- 1The First Clinical Medical College, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang, China
- 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 3Institute of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 4The Second Clinical Medical College, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang, China
Hyperlipidemia-associated acute pancreatitis (HLAP), an acute inflammatory disorder triggered by dyslipidemia, has witnessed a rising global incidence with significant health implications. The pathogenesis of HLAP involves complex interactions among lipid metabolism dysregulation, inflammatory cascades, and oxidative stress. Conventional therapeutic approaches, while providing partial symptomatic relief, exhibit limitations in addressing individual variability. Precision nutrition management emerges as a novel paradigm integrating multi-omics profiling (genomic, metabolomic) and clinical parameters to develop personalized intervention strategies. This comprehensive review analyzes the pathophysiological mechanisms linking lipid dyshomeostasis to HLAP progression, systematically evaluates the scientific foundation for precision nutrition interventions, and identifies key gaps in current implementation strategies. Furthermore, we examine current research limitations and outline future avenues for enhancing therapeutic efficacy via personalized nutritional interventions.
1 Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP), a gastrointestinal emergency with multifactorial etiology, demonstrates increasing epidemiological association with hyperlipidemia (1). Globally, hyperlipidemia accounts for 10% of AP cases, characterized by heightened clinical severity and elevated recurrence rates (2). In China, hyperlipidemia has surpassed alcohol consumption to become the second most prevalent AP etiology following cholelithiasis (3). A retrospective Chinese cohort study (2001–2016, n = 475 moderate–severe AP patients) revealed 108 HLAP cases (22.7%), with HLAP prevalence increasing from 14.3 to 35.5% during the study period, contrasting with declining rates of biliary pancreatitis (4). Epidemiological trends further show a 2.6-fold increase in HLAP incidence over the past decade, coinciding with the global rise in metabolic syndrome and obesity (5).
The pathognomonic feature of HLAP involves serum triglyceride (TG) concentrations exceeding 11.30 mmol/L (1,000 mg/dL) after excluding biliary, alcoholic, and other etiologies (6). Mechanistically, excessive TG hydrolysis generates cytotoxic free fatty acids that induce pancreatic capillary endothelial damage and acinar cell apoptosis (7). Clinically, HLAP demonstrates greater propensity for progression to necrotizing pancreatitis compared to other AP subtypes (8). Population-level analyses reveal a dose-dependent relationship between hypertriglyceridemia and AP risk: each 100 mg/dL increment above normal TG levels (150 mg/dL) elevates AP risk by 4%, with exponential risk escalation beyond 500 mg/dL (9).
The hypercatabolic state in early HLAP induces rapid-onset negative nitrogen balance and hypoalbuminemia, exacerbating malnutrition while compounding gastrointestinal complications including abdominal pain, intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction, and malabsorption (10). Traditional nutritional interventions, although temporarily alleviating hyperlipidemia and inflammation, lack personalization and frequently result in suboptimal, inconsistent clinical outcomes. This is primarily due to the inadequate integration of individual metabolic phenotypes, genetic susceptibilities, and inflammatory profiles (11).
The advent of precision medicine has catalyzed paradigm shifts in therapeutic approaches. Precision nutrition management employs multi-omics integration (genomic, metabolomic, and clinical data) to formulate tailored dietary regimens (12). This strategy shows particular promise in HLAP management by addressing individual variations in lipid metabolism pathways, inflammatory responses, and nutrient utilization efficiency. Compared to conventional one-size-fits-all approaches, precision nutrition offers mechanistic-driven solutions to optimize therapeutic outcomes and prevent disease recurrence.
2 Pathogenesis of HLAP
The pathophysiological mechanisms of HLAP are complex, involving dysregulated lipid metabolism, inflammation activation, pancreatic microcirculatory disturbances, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance, among multiple interacting pathways (13–16). The core pathological processes revolve around excessive free fatty acids (FFA) release, microcirculatory damage, and the amplification of systemic inflammatory responses (Figure 1).
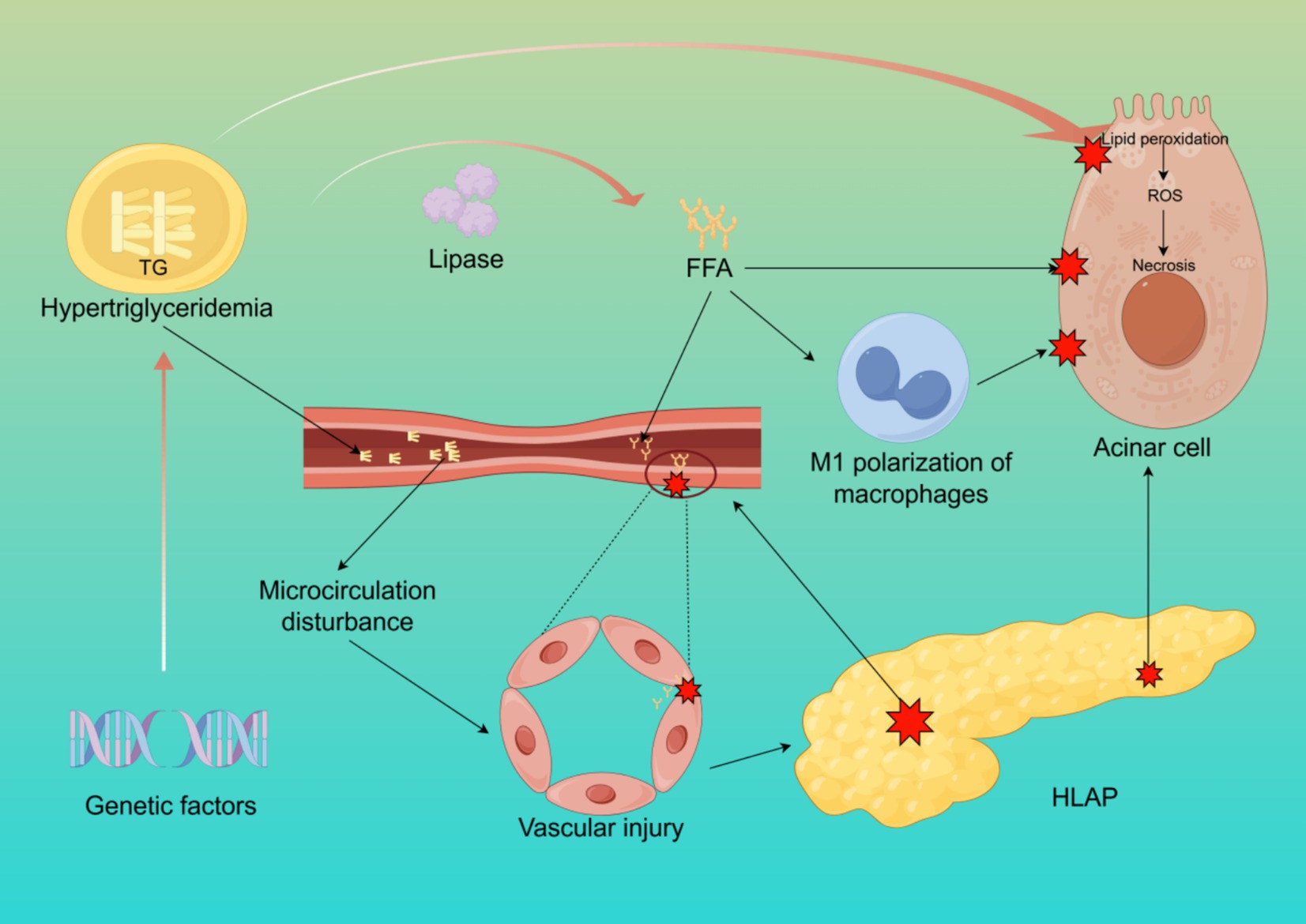
Figure 1. The pathogenesis of HLAP. This figure illustrates the core mechanisms of HLAP, including elevated triglyceride hydrolysis into free fatty acids, acinar cell injury, endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and activation of inflammatory pathways. Created with Figdraw.com.
