.005
2. Qing, P, Wang, YZ, Li, J, and Min, S. The greater food approach and national nutritional health. Issues Agricult Econ. (2023) 5:61–73. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.iae.2023.05.006
3. He, YN, Fang, YH, and Xia, J. Update of the Chinese diet balance index: DBI_16. Acta Nutr Sin. (2018) 40:526–30. doi: 10.13325/j.cnki.acta.nutr.sin.2018.06.003
4. Wang, YY, Su, X, Chen, Y, Wang, Y, Zhou, J, Liu, T, et al. Unfavorable dietary quality contributes to elevated risk of ischemic stroke among residents in Southwest China: based on the Chinese diet balance index 2016 (DBI_16). Nutrients. (2022) 14:694. doi: 10.3390/nu14030694
5. Ward, SJ, Coates, AM, Baldock, KL, Stanford, TE, and Hill, AM. Better diet quality is associated with reduced body pain in adults regardless of adiposity: findings from the Whyalla intergenerational study of health. Nutr Res. (2024) 130:22–33. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2024.08.002
6. Gao, Y, Zheng, ZH, and Henneberry, SR. Is nutritional status associated with income growth? Evidence from Chinese adults. China Agricult Econ Rev. (2020) 12:507–25. doi: 10.1108/CAER-11-2019-0216
7. Li, Y, and Li, T. The impact of income growth on the nutritional structure of poverty-alleviated rural families: empirical evidence from 1026 households in Ningxia. Resour Sci. (2023) 45:2064–75. doi: 10.18402/resci.2023.10.11
8. Zhai, TC, and Hu, BC. An analysis on the evolution of food consumption habits of Chinese rural residents. Chinese Rural Econ. (2017) 8:61–74. doi: 10.20077/j.cnki.11-1262/f.2017.08.005
9. Wen, JS, Han, XR, and Zheng, ZH. Habit formation effect of food consumption and its impact on overweight and obesity in rural China. J Agrotech Econ. (2024) 4:18–38. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2024.04.001
10. Koppmair, S, Kassie, M, and Qaim, M. Farm production, market access and dietary diversity in Malawi. Public Health Nutr. (2017) 20:325–35. doi: 10.1017/S1368980016002135
11. Huang, Y, and Tian, X. Food accessibility, diversity of agricultural production and dietary pattern in rural China. Food Policy. (2019) 84:92–102. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2019.03.002
12. Wang, XB, Zhao, LQ, Min, S, and Wang, Y. Rural food market, food consumption, and nutritional health: examination based on the IV-LASSO method. Issues Agricult Econ. (2024) 8:25–41. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.iae.2024.08.006
13. Ning, GJ, and Gong, JJ. Nutritional effect of government transfer payments: analysis of nutritional assistance to rural low-income poor families under the background of rural vitalization. Comparat Econ Soc Syst. (2022) 3:88–99.
14. Bhandari, R, and Smith, FJ. Education and food consumption patterns in China: household analysis and policy implications. J Nutr Educ. (2000) 32:214–24. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3182(00)70559-0
15. Popkin, BM, Zizza, C, and Siega-Riz, AM. Who is leading the change? U.S. dietary quality comparison between 1965 and 1996. Am J Prev Med. (2003) 25:1–8. doi: 10.1016/S0749-3797(03)00099-0
16. Worsley, A, Blasche, R, Ball, K, and Crawford, D. The relationship between education and food consumption in the 1995 Australian National Nutrition Survey. Public Health Nutr. (2004) 7:649–63. doi: 10.1079/PHN2003577
17. Barker, M, Lawrence, W, Crozier, S, Robinson, S, Baird, J, Margetts, B, et al. Educational attainment, perceived control and the quality of Women’s diet. Appetite. (2009) 52:631–6. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2009.02.011
18. Chen, YY, and Li, HB. Mother's education and child health: is there a nurturing effect? J Health Econ. (2009) 28:413–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jhealeco.2008.10.005
19. Wang, Y, and He, XR. How does education generate health benefits? — evidence from the perspectives of food and nutrition intake. J Northwest Polytech Univ. (2016) 3:37-43+10.
