- 1Department of Neurology, Kunshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunshan, Jiangsu, China
- 2Department of Computer and Information Engineering, Kunsan National University, Gunsan, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shenzhen People’s Hospital (The Second Clinical Medical College, Jinan University, The First Affiliated Hospital, Southern University of Science and Technology), Shenzhen, China
- 4Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, United States
- 5Molecular Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
Background: Depression remains a significant global health issue, yet the combined influence of dietary quality and extreme pessimistic thoughts on depressive risk is not fully understood. This study evaluated whether a Balanced Healthy Eating Index (BHEI) and extreme pessimism independently and jointly predict depression in adults.
Materials and methods: We analyzed data from 17,575 participants aged 18–65 years in the 2007–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). BHEI scores above 62 were classified as meeting healthy dietary standards. Logistic regression models assessed the associations between substandard BHEI, extreme pessimism (frequent thoughts of being better off dead), and self-reported depression (PHQ-9 ≥ 10). Models were adjusted for age, sex, ethnicity, BMI, total energy intake, smoking status, alcohol use, and physical activity.
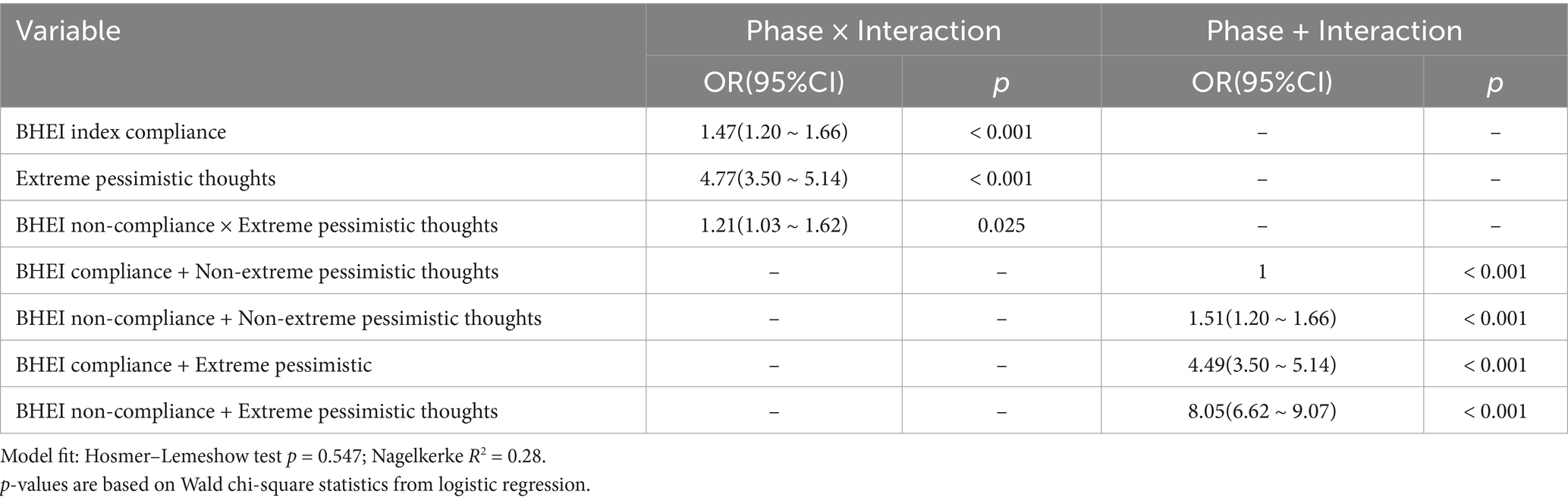
Results: Participants failing to meet the BHEI threshold had increased odds of depression (OR = 1.55, 95% CI: 1.37–1.76). Extreme pessimism further elevated depression risk (OR = 4.17, 95% CI: 3.40–4.41). An interaction effect showed that individuals with both substandard BHEI and extreme pessimism faced even higher odds of depression (OR = 8.05, 95% CI: 6.62–9.07), suggesting a multiplicative relationship.
Conclusion: Both low-quality diets and extreme pessimistic thinking were significantly associated with depression risk, and the combination was particularly impactful. Future longitudinal studies are warranted to clarify causal pathways and to determine whether improving dietary patterns or mitigating extreme pessimism could reduce depression prevalence.
1 Introduction
Depressive disorders pose a substantial global health burden, affecting people across populations and contributing to increased morbidity, mortality, and economic costs (1, 2). According to existing epidemiological evidence, depression prevalence varies notably by demographic characteristics such as age, gender, socioeconomic status, and chronic comorbidities (3, 4). Gender is frequently reported as a determinant, with women exhibiting higher rates of depression than men, potentially due to hormonal fluctuations and psychosocial factors (5). Genetic predispositions, indicated by the familial aggregation of depressive disorders, further increase susceptibility (6). Additionally, modifiable lifestyle behaviors, including tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and physical inactivity, have been consistently linked to higher depression risk (7, 8). Chronic health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, also elevate the risk of depressive symptoms and complicate treatment outcomes (9, 10). Moreover, socioeconomic variables, such as marital status, income, education level, and stressful life events, significantly influence depressive symptomatology (11–14). Given these multifactorial influences, there is growing interest in the role nutritional factors play in the onset and progression of depressive symptoms.
