- 1Department of Endocrinology & Rheumatology, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences Affiliated Zhoupu Hospital, Shanghai, China
- 2Graduate School, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
Objective: Hemoglobin to red blood cell distribution width ratio (HRR) is a novel prognostic indicator of disease, and is also associated with a variety of chronic systemic diseases. However, there are fewer studies on the relationship between HRR and albuminuria. This study aimed to investigate the association between the two subjects.
Methods: A total of 13,971 participants aged 20 and older in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) between 2007 and 2018. The HRR is the ratio of hemoglobin to the width of the red blood cell distribution. Smoothed curve fitting and multivariate segmented linear regression models were used to study the relationship between HRR and albuminuria. Finally, subgroup analysis and interaction tests were performed to test the stability of the results.
Results: The results of the univariate analysis showed that HRR was negatively associated with albuminuria (OR = 0.86, p < 0.0001). After further adjustment of potential confounding factors, the smooth curve fitting showed that HRR was nonlinearly related to albuminuria. The inflection point of HRR in multiple segmented linear regression analysis was 1.213. Specifically, when HRR <1.213, (OR = 0.93, 95% CI 0.90, 0.97; p = 0.0007); when HRR ≥ 1.213, (OR = 1.24, 95% CI 1.08, 1.43; p < 0.0001). Subgroup analyses revealed that this association exists as stable in different populations.
Conclusion: There was a nonlinear correlation between HRR and albuminuria in adults aged 20 or older in the United States.
Introduction
Albuminuria, characterized by abnormal excretion of protein in the urine, it is usually expressed as the ratio of urinary albumin to creatinine in urine (UACR) over 30 mg/g (1, 2). Microalbuminuria is an early stage of glomerular disease, and the presence of albuminuria indicates an impaired glomerular filtration barrier, the first line of defense for the maintenance of the renal selective permeability (3, 4). Previous studies have shown that even low levels of albuminuria are associated with diabetic nephropathy, all-cause death, and cardiovascular death (5, 6). This damage triggers a range of harmful effects over time. Persistent albuminuria was not only associated with increased likelihood of developing end-stage renal disease but also with the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events (4, 7). Therefore, early detection and effective management of albuminuria is essential to reduce the risk of renal failure and associated complications.
HRR was originally proposed as a new combinatorial biomarker by Sun et al. (8) in the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression Study. HRR has been widely used to assess various diseases such as cancer (9), cardiovascular disease (10), cerebrovascular disease (11, 12), and bone mineral density (13) etc. HRR, calculated by dividing hemoglobin by red blood cell distribution width ratio (RDW), is a new inflammatory marker that better reflects the function of red blood cells. Given the emerging evidence that inflammation plays a key role in the pathophysiology of albuminuria (14, 15), the potential association between HRR and albuminuria has been noted. HRR is unique in its ability to reflect subtle changes in blood parameters that may not be detected when analyzing hemoglobin or red blood cell distribution width (RDW) alone.
In the assessment and diagnosis of the disease, the complete blood cell count (CBC) plays a key role in revealing the blood health status of individuals (16). Hemoglobin is an important parameter of CBC. It is a protein rich in red blood cells (RBC), which mainly plays the role of oxygen transport molecule (17). Due to the direct link between blood circulation and tissue oxygen supply, the hemoglobin level is closely related with the occurrence and development of albuminuria. However, previous studies on the relationship between hemoglobin levels and albuminuria have drawn inconsistent conclusions. A retrospective cohort study in Japan found that low hemoglobin concentration was associated with the progression and development of albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes (18). However, another study showed that patients with erycytosis (female, hemoglobin 190 g / L or above; male, 210 g/L or above) had a median urinary protein level of 2.5 g/24 h, and the kidney is one of the most severely affected organs (19). Furthermore, a cross-sectional study with a total population of 8,868 found that, after adjusting for all latent variables, hemoglobin levels showed a U-type association with albuminuria, with an inflection point of 15.5 g/dL, both lower and higher hemoglobin levels were associated with the development of albuminuria (20). RDW is another important parameter of CBC and is used to measure variability in RBC counts. Existing studies found a significant negative relationship between RDW and renal function, and this association remained highly significant even after multivariable adjustment for comorbidities, iron deficiency, inflammation and nutritional status (21). HRR is a ratio that combines hemoglobin and RDW, and there is a lack of clarity regarding the relationship between HRR and albuminuria; therefore, we conducted the present study to examine the relationship between HRR and albuminuria in the United States adults.
Materials and methods
Study population
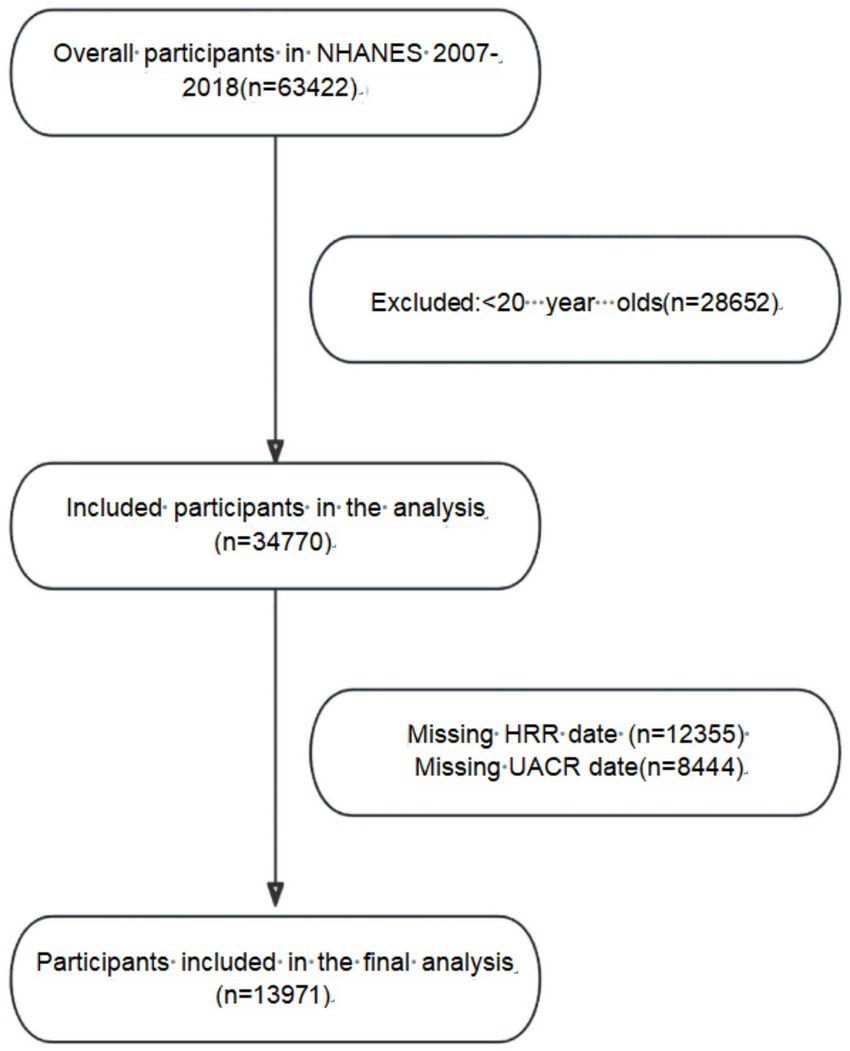
Data for this study were obtained from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey of the National Center for Health Statistics (NHANES), the project was approved by the Ethics Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), and all participants signed written informed consent before enrollment. This study covers the data from 2007 to 2018, involving a total of 63,422 subjects. During the screening process, we excluded participants under 20 years (28652), participants with incomplete urinary albumin creatinine ratio (UACR) data (8444) and participants with incomplete HRR data (12355). A total of 13,971 individuals were ultimately included in the study. The specific screening process is shown in Figure 1.
