- 1Department of Rehabilitation, Shanghai Fourth People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
- 2School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Rehabilitation, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 4Engineering Research Center for Medical Surgery and Rehabilitation Robotics Technology of Liaoning Provincial, Shenyang, China
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent whole-joint disease characterized by cartilage degradation, subchondral bone remodeling, synovial inflammation, and systemic metabolic dysregulation, imposing significant health and socioeconomic burdens globally. Conventional treatments primarily offer symptomatic relief without addressing the underlying disease mechanisms. Recently, intermittent fasting (IF), defined by cyclic caloric restriction and metabolic switching, has emerged as a promising lifestyle intervention with therapeutic potential for OA. Preclinical and preliminary clinical studies suggest that IF beneficially impacts OA pathogenesis by improving metabolic profiles, reducing systemic and local joint inflammation, activating cellular protective autophagy pathways, and positively modulating the gut microbiota. This review systematically synthesizes current mechanistic insights, preclinical findings, and emerging clinical evidence regarding IF’s role in OA prevention and treatment. We also address practical considerations for implementing IF in clinical practice and outline future research priorities necessary to validate and optimize IF protocols tailored for OA management.
1 Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a whole-joint disease characterized by structural alterations involving hyaline articular cartilage, subchondral bone, ligaments, the joint capsule, synovium, and periarticular muscles (1–3). According to the Global Burden of Disease study, OA is one of the leading causes of chronic pain and functional impairment among older adults, affecting approximately 595 million individuals worldwide (1), resulting in a significant public health and socioeconomic burden (4–6). Conventional therapies for OA primarily focus on symptom relief but fail to fundamentally reverse disease progression. Additionally, pharmacological interventions may present adverse effects, while joint replacement surgery is associated with high costs and postoperative risks (7, 8). Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop novel therapeutic strategies, especially those targeting early pathological changes in OA, aiming to halt or delay disease progression, enhance patients’ quality of life, and reduce long-term healthcare costs (1, 3, 9, 10).
In recent years, significant advancements have been made in understanding the etiology and pathogenesis of OA. The conceptual framework has gradually evolved from the traditional viewpoint of “pure mechanical wear” to a multifaceted interaction involving metabolic disturbances, inflammatory processes, and immune dysregulation, etc (11–14). Current studies indicate that obesity, insulin resistance, dysregulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, and chronic low-grade inflammation may accelerate the onset and progression of OA (1, 9, 15, 16). Extensive research supports dietary interventions as promising strategies for preventing or managing OA, highlighting their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anabolic potentials, thus offering a feasible approach for reducing the disease burden (17).
Recently, intermittent fasting (IF) has attracted scholarly interest regarding its potential application in OA prevention and management (18). Studies suggest that IF, characterized by periodic restriction of caloric intake, induces metabolic switching, improves insulin sensitivity, reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and positively modulates the immune microenvironment (19–22). These mechanisms collectively suggest a promising therapeutic potential for OA treatment and prevention (17, 23). As a lifestyle intervention affecting systemic metabolic and immune status, IF has the potential to shift the traditional treatment paradigm, which primarily focuses on local joint pathology, toward a broader, systemic modulation involving metabolism, inflammation, and gut microbiota (24).
This review focuses on recent advances concerning IF for OA, systematically summarizing the potential underlying mechanisms, evidence from animal studies and clinical trials, and discussing practical considerations and future research directions. We have searched the Pubmed and Embase databases to identify relevant literatures regardless of study type. To construct the search strategy, the concepts of “subjects: OA” and “intervention: IF” were combined with the “AND” operator. For each concept, we combined synonyms and Medical Subject Headings terms with the “OR” operator. In addition, we have handsearched the reference lists of relevant literatures to identify any related studies. Our aim is to provide a comprehensive and insightful overview of this emerging interdisciplinary field to support the scientific evaluation and practical application of IF as a non-pharmacological intervention for OA.
2 Overview of IF
2.1 Definition and common patterns
Intermittent fasting is a dietary pattern characterized by intentional restriction or complete cessation of energy intake during specific periods. Its fundamental principle involves triggering metabolic adaptations through cyclic periods of “feeding-fasting” (20, 25). IF has been demonstrated to provide numerous health benefits, such as weight loss (26, 27), regulation of body composition (28–30), reduction of inflammation (31, 32), alleviation of oxidative stress (33), improvement of insulin resistance (26, 34), promotion of neuronal regeneration and repair (35), acceleration of wound healing (36), and deceleration of cancer progression (37, 38). Commonly practiced IF patterns include (39):
• Alternate-day fasting (ADF): This regimen alternates between “fasting days” and “feast days”. On fasting days, individuals either consume only water (known as “zero-calorie alternate-day fasting”) (40) or restrict their caloric intake to approximately 25% of their daily energy requirements (around 500 kcal/day), termed “modified alternate-day fasting” (41). On feast days, there are no specific limitations regarding food types or quantities consumed.
• The 5:2 fasting diet: A modified form of ADF, this pattern involves normal eating for 5 days each week and caloric restriction to 500–600 kcal for the remaining 2 days (42).
• Time-restricted feeding (TRF): Unlike ADF and the 5:2 fasting diet, TRF restricts daily food consumption to a specific time window (43). Specifically, TRF limits the feeding period to certain hours each day (typically 4–8 h), with fasting (consumption limited to water or zero-calorie beverages) occurring during the remaining hours (30). As a distinct form of IF, TRF does not require individuals to monitor caloric intake or count calories during the eating window (44).
While these IF modalities differ in terms of fasting duration and frequency, they all aim to induce a state of energy deprivation, thereby promoting metabolic switching in the body (19, 45).
2.2 Physiological and metabolic basis of IF
The primary physiological mechanism underlying IF is known as “metabolic switching,” where the body transitions from primarily utilizing glucose as an energy source to predominantly relying on fatty acid oxidation and ketogenesis (20, 45). During fasting periods, hepatic glycogen reserves gradually become depleted, accelerating lipolysis and the subsequent generation of ketone bodies (e.g., β-hydroxybutyrate). These ketones serve not only as alternative energy substrates but also as signaling molecules that regulate inflammation, autophagy, and stress responses (19, 39). Ketone bodies produced during fasting significantly influence the expression and activity of various key proteins and molecules, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), sirtuins, fibroblast growth factors, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +), all of which play critical roles in health and aging (25). By interacting with these cellular pathways, ketone bodies exert profound systemic metabolic effects (36). Furthermore, IF may regulate cellular energy metabolism and oxidative stress by lowering insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) levels and activating signaling pathways such as AMPK and SIRT1 (21). Compared to continuous caloric restriction (CR), IF demonstrates advantages in preserving lean body mass and generally shows higher adherence rates (22, 46).
Research has indicated that IF not only promotes weight loss and reduces free radical generation but also induces adaptive cellular responses, enhancing stress resistance and suppressing inflammation (47). IF triggers coordinated adaptive stress responses at the cellular level, resulting in upregulation of antioxidant defenses, DNA repair, protein quality control, mitochondrial biogenesis, and autophagy, coupled with a reduction in inflammation (48, 49). Through intermittent metabolic switching, cellular and molecular mechanisms enhance organ functionality and improve resistance to stress and disease (25). During energy restriction, depletion of hepatic glycogen stores initiates metabolic switching, reducing fatty acid and ketone utilization (26). To accommodate this bioenergetic challenge, cells and organ systems activate multiple signaling pathways, which enhance mitochondrial function, boost stress resistance and antioxidant defense, diminish insulin signaling and global protein synthesis, and upregulate autophagy to clear damaged molecules and recycle cellular components (50–52). Conversely, during feeding periods, cells engage in tissue-specific growth and plasticity processes (53).
2.3 Association of IF with chronic disease management
Recently, IF has emerged as a popular strategy for managing various chronic diseases. Its extensive modulatory effects on metabolic pathways underscore its promise as a nutritional intervention to counteract obesity and associated metabolic disorders (48, 54). Studies suggest that IF holds potential therapeutic benefits for obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain neurodegenerative conditions (19, 20, 55). Extensive evidence indicates that IF can decelerate cellular aging through multiple mechanisms, including the switching of metabolic rhythms to promote health span and mitigate age-related pathologies (56). Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated that IF restores metabolic homeostasis in patients with obesity and metabolic syndrome by ameliorating adiposity, lipid dysregulation and hypertension (57, 58). In the context of cardiometabolic disease, IF confers cardiovascular protection by lowering blood pressure, improving lipid profiles and reducing key atherogenic risk factors (59). Moreover, the enforced metabolic shift induced by IF may disrupt the vicious cycle of metaflammation, modulate cell- and tissue-specific immunometabolic responses, and reestablish endocrine control of energy balance (60).
As a non-pharmacological intervention, IF represents a potent tool in the comprehensive management of a wide spectrum of metabolic disorders. These chronic diseases share common pathological features of metabolic disturbances and chronic low-grade inflammation, which are also critical in the pathogenesis of OA. Consequently, increasing attention has been directed toward the application of IF in musculoskeletal disorders, particularly regarding its effects on bone and cartilage tissues (21, 61). Preliminary evidence indicates that IF might benefit bone and joint health by improving bone density and reducing inflammatory markers (39). Additionally, studies have shown that IF can alleviate symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis (62–64), and significantly improve disease activity and symptoms such as dactylitis in patients with psoriatic arthritis, independent of weight loss. These beneficial effects might relate to IF’s immunomodulatory properties (65).
3 Osteoarthritis pathogenesis beyond mechanical stress
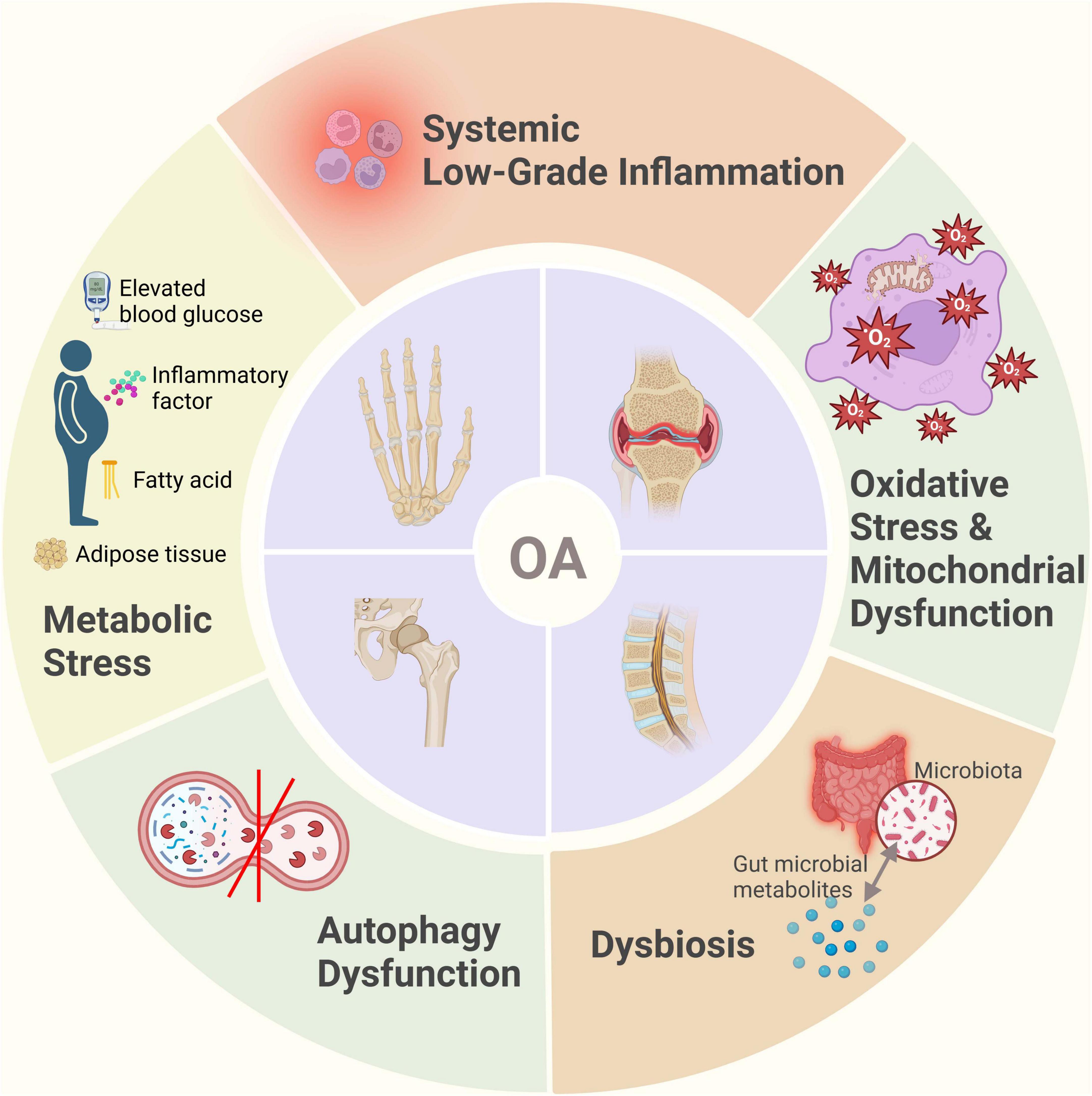
OA was traditionally regarded as a result of mechanical “wear and tear,” but recent research has demonstrated a more complex pathogenesis (10, 14). It typically involves cartilage, subchondral bone, and synovial tissue, each engaging in intricate cellular and molecular interactions (66). Damage to the cartilage extracellular matrix triggers the innate immune response through the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), resulting in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and matrix-degrading enzymes (67). Under metabolic stress, chondrocytes exhibit accelerated glycolysis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and impaired autophagy (68). Mild synovitis develops early in OA progression, where synovial immune cells produce inflammatory mediators such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and activated metalloproteinases (MMPs), further accelerating cartilage degradation (69). This creates a vicious cycle of inflammation and tissue damage (67). It is now widely recognized that OA is not restricted to the joint alone, but also involves systemic immune dysregulation that impacts the entire body (70).
