- 1Department of Bone Tumor, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Yunnan Cancer Hospital, Kunming, China
- 2School of Nursing, Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
- 3Department of Nursing, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Yunnan Cancer Hospital, Kunming, China
- 4Department of Nutrition, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Yunnan Cancer Hospital, Kunming, China
- 5Alice Lee Centre for Nursing Studies, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
Background: Sarcopenia screening in bone tumor patients is challenging due to limited awareness, complex procedures, and high costs-especially since most research targets older adults, overlooking younger patients in this group. This study aims to compare the screening efficacy of five different tools for sarcopenia, and to identify the most appropriate screening tool for patients with bone tumors.
Methods: The five sarcopenia screening tools assessed were SARC-F, SARC-Calf, SARC-F + EBM, and the Chinese versions of the Mini-Sarcopenia Risk Assessment scales (MSRA-5 and MSRA-7). The 2019 Asia Working Group for Sarcopenia (AWGS) criteria served as the reference standard for sarcopenia screening.
Results: Among 300 bone tumor patients, 26% were found to have sarcopenia based on AWGS 2019 criteria. The screening tools varied in performance, with SARC-Calf showing the highest sensitivity and MSRA-7 the lowest specificity. Positive and negative predictive values were moderate across tools, with combined screening methods generally improving sensitivity. The highest overall accuracy (AUC) was observed when using a combination of SARC-F, SARC-Calf, and EBM, which provided both high sensitivity and acceptable specificity.
Conclusion: The SARC-Calf and SARC-F + EBM tools demonstrated high accuracy in screening sarcopenia among bone tumor patients. The combined use of SARC-F, SARC-Calf, and SARC-F + EBM yielded superior screening performance, making them suitable for preliminary sarcopenia screening in this patient population.
1 Introduction
Bone tumors originate from bone tissue or other components within the bone, encompassing primary bone tumors as well as metastases from other malignancies, most commonly from the lungs and breasts. Bone metastases affect over 1.5 million cancer patients globally and spread through the blood or lymphatic system (1). Primary bone tumors, although rare, account for approximately 2–3% of all cancers and are frequently located at the ends of long bones, such as the distal femur, proximal tibia, and proximal humerus (2). In China, an estimated 24,200 bone tumor cases were reported in 2015, representing about 0.62% of all cancers (3). Factors such as chemotherapy, immunodeficiency, tumor-induced catabolism, fear of movement, pain, and poor sleep contribute to an increased risk of muscle loss in bone tumor patients (4, 5).
Sarcopenia is a progressive, systemic condition characterized by the loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, and physical performance (6). The prevalence of sarcopenia varies according to diagnostic criteria and environmental factors, ranging from 5.5 to 25.7% (7). Among cancer patients, sarcopenia prevalence can be as high as 43% (8), significantly impacting clinical outcomes, such as increased chemotherapy toxicity, higher rates of complications, prolonged hospital stays, reduced quality of life, and elevated mortality risk (6, 9).
The diagnosis of sarcopenia is challenging due to variability in measurement techniques and diagnostic thresholds. Commonly used methods include computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), ultrasound, and bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) (6). While CT and MRI are considered the gold standards for assessing muscle mass, their high costs, limited accessibility, and need for specialized personnel restrict their routine use (10). DXA provides inconsistent results across different instrument brands, and ultrasound lacks standardized cutoff values (11, 12). BIA, although affordable, is affected by factors such as body composition and fluid retention.
Given these limitations, screening tools like the SARC-F (strength, assistance with walking, rise from a chair, climb stairs and falls), SARC-CalF (SARC-F combined with calf circumference), EBM (elderly and body mass index information), Mini sarcopenia risk assessment-5 (MSRA-5), and Mini sarcopenia risk assessment-7 (MSRA-7) have gained attention as alternatives for early detection of sarcopenia (7). The 2018 European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People (EWGSOP) and the 2019 Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia (AWGS) recommend using screening tools to identify individuals at risk of sarcopenia to facilitate timely intervention (6, 13). However, these tools have primarily been validated in older adults and patients with other chronic conditions (1). Research on sarcopenia screening in cancer patients, especially those with bone tumors, remains limited, necessitating further investigation into the efficacy and applicability of these tools in this study population. Therefore, this study aims to compare the screening efficacy of five different tools for sarcopenia, and to identify the most appropriate screening tool for patients with bone tumors.
2 Materials and methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted at a provincial cancer hospital between August 2023 and November 2023. It is part of a broader investigation into the development and application of a risk prediction model for sarcopenia in patients with bone tumors. The study obtained the ethical approval from the studied hospital’s ethics committee (SLKYLX2023-171). All participants provided written informed consent and voluntarily took part in the study.
2.1 Study participants
All study participants were recruited using convenience sampling. The inclusion criteria were: (1) a diagnosis of primary or metastatic bone tumors; (2) a disease duration of at least 3 months; and (3) age 18 years or older. The exclusion criteria included: (1) presence of lower limb edema; (2) mental disorders; (3) severe hearing, vision, or speech impairments; (4) inability to stand; (5) presence of metallic implants; (6) limb amputations; (7) limbs wrapped in bandages or casts; and (8) use of medications that could affect body composition measurements.
