- Wenzhou Central Hospital, Wenzhou, China
Background: Testosterone deficiency is a prevalent condition among males and warrants greater attention. The balance between oxidative and antioxidant capacity plays a critical role in testosterone deficiency.
Methods: This study conducted a secondary analysis using data from three cycles of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2011–2016). The oxidative balance score (OBS) and testosterone levels were derived from interview data and laboratory measurements. Weighted logistic regression was employed to explore the relationship between OBS and testosterone deficiency. Subgroup analyses, sensitivity analyses, and p-value for interaction were also performed.
Results: The analysis encompassed a cohort of 3,578 participants who met the eligibility criteria. The prevalence of testosterone deficiency among participants was 23.69%. OBS was inversely correlated with testosterone deficiency, with each unit increase in OBS associated with a 3% reduction in the risk of testosterone deficiency (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.95 to 0.99). The highest OBS group exhibited a 38% lower risk of testosterone deficiency (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40 to 0.96) Compared to the lowest OBS group. Furthermore, lifestyle OBS was also negatively correlated with testosterone deficiency. In, subgroup analyses, the inverse association between OBS and testosterone deficiency was most pronounced in subgroups characterized by educational background beyond high school, PIR > 3, and absence of hypertension or diabetes.
Conclusion: Higher OBS was inversely correlated with testosterone deficiency in males. This study underscores the importance of comprehensive antioxidant approaches, particularly lifestyle OBS, in male testosterone deficiency.
1 Introduction
The health concerns of males should not be overlooked or marginalized. In the adult male population of the United States, the prevalence of low testosterone is approximately 5.6%. With the progression of societal aging, the socio-medical burden associated with testosterone deficiency is further exacerbated (1). Testosterone plays a pivotal role in the maintenance of male characteristics and the development of the musculoskeletal system (2). Despite the development of certain pharmacological interventions for treatment, these measures are unable to fundamentally alter the current situation (3, 4). Low testosterone levels are associated with various diseases, such as osteoarthritis, cardiovascular disease, and pulmonary health (5–7). Consequently, addressing the current prevalence of male testosterone deficiency and developing evidence-based intervention strategies carries epoch-making significance for alleviating both societal and healthcare burdens.
Previous studies on the effect of diet and lifestyle on testosterone levels have shortcomings or limitations, which may prevent people (men) from doing a good job of intervention according to diet and lifestyle. For example, the oxidative properties of foods and medications encountered in daily life can significantly influence testosterone levels. Sodium fluoride, a substance widely present in drinking water and food, can influence testosterone production by altering oxidative stress levels in the testes (8). Vitamin C, acting as an antioxidant, can reverse the decreased testosterone levels induced by lead exposure (9). Low levels of vitamin B12 are associated with an increased risk of testosterone deficiency (10). The antioxidant properties of curcumin also significantly influence testosterone levels in the body (11). However, human dietary intake inherently comprises complex combinations of nutrients rather than isolated compounds. Of particular importance is the recognition that environmental xenobiotics can exert testosterone-disrupting effects through oxidative mechanisms. Glyphosate has been demonstrated to elevate oxidative levels (12), and exposure to glyphosate in the environment has been shown to reduce levels of sex hormones, including testosterone (13). Male non-smokers exhibit significantly higher testosterone levels compared to the median testosterone level of the general male population (14). Multiple lifestyle factors should be systematically incorporated into the research framework. Therefore, modulating the body’s oxidative balance may offer promising prospects for individuals with low testosterone levels. Current research has primarily concentrated on the effects of modifying individual oxidative factors on testosterone levels, overlooking the broader role of overall oxidative status in testosterone regulation. However, there is an Oxidative Balance Score (OBS), that provides a comprehensive assessment of systemic redox homeostasis, offering distinct advantages over isolated examinations of dietary or lifestyle factors. Its principal strength lies in the holistic evaluation of human physiology, which integrates both pro-oxidant and antioxidant exposures, accounts for biological interactions between nutritional and behavioral components, and reflects the organism’s net oxidative stress burden. It provides a basis for future research and the formulation of relevant preventive healthcare measures.
A higher OBS indicates a stronger antioxidative capacity and it has emerged in recent years as a significant metric for assessing the balance between oxidative and antioxidative capacities within the body. Currently, OBS has been demonstrated to be associated with conditions such as sleep disorders and pulmonary diseases, showcasing its considerable potential for clinical application (15, 16). Previous studies have highlighted the intricate relationship between dietary/lifestyle factors and low testosterone levels, yet there is a notable lack of research focusing on the role of antioxidative status in populations with low testosterone. Consequently, the potential association between overall oxidative-antioxidative status and low testosterone represents a promising area of investigation. We hypothesize that there exists an inverse correlation between OBS and the risk of testosterone deficiency. Understanding this relationship is crucial for the management of male testosterone deficiency. We anticipate that integrated antioxidant approaches combining dietary and lifestyle interventions will provide effective prevention and clinical guidance for males with testosterone deficiency.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population and design
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) provides comprehensive data on disease and nutritional status across a broad segment of the U. S. population, encompassing physical examinations, laboratory tests, and questionnaire surveys, making its data highly representative. As such, it serves as a valuable resource for generating evidence and references to inform public health policies aimed at disease prevention.
