- 1Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, China
- 2University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
- 3Hefei Normal University, Hefei, China
- 4Faculty of Sports and Exercise Science, Universiti Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- 5College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
- 6Progression School of Upper Secondary, Beijing College of Finance and Commerce, Beijing, China
- 7Department of Physical Education and Research, Central South University, Changsha, China
Objectives: To investigate the association between Lactobacillus levels, depressive mood, and body mass index (BMI) among Chinese college students. In addition, to examine whether depressive mood mediates the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI and whether physical activity (PA) moderates this association.
Methods: This cross-sectional study recruited 423 Chinese college students using a multi-stage stratified sampling method. Lactobacillus levels were measured from stool samples, depressive mood was assessed using a well-designed depression scale, PA was tracked with accelerometers, and BMI was calculated using calibrated electronic scales. Confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, regression analysis, and tests for mediation and moderation effects were conducted using SPSS and AMOS software.
Results: Lactobacillus levels exhibited significant negative correlations with depressive moods (r = −0.131, p < 0.01) and BMI (r = −0.113, p < 0.05), while depressive mood showed a positive correlation with BMI (r = 0.117, p < 0.05). Mediation analysis revealed that depressive moods mediated the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI, with an indirect effect of −0.021 (95% CI: −0.062 to −0.001). PA significantly moderated the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI, as evidenced by an interaction coefficient of 0.009 (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Depressive mood could mediate the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI, with PA playing a moderating role. This study provides new evidence for weight and depression management in college students.
1 Introduction
Obesity has emerged as a global health challenge, with its prevalence rising at an alarming rate (1). Obesity and overweight are major risk factors for various chronic diseases, including diabetes (2), cancer (3), cardiovascular diseases (4), and hypertension (5). BMI, defined as the ratio of weight (kg) to the square of height (m2), is a commonly used indicator for classifying overweight and obesity in adults. BMI categorizes overweight as 25–29.9 and obesity as ≥30 (6). In China, the adult obesity rate has reached 16.4% (7), higher than the global average (8). College students, burdened by academic pressure, insufficient PA, and prolonged sedentary behavior, also experience a notably high prevalence of obesity (9).
Growing evidence suggests that gut microbiota plays a critical role in the development of obesity (10), offering new possibilities for microbiota-mediated weight management interventions. Obesity is closely associated with changes in gut microbiota composition, such as alterations in the Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio and levels of specific microbial genera (11). Probiotics, which are live microorganisms that enhance gut microbiota function, benefit the host, with Lactobacillus being the most prominent type (12). Currently, probiotic supplementation is gaining acceptance as an obesity intervention, with several reviews confirming its significant role in managing obesity (13, 14). Studies indicate that Lactobacillus can effectively alleviate obesity symptoms by reducing blood lipids, improving gut microbiota, regulating the immune system, and influencing metabolism (14–17). Notably, recent findings further reveal that gut microbiota-based interventions, including probiotics, synbiotics, and prebiotics, hold promising prospects for addressing diabetes (18), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (19), and their related metabolic complications.
Beyond its role in host metabolism, the gut microbiota communicates with the central nervous system via the microbiota–gut–brain axis, thereby modulating mood and behavior (20, 21). Among them, depression is highly prevalent in college students and ranks as the fourth leading cause of suicide among individuals aged 15–29 (22). Research has indicated that the composition of gut microbiota may help mitigate depression (23), and such microorganisms are termed psychobiotics. Psychobiotics, primarily including Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, can produce neuroactive substances such as gamma-aminobutyric acid and serotonin (24). In rodent models, Lactobacillus has been shown to prevent postpartum depression via the microbiota-gut-brain axis (25). Additionally, Lactobacillus can alleviate depression-like symptoms caused by dendritic cytokine deficiencies (26).
Obesity and depression frequently co-occur and interact in a self-perpetuating cycle. The risk of depression increases by 55% when BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, and the association between obesity and depression is even stronger when BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2 (27). Blasco et al. (28) conducted a longitudinal study on obesity and depression mood between 2012 and 2017, highlighting depression as a risk factor for obesity. Contemporary understanding of depression has evolved, recognizing weight gain and increased appetite as key “typical” core symptoms (29). A national survey of 43,093 U.S. adults, for instance, found that the prevalence of major depressive disorder with atypical features was nearly 40% higher than that of the disorder without atypical features (30). Depressed individuals often improve their mood by consuming high-fat, high-sugar “comfort foods” (29), a process that is linked to excessive activation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, elevated cortisol levels, fat accumulation, and insulin resistance (31), all of which may contribute to weight gain. Therefore, effectively addressing depressive symptoms is expected to mitigate the obesity-promoting tendencies mentioned above.
Overall, Lactobacillus can directly reduce BMI and effectively alleviate depressive mood levels, and the latter, in turn, contributes to BMI reduction. Thus, it is plausible to hypothesize that depressive mood mediates the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI. Additionally, existing evidence suggests that PA moderates this association. To our knowledge, no prior studies have examined whether depressive mood mediates the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI, nor have they investigated whether PA moderates this association. Addressing this knowledge gap is essential, as the findings could provide preliminary empirical evidence on the mediating role of depressive mood and the moderating effect of PA on this association. Moreover, these findings provide a scientific foundation for designing targeted mental health and weight management interventions tailored to college students.
Therefore, this research conducted a cross-sectional study to investigate the association among Lactobacillus levels, depressive mood, and BMI in college students, as well as the moderating effect of PA on the association. This study aims to address three primary questions: (1) What is the association among Lactobacillus levels, depressive mood, and obesity in Chinese college students? (2) Does depressive mood mediate the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI? (3) Does PA moderate the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI?