2.2 AWGS 2019 sarcopenia diagnosis
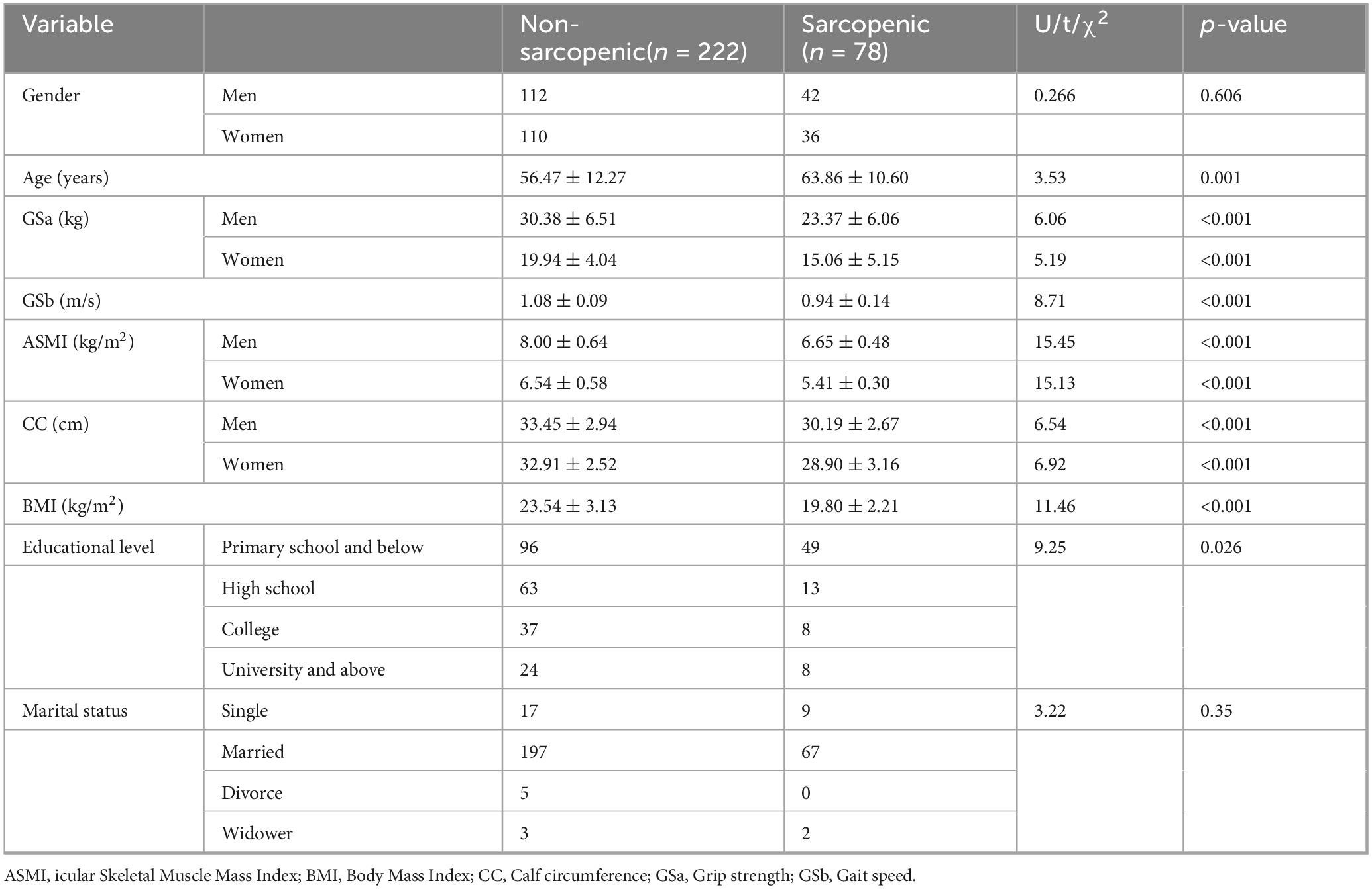
According to the 2019 AWGS criteria (7), sarcopenia is diagnosed based on three key components: (1) Muscle Strength: Defined as reduced grip strength, with thresholds of < 28 kg for men and < 18 kg for women; (2) Muscle Mass: Assessed using bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), with an icular skeletal muscle mass index of < 7.0 kg/m2 for men and < 5.7 kg/m2 for women; (3) Physical Performance: Evaluated by gait speed, where a speed of < 1 m/s over a 6-m walk indicates impaired performance.
2.3 Data collection tools
2.3.1 General information sheet
This information sheet was developed based on a comprehensive literature review to collect demographic and clinical information. This included details such as age, gender, education level, marital status, icular skeletal muscle mass index, body mass index, calf circumference, grip strength, and gait speed.
2.3.2 SARC-F questionnaire
The SARC-F, developed by Malmstrom and Morley (14), assesses five domains: strength, assistance in walking, rising from a chair, climbing stairs, and fall history. Each item is scored from 0 to 2, with the total score ranging from 0 to 10. A score of ≥ 4 suggests a high risk of sarcopenia. The scale was translated into Chinese: its reliability (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.849), and the criterion-related validity (r = 0.878) (15).
2.3.3 SARC-Calf questionnaire
The SARC-Calf integrates the SARC-F with calf circumference measurements developed by Barbosa-Silva et al. (16). For males with a calf circumference ≤ 34 cm or females with ≤ 33 cm, 10 points are added to the SARC-F score. The total possible score ranges from 0 to 20, with a score of ≥ 11 indicating a high risk of sarcopenia.
2.3.4 SARC-F + EBM questionnaire
The SARC-F + EBM, developed by Kurita et al. (17), combines the SARC-F with an expanded body mass index (EBM) assessment, incorporating calf circumference measurements. A total score of ≥ 11 points denote a high risk of sarcopenia.
2.3.5 MSRA-5 and MSRA-7 questionnaires
The Mini Sarcopenia Risk Assessment (MSRA) was developed by Rossi et al. (18), and later translated into Chinese by Yang et al. (19). The MSRA-5 consists of five items: age, history of hospital stays, physical activity level, daily meals, and weight loss, with a total score of ≤ 45 indicating sarcopenia risk. The MSRA-7 expands on this by including dairy and protein consumption, and a score of ≤ 30 suggests a sarcopenia risk.
2.4 Data collection
One nurse researcher (the first author) collected the data. Within 24 h of admission, eligible patients were informed about the study, and written consent was obtained. They were then asked to complete the five questionnaires, with assistance provided if needed. Calf circumference was measured three times while patients were seated with their dominant leg exposed, and the average of the three measurements was recorded. Before treatment, assessments of grip strength, walking speed, and icular skeletal muscle mass index were conducted. Grip strength was measured using an electronic grip strength meter (Xiangshan EH-101) with the dominant hand, or with the unaffected hand for patients with arm tumors, and the highest value from three attempts was recorded. Walking speed was measured twice over a 6-m distance, and the average speed was calculated. The icular skeletal muscle mass was assessed using an InBody 770 body composition analyzer.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS version 25.0. Continuous variables were presented as means with standard deviations, while categorical variables were reported as frequencies and percentages. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated based on the 2019 sarcopenia diagnostic criteria, and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) along with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. For each screening tool, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), kappa value, and their respective 95% CIs were compared. The DeLong test was employed to evaluate differences between the AUCs of the screening tools. Youden’s index was calculated to identify optimal cutoff points. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of study participants
This study included 300 bone tumor patients, aged 19–81 years, with a median age of 58 years (mean = 55.18, SD, 14.28 years). Based on the AWGS 2019 sarcopenia diagnostic criteria, the prevalence of sarcopenia among bone tumor patients was 26%. The difference of characteristics of patients with sarcopenia and without sarcopenia was presented in Table 1.