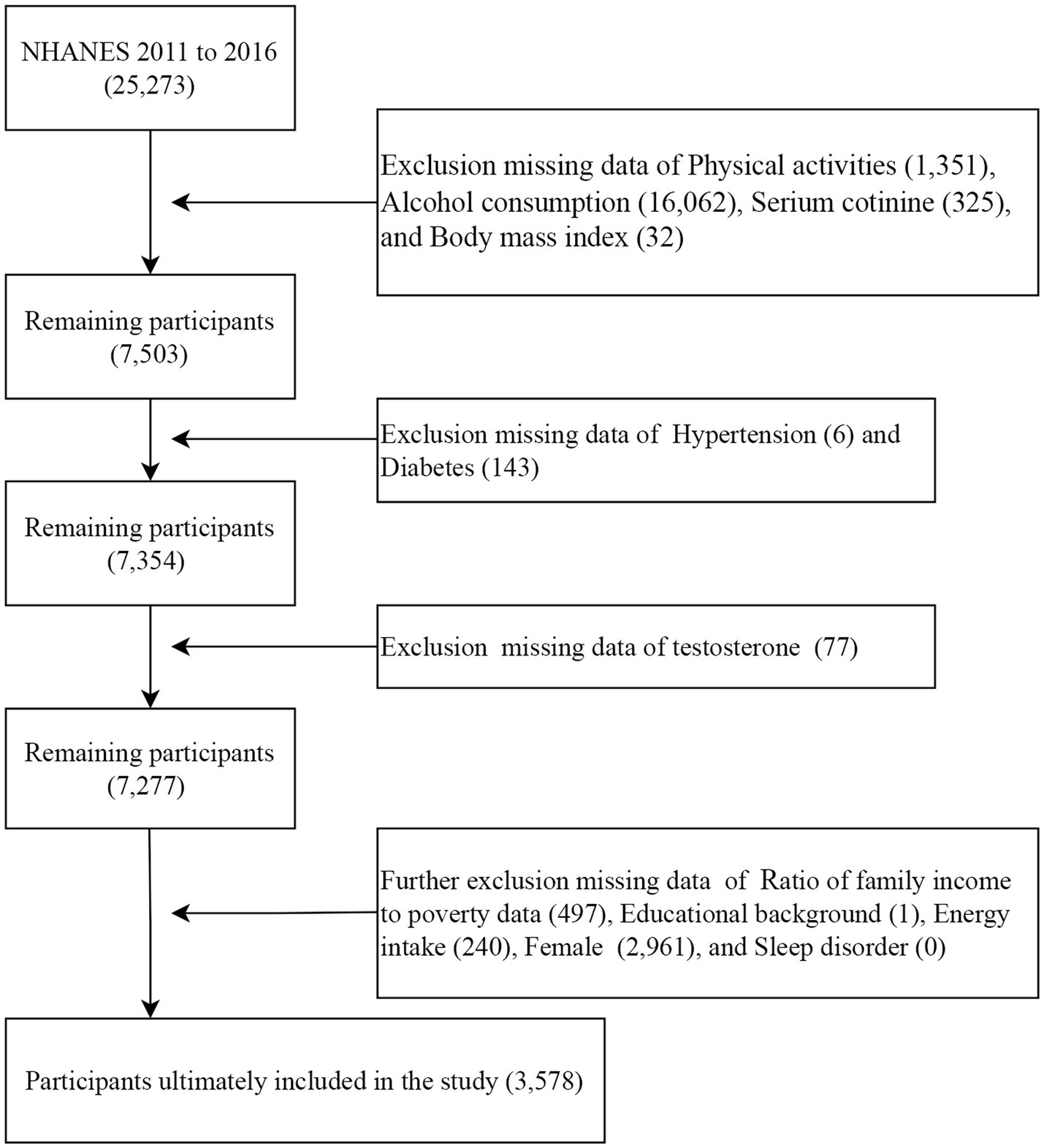
This study analyzed data from three NHANES survey cycles (2011–2012, 2013–2014, and 2015–2016). These cycles were selected because they contain complete data necessary for calculating the OBS as well as testosterone measurements. First, 25,273 participants with complete dietary OBS data were included. Second, participants with missing data on physical activities (1,351), alcohol consumption (16,062), serum cotinine (352), and body mass index (BMI) (17) were excluded. Third, participants with missing data on hypertension (6) and diabetes (143) were excluded. Then, participants with missing data on testosterone level (77) were excluded. In addition, participants with missing data on PIR (497), educational background (1), energy intake (240), females (2,961), and sleep disorder (0) were also excluded. The analysis for this study ultimately included a total of 3,578 participants (Figure 1).
2.2 Ethics statement
This study analyzed de-identified data from NHANES, which obtained the National Center for Health Statistics institutional review board approval and participant consent during primary data collection (Protocol #2011–17). The use of public data was exempt from further review per institutional guidelines.
2.3 Exposure definition
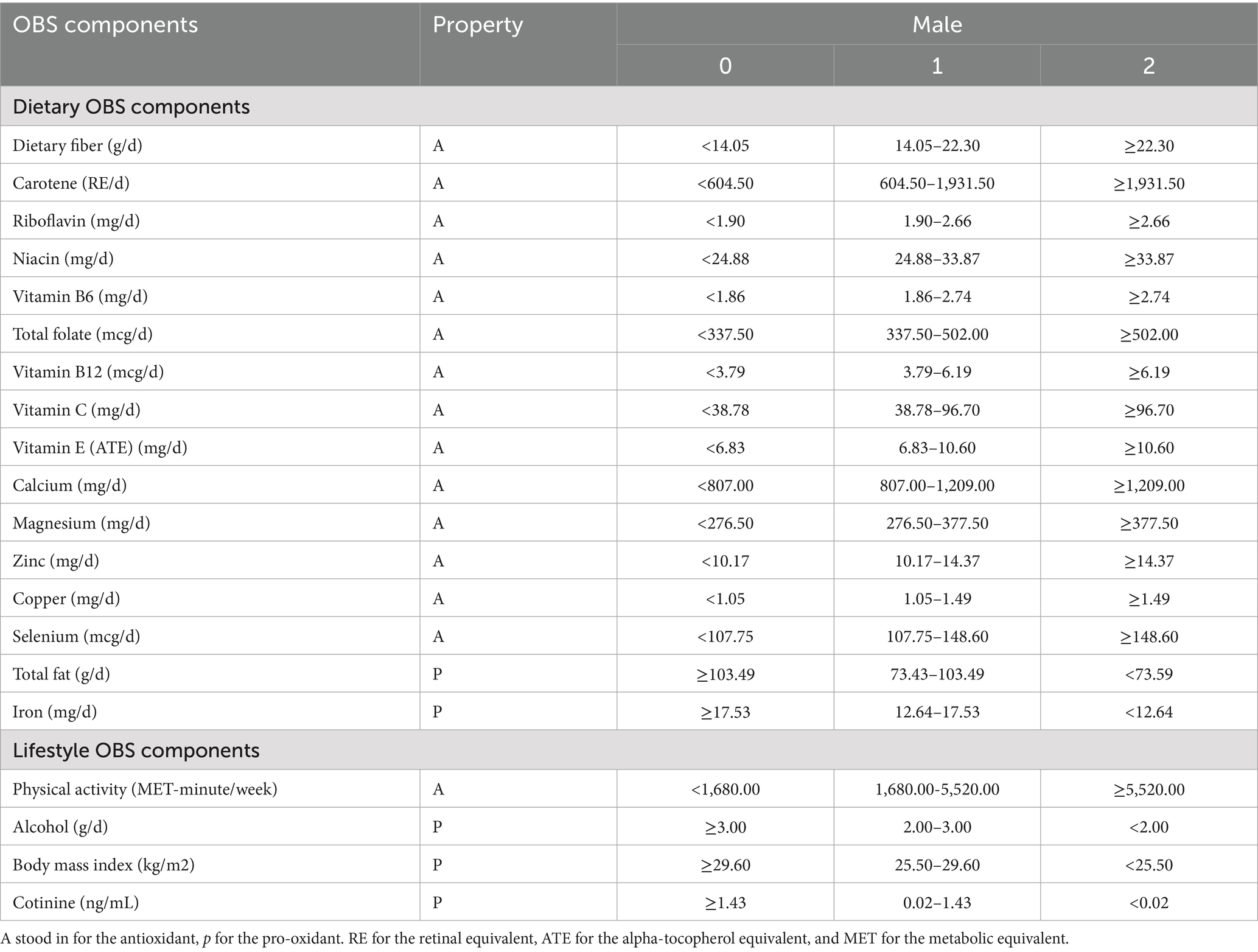
The OBS comprises a total of 5 pro-oxidants and 15 antioxidants. OBS was further divided into dietary OBS and lifestyle OBS. First, information required to calculate the OBS for each participant was collected. To ensure the accuracy of dietary intake, the final intake values were calculated based on the results of the average of the two 24-h interviews. Second, lifestyle OBS includes alcohol consumption, serum cotinine, BMI, and physical activity. Average alcohol consumption over the past 12 months was defined as alcohol intake. Given the increased exposure to secondhand smoke, this study measured smoking utilized serum cotinine levels, a metabolite of cigarette smoke. Physical activity was defined using the formula from this literature (18).
