- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin, China
- 2Medical School of Tianjin University, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China
Objective: Lifestyle factors play a critical role in osteoporosis management and are closely linked to the development and progression of comorbid depression. This study examines lifestyle patterns and their association with depression in individuals with osteopenia or osteoporosis, while assessing the mediating role of the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII).
Methods: Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2009–2020 were analyzed using latent class analysis (LCA) to classify 3,384 adults based on their lifestyle behaviors. A generalized linear model (GLM) evaluated the effects of lifestyle patterns on depression, and mediation analysis tested associations between these patterns, DII, and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) scores.
Results: LCA identified three lifestyle groups: healthy but inactive (34.16%), unhealthy (8.78%), and sedentary (57.06%). The unhealthy (OR = 2.848, 95% CI = 1.550–5.234, p = 0.001) and sedentary (OR = 1.600, 95% CI = 1.127–2.271, p = 0.009) groups were associated with higher depression risk in women. DII partially mediated the relationships between unhealthy lifestyle and PHQ-9 (effect coefficient = 0.095, 95% CI: 0.056–0.135) and between sedentary lifestyle and PHQ-9 (effect coefficient = 0.059, 95% CI: 0.017–0.115).
Conclusion: These findings suggest that lifestyle patterns significantly influence depression in women with osteopenia or osteoporosis, with DII serving as a partial mediator.
1 Introduction
Osteoporosis is a chronic systemic skeletal disorder characterized by reduced bone mass and deterioration of bone microarchitecture (1), with its progressive nature posing significant public health challenges (2). Globally, approximately one-third of women and one-fifth of men aged 50 and above develop osteoporosis, exhibiting an estimated prevalence of 18.3% (3, 4). In the United States alone, 14.1 million adults aged 50 and above are currently diagnosed with osteoporosis, with prevalence rates continuing to increase (5, 6). As populations age, the growing number of osteoporosis cases warrants greater focus on its comorbidity with chronic diseases, which substantially compromises patients’ quality of life (7). Bone undergoes dynamic remodeling throughout life, and recent discoveries of its endocrine functions have established the bone–brain axis as a conceptual framework for studying neural function and behavior (8). Bone-derived signaling molecules contribute to both neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression and neurodegenerative conditions (9). The ICD-11 classifies depression as a syndrome involving distinct clinical symptoms and behavioral manifestations that impair functioning and cause distress (10). In osteoporosis patients, depression correlates with poorer clinical outcomes, including restricted physical activity and unhealthy lifestyle patterns (4, 11).
The relationship between osteoporosis and depression involves complex bidirectional mechanisms, though lifestyle factors play a central moderating role in their development and progression (8, 12, 13). Reduced mobility from osteoporosis often impairs patients’ ability to perform daily activities, while simultaneously isolating them from social support systems, creating conditions that foster maladaptive behaviors (14). These behavioral patterns—including physical inactivity, sleep dysregulation, and substance abuse—collectively contribute to neurobiological changes that elevate depression risk (15–19). Chronic sleep disturbances, for example, alter hormonal homeostasis and amplify inflammatory cascades known to underlie depressive pathophysiology (15). Nicotine exposure from smoking modulates nAChR-mediated neurotransmission, directly affecting neural circuits involved in stress adaptation and mood regulation (16). Alcohol-induced metabolic dysregulation further compounds emotional instability, establishing a self-perpetuating cycle of depressive symptomatology (17). The activity restriction inherent to osteoporosis frequently precipitates a sedentary lifestyle that independently predicts depression onset (18), whereas exercise demonstrates antidepressant effects through neurotrophic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms (19). Existing research has extensively focused on discrete behavioral factors rather than examining the heterogeneous lifestyle profiles that may differentially influence depression risk in osteoporotic populations. Characterizing these multidimensional behavioral patterns could support more precise preventive interventions and treatment approaches.
In osteoporosis management, dietary habits substantially influence bone mineral density and complication risks (20). Patients with osteoporosis often follow pro-inflammatory diets, which may contribute to depression pathogenesis (21, 22). The Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) quantifies diet-induced inflammation, enabling assessment of its health effects (23). Pro-inflammatory diets—high in saturated fats, trans fats, and refined sugars—correlate with elevated DII scores and depression risk (24), whereas anti-inflammatory diets abundant in omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, and produce yield lower DII scores and reduced depression incidence (25). These dietary differences regulate bone mass and simultaneously provide nutrients that support mood and cognition. Healthy lifestyles combining physical activity, adequate sleep, and limited alcohol and tobacco use further promote anti-inflammatory dietary patterns. This reciprocal relationship between lifestyle and diet may improve overall health outcomes (26, 27). The DII potentially mediates the association between osteoporosis-related lifestyle factors and depression, indicating that dietary inflammation modulates their link to depressive symptoms.
This study examined the association between lifestyle factors, dietary inflammation, and depression risk in adults with osteopenia or osteoporosis. We assessed lifestyle characteristics in this population, evaluated relationships between lifestyle factors and depression, and determined whether the DII mediates these associations. The DII may differentially influence depression risk depending on distinct lifestyle patterns among individuals with osteopenia or osteoporosis. These findings could guide targeted interventions combining lifestyle adjustments and dietary approaches to reduce the depression burden in this patient group.
2 Methods
2.1 Study population
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a cross-sectional, population-based study designed to assess the health status, nutritional habits, and lifestyle of non-institutionalized U. S. civilians. We analyzed NHANES data from three survey cycles (2009–2010, 2013–2014, and 2017–2020). The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) provides full documentation of the study design and data collection procedures (28, 29). A total of 14,360 participants aged 20 years or older were identified, and 3,384 participants with complete data entered the final analysis. To account for potential bias introduced by missing values, we retained only complete-case observations in the analysis. The detailed screening process is shown in Supplementary Figure S1.