3.2 Accuracy analysis of five sarcopenia screening tools
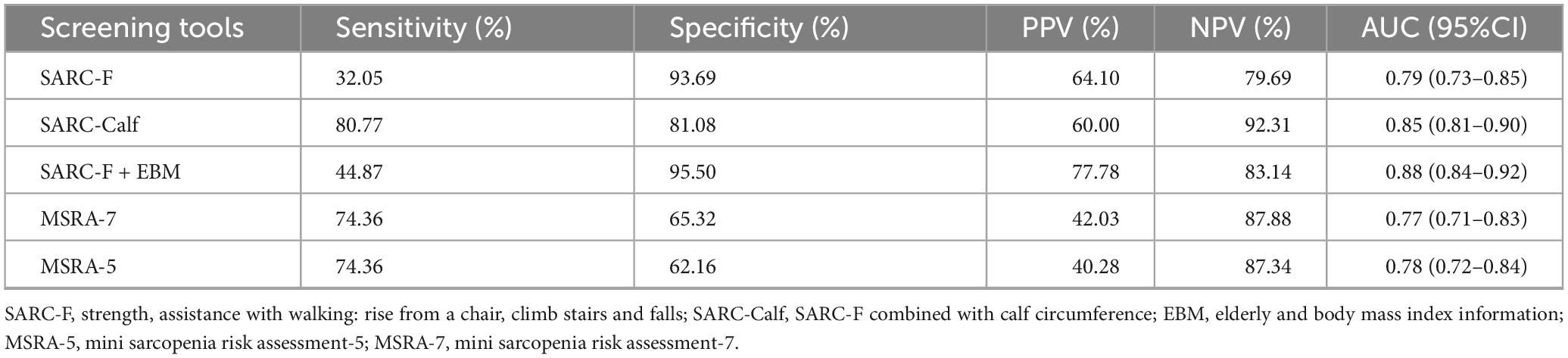
Using the AWGS 2019 diagnostic criteria as a reference, we assessed the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and AUC for five sarcopenia screening tools. The results are summarized in Table 2.
3.3 Optimal cutoff values for the five sarcopenia screening tools
Among the five screening tools, the SARC-F + EBM questionnaire showed the highest AUC (0.88) with an optimal cutoff point of 10.5. The ROC curve is shown in Figure 1. At this cutoff, the sensitivity and specificity were 61.5 and 93.7%, respectively (Supplementary Table 1).
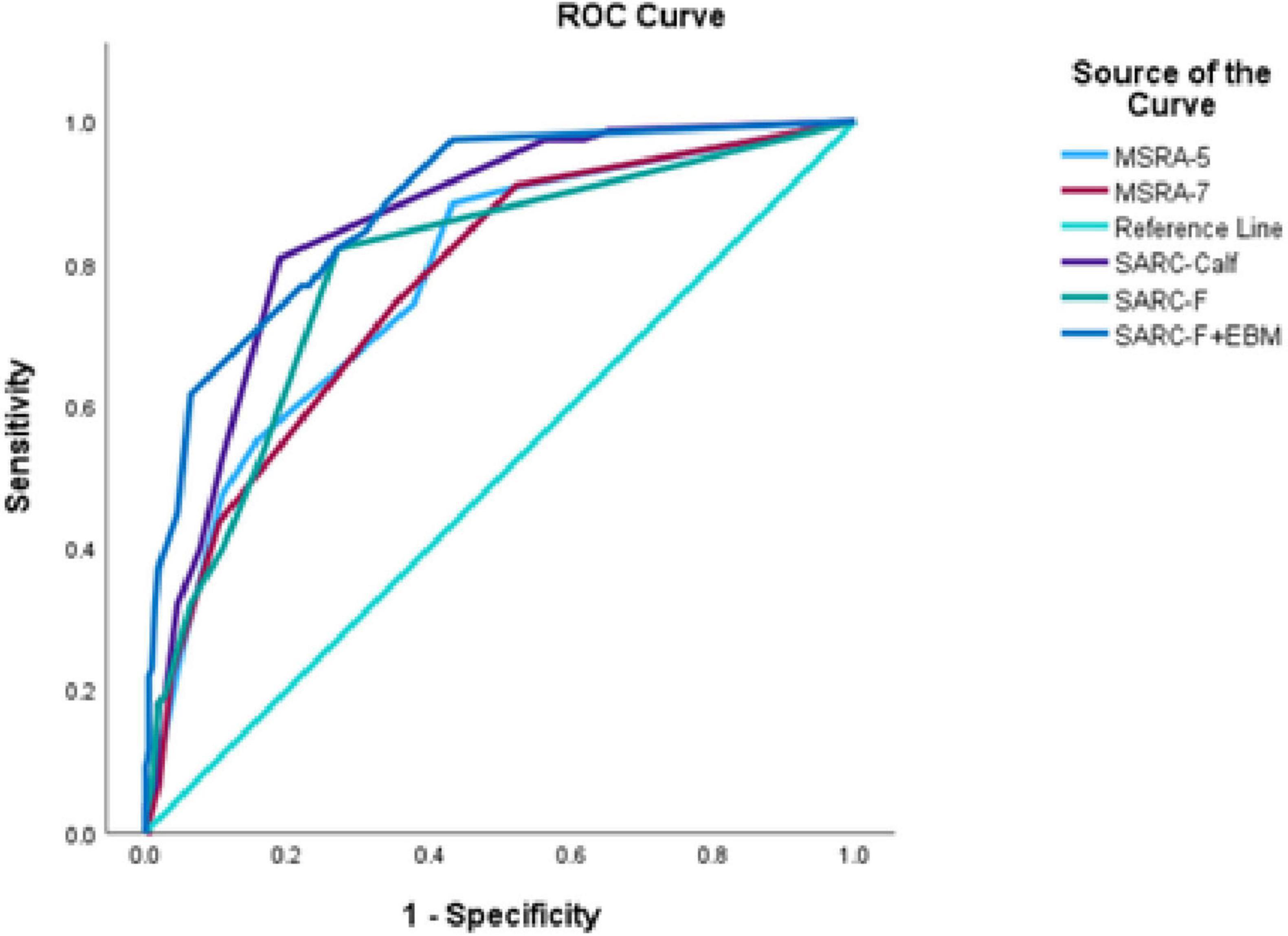
Figure 1. Comparisons of five screening tools for sarcopenia based on AWGS 2019. SARC-F, strength, assistance with walking, rise from a chair, climb stairs and falls; SARC-Calf, SARC-F combined with calf circumference; EBM, elderly and body mass index information; MSRA-5, mini sarcopenia risk assessment-5; MSRA-7, mini sarcopenia risk assessment-7.