In this study, each component of the Oxidative Balance Score (OBS) was assigned a score based on its tertile distribution. Specifically, antioxidant components were scored as high (2), medium (1), and low (0) levels, respectively, while pro-oxidant components were scored inversely. The aggregate sum of their addition was denoted as OBS (Table 1). Additionally, the lifestyle/dietary OBS were also calculated separately. The scoring system is designed to quantitatively reflect systemic oxidative stress homeostasis.
2.4 Outcome definitions
Specimens were collected by professionally trained personnel. Total testosterone levels in serum were measured using isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (ID-LC–MS/MS). A testosterone level below 300 ng/dL is defined as testosterone deficiency (19).
2.5 Covariates definitions
There were some covariates considered in this study, including age, race/ethnicity, poverty-to-income ratio (PIR), educational background, total energy intake, diabetes status, and hypertension status. Extreme dietary intake will be excluded (<800 or >4,200 kcal day−1 for males) (20). Given the well-established association between hypertension, diabetes, and testosterone deficiency in males (21, 22). Therefore, hypertension and diabetes were incorporated as covariates in this study. The presence of chronic diseases was determined based on self-reported hypertension or diabetes. Numerous studies have reported a robust association between sleep disorder and testosterone deficiency (23, 24). Therefore, we incorporated sleep disorders as a covariate in the study, defined based on self-reported sleep disorder questionnaires (25).
2.6 Statistical analysis
The data in this study were available directly from the official NHANES website. During the data analysis process, the data were weighted to ensure representativeness. Normality tests were conducted for continuous variables, and non-normally distributed continuous variables were expressed using medians. Categorical variables were presented as unweighted frequencies (weighted percentages).
When examining the baseline characteristics across OBS quartiles, categorical variables were analyzed using the Rao-Scott chi-square test, while non-normally distributed continuous variables were assessed using the Kruskal-Wallis test. Weighted logistic regression was employed to investigate the potential relationship between OBS and low testosterone in males.
This study further stratified OBS into lifestyle OBS and dietary OBS to separately examine their associations with low testosterone in males. Additionally, subgroup analyses were performed to identify high-risk populations. Finally, sensitivity analyses were also included in this study to ensure the robustness of the findings. All analyses in this study were conducted using R (version 4.2.2), and a two-sided p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics of participants stratified by OBS quartiles
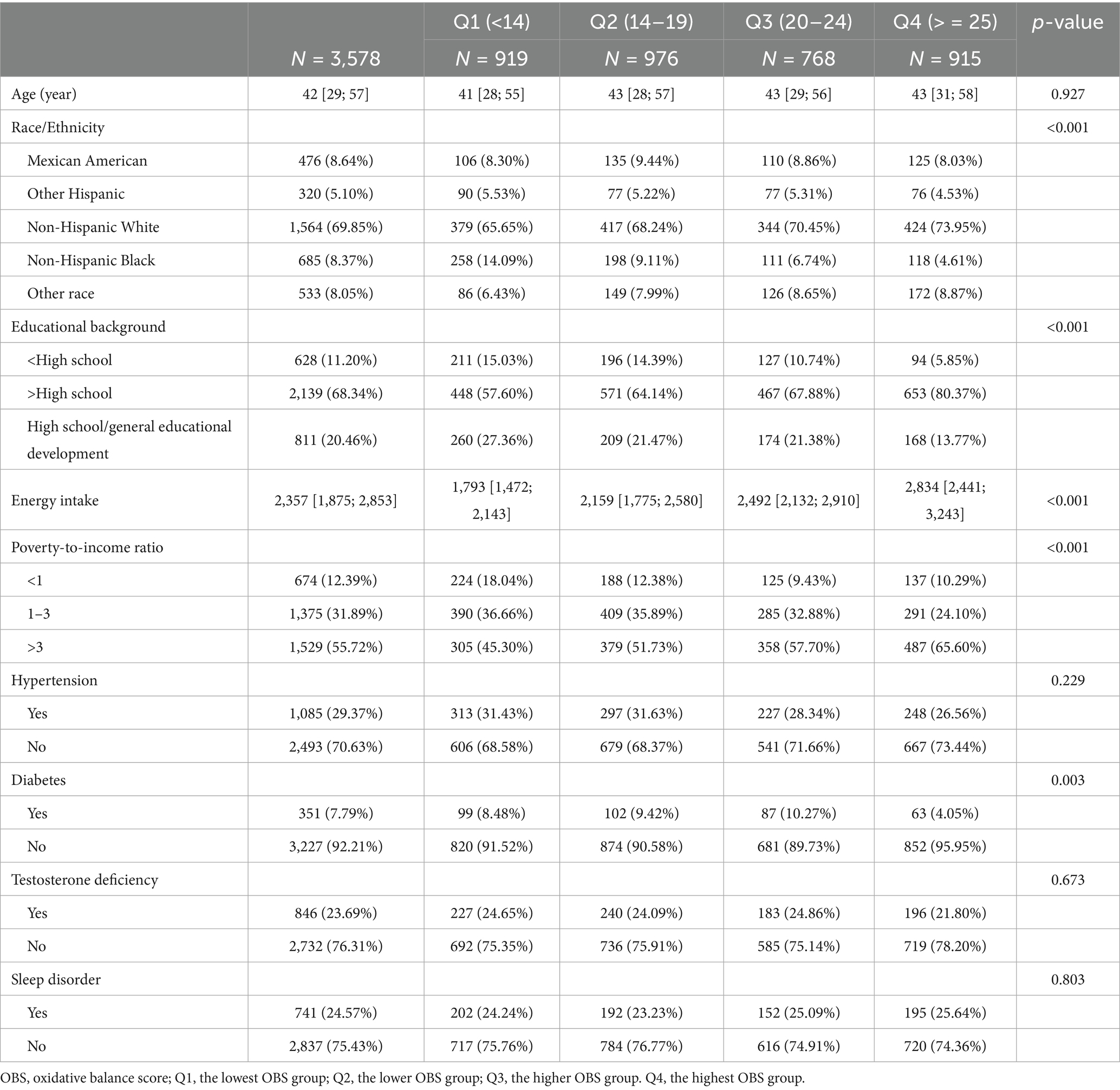
A total of 3,578 male participants with a median age of 42 years were comprised in this study (Table 2). The prevalence of testosterone deficiency among participants was 23.69%. The majority of the participants were Non-Hispanic White. Participants in the highest OBS group, compared to those in the lowest OBS group, were more likely to have an educational background above high school, a PIR greater than 3, a higher energy intake, and no diabetes (all p values less than 0.05).
