- 1Department of General Surgery, Liuzhou People's Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi Medical University, Liuzhou, China
- 2Liuzhou Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases Precision Diagnosis Research Center of Engineering Technology, Liuzhou People's Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi Medical University, Liuzhou, China
- 3Pathology Department, Liuzhou People's Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi Medical University, Liuzhou, China
- 4Emergency Medicine Department, Liuzhou People's Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi Medical University, Liuzhou, China
- 5Guangxi Clinical Key Specialty (Emergency Medicine Department), Liuzhou, China
Introduction: Gallbladder and Biliary Tract Cancer (GBTC) accounts for a notable proportion of cancer cases worldwide. This study aims to assess the burden of GBTC among aged 55 years and older, enhancing our understanding of its trends and their relationship with Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) across regions and countries.
Methods: We used the data from the Global Burden of Disease study from 2010 to 2021 to analyze GBTC incidence, death numbers, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) and their respective rates for individuals aged 55 years and older. We also reported the GBTC percentage trend during this period.
Results: The global incidence and death cases of GBTC changed significantly between 2010 and 2021. Compared to 2010, GBTC incidence and deaths increased by 35.9% and 29.7% individually in 2021. High-income Asia Pacific was the region with the highest age-standardized incidence, deaths, and DALYs in 2021, and China was the country with the largest number of incidence cases, deaths, and DALYs in 2021. Furthermore, the highest age-standardized incidence rate and age-standardized death rate occurred in Japan. Among individuals aged 55 years and older, the highest incident and death cases were observed in 70–74 age group, and females were more suffered from GBTC than males between 2010 and 2021.
Conclusion: GBTC remains a substantial and growing global health burden, particularly among females and the aged from 2010 to 2021. The absolute number of GBTC cases continued to rise over the past decade in aged 55 years and older.
1 Introduction
Although gallbladder and biliary tract cancers (GBTC) are relatively rare globally, their prognosis remains poor, with a 5-year survival rate under 20% in most European countries (1). Recent years have witnessed an alarming rise in GBTC prevalence (2, 3), making it a significant health burden worldwide, especially in China (4). GBTC is categorized by anatomical location as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, perihilar cholangiocarcinoma, distal cholangiocarcinoma, and gallbladder cancer (5). The prognosis for both gallbladder cancer and cholangiocarcinoma are generally poor, with median survival rate ranging from ~3–6 months in unresectable cases (4). Even after complete resection, the overall 5-year survival rate remains disappointingly low (6). The incidence and epidemiology of GBTC are complex and vary widely. Gallbladder cancer constitutes 80%−95% of biliary tract cancers (3, 7). Notably, according to our previous study geographic variations significantly influence the incidence of GBTC, with highest age-standardized incidence rates (ASIR) observed in high-income Asia Pacific and southern Latin America in 2017, particular in countries like Japan and Chile (7–9).
Simultaneously, the global population aging—driven by increasing life expectancy and population growth, particularly in China and India—is expected to intensify the burden of chronic diseases, including cancers. By 2050, it is projected that over 0.75 billion people aged sixty and older will reside in these two nations, comprising 38.5% of the world's sixty-plus population (10). Previous study showed that cancer incidence is notably higher among aging populations, especially those aged 55 years and older, who often face age-related functional declines and multi-system diseases (11, 12). In our global burden of diseases (GBD) 2017 study also showed that the incidence and deaths number of age above 55 groups was higher than age below 55 groups (9). Therefore, it is crucial to consider GBTC disease burden in this age group, as the impact on families and society could be substantial and help policy makers in implementing effective policies.
While several studies have estimated the GBTC burden, indicating GBTC is still a major public issue (9, 13), most studies have focused on general populations across all age groups and the past 30 years burden, with little emphasis on older adults, who are more susceptible to GBTC (14–16). Until now, no previous studies have specifically focused on the GBTC burden in individuals aged 55 and older, especially the trends of GBTC over the past decade. To address this gap, this study presents estimates of the number of cases and age-standardized rates (ASRs) for GBTC incidence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) across 204 countries and territories from 2010 to 2021 for individuals aged 55 years and older (17). These estimates are stratified by age, sex, and the Socio-Demographic Index (SDI). To our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the relationship between trends in GBTC and SDI at both regional and national levels over this period and age groups.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Overviews
The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study was initiated to provide a comprehensive, publicly accessible resource for global disease burden metrics. Data were collected from 204 countries and territories, which were grouped into 21 regions. These countries were further classified into five SDI levels—high, high-middle, middle, low-middle, and low—using data spanning from 2010 to 2021. The Global Health Data Exchange (http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool) provides detailed datasets on incidence, mortality, DALYs, Years of Life Lost (YLLs), and Years of Lived Disability (YLDs). The methodologies employed to derive these metrics have been thoroughly documented in previous research (17, 18). This study was conducted in compliance with the Guidelines for Accurate and Transparent Health Estimates Reporting (GATHER) (19).
2.2 Data sources
The GBD estimation process integrates multiple relevant data sources for each disease or injury, including censuses, household surveys, civil registration and vital statistics, disease registries, health service use, air pollution monitors, satellite imaging, disease notifications, and other sources (20). All cancers were coded as C23 through C24.9 based on the 11th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) were included in this study (20). Intrahepatic bile duct cancer (ICD-10 code C22.1) was excluded to avoid overlap with others research.
2.3 Statistical analysis
In our study, we utilized the ASIR, age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) and age-standardized disability-adjusted life year (ASDR) to quantify the trends in the global, regions and countries GBTC burden. DALYs were employed to evaluate GBTC's societal impact and inform public health strategies. IHME calculated the percentage change in each metric between 2010 and 2021 by subtracting the 2010 value from the 2021 value and then dividing by the 2010 baseline. Specifically, the trend of incidence, death, and DALYs of were assessed in this way to quantify (18). All data were drawn from the GBD database. All data statistics were analyzed using the R statistical software program (version 3.6.3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing). P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
2.4 Uncertainty analysis
We report the 95% uncertainty intervals (UIs) for all estimates. The 95% UI represents the range from the 2.5th to the 97.5th percentile of the calculated parameters based on the disease data.
2.5 Mortality estimates
First, by using data sources that reported accurate incidence and mortality rates in the same year, the mortality-to-incidence ratio (MIR) for GBTC was estimated using a linear mixed-effects model with the Healthcare Access and Quality (HAQ) Index, age, and sex as covariates. Second, the MIR was combined with cancer registry incidence data to estimate mortality. Third, the estimated mortality for GBTC was combined with observed mortality (from vital registrations) and entered into the Cause of Death Ensemble Model (CODEm). CODEm was then used to predict GBTC mortality for all locations, years, sexes, and ages. Finally, the CoD Correct algorithm was used to adjust the sum of predicted single-cause mortality (CODEm results) to be consistent with the all-cause mortality estimation (9).
2.6 Socio-demographic index
The SDI was calculated based on the total fertility rate for those aged under 25 years, the average education level, and the per capita income of the female population aged over 15 years. It serves as a composite indicator to measure a country or region's per capita income, mean education level, and total fertility rate.
3 Results
3.1 Global burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer
Globally in 2021, the number of GBTC deaths was 155,077 (95% UI: 129,703 to 174,512) in aged ≥55 group (Table 1, Figure 1A), while in 2010, the number of deaths cases were 119,606 (95% UI: 102,399 to 132,423). The ASMR decreased from 11.1 (95% UI: 9.5 to 12.3) per 100,000 population in 2010 to 10.4 (95% UI: 8.7 to 11.7) per 100,000 population in 2021 in aged 55 years and older group (Figure 1B, Table 1). Globally, the number of GBTC incidence cases was 141,299 (95% UI: 121,392 to 154,339) in 2010, which increased to 192,028 (95% UI: 163,007 to 216,508) in 2021 (Table 1, Figure 1C). Over the past decade, there has been a slight decrease in the overall ASIR for GBTC among individuals aged 55 years and older worldwide. In 2010, the ASIR was 13.1 per 100,000 population, whereas in 2021, it decreased to 12.9 per 100,000 population, representing a 1.4% reduction in incidence (Figure 1D, Table 1).