Dietary factors have emerged as potential preventive and adjunct therapeutic targets for depressive disorders. Emerging research suggests that nutritional intake can influence mental health through pathways such as inflammation, oxidative stress, and gut–brain axis interactions (15, 16). Evaluations of diet quality and its association with mental health have utilized various dietary indices, among which the Healthy Eating Index (HEI), including the Healthy Eating Index, stand out due to their broad application in assessing dietary guideline adherence (17). These indices summarize multiple dietary components—such as fruit, vegetables, whole grains, saturated fat, and added sugars—into composite scores to provide a holistic assessment of dietary quality (17, 18). Prior research linking dietary patterns assessed by HEI to depression revealed mixed findings. Some studies report inverse associations, suggesting that healthy dietary patterns are protective against depression (19–23). However, the mechanisms by which dietary, behavioral, and sociodemographic determinants play a role in influencing mental health outcomes remain complex (24, 25). Thus, further research leveraging robust population-based data are warranted to better delineate how specific dietary components may impact depression risk.
Against this background, the present study aims to investigate the association between different forms of the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) and depression among adults aged 18 and 65 years, drawing data from the 2007–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) (26). Additionally, we seek to explore the potential mediating role of extreme pessimistic thoughts—conceptualized here as instances where respondents frequently consider that they might be “Thought you would be better off dead” on the link between diet quality and depressive symptomatology (27). By leveraging the comprehensive scope of NHANES, which includes detailed dietary intake data, demographic information, and mental health assessments, we aim to illuminate whether specific dimensions of healthy eating can forecast reduced susceptibility to depression and whether extreme pessimistic thinking independently mediates that relationship (28). This study seeks to establish whether adherence to a healthy diet is associated with reduced depressive symptoms and whether extreme pessimistic thoughts mediate this association, thereby highlighting potential cognitive and behavioral intervention points.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data sources
NHANES is a periodic cross-sectional survey designed to assess the health status of the US population. It is conducted every 2 years and uses a multistage probability sampling design to ensure a nationally representative sample from different geographical regions of the United States. The database consistently assesses depression using the 9-item Mental Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9). Due to the disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, the scarcity and complexity of data collected after 2019 may not accurately reflect the prevalence of depression in the current population. Therefore, to ensure data consistency and reliability, the NHANES cycle from 2007 to 2018 was selected for our analyses (29).
2.2 Research participants
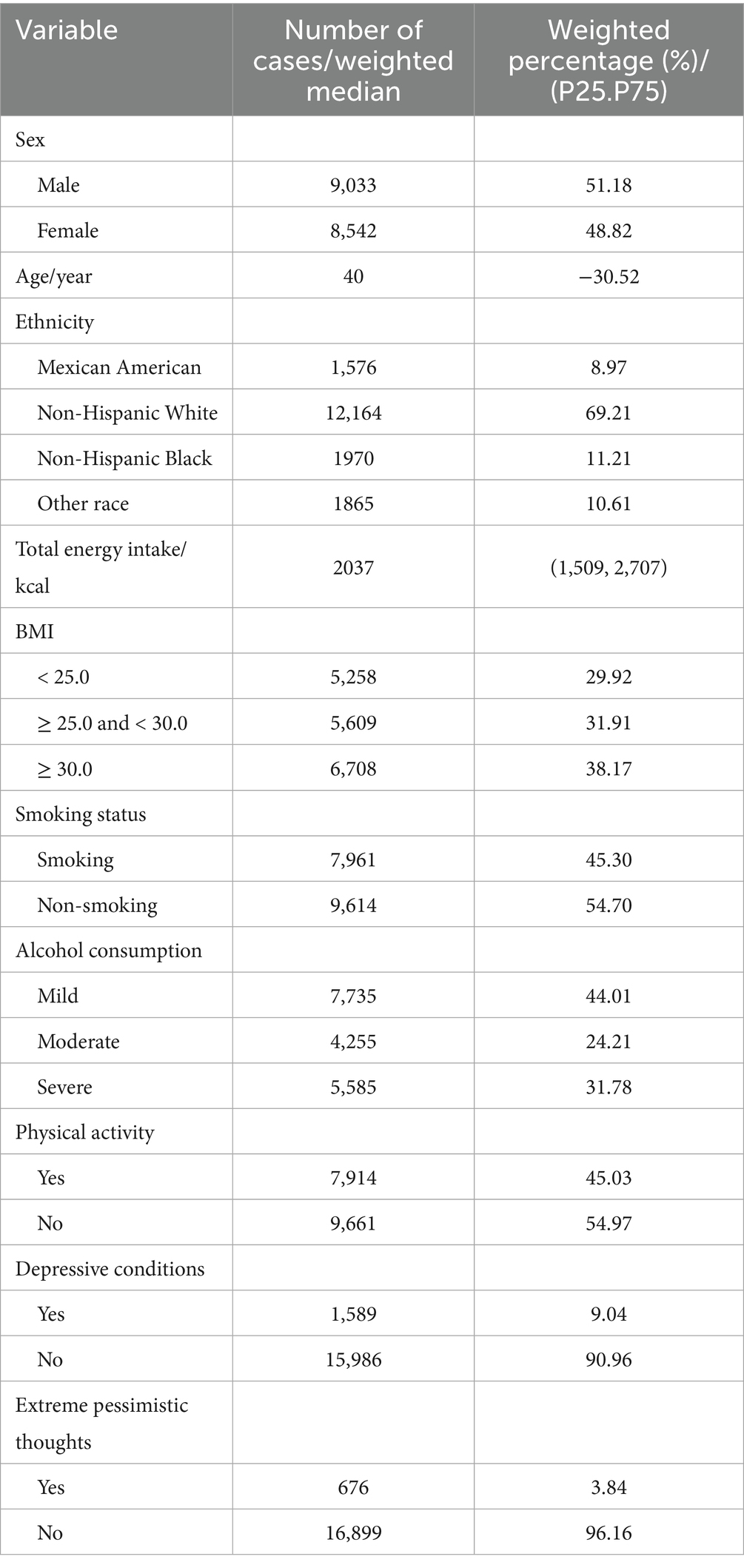
Participants aged between 18 and 65 years who underwent dietary survey data, as well as psychological questionnaires, were included in this study. Subjects with incomplete demographic, dietary, or questionnaire data were excluded; those indexed to the abnormal energy intake criteria were excluded; and those with other dietary abnormalities were excluded. A total of 17,575 subjects met these criteria and were included in the analysis, as detailed in Table 1.