2.1 Cytotoxicity of FFA
In hyperlipidemic conditions, elevated TG levels in the bloodstream are hydrolyzed by pancreatic lipase, releasing large amounts of FFA. These FFA, primarily composed of palmitic acid (PA), are unsaturated fatty acids (17). Under normal conditions, FFA bind to plasma albumin for systemic transport and oxidation. However, when the concentration of FFA exceeds the binding capacity of albumin, excess FFA remain unbound in the bloodstream, leading to cytotoxic effects on pancreatic acinar and vascular endothelial cells through lipid peroxidation of cell membranes (18). Studies have shown that unsaturated fatty acids exhibit higher toxicity than saturated fatty acids (19). Damage to pancreatic capillaries results in pancreatic ischemia, intracellular pH reduction in acinar cells, and the formation of an acidic environment, which further activates trypsinogen and enhances FFA toxicity, leading to autodigestion of pancreatic acinar cells. Additionally, excessive FFA and TG levels increase blood viscosity, further impairing pancreatic circulation and exacerbating local inflammation (20). Research on isolated pancreatic acinar cells has demonstrated that exposure to FFA significantly elevates levels of hydroperoxidized phosphatidylcholine, indicating that FFA mediate lipid peroxidation and disrupt cell membranes, causing direct injury to pancreatic acinar cells (21). Another study observed that adding FFA to cultured rat pancreatic acinar cells resulted in damage that was positively correlated with both FFA concentration and exposure duration (22). Excessive FFA also induce M1 polarization of macrophages and mediate inflammatory responses and pyroptosis in pancreatic acinar cells (23).
2.2 Pancreatic microcirculatory disturbances
Microcirculation refers to the network responsible for the transport of substances, energy, and signals at the tissue and cellular levels. Proper microcirculatory perfusion is crucial for maintaining normal physiological metabolism in organs (24). Hyperlipidemia increases plasma viscosity and reduces erythrocyte deformability, leading to decreased pancreatic microcirculatory perfusion (25). Furthermore, excessive FFA accumulation promotes platelet activation and the coagulation cascade, resulting in microthrombus formation, which aggravates pancreatic ischemia and hypoxia (8). Ischemic injury can cause acinar cell necrosis, exacerbating local inflammation and edema, and in severe cases, leading to necrotizing pancreatitis (26). Pancreatic microcirculatory disturbances manifest as chylomicron aggregation blocking capillaries, leading to abnormal hemorheology, hypercoagulation, and microthrombosis, as well as increased vascular permeability due to microvascular spasms and endothelial damage. Additionally, ischemia–reperfusion injury contributes to oxidative stress through increased free radical generation (27, 28).
2.3 Oxidative stress and inflammatory cascade response
Oxidative stress refers to an imbalance between oxidative and antioxidative processes within the body, with lipid peroxidation playing a pivotal role in HLAP progression (29). Excessive triglyceride oxidation in the pancreas generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxidation products, further damaging DNA, proteins, and lipids, thereby exacerbating pancreatic injury (30). Moreover, FFA stimulate macrophage activation, triggering a systemic inflammatory response that leads to a “cytokine storm,” which can ultimately result in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) and increased HLAP mortality (31). Animal studies have demonstrated that alleviating oxidative stress-related pancreatic damage can mitigate AP severity (32). Oxidative stress activation promotes the recruitment of inflammatory cells, further aggravating pancreatic tissue damage, whereas antioxidant therapy significantly reduces pancreatic and other organ injuries associated with AP (33).
2.4 Genetic and acquired lipid metabolism defects
Familial hypertriglyceridemia (HTG) has long been recognized as a disorder characterized by increased very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles and an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern (34). In the genomic era, it has been established that while familial HTG can be clustered within families, it is a polygenic disorder, with phenotypic expression influenced by environmental factors. Clinically, it is characterized by moderate HTG, which increases cardiovascular risk, while in rare cases, it presents with severe HTG and an elevated risk of AP (35). Some HLAP patients exhibit lipid metabolism-related genetic mutations, such as mutations in the LPL and APOC2 genes, which lead to impaired chylomicron clearance, resulting in familial chylomicronemia and significantly increasing the risk of HLAP (36–39). Understanding these genetic factors is crucial for identifying high-risk individuals and implementing targeted preventive strategies.
3 Theoretical basis of precision nutrition management
An increasing number of studies suggest that an individual’s genetic background significantly influences their response to dietary interventions (40). For instance, the ability to digest lactose in adulthood is more common in Northern Europeans than in East Asians (41). Therefore, precise nutritional interventions should be tailored based on an individual’s genotype, metabolic phenotype, and lifestyle to enhance intervention effectiveness and prevent and treat related diseases (42).
3.1 Association between genomics and nutritional interventions
Recent genomic studies indicate that genes related to lipid metabolism, inflammatory responses, and autophagy regulation in pancreatic cells play crucial roles in the development and progression of HLAP (29, 43). Specific gene variants, such as APOE and LPL mutations, have been shown to be closely associated with hyperlipidemia and pancreatitis (44–46). These genes are critical in lipid metabolism, cholesterol transport, and pancreatic cell injury repair. Polymorphisms in the FTO gene have been linked to fat accumulation and obesity, while variations in the APOA5 gene affect triglyceride metabolism and regulate lipid levels (47, 48). Nutrigenomics explores how dietary factors influence gene expression, subsequently affecting protein and metabolite levels (49). The interaction between genes and diet may play a vital role in metabolic and inflammatory responses, providing a theoretical foundation for developing precision nutritional intervention strategies.
3.2 Metabolomics as a new target for personalized interventions
Metabolomics is a high-throughput analytical science that systematically identifies and quantifies small-molecule metabolites (<1,500 Da) within biological systems to understand their dynamic changes in response to genetic, environmental, or pathological perturbations. It plays a key role in precision nutrition development, primarily focusing on food intake biomarkers, metabolic phenotypes, and responses to interventions (50). Studies have revealed metabolic reprogramming in multiple pathways in HLAP patients, particularly in fatty acid metabolism, cholesterol metabolism, and amino acid metabolism (14, 51, 52). For instance, abnormal elevations in triglycerides (TG) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL), along with imbalances in insulin resistance markers (e.g., branched-chain amino acids) and oxidative stress products (e.g., malondialdehyde), provide potential targets for personalized interventions (53, 54). These metabolic features not only reveal core disease mechanisms—such as chylomicronemia-induced pancreatic microcirculatory disturbances—but also guide targeted nutritional regulation strategies, such as increasing omega-3 fatty acids to modulate lipid metabolism, supplementing dietary fiber to enhance short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production by gut microbiota, or using antioxidant nutrients (e.g., vitamin C) to mitigate oxidative damage (55–58). Comprehensive metabolite analysis in patients enables a more accurate assessment of individual metabolic states, providing a scientific basis for personalized nutritional interventions.