3.1 Metabolic disorders
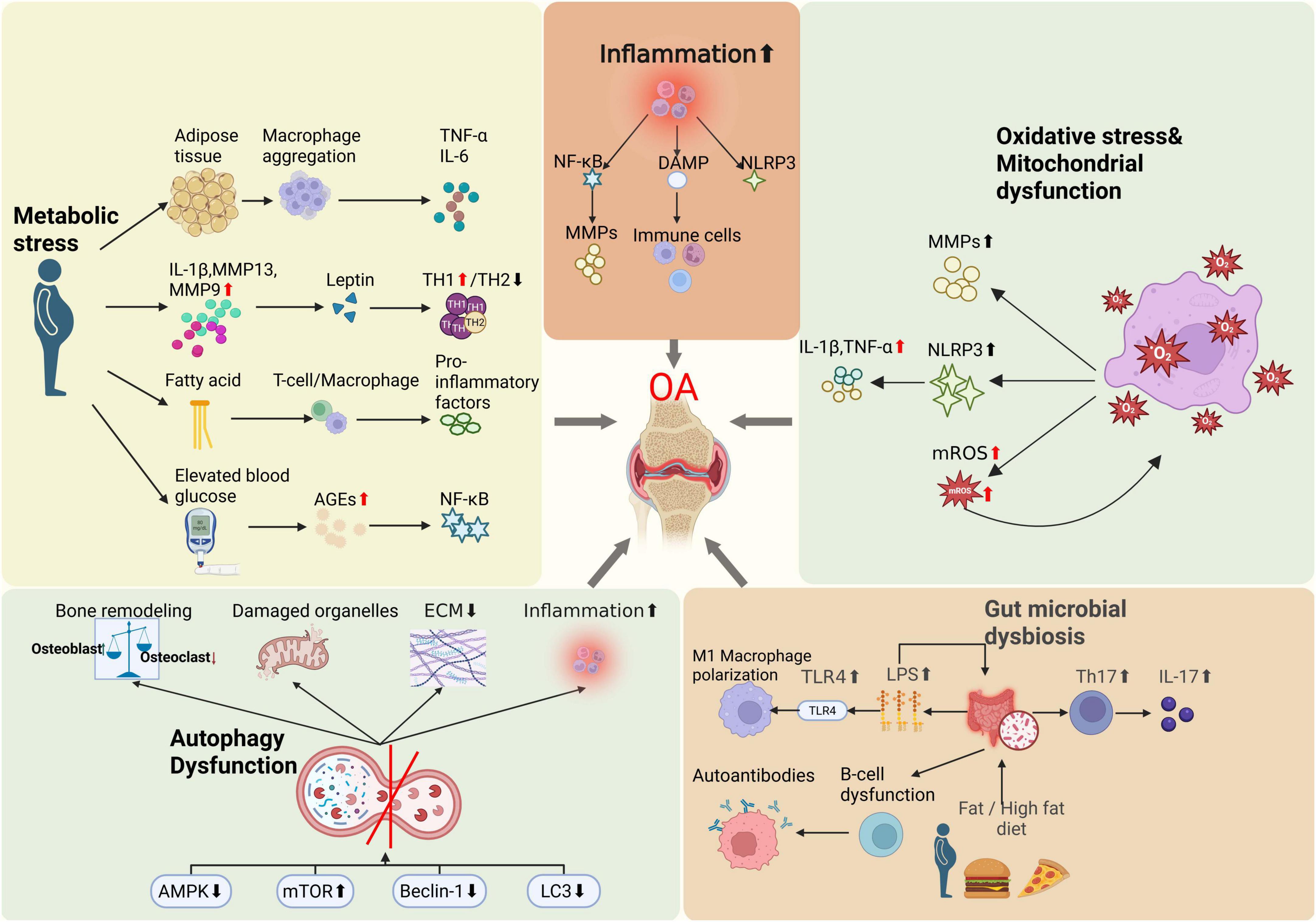
In addition to local joint mechanisms, systemic metabolic and inflammatory states significantly influence OA pathogenesis, particularly evident in obesity-associated OA. Epidemiological evidence shows that obesity substantially increases the risk of knee OA (KOA), and even non-weight-bearing joints (e.g., finger joints) are more commonly affected in obese individuals (71, 72). These findings suggest that obesity promotes OA through systemic metabolic and inflammatory pathways, beyond mere mechanical loading. Adipose tissue hypertrophy leads to macrophage infiltration and secretion of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, initiating systemic chronic low-grade inflammation (71, 73–75). These inflammatory mediators infiltrate the joint via synovial fluid, exacerbating cartilage degradation and synovial inflammation (76). A meta-analysis has revealed that circulating adiponectin concentrations are significantly elevated OA patients compared to healthy controls (77). Additionally, elevated leptin levels in obesity promote local joint inflammation and cartilage matrix degradation, indicating leptin as a critical mediator linking obesity and OA (71). Leptin, acting either autonomously or synergistically with other pro-inflammatory mediators, directly targets chondrocytes, synoviocytes and osteoblasts to profoundly influence the progression of osteoarthritis (78, 79). Inflammatory and catabolic factors such as IL-1β, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and MMP-13 have been shown to upregulate leptin expression within joint tissues (80, 81). Elevated leptin levels, in turn, skew immune responses toward a T helper 1 (TH1) cytokine profile while suppressing TH2 cytokines (82). This shift exacerbates intra-articular inflammation and accelerates cartilage matrix degradation, thereby hastening disease progression (83–85). Notably, obese animal models deficient in leptin signaling do not develop systemic inflammation or KOA, highlighting leptin’s pivotal role in osteoarthritic pathobiology (86). Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia further exacerbate OA progression, with elevated insulin levels inducing abnormal chondrocyte differentiation and cartilage hypertrophy, thus accelerating cartilage degeneration (18). Under insulin-resistant conditions, articular chondrocytes exhibit reduced sensitivity to insulin, resulting in disrupted intracellular signaling that impairs cartilage matrix synthesis and repair (87). Chronic hyperglycemia drives the accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) within chondrocytes, engagement of AGEs with their cell-surface receptors activates pro-inflammatory pathways -most notably NF-κB- thereby promoting chondrocyte apoptosis and matrix breakdown (88, 89). Moreover, diabetic microvascular complications compromise subchondral perfusion, diminish nutrient exchange and alter synovial fluid composition, collectively accelerating cartilage degeneration (90).
Fatty acid metabolism dysregulation also plays a pivotal role in OA progression (91). Fatty acids, essential for cellular energy metabolism, significantly influence immune cell function and bone metabolism (92, 93). Recent studies indicate that dysregulated fatty acid metabolism in subchondral bone could trigger local metabolic imbalances, enhancing immune cell activation and inflammatory responses (94). For example, abnormal fatty acid metabolism in KOA could stimulate macrophages and T cells to secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, exacerbating cartilage damage and bone loss (95). Investigations have consistently demonstrated a positive association between hypercholesterolemia and OA (96, 97). Elevated plasma cholesterol levels inhibit LRP3 expression in chondrocytes, disrupting extracellular matrix turnover and precipitating cartilage degeneration (98). Concomitantly, heightened circulating cholesterol and triglycerides, along with dysfunctional high-density lipoprotein, drive ectopic ossification and bone-marrow lesion formation—mechanisms that exacerbate cartilage loss in KOA and accelerate joint pathology (99, 100). Moreover, metabolic syndrome contributes to osteoarthritic pain through non-mechanical pathways, including systemic inflammation, dysregulated endocannabinoid signaling, transient receptor potential vanillic acid subfamily member 1 (TRPV1) channel activation, and gut microbiota imbalances, further underscoring lipid metabolism’s pivotal role in OA pathogenesis (101, 102).
Moreover, metabolic dysregulation not only perturbs chondrocyte bioenergetics but also inflicts direct damage through mechanisms such as inflammation and oxidative stress, leading to chondrocyte apoptosis and dysfunction that exacerbate cartilage degeneration (103, 104). Studies have shown that diet-induced obesity is associated with elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, including leptin and IL-1α, which correlate with the progression of OA, underscoring metabolic abnormalities’ role in driving inflammatory cascades that exacerbate joint pathology (105). Consequently, OA is increasingly considered a joint manifestation of metabolic syndrome, suggesting metabolic modulation could influence OA progression.
3.2 Chronic inflammation
Although OA was historically perceived primarily as a degenerative condition, recent studies emphasize the crucial role of chronic inflammation in OA progression (70, 106). Another hallmark of inflammation is the chronic activation of the immune system: senescent immune cells acquire a pro-inflammatory phenotype, while microbial infection or gut dysbiosis can both initiate and modulate this persistent inflammatory state (107). Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) significantly contribute to systemic inflammation and joint destruction. Mitochondrial stress responses and dysregulated glucose and lipid metabolism also promote DAMP production (108). DAMPs exacerbate joint tissue damage by activating immune cells, promoting inflammation, inducing cartilage matrix degradation, and triggering chondrocyte apoptosis (109, 110). Increased cytokines and chemokines within OA joints activate NLRP3 inflammasomes in chondrocytes and synoviocytes, further accelerating joint destruction (21). Persistent low-grade inflammation in OA is in part driven by sustained activation of signaling cascades such as NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) (111). As a master transcriptional regulator of the inflammatory response, NF-κB is activated by diverse pro-inflammatory stimuli and orchestrates the expression of cytokines and MPPs (112). Chronic inflammation also induces synovial hyperplasia and leukocyte infiltration, culminating in synovitis that exacerbates joint inflammation and tissue damage (113, 114). Moreover, the inflammatory milieu perturbs bone remodeling, skewing the balance toward osteoclast-mediated resorption over osteoblast-driven formation and thereby accelerates structural joint deterioration (115, 116).
3.3 Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
Mitochondrial dysfunction is characterized by mitochondrial DNA damage, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, reduced oxidative phosphorylation efficiency, and increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Collectively, these alterations lead to impaired mitochondrial function, negatively affecting normal cellular metabolism and function (117). Oxidative stress arises from an imbalance between ROS production and the cellular antioxidant defense capacity, playing a pivotal role in OA pathogenesis (118). Elevated oxidative stress observed in OA joints contributes significantly to chronic inflammation and results from excessive ROS production (69). Furthermore, mitochondrial damage activates the NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, which triggers excessive secretion of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β and TNF-α, exacerbating chondrocyte inflammation and promoting apoptosis (119). Mitochondrial dysfunction not only amplifies cartilage degradation by activating inflammatory signaling cascades and upregulating matrix metalloproteinases, but also compromises chondrocyte bioenergetics and survival through impaired adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis and disrupted calcium homeostasis (120, 121). Research has shown that excessive generation of ROS establishes a deleterious positive feedback loop wherein ROS-induced mitochondrial damage further amplifies ROS production, which plays a key driving role in the pathogenesis of OA (122). Specifically, elevated ROS levels compromise mitochondrial integrity, leading to increased mitochondrial ROS (mROS) generation and establishing a self-amplifying cycle of oxidative damage and organelle dysfunction. This vicious feedback loop perpetuates mitochondrial impairment, exacerbates chondrocyte injury, and accelerates OA pathology (123). In addition, oxidative stress also inhibits mitochondrial autophagy, making it difficult for damaged mitochondria to be cleared in a timely manner, further exacerbating mitochondrial dysfunction and chondrocyte damage, ultimately promoting the pathological process of OA (124, 125).
3.4 Autophagy dysfunction
Autophagy dysfunction plays a crucial role in OA pathogenesis (126). It prevents efficient clearance of damaged organelles and proteins, leading to cellular homeostasis disruption, accelerated chondrocyte senescence, and apoptosis. Autophagy impairment also exacerbates inflammation and cartilage matrix degradation (127). Autophagy can regulate the function of immune cells in joints by reducing the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting the inflammatory process of OA (128, 129). In bone cells, autophagy also plays an important role in regulating the balance between bone formation and resorption, ensuring normal bone metabolism (130). Dysfunction of autophagy may lead to abnormal bone cell function, which in turn affects the overall health of bones (131). Dysfunctional autophagy is closely linked to aberrant activation of signaling pathways, including excessive mTOR activation, suppressed AMPK signaling, and disruption of Beclin1 and LC3 pathways (132). Targeting these autophagy pathways may offer potential strategies for OA prevention and treatment (133, 134).
3.5 Gut microbiota dysbiosis
Gut microbiota dysbiosis refers to the disruption of intestinal microbial equilibrium caused by external factors such as diet, infections, aging, and genetics. This disruption leads to alterations in the structure, function, and diversity of gut microbiota, consequently resulting in various pathological conditions and diseases (135). Obesity and high-fat diets have been recently implicated in gut dysbiosis, potentially influencing OA development through the gut-joint axis (24, 136, 137). Dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota contributes to systemic inflammation and immune dysregulation, ultimately affecting cartilage and the joint microenvironment (138). High-fat diets increase the proportion of Gram-negative bacteria in the gut, enhancing the production of endotoxins such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which increase intestinal barrier permeability and lead to leakage of inflammatory metabolites like LPS into systemic circulation, thereby inducing systemic low-grade inflammation (137, 139). Elevated LPS levels activate the TLR4 pathway, promote M1 macrophage polarization, release pro-inflammatory cytokines, and intensify tissue inflammatory damage (140). Additionally, beneficial gut bacteria produce extracellular vesicles transported to host bone cells, participating in the regulation of bone metabolism (141). In a rat model of high-fat, high-sucrose diet-induced obesity, gut microbiota dysbiosis was closely linked to elevated systemic LPS levels, enhanced serum and local inflammatory signatures, and aggravated joint damage (142). Mouse studies have demonstrated that obesity induced by a high-fat diet can alter the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, promoting inflammatory bacteria growth, elevating circulating LPS levels, and exacerbating joint inflammation (143). Conversely, prebiotic fructooligosaccharides, which modulate gut microbiota, reduce systemic inflammation in obese mice and significantly mitigate cartilage damage in traumatic knee OA (71). These findings suggest that targeting gut microbiota to modulate inflammation represents a promising new intervention strategy for OA (24). Emerging evidence indicates that gut microbiota modulate joint immunity by regulating immune cell differentiation and function (144, 145). Specific microbial taxa have been shown to skew T cell polarization toward the pro-inflammatory Th17 phenotype, thereby increasing IL-17 production and amplifying joint inflammation (146). Concurrently, dysbiosis may disrupt B cell homeostasis, leading to aberrant autoantibody generation and exacerbation of joint tissue damage (147). Furthermore, microbial metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), notably butyrate, exert anti-inflammatory effects, potentially suppressing joint inflammation by enhancing regulatory T-cell activity, highlighting their crucial role in mediating gut microbiota effects on joint health (24).
In summary, the development of OA is not limited to local joint pathology but results from complex interactions involving systemic metabolism, immune regulation, and gut microbiota, among other factors (Figures 1, 2). This understanding provides a theoretical foundation for systemic interventions in OA management, such as dietary modulation.