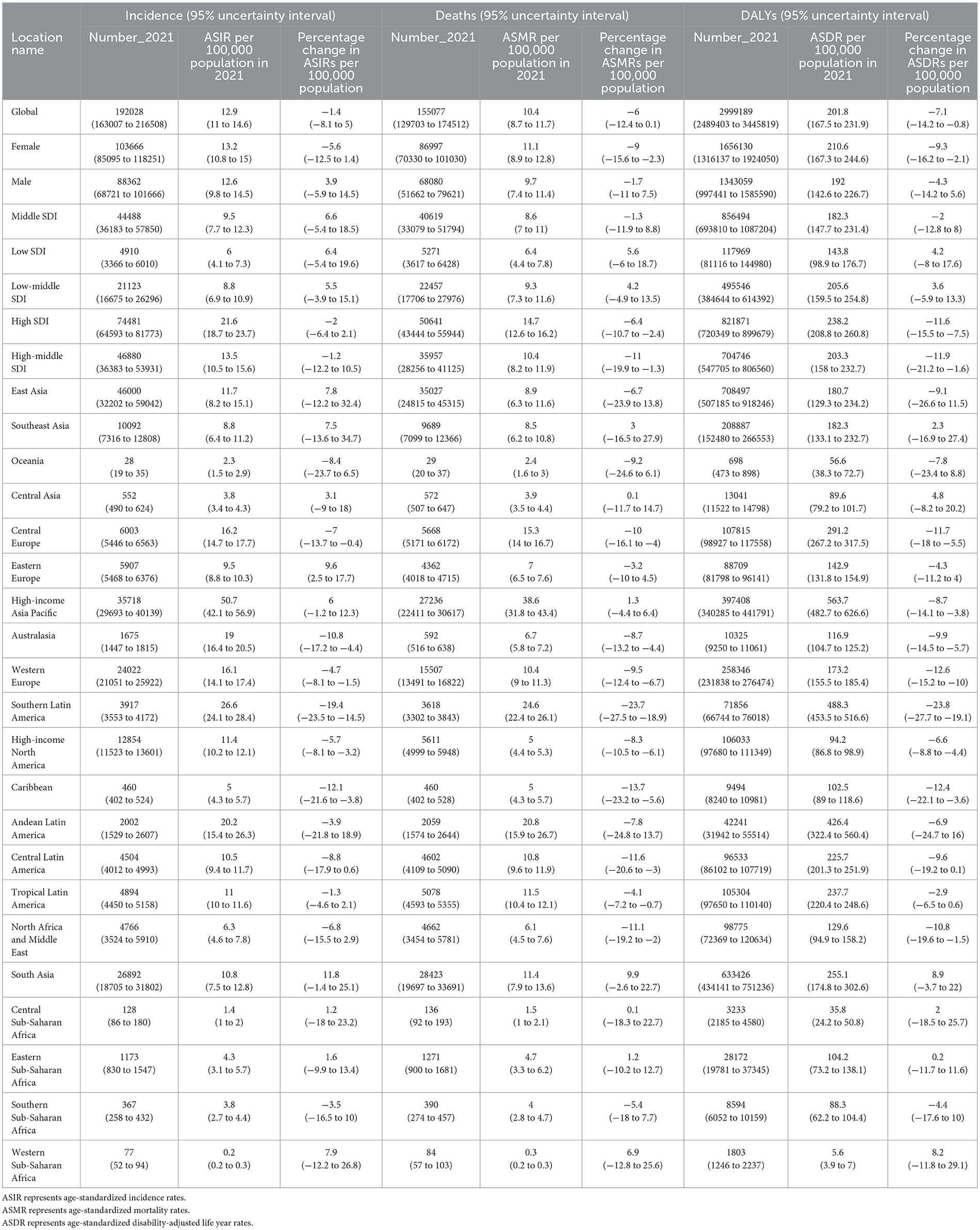
Table 1. Deaths, incidence cases, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for GBTC in 2021 and percentage change in age-standardized rates (ASRs) per 100,000 population from 2010 to 2021 by global, 5 SDI, 21 regions burden for the population aged 55 years and older of disease.
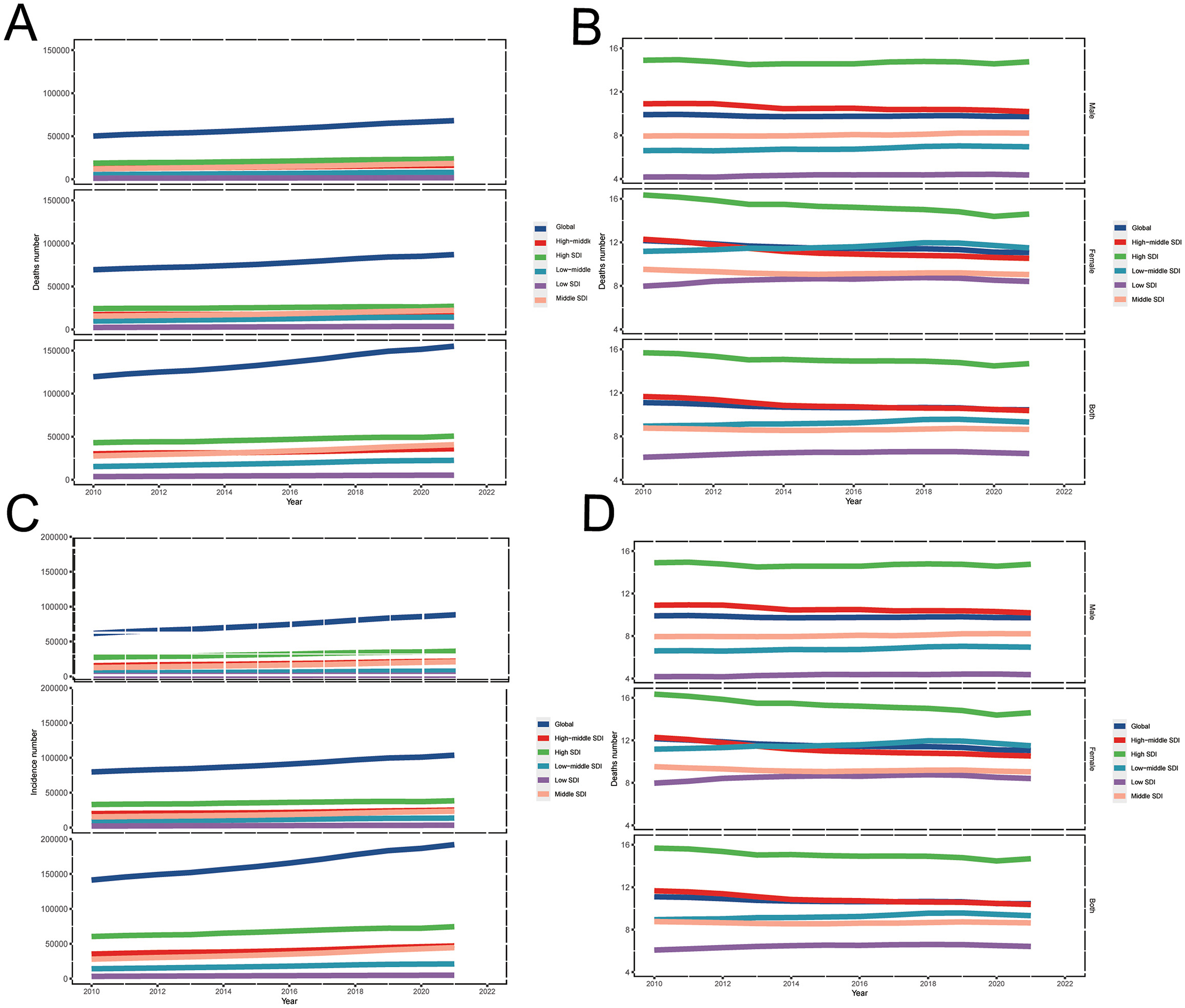
Figure 1. Trends in GBTC burden of (A) deaths cases, (B) ASMR, (C) incident cases, and (D) ASIR across global and 5 SDI regions, from 2010 to 2021 for aged 55 years and older. GBTC, gallbladder and biliary tract cancer; ASMR, age-standardized death rate; ASIR, age-standardized incidence rate; SDI, Socio-Demographic Index.
Globally in 2010, GBTC DALYs cases accounted for 2,341,779 (95% UI: 1,970,210 to 2,623,883). By 2021, the number of DALYs cases had risen to 2,999,189 (95% UI: 2,489,403 to 3,445,819), representing a 28.1% increase (Table 1). The ASDR of GBTC in aged 55 years and older were 217.0 (95% UI: 182.8 to 243.5) per 100,000 population in 2010 and, 201.8 (95% UI: 167.5 to 231.9) per 100,000 population in 2021, a 7.1% (95% UI: −14.2% to −0.8%) decrease from 2010 to 2021 (Table 1).