2.3 Depression criteria
Depressive symptoms are the outcome measure. The PHQ-9 depression screening scale consists of 9 items, each of which is scored on a 4-point scale of 0, 1, 2, and 3, for a total score of 27, with a score of 0 to 9 indicating no depression and a score of 10 to 27 indicating the presence of depression (30). Depressive symptoms were measured using the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), a validated self-report instrument commonly applied to both clinical and population-based studies. In NHANES, this questionnaire is administered via the Audio Computer-Assisted Self-Interview (ACASI) system at the Mobile Examination Center. Each item is scored from 0 (not at all) to 3 (nearly every day), with a total score ranging from 0 to 27. Extreme pessimistic thoughts were assessed using item 9 of the PHQ-9, which inquires about thoughts of death or self-harm.
Extreme pessimism was defined based on item 9 of the PHQ-9, which captures passive or active thoughts of death or self-harm. While this item is often used as a proxy for hopelessness in depression research, it reflects only the most severe end of pessimistic thinking.
2.4 Extreme pessimistic tendency criterion
To assess the presence of extreme pessimistic thoughts, participants were scored on their responses to item DPQ090 from the PHQ-9 questionnaire, which specifically asked the following question: “Over the last 2 weeks, how often have you been bothered by the following problems: Thoughts that you would be better off dead or of hurting yourself in some way?” Responses were categorized into four frequencies: 0 (not at all), 1 (several days), 2 (more than half of the days), and 3 (almost every day). Participants who answered ‘refused’ or ‘do not know’ were excluded from the analysis. For this study, individuals who selected responses coded as 1, 2, or 3 were classified as having suicidal ideation.
2.5 Balanced Healthy Eating Index (BHEI)
In this study, we used the standard Healthy Eating Index (HEI) as an established measure of dietary quality, and building on this approach, we introduced a Balanced Healthy Eating Index (BHEI) framework that incorporates some scaling adjustments to provide a refined assessment perspective by reweighting specific components. To enhance its specificity for depression-related outcomes, we retained the original 13 components of the HEI-2015 but adjusted their relative weights based on existing literature and exploratory analyses. The final BHEI score was normalized to 100 to ensure comparability across participants.
The dietary data used to construct the BHEI were derived from two 24-h dietary recall interviews conducted as part of NHANES. Nutrient and food group information were obtained from the dietary component files. The BHEI was calculated following previously established scoring protocols developed for NHANES-based diet quality assessment. For this analysis, participants with BHEI scores above 62 were considered to have reached a threshold for healthy eating.
2.6 Covariates
Covariates, include age, sex, race (Mexican American, non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, other), BMI (non-overweight BMI < 25.00 kg/m2, overweight 25.00 ≤ BMI < 30.00 kg/m2, and obese BMI ≥ 30.00 kg/m2), smoking history (more than 100 cigarettes, less than 100 cigarettes, or never smoked), alcohol consumption (heavy, moderate, and light), and physical activity (moderate to no activity).
2.7 Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 27.0 and R 4.4.2. In accordance with NHANES analytical guidelines, data were weighted using the wtmec2yr variable to account for the complex survey design and 2-year sampling cycles.
Logistic regression models were used to examine the associations between the Balanced Healthy Eating Index (BHEI), pessimism, and depression. Interaction effects were also tested to assess the joint relationship between dietary quality and pessimism.
Three hierarchical models were constructed: Model 1 was adjusted for demographic variables (age, gender, race/ethnicity, education, and income); Model 2 was additionally adjusted for lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking, alcohol use, and BMI); and Model 3 further included psychological variables (e.g., sleep quality and antidepressant use).