3.3 Integration of microbiome and precision nutrition management
Emerging research suggests that the microbiome can potentially influence human physiology by participating in digestion, nutrient absorption, mucosal immune responses, and the synthesis or regulation of various bioactive compounds (59–61). Consequently, diet-induced microbial changes may contribute to disease onset and progression (62). The gut microbiota plays a significant role in the development of AP, characterized by a reduction in beneficial bacteria and an increase in opportunistic pathogens. This imbalance leads to decreased SCFA secretion and epithelial damage, thereby compromising the intestinal mucosal barrier (63). One study found that 59% of AP patients exhibited intestinal barrier damage and increased mucosal permeability, leading to bacterial translocation, pancreatic necrosis, infection, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) (64). A randomized controlled trial demonstrated that probiotics improved gut barrier function and modulated microbiota composition in severe AP (SAP) patients, reducing inflammatory cytokine levels, alleviating abdominal pain, mitigating pancreatic edema, and shortening bowel movement recovery time and hospital stays (65). Similar results were observed in another randomized controlled trial involving mild AP (66). Soluble dietary fiber (SDF) influences intestinal integrity and regulates gut microbiota (67). A single-blind randomized controlled study found that SDF reduced the time needed to achieve energy targets during enteral nutrition (EN), improved gut permeability and motility disorders, and decreased feeding intolerance in SAP patients (68). Therefore, the microbiome provides a “microbiota-metabolism” regulatory target for the personalized nutritional design of HLAP, advancing a more precise disease management model.
4 Precision nutritional interventions for HLAP
4.1 Conventional nutritional support
The primary management goals in the acute phase of HLAP are to minimize pancreatic stimulation, control inflammatory responses, and support energy metabolism. Previous studies have suggested that higher serum triglyceride (TG) levels are associated with a greater tendency for HLAP to become severe, a shorter time to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), and a higher incidence of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) (69). During fasting in AP patients, negative nitrogen balance is common, making nutritional support an essential component of HLAP management (70). During the course of pancreatitis, pancreatic exocrine function is suppressed; thus, food intake or artificial nutrition does not stimulate exocrine secretion (71). For patients who can tolerate oral feeding, an initial low-fat solid diet is recommended (72). Early oral feeding may shorten hospital stays in these patients (73).
For patients with severe acute pancreatitis, appropriate clinical nutrition strategies are necessary, with enteral nutrition (EN) being preferred (74, 75). EN helps maintain intestinal mucosal integrity, stimulates intestinal motility, increases visceral blood flow, prevents bacterial overgrowth, and reduces microbial translocation (76). Studies have shown that initiating nutrition within 24–72 h of admission reduces bacterial translocation, thereby mitigating systemic inflammation while preserving intestinal integrity and microbiome composition (77). Compared to parenteral nutrition (PN), EN is more effective in maintaining gut barrier function and reducing the risk of infections and pancreatic complications (78). A systematic review provided strong evidence supporting the advantages of EN in reducing infectious complications and mortality in AP patients (79). Special formulations with low fat and low osmolarity are recommended to minimize the burden on pancreatic enzyme secretion. For patients without respiratory failure, who are conscious, free from nausea and vomiting, and without significant gastrointestinal obstruction, an oral nutrition trial should be initiated immediately (80). In summary, guidelines recommend that AP patients receive EN rather than PN unless contraindications or intolerance to EN exist (81, 82). The European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) recommends early EN via nasogastric tube, with nasojejunal feeding preferred if intolerance occurs (82). Given that “waking up the gut” is more beneficial than “gut rest,” patients with mild HLAP should be allowed oral feeding within 24 h if tolerated. However, patients with moderate to severe HLAP (acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE-I) >8) who experience hemodynamic instability and require vasopressor support are often unable to tolerate oral feeding due to the increased risk of non-occlusive mesenteric ischemia (3). For these patients, EN should be initiated via a feeding tube within 24 h of hemodynamic stabilization (83, 84). Studies have shown that the improvement in nutritional status and tolerance of EN in HLAP patients is related to the choice between nasogastric and nasojejunal feeding tubes (85). Currently, high-quality evidence comparing nasogastric and nasojejunal tube feeding is lacking. Although nasojejunal feeding reduces the risk of aspiration and pancreatic stimulation, its placement requires endoscopic and/or fluoroscopic guidance or specialized equipment. In contrast, nasogastric tubes are easier to insert and can be placed at the bedside (Table 1) (86).
4.2 Immunonutrition support
Immunonutrition involves the addition of immune-enhancing nutrients to conventional nutrition, aiming to improve inflammatory responses, malnutrition, metabolic abnormalities, and immune imbalances (87, 88). Recent studies have highlighted the benefits of immunonutrition (89–91). Key immunonutrients include omega-3 fatty acids, glutamine, arginine, and nucleotides (92). Omega-3 fatty acids competitively inhibit the arachidonic acid metabolic pathway, reducing the synthesis of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins and leukotrienes, thereby mitigating pancreatic inflammation (93, 94). Glutamine, a non-essential amino acid, plays a role in protein synthesis, energy supply, and immune support, with increased demand during stress conditions (95). As the primary energy source for intestinal immune cells, glutamine helps maintain gut barrier integrity and reduces bacterial translocation and infections (96). However, studies comparing EN with and without glutamine supplementation have shown no significant advantage with glutamine (97, 98). Nonetheless, compared to standard PN, PN supplemented with glutamine and omega-3 fatty acids has been associated with improved outcomes (99, 100). Arginine, a conditionally essential amino acid found in meat, fish, and nuts, promotes nitric oxide (NO) synthesis, improves microcirculation, and enhances T-cell and macrophage function (101, 102). Some studies have linked immunonutrition to reduced AP mortality, lower infection rates, and shorter hospital stays (103). However, a meta-analysis found no significant benefit of immunonutrition over standard EN in terms of overall infection rates and mortality (104). The safety and efficacy of immunonutrition remain inconclusive, requiring further research (Table 2) (105).
4.3 Precision nutrition strategies
Precision nutrition emphasizes individualized nutritional interventions based on lipid metabolism characteristics, genetic susceptibility, inflammatory status, and gut microbiota composition to optimize triglyceride levels, reduce pancreatic inflammation, and promote pancreatic recovery (Figure 2) (106).