Exposure variables and outcome definition
The exposure variable in this study was HRR. The HRR value of each subject was calculated by dividing hemoglobin (unit: grams/deciliter, g/dL) by RDW, and the results were rounded to two decimal places. Blood samples from NHANES participants were collected at standardized flow sampling centers. The NHANES Laboratory/Medical Technician Operation Manual details the specific procedures for sample collection and processing. CBC parameters including hemoglobin and RDW were derived using the Beckman Coulter methodology.
The definition of proteinuria is based on the urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR), which is calculated by dividing the concentration of urinary albumin (mg) by the concentration of urinary creatinine (g). UACR> 30 mg/g is defined as albuminuria (2). The researchers collected urine samples from NHANES participants at standardized mobile testing centers. Urinary albumin levels were measured using solid-phase fluorescence immunoassay, while urinary creatinine levels were assessed using enzymatic methods.
Covariates
Based on previous studies (22), this research included the following covariates: age, gender, race, poverty-income ratio (PIR), education level, body mass index (BMI), smoking and alcohol consumption status, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (CR), uric acid (UA), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), fasting blood glucose (FBG), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), as well as hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Demographic data were collected through questionnaires. The specific items included: age (years); gender (male or female); ethnicity (Mexican American, other Hispanic, non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, and other ethnic groups); education level (less than high school, high school, more than high school); and poverty income ratio (PIR).
The physical examination included measurements of height, weight, systolic blood pressure (SBP), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP). BMI was calculated based on height (HT, meters) and weight (WT, kilograms) using the formula BMI = WT/(HT)^2.
Laboratory data included BUN, CR, UA, ALT, AST, LDL-C, HDL-C, TG, TC, FBG, HbA1c and eGFR, among which eGFR was calculated by CKD-EPI formula (23).
We collected participants’ personal behaviors, medical history, and medication use through questionnaires. The criteria included: (1) Those who have smoked at least 100 cigarettes in their lifetime are classified as smokers; (2) Those who have consumed at least 12 alcoholic beverages in the past 12 months are classified as drinkers; (3) Hypertension was defined as three consecutive measurements showing an average SBP ≥ 140 mmHg and/or DBP ≥ 90 mmHg, or two or more participants being diagnosed with hypertension or prescribed antihypertensive medications; (4) Diabetes was defined as being diagnosed by a physician, taking anti-diabetic medications, using insulin, or having FBG ≥ 7.0 mmol/LmM or HbA1c ≥ 6.5%; (5) CVD were self-reported conditions including coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, heart failure, myocardial infarction, and/or stroke.
Statistical analysis
If the continuous variables meet normal distribution, expressed as mean ± standard deviation; If the continuous variable shows a skewed distribution, expressed as the median (Q1-Q3), Categorical variables were expressed as percentages. First, the linear relationship between HRR and albuminuria was analyzed using univariate logistic regression, and then, after adjusting for potential confounders, the nonlinear relationship between HRR and albuminuria was investigated using smoothed curve fitting and multivariate segmented linear regression models. Finally, subgroup analysis and interaction tests were performed to determine the stability of the relationship between HRR and albuminuria in different populations by age (≥60, <60 years), gender (male, female), BMI (≥25, <25), eGFR (≥60, <60), race, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, smoking and drinking status. The missing covariates were reanalyzed after multiple interpolation, and multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to ensure the stability of the research results (24, 25). A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All data were analyzed using the statistical packages R (2The R Foundation) and EmpowerStats (3X&Y Solutions, Inc., Boston, MA, USA conduct).
