- 1School of Chinese Medicine, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China
- 2Medical Department, Hubei Enshi College, Enshi, Hubei, China
- 3Fifth People’s Hospital of Jinan, Jinan, Shangdong, China
- 4Enshi Central Hospital, Enshi, Hubei, China
- 5Department of Pulmonary Disease Diabetes Mellitus, The Central Hospital of Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Enshi, Hubei, China
Objective: This study aimed to assess the association between the advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) and the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (DR) in a nationally representative sample of US adults with diabetes.
Methods: We used cross-sectional data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning 1999 to 2018. ALI was calculated from the body mass index (BMI), albumin levels, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), providing an integrative measure of inflammatory and nutritional metabolic status. A history of diabetes was obtained through self-report. Logistic regression models were used to investigate the relationship between ALI and DR prevalence, adjusting for multiple potential confounders. Additionally, restricted cubic spline (RCS) analyses were used to explore potential non-linear associations.
Results: A total of 3,952 diabetic participants were included, of whom 813 had DR. Logistic regression analysis shows that higher ALI values are significantly correlated with a decrease in DR prevalence. Compared to the lowest ALI quartile, the highest quartile was associated with a 27% decrease in DR prevalence after full adjustment. Subgroup analyses showed that the relationship remained stable across most demographic and clinical strata, although racial differences were also observed. Furthermore, RCS analyses revealed an L-shaped relationship between ALI and DR prevalence.
Conclusion: In the US adult diabetic population, lower ALI levels were associated with greater DR prevalence, and this relationship displayed an L-shaped, non-linear pattern. These findings suggest that monitoring and managing ALI may be beneficial in reducing the risk of DR. Future longitudinal studies are needed to clarify the causality and evaluate the impact of ALI-targeted interventions in clinical practice.
1 Introduction
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is one of the most prevalent and severe microvascular complications of diabetes, characterized by pathological alterations in the retinal vasculature triggered by persistent hyperglycemia. This condition leads to endothelial damage, increased vascular permeability, microhemorrhage, and neovascularization, potentially resulting in visual impairment (1, 2). Current treatments for DR include laser photocoagulation, intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF agents, and surgical procedures, such as vitrectomy (3). However, the multifactorial nature of DR, which involves hyperglycemia-induced metabolic disturbances, low-grade inflammation, and complex lipid dysregulation, poses significant challenges. Therefore, developing robust strategies for prevention, early detection, and timely intervention remains imperative (4–6).
Globally, approximately the 30–40% of individuals with diabetes develop DR, creating substantial clinical, economic, and psychological burden. With diabetes prevalence rising worldwide, identifying accessible and integrative biomarkers that reflect underlying metabolic and inflammatory processes is crucial for improving risk stratification and guiding targeted interventions (7–9).
In recent years, the advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI), originally introduced as a prognostic indicator in patients with advanced lung cancer, has gained attention in various diseases. ALI integrates metrics such as body mass index, albumin levels, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, combining nutritional status and systemic inflammatory burden into a single measure. Although initially established in oncology, research suggests that ALI may have predictive value in metabolic and vascular conditions (10–12). However, its role in diabetic microvascular complications, including DR, remains underexplored.
Drawing on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 1999 to 2018, the present cross-sectional study investigated the association between ALI and DR prevalence among US adults with diabetes. This is the first comprehensive effort to evaluate this integrated inflammation-nutrition index in the context of DR risk. Confirming this relationship could facilitate new approaches for risk profiling and interventions tailored to the inflammatory and nutritional dimensions of DR pathogenesis (13). To our knowledge, this is the first large-scale epidemiological study to investigate the relationship between ALI and DR in a nationally representative sample. By repurposing ALI—originally developed for oncology—as a potential biomarker for diabetic microvascular complications, we introduce a novel perspective that integrates inflammatory and nutritional dimensions into DR risk assessment. The findings of this study will not only offer novel insights into the systemic nature of DR pathogenesis but also guide future longitudinal and interventional research aimed at improving clinical outcomes for individuals with diabetes through targeted anti-inflammatory and nutritional interventions.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Source of data and study population
The data for this study were obtained from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), a long-standing program initiated in the late 1960s to assess the health and nutritional status of the US population. The NHANES employs a complex multistage probability sampling design to ensure national representativeness. Data are released biennially, and encompass a comprehensive array of demographic, health, nutritional, and biochemical variables. The most recent available dataset extends to 2018, encompassing a wealth of health and nutrition-related information. The NHANES aims to monitor and evaluate the health of US residents, providing critical scientific evidence to support public health policies and clinical practices (14).