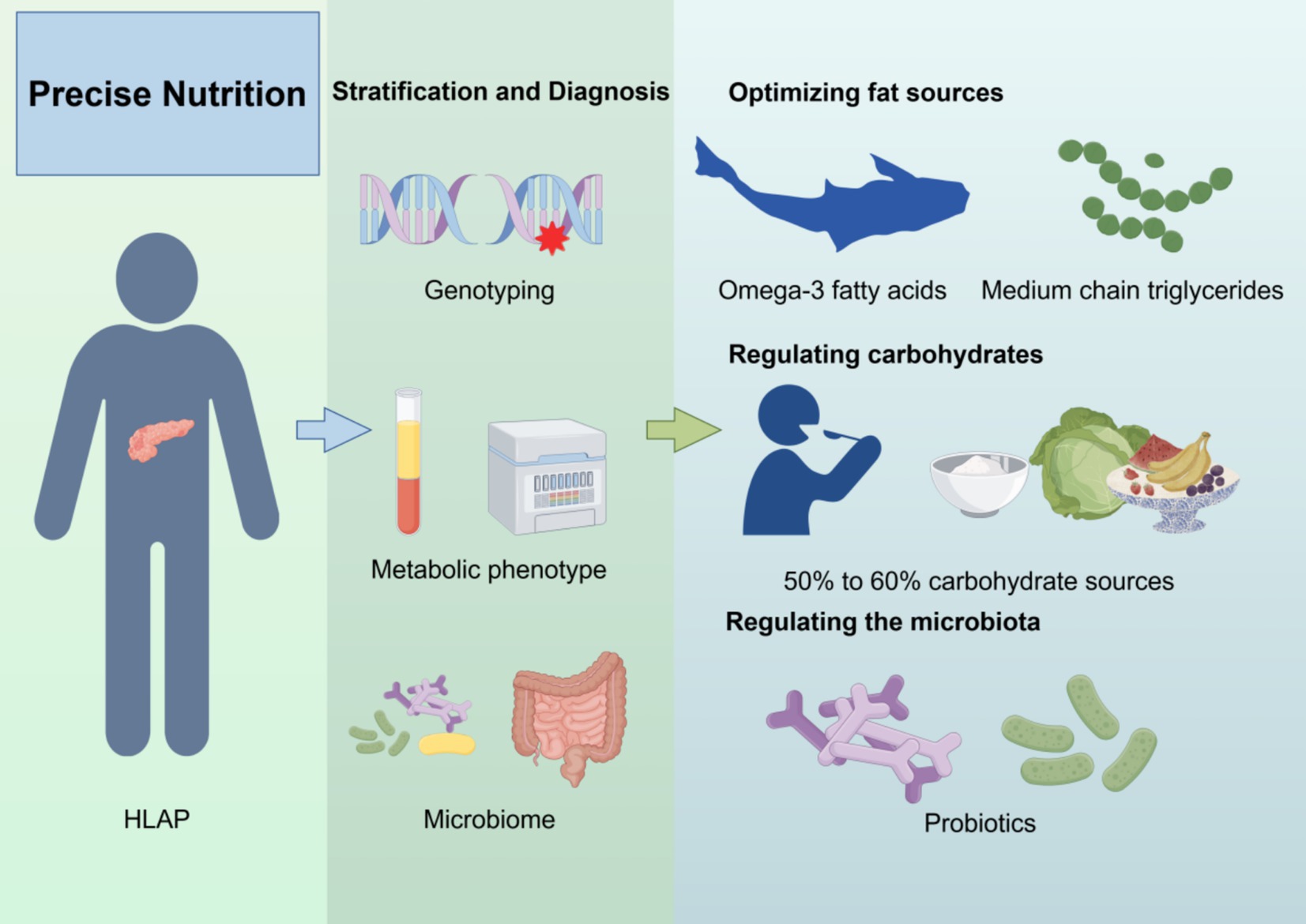
Figure 2. Precision nutrition strategy for HLAP patients. The diagram outlines four components of precision nutrition: (1) lipid source optimization, (2) macronutrient regulation, (3) gut microbiota modulation, and (4) genotype-based dietary adjustment. Created with Figdraw.com.
To facilitate clinical translation and decision-making, a personalized nutrition framework for HLAP management can be constructed with four key components: (1) lipid source optimization, (2) macronutrient regulation, (3) gut microbiota modulation, and (4) genotype-based dietary customization. Each component is tailored to the patient’s metabolic and genomic profile.
First, optimizing fat sources is crucial. Saturated and trans fats should be avoided, while foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., deep-sea fish, flaxseeds, walnuts) should be increased (107, 108). Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation and improve lipid metabolism (109). Additionally, medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are directly metabolized by the liver and do not require pancreatic lipase, may serve as a safer fat source for HLAP patients (110). Second, carbohydrate intake should be regulated, with total carbohydrate intake kept below 50–60% of daily calories and primarily sourced from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables rich in fiber (111). One study suggested that replacing 1% of energy intake from carbohydrates with fat sources could reduce serum TG levels by an estimated 1–2% (112).
Regulating gut microbiota is another key component of precision nutrition. Gut dysbiosis in HLAP exacerbates inflammation, so supplementing with probiotics (e.g., Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus) and prebiotics (e.g., fructooligosaccharides, inulin), as well as consuming foods rich in SCFA (e.g., oats, nuts), may help maintain gut barrier function and reduce enterogenic infections (113). Furthermore, personalized nutrition interventions should incorporate genomic and metabolomic profiles. For instance, patients with APOA5 gene mutations should strictly limit saturated fat intake and increase omega-3 fatty acid consumption (48). Meanwhile, in individuals with PPARG gene mutations, omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to regulate lipid metabolism, significantly reducing LDL-C, total cholesterol, and serum TG levels within 3 months (Table 3) (114). This integrative framework allows clinicians to match specific nutritional components with the patient’s phenotype and genotype, forming the basis for truly personalized dietary therapy. Overall, precision nutrition offers an individualized strategy for HLAP management. By integrating lipid metabolism regulation, inflammation control, gut microbiome balance, and genetic analysis, tailored nutritional plans can be developed to minimize pancreatic damage, enhance treatment efficacy, and improve long-term health outcomes while reducing HLAP recurrence.
Despite the promising theoretical and experimental foundation, the clinical implementation of precision nutrition in HLAP remains at an early stage. Translating these strategies into routine practice requires a critical evaluation of existing barriers.
5 Limitations and future directions
First, the heterogeneity of HLAP pathophysiology (e.g., genetic background, metabolic phenotypes, and secondary factors) results in insufficient evidence for individualized interventions. Most existing studies focus on “triglyceride thresholds,” with limited stratified research on lipid tolerance dynamics, specific fatty acid effects, and varying nutritional needs across different disease phases (acute vs. chronic). Second, technical barriers exist in integrating multimodal data, such as real-time metabolic monitoring (lipidomics, gut microbiota metabolites), clinical adoption challenges, and the absence of quantitative models for gene–environment interactions, restricting dynamic precision adjustments. Additionally, clinical implementation faces challenges such as balancing strict fat restriction in the acute phase with the risk of malnutrition, poor dietary adherence in the chronic phase, and the lack of multidisciplinary collaboration mechanisms. Moreover, several practical barriers hinder the clinical translation of precision nutrition. High costs and limited accessibility of genomic and metabolomic testing restrict large-scale screening, especially in resource-limited settings. Real-time monitoring of lipid metabolism and gut microbiota remains technically complex and is not yet feasible in most clinical workflows. To address these gaps, future studies should incorporate stratified randomized trials based on genetic and metabolic profiles, develop point-of-care tools for dynamic lipid and microbiota monitoring, and apply predictive models (e.g., machine learning) to guide individualized nutrition. Real-world studies assessing feasibility, adherence, and cost-effectiveness will be essential to support clinical translation.