Results
Subject population description
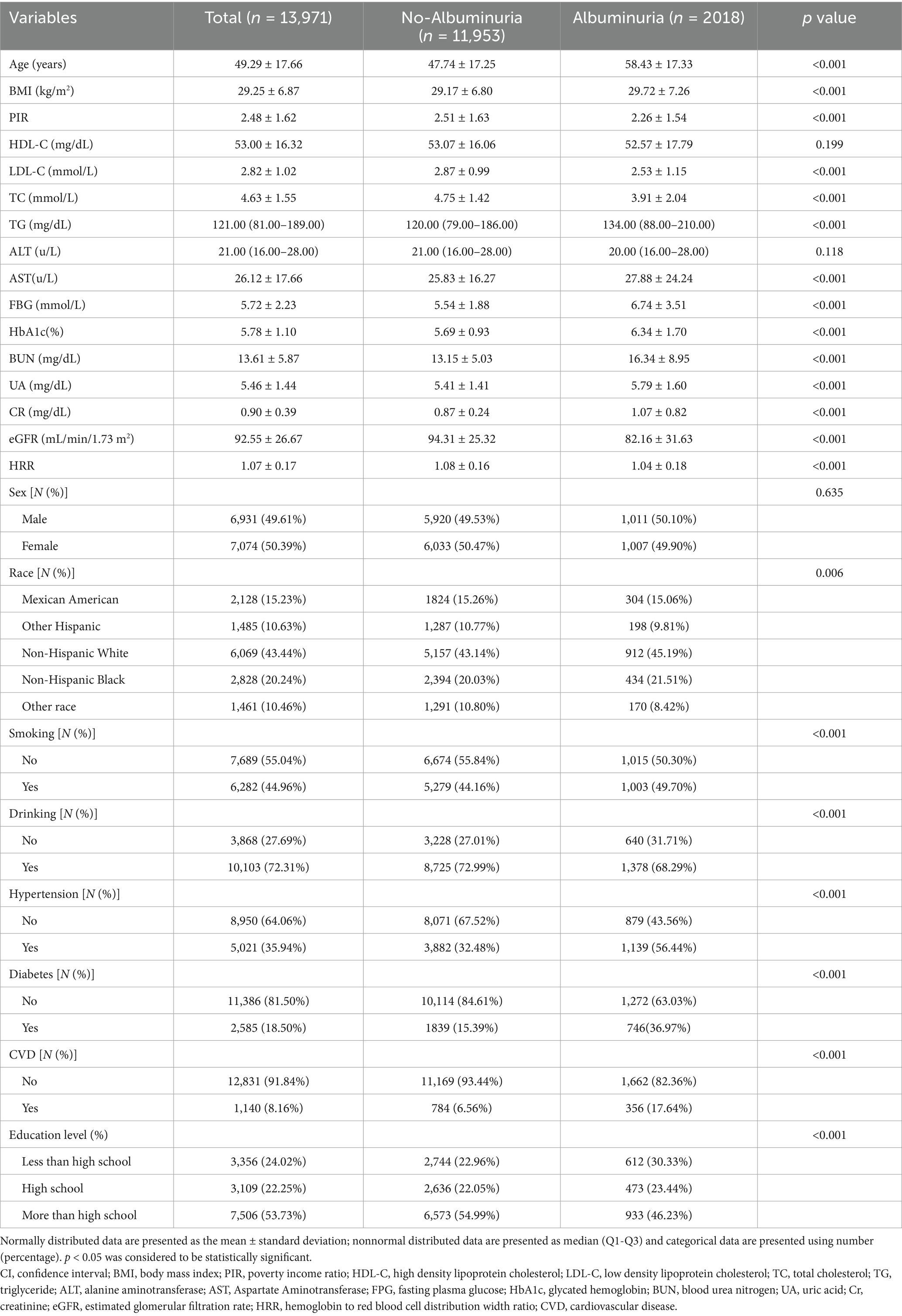
Table 1 describes the baseline characteristics of the researchers. A total of 13,971 investigators were included in this study, of whom 6,931 (49.61%) were males and 7,074 (50.39%) were females. The mean age was 49.29 ± 17.66 years; mean HRR was 1.07 ± 0.17 and overall prevalence of albuminuria was 12.1%. Among the study population, 35.94% were patients with hypertension, 18.50% were patients with diabetes and 8.16% were patients with CVD.
Compared with subjects without albuminuria, subjects in the albuminuria group were older and had higher BMI, TG, AST, FBG, HbA1c, BUN, UA, CR, instead, the albuminuria group had lower PIR, LDL-C, TC, eGFR, and HRR. In addition, adults with albuminuria tend to smoke, drink alcohol, have a low level of education, and have a higher prevalence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and CVD. However, there was no significant difference in gender, ALT, and HDL-C groups (p > 0.05).
Factors associated with albuminuria
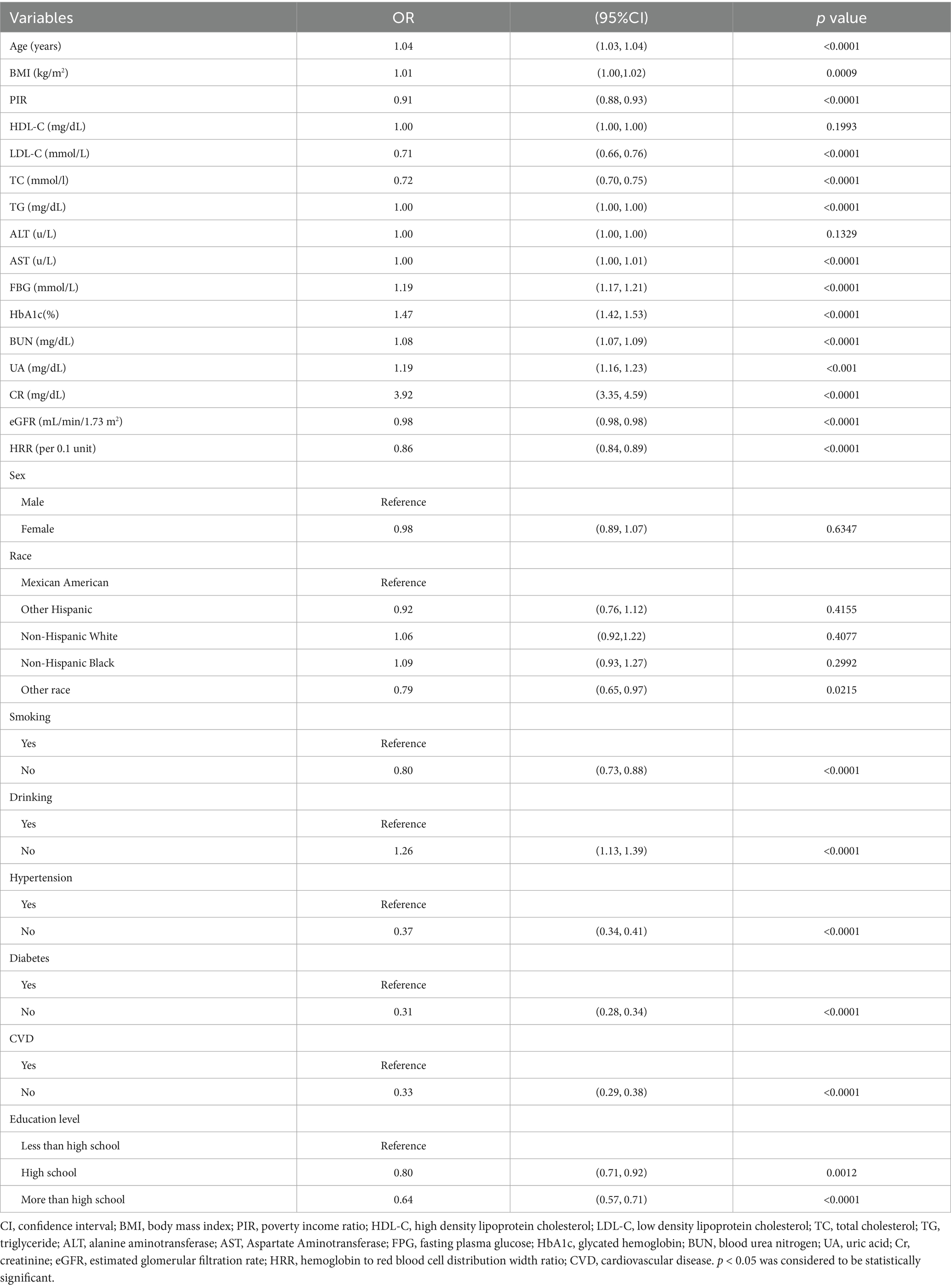
Table 2 describes the results of the univariate analysis. For the unadjusted model, HRR was significantly negatively correlated with albuminuria (p < 0.001). In addition, other variables significantly associated with albuminuria were age, BMI, PIR, LDL-C, TC, TG, AST, FBG, HbA1c, BUN, UA, CR, eGFR, smoking, alcohol consumption, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, CVD, and education level (p < 0.05).