4 Potential biological mechanisms of IF in the prevention and treatment of OA
4.1 Improvement of metabolic markers and cartilage protection
IF induces periodic low-energy intake, driving a metabolic switch that enhances lipolysis and ketone body production (20). In the osteoarthritic joint environment, improving chondrocyte energy homeostasis supports the synthesis and repair capacity of the cartilage extracellular matrix. Activation of the AMPK/SIRT1 axis promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy, while concurrently suppressing catabolic mediators such as hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α), thereby slowing cartilage degeneration (19). Additionally, IF increases free fatty acid (FFA) levels, leading to elevated production and release of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) (63). Evidence indicates that FGF21 not only regulates glucose and lipid metabolism but may also significantly influence cartilage metabolism and inflammatory responses, thereby impacting OA onset and progression (148). Moreover, IF-induced reductions in insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentrations exert protective effects on cartilage. Elevated insulin and IGF-1 conditions can disrupt chondrocyte metabolism, potentially accelerating OA progression (18, 149, 150). IF enhances insulin sensitivity, reducing fasting insulin levels and thereby mitigating hyperinsulinemia. It has been reported (18) that elevated fasting insulin in OA patients may exacerbate cartilage matrix degradation, whereas IF can lower fasting insulin by approximately 20%–30%, thus reducing metabolic stress on cartilage. Furthermore, IF typically improves lipid profiles-especially reducing triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-and beneficially modulates adipokines by decreasing leptin and increasing adiponectin levels (63). These metabolic adjustments may alleviate the detrimental metabolic load on articular cartilage and synovium (151). For instance, decreased leptin levels reduce stimulation of MMP production in chondrocytes, while increased adiponectin exerts anti-inflammatory effects and promotes matrix synthesis (152). It was reported that (25, 79, 153) serum leptin levels in KOA patients correlated with pain severity and structural damage, and dietary interventions lowering leptin may slow cartilage degeneration to some extent. Thus, through multilayered metabolic improvements (e.g., reduced insulin and leptin, improved lipid profiles), IF may foster a systemic metabolic environment that is beneficial to joint health, ultimately delaying OA progression.
4.2 Anti-inflammatory effects and immunomodulation
Metabolic changes induced by IF directly reduce systemic inflammation. Under fasting conditions, metabolites such as β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) are produced, which have demonstrated inhibitory effects on inflammatory pathways including the NLRP3 inflammasome (18). Clinical studies have consistently shown that various forms of IF effectively decrease chronic inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), TNF-α, and IL-6 (154–156). For OA, these changes imply that IF can alleviate local joint inflammation. A systematic review focused on chronic pain noted that in OA patients, IF-induced fat loss reduces adipose-derived pro-inflammatory cytokines, consequently lowering inflammation both systemically and within joint tissues (157). Additionally, IF may decrease the proportion of pro-inflammatory synovial macrophages and enhance peripheral regulatory T-cell populations, thus improving immune balance (158). In rheumatoid arthritis (RA) studies, patients undergoing strict fasting for seven or more days experienced significant reductions in joint swelling and tenderness, along with notable alterations in serum IL-6 and IL-1 receptor antagonist concentrations (18). Although OA inflammation is typically less severe compared to RA, chronic low-grade inflammation persists throughout the OA disease process (14). IF exerts its anti-inflammatory effects through multiple mechanisms: firstly, by reducing visceral adiposity and gut-derived inflammatory mediators; secondly, by directly modulating cellular metabolic pathways, leading to decreased expression of pro-inflammatory genes, thereby potentially attenuating the inflammatory drivers of OA (20). Furthermore, IF-mediated suppression of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways contributes significantly to decreased inflammation both locally in joints and systemically (159). IF may also modify adipokine secretion profiles and regulate immune cell functions and pro-inflammatory cytokine networks, thus alleviating synovial inflammation (160, 161). Of note, recent discoveries regarding the neuropeptide Y (NPY) pathway offer novel insights into the mechanisms underlying IF’s anti-inflammatory effects in OA. New animal studies suggest that osteocytes overproduce NPY during OA progression, promoting inflammation and osteoclastogenesis, whereas IF significantly inhibits osteocytic NPY overproduction (162). Further experiments indicated that osteocyte-specific NPY knockout markedly attenuated surgically-induced OA inflammation and bone destruction, and notably, the protective effects of IF against OA were abolished in the absence of NPY. These findings strongly suggest that IF may exert its anti-inflammatory and bone-protective effects via downregulation of osteocyte-derived NPY, establishing the NPY pathway as an innovative key mechanism by which IF impacts OA pathogenesis.
4.3 Autophagy activation and cellular protection
Autophagy is an essential cellular self-protective mechanism that plays a crucial role in maintaining the homeostasis of chondrocytes and the cartilage extracellular matrix (163). The aging and cell death observed in osteoarthritic cartilage are closely associated with impaired autophagic activity (164, 165). Under physiological conditions, chondrocytes depend on moderate autophagy to eliminate damaged organelles; however, the expression of autophagy-related proteins, such as Beclin-1 and LC3, is diminished in aged and osteoarthritic cartilage. This reduction results in the accumulation of intracellular damaged products and decreased chondrocyte viability (166, 167). Fasting activates autophagy by restricting energy intake and plays a significant role in regulating mitochondrial network homeostasis (168). IF is widely recognized as a robust inducer of autophagy: during fasting periods, activation of the energy-sensing pathway AMPK and inhibition of mTOR enhance autophagosome formation (45). A recent study by Zhang et al. (23) underscored the importance of IF-induced autophagy in protecting cartilage. They demonstrated that IF significantly activates selective mitophagy in chondrocytes, which facilitates the clearance of damaged mitochondria, reduces oxidative stress and apoptosis, and ultimately prevents OA progression in mouse models. Specifically, Optineurin (Optn) gene knockout mice exhibited accelerated cartilage degeneration and OA phenotype, whereas IF treatment restored mitophagy through the OPTN pathway and significantly alleviated cartilage lesions. These findings suggest that maintaining chondrocyte autophagy is crucial for combating OA, and IF provides a systemic means to enhance autophagic activity. In addition to chondrocytes, IF also modulates autophagy in other joint cells. For example, IF can induce autophagy in synovial fibroblasts, thereby suppressing synovial hyperproliferation and inflammatory mediator release (63, 64). Furthermore, IF may promote macrophage polarization toward the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, a process closely linked with enhanced autophagy (158). Taken together, IF exerts protective effects at the cellular level by activating autophagy, facilitating the clearance of damage-associated factors in degenerative tissues, and counteracting age- and inflammation-related damage, ultimately slowing the pathological progression of OA (33).
4.4 Gut microbiota-joint axis
The impact of IF on gut microbiota represents a crucial aspect of its underlying mechanisms (45). Fasting-feeding cycles can alter nutrient availability patterns within the gut, thus reshaping microbial composition and the profile of microbial metabolites (169, 170). Recent studies have demonstrated that IF enhances gut microbial diversity, increases beneficial bacterial populations, promotes SCFAs production, and concurrently reduces pro-inflammatory bacteria and harmful metabolites (171, 172). For instance, a study conducted in hypertensive rats found that ADF increased the abundance of beneficial microbes, such as Bifidobacterium, and elevated bile acid-related microbial metabolites, which contributed to reduced blood pressure and systemic inflammation (158). In obese individuals, an 8-week intervention combining IF with a high-protein diet significantly enriched Christensenellaceae in fecal microbiota-a bacterial family associated with healthy, lean phenotypes (173). These microbiota changes correlated with improved gastrointestinal symptoms and reduced systemic metabolic inflammation markers. IF has also been suggested to exert anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects by modulating gut microbiota (48). Animal studies further indicated that IF partially restores gut microbiota balance in obesity models, alleviating inflammatory burden and slowing joint degeneration (19). The beneficial effects of improved gut microbiota composition on OA may be explained by several mechanisms. Enhanced gut barrier integrity, due to increased abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria and probiotics, reduces translocation of inflammatory molecules like LPS (137). Additionally, SCFAs such as butyrate and propionate, produced by beneficial bacteria, enter systemic circulation and can directly inhibit joint inflammation and enhance chondrocyte energy metabolism (24). Furthermore, IF may modulate gut immune environments by increasing anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells and reducing pro-inflammatory Th17 cells within gut-associated lymphoid tissues, thereby alleviating systemic inflammation (170). Although direct evidence linking IF, gut microbiota, and OA remains limited, considering the crucial role of gut microbiota in obesity and inflammation, IF-mediated reshaping of the gut-joint axis may represent a novel therapeutic strategy for reducing joint inflammation induced by gut dysbiosis and ultimately preventing OA progression.
In summary, IF may confer beneficial effects on OA through multiple mechanisms, including metabolic optimization, anti-inflammatory immunomodulation, autophagy activation, and gut microbiota regulation (Figure 3).
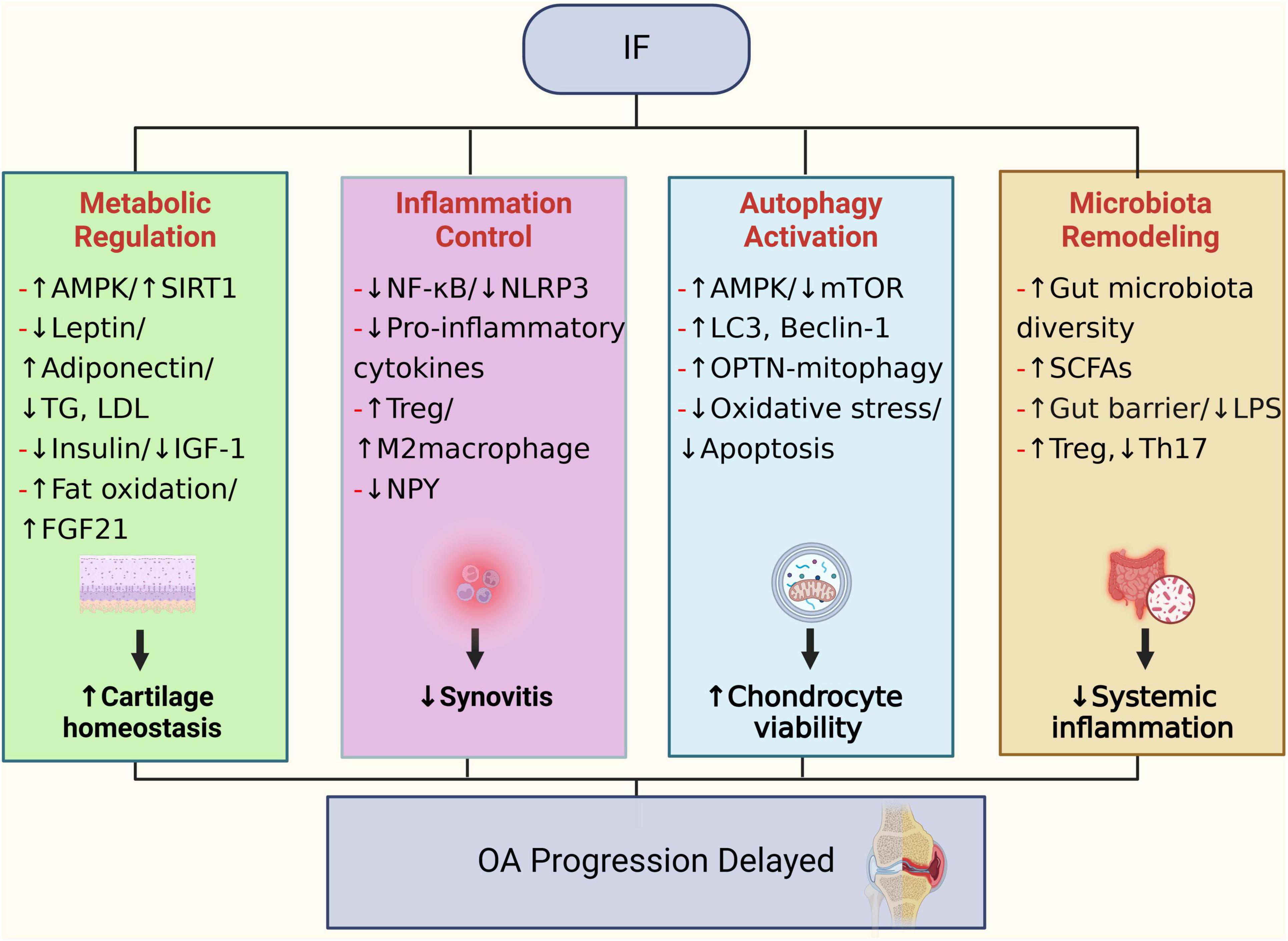
Figure 3. Potential biological mechanisms through which IF may contribute to the prevention and treatment of OA.
