- 1Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Hebei General Hospital, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 2Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Hebei General Hospital, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 3Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Hebei General Hospital, North China University of Science and Technology, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
Objective: To compare the effects of different vitamins on patients with septic shock (SS) through Bayesian network meta-analysis.
Methods: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on vitamins for septic shock patients were retrieved from PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, etc. The retrieval time was set from the establishment of the database to May 20, 2024. All relevant studies on vitamin treatment for septic shock were retrieved and screened according to the established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay, mechanical ventilation time, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scores after 24 h, total hospital stay, and 28-day mortality were used as outcome measures. The quality of the included studies was evaluated for risk of bias, and R software was used for data analysis.
Results: A total of 36 articles were included in the analysis, covering 4,473 patients with septic shock. The vitamins included vitamin B (VB), vitamin C (VC), vitamin D (VD), vitamin E (VE), hydroxocobalamin (HYD), and vitamin combinations such as hydrocortisone plus vitamin C plus vitamin B (HYDVCVB), vitamin D plus probiotics (VDP), vitamin C plus vitamin B (VCVB), and hydrocortisone plus vitamin C (HYDVC). The network meta-analysis results showed that in terms of ICU length of stay, VD was superior to the control group [mean difference (MD) = 4.57, 95% CI (1.01, 9.69)] and HYDVCVB [MD = 5.4, 95% CI (0.51, 11.66)], with statistically significant differences. In terms of mechanical ventilation time, VC, VD, VCVB, and HYDVCVB showed no statistically significant differences compared to the control group. Regarding the SOFA score after 24 h, VDP was superior to the control group [MD = 2.98, 95% CI (0.27, 5.62)], as well as HYDVCVB [MD = 3.32, 95% CI (0.59, 6.04)], VB [MD = 2.96, 95% CI (0.18, 5.67)], VC [MD = 2.91, 95% CI (0.17, 5.57)], VCVB [MD = 3.18, 95% CI (0.31, 5.9)], and VD [MD = 2.91, 95% CI (0.05, 5.71)], with statistically significant differences. In terms of total hospital stay, VD was superior to the control group [MD = 7.61, 95% CI (2.59, 12.63)], as well as HYDVCVB [MD = 7.71, 95% CI (2.55, 12.9)], VB [MD = 7.6, 95% CI (0.84, 14.39)], VC [MD = 9.93, 95% CI (3.9, 15.92)], and VCVB [MD = 8.1, 95% CI (1.79, 14.41)], with statistically significant differences. Regarding 28-day mortality, VB, VC, VD, VDP, VCVB, HYDVCVB showed no statistically significant differences compared to the control group.
Conclusion: In patients with septic shock, the use of VD shows certain advantages in reducing ICU length of stay and total hospital length of stay. Moreover, its combination with probiotics may help reduce the SOFA scores after 24 h. However, these interventions have not significantly impacted 28-day mortality or mechanical ventilation time.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, PROSPERO: CRD42024599094.
1 Introduction
Sepsis is a severe inflammatory response syndrome that is triggered by an excessive immune response to infection and is a life-threatening organ dysfunction (1). It can be identified by an acute change in the Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score of at least 2 points following infection. Septic shock (SS) is defined as a subset of sepsis characterized by circulatory, cellular, and metabolic abnormalities, which are associated with a higher risk of death. Clinically, it is defined as patients who meet the diagnostic criteria for sepsis and who, despite adequate fluid resuscitation, require vasopressors to maintain a mean arterial pressure of at least 65 mmHg and have a lactate level >2 mmol/L (2). Despite years of research and therapeutic advancements, sepsis and septic shock remain one of the most common reasons for intensive care unit (ICU) admissions, posing a significant burden on the healthcare system, with 18.6 cases per 1,000 hospital admissions related to this condition, and a mortality rate exceeding 50% in patients with SS (3–5). Moreover, the higher incidence of sepsis in resource-limited settings further underscores the necessity for ongoing efforts to enhance prevention, clinical recognition, and treatment to reduce the global burden of this disease (2, 6, 7).
Restoring hemodynamic stability and therapeutic options for treating critically ill patients with sepsis or septic shock include fluid resuscitation, antimicrobial therapy, vasopressors, mechanical ventilation, and adjunctive metabolic therapy, which may involve the use of vitamin C (VC), thiamine, and corticosteroids either alone or in various combinations (8–10). Vitamins are essential micronutrients that play a key role in many biological pathways associated with sepsis, including those leading to anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects (11, 12). In addition, relative vitamin deficiency in plasma is common during sepsis, and vitamin therapy has been associated with improved outcomes in some observational and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving adult and pediatric sepsis patients (13–16). The biological plausibility and supportive clinical evidence for some major vitamins [such as vitamin C, thiamine, and vitamin D (VD)] form a strong argument for their use in sepsis. However, to date, the results of vitamin supplementation in large multicenter randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies have been inconsistent. Overall, the evidence for the role of vitamins in sepsis remains mixed.
Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis to analyze the evidence from randomized controlled trials to assess the efficacy and safety of different vitamins in critically ill adult and pediatric patients, particularly those with septic shock.
2 Methods and data
2.1 Methods
The NMA adhered to the guidelines outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (17) and was registered on the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), with the registration No. of CRD42024599094.
2.2 Literature retrieval
RCTs investigating the role of various vitamins on individuals with SS were retrieved in Cochrane, PubMed, Embase and Web of Science spanning from the establishment of each database to May 2024. The search strategy incorporated a blend of MeSH and free-text terms associated with vitamins and SS. The comprehensive search strategy can be found in Supplementary material S1.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Adults and children who met the diagnostic criteria for SS in the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (13) revised in 2016 were included. The vitamins included vitamin B (VB), vitamin C (VC), vitamin D (VD), vitamin E (VE), hydroxocobalamin (HYD), and vitamin combinations such as hydrocortisone plus vitamin C plus vitamin B (HYDVCVB), vitamin D plus probiotics (VDP), vitamin C plus vitamin B (VCVB), and hydrocortisone plus vitamin C (HYDVC), while the control group adopted placebo. The primary outcomes assessed encompassed hospital stay duration, 28-day death rate, SOFA scores after 24 h, mechanical ventilation duration, and ICU stay. The study type was RCT.
Duplicates, animal experiments, case explorations, meeting abstracts, reviews, articles with unavailable full texts, and studies involving participants with other organ comorbidities were ruled out.
2.4 Data retrieval
Two reviewers autonomously retrieved the articles based on the pre-given criteria. Any discrepancies were addressed through discussion or consulting with a third party to reach an agreement. Information gathered from the selected articles encompassed essential elements like the primary author, publication year, region, sample size, sex, average age, interventions adopted, and outcome metrics.
2.5 Quality assessment
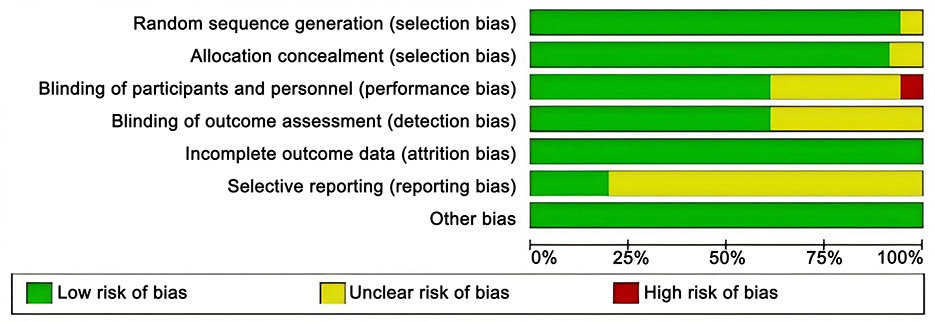
Two investigators autonomously evaluated the risk of bias as low, unclear, or high utilizing the tools provided by Cochrane Collaboration (18). In instances of disagreement, a third party was engaged to help reach an agreement. The evaluation encompassed seven domains, including random sequence generation (selection bias), concealment of allocation (selection bias), blinding of personnel and participants (implementation bias), blinding of outcome assessors (detection bias), completeness of outcome data (follow-up bias), selective outcome reporting (reporting bias), and other possible sources of bias. Every enrolled research was individually assessed based on these criteria. Studies meeting all criteria were deemed “low risk” of bias, indicative of high quality and negligible overall bias. Studies that partially fulfilled the criteria were labeled as “unclear risk,” indicating a moderate likelihood of bias. Studies that did not meet any criteria were designated as “high risk,” indicating elevated bias risk and diminished study quality.