3.2 Baseline characteristics for the presence or absence of testosterone deficiency
Compared to males without testosterone deficiency, those with testosterone deficiency were older, more likely to suffer from diabetes, hypertension, and sleep disorder, and also exhibited lower lifestyle OBS (all p-values < 0.05; Table 3).
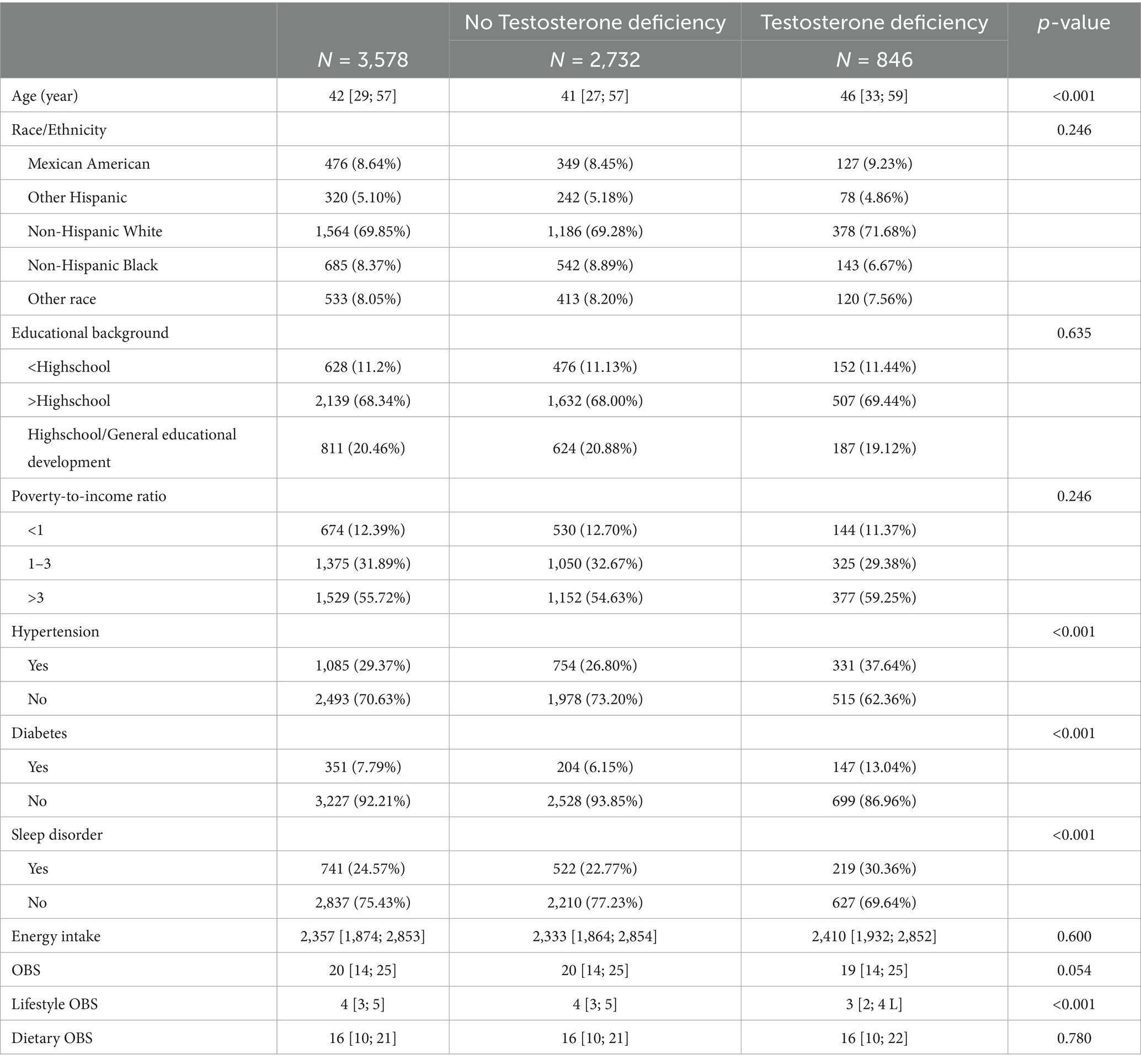
Table 3. Baseline characteristics of participants stratified by the presence or absence of testosterone deficiency.
3.3 The relationship between OBS and testosterone deficiency
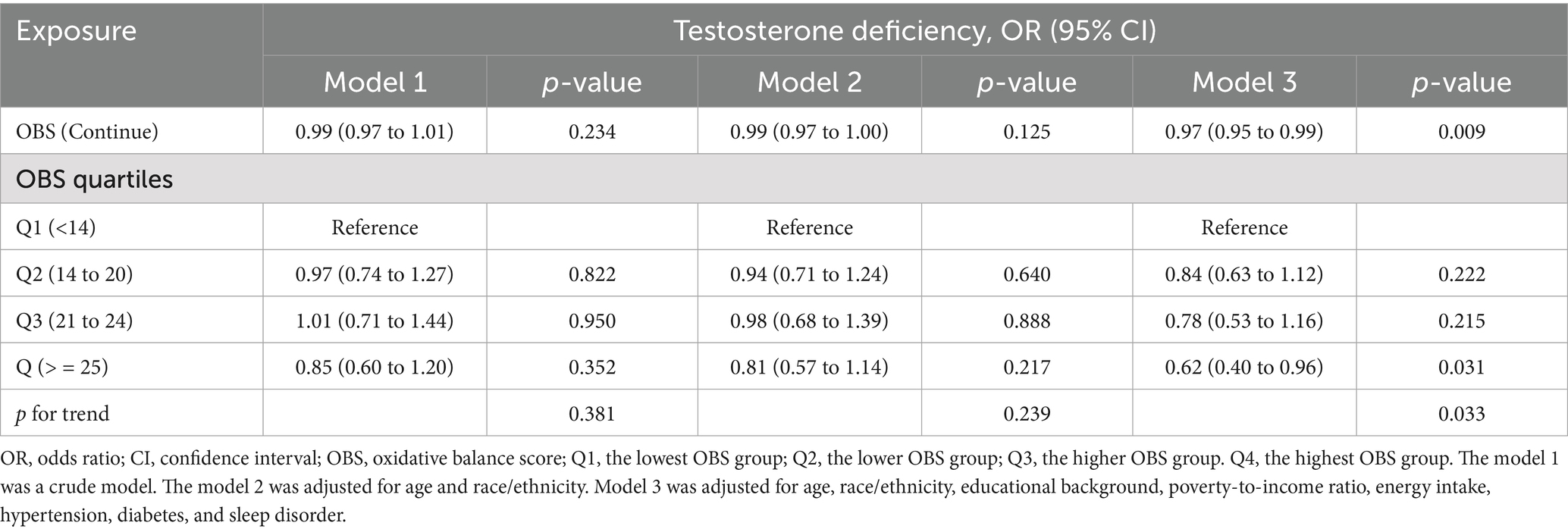
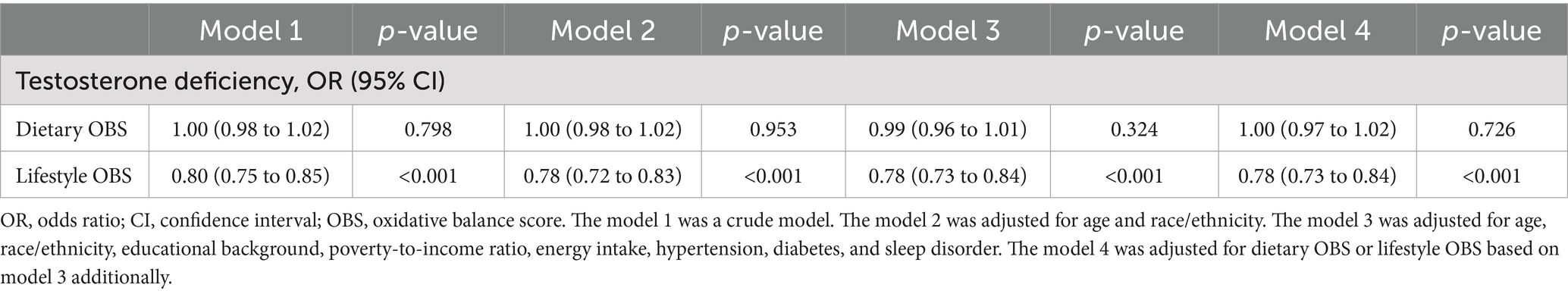
As demonstrated in Table 4, no significant association was observed between OBS and testosterone deficiency in the unadjusted Model 1. However, a significant inverse correlation between OBS and testosterone deficiency emerged (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.95 to 0.99) after adjusting for all covariates. Furthermore, when using the lowest OBS group as the reference, the highest OBS group demonstrated a 38% lower risk of testosterone deficiency (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40 to 0.96), and the p for trend was less than 0.05. The restricted cubic spline (RCS) plot revealed a nonlinear association (p for nonlinear = 0.473) between OBS and testosterone deficiency in males (Figure 2).