3.4 AUC Comparison between the five screening tools
The AUC comparison revealed that the SARC-F + EBM questionnaire had a significantly higher AUC of 0.88 than the SARC-F, MSRA-7, and MSRA-5 questionnaires. Similarly, the SARC-Calf questionnaire had a higher AUC of 0.85 than the SARC-F, MSRA-7, and MSRA-5 questionnaires. There were no significant differences in AUC between the other tools (Table 3).
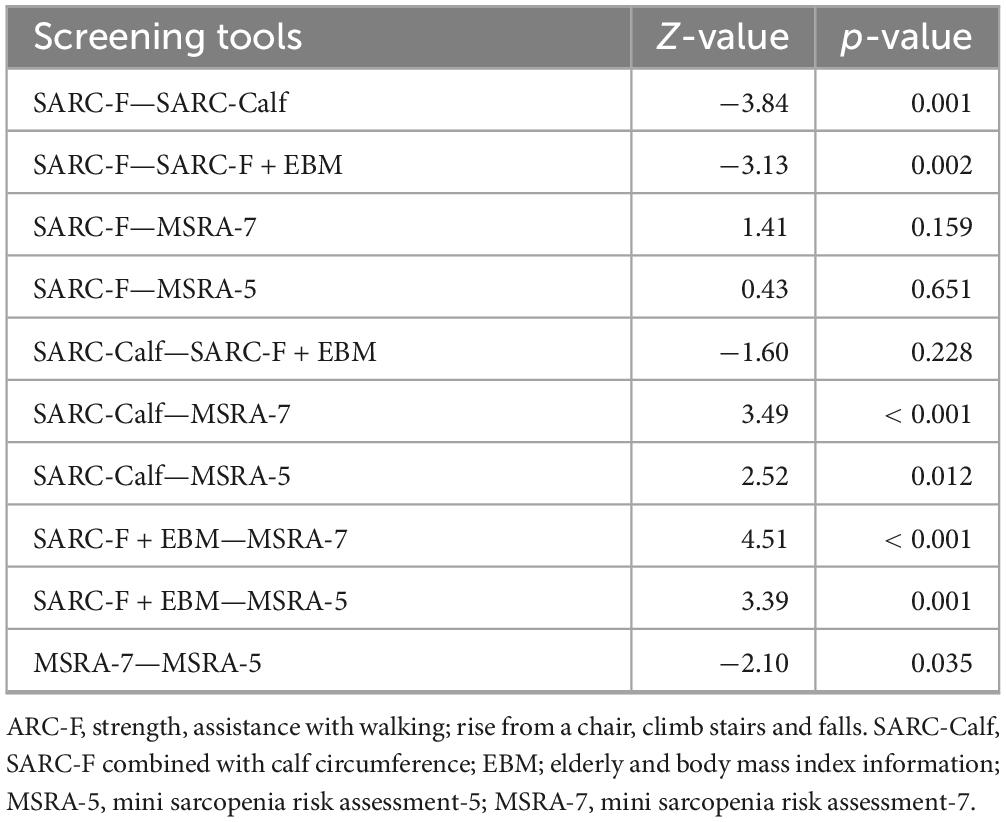
Table 3. The results of pairwise comparison of the area under the ROC curve of 5 screening tools (N = 300).
3.5 Comparison of sarcopenia screening results of the five tools with AWGS 2019 sarcopenia diagnostic criteria
Based on the screening results of the five tools, patients were classified into sarcopenia and non-sarcopenia groups. A comparison with the AWGS 2019 diagnostic criteria showed that the Kappa values for the SARC-F, SARC-Calf, SARC-F + EBM, MSRA-7, and MSRA-5 questionnaires were 0.307, 0.556, 0.468, 0.321, and 0.288, respectively (all P < 0.001), indicating moderate agreement (Table 4).
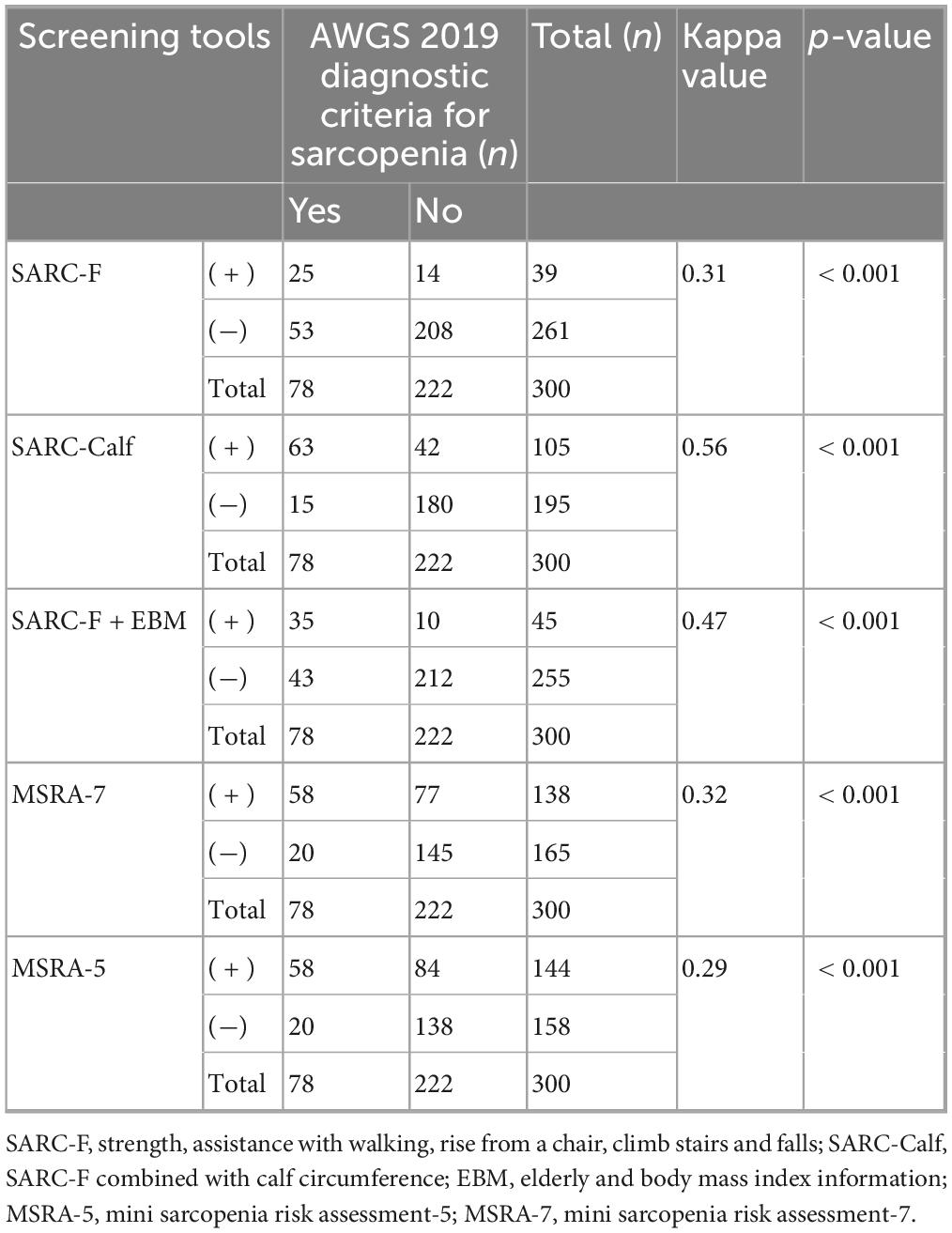
Table 4. Comparison of screening results of 5 sarcopenia screening tools with AWGS 2019 diagnostic criteria for sarcopenia (N = 300).