5 Preclinical evidence
5.1 In vivo studies
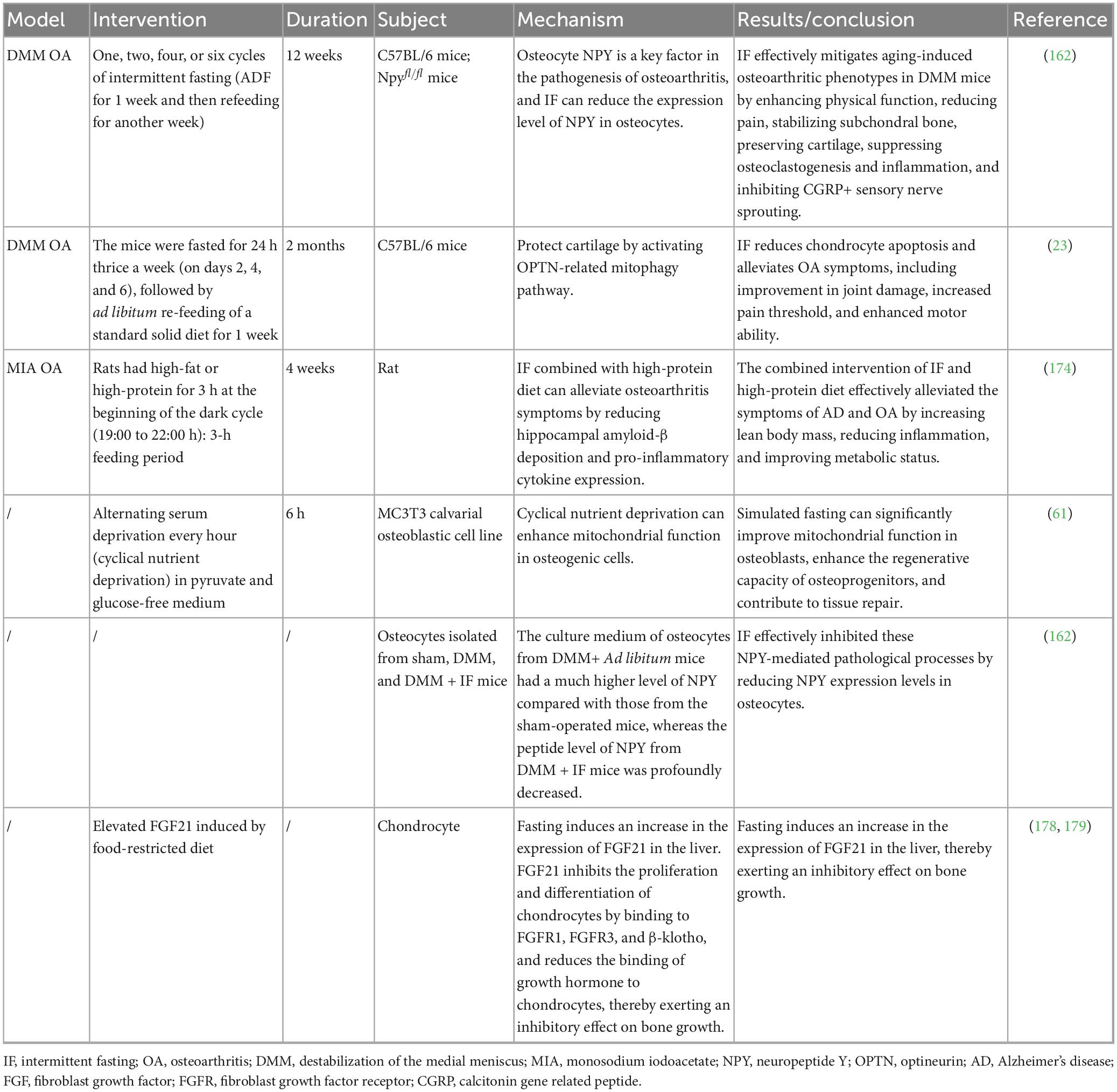
To investigate the therapeutic effects of IF on OA, various animal model studies have been conducted. Qian et al. (162) employed a mouse model of destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM)-induced KOA. After surgery for 1 week, these mice or the sham-operated mice received one, two, four, or six cycles of IF (ADF for 1 week and then refeeding for another week) or ad libitum feeding. They observed that IF treatment effectively preserved subchondral bone microarchitecture and attenuated cartilage degeneration. Moreover, IF-treated mice exhibited significantly improved outcomes in gait analysis, rotarod performance, balance beam tests, and pain sensitivity assays compared to controls, suggesting that IF enhances joint function and alleviates pain perception in OA animals. These findings provided initial evidence that IF could mitigate structural deterioration and symptoms associated with OA. Importantly, the study identified NPY as a crucial mediator of IF’s protective effects. Increased NPY expression was detected in the bone tissues of OA mice, whereas IF significantly downregulated osteocytic NPY levels. Furthermore, IF’s beneficial effects on OA were diminished in osteocyte-specific NPY-knockout mice, with some parameters even showing a slight worsening trend. These observations highlight NPY’s pivotal role in the IF-mediated alleviation of OA pathology. Thus, by reducing osteocytic NPY expression, IF effectively suppresses pathological processes such as inflammation, osteoclastogenesis, and neurogenic fiber proliferation in OA, representing a novel finding that emphasizes the essential role of bone tissues in IF-induced joint protection. Another notable study by Zhang et al. (23) focused on IF-mediated mitochondrial autophagy (mitophagy) in chondrocytes. Using Optineurin (Optn)-knockout mice to model impaired autophagy, the researchers demonstrated that Optn deficiency exacerbated chondrocyte injury and OA-like pathology. The mice were fasted for 24 h thrice a week (on days 2, 4, and 6), followed by ad libitum re-feeding of a standard solid diet for 1 week. This fasting-refeeding cycle was repeated for 2 months. ADF significantly activated OPTN-dependent mitophagy in wild-type OA mice, leading to efficient clearance of damaged mitochondria, and subsequently suppressed cartilage degeneration and joint inflammation. However, IF failed to prevent OA progression in Optn-deficient mice, indicating that the protective effect of IF on cartilage is primarily mediated via the OPTN-associated mitophagy pathway. Histological analyses revealed higher proteoglycan content, lower chondrocyte apoptosis rates, and reduced oxidative stress markers in synovial and subchondral bone tissues following IF treatment. These findings provide robust preclinical evidence demonstrating that autophagy activation is a critical mechanism underlying IF’s anti-OA effects. Collectively, these two animal studies support the multifaceted benefits of IF in OA models, including attenuated inflammation, reduced osteoclast activity, and cartilage protection, consistent with previously discussed mechanistic analyses. Additionally, some relevant investigations on IF in metabolic OA contexts are noteworthy. For instance, Park and Shin (174) studied a KOA rat model accompanied by obesity. In the IF groups, rats had a high-protein or high-fat diet for 3h at the beginning of the dark cycle (19.00 to 22.00 h), the mealtime of the rats corresponded to the morning for humans. The 3-h feeding period is similar to the 16-h fasting and 8-h feeding for humans in their previous and preliminary studies. Mimicking postmenopausal metabolic conditions and introducing Alzheimer’s-like pathological states to exacerbate systemic inflammation, their study revealed that a high-protein diet combined with IF effectively decreased body fat mass, increased lean body mass, and simultaneously reduced the joint expression of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α without significantly reducing total caloric intake. Histological examination of joint tissues indicated less cartilage erosion and bone resorption in IF-treated animals compared to controls. These findings suggest that dietary composition adjustments—particularly increased protein intake—may enhance the beneficial effects of IF on OA, notably by preventing muscle loss. This provides valuable guidance for clinical practice, indicating that older OA patients employing IF should ensure adequate protein consumption to optimize outcomes between weight loss and muscle preservation.
Glucosamine (GlcN) is widely used to alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis; however, its clinical efficacy is limited by poor bioavailability (175, 176). A recent animal study (177) investigated strategies to enhance GlcN absorption by leveraging circadian rhythms and feeding patterns (although not in OA models). The findings demonstrated that administering GlcN during the peak expression of its intestinal transporters (22:00) under fasting conditions significantly increased its systemic bioavailability. These insights suggest a promising chronopharmacological approach to optimize GlcN delivery in humans, potentially improving therapeutic outcomes for OA and related disorders.
5.2 In vitro studies
A study showed that the fasting mimicking diet can significantly improve the mitochondrial function of osteoblasts, enhance the regenerative ability of osteoprogenitors, aid in tissue repair, and regulate the expression of related genes. This discovery provides a new perspective for understanding the role of fasting in bone health (61). Another in vitro study (162) reported that NPY significantly promoted inflammatory cytokine expression in monocyte/macrophage populations, facilitated osteoclast differentiation, and enhanced neuronal neurite outgrowth. IF effectively inhibited these NPY-mediated pathological processes by reducing NPY expression levels in osteocytes, further elucidating the potential mechanisms underlying IF-mediated relief of OA symptoms.
There are research results showing that (178) in food-restricted mice, the expression of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) in the tibial growth plates is greater than that in mice fed randomly. FGF21 has a pathogenic effect of inhibiting bone growth during long-term malnutrition. Another study on the same team showed that (179) fasting would induce an increase in the expression of FGF21, and the increase in FGF21 would inhibit the proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes, reduce the binding of growth hormone to chondrocytes, and have a significant inhibitory effect on bone growth. However, there are also experiments showing that FGF21 can protect chondrocytes from apoptosis, senescence and extracellular matrix catabolism by up-regulating autophagic flux, thereby alleviating the progression of osteoarthritis (180). This suggests that when exploring the impact of fasting on osteoarthritis, it is necessary to comprehensively consider its possible dual effects. Preclinical studies on the effect of IF in OA are presented in Table 1.
6 Clinical evidence
6.1 Observational studies
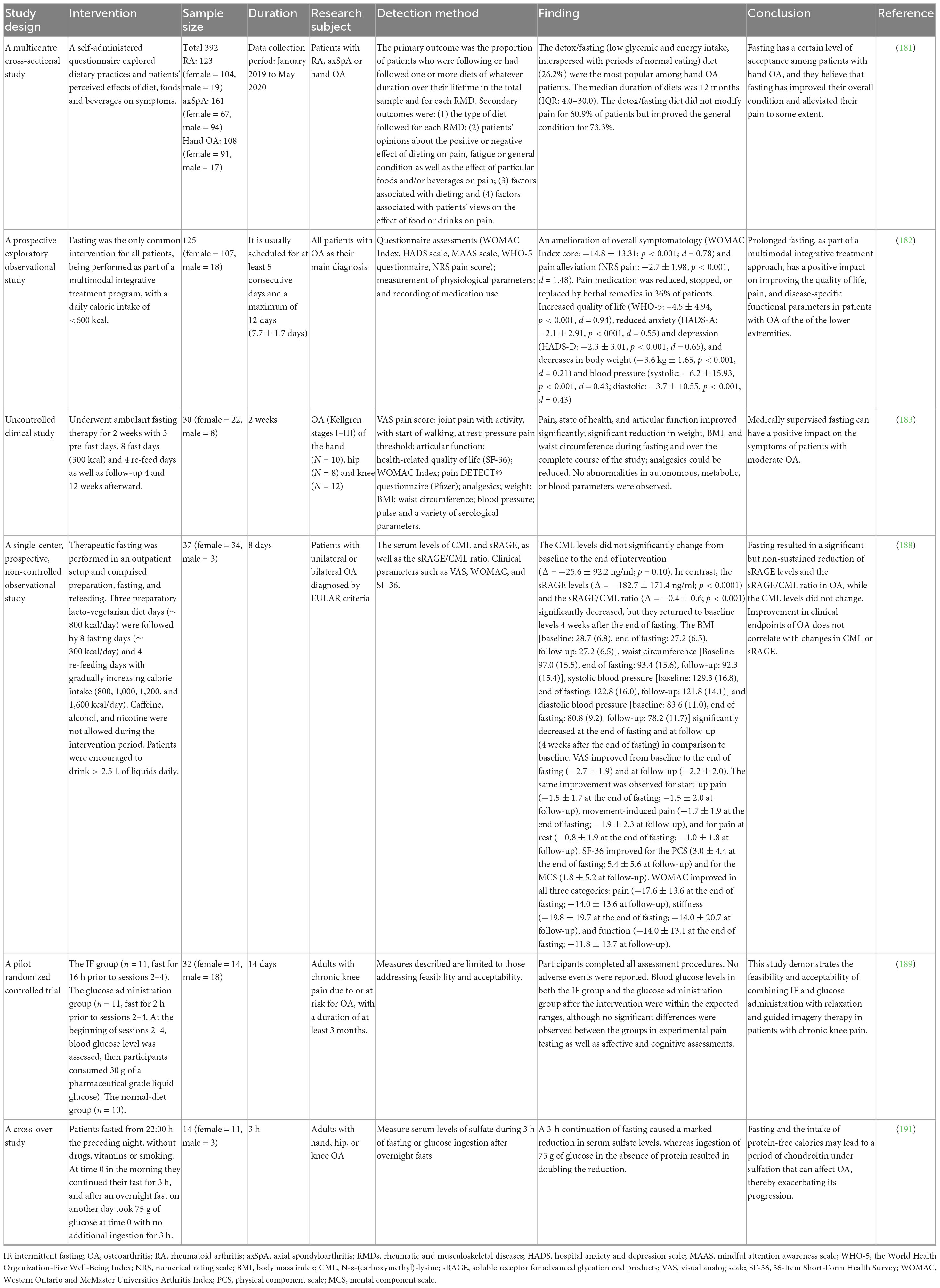
Population cohort studies have reported subjective improvement in joint symptoms among individuals engaging in fasting practices driven by cultural or religious reasons, such as Ramadan fasting (62). However, these observational studies typically lacked rigorous control of confounding factors and objective evaluation of joint structural changes. Additionally, a multicenter cross-sectional study (181) indicated that fasting was relatively well-accepted by OA patients, particularly among those with hand OA, who reported overall improvement and pain relief following fasting practices. In a prospective exploratory observational study involving 125 OA patients (182), patients started fasting on the second day. It is usually scheduled for at least five consecutive days and a maximum of 12 days, with the length depending on the individual constitution of the patient and the regulation of the inpatient stay according to diagnosis and disease severity. During fasting, only natural juices, unsweetened herbal teas, and water are consumed. The daily caloric intake is between 200 and 300 calories. The study demonstrated that fasting significantly improved overall symptoms (mean WOMAC index reduction of 14.8 points), alleviated pain (mean NRS pain score reduction of 2.7 points), and reduced analgesic medication usage, with 36% of participants decreasing analgesic doses, discontinuing medication, or switching to herbal treatments. Furthermore, fasting enhanced patients’ quality of life (mean WHO-5 score increase of 4.5 points), reduced anxiety and depressive symptoms (mean reductions of 2.1 and 2.3 points in HADS-A and HADS-D, respectively), and facilitated weight loss and blood pressure reduction. Researchers believe that short-term fasting can be used as an adjunct to multimodal therapy to alleviate OA symptoms by rapidly reducing inflammation and weight. This prospective study provides direct human evidence for the use of IF in OA. However, it should be noted that this plan has a high intensity and should not be implemented frequently for a long time. Its long-term effectiveness and safety still need to be evaluated. Collectively, these findings indicate that extended fasting periods within multimodal therapeutic strategies may positively affect pain, functional status, and quality of life in knee and hip OA patients, although future randomized controlled trials are necessary to confirm these observations. Another outpatient fasting intervention study (183) lasting 2 weeks evaluated effects on pain, general health status, and joint function in OA patients. The study consisted of a 3-day preparatory period, an 8-day fasting period (approximately 300 kcal/day), and a 4-day recovery phase, with follow-ups at 4 and 12 weeks post-intervention. Results showed significant reductions in pain intensity during the fasting period and throughout the entire study duration, as well as improvements in joint function and overall health status. Analgesic medication use was also significantly reduced during fasting. These studies collectively provide preliminary evidence supporting the beneficial effects of fasting interventions for OA symptoms and suggest outpatient fasting under medical supervision may offer therapeutic potential for patients with OA.