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and participants
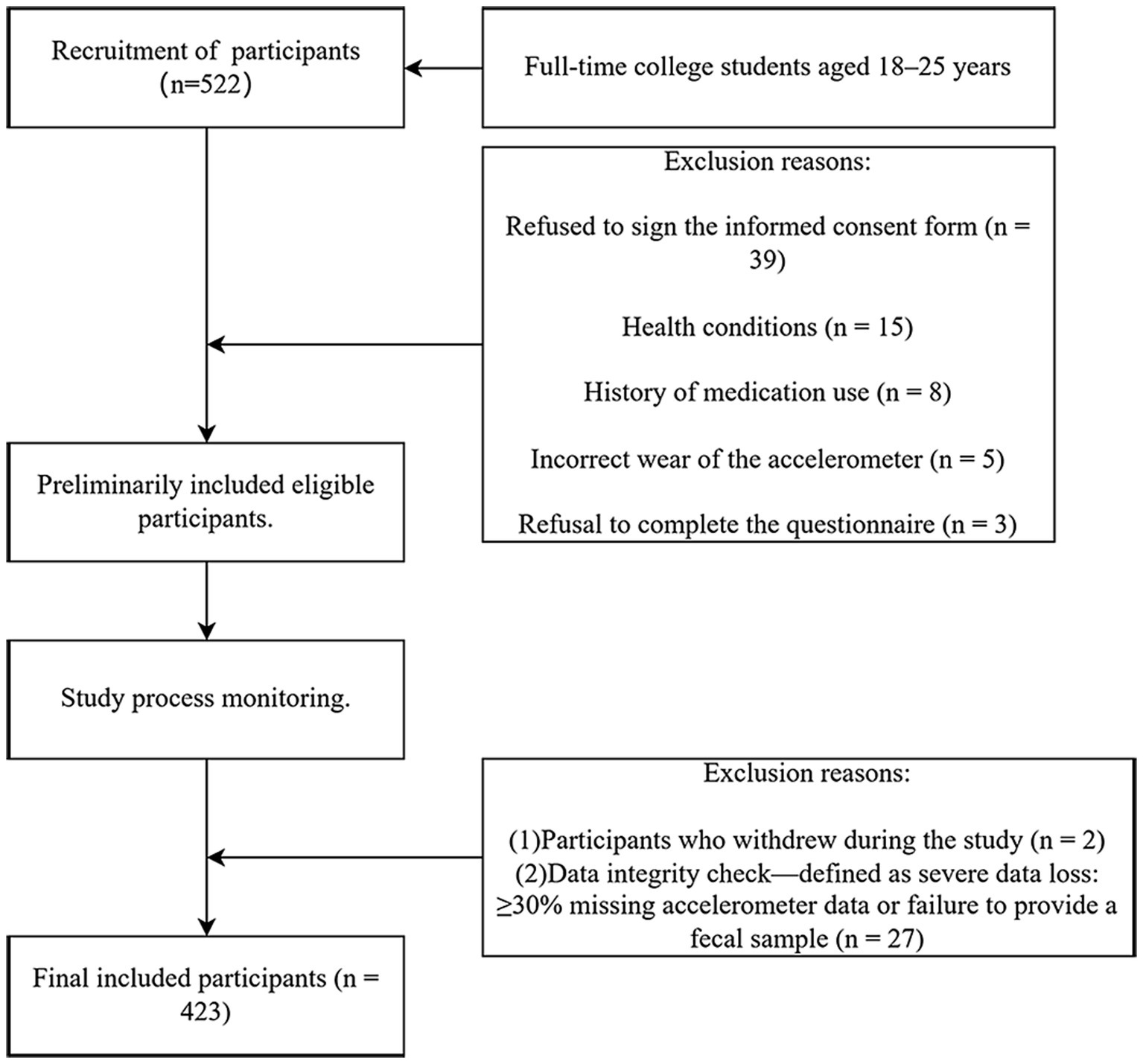
A multi-stage stratified sampling method was employed to recruit college students from multiple universities, ensuring the diversity and representativeness of the sample. Inclusion criteria included full-time college students aged 18–25 years who could understand and voluntarily sign an informed consent form, had no severe chronic diseases (e.g., cardiovascular diseases or diabetes), no history of mental disorders (e.g., diagnosed depression or anxiety), and no use of probiotics or antibiotics in the past three months. Exclusion criteria encompassed inability to properly wear or use the research equipment (e.g., accelerometers); refusal to participate in the questionnaire survey or provide stool samples; withdrawal from the study, or severe data missing. Severe data missing was defined as a participant missing ≥30% of their accelerometer data or failing to provide a stool sample. Ultimately, 27 participants were excluded due to severe data loss. After rigorous screening (Figure 1), a total of 423 college students were included in this study. To improve participant compliance, the study provided a gift card incentive to each student who completed the data collection process. The study received approval from the Biomedical Ethics Committee of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (SWYX-Y-2021-53).
2.2 Measurements
2.2.1 Lactobacillus
Under professional supervision, students collected stool samples in sterile containers in the morning, which were promptly stored in low-temperature preservation boxes. The samples were swiftly transported to a specialized laboratory, where advanced molecular biological techniques, such as quantitative fluorescence PCR, were employed to accurately detect Lactobacillus using specific primers. Based on the results, Lactobacillus levels were categorized as abnormal (coded as 0) or normal (coded as 1). Based on the reference standard for healthy population microbiome research (32), this study classified a relative abundance of Lactobacillus below 1% as abnormal and ≥ 1% as normal. In subsequent sensitivity analyses, mediation models were re-estimated using the raw abundance values, and the core findings remained essentially unchanged (Supplementary materials 1, 2).
2.2.2 Depressive mood
The depressive mood scale used in this study was developed based on Radloff’s CES-D scale (33) and the shortened version proposed by Kohout et al. (34). The scale is designed to measure depressive mood states over the past two weeks (e.g., sadness, hopelessness), rather than clinical depression. It contains 9 items, scored on a 4-point scale ranging from “never” to “always,” scored 1 to 4. Its Cronbach’s α coefficient was 0.944, indicating high internal consistency and reliability for measuring depressive mood traits. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) showed model fit indices as chi-square = 163.789 (df = 27), chi-square/df = 6.066 (p < 0.000), GFI = 0.912, AGFI = 0.854, CFI = 0.956, RMSEA = 0.110, and RMR = 0.036. According to SEM fit criteria (35), an RMSEA ≤ 0.08 is considered indicative of a good fit, while values between 0.08 and 0.12 fall within an acceptable range. In the present study, RMSEA was 0.110. Although this exceeds the ideal threshold, when taking into account the sample size and the short-form nature of the scale, this result remains within the acceptable range. Overall, it suggests that the scale demonstrates satisfactory structural validity.
2.2.3 PA
Each participant was provided with a high-precision accelerometer (ActiGraph, Pensacola, Florida) and instructed on its use and precautions. Participants were required to wear the accelerometer on their waist continuously for 7 days, except during sleep, bathing, or other special circumstances, to ensure data integrity and accuracy. The accelerometer recorded acceleration data during daily activities, which was analyzed using specialized software (e.g., ActiGraph’s proprietary software) to calculate daily PA levels. The study primarily used the average daily total activity as the core indicator, derived by dividing the total weekly activity by 7.
2.2.4 BMI
Body weight (accurate to 0.1 kg) and height (accurate to 0.01 m) were measured using rigorously calibrated electronic scales (brand: Omron, model: HBF-260 T1) and stadiometers (brand: Shanghe, model: SH-200G), respectively. BMI was calculated using the international standard formula: BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height2 (m2). BMI was used as a key indicator to assess obesity levels among college students.
2.3 Statistical methods
Data analysis was conducted using SPSS 26.0 and AMOS 24.0. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize basic characteristics. Bivariate correlation analysis was performed to examine interdimensional association and measure the strength of correlation between variables, with results expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Confirmatory factor analysis was performed on the scale using AMOS 24.0, evaluating structural validity with relevant fit indices. The indirect effect’s 95% confidence interval was estimated using the bias-corrected percentile method, with 5,000 bootstrap replications to minimize sampling bias (36). PA was added as a moderator in a moderation analysis. Interaction term coefficients were tested for significance to determine moderation, and the Johnson-Neyman method in PROCESS was applied to generate moderation effect plots. Unlike simple slope analysis, which evaluates the effect of the independent variable at selected moderator values, the Johnson–Neyman technique is appropriate when we want to determine comprehensively and precisely at which points across the moderator’s entire range the interaction effect is significant. Simple slope analysis only illustrates the IV–DV relationship at specific moderator values, whereas the Johnson–Neyman technique calculates the critical values of the moderator (e.g., PA) to identify the exact interval in which the main effect is significant.