3.6 Combined use of SARC-F and MSRA screening tools
When the SARC-F and SARC-Calf tools were used together, the AUC under the ROC curve was 0.86. Combining SARC-F with SARC-F + EBM resulted in an AUC of 0.88. Using all three tools (SARC-F, SARC-Calf, and SARC-F + EBM) together further increased the AUC to 0.89. In contrast, when MSRA-7 and MSRA-5 were combined, the AUC was 0.78. The corresponding ROC curves are shown in Figure 2, and results are summarized in Table 5.
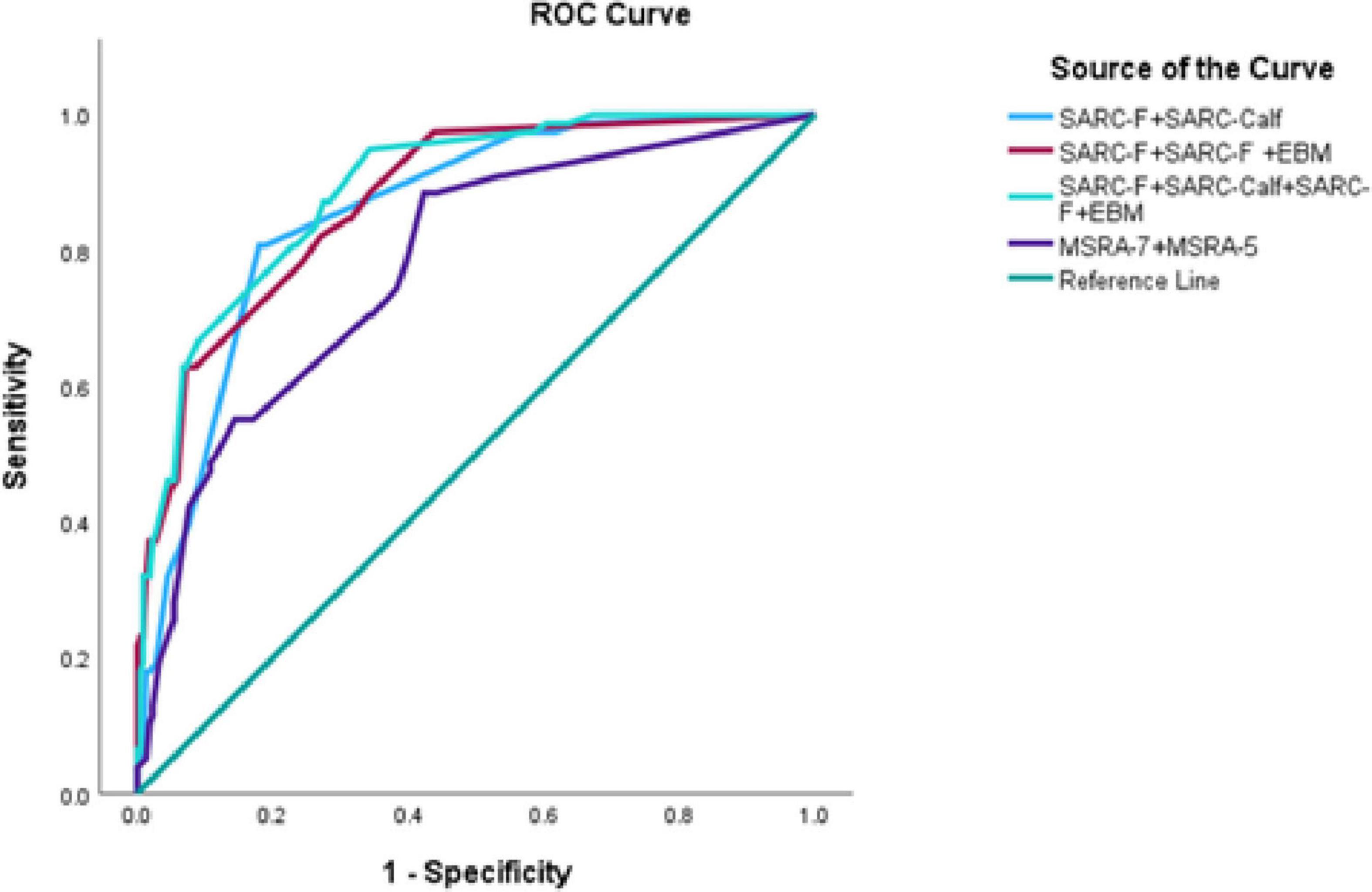
Figure 2. Comparisons of combined use of screening tools for sarcopenia based on AWGS 2019. SARC-F, strength, assistance with walking, rise from a chair, climb stairs and falls; SARC-Calf, SARC-F combined with calf circumference; EBM, elderly and body mass index information; MSRA-5, mini sarcopenia risk assessment-5; MSRA-7, mini sarcopenia risk assessment-7.