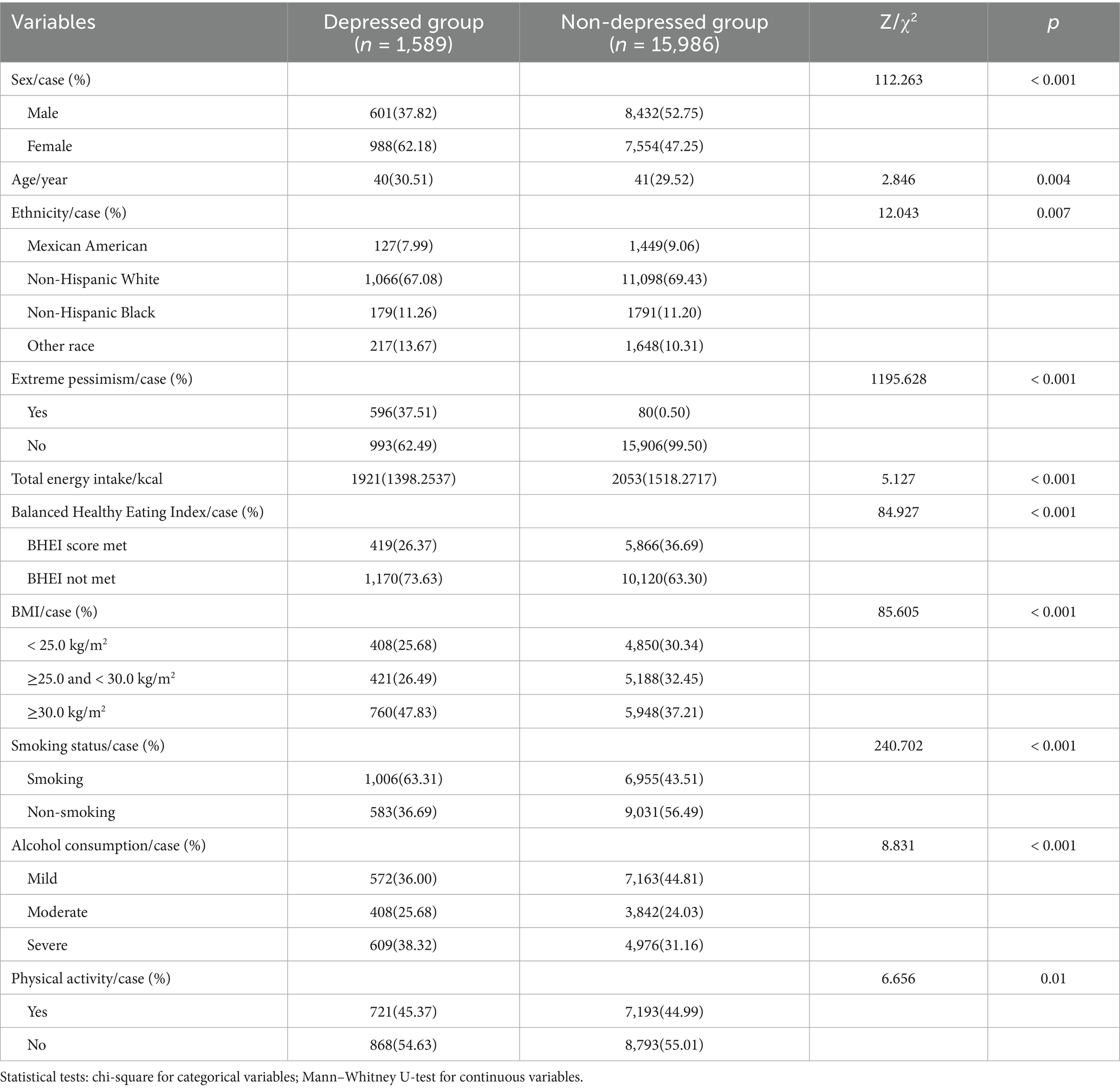
For group comparisons, chi-square tests were applied to categorical variables. For continuous variables, normality was tested using the Shapiro–Wilk test. As most continuous variables were not normally distributed, the non-parametric Mann–Whitney U-test was used.
The performance of logistic regression models was assessed using the Hosmer–Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test and Nagelkerke pseudo R2 to evaluate model calibration and explanatory power.
3 Results
Baseline demographic characteristics are presented in Table 1. Group-wise distributions of depression-related factors are summarized in Table 2.
3.1 Participant characteristics
A total of 17,575 subjects were included in this study, predominantly non-Hispanic White, with a majority of participants being non-smokers and light drinkers, a high proportion of people with a BMI above the normal range, and a high proportion of people who did not meet the BHEI. The distribution of general demographic characteristics is shown in Table 1.
The distribution of depression characteristics among NHANES study participants from 2007 to 2018 is shown in Table 2.