3 Results
3.1 Demographic information
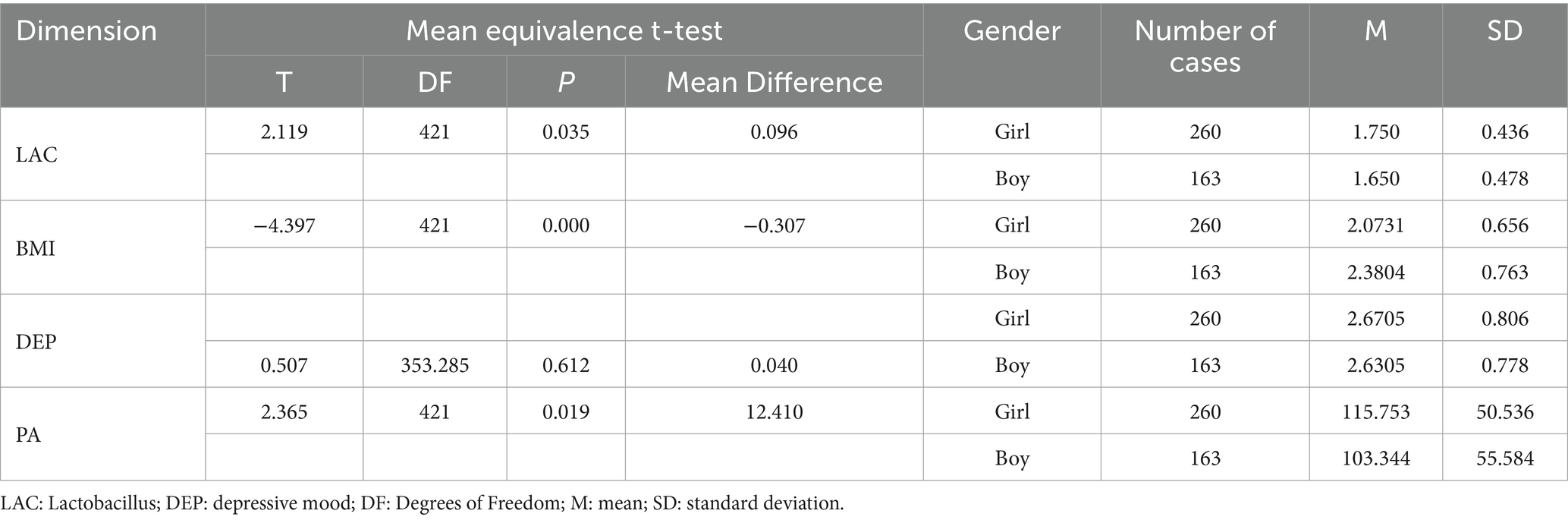
Independent samples t-tests were conducted to examine gender differences in Lactobacillus levels, BMI, depressive mood, and PA. Results indicated no significant gender difference in depressive mood (p = 0.612), whereas significant differences were identified for PA (p = 0.019) and Lactobacillus (p = 0.010), with girls outperforming boys in both. Significant gender differences were also observed in BMI, with boys outperforming girls (see Table 1).
3.2 Correlation analysis of variables
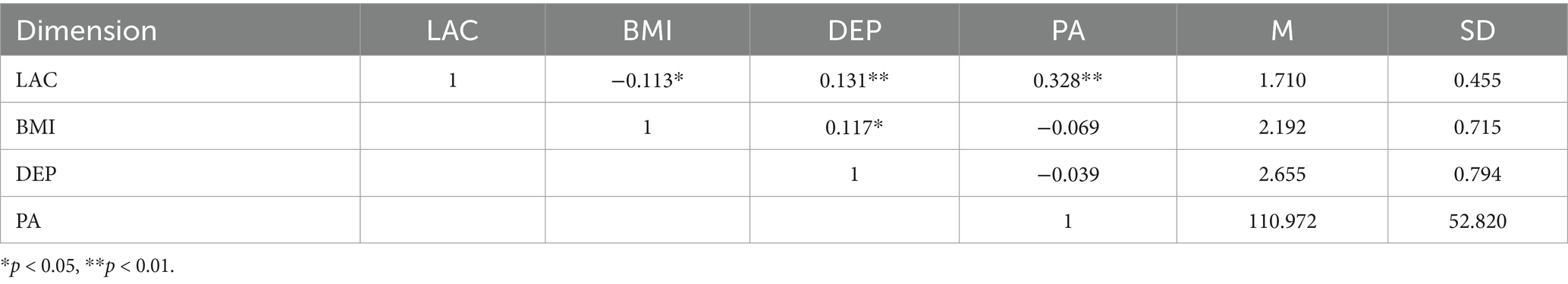
Pearson correlation analysis was conducted for all variables, as presented in Table 2. Lactobacillus was significantly positively correlated with depressive mood (r = 0.131, p < 0.01) and PA (r = 0.328, p < 0.01) but significantly negatively correlated with BMI (r = −0.113, p < 0.05). BMI showed a significant positive correlation with depressive mood (r = 0.117, p < 0.05), whereas both BMI and depressive mood exhibited non-significant negative correlations with PA (r = −0.069, p > 0.05; r = −0.039, p > 0.05).
3.3 Mediation effect of depressive mood
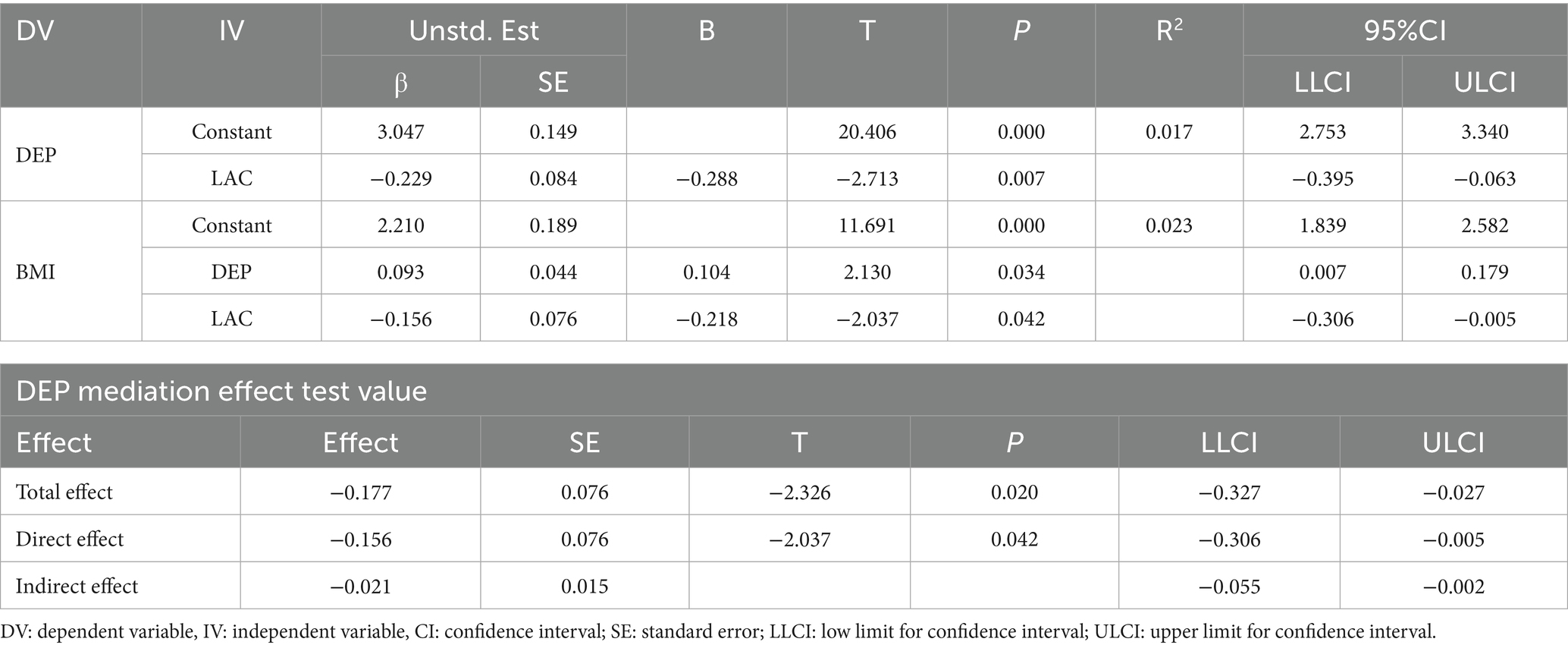
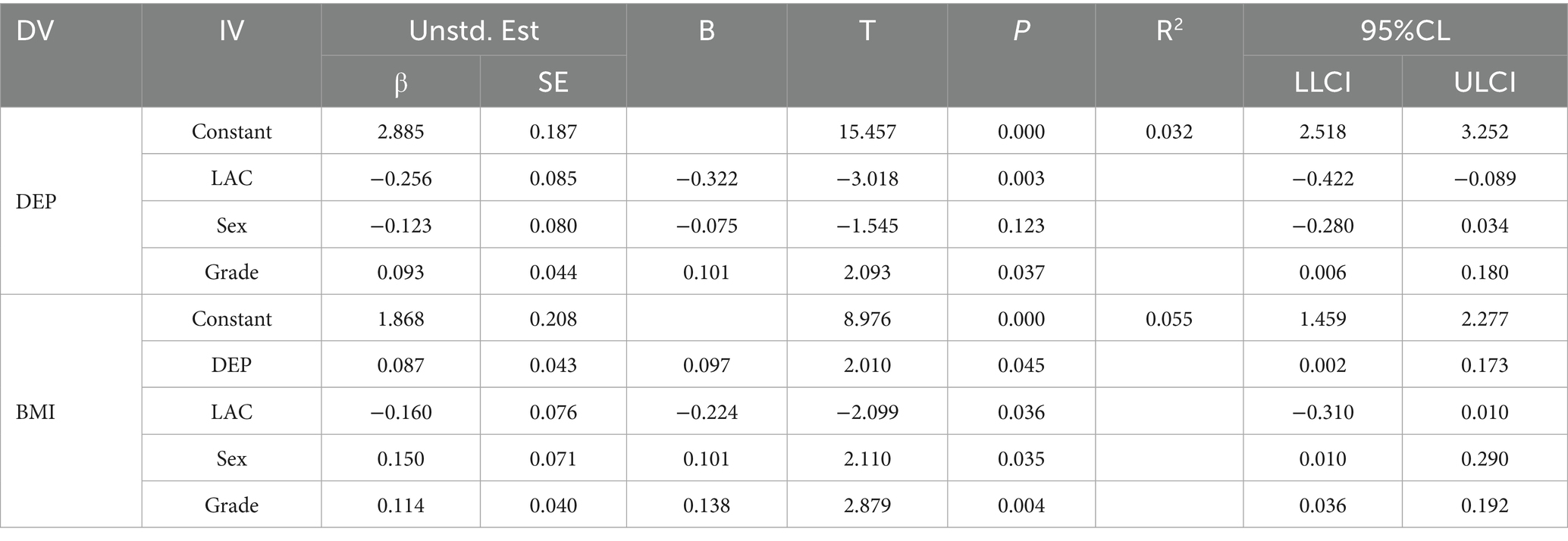
Model 4 of the SPSS PROCESS was utilized to examine the mediating effect of depressive mood in the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI among college students. As shown in Table 3, after controlling for constants, Lactobacillus levels have a significant negative impact on depressive mood (β = −0.229, SE = 0.084, t = −2.713, p = 0.007). This indicates that higher levels of Lactobacillus are associated with lower levels of depressive mood. Lactobacillus levels also have a significant negative impact on BMI (β = −0.156, SE = 0.076, t = −2.037, p = 0.042), suggesting that higher levels of Lactobacillus are associated with lower BMI. Lactobacillus levels have a significant positive impact on BMI (β = 0.093, SE = 0.044, t = −2.103, p = 0.034), indicating that lower depressive mood is associated with lower obesity. In the mediation effect test, the total effect is −0.177 with a 95% CI (−0.327, −0.027), the direct effect is −0.156 with a 95% CI (−0.306, −0.005), and the indirect effect is −0.021 with a 95% CI (−0.062, −0.001), not including zero. These results suggest a significant mediating trend.
3.4 Mediation analysis with covariates controlled
