- 1College of Physical Education, Kashgar University, Kashgar, China
- 2Department of Physical Education, Shandong Jiaotong University, Jinan, China
- 3Department of Aviation Security, China Civil Aviation Flight Academy, Guanghan, China
- 4School of Aviation Sports, China Civil Aviation Flight Academy, Guiyang, China
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the effects of vitamin supplementation, exercise, and their combined interventions on insulin resistance and related outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). Additionally, it examined the dose–response relationships between vitamin dosage, exercise intensity, and improvements in insulin resistance.
Methods: Relevant studies investigating the impact of vitamin supplementation and exercise interventions on insulin resistance in T2D patients were systematically retrieved from authoritative domestic and international databases, followed by comprehensive synthesis and analysis.
Results: Traditional meta-analyses revealed that both short-term (<12 weeks) and long-term (>12 weeks) interventions significantly improved insulin resistance and related outcomes. The exceptions included vitamin supplementation alone, which did not significantly improve glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c); neither exercise alone or vitamin supplementation alone, which failed to significantly reduce fasting blood glucose; and combined exercise interventions, which had no significant effects on insulin levels. All other interventions yielded significant benefits. Network meta-analysis revealed that, compared with the control group, probiotics provided the greatest improvement in insulin resistance. Vitamin D was most effective at improving HbA1c, whereas vitamin C had the strongest effects on fasting blood glucose and insulin indices. Dose-subgroup analysis indicated that vitamin supplementation up to 2000 IU/day most effectively reduced fasting blood glucose (p < 0.01) but had no significant effects on HbA1c or insulin (all p > 0.05). A dosage of 2,100–4,000 IU/day produced the most pronounced improvements in HbA1c (p < 0.01) and insulin (p < 0.05) but did not significantly affect insulin resistance or fasting blood glucose (all p > 0.05). Supplementation at 4100–7500 IU/day yielded the greatest improvements in insulin resistance (p < 0.01) but had no significant effect on HbA1c (p > 0.05). Exercise interventions with an intensity of ≤4 METs, performed three times per week, significantly improved insulin resistance, HbA1c, and insulin indices. Sessions lasting ≤60 min produced optimal benefits for insulin resistance and insulin measures, whereas sessions ≤45 min were most effective for HbA1c and fasting blood glucose.
Conclusion: Vitamin supplementation at 4100–7500 IU/day combined with moderate-intensity exercise (approximately 4 METs) performed three times per week with each session lasting 45–60 min, yielded the most favorable improvements in insulin resistance and related metabolic outcomes in T2D patients.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD420250655264.
Introduction
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 180 million people worldwide have diabetes, and this number is projected to rise to 360 million by 2030. Each year, diabetes contributes to an estimated 2.9 million deaths, making it a major global public health challenge (1). Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), also known as non–insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), accounts for more than 90% of all diabetes cases and occurs predominantly in middle-aged and older adults (1).
Insulin resistance (IR), a key pathophysiological feature of T2DM, is closely linked to the development and progression of the disease. Most patients with T2DM present with IR, which is defined as a diminished responsiveness of insulin-target tissues to elevated insulin levels. This impaired response reduces the body’s ability to regulate blood glucose, leading to chronic hyperglycemia. Over time, persistent hyperglycemia induces β-cell dysfunction and failure, resulting in chronic hyperinsulinemia and ultimately progressing to T2DM (2, 3). Importantly, prediabetes represents a transitional stage between normal glucose tolerance and T2DM and serves as a critical warning period (4). Individuals in this stage already exhibit insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, both of which contribute to the onset and persistence of T2DM. Insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion jointly characterize this stage. Furthermore, IR and T2DM are strongly associated with obesity (5).
Current interventions for prediabetes and T2DM include vitamin supplementation and exercise. Vitamin supplementation plays an important role in suppressing inflammation, controlling blood glucose, and enhancing insulin secretion. Exercise, considered one of the five cornerstones of T2DM management, is valued for its affordability, convenience, and systemic health benefits. Research has shown that exercise improves obesity-related outcomes and reduces glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and fasting insulin (FINS) levels. However, the effects of vitamins on diabetes remain a subject of debate, and the optimal parameters of exercise—such as duration, intensity, and type—have not been clearly defined (1). In addition, although some studies suggest that combining exercise with dietary and lifestyle interventions achieves greater benefits in weight reduction and prevention or management of T2DM than exercise alone, the overall effectiveness of these combined approaches requires further validation.
To address these gaps, the present study employed a network meta-analysis to evaluate the effects of vitamin supplementation, exercise interventions, and their combination on insulin resistance in patients with T2DM. Furthermore, a dose–response meta-analysis was conducted to identify the optimal dosage of vitamin supplementation and exercise parameters, aiming to provide evidence-based recommendations for the management of insulin resistance in T2DM patients.
Research subjects and methods
This study followed the PRISMA 2020 guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses and has been registered on the international PROSPERO platform, with the registration number CRD420250655264.
Literature search strategy
A comprehensive search was conducted in both domestic and international academic databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Library, the China Biomedical Literature Database, CNKI, the Wanfang Database, and the VIP Database. The search was limited to publications in Chinese and English, with a cutoff date of December 24, 2024. The Chinese search terms included: vitamin and exercise or training or “physical activity and type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance.” The English search terms included: “insulin resistance” OR “Insulin resistance” OR “Metabolic syndrome” OR “insulin resistance factor uremia” OR “Pseudoacromegaly with Severe Insulin Resistance” OR “HAIR-AN syndrome” AND “type 2 diabetes” OR “Diabetes Mellitus Type 2” OR “Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young” OR “Type 2” OR “T2DM” AND “vitamin” AND “sport” OR “exercise” OR “physical activity” OR “training.” Please refer to Appendix 2 for the specific process.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies were included according to the PICOST framework. Eligibility criteria: Population (P): Patients diagnosed with T2DM, regardless of age, sex, or disease duration. Patients with or without additional complications were considered. Intervention (I): Vitamin supplementation (e.g., vitamin D, vitamin E, folic acid), with no restrictions on dosage or frequency. Exercise interventions (including aerobic exercise, resistance training, traditional exercise, and aquatic exercise), with no restrictions on frequency, duration, or type. Combined interventions of exercise plus vitamin supplementation, with no restrictions on vitamin type, exercise modality, frequency, or dosage. Comparison (C): Control groups received placebo supplementation without vitamins and maintained usual physical activity. Outcomes (O): Insulin resistance and related metabolic indicators. Study design (S): Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), with no language restrictions. Time frame (T): No restrictions on intervention duration.
Exclusion criteria: Studies were excluded if they met any of the following conditions: reviews, theoretical studies, animal experiments, or conference abstracts; interventions not involving exercise, vitamin supplementation, or their combination; or data reported without means ± standard deviations.
Literature screening and data extraction
Two independent researchers screened the literature according to the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. A third researcher resolved any disagreements. The selection process included the following steps: 1. Identification and removal of duplicate records. 2. Title screening to exclude survey studies, reviews, studies with unrelated interventions, and animal experiments. 3. Abstract and full-text screening to exclude studies with incomplete data, unclear interventions, or undefined outcome measures; and 4. Verification of eligible studies was performed by a third researcher. Final confirmation of the included studies and extraction of relevant data. Data extraction included the following: study characteristics: first author and year of publication. Participant information: Age, sex, and sample size of the experimental and control groups. Study design: type of intervention, duration, frequency, and evaluation indicators. Outcomes of interest: IR, fasting blood sugar (FBS), HbA1c, FINS, TC, TG, LDL-C, and hHDL-C. To ensure consistency, all outcome measures were converted to international standard units. For example, blood glucose values reported in mg/dL were converted to mmol/L. Insulin resistance was assessed via the homeostasis model assessment of IR (HOMA-IR).
Quality assessment
Two researchers independently evaluated the methodological quality of the included studies via the Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool. The assessment covered seven domains, including random sequence generation, allocation concealment, and blinding. A third researcher resolved any disagreements.
Statistical analysis
This study used Stata software to conduct a meta-analysis of intervention effects on the outcome measures from the included studies. All primary indicators—including IR, FINS, FBS, and HbA1c—were treated as continuous variables. The network meta-analysis employed Stata to perform traditional meta-analysis and dose–subgroup analyses. R software (version 4.4.1) was used to test model consistency, assess convergence, generate cumulative ranking results, and evaluate publication bias.
Assessment of evidence quality
This study applied the GRADE approach to evaluate the quality of evidence for the included outcomes. The assessment considered five domains: risk of bias, indirectness, inconsistency, imprecision, and publication bias. On the basis of these domains, each outcome was graded as very low, low, moderate, or high quality.
Results
Literature selection results
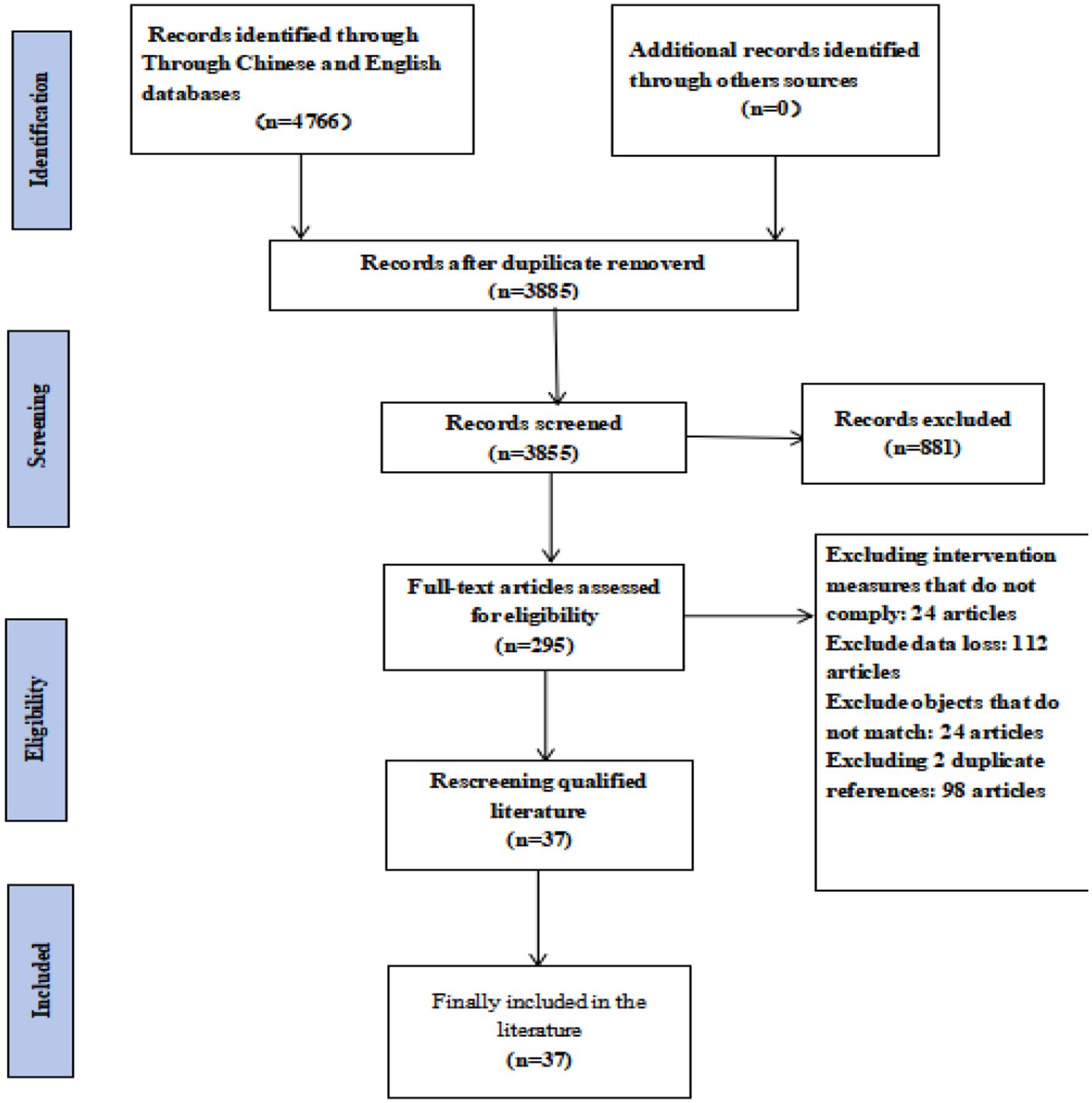
A total of 4,766 articles were initially retrieved from domestic and international databases. After removing duplicates, animal studies, and other ineligible records, 295 articles remained for preliminary screening. Following full-text review, 37 studies met the inclusion criteria (Figure 1). These included 5 two-arm trials, 6 studies with dual interventions, and 12 studies with multiple interventions.
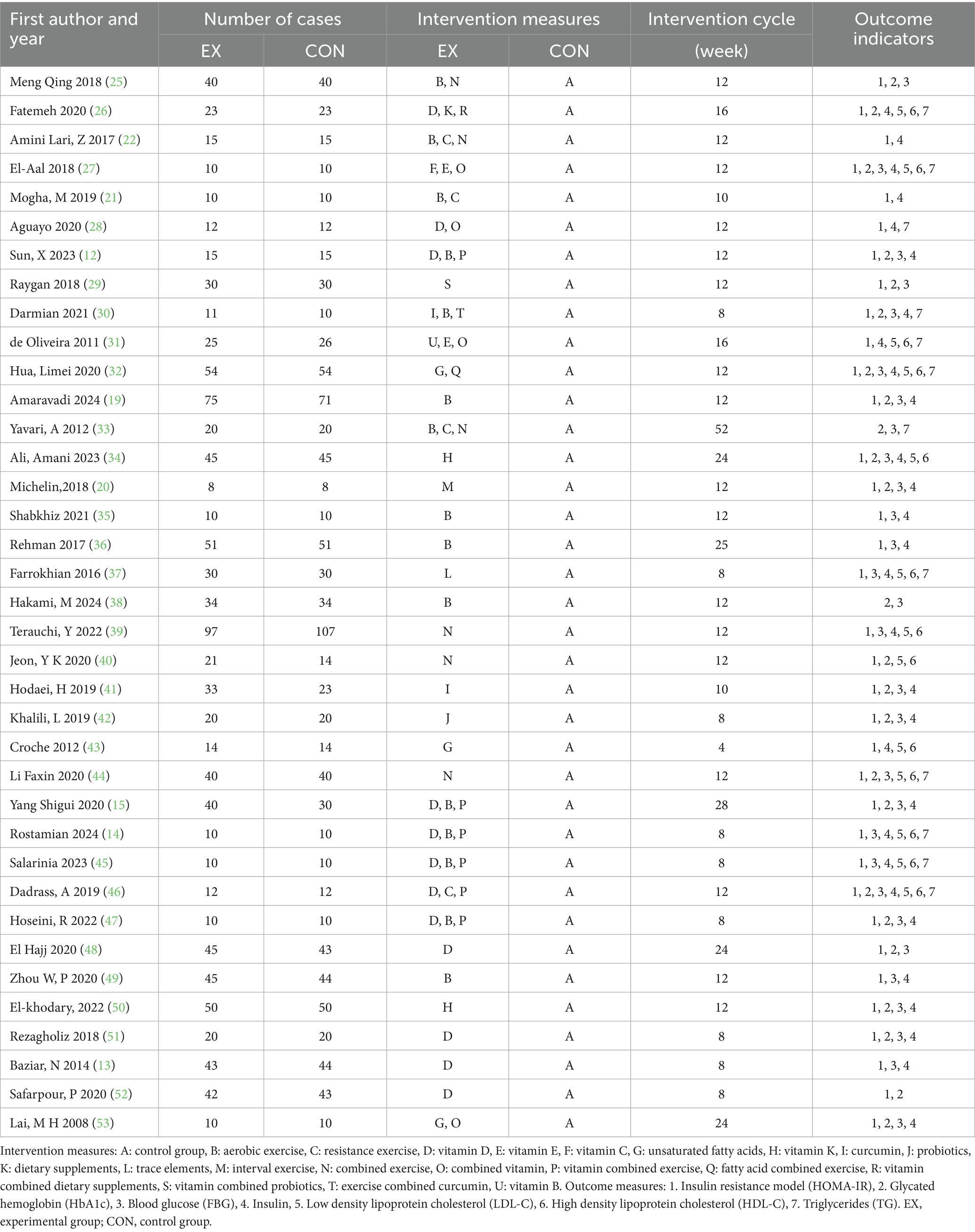
The baseline characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1. Overall, 2,828 patients with type 2 diabetes were enrolled, with 1,672 participants in the test group (T) and 1,156 in the control group (C). Interventions included vitamin C, trace element, vitamin D, aerobic exercise, resistance training, unsaturated fatty acid, combined exercise, combined vitamin supplementation, and exercise plus vitamin supplementation. All interventions lasted at least 8 weeks.
Risk of bias assessment
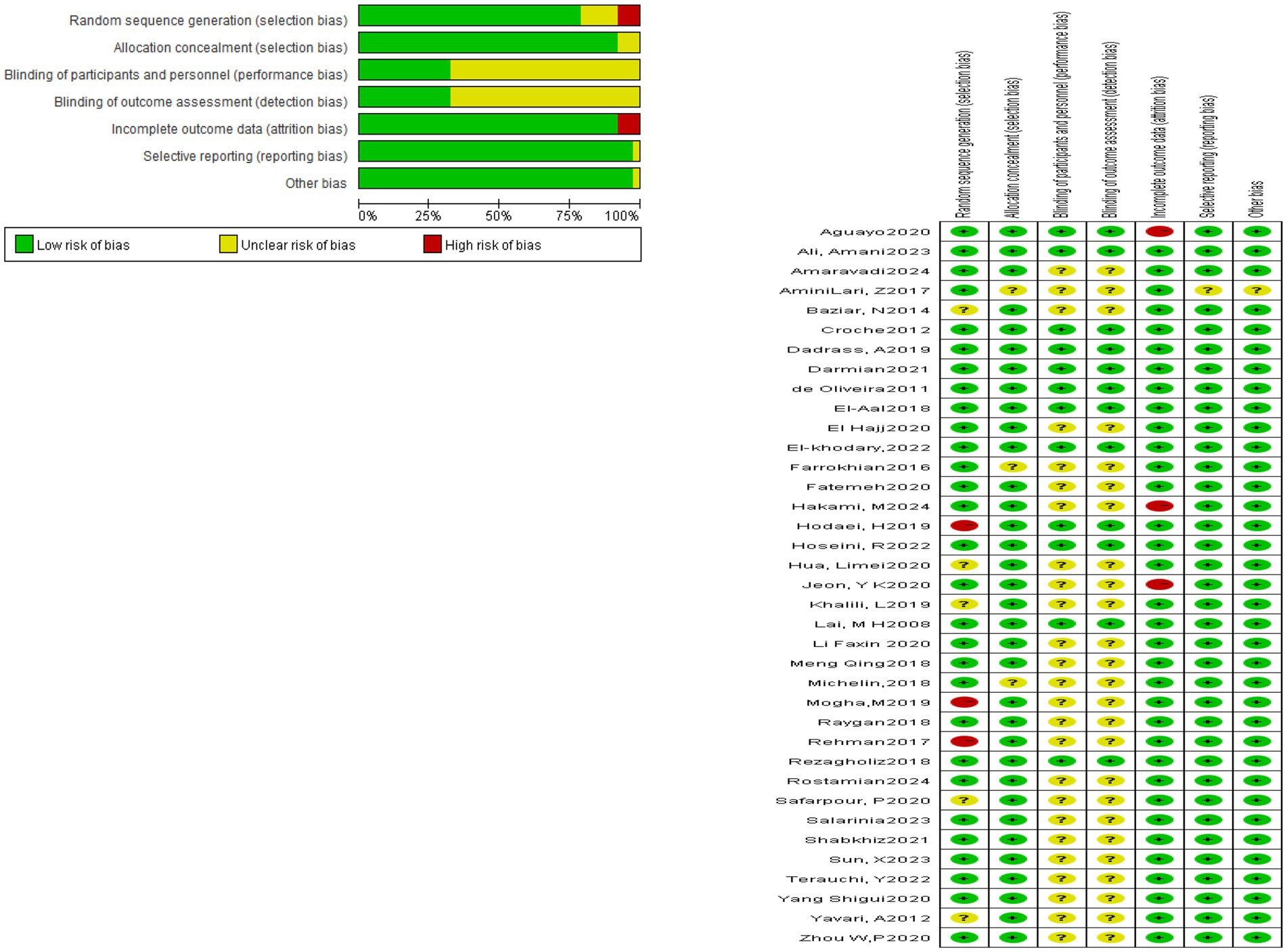
All 37 included studies reported the use of randomization. However, 31 studies did not provide detailed descriptions of the randomization method. One study used computer-generated randomization, one applied block randomization, one adopted sealed envelopes, and one used a random number generator. Among the included studies, three explicitly implemented single-blinding, nine applied double-blinding, and the remaining studies did not mention blinding procedures. Three studies presented a potential risk of incomplete outcome data. With respect to participant characteristics, 29 studies included patients with comorbidities. The reported comorbidities included coronary heart disease in two studies, hyperlipidemia in one study, and hypertension in one study. The detailed results are presented in Figure 2.
Traditional meta-analysis results
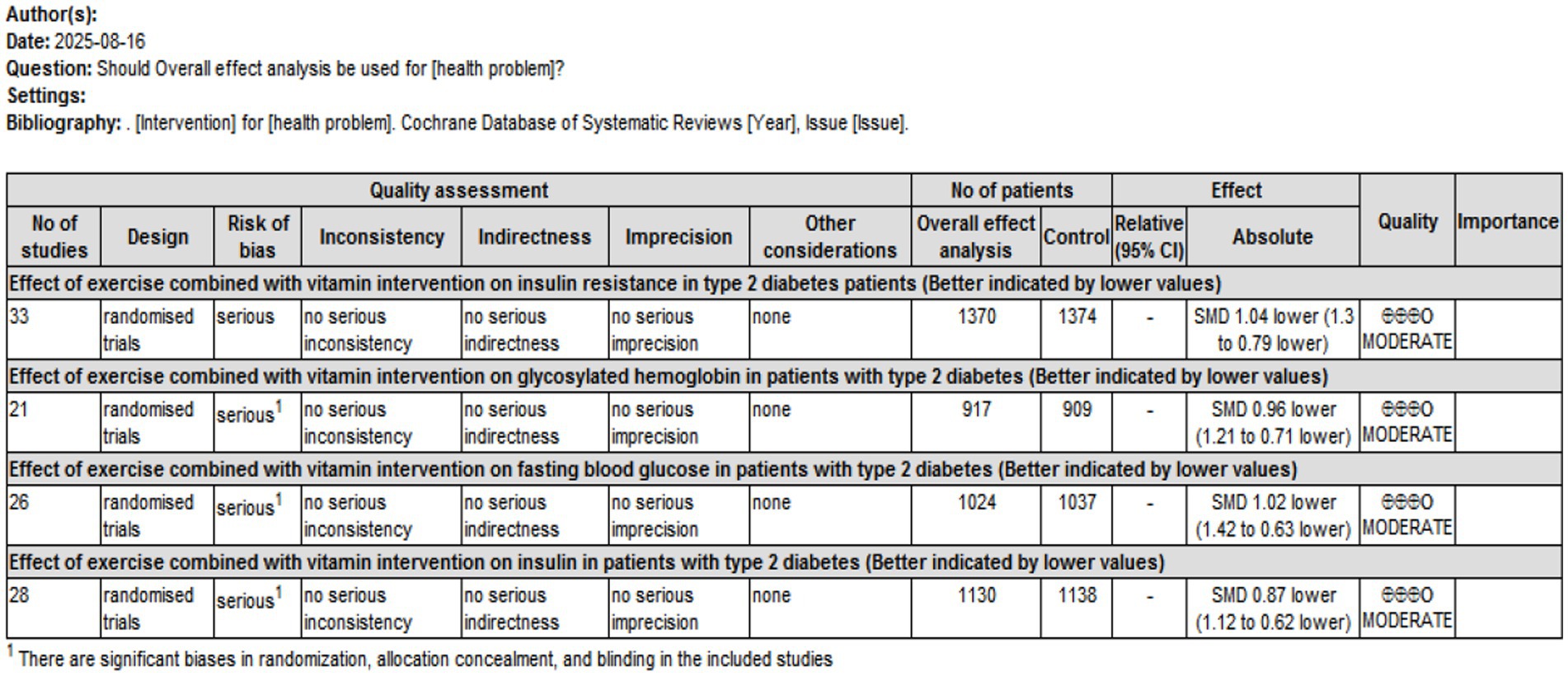
A total of 33, 21, 26, and 28 studies were included to assess the effects of interventions on IR, HbA1c, FBS, and FINS, respectively. Overall effect analyses indicated significant heterogeneity across studies (IR: p < 0.01, I2 = 90.8%; HbA1c: p < 0.01, I2 = 85.1%; FBS: p < 0.01, I2 = 93.8%; FINS: p < 0.01, I2 = 86.4%), suggesting the use of a random effects model. The results demonstrated that, compared with controls, interventions significantly reduced IR and associated metabolic indicators: IR: SMD = −1.217, 95% CI [−1.490, −0.945], p < 0.01; HbA1c: SMD = −1.061, 95% CI [−1.315, −0.807], p < 0.01; FBS: SMD = −1.122, 95% CI [−1.505, −0.740], p < 0.01; FINS: SMD = −0.908, 95% CI [−1.152, −0.665], p < 0.01.
Subgroup analyses revealed that single exercise, combined exercise, single supplementation with vitamins, unsaturated fatty acids, or trace elements, and combined interventions with vitamins, unsaturated fatty acids, trace elements, or exercise significantly reduced IR (SMD range: −0.854 to −1.916, all p < 0.05). Single exercise significantly reduced IR (SMD range: −0.854 to −1.916, all p < 0.05). Single exercise, combined exercise, single supplementation, and combined interventions significantly improved HbA1c (SMD range: −0.957 to −1.534, all p < 0.05). However, combined supplementation with vitamins, unsaturated fatty acids, and trace elements alone did not significantly affect HbA1c (SMD = −0.247, 95% CI [−1.169, 0.676], p > 0.05). Single exercise and single supplementation did not significantly reduce FBS (SMD = −0.684, 95% CI [−1.543, 0.174], p > 0.05; SMD = −1.063, 95% CI [−1.505, 0.621], p > 0.05). In contrast, combined vitamin/unsaturated fatty acids/trace elements, combined exercise, and unsaturated fatty acids/trace elements plus exercise significantly reduced the FBS (SMD range: −0.598 to −5.001, all p < 0.01). Single exercise, single supplementation, combined vitamin supplementation, and other combined interventions significantly reduced insulin levels (SMD range: −0.715 to −1.718, all p < 0.05), whereas combined exercise alone did not significantly affect insulin (SMD = 0.024, 95% CI [−0.521, 0.568], p > 0.05).
Intervention duration analysis revealed that short-term (<12 weeks), medium-term (12 weeks), and long-term (>12 weeks) interventions significantly reduced IR, insulin, and HbA1c (all p < 0.01). Interventions shorter than 12 weeks or longer than 12 weeks also significantly reduced FBS, whereas 12-week interventions did not significantly affect FBS (SMD = −0.479, 95% CI [−1.094, 0.135], p > 0.05). The detailed results are presented in Table 2.
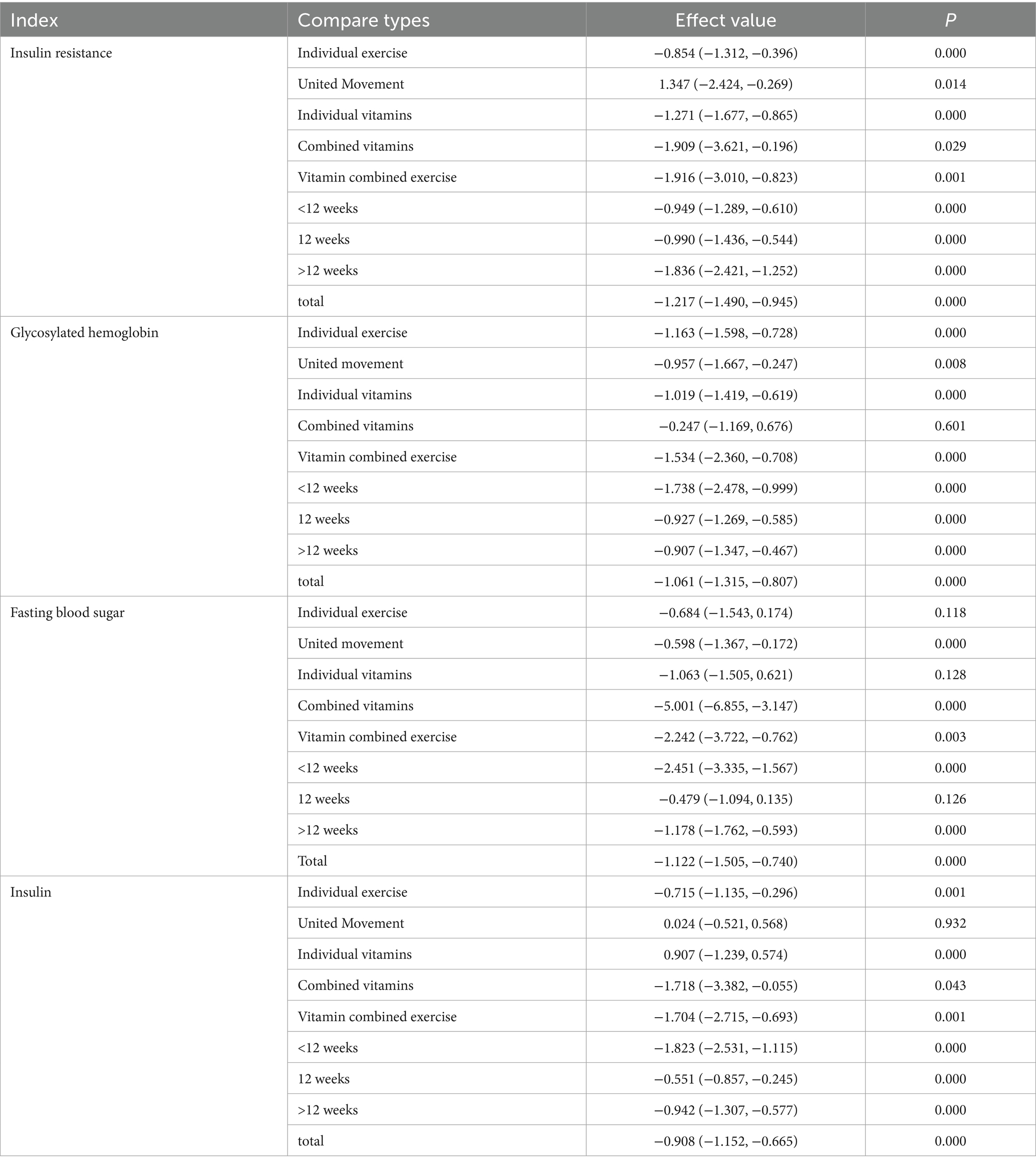
Table 2. Subgroup analysis of exercise combined with vitamin intervention on insulin resistance and corresponding indicators.
Dosage subgroup analysis
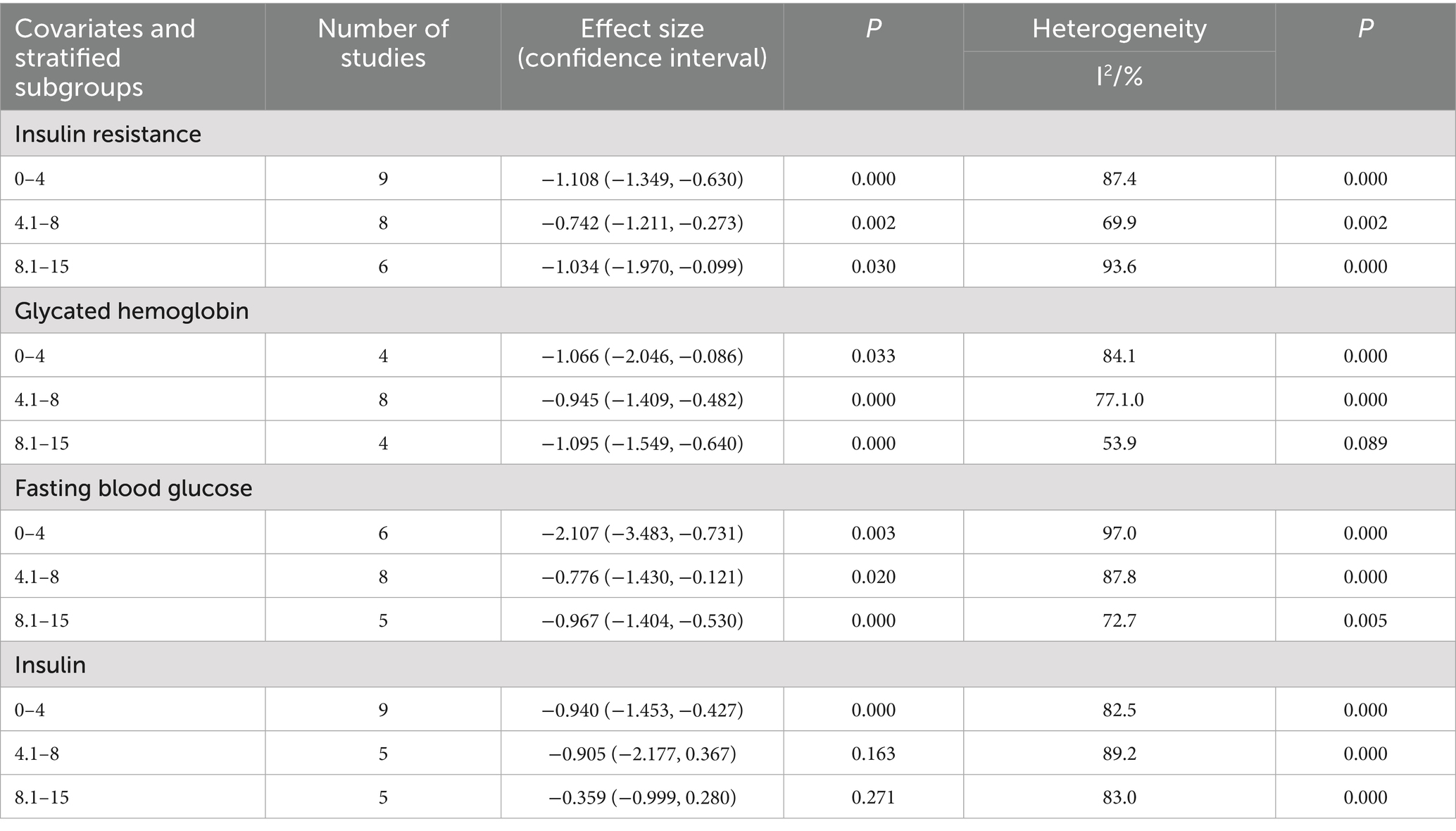
This study collected and standardized intervention doses to quantify the effects of vitamin supplementation and exercise on insulin resistance. For fat-soluble vitamin interventions, 0 IU/day served as the reference, and for exercise interventions, 0 MET·hour served as the reference. The study then conducted a quantitative assessment of the relationships between vitamin dose, exercise intensity, and IR in patients with type 2 diabetes. The dose–response meta-analysis revealed that fat-soluble vitamin supplementation up to 2,000 IU/day produced the greatest improvement in fasting blood glucose (FBS) (p < 0.01) but had no significant effect on hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) or insulin levels (both p > 0.05). Doses of 2,100–4,000 IU/day optimized improvements in HbA1c (p < 0.01) and insulin (p < 0.05) but did not significantly affect insulin resistance or FBS (both p > 0.05). Doses of 4,100–7,500 IU/day achieved the greatest reduction in insulin resistance (p < 0.01) without significantly affecting HbA1c (p > 0.05). With respect to exercise interventions, intensities ≤4 MET significantly improved insulin resistance and insulin levels (both p < 0.01) and significantly affected HbA1c (p < 0.01) and FBS (p < 0.05). Intensities of 4.1–8 MET optimized HbA1c outcomes (p < 0.01) but did not significantly affect FINS levels (p > 0.05). Intensities of 8.1–15 MET significantly improved HbA1c and FBS (both p < 0.01) but did not significantly influence IR or FINS (both p > 0.05). An intervention frequency of three sessions per week significantly improved IR, HbA1c, and FINS outcomes. Single-session durations ≤60 min produced the greatest improvements in IR and FINS levels, whereas durations ≤45 min were most effective for HbA1c and FBS.
On the basis of these findings, fat-soluble vitamin supplementation at 4,100–7,500 IU/day combined with exercise at approximately 4 METs, performed three times per week, with each session lasting 45–60 min, is recommended to achieve optimal improvements in insulin resistance and related metabolic indicators in patients with type 2 diabetes. The detailed results are presented in Tables 3–5.
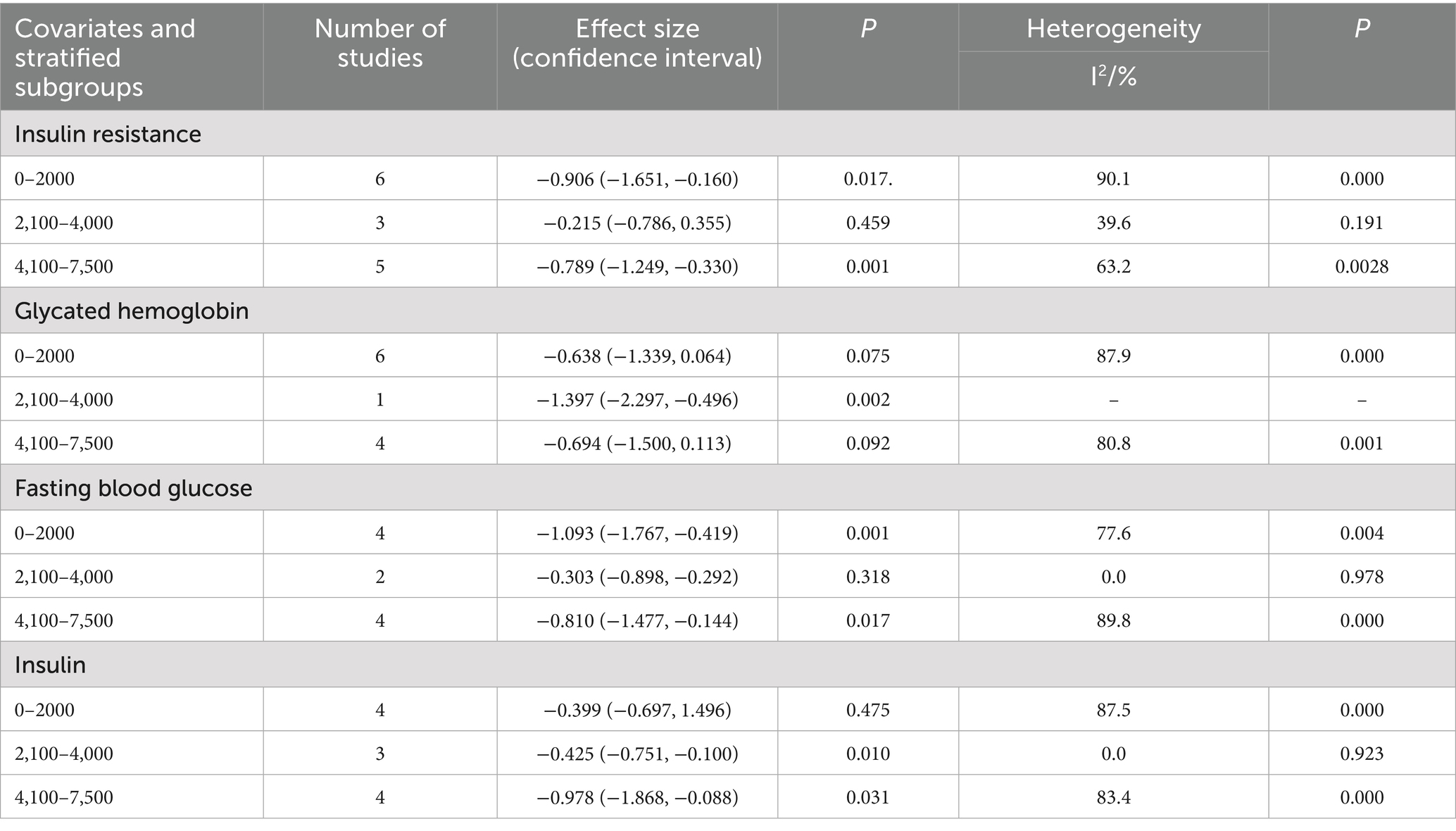
Table 3. Subgroup reactions of vitamin supplementation to insulin resistance and corresponding indicator doses.
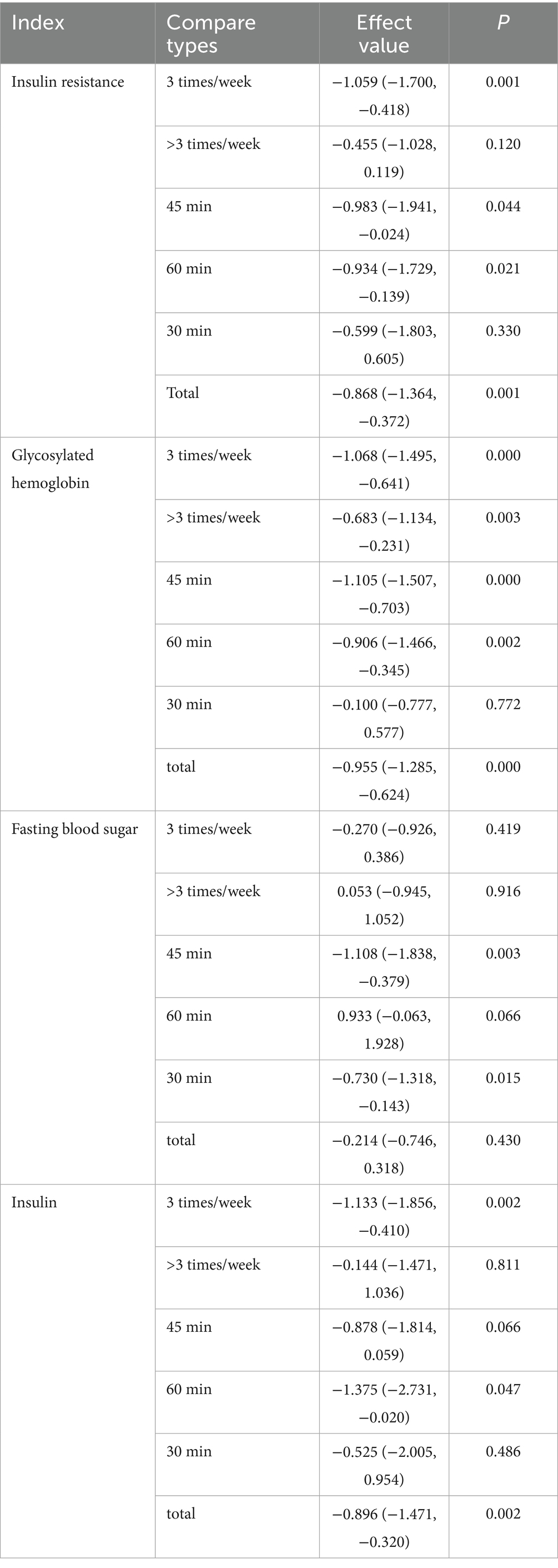
Table 5. Subgroup analysis of exercise intervention frequency and duration of single exercise intervention.
Network meta-analysis results
Network plot
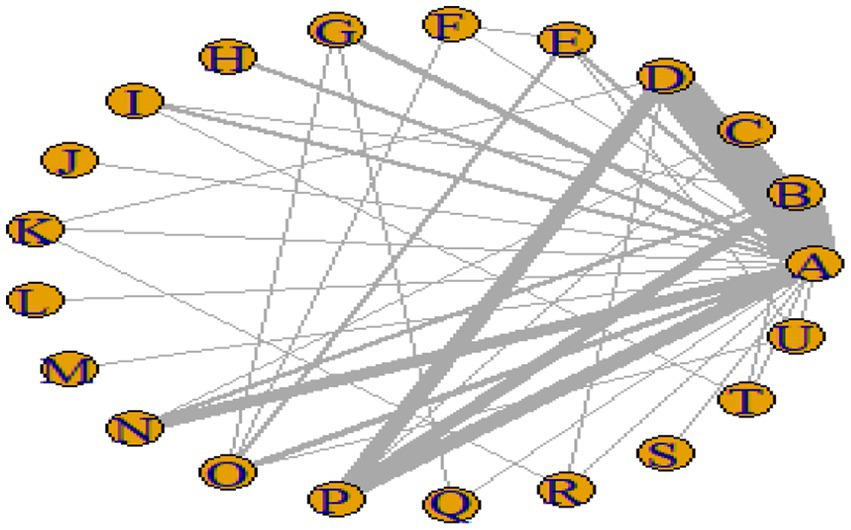
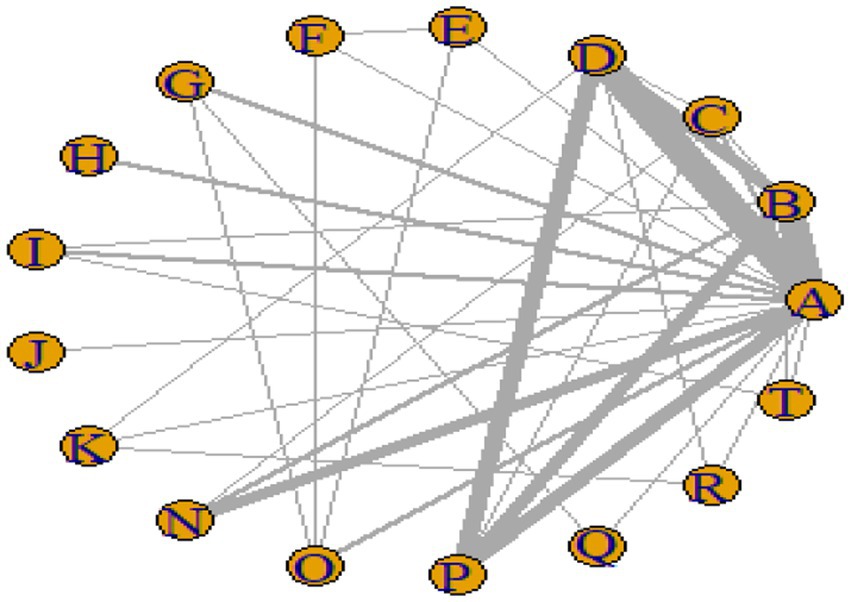
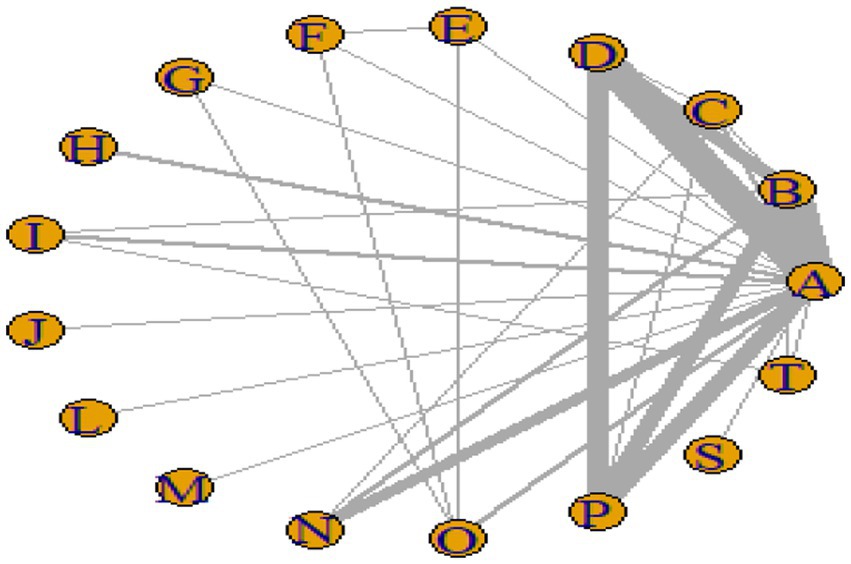