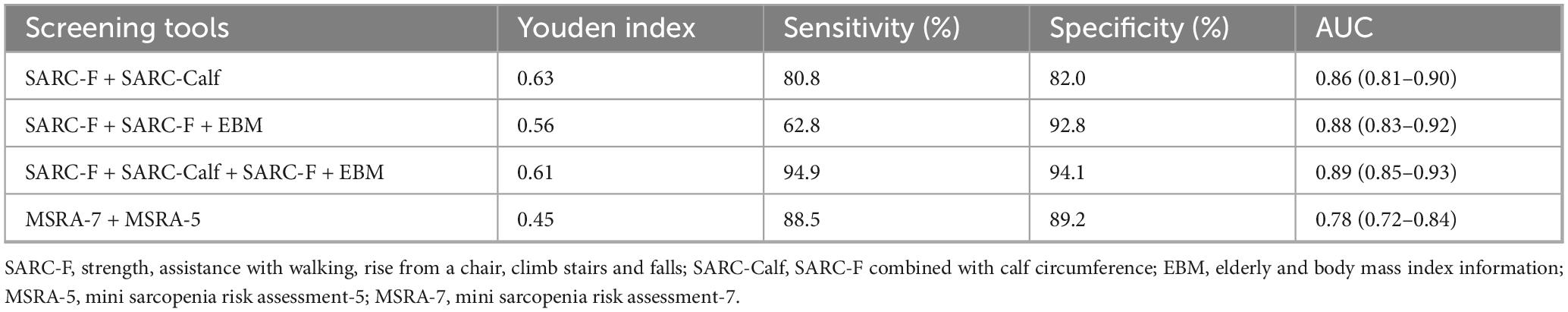
Table 5. Comparison results of combined use of SARC-F related scales and MSRA related scales (N = 300).
4 Discussion
This study, using the AWGS 2019 sarcopenia screening criteria (20), found that the prevalence of sarcopenia in bone tumor patients was 26%, higher than previous similar studies with a prevalence of 22% (21–23). This may be due to bone tumors compressing spinal cord nerves, leading to paralysis and reduced physical activity (24). Additionally, bone tumor patients are less likely to experience early-stage digestive dysfunction compared to patients with gastrointestinal cancers, where insufficient nutritional intake increases the risk of sarcopenia (4, 25). Although the findings differ across studies, they highlight that sarcopenia in bone tumor patients is a significant concern (21, 22).
Most research on sarcopenia focuses on older adults, but bone tumor patients include younger individuals. The lack of awareness about sarcopenia, coupled with its complex screening process and the high costs of assessment, makes it challenging to screen these patients effectively (13). Therefore, healthcare professionals should emphasize early screening and prevention of sarcopenia in bone tumor patients to delay its onset and mitigate complications. Given the unique risks in bone tumor patients, Distinguishing sarcopenia from cachexia is essential, as they are distinct but can coexist, particularly in cancer settings (26, 27). Future research should address this overlap to refine screening and intervention strategies for all age groups affected by bone tumors.
In this study, the SARC-F questionnaire had high specificity but low sensitivity, consistent with previous research, indicating its limited ability to detect sarcopenia, leading to a high misdiagnosis rate. This is because SARC-F mainly reflects muscle strength and physical performance but does not assess muscle mass, a key diagnostic criterion for sarcopenia (28). The ROC analysis revealed an optimal cutoff value of 0.5, which aligns with Ma et al.’s findings (29), but differs from other studies (30, 31) due to regional and population differences. Adjusting the cutoff improved the sensitivity and balanced specificity, enhancing the screening performance of SARC-F for bone tumor patients. This suggests that clinicians need to determine optimal cutoff values tailored to specific populations to maximize the effectiveness of screening tools.
The SARC-Calf questionnaire, which incorporates calf circumference, showed higher sensitivity and specificity compared to SARC-F, offering better diagnostic value (Kappa value of 0.556). However, it still demonstrated low PPV and high NPV, consistent with previous research (32). Calf circumference is a reliable marker of skeletal muscle mass (33) and has been validated in diagnosing sarcopenia among older adults (7), patients with chronic liver diseases (34), and stroke survivors (35). However, the optimal cutoff value varies by study and population. For example, studies in Turkey and Taiwan found cutoffs of 33 cm for men and 32–33 cm for women (7, 36), while Japanese researchers recommend 34 cm for men and 33 cm for women (37). These variations may stem from differences in ethnicity, culture, and lifestyle (38). The AWGS2019-recommended cutoffs used in this study were appropriate for this population.
The SARC-F + EBM questionnaire, which adds age and BMI to the SARC-F tool, had higher sensitivity, specificity, and overall diagnostic performance than SARC-F alone, consistent with previous research (17). This is particularly meaningful for elderly patients with bone tumors, who are at greater risk of muscle loss due to reduced mobility and long-term bed rest. Moreover, studies have shown that low BMI (≤ 21 kg/m2) is associated with undernutrition, which increases the risk of sarcopenia (39, 40). Bone tumor patients often experience malnutrition due to chemotherapy-related gastrointestinal side effects and cachexia, further increasing sarcopenia risk. With an AUC of 0.88, the SARC-F + EBM tool demonstrated strong screening performance.
The MSRA-7 questionnaire showed high sensitivity but lower specificity and a lower PPV. Among the five screening tools, it had the smallest AUC (0.77). One possible explanation is that patients undergoing chemotherapy may have been hospitalized frequently during the past year, affecting their scores, even though their condition may have improved post-chemotherapy. Furthermore, the inclusion of daily dairy consumption as a factor may not align with typical Chinese dietary habits, impacting the tool’s performance. After removing dairy and protein consumption items, the MSRA-5 questionnaire performed better in terms of sensitivity and specificity, though its agreement with diagnostic outcomes was still suboptimal. Future research should aim to revise the MSRA tool for better applicability in bone tumor patients in China.
When SARC-F-related scales and MSRA-related scales were used in combination, the diagnostic performance improved. Specifically, the combined use of SARC-F, SARC-Calf, and SARC-F + EBM yielded the best diagnostic results, offering a comprehensive evaluation of muscle strength, physical performance, muscle mass, age, and nutrition. This combination provides a more practical and efficient method for early screening of sarcopenia in bone tumor patients.
Bone tumors and sarcopenia are interrelated. The disease itself, alongside treatments and psychological stressors, increases the prevalence of sarcopenia in bone tumor patients. Nurses play a crucial role in early detection, assessment, and intervention, making it essential to incorporate validated and practical sarcopenia screening tools into routine nursing assessments. By identifying patients at risk of sarcopenia early, nurses can implement tailored interventions that focus on maintaining or improving muscle strength, nutritional status, and overall physical function. This proactive approach can enhance postoperative recovery, reduce the severity of chemotherapy side effects, shorten hospital stays, and lower healthcare costs among bone tumor patients.
Additionally, the study highlights the importance of individualized patient education. Nurses can educate bone tumor patients and their families about the risks of sarcopenia, the importance of maintaining muscle mass through proper nutrition and physical activity, and how to recognize early signs of sarcopenia. These efforts can empower patients to take an active role in their care, potentially improving outcomes and quality of life in bone tumor patients. The study underscores the need for further research to validate and refine sarcopenia screening tools specifically for bone tumor patients, considering the unique characteristics of this population.