6.2 Small-scale clinical trials and preliminary findings
Currently, direct clinical trials evaluating IF specifically for OA patients remain limited, though some related studies provide indirect evidence supporting its potential benefits. Extensive weight-loss clinical trials have clearly established the significance of weight reduction in improving OA symptoms (184, 185). While traditional weight-loss approaches rely heavily on continuous calorie restriction, IF serves as an alternative dietary strategy that demonstrates comparable weight-loss efficacy and adherence in obese populations (173). It is reasonable to hypothesize that IF-induced weight reduction would yield similar symptom relief in overweight OA patients (150). Meanwhile, studies have shown that IF can potentially treat different types of chronic pain through various mechanisms, providing a new non-invasive treatment approach for chronic pain management (18). A study proposed that decreased fasting insulin levels might play a crucial role in alleviating insulin resistance and inflammation in cartilage tissues (186). Concurrently, IF improved patients’ mood and sleep quality, potentially enhancing participation in rehabilitative exercises (187). Although this study was limited by its small sample size, these preliminary results highlight the need for larger, rigorous trials assessing the efficacy of IF in OA symptom management. A single-center, prospective, non-controlled observational study (188) involving 37 OA patients demonstrated that IF significantly improved joint pain, physical function, and quality of life. Notably, these clinical benefits were not only observed during the fasting period but also persisted during the post-fasting follow-up, suggesting that IF may confer sustained therapeutic effects in OA. Interestingly, the intervention had no significant impact on serum levels of N-ε-(carboxymethyl)-lysine (CML) or soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE), indicating that its benefits may not be mediated through modulation of these biochemical markers. The fasting protocol consisted of three distinct phases: a preparatory phase involving a low-calorie (∼ 800 kcal/day) lacto-vegetarian diet for 3 days; a fasting phase with severe caloric restriction (∼ 300 kcal/day) for 8 days; and a refeeding phase over 4 days with a stepwise increase in caloric intake (800, 1000, 1200, and 1600 kcal/day). During the fasting phase, intake of caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine was prohibited, and patients were encouraged to consume more than 2.5 liters of fluids daily. Researchers concluded that short-term fasting could serve as an adjunctive component within multimodal OA therapies, providing rapid reductions in inflammation and body weight to alleviate joint symptoms. However, the intensity of such fasting protocols may not be suitable for frequent or prolonged use, and long-term efficacy and safety warrant further investigation. A randomized controlled trial involving 32 patients with OA or chronic knee pain at risk of OA assessed the feasibility and acceptability of dietary interventions combined with relaxation and guided imagery therapy (189). Participants were allocated to three groups: IF, glucose-management, or normal-diet controls. Over a period of approximately 2 weeks, participants completed four experimental sessions. Those assigned to IF group were instructed to fast for 16 h prior to sessions 2–4. Specifically, they were asked to refrain from consuming any food or caloric beverages after 6:00 or 7:00 p.m. on the evening preceding each session, allowing only non-caloric drinks or black coffee during the fasting window. On non-session days, participants were advised to maintain their habitual dietary patterns. Individuals in the glucose administration group were instructed to fast for 2 h before sessions 2–4, while following their usual diet on all other days. Participants in the normal diet control group were asked to maintain their regular eating habits throughout the entire study duration. Compliance was high across all groups, with both IF and glucose-management groups achieving expected blood glucose ranges. Although no significant differences in experimental pain measures or mood and cognitive assessments were observed among the groups, the study importantly demonstrated that dietary interventions—IF and glucose management—are both feasible and acceptable adjuncts to chronic pain treatment when combined with relaxation and guided imagery. Moreover, several studies focusing on RA support potential fasting-related benefits for inflammatory joint disorders (190). For example, the “To eat or not to eat” trial compared a 7-day water-porridge fast followed by a plant-based diet against a purely anti-inflammatory diet in RA patients. Although there were no significant differences in disease activity scores between groups, fasting patients reported short-term improvement in joint pain and morning stiffness. Given the tolerability and symptom improvements observed in RA fasting studies, researchers suggest exploring similar approaches in OA populations.
A crossover study involving 14 patients with hand, hip, or knee OA reported that fasting combined with caloric intake devoid of protein may impair cartilage sulfation, potentially influencing OA pathogenesis (191). In this study, participants refrained from food, medications, vitamins, and smoking from 10:00 p.m. the night prior. On one test day, they continued fasting for an additional 3 h in the morning. On a separate day, following the same overnight fast, they ingested 75 grams of glucose at midnight and again remained fasted for the subsequent 3 h. Serum sulfate levels were measured across both conditions. Results showed a mean 9.3% reduction in serum sulfate levels after fasting alone, which was further exacerbated to an average 18.9% decrease following glucose ingestion, indicating that both fasting and postprandial glycemic shifts may suppress systemic sulfate availability. As sulfate is essential for proteoglycan sulfation in cartilage, these findings suggest that prolonged fasting and insufficient protein intake may negatively affect cartilage integrity. The study underscores the importance of adequate protein consumption and cautions against extended fasting regimens in individuals with OA.
Overall, large-scale randomized controlled trials specifically evaluating IF for OA are currently lacking. However, combined evidence from weight-loss studies, observational fasting trials, and investigations in related inflammatory joint diseases collectively support IF’s potential to relieve joint symptoms and reduce inflammation markers (18, 48, 192). Clinical studies on the effect of IF in OA are presented in Table 2.
Despite recent progress, research on the IF-OA relationship still faces limitations. The number of randomized controlled trials involving IF interventions in OA patients remains limited, often characterized by small sample sizes, short durations, and absence of long-term follow-up. Future large-scale, multicenter randomized controlled trials are required to validate IF’s clinical effectiveness on OA symptoms, radiographic outcomes, and cartilage biomarkers (e.g., type II collagen C-terminal peptide, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein). Additionally, further investigation should address the safety and compliance of IF regimens in older adults or those with comorbidities such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
7 Practical considerations and future directions
7.1 Adherence and safety
Research indicates that IF rarely produces adverse gastrointestinal, neurological, hormonal, or metabolic outcomes (39, 193, 194). For OA patients, the selection of an appropriate IF regimen should be based on individual lifestyle patterns and compliance capabilities. Patients with regular daily routines may find TRF-such as skipping breakfast and limiting eating to between noon and 8:00 PM-relatively easy to incorporate, as it aligns closely with circadian rhythms and reduces perceived hunger. For younger and middle-aged patients needing to accommodate family meals or social interactions, the 5:2 diet, which allows the consumption of approximately 500–600 kcal of simple foods on two fasting days per week, offers greater flexibility while maintaining normal eating on non-fasting days. Conversely, alternate-day fasting, despite significant clinical benefits demonstrated in research, is associated with fluctuating energy states that may disrupt work and daily routines, potentially limiting its suitability for general OA populations. Moreover, patients requiring medication at specific times may face difficulties adhering to certain time-restricted eating schedules. Thus, these individuals should collaborate with their clinicians to develop a fasting regimen that integrates effectively with their medication protocols (39). Patient adherence is critical for achieving therapeutic outcomes with IF. Evidence suggests that patients who consistently adhere to IF experience significantly better improvements in pain relief and functional outcomes after 3 months compared to those who discontinue early (18). Therefore, healthcare providers should offer comprehensive health education and ongoing support to patients by clearly explaining the scientific basis and potential benefits of IF, assisting with detailed meal planning, providing practical strategies to manage potential discomfort such as hunger and dizziness, and scheduling regular follow-ups to encourage continued adherence. For patients with cognitive impairment or poor self-control, IF implementation is not advisable, as it may elevate the risk of nutritional deficiencies or other health complications.
7.2 Monitoring potential risks
Although most studies have concluded that IF is safe for metabolically healthy adults (18), caution remains necessary for OA patients, who are often older adults with comorbidities. Several potential risks warrant consideration. First, hypoglycemia and hypotension: fasting may lead to reduced blood glucose, particularly in patients receiving diabetes medications; orthostatic hypotension can also occur due to prolonged periods without food intake. Patients should be instructed on blood glucose monitoring and, when necessary, consume small amounts of sugary beverages to correct hypoglycemia during fasting, as well as advised on gradual posture changes to prevent dizziness. Second, gout: fasting elevates ketone levels and may transiently increase serum uric acid; therefore, patients with gout should adopt IF carefully under medical supervision (158). Third, gallstones: rapid weight loss and extended fasting periods may increase the risk of bile stasis, and previous studies have documented higher gallstone incidences following significant rapid weight reductions (195). OA patients with a history of gallbladder disease require regular monitoring. Fourth, IF is contraindicated in children under 12 years, pregnant or breastfeeding women, as safety studies are currently lacking in these groups. Fifth, dietary composition warrants critical attention. Protein malnutrition and inadequate vitamin intake represent key nutritional risks during IF regimens (196). Protein is essential for preserving muscle mass and joint integrity, while vitamins support immune competence, cellular repair, and metabolic homeostasis. In addition, during IF, patients also need to maintain the health of their gut microbiota through fiber rich foods to indirectly support joint function, while ensuring calcium intake to protect bone health (39). It is worth noting that insufficient caloric intake, dehydration, and elevated stress hormone levels—commonly associated with restrictive diets—can lead to transient symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and nausea. However, these effects are typically alleviated upon refeeding (56). Overall, IF should be practiced under medical supervision, including clear emergency guidelines, such as immediate cessation of fasting and seeking medical attention if severe adverse events occur. With proper regimen selection and clinical guidance, most patients can successfully navigate the adaptation phase and safely benefit from IF.
7.3 Patient selection and individualized protocols
Based on existing evidence, overweight or obese patients with KOA may represent the primary candidate population for IF interventions. Weight reduction in these individuals clearly improves OA outcomes, and IF offers an alternative weight-loss approach that many patients find more sustainable than daily calorie restriction (173). For OA patients who have a normal body weight but exhibit metabolic disturbances, such as prediabetes or hyperinsulinemia, IF might also confer benefits by improving metabolic profiles; however, careful nutritional assessment is necessary to avoid excessive weight loss. Individualization of IF protocols is especially important in older adults (≥65 years) with OA, given the higher risk of sarcopenia. These patients should ensure adequate daily protein intake, preferably consuming high biological-value proteins within their eating window to preserve muscle mass (197). Furthermore, patients with concurrent diabetes and those receiving hypoglycemic medications should consult their physicians before initiating IF to adjust medication dosages and prevent hypoglycemic episodes. In clinical practice, the implementation of IF should adhere to a principle of “start low, monitor closely, and adjust gradually.” For example, initiating a 12-h daily fast (from 8 PM to 8 AM) and progressively extending fasting duration or transitioning to a 5:2 regimen should be based on patient tolerance and observed efficacy.
7.4 Combining IF with other interventions
The synergistic potential of combining IF with exercise therapy, pharmacological treatments (such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs] or slow-acting osteoarthritis agents), and joint-protective nutrients (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D) is an emerging area of interest (10). A multimodal therapeutic approach is recommended, as IF does not conflict with existing treatments but rather complements exercise and nutritional supplementation strategies. First, IF aligns well with anti-inflammatory dietary concepts (18); thus, dietary patterns enriched in omega-3 fatty acids, dietary fiber, and antioxidants can be integrated alongside IF to enhance anti-inflammatory benefits. Second, moderate strength training and aerobic exercise during IF periods may further promote fat utilization and muscle protein synthesis, significantly improving joint function. A community-based study demonstrated that combining dietary restriction with exercise resulted in a 50% greater reduction in knee pain compared to dietary restriction alone, suggesting additive benefits for mobility improvement (184). Therefore, IF should be promoted as part of a comprehensive lifestyle intervention plan rather than as an isolated or replacement therapy for OA patients. Additionally, IF may beneficially interact with supplements such as probiotics or prebiotics, which could further optimize gut microbiota composition, or protein hydrolysis enzyme inhibitors (e.g., quercetin) that potentially amplify fasting-induced metabolic effects. These interactions warrant investigation in future studies. It is important to emphasize that IF cannot replace surgical interventions such as joint arthroplasty in advanced OA cases; however, it could play an essential role in perioperative weight management and metabolic optimization, improving surgical tolerance and postoperative recovery outcomes. Caution is warranted when combining IF with exercise interventions. The fasting window may predispose individuals to hypoglycemia and insufficient energy availability, potentially impairing physical performance and post-exercise recovery (198). This concern is particularly relevant for individuals with irregular daily routines or those requiring frequent caloric intake to sustain metabolic demands. Adhering to fixed schedules for both feeding and training may thus pose practical challenges. To mitigate these risks, it is advisable to adapt exercise timing in alignment with the fasting cycle, avoiding high-intensity workouts during periods of low blood glucose to optimize both safety and efficacy.
7.5 Limitations and future research priorities
Limitations: Significant physiological, metabolic, and lifespan differences between animal models (such as mice and rats) and humans must be acknowledged (56). For example, mice exhibit markedly higher metabolic rates than humans and may respond differently to nutritional changes. Furthermore, disease models in animals may not fully replicate the complexity of human conditions. In human studies, adherence to IF protocols may influence outcomes, and individual variability in response to IF is common (189). Some studies also exhibit methodological limitations (182), such as the absence of appropriate control groups, lack of detailed data on participants’ overall dietary behaviors, and insufficient tracking of dietary changes during follow-up. These factors hinder accurate attribution of observed effects to IF alone, as changes in post-discharge diet may also play a role. Moreover, long-term therapeutic fasting is often combined with exercise or mind–body interventions to alleviate hunger or adverse symptoms, potentially introducing confounding variables and masking possible side effects of IF (199). In addition, most human trials to date involve relatively short intervention periods, providing limited evidence regarding the long-term health effects of IF.
Despite preliminary evidence supporting the potential of IF for OA management, several important scientific questions remain to be addressed:
(1) Clinical efficacy evidence: There is an urgent need for large-scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to rigorously evaluate the effects of IF on OA-related pain, functional outcomes, and radiographic progression, particularly in comparison with traditional continuous calorie restriction diets. Such trials should include distinct patient subgroups (e.g., obese vs. non-obese OA patients) to identify populations that could derive the greatest benefit from IF.
(2) Mechanistic biomarkers: Future investigations should delve deeper into the molecular mechanisms by which IF influences OA. Advanced technologies such as single-cell sequencing and tissue organoids can be employed to elucidate multidimensional effects of IF on chondrocytes, osteocytes, and synovial cells, with special emphasis on novel neuroendocrine pathways like NPY. Imaging techniques, such as MRI T2 mapping, should be utilized to quantitatively assess cartilage quality and structural changes, while biochemical markers in serum and synovial fluid (e.g., type II collagen C-terminal peptide, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein) could serve as sensitive indicators of IF intervention efficacy (182).
(3) Optimization of IF protocols: Comparative analyses of different IF regimens (e.g., alternate-day fasting vs. 16:8 fasting), varying fasting durations (such as 14 vs. 18 h daily), and their respective impacts on OA outcomes are necessary to define the optimal fasting strategy. Additionally, the relationship between intervention duration and effectiveness should be explored to ascertain whether sustained adherence yields cumulative benefits.
(4) Combined interventions and functional recovery: Evaluating the potential synergy of IF with exercise rehabilitation programs and pharmacological therapies (e.g., analgesics, disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs) could reveal important interactions, such as reducing reliance on NSAIDs or enhancing the efficacy of joint-protective supplements (e.g., glucosamine).
(5) Special populations and risk management: Special attention is needed regarding safety, efficacy, and nutritional status monitoring of IF interventions among older OA patients and those with comorbid conditions, including metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and osteoporosis risk, to minimize adverse outcomes.