In the worldwide, the percentage of ASMR [−6.0% (95% UI: −12.4% to 0.1%)] and ASIR [−1.4% (95% UI: −8.1% to 5.0%)] were both showed a declined trends from 2010 to 2021 (Table 1). However, absolute numbers rose from 2010 to 2021, namely, the number of deaths were increase 29.7% (95% UI: 20.8% to 38.0%) and incidence were 35.9% (95% UI: 26.7% to 44.9%; Table 1).
3.2 Regional burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer
In 2021, the highest ASIR for individuals aged 55 years and older was observed in the High-income Asia Pacific region for both sexes, with a rate of 50.7 per 100,000 population (95% UI: 42.1 to 56.9), followed by Southern Latin America [26.6 per 100,000 (95% UI: 24.1 to 28.4)], and Andean Latin America [20.2 per 100,000 (95% UI: 15.4 to 26.3), Figure 2A, Table 1]. In the same time, East Asia has the largest incidence number than the other regions (Figure 2C). In contrast, the lowest ASIRs were recorded in Western Sub-Saharan Africa [0.2 per 100,000 (95% UI: 0.2 to 0.3)], Central Sub-Saharan Africa [1.4 per 100,000 (95% UI: 1.0 to 2.0)], and Oceania [2.3 per 100,000 (95% UI: 1.5 to 2.9), Figure 2A, Table 1].
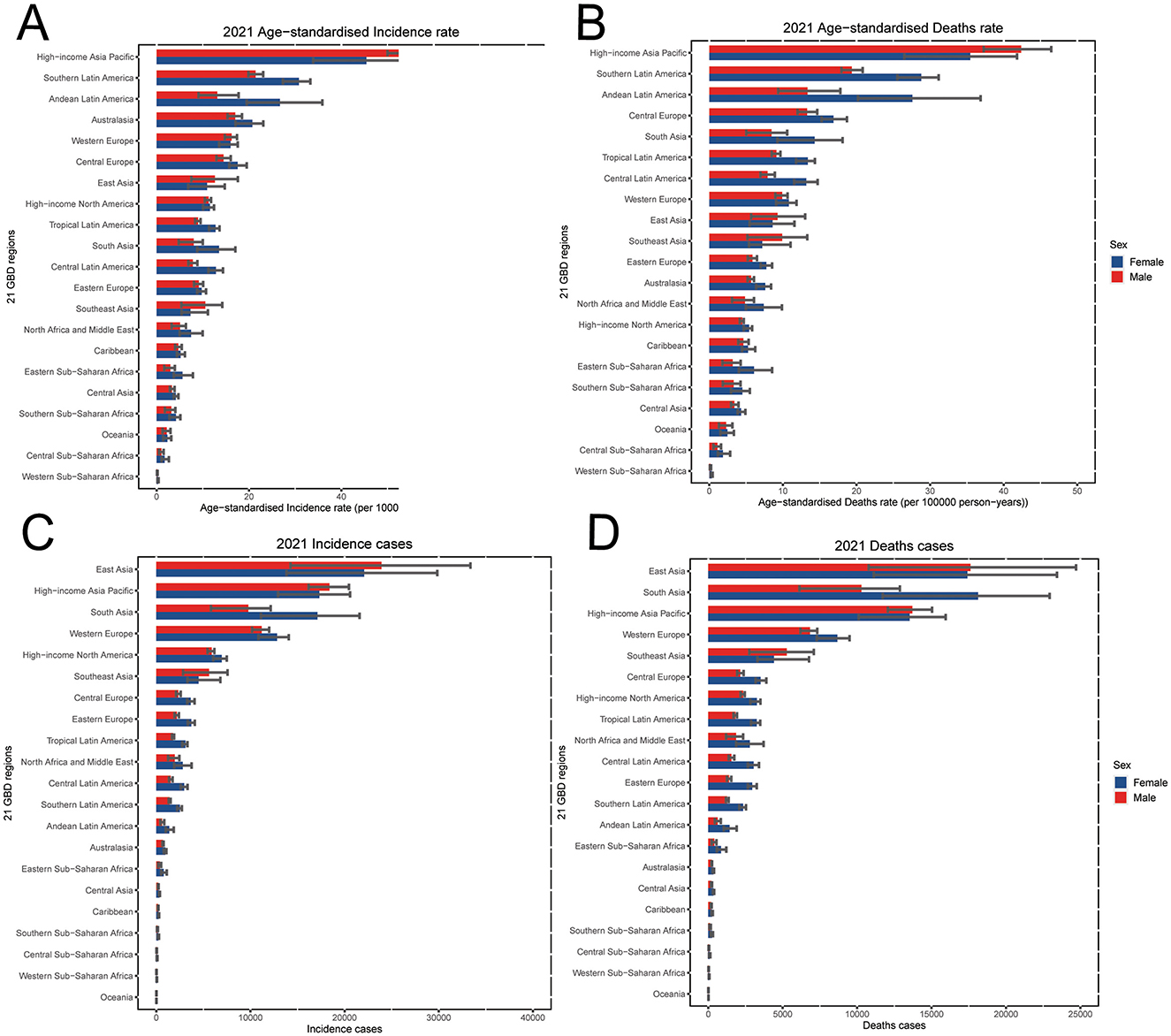
Figure 2. In 2021, the GBTC burden of 21 regions for individuals aged 55 years and older, including (A) ASIR, (B) ASMR, (C) incidence cases and (D) death cases by sexes. GBTC, gallbladder and biliary tract cancer; ASIR, age-standardized incidence rate; ASMR, age-standardized death rate.
At the regional level, the highest ASMR in 2021 was also found in the High-income Asia Pacific region [38.6 per 100,000 population (95% UI: 31.8 to 43.4)], followed by Southern Latin America [24.6 per 100,000 (95% UI: 22.4 to 26.1)], and Andean Latin America [20.8 per 100,000 (95% UI: 15.9 to 26.7), Figure 2B, Table 1]. And the East Asia had the highest death number than the other regions (Figure 2D). Conversely, the lowest ASMRs of GBTC for individuals aged 55 years and older were found in Western Sub-Saharan Africa [0.3 per 100,000 (95% UI: 0.2 to 0.3)], Central Sub-Saharan Africa [1.5 per 100,000 (95% UI: 1.0 to 2.1)], and Oceania at 2.4 per 100,000 (95% UI: 1.6 to 3.0; Figure 2B, Table 1).
Regarding the ASDR for GBTC in 2021 among those aged 55 years and older, the lowest burdens were observed in Western Sub-Saharan Africa [5.6 per 100,000 (95% UI: 3.9 to 7.0)], Central Sub-Saharan Africa [35.8 per 100,000 (95% UI: 24.2 to 50.8)], and Oceania [56.6 per 100,000 (95% UI: 38.3 to 72.7), Supplementary Figure 1]. In contrast, the highest ASDRs were found in the High-income Asia Pacific [563·7 per 100,000 (95% UI: 482.7 to 626.6)], Southern Latin America [488.3 per 100,000 (95% UI: 453.5 to 516.6)], and Andean Latin America [426.4 per 100,000 (95% UI: 322.4 to 560.4)] regions among the 21 GBD regions for the population aged 55 years and older (Supplementary Figure 1).
Despite regional variation in incidence numbers, all 21 GBD regions experienced increasing trends between 2010 and 2021. Southeast Asia [66.4% (95% UI: 33.9% to 108.6%)], South Asia [60.5% (95% UI: 41.6% to 79.6%)] and East Asia [58.0% (95% UI: 28.6% to 94.0%)] showed the largest increasing trends of incidence number during this period (Supplementary Table 1). South Asia [11.8% (95% UI: −1.4% to 25.1%)], Eastern Europe [9.6% (95% UI: 2.5% to 17.7%)] and Western Sub-Saharan Africa [7.9% (95% UI: −12.2% to 26.8%)] were top three increased in the percentage of ASIR from 2010 to 2021 (Table 1). Meanwhile, Southern Lartin America [−19.4% (95% UI: −23.5% to −14.5%)], Caribbean [−12.1% (95% UI: −21·6% to −3·8%)] and Australasia [−10.8% (95% UI: −17.2% to −4.4%)] were top three decreased in ASIR (Table 1). The regional changes in death counts did not always parallel incidence. Southeast Asia [59.5% (95% UI: 29.3% to 98.1%)] saw the greatest increase in deaths, whereas Southern Latin America had the largest decrease [−2.6% (95% UI: −7.4% to 3.5%), Supplementary Table 1]. For ASMR between 2010 and 2021, South Asia and Southern Latin America showed the largest increased and decrease trend, respectively (Table 1).