2.6 Data analysis
An NMA was conducted utilizing a prior vague random effects model with the R 4.4.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing). A Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) technique was utilized (19) to derive the optimal combined estimate and probabilities associated with each protocol. Continuous findings were presented as the posterior mean difference (MD) accompanied by the respective 95% confidence interval (95% CI). The combined effect indicators of binary variables were represented by odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI. The Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking curve (SUCRA) percentages were computed to evaluate the probability of each approach being the most favorable. Network and funnel graphs were visualized utilizing Stata (v15.0) with an incorporated metan command. Within the network diagrams, individual nodes represented medications, with the connections illustrating the comparisons made between them. The size of each circle had a positive correlation with the sample size (number of patients enrolled). Cumulative probability graphs were visualized utilizing the ggplot 2 package.
3 Results
3.1 Data screening and findings
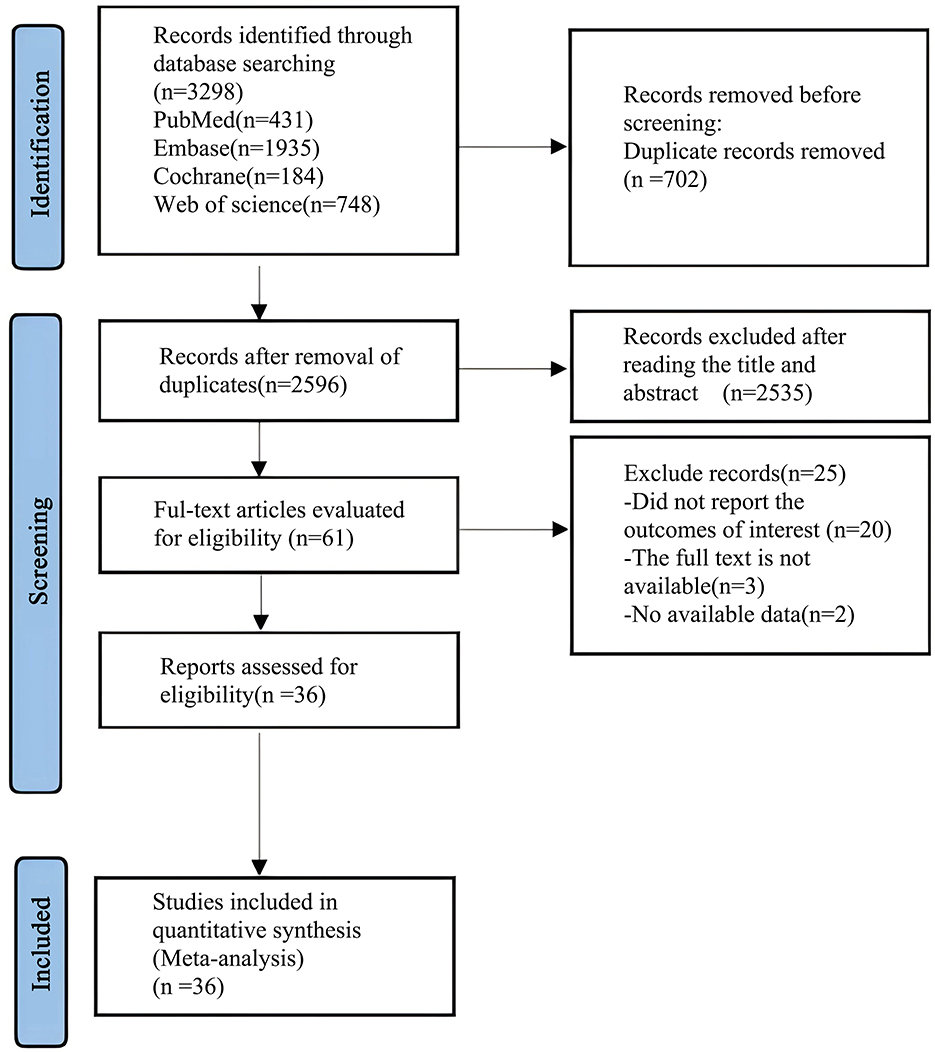
A preliminary search of the databases yielded 3,298 articles. After removing 702 duplicates, 2,535 articles were excluded based on the review of titles and abstracts. A further 25 articles were excluded after full-text review, leaving a final total of 36 articles (20–54) for analysis. The process of literature screening is shown in Figure 1: flowchart of literature search.
3.2 Basic characteristics of articles and risk of bias evaluation
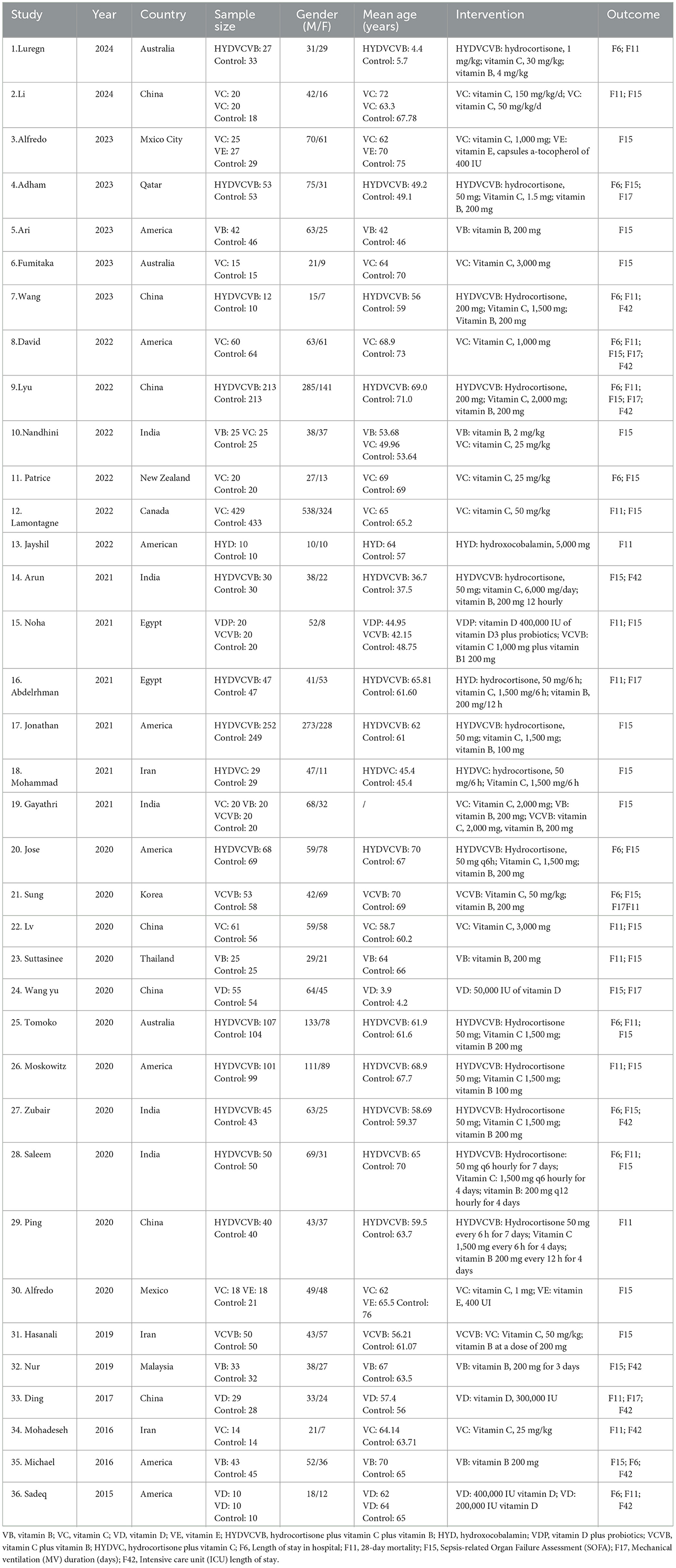
Altogether 36 articles (20–54) were included in the analysis, involving 4,473 patients with SS. Vitamins included VB, VC, VD, VE, HYD, and vitamin combinations included HYDVCVB, VDP, VCVB, and HYDVC. Table 1 outlines the characteristics of the articles. The blinding method applied in the included articles was clearly explained, and the high risk was mainly caused by deviations in planned interventions. The assessment of the risk of bias in the enrolled articles is depicted in Figure 2.
3.3 NMA results
3.3.1 Effect of treatment on ICU length of stay
Ten studies (26–28, 33, 46, 51–54) mentioned the impact of different vitamin treatments on ICU length of stay, as shown in Figure 3. From the network diagram, we found that direct comparisons were formed, among which the number of studies comparing HYDVCVB with the control group was the largest. The network relationship diagram is shown in Figure 3A. In the forest plot, compared with the control group [MD = −4.6, 95% CI (−9.7, −1.0)], VD could reduce the number of days of ICU stay. The forest plot is shown in Figure 3B. In the league table, it is further shown that compared with the control group [MD = 4.57, 95% CI (1.01, 9.69)] and HYDVCVB [MD = 5.4, 95% CI (0.51, 11.66)], VD has an advantage in shortening ICU length of stay, and the differences are all statistically significant. See Supplementary Table S1 for details. According to the Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) line chart, VD has the largest area, indicating that the effect of VD in shortening ICU length of stay in septic shock may be the best. The SUCRA plot is detailed in Figure 3C.