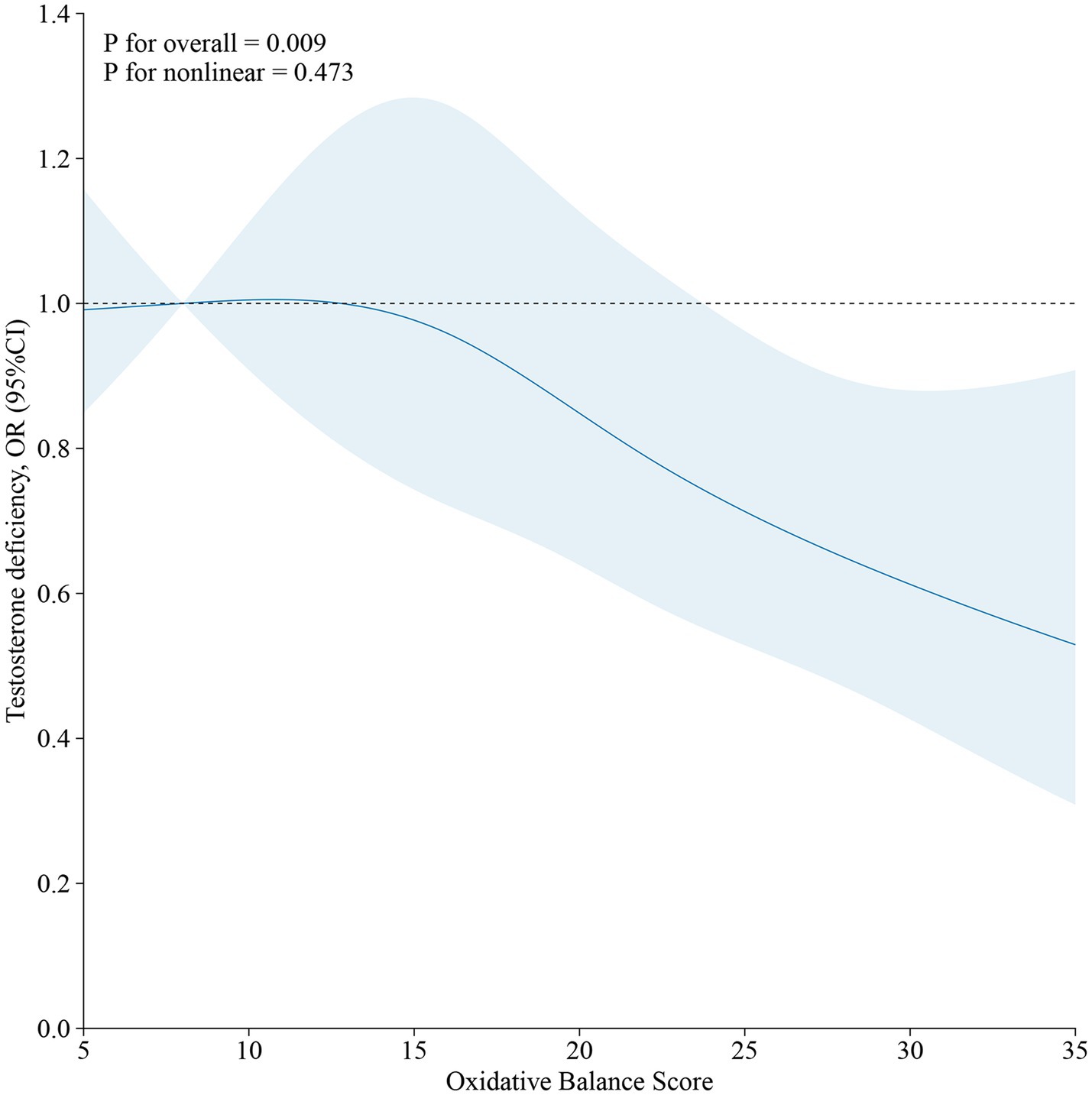
Figure 2. The restricted cubic spline (RCS) of the relationship between OBS and testosterone deficiency in males.
3.4 Dietary/lifestyle OBS and its association with testosterone deficiency
This study further investigated the relationship between lifestyle OBS/dietary OBS and testosterone deficiency. The multivariable analysis (Table 5) revealed that higher lifestyle OBS scores were independently associated with a 22% reduced risk of testosterone deficiency (OR, 0.78, 95% CI, 0.73 to 0.84), whereas no significant association was found for dietary OBS.