4.1 Study limitations
This study compared the effectiveness of five sarcopenia screening tools in bone tumor patients, identifying the best tools for early detection and providing a basis for prevention and further research. Although these tools were primarily developed for elderly populations, the inclusion of younger patients (≥ 18 years old) highlighted that sarcopenia can also affect non-elderly individuals. This emphasizes the need for healthcare professionals to pay greater attention to sarcopenia in bone tumor patients. However, the study has several limitations. First, the sample was small and drawn from a single hospital. Future studies should expand the sample size and include multicenter surveys of different types and stages of bone tumors to enhance the predictive power of these tools. Second, the study did not conduct longitudinal follow-up or evaluate the predictive value of the tools for adverse outcomes. Third, while BIA was used for muscle measurement, more accurate methods, such as CT, MRI, or dual-energy X-ray, could provide more precise assessments. Furthermore, the study focused on a specific cancer type and a particular ethnic group, which may limit the applicability of the findings to other cancer types or ethnicities. Finally, this study is the use of single-center, convenience-based sampling and the cross-sectional nature of the study, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
4.2 Study implications
This study identified the SARC-F + EBM questionnaire and the combined use of SARC-F, SARC-Calf, and SARC-F + EBM as the top-performing tools for sarcopenia screening in bone tumor patients. The SARC-F + EBM demonstrated exceptional diagnostic performance, with high sensitivity, specificity, and an AUC of 0.88, making it highly effective for early detection. The combined approach further improved accuracy by comprehensively assessing muscle strength, physical performance, muscle mass, age, and nutritional status. For practical implementation, healthcare professionals should prioritize early screening using these validated tools in clinical settings, particularly for bone tumor patients at risk due to reduced mobility or malnutrition. Nurses should be trained to incorporate these tools into routine assessments to facilitate timely intervention. Additionally, individualized patient education on maintaining muscle mass through nutrition and physical activity is essential to improve outcomes. Further research is recommended to refine these tools for bone tumor patients and adapt them to diverse populations.
5 Conclusion
The study concludes that among these five screening tools for sarcopenia in bone tumor patients, the SARC-F + EBM and SARC-Calf methods exhibit higher accuracy than the SARC-F, MSRA-7, and MSRA-5 tools, for identifying sarcopenia in patients with bone tumors. These two tools are recommended as the most effective for clinical healthcare professionals in screening for sarcopenia. Furthermore, the combined use of SARC-F, SARC-Calf, and SARC-F + EBM yields even greater screening efficacy.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
This study involving human subjects was approved by the Ethics Committee of Yunnan Cancer Hospital (SLKYLX2023-171). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
JY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. QG: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft. LZ: Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JC: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by 2023 Teaching Alliance Undergraduate Education and Teaching Research Project of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University (JXYJ20230105).
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants involved in this study for their contributions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1584706/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Chaiamnuay S, Kanjanavaikoon N, Saisirivechakun P. Comparative evaluation of screening tools for sarcopenia in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:14407. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65120-2
2. Coleman R, Croucher P, Padhani A, Clézardin P, Chow E, Fallon M, et al. Bone metastases. Nat Rev Dis Prim. (2020) 6:83. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00216-3
3. Xi Y, Qiao L, Na B, Liu H, Zhang S, Zheng R, et al. Primary malignant bone tumors incidence, mortality, and trends in China from 2000 to 2015. Chin Med J (Engl). (2023) 136:2037–43. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002547
4. Davis M, Panikkar R. Sarcopenia associated with chemotherapy and targeted agents for cancer therapy. Ann Palliat Med. (2019) 8:86–101. doi: 10.21037/apm.2018.08.02
5. Simonsen C, de Heer P, Bjerre ED, Suetta C, Hojman P, Pedersen B, et al. Sarcopenia and postoperative complication risk in gastrointestinal surgical oncology: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg. (2018) 268:58–69. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002679
6. Cruz-Jentoft A, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. (2019) 48:16–31. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afy169
7. Chen L, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung T, Chou M, Iijima K, et al. Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2020) 21:300–07.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012
8. Welford J, Rafferty R, Hunt K, Short D, Duncan L, Ward A, et al. The clinical frailty scale can indicate prognosis and care requirements on discharge in oncology and haemato-oncology inpatients: a cohort study. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). (2022) 31:e13752. doi: 10.1111/ecc.13752
9. Hansen T, Omland L, von Heymann A, Johansen C, Clausen M, Suetta C, et al. Development of sarcopenia in patients with bladder cancer: a systematic review. Semin Oncol Nurs. (2021) 37:151108. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2020.151108
10. Ní Bhuachalla ÉB, Daly LE, Power DG, Cushen SJ, MacEneaney P, Ryan AM. Computed tomography diagnosed cachexia and sarcopenia in 725 oncology patients: is nutritional screening capturing hidden malnutrition? J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2018) 9:295–305. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12258
11. Baracos V, Mazurak V, Bhullar A. Cancer cachexia is defined by an ongoing loss of skeletal muscle mass. Ann Palliat Med. (2019) 8:3–12. doi: 10.21037/apm.2018.12.01
12. Stringer H, Wilson D. The role of ultrasound as a diagnostic tool for sarcopenia. J Frailty Aging. (2018) 7:258–61. doi: 10.14283/jfa.2018.24
13. Chen C, Tseng W, Yang Y, Chen C, Lin L, Chen F, et al. Calf circumference as an optimal choice of four screening tools for sarcopenia among ethnic chinese older adults in assisted living. Clin Interv Aging. (2020) 15:2415–22. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S287207
14. Malmstrom T, Morley JE. SARC-F: a simple questionnaire to rapidly diagnose sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2013) 14:531–2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.05.018
15. Wang X. The sinicization of the questionnaire for sarcopenia in the elderly and the therapeutic effect of exercise therapy on sarcopenia: a meta-analysis. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Medical University (2018).