After controlling for covariates such as sex and grade level, the mediation analysis yielded clearer results. As shown in Table 4, the Lactobacillus (LAC) exerted a significant negative effect on DEP (β = −0.256, p = 0.003), representing a “net effect” after eliminating confounding factors, which authentically reflects their association. Grade level showed a significant positive effect on DEP (β = 0.093, p = 0.037), while the effect of sex was nonsignificant (p = 0.123). For BMI, both sex (β = 0.150, p = 0.035) and grade level (β = 0.114, p = 0.004) had significant positive effects. Without covariate adjustment, these factors could conflate the relationship between LAC and BMI, leading to biased estimates. Moreover, after covariate adjustment, the direct effects of LAC (p = 0.036) and DEP (p = 0.045) on BMI remained significant. Compared to the unadjusted model, this approach more accurately isolates the independent effects of each variable, providing a robust basis for dissecting their interrelationships.
3.5 Test of the moderating effect of PA using a mixed model
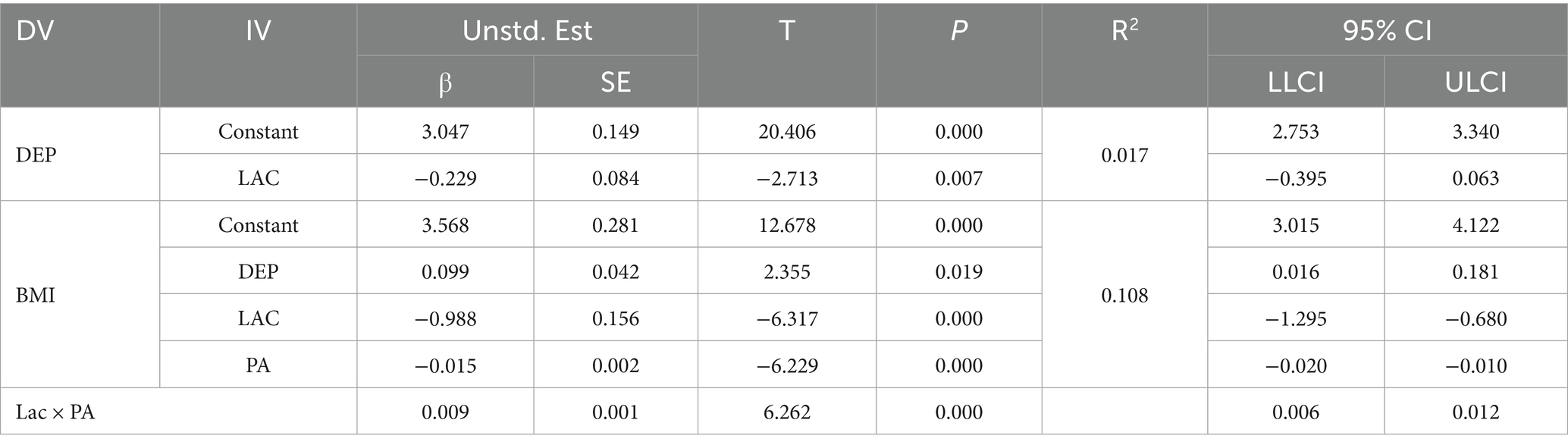
Utilizing SPSS PROCESS Model 5, this study conducted a mixed model analysis to investigate the association between Lactobacillus levels, depressive mood, and BMI. The results showed significant effects (Table 5): for depressive mood as the dependent variable, the intercept was 3.047 with a SE of 0.149, yielding a t-value of 20.406 and a highly significant p-value (<0.001). Lactobacillus levels were significantly inversely correlated with Lactobacillus (β = −0.229, SE = 0.084, t = −2.713, p = 0.007), suggesting that higher Lactobacillus levels are associated with lower depressive mood. For BMI, the intercept coefficient was 3.568 (SE = 0.281, t = 12.678, p < 0.001), with Lactobacillus levels positively correlated with BMI (β = 0.099, SE = 0.042, t = 2.355, p = 0.019), indicating that higher depressive mood is associated with higher BMI. Lactobacillus had a significant negative impact on BMI (β = −0.988, SE = 0.156, t = −6.317, p < 0.001), and PA also demonstrated a negative effect (β = −0.015, SE = 0.002, t = −6.229, p < 0.001). The interaction term Lactobacillus x PA positively influenced BMI (β = 0.009, SE = 0.001, t = 6.262, p < 0.001). These findings elucidate the significant roles of each variable and their interactions, offering a strong foundation for further exploration of these associations.