20. Li, RB. How does education affect health: an empirical analysis of the cross-spouse effect. Populat Dev. (2024) 30:77–87.
21. Wardle, J, Parmenter, K, and Waller, J. Nutrition knowledge and food intake. Appetite. (2000) 34:269–75. doi: 10.1006/appe.1999.0311
22. McKernan Boulanger, P, Perez-Escamilla, R, Himmelgreen, D, Segura-Millan, S, and Haldeman, L. Determinants of nutrition knowledge among low-income Latino caretakers in hart ford, conn. J Am Diet Assoc. (2002) 102:978–81. doi: 10.1016/S0002-8223(02)90223-3
23. Johansson, L, Thelle, DS, Solvoll, K, Bjørneboe, G-E, and Drevon, CA. Healthy dietary habits in relation to social determinants and lifestyle factors. Br J Nutr. (1999) 81:211–20. doi: 10.1017/S0007114599000409
24. Behrman, JR. Household behavior, preschool child health and nutrition, and the role of information In: P Pinstrup-Andersen, D Pelletier, and H Alderman, editors. Child growth and nutrition in developing countries: Priorities for action. New York: Cornell University Press (1995)
25. Shelton, NJ. What not to eat: inequalities in healthy eating behavior, evidence from the 1998 Scottish health survey. J Public Health. (2005) 27:36–44. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdh191
26. Li, L, Bai, JF, and Zhang, CP. Can migration of rural-to-urban workers increase the left-behind household members’ meat demand? J Agrotech Econ. (2019) 9:27–37. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2019.09.003
27. Hao, JH, Wang, F, and Huang, JQ. Male labor migration, women empowerment and household protein intake: evidence from less developed rural areas in China. Chinese Rural Econ. (2021) 8:125–44. doi: 10.20077/j.cnki.11-1262/f.2021.08.007
28. Gupta, S, Pingali, P, Pinstrupandersen, P, and Kydd, J. Women’s empowerment and nutrition status: the case of iron deficiency in India. Food Policy. (2019) 88:101763–11. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2019.101763
29. Bonis-Profumo, G, Stacey, N, and Brimblecombe, J. Measuring women’s empowerment in agriculture, food production, and child and maternal dietary diversity in Timor-Leste. Food Policy. (2021) 102:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2021.102102
30. Gupta, S, Seth, P, Vemireddy, V, and Pingali, P. Women’s empowerment and intra-household diet diversity across the urban continuum: evidence from India’s DHS. J Food Policy. (2024) 128:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2024.102680
31. Fan, HL, and Xin, BY. Elderly care and rural women’s non-farm employment in China: micro data evidence from China. Chinese Rural Econ. (2019) 2:98–114. doi: 10.20077/j.cnki.11-1262/f.2019.02.006
32. Zhou, C, Sylvia, S, Zhang, L, Luo, R, Yi, H, Liu, C, et al. China’s left-behind children: impact of parental migration on health, nutrition, and educational outcomes. Health Aff. (2015) 34:1964–71. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2015.0150
33. Lin, Q, Adab, P, Hemming, K, Yang, L, and Qin, H. Health allowance for improving the nutritional status and development of 3–5-year-old left-behind children in poor rural areas of China: study protocol for a cluster randomised trial. Trials. (2015) 16:361. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0897-5
34. Tian, X, Huang, YY, Zhong, L, and Wang, H. Nutritional status of left-behind children in rural China. China Econ Q. (2018) 1:247–76. doi: 10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2017.04.10
35. Bennett, MK. International contrasts in food consumption. Geogr Rev. (1941) 31:365–76. doi: 10.2307/210172
Keywords: women’s educational attainment, dietary quality, full-time farming, diet balance index, China food pagoda
Citation: Li R, Ye L and Han J (2025) Women’s educational attainment, full-time farming, and household dietary quality in rural China. Front. Nutr. 12:1560455. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1560455
Edited by:
Monica Trif, Centre for Innovative Process Engineering, GermanyReviewed by:
Claudia Terezia Socol, University of Oradea, RomaniaSubhashis Sahu, University of Kalyani, India
Copyright © 2025 Li, Ye and Han. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rong Li, bHJAaHp1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Rong Li
Rong Li Linxiang Ye3
Linxiang Ye3