6 Conclusion
HLAP is a complex disease requiring multidisciplinary collaboration. Precision nutrition, an emerging therapeutic strategy, integrates genomics, metabolomics, and gut microbiome data to provide personalized nutritional interventions. With advances in technology and further clinical research, precision nutrition has the potential to significantly improve HLAP treatment outcomes, enhance patient prognosis, and reduce recurrence rates.
Author contributions
JM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. XH: Writing – review & editing. YM: Writing – review & editing. YG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the use of Figdraw (www.figdraw.com) to create all figures.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Szatmary, P, Grammatikopoulos, T, Cai, W, Huang, W, Mukherjee, R, Halloran, C, et al. Acute pancreatitis: diagnosis and treatment. Drugs. (2022) 82:1251–76. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01766-4
2. Ewald, N, Hardt, PD, and Kloer, HU. Severe hypertriglyceridemia and pancreatitis: presentation and management. Curr Opin Lipidol. (2009) 20:497–504. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e3283319a1d
3. Zhu, Y, Pan, X, Zeng, H, He, W, Xia, L, Liu, P, et al. A study on the etiology, severity, and mortality of 3260 patients with acute pancreatitis according to the revised Atlanta classification in Jiangxi, China over an 8-year period. Pancreas. (2017) 46:504–9. doi: 10.1097/mpa.0000000000000776
4. Jin, M, Bai, X, Chen, X, Zhang, H, Lu, B, Li, Y, et al. A 16-year trend of etiology in acute pancreatitis: the increasing proportion of hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis and its adverse effect on prognosis. J Clin Lipidol. (2019) 13:947–53.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.09.005
5. Lin, XY, Zeng, Y, Zhang, ZC, Lin, ZH, Chen, LC, and Ye, ZS. Incidence and clinical characteristics of Hypertriglyceridemic acute pancreatitis: a retrospective single-center study. World J Gastroenterol. (2022) 28:3946–59. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3946
6. Valdivielso, P, Ramírez-Bueno, A, and Ewald, N. Current knowledge of Hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis. Eur J Intern Med. (2014) 25:689–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2014.08.008
7. Sun, Q, Du, L, Ren, Q, Zhu, G, Zhang, B, Su, A, et al. Hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, body mass index, and the risk of acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. (2024) 69:3413–25. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08493-8
8. Gu, X, Huang, Z, Ying, X, Liu, X, Ruan, K, Hua, S, et al. Ferroptosis exacerbates Hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis by enhancing lipid peroxidation and modulating the immune microenvironment. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:242. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02007-1
9. Tenner, S, Vege, SS, Sheth, SG, Sauer, B, Yang, A, Conwell, DL, et al. American College of Gastroenterology guidelines: management of acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. (2024) 119:419–37. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002645
10. Rashid, N, Sharma, PP, Scott, RD, Lin, KJ, and Toth, PP. All-cause and acute pancreatitis health care costs in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia. Pancreas. (2017) 46:57–63. doi: 10.1097/mpa.0000000000000704
11. Krishna, S, and Davoren, P. A three-year review of the management of hypertriglyceridaemia-induced pancreatitis. Metabolism. (2021) 116:154485. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154485
12. Marcum, JA. Nutrigenetics/nutrigenomics, personalized nutrition, and precision healthcare. Curr Nutr Rep. (2020) 9:338–45. doi: 10.1007/s13668-020-00327-z
13. Liu, G, Liu, F, Xiao, L, Kuang, Q, He, X, Wang, Y, et al. Treatment of Hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis with modified Dachengqi decoction combining with conventional therapy based on “six-hollow-organs to be unblocked” theory. Ann Palliat Med. (2020) 9:2045–53. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1106
14. Ren, D, Li, Y, Zhang, G, Li, T, and Liu, Z. Lipid metabolic profiling and diagnostic model development for Hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis. Front Physiol. (2024) 15:1457349. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1457349
15. Gan, SI, Edwards, AL, Symonds, CJ, and Beck, PL. Hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis: A case-based review. World J Gastroenterol. (2006) 12:7197–202. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7197
16. Zuo, Z, Liu, S, Pang, W, Lu, B, Sun, W, Zhang, N, et al. Beneficial effect of kidney bean resistant starch on hyperlipidemia-induced acute pancreatitis and related intestinal barrier damage in rats. Molecules. (2022) 27:783. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092783
17. Carta, G, Murru, E, Banni, S, and Manca, C. Palmitic acid: physiological role, metabolism and nutritional implications. Front Physiol. (2017) 8:902. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00902
18. Yang, F, Wang, Y, Sternfeld, L, Rodriguez, JA, Ross, C, Hayden, MR, et al. The role of free fatty acids, pancreatic lipase and ca+ Signalling in injury of isolated acinar cells and pancreatitis model in lipoprotein lipase-deficient mice. Acta Physiol. (2009) 195:13–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2008.01933.x
19. Phillips, AE, Wilson, A, Papachristou, G, and Whitcomb, DJP. Is there a threshold unsaturated free fatty acid (Uffa) level causing cell toxicity and death in acute pancreatitis, and are Uffas more toxic than their saturated counterparts? Pancreatology. (2017) 17:S2–3. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2017.05.007
20. Inayat, F, Zafar, F, Riaz, I, Younus, F, Baig, AS, and Imran, Z. Hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis: is insulin monotherapy a feasible therapeutic option? Cureus. (2018) 10:e3461. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3461
21. Morita, Y, Yoshikawa, T, Takeda, S, Matsuyama, K, Takahashi, S, Yoshida, N, et al. Involvement of lipid peroxidation in free fatty acid-induced isolated rat pancreatic acinar cell injury. Pancreas. (1998) 17:383–9. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199811000-00009
22. Mössner, J, Bödeker, H, Kimura, W, Meyer, F, Böhm, S, and Fischbach, W. Isolated rat pancreatic acini as a model to study the potential role of lipase in the pathogenesis of acinar cell destruction. Int J Pancreatol. (1992) 12:285–96. doi: 10.1007/bf02924368
23. Xia, W, Lu, Z, Chen, W, Zhou, J, and Zhao, Y. Excess fatty acids induce pancreatic acinar cell Pyroptosis through macrophage M1 polarization. BMC Gastroenterol. (2022) 22:72. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02146-8
24. Jacob, M, Chappell, D, and Becker, BF. Regulation of blood flow and volume exchange across the microcirculation. Crit Care. (2016) 20:319. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1485-0
25. de Pretis, N, Amodio, A, and Frulloni, L. Hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis: epidemiology, pathophysiology and clinical management. United European Gastroenterol J. (2018) 6:649–55. doi: 10.1177/2050640618755002
26. Bhatia, M. Apoptosis versus necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2004) 286:G189–96. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00304.2003
27. Kotan, R, Peto, K, Deak, A, Szentkereszty, Z, and Nemeth, N. Hemorheological and microcirculatory relations of acute pancreatitis. Meta. (2022) 13:4. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010004