3.3 204 countries and territories burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer
At the national and territories level in 2021, China (44,513; 95% UI: 30,655 to 57,373), Japan (28,358; 95% UI: 22,977 to 31,518) and India (21,569; 95% UI: 14,886 to 25,381) had the highest number of incident cases, and the highest number of deaths were China (33,806; 95% UI: 23,681 to 43,755), India (22,728; 95% UI: 15,624 to 26,748) and Japan (21,786; 95% UI: 17,687 to 24,178; Figures 3A, B, Supplementary Tables 2-S1, S2). In 2021, Japan suffered the highest ASIR (54.3 per 100,000; 95% UI: 44.0 to 60.4), ASMR (41.7 per 100,000; 95% UI: 33.9 to 46.3) (Figures 3A, B; Supplementary Figure 3, Tables 2-S1, S2). Whereas, Gambia, the Tokelau Islands, and Niue suffer the lowest burden in 2021. From 2010 to 2021, percentage changes in ASIR and ASMR varied across all countries and territories. Armenia showed the largest increase in ASIR (115.6%; 95% UI: 72.6% to 168.5%) and ASMR (110.2%; 95% UI: 68.3% to 161.2%), followed by Georgia and Uzbekistan (Figure 3C; Supplementary Figure 4, Tables 2-S1, S2). In contrast, United Arab Emirates experienced the most significant decreases in ASIR (−42.9%; 95% UI: −59.0% to 16.1%) and ASMR (−45.6%; 95% UI: −40.9% to −20.3%; Supplementary Tables 2-S1, S2).
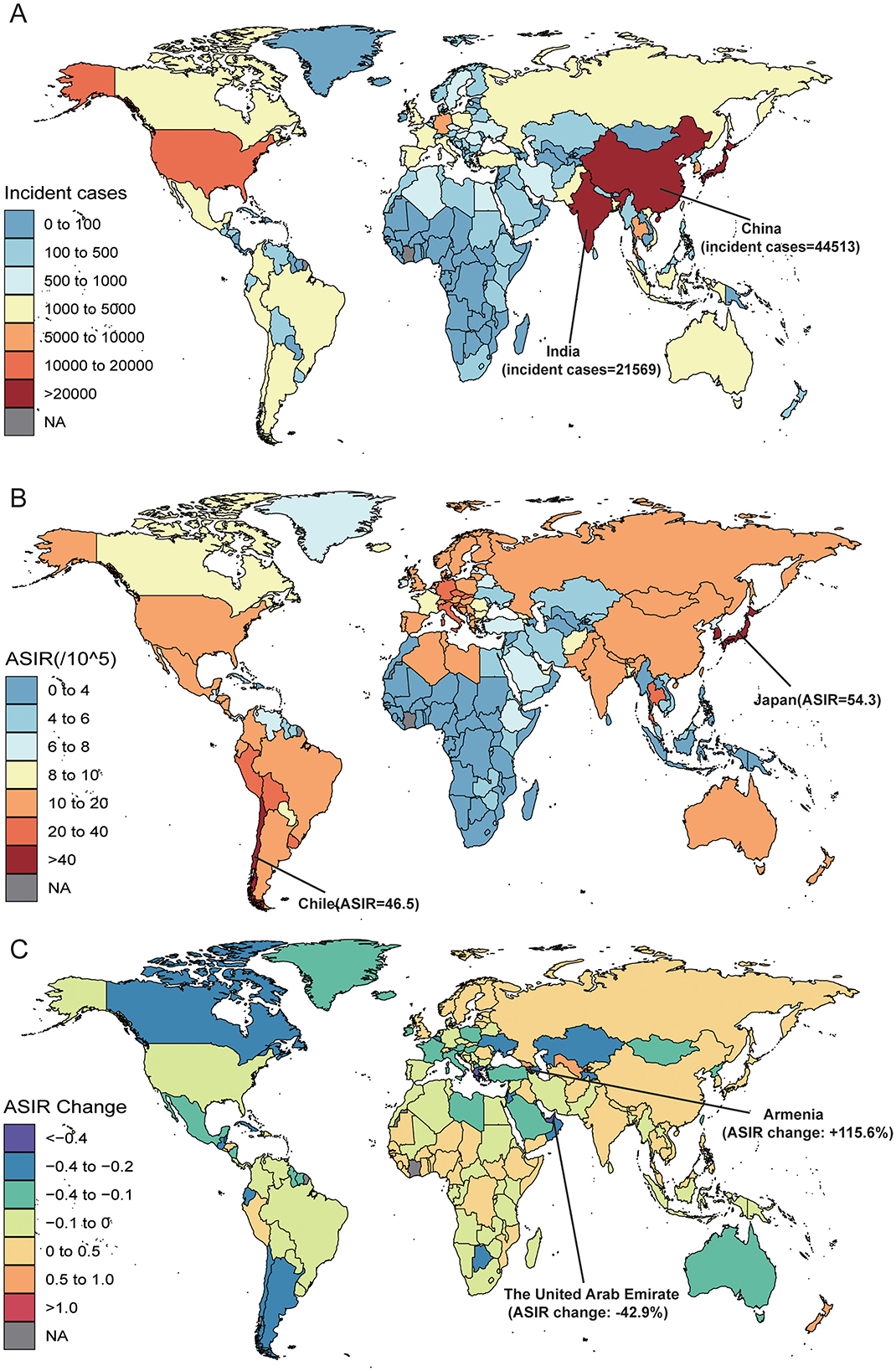
Figure 3. The Gallbladder and Biliary Tract Cancer (GBTC) burden of 204 countries and territories, for aged 55 years and older, including (A) the incidence cases of GBTC in 2021, (B) the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) of GBTC in 2021, and (C) from 2010 to 2021, the annual percent change of ASIR. GBTC indicates gallbladder and biliary tract cancer; ASIR, age-standardized incidence rate.
In 2021, China [683,908 (95% UI: 482,234 to 886,803)] had the highest number of DALYs related to the burden of GBTC among individuals aged ≥55, followed by India and Japan (Supplementary Figure 5, Table 2-S3). The lowest number of DALYs were observed in Gambia, the Tokelau Islands, and Niue (Supplementary Table 2-S3). The highest ASDR for GBTC aged ≥ 55 in 2021 was recorded in Chile [805.4 per 100,000 (95% UI: 736.1 to 872.7)], followed by Thailand and Bolivia (Supplementary Figure 6, Table 2-S3). Conversely, the lowest ASDRs were recorded in Gambia (approaching 0.0), the Tokelau Islands and Niue (Supplementary Table 2-S3). Most countries and territories showed increasing trends in ASDR among individuals aged ≥55 from 2010 to 2021. From 2010 to 2021 the largest increases in ASDR were observed in Armenia [114.8% (95% UI: 71.3% to 168.0%)], followed by Georgia and Uzbekistan (Supplementary Figure 7, Table 2-S3). The largest decreases in ASDR were found in United Arab Emirates, Greece, and San Marino (Supplementary Table 2-S3).
3.4 The burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer between regions, countries and SDI
Our results showed that the ASDR of GBTC aged ≥55 was positively correlated with the SDI at the regional level from 2010 to 2021 (Figure 4). The lowest ASDR was associated with an SDI value of ~0.371. Notably, regions such as High-Income Asia Pacific, Southern Latin America, Andean Latin America, and South Asia exhibited higher-than-expected ASDR levels, while areas including Eastern Europe, High-Income North America, Central Asia, and Southern Sub-Saharan Africa consistently showed lower-than-expected ASDR values (Figure 4). A similar trend was observed for the relationship between ASMR and ASIR with SDI (Supplementary Figures 8A, B).