2.2 Assessment of osteopenia and osteoporosis
Bone mineral density (BMD) was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) using QDR 4500A fan-beam densitometers (Hologic, Inc., Bedford, MA, USA). Standard left hip scans provided total BMD values for the femur, femoral neck, and trochanters. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines osteopenia and osteoporosis in adults aged ≥50 years as BMD values that are 1–2.5 standard deviations (SD) or >2.5 SD below the young adult mean (20–29 years), respectively (30). These diagnostic thresholds apply equally to both sexes and collectively indicate low bone density (31). Patients with concurrent comorbidities were excluded from the analysis.
2.3 Assessment of lifestyle behavior
Lifestyle behavior data were obtained via in-person questionnaires and 24-h dietary recalls. Five dichotomized lifestyle variables were analyzed: cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, sleep duration, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA), and sedentary behavior. Participants who reported smoking ≥100 cigarettes in their lifetime were classified as unhealthy smokers (coded 1) (32). Unhealthy alcohol consumption was defined as >2 drinks/day for men or >1 drink/day for women, consistent with Dietary Guidelines for Americans (coded 1) (33). Sleep durations <6 h or >8 h, regardless of weekday/weekend patterns, were considered unhealthy (coded 1) (34). According to WHO guidelines, participants who failed to meet the weekly thresholds of 150 min of moderate-intensity activity, 75 min of vigorous-intensity activity, or equivalent combinations were classified as physically inactive (coded 1) (35). Sedentary behavior, defined as >7.5 sitting h/day based on previous studies, was similarly categorized as unhealthy (coded 1) (35, 36).
2.4 Assessment of dietary inflammatory index (DII)
The NHANES collected dietary intake data through two 24-h recall interviews, during which participants reported all foods and beverages consumed on the preceding day. Energy and nutrient intakes were derived from these self-reported quantities.
A modified version of the Shivappa et al. (23, 37) methodology was used to calculate the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII), incorporating 27 dietary components such as macronutrients, vitamins (A, B6, B12, C, D, E), minerals (Fe, Mg, Zn, Se), fatty acids (MUFA, PUFA, n-3, n-6), and bioactive compounds (caffeine, β-carotene). Although fewer than 30 nutrients were considered, the DII remained a valid measure (23).
For DII computation, individual nutrient intakes were standardized into z-scores by centering them on global mean values and scaling by standard deviations. These z-scores were converted to percentiles, symmetrically adjusted to a − 1 to +1 range, and then transformed by doubling, subtracting from 1, and multiplying by nutrient-specific inflammatory weights. The final DII score represented the sum of these weighted values (23). Given the study population’s age (>50 years) and consistent dietary habits, the DII provided a reliable inflammatory assessment.
2.5 Assessment of depressive symptoms
The Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) is a nine-item instrument validated for assessing depressive symptoms based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV (DSM-IV) criteria. The NHANES used the PHQ-9 to measure depressive symptoms among participants during the 2 weeks preceding the survey (38).
Participants rated the frequency of nine DSM-IV-defined depressive symptoms over this period using a 4-point scale: 0 (“not at all”), 1 (“several days”), 2 (“more than half the days”), or 3 (“nearly every day”). Total scores ranged from 0 to 27, with a threshold of ≥10 suggesting clinically significant depressive symptoms (39).
2.6 Covariates
The analysis adjusted for several potential confounders: age, sex, ethnicity (non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, and others), education level (less than high school, high school or equivalent, and college or above), self-reported household income, and body mass index (BMI). Household income was measured using the poverty–income ratio (PIR) and categorized into high (PIR > 3.5), middle (PIR 1.3–3.5), and low (PIR ≤ 1.3) categories (40). BMI was grouped into normal or low weight (<25.0 kg/m2), overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2), and obese (≥30.0 kg/m2) (39).
2.7 Data analysis
All data were integrated according to the NHANES protocols, incorporating masked variance and applying the recommended weighting methodology. Latent class analysis (LCA) identified underlying subgroups based on five lifestyle behaviors, with model selection guided by the Akaike information criterion (AIC), Bayesian information criterion (BIC), sample-size adjusted BIC (aBIC), Bootstrap likelihood ratio test (BLRT), and adjusted Lo–Mendell–Rubin test (aLMR). To assess associations between lifestyle patterns and depression in participants with osteopenia or osteoporosis, we employed a generalized linear model (GLM). Mediation analysis further examined relationships among lifestyle patterns, dietary inflammatory index (DII), and PHQ-9 scores in this population. LCA was performed using MPlus 8.3, while mediation analyses utilized IBM SPSS 26.0 with PROCESS Macro Model 4. The remaining statistical procedures were conducted in R 4.2.2, with statistical significance set at a p-value of < 0.05 (two-tailed).