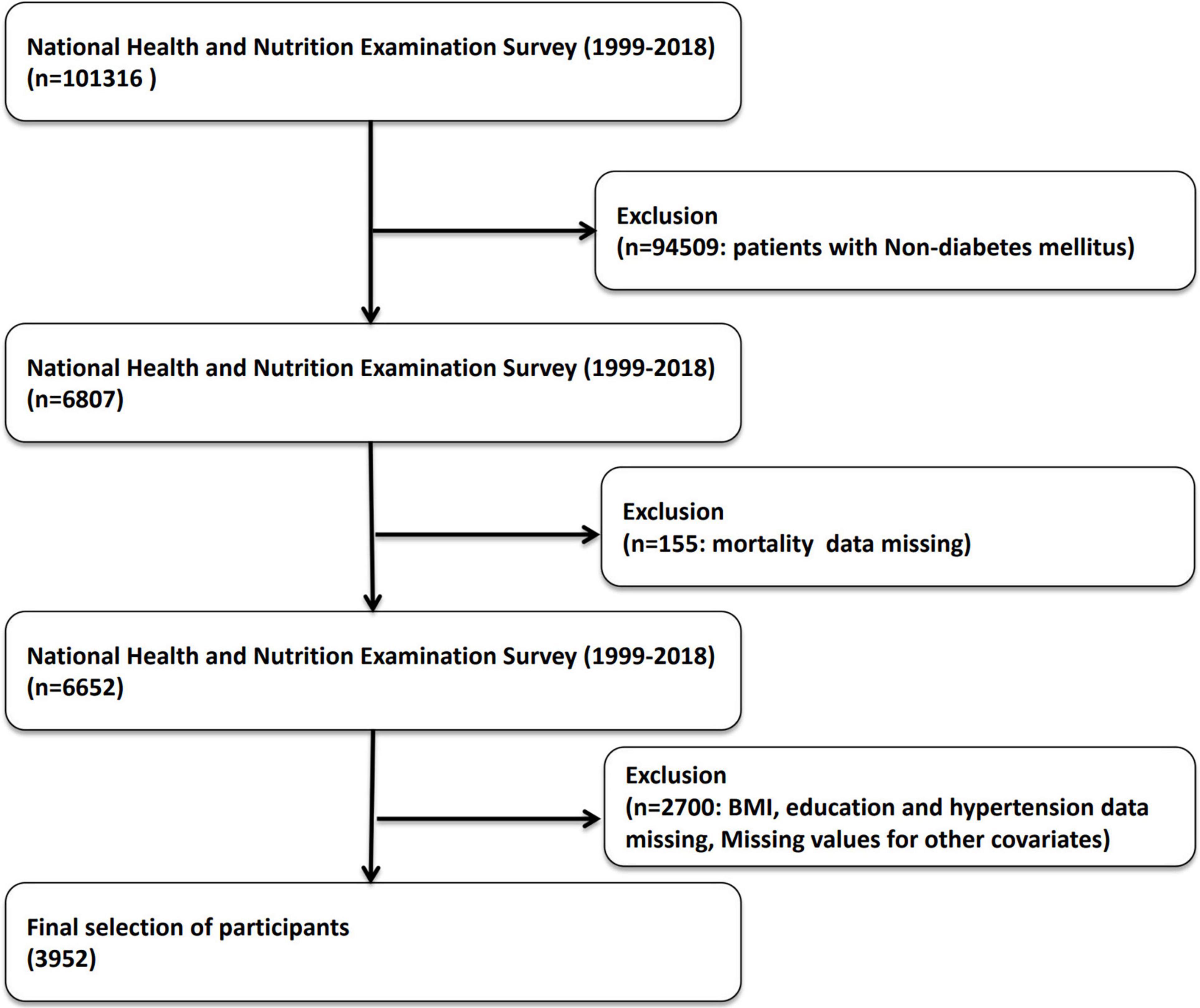
This study utilized a cross-sectional design, focusing on participants with diabetes in the NHANES from 1999 to 2018. NHANES data are collected continuously and released every two years, providing nationally representative information. The initial study population included 101,316 individuals. Participants were excluded based on the following criteria: (1) absence of diabetes data and (2) missing covariate data. After applying these exclusion criteria, 3,952 diabetic patients were included in the analysis (see Figure 1). This study evaluated the cross-sectional relationship between advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) and prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (DR).
2.2 Definition of ALI
ALI served as the primary exposure variable in this study and was calculated using the following formula: ALI = BMI × Albumin/NLR, where BMI is body mass index (kg/m2), Albumin is serum albumin level (g/dL), and NLR is neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. ALI reflects an individual’s systemic inflammatory status and nutritional profile, offering a composite metric with a demonstrated predictive value in various diseases. Its emerging role as a biomarker of inflammation and lipid metabolism highlights its relevance in microvascular complications such as DR (15).
2.3 Assessment of DM and diabetic visual impairment
Diabetes was defined as having a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level of more than 126 mg/dL or a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of at least 6.5% or having a physician-diagnosed diagnosis of DM. Diabetic retinopathy (DR) was identified through the NHANES standardized questionnaire protocol, which includes validated health condition assessment questions administered by trained interviewers. Participants were classified as having DR based on their response to the specific question “Has diabetes affected your eyes/have you had retinopathy?” This methodology aligns with NHANES-recommended practices for population health surveillance and epidemiological research. The use of this assessment approach enables comprehensive analysis across multiple survey cycles (1999–2018), facilitating robust statistical power and nationally representative estimates that would be challenging to achieve with clinical examinations in such a large-scale population study.
2.4 Measurement of covariates
Multiple potential confounders were incorporated as covariates, including age, sex, race, education level, income level (Poverty Income Ratio, PIR), smoking and alcohol use, history of angina, myocardial infarction, heart failure, hypertension, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) level, and total cholesterol level. Specific measurement protocols for these covariates are detailed on the NHANES website (NHANES, CDC).