(6) Alternative strategies: For patients unable to adhere to dietary changes, pharmaceutical mimetics of IF, such as low-dose mTOR inhibitors or AMPK activators, could be explored to stimulate similar beneficial metabolic pathways without the necessity of fasting (23).
8 Conclusion
The complex pathogenesis of OA limits the effectiveness of conventional therapies targeting single mechanisms, highlighting the need for systemic therapeutic strategies. IF, as a systemic dietary intervention, offers novel therapeutic potential for OA prevention and management. This review summarizes recent mechanistic and preliminary clinical evidence demonstrating that IF exerts multifaceted effects addressing critical pathological aspects of OA. Animal studies have shown that IF alleviates cartilage degradation, inhibits synovial inflammation, and corrects abnormal bone remodeling processes, highlighting emerging molecular mechanisms such as NPY signaling (162). Preliminary clinical observations further suggest that IF can feasibly improve pain and functional outcomes in OA patients (182). Nonetheless, current evidence primarily derives from preclinical and small-scale clinical studies; therefore, robust, long-term clinical trials are essential to definitively establish the efficacy and safety of IF for OA patients. Practically, IF protocols must be individually tailored according to patient characteristics and integrated into comprehensive intervention programs alongside weight management, exercise, and other lifestyle modifications. With increasing mechanistic insights and clinical data accumulation, IF is poised to evolve from a complementary lifestyle modification to an integral component of holistic OA management, representing a promising non-pharmacological and non-surgical therapeutic option. In conclusion, IF demonstrates considerable potential in OA prevention and treatment, offering new hope in addressing the growing global burden of osteoarthritis.
Author contributions
NS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. YZ: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JW: Writing – review and editing. AZ: Writing – review and editing. YH: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82405529), the Hongkou Clinical Support Key Specialty Project of Shanghai (No. HKLCFC202406), the Research Startup Fund of Shanghai Fourth People’s Hospital (No. sykyqd02601), and the Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Specialty Capacity Enhancement Project (No. QJZXYJK-202404).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kloppenburg M, Namane M, Cicuttini F. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. (2025) 405:71–85. doi: 10.1016/s0140-673602322-5
2. Hodgkinson T, Kelly D, Curtin C, O’Brien F. Mechanosignalling in cartilage: an emerging target for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) 18:67–84. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00724-w
3. Katz J, Arant K, Loeser R. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a review. JAMA. (2021) 325:568–78. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.22171
4. Hunter D, March L, Chew M. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond - Authors’ reply. Lancet. (2021) 397:1060. doi: 10.1016/s0140-673600205-1
5. Yang G, Wang J, Liu Y, Lu H, He L, Ma C, et al. Burden of knee osteoarthritis in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). (2023) 75:2489–500. doi: 10.1002/acr.25158
6. Gbd 2021 Osteoarthritis Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990-2020 and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. (2023) 5:e508–22. doi: 10.1016/s2665-991300163-7
8. Tang S, Zhang C, Oo WM, Fu K, Risberg MA, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, et al. 6.osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Prim. (2025) 11:10. doi: 10.1038/s41572-025-00594-6
10. Gezer H, Ostor A. 7.What is new in pharmacological treatment for osteoarthritis? Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2023) 37:101841. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2023.101841
11. Robinson WH, Lepus CM, Wang Q, Raghu H, Mao R, Lindstrom TM, et al. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2016) 12:580–92. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.136
12. Loeser R, Collins J, Diekman B. Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2016) 12:412–20. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.65
13. Mobasheri A, Rayman M, Gualillo O, Sellam J, van der Kraan P, Fearon U. The role of metabolism in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2017) 13:302–11. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.50
14. Coaccioli S, Sarzi-Puttini P, Zis P, Rinonapoli G, Varrassi G. Osteoarthritis: new insight on its pathophysiology. J Clin Med. (2022) 11:6013. doi: 10.3390/jcm11206013
15. Xie Y, Lv Z, Li W, Lin JT, Sun W, Guo H, et al. JP4-039 protects chondrocytes from ferroptosis to attenuate osteoarthritis progression by promoting Pink1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy. J Orthop Transl. (2025) 51:132–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.01.001
16. Yang D, Xu J, Xu K, Xu P. Skeletal interoception in osteoarthritis. Bone Res. (2024) 12:22. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00328-6
17. Buck A, Vincent H, Newman C, Batsis JA, Abbate LM, Huffman KF, et al. Evidence-based dietary practices to improve osteoarthritis symptoms: an umbrella review. Nutrients. (2023) 15:3050. doi: 10.3390/nu15133050
18. Caron J, Kreher M, Mickle A, Wu S, Przkora R, Estores IM, et al. Intermittent fasting: potential utility in the treatment of chronic pain across the clinical spectrum. Nutrients. (2022) 14:2536. doi: 10.3390/nu14122536
19. Patterson R, Sears D. Metabolic effects of intermittent fasting. Annu Rev Nutr. (2017) 37:371–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064634
20. de Cabo R, Mattson M. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:2541–51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1905136
21. Veronese N, Reginster J. The effects of calorie restriction, intermittent fasting and vegetarian diets on bone health. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2019) 31:753–8. doi: 10.1007/s40520-019-01174-x
22. Chen Y, Tsai H, Tu Y, Chen L. Effects of different types of intermittent fasting on metabolic outcomes: an umbrella review and network meta-analysis. BMC Med. (2024) 22:529. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03716-1
23. Zhang M-N, Duan R, Chen G-H, Chen M-J, Hong C-G, Wang X, et al. Fasting activates optineurin-mediated mitophagy in chondrocytes to protect against osteoarthritis. Commun Biol. (2025) 8:68. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07541-x
24. Wei Z, Li F, Pi G. Association between gut microbiota and osteoarthritis: a review of evidence for potential mechanisms and therapeutics. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:812596. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.812596
25. Mattson M, de Cabo R. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on health, aging, and disease. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:1773–4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2001176
26. Teong XT, Liu K, Vincent AD, Bensalem J, Liu B, Hattersley KJ, et al. Intermittent fasting plus early time-restricted eating versus calorie restriction and standard care in adults at risk of type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Nat Med. (2023) 29:963–72. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02287-7
27. Harvie M, Haiba M. The impact of intermittent energy restriction on women’s health. Proc Nutr Soc. (2025) 1:1–10. doi: 10.1017/s0029665125000059
28. Kapogiannis D, Manolopoulos A, Mullins R, Avgerinos K, Delgado-Peraza F, Mustapic M, et al. Brain responses to intermittent fasting and the healthy living diet in older adults. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:1900–4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.07.012
29. Willoughby D, Hewlings S, Kalman D. Body composition changes in weight loss: strategies and supplementation for maintaining lean body mass, a brief review. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1876. doi: 10.3390/nu10121876
30. Chow LS, Manoogian ENC, Alvear A, Fleischer JG, Thor H, Dietsche K, et al. Time-restricted eating effects on body composition and metabolic measures in humans who are overweight: a feasibility study. Obesity (Silver Spring). (2020) 28:860–9. doi: 10.1002/oby.22756
31. Han K, Singh K, Rodman MJ, Hassanzadeh S, Wu K, Nguyen A, et al. Fasting-induced FOXO4 blunts human CD4(+) T helper cell responsiveness. Nat Metab. (2021) 3:318–26. doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00356-0
32. Minciuna I, Gallage S, Heikenwalder M, Zelber-Sagi S, Dufour J. Intermittent fasting-the future treatment in NASH patients? Hepatology. (2023) 78:1290–305. doi: 10.1097/hep.0000000000000330
33. Milan M, Brown J, O’Reilly CL, Bubak MP, Negri S, Balasubramanian P, et al. Time-restricted feeding improves aortic endothelial relaxation by enhancing mitochondrial function and attenuating oxidative stress in aged mice. Redox Biol. (2024) 73:103189. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103189
34. Horne B, Grajower M, Anderson J. Limited evidence for the health effects and safety of intermittent fasting among patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA. (2020) 324:341–2. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.3908
35. Serger E, Luengo-Gutierrez L, Chadwick JS, Kong G, Zhou L, Crawford G, et al. The gut metabolite indole-3 propionate promotes nerve regeneration and repair. Nature. (2022) 607:585–92. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04884-x
36. Petersen MC, Gallop MR, Ramos SF, Zarrinpar A, Broussard JL, Chondronikola M, et al. Complex physiology and clinical implications of time-restricted eating. Physiol Rev. (2022) 102:1991–2034. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00006.2022
37. Gallage S, Ali A, Barragan Avila J, Seymen N, Ramadori P, Joerke V, et al. A 5:2 intermittent fasting regimen ameliorates NASH and fibrosis and blunts HCC development via hepatic PPARα and PCK1. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:1371–93.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.04.015
38. Shams-White M, Goldbaum A, Agurs-Collins T, Czajkowski S, Herrick KA, Nebeling L, et al. Time-restricted eating and cancer: lessons learned and considerations for a path forward. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2024) 12:djae331. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djae331
39. Varady K, Cienfuegos S, Ezpeleta M, Gabel K. Clinical application of intermittent fasting for weight loss: progress and future directions. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2022) 18:309–21. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00638-x
40. Stekovic S, Hofer S, Tripolt N, Aon MA, Royer P, Pein L, et al. Alternate day fasting improves physiological and molecular markers of aging in healthy, non-obese humans. Cell Metab. (2020) 31:878–81. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.02.011
41. Trepanowski JF, Kroeger CM, Barnosky A, Klempel MC, Bhutani S, Hoddy KK, et al. Effect of alternate-day fasting on weight loss, weight maintenance, and cardioprotection among metabolically healthy obese adults: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. (2017) 177:930–8. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0936
42. Schübel R, Nattenmüller J, Sookthai D, Nonnenmacher T, Graf ME, Riedl L, et al. Effects of intermittent and continuous calorie restriction on body weight and metabolism over 50 wk: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. (2018) 108:933–45. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy196
43. Cienfuegos S, Gabel K, Kalam F, Ezpeleta M, Wiseman E, Pavlou V, et al. Effects of 4- and 6-h time-restricted feeding on weight and cardiometabolic health: a randomized controlled trial in adults with obesity. Cell Metab. (2020) 32:366-78.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.018
44. Tinsley GM, Moore ML, Graybeal AJ, Paoli A, Kim Y, Gonzales JU, et al. Time-restricted feeding plus resistance training in active females: a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr. (2019) 110:628–40. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqz126
45. Mattson M. The cyclic metabolic switching theory of intermittent fasting. Nat Metab. (2025) 7:665–78. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01254-5
46. Varady K. Intermittent fasting is gaining interest fast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2021) 22:587. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00377-3
47. Wilhelmi de Toledo F, Grundler F, Sirtori CR, Ruscica M. Unravelling the health effects of fasting: a long road from obesity treatment to healthy life span increase and improved cognition. Ann Med. (2020) 52:147–61. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1770849
48. Morales-Suarez-Varela M, Collado Sánchez E, Peraita-Costa I, Llopis-Morales A, Soriano J. Intermittent fasting and the possible benefits in obesity, diabetes, and multiple sclerosis: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3179. doi: 10.3390/nu13093179
49. Parrotta M, Colangeli L, Scipione V, Vitale C, Sbraccia P, Guglielmi V. Time restricted eating: a valuable alternative to calorie restriction for addressing obesity? Curr Obes Rep. (2025) 14:17. doi: 10.1007/s13679-025-00609-z
50. Stockman M, Thomas D, Burke J, Apovian C. Intermittent fasting: is the wait worth the weight? Curr Obes Rep. (2018) 7:172–85. doi: 10.1007/s13679-018-0308-9
51. Zhang A, Wang J, Zhao Y, He Y, Sun N. Intermittent fasting, fatty acid metabolism reprogramming, and neuroimmuno microenvironment: mechanisms and application prospects. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1485632. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1485632
52. Borgundvaag E, Mak J, Kramer C. Metabolic impact of intermittent fasting in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2021) 106:902–11. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa926
53. Vasim I, Majeed C, DeBoer M. Intermittent fasting and metabolic health. Nutrients. (2022) 14:631. doi: 10.3390/nu14030631
54. Cheng W, Desmet L, Depoortere I. Time-restricted eating for chronodisruption-related chronic diseases. Acta Physiol (Oxf). (2023) 239:e14027. doi: 10.1111/apha.14027
55. Jamshed H, Beyl R, Della Manna D, Yang E, Ravussin E, Peterson C. Early time-restricted feeding improves 24-hour glucose levels and affects markers of the circadian clock, aging, and autophagy in humans. Nutrients. (2019) 11:1234. doi: 10.3390/nu11061234
56. Strilbytska O, Klishch S, Storey K, Koliada A, Lushchak O. Intermittent fasting and longevity: from animal models to implication for humans. Ageing Res Rev. (2024) 96:102274. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102274
57. Silva A, Direito M, Pinto-Ribeiro F, Ludovico P, Sampaio-Marques B. Effects of intermittent fasting on regulation of metabolic homeostasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis in health and metabolic-related disorders. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:3699. doi: 10.3390/jcm12113699
58. Ezzati A, Rosenkranz S, Phelan J, Logan C. The effects of isocaloric intermittent fasting vs daily caloric restriction on weight loss and metabolic risk factors for noncommunicable chronic diseases: a systematic review of randomized controlled or comparative trials. J Acad Nutr Diet. (2023) 123:318–29.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2022.09.013
59. Zhu S, Surampudi P, Rosharavan B, Chondronikola M. Intermittent fasting as a nutrition approach against obesity and metabolic disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2020) 23:387–94. doi: 10.1097/mco.0000000000000694
60. Marko D, Conn M, Schertzer J. Intermittent fasting influences immunity and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2024) 35:821–33. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2024.04.014
61. Reeves J, Tournier P, Becquart P, Carton R, Tang Y, Vigilante A, et al. Rejuvenating aged osteoprogenitors for bone repair. Elife. (2024) 13:R104068. doi: 10.7554/eLife.104068
62. Ben Nessib D, Maatallah K, Ferjani H, Kaffel D, Hamdi W. The potential effect of Ramadan fasting on musculoskeletal diseases: new perspectives. Clin Rheumatol. (2021) 40:833–9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05297-9
63. Barati M, Ghahremani A, Namdar Ahmadabad H. Intermittent fasting: a promising dietary intervention for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2023) 22:103408. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103408
64. Tavakoli A, Akhgarjand C, Ansar H, Houjaghani H, Khormani A, Djafarian K, et al. The effects of intermittent fasting on antioxidant and inflammatory markers and liver enzymes in postmenopausal, overweight and obese women with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:2357. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86734-0
65. Adawi M, Damiani G, Bragazzi N. The impact of intermittent fasting (Ramadan fasting) on psoriatic arthritis disease activity, enthesitis, and dactylitis: a multicentre study. Nutrients. (2019) 11:301. doi: 10.3390/nu11030601