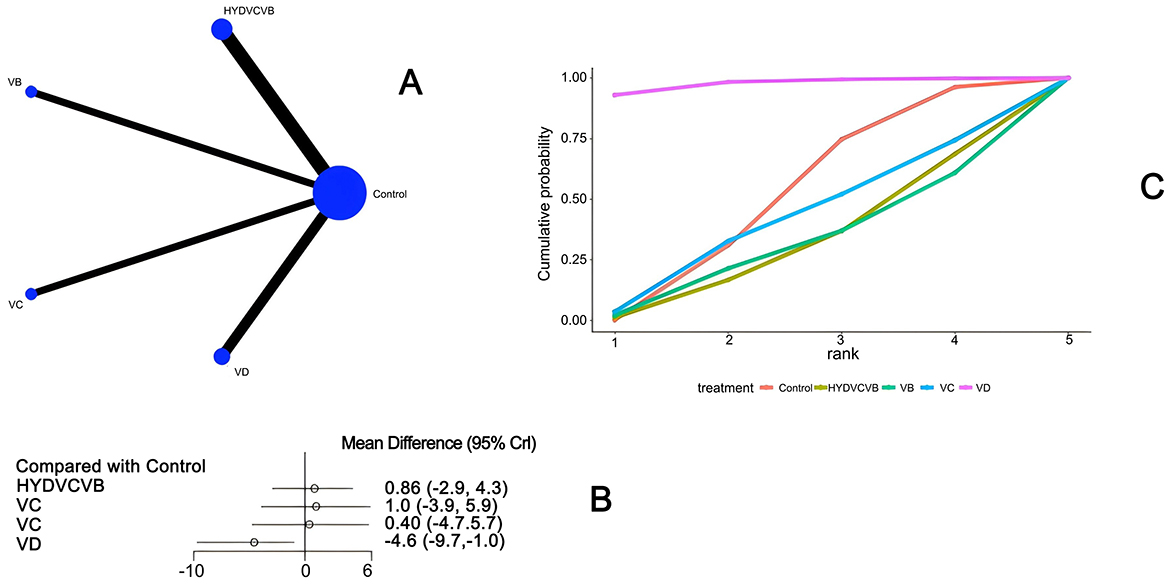
Figure 3. The impact of various vitamins on ICU duration of stay. (A) Network diagram illustrating the impact of various vitamins on ICU length of stay. (B) Forest plot illustrating the impact of various vitamins on ICU length of stay. (C) SUCRA plot illustrating the impact of various vitamins on ICU length of stay.
3.3.2 Effect of treatment on mechanical ventilation duration
Seven studies (23, 27, 28, 35, 40, 43, 52) have examined the impact of different vitamin treatments on the duration of mechanical ventilation, as shown in Figure 4. The network diagram reveals that direct comparisons were formed, with the most studies comparing HYDVCVB to the control group. The detailed network relationship diagram is presented in Figure 4A. In the forest plot analysis, no significant differences were found when comparing HYDVCVB, VC, VCVB, and VD to the control group. The specific forest plot is detailed in Figure 4B. Furthermore, the league table also indicates that there were no statistically significant differences when comparing HYDVCVB, VC, VCVB, and VD to the control group. The detailed league table is provided in Supplementary Table S2. The Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) plot is shown in Figure 4C. In summary, the application of HYDVCVB, VC, VCVB, and VD in septic shock does not significantly affect the duration of mechanical ventilation.
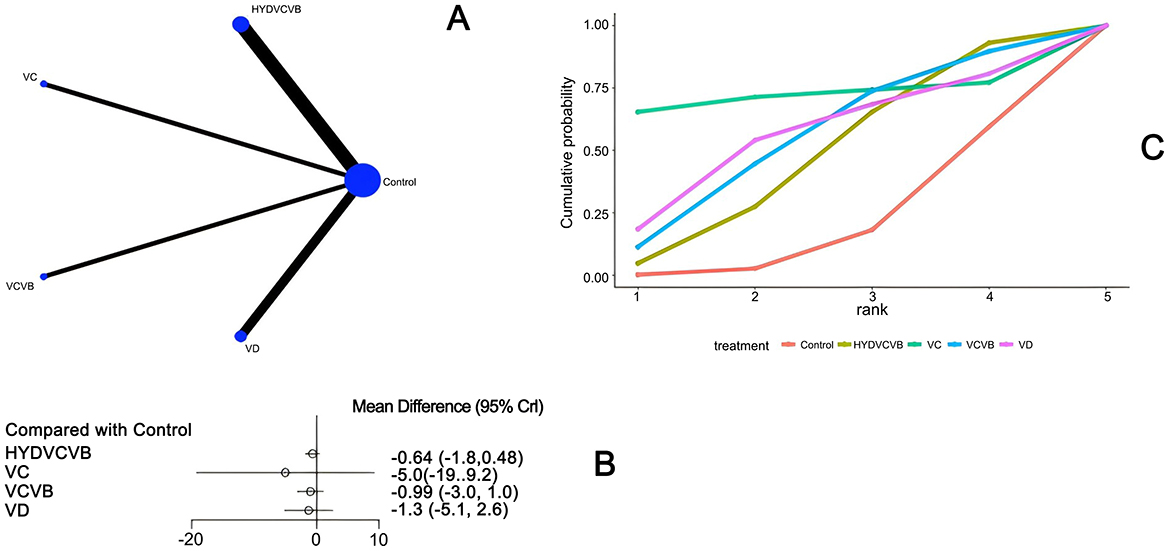
Figure 4. The effect of different vitamins on mechanical ventilation duration. (A) Network diagram illustrating the effect of treatment on mechanical ventilation duration. (B) Forest plot illustrating the effect of treatment on mechanical ventilation duration. (C) SUCRA plot illustrating the effect of treatment on mechanical ventilation duration.
3.3.3 Effect of treatment on SOFA score after 24 h
Twenty-eight studies (21–25, 27–31, 33, 34, 36–47, 49–51) have examined the impact of different vitamins on the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score 24 h after treatment, as shown in Figure 5. The network diagram reveals that direct comparisons were formed, with the most studies comparing Vitamin C to the control group. The detailed network relationship diagram is presented in Figure 5A. In the forest plot analysis, Vitamin D plus probiotics (VDP) was found to significantly reduce the SOFA score 24 h after treatment when compared to the control group [MD = −3.0, 95% CI (−5.6, −0.27)]. This indicates that VDP can effectively lower the SOFA score. The specific forest plot is detailed in Figure 5B. The league table further highlights that VDP has a significant advantage in reducing the SOFA score 24 h after treatment when compared to the control group [MD = 2.98, 95% CI (0.27, 5.62)], HYDVCVB [MD = 3.32, 95% CI (0.59, 6.04)], vitamin B [MD = 2.96, 95% CI (0.18, 5.67)], vitamin C [MD = 2.91, 95% CI (0.17, 5.57)], VCVB [MD = 3.18, 95% CI (0.31, 5.9)], and vitamin D [MD = 2.91, 95% CI (0.05, 5.71)]. These differences are statistically significant, suggesting that VDP is more effective in reducing the SOFA score. The detailed league table is provided in Supplementary Table S3. The Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) plot shows that VDP has the largest SUCRA value, indicating that VDP may be the most effective treatment for reducing the SOFA score 24 h after treatment in patients with septic shock. The SUCRA plot is detailed in Figure 5C.