2.5 Statistical analysis
All analyses were performed using SAS (version 9.4) and R (version 4.0.3) software. Continuous variables are expressed as medians with interquartile ranges, while categorical variables are represented as percentages. The Chi-square test was used to assess differences in categorical variables, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used to analyze continuous variables. Logistic regression models were used to explore the relationship between ALI and DR prevalence, with DR as the binary dependent variable. The study tested ALI both as a continuous variable and categorized into quartiles: Model 1: Unadjusted. Model 2: Adjusted for age, sex, race, education, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Model 3: Further adjusted for history of angina, myocardial infarction, heart failure, and hypertension. Model 4: Additionally adjusted for HDL and total cholesterol levels.
Restricted cubic spline (RCS) fitting were used to investigate the potential non-linear relationships between ALI and DR prevalence. Stratified analyses and interaction tests were conducted across subgroups defined by age, sex, race, education, income, smoking, alcohol consumption, and comorbidities including cardiovascular history. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics of the study population
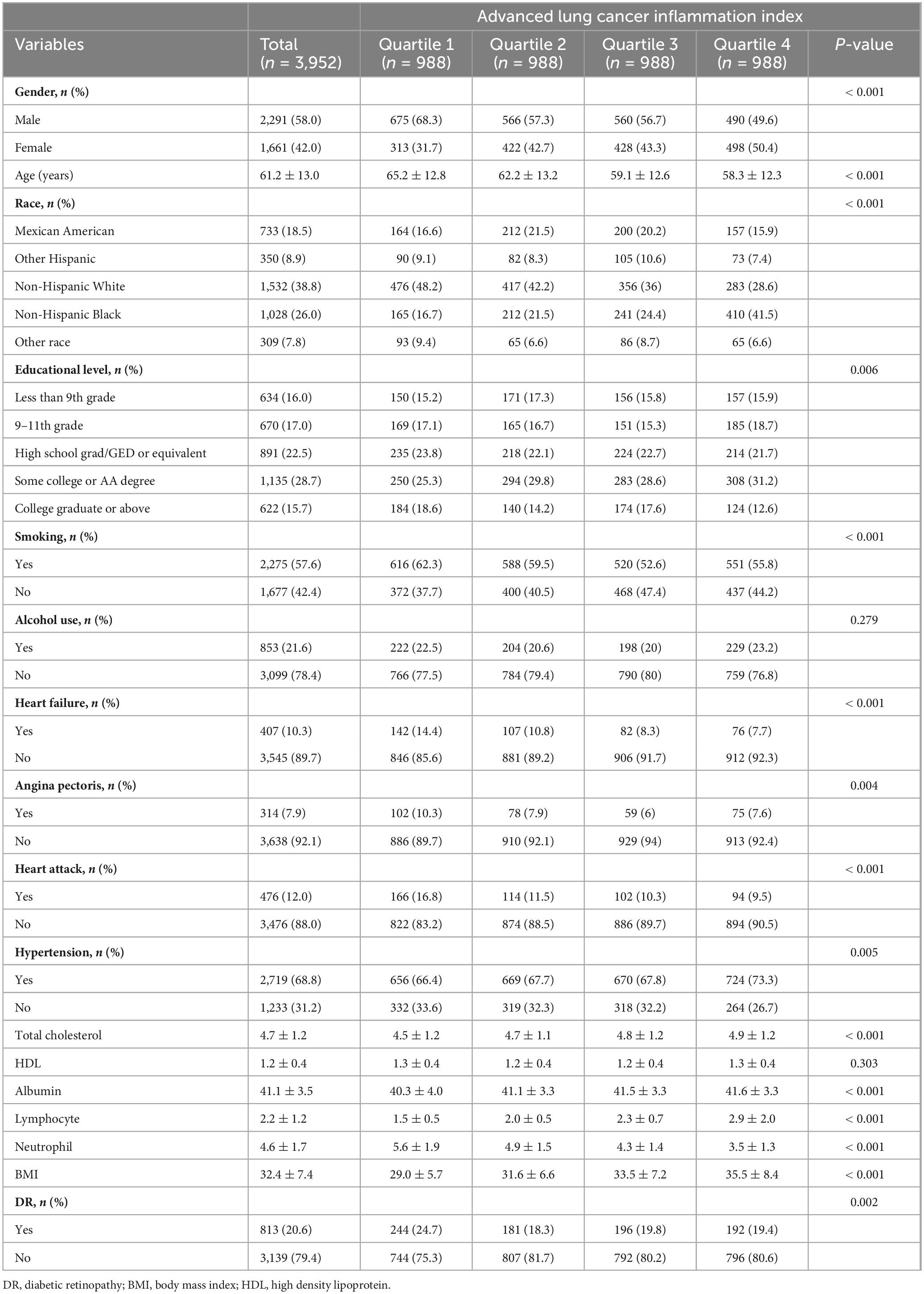
A total of 3,952 patients with diabetes, comprising 2,291 males and 1,661 females. Among all participants, 813 had diabetic retinopathy (DR), while 3,139 did not. Table 1 shows that participants in the higher quartiles of ALI generally exhibited lower age and higher BMI values. Significant differences (all P < 0.05) were observed among the different ALI quartiles in terms of race, education level, smoking status, history of angina, myocardial infarction, heart failure, and hypertension. Specifically, higher ALI quartiles were associated with higher BMI and lower age. Additionally, the high ALI group had a higher proportion of African Americans, lower education levels, and a higher prevalence of smoking.