3.2 Mutual relationships
3.2.1 Relationship between the BHEI index and depression
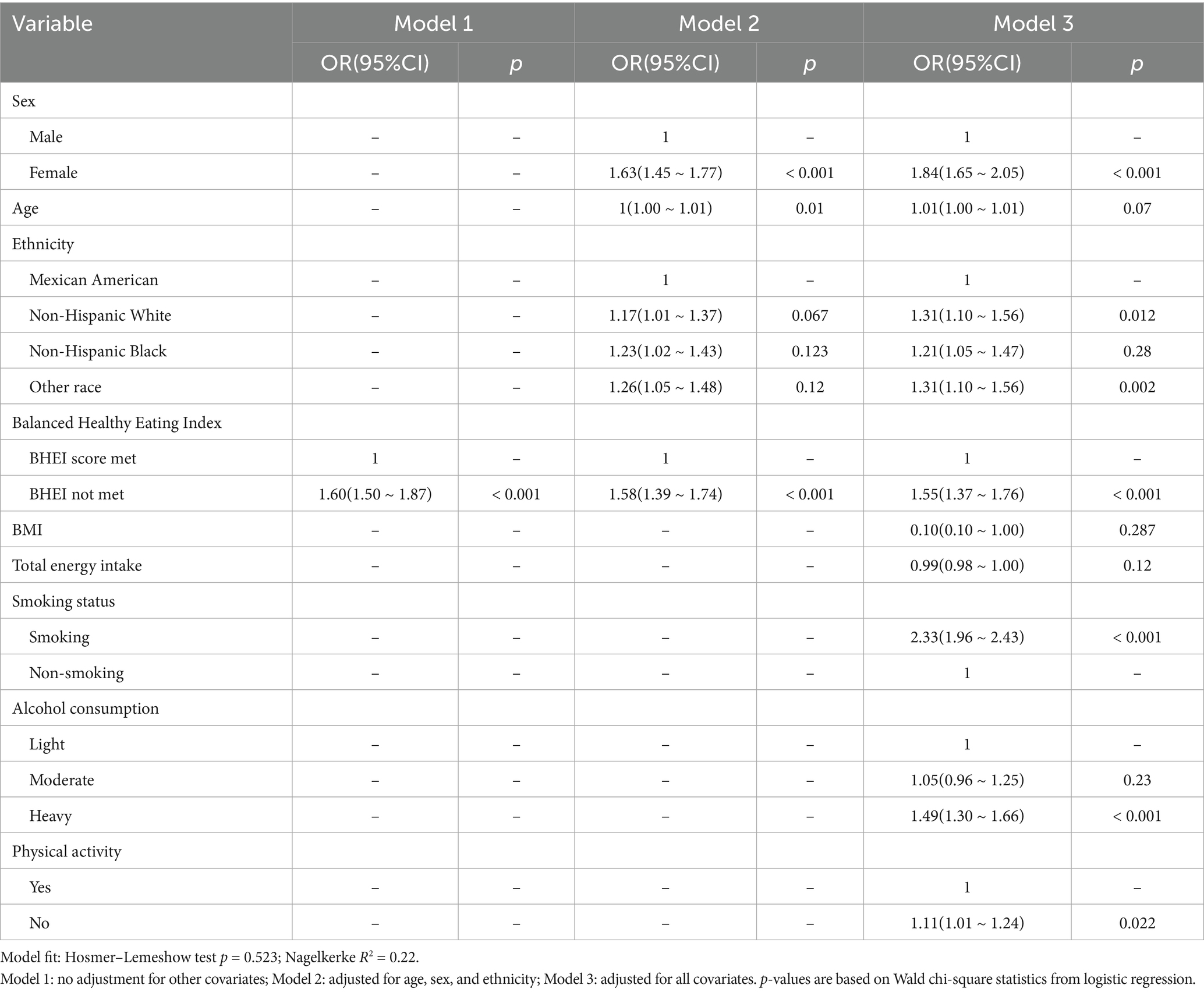
Logistic regression models were utilized to investigate the association between dietary inflammation and depression, using the non-depressed group as the reference. The corresponding results are summarized in Table 3. In all three models, dietary inflammation was significantly and positively associated with depression (p < 0.001). In Model 1, participants in the BHEI non-adherent group had a significantly higher risk of depression compared to the anti-inflammatory dietary group (OR = 1.60, 95% CI = 1.50–1.87, p < 0.001). In Model 1, participants in the BHEI non-adherent group had a significantly higher risk of depression compared to the anti-inflammatory dietary group (OR = 1.60, 95% CI = 1.50–1.87, p < 0.001). In Model 2, after adjusting for age, gender, and ethnicity, the risk of depression remained significantly elevated in the BHEI non-adherent group (OR = 1.58, 95% CI = 1.31–1.77, p < 0.001). In Model 3, after adjusting for age, gender, ethnicity, BMI, total energy intake, alcohol consumption, smoking status, and physical activity, participants in the BHEI non-adherent group still exhibited a significantly increased risk of depression (OR = 1.55, 95% CI = 1.37–1.76, p < 0.001).
3.2.2 Relationship between extreme pessimistic thoughts and depression
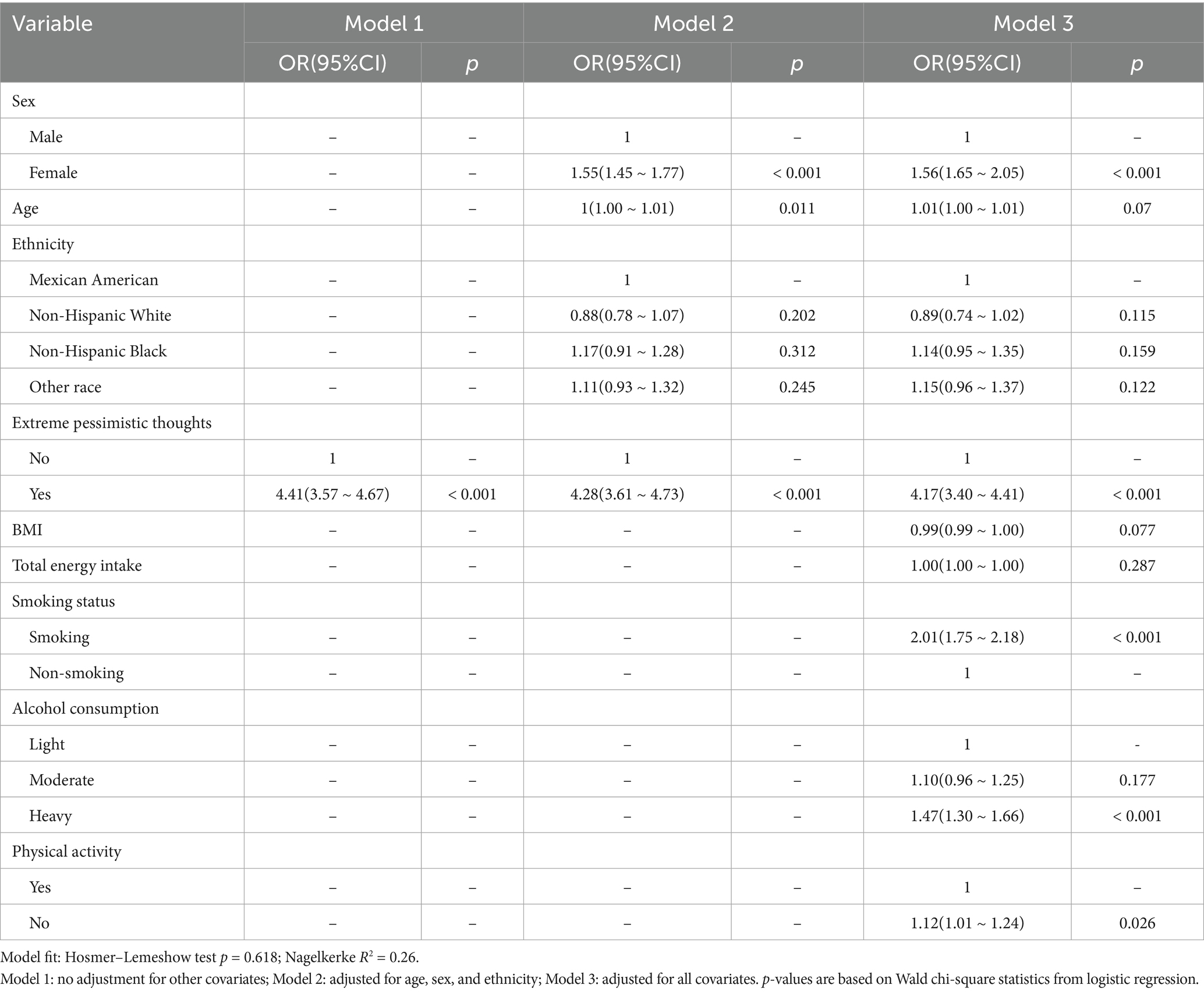
Logistic regression models were used to investigate the association between extreme pessimism and depression. The results are presented in Table 4. Compared to the non-depressed population, participants with extreme pessimism had a significantly increased risk of depression across Models 1, 2, and 3 (p < 0.001).
3.2.3 Interaction between BHEI index and extreme pessimistic thoughts
After adjusting for age, gender, ethnicity, BMI, total energy intake, alcohol consumption, smoking status, and physical activity, the interaction between extreme pessimism and BHEI status remained significantly associated with depression (p < 0.05). The results are summarized in Table 5. Compared to the non-pessimistic population with adequate BHEI scores, failure to meet the BHEI standard and extreme pessimism were each independently associated with increased odds of depression (p < 0.05). Notably, individuals with both substandard BHEI scores and extreme pessimism exhibited the highest risk of depression. Notably, the combination of low BHEI and extreme pessimism showed a markedly elevated depression risk (OR = 8.05), exceeding the effect of either factor alone.