3 Results
3.1 Demographics
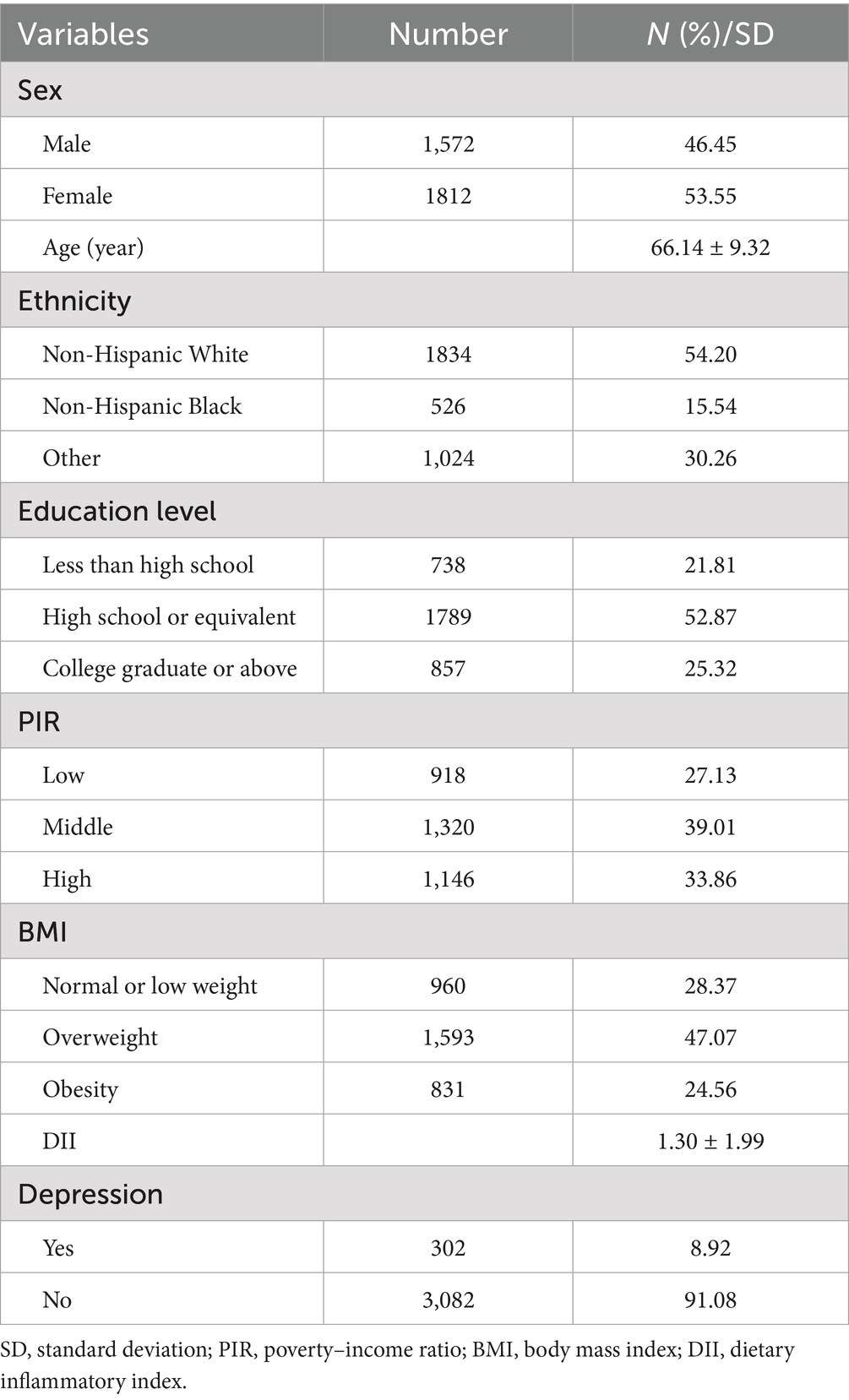
Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of participants with osteopenia and osteoporosis from the NHANES 2009–2010, 2013–2014, and 2017–2020 cycles. The study population comprised 3,384 individuals with a mean (SE) age of 66.14 (9.32) years. Participants showed a mean (SE) DII score of 1.30 (1.99), while 302 individuals (8.92%) exhibited depressive symptoms.
3.2 Latent class analysis of lifestyle behavior
Supplementary Table S1 displays the LCA model results, including fit indices for solutions ranging from 1 to 5 classes. The 4-class model showed non-significant LMR and BLRT values, along with one class comprising less than 5% of the sample, while the 3-class solution demonstrated superior interpretability and the lowest AIC, BIC, and aBIC values.
Figure 1 illustrates the conditional probabilities of lifestyle behaviors across classes. Class 1 exhibited relatively low probabilities for smoking (40.6%), alcohol consumption (0%), and sedentary behavior (20.1%), contrasting with Classes 2 and 3. Class 2 displayed notably high probabilities for smoking (59.1%), alcohol consumption (99.9%), sleep disturbances (38.2%), and physical inactivity (47.1%). Although Class 3 showed the highest sedentary behavior probability (51.2%), its probabilities for sleep disturbances (28.7%) and inactivity (0%) remained lower than other classes. Based on these patterns, we classified Class 1 (n = 1,156, 34.16%) as “healthy but inactive,” Class 2 (n = 297, 8.78%) as “unhealthy,” and Class 3 (n = 1,931, 57.06%) as “sedentary.”
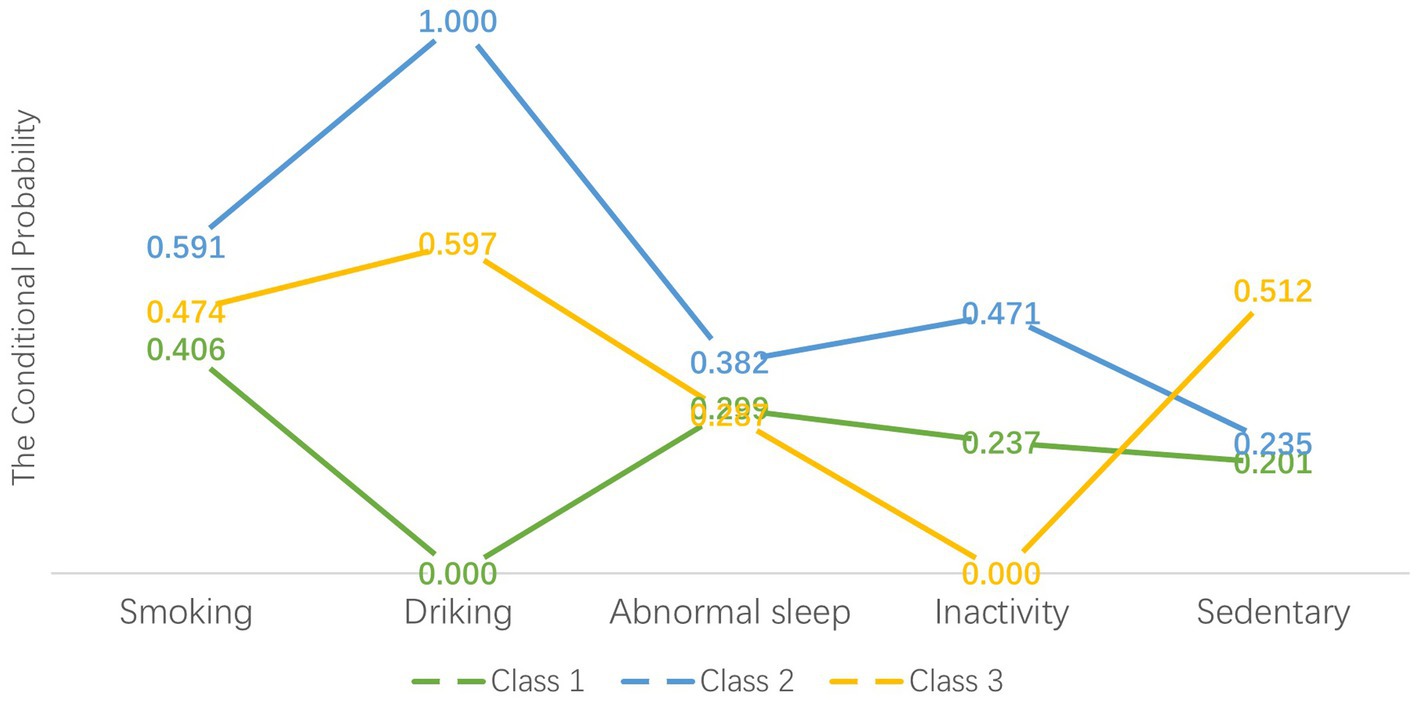
Figure 1. Item-response probabilities of lifestyle behaviors by the three latent class groups. “Healthy but inactivity” group (Class 1) represented 34.16% of the sample (n = 1,156). “Unhealthy” group (Class 2) accounted for 8.78% of the full sample (n = 297). “Sedentary” group (Class 3) represented 57.06% of the sample (n = 1,931).