3.2 Association between ALI and prevalence of diabetic retinopathy
Our analysis indicated that higher levels of ALI were significantly associated with an decreased prevalence of DR. In the unadjusted model, compared to participants in the lowest quartile of ALI, those in the second, third, and fourth quartiles had odds ratios (OR) for DR of 0.68 (95% CI: 0.55–0.85), 0.75 (95% CI: 0.61–0.93), and 0.74 (95% CI: 0.59–0.91). After adjusting for age, sex, race, education level, smoking, and alcohol consumption in Model 2, the ORs were 0.7 (95% CI: 0.56–0.87), 0.77 (95% CI: 0.62–0.96), and 0.73 (95% CI: 0.58–0.92) for the second, third, and fourth quartiles, respectively, remaining statistically significant (Table 2). These results suggest that ALI, as a composite indicator, is inversely associated with DR prevalence, with higher ALI values corresponding to lower odds of DR.
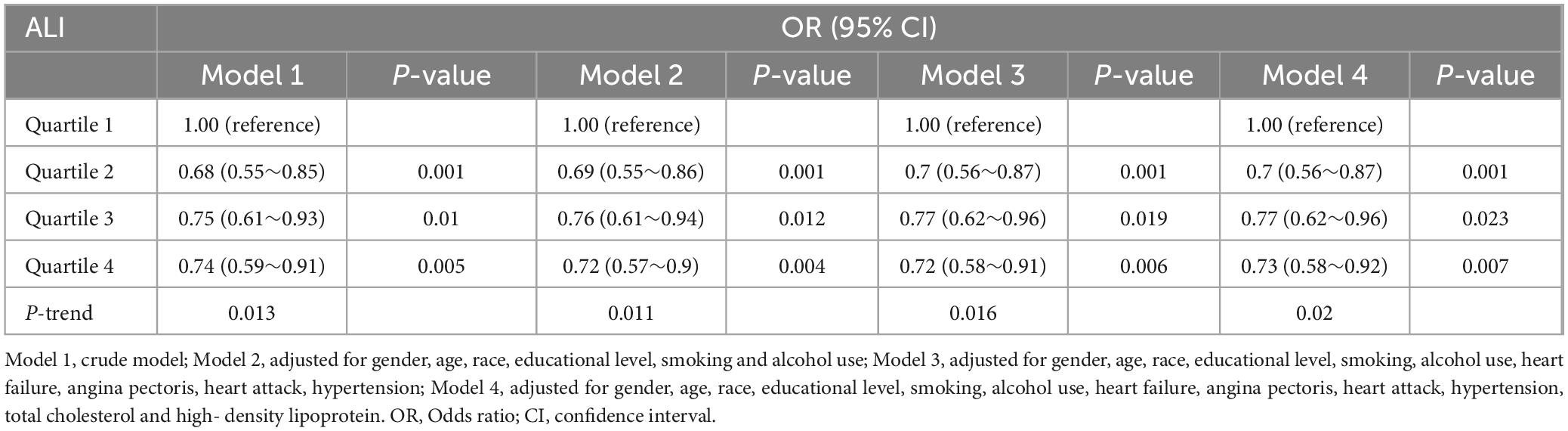
Table 2. Association between advanced lung cancer inflammation index and the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy.
3.3 Results of restricted cubic spline analysis
After adjusting for all covariates, we utilized restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis to explore the relationship between ALI and the prevalence of DR. The results demonstrated a significant non-linear relationship between the two variables (Figure 2). Specifically, the ALI and DR prevalence exhibited an L-shaped curve, indicating that the protective effect of ALI against DR is most pronounced at lower ALI values and tends to plateau at higher values. Specifically, DR risk decreases sharply as ALI increases from the lowest values until approximately the median, after which additional increases in ALI confer diminishing protective benefits. From a clinical perspective, this relationship holds significant importance. This finding suggests that ALI may serve as a simple clinical tool for identifying high-risk DR patients, particularly for those individuals with notably low ALI values.