3.6 Johnson-Neyman moderation effect model
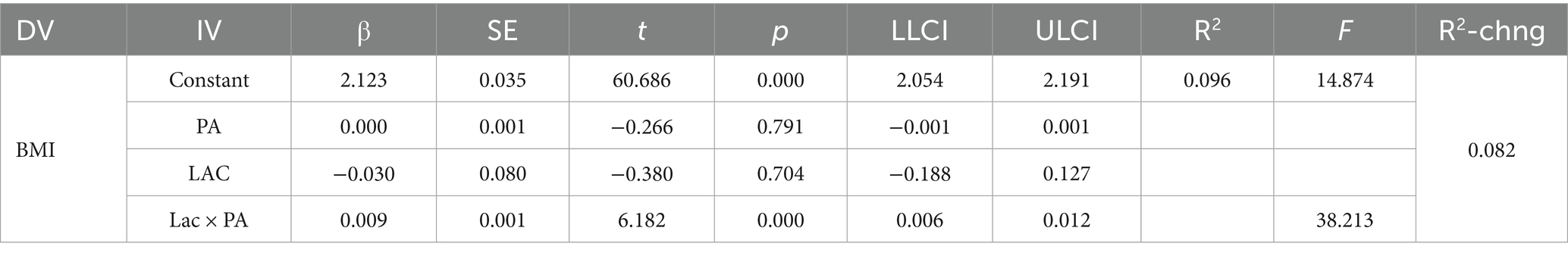
The moderating effect of PA was tested using SPSS PROCESS Model 1. As shown in Table 6, the interaction term Lactobacillus × PA yielded a coefficient (β) of 0.009, with a SE of 0.001, a t-value of 6.182, and a p-value of 0.000. The 95% CI (0.006, 0.012) confirmed the significant effect, indicating a notable interaction between Lactobacillus levels and PA that impacts the dependent variable. The overall model explained 9.6% of the variance in the dependent variable (R2 = 0.096), with an F-value of 14.874 and a p-value of less than 0.001, demonstrating the significance of the entire model.
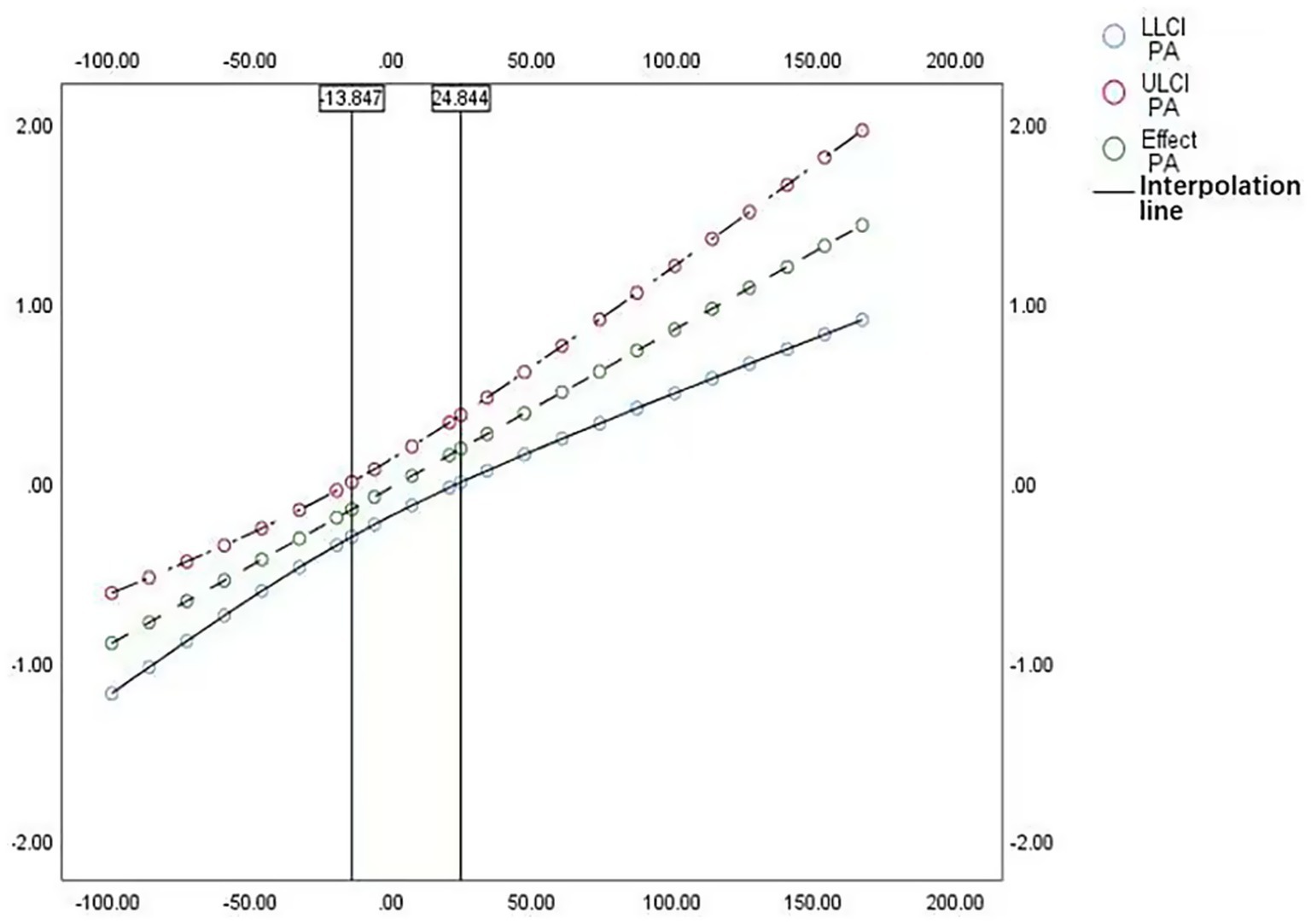
To better elucidate the moderating role of PA, we employed the Johnson-Neyman technique to identify the range of values where the moderation effect is significant. As shown in Figure 2, the moderation effect is statistically significant within the left interval below −13.847 and the right interval above 24.844. Specifically, when PA < −13.847 or PA > 24.844, the effect of Lactobacillus on BMI varies significantly as PA changes; between these two critical values, the moderation effect is not significant. Interpreting the moderation in terms of these thresholds and intervals provides a more intuitive understanding of how the effect behaves across the full range of the moderator, rather than relying solely on the interaction-term coefficient.