3.3 Univariate analysis among lifestyle patterns
Sex, age, ethnicity, and educational level differed significantly across the three lifestyle behavior patterns (sex: χ2 = 147.700, p < 0.001; age: F = 26.375, p < 0.001; ethnicity: χ2 = 83.386, p < 0.001; education: χ2 = 30.288, p < 0.001), as detailed in Supplementary Table S2.
3.4 Effects of lifestyle patterns and DII on depression
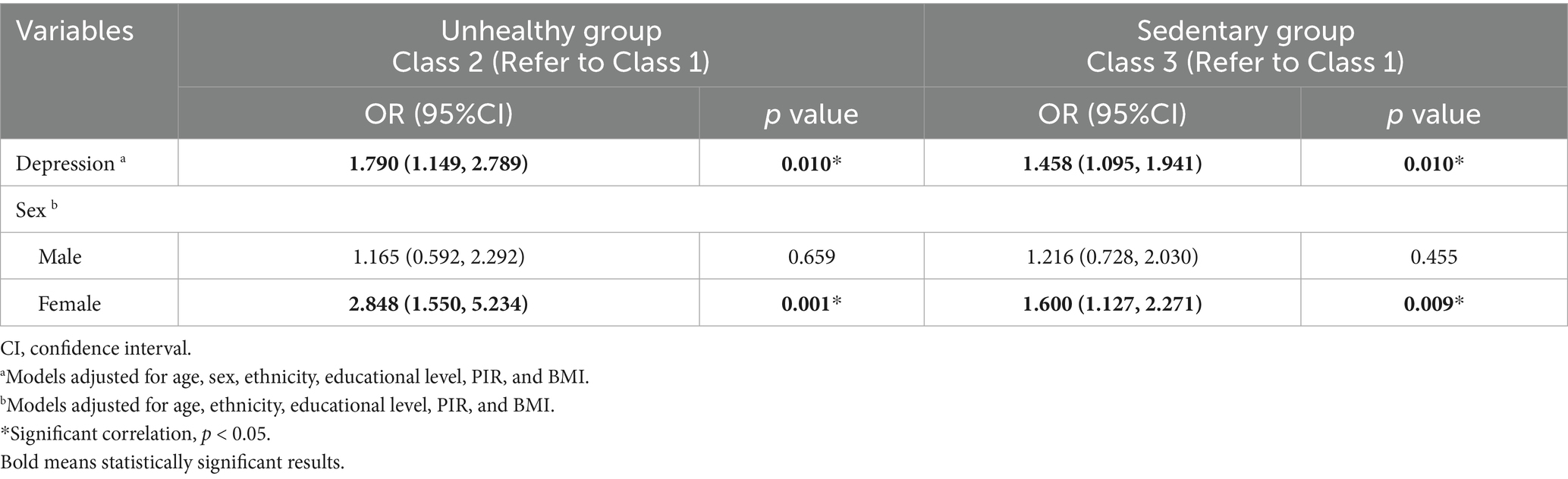
After adjusting for age, ethnicity, educational level, PIR, and BMI, women with osteopenia or osteoporosis in the unhealthy (OR = 2.848, 95% CI = 1.550–5.234, p = 0.001) and sedentary (OR = 1.600, 95% CI = 1.127–2.271, p = 0.009) groups exhibited higher depression risk than those in the healthy but inactive group (Table 2).
DII scores (H = 7.675, p = 0.022) differed significantly across the three lifestyle behavior patterns among women (Supplementary Table S3). Higher DII scores were associated with increased depression risk (OR = 1.127, 95% CI = 1.051–1.210, p < 0.001) (Supplementary Table S4).
3.5 Lifestyle patterns, DII, and PHQ-9 scores
DII, lifestyle patterns, and PHQ-9 scores showed significant intercorrelations in women with osteopenia or osteoporosis (Supplementary Table S5). Mediation analysis revealed that DII partially accounted for the associations between both unhealthy lifestyle patterns and PHQ-9 scores (β = 0.095, 95% CI: 0.056–0.135) and sedentary behavior and PHQ-9 scores (β = 0.059, 95% CI: 0.017–0.115). These mediation effects corresponded to 4.63 and 6.22% of the total associations between lifestyle factors and depressive symptoms, respectively (Supplementary Table S6; Figure 2).