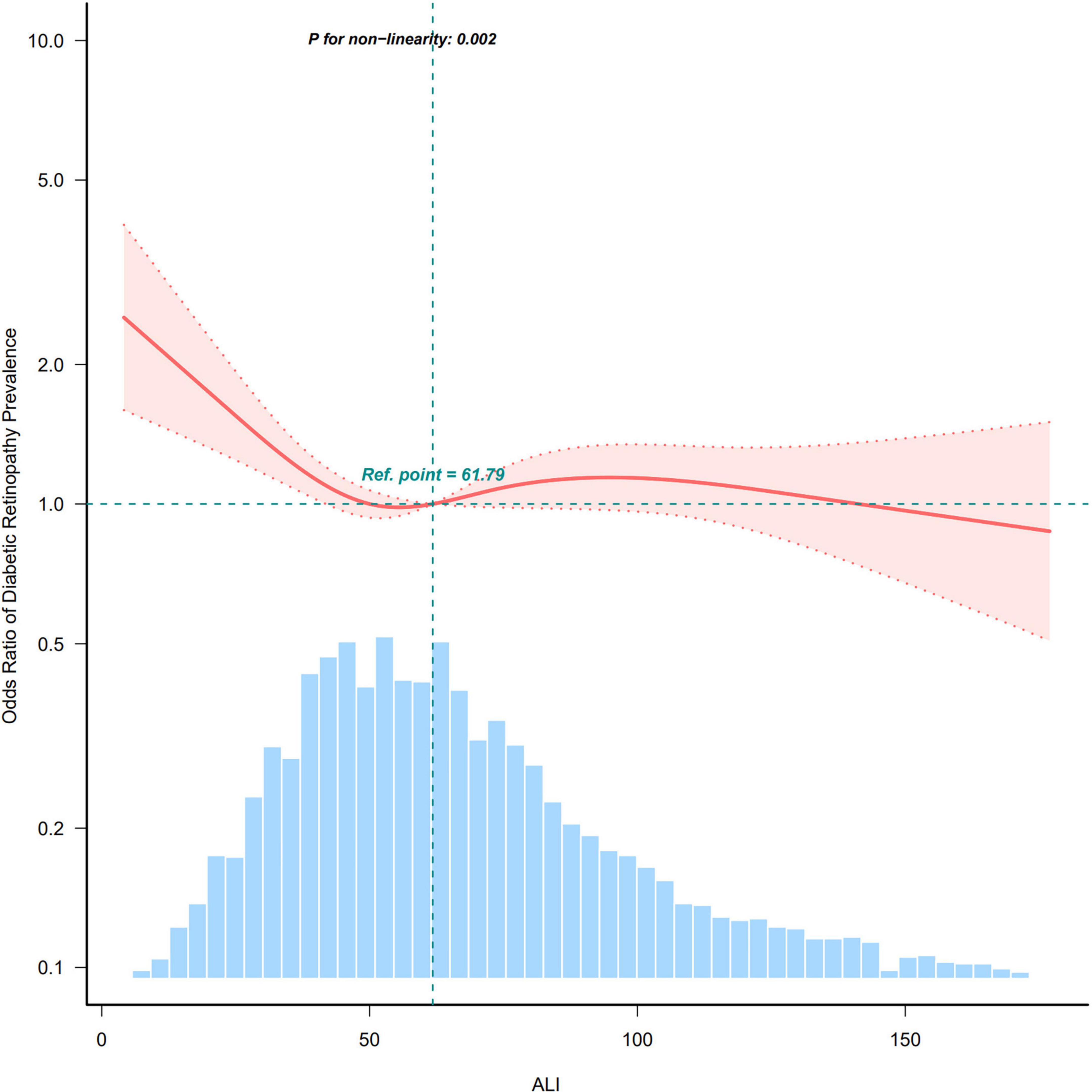
Figure 2. Restricted cubic spline curve illustrating the relationship between ALI and DR prevalence.
3.4 Subgroup analysis
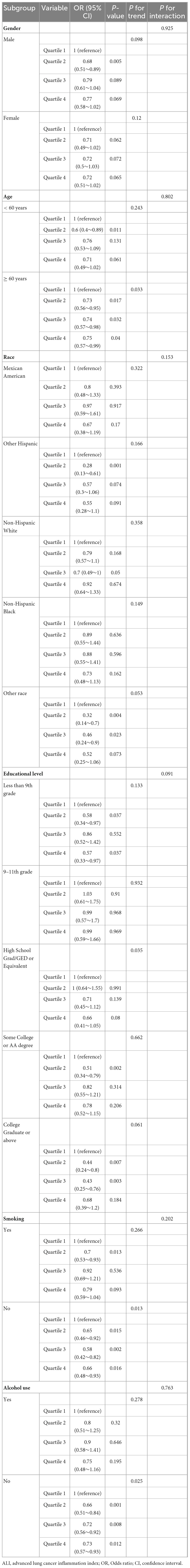
To verify the stability of the association between ALI and DR prevalence across different populations, multifactorial subgroup analyses were conducted (Table 3). The analyses included subgroups based on sex, age, race, education level, income level (PIR), smoking, alcohol consumption, history of myocardial infarction, history of heart failure, history of angina, hypertension, and diabetes. The results indicated that, except for race, the association between ALI and DR remained consistent across all subgroups, suggesting that the negative association between ALI and DR has high generalizability and stability. The protective association between higher ALI and lower DR prevalence was significantly stronger in African–American populations compared to other racial groups (P < 0.05). This suggests that African Americans may particularly benefit from interventions targeting ALI components, though the mechanisms underlying this racial difference require further investigation.
4 Discussion
This study utilized a nationally representative sample of American adults with diabetes to explore the relationship between the advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) and the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (DR). ALI integrates body mass index (BMI), albumin levels, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), thus reflecting systemic inflammatory, nutritional, and metabolic states. Our analysis revealed a significant L-shaped, non-linear association between ALI and DR prevalence. These observations suggest an association between systemic inflammatory-nutritional states and retinal microvascular status. Furthermore, racial differences moderated this association, underscoring the interplay between genetic, cultural, and socioeconomic factors in DR pathogenesis. These findings expand the applicability of ALI beyond oncology, highlighting its utility in systemic diseases and underscoring the need for a holistic approach for DR risk assessment (4, 16).