Independent correlation between HRR and albuminuria by multivariate piecewise linear regression
After adjusting for gender, age, BMI, PIR, TC, TG, ALT, AST, BUN, UA, CR, eGFR, ethnicity, smoking, drinking status, hypertension, diabetes, CVD, and education level, a smooth curve fit showed a nonlinear relationship between HRR and albuminuria (shown in Figure 2). The inflection point of the HRR was then determined by threshold effects analysis, and the data indicated an inflection point of 1.213 for the HRR. When HRR < 1.213, each 0.1 unit increase in HRR was associated with a 7% reduction in the risk of albuminuria (OR = 0.93, 95% CI 0.90, 0.97; p = 0.0007), and conversely, when HRR ≥ 1.213, each 0.1 unit increase in HRR was associated with a 24% increase in the risk of albuminuria (OR = 1.24, 95% CI 1.08, 1.43; p < 0.0001) (as shown in Table 3).
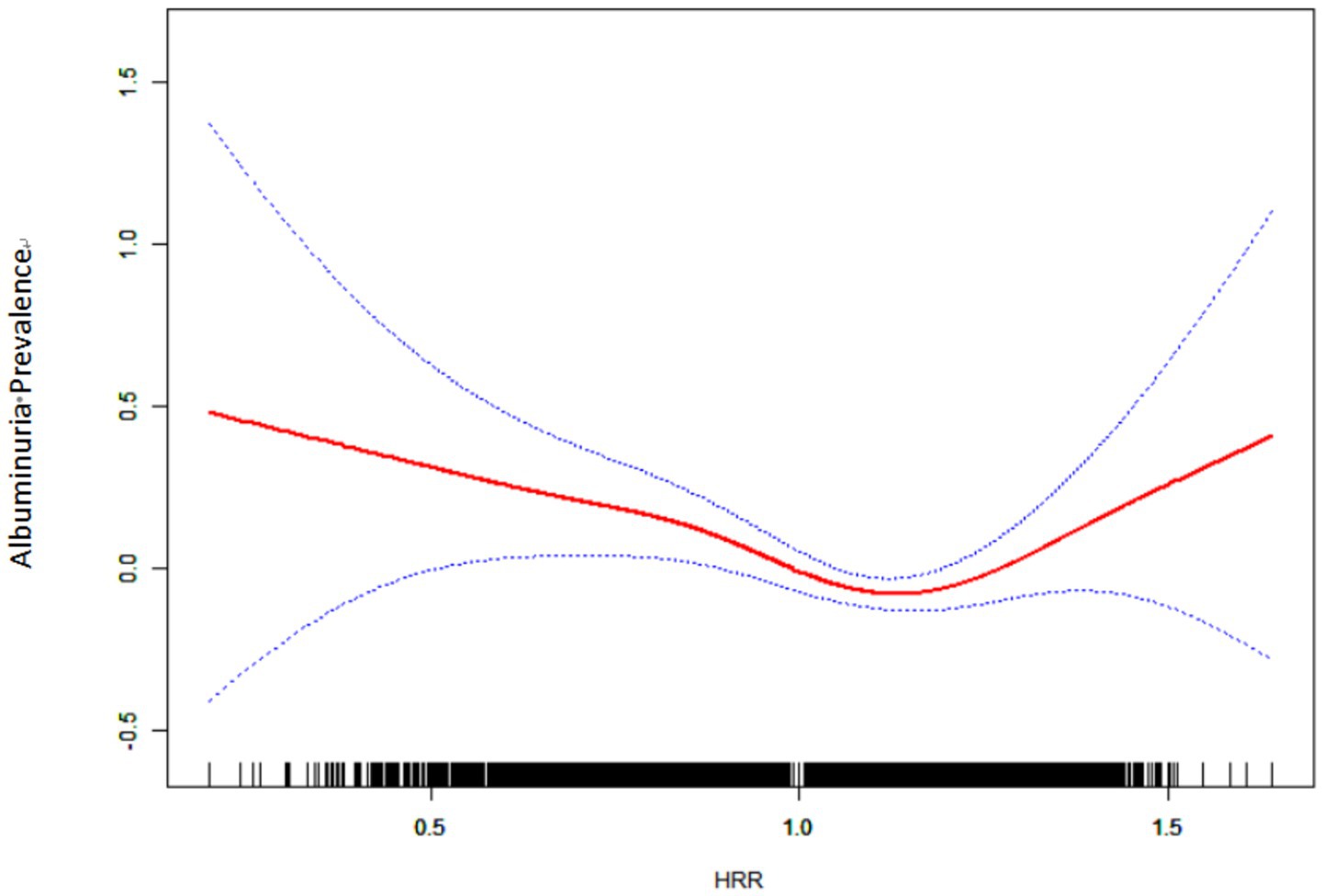
Figure 2. Relationship between HRR and albuminuria by smooth curve fitting. Red band represents the smooth curve fit between variables. Blue bands represent the 95% confidence interval from the fit. Adjustment variables: sex, age, BMI, PIR; TC; TG; ALT; AST; BUN; UA; Cr; eGFR; Race; Smoking; Drinking; Hypertension; Diabetes; CVD; Education level. CI, confidence interval; BMI, body mass index; PIR, poverty income ratio; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, Aspartate Aminotransferase; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; UA, uric acid; Cr, creatinine; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HRR, hemoglobin to red blood cell distribution width ratio; CVD, cardiovascular disease. p < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
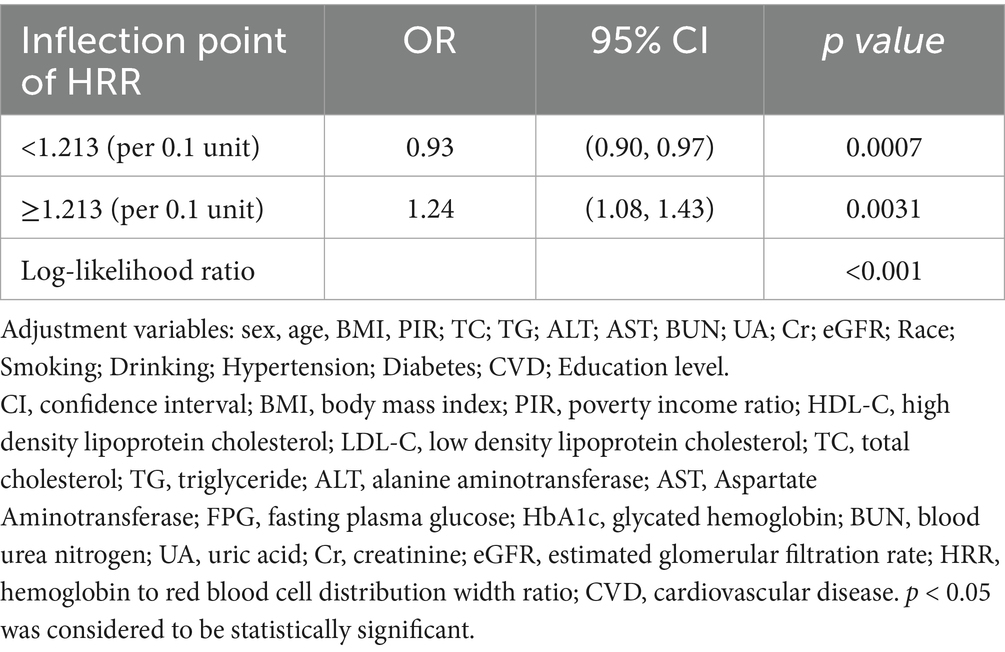
Table 3. Independent correlation between HRR and albuminuria by multivariate piecewise linear regression.
Subgroup analysis
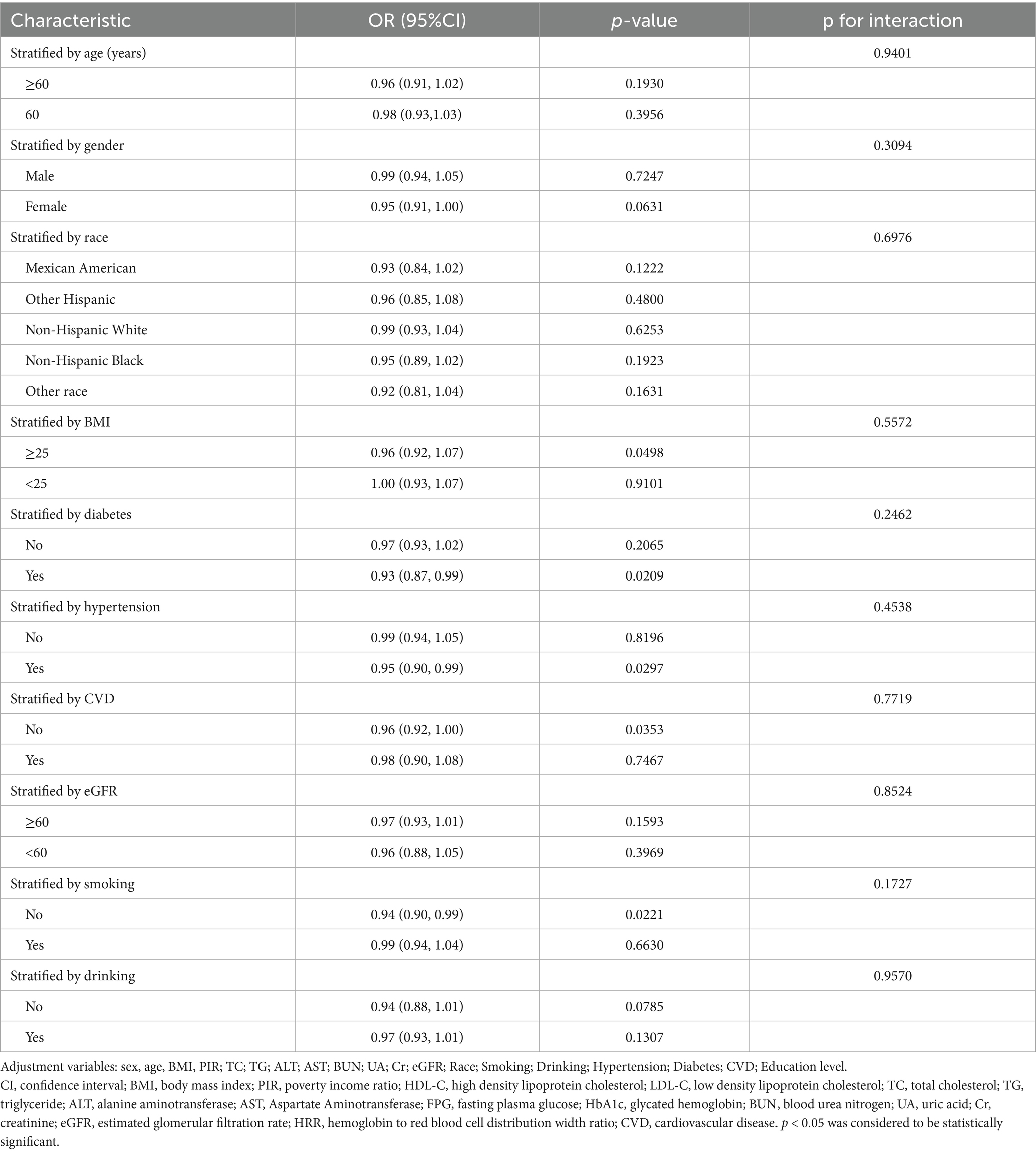
To assess the consistency of the correlation between HRR and albuminuria. We performed subgroup analyses and interaction tests based on age, gender, race, BMI, diabetes, hypertension, CVD, eGFR, and smoking and drinking status (as shown in Table 4), and the results showed consistent results for this association (interaction p > 0.05).