28. Cuthbertson, CM, and Christophi, C. Disturbances of the microcirculation in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. (2006) 93:518–30. doi: 10.1002/bjs.5316
29. Qiu, M, Huang, Y, Zhou, X, Yu, J, Li, J, Wang, W, et al. Hyperlipidemia exacerbates acute pancreatitis via interactions between P38mapk and oxidative stress. Cell Signal. (2025) 125:111504. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111504
30. Xia, CC, Chen, HT, Deng, H, Huang, YT, and Xu, GQ. Reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress in acute pancreatitis: pathogenesis and new therapeutic interventions. World J Gastroenterol. (2024) 30:4771–80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4771
31. Cheng, X, Zhan, Y, Wang, Z, Wang, F, Zeng, X, Mao, Y, et al. A single-center experience of non-bioartificial Dfapp support systems among Chinese patients with Hyperlipidemic moderate/severe acute pancreatitis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:1128. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51761-w
32. Hagar, HH, Almubrik, SA, Attia, NM, and Aljasser, SN. Mesna alleviates Cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis by inhibiting the inflammatory response and oxidative stress in experimental rats. Dig Dis Sci. (2020) 65:3583–91. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06072-1
33. Tang, N, Li, W, Shang, H, Yang, Z, Chen, Z, and Shi, G. Irisin-mediated Keap1 degradation alleviates oxidative stress and ameliorates pancreatitis. Immunol Res. (2025) 73:37. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09588-0
34. Cruz-Bautista, I, Huerta-Chagoya, A, Moreno-Macías, H, Rodríguez-Guillén, R, Ordóñez-Sánchez, ML, Segura-Kato, Y, et al. Familial hypertriglyceridemia: an entity with distinguishable features from other causes of hypertriglyceridemia. Lipids Health Dis. (2021) 20:14. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01436-6
35. Lahoz, C, and Mostaza, JM. Familial hypertriglyceridemia/polygenic hypertrigliceridemia. Clin Invest Arterioscler. (2021) 33:37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.arteri.2020.12.014
36. Paquette, M, Amyot, J, Fantino, M, Baass, A, and Bernard, S. Rare variants in triglycerides-related genes increase pancreatitis risk in multifactorial Chylomicronemia syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2021) 106:e3473–82. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab360
37. Dron, JS, Wang, J, Cao, H, McIntyre, AD, Iacocca, MA, Menard, JR, et al. Severe hypertriglyceridemia is primarily polygenic. J Clin Lipidol. (2019) 13:80–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2018.10.006
38. Baass, A, Paquette, M, Bernard, S, and Hegele, RA. Familial Chylomicronemia syndrome: an under-recognized cause of severe Hypertriglyceridaemia. J Intern Med. (2020) 287:340–8. doi: 10.1111/joim.13016
39. Wang, M, Zhou, Y, He, X, Deng, C, Liu, X, Li, J, et al. Two novel mutations of the Lpl gene in two Chinese family cases with familial chylomicronemia syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. (2021) 521:264–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2021.07.022
40. Mishra, UN, Jena, D, Sahu, C, Devi, R, Kumar, R, Jena, R, et al. Nutrigenomics: an inimitable interaction amid genomics, nutrition and health. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. (2022) 82:103196. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2022.103196
41. Lapides, RA, and Savaiano, DA. Gender, age, race and lactose intolerance: is there evidence to support a differential symptom response? A scoping review. Nutrients. (2018) 10:956. doi: 10.3390/nu10121956
42. Singar, S, Nagpal, R, Arjmandi, BH, and Akhavan, NS. Personalized nutrition: tailoring dietary recommendations through genetic insights. Nutrients. (2024) 16:673. doi: 10.3390/nu16162673
43. Chaoqun, H, Rong, Y, Yunpeng, P, Xiaole, Z, Wanli, G, Chenyuan, S, et al. Rna sequence analysis reveals pathways and candidate genes associated with pancreatic acinar cells injury in a mouse pancreatitis model. Tissue Cell. (2022) 79:101940. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2022.101940
44. Cheung, B, Tedder, B, Schaefer, E, and Hegele, R. Severe combined hyperlipidemia, heterozygous Apoe P.V254e, pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, and plantar xanthomas*. J Clin Lipidol. (2019) 13:e24–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.04.044
45. Kawashiri, MA, Higashikata, T, Mizuno, M, Takata, M, Katsuda, S, Miwa, K, et al. Long-term course of lipoprotein lipase (Lpl) deficiency due to homozygous Lpl(Arita) in a patient with recurrent pancreatitis, retained glucose tolerance, and atherosclerosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2005) 90:6541–4. doi: 10.1210/jc.2005-1098
46. Keilson, LM, Vary, CP, Sprecher, DL, and Renfrew, R. Hyperlipidemia and pancreatitis during pregnancy in two sisters with a mutation in the lipoprotein lipase gene. Ann Intern Med. (1996) 124:425–8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-124-4-199602150-00007
47. García-Pastor, T, Muñoz-Puente, I, Pérez-Pelayo, M, Púa, I, Roberts, JD, and Del Coso, J. Maximal fat oxidation during exercise in healthy individuals: lack of genetic association with the Fto Rs9939609 polymorphism. Genes. (2024) 16:4. doi: 10.3390/genes16010004
48. Makhmudova, U, Schulze, PC, Lorkowski, S, März, W, Geiling, JA, and Weingärtner, O. Monogenic hypertriglyceridemia and recurrent pancreatitis in a homozygous carrier of a rare Apoa5 mutation: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2024) 18:278. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04532-0
49. Ferguson, LR, De Caterina, R, Görman, U, Allayee, H, Kohlmeier, M, Prasad, C, et al. Guide and position of the International Society of Nutrigenetics/nutrigenomics on personalised nutrition: part 1 - fields of precision nutrition. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. (2016) 9:12–27. doi: 10.1159/000445350
50. Brennan, L, and de Roos, B. Role of metabolomics in the delivery of precision nutrition. Redox Biol. (2023) 65:102808. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102808
51. Zhou, X, Jin, S, Pan, J, Lin, Q, Yang, S, Lu, Y, et al. Relationship between cholesterol-related lipids and severe acute pancreatitis: from bench to bedside. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:729. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051729
52. Simon, P, Weiss, FU, Zimmer, KP, Koch, HG, and Lerch, MM. Acute and chronic pancreatitis in patients with inborn errors of metabolism. Pancreatology. (2001) 1:448–56. doi: 10.1159/000055846
53. Yang, AL, and McNabb-Baltar, J. Hypertriglyceridemia and acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. (2020) 20:795–800. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.06.005
54. Kortesniemi, M, Noerman, S, Kårlund, A, Raita, J, Meuronen, T, Koistinen, V, et al. Nutritional metabolomics: recent developments and future needs. Curr Opin Chem Biol. (2023) 77:102400. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2023.102400
55. Rawla, P, Sunkara, T, Thandra, KC, and Gaduputi, V. Hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis: updated review of current treatment and preventive strategies. Clin J Gastroenterol. (2018) 11:441–8. doi: 10.1007/s12328-018-0881-1
56. Luna-Castillo, KP, Olivares-Ochoa, XC, Hernández-Ruiz, RG, Llamas-Covarrubias, IM, Rodríguez-Reyes, SC, Betancourt-Núñez, A, et al. The effect of dietary interventions on hypertriglyceridemia: from public health to molecular nutrition evidence. Nutrients. (2022) 14:104. doi: 10.3390/nu14051104
57. Nie, Y, and Luo, F. Dietary Fiber: an opportunity for a global control of hyperlipidemia. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:5542342. doi: 10.1155/2021/5542342