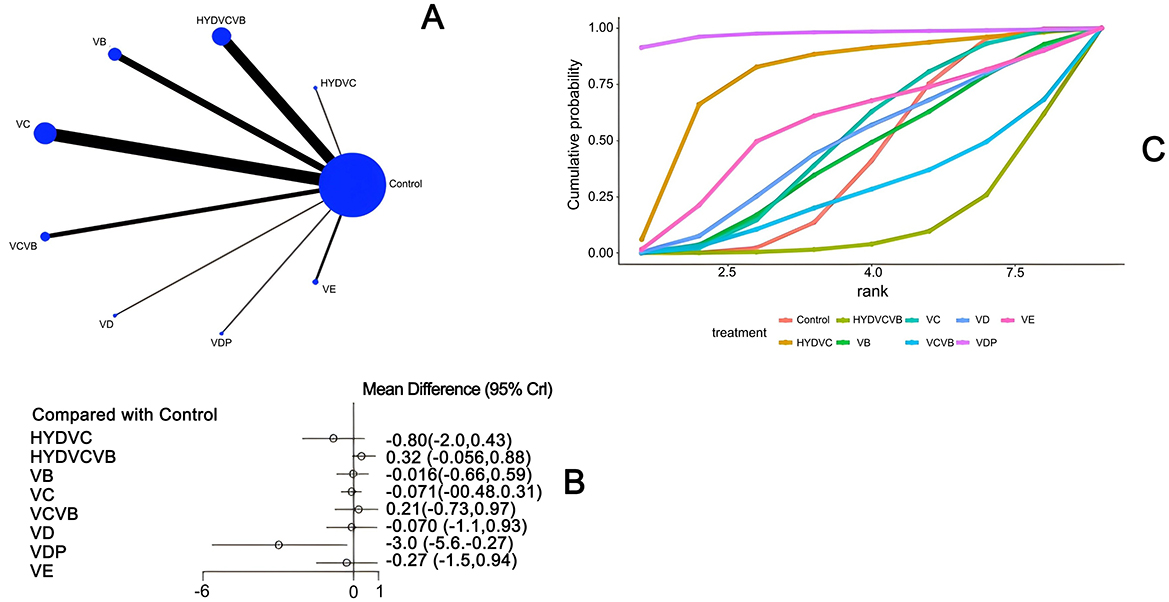
Figure 5. The effect of different vitamins on SOFA scores after 24 h. (A) Network diagram illustrating the effect of treatment on SOFA score after 24 h. (B) Forest plot illustrating the effect of treatment on SOFA score after 24 h. (C) SUCRA plot illustrating the effect of treatment on SOFA score after 24 h.
3.3.4 Effect of treatment on total length of hospital stay
Thirteen studies (20, 23, 26–28, 30, 39, 40, 44, 46, 47, 54) have examined the impact of different vitamin treatments on the total length of hospital stay, as shown in Figure 6. The network diagram reveals that direct comparisons were formed, with the most studies comparing HYDVCVB to the control group. The detailed network relationship diagram is presented in Figure 6A. In the forest plot analysis, vitamin D (VD) was found to significantly reduce the total length of hospital stay when compared to the control group [MD = −7.6, 95% CI (−13.0, −2.6)]. This indicates that VD can effectively shorten the total hospital stay. The specific forest plot is detailed in Figure 6B. The league table further highlights that VD has a significant advantage in reducing the total length of hospital stay when compared to the control group [MD = 7.61, 95% CI (2.59, 12.63)], HYDVCVB [MD = 7.71, 95% CI (2.55, 12.9)], vitamin B [MD = 7.6, 95% CI (0.84, 14.39)], vitamin C [MD = 9.93, 95% CI (3.9, 15.92)], and VCVB [MD = 8.1, 95% CI (1.79, 14.41)]. These differences are statistically significant, suggesting that VD is more effective in reducing the total length of hospital stay. The detailed league table is provided in Supplementary Table S4. The Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) plot shows that VD has the largest SUCRA value, indicating that VD may be the most effective treatment for reducing the total length of hospital stay in patients with septic shock. The SUCRA plot is detailed in Figure 6C.
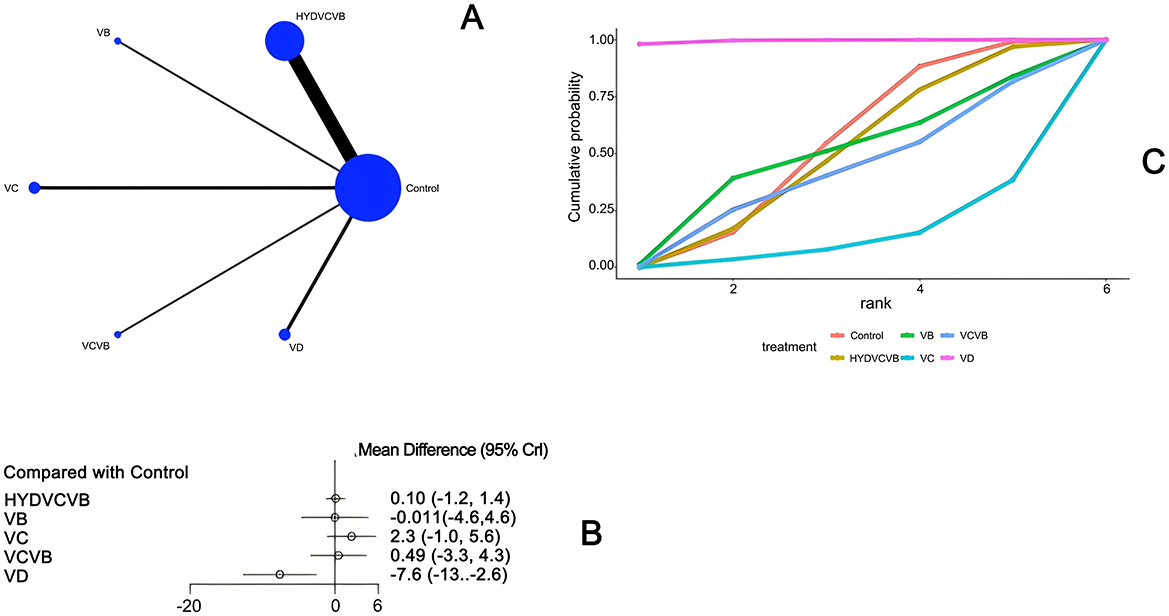
Figure 6. The effect of treatment on total length of hospital stay. (A) Network diagram illustrating the effect of treatment on total length of hospital stay. (B) Forest plot illustrating the effect of treatment on total length of hospital stay. (C) SUCRA plot illustrating the effect of treatment on total length of hospital stay.
3.3.5 Effect of treatment on 28-day mortality
Nineteen studies (20, 21, 26–28, 31, 32, 34, 35, 40–42, 44, 45, 47, 48, 52–54) have examined the impact of different vitamin treatments on 28-day mortality, as shown in Figure 7. The network diagram reveals that direct comparisons were formed, with the most studies comparing HYDVCVB to the control group. The detailed network relationship diagram is presented in Figure 7A. In the forest plot analysis, no significant differences were found when comparing HYD, HYDVCV, VB, VC, VCVB, VD, and VDP to the control group. The specific forest plot is detailed in Figure 7B. The league table further indicates that there were no statistically significant differences when comparing HYD, HYDVCV, VB, VC, VCVB, VD, and VDP to the control group. The detailed league table is provided in Supplementary Table S5. The Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) plot is shown in Figure 7C. In summary, the application of HYD, HYDVCV, VB, VC, VCVB, VD, and VDP in septic shock does not significantly affect 28-day mortality.
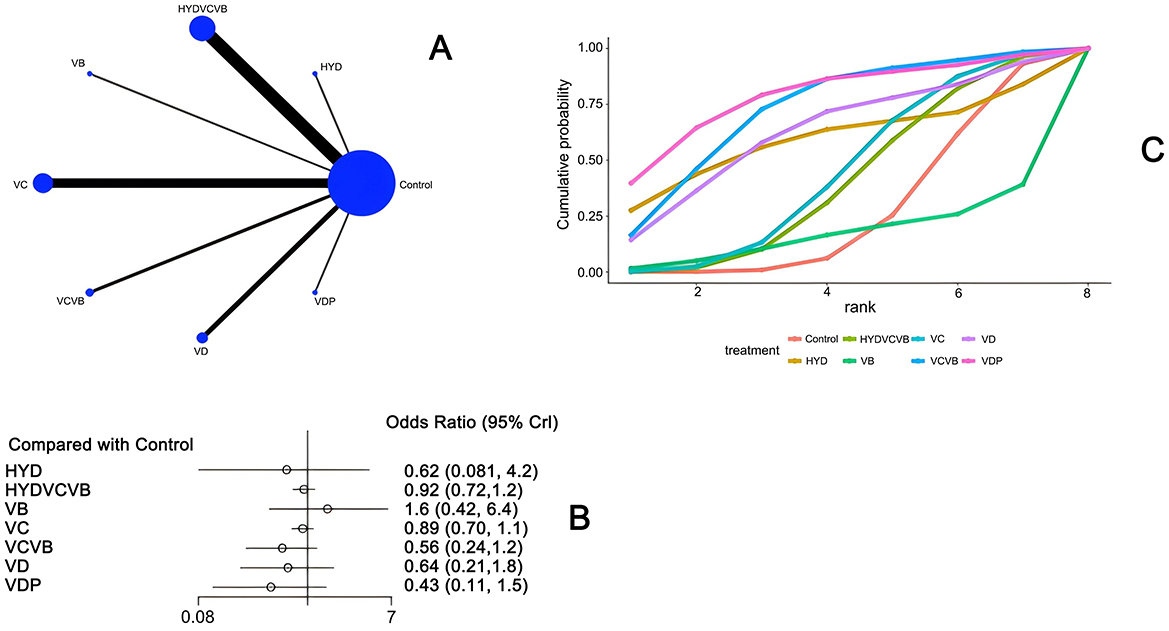
Figure 7. The effect of treatment on 28-day mortality. (A) Network diagram illustrating the effect of treatment on 28-day mortality. (B) Forest plot illustrating the effect of treatment on 28-day mortality. (C) SUCRA plot illustrating the effect of treatment on 28-day mortality.