Reframing DR within the broader context of systemic health, this study challenges the traditional focus on hyperglycemia-induced microvascular damage (17). While chronic hyperglycemia disrupts endothelial function, induces oxidative stress, and increases vascular permeability (18, 19), our findings suggest that inflammatory and nutritional imbalances are equally pivotal. Additionally, glycoxidation of protein by reactive carbonyl compounds like methylglyoxal has been shown to disturb structural integrity and increase immunogenicity of important serum proteins like IgG, thereby contributing to inflammation and immune dysregulation in T2DM (20). The L-shaped association we observed underscores this complexity: lower ALI values may represent inadequate nutrition and increased inflammation, impairing repair mechanisms of retinal vasculature (21), while higher ALI values likely signify a more favorable metabolic environment with better nutritional status and lower inflammatory burden (22, 23). These observations align with emerging research on the role of inflammation in DR pathogenesis, where pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1β exacerbate vascular leakage and pathological angiogenesis (7). A comparison with existing literature further corroborates the clinical relevance of ALI (24). Previous studies have linked ALI to outcomes in coronary heart disease, chronic kidney disease, and diabetic nephropathy, suggesting shared pathophysiological pathways rooted in systemic inflammation and metabolic dysregulation. By demonstrating the association between ALI and DR, our study broadens its clinical scope, establishing it as a systemic health indicator rather than an organ-specific biomarker. Leveraging NHANES data ensures external validity and reduces selection bias, while our advanced statistical methods enable rigorous examination of non-linearities and effect modifiers. These methodological strengths underscore our findings: ALI appears to correlate with DR risk based on underlying systemic health. This perspective aligns with integrated care paradigms that emphasize the interplay between systemic and localized disease processes (25–27).
The potential mechanisms linking ALI to diabetic retinopathy are multifaceted. Chronic hyperglycemia triggers a cascade of deleterious changes in the retina, but the three components of ALI collectively reflect additional dimensions of systemic health that may influence retinal microvascular integrity. BMI correlates with metabolic states—high BMI indicates insulin resistance (28), while low BMI may signal malnutrition; albumin reflects nutritional and inflammatory status—low albumin implies chronic inflammation and catabolic stress (29); and NLR serves as a marker of systemic inflammation—elevated NLR indicates neutrophil predominance and lymphocyte suppression (30). By combining these factors, ALI transcends isolated biomarkers to provide a comprehensive measure of the patient’s physiological milieu (31). Poor nutritional status, as reflected by low albumin levels, compromises tissue repair mechanisms and antioxidant defenses, rendering the retina more vulnerable to metabolic insults (11). Furthermore, an abnormal body mass index, whether too low or excessively high, modulates insulin sensitivity, lipid profiles, and adipokine secretion, potentially amplifying microvascular damage (32) The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio emphasizes the chronic inflammatory milieu that may accelerate these processes through increased oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and vascular permeability. This systemic environment likely influences the delicate balance between damage and repair in retinal tissues, with lower ALI reflecting conditions that favor microvascular deterioration. Research suggests that inflammatory cells infiltrate the retina early in DR, where pro-inflammatory cytokines exacerbate vascular leakage and promote neovascularization (9). Thus, ALI emerges as a sentinel that reflects the systemic environment from which DR evolves. Rather than focusing exclusively on advanced retinal changes, ALI may potentially serve as an early indicator of systemic disturbances that precede clinically detectable retinopathy, though longitudinal studies are needed to confirm this temporal relationship.
The potential clinical implications of incorporating ALI into research on diabetes management warrant consideration, though our cross-sectional findings cannot establish causality. Current DR screening protocols primarily focus on glycemic control, diabetes duration, and periodic retinal examination. Evaluating whether complementing these approaches with ALI measurements provides clinically meaningful insights into patients’ systemic environment would require prospective clinical trials. If such studies confirm our findings, several potential applications might emerge. Patients with diabetes who exhibit lower ALI levels might benefit from more frequent retinal screening, even in the absence of other risk factors. Targeted nutritional interventions to improve serum albumin levels and anti-inflammatory strategies to reduce NLR could represent novel approaches to DR prevention, though these require prospective evaluation (33). In resource-limited settings where advanced imaging is inaccessible, ALI’s simplicity and cost-effectiveness could theoretically make it a practical complementary tool for risk stratification, though implementation would require validation studies. As healthcare paradigms shift toward precision medicine and prevention-focused strategies, integrative biomarkers like ALI align with these trends. Beyond individual care, the adoption of ALI has potential broader implications for public health research addressing diabetes complications. Replication of our findings across diverse populations could encourage further investigation into nutritional and inflammatory pathways in DR pathogenesis. On a population level, ALI distributions could identify at-risk subgroups, potentially guiding targeted research into community initiatives such as culturally sensitive dietary programs and exercise campaigns (26, 34–36). This research direction, focusing on upstream factors rather than downstream complications, may ultimately contribute to improved patient outcomes and more efficient use of healthcare resources. However, we emphasize that these potential applications require confirmation through longitudinal and interventional studies before any clinical implementation can be recommended.