3.5 Additional analyses
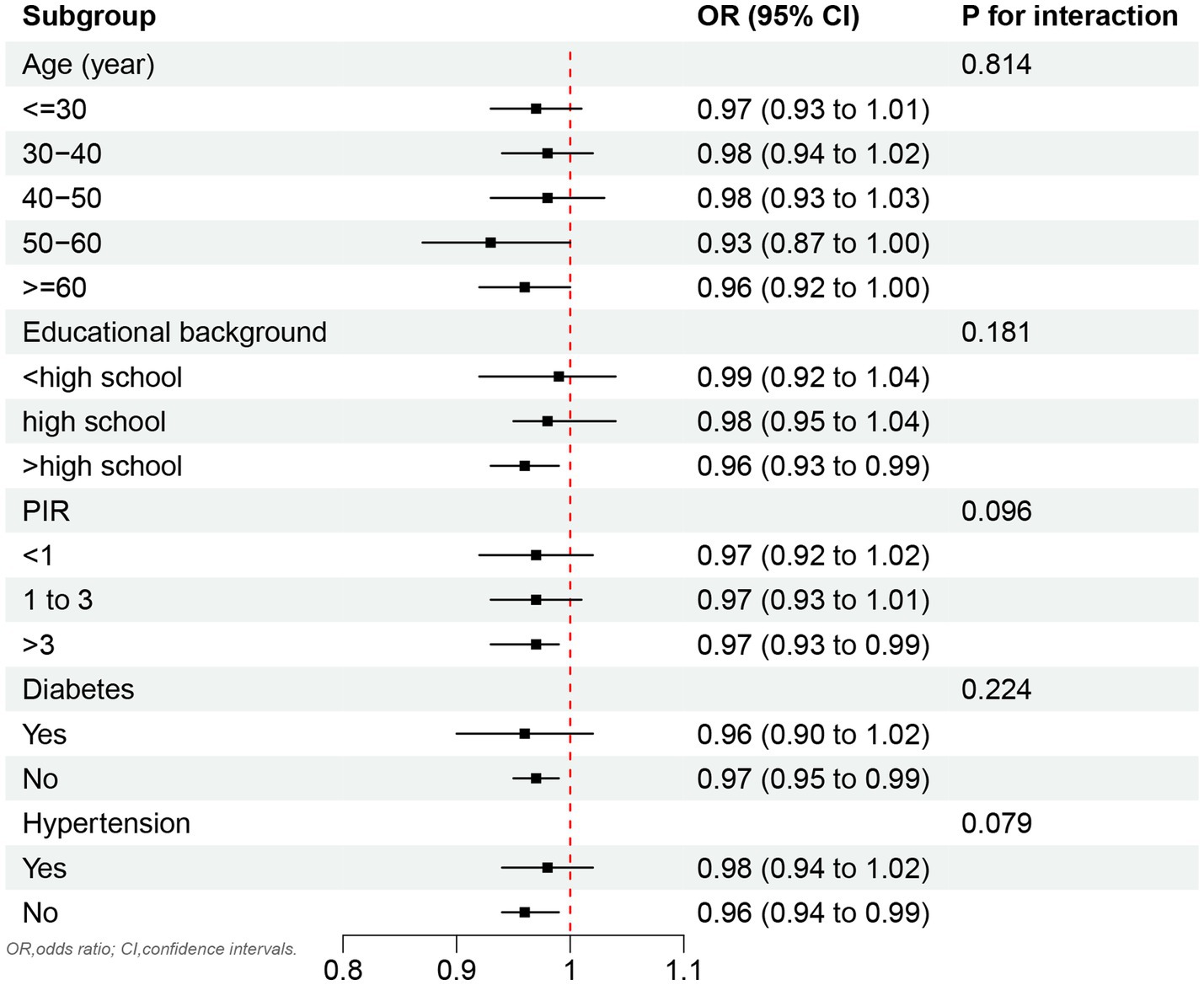
As shown in Figure 3, no significant association was observed between OBS and testosterone deficiency across the stratified age groups. However, a significant inverse correlation between OBS and testosterone deficiency was identified in subgroups with an educational background above high school, as well as in individuals without hypertension and diabetes.
Importantly, the relationship between OBS and testosterone deficiency remained highly robust, even after the sequential removal of each OBS component (Supplementary material S1).
4 Discussion
In this study, which utilized a nationally representative sample of the U. S. population, we primarily identified an inverse association between OBS and testosterone deficiency in males. The highest OBS group exhibited a 38% reduction in the risk of testosterone deficiency compared to the lowest OBS group. A significant inverse correlation was observed between lifestyle OBS and testosterone deficiency, whereas no such association was found for dietary OBS. Furthermore, factors such as educational level, socioeconomic status, and people without chronic conditions (e.g., hypertension and diabetes) appeared to influence this relationship.
Research on the relationship between diet and disease has consistently been a prominent area of interest, and this holds true for studies focusing on testosterone deficiency as well. Although the dietary OBS alone did not demonstrate a statistically significant association with testosterone deficiency in males, the composite OBS showed a robust inverse correlation. This discrepancy warrants thorough discussion. The Mediterranean diet, which includes a variety of antioxidant-rich components, has been shown to significantly elevate testosterone levels when adhered to over the long term (26). In men, dietary fiber intake is associated with a modest increase in testosterone levels, which can be attributed to the influence of dietary factors on hormonal metabolism (27). However, studies have also revealed that men adhering to a low-fat diet tend to exhibit lower testosterone levels (28). Zinc, a widely recognized antioxidant, plays a critical role in testicular metabolism, and its deficiency may consequently affect testosterone levels (29). Basic research has also demonstrated that the combined application of zinc and selenium enhances testosterone levels by strengthening antioxidant mechanisms (30). Nicotinic acid intake has been shown to reverse the decline in testosterone levels caused by testicular damage, demonstrating a positive effect on improving testicular function (31). Surprisingly, a high-fat diet in parental generations can lead to the occurrence of testosterone deficiency in offspring (32). However, a study has also shown no association between cholesterol intake and testosterone levels (17). From these research findings, it is evident that most studies have focused on the impact of a single dietary modification on testosterone deficiency, without considering multiple or overall dietary patterns. Therefore, this study, which integrates numerous dietary factors to investigate their relationship with testosterone deficiency, is well-justified, and its results are likely to be more reliable. Consequently, an integrated assessment incorporating both dietary and lifestyle factors is essential for advancing our understanding of disease pathogenesis. A comprehensive, multidimensional approach represents a fundamental prerequisite for elucidating disease mechanisms.
Many lifestyle habits can also significantly influence testosterone levels. Long-term alcohol consumption can impair the male gonadal axis and lead to a reduction in testosterone levels (33). Cotinine, a metabolite of cigarette smoke, exhibits a non-linear relationship with testosterone levels. Once cotinine levels in the body reach a certain threshold, they are negatively correlated with testosterone (34). However, previous studies have also indicated that smokers tend to have higher testosterone levels compared to non-smokers (35). Moderate physical activities can increase testosterone levels, thereby maintaining male physiological functions and combating aging (36). In males, there exists an inverse correlation between obesity and testosterone levels (37). Fat accumulation due to obesity leads to increased oxidative stress levels in males (38). The BMI levels are positively correlated with testosterone deficiency, suggesting that addressing obesity may offer a feasible approach to mitigating this condition (39). In this study, it was also demonstrated that lifestyle OBS is inversely correlated with testosterone deficiency. Promoting a healthy lifestyle is therefore essential, as modifying lifestyle habits appears to be a viable approach. However, further prospective studies are needed to validate these findings.