4 Discussion
This study utilized NHANES data (2007–2018) to investigate the associations among the Balanced Healthy Eating Index (BHEI), extreme pessimism, depression, and their interactions. The results indicated that substandard dietary patterns (failing to meet the BHEI criteria) and extreme pessimism were each significantly associated with an increased risk of depression. Furthermore, interaction analyses revealed that participants simultaneously exhibiting substandard dietary patterns and extreme pessimism had the highest risk for depressive symptoms. This finding suggests a compounding effect, whereby poor diet and extreme cognition amplify one another’s impact on depressive symptoms. These findings are consistent with previous studies suggesting that low-quality diets increase the likelihood of mood disturbances, potentially due to nutritional deficiencies, pro-inflammatory processes, or metabolic dysregulation (16, 24). Finally, due to the cross-sectional design of NHANES, the possibility of reverse causality cannot be ruled out. For example, individuals with depression may adopt poorer dietary habits or experience increased pessimism as a consequence of their mental health status.
Our findings are consistent with a growing body of evidence highlighting the association between dietary quality and depression. For instance, several observational studies have reported that higher adherence to healthy dietary patterns, particularly the Mediterranean diet, is associated with a reduced risk of depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder (31, 32). Similarly, randomized controlled trials have shown that dietary interventions can lead to significant improvements in depressive symptoms, especially among young adults (33). A systematic review by Patsalos et al. (34) further emphasized the role of dietary improvement in managing depressive symptoms in overweight and obese individuals. In line with these findings, de Oliveira Meller et al. (35) reported that individuals with lower diet quality had a significantly higher likelihood of experiencing depressive episodes. These studies support the notion that dietary quality may influence mental health outcomes through multiple biological and psychosocial mechanisms (31). Collectively, our study adds to this literature by introducing the BHEI as a refined measure of diet quality and demonstrating its association with depressive risk and extreme pessimistic thinking in a large nationally representative population.