Discussion
In this cross-sectional study, we observed a negative correlation between HRR and albuminuria in American adults, which remained stable in fully adjusted models. Smooth curve fitting suggested a nonlinear relationship between HRR and albuminuria with a turning point at 1.213.
It is well known that albuminuria is closely associated with the development of diabetic nephropathy and end-stage renal disease (5). Our study found that albumin decreased with increasing HRR when the HRR was below 1.213. This is similar to the findings of the previous studies. A cross-sectional study conducted by Lin Ning et al. has demonstrated a negative linear association between HRR and CKD, with higher HRR levels indicating a lower prevalence of CKD (22). To investigate the relationship between complete blood count parameters and the incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) and mortality in patients with Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), 585 adult HLH patients were enrolled in Sichuan, China, and a logistic regression model of AKI and 28-day mortality was developed. The multifactorial logistic regression model showed that low HRR (HRR < 0.49) was an independent risk factor for AKI (OR = 1.692) (26). In addition, a retrospective study of 198 patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) suggests that low HRR may be considered a new indicator of shorter survival in patients with RCC (27). Since HRR calculation is based on hemoglobin and red RDW, its decrease may be due to low HGB value, high RDW value or both. Previous studies have shown that hemoglobin (every 1 g/dL increase) is negatively correlated with albuminuria (OR 0.92; 95%CI 0.87–0.97) (20). At the same time, elevated RDW is associated with impaired microcirculation function and further increases the risk of albuminuria (28). The possible mechanisms are as follows: First, low HRR levels usually reflect the potential state of chronic inflammation, which plays a key role in the occurrence of albuminuria (8, 29–31). Chronic inflammation inhibits erythropoiesis, leading to decreased hemoglobin, while increasing RDW by disrupting red blood cell maturation and promoting anisocytosis. This imbalance not only indicates impaired hematopoietic function, but also relates to microcirculatory energy impairment (32). Secondly, low HRR levels may indicate impaired oxygen-carrying capacity, which may lead to tissue hypoxia and promote the occurrence of albuminuria (33).
In this study, we used the smooth curve fitting method to describe the nonlinear association and saturation phenomenon between HRR and albuminuria. The saturation effect value of 1.213 may have physiological significance in the relationship between HRR and albuminuria. When HRR is lower than this threshold, HRR may play a stronger protective role in the occurrence of albuminuria; when HRR exceeds this threshold, HRR is positively correlated with the occurrence of albuminuria. The interpretation of this finding needs to be combined with the pathophysiological basis, common influencing factors and interactions of hemoglobin and RDW. Low level HRR is often dominated by chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, which further leads to systemic vascular endothelial dysfunction, glomerular filtration barrier damage, and increased urinary albumin excretion rate (34, 35). However, high levels of HRR often represent a state of high blood viscosity or excessive erythrocyte production, which increases glomerular pressure and accelerates the formation of albuminuria (36). Previous studies have focused on the negative association between HRR and diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and nephropathy (9, 10, 12, 22). The current study lacks evidence that albuminuria increases with HRR. To our knowledge, only one retrospective study of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients has reported a correlation between higher HRR and poorer prognosis. In the low HRR group, overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were 44.4 months (95% CI: 4.9–83.8) and 15.7 months (95% CI: 0.1–36.2), respectively, but not attainable in the high HRR group (p < 0.001), Multivariate analysis showed that low HRR was an independent factor of OS (p = 0.004, HR = 3.07, 95% CI:1.444–6.529) and DFS (p < 0.001, HR = 3.94, 95% CI:1.883–8.244). A possible explanation for this is that the study focused on cancer patients receiving chemotherapy and radiotherapy, whose hemoglobin levels varied to varying degrees (37). In addition, a cross-sectional study of 8,868 people found a U-shaped correlation between hemoglobin levels and albuminuria, with an inflection point of 15.5 g/dL, and both high and low levels of hemoglobin were associated with the occurrence of albuminuria (20). It is important to note that although we observed a nonlinear association and saturation between HRR and albuminuria, further studies are needed to determine the optimal level of HRR.
In conclusion, HRR can comprehensively reflect the multifaceted changes in blood status. When anemia is accompanied by inconsistencies in red blood cell production, HRR can more sensitively reflect the pathological status of the patient, which may indicate a wider range of hematological abnormalities and metabolic disorders. In addition, HRR detection is simple to operate and low cost, making it highly accessible and valuable in resource-limited environments. Therefore, HRR provides a new perspective for the early screening of albuminuria.
Subgroup analysis showed that the negative correlation between HRR and albuminuria was more obvious in non-smokers, which may be because smoking itself can lead to various changes in blood status. Previous studies have shown that the red blood cell count and hemoglobin level of patients with smoking showed an increasing trend, which weakened the correlation between HRR and albuminuria (38, 39). It is well known that obesity, hypertension, and diabetes are often accompanied by chronic low-grade systemic inflammation. Inflammatory mediators can lead to red blood cell destruction and suppress erythropoiesis, increasing RDW and exacerbating oxygen transport abnormalities (40–42). Therefore, these populations should pay attention to HRR levels. However, we did not observe similar phenomena in patients with CVD, which requires further research to clarify the exact mechanisms and clinical significance in CVD populations.