4 Discussion
4.1 Gender differences
From a gender perspective, our study revealed that females exhibited significantly higher Lactobacillus levels than males, which aligns with previous research. Previous studies suggest that gender influences gut microbiota composition, serving as a key determinant of microbial diversity and function (37). Our results highlight the importance of incorporating gender as a crucial variable in studies on the health effects of gut microbiota. In terms of BMI, males exhibited significantly lower levels than females, in line with established gender differences. This difference likely stems from gender-related variations in fat distribution and metabolic rates (38). These results provide additional evidence for the role of gender in weight management and underscore its implications for developing targeted interventions. Although our study found no significant gender differences in depressive mood, this does not diminish the role of gender in psychological health. However, other studies suggest that gender differences exist in the experience and expression of depressive mood (39). The absence of significant findings may stem from limitations such as sample size or measurement tools, highlighting the need for further investigation. In terms of physical activity, females were significantly more active than males, particularly in specific activity types, consistent with epidemiological evidence (40). This finding has important implications for designing gender-specific exercise interventions to enhance program effectiveness in promoting health across populations.
4.2 Correlations among variables
Among college students, the positive correlation between Lactobacillus levels and depressive mood reveals the intricate link between gut microbiota and mental health. This finding is consistent with existing evidence suggesting that the gut microbiome influences mood and behavior via the gut-brain axis (41). As a beneficial bacterium, the abundance of Lactobacillus in the gut may play a positive role in enhancing mental health (42). The observed positive association between Lactobacillus levels and PA offers new insights into the interplay between gut microbiota and lifestyle. This suggests that engaging in PA not only enhances physical health but may also exert a positive influence on mental well-being by fostering the proliferation of beneficial gut bacteria. The significant inverse correlation between Lactobacillus levels and BMI provides valuable insights into the role of gut microbiota in weight regulation. This finding suggests a potential role of Lactobacillus in regulating energy balance and fat metabolism, thereby contributing to weight maintenance.
4.3 Mediation effect of depressive mood
The study found a significant negative correlation between Lactobacillus levels and depressive mood, consistent with previous research (41). The prior research has indicated that the gut microbiota may influence mood and behavior through the gut-brain axis (41). Our results provide further evidence, suggesting that Lactobacillus may positively impact mental health by modulating the synthesis and release of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine. Additionally, Lactobacillus is believed to regulate the body’s response to stress, thereby potentially mitigating depression and anxiety (43). Another noteworthy finding is the significant negative correlation between Lactobacillus levels and BMI (44, 45), consistent with the previous research (46). Notably, the cross-sectional design of this study reveals only associations among Lactobacillus levels, BMI, and depressive mood, and cannot establish causality; therefore, these findings should be interpreted cautiously in clinical practice. Previous experimental studies have demonstrated that supplementation with psychobiotics (Lactobacillus) caneduce obesity (47) and depression (48) in adults. Lactobacillus supplementation may serve as a promising intervention to mitigate obesity and depression among college students. We also observed a significant positive relationship between depressive mood and BMI. As supported by existing literature, depressive mood may contribute to unhealthy eating behaviors, such as emotional eating, which in turn may influence BMI and waist circumference (49). This positive correlation suggests that depressive mood might lead individuals to engage in unhealthy eating behaviors, such as emotional eating. Our findings further substantiate this perspective, highlighting the critical role of mental health in weight management. Moreover, depressive mood might influence lifestyle choices, including overeating and physical inactivity, thereby affecting BMI (31).
Although the mediating effect of depressive mood between Lactobacillus levels and BMI was statistically significant, its effect size was small. This finding suggests that other factors, such as dietary habits (50), lifestyle (51), and genetic predispositions (52), may serve as additional mediators in this association. These factors could influence weight management by modulating the composition and functionality of the gut microbiota. Furthermore, the results revealed a significant negative effect of Lactobacillus on BMI, potentially attributable to its regulatory influence on the gut environment. Lactobacillus may affect energy absorption and metabolism by fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria while suppressing harmful ones, thereby influencing BMI.
4.4 Moderating role of PA
The significant moderating effect of physical activity (PA) on the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI highlights the crucial role of PA in modulating the relationship between gut microbiota and health outcomes (53, 54). PA may enhance the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus, by improving blood circulation, promoting intestinal motility, and optimizing the gut environment. Mixed model analyses revealed negative coefficients for both Lactobacillus and PA, indicating their independent associations with lower BMI. However, the interaction term between Lactobacillus and PA showed a positive coefficient for BMI, suggesting that higher PA levels may weaken the effect of Lactobacillus in reducing BMI. That is, the BMI-lowering effect of Lactobacillus appeared less pronounced among individuals with high PA levels compared to those with lower PA levels. This suggests that the interaction between Lactobacillus and PA is non-additive in nature. At higher levels of PA, other factors—such as different microbial populations, dietary habits, or genetic influences—may exert a more dominant impact on BMI regulation. Previous research has shown that PA, particularly when combined with dietary interventions, can induce substantial changes in gut microbiota composition, including increased Lactobacillus abundance. These microbial shifts are strongly associated with weight loss and BMI reduction (55).
The Johnson-Neyman technique was employed to examine in detail the moderating effect of physical activity (PA) on the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI. The results indicated that this moderating effect was particularly significant when PA levels were below −13.847 or above 24.844, highlighting the nuanced role of PA in the Lactobacillus-BMI relationship across different activity levels. Notably, at higher levels of PA, the inverse association between Lactobacillus and BMI was more pronounced, suggesting that PA may enhance the potential benefits of Lactobacillus in weight management. However, the moderating effect identified in this study remains correlational in nature, precluding causal inference. Encouragingly, previous experimental and longitudinal studies have shown that probiotic supplementation combined with PA can produce synergistic effects in reducing BMI (56). Such combined intervention strategies present promising approaches for clinical application. Overall, in evaluating the role of gut microbiota in weight regulation, our study underscores the importance of increasing PA levels and offers valuable insights for future research and intervention strategies.
4.5 Strengths and limitations
Regarding measurement tools, a key advantage of this study is the application of a high-precision accelerometer (ActiGraph, Pensacola, Florida) for objectively measuring PA, thus eliminating the recall bias typically associated with self-reported questionnaires. Additionally, the study utilized the validated 9-item short version of the CES-D (α = 0.944), which provides superior measurement accuracy relative to non-standardized scales. Methodologically, the study applied advanced statistical techniques, including mixed models and the Johnson-Neyman method, which improved the precision and robustness of the results. Additionally, by integrating Lactobacillus levels, depressive mood, PA, and BMI, the study established a multivariate analytical framework, facilitating a deeper comprehension of the intricate interrelations among these variables.