Before concluding, it is important to acknowledge several limitations of this study. The cross-sectional design precludes definitive conclusions about causality, as the temporal relationship between ALI elevation and DR development remains undetermined—whether high ALI predisposes individuals to DR or if early DR alters systemic parameters reflected in ALI components. Prospective longitudinal studies are needed to establish these temporal sequences and evaluate if ALI modification reduces DR risk. A notable limitation is our use of self-reported DR data rather than clinical verification, potentially underestimating DR prevalence, especially in milder cases. While pragmatic for large-scale surveys like NHANES, incorporating retinal imaging or standardized ophthalmoscopy would substantially enhance diagnostic accuracy in future studies. The absence of comprehensive glycemic control assessment, particularly HbA1c measurements, represents a significant methodological limitation that introduces interpretative complexity to our findings. Additionally, while ALI integrates key inflammatory and metabolic indicators, its current formulation omits critical variables including glycemic control, blood pressure measurements, and angiogenic factors such as VEGF. Refining ALI or combining it with complementary markers could significantly improve its clinical utility (37). Important unmeasured confounders—genetic factors, dietary patterns, and psychosocial stressors—likely contribute to unexplained variability despite our adjustment efforts. Furthermore, our study did not differentiate between non-proliferative and proliferative DR stages. Future research should explore whether the relationship between ALI and DR varies by retinopathy severity, which could facilitate more targeted preventive strategies. The study’s strengths lie in its large, diverse NHANES sample, enhancing external validity. However, the relatively modest number of DR cases limits statistical power for subgroup analyses and may obscure important interactions. Future pooled analyses across multiple datasets could provide more precise population-specific ALI thresholds and clarify their role in DR pathophysiology (38).
In conclusion, this cross-sectional study identifies a significant inverse association between ALI and DR prevalence, suggesting potential utility of ALI as a risk stratification tool. While our findings suggest ALI could be relevant to DR pathophysiology, prospective studies are necessary before recommending its integration into routine clinical practice.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because Ethics approval and consent to participate the protocols for NHANES were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the National Center for Health Statistics, CDC (https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/default.aspx). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JP: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Software, Conceptualization. ZC: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review and editing, Software. YW: Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Methodology. KW: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Resources. FW: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Data curation, Conceptualization. JX: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Hubei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant No. ZY2023Q028), the Enshi Prefecture Science and Technology Program (Grant No. XYJ2023000019), and the Enshi Prefecture “Sailing Special” Science and Technology Plan Project in 2024.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Jenkins A, Joglekar M, Hardikar A, Keech A, O’Neal D, Januszewski A. Biomarkers in diabetic retinopathy. Rev Diabet Stud. (2015) 12:159–95. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2015.12.159
2. Simó-Servat O, Simó R, Hernández C. Circulating biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy: An overview based on physiopathology. J Diabetes Res. (2016) 2016:5263798. doi: 10.1155/2016/5263798
3. Ren J, Zhang S, Pan Y, Jin M, Li J, Luo Y, et al. Diabetic retinopathy: Involved cells, biomarkers, and treatments. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:953691. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.953691
4. Ramos H, Hernández C, Simó R, Simó-Servat O. Inflammation: The link between neural and vascular impairment in the diabetic retina and therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:8796. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108796
5. Cunha-Vaz J, Ribeiro L, Lobo C. Phenotypes and biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. (2014) 41:90–111. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2014.03.003
6. Kwan C, Fawzi A. Imaging and biomarkers in diabetic macular edema and diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diab Rep. (2019) 19:95. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1226-2
7. Tang L, Xu G, Zhang J. Inflammation in diabetic retinopathy: Possible roles in pathogenesis and potential implications for therapy. Neural Regen Res. (2023) 18:976–82. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.355743
8. Vujosevic S, Simó R. Local and systemic inflammatory biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy: An integrative approach. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. (2017) 58:BIO68–75. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-21769
9. Youngblood H, Robinson R, Sharma A, Sharma S. Proteomic biomarkers of retinal inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:4755. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194755
10. Maeda D, Kanzaki Y, Sakane K, Ito T, Sohmiya K, Hoshiga M. Prognostic impact of a novel index of nutrition and inflammation for patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Heart Vessels. (2020) 35:1201–8. doi: 10.1007/s00380-020-01590-4
11. Martinez B, Peplow P. MicroRNAs as biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy and disease progression. Neural Regen Res. (2019) 14:1858–69. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.259602
12. Khan A, Rahmani A, Aldebasi Y. Diabetic retinopathy: Recent updates on different biomarkers and some therapeutic agents. Curr Diabetes Rev. (2018) 14:523–33. doi: 10.2174/1573399813666170915133253
13. Liu S, Ju Y, Gu P. Experiment-based interventions to diabetic retinopathy: Present and advances. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:7005. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137005
14. Chen Y, Xiang X, Wu Y, Han S, Huang Z, Wu M. Magnesium depletion score predicts diabetic retinopathy risk among diabetes: Findings from NHANES 2005-2018. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2023) 201:2750–6. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03384-3
15. Chen Y, Guan M, Wang R, Wang X. Relationship between advanced lung cancer inflammation index and long-term all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: NHANES, 1999-2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1298345. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1298345
16. Soltani S, Ashoori M, Dehghani F, Meshkini F, Clayton Z, Abdollahi S. Effects of probiotic/synbiotic supplementation on body weight in patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized-controlled trials. BMC Endocr Disord. (2023) 23:86. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01338-x
17. Whitehead M, Wickremasinghe S, Osborne A, Van Wijngaarden P, Martin K. Diabetic retinopathy: A complex pathophysiology requiring novel therapeutic strategies. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2018) 18:1257–70. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2018.1545836
18. Lechner J, O’Leary O, Stitt A. The pathology associated with diabetic retinopathy. Vis Res. (2017) 139:7–14. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2017.04.003
19. Duh E, Sun J, Stitt A. Diabetic retinopathy: Current understanding, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. JCI Insight. (2017) 2:e93751. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.93751
20. Islam S, Moinuddin, Mir AR, Arfat MY, Alam K, Ali A. Studies on glycoxidatively modified human IgG: Implications in immuno-pathology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Biol Macromol. (2017) 104:19–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.190
21. Wan H, Cai Y, Wang Y, Fang S, Chen C, Chen Y, et al. The unique association between the level of peripheral blood monocytes and the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy: A cross-sectional study. J Transl Med. (2020) 18:248. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02422-9
22. Sharma A, Arora D. Role of inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. In: GL Giudice editor. Diabetic eye disease–from therapeutic pipeline to the real world. London: IntechOpen (2021).