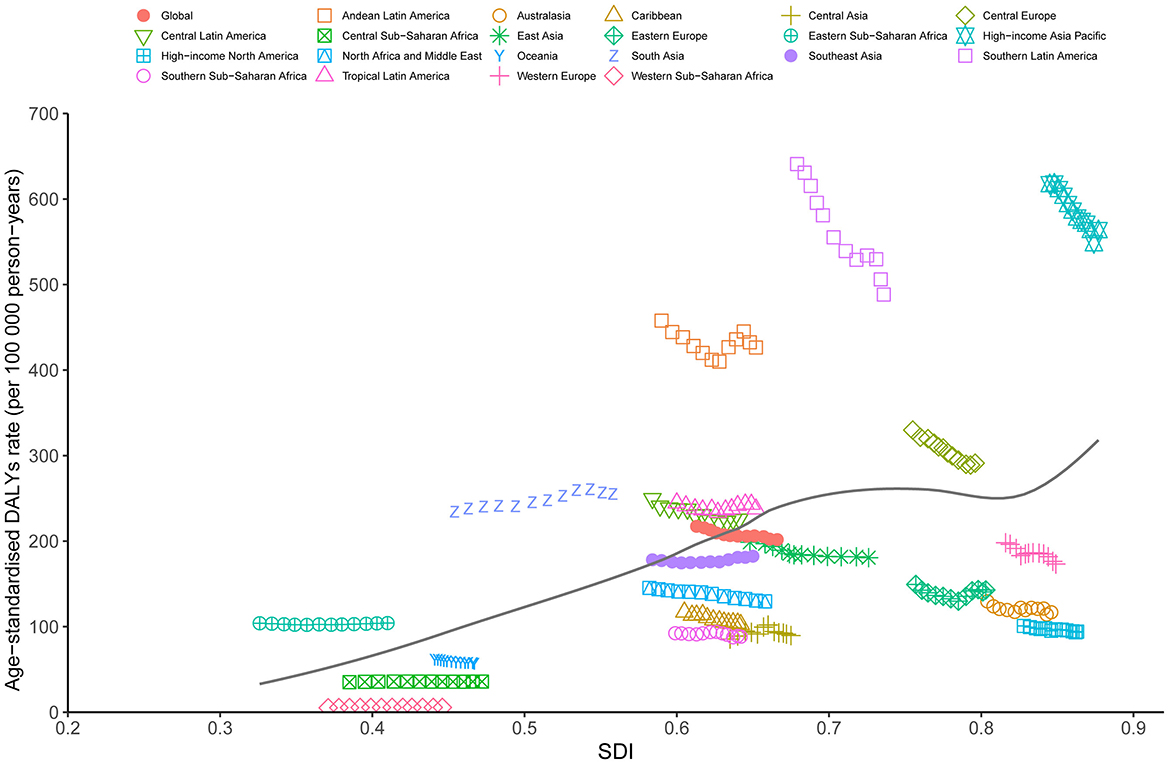
Figure 4. Trends in age-standardized DALYs rate (ASDR) for GBTC across 21 regions burden of disease is illustrated by SDI, from 2010 to 2021 for aged 55 years and older. The black line indicates expected values. GBTC, gallbladder and biliary tract cancer; ASDR, age-standardized disability-adjusted life years rate; SDI, Socio-Demographic Index.
The analysis of DALYs for GBTC across 204 countries from 2010 to 2021 also revealed a general positive association between DALYs and SDI (Figure 5). The lowest ASDR among these countries was observed at an SDI value of around 0.410. Countries such as Chile, Thailand, Bolivia, Japan, and South Korea displayed significantly higher DALY rates than expected based on their SDI levels. Conversely, nations including Gambia, Niger, Liberia, Benin, and Mauritania reported markedly lower rates than anticipated (Figure 5). Additionally, ASIR and ASMR followed trends similar to ASDR from 2010 to 2021 (Supplementary Figures 9A, B).
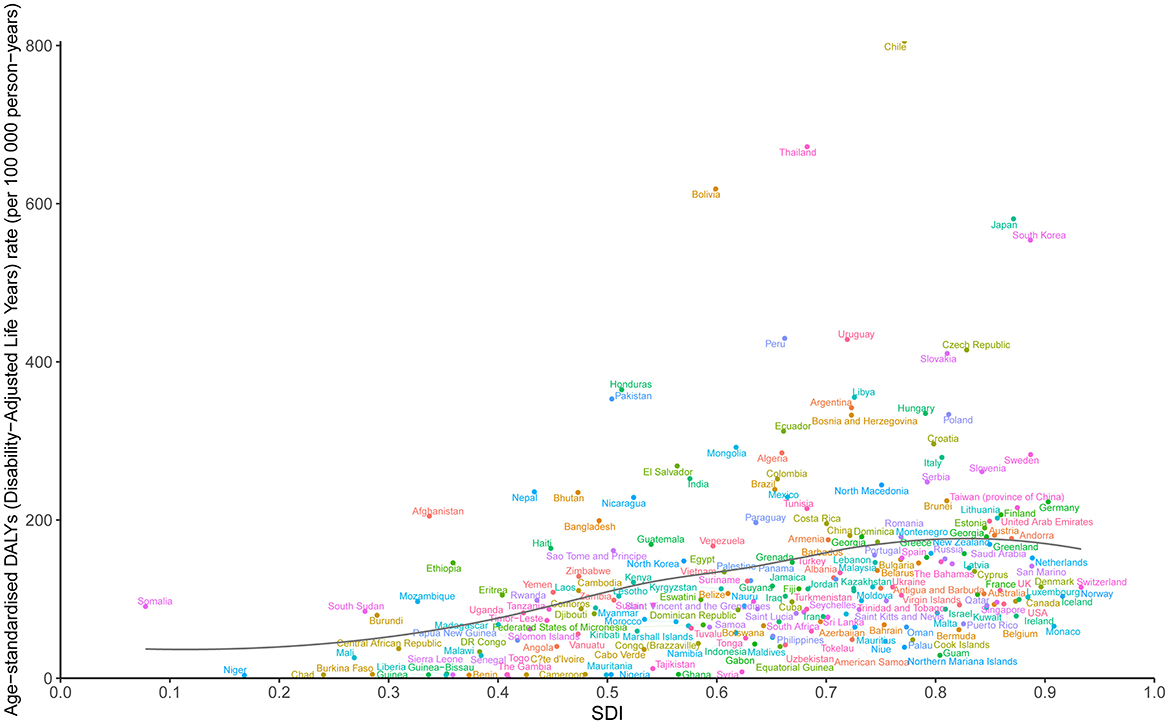
Figure 5. Trends in age-standardized DALYs rate (ASDR) for GBTC across 204 countries and territories burden of disease is illustrated by SDI, from 2010 to 2021 for aged 55 years and older. The black line indicates expected values. GBTC, gallbladder and biliary tract cancer; ASDR, age-standardized disability-adjusted life years rate; SDI, Socio-Demographic Index.
3.5 The burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer between age and sex pattern
In 2021, the GBTC incidence, death cases, and DALYs varied by sex and age. The number of GBTC cases showed an increasing trend with age in both males and females, peaking in the 70–74 age group, followed by a slight annual decline (Figure 6A). Females consistently exhibiting a higher burden of incidence and death burden than males. Additionally, the incidence rate of GBTC generally increased with age, reaching its highest point in the 90–94 age group (Figure 6A). After this peak, the incidence rate declined rapidly in males but continued upward in females. This same trend was also observed in death cases rates (Figure 6B).