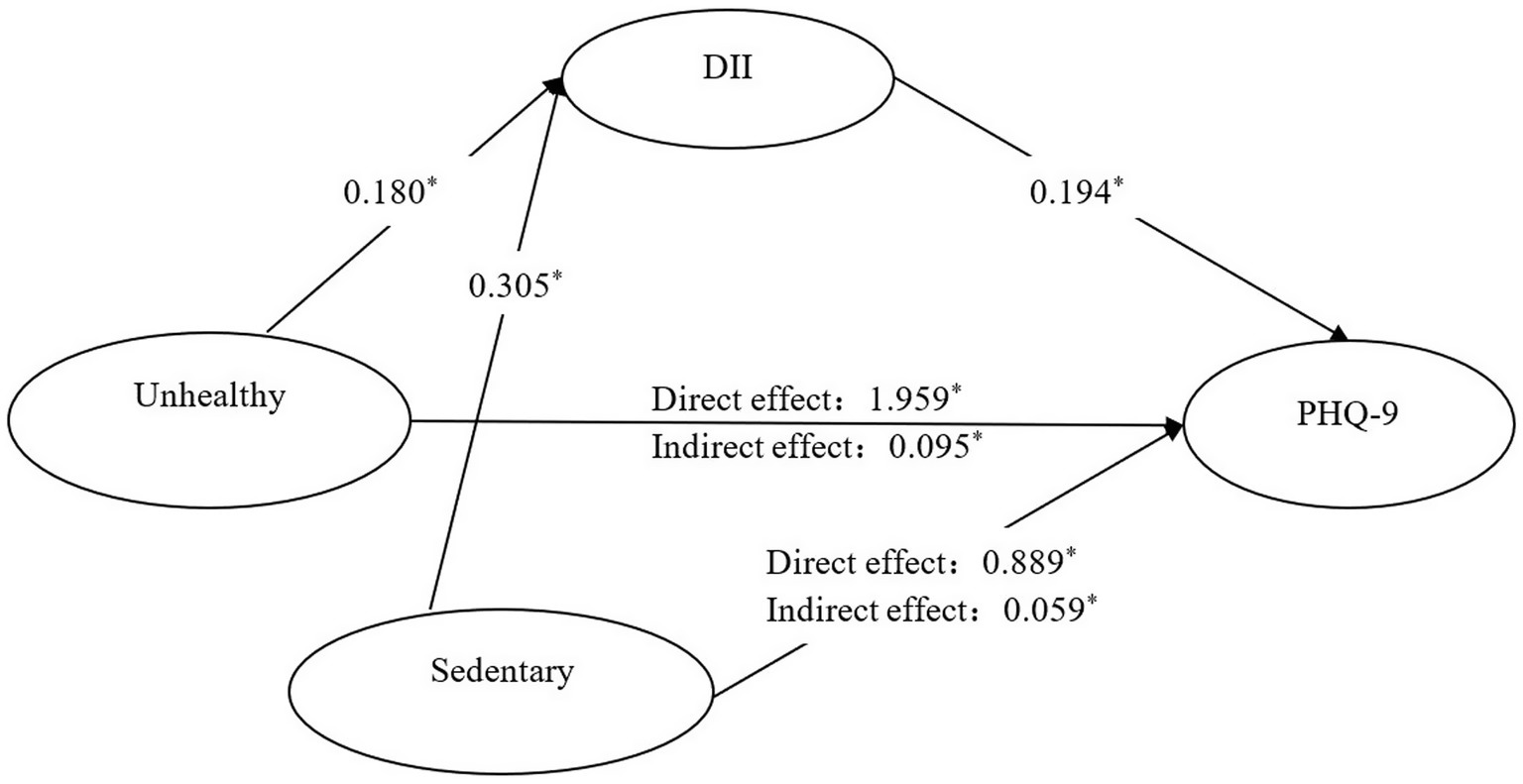
Figure 2. Mediating effect of DII in the relationship between lifestyle patterns and PHQ-9 among adults with osteopenia or osteoporosis. *: p < 0.05; coefficients have been standardized; Reference group: Healthy but inactivity group. Path 1: Unhealthy group→DII → PHQ-9. Path 2: Sedentary group→DII → PHQ-9.
4 Discussion
Our analysis of lifestyle behaviors in adults with osteopenia and osteoporosis revealed three distinct patterns: healthy, unhealthy, and sedentary, each characterized by at least one unhealthy behavior. The distribution of these patterns varied across demographic groups, with osteoporosis and osteopenia patients predominantly clustered in the sedentary group (60.75% of men and 53.86% of women). Men were significantly overrepresented in the unhealthy group compared to women (13.61% versus 4.58%), which was consistent with established gender disparities in smoking and alcohol consumption (41, 42), although alcohol consumption has increased among women in recent years. Participant age differed markedly among the groups, with the lowest mean age in the healthy but inactive group and the highest in the unhealthy group, reflecting the known age-related accumulation of risk behaviors that may accelerate chronic disease development (43). As anticipated, the unhealthy group showed the highest mean DII scores, while the healthy but inactive group displayed the lowest, corroborating evidence linking healthy lifestyles with anti-inflammatory diets (26, 27). These results demonstrate how lifestyle factors interact synergistically to influence health outcomes (44). The high frequency of concurrent unhealthy behaviors in our cohort underscores the need for integrated interventions targeting multiple risk factors simultaneously, which could substantially improve overall health and reduce comorbidity burdens in this population.
Significant disparities emerged in depression risk associated with lifestyle factors, particularly among women with osteopenia or osteoporosis. This finding raises critical questions about potential gender differences in the pathways linking these conditions to comorbid depression. Our study focused exclusively on adults aged 50 and above, particularly women, who typically undergo perimenopause—a period marked by hormonal fluctuations that may simultaneously increase susceptibility to both bone loss and depression (45). The anti-inflammatory properties of estrogen suggest a possible mechanism, as declining levels in postmenopausal women could exacerbate depression through inflammatory pathways (46). Gender-specific neuroendocrine stress responses may further contribute to this phenomenon (47). Depression also manifests differently between genders (48), with women generally experiencing more severe and persistent symptoms than men (49). Notably, lifestyle factors interact with depression risk in a gender-dependent manner: Fan et al. demonstrated stronger associations between tobacco smoke exposure and depressive symptoms in women than men (50), while sleep patterns disproportionately affect women’s mental health (51). These observations position gender as a key modifier of depression risk, particularly regarding lifestyle interventions. Women with osteopenia or osteoporosis may therefore derive greater mental health benefits from lifestyle improvements, whereas additional factors—including independent effects or behavioral interactions—likely influence outcomes in men. Further investigation should clarify the complex interplay between lifestyle factors, mediating mechanisms, and depression development in this patient population.
Our findings reveal the unique role of the DII in linking lifestyle factors to depression, demonstrating the need for targeted interventions. Among women with osteopenia or osteoporosis, the DII partially mediated associations between unhealthy dietary patterns and PHQ-9 scores, as well as between sedentary behavior and depressive symptoms. These observations imply that dietary interventions reducing inflammation could effectively mitigate depression risk in this population. Shifting toward anti-inflammatory diets while minimizing pro-inflammatory food intake may substantially decrease PHQ-9 scores and depression incidence. However, integrating dietary modifications with broader lifestyle interventions targeting multiple risk factors may yield greater benefits for depressive symptom relief. The pronounced mediating effect of the DII underscores the critical role of dietary management—particularly anti-inflammatory eating patterns—in alleviating depression among osteopenic and osteoporotic patients. This finding corroborates existing evidence that anti-inflammatory diets positively influence mental health (26, 27), suggesting that such diets may buffer depression’s effects on inflammatory markers (52). Chronic low-grade inflammation has been implicated in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Research consistently shows that diets rich in sugar, refined carbohydrates, saturated fats, and processed meats exacerbate inflammation and are associated with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, and cognitive impairment. Recent studies further connect these pro-inflammatory diets with elevated depression risk in adults (53). Since proper neurotransmitter synthesis requires adequate amino acids, minerals, and vitamins, nutritional deficiencies may simultaneously affect depression susceptibility and HPA axis function (54). However, the incomplete mediation observed suggests that additional pathways beyond inflammation alone may be involved. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D is not only significantly associated with BMD but also potentially with symptoms of depression (55). In addition, the role of vitamin D in neuroendocrine regulation and bone homeostasis should not be ignored (56). Future research needs to explore its regulatory pathways further, particularly in conjunction with vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms. Other potential pathways of influence include gut flora, which may be involved in the co-morbid mechanisms of depression and bone loss through immune regulation (e.g., Th17/Treg balance), short-chain fatty acid metabolism, and other related pathways. A clinical study found that the gut microbiota of patients with inflammatory depression exhibited a higher level of Anaplasma spp. and a lower level of Clostridium spp. and an increase in butyrate metabolism of abnormal SCFA-producing bacteria (57). Longitudinal investigations are needed to clarify these complex relationships and assess the effectiveness of tailored dietary and lifestyle interventions for individuals with osteopenia and osteoporosis. Additionally, clinical trials must establish optimal implementation strategies to translate these findings into improved mental and physical health outcomes.
To our knowledge, this study provides the first examination of how lifestyle patterns and dietary inflammation jointly influence depression risk in adults with osteopenia or osteoporosis. The results reveal distinct mediating effects of the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) in this relationship, highlighting the need for targeted interventions. The large, nationally representative NHANES sample strengthens the reliability of these findings and their applicability to U. S. adults with compromised bone health. Several limitations warrant consideration. First, the DII calculation incorporated only 27 food parameters due to data constraints, potentially limiting the assessment’s thoroughness regarding dietary inflammation. Second, while validated instruments were used, the dependence on self-reported dietary recalls and PHQ-9 depression screening introduces potential recall bias. Although depressive states were categorized using established criteria, future work should use more nuanced analytical methods. Third, the cross-sectional design prevents causal inference, underscoring the need for longitudinal studies to clarify temporal relationships among these factors. Future research should broaden the scope to include individuals across the bone density spectrum, even without clinical diagnoses, to better inform prevention efforts. Additionally, our findings require validation in non-U. S. populations. Finally, unmeasured medication use may have confounded the observed associations between depression and dietary behaviors.
5 Conclusion
Adults with osteopenia or osteoporosis typically demonstrate lifestyle patterns involving at least one unhealthy behavior. These patterns correlate with increased depression risk in women. The Dietary Inflammatory Index mediates this relationship through multiple pathways, highlighting the need for population-specific interventions that account for varying lifestyle profiles.
Data availability statement
The publicly available data sets used in this study can be found at: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/default.aspx.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by NCHS Research Ethics Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
BW: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YF: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. ST: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft. WG: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft. YL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CD: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Tianjin Education Commission Research Project (grant number 2022KJ240). The sponsor or funding organization had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all National Center for Health Statistics staff for their assistance in explaining and accessing NHANES variables and thank NHANES participants and the data collection team for making this survey possible.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1578954/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Compston, JE, McClung, MR, and Leslie, WD. Osteoporosis. Lancet. (2019) 393:364–76. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32112-3
2. Khosla, S, and Hofbauer, LC. Osteoporosis treatment: recent developments and ongoing challenges. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2017) 5:898–907. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30188-2
3. Aibar-Almazán, A, Voltes-Martínez, A, Castellote-Caballero, Y, Afanador-Restrepo, DF, Carcelén-Fraile, MDC, and López-Ruiz, E. Current status of the diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:9465. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169465
4. Chen, K, Wang, T, Tong, X, Song, Y, Hong, J, Sun, Y, et al. Osteoporosis is associated with depression among older adults: a nationwide population-based study in the USA from 2005 to 2020. Public Health. (2024) 226:27–31. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2023.10.022
5. Sarafrazi, N, Wambogo, EA, and Shepherd, JA. Osteoporosis or low bone mass in older adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief. (2021) 405:1–8. doi: 10.15620/cdc:103477
6. Salari, N, Ghasemi, H, Mohammadi, L, Behzadi, M, Rabieenia, E, Shohaimi, S, et al. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2021) 16:609. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02772-0
7. Guo, X, She, Y, Liu, Q, Qin, J, Wang, L, Xu, A, et al. Osteoporosis and depression in perimenopausal women: from clinical association to genetic causality. J Affect Disord. (2024) 356:371–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.04.019
8. Kashfi, SS, Abdollahi, G, Hassanzadeh, J, Mokarami, H, and Khani Jeihooni, A. The relationship between osteoporosis and depression. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:11177. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15248-w
9. Ma, C, Zhang, Y, Cao, Y, Hu, CH, Zheng, CX, Jin, Y, et al. Autonomic neural regulation in mediating the brain-bone axis: mechanisms and implications for regeneration under psychological stress. QJM. (2024) 117:95–108. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcad108
11. Shi, L, Zhou, X, Gao, Y, Li, X, Fang, R, and Deng, X. Evaluation of the correlation between depression and physical activity among older persons with osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study. Front Psych. (2023) 14:1193072. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1193072
12. He, B, Lyu, Q, Yin, L, Zhang, M, Quan, Z, and Ou, Y. Depression and osteoporosis: a Mendelian randomization study. Calcif Tissue Int. (2021) 109:675–84. doi: 10.1007/s00223-021-00886-5
13. Kerr, C, Bottomley, C, Shingler, S, Giangregorio, L, de Freitas, HM, Patel, C, et al. The importance of physical function to people with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. (2017) 28:1597–607. doi: 10.1007/s00198-017-3911-9
14. Becofsky, K, Baruth, M, and Wilcox, S. Physical activity mediates the relationship between program participation and improved mental health in older adults. Public Health. (2016) 132:64–71. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2015.07.040
15. Li, J, Cao, D, Huang, Y, Chen, Z, Wang, R, Dong, Q, et al. Sleep duration and health outcomes: an umbrella review. Sleep Breath. (2022) 26:1479–501. doi: 10.1007/s11325-021-02458-1
16. Terry, AV Jr, Jones, K, and Bertrand, D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in neurological and psychiatric diseases. Pharmacol Res. (2023) 191:106764. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106764
17. Nunes, EV. Alcohol and the etiology of depression. Am J Psychiatry. (2023) 180:179–81. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.20230004
18. Onagbiye, S, Guddemi, A, Baruwa, OJ, Alberti, F, Odone, A, Ricci, H, et al. Association of sedentary time with risk of cardiovascular diseases and cardiovascular mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Prev Med. (2024) 179:107812. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2023.107812
19. Bellón, JÁ, Conejo-Cerón, S, Sánchez-Calderón, A, Rodríguez-Martín, B, Bellón, D, Rodríguez-Sánchez, E, et al. Effectiveness of exercise-based interventions in reducing depressive symptoms in people without clinical depression: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Psychiatry. (2021) 219:578–87. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2021.5
20. Quattrini, S, Pampaloni, B, Gronchi, G, Giusti, F, and Brandi, ML. The Mediterranean diet in osteoporosis prevention: an insight in a Peri- and post-menopausal population. Nutrients. (2021) 13:531. doi: 10.3390/nu13020531
21. Ayyadurai, VAS, Deonikar, P, and Bannuru, RR. Attenuation of low-grade chronic inflammation by phytonutrients: a computational systems biology analysis. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2022) 49:425–35. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.03.010
22. Wang, B, Fan, Y, Wang, X, Zeng, X, Zeng, S, Jia, H, et al. Influence of lifestyle patterns on depression among adults with diabetes: a mediation effect of dietary inflammatory index. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:1779. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19319-7
23. Shivappa, N, Steck, SE, Hurley, TG, Hussey, JR, and Hébert, JR. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. (2014) 17:1689–96. doi: 10.1017/S1368980013002115
24. Shakya, PR, Melaku, YA, Shivappa, N, Hébert, JR, Adams, RJ, Page, AJ, et al. Dietary inflammatory index (DII®) and the risk of depression symptoms in adults. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:3631–42. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.12.031
25. Gabriella, M, Shakila, M, Qiaowei, L, Wendy, L, Amy, R, and Venkat, B. Mental health consequences of dietary restriction: increased depressive symptoms in biological men and populations with elevated BMI. BMJ Nutr Prev Health. (2025) 10:1167. doi: 10.1136/bmjnph-2025-001167
26. Joshi, MR, Joshi, M, Mundra, A, M, R, Kolhe, R, Kirubakaran, R, et al. Community-based health promotion interventions to reduce risk factors of non-communicable diseases among adolescent and young adults in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health. (2025) 243:105714. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2025.03.026
27. Karageorgou, D, Magriplis, E, Mitsopoulou, AV, Dimakopoulos, I, Bakogianni, I, Micha, R, et al. Dietary patterns and lifestyle characteristics in adults: results from the Hellenic National Nutrition and health survey (HNNHS). Public Health. (2019) 171:76–88. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2019.03.013
28. National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2024) NCHS research ethics review board approval. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about/erb.html?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/irba98.htm (Accessed December 18, 2024).
29. CDC. (2024) NHANES - about the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about_nhanes.htm (Accessed December 18, 2024).
31. Sun, C, Yang, X, and Feng, X. Obesity paradox: association between lipid metabolism indices and skeletal muscle mass in older adults: the mediating role of uric acid. Acta Diabetol. (2025) 2025:527. doi: 10.1007/s00592-025-02527-x
32. Chang, HJ, Lin, KR, Lin, MT, and Chang, JL. Associations between lifestyle factors and reduced kidney function in US older adults: NHANES 1999-2016. Int J Public Health. (2021) 66:1603966. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2021.1603966
33. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture. (2020). Dietary guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025. Retrieved from https://health.gov/our-work/nutrition-physical-activity/dietary-guidelines/current-dietary-guidelines
34. Lallukka, T, Sivertsen, B, Kronholm, E, Bin, YS, Øverland, S, and Glozier, N. Association of sleep duration and sleep quality with the physical, social, and emotional functioning among Australian adults. Sleep Health. (2018) 4:194–200. doi: 10.1016/j.sleh.2017.11.006
35. WHO. WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Geneva: World Health Organization (2020).
36. Ekelund, U, Tarp, J, Steene-Johannessen, J, Hansen, BH, Jefferis, B, Fagerland, MW, et al. Dose-response associations between accelerometry measured physical activity and sedentary time and all cause mortality: systematic review and harmonised meta-analysis. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4570. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4570
37. Mohammadi, S, Hosseinikia, M, Ghaffarian-Bahraman, A, Clark, CCT, Davies, IG, Yousefi Rad, E, et al. Dietary inflammatory index and elevated serum C-reactive protein: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Sci Nutr. (2023) 11:5786–98. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3553
38. Ford, J, Thomas, F, Byng, R, and McCabe, R. Use of the patient health questionnaire (PHQ-9) in practice: interactions between patients and physicians. Qual Health Res. (2020) 30:2146–59. doi: 10.1177/1049732320924625
39. Ba, DM, Gao, X, Al-Shaar, L, et al. Mushroom intake and depression: a population-based study using data from the US National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES), 2005-2016. J Affect Disord. (2021) 294:686–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.07.080
40. Fryar, CD, Wright, JD, Eberhardt, MS, and Dye, BA. Trends in nutrient intakes and chronic health conditions among Mexican-American adults, a 25-year profile: United States, 1982–2006. United States: US Department of Health and Human Services (2012).
41. Alam, F, and Silveyra, P. Sex differences in E-cigarette use and related health effects. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2023) 20:7079. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20227079
42. Agabio, R, Pisanu, C, Gessa, GL, and Franconi, F. Sex differences in alcohol use disorder. Curr Med Chem. (2017) 24:2661–70. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666161202092908
43. Cho, H, and Lee, H. Latent class analysis of health lifestyle among older adults living alone and associations with life satisfaction and depressive symptoms. J Affect Disord. (2024) 361:172–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.05.162
44. Che, W, Wang, C, Tao, S, Li, T, Xie, Y, Tao, F, et al. The association of chronotype, sleep duration and trajectories of health-risk behaviors among college students: a cohort study. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. (2025) 19:4. doi: 10.1186/s13034-025-00861-0
45. Shitomi-Jones, LM, Dolman, C, Jones, I, Kirov, G, Escott-Price, V, Legge, SE, et al. Exploration of first onsets of mania, schizophrenia spectrum disorders and major depressive disorder in perimenopause. Nat Ment Health. (2024) 2:1161–8. doi: 10.1038/s44220-024-00292-4
46. Zhang, Y, Tan, X, and Tang, C. Estrogen-immuno-neuromodulation disorders in menopausal depression. J Neuroinflammation. (2024) 21:159. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03152-1
47. Heck, AL, and Handa, RJ. Sex differences in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis' response to stress: an important role for gonadal hormones. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2019) 44:45–58. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0167-9
48. Bondy, E, Norton, SA, Voss, M, Marks, RB, Boudreaux, MJ, Treadway, MT, et al. Inflammation is associated with future depressive symptoms among older adults. Brain Behav Immun Health. (2021) 13:100226. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100226
49. Senoo, K, Kaneko, H, Ueno, K, Suzuki, Y, Okada, A, Fujiu, K, et al. Sex differences in the association between depression and incident cardiovascular disease. JACC Asia. (2024) 4:279–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jacasi.2023.11.015
50. Fan, Z, Gong, X, Xu, H, Wang, H, Zeng, N, Li, L, et al. Gender differences in the associations between tobacco smoke exposure and depressive symptoms among U.S. adults: NHANES 2007-2018. J Psychiatr Res. (2022) 146:249–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.11.013
51. Montagni, I, Qchiqach, S, Pereira, E, Tully, PJ, and Tzourio, C. Sex-specific associations between sleep and mental health in university students: a large cross-sectional study. J Am Coll Heal. (2020) 68:278–85. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2018.1546183
52. Pierret, ACS, Mizuno, Y, Saunders, P, Lim, E, de Giorgi, R, Howes, OD, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and mental health: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. (2025) 14:e250679. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2025.0679
53. Juliana, MM, Isabelly, GS, Renato, NS, and Luiz, GSB. Exploring the links between pro-inflammatory diets, gut dysbiosis, serotonin, and their implications for psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Behav Immun Integr. (2024) 8:100097. doi: 10.1016/j.bbii.2024.100097
54. Belliveau, R, Horton, S, Hereford, C, Ridpath, L, Foster, R, and Boothe, E. Pro-inflammatory diet and depressive symptoms in the healthcare setting. BMC Psychiatry. (2022) 22:125. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-03771-z
55. Atteritano, M, Lasco, A, Mazzaferro, S, Macrì, I, Catalano, A, Santangelo, A, et al. Bone mineral density, quantitative ultrasound parameters and bone metabolism in postmenopausal women with depression. Intern Emerg Med. (2013) 8:485–491. doi: 10.1007/s11739-011-0628-1
56. Bertone-Johnson, ER, Powers, SI, Spangler, L, Brunner, RL, Michael, YL, Larson, JC, et al. Vitamin D intake from foods and supplements and depressive symptoms in a diverse population of older women. Am J Clin Nutr. (2011) 94:1104–1112. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.111.017384
Keywords: dietary inflammation index, depression, lifestyle patterns, osteopenia, osteoporosis, NHANES
Citation: Wang B, Fan Y, Tang S, Guo W, Li Y and Dai C (2025) Dietary inflammatory index mediation lifestyle patterns and depression among women with osteopenia or osteoporosis. Front. Nutr. 12:1578954. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1578954
Edited by:
Marija Takic, University of Belgrade, SerbiaReviewed by:
Antonino Catalano, University of Messina, ItalyFatemeh Pourteymour Fard Tabrizi, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Xin Chen, Tongji University, China
Małgorzata Natalia Słoma-Krześlak, Śląskiego Uniwersytetu Medycznego, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Fan, Tang, Guo, Li and Dai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yin Li, bGl5aW45OUB0bXUuZWR1LmNu; Chenlin Dai, ZGFpYW5kemhhbmdAc2luYS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Baoping Wang1†
Baoping Wang1† Yuxin Fan
Yuxin Fan Yin Li
Yin Li