This study has four notable limitations. First, the cross-sectional design constrains the ability to establish causal relationships. Future research should adopt longitudinal designs to provide deeper insights into the dynamic relationships among these variables. Second, the inherent limitations of self-reported measures cannot be disregarded, as participant subjectivity may compromise data reliability. To enhance measurement precision, future studies should incorporate objective assessments, such as physiological monitoring and biomarker analysis. Third, this study did not comprehensively account for environmental factors that may influence gut microbiota and BMI, including campus environment, seasonal variations, and socioeconomic status. The omission of these variables may have introduced confounding effects. Therefore, future studies should be conducted under more rigorously controlled conditions to mitigate the influence of these potential confounders. Lastly, although the model captures the key relationships among variables, the R2 value of 0.096 indicates that only 9.6% of the variance in BMI is explained, potentially due to unmeasured confounders such as dietary patterns, sleep quality, and stress levels. Future research may benefit from the dynamic collection of multidimensional behavioral data or from implementing machine learning approaches to uncover potential nonlinear associations. Even when R2 values are relatively low (e.g., 0.1–0.5), a model can still be considered meaningful if key predictors reach statistical significance (57). This study emphasizes theoretical validation over predictive accuracy, and the value of the model is supported by significant mediation and moderation effects.
5 Conclusion
This study utilized a cross-sectional design with 423 college students to investigate the association among Lactobacillus levels, depressive mood, PA, and BMI. The results demonstrated that Lactobacillus levels were significantly negatively correlated with both depressive mood and BMI. Depressive mood served as a mediator in the relationship between Lactobacillus levels and BMI, while PA significantly moderated the effect of Lactobacillus on BMI. These findings revealed that depressive mood could mediate the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI, and underscores the critical moderating role of PA. This study offers new insights into how PA modulates the association between Lactobacillus levels and BMI, providing valuable implications for targeted weight management and mental health interventions among college students.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Biomedical Ethics Committee of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QY: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZQ: Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YQ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study is funded by the 2023 National Social Science Fund of China Youth Project (23CTY007).
Acknowledgments
This study gratefully acknowledges the voluntary participation of college student in this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1603169/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Blüher, M. Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2019) 15:288–98. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0176-8
2. Klein, S, Gastaldelli, A, Yki-Järvinen, H, and Scherer, PE. Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell Metab. (2022) 34:11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.12.012
3. Kyrgiou, M, Kalliala, I, Markozannes, G, Gunter, MJ, Paraskevaidis, E, Gabra, H, et al. Adiposity and cancer at major anatomical sites: umbrella review of the literature. BMJ. (2017):j477. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j477
4. Koliaki, C, Liatis, S, and Kokkinos, A. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: revisiting an old relationship. Metabolism. (2019) 92:98–107. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.10.011
5. Seravalle, G, and Grassi, G. Obesity and hypertension In: SI Ahmad, editor. Obesity: Clinical, surgical and practical guide. Springer, Cham. (2024) 65–79.
6. WHO Consultation on Obesity. Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. World Health Organization technical report series. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. (2000);894:1–253.
7. Pan, X-F, Wang, L, and Pan, A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. Lancet Diab Endocrinol. (2021) 9:373–92. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00045-0
8. Collaborators GO. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:13–27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1614362
9. Pelletier, JE, Lytle, LA, and Laska, MN. Stress, health risk behaviors, and weight status among community college students. Health Educ Behav. (2016) 43:139–44. doi: 10.1177/1090198115598983
10. Kang, Y, Kang, X, Yang, H, Liu, H, Yang, X, Liu, Q, et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates obesity in mice through modulation of gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal permeability. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 175:106020. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.106020
11. Ley, RE, Turnbaugh, PJ, Klein, S, and Gordon, JI. Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. (2006) 444:1022–3. doi: 10.1038/4441022a
12. Wang, M, Zhang, B, Hu, J, Nie, S, Xiong, T, and Xie, M. Intervention of five strains of Lactobacillus on obesity in mice induced by high-fat diet. J Funct Foods. (2020) 72:104078. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104078
13. Qiu, X, Wu, Q, Li, W, Tang, K, and Zhang, J. Effects of Lactobacillus supplementation on glycemic and lipid indices in overweight or obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. (2022) 41:1787–97. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2022.06.030
14. Crovesy, L, Ostrowski, M, Ferreira, D, Rosado, E, and Soares-Mota, M. Effect of Lactobacillus on body weight and body fat in overweight subjects: a systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. Int J Obes. (2017) 41:1607–14. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2017.161
15. Drissi, F, Raoult, D, and Merhej, V. Metabolic role of lactobacilli in weight modification in humans and animals. Microb Pathog. (2017) 106:182–94. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.03.006
16. Kadooka, Y, Sato, M, Imaizumi, K, Ogawa, A, Ikuyama, K, Akai, Y, et al. Regulation of abdominal adiposity by probiotics (Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055) in adults with obese tendencies in a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2010) 64:636–43. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2010.19
17. Cerdó, T, García-Santos, JAG, Bermúdez, M, and Campoy, C. The role of probiotics and prebiotics in the prevention and treatment of obesity. Nutrients. (2019) 11:635. doi: 10.3390/nu11030635
18. Młynarska, E, Wasiak, J, Gajewska, A, Steć, G, Jasińska, J, Rysz, J, et al. Exploring the significance of gut microbiota in diabetes pathogenesis and management—a narrative review. Nutrients. (2024) 16:1938. doi: 10.3390/nu16121938
19. Naghipour, A, Amini-Salehi, E, Orang Gorabzarmakhi, M, Shahdkar, M, Fouladi, B, Alipourfard, I, et al. Effects of gut microbial therapy on lipid profile in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an umbrella meta-analysis study. Syst Rev. (2023) 12:144. doi: 10.1186/s13643-023-02299-x
20. Lonstein, JS, Meinhardt, TA, Pavlidi, P, Kokras, N, Dalla, C, Charlier, TD, et al. Maternal probiotic Lactocaseibacillus rhamnosus HN001 treatment alters postpartum anxiety, cortical monoamines, and the gut microbiome. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2024) 165:107033. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2024.107033
21. Mudaliar, SB, Poojary, SS, Bharath Prasad, AS, and Mazumder, N. Probiotics and paraprobiotics: effects on microbiota-gut-brain axis and their consequent potential in neuropsychiatric therapy. Probiot Antim Prot. (2024) 16:1440–1464. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10214-6
22. Evans-Lacko, S, Aguilar-Gaxiola, S, Al-Hamzawi, A, Alonso, J, Benjet, C, Bruffaerts, R, et al. Socio-economic variations in the mental health treatment gap for people with anxiety, mood, and substance use disorders: results from the WHO world mental health (WMH) surveys. Psychol Med. (2018) 48:1560–71. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717003336
23. Du, Y, Gao, X-R, Peng, L, and Ge, J-F. Crosstalk between the microbiota-gut-brain axis and depression. Heliyon. (2020) 6:e04097. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04097
24. Dinan, TG, Stanton, C, and Cryan, JF. Psychobiotics: a novel class of psychotropic. Biol Psychiatry. (2013) 74:720–6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.05.001
25. Yang, Y, Zhao, S, Yang, X, Li, W, Si, J, and Yang, X. The antidepressant potential of lactobacillus casei in the postpartum depression rat model mediated by the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neurosci Lett. (2022) 774:136474. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2022.136474
26. Zhou, H, Wang, R, Zhang, S, Zhang, X, Zhou, H, Wen, T, et al. Depression-like symptoms due to Dcf1 deficiency are alleviated by intestinal transplantation of Lactobacillus murine and Lactobacillus reuteri. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2022) 593:137–43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.01.026
27. Mansur, RB, Brietzke, E, and McIntyre, RS. Is there a “metabolic-mood syndrome”? A review of the relationship between obesity and mood disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2015) 52:89–104. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.12.017
28. Blasco, BV, García-Jiménez, J, Bodoano, I, and Gutiérrez-Rojas, L. Obesity and depression: its prevalence and influence as a prognostic factor: a systematic review. Psychiatry Investig. (2020) 17:715–24. doi: 10.30773/pi.2020.0099
29. Privitera, GJ, Misenheimer, ML, and Doraiswamy, PM. From weight loss to weight gain: appetite changes in major depressive disorder as a mirror into brain-environment interactions. Front Psychol. (2013) 4:873. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00873
30. Blanco, C, Vesga-López, O, Stewart, JW, Liu, S-M, Grant, BF, and Hasin, DS. Epidemiology of major depression with atypical features: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions (NESARC). J Clin Psychiatry. (2012) 73:224. doi: 10.4088/JCP.10m06227
31. Milaneschi, Y, Simmons, WK, van Rossum, EF, and Penninx, BW. Depression and obesity: evidence of shared biological mechanisms. Mol Psychiatry. (2019) 24:18–33. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0017-5
32. Qin, JJ, Li, RQ, Raes, J, Arumugam, M, Burgdorf, KS, Manichanh, C, et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature. (2010) 464:59–U70. doi: 10.1038/nature08821
33. Radloff, LS. The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas. (1977) 1:385–401. doi: 10.1177/014662167700100306
34. Kohout, FJ, Berkman, LF, Evans, DA, and Cornoni-Huntley, J. Two shorter forms of the CES-D (center for epidemiological studies depression) depression symptoms index. J Aging Health. (1993) 5:179–93.