58. Hannan, PA, Khan, JA, Ullah, I, and Ullah, S. Synergistic combinatorial Antihyperlipidemic study of selected natural antioxidants; modulatory effects on lipid profile and endogenous antioxidants. Lipids Health Dis. (2016) 15:151. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0323-3
59. Heintz-Buschart, A, and Wilmes, P. Human gut microbiome: function matters. Trends Microbiol. (2018) 26:563–74. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.11.002
60. Qian, G, and Ho, JWK. Challenges and emerging systems biology approaches to discover how the human gut microbiome impact host physiology. Biophys Rev. (2020) 12:851–63. doi: 10.1007/s12551-020-00724-2
61. Brown, EM, Clardy, J, and Xavier, RJ. Gut microbiome lipid metabolism and its impact on host physiology. Cell Host Microbe. (2023) 31:173–86. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2023.01.009
62. Kolodziejczyk, AA, Zheng, D, and Elinav, E. Diet-microbiota interactions and personalized nutrition. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2019) 17:742–53. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0256-8
63. Wang, Z, Guo, M, Yang, S, Chen, Y, Cheng, J, Huang, Z, et al. Intestinal microflora and metabolites affect the progression of acute pancreatitis (Ap). Gut pathogens. (2024) 16:64. doi: 10.1186/s13099-024-00652-6
64. Li, XY, He, C, Zhu, Y, and Lu, NH. Role of gut microbiota on intestinal barrier function in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. (2020) 26:2187–93. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2187
65. Zhao, Y, Zhang, R, Wang, S, Yang, C, Wang, Y, Fan, H, et al. Observation on the therapeutic effect of probiotics on early Oral feeding in the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Front Med. (2024) 11:1492108. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1492108
66. Wan, YD, Zhu, RX, Bian, ZZ, and Sun, TW. Effect of probiotics on length of hospitalization in mild acute pancreatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol. (2021) 27:224–32. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i2.224
67. Guan, ZW, Yu, EZ, and Feng, Q. Soluble dietary fiber, one of the most important nutrients for the gut microbiota. Molecules. (2021) 26:802. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226802
68. Chen, T, Ma, Y, Xu, L, Sun, C, Xu, H, and Zhu, J. Soluble dietary Fiber reduces feeding intolerance in severe acute pancreatitis: a randomized study. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2021) 45:125–35. doi: 10.1002/jpen.1816
69. Wen, S, Zhang, Y, Zhao, G, Tu, Z, Zhang, K, and Cui, Y. Association of Admission Serum Triglyceride Levels with intensive care unit hospitalization rates in acute pancreatitis patients: a retrospective study. Medicine. (2024) 103:e38265. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000038265
70. Abou-Assi, S, and O’Keefe, SJJJ. Nutrition in acute pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. (2001) 32:203–9. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200103000-00004
71. Plauth, M, Schütz, T, Pirlich, M, and Canbay, A. Ernährungsmedizin udDSCJA S3-Leitlinie Der Deutschen Gesellschaft Für Ernährungsmedizin (Dgem) in Zusammenarbeit Mit Der Geskes. Der Ake Und Der Dgvs. (2014) 39:e1–e42. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1360016
72. Lariño-Noia, J, Lindkvist, B, Iglesias-García, J, Seijo-Ríos, S, Iglesias-Canle, J, and Domínguez-Muñoz, JE. Early and/or immediately full caloric diet versus standard refeeding in mild acute pancreatitis: a randomized open-label trial. Pancreatology. (2014) 14:167–73. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2014.02.008
73. Vaughn, VM, Shuster, D, Rogers, MAM, Mann, J, Conte, ML, Saint, S, et al. Early versus delayed feeding in patients with acute pancreatitis: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. (2017) 166:883–92. doi: 10.7326/m16-2533
74. Kalfarentzos, F, Kehagias, J, Mead, N, Kokkinis, K, and Gogos, CA. Enteral nutrition is superior to parenteral nutrition in severe acute pancreatitis: results of a randomized prospective trial. Br J Surg. (1997) 84:1665–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.1998.00812.x
75. Wereszczynska-Siemiatkowska, U, Swidnicka-Siergiejko, A, Siemiatkowski, A, and Dabrowski, A. Early enteral nutrition is superior to delayed enteral nutrition for the prevention of infected necrosis and mortality in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. (2013) 42:640–6. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318271bb61
76. Schörghuber, M, and Fruhwald, S. Effects of enteral nutrition on gastrointestinal function in patients who are critically ill. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 3:281–7. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(18)30036-0
77. Petrov, MS, and Windsor, JA. Nutritional management of acute pancreatitis: the concept of ‘gut rousing’. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2013) 16:557–63. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283638ed1
78. McClave, SA, and Martindale, RG. What is the role of parenteral nutrition in the management of the patient with severe acute pancreatitis? Nutr Clin Pract. (2024) 40:266. doi: 10.1002/ncp.11266
79. Petrov, MS, Pylypchuk, RD, and Emelyanov, NV. Systematic review: nutritional support in acute pancreatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2008) 28:704–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03786.x
80. Baron, TH, DiMaio, CJ, Wang, AY, and Morgan, KA. American gastroenterological association clinical practice update: management of pancreatic necrosis. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:67–75e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.064
81. Vege, SS, DiMagno, MJ, Forsmark, CE, Martel, M, and Barkun, AN. Initial medical treatment of acute pancreatitis: American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review. Gastroenterology. (2018) 154:1103–39. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.031
82. Arvanitakis, M, Ockenga, J, Bezmarevic, M, Gianotti, L, Krznarić, Ž, Lobo, DN, et al. Espen guideline on clinical nutrition in acute and chronic pancreatitis. Clinic Nutr. (2020) 39:612–31. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.01.004
83. Stigliano, S, Sternby, H, de Madaria, E, Capurso, G, and Petrov, MS. Early Management of Acute Pancreatitis: a review of the best evidence. Diges Liver Dis. (2017) 49:585–94. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.01.168
84. Shu, H, Liu, K, He, Q, Zhong, F, Yang, L, Li, Q, et al. Ulinastatin, a protease inhibitor, may inhibit allogeneic blood transfusion-associated pro-inflammatory cytokines and systemic inflammatory response syndrome and improve postoperative recovery. Blood Trans. (2014) 12 Suppl 1:s109–18. doi: 10.2450/2013.0224-12
85. Crockett, SD, Wani, S, Gardner, TB, Falck-Ytter, Y, and Barkun, AN. American gastroenterological association institute guideline on initial management of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2018) 154:1096–101. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.032
86. Blaszczak, AM, Krishna, SG, Hart, PA, Bradley, D, Hsueh, W, Lara, LF, et al. Class iii obesity rather than metabolic syndrome impacts clinical outcomes of acute pancreatitis: a propensity score weighted analysis. Pancreatology. (2020) 20:1287–95. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.08.011
87. Cintoni, M, and Mele, MC. The role of Immunonutrition in patients. Nutrients. (2023) 15:780. doi: 10.3390/nu15030780
88. Oláh, A, and Romics, L. Enteral nutrition in acute pancreatitis: a review of the current evidence. World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:16123–31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16123