Study strengths and limitations
This study has the following advantages. First, the data were obtained from the NHANES database, which has a large sample size. We included various covariates to adjust for potential confounding factors to enhance the reliability of the results. Second, UACR is an accurate and sensitive indicator with fewer influencing factors and is relatively stable in individuals, allowing for a better assessment of early kidney damage. Finally, through smooth curve fitting and multiple piecewise linear regression model, this study found that there was a nonlinear relationship between HRR and albuminuria.
However, this study has some limitations. First, because of the cross-sectional study design, we were unable to determine causality. Secondly, the subjects of this study were adults aged 20 or older in the United States, and the results could not be generalized to people outside the NHANES sample. Third, although we have adjusted for a variety of confounding factors, there may still be unconsidered confounding factors, such as inflammatory markers and dietary differences, that may affect the conclusions. More prospective studies and clinical trials will be needed to confirm our findings and explore potential mechanisms of action.
Conclusion
There was a nonlinear correlation between HRR and albuminuria in adults aged 20 or older in the United States. Further prospective research and clinical trials are necessary to confirm our findings and potential mechanisms.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material. Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
GXL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition. GCL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Software. WYX: Writing – review & editing, Software. YPY: Writing – review & editing, Software. J-aZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Visualization. JZ: Visualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the following funds: Talent Project of Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences Affiliated Zhoupu Hospital [ZPRC-2024A-03], Key discipline project of Shanghai Pudong New Area Health Commission [PWZxk2022–22], and Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission [202240113].
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all participants in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Molitoris, BA, Sandoval, RM, Yadav, S, and Wagner, MC. Albumin uptake and processing by the proximal tubule: physiological, pathological, and therapeutic implications. Physiol Rev. (2022) 102:1625–67. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00014.2021
2. Cho, YT, Chen, CW, Chen, MP, Hu, JL, Su, H, Shiea, J, et al. Diagnosis of albuminuria by tryptic digestion and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. (2013) 420:76–81. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2012.12.016
3. Heerspink, H, Greene, T, Tighiouart, H, Gansevoort, RT, Coresh, J, Simon, AL, et al. Change in albuminuria as a surrogate endpoint for progression of kidney disease: a meta-analysis of treatment effects in randomised clinical trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2019) 7:128–39. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30314-0
4. Matsushita, K, van der Velde, M, Astor, BC, Woodward, M, Levey, AS, de Jong, PE, et al. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: a collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet. (2010) 375:2073–81. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60674-5
5. Pichaiwong, W, Homsuwan, W, and Leelahavanichkul, A. The prevalence of normoalbuminuria and renal impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Nephrol. (2019) 92:73–80. doi: 10.5414/CN109606
6. Kang, M, Kwon, S, Lee, J, Shin, JI, Kim, YC, Park, JY, et al. Albuminuria within the Normal range can predict all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality. Kidney360. (2022) 3:74–82. doi: 10.34067/KID.0003912021
7. Vestergaard, A, Jensen, SK, Heide-Jorgensen, U, Frederiksen, LE, Birn, H, Jarbol, DE, et al. Risk factor analysis for a rapid progression of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2024) 39:1150–8. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad271
8. Sun, P, Zhang, F, Chen, C, Bi, X, Yang, H, An, X, et al. The ratio of hemoglobin to red cell distribution width as a novel prognostic parameter in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective study from southern China. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:42650–60. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9516
9. Chi, G, Lee, JJ, Montazerin, SM, and Marszalek, J. Prognostic value of hemoglobin-to-red cell distribution width ratio in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomark Med. (2022) 16:473–82. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2021-0577
10. Qu, J, Zhou, T, Xue, M, Sun, H, Shen, Y, Chen, Y, et al. Correlation analysis of hemoglobin-to-red blood cell distribution width ratio and frailty in elderly patients with coronary heart disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:728800. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.728800
11. Liu, J, and Wang, J. Association between hemoglobin-to-red blood cell distribution width ratio and hospital mortality in patients with non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1180912. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1180912
12. Xiong, Y, Xie, S, Yao, Y, Chen, Y, Ding, J, Zhou, R, et al. Hemoglobin-to-red blood cell distribution width ratio is negatively associated with stroke: a cross-sectional study from NHANES. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:28098. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79520-x
13. Xiao, Y, Pan, H, Huang, R, Wu, P, Peng, C, Luo, J, et al. Association of hemoglobin-to-red blood cell distribution width ratio and bone mineral density in older adults. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2024) 25:866. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07984-z
14. Ma, X, Qian, Y, Qian, C, Lin, H, and Sun, Y. Association between inflammation indicators and albuminuria in US adults: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:21496. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06540-6
15. Ding, L, Guo, H, Zhang, C, Jiang, B, Zhang, S, and Zhang, J. Association between dietary inflammation index and albuminuria: results from the National Health and nutrition examination survey. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1361890. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1361890
16. Palladino, M. Complete blood count alterations in COVID-19 patients: a narrative review. Biochem Med (Zagreb). (2021) 31:30501. doi: 10.11613/BM.2021.030501
17. Ciaccio, C, Coletta, A, and Coletta, M. Role of hemoglobin structural-functional relationships in oxygen transport. Mol Asp Med. (2022) 84:101022. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2021.101022
18. Okada, H, Hasegawa, G, Tanaka, M, Osaka, T, Shiotsu, Y, Narumiya, H, et al. Association between hemoglobin concentration and the progression or development of albuminuria in diabetic kidney disease. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e129192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129192
19. Wang, H, Tang, C, Dang, Z, Yong, A, Liu, L, Wang, S, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of high-altitude polycythemia-related kidney disease in Tibetan inhabitants. Kidney Int. (2022) 102:196–206. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.03.027