66. Goldring S, Goldring M. Changes in the osteochondral unit during osteoarthritis: structure, function and cartilage-bone crosstalk. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2016) 12:632–44. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.148
67. Miller R, Malfait A, Miller R. The innate immune response as a mediator of osteoarthritis pain. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2020) 28:562–71. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.11.006
68. Coryell P, Diekman B, Loeser R. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2021) 17:47–57. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00533-7
69. Sanchez-Lopez E, Coras R, Torres A, Lane N, Guma M. Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis progression. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) 18:258–75. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00749-9
70. Moulin D, Sellam J, Berenbaum F, Guicheux J, Boutet M. The role of the immune system in osteoarthritis: mechanisms, challenges and future directions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2025) 21:221–36. doi: 10.1038/s41584-025-01223-y
71. Schott E, Farnsworth C, Grier A. Targeting the gut microbiome to treat the osteoarthritis of obesity. JCI Insight. (2018) 3:e95997. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.95997
72. Courties A, Berenbaum F, Sellam J. The phenotypic approach to osteoarthritis: a look at metabolic syndrome-associated osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. (2019) 86:725–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2018.12.005
73. Collins K, Lenz K, Pollitt E, Ferguson D, Hutson I, Springer LE, et al. Adipose tissue is a critical regulator of osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2021) 118:e2021096118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2021096118
74. Binvignat M, Sellam J, Berenbaum F, Felson D. The role of obesity and adipose tissue dysfunction in osteoarthritis pain. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2024) 20:565–84. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01143-3
75. Szilagyi IA, Nguyen NL, Boer CG, Schiphof D, Ahmadizar F, Kavousi M, et al. Metabolic syndrome, radiographic osteoarthritis progression and chronic pain of the knee among men and women from the general population: the Rotterdam study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2024) 69:152544. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2024.152544
76. Kardos D, Marschall B, Simon M, Hornyák I, Hinsenkamp A, Kuten O, et al. Investigation of cytokine changes in osteoarthritic knee joint tissues in response to hyperacute serum treatment. Cells. (2019) 8:824. doi: 10.3390/cells8080824
77. Tang Q, Hu Z, Shen L, Shang P, Xu H, Liu H. Association of osteoarthritis and circulating adiponectin levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. (2018) 17:189. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0838-x
78. Liu Z, Xie W, Li H, Liu X, Lu Y, Lu B, et al. Novel perspectives on leptin in osteoarthritis: focus on aging. Genes Dis. (2024) 11:101159. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.101159
79. Scotece M, Mobasheri A. Leptin in osteoarthritis: focus on articular cartilage and chondrocytes. Life Sci. (2015) 140:75–8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.05.025
80. Gao Y, Zhao C, Liu B, Dong N, Ding L, Li YR, et al. An update on the association between metabolic syndrome and osteoarthritis and on the potential role of leptin in osteoarthritis. Cytokine. (2020) 129:155043. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155043
81. Abella V, Scotece M, Conde J, Pino J, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Gómez-Reino JJ, et al. Leptin in the interplay of inflammation, metabolism and immune system disorders. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2017) 13:100–9. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.209
82. Ouchi N, Parker J, Lugus J, Walsh K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2011) 11:85–97. doi: 10.1038/nri2921
83. Jansen NEJ, Molendijk E, Schiphof D, Meurs JBJ, Oei EHG, Middelkoop M, et al. Metabolic syndrome and the progression of knee osteoarthritis on MRI. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2023) 31:647–55. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2023.02.003
84. Wang T, He C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: the link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2018) 44:38–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.10.002
85. Kroon FPB, Veenbrink AI, Mutsert R, Visser AW, Dijk K W, Cessie S, et al. The role of leptin and adiponectin as mediators in the relationship between adiposity and hand and knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2019) 27:1761–7. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.08.003
86. Griffin T, Huebner J, Kraus V, Guilak F. Extreme obesity due to impaired leptin signaling in mice does not cause knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. (2009) 60:2935–44. doi: 10.1002/art.24854
87. Sampath S, Venkatesan V, Ghosh S, Kotikalapudi N. Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Osteoarthritis-An Updated Review. Curr Obes Rep. (2023) 12:308–31. doi: 10.1007/s13679-023-00520-5
88. Veronese N, Cooper C, Reginster JY, Hochberg M, Branco J, Bruyère O, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2019) 49:9–19. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.01.005
89. Suzuki A, Yabu A, Nakamura H. Advanced glycation end products in musculoskeletal system and disorders. Methods. (2022) 203:179–86. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.09.012
90. Louati K, Vidal C, Berenbaum F, Sellam J. Association between diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis: systematic literature review and meta-analysis. RMD Open. (2015) 1:e000077. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2015-000077
91. Maniglio M, Loisay L, de Haro D, Antoniadis A, Hügle T, Geurts J. Subchondral bone marrow adipose tissue lipolysis regulates bone formation in hand osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2025) 33:322–9. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2024.12.005
92. Mustonen A, Nieminen P. Fatty Acids and Oxylipins in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis-a Complex Field with Significant Potential for Future Treatments. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2021) 23:41. doi: 10.1007/s11926-021-01007-9
93. Van Pevenage P, Birchmier J, June R. Utilizing metabolomics to identify potential biomarkers and perturbed metabolic pathways in osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2023) 59:152163. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2023.152163
94. Ma Y, Liu Y, Luo D, Guo Z, Xiang H, Chen B, et al. Identification of biomarkers and immune infiltration characterization of lipid metabolism-associated genes in osteoarthritis based on machine learning algorithms. Aging (Albany NY). (2024) 16:7043–59. doi: 10.18632/aging.205740
95. Wang F, Ma L, Ding Y, He L, Chang M, Shan Y, et al. Fatty acid sensing GPCR (GPR84) signaling safeguards cartilage homeostasis and protects against osteoarthritis. Pharmacol Res. (2021) 164:105406. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105406
96. Papathanasiou I, Anastasopoulou L, Tsezou A. Cholesterol metabolism related genes in osteoarthritis. Bone. (2021) 152:116076. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2021.116076
97. Cho B, Kim D, Kwon H, Yang I, Lee W, Park K. Cross-sectional association between hypercholesterolemia and knee pain in the elderly with radiographic knee osteoarthritis: data from the korean national health and nutritional examination survey. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:933. doi: 10.3390/jcm10050933
98. Cao C, Shi Y, Zhang X, Li Q, Zhang J, Zhao F, et al. Cholesterol-induced LRP3 downregulation promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by targeting Syndecan-4. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:7139. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34830-4
99. Triantaphyllidou I, Kalyvioti E, Karavia E, Lilis I, Kypreos K, Papachristou D. Perturbations in the HDL metabolic pathway predispose to the development of osteoarthritis in mice following long-term exposure to western-type diet. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2013) 21:322–30. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2012.11.003
100. Courties A, Sellam J, Berenbaum F. Metabolic syndrome-associated osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2017) 29:214–22. doi: 10.1097/bor.0000000000000373
101. Niu J, Clancy M, Aliabadi P, Vasan R, Felson D. Metabolic syndrome, its components, and knee osteoarthritis: the Framingham osteoarthritis study. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2017) 69:1194–203. doi: 10.1002/art.40087
102. Valdes A. Metabolic syndrome and osteoarthritis pain: common molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic implications. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2020) 28:7–9. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.06.015
103. Kluzek S, Newton J, Arden N. Is osteoarthritis a metabolic disorder? Br Med Bull. (2015) 115:111–21. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldv028
104. Tang YH, Yue Z-S, Zheng W-J, Shen H-F, Zeng L-R, Hu Z-Q, et al. 4-Phenylbutyric acid presents therapeutic effect on osteoarthritis via inhibiting cell apoptosis and inflammatory response induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. (2018) 65:540–6. doi: 10.1002/bab.1642
105. Peiris C, Culvenor A. Metabolic syndrome and osteoarthritis: implications for the management of an increasingly common phenotype. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2023) 31:1415–7. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2023.06.004
106. Olivotto E, Trisolino G, Belluzzi E, Lazzaro A, Strazzari A, Pozzuoli A, et al. Macroscopic synovial inflammation correlates with symptoms and cartilage lesions in patients undergoing arthroscopic partial meniscectomy: a clinical study. J Clin Med. (2022) 11:4330. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154330
107. Fulop T, Witkowski J, Olivieri F, Larbi A. The integration of inflammaging in age-related diseases. Semin Immunol. (2018) 40:17–35. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2018.09.003
108. Yuan F, Tang Y, Zheng F, Xie Q. Analyzing the role of specific damage-associated molecular patterns-related genes in osteoarthritis and investigating the association between β-amyloid and apolipoprotein E isoforms. J Innate Immun. (2024) 16:501–12. doi: 10.1159/000541542
109. Semenistaja S, Skuja S, Kadisa A, Groma V. Healthy and osteoarthritis-affected joints facing the cellular crosstalk. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4120. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044120
110. Palumbo A, Atzeni F, Murdaca G, Gangemi S. The role of alarmins in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: HMGB1, S100B and IL-33. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:2143. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512143
111. Liang W, Feng R, Li X, Duan X, Feng S, Chen J, et al. A RANKL-UCHL1-sCD13 negative feedback loop limits osteoclastogenesis in subchondral bone to prevent osteoarthritis progression. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:8792. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53119-2
112. Motta F, Barone E, Sica A, Selmi C. Inflammaging and Osteoarthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2023) 64:222–38. doi: 10.1007/s12016-022-08941-1
113. Nedunchezhiyan U, Varughese I, Sun A, Wu X, Crawford R, Prasadam I. Obesity, inflammation, and immune system in osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:907750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.907750
114. Knights A, Redding S, Maerz T. Inflammation in osteoarthritis: the latest progress and ongoing challenges. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2023) 35:128–34. doi: 10.1097/bor.0000000000000923
115. Zhang P, Zhai H, Zhang S, Ma X, Gong A, Xu Z, et al. GDF11 protects against mitochondrial-dysfunction-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation to attenuate osteoarthritis. J Adv Res. (2024) 73:501–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.08.001
116. Zhang Y, Li S, Jin P, Shang T, Sun R, Lu L, et al. Dual functions of microRNA-17 in maintaining cartilage homeostasis and protection against osteoarthritis. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:2447. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30119-8
117. Papatriantafyllou M. PDZK1 downregulation linked to mitochondrial dysfunction in OA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2024) 20:597. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01157-x
118. Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, et al. Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:8416763. doi: 10.1155/2017/8416763
119. Deng Z, Long D, Li C, Liu H, Li W, Zhong Y, et al. IRF1-mediated upregulation of PARP12 promotes cartilage degradation by inhibiting PINK1/Parkin dependent mitophagy through ISG15 attenuating ubiquitylation and SUMOylation of MFN1/2. Bone Res. (2024) 12:63. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00363-3
120. Xiang J, Yang X, Tan M, Guo J, Ye Y, Deng J, et al. NIR-enhanced Pt single atom/g-CN nanozymes as SOD/CAT mimics to rescue ATP energy crisis by regulating oxidative phosphorylation pathway for delaying osteoarthritis progression. Bioact Mater. (2024) 36:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.02.018
121. Li Y, Yang J, Chen X, Hu H, Lan N, Zhao J, et al. Mitochondrial-targeting and NIR-responsive MnO@PDA@Pd-SS31 nanozymes reduce oxidative stress and reverse mitochondrial dysfunction to alleviate osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. (2024) 305:122449. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122449
122. Liu L, Zhang W, Liu T, Tan Y, Chen C, Zhao J, et al. The physiological metabolite α-ketoglutarate ameliorates osteoarthritis by regulating mitophagy and oxidative stress. Redox Biol. (2023) 62:102663. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102663
123. Ansari M, Ahmad N, Haqqi T. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 129:110452. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110452
124. Riegger J, Schoppa A, Ruths L, Haffner-Luntzer M, Ignatius A. Oxidative stress as a key modulator of cell fate decision in osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: a narrative review. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2023) 28:76. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00489-y
125. Liu D, Cai Z-J, Yang Y-T, Lu W-H, Pan L-Y, Xiao W-F, et al. Mitochondrial quality control in cartilage damage and osteoarthritis: new insights and potential therapeutic targets. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2022) 30:395–405. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2021.10.009
126. Sun K, Jing X, Guo J, Yao X, Guo F. Mitophagy in degenerative joint diseases. Autophagy. (2021) 17:2082–92. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1822097
127. Dong J, Zhang K-J, Li G-C, Chen X-R, Lin J-J, Li J-W, et al. CDDO-Im ameliorates osteoarthritis and inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis in mice via enhancing Nrf2-dependent autophagy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2022) 43:1793–802. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00782-6
128. Wang J, Zhang Y, Cao J, Wang Y, Anwar N, Zhang Z, et al. The role of autophagy in bone metabolism and clinical significance. Autophagy (2023) 19:2409–27. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2186112
129. Qin J, Zhang J, Wu JJ, Ru X, Zhong Q-L, Zhao JM, et al. Identification of autophagy-related genes in osteoarthritis articular cartilage and their roles in immune infiltration. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1263988. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1263988
130. Wang S, Deng Z, Ma Y, Jin J, Qi F, Li S, et al. The Role of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Bone Metabolic Disorders. Int J Biol Sci. (2020) 16:2675–91. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.46627
131. Guo Y, Jia X, Cui Y, Song Y, Wang S, Geng Y, et al. Sirt3-mediated mitophagy regulates AGEs-induced BMSCs senescence and senile osteoporosis. Redox Biol. (2021) 41:101915. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101915
132. Xu K, He Y, Moqbel S, Zhou X, Wu L, Bao J. SIRT3 ameliorates osteoarthritis via regulating chondrocyte autophagy and apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. (2021) 175:351–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.029
133. Yan J, Shen M, Sui B, Lu W, Han X, Wan Q, et al. Autophagic LC3(+) calcified extracellular vesicles initiate cartilage calcification in osteoarthritis. Sci Adv. (2022) 8:eabn1556. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn1556
134. Duan R, Xie H, Liu Z. The role of autophagy in osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:608388. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.608388
135. Chen Y, Zhou J, Wang L. Role and mechanism of gut microbiota in human disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2021) 11:625913. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.625913