89. Xue, P, Deng, LH, Xia, Q, Zhang, ZD, Hu, WM, Yang, XN, et al. Impact of alanyl-glutamine dipeptide on severe acute pancreatitis in early stage. World J Gastroenterol. (2008) 14:474–8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.474
90. Asrani, V, Chang, WK, Dong, Z, Hardy, G, Windsor, JA, and Petrov, MS. Glutamine supplementation in acute pancreatitis: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pancreatology. (2013) 13:468–74. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2013.07.282
91. Jafari, T, Feizi, A, Askari, G, and Fallah, AA. Parenteral Immunonutrition in patients with acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Clini Nutr. (2015) 34:35–43. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.05.008
92. Tao, X, Yang, Y, Xu, S, and Xiong, Q. Efficacy of immune nutrients in severe acute pancreatitis: a network Meta-analysis. Medicine. (2023) 102:e35615. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000035615
93. Heller, AR. Pharmaconutrition with Omega-3 fatty acids: status quo and further perspectives. Mini Rev Med Chem. (2008) 8:107–15. doi: 10.2174/138955708783498122
94. Shibabaw, T. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: anti-inflammatory and anti-hypertriglyceridemia mechanisms in cardiovascular disease. Mol Cell Biochem. (2021) 476:993–1003. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03965-7
95. Cruzat, V, Macedo Rogero, M, Noel Keane, K, Curi, R, and Newsholme, P. Glutamine: metabolism and immune function, supplementation and clinical translation. Nutrients. (2018) 10:564. doi: 10.3390/nu10111564
96. Perna, S, Alalwan, TA, Alaali, Z, Alnashaba, T, Gasparri, C, Infantino, V, et al. The role of glutamine in the complex interaction between gut microbiota and health: a narrative review. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:232. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205232
97. Arutla, M, Raghunath, M, Deepika, G, Jakkampudi, A, Murthy, HVV, Rao, GV, et al. Efficacy of enteral glutamine supplementation in patients with severe and predicted severe acute pancreatitis- a randomized controlled trial. Indian J Gastroenterol. (2019) 38:338–47. doi: 10.1007/s12664-019-00962-7
98. Singh, N, Mishra, SK, Sachdev, V, Sharma, H, Upadhyay, AD, Arora, I, et al. Effect of Oral glutamine supplementation on gut permeability and Endotoxemia in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: a randomized controlled trial. Pancreas. (2014) 43:867–73. doi: 10.1097/mpa.0000000000000124
99. Sahin, H, Mercanligil, SM, Inanç, N, and Ok, E. Effects of glutamine-enriched Total parenteral nutrition on acute pancreatitis. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2007) 61:1429–34. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602664
100. Wang, X, Li, W, Li, N, and Li, J. Omega-3 fatty acids-supplemented parenteral nutrition decreases Hyperinflammatory response and attenuates systemic disease sequelae in severe acute pancreatitis: a randomized and controlled study. JPEN. (2008) 32:236–41. doi: 10.1177/0148607108316189
101. Górska-Warsewicz, H, Laskowski, W, Kulykovets, O, Kudlińska-Chylak, A, Czeczotko, M, and Rejman, K. Food products as sources of protein and amino acids-the case of Poland. Nutrients. (2018) 10:977. doi: 10.3390/nu10121977
102. Lorin, J, Zeller, M, Guilland, JC, Cottin, Y, Vergely, C, and Rochette, L. Arginine and nitric oxide synthase: regulatory mechanisms and cardiovascular aspects. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2014) 58:101–16. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201300033
103. Zhou, J, Xue, Y, Liu, Y, Li, XK, Tong, ZH, and Li, WQ. The effect of Immunonutrition in patients with acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Hum Nutr Diet. (2021) 34:429–39. doi: 10.1111/jhn.12816
104. Petrov, MS, Atduev, VA, and Zagainov, VE. Advanced enteral therapy in acute pancreatitis: is there a room for immunonutrition? A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. (2008) 6:119–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2008.01.003
105. Poropat, G, Giljaca, V, Hauser, G, and Štimac, D. Enteral nutrition formulations for acute pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2015) 2015:CD010605. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010605.pub2
106. Rodgers, GP, and Collins, FS. Precision nutrition-the answer to “what to eat to stay healthy”. JAMA. (2020) 324:735–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.13601
107. Hwang, WM, Bak, DH, Kim, DH, Hong, JY, Han, SY, Park, KY, et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may attenuate Streptozotocin-induced pancreatic Β-cell death via autophagy activation in Fat1 transgenic mice. Endocrinol Metabol. (2015) 30:569–75. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.569
108. Skulas-Ray, AC, Wilson, PWF, Harris, WS, Brinton, EA, Kris-Etherton, PM, Richter, CK, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids for the Management of Hypertriglyceridemia: a science advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2019) 140:e673–91. doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000000709
109. Shahidi, F, and Ambigaipalan, P. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and their health benefits. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. (2018) 9:345–81. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-111317-095850
110. Shemesh, E, and Zafrir, B. Hypertriglyceridemia-related pancreatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes: links and risks. Diab Metab Syndr Obes. (2019) 12:2041–52. doi: 10.2147/dmso.S188856
111. Gao, L, and Li, WJJ. Hypertriglyceridemia and acute pancreatitis: clinical and basic research—a narrative review. J Pancreatol. (2024) 7:53–60. doi: 10.1097/JP9.0000000000000153
112. Mensink, RP, Zock, PL, Kester, AD, and Katan, MB. Effects of dietary fatty acids and carbohydrates on the ratio of serum total to HDL cholesterol and on serum lipids and apolipoproteins: a meta-analysis of 60 controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. (2003) 77:1146–55. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/77.5.1146
113. Li, X, Zheng, P, Zou, Y, Guan, L, Li, N, Liu, J, et al. Dietary inulin ameliorates obesity-induced severe acute pancreatitis via gut-pancreas Axis. Gut Microbes. (2024) 16:2436949. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2436949
114. Pokushalov, E, Ponomarenko, A, Bayramova, S, Garcia, C, Pak, I, Shrainer, E, et al. Evaluating the impact of omega-3 fatty acid (Soloways(tm)) supplementation on lipid profiles in adults with Pparg polymorphisms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients. (2023) 16:97. doi: 10.3390/nu16010097
Keywords: hyperlipidemia, acute pancreatitis, precision nutrition, clinical nutrition, mechanism, multi-omics integration, personalized medicine
Citation: Ma J, Wan X, Liu J, Hu X, Ma Y and Gao Y (2025) Precision nutrition management in hyperlipidemia-associated acute pancreatitis: mechanistic insights and personalized therapeutic approaches. Front. Nutr. 12:1583889. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1583889
Edited by:
Teresa Perra, Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Sassari, ItalyReviewed by:
Xiao-lei Shi, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, ChinaSuprit Malali, Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Wan, Liu, Hu, Ma and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yunhai Gao, bG56eTEyM25AMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jingyuan Ma
Jingyuan Ma Xing Wan
Xing Wan Jifeng Liu
Jifeng Liu Xuyang Hu4
Xuyang Hu4