20. Yin, R, and Hu, Z. U-shaped association between hemoglobin levels and albuminuria in US adults: a cross-sectional study. Int Urol Nephrol. (2025) 57:561–9. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04200-8
21. Ujszaszi, A, Molnar, MZ, Czira, ME, Novak, M, and Mucsi, I. Renal function is independently associated with red cell distribution width in kidney transplant recipients: a potential new auxiliary parameter for the clinical evaluation of patients with chronic kidney disease. Br J Haematol. (2013) 161:715–25. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12315
22. Ning, L, Tang, J, Chen, Z, Zeng, X, Liu, Q, Tan, L, et al. Association between hemoglobin-to-red blood cell distribution width ratio and chronic kidney disease: a cross sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). (2024) 103:e40224. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040224
23. Levey, AS, Stevens, LA, Schmid, CH, Zhang, YL, Castro, AR, Feldman, HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. (2009) 150:604–12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006
24. Groenwold, RH, White, IR, Donders, AR, Carpenter, JR, Altman, DG, and Moons, KG. Missing covariate data in clinical research: when and when not to use the missing-indicator method for analysis. CMAJ. (2012) 184:1265–9. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.110977
25. White, IR, Royston, P, and Wood, AM. Multiple imputation using chained equations: issues and guidance for practice. Stat Med. (2011) 30:377–99. doi: 10.1002/sim.4067
26. Chen, X, Wang, S, Yang, J, Wang, X, Yang, L, and Zhou, J. The predictive value of hematological inflammatory markers for acute kidney injury and mortality in adults with hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective analysis of 585 patients. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 122:110564. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110564
27. Yilmaz, H, Yilmaz, A, and Demirag, G. Prognostic significance of hemoglobin-to-red cell distribution width ratio in patients with metastatic renal cancer. Future Oncol. (2021) 17:3853–64. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0040
28. Uzun, F, Guner, A, Pusuroglu, H, Demir, AR, Gunduz, S, Gurbak, I, et al. Association of red blood cell distribution width, systemic-immune-inflammation index and poor cardiovascular outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. (2022) 44:530–8. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2022.2079668
29. Zhao, W, Shi, M, and Zhang, J. Preoperative hemoglobin-to-red cell distribution width ratio as a prognostic factor in pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:42. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6348
30. Yu, Z, Zhang, T, and Shen, J. Low hemoglobin-to-red cell distribution width ratio is associated with mortality in patients with HBV-related decompensated cirrhosis. Biomed Res Int. (2022) 2022:5754790. doi: 10.1155/2022/5754790
31. Su, YC, Wen, SC, Li, CC, Su, HC, Ke, HL, Li, WM, et al. Low hemoglobin-to-red cell distribution width ratio is associated with disease progression and poor prognosis in upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Biomedicine. (2021) 9:672. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060672
32. Wang, B, Li, ZL, Zhang, YL, Wen, Y, Gao, YM, and Liu, BC. Hypoxia and chronic kidney disease. EBioMedicine. (2022) 77:103942. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103942
33. Kadatane, SP, Satariano, M, Massey, M, Mongan, K, and Raina, R. The role of inflammation in CKD. Cells. (2023) 12:1581. doi: 10.3390/cells12121581
34. Singh, AK, Kolligundla, LP, Francis, J, and Pasupulati, AK. Detrimental effects of hypoxia on glomerular podocytes. J Physiol Biochem. (2021) 77:193–203. doi: 10.1007/s13105-021-00788-y
35. Takahashi, N, Yoshida, H, Kimura, H, Kamiyama, K, Kurose, T, Sugimoto, H, et al. Chronic hypoxia exacerbates diabetic glomerulosclerosis through mesangiolysis and podocyte injury in db/db mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2020) 35:1678–88. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa074
36. Palubiski, LM, O'Halloran, KD, and O'Neill, J. Renal physiological adaptation to high altitude: a systematic review. Front Physiol. (2020) 11:756. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00756
37. Bozkaya, Y, Dilber, M, Bilgili, AM, and Aktas, C. A new prognostic parameter associated with recurrence in patients with nasopharyngeal cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy: the ratio of the hemoglobin-to-red cell distribution width. Cureus. (2023) 15:e39907. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39907
38. Kiraz, M, and Demir, E. Relationship of lumbar disc degeneration with hemoglobin value and smoking. Neurochirurgie. (2020) 66:373–7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuchi.2020.06.133
39. Pedersen, KM, Colak, Y, Ellervik, C, Hasselbalch, HC, Bojesen, SE, and Nordestgaard, BG. Smoking and increased White and red blood cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39:965–77. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.312338
40. Guzik, TJ, Nosalski, R, Maffia, P, and Drummond, GR. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2024) 21:396–416. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00964-1
41. Luc, K, Schramm-Luc, A, Guzik, TJ, and Mikolajczyk, TP. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J Physiol Pharmacol. (2019) 70. doi: 10.26402/jpp.2019.6.01
42. Saltiel, AR, and Olefsky, JM. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest. (2017) 127:1–4. doi: 10.1172/JCI92035
Glossary
CI - confidence interval
BMI - body mass index
PIR - poverty income ratio
HDL-C - high density lipoprotein cholesterol
LDL-C - low density lipoprotein cholesterol
TC - total cholesterol
TG - triglyceride
ALT - alanine aminotransferase
AST - Aspartate Aminotransferase
FPG - fasting plasma glucose
HbA1c - glycated hemoglobin
BUN - blood urea nitrogen
UA - uric acid
Cr - creatinine
eGFR - estimated glomerular filtration rate
HRR - hemoglobin to red blood cell distribution width ratio
CVD - cardiovascular disease
CBC - complete blood cell count
RBC - red blood cells
CKD - chronic kidney disease
RDW - cell distribution width
NHANES - National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey of the National Center for Health Statistics
NCHS - National Center for Health Statistics
ACR - albumin creatinine ratio
AKI - acute kidney injury
HLH - hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
RCC - renal cell carcinoma
ROS - reactive oxygen species
OS - overall survival
DFS - disease-free survival
COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Keywords: hemoglobin to red cell distribution width ratio, albuminuria, NHANES, cross-sectional study, nonlinear correlation
Citation: Li G, Li G, Xu W, Yang Y, Zhang J-a and Zhang J (2025) Relationship between hemoglobin and red blood cell distribution width ratio and albuminuria in the United States adults aged 20 years and above: a cross-sectional analysis. Front. Nutr. 12:1572196. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1572196
Edited by:
Lei Qin, University of International Business and Economics, ChinaReviewed by:
Zhaoxiang Wang, First People's Hospital of Kunshan, ChinaEdward Kurnia Setiawan Limijadi, Diponegoro University, Indonesia
Jingru Zhao, Hebei General Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Li, Xu, Yang, Zhang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jin-an Zhang, emhhbmdqaW5hbkBob3RtYWlsLmNvbQ==: Jing Zhang, amVubnkxOTc2NTRAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Guangxin Li
Guangxin Li Guangchao Li2
Guangchao Li2