3.4 Publication bias assessment
A funnel graph was adopted to assess the publication bias of ICU duration, mechanical ventilation time, SOFA score, total hospital stay, and 28-day death rate. The findings indicated a high likelihood of publication bias in mechanical ventilation duration, as illustrated in Supplementary material S2 (Figures S1–S5).
4 Discussion
At present, several common vitamins (VA, VB, VC, VD, and VE) in the treatment of sepsis has been covered both domestically and internationally, but most studies compare the efficacy of a single vitamin to a control group. The evaluation and ranking of the effects of different vitamin interventions on sepsis patients are not clear. Therefore, this study uses the Bayesian network meta-analysis method to evaluate the impact of different vitamins on septic shock patients, which is the innovation of this paper.
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection and is a major cause of high morbidity and mortality worldwide. Since there are no direct treatments targeting the pathogenesis of sepsis, clinical management relies on early recognition and prompt administration of antibiotics, intravenous fluids, and appropriate vasopressors (55). Over the past three decades, numerous epidemiological studies have shown a strong correlation between VD deficiency and the incidence of various infectious diseases, including sepsis (56–59). Therefore, the development of new adjuvant therapies can help improve disease prognosis or enhance therapeutic effects.
VD is a steroid hormone and a key nutrient that is reported to control a wide range of physiological processes (60). VD is available in several forms, existing as D2 and D3. In the body, D2 and D3 undergo two consecutive hydroxylation steps in the liver and are then converted into their active compounds in the kidneys, which are 25(OH)D3 calcidiol (a clinical marker of plasma VD levels) and 1,25(OH)2D3 calcitriol (61). Although there is no consensus in the literature on the plasma concentration of 25(OH)D used to define VD deficiency, it is a very common condition worldwide (62–64). Low plasma VD levels are observed in 79%−98% of intensive care unit patients, including sepsis cases (65–67). The risk of sepsis and its consequences (such as mortality, hospital stay, and organ failure) is positively correlated with VD deficiency (65, 68). Trongtrakul and Feemuchang found that three-quarters of patients diagnosed with severe sepsis had low plasma VD levels, with higher mortality rates, especially when VD plasma levels were severely deficient (25(OH)D < 30 nmol/L) (69). Therefore, restoring VD to optimal plasma levels may have an important impact on the development and outcome of sepsis. There are also studies showing that VD administration leads to a significant increase in the expression of the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin (LL-37) (70) in white blood cell mRNA and plasma cathelicidin, a significant decrease in IL-1β and IL-6 in sepsis patients (54), and a reduction in 30-day ICU readmission rates in sepsis cases, a reduction in hospital mortality in critically ill patients with severe VD deficiency (25(OH)D3 ≤ 30 nmol/L) (71), a significant reduction in hospital stay (72), a reduction in mechanical ventilation time and hospital stay, and a reduction in mortality in critically ill patients in the ICU (73). This study shows that among septic shock patients, VD may be the most effective in reducing ICU hospital stay and total hospital stay.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 27 studies, including 17 case-control studies and 10 cohort studies, found that the levels of 25-(OH)D in mothers and newborns with sepsis were significantly lower than those in non-septic children (P < 0.001). In addition, the proportion of severe VD deficiency in the sepsis group was significantly higher than in the non-sepsis group (OR = 2.66, 95% confidence interval CI = 1.13–6.25, P < 0.001). In this study, the incidence of sepsis in children with lower 25-(OH)D levels was 30.4%, while in children with higher 25-(OH)D levels it was 18.2%, but there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of mechanical ventilation rate and 30-day mortality (74). VD supplementation may become a new adjuvant therapy for sepsis in children. However, the current research results on the relationship between VD supplementation and the occurrence of sepsis in children are still controversial, and further research is needed to determine the role of VD supplementation in pediatric sepsis.
Sepsis patients often have intestinal dysbiosis, characterized by a decrease in beneficial bacteria and an increase in harmful bacteria. This imbalance can lead to impaired intestinal barrier function and increase the risk of systemic inflammatory responses (75). A study found that the abundance of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus in the gut microbiota of sepsis patients was significantly reduced, while the abundance of Bacteroides and Proteobacteria was significantly increased (54, 76). VD can modulate the composition of the gut microbiota through its active form 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25-(OH)2D3). Studies have shown that the activation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria (such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus) while inhibiting the proliferation of harmful bacteria (such as Bacteroides and Proteobacteria) (77, 78). In addition, VD reduces the production of inflammatory mediators by modulating the gut microbiota. Beneficial bacteria (such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus) can produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have anti-inflammatory effects and can modulate the function of immune cells to reduce inflammatory responses (79). A study found that VD supplementation can significantly increase the levels of SCFAs in the gut, thereby reducing the production of inflammatory mediators and improving the gut microenvironment (80). There are also studies that have found that early sepsis patients treated with a combination of probiotics [Winclove 607 based on Omnibiotic(R) 10 AAD] for 28 days did not change gut permeability, but endotoxins, endotoxin-binding proteins, and peptidoglycans increased. It can be seen that probiotic intervention successfully increased the probiotic strains in the feces and improved functional diversity (74). In severe sepsis children, supplementing with probiotics for 7 days can significantly reduce the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, increase anti-inflammatory cytokines, significantly reduce the sequential organ failure assessment score, but there is no significant improvement in mortality (75). Probiotics, as non-pathogenic microorganisms, have a positive impact on specific beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and yeast, shaping the gut microbiota and restoring the composition of gut microbiota metabolites, reducing the susceptibility to sepsis (81–83). In addition, VD deficiency can lead to perturbations in the gut microbiome (84), and VD and VDR play an important role in maintaining the balance of the gut microbiota (85), which in turn enhances immunity to gut and systemic pathogens (86). Therefore, VD combined with probiotics can be a sepsis intervention method to restore balanced gut microbiota. This study shows that among septic shock patients, VD combined with probiotics may have an advantage in reducing the SOFA score after 24 h, and more high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed in the future to further verify its clinical value.
Cobalamin (vitamin B12) is an essential trace nutrient found in animal proteins, playing an important role in the function of the central nervous system and bone marrow (87). Vitamin B12 has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties and plays an important role in the pathophysiological process of sepsis (87–90). These effects specifically include: (1) selectively inhibiting inducible nitric oxide synthase, thereby reducing the production of nitric oxide. (2) Reducing the generation of reactive oxygen species by optimizing the use of glutathione. (3) Increasing the synthesis of acetylcholine and enhancing the function of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. (4) Promoting the process of oxidative phosphorylation. (5) Enhancing antibacterial capacity. (6) Regulating the activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) (89, 91). Although cobalamin has many theoretical advantages and has shown good tolerance when administered intravenously in high doses for cyanide poisoning treatment (89, 91), its potential benefits in prospective clinical trials have not been confirmed and further exploration is needed.
In recent years, the potential role of VC in the treatment of septic shock has gradually received attention. VC is a powerful antioxidant and a cofactor for many biosynthetic enzymes, involved in the synthesis of endogenous vasopressin and norepinephrine (92). Since the human body cannot synthesize VC endogenously, and the serum VC levels of sepsis patients are usually low (93), supplementing VC has become a possible treatment option. Early studies have confirmed that intravenous VC (IVVC) is associated with reduced sepsis inflammatory response and improved outcomes (94, 95). However, the current research results on the efficacy of VC in treating sepsis or septic shock are not consistent. A meta-analysis including 18 randomized controlled trials with a total of 3,364 patients showed that IVVC treatment can significantly improve the ΔSOFA score and shorten the use of vasopressors, but it is not related to a reduction in short-term mortality (96). In addition, favorable outcomes have been reported in some meta-analyses for the VC group (97, 98). However, the existing evidence is still inconsistent. In another recent meta-analysis, intravenous VC seems to be ineffective in sepsis (99). The 2021 “Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for the Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock” suggests that for patients with sepsis or septic shock, the use of IVVC is not recommended and is only weakly recommended based on low-quality evidence (100).
In 2017, Paul Marik published for the first time the “sepsis cocktail” therapy (that is, the combined use of vitamin C, hydrocortisone, and thiamine), and reported its potential benefits in reducing mortality in sepsis patients, reducing the use of vasopressors, and reducing organ damage (95). This study was a single-center before-and-after study, and although the results were encouraging, it was also criticized mainly for the lack of support from randomized controlled trials (RCTs). In addition, multiple RCT studies and meta-analysis results have shown that the combination of vitamin C, hydrocortisone, and thiamine does not significantly improve mortality (44, 45, 101, 102).