35. Hu, L, and Bentler, PM. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct Equ Model Multidiscip J. (1999) 6:1–55. doi: 10.1080/10705519909540118
36. Bolin, JH. Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: a regression-based approach. J Educ Meas. (2014) 51:335–7.
37. Campaniello, D, Corbo, MR, Sinigaglia, M, Speranza, B, Racioppo, A, Altieri, C, et al. How diet and physical activity modulate gut microbiota: evidence, and perspectives. Nutrients. (2022) 14:2456. doi: 10.3390/nu14122456
38. Karnes, JH, Arora, A, Feng, J, Steiner, HE, Sulieman, L, Boerwinkle, E, et al. Racial, ethnic, and gender differences in obesity and body fat distribution: an all of us research program demonstration project. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0255583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255583
39. Salk, RH, Hyde, JS, and Abramson, LY. Gender differences in depression in representative national samples: Meta-analyses of diagnoses and symptoms. Psychol Bull. (2017) 143:783–822. doi: 10.1037/bul0000102
40. Castro, EA, Carraça, EV, Cupeiro, R, López-Plaza, B, Teixeira, PJ, González-Lamuño, D, et al. The effects of the type of exercise and physical activity on eating behavior and body composition in overweight and obese subjects. Nutrients. (2020) 12:557. doi: 10.3390/nu12020557
41. Cryan, JF, and Dinan, TG. Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2012) 13:701–12. doi: 10.1038/nrn3346
42. Ait-Belgnaoui, A, Colom, A, Braniste, V, Ramalho, L, Marrot, A, Cartier, C, et al. Probiotic gut effect prevents the chronic psychological stress-induced brain activity abnormality in mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2014) 26:510–20. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12295
43. Merchak, AR, Wachamo, S, Brown, LC, Thakur, A, Moreau, B, Brown, RM, et al. Lactobacillus from the altered Schaedler Flora maintain IFNγ homeostasis to promote behavioral stress resilience. Brain Behav Immun. (2024) 115:458–69. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.11.001
44. Stunkard, AJ, Faith, MS, and Allison, KC. Depression and obesity. Biol Psychiatry. (2003) 54:330–7. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(03)00608-5
46. Le Chatelier, E, Nielsen, T, Qin, J, Prifti, E, Hildebrand, F, Falony, G, et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature. (2013) 500:541–6. doi: 10.1038/nature12506
47. Michael, D, Jack, A, Masetti, G, Davies, T, Loxley, K, Kerry-Smith, J, et al. A randomised controlled study shows supplementation of overweight and obese adults with lactobacilli and bifidobacteria reduces bodyweight and improves well-being. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:4183. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60991-7
48. Ho, Y-T, Tsai, Y-C, Kuo, TB, and Yang, CC. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on depressive symptoms and sleep quality in self-reported insomniacs: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial. Nutrients. (2021) 13:2820. doi: 10.3390/nu13082820
49. Konttinen, H, van Strien, T, Männistö, S, Jousilahti, P, and Haukkala, A. Depression, emotional eating and long-term weight changes: a population-based prospective study. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. (2019) 16:28. doi: 10.1186/s12966-019-0791-8
50. Ding, M, Ellervik, C, Huang, T, Jensen, MK, Curhan, GC, Pasquale, LR, et al. Diet quality and genetic association with body mass index: results from 3 observational studies. Am J Clin Nutr. (2018) 108:1291–300. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy203
51. Corella, D, Arnett, DK, Tucker, KL, Kabagambe, EK, Tsai, M, Parnell, LD, et al. A high intake of saturated fatty acids strengthens the association between the fat mass and obesity-associated gene and BMI. J Nutr. (2011) 141:2219–25. doi: 10.3945/jn.111.143826
52. Holzapfel, C, Grallert, H, Huth, C, Wahl, S, Fischer, B, Döring, A, et al. Genes and lifestyle factors in obesity: results from 12,462 subjects from MONICA/KORA. Int J Obes. (2010) 34:1538–45. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2010.79
53. Zhang, L, Liu, Y, Wang, X, and Zhang, X. Physical exercise and diet: regulation of gut microbiota to prevent and treat metabolic disorders to maintain health. Nutrients. (2023) 15:4183. doi: 10.3390/nu15061539
54. Dorelli, B, Gallè, F, De Vito, C, Duranti, G, Iachini, M, Zaccarin, M, et al. Can physical activity influence human gut microbiota composition independently of diet? A systematic review. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1890. doi: 10.3390/nu13061890
55. Santacruz, A, Marcos, A, Wärnberg, J, Martí, A, Martin-Matillas, M, Campoy, C, et al. Interplay between weight loss and gut microbiota composition in overweight adolescents. Obesity (Silver Spring). (2009) 17:1906–15. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.112
56. Kilic Yildirim, G, Dinleyici, M, Vandenplas, Y, and Dinleyici, EC. Effects of multispecies Synbiotic supplementation on anthropometric measurements, glucose and lipid parameters in children with exogenous obesity: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (Probesity-2 trial). Front Nutr. (2022) 9:898037. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.898037
Keywords: Lactobacillus, depressive mood, physical activity, body mass index, university students
Citation: Wu Y, Yi Q, Qi Z, Yin Y and Qi Y (2025) Association between lactobacillus levels, depressive mood, and BMI in college students: the moderating role of physical activity. Front. Nutr. 12:1603169. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1603169
Edited by:
Eric Gumpricht, Independent Researcher, Gilbert, AZ, United StatesReviewed by:
Ehsan Amini-Salehi, Gilan University of Medical Sciences, IranHuaicheng Wang, Sun Yat-sen University, China
Bilal Hotayt, Independent Researcher, Beirut, Lebanon
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Yi, Qi, Yin and Qi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qing Yi, eXFmZDYwNkAxNjMuY29t
 Youliang Wu1,2,3
Youliang Wu1,2,3 Qing Yi
Qing Yi Yao Yin
Yao Yin Yufei Qi
Yufei Qi