16. Barbosa-Silva T, Menezes A, Bielemann R, Malmstrom T, Gonzalez M, Enhancing S. Improving sarcopenia screening in the clinical practice. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2016) 17:1136–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2016.08.004
17. Kurita N, Wakita T, Kamitani T, Wada O, Mizuno K. SARC-F validation and SARC-F+EBM derivation in musculoskeletal disease: the SPSS-OK study. J Nutr Health Aging. (2019) 23:732–8. doi: 10.1007/s12603-019-1222-x
18. Rossi A, Micciolo R, Rubele S, Fantin F, Caliari C, Zoico E, et al. Assessing the risk of sarcopenia in the elderly: the mini sarcopenia risk assessment (MSRA) questionnaire. J Nutr Health Aging. (2017) 21:743–9. doi: 10.1007/s12603-017-0921-4
19. Yang M, Hu X, Xie L, Zhang L, Zhou J, Lin J, et al. Validation of the Chinese version of the mini sarcopenia risk assessment questionnaire in community-dwelling older adults. Medicine (Baltimore). (2018) 97:e12426. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012426
20. Oh M, Shin H, Kim K, Won C, Kim M. Combinations of sarcopenia diagnostic criteria by asian working group of sarcopenia (AWGS) 2019 guideline and incident adverse health outcomes in community-dwelling older adults. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2023) 24:1185–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2023.04.005
21. Ban Y, Manabu H, Oebisu N, Shimatani A, Takada N, Nakamura H. Outcomes of sarcopenia treatment for malignant bone and soft tissue tumors in elderly patients. Cancer Diagn Progn. (2022) 2:194–200. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10094
22. Oflazoglu U, Alacacioglu A, Varol U, Kucukzeybek Y, Salman T, Taskaynatan H, et al. Prevalence and related factors of sarcopenia in newly diagnosed cancer patients. Support Care Cancer. (2020) 28:837–43. doi: 10.1007/s00520-019-04880-4
23. Surov A, Wienke A. Prevalence of sarcopenia in patients with solid tumors: a meta-analysis based on 81,814 patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2022) 46:1761–8. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2415
24. Migliorini F, Maffulli N, Trivellas A, Eschweiler J, Tingart M, Driessen A. Bone metastases: a comprehensive review of the literature. Mol Biol Rep. (2020) 47:6337–45. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05684-0
25. Haiducu C, Buzea A, Mirea L, Dan G. The prevalence and the impact of sarcopenia in digestive cancers. A systematic review. Rom J Intern Med. (2021) 59:328–44. doi: 10.2478/rjim-2021-0026
26. Fearon K, Strasser F, Anker S, Bosaeus I, Bruera E, Fainsinger R, et al. Definition and classification of cancer cachexia: an international consensus. Lancet Oncol. (2011) 12:489–95. doi: 10.1016/S1470-204570218-7
27. Sun Q, Jiang X, Qin R, Yang Y, Gong Y, Wang K, et al. Sarcopenia among older patients with cancer: a scoping review of the literature. J Geriatr Oncol. (2022) 13:924–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2022.03.008
28. Rathnayake N, Abeygunasekara T, Liyanage G, Subasinghe S, De Zoysa W, Palangasinghe D, et al. SARC-F: an effective screening tool for detecting sarcopenia and predicting health-related quality of life in older women in Sri Lanka. BMC Geriatr. (2025) 25:129. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-05786-z
29. Ma Y, Wu Y, Dou J. Comparison of the validity of 4 community sarcopenia screening tools for MHD sarcopenia patients. Chin Nurs Res. (2022) 36:2886–91.
30. Hanai T, Hiraoka A, Shiraki M, Sugimoto R, Taniki N, Hiramatsu A, et al. Utility of the SARC-F questionnaire for sarcopenia screening in patients with chronic liver disease: a multicenter cross-sectional study in Japan. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:3448. doi: 10.3390/jcm10153448
31. Wu T, Liaw C, Chen F, Kuo K, Chie W, Yang R. Sarcopenia screened with SARC-F questionnaire is associated with quality of life and 4-year mortality. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2016) 17:1129–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2016.07.029
32. Mo Y, Zhong J, Dong X, Su Y, Deng W, Yao X, et al. Comparison of three screening methods for sarcopenia in community-dwelling older persons. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2021) 22:746–50.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2020.05.041
33. Gonzalez M, Mehrnezhad A, Razaviarab N, Barbosa-Silva T, Heymsfield S. Calf circumference: cutoff values from the NHANES 1999-2006. Am J Clin Nutr. (2021) 113:1679–87. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqab029
34. Nishikawa H, Yoh K, Enomoto H, Iwata Y, Sakai Y, Kishino K, et al. Calf circumference as a useful predictor of sarcopenia in patients with liver diseases. In Vivo. (2020) 34:2561–9. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12073
35. Inoue T, Maeda K, Shimizu A, Nagano A, Ueshima J, Sato K, et al. Calf circumference value for sarcopenia screening among older adults with stroke. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2021) 93:104290. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2020.104290
36. Bahat G, Oren M, Yilmaz O, Kılıç C, Aydin K, Karan M. Comparing SARC-F with SARC-CalF to screen sarcopenia in community living older adults. J Nutr Health Aging. (2018) 22:1034–8. doi: 10.1007/s12603-018-1072-y
37. Xu Z, Zhang P, Chen Y, Jiang J, Zhou Z, Zhu H. Comparing SARC-CalF with SARC-F for screening sarcopenia in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:803924. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.803924
38. Kandinata S, Widajanti N, Ichwani J, Firdausi H, Aryana I, Alkaff F. Diagnostic performance of calf circumference, SARC-F, and SARC-CalF for possible sarcopenia screening in Indonesia. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:9824. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36585-4
39. Lau E, Lynn H, Woo J, Kwok T, Melton L. Prevalence of and risk factors for sarcopenia in elderly Chinese men and women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2005) 60:213–6. doi: 10.1093/gerona/60.2.213
Keywords: sarcopenia, screening tool, sensitivity and specificity, bone tumor, Chinese patients
Citation: Yu J, Guan Q, Chen Y, Zhou L, Chen J and Zeng Y (2025) Comparative assessment of sarcopenia screening tools for patients with bone tumors: insights for enhanced clinical application. Front. Nutr. 12:1584706. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1584706
Received: 27 February 2025; Accepted: 11 July 2025;
Published: 04 August 2025.
Edited by:
Sofi G. Julien, Holy Spirit University of Kaslik, LebanonReviewed by:
Mireille Serhan, University of Balamand, LebanonRamesh Bhandari, KLE College of Pharmacy, India
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Guan, Chen, Zhou, Chen and Zeng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jian Chen, bnVyc2luZ2RpcmVjdG9yMDFAZ21haWwuY29t; Yingchun Zeng, Y2hsb2V6ZW5neWNAaG90bWFpbC5jby51aw==
†These authors share first authorship
‡ORCID: Yingchun Zeng, orcid.org/0000-0001-9250-4086
 Jun Yu1,2†
Jun Yu1,2† Yingchun Zeng
Yingchun Zeng