Although this study explored the differences between different vitamins, we found in the league table that the differences between the top-ranked interventions are not obvious. Because for the selection of vitamins, we need more research to support our views, but this can also provide a treatment option for sepsis shock patients. Limitations of this study: all studies included in this study were in English, which may introduce some bias and affect the generalizability of the results. Secondly, some studies did not mention the method of random grouping, did not describe allocation concealment in detail, and did not mention the use of blinding. Therefore, more high-quality, large-scale, multicenter randomized controlled trials are needed to further verify the clinical effects of these interventions.
5 Conclusion
In patients with septic shock, the use of vitamin D shows certain advantages in reducing the number of days of ICU stay and the total length of hospital stay, and its combination with probiotics may help to lower the SOFA score after 24 h. However, these interventions have not significantly affected the 28-day mortality rate or the duration of mechanical ventilation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JT: Writing – original draft, Software. LL: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. DL: Writing – original draft, Software, Methodology. YL: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Validation. GS: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. WS: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. XY: Writing – original draft, Data curation. LS: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. HZ: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. SR: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Key Specialty Project and also this study was supported by the Mechanisms of acute gastrointestinal impairment and strategies for optimizing early enteral nutrition in patients with sepsis (ZF2023200).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1566422/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
VB, vitamin B; VC, vitamin C; VD, vitamin D; VE, vitamin E; HYD, hydroxocobalamin; HYDVCVB, hydrocortisone plus vitamin C plus vitamin B; HYDVC, hydrocortisone plus vitamin C; VDP, vitamin D plus probiotics; VCVB, vitamin C plus vitamin B; SS, septic shock; NMA, network meta-analysis; RCTs, Randomized controlled trials; ROB, risk of bias; ICU, intensive care unit; SOFA, Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment; PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; PROSPERO, Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews; MCMC, Markov Chain Monte Carlo; SUCRA, Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking curve; IVVC, Intravenous Vitamin C.
References
1. Hager DN, Hooper MH, Bernard GR, Busse LW, Ely EW, Fowler AA, et al. The vitamin C, thiamine and steroids in sepsis (VICTAS) protocol: a prospective, multi-center, double-blind, adaptive sample size, randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Trials. (2019) 20:1–16. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3254-2
2. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The Third International Consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315:801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
3. Kadri SS, Rhee C, Strich JR, Morales MK, Hohmann S, Menchaca J, et al. Estimating ten-year trends in septic shock incidence and mortality in United States academic medical centers using clinical data. Chest. (2017) 151:278–85. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.07.010
4. Gaieski DF, Edwards JM, Kallan MJ, Carr BG. Benchmarking the incidence and mortality of severe sepsis in the United States. Crit Care Med. (2013) 41:1167–74. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827c09f8
5. Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Suzuki S, Pilcher D, Bellomo R. Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000-2012. JAMA. (2014) 311:1308–16. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.2637
6. Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. (2020) 395:200–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7
7. Sakr Y, Jaschinski U, Wittebole X, Szakmany T, Lipman J, Ñamendys-Silva SA, et al. Sepsis in intensive care unit patients: worldwide data from the intensive care over nations audit. Open forum Infect Dis. (2018) 5:313. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofy313
8. Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. (2017) 43:304–77. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6
9. Fujii T, Deane AM, Nair P. Metabolic support in sepsis: corticosteroids and vitamins: the why, the when, the how. Curr Opin Crit Care. (2020) 26:363–8. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000736
10. Fujii T, Salanti G, Belletti A, Bellomo R, Carr A, Furukawa TA, et al. Effect of adjunctive vitamin C, glucocorticoids, and vitamin B1 on longer-term mortality in adults with sepsis or septic shock: a systematic review and a component network meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. (2022) 48:16–24. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06558-0
11. Corcoran TB, O'Neill MA, Webb SA, Ho KM. Prevalence of vitamin deficiencies on admission: relationship to hospital mortality in critically ill patients. Anaesth Intens Care. (2009) 37:254–60. doi: 10.1177/0310057X0903700215
12. Gerasimidis K. Assessment and interpretation of vitamin and trace element status in sick children: a position paper from the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology, and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2020) 70:873–81. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002688
13. Donnino MW, Andersen LW, Chase M, Berg KM, Tidswell M, Giberson T, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of thiamine as a metabolic resuscitator in septic shock: a pilot Study. Crit Care Med. (2016) 44:360–7. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001572
14. Fowler AA. Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure: the CITRIS-ALI Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. (2019) 322:1261–70. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.11825
15. Wald EL. Hydrocortisone-ascorbic acid-thiamine use associated with lower mortality in pediatric septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2020) 201:863–7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201908-1543LE
16. Wang Y, Shi C, Yang Z, Chen F, Gao L. Vitamin D deficiency and clinical outcomes related to septic shock in children with critical illness: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2019) 73:1095–101. doi: 10.1038/s41430-018-0249-0
17. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. (2009) 6:e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
18. Eldridge S, Campbell M, Campbell M, Dahota A, Giraudeau B, Higgins J, et al. Revised Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool for Randomized Trials (RoB 2.0). Available online at: https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/rob-2-0-tooV/archive rob-2-0-2016 (Accessed October 20, 2016).
19. Jansen JP. Bayesian meta-analysis of multiple treatment comparisons: an introduction to mixed treatment comparisons. Value Health. (2008) 11:956–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2008.00347.x
20. Luregn JS, Raman S, Buckley D, George S, King M, Ridolfi R, et al. Resuscitation with vitamin C, hydrocortisone, and thiamin in children with septic shock: a multicenter randomized pilot study. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2024) 25:159–70. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000003503
21. Wenwen Li. Ranran Zhao, Shanshan Liu, Ma C, Wan X. High-dose vitamin C improves norepinephrine level in patients with septic shock: a single-center, prospective, randomized controlled trial. Medicine. (2024) 103:e37838. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037838
22. Aisa-Álvarez A, Pérez-Torres I, Guarner-Lans V, Manzano-Pech L, Cruz-Soto R, Márquez-Velasco R, et al. Randomized clinical trial of antioxidant therapy patients with septic shock and organ dysfunction in the ICU: SOFA score reduction by improvement of the enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant system. Cells. (2023) 12:1330. doi: 10.3390/cells12091330
23. Mohamed A, Abdelaty M, Saad MO, Shible A, Mitwally H, Akkari AR, et al. Evaluation of hydrocortisone, vitamin C, and thiamine for the treatment of septic shock: a randomized controlled trial (The Hyvits Trial). Shock. (2023) 59:697–701. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002110
24. Moskowitz A, Berg KM, Grossestreuer AV, Balaji L, Liu X, Cocchi MN, et al. Thiamine for Renal Protection in Septic Shock (TRPSS): a randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2023) 208:570–8. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202301-0034OC
25. Yanase F, Spano S, Maeda A, Chaba A, Naorungroj T, Ow CPC, et al. Mega-dose sodium ascorbate: a pilot, single-dose, physiological effect, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Crit Care. (2023) 27:371. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04644-x
26. Wang J, Song Q, Yang S, Wang H, Meng S, Huang L, et al. Effects of hydrocortisone combined with vitamin C and vitamin B1 versus hydrocortisone alone on microcirculation in septic shock patients: a pilot study. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. (2023) 84:111–23. doi: 10.3233/CH-221444
27. Wacker DA, Burton SL, Berger JP, Hegg AJ, Heisdorffer J, Wang Q, et al. Evaluating vitamin C in septic shock: a randomized controlled trial of vitamin C monotherapy. Crit Care Med. (2022) 50:e458–67. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005427
28. Lyu QQ, Zheng R, Chen Q-H, Yu J-Q, Shao J, Gu X-H. Early administration of hydrocortisone, vitamin C, and thiamine in adult patients with septic shock: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Crit Care. (2022) 26:295. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04175-x
29. Nandhini N, Malviya D, Parashar S, Pandey C, Nath SS, Tripathi M. Comparison of the effects of vitamin C and thiamine on refractory hypotension in patients with sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. (2022) 12:138–45. doi: 10.4103/ijciis.ijciis_107_21
30. Rosengrave P, Spencer E, Williman J, Mehrtens J, Morgan S, Doyle T, et al. Intravenous vitamin C administration to patients with septic shock: a pilot randomised controlled trial. Crit Care. (2022) 26:26. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-03900-w
31. Lamontagne F, Masse MH, Menard J, Sprague S, Pinto R, Heyland DK, et al. Intravenous vitamin C in adults with sepsis in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386:2387–98. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2200644
32. Patel JJ, Willoughby R, Peterson J, Carver T, Zelten J, Markiewicz A, et al. High-dose IV hydroxocobalamin (Vitamin B12) in septic shock: a double-blind, allocation-concealed, placebo-controlled single-center pilot randomized controlled trial (The Intravenous Hydroxocobalamin in Septic Shock Trial). Chest. (2023) 163:303–12. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.09.021
33. Yadav AK, Singh VK, Singh GP, Singh V. Outcome of Ulinastatin vs metabolic resuscitation using ascorbic acid, thiamine and glucocorticoid in early treatment of sepsis- a randomised controlled trial. J Clin Diagn Res. (2021) 15:UC36–9. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2021/47233.14946
34. Kamel NA, Soliman MM, Abo-Zeid MA, Shaaban MI. Effect of anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial cosupplementations on sepsis prevention in critically ill trauma patients at high risk for sepsis. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:792741. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.792741
35. Hussein AA, Sabry NA, Abdalla MS, Farid SF. A prospective, randomised clinical study comparing triple therapy regimen to hydrocortisone monotherapy in reducing mortality in septic shock patients. Int J Clin Pract. (2021) 75:e14376. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.14376
36. Sevransky JE, Rothman RE, Hager DN, Bernard GR, Brown SM, Buchman TG, et al. Effect of vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone on ventilator- and vasopressor-free days in patients with sepsis: the VICTAS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2021) 325:742–50. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.24505
37. Jamshidi MR, Zeraati MR, Forouzanfar B, Tahrekhani M, Motamed N. Effects of triple combination of hydrocortisone, thiamine, and Vitamin C on clinical outcome in patients with septic shock: a single-center randomized controlled trial. J Res Med Sci. (2021) 26:47. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_593_19
38. Ap GR, Daga MK, Mawari G, Koner BC, Singh VK, Kumar N, et al. Effect of supplementation of vitamin C and thiamine on the outcome in sepsis: South East Asian Region. J Assoc Physicians India. (2022) 70:11–2.