The finding that pessimistic thinking further increases the risk of depression highlights the multifactorial nature of mental health. Specifically, cognitive and emotional factors may exacerbate the negative effects of poor dietary habits on mood. Although key confounders—including age, sex, ethnicity, total energy intake, BMI, physical activity, alcohol consumption, and smoking status—were considered, residual confounding or reverse causation cannot be ruled out. For instance, individuals experiencing undiagnosed depressive symptoms might adopt unhealthy dietary habits, leading to a bidirectional relationship that complicates causal inference. Longitudinal and intervention studies are required to determine whether improving dietary quality can alleviate pessimistic thinking, or conversely, if enhancing cognitive functioning indirectly promotes healthier dietary behaviors. Future prospective studies could better clarify the temporal sequence of these factors, thereby informing targeted preventive strategies. One limitation is the operationalization of extreme pessimism using only a single PHQ-9 item, which may not fully capture the broader spectrum of negative cognitive styles and may lead to an underestimation of more moderate pessimistic tendencies.
Additionally, the reliance on self-reported dietary data in this study may have introduced measurement errors or recall bias. Future research should use prospective or longitudinal study designs, incorporate more comprehensive assessments of psychosocial stressors, and utilize objective dietary measures (e.g., biomarkers). Such refinements may help elucidate the mechanisms linking dietary quality, pessimistic cognition, and depressive outcomes. Given the cross-sectional nature of the NHANES data, the associations identified in this study do not imply causality.
5 Conclusion
This population-based cross-sectional study indicates that both suboptimal dietary quality (assessed by the Balanced Healthy Eating Index, BHEI) and extreme pessimistic thoughts are significantly associated with increased depression risk among adults aged 18–65 years. Moreover, the interaction between these two factors indicates a multiplicative effect on depressive symptoms, highlighting the importance of integrating nutritional and psychological interventions. Due to the inherent limitations of the cross-sectional design, this study cannot establish causality. Nevertheless, the findings highlight the potential importance of diet quality and extreme pessimism on depression risk. Further prospective and interventional studies are necessary to clarify temporal relationships and determine whether modifying dietary practices or pessimistic tendencies can effectively reduce depression incidence or severity.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the First Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
YL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SB: Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. CL: Investigation, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. FL: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ML: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing. GY: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Conceptualization, Project administration, Validation, Funding acquisition, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Guangzhou Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine Science and Technology Project Scientific Research Establishment Fund (Grant No. 20222A010039), the Kunsan National University Scientific Research Fund (No. 2023H052), and the Suzhou City Applied Basic Research and Science and Technology Innovation Project (SYWD2024196).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1590171/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Friedrich, MJ. Depression is the leading cause of disability around the world. JAMA. (2017) 317:1517–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.3828
2. Greenberg, PE, Fournier, A-A, Sisitsky, T, Pike, CT, and Kessler, RC. The economic burden of adults with major depressive disorder in the United States (2005 and 2010). J Clin Psychiatry. (2015) 76:155–62. doi: 10.4088/JCP.14m09298
3. Zajkowska, Z, Walsh, A, Zonca, V, Gullett, N, Pedersen, GA, Kieling, C, et al. A systematic review of the association between biological markers and environmental stress risk factors for adolescent depression. J Psychiatr Res. (2021) 138:163–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.04.003
4. Alegría, M, NeMoyer, A, Falgàs Bagué, I, Wang, Y, and Alvarez, K. Social determinants of mental health: where we are and where we need to go. Curr Psychiatry Rep. (2018) 20:1–13. doi: 10.1007/s11920-018-0969-9
5. Hankin, BL, and Abramson, LY. Development of gender differences in depression: description and possible explanations. Ann Med. (1999) 31:372–9. doi: 10.3109/07853899908998794
6. Lau, JYF, and Eley, TC. The genetics of mood disorders. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. (2010) 6:313–37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.121208.131308
7. Lenz, BK. Tobacco, depression, and lifestyle choices in the pivotal early college years. J Am Coll Heal. (2004) 52:213–20. doi: 10.3200/JACH.52.5.213-220
8. Lopresti, AL, Hood, SD, and Drummond, PD. A review of lifestyle factors that contribute to important pathways associated with major depression: diet, sleep and exercise. J Affect Disord. (2013) 148:12–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.01.014
9. Lin, R. “Central obesity may affect bone development in adolescents: association between abdominal obesity index ABSI and adolescent bone mineral density.” BMC Endocrine Disorders. (2004) 24:81.