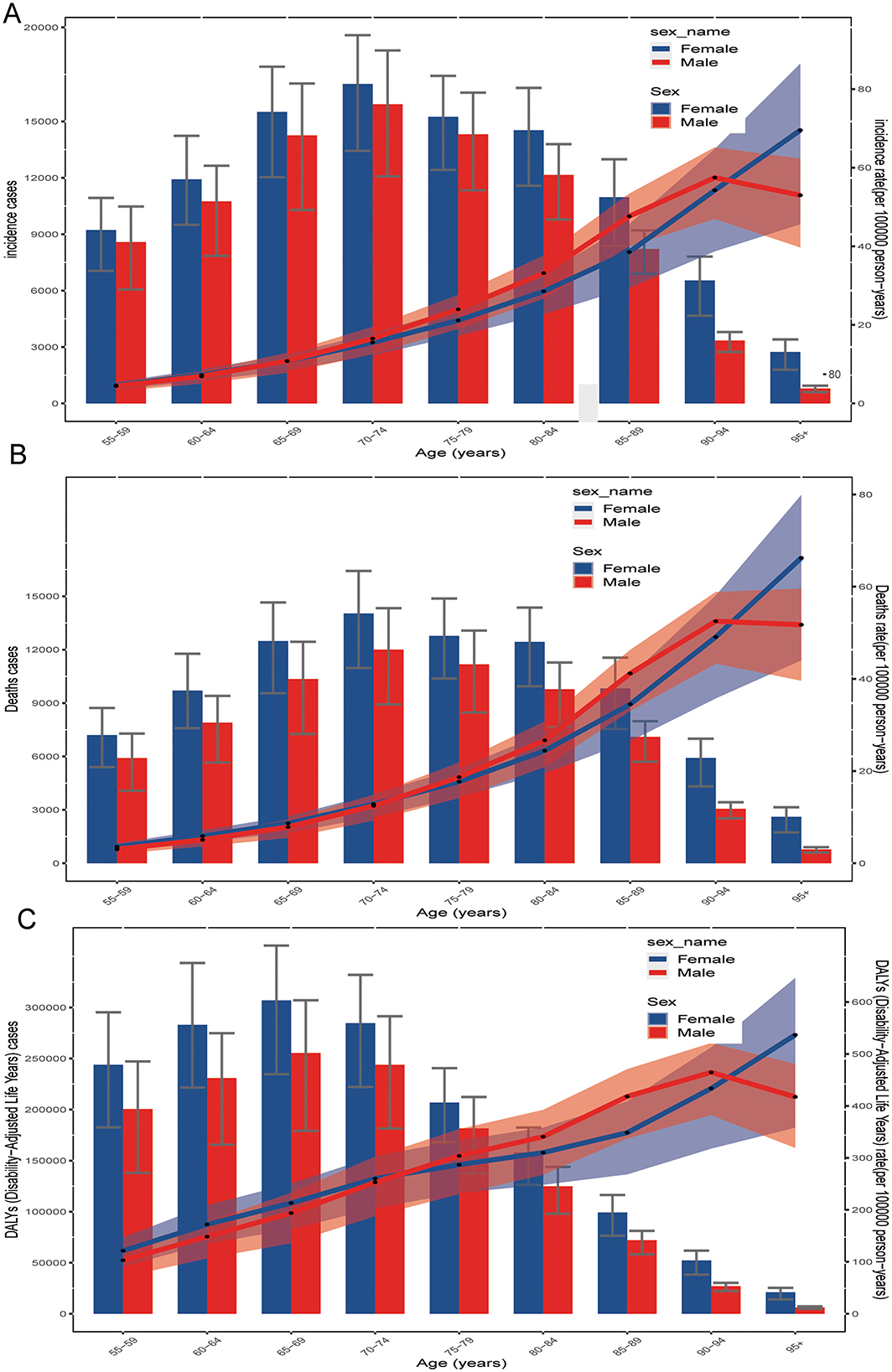
Figure 6. Age-specific numbers of (A) incidence cases, (B) death cases, and (C) disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) from GBTC in 2021 both are illustrated by age and sex, which aged 55 years and older. GBTC, gallbladder and biliary tract cancer; DALYs, disability-adjusted life years.
The pattern of DALYs differed somewhat. GBTC DALYs increased steadily with age, peaking in the 65–69 age group for both sexes, and then gradually declining in older age groups (Figure 6C). The DALY rate, like the incidence rate, generally increased with age, peaking in the 90–94 age group. After this peak, the DALY rate declined rapidly in males but continued to rise in females (Figure 6C).
3.6 Risk factors
GBD estimates identify elevated body-mass index (BMI) as the only major risk factor driving GBTC-related deaths and DALYs, and they demonstrate that GBTC burden varies markedly by age, sex, and region (Supplementary Figure 10). In our analysis of adults aged ≥55 years, the contribution of high BMI to both mortality and DALYs was particularly pronounced among those aged 55–59. In 2021, globally, 11.6% of GBTC deaths (10.3% in males; 12.6% in females) and 12.0% of DALYs (10.7% in males; 13.1% in females) were attributable to elevated BMI (Supplementary Figures 10A, B). Across the five SDI regions, the high-middle SDI category exhibited the highest BMI-attributable mortality proportion–14.1% overall (12.4% in males; 15.6% in females)—whereas the low SDI region showed the lowest proportion at 5.8% (4.9% in males; 6.3% in females; Supplementary Figures 10C, D).
4 Discussion
GBTC is relatively uncommon compared to other cancers, but recent evidence indicates increasing increase in incidence, mortality, and DALYs. Our study showed the most up-to-date and comprehensive data on GBTC aged 55 years and older from 2010 to 2021, revealing a substantial and rising global health burden, particularly among women and older adults. This finding underscores the need for focused prevention and treatment strategies for some specific groups. Additionally, our study emphasizes emphasize the critical role of improving early diagnosis rates to boost the chances of successful surgical interventions.
We found that the number of incidence cases and death of GBTC aged 55 years and older increased globally from 2010 to 2021, Whereas the ASR of GBTC for this age group were decreased during the past 10 years, consistent with previous studies (9, 21). A recent study predicted that global ASR of GBTC incidence and mortality would continue to decline from 2020 to 2030 (21). Nevertheless, researchers note that despite these ASR reductions, the absolute number of new cases and deaths may rise slightly in certain regions in certain regions (22). These global disparities in ASIR and ASMR stem from various complex factors, including local dietary habits, socioeconomic inequalities, environmental risk factors, genetic predisposition, and the prevalence of gallstone disease. Moreover, limited access to diagnostic tools and inconsistent data quality, especially in low- and lower-middle-income countries, significantly influence these trends (9, 13, 23, 24).
Several researchers have reported substantial geographic variation, with certain Asian regions showing notably high figures (9, 25, 26). Among the 21 GBD regions analyzed for GBTC burden in aged 55 years and older, our study found that the High-income Asia Pacific region (Japan and Korea) had the highest ASR in 2021. This elevated ASR may be linked to greater prevalence of clonorchiasis, hepatitis B, and obesity. Furthermore, liver fluke infections resulting from raw fish consumption in this area represent a key risk factor (27–29). Additional contributors to this region's high GBTC burden include unhealthy dietary patterns—such as excessive salt intake from salted fish, pickles, and cured meats—along with smoking and heavy alcohol use (9, 30, 31). Additionally, disparities in access to quality healthcare, particularly for early detection and treatment, may further amplify the burden of GBTC in different region. Socioeconomic development, dietary habits, population growth, and improvements in detection measures in these regions likely play significant roles in influencing this burden (32). Tumor development and progression are intricate processes driven by multiple carcinogenic factors. Consequently, the trends in GBTC morbidity and mortality are complex, underscoring the necessity for comprehensive, the need for tailored, region-specific interventions to improve healthcare access and prevention efforts. Implementing effective and feasible strategies for prevention, early detection, and treatment in these high-risk regions is essential to addressing the global GBTC burden.
In 2021, China had the highest number of GBTC incidence cases and deaths, largely due to its large population. A previous study reported that China had 254 million individuals aged 60 or older in 2019, this number is expected to rise to 402 million by 2040, which would account for approximately 28% of the total population (33). Studies also forecast a steady increase in GBTC incidence and mortality in China from 2020 to 2044 (22), driven by an aging population and demographic shifts that are expected to elevate age-standardized cancer rates (22, 25, 34). Additional factors, such as improved diagnostic, a shift from grain-based to high-energy, high-fat Western diets, rising body mass index (BMI), and viral hepatitis, further contribute to China's increased GBTC burden (22, 34–38). Japan recorded the highest ASIR and the ASMR, potentially tied to a higher prevalence of biliary tree malformations, growing obesity rates, an aging populace, and advanced diagnostic technologies (9, 37, 39). From 2010 to 2021, Armenia and Georgia saw the largest increases in GBTC burden among individuals aged 55 years and older. This mirrors the trend observed from 1990 to 2017 in these countries, indicating that the rising burden has continued over the past 4 years. This persistence suggests a lack of effective strategies to control GBTC in these regions, emphasizing the urgent need for policymakers to prioritize targeted interventions and preventive efforts. For example, tailored strategies should reflect each country's unique circumstances, including cultural practices, available resources, healthcare systems, and cancer awareness levels.
We also observed a significant disparity in the burden of GBTC between males and females, with females experiencing a higher burden—a finding consistent with prior research despite varying age groups (26, 37, 40, 41). The gender disparity in GBTC incidence may partly attributed to genetic and hormonal factors, as females have elevated estrogen levels during reproductive years, potentially increasing their risk (42–44). A previous report found that from 2011 to 2019, younger individuals (aged 20–54) accounted for just 10.1% of biliary tract cancer cases, while those aged 55–84 comprised 89.9% (45). Another study also reported that the incidence of GBTC in older patients was nearly double that of younger patients (46–48). Therefore, our research focused on the population aged 55 years and older and found that the number of incidence cases and deaths showed a generally increasing trend with age. Both the GBD 2017 (9) and GBD 2021 studies demonstrated that individuals aged 65–79 had a higher incidence and mortality rates. Several studies have identified older age as a significant independent risk factor for poor outcomes in patients with GBTC (32, 49, 50). These findings suggest that GBTC poses a significant threat to the elderly population, particularly affecting quality of life in the later stages and influencing therapeutic strategies (48, 51). Therefore, developing gender- and age-specific strategies to address GBTC's unique risk factors is essential. Screening programs for GBTC should be tailored to the specific needs of different age groups and genders, and future research should explore how genetics, hormones, lifestyle, and healthcare access shape these patterns. For example, screening women aged 70–74, launching dietary campaigns to discourage raw fish consumption, and promoting physical activity to reduce BMI and obesity could prove effective.