23. Araújo R, Bitoque D, Silva G. Dual-acting antiangiogenic gene therapy reduces inflammation and regresses neovascularization in diabetic mouse retina. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2020) 22:329–39. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.08.036
24. Guo H, Wan C, Zhu J, Jiang X, Li S. Association of systemic immune-inflammation index with insulin resistance and prediabetes: A cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1377792. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1377792
25. Sheu W, Lin K, Wang J, Lai D, Lee W, Lin F, et al. Therapeutic potential of Tpl2 (tumor progression locus 2) inhibition on diabetic vasculopathy through the blockage of the inflammasome complex. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2021) 41:e46–62. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315176
26. Gouliopoulos N, Kalogeropoulos C, Lavaris A, Rouvas A, Asproudis I, Garmpi A, et al. Association of serum inflammatory markers and diabetic retinopathy: A review of literature. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2018) 22:7113–28. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201811_16243
27. Victor A, Sitompul R. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy: An overview of vitreous immune and biomarkers. London: IntechOpen (2018).
28. Jiang Y, Fan H, Xie J, Xu Y, Sun X. Association between adipocytokines and diabetic retinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1271027. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1271027
29. Li X, Hao W, Yang N. Inverse association of serum albumin levels with diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients: A cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:4016. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54704-7
30. Li J, Wang X, Jia W, Wang K, Wang W, Diao W, et al. Association of the systemic immuno-inflammation index, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio with diabetic microvascular complications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1367376. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1367376
31. Li Y, Hu B, Lu L, Li Y, Caika S, Song Z, et al. Development and external validation of a predictive model for type 2 diabetic retinopathy. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:16741. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67533-5
32. Pachpute A, Jha R, Kachawa K. Diabetic retinopathy disease. Int J Health Sci. (2022) 6:481–7. doi: 10.53730/ijhs.v6nS2.5042
33. Rübsam A, Parikh S, Fort P. Role of inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:942. doi: 10.3390/ijms19040942
34. Forrester J, Kuffova L, Delibegovic M. The role of inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:583687. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.583687
35. Platania C, Maisto R, Trotta M, D’Amico M, Rossi S, Gesualdo C, et al. Retinal and circulating miRNA expression patterns in diabetic retinopathy: An in silico and in vivo approach. Br J Pharmacol. (2019) 176:2179–94. doi: 10.1111/bph.14665
36. Zapadka T, Lindstrom S, Taylor B, Lee C, Tang J, Taylor Z, et al. RORγt inhibitor-SR1001 halts retinal inflammation, capillary degeneration, and the progression of diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:3547. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103547
37. Adki K, Kulkarni Y. Potential biomarkers in diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diabetes Rev. (2020) 16:971–83. doi: 10.2174/1573399816666200217092022
Keywords: advanced lung cancer inflammation index, diabetic retinopathy, inflammation, nutrition, metabolic health, NHANES, non-linear association
Citation: Peng J, Chen Z, Wang Y, Wang K, Wu F and Xiang J (2025) Nutritional-inflammatory status and diabetic retinopathy: exploring the association between advanced lung cancer inflammation index and retinal complications in diabetes. Front. Nutr. 12:1602361. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1602361
Received: 29 March 2025; Accepted: 05 June 2025;
Published: 30 June 2025.
Edited by:
Raminderjit Kaur, Case Western Reserve University, United StatesReviewed by:
Sidra Islam, Case Western Reserve University, United StatesKang Qin, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, United States
Niu Jinliang, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Peng, Chen, Wang, Wang, Wu and Xiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Wu, d2YzNzk3Mzg4NjNAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Jianjun Xiang, eGlhbmcyMDI0MTIxOUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jinxiang Peng1,2†
Jinxiang Peng1,2† Zhuang Chen
Zhuang Chen Feng Wu
Feng Wu