39. Iglesias J, Vassallo AV, Patel VV, Sullivan JB, Cavanaugh J, Elbaga Y. Outcomes of metabolic resuscitation using ascorbic acid, thiamine, and glucocorticoids in the early treatment of sepsis: the ORANGES Trial. Chest. (2020) 158:164–73. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.049
40. Hwang SY, Ryoo SM, Park JE, Jo YH, Jang DH, Suh GJ, et al. Combination therapy of vitamin C and thiamine for septic shock: a multi-centre, double-blinded randomized, controlled study. Intensive Care Med. (2020) 46:2015–25. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06191-3
41. Lv SJ, Zhang GH, Xia JM, Yu H, Zhao F. Early use of high-dose vitamin C is beneficial in treatment of sepsis. Ir J Med Sci. (2020) 190:1183–8. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02394-1
42. Petsakul S, Morakul S, Tangsujaritvijit V, Kunawut P, Singhatas P, Sanguanwit P. Effects of thiamine on vasopressor requirements in patients with septic shock: a prospective randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. (2020) 20:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-01195-4
43. Wang Y, Yang Z, Gao L, Cao Z, Wang Q. Effects of a single dose of vitamin D in septic children: a randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial. J Int Med Res. (2020) 48:0300060520926890. doi: 10.1177/0300060520926890
44. Fujii T, Luethi N, Young PJ, Frei DR, Eastwood GM, French CJ, et al. Effect of vitamin C, hydrocortisone, and thiamine vs hydrocortisone alone on time alive and free of vasopressor support among patients with septic shock: the VITAMINS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. (2020) 323:423–31. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.22176
45. Moskowitz A, Huang DT, Hou PC, Gong J, Doshi PB, Grossestreuer AV, et al. Effect of ascorbic acid, corticosteroids, and thiamine on organ injury in septic shock: the ACTS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. (2020) 324:642–50. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.11946
46. Mohamed ZU, Prasannan P, Moni M, Edathadathil F, Prasanna P, Menon A, et al. Vitamin C therapy for routine care in septic shock (ViCTOR) trial: effect of intravenous vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone administration on inpatient mortality among patients with septic shock. Indian J Crit Care Med. (2020) 24:653. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23517
47. Wani SJ, Mufti SA, Jan RA, Shah SU, Qadri SM, Khan UH, et al. Combination of vitamin C, thiamine and hydrocortisone added to standard treatment in the management of sepsis: results from an open label randomised controlled clinical trial and a review of the literature. Infect Dis. (2020) 52:271–8. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2020.1718200
48. Chang P, Liao Y, Guan J, Guo Y, Zhao M, Hu J, et al. Combined treatment with hydrocortisone, vitamin C, and thiamine for sepsis and septic shock: a randomized controlled trial. Chest. (2020) 158:174–82. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.065
49. Aisa-Alvarez A, Soto ME, Guarner-Lans V, Camarena-Alejo G, Franco-Granillo J, Martínez-Rodríguez EA, et al. Usefulness of antioxidants as adjuvant therapy for septic shock: a randomized clinical trial. Medicina. (2020) 56:619. doi: 10.3390/medicina56110619
50. Karimpour H, Bahrami A, Amini S, Rezaei M, Amini-Saman J, Shahbazi F. Effects of a high dose of vitamin C along with thiamine in critically-ill patients with septic shock: a preliminary study. JPRI. (2019) 29:1–7. doi: 10.9734/jpri/2019/v29i530248
51. Harun NF, Cheah SK, Yusof AM, Lau CL. Intravenous thiamine as an adjuvant therapy for hyperlactatemia in septic shock patients. Crit Care Shock. (2019) 22:288–98.
52. Ding F, Zang B, Fu J, Ji K. Effect of vitamin D on the severity and prognosis of patients with sepsis: a prospective randomized double-blind placebo study. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. (2017) 29:106–10. doi: 10.3760/cma.J.issn.2095-4352.2017.02.003
53. Zabet MH, Mohammadi M, Ramezani M, Khalili H. Effect of high-dose Ascorbic acid on vasopressor's requirement in septic shock. J Res Pharm Pract. (2016) 5:94–100. doi: 10.4103/2279-042X.179569
54. Quraishi SA, De Pascale G, Needleman JS, Nakazawa H, Kaneki M, Bajwa EK, et al. Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation on vitamin D status and cathelicidin levels in sepsis: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Crit Care Med. (2015) 43:1928–37. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001148
55. Wang Y, Lin H, Lin BW, Lin JD. Effects of different ascorbic acid doses on the mortality of critically ill patients: a meta-analysis. Ann Intensive Care. (2019) 9:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13613-019-0532-9
56. Laaksi I, Ruohola JP, Tuohimaa P, Auvinen A, Haataja R, Pihlajamäki H, et al. An association of serum vitamin D concentrations < 40 nmol/L with acute respiratory tract infection in young Finnish men. Am J Clin Nutr. (2007) 86:714–7. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/86.3.714
57. Upala S, Sanguankeo A, Permpalung N. Significant association between vitamin D deficiency and sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. (2015) 15:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12871-015-0063-3
58. Zhou W, Mao S, Wu L, Yu J. Association between vitamin D status and sepsis. Clin Lab. (2018) 64:451–60. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2017.170919
59. McNally JD, Leis K, Matheson LA, Karuananyake C, Sankaran K, Rosenberg AM. Vitamin D deficiency in young children with severe acute lower respiratory infection. Pediatr Pulmonol. (2009) 44:981–8. doi: 10.1002/ppul.21089
60. Tintut Y, Demer LL. Potential impact of the steroid hormone, vitamin D, on the vasculature vitamin D-hormones and cardiovascular disease. Am Heart J. (2021) 239:147–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2021.05.012
61. Demer LL, Hsu JJ, Tintut Y. Steroid hormone vitamin D: implications for cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. (2018) 122:1576–85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.311585
62. Roth DE, Abrams SA, Aloia J, Bergeron G, Bourassa MW, Brown KH, et al. Global prevalence and disease burden of vitamin D deficiency: a roadmap for action in low-and middle-income countries. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2018) 1430:44–79. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13968
63. Giustina A, Adler RA, Binkley N, Bollerslev J, Bouillon R, Dawson-Hughes B, et al. Consensus statement from 2nd International Conference on Controversies in vitamin D. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. (2020) 21:89–116. doi: 10.1007/s11154-019-09532-w
64. Mogire RM, Mutua A, Kimita W, Kamau A, Bejon P, Pettifor JM, et al. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. (2020) 8:e134–42. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30457-7
65. Kempker JA, Tangpricha V, Ziegler TR, Martin GS. Vitamin D in sepsis: from basic science to clinical impact. Crit Care. (2012) 16:1–6. doi: 10.1186/cc11252
66. Azim A, Ahmed A, Yadav S, Baronia AK, Gurjar M, Godbole MM, et al. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in critically ill patients and its influence on outcome: experience from a tertiary care centre in North India (an observational study). J Intensive Care. (2013) 1:1–5. doi: 10.1186/2052-0492-1-14
67. Amrein K, Papinutti A, Mathew E, Vila G, Parekh D. Vitamin D and critical illness: what endocrinology can learn from intensive care and vice versa. Endocr Connect. (2018) 7:R304–15. doi: 10.1530/EC-18-0184
68. de Haan K, Groeneveld AB, de Geus HR, Egal M, Struijs A. Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for infection, sepsis and mortality in the critically ill: systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. (2014) 18:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0660-4
69. Trongtrakul K, Feemuchang C. Prevalence and association of vitamin D deficiency and mortality in patients with severe sepsis. Int J Gen Med. (2017) 10:415–21. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S147561
70. Leaf DE, Raed A, Donnino MW, Ginde AA, Waikar SS. Randomized controlled trial of calcitriol in severe sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2014) 190:533–41. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201405-0988OC