Social factors are closely associated with the development of diseases. Patients with private insurance can utilize telemedicine for the diagnosis and treatment of testosterone deficiency, indicating that individuals require a certain level of financial resources and capability (40). Males with testosterone deficiency who struggle with adverse socioeconomic conditions appear less likely to seek or adhere to formal treatment regimens (41). Furthermore, males with type 2 diabetes often exhibit testosterone deficiency, which provides new insights into the prevention of testosterone deficiency in non-diabetic individuals (42). Particularly in obese populations, educational level and hypertension serve as significant mediators between obesity and testosterone deficiency (43). Therefore, the findings of this study also highlight the importance of identifying social heterogeneity and integrating male lifestyle factors to develop appropriate health policies.
This study revealed the relationship between OBS and testosterone deficiency, offering several strengths. First, the participants represent a diverse and nationally representative sample of the U. S. population, accurately reflecting its demographic variability. Second, the analysis incorporated weighted data processing, ensuring the representativeness and robustness of the results. Third, the study utilized high-quality data from a publicly accessible database that provides comprehensive health and nutritional information. However, the limitations of this study must also be acknowledged. First, the primary limitation is that the study relies on cross-sectional data, making it difficult to infer causal relationships. Second, some data were based on participant recall, which introduces potential bias. However, the large sample size of this study may help mitigate this issue. Third, the exclusion of participants with significant missing data led to substantial sample attrition, though the results remain relatively robust and realistic. In addition, prospective studies incorporating computer-aided sperm analysis parameters are needed to fully elucidate these relationships.
In addition, although we performed a sensitivity analysis by removing individual OBS components in sequence, we acknowledge that this method may have limited ability to assess the robustness of the association, especially given the lack of an independent relationship between Dietary OBS and testosterone deficiency. This approach offers preliminary insight but may not fully reflect the complex interplay between lifestyle and dietary contributors to oxidative stress. Future studies should explore alternative methods, such as weighted composite scores or interaction models, to better delineate the independent and joint effects of OBS components. The study adjusted for potential confounding factors, the study only showed that OBS was associated with testosterone deficiency, however, higher OBS may represent individuals with other healthier lifestyles, which may also affect testosterone levels. Future studies in this domain are warranted to further elucidate these mechanisms.
5 Conclusion
In summary, the study demonstrated that higher OBS, particularly the lifestyle OBS, was significantly associated with reduced risk of testosterone deficiency in males. These findings highlight the crucial role of dietary and lifestyle antioxidants in male testosterone deficiency. However, further multicenter, large-scale prospective studies are required to validate these findings. In conclusion, this study offers a novel perspective for the treatment and management of male testosterone deficiency, leveraging this relationship.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found at: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the National Center for Health Statistics institutional review board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
ZZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Software. KZ: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing, Validation. XJ: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. XW: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing, Visualization. XZ: Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Supervision, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1577823/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Foster, J, Wright, P, Rao, PM, Edwards, D, Greenwood, M, Wayman, R, et al. Improving the recognition, diagnosis, and Management of Male Testosterone Deficiency across the Nhs: a Delphi consensus. J Sex Med. (2025) 1:130. doi: 10.1093/jsxmed/qdaf130
2. Ortega-de Los Ríos, L, Getino, L, Galán, B, García, JL, Luengo, JM, Chamizo-Ampudia, A, et al. Unlocking testosterone production by biotransformation: engineering a fungal model of aspergillus Nidulans strain deficient in steroid 11α-hydroxylase activity and expressing 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzyme as proof of concept. Biomol Ther. (2024) 14:1502. doi: 10.3390/biom14121502
3. Grossmann, M, Anawalt, BD, and Yeap, BB. Testosterone therapy in older men: clinical implications of recent landmark trials. Eur J Endocrinol. (2024) 191:R22–r31. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvae071
4. Sun, L, Huang, J, Wang, X, Huang, P, Dong, B, Liang, Z, et al. Enucleated bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells regulate immune microenvironment and promote testosterone production through Efferocytosis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2025) 23:21. doi: 10.1186/s12958-025-01352-9
5. Du, D, Ran, B, Xu, D, Liu, L, Hu, X, Zeng, T, et al. Sex hormones and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional study and Mendelian randomization analysis. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2024) 19:1649–60. doi: 10.2147/copd.S463849
6. Ma, N, and Gao, F. Correlation between low testosterone levels and the risk of osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional analysis of Nhanes data (2011-2016). BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2025) 26:23. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08272-6
7. Wu, X, Zhang, Y, and Zhang, X. Association between serum testosterone level and cardiovascular health in us male adults: results from the 2013-2016 Nhanes. J Sex Med. (2025) 22:265–73. doi: 10.1093/jsxmed/qdae196
8. Talebi, SF, Seify, M, Bhandari, RK, Shoorei, H, and Oskuei, SD. Fluoride-induced testicular and ovarian toxicity: evidence from animal studies. Biol Res. (2025) 58:6. doi: 10.1186/s40659-025-00586-6
9. Zhao, ZM, Mei, S, Zheng, QY, Wang, J, Yin, YR, Zhang, JJ, et al. Melatonin or vitamin C attenuates Lead acetate-induced testicular oxidative and inflammatory damage in mice by inhibiting oxidative stress mediated Nf-Κb signaling. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2023) 264:115481:115481. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115481
10. Rastegar Panah, M, Jarvi, K, Lo, K, and El-Sohemy, A. Vitamin B (12) is associated with higher serum testosterone concentrations and improved androgenic profiles among men with infertility. J Nutr. (2024) 154:2680–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.06.013
11. Saleem, HM, Al-Hetty, H, Ahmed, AT, Awad, MM, Al-Ani, MQ, Al-Darraji, MN, et al. Effect of curcumin on lipid mediators, glycemic index, and oxidative stress and inflammation biomarkers in polycystic ovary syndrome: future directions and current knowledge - a systematic review. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. (2025) 177:106947:106947. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2024.106947
12. Hentges, CR, Schuck, LK, De Abreu, CC, Tozetti, AM, and Oliveira, GT. Impact of environmentally relevant concentrations of glyphosate on Boana faber tadpoles exposed in the laboratory: morphological and functional markers. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. (2025) 114:104643:104643. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2025.104643
13. Sun, X, Zhang, H, Huang, X, Yang, D, Wu, C, Liu, H, et al. Associations of glyphosate exposure and serum sex steroid hormones among 6-19-year-old children and adolescents. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2024) 275:116266:116266. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116266