Although we previously reported the association between GBTC burden and SDI and HAQ, finding a negative correlation between GBTC burden and SDI across all age groups from 1990 to 2017 (9), and another study observed lower incidence of cholangiocarcinoma in high-income countries (52). However, we found a positive correlation between the GBTC burden and SDI in individuals aged 55 years and older from 2010 to 2021. This suggested that elderly GBTC patients in higher SDI regions or countries were face higher disease burden compared to lower SDI regions or countries. The discrepancy between the two studies may stem from differences in the age groups and study periods included. In our previous study, all age groups from 1990 to 2019 were considered, while the current study focuses on patients aged ≥55 from 2010 to 2021. Previous study showed that higher SDI regions are generally higher obesity rates, driven by lifestyle factors like high-calorie diets and reduced physical activity (53). In addition, Gallbladder and biliary diseases, particularly gallbladder cancer, are associated with higher BMI or obesity, which tend to have a higher prevalence in high-SDI regions (54). Therefore, greater attention should be focus on individuals aged 55 years and older in high-SDI regions. In addition, lower burden of GBTC in low SDI region may due to lower rate of obesity. However, although lower SDI regions have lower ASR, but we cannot overlook the burden of these regions, because there may be limited healthcare resources, lower educational attainment, and higher environmental risk exposures, which may lead to delays in GBTC diagnosis or undiagnosed and treatment (55).
Our study provided a high-quality analysis of global, regional, and national burden of GBTC from 2010 to 2021, focusing on individuals aged 55 and older. However, some limitations of this study warrant consideration. Firstly, this study is a secondary analysis of GBD data, and as with many GBD-based studies, the accuracy and reliability of the estimates depend heavily on the quality and quantity of the input data used for modeling. Secondly, the GBD data in this study covers only the period from 2010 to 2021, potentially introducing uncertainties and biases in the estimates. Furthermore, incorporating additional cancer databases could enhance the analysis's comprehensiveness and objectivity. Thirdly, this study does not investigate GBTC's economic impact or detail prevention strategies across different regions and countries, specifically, in low-SDI areas, underreporting, incomplete registries, and ICD coding changes may affect the results. So, significant variations may exist between low- and middle-income countries and high-income countries. Finally, this study focuses on individuals aged 55 years and older but lacks analysis of those under 55, who still represent a significant proportion of GBTC cases. Future research should include both age groups to assess age-related risk factors and further investigate gender differences in incidence.
In summary, our study examined the burden of GBTC among individuals aged 55 years and older, highlighting an escalating public health challenge with notable variations across age, sex, and geographic regions. Although ASRs of GBTC in this age group decreased from 2010 to 2021, the absolute number of GBTC cases continued to rise over the past decade. This underscores the need for a comprehensive and coordinated global response to this complex disease. Our findings may guide the development of strategies and interventions to prevent and manage GBTC risk factors effectively.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
Since the GBD database does not involve direct participation of human subjects, ethical approval was not required for this study.
Author contributions
ML: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JL: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. ShuangjiL: Writing – review & editing. MZ: Writing – review & editing. ShuanL: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. TG: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. MW: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ShunL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. QL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. GP: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. JY: Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. GO: Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by Guangxi Science and Technology Project (Guike AB23026016); Liuzhou Science and Technology Project (2022CAC0209), Youth Science Foundation of Guangxi Medical University (GXMUYSF202451), Guangxi Key Laboratory of Early Prevention and Treatment for Regional High Frequency Tumor (No. GKE-KF202303), Clinical Key Specialty (Emergency Medicine Department) in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (No. GWYF [2023] 26) and the “Ascent Plan” Construction Project of Key Clinical Specialties in Liuzhou City (Key Cultivation of National Key Clinical Specialties - Emergency Medicine Department) (No. LWYBH [2024] 12).
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation and their collaborators provided epidemic, publicly available data for this research, while the Health Research Center of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences funded the investigation of social determinants. The findings presented in this thesis constitute original research that has not been previously published or shared online. The datasets analyzed during the current study are available in GBD database: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1561712/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Lepage C, Capocaccia R, Hackl M, Lemmens V, Molina E, Pierannunzio D, et al. Survival in patients with primary liver cancer, gallbladder and extrahepatic biliary tract cancer and pancreatic cancer in Europe 1999–2007: results of EUROCARE-5. Eur J Cancer. (2015) 51:2169–78. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.07.034
2. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
3. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
4. Ren T, Li Y, Zhang X, Geng Y, Shao Z, Li M, et al. Protocol for a gallbladder cancer registry study in China: the Chinese research group of gallbladder cancer (CRGGC) study. BMJ Open. (2021) 11:e038634. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038634
5. Rizvi S, Khan SA, Hallemeier CL, Kelley RK, Gores GJ. Cholangiocarcinoma – evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2018) 15:95–111. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.157
6. Jarnagin WR, Shoup M. Surgical management of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. (2004) 24:189–99. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-828895
7. Sharma A, Sharma KL, Gupta A, Yadav A, Kumar A. Gallbladder cancer epidemiology, pathogenesis and molecular genetics: recent update. World J Gastroenterol. (2017) 23:3978–98. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3978
8. Miranda-Filho A, Piñeros M, Ferreccio C, Adsay V, Soerjomataram I, Bray F, et al. Gallbladder and extrahepatic bile duct cancers in the Americas: incidence and mortality patterns and trends. Intl J Cancer. (2020) 147:978–89. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32863
9. Ouyang G, Liu Q, Wu Y, Liu Z, Lu W, Li S, et al. The global, regional, and national burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer and its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories, 1990 to 2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Cancer. (2021) 127:2238–50. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33476
10. Chatterji S, Kowal P, Mathers C, Naidoo N, Verdes E, Smith JP, et al. The health of aging populations in China and India. Health Aff. (2008) 27:1052–63. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.27.4.1052
11. Miranda-Filho A, Bray F, Charvat H, Rajaraman S, Soerjomataram I. The world cancer patient population (WCPP): an updated standard for international comparisons of population-based survival. Cancer Epidemiol. (2020) 69:101802. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2020.101802
12. Gao TY, Tao YT Li HY, Liu X, Ma YT Li HJ, et al. Cancer burden and risk in the Chinese population aged 55 years and above: a systematic analysis and comparison with the USA and western Europe. J Glob Health (2024) 14:04014. doi: 10.7189/jogh.14.04014
13. Khanali J, Malekpour MR, Azangou-Khyavy M, Saeedi Moghaddam S, Rezaei N, Kolahi AA, et al. Global, regional, and national quality of care of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 1990–2017. Int J Equity Health. (2021) 20:259. doi: 10.1186/s12939-021-01596-y
14. Liu C, Du S, Liu X, Niu W, Song K, Yu J. Global, regional, and national burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer, 1990 to 2021 and predictions to 2045: an analysis of the global burden of disease study 2021. J Gastrointest Surg. (2025) 29:101968. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2025.101968
15. Lei S, Huang G, Li X, Xi P, Yao Z, Lin X. Global burden, trends, and inequalities of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer, 1990–2021: a decomposition and age-period-cohort analysis. Liver Int. (2025) 45:e16199. doi: 10.1111/liv.16199
16. Hu Z, Wang X, Zhang X, Sun W, Mao J. An analysis of the global burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer attributable to high BMI in 204 countries and territories: 1990–2021. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1521770. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1521770
17. Mettananda KCD, Mettananda S. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet. (2024) 403:2162–203. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00933-4
18. Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Aali A, Abate YH, Abbafati C, Abbastabar H, et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. (2024) 403:2133–61. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8