71. Amrein K, Schnedl C, Holl A, Riedl R, Christopher KB, Pachler C, et al. Effect of high-dose vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in critically ill patients with vitamin D deficiency: the VITdAL-ICU randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2014) 312:1520–30. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.13204
72. Han JE, Jones JL, Tangpricha V, Brown MA, Brown LAS, Hao L, et al. High dose vitamin D administration in ventilated intensive care unit patients: a pilot double blind randomized controlled trial. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. (2016) 4:59–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jcte.2016.04.004
73. Miri M, Kouchek M, Rahat Dahmardeh A, Sistanizad M. Effect of high-dose vitamin D on duration of mechanical ventilation in ICU patients. Iran J Pharm Re. (2019) 18:1067. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.1100647
74. Yu W, Ying Q, Zhu W, Huang L, Hou Q. Vitamin D status was associated with sepsis in critically ill children: a PRISMA compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. (2021) 100:e23827. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023827
75. Piccioni A, Spagnuolo F, Candelli M, Voza A, Covino M, Gasbarrini A, et al. The gut microbiome in sepsis: from dysbiosis to personalized therapy. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:6082. doi: 10.3390/jcm13206082
76. De Pascale G, Vallecoccia MS, Schiattarella A, Di Gravio V, Cutuli SL, Bello G, et al. Clinical and microbiological outcome in septic patients with extremely low 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels at initiation of critical care. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2016) 22:e7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.12.015
77. Fakhoury HMA, Kvietys PR, AlKattan W, Anouti FA, Elahi MA, Karras SN, et al. Vitamin D and intestinal homeostasis: barrier, microbiota, and immune modulation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2020) 200:105663. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105663
78. Greenstein RJ, Su L, Brown ST. Vitamins A & D inhibit the growth of mycobacteria in radiometric culture. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e29631. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029631
79. Gioia C, Lucchino B, Tarsitano MG, Iannuccelli C, Di Franco M. Dietary habits and nutrition in rheumatoid arthritis: can diet influence disease development and clinical manifestations? Nutrients. (2020) 12:1456. doi: 10.3390/nu12051456
80. Wellington VNA, Sundaram VL, Singh S, Sundaram U. Dietary supplementation with vitamin D, fish oil or resveratrol modulates the gut microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 23:206. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010206
81. Fu Y, Zhang S, Yue Q, An Z, Zhao M, Zhao C, et al. The preventative effects of Lactococcus Lactis metabolites against LPS-in-ducedsepsis. Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1404652. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1404652
82. Potruch A, Schwartz A, Ilan Y. The role of bacterial translocation in sepsis: a new target for therapy. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. (2022) 15:17562848221094214. doi: 10.1177/17562848221094214
83. Chang BT, Wang Y, Tu WL, Zhang ZQ, Pu YF, Xie L, et al. Regulatory effects of mangiferinon LPS-induced inflammatory responses and intest inalflora imbalance during sepsis. Food Sci Nutr. (2024) 12:2068–80. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3907
84. Stadlbauer V, Horvath A, Komarova I, Schmerboeck B, Feldbacher N, Klymiuk I, et al. Dysbiosis in early sepsis/can be modulated by a multispecies probiotic: a randomised controlled pilot trial. Benef Microbes. (2019) 10:265–78. doi: 10.3920/BM2018.0067
85. Angurana SK, Bansal A, Singhi S, Aggarwal R, Jayashree M, Salaria M, et al. Evaluation of effect of pro-biotics on cytokine levels in critically ill children with severe sepsis: a double - blind, placebo - controlled trial. Crit Care Med. (2018) 46:1656–64. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003279
86. Haak BW, Wiersinga WJ. The role of the gut microbiota in sepsis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 2:135–43. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30119-4
87. Romain M, Sviri S, Linton DM, Stav I, van Heerden PV. The role of vitamin B12 in the critically ill—a review. Anaesth Intensive Care. (2016) 44:447–52. doi: 10.1177/0310057X1604400410
88. Birch CS, Brasch NE, McCaddon A, Williams JH. A novel role for vitamin B12: cobalamins are intracellular antioxidants in vitro. Free Radic Biol Med. (2009) 47:184–8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.04.023
89. Manzanares W, Hardy G. Vitamin B12: the forgotten micronutrient for critical care. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2010) 13:662–8. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32833dfaec
90. Weinberg JB, Chen Y, Jiang N, Beasley BE, Salerno JC, Ghosh DK. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase by cobalamins and cobinamides. Free Radic Biol Med. (2009) 46:1626–32. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.03.017
91. Wheatley C. A scarlet pimpernel for the resolution of inflammation? The role of supra-therapeutic doses of cobalamin, in the treatment ofsystemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic or traumatic shock. Med Hypotheses. (2006) 67:124–42. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2006.01.036
92. Carr AC, Shaw GM, Fowler AA, Natarajan R. Ascorbate-dependent vasopressor synthesis: a rationale for vitamin C administration in severe sepsis and septic shock? Crit Care. (2015) 19:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-1131-2
93. Belsky JB, Wira CR, Jacob V, Sather JE, Lee PJ. A review of micronutrients in sepsis: the role of thiamine, l-carnitine, vitamin C, selenium and vitamin D. Nutr Res Rev. (2018) 31:281–90. doi: 10.1017/S0954422418000124
94. Fowler AA, Syed AA III, Knowlson S, Sculthorpe R, Farthing D, DeWilde C, et al. Phase I safety trial of intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with severe sepsis. J Transl Med. (2014) 12:1–10. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-32
95. Marik PE, Khangoora V, Rivera R, Hooper MH, Catravas J. Hydrocortisone, vitamin C, and thiamine for the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock: a retrospective before-after study. Chest. (2017) 151:1229–38. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.11.036
96. Liang B, Su J, Shao H, Chen H, Xie B. The outcome of IV vitamin C therapy in patients with sepsis or septic shock: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Critical Care. (2023) 27:109. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04392-y
97. Li J. Evidence is stronger than you think: a meta-analysis of vitamin C use in patients with sepsis. Crit Care. (2018) 22:258–67. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2191-x
98. Muhammad M, Jahangir A, Kassem A, Sattar SBA, Jahangir A, Sahra S, et al. The role and efficacy of vitamin C in sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Respir Med. (2022) 90:281–99. doi: 10.3390/arm90040038
99. Cai B, Lv X, Lin M, Feng C, Chen C. Clinical efficacy and safety of vitamin C in the treatment of septic shock patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Palliat Med. (2022) 11:1369–80. doi: 10.21037/apm-22-225
100. Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. (2021) 47:1181–247. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y
101. Putzu A, Daems AM, Lopez-Delgado JC, Giordano VF, Landoni G. The effect of vitamin C on clinical outcome incritically ill patients: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Care Med. (2019) 47:774–83. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003700
Keywords: vitamins, septic shock, network meta-analysis, vitamin D, shock
Citation: Tian J, Long L, Li D, Liang Y, Sun G, Song W, Yue X, Shen L, Zhao H and Ren S (2025) Effects of different vitamins on individuals with septic shock: a Bayesian NMA of RCTs. Front. Nutr. 12:1566422. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1566422
Received: 24 January 2025; Accepted: 25 July 2025;
Published: 13 August 2025.
Edited by:
Dieter Kabelitz, University of Kiel, GermanyReviewed by:
Manjusha Biswas, University Hospital Bonn, GermanyShivang Sharma, Johns Hopkins University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Tian, Long, Li, Liang, Sun, Song, Yue, Shen, Zhao and Ren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shan Ren, cnMxMjI2QHNpbmEuY29t
 Jinjin Tian1
Jinjin Tian1 Limin Shen
Limin Shen Heling Zhao
Heling Zhao Shan Ren
Shan Ren