- 1The First Clinical College, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China
- 2Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China
- 3Institute of Literature in Chinese Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China
Background: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. This study investigates the association between H. pylori seropositivity and the newly proposed hemoglobin A1c/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (HbA1c/HDL-C ratio) in a nationally representative U.S. population.
Methods: Data from the 1999–2000 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) were analyzed. Multivariable linear regression models assessed the association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio. Subgroup analyses were performed to evaluate the consistency of the association across different demographic and clinical strata. Generalized additive models with smoothing splines and threshold effect analysis was conducted to identify potential nonlinear relationships.
Results: The cross-sectional analysis comprised 2,909 participants, including 1,254 with H. pylori seropositivity. After multivariable adjustment, a significant positive association was found between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio (β: 0.28, 95% CI: 0.13, 0.42). Subgroup analyses revealed a stronger association among non-diabetic individuals compared to diabetic individuals. A “L”-shaped relationship was observed, with an inflection point at an HbA1c/HDL-C ratio of 4.81. Below this threshold, H. pylori seropositivity was positively associated with the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio. Above this threshold, the association was no longer statistically significant.
Conclusion: This study identifies a significant association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio, suggesting that metabolic dysfunction may be linked to H. pylori infection. Future longitudinal studies are needed to establish causality and explore underlying mechanisms.
1 Introduction
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is one of the most prevalent chronic bacterial infections in the world, affecting about half of the global population (1, 2). It is a major cause of several gastrointestinal disorders, including chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer and gastric cancer (3, 4). In addition, many extra-gastric diseases have been shown to be associated with H. pylori infection, such as metabolic, cardiovascular and neurological disorders (5–7).
Emerging evidence suggests that H. pylori infection may contribute to systemic metabolic disturbances, including insulin resistance (IR) and metabolic syndrome (8–10). This association appears to be bidirectional, with individuals who already exhibit metabolic disturbances being more prone to persistent H. pylori infection (11). However, the existing literature presents inconsistent results, underscoring the necessity for novel biomarkers to disentangle this intricate interplay. In recent years, the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio has been introduced as a comprehensive indicator of both glucose and lipid metabolism. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), a marker reflecting average blood glucose levels over the past 2–3 months, provides insight into long-term glycemic control (12, 13). On the other hand, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, plays a key role in lipid metabolism and is generally regarded as a protective factor against cardiovascular diseases (14). Thus, the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio serves as a refined measure of the interplay between glucose regulation and lipid balance, offering valuable information about overall metabolic state. This ratio has gained considerable attention for its potential in assessing the risk of various conditions, including carotid atherosclerosis (15), stroke (16), and metabolic associated fatty liver disease (17). Despite its promising clinical significance, no studies have yet examined the relationship between the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio and H. pylori infection.
This study aims to investigate the association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio in a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults. By exploring this relationship, we seek to identify potential metabolic markers for H. pylori susceptibility and provide new insights into the interplay between metabolic health and infectious diseases.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design and population
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a nationally representative, cross-sectional program designed to assess the health and nutritional status of the non-institutionalized civilian population in the U.S. (18, 19). Employing a complex, multi-stage probability sampling design, NHANES collects data through structured interviews, standardized physical examinations, and comprehensive laboratory analyses, providing a robust platform for evaluating a wide range of health indicators (19–21). All study protocols were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
This study utilized data from the 1999–2000 NHANES cycle. Initially, 4,480 participants aged 20 years or older were included. After excluding individuals with incomplete data on the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio (n = 764) and H. pylori serological status (n = 116), as well as those with missing covariates such as education level (n = 13), marital status (n = 431), poverty income ratio (PIR) (n = 484), drinking status (n = 143), smoking status (n = 3), and body mass index (BMI) (n = 17), a total of 2,909 participants were included in the final analysis (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Flow chart of participants selection. H. pylori, Helicobacter pylori; PIR, poverty income ratio; BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
2.2 Assessment of Helicobacter pylori seropositivity status
Helicobacter pylori seropositivity status was assessed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to quantify anti-H. pylori immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody levels (22). Participants were classified into two groups based on established ELISA cutoff values: H. pylori-positive (optical density [OD] value ≥1.1) and H. pylori-negative (OD value < 0.9). Ambiguous results within the range of 0.9 to 1.1 were excluded from the analysis to ensure precise statistical outcomes, consistent with previous epidemiological studies (23–25).
2.3 Assessment of the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio
Fasting blood samples were analyzed to measure HbA1c and HDL-C levels. The HbA1c/HDL-C ratio was calculated by dividing HbA1c (%) by HDL-C (mg/dL) (15). Participants were categorized into quartiles (Q1 to Q4) based on their HbA1c/HDL-C ratio values, with quartile thresholds determined by dividing the study population into four equal groups.