19. Stevens GA, Alkema L, Black RE, Boerma JT, Collins GS, Ezzati M, et al. Guidelines for accurate and transparent health estimates reporting: the GATHER statement. Lancet. (2016) 388:e19–23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30388-9
20. GBD 2019 Adolescent Young Adult Cancer Collaborators. The global burden of adolescent and young adult cancer in 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:27–52. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00581-7
21. Su J, Liang Y, He X. Global, regional, and national burden and trends analysis of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer from 1990 to 2019 and predictions to 2030: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front Med. (2024) 11:1384314. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1384314
22. Chen S, Han K, Song Y, Liu S, Li X, Wang S, et al. Current status, trends, and predictions in the burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer in China from 1990 to 2019. Chin Med J. (2022) 135:1697–706. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002258
23. Hughes T, O'Connor T, Techasen A, Namwat N, Loilome W, Andrews RH, et al. Opisthorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma in Southeast Asia: an unresolved problem. Int J General Med. (2017) 10:227–37. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S133292
24. Boffetta P, Donato F, Gouas D, Da Costa AN, Abedi-Ardekani B, Hainaut P. Cancers of the intestine, the liver, and the biliary tract. In:Anttila S, Boffetta P, , editors. Occupational Cancers. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2020), p. 179–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-30766-0_8
25. Bergquist A, Von Seth E. Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. (2015) 29:221–32. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2015.02.003
26. Randi G, Franceschi S, La Vecchia C. Gallbladder cancer worldwide: geographical distribution and risk factors. Int J Cancer. (2006) 118:1591–602. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21683
27. Kim BW, Oh CM, Choi HY, Park JW, Cho H, Ki M. Incidence and overall survival of biliary tract cancers in South Korea from 2006 to 2015: using the national health information database. Gut Liver. (2019) 13:104–13. doi: 10.5009/gnl18105
28. Woo S, Kim Y, Hwang S, Chon HJ. Epidemiology and genomic features of biliary tract cancer and its unique features in Korea. J Liver Cancer. (2025) 25:41–51. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2025.02.27
29. Makiuchi T, Sobue T. Descriptive epidemiology of biliary tract cancer incidence and geographic variation in Japan. Eur J Cancer Prev. (2023) 32:2–9. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0000000000000758
30. Shin HR, Carlos MC, Varghese C. Cancer control in the Asia Pacific Region: current status and concerns. Jpn J Clin Oncol. (2012) 42:867–81. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hys077
31. Nomura S, Sakamoto H, Glenn S, Tsugawa Y, Abe SK, Rahman MM, et al. Population health and regional variations of disease burden in Japan, 1990–2015: a systematic subnational analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. (2017) 390:1521–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31544-1
32. Zhu H, Ji K, Wu W, Zhao S, Zhou J, Zhang C, et al. Describing treatment patterns for elderly patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and predicting prognosis by a validated model: a population-based study. J Cancer. (2021) 12:3114–25. doi: 10.7150/jca.53978
33. None TL. Population ageing in China: crisis or opportunity? Lancet. (2022) 400(10366). doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02410-2
34. Ju W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, Sun K, Wang S, et al. Cancer statistics in Chinese older people, 2022: current burden, time trends, and comparisons with the US, Japan, and the Republic of Korea. Sci China Life Sci. (2023) 66:1079–91. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2218-x
35. Xie C, Shi D, Lin H, Liu Y, Liu W, Yin P. Spatial patterns of gallbladder and biliary tract carcinoma in China from 1990 to 2019: an analysis at the provincial level. Cureus. (2023) 15:e42796. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42796
36. Liu Z, Shi O, Zhang T, Jin L, Chen X. Disease burden of viral hepatitis A, B, C and E: a systematic analysis. J Viral Hepat. (2020) 27:1284–96. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13371
37. Torre LA, Siegel RL, Islami F, Bray F, Jemal A. Worldwide burden of and trends in mortality from gallbladder and other biliary tract cancers. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 16:427–37. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.08.017
38. Tan DJH, Ng CH, Muthiah M, Yong JN, Chee D, Teng M, et al. Rising global burden of cancer attributable to high BMI from 2010 to 2019. Metabolism. (2024) 152:155744. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155744
39. Zhang Y, Yang C, Huang M. Global, regional, and national burden of biliary tract cancer from 1990 to 2017 based on the 2017 global burden of disease study. Cancer Epidemiol. (2021) 73:101949. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2021.101949
40. Vuthaluru S, Sharma P, Chowdhury S, Are C. Global epidemiological trends and variations in the burden of gallbladder cancer. J Surg Oncol. (2023) 128:980–8. doi: 10.1002/jso.27450
41. de Savornin Lohman E, de Bitter T, Verhoeven R, van der Geest L, Hagendoorn J, Haj Mohammad N, et al. Trends in treatment and survival of gallbladder cancer in the Netherlands; identifying gaps and opportunities from a nation-wide cohort. Cancers. (2020) 12:918. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040918
42. Brown KE, Hirshberg JS, Conner SN. Gallbladder and biliary disease in pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol. (2020) 63:211–25. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000496
43. Gupta P, Agarwal A, Gupta V, Singh PK, Pantola C, Amit S. Expression and clinicopathological significance of estrogen and progesterone receptors in gallbladder cancer. Gastrointest Cancer Res. (2012) 5:41–7.
44. Li ZZ, Guan LJ, Ouyang R, Chen ZX, Ouyang GQ, Jiang HX. Global, regional, and national burden of gallbladder and biliary diseases from 1990 to 2019. World J Gastrointest Surg. (2023) 15:2564–78. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i11.2564
45. Rahman R, Ludvigsson JF, von Seth E, Lagergren J, Bergquist A, Radkiewicz C. Age trends in biliary tract cancer incidence by anatomical subtype: a Swedish cohort study. Eur J Cancer. (2022) 175:291–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2022.08.032
46. Zhang H. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and surgical management. Cancer Lett. (2016) 379:198–205. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.09.008
47. Saha SK, Zhu AX, Fuchs CS, Brooks GA. Forty-year trends in cholangiocarcinoma incidence in the US: intrahepatic disease on the rise. Oncologist. (2016) 21:594–9. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0446
48. Vitale A, Spolverato G, Bagante F, Gani F, Popescu I, Marques HP, et al. A multi-institutional analysis of elderly patients undergoing a liver resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: liver resection for ICC among the elderly. J Surg Oncol. (2016) 113:420–6. doi: 10.1002/jso.24148
49. Jackson MW, Amini A, Jones BL, Rusthoven CG, Schefter TE, Goodman KA. Treatment selection and survival outcomes with and without radiation for unresectable, localized intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer J. (2016) 22:237–42. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000213
50. Kizy S, Altman AM, Marmor S, Wirth K, Ching Hui JY, Tuttle TM, et al. Surgical resection of lymph node positive intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma may not improve survival. HPB. (2019) 21:235–41. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2018.08.006
51. McNamara MG. Outcomes in older patients with biliary tract cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2021) 47:569–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2020.03.202
52. Valle JW, Kelley RK, Nervi B, Oh DY, Zhu AX. Biliary tract cancer. Lancet. (2021) 397:428–44. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00153-7
53. Ng M, Gakidou E, Lo J, Abate YH, Abbafati C, Abbas N, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of adult overweight and obesity, 1990–2021, with forecasts to 2050: a forecasting study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. (2025) 405:813–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(25)00355-1
54. Liu S, Yi M, Qin J, Lei F, Lin L, Li Y, et al. The increasing incidence and high body mass index-related burden of gallbladder and biliary diseases – a results from global burden of disease study 2019. Front Med. (2022) 9 doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1002325
Keywords: gallbladder and biliary tract cancer, GBD, incidence, death, DALYs, 55 years and older
Citation: Li M, Li J, Li S, Zhang M, Li S, Zhao J, Gan T, Wu M, Luo S, Liang Y, Li Q, Pan G, Yang J and Ouyang G (2025) Global, regional, and national burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer among adults aged 55 years and older, 2010–2021. Front. Nutr. 12:1561712. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1561712
Received: 16 January 2025; Accepted: 04 June 2025;
Published: 01 July 2025.
Edited by:
Evelyn Nunes Goulart Da Silva Pereira, Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (Fiocruz), BrazilReviewed by:
Zhaojun Wang, Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaSatish Patil, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Copyright © 2025 Li, Li, Li, Zhang, Li, Zhao, Gan, Wu, Luo, Liang, Li, Pan, Yang and Ouyang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianqing Yang, eWFuZ2ppYW5xaW5neHlAc2luYS5jb20=; Guoqing Ouyang, b3V5YW5nZ3VvcWluZ0BzdHUuZ3htdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Mingjuan Li
Mingjuan Li Jiaguang Li3†
Jiaguang Li3† Shuang Li
Shuang Li Tao Gan
Tao Gan Shunwen Luo
Shunwen Luo Yunying Liang
Yunying Liang Qiuyun Li
Qiuyun Li Guoqing Ouyang
Guoqing Ouyang