136. Yu F, Zhu C, Wu W. Senile osteoarthritis regulated by the gut microbiota: from mechanisms to treatments. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:1505. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041505
137. Biver E, Berenbaum F, Valdes AM, Carvalho IA, Bindels LB, Brandi ML, et al. Gut microbiota and osteoarthritis management: an expert consensus of the European society for clinical and economic aspects of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal diseases (ESCEO). Ageing Res Rev. (2019) 55:100946. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.100946
138. Geng J, Ni Q, Sun W, Li L, Feng X. The links between gut microbiota and obesity and obesity related diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 147:112678. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112678
139. Romero-Figueroa M, Ramírez-Durán N, Montiel-Jarquín A, Horta-Baas G. Gut-joint axis: gut dysbiosis can contribute to the onset of rheumatoid arthritis via multiple pathways. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1092118. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1092118
140. Ahuja A, Kim E, Sung G, Cho J. STAT3 differentially regulates TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses in early or late phases. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:7675. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207675
141. Favazzo LJ, Hendesi H, Villani DA, Soniwala S, Dar Q-A, Schott EM, et al. The gut microbiome-joint connection: implications in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2020) 32:92–101. doi: 10.1097/bor.0000000000000681
142. Rios J, Bomhof M, Reimer R, Hart D, Collins K, Herzog W. Protective effect of prebiotic and exercise intervention on knee health in a rat model of diet-induced obesity. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:3893. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40601-x
143. Guss JD, Ziemian SN, Luna M, Sandoval TN, Holyoak DT, Guisado GG, et al. The effects of metabolic syndrome, obesity, and the gut microbiome on load-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2019) 27:129–39. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.07.020
144. Liu S, Li G, Xu H, Wang Q, Wei Y, Yang Q, et al. “Cross-talk” between gut microbiome dysbiosis and osteoarthritis progression: a systematic review. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1150572. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1150572
145. He J, Chu Y, Li J, Meng Q, Liu Y, Jin J, et al. Intestinal butyrate-metabolizing species contribute to autoantibody production and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Adv. (2022) 8:eabm1511. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm1511
146. Sano T, Kageyama T, Fang V, Kedmi R, Martinez CS, Talbot J, et al. Redundant cytokine requirement for intestinal microbiota-induced Th17 cell differentiation in draining lymph nodes. Cell Rep. (2021) 36:109608. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109608
147. Chen Y, Wang X, Zhang C, Liu Z, Li C, Ren Z. Gut microbiota and bone diseases: a growing partnership. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:877776. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.877776
148. Li H-Z, Zhang J-L, Yuan D-L, Xie W-Q, Ladel CH, Mobasheri A, et al. Role of signaling pathways in age-related orthopedic diseases: focus on the fibroblast growth factor family. Mil Med Res. (2024) 11:40. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00544-5
149. Belluzzi E, Hadi HE, Granzotto M, Rossato M, Ramonda R, Macchi V, et al. Systemic and Local Adipose Tissue in Knee Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. (2017) 232:1971–8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25716
150. Atukorala I, Makovey J, Lawler L, Messier S, Bennell K, Hunter D. Is There a Dose-Response Relationship Between Weight Loss and Symptom Improvement in Persons With Knee Osteoarthritis? Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). (2016) 68:1106–14. doi: 10.1002/acr.22805
151. Ge M, Sun W, Xu T, Yang R, Zhang K, Li J, et al. Multi-omics analysis of synovial tissue and fluid reveals differentially expressed proteins and metabolites in osteoarthritis. J Transl Med. (2025) 23:285. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06310-y
152. Hamada D, Maynard R, Schott E, Drinkwater CJ, Ketz JP, Kates SL, et al. Suppressive effects of insulin on tumor necrosis factor-dependent early osteoarthritic changes associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2016) 68:1392–402. doi: 10.1002/art.39561
153. Ding C, Parameswaran V, Cicuttini F, Burgess J, Zhai G, Quinn S, et al. Association between leptin, body composition, sex and knee cartilage morphology in older adults: the Tasmanian older adult cohort (TASOAC) study. Ann Rheum Dis. (2008) 67:1256–61. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.082651
154. Choi I, Lee C, Longo V. Nutrition and fasting mimicking diets in the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases and immunosenescence. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2017) 455:4–12. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.01.042
155. Buono R, Longo V. When fasting gets tough, the tough immune cells get going-or die. Cell. (2019) 178:1038–40. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.052
156. Jordan S, Tung N, Casanova-Acebes M, Chang C, Cantoni C, Zhang D, et al. Dietary intake regulates the circulating inflammatory monocyte pool. Cell. (2019) 178:1102–14.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.050
157. Chen D, Shen J, Zhao W, Wang T, Han L, Hamilton JL, et al. 5.Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res. (2017) 5:16044. doi: 10.1038/boneres.2016.44
158. Shi H, Zhang B, Abo-Hamzy T, Nelson JW, Ambati CSR, Petrosino JF, et al. Restructuring the gut microbiota by intermittent fasting lowers blood pressure. Circ Res. (2021) 128:1240–54. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.120.318155
159. Neudorf H, Little J. Impact of fasting & ketogenic interventions on the NLRP3 inflammasome: a narrative review. Biomed J. (2024) 47:100677. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.100677
160. Li G, Xie C, Lu S, Nichols RG, Tian Y, Li L, et al. Intermittent fasting promotes white adipose browning and decreases obesity by shaping the gut microbiota. Cell Metab. (2017) 26:672–85.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.08.019
161. Nagai M, Noguchi R, Takahashi D, Morikawa T, Koshida K, Komiyama S, et al. Fasting-refeeding impacts immune cell dynamics and mucosal immune responses. Cell. (2019) 178:1072–87.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.047
162. Qian Y-X, Rao S-S, Tan Y-J, Wang Z, Yin H, Wan T-F, et al. Intermittent fasting targets osteocyte neuropeptide y to relieve osteoarthritis. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11:e2400196. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400196
163. Deng Y, Hou M, Wu Y, Liu Y, Xia X, Yu C, et al. SIRT3-PINK1-PKM2 axis prevents osteoarthritis via mitochondrial renewal and metabolic switch. Bone Res. (2025) 13:36. doi: 10.1038/s41413-025-00413-4
164. He H, Huang C, Huang H, Lan N, Liu S, Luo Y, et al. Zn(2+)-driven metformin conjugated with siRNA attenuates osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting NF-κB signaling and activating autophagy. Biomaterials. (2025) 319:123210. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2025.123210
165. Li L, Li J, Li J-J, Zhou H, Zhu X-W, Zhang P-H, et al. Chondrocyte autophagy mechanism and therapeutic prospects in osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1472613. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1472613
166. Wen R, Huang R, Xu K, Yi X. Insights into the role of histone lysine demethylases in bone homeostasis and skeletal diseases: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 306:141807. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.141807
167. Kao W, Chen J, Liu P, Lu CC, Lin SY, Chuang SC, et al. The role of autophagy in osteoarthritic cartilage. Biomolecules. (2022) 12:1357. doi: 10.3390/biom12101357
168. Weir H, Yao P, Huynh F, Escoubas CC, Goncalves RL, Burkewitz K, et al. Dietary restriction and AMPK increase lifespan via mitochondrial network and peroxisome remodeling. Cell Metab. (2017) 26:884–96.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.024
169. Zeb F, Osaili T, Obaid R, Naja F, Radwan H, Cheikh Ismail L, et al. Gut microbiota and time-restricted feeding/eating: a targeted biomarker and approach in precision nutrition. Nutrients. (2023) 15:259. doi: 10.3390/nu15020259
170. Saglam D, Colak G, Sahin E, Ekren B, Sezerman U, Bas M. Effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting on gut microbiome: is the diet key? Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1203205. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1203205
171. Liu J, Zhong Y, Luo X, Ma Y, Liu J, Wang H. Intermittent fasting reshapes the gut microbiota and metabolome and reduces weight gain more effectively than melatonin in mice. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:784681. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.784681
172. Rinninella E, Cintoni M, Raoul P, Ianiro G, Laterza L, Lopetuso LR, et al. Gut microbiota during dietary restrictions: new insights in non-communicable diseases. Microorganisms. (2020) 8:1140. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8081140
173. Mohr AE, Sweazea KL, Bowes DA, Jasbi P, Whisner CM, Sears DD, et al. Gut microbiome remodeling and metabolomic profile improves in response to protein pacing with intermittent fasting versus continuous caloric restriction. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:4155. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48355-5
174. Park S, Shin B. Intermittent fasting with a high-protein diet mitigated osteoarthritis symptoms by increasing lean body mass and reducing inflammation in osteoarthritic rats with Alzheimer’s disease-like dementia. Br J Nutr. (2022) 127:55–67. doi: 10.1017/s0007114521000829
175. Fransen M, Agaliotis M, Nairn L, Votrubec M, Bridgett L, Su S, et al. Glucosamine and chondroitin for knee osteoarthritis: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating single and combination regimens. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:851–8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203954
176. Sumsuzzman D, Khan Z, Jung J, Hong Y, Yang WJ, Park K, et al. Comparative efficacy of glucosamine-based combination therapies in alleviating knee osteoarthritis pain: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:7444. doi: 10.3390/jcm13237444
177. Seto Y, Yoshihashi T, Tomonari M, To H. Absorption of glucosamine is improved by considering circadian rhythm and feeding time in rats. Chronobiol Int. (2020) 37:1528–37. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2020.1784189
178. Kubicky R, Wu S, Kharitonenkov A, De Luca F. Role of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) in undernutrition-related attenuation of growth in mice. Endocrinology. (2012) 153:2287–95. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1909
179. Wu S, Levenson A, Kharitonenkov A, De Luca F. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) inhibits chondrocyte function and growth hormone action directly at the growth plate. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:26060–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.343707
180. Lu H, Jia C, Wu D, Jin H, Lin Z, Pan J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) alleviates senescence, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via the SIRT1-mTOR signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:865. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04157-x
181. Renard D, Tuffet S, Dieud P, Claudepierre P, Gossec L, Fautrel B, et al. Factors associated with dietary practices and beliefs on food of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: a multicentre cross-sectional study. Joint Bone Spine. (2025) 92:105778. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2024.105778
182. Koppold D, Kandil F, Güttler O, Müller A, Steckhan N, Meiß S, et al. Effects of prolonged fasting during inpatient multimodal treatment on pain and functional parameters in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a prospective exploratory observational study. Nutrients. (2023) 15:2695. doi: 10.3390/nu15122695
183. Schmidt S, Stange R, Lischka E, Kiehntopf M, Deufel T, Loth D, et al. [Uncontrolled clinical study of the efficacy of ambulant fasting in patients with osteoarthritis]. Forsch Komplementmed. (2010) 17:87–94. doi: 10.1159/000285479
184. Messier S, Beavers D, Queen K. Effect of diet and exercise on knee pain in patients with osteoarthritis and overweight or obesity: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2022) 328:2242–51. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.21893
185. Messier SP, Mihalko SL, Legault C, Miller GD, Nicklas BJ, DeVita P, et al. Effects of intensive diet and exercise on knee joint loads, inflammation, and clinical outcomes among overweight and obese adults with knee osteoarthritis: the IDEA randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2013) 310:1263–73. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.277669
186. Ribeiro M, López de Figueroa P, Blanco FJ, Mendes AF, Caramés B. Insulin decreases autophagy and leads to cartilage degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartil. (2016) 24:731–9. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.10.017
187. Phillips K, Clauw D. Central pain mechanisms in chronic pain states–maybe it is all in their head. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2011) 25:141–54. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2011.02.005
188. Drinda S, Franke S, Schmidt S, Stoy K, Lehmann T, Wolf G, et al. AGE-RAGE interaction does not explain the clinical improvements after therapeutic fasting in osteoarthritis. Complement Med Res. (2018) 25:167–72. doi: 10.1159/000486237
189. Pratscher S, Mickle A, Marks J, Rocha H, Bartsch F, Schmidt J, et al. Optimizing chronic pain treatment with enhanced neuroplastic responsiveness: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1556. doi: 10.3390/nu13051556
190. Hartmann A, Dell’Oro M, Spoo M, Fischer JM, Steckhan N, Jeitler M, et al. To eat or not to eat-an exploratory randomized controlled trial on fasting and plant-based diet in rheumatoid arthritis (NutriFast-Study). Front Nutr. (2022) 9:1030380. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1030380
191. Blinn C, Biggee B, McAlindon T, Nuite M, Silbert J. Sulphate and osteoarthritis: decrease of serum sulphate levels by an additional 3-h fast and a 3-h glucose tolerance test after an overnight fast. Ann Rheum Dis. (2006) 65:1223–5. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.052571
192. Mattson M, Longo V, Harvie M. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res Rev. (2017) 39:46–58. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.10.005
193. Hoddy K, Kroeger C, Trepanowski J, Barnosky A, Bhutani S, Varady K. Safety of alternate day fasting and effect on disordered eating behaviors. Nutr J. (2015) 14:44. doi: 10.1186/s12937-015-0029-9
194. Harvie M, Pegington M, Mattson M, Frystyk J, Dillon B, Evans G, et al. The effects of intermittent or continuous energy restriction on weight loss and metabolic disease risk markers: a randomized trial in young overweight women. Int J Obes (Lond). (2011) 35:714–27. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2010.171
195. Kim H, Kang T, Kim M, Swan H, Park S. Long-term weight patterns and physical activity in gallstones. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:25817. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77218-8
196. Grajower M, Horne B. Clinical management of intermittent fasting in patients with diabetes mellitus. Nutrients. (2019) 11:873. doi: 10.3390/nu11040873
197. Park S, Kang S, Kim D, Zhang T. Protection against osteoarthritis symptoms by aerobic exercise with a high-protein diet by reducing inflammation in a testosterone-deficient animal model. Life (Basel). (2022) 12:177. doi: 10.3390/life12020177
198. Hays H, Sefidmooye Azar P, Kang M, Tinsley G, Wijayatunga N. Effects of time-restricted eating with exercise on body composition in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). (2025) 49:755–65. doi: 10.1038/s41366-024-01704-2
Keywords: osteoarthritis, intermittent fasting, metabolic regulation, inflammation, gut microbiota
Citation: Sun N, Zhao Y, Wang J, Zhang A and He Y (2025) Intermittent fasting in osteoarthritis: from mechanistic insights to therapeutic potential. Front. Nutr. 12:1604872. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1604872
Received: 02 April 2025; Accepted: 04 July 2025;
Published: 21 July 2025.
Edited by:
Amin Gasmi, Francophone Society of Nutritherapy and Applied Nutrigenetics, FranceReviewed by:
Samuel Pragasam, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, IndiaSabine Chmelar, St. Pölten University of Applied Sciences, Austria
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Zhao, Wang, Zhang and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Anren Zhang, YW5yZW4wMTI0QDE2My5jb20=; Yu He, aGV5dUBjbXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Nianyi Sun
Nianyi Sun Yinuo Zhao1,2†
Yinuo Zhao1,2† Junyu Wang
Junyu Wang Yu He
Yu He