14. Platz, EA, Barber, JR, Chadid, S, Lu, J, Dobs, AS, Kanarek, NF, et al. Nationally representative estimates of serum testosterone concentration in never-smoking, lean men without aging-associated comorbidities. J Endocr Soc. (2019) 3:1759–70. doi: 10.1210/js.2019-00151
15. Lei, X, Xu, Z, and Chen, W. Association of Oxidative Balance Score with sleep quality: Nhanes 2007-2014. J Affect Disord. (2023) 339:435–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.07.040
16. Xu, Z, Lei, X, and Chen, C. Antioxidant diet/lifestyle could mitigate the adverse impacts of urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on lung function. Environ Res. (2024) 246:118099. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118099
17. Gomes, GK, de Branco, FMS, Santos, HO, Pereira, JL, Orsatti, FL, and de Oliveira, EP. Cholesterol intake and serum Total cholesterol levels are not associated with Total testosterone levels in men: a cross-sectional study from Nhanes 2013-2014. Lipids Health Dis. (2023) 22:168. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01928-7
18. Tian, X, Xue, B, Wang, B, Lei, R, Shan, X, Niu, J, et al. Physical activity reduces the role of blood cadmium on depression: a cross-sectional analysis with Nhanes data. Environ Pollut. (2022) 304:119211. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119211
19. Mulhall, JP, Trost, LW, Brannigan, RE, Kurtz, EG, Redmon, JB, Chiles, KA, et al. Evaluation and Management of Testosterone Deficiency: Aua guideline. J Urol. (2018) 200:423–32. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.115
20. Zhang, W, Peng, SF, Chen, L, Chen, HM, Cheng, XE, and Tang, YH. Association between the oxidative balance score and telomere length from the National Health and nutrition examination survey 1999-2002. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:1345071. doi: 10.1155/2022/1345071
21. Ahmed, F, Hetty, S, Laterveer, R, Surucu, EB, Mathioudaki, A, Hornbrinck, E, et al. Altered expression of aromatase and estrogen receptors in adipose tissue from men with obesity or type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2025) 1:38. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaf038
22. Negretto, LAF, Rassi, N, Soares, LR, Saraiva, ABC, Teixeira, MEF, Santos, LDR, et al. Testosterone deficiency in hypertensive men: prevalence and associated factors. Arq Bras Cardiol. (2024) 121:e20230138. doi: 10.36660/abc.20230138
23. Patel, P, Shiff, B, Kohn, TP, and Ramasamy, R. Impaired sleep is associated with low testosterone in us adult males: results from the National Health and nutrition examination survey. World J Urol. (2019) 37:1449–53. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2485-2
24. Wittert, G. The relationship between sleep disorders and testosterone. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. (2014) 21:239–43. doi: 10.1097/med.0000000000000069
25. Yang, Q, Zhang, J, and Fan, Z. The association between sleep disorder and female infertility: a mediation analysis of inflammatory and oxidative markers. Mediat Inflamm. (2025) 2025:4572392. doi: 10.1155/mi/4572392
26. Corsetti, V, Notari, T, and Montano, L. Effects of the low-carb organic Mediterranean diet on testosterone levels and sperm DNA fragmentation. Curr Res Food Sci. (2023) 7:100636:100636. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2023.100636
27. Allen, NE, and Key, TJ. The effects of diet on circulating sex hormone levels in men. Nutr Res Rev. (2000) 13:159–84. doi: 10.1079/095442200108729052
28. Fantus, RJ, Halpern, JA, Chang, C, Keeter, MK, Bennett, NE, Helfand, B, et al. The association between popular diets and serum testosterone among men in the United States. J Urol. (2020) 203:398–404. doi: 10.1097/ju.0000000000000482
29. Marín de Jesús, S, Vigueras-Villaseñor, RM, Cortés-Barberena, E, Hernández-Rodriguez, J, Montes, S, Arrieta-Cruz, I, et al. Zinc and its impact on the function of the testicle and epididymis. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:991. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168991
30. Sahu, C, and Jena, G. Combination treatment of zinc and selenium intervention ameliorated Bpa-exposed germ cell damage in Sd rats: elucidation of molecular mechanisms. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol. (2024) 397:6685–704. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03044-4
31. Azimi Zangabad, E, Shomali, T, and Roshangar, L. Effects of pharmacological doses of niacin on subacute glucocorticoid-induced testicular damage in rats. Pharmacol Res Perspect. (2023) 11:e01128:e01128. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1128
32. Sertorio, MN, César, H, de Souza, EA, Mennitti, LV, Santamarina, AB, De Souza Mesquita, LM, et al. Parental high-fat high-sugar diet intake programming inflammatory and oxidative parameters of reproductive health in male offspring. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:867127. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.867127
33. Santi, D, Cignarelli, A, Baldi, M, Sansone, A, Spaggiari, G, Simoni, M, et al. The chronic alcohol consumption influences the gonadal Axis in men: results from a Meta-analysis. Andrology. (2024) 12:768–80. doi: 10.1111/andr.13526
34. Liu, M, Gou, Y, Zou, B, Li, X, and Yang, P. Association between serum cotinine and Total testosterone in adult males based on Nhanes 2011-2016. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:23042. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74482-6
35. Field, AE, Colditz, GA, Willett, WC, Longcope, C, and McKinlay, JB. The relation of smoking, age, relative weight, and dietary intake to serum adrenal steroids, sex hormones, and sex hormone-binding globulin in middle-aged men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1994) 79:1310–6. doi: 10.1210/jcem.79.5.7962322
36. Abdel-Sater, KA. Testosterone in long-term sedentary aging males: effect of antiaging strategies. Physiol Int. (2025) 112:1–11. doi: 10.1556/2060.2024.00486
37. Guo, W, Zhao, S, Chang, Q, Sun, J, Fan, Y, and Liu, J. Negative association between 15 obesity- and lipid-related indices and testosterone in adult males: a population based cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis. (2025) 24:24. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02436-6
38. Mele, VG, Chioccarelli, T, Finamore, R, D'Agostino, A, d'Agostino, M, Cimini, D, et al. Antioxidants positively regulate obesity dependent Circrnas - sperm quality - functional Axis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1290971. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1290971
39. Iftikhar, M, Shah, N, Khan, I, Shah, MM, and Saleem, MN. Association between body mass index (Bmi), vitamin D, and testosterone levels. Cureus. (2024) 16:e71509. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71509
40. Jesse, E, Sellke, N, Rivero, MJ, Muncey, W, Ghayda, RA, Loeb, A, et al. Practice comparison and cost analysis of direct-to-consumer telemedicine platforms offering testosterone therapy. J Sex Med. (2022) 19:1608–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2022.03.609
41. Ali, K, Talati, J, Mikulas, C, Quan, A, and Reddy, P. Testosterone therapy for the treatment of unexplained Anemia in men with hypogonadism. Cureus. (2024) 16:e66887. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66887
42. Kivrak, M, Avci, U, Uzun, H, and Ardic, C. The impact of the smote method on machine learning and ensemble learning performance results in addressing class imbalance in data used for predicting Total testosterone deficiency in type 2 diabetes patients. Diagnostics (Basel). (2024) 14:634. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14232634
Keywords: testosterone deficiency, oxidative balance score, lifestyle, dietary, NHANES
Citation: Zhuge Z, Zheng K, Ji X, Wang X and Zhang X (2025) Association between the oxidative balance score and testosterone deficiency in males: a cross-sectional study. Front. Nutr. 12:1577823. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1577823
Edited by:
Weimin Guo, Boston University, United StatesReviewed by:
Tarique Hussain, Nuclear Institute for Agriculture and Biology, PakistanYu Wang, Jinan University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhuge, Zheng, Ji, Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuena Zhang, emhhbmd4dWVuYTI5QDE2My5jb20=
 Ze Zhuge
Ze Zhuge Xiaojun Ji
Xiaojun Ji Xuena Zhang
Xuena Zhang