10. Lorant, V, Deliège, D, Eaton, W, Robert, A, Philippot, P, and Ansseau, M. Socioeconomic inequalities in depression: a meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. (2003) 157:98–112. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwf182
11. Araya, R, Lewis, G, Rojas, G, and Fritsch, R. Education and income: which is more important for mental health? J Epidemiol Community Health. (2003) 57:501–5. doi: 10.1136/jech.57.7.501
12. Opie, RS, Itsiopoulos, C, Parletta, N, Sanchez-Villegas, A, Akbaraly, TN, Ruusunen, A, et al. Dietary recommendations for the prevention of depression. Nutr Neurosci. (2017) 20:161–71. doi: 10.1179/1476830515Y.0000000043
13. Ortega, MA, Fraile-Martínez, Ó, García-Montero, C, Alvarez-Mon, MA, Lahera, G, Monserrat, J, et al. Biological role of nutrients, food and dietary patterns in the prevention and clinical management of major depressive disorder. Nutrients. (2022) 14:3099. doi: 10.3390/nu14153099
14. Naska, A, Lagiou, A, and Lagiou, P. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiological research: current state of the art and future prospects. F1000Res. (2017) 6:926. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.10703.1
15. Kaplan, BJ, Crawford, SG, Field, CJ, and Simpson, JSA. Vitamins, minerals, and mood. Psychol Bull. (2007) 133:747–60. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.133.5.747
16. Beurel, E, Toups, M, and Nemeroff, CB. The bidirectional relationship of depression and inflammation: double trouble. Neuron. (2020) 107:234–56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.06.002
17. Krebs-Smith, SM, Pannucci, TE, Subar, AF, Kirkpatrick, SI, Lerman, JL, Tooze, JA, et al. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J Acad Nutr Diet. (2018) 118:1591–602. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
18. Shams-White, MM, Pannucci, TRE, Lerman, JL, Herrick, KA, Zimmer, M, Meyers Mathieu, K, et al. Healthy eating index-2020: review and update process to reflect the dietary guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. J Acad Nutr Diet. (2023) 123:1280–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2023.05.015
19. Ljungberg, T, Bondza, E, and Lethin, C. Evidence of the importance of dietary habits regarding depressive symptoms and depression. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:1616. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051616
20. Murakami, K, and Sasaki, S. Dietary intake and depressive symptoms: a systematic review of observational studies. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2010) 54:471–88. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200900157
21. Lassale, C, Batty, GD, Baghdadli, A, Jacka, F, Sánchez-Villegas, A, Kivimäki, M, et al. Healthy dietary indices and risk of depressive outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Mol Psychiatry. (2019) 24:965–86. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0237-8
22. Akbaraly, TN, Brunner, EJ, Ferrie, JE, Marmot, MG, Kivimaki, M, and Singh-Manoux, A. Dietary pattern and depressive symptoms in middle age. Br J Psychiatry. (2009) 195:408–13. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.108.058925
23. McLaren, L. Socioeconomic status and obesity. Epidemiol Rev. (2007) 29:29–48. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxm001
24. Liese, AD, Krebs-Smith, SM, Subar, AF, George, SM, Harmon, BE, Neuhouser, ML, et al. The dietary patterns methods project: synthesis of findings across cohorts and relevance to dietary guidance. J Nutr. (2015) 145:393–402. doi: 10.3945/jn.114.205336
25. Schweren, LJS, Larsson, H, Vinke, PC, Li, L, Kvalvik, LG, Arias-Vasquez, A, et al. Diet quality, stress and common mental health problems: a cohort study of 121,008 adults. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:901–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.06.016
26. Shi, J, Liang, Z, Zhang, X, Ren, S, Cheng, Y, Liu, Y, et al. Association of physical activity and dietary inflammatory index with overweight/obesity in US adults: NHANES 2007–2018. Environ Health Prev Med. (2023) 28:40–08. doi: 10.1265/ehpm.23-00016
27. Hunter, EC, and O'Connor, RC. Hopelessness and future thinking in parasuicide: the role of perfectionism. Br J Clin Psychol. (2003) 42:355–65. doi: 10.1348/014466503322528900
28. Ahluwalia, N, Dwyer, J, Terry, A, Moshfegh, A, and Johnson, C. Update on NHANES dietary data: focus on collection, release, analytical considerations, and uses to inform public policy. Adv Nutr. (2016) 7:121–34. doi: 10.3945/an.115.009258
29. Cowan, AE, Tooze, JA, Gahche, JJ, Eicher-Miller, HA, Guenther, PM, Dwyer, JT, et al. Trends in overall and micronutrient-containing dietary supplement use in US adults and children, NHANES 2007–2018. J Nutr. (2022) 152:2789–801. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxac168
30. He, K, Pang, T, and Huang, H. The relationship between depressive symptoms and BMI: 2005–2018 NHANES data. J Affect Disord. (2022) 313:151–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.06.046
31. Marx, W, Lane, M, Hockey, M, Aslam, H, Berk, M, and Jacka, F. Diet and depression: exploring the biological mechanisms of action. Mol Psychiatry. (2021) 26:134–50. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-00925-x
32. Yin, W, Löf, M, Chen, R, Hultman, CM, and Fang, F. Mediterranean diet and depression: a population-based cohort study. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. (2021) 18:153. doi: 10.1186/s12966-021-01227-3
33. Bayes, J, Schloss, J, and Sibbritt, D. The effect of a Mediterranean diet on the symptoms of depression in young males (the “AMMEND: a Mediterranean diet in MEN with depression” study): a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. (2022) 116:572–80. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac106
34. Patsalos, O, Keeler, JL, Schmidt, U, and Campbell, IC. Diet, obesity, and depression: a systematic review. J Pers Med. (2021) 11:176. doi: 10.3390/jpm11030176
Keywords: Balanced Healthy Eating Index, extreme pessimism, depression, NHANES, diet quality
Citation: Liu Y, Bao S, Li C, Li F, Liang M and Yang G (2025) Association between the Balanced Healthy Eating Index and depression and the mediating role of extreme pessimistic thoughts: an analysis from the health and nutrition database. Front. Nutr. 12:1590171. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1590171
Edited by:
Kankan Zhang, Guizhou University, ChinaReviewed by:
Seydi Yıkmış, Namik Kemal University, TürkiyeFlávia Dos Santos Barbosa Brito, Rio de Janeiro State University, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Bao, Li, Li, Liang and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guang Yang, MTM2NTU2OTU0NTBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Yantong Liu
Yantong Liu Shengyong Bao
Shengyong Bao Chuang Li
Chuang Li Feifei Li5
Feifei Li5 Mingqian Liang
Mingqian Liang