2.4 Assessment of covariates
To ensure comprehensive adjustments in the analysis, relevant sociodemographic characteristics, lifestyle behaviors, and comorbid health conditions were included as covariates. Sociodemographic variables encompassed age, sex, race, education level, marital status, and PIR. Lifestyle factors included drinking status (classified as <12 or ≥12 alcoholic drinks per year) and smoking status (categorized as never, former, or current smoker). Health conditions were assessed using a combination of self-reported data and objective clinical measurements. BMI was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (kg/m2) and classified into normal weight (<25), overweight (≥25 and <30), and obesity (≥30) (26). Hypertension was defined as a self-reported physician diagnosis, use of antihypertensive medications, or elevated blood pressure (systolic ≥130 mmHg or diastolic ≥80 mmHg) (27). Cardiovascular disease, encompassing coronary heart disease, angina, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, and stroke, was ascertained through self-reported diagnoses provided by healthcare professionals (28).
2.5 Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using appropriate NHANES sampling weights to account for the complex, multi-stage cluster survey design. Baseline characteristics of participants were described using weighted means (95% confidence intervals [CIs]) for continuous variables and weighted percentages (95% CIs) for categorical variables. Differences in baseline characteristics were assessed using weighted linear regression for continuous variables and weighted chi-square test for categorical variables.
The association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio was evaluated using multivariable linear regression models. Crude model was unadjusted, Model 1 adjusted for age, sex, and race, and Model 2 further adjusted for education, marital status, PIR, drinking status, smoking status, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Results were reported as beta (β) coefficients with corresponding 95% CIs. Subgroup analyses were conducted to examine the association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio across different age, sex, race, PIR, BMI, and disease histories (hypertension and cardiovascular disease). Interaction tests were used to evaluate the consistency of these associations across subgroups.
As a sensitivity analysis, we performed logistic regression analyses with H. pylori seropositivity as the dependent variable and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio as the independent variable. Both continuous and quartile-based forms of the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio were included in the regression analyses. Results were reported as odds ratios (ORs) with corresponding 95% CIs.
To explore potential non-linear relationships between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio, generalized additive models with smoothing splines were employed. Additionally, recursive algorithms and two-stage logistic models were utilized to detect any potential inflection points in the relationship. Likelihood ratio tests were performed to compare the fit of single logistic regression models with that of two-stage logistic models.
All analyses were performed using R (http://www.R-project.org, version 4.3.1) and EmpowerStats (http://www.empowerstats.com, version 4.2). Statistical significance was defined as a two-sided p value < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
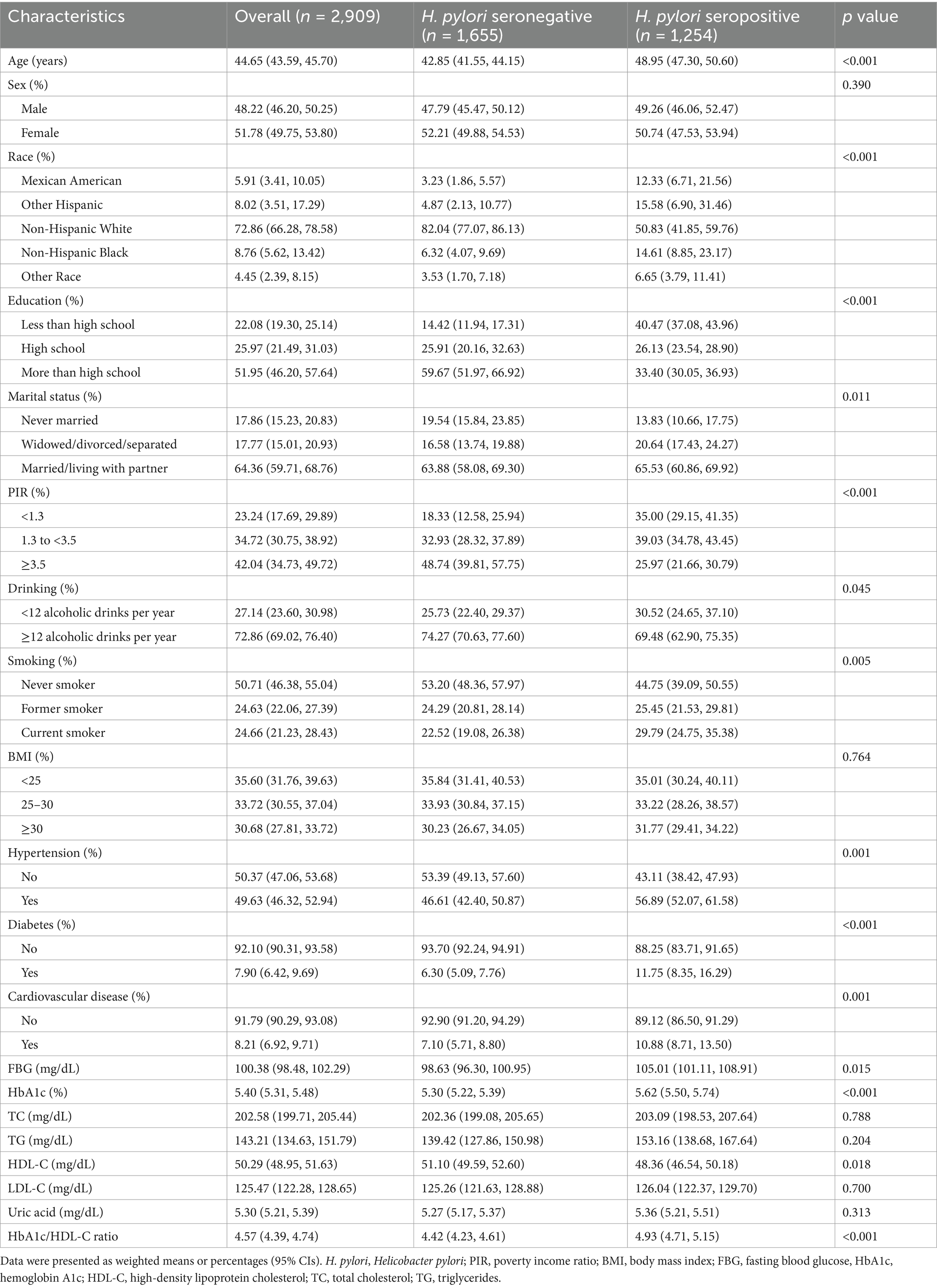
This analysis included 2,909 U.S. adults with a weighted mean age of 44.65 years (95% CI: 43.59, 45.70), of whom 48.22% were male and 43.8% exhibited H. pylori seropositive. Table 1 summarizes the comparative analysis of demographic, socioeconomic, and clinical characteristics between H. pylori seropositive and seronegative participants. Within the H. pylori seropositive group, there was a greater proportion of older individuals and Mexican Americans. They also had lower levels of education, lower PIR, and were more likely to be married or living with a partner. Additionally, H. pylori seropositive participants were more likely to be smokers and less likely to consume alcohol. Furthermore, individuals with H. pylori seropositive exhibited higher prevalence rates of hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. However, traditional metabolic markers, such as TC, TG, LDL-C, and uric acid, did not differ significantly between the two groups. Notably, the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio was significantly higher among H. pylori seropositive participants.
3.2 Association between Helicobacter pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio
Table 2 presents the associations between H. pylori seropositivity and HbA1c/HDL-C ratio. The results indicated that H. pylori seropositivity was positively associated with the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio in the unadjusted model (β: 0.55, 95% CI: 0.41, 0.69), the partially adjusted model (β: 0.36, 95% CI: 0.22, 0.51), and the fully adjusted model (β: 0.28, 95% CI: 0.13, 0.42).
3.3 Subgroup analysis
Subgroup analyses and interaction tests were conducted to evaluate the consistency of the association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio across various demographic and clinical subgroups, including age, sex, race, PIR, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease (Figure 2). The positive association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio was generally consistent across most subgroups (P for interaction >0.05). However, a significant interaction was identified for diabetes status (P for interaction = 0.038). Specifically, the association was stronger in individuals without diabetes (β: 0.31, 95% CI: 0.19, 0.43) compared to those with diabetes (β: 0.21, 95% CI: −0.03, 0.45).
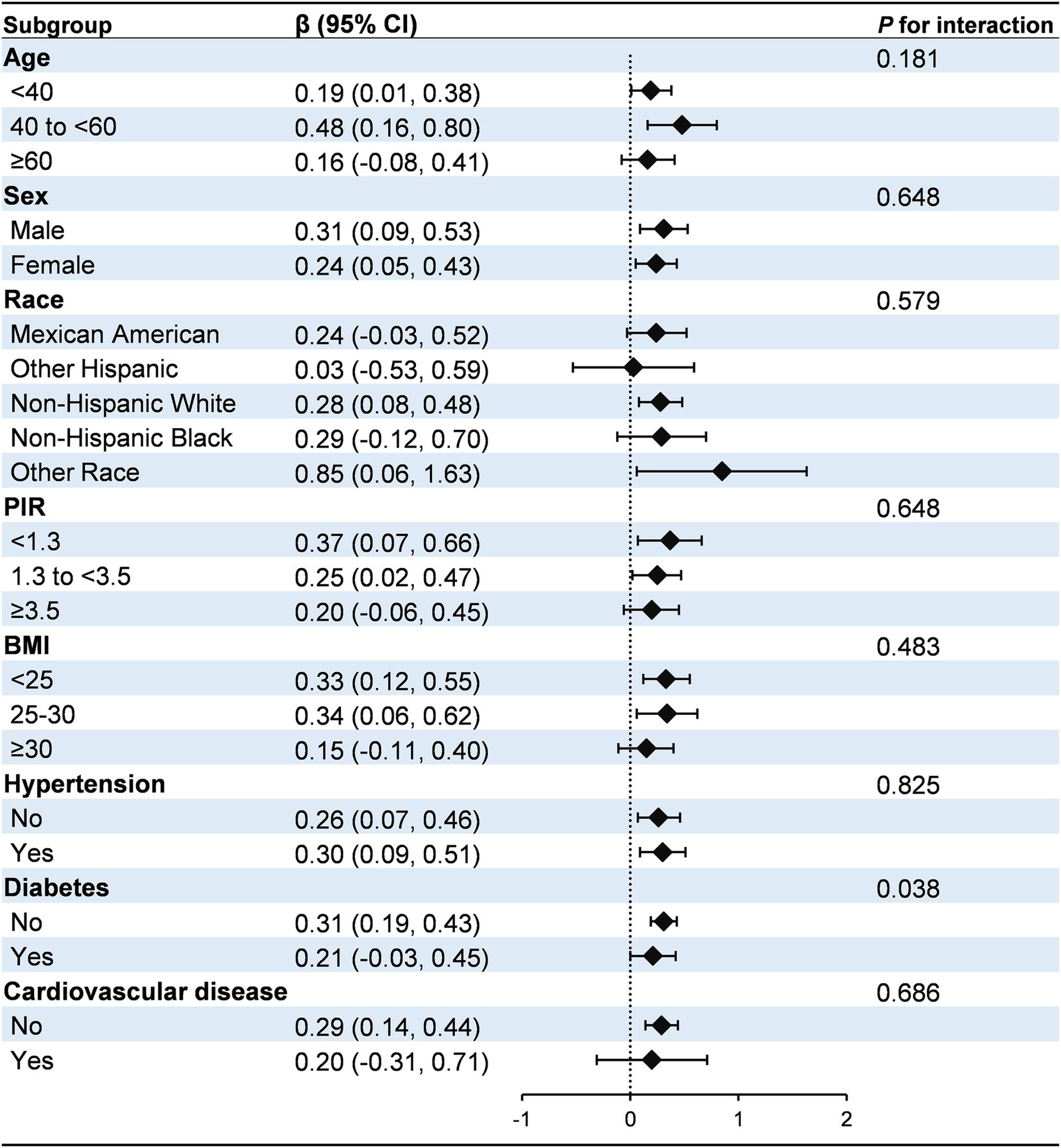
Figure 2. Subgroup analysis for the association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio. The model was adjusted for age, sex, race, education, marital status, PIR, drinking, smoking, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes was identified based on self-reported physician diagnosis, use of insulin or glucose-lowering medications, fasting blood glucose levels ≥126 mg/dL, or glycated hemoglobin levels ≥6.5%. PIR, poverty income ratio; BMI, body mass index.
3.4 Sensitivity analysis
To further validate the robustness of our findings, we conducted additional sensitivity analyses. In the fully adjusted model, participants in the highest quartile (Q4) of the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio exhibited an 84% increased probability of H. pylori seropositivity (OR: 1.75, 95% CI: 1.38, 2.44) compared to those in the lowest quartile (Q1). Notably, trend tests confirmed the statistical significance of the overall positive association between the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio and H. pylori seropositivity (all P for trend <0.05) (Supplementary Table 1).
3.5 Dose–response relationship between Helicobacter pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio
Generalized additive models with smoothing splines revealed a nonlinear, L-shaped association between the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio and H. pylori seropositivity (Figure 3). Threshold effect analysis identified an inflection point at an HbA1c/HDL-C ratio of 4.81. Below this threshold, a significant positive association was observed between the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio and H. pylori seropositivity (OR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.14, 1.46), whereas no significant association was observed above the threshold (OR: 1.02, 95% CI: 0.96, 1.09). The log-likelihood ratio test confirmed the superiority of the two-piecewise linear regression model over the one-line linear model (p = 0.003) (Supplementary Table 2). We constructed stratified curves for the association between the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio and H. pylori seropositivity by diabetes status (Supplementary Figure 1). In non-diabetic individuals, the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio exhibited a linear association with H. pylori seropositivity (OR: 1.19, 95% CI: 1.10, 1.28), and the log-likelihood ratio test (p = 0.205) supported the adequacy of the linear model. Among diabetic individuals, no significant association between the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio and H. pylori seropositivity was found (Supplementary Table 3).

Figure 3. The association between the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio and H. pylori seropositivity. The red line represents the smooth curve fit between variables, with blue bands representing the 95% CI of the fit. The model was adjusted for age, sex, race, education, marital status, PIR, drinking, smoking, BMI, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. H. pylori, Helicobacter pylori; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
4 Discussion
In this cross-sectional study conducted among U.S. population, we identified a significant positive association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio. Notably, we observed a “L”-shaped relationship between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio, with an inflection point at 4.81. Below this threshold, H. pylori seropositivity was positively associated with the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio. However, above this value, no significant association was detected.
H. pylori infection may increase the risk of metabolic dysfunction. A systematic review has reported a positive correlation between H. pylori infection and metabolic syndrome, with infected individuals exhibiting elevated levels of TG, fasting blood glucose (FBG), BMI, and reduced HDL-C (29). Several studies have also demonstrated that H. pylori infection is linked to abnormal glucose metabolism and an increased risk of diabetes (30–32). Specifically, individuals with H. pylori infection exhibit significantly higher HbA1c levels compared to uninfected individuals, and a positive correlation has been observed between H. pylori infection and elevated HbA1c levels in diabetic patients (33). These findings suggest that H. pylori infection may be closely associated with IR-related disorders. However, the relationship between H. pylori infection and markers such as HbA1c and IR remains controversial. For instance, a large cross-sectional study involving 37,263 participants found that H. pylori infection was associated only with dyslipidemia, showing no significant correlation with FBG or HbA1c levels (34). In addition to its potential impact on glucose metabolism, H. pylori infection has been shown to significantly influence lipid profiles. Studies indicate that individuals with H. pylori infection tend to exhibit elevated levels of TC, TG and LDL-C, alongside reduced HDL-C levels (35–37). Notably, the prevalence of dyslipidemia is significantly lower in individuals who have undergone H. pylori eradication compared to those with active infection (38). Eradication of H. pylori has been associated with improved lipid profiles, including increased HDL-C levels and decreased TG and LDL-C levels (39, 40). These findings demonstrate the complexity of the relationship between H. pylori infection and metabolic disorders and suggest that more research is needed to focus on the association between H. pylori infection and abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism.
Glucose and lipid metabolism interact through complex physiological and pathological processes (41, 42). The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, derived from FPG and TG levels, has emerged as a reliable marker of IR and metabolic dysfunction (43, 44). Previous studies have shown that an elevated TyG index is associated with an increased risk of H. pylori infection (24, 45). Compared to the short-term glucose indicators used in the TyG index, HbA1c reflects long-term glucose control and provides a more stable measure than fasting glucose (46). Our findings are consistent with studies using the TyG index, revealing the close association between H. pylori seropositivity and glycolipid metabolism. The HbA1c/HDL-C ratio may offer more stable and clinically meaningful insights into the relationship between H. pylori infection and metabolic dysfunction.
In this study, we identified a saturation effect in the relationship between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio using segmented regression analysis. Within the lower range of the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio, mild disturbances in glucose and lipid metabolism were associated with a higher probability of H. pylori seropositivity. However, beyond a certain threshold, this association was no longer significant. This saturation effect aligns with previous observations of nonlinear relationships between metabolic indicators and health outcomes (16, 47), suggesting that the association between metabolic status and H. pylori infection may vary depending on the severity of metabolic disturbances.
Subgroup analyses revealed that the association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio was more pronounced in individuals without diabetes than in those with diabetes. This discrepancy may be attributed to the complex metabolic disturbances in individuals with diabetes, characterized by hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia, which could obscure the relationship between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio (48, 49). Unfortunately, our study lacked detailed data on disease duration, treatment regimens, and the presence of complications, limiting our ability to explore these potential influences. Additionally, glycemic and lipid-lowering therapies, which are common in diabetes management, may alter the measurement of the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio and impact H. pylori colonization or eradication, thereby attenuating the observed association (50, 51). Our findings suggest that H. pylori seropositivity is positively associated with the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio, especially in non-diabetic populations. Future research should explore the mechanisms underlying this association and develop personalized strategies for metabolic management.
The potential mechanisms underlying the association between the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio and H. pylori infection are multifaceted. H. pylori infection induces systemic inflammation through the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6, which disrupt insulin signaling pathways and exacerbate insulin resistance (52, 53). Moreover, H. pylori infection may alter the gastric environment, influencing gut microbiota composition and contributing to systemic inflammation and metabolic dysregulation (54, 55). The relationship between metabolic disorders and H. pylori infection appears to be bidirectional. Metabolic dysfunction, characterized by IR, hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia, promotes oxidative stress and impairs gastric mucosal defenses, thereby creating a favorable environment for H. pylori colonization and persistence (10, 56, 57). Additionally, IR-related autonomic dysfunction may slow gastrointestinal motility and reduce gastric acid secretion, further facilitating H. pylori survival (58–60). These interconnected mechanisms highlight the complex interplay between metabolic health and H. pylori infection, with the exact mechanisms warranting further investigation.
This study is the first to investigate the association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio. A key strength of this study is its use of a large, nationally representative sample of U.S. adults, which enhances the generalizability of the findings to broader populations. However, several limitations should be noted. First, as a cross-sectional study, it cannot establish a causal relationship between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio. Further longitudinal studies are needed to clarify the directionality of this association. Second, the NHANES database provides only serological data on H. pylori infection status, which precludes differentiation between past and current infections among seropositive participants. Although serology is a widely used and reliable method for assessing H. pylori status in large epidemiological studies (25, 28), it does not capture the activity of infection, thereby limiting our ability to assess the relationship between chronic versus acute infection and metabolic disturbances. Third, there may be unmeasured confounding factors, such as genetic predisposition, unaccounted medication use, and environmental influences, which could affect the observed association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio. Finally, the study focused exclusively on a U.S. population, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other ethnic or geographic groups.
5 Conclusion
This study identifies a positive association between H. pylori seropositivity and the HbA1c/HDL-C ratio in a nationally representative sample. The findings suggest that this metabolic marker may serve as a potential indicator of H. pylori infection in clinical settings. Future longitudinal studies are needed to establish causality and explore underlying mechanisms.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the National Center for Health Statistics Research Ethics Review Board provided ethics approval (Protocol #98-12). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
CX: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. X-yJ: Data curation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. J-mL: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. Y-fZ: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. J-yH: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. C-CL: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. HS: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by High-level Key Discipline Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Guozhong Pharmaceutical Renjiao Letter [2022] No. 75 and [2023] No. 85) and the study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China [grant number 2022YFC3500201].
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all NHANES staff and participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1589510/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Li, Y, Choi, H, Leung, K, Jiang, F, Graham, DY, and Leung, WK. Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection between 1980 and 2022: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:553–64. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00070-5
2. Chen, YC, Malfertheiner, P, Yu, HT, Kuo, CL, Chang, YY, Meng, FT, et al. Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and incidence of gastric Cancer between 1980 and 2022. Gastroenterology. (2024) 166:605–19. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.022
3. Malfertheiner, P, Camargo, MC, El-Omar, E, Liou, JM, Peek, R, Schulz, C, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2023) 9:19. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00431-8
4. Usui, Y, Taniyama, Y, Endo, M, Koyanagi, YN, Kasugai, Y, Oze, I, et al. Helicobacter pylori, homologous-recombination genes, and gastric Cancer. N Engl J Med. (2023) 388:1181–90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2211807
5. Kountouras, J, Papaefthymiou, A, Polyzos, SA, Liatsos, C, Tzitiridou-Chatzopoulou, M, Chatzopoulos, D, et al. Potential impact of Helicobacter pylori and metabolic syndrome-related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease on cardio-cerebrovascular disease. Metabolism. (2022) 135:155276. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155276
6. Sun, L, Zheng, H, Qiu, M, Hao, S, Liu, X, Zhu, X, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of cardiovascular disease. Helicobacter. (2023) 28:e12967. doi: 10.1111/hel.12967
7. Wang, F, Yao, Z, Jin, T, Mao, B, Shao, S, and Shao, C. Research progress on Helicobacter pylori infection related neurological diseases. Ageing Res Rev. (2024) 99:102399. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102399
8. Chen, C, Zhang, C, Wang, X, Zhang, F, Zhang, Z, Ma, P, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection may increase the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via promoting liver function damage, glycometabolism, lipid metabolism, inflammatory reaction and metabolic syndrome. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 32:857–66. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001601
9. Izhari, MA, Al Mutawa, OA, Mahzari, A, Alotaibi, EA, Almashary, MA, Alshahrani, JA, et al. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection-associated dyslipidemia in the Asir region of Saudi Arabia. Life (Basel). (2023) 13:2206. doi: 10.3390/life13112206
10. Qiu, J, Yu, Y, Liu, D, Chen, S, Wang, Y, Peng, J, et al. Association between non-insulin-based insulin resistance surrogate makers and Helicobacter pylori infection: a population-based study. BMC Gastroenterol. (2025) 25:25. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03610-x
11. Baradaran, A, Dehghanbanadaki, H, Naderpour, S, Pirkashani, LM, Rajabi, A, Rashti, R, et al. The association between Helicobacter pylori and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. (2021) 7:15. doi: 10.1186/s40842-021-00131-w
12. Balintescu, A, and Mårtensson, J. Hemoglobin A1c and permissive hyperglycemia in patients in the intensive care unit with diabetes. Crit Care Clin. (2019) 35:289–300. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2018.11.010
13. Yazdanpanah, S, Rabiee, M, Tahriri, M, Abdolrahim, M, Rajab, A, Jazayeri, HE, et al. Evaluation of glycated albumin (GA) and GA/HbA1c ratio for diagnosis of diabetes and glycemic control: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. (2017) 54:219–32. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2017.1299684
14. Mineo, C, and Shaul, PW. Novel biological functions of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Circ Res. (2012) 111:1079–90. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.258673
15. Hu, X, Li, W, Wang, C, Zhang, H, Lu, H, Li, G, et al. Association between the plasma-glycosylated hemoglobin A1c/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and carotid atherosclerosis: a retrospective study. J Diabetes Res. (2021) 2021:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2021/9238566
16. Huang, C, You, H, Zhang, Y, Fan, L, Feng, X, and Shao, N. Association between the hemoglobin A1c/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and stroke incidence: a prospective nationwide cohort study in China. Lipids Health Dis. (2025) 24:25. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02438-4
17. He, S, Lu, S, Yu, C, Kuang, M, Qiu, J, Sheng, G, et al. The newly proposed plasma-glycosylated hemoglobin A1c/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio serves as a simple and practical indicator for screening metabolic associated fatty liver disease: an observational study based on a physical examination population. BMC Gastroenterol. (2024) 24:274. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03362-0
18. Ogden, CL, Carroll, MD, Kit, BK, and Flegal, KM. Prevalence of obesity and trends in body mass index among US children and adolescents, 1999-2010. JAMA. (2012) 307:483–90. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.40
19. Xu, C, Song, Z, Wang, JN, and Li, CC. Association of visceral adiposity index with phenotypic age acceleration: insight from NHANES 1999-2010. J Nutr Health Aging. (2024) 28:100323. doi: 10.1016/j.jnha.2024.100323
20. Paulose-Ram, R, Graber, JE, Woodwell, D, and Ahluwalia, N. The National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES), 2021-2022: adapting data collection in a COVID-19 environment. Am J Public Health. (2021) 111:2149–56. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2021.306517
21. Song, Z, Gu, HQ, and Xu, C. Association of the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatic steatosis in United States adults: insights from NHANES 2017-2020. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1540903. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1540903
22. Berrett, AN, Gale, SD, Erickson, LD, Brown, BL, and Hedges, DW. Folate and inflammatory markers moderate the association between Helicobacter pylori exposure and cognitive function in US adults. Helicobacter. (2016) 21:471–80. doi: 10.1111/hel.12303
23. Xiong, YJ, Du, LL, Diao, YL, Wen, J, Meng, XB, Gao, J, et al. Association of dietary inflammatory index with helicobacter pylori infection and mortality among US population. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:538. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04398-8
24. Zhu, XY, Xiong, YJ, Meng, XD, Xu, HZ, Huo, L, and Deng, W. Association of triglyceride-glucose index with helicobacter pylori infection and mortality among the US population. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2024) 16:187. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01422-9
25. Qiu, J, Fang, H, Liu, D, Lai, Q, Xie, J, Wang, Y, et al. Accelerated biological aging mediates the association between inflammatory markers with Helicobacter pylori infection and mortality. J Transl Med. (2025) 23:174. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06189-9
26. Chen, C, Ye, Y, Zhang, Y, Pan, XF, and Pan, A. Weight change across adulthood in relation to all cause and cause specific mortality: prospective cohort study. BMJ. (2019) 367:l5584. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l5584
27. Whelton, PK, Carey, RM, Aronow, WS, Casey, DE Jr, Collins, KJ, Dennison, C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2018) 71:e127–248. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.006
28. Tang, C, Zhang, Q, Zhang, C, Du, X, Zhao, Z, and Qi, W. Relationships among Helicobacter pylori seropositivity, the triglyceride-glucose index, and cardiovascular disease: a cohort study using the NHANES database. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:441. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02536-0
29. Upala, S, Jaruvongvanich, V, Riangwiwat, T, Jaruvongvanich, S, and Sanguankeo, A. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dig Dis. (2016) 17:433–40. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12367
30. Hsieh, MC, Wang, SS, Hsieh, YT, Kuo, FC, Soon, MS, and Wu, DC. Helicobacter pylori infection associated with high HbA1c and type 2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Investig. (2013) 43:949–56. doi: 10.1111/eci.12124
31. Wan, Z, Song, L, Hu, L, Hu, M, Lei, X, Huang, Y, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with diabetes among Chinese adults. J Diabetes Investig. (2020) 11:199–205. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13102
32. Mansori, K, Moradi, Y, Naderpour, S, Rashti, R, Moghaddam, AB, Saed, L, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection as a risk factor for diabetes: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. BMC Gastroenterol. (2020) 20:77. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01223-0
33. Chen, J, Xing, Y, Zhao, L, and Ma, H. The association between Helicobacter pylori infection and glycated hemoglobin a in diabetes: a Meta-analysis. J Diabetes Res. (2019) 2019:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2019/3705264
34. Kim, TJ, Lee, H, Kang, M, Kim, JE, Choi, YH, Min, YW, et al. Helicobacter pylori is associated with dyslipidemia but not with other risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:38015. doi: 10.1038/srep38015
35. Shimamoto, T, Yamamichi, N, Gondo, K, Takahashi, Y, Takeuchi, C, Wada, R, et al. The association of Helicobacter pylori infection with serum lipid profiles: An evaluation based on a combination of meta-analysis and a propensity score-based observational approach. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0234433. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234433
36. Tali, LDN, Faujo, GFN, Konang, JLN, Dzoyem, JP, and Kouitcheu, LBM. Relationship between active Helicobacter pylori infection and risk factors of cardiovascular diseases, a cross-sectional hospital-based study in a sub-Saharan setting. BMC Infect Dis. (2022) 22:731. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07718-3
37. Nigatie, M, Melak, T, Asmelash, D, and Worede, A. Dyslipidemia and its associated factors among Helicobacter pylori-infected patients attending at University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Gondar, north-West Ethiopia: a comparative cross-sectional study. J Multidiscip Healthc. (2022) 15:1481–91. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S368832
38. Park, Y, Kim, TJ, Lee, H, Yoo, H, Sohn, I, Min, YW, et al. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection decreases risk for dyslipidemia: a cohort study. Helicobacter. (2021) 26:e12783. doi: 10.1111/hel.12783
39. Iwai, N, Okuda, T, Oka, K, Hara, T, Inada, Y, Tsuji, T, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication increases the serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol level in the infected patients with chronic gastritis: a single-center observational study. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0221349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221349
40. Mokhtare, M, Mirfakhraee, H, Arshad, M, Samadani Fard, SH, Bahardoust, M, Movahed, A, et al. The effects of helicobacter pylori eradication on modification of metabolic syndrome parameters in patients with functional dyspepsia. Diabetes Metab Syndr. (2017) 11:S1031–5. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2017.07.035
41. Agbu, P, and Carthew, RW. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2021) 22:425–38. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00354-w
42. Wat, LW, and Svensson, KJ. Novel secreted regulators of glucose and lipid metabolism in the development of metabolic diseases. Diabetologia. (2024) 67:2626–36. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06253-x
43. Dang, K, Wang, X, Hu, J, Zhang, Y, Cheng, L, Qi, X, et al. The association between triglyceride-glucose index and its combination with obesity indicators and cardiovascular disease: NHANES 2003-2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:8. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02115-9
44. Yao, Y, Wang, B, Geng, T, Chen, J, Chen, W, and Li, L. The association between TyG and all-cause/non-cardiovascular mortality in general patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is modified by age: results from the cohort study of NHANES 1999-2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:43. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02120-6
45. Liu, W, An, J, Jiao, C, Guo, J, Zhang, L, Jin, H, et al. Association of triglyceride-glucose index with Helicobacter pylori infection in the 1999-2000 NHANES cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:387. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84536-4
46. American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care. (2021) 44:S15–33. doi: 10.2337/dc21-S002
47. Chen, Y, Yang, C, You, N, and Zhang, J. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori and glycated hemoglobin: a cohort study. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1196338. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1196338
48. Kløve, S, Stinson, SE, Romme, FO, Butt, J, Graversen, KB, Lund, MAV, et al. Helicobacter pylori seropositivity associates with hyperglycemia, but not obesity, in Danish children and adolescents. BMC Med. (2024) 22:379. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03591-w
49. Yang, C, You, N, Chen, Y, and Zhang, J. Helicobacter pylori infection increases the risk of dyslipidemia in Chinese diabetic population: a retrospective cross-sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. (2024) 24:730. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09597-2
50. Courtois, S, Bénéjat, L, Izotte, J, Mégraud, F, Varon, C, Lehours, P, et al. Metformin can inhibit Helicobacter pylori growth. Future Microbiol. (2018) 13:1575–83. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2018-0184
51. Ness, A, Levi, Z, Belfer, RG, Dickman, R, and Boltin, D. Improvement in Helicobacter pylori eradication among adults receiving Semaglutide: a population-based propensity-score-adjusted analysis. Helicobacter. (2025) 30:e70014. doi: 10.1111/hel.70014
52. Tang, L, Tang, B, Lei, Y, Yang, M, Wang, S, Hu, S, et al. Helicobacter pylori-induced Heparanase promotes H. pylori colonization and gastritis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:675747. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.675747
53. Zhou, X, Liu, W, Gu, M, Zhou, H, and Zhang, G. Helicobacter pylori infection causes hepatic insulin resistance by the c-Jun/miR-203/SOCS3 signaling pathway. J Gastroenterol. (2015) 50:1027–40. doi: 10.1007/s00535-015-1051-6
54. Chen, CC, Liou, JM, Lee, YC, Hong, TC, El-Omar, EM, and Wu, MS. The interplay between Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes. (2021) 13:1–22. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1909459
55. Nabavi-Rad, A, Sadeghi, A, Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H, Yadegar, A, Smith, SM, and Zali, MR. The double-edged sword of probiotic supplementation on gut microbiota structure in Helicobacter pylori management. Gut Microbes. (2022) 14:2108655. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2108655
56. Aslan, M, Horoz, M, Nazligul, Y, Bolukbas, C, Bolukbas, FF, Selek, S, et al. Insulin resistance in H pylori infection and its association with oxidative stress. World J Gastroenterol. (2006) 12:6865–8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6865
57. Sheu, SM, Cheng, H, Kao, CY, Yang, YJ, Wu, JJ, and Sheu, BS. Higher glucose level can enhance the H. pylori adhesion and virulence related with type IV secretion system in AGS cells. J Biomed Sci. (2014) 21:96. doi: 10.1186/s12929-014-0096-9
58. Kountouras, J, Boziki, M, Kazakos, E, Theotokis, P, Kesidou, E, Nella, M, et al. Impact of Helicobacter pylori and metabolic syndrome on mast cell activation-related pathophysiology and neurodegeneration. Neurochem Int. (2024) 175:105724. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105724
59. Abdalla, MMI. Enteric neuropathy in diabetes: implications for gastrointestinal function. World J Gastroenterol. (2024) 30:2852–65. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i22.2852
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori , hemoglobin A1c/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio, metabolic dysfunction, NHANES, cross-sectional study
Citation: Xu C, Jiang X-y, Liao J-m, Zhao Y-f, Hu J-y, Li C-C and Shen H (2025) Association between Helicobacter pylori seropositivity and the hemoglobin A1c/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in U.S. adults: evidence from NHANES. Front. Nutr. 12:1589510. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1589510
Edited by:
Fernando Javier Barreyro, National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET), ArgentinaReviewed by:
Yujun Xiong, Peking University, ChinaZerihun Assefa, North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University, United States
Emmanuel Tagoe, University of Ghana, Ghana
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Jiang, Liao, Zhao, Hu, Li and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chong-Chao Li, bGljaG9uZ2NoYW9Abmp1Y20uZWR1LmNu; Hong Shen, c2hlbmhvbmc5OTlAbmp1Y20uZWR1LmNu
 Cheng Xu
Cheng Xu Xin-yi Jiang1,2
Xin-yi Jiang1,2 Hong Shen
Hong Shen