- Department of Biochemistry, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Background/objectives: Oxidative stress, organ impairments, and gastrointestinal abnormalities are the most common systemic dysfunctions that accompanied the neurodevelopmental condition, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Emerging evidence suggests that increased propionic acid (PPA) levels contribute to ASD pathophysiology through oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and disruption of the gut-liver-brain axis. Thanks to its strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potencies, luteolin, has shown to be promising in alleviating these effects. This study investigated the therapeutic and protective effects of luteolin in a PPA-induced rodent model of ASD by assessing oxidative stress, intestinal permeability, and liver and kidney dysfunction biomarkers.
Methods: Fifty young male albino rats were divided into five groups: control, PPA-treated, luteolin-treated, therapeutic (PPA followed by luteolin), and protective (luteolin followed by PPA). Oxidative stress markers (GSH, lipid peroxides, GST, SOD, and catalase), serum zonulin, liver enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP) and renal function markers (urea nitrogen, creatinine) were investigated. ROC analysis evaluated the diagnostic potential of these biomarkers, while Spearman correlation analysis explored interrelationships among parameters.
Results: PPA administration significantly reduced antioxidant defenses, including GSH, GST, SOD, and catalase, while increasing lipid peroxidation and inducing hepatic and renal dysfunction, as evidenced by elevated ALT, AST, ALP, urea nitrogen, and creatinine levels, along with increased zonulin levels. Luteolin intervention effectively reversed these alterations by restoring antioxidant capacity, lowering zonulin levels, and improving liver and kidney function. ROC analysis demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy (AUC = 1.000) for oxidative stress and organ dysfunction markers in the PPA-treated group, while luteolin treatment significantly enhanced biomarker sensitivity and specificity. Spearman correlation analysis revealed strong negative correlations between antioxidants and oxidative stress markers (p < 0.001) and positive correlations between zonulin and liver/kidney dysfunction indicators (p < 0.001), further confirming the systemic impact of PPA.
Conclusion: Luteolin effectively alleviated oxidative stress, restored antioxidant defenses, and enhanced liver, kidney, and intestinal barrier functions in a PPA-induced ASD model. These findings underscored its therapeutic potential as a natural intervention for ASD-related systemic dysfunctions. Further clinical studies are needed to evaluate its translational applicability in ASD management.
1 Introduction
Repetitive behaviors as well as impairments in communication skills and social interaction are the main characteristics of the neurodevelopmental disorder, autism spectrum disorder (ASD) (1, 2). Globally, ASD impacts about 1 in 54 children, with a higher prevalence among males (3). In addition to its hallmark symptoms, ASD is often accompanied by systemic dysfunctions, including oxidative stress, gastrointestinal (GI) issues and organ-specific abnormalities. Genetic predispositions, environmental effects and gut microbiota (GM) abnormalities are all involved in its pathophysiology (4). ASD is frequently associated with heightened oxidative stress, which contributes to neuroinflammation and behavioral disturbances (5). Altered GM and increased intestinal permeability are typical co-morbidities associated with gut-brain axis dysfunction in ASD (4, 6). Additionally, several researchers are beginning to view autism as a systemic disorder with a potential impact on various organs and physiological system, including the liver (7, 8). A recent study by Ahmed et al. (8) demonstrated liver dysfunction and elevated liver enzymes in autistic children compared to controls. Additionally, it has been discovered that children with autism spectrum disorder have greater levels of bacterial metabolites, which have been linked to both acute renal damage and chronic kidney disease (9, 10).
Propionic acid (PPA) is a short-chain fatty acid naturally found in dairy products such as milk, yogurt and cheese (11, 12). It is mainly produced in the colon when GM ferment undigested food. Once absorbed into the bloodstream, PPA can reach adipose tissue, where it lowers plasma fatty acid levels by inhibiting lipolysis, promoting lipogenesis in fat tissues and suppressing fatty acid synthesis in the liver (13). While PPA is crucial for normal immune and physiological functions, elevated levels can disrupt these processes and lead to adverse effects (14). PPA has the ability to cross barriers in the gut, liver, blood, and brain, allowing it to reach the central nervous system (15). Within the brain, PPA penetrates cell membranes and accumulates inside, causing the cells to become more acidic (16, 17). This acidification disrupts neurotransmitter release, potentially affecting neuronal communication and behavior (18, 19). PPA is also implicated in metabolic disturbances, including inhibition of ureagenesis, disruption of fatty acid metabolism (20), and induction of oxidative stress (21, 22). Its ability to traverse the gut-liver-brain axis facilitates systemic effects, contributing to liver dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative damage (15).
Medicinal plants are rich in natural compounds that have been widely studied for their pharmacological effects on various conditions, including cancer, inflammation, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative disorders (23, 24). Flavonoids, key bioactive compounds derived from plants, play essential roles in plant defense and offer a range of health benefits, including anticoagulant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antimicrobial, and antidepressant effects (25, 26). Their antioxidant properties largely contribute to these benefits. Indeed, the phenolic structure of flavonoids helps neutralizing free radicals and mitigate oxidative stress by decreasing lipid peroxidation and enhancing antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) (27, 28).
Luteolin (3,4,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is a natural flavonoid found in various foods such as carrots, apples, cabbage, and certain medicinal plants. It exhibits a range of pharmacological effects, including anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties (29). The structure of luteolin is directly linked to its antioxidant capacity and its ability to resist oxidation through metal ion chelation (30–33). Studies have shown that luteolin reduces oxidative stress, regulates inflammatory pathways and restores the integrity of the gut-liver-kidney axis. Specifically, luteolin provides renoprotective benefits, protecting against renal damage caused by ischemia, nephrotoxic drugs, and sepsis (34–36). The co-administration of this bioactive flavonoid as part of preoperative nutrition has been shown to reduce ischemia–reperfusion injury and minimize intestinal apoptosis (37). Luteolin is also an attractive candidate for developing liver-protective drugs. It targets proinflammatory interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-18 pathways, significantly alleviating inflammation and steatosis while restoring normal levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and maintaining a proper balance between reactive oxygen species and antioxidant enzymes (38). In addition, luteolin has demonstrated therapeutic potential in neurological disorders. A clinical study found that a dietary supplement containing luteolin significantly improved social interaction in children with ASDs (39). More recent research has further confirmed luteolin’s promise as a therapeutic option for reducing ASD symptoms (40). In the present study, the effect of luteolin was investigated in a PPA-induced ASD rat model, focusing on gut leakiness, liver and renal dysfunctions, as well as oxidative stress.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animals and experimental design
Animal experiment was carried out in the Experimental Surgery and Animal Laboratory at the College of Medicine, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. 50 young male albino rats (80–100 g, 3 weeks old) were housed in cages measuring 40 × 35 × 20 cm3 under controlled environmental conditions, with a temperature maintained at 21 ± 1°C and a 12-h light/dark cycle (lights on at 9:00 AM and off at 9:00 PM) and an unrestricted access to water and standard laboratory feed pellets. The experimental procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Research at King Saud University, Riyadh (Approval No. KSU-SE-23-26).
The animals were randomly assigned to five groups, each consisting of 10 rats: Group I (Control group): received phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) only. Group II (PPA-intoxicated group): administered PPA at a dose of 250 mg/kg daily for 3 days. Group III (Luteolin-treated group): given luteolin at a dose of 50 mg/kg per day for 27 days. The 50 mg/kg dose of luteolin was selected based on previous studies showing its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects in rats, including models of neurotoxicity (41) and inflammation (42), supporting its use in the PPA-induced ASD model. Group IV (Therapeutic group): received PPA (250 mg/kg daily for 3 days), followed by luteolin (50 mg/kg per day for 27 days). Group V (Protective group): pre-treated with luteolin (50 mg/kg per day for 27 days), followed by PPA administration (250 mg/kg daily for 3 days).
2.2 Serum and tissue collection
On day 28, blood samples were collected via direct cardiac puncture into plain tubes without anticoagulant. Serum was separated by centrifugation at 3,000 rpm at 4°C for 10 min.
Meanwhile, the liver and kidney were carefully excised, washed, and sliced into ~1 g fragments. The tissue samples were homogenized in 10 mL of double-distilled water for 3 min using a Teflon homogenizer (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). The homogenates were then centrifuged at 4,000 g for 20 min to remove debris. Both tissue homogenates and serum samples were stored at −80°C until further use.
2.3 Biochemical analysis
A panel of selected biochemical markers was measured across all study groups. Oxidative stress biomarkers, including glutathione (GSH) (43), lipid peroxides (44), glutathione-S-transferase (GST) (45), SOD (46), and catalase (47), were analyzed in serum, liver, and kidney tissue homogenates.
Serum zonulin (Cat No. MBS2606662) and urea nitrogen (Cat No. MAK006) were quantified using ELISA kits from MyBioSource and Sigma-Aldrich, respectively, following the manufacturers’ instructions. Additionally, alanine aminotransferase (ALT, Cat No. EL07-150), aspartate aminotransferase (AST, Cat No. EL15-150), alkaline phosphatase (ALP, Cat No. EL04L-150), and creatinine (Cat No. EL33K-1000) levels were assessed in serum samples using colorimetric kits from United Diagnostics Industry, Dammam, KSA, according to the manufacturers’ protocols.
All measurements were performed in triplicate, with the mean of three readings calculated.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Data were expressed as mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis tests assessed group differences, followed by the Least Significant Difference (LSD) or Mann–Whitney tests for multiple comparisons. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis evaluated the diagnostic performance of biochemical parameters, reporting Area Under the Curve (AUC), sensitivity and specificity. Parameters with high AUC values were strong biomarker candidates. Spearman correlation analysis explored relationships between biochemical parameters, reporting correlation coefficients (R) and p values.
3 Results
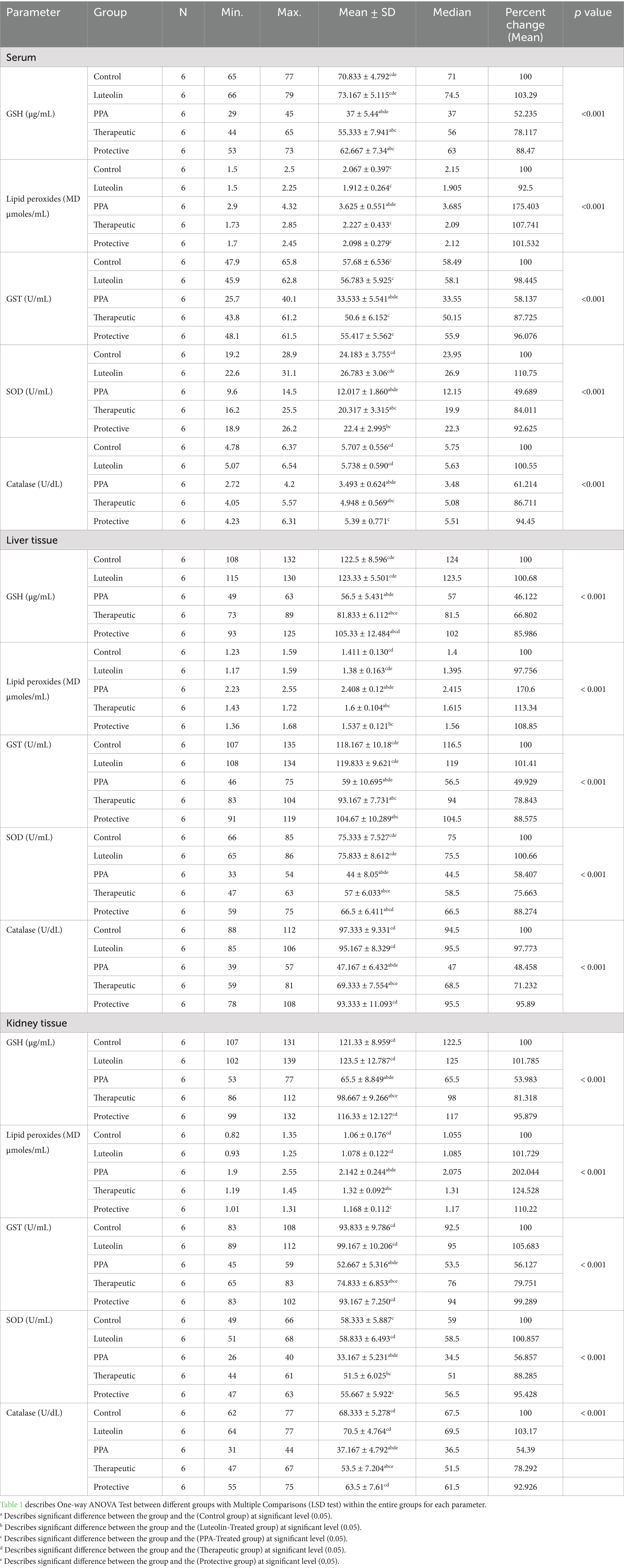
Biochemical assessments revealed that PPA exposure significantly disrupted redox homeostasis, marked by a notable reduction in GSH and antioxidant enzyme activities, with a concomitant increase in lipid peroxides across serum, liver, and kidney samples. These findings highlighted oxidative stress as a hallmark of PPA toxicity (Table 1; Figure 1).
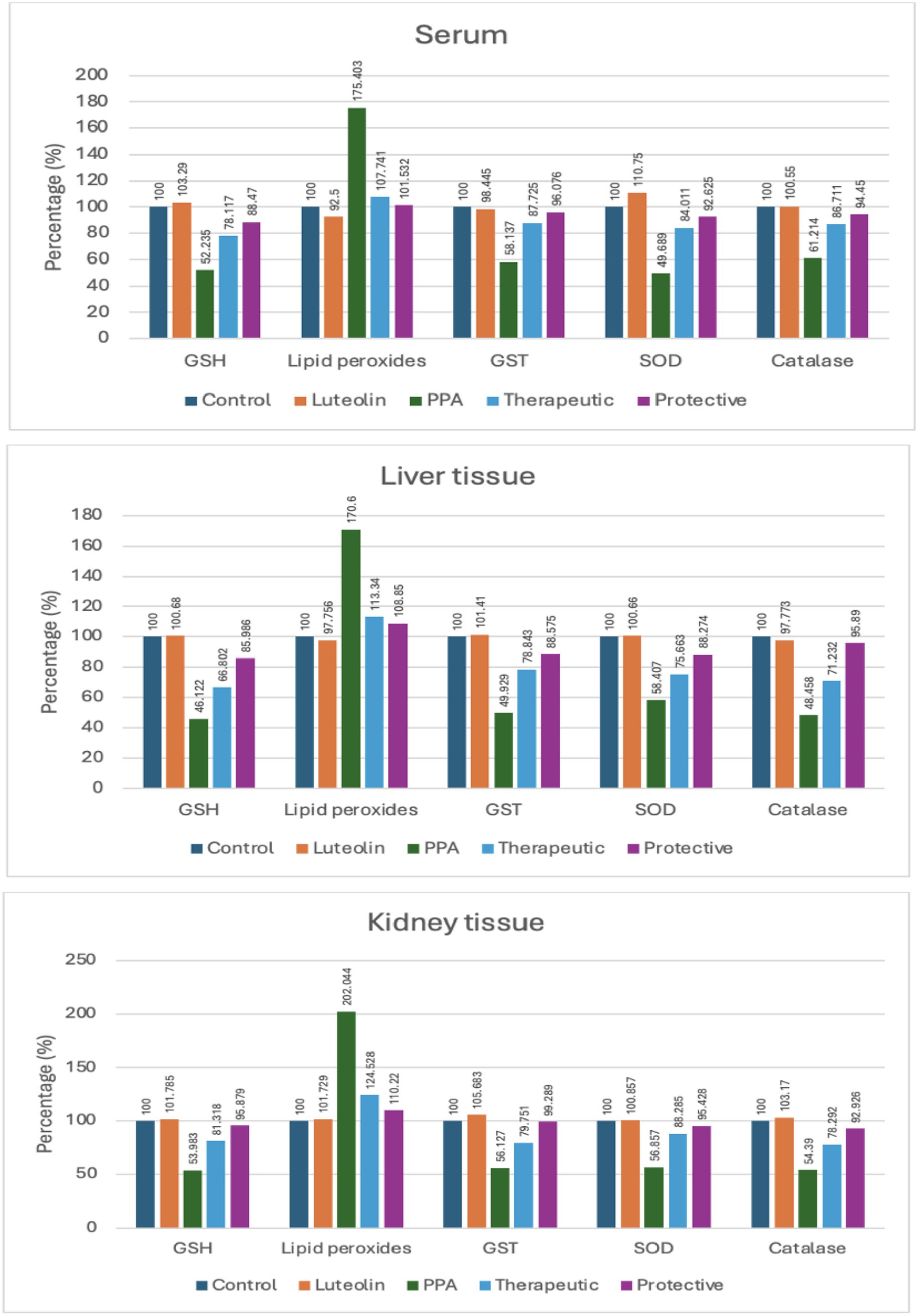
Figure 1. Percent change of oxidative stress biomarkers in serum, liver, and kidney tissues of experimental groups (Control, Luteolin, PPA, Therapeutic and Protective). Data were expressed as percentage relative to control group (set at 100%). GSH, Reduced Glutathione; GST, Glutathione S-Transferase; SOD, Superoxide Dismutase; PPA, Propionic Acid.
Luteolin treatment whether administered as a preventive or therapeutic intervention effectively restored antioxidant balance. GSH levels, suppressed by PPA, were markedly elevated in luteolin-treated groups, with the protective protocol demonstrating slightly superior outcomes. Similarly, lipid peroxidation, significantly elevated by PPA, was remarkably reduced following luteolin administration, nearing control levels, particularly in the protective group (Table 1; Figure 1).
The activities of key enzymatic antioxidants, including GST, SOD and catalase, were also significantly impaired by PPA. Interestingly, luteolin co-administration restored these activities in both liver and kidney tissues, with the protective regimen showing greater efficacy in normalizing catalase activity (Table 1; Figure 1).
In addition to oxidative stress markers, zonulin levels a biomarker of intestinal permeability—were markedly increased by PPA but significantly reduced in both luteolin-treated groups. These results underscored luteolin’s ability to maintain intestinal barrier integrity (Table 2; Figure 2).
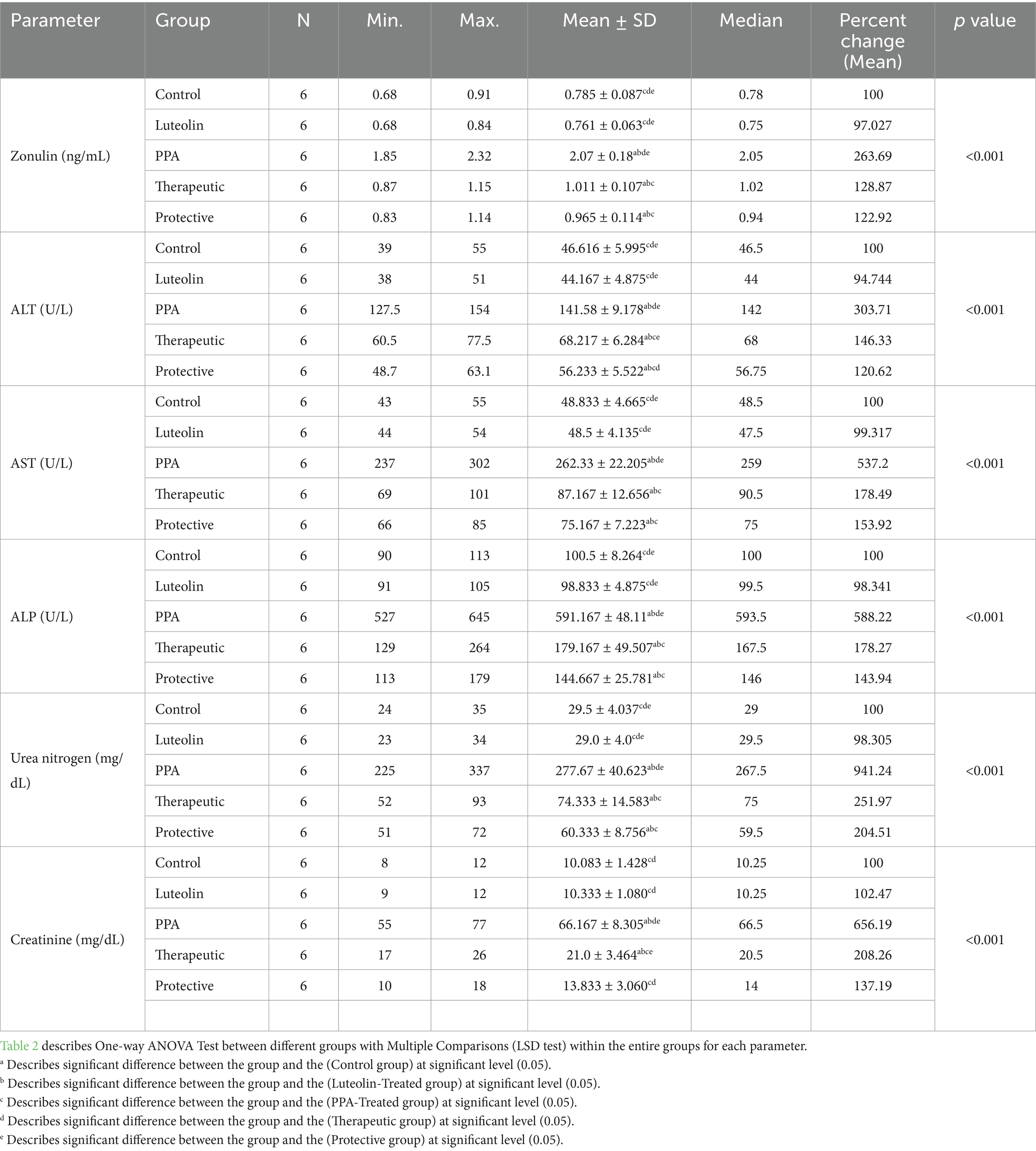
Table 2. Comparative analysis of serum zonulin, liver enzymes and kidney function biomarkers between different groups.
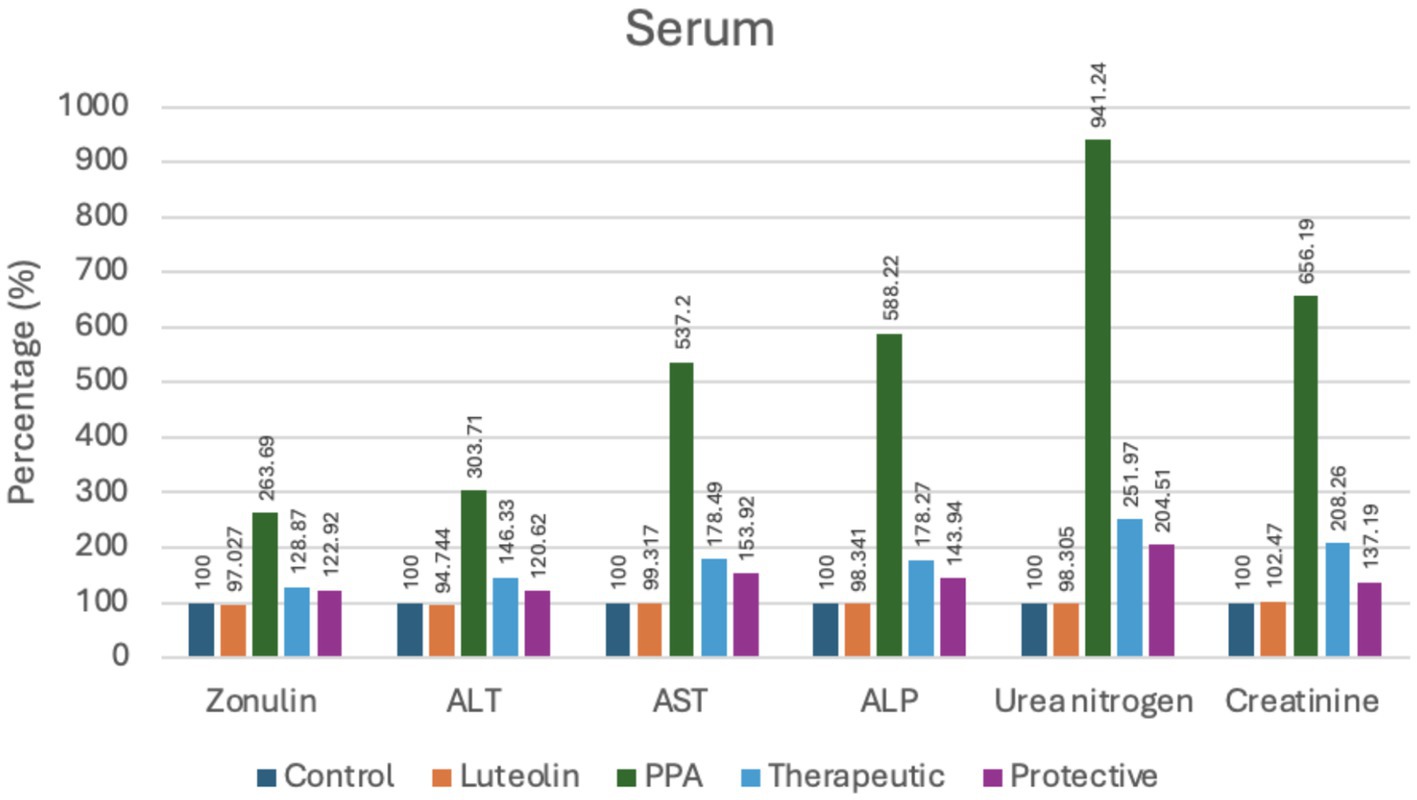
Figure 2. Percent change of serum markers indicating intestinal permeability, liver and kidney function in experimental groups (Control, Luteolin, PPA, Therapeutic and Protective). Data were expressed as percentage relative to control group (set at 100%). ALT, Alanine Aminotransferase; AST, Aspartate Aminotransferase; ALP, Alkaline Phosphatase; PPA, Propionic Acid.
Liver function biomarkers (ALT, AST and ALP) and renal function markers (urea nitrogen and creatinine) were also severely elevated following PPA exposure, indicating multi-organ impairment. Notably, luteolin administration substantially ameliorated these alterations, with the protective approach yielding values closer to baseline compared to the therapeutic group (Table 2; Figure 2).
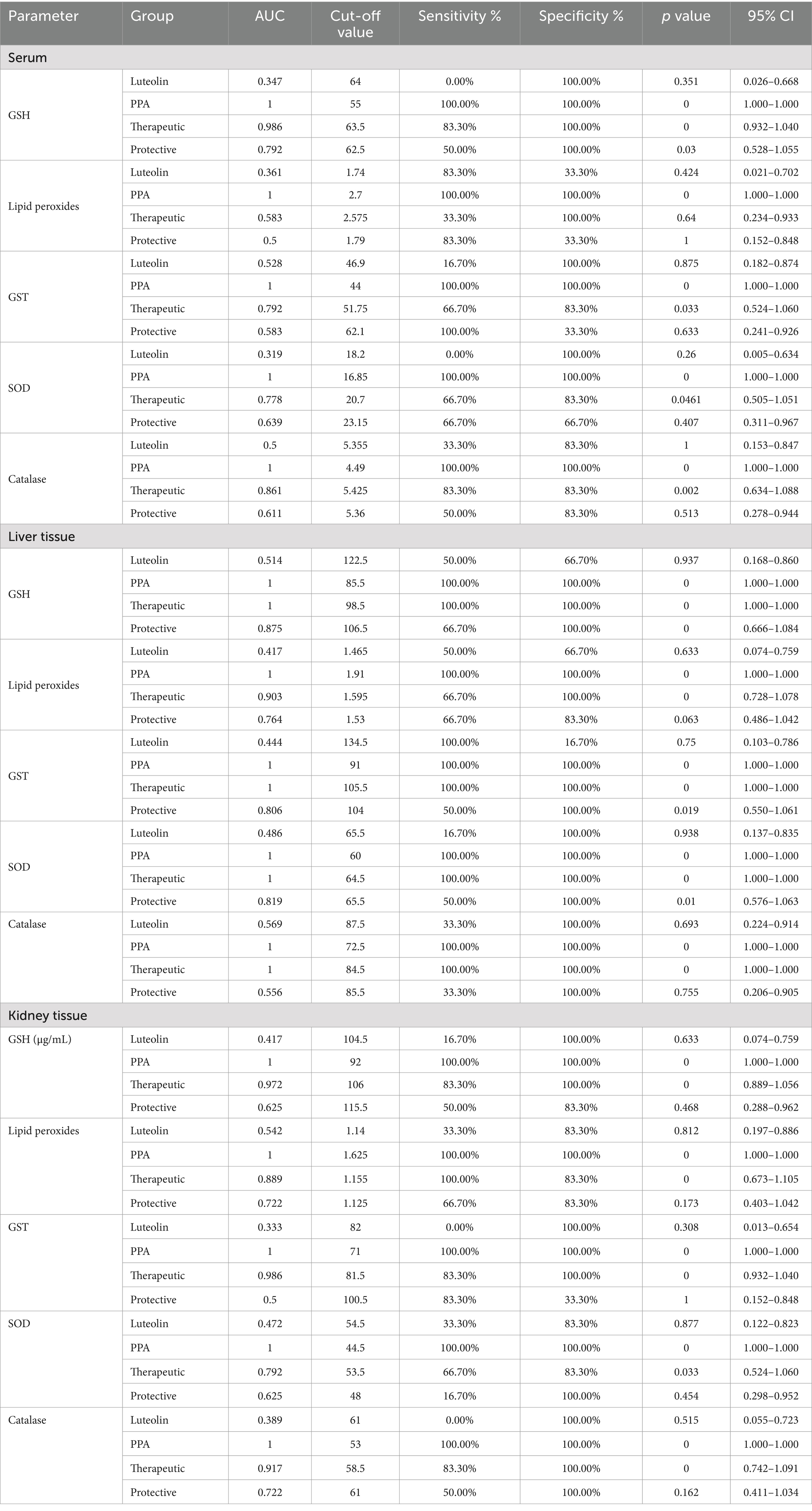
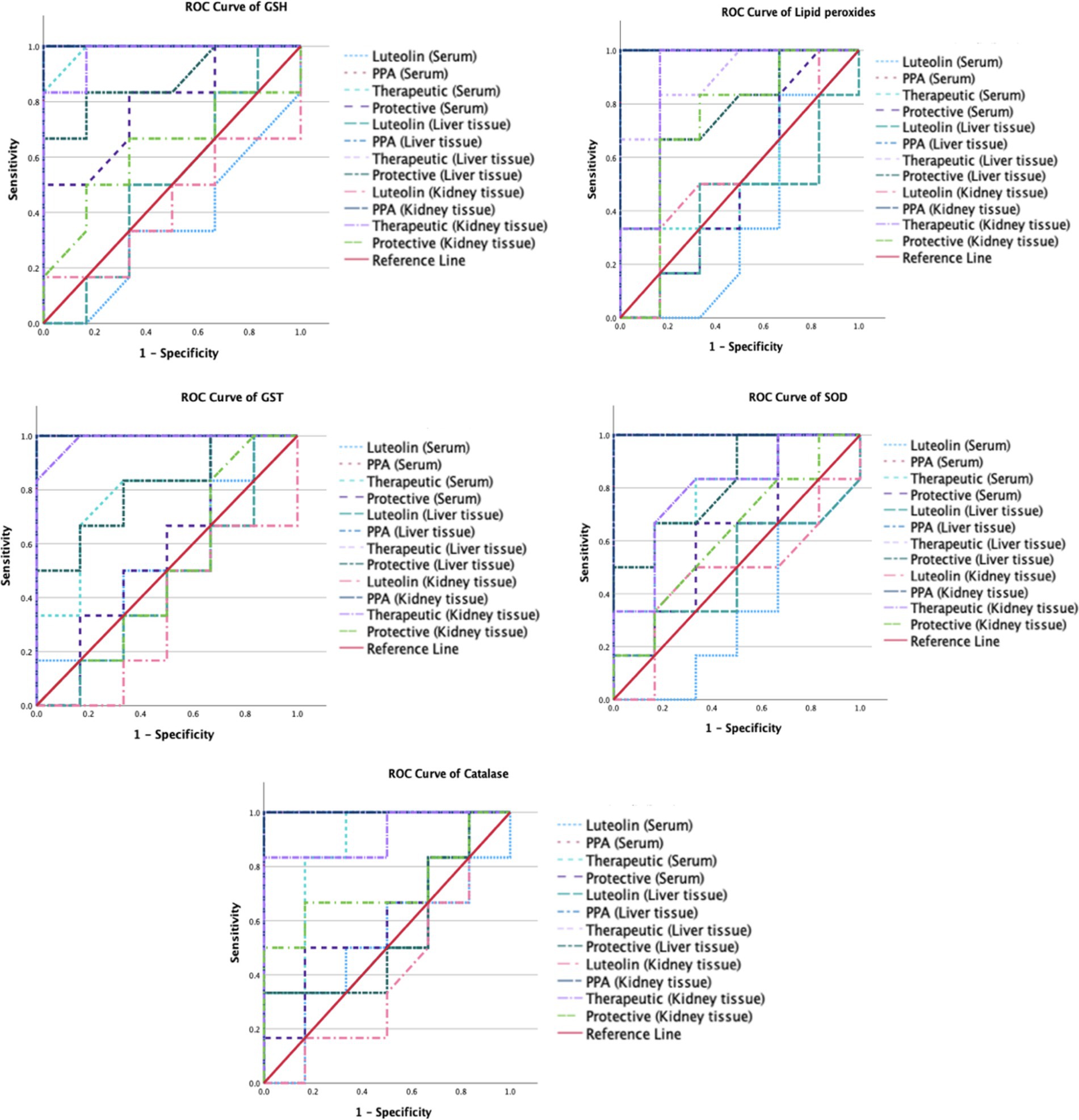
The ROC analysis was conducted to evaluate the diagnostic performance of multiple biochemical markers across all experimental groups (Tables 3, 4; Figures 3,4). In the PPA-treated group, all biomarkers exhibited outstanding diagnostic accuracy, with AUC values of 1.0, confirming the significant biochemical and physiological disturbances induced by PPA. In contrast, the luteolin-only group showed low to moderate diagnostic performance across most parameters, with AUC values generally below 0.7, indicating limited predictive power when administered without PPA exposure.
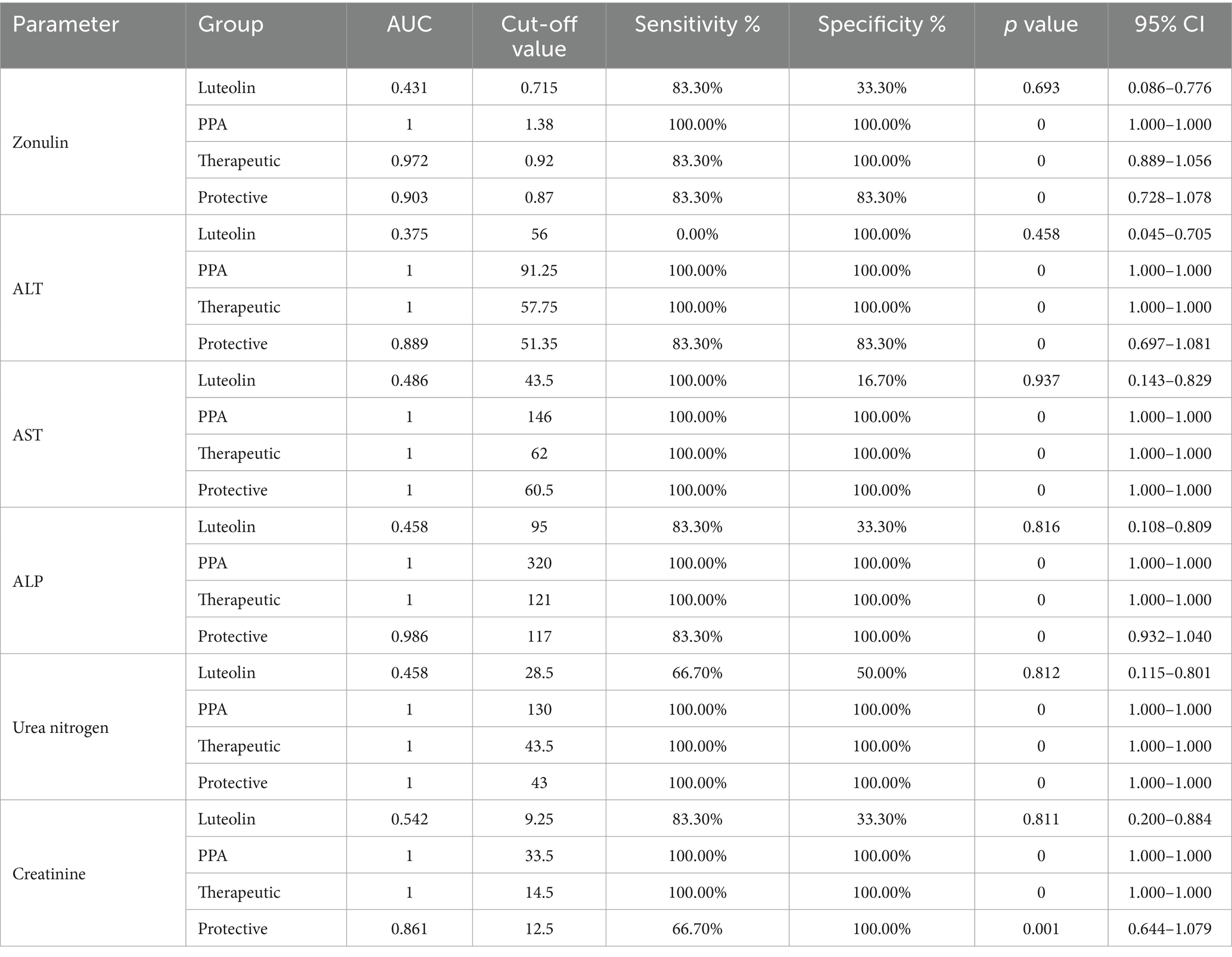
Table 4. ROC analysis of several biomarkers of intestine (Zonulin), liver (ALT, AST & ALP), and renal (urea and creatinine) functioning in the different groups.
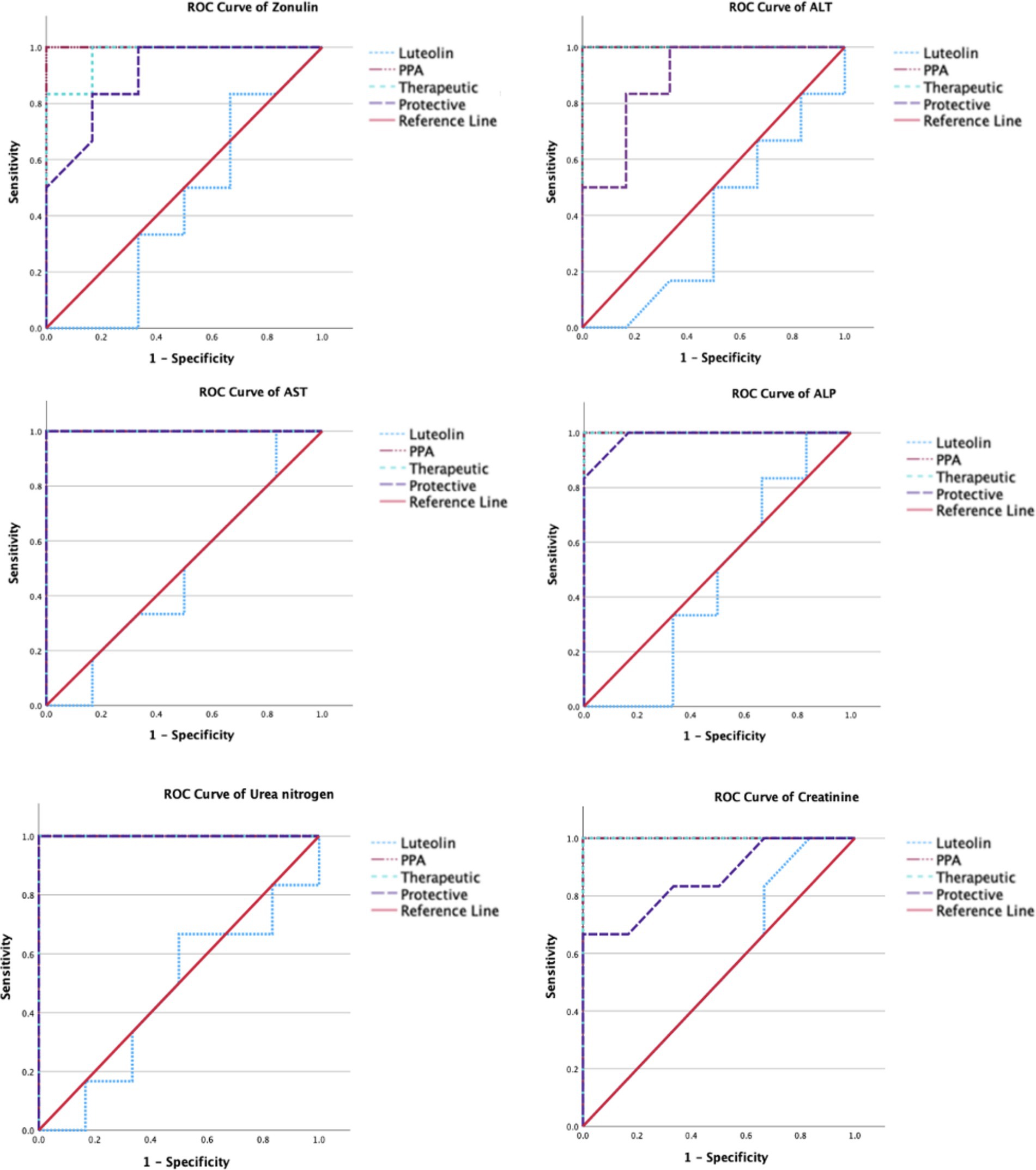
Figure 4. ROC curves of several biomarkers of intestine (Zonulin), liver (ALT, AST & ALP), and renal (urea and creatinine) functioning in the different groups.
Luteolin co-administration in the therapeutic and protective groups substantially enhanced the diagnostic accuracy of numerous markers. In the therapeutic group, several serum and tissue biomarkers such as GSH, ALT, AST, ALP and lipid peroxides exhibited excellent performance (AUC > 0.9), reflecting luteolin’s robust capacity to mitigate PPA-induced biochemical alterations. Similarly, the protective group demonstrated marked improvement in AUC values for key oxidative stress and organ function biomarkers, though to a slightly lesser extent than the therapeutic group. These findings collectively emphasize the potential of luteolin in both preventing and reversing PPA-induced oxidative and functional impairments.
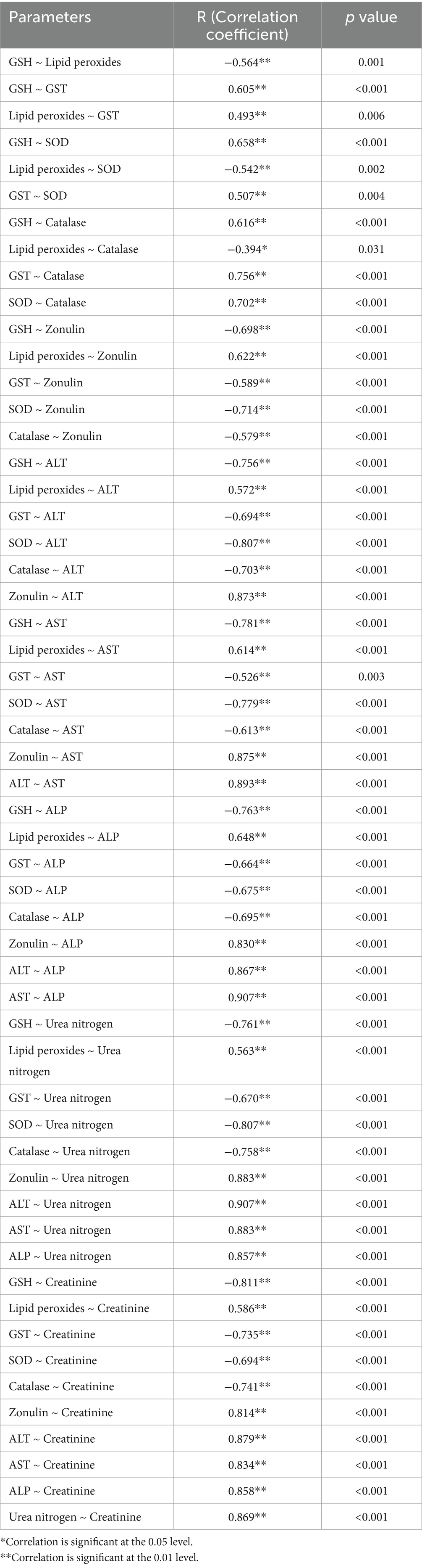
Spearman’s correlation analysis revealed significant interrelationships among biochemical parameters, highlighting the interconnected roles of oxidative stress, intestinal permeability, and liver and kidney function (Table 5). Antioxidants such as GSH, GST, SOD and catalase exhibited strong positive correlations. In contrast, lipid peroxides showed negative correlations with antioxidants. Zonulin displayed a strong negative correlation with antioxidants but was positively correlated with lipid peroxides, ALT and AST. Liver function markers (ALT and AST) were highly correlated with each other and with zonulin, while showing strong negative correlations with antioxidants such as GSH. Similarly, kidney function markers (urea nitrogen and creatinine) were strongly correlated and also positively associated with zonulin. However, they exhibited negative correlations with antioxidants, including GSH.
4 Discussion
This study demonstrated the promising therapeutic and preventive potential of luteolin in mitigating PPA-induced oxidative stress, intestinal barrier dysfunction, and hepatic and renal impairments in a rodent model of ASD. Through biochemical assessments and robust statistical analyses including Spearman correlations and ROC curve evaluations, luteolin showed a strong capacity to restore antioxidant defense mechanisms, reinforce intestinal barrier integrity, and normalize liver and kidney function biomarkers.
Emerging research also underscores the pivotal role of the gut–liver and gut–kidney axes in systemic health. The gut–liver axis facilitates metabolite and immune communication via the portal vein, and its disruption via dysbiosis and increased intestinal permeability can promote hepatic inflammation and oxidative stress (48). Similarly, the gut–kidney axis links microbial metabolites to renal function, with permeability alterations leading to uremic toxin translocation and kidney injury (49). In the current model, PPA-induced permeability may have facilitated harmful microbial product transfer to the liver and kidneys, exacerbating damage. The protective effects of luteolin may thus be partially attributed to its capacity to modulate gut microbiota and enhance intestinal barrier integrity, thereby attenuating pathological processes along these axes (50).
PPA administration lead to increased intestinal permeability, reflected in elevated serum zonulin levels, and widespread oxidative stress, marked by depleted antioxidant enzymes (GSH, GST, SOD, catalase) and increased lipid peroxidation. These results are consistent with previous studies by Kara et al. (51) and Esnafoglu et al. (52), who reported higher zonulin levels in individuals with ASD, indicating a disrupted intestinal barrier. This “leaky gut” state facilitates the entry of microbial products into circulation, exacerbating systemic inflammation and oxidative damage a key mechanism of PPA toxicity (19). Our findings confirmed significantly reduced antioxidant levels and elevated oxidative markers. These results aligned with previous studies reporting oxidative stress in serum (53), liver tissues (15), brain tissues (54, 55), and systemic oxidative stress studies (21, 22).
These oxidative disruptions were strongly correlated with hepatic and renal dysfunction, as reflected in elevated ALT, AST, urea nitrogen, and creatinine, reinforcing previous evidence of PPA-induced multi-organ toxicity (14, 15, 54). However, luteolin intervention, particularly in the protective group, markedly reversed these effects, confirming its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions. Luteolin treatment significantly improved hepatic oxidative balance likely due to free radical scavenging and upregulation of antioxidant enzymes (27). This finding could be supported by Yao et al. (56) who underlined the hepatoprotective properties of luteolin, especially through the upregulation of antioxidant defenses, including SOD and GSH and the inhibition of oxidative stress markers such as malondialdehyde. This could explain the pronounced recovery observed in liver tissues, where luteolin’s activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway plays a crucial role (57).
Similarly, kidney tissues responded favorably to luteolin which was consistent with previous studies such as that by Birman et al. (58), where luteolin restored nitric oxide synthase activity and reduced iNOS levels, contributing to renal antioxidative effects. In the current study, both the therapeutic and protective groups restored antioxidant defenses, with the protective group showing greater recovery, supporting luteolin’s role as a potent antioxidant (29). Luteolin’s phenolic structure enhances its free radical scavenging capacity through hydrogen atom donation, reducing oxidative stress markers such as lipid peroxides, as previously reported by Procházková et al. (27) and Wu et al. (28). Both luteolin-treated groups demonstrated a reduction in these markers, restoring near-normal levels, further confirming its hepatoprotective and renoprotective effects (34, 56, 59). Additionally, luteolin’s ability to modulate inflammatory pathways, including IL-1 and IL-18, likely contributes to its protective effects (39).
Elevated zonulin levels in ASD have been associated with greater symptom severity, pointing to a link between intestinal permeability and metabolic disruption (51, 52, 60). In this study, luteolin significantly reduced serum zonulin in both therapeutic and protective groups, suggesting its role in preserving intestinal barrier integrity (50, 61). Interestingly, a significant inverse correlation was found between antioxidant levels (such as GSH and SOD) and serum zonulin, suggesting that oxidative stress contributes directly to intestinal barrier dysfunction. This finding was in line with a recent study by Yuan et al. (62) that demonstrated luteolin’s ability to restore barrier integrity in a Caco-2 cell model by reducing ROS, increasing antioxidant enzyme activity (SOD and GSH), and upregulating tight junction proteins like ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1. The study also showed that luteolin’s protective effects involve activation of Nrf2 signaling and suppression of ERK and NF-κB/MLCK pathways. These results highlighted the importance of antioxidant defense in modulating intestinal permeability, and supported the use of luteolin as a dietary supplement to preserve gut integrity under oxidative stress conditions.
Correlation analysis further illuminated the underlying pathophysiology, revealing strong negative correlations between oxidative stress markers and antioxidants, and positive correlations with liver and kidney damage parameters (e.g., ALT, AST, creatinine). These findings underscored oxidative stress as a central driver of PPA-induced multi-organ damage and highlighted the importance of antioxidant defense in mitigating systemic toxicity. The antioxidant and protective role of luteolin was well supported by previous research. For instance, Owumi et al. (63) demonstrated that luteolin co-treatment alleviated doxorubicin-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, while improving antioxidant status, tissue integrity, and survival. This reinforces luteolin’s potential as a chemoprotective agent in oxidative stress-related pathologies.
Furthermore, the ROC analysis could provide valuable insights into the diagnostic efficacy of various biomarkers for detecting PPA-induced oxidative stress and organ dysfunction, as well as the therapeutic and protective potential of luteolin. In the PPA group, nearly all biomarkers had AUC = 1.00, indicating severe systemic damage with high diagnostic accuracy (15, 64, 65). Upon luteolin treatment, the therapeutic group exhibited notable improvements. Serum GSH levels, for instance, achieved an AUC of 0.986, with 83.3% sensitivity and 100% specificity, highlighting a significant recovery in antioxidant capacity. Consistent with Ben Bacha et al. (55), luteolin demonstrated neuroprotective and neurotherapeutic properties, effectively counteracting oxidative stress and cognitive impairment. Similarly, liver enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP) and renal function biomarkers (urea nitrogen, creatinine) maintained an AUC of 1.000, indicating complete restoration of liver and kidney functions. These findings aligned with previous research on luteolin’s antioxidative and organ-protective properties. For instance, Yao et al. (56) explored its pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics in mitigating liver injury, while Diniz et al. (29) highlighted its renoprotective effects against kidney damage.
In the protective group, while some biomarkers, such as AST and urea nitrogen, retained an AUC of 1.000, others, like serum GSH, exhibited reduced sensitivity (50.0%) despite (100%) specificity, resulting in a lower AUC of 0.792. This suggested that preventive luteolin administration provided partial protection against PPA-induced oxidative stress and organ dysfunction. These findings could be supported by previous researches exploring luteolin’s protective effects in oxidative stress models. For instance, Al-Dbass et al. (53) investigated the protective and therapeutic potential of N-acetyl-cysteine against PPA-induced neurotoxicity, utilizing ROC analysis to evaluate various biomarkers. This study might offer a comparative perspective on antioxidant interventions, reinforcing the relevance of luteolin in mitigating oxidative damage.
Although the current findings were based on a PPA-induced model of ASD, which primarily reflected environmental and metabolic contributions, the observed therapeutic effects of luteolin particularly its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and gut-protective properties suggested that it may also be beneficial in genetic models of autism. Future studies using established genetic mouse models such as Shank3 or Fmr1 mutants could provide further insights into the broader applicability of luteolin as a neuroprotective and disease-modifying agent in ASD.
5 Conclusion
This study highlighted the detrimental effects of PPA-induced oxidative stress, increased intestinal permeability, and organ dysfunction, reinforcing its role in metabolic disturbances and ASD. The findings demonstrated that luteolin effectively mitigated these effects by restoring antioxidant defenses, improving biochemical markers, and preserving gut–liver–kidney homeostasis. Its ability to modulate oxidative stress pathways and gut–organ communication underscores luteolin’s potential as both a therapeutic and protective agent. Overall, this study showed promise for the use of evidence-based dietary interventions in ASD. Future study should concentrate on luteolin’s molecular mechanisms in order to optimize its therapeutic application.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the experimental procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Research at King Saud University, Riyadh (Approval No. KSU-SE-23-26). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
AK: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. AlA: Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. ArA: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. EA-S: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Software, Writing – review & editing. AB: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to Ongoing Funding Research Program, (ORF-2025-237), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, for funding this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing (2013).
2. Lord, C, Elsabbagh, M, Baird, G, and Veenstra-Vanderweele, J. Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet (London, England). (2018) 392:508–20. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31129-2
3. Maenner, MJ, Shaw, KA, Baio, J, Patrick, M, DiRienzo, M, Christensen, DL, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years - autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2016. MMWR Surveill Summ. (2020) 69:1–12. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6904a1
4. Dargenio, VN, Dargenio, C, Castellaneta, S, De Giacomo, A, Laguardia, M, Schettini, F, et al. Intestinal barrier dysfunction and microbiota-gut-brain axis: possible implications in the pathogenesis and treatment of autism spectrum disorder. Nutrients. (2023) 15:1620. doi: 10.3390/nu15071620
5. Usui, N, Kobayashi, H, and Shimada, S. Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorder. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:5487. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065487
6. Fattorusso, A, Di Genova, L, Dell'Isola, GB, Mencaroni, E, and Esposito, S. Autism spectrum disorders and the gut microbiota. Nutrients. (2019) 11:521. doi: 10.3390/nu11030521
7. Trinchese, G, Cimmino, F, Cavaliere, G, Catapano, A, Fogliano, C, Lama, A, et al. The hepatic mitochondrial alterations exacerbate meta-inflammation in autism spectrum disorders. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). (2022) 11:1990. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101990
8. Ahmed, JMY, Omear, HA-H, and Hasan, AH. Liver enzyme activity in children with autism spectrum disorder. Afr J Biomed Res. (2024) 27:6932–9. doi: 10.53555/734f1z11
9. Clothier, J, and Absoud, M. Autism spectrum disorder and kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany). (2021) 36:2987–95. doi: 10.1007/s00467-020-04875-y
10. Hill, ZR, Flynn, CK, and Adams, JB. Indoxyl sulfate and autism spectrum disorder: a literature review. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:12973. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312973
11. Langsrud, T, and Reinbold, GW. Flavor development and microbiology of Swiss cheese–a review. J Food Prot. (1973) 36:487–90. doi: 10.4315/0022-2747-36.9.487
12. Fernandez-Garcia, E, and McGregor, JU. Determination of organic acids during the fermentation and cold storage of yogurt. J Dairy Sci. (1994) 77:2934–9. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(94)77234-9
13. Venema, K. Role of gut microbiota in the control of energy and carbohydrate metabolism. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2010) 13:432–8. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32833a8b60
14. Greenman, N, Abdelli, LS, Hassouneh, SA, Ali, S, Johnston, C, Naser, SA, et al. Impact of propionic acid-rich diets on microbial composition of the murine gut microbiome. Front Microb. (2024) 3:1451735. doi: 10.3389/frmbi.2024.1451735
15. Al-Daihan, S, and Shafi Bhat, R. Impact of propionic acid on liver damage in rats. Int J Mol Cell Med. (2015) 4:188–95.
16. Karuri, AR, Dobrowsky, E, and Tannock, IF. Selective cellular acidification and toxicity of weak organic acids in an acidic microenvironment. Br J Cancer. (1993) 68:1080–7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.485
17. Cannizzaro, C, Monastero, R, Vacca, M, and Martire, M. [3H]-DA release evoked by low pH medium and internal H+ accumulation in rat hypothalamic synaptosomes: involvement of calcium ions. Neurochem Int. (2003) 43:9–17. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(02)00211-5
18. Severson, CA, Wang, W, Pieribone, VA, Dohle, CI, and Richerson, GB. Midbrain serotonergic neurons are central pH chemoreceptors. Nat Neurosci. (2003) 6:1139–40. doi: 10.1038/nn1130
19. MacFabe, DF, Cain, DP, Rodriguez-Capote, K, Franklin, AE, Hoffman, JE, Boon, F, et al. Neurobiological effects of intraventricular propionic acid in rats: possible role of short chain fatty acids on the pathogenesis and characteristics of autism spectrum disorders. Behav Brain Res. (2007) 176:149–69. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2006.07.025
20. Glasgow, AM, and Chase, HP. Effect of propionic acid on fatty acid oxidation and ureagenesis. Pediatr Res. (1976) 10:683–6. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197607000-00010
21. Khalil, SR, Abd-Elhakim, YM, Selim, ME, and Al-Ayadhi, LY. Apitoxin protects rat pups brain from propionic acid-induced oxidative stress: the expression pattern of Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 apoptotic genes. Neurotoxicology. (2015) 49:121–31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2015.05.011
22. Erten, F. Lycopene ameliorates propionic acid-induced autism spectrum disorders by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress in rats. J Food Biochem. (2021) 45:e13922. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13922
23. Tapsell, LC, Hemphill, I, Cobiac, L, Patch, CS, Sullivan, DR, Fenech, M, et al. Health benefits of herbs and spices: the past, the present, the future. Med J Aust. (2006) 185:S1–S24. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2006.tb00548.x
24. Meena, S, Kanthaliya, B, Joshi, A, Khan, F, and Arora, J. Biologia futura: medicinal plants-derived bioactive peptides in functional perspective-a review. Biologia futura. (2020) 71:195–208. doi: 10.1007/s42977-020-00042-4
25. Wang, TY, Li, Q, and Bi, KS. Bioactive flavonoids in medicinal plants: structure, activity and biological fate. Asian J Pharm Sci. (2018) 13:12–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2017.08.004
26. Gupta, G, Siddiqui, MA, Khan, MM, Ajmal, M, Ahsan, R, Rahaman, MA, et al. Current pharmacological trends on Myricetin. Drug Res. (2020) 70:448–54. doi: 10.1055/a-1224-3625
27. Procházková, D, Boušová, I, and Wilhelmová, N. Antioxidant and prooxidant properties of flavonoids. Fitoterapia. (2011) 82:513–23. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2011.01.018
28. Wu, S, Zhang, Y, Ren, F, Qin, Y, Liu, J, Liu, J, et al. Structure-affinity relationship of the interaction between phenolic acids and their derivatives and β-lactoglobulin and effect on antioxidant activity. Food Chem. (2018) 245:613–9. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.122
29. Diniz, LRL, Elshabrawy, HA, Souza, MTS, Duarte, ABS, Madhav, N, and de Sousa, DP. Renoprotective effects of Luteolin: therapeutic potential for COVID-19-associated acute kidney injuries. Biomol Ther. (2022) 12:1544. doi: 10.3390/biom12111544
30. Lin, Y, Shi, R, Wang, X, and Shen, HM. Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. (2008) 8:634–46. doi: 10.2174/156800908786241050
31. Nabavi, SF, Braidy, N, Gortzi, O, Sobarzo-Sanchez, E, Daglia, M, Skalicka-Woźniak, K, et al. Luteolin as an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agent: a brief review. Brain Res Bull. (2015) 119:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.09.002
32. Imran, M, Rauf, A, Abu-Izneid, T, Nadeem, M, Shariati, MA, Khan, IA, et al. Luteolin, a flavonoid, as an anticancer agent: a review. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 112:108612. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108612
33. Manzoor, MF, Ahmad, N, Ahmed, Z, Siddique, R, Zeng, XA, Rahaman, A, et al. Novel extraction techniques and pharmaceutical activities of luteolin and its derivatives. J Food Biochem. (2019) 43:e12974. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12974
34. Domitrović, R, Cvijanović, O, Pugel, EP, Zagorac, GB, Mahmutefendić, H, and Škoda, M. Luteolin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice through inhibition of platinum accumulation, inflammation and apoptosis in the kidney. Toxicology. (2013) 310:115–23. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2013.05.015
35. Arslan, BY, Arslan, F, Erkalp, K, Alagöl, A, Sevdi, MS, Yıldız, G, et al. Luteolin ameliorates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in the rat models. Ren Fail. (2016) 38:1735–40. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2016.1229995
36. Dar, AA, Fehaid, A, Alkhatani, S, Alarifi, S, Alqahtani, WS, Albasher, G, et al. The protective role of luteolin against the methotrexate-induced hepato-renal toxicity via its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2021) 40:1194–207. doi: 10.1177/0960327121991905
37. van Hoorn, DE, Nijveldt, RJ, Boelens, PG, Hofman, Z, van Leeuwen, PA, and van Norren, K. Effects of preoperative flavonoid supplementation on different organ functions in rats. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2006) 30:302–8. doi: 10.1177/0148607106030004302
38. Abu-Elsaad, N, and El-Karef, A. Protection against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through targeting IL-18 and IL-1alpha by luteolin. Pharmacol Rep. (2019) 71:688–94. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2019.03.009
39. Taliou, A, Zintzaras, E, Lykouras, L, and Francis, K. An open-label pilot study of a formulation containing the anti-inflammatory flavonoid luteolin and its effects on behavior in children with autism spectrum disorders. Clin Ther. (2013) 35:592–602. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.04.006
40. Mehdar, KM, and Alqahtani, SM. Protective effects of luteolin on a rat model of autism: an analysis of luteolin flavonoid’s effects on rat behaviour, histology, and cerebellar pathology. Int J Pharmacol. (2024) 20:942–55. doi: 10.3923/ijp.2024.942.955
41. Albrakati, A. The potential neuroprotective of luteolin against acetamiprid-induced neurotoxicity in the rat cerebral cortex. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1361792. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1361792
42. Lodhi, S, Vadnere, GP, Patil, KD, and Patil, TP. Protective effects of luteolin on injury induced inflammation through reduction of tissue uric acid and pro-inflammatory cytokines in rats. J Tradit Complement Med. (2019) 10:60–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2019.02.004
43. Beutler, E, Duron, O, and Kelly, BM. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med. (1963) 61:882–8.
44. Ruiz-Larrea, MB, Leal, AM, Liza, M, Lacort, M, and de Groot, H. Antioxidant effects of estradiol and 2-hydroxyestradiol on iron-induced lipid peroxidation of rat liver microsomes. Steroids. (1994) 59:383–8. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(94)90006-x
45. Habig, WH, Pabst, MJ, and Jakoby, WB. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. (1974) 249:7130–9. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)42083-8
46. McCord, JM, and Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. (1969) 244:6049–55. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)63504-5
47. Maehly, AC, and Chance, B. The assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Biochem Anal. (1954) 1:357–424. doi: 10.1002/9780470110171.ch14
48. Albillos, A, de Gottardi, A, and Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: pathophysiological basis for therapy. J Hepatol. (2020) 72:558–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.003
49. Tsuji, K, Uchida, N, Nakanoh, H, Fukushima, K, Haraguchi, S, Kitamura, S, et al. The gut-kidney Axis in chronic kidney diseases. Diagnostics. (2025) 15:21. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15010021
50. Yang, S, Duan, H, Yan, Z, Xue, C, Niu, T, Cheng, W, et al. Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by modulating gut microbiota and plasma metabolism. Nutrients. (2025) 17:203. doi: 10.3390/nu17020203
51. Kara, H, Burak Açıkel, S, Çetinkaya, M, and Çiğdem Tuncer, S. Serum Zonulin levels are higher among children with autism Spectrum disorders and correlated with social impairment. Alpha Psychiatry. (2021) 22:250–6. doi: 10.1530/alphapsychiatry.2021.21152
52. Esnafoglu, E, Cırrık, S, Ayyıldız, SN, Erdil, A, Ertürk, EY, Daglı, A, et al. Increased serum Zonulin levels as an intestinal permeability marker in autistic subjects. J Pediatr. (2017) 188:240–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.04.004
53. Al-Dbass, AM. N-acetylcysteine reduces the neurotoxic effects of propionic acid in rat pups. J King Saud Univ Sci. (2014) 26:254–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2013.08.006
54. Fontella, FU, Pulrolnik, V, Gassen, E, Wannmacher, CM, Klein, AB, Wajner, M, et al. Propionic and L-methylmalonic acids induce oxidative stress in brain of young rats. Neuroreport. (2000) 11:541–4. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200002280-00023
55. Ben Bacha, A, Alonazi, M, Aljehani, EM, Alabdali, AN, Bhat, R, Almuayrifi, M, et al. Luteolin ameliorating effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in an ASD rodent model. Int J Pharmacol. (2024) 20:1479–87. doi: 10.3923/ijp.2024.1479.1487
56. Yao, C, Dai, S, Wang, C, Fu, K, Wu, R, Zhao, X, et al. Luteolin as a potential hepatoprotective drug: molecular mechanisms and treatment strategies. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 167:115464. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115464
57. Suraweera, L, Rupasinghe, HPV, Dellaire, G, and Xu, Z. Regulation of Nrf2/ARE pathway by dietary flavonoids: a friend or foe for cancer management? Antioxidants. (2020) 9:973. doi: 10.3390/antiox9100973
58. Birman, H, Dar, KA, Kapucu, A, Acar, S, and Uzüm, G. Effects of Luteolin on liver, kidney and brain in pentylentetrazol-induced seizures: involvement of metalloproteinases and NOS activities. Balkan Med J. (2012) 29:188–96. doi: 10.5152/balkanmedj.2011.030
59. Kolankaya, D, and Korkmaz, A. Luteolin prevents ischemia/reperfusion-induced damage in the rat kidney. Toxicol Lett. (2008) 180:S50. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.06.615
60. Al-Ayadhi, L, Zayed, N, Bhat, RS, Moubayed, NMS, Al-Muammar, MN, El-Ansary, A, et al. The use of biomarkers associated with leaky gut as a diagnostic tool for early intervention in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review. Gut Pathog. (2021) 13:54. doi: 10.1186/s13099-021-00448-y
61. Xie, X, Zhao, M, Huang, S, Li, P, Chen, P, Luo, X, et al. Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis by restoring the balance of NCR−ILC3/NCR+ILC3 to repairing impaired intestinal barrier. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 112:109251. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109251
62. Yuan, J, Che, S, Ruan, Z, Song, L, Tang, R, and Zhang, L. Regulatory effects of flavonoids luteolin on BDE-209-induced intestinal epithelial barrier damage in Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Food Chem Toxicol. (2021) 150:112098. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112098
63. Owumi, SE, Lewu, DO, Arunsi, UO, and Oyelere, AK. Luteolin attenuates doxorubicin-induced derangements of liver and kidney by reducing oxidative and inflammatory stress to suppress apoptosis. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2021) 40:1656–72. doi: 10.1177/09603271211006171
64. El-Ansary, AK, Ben Bacha, A, and Kotb, M. Etiology of autistic features: the persisting neurotoxic effects of propionic acid. J Neuroinflammation. (2012) 9:74. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-74
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder, luteolin, oxidative stress, leaky gut, liver, kidney
Citation: Khayyat AIA, Alabdali AN, Alonazi M, Alzahrani AA, Al-Shehri E and Ben Bacha A (2025) Luteolin mitigates oxidative stress and multi-organ impairment in a propionic acid-induced rodent model of autism. Front. Nutr. 12:1583119. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1583119
Edited by:
Marija Takic, University of Belgrade, SerbiaReviewed by:
Luca Pangrazzi, University of Innsbruck, AustriaMarko Miler, University of Belgrade, Serbia
Copyright © 2025 Khayyat, Alabdali, Alonazi, Alzahrani, Al-Shehri and Ben Bacha. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abir Ben Bacha, YWFsZ2hhbm91Y2hpQGtzdS5lZHUuc2E=
 Arwa Ishaq Abdulmalik Khayyat
Arwa Ishaq Abdulmalik Khayyat Altaf N. Alabdali
Altaf N. Alabdali Mona Alonazi
Mona Alonazi Areej Ali Alzahrani
Areej Ali Alzahrani Eman Al-Shehri
Eman Al-Shehri Abir Ben Bacha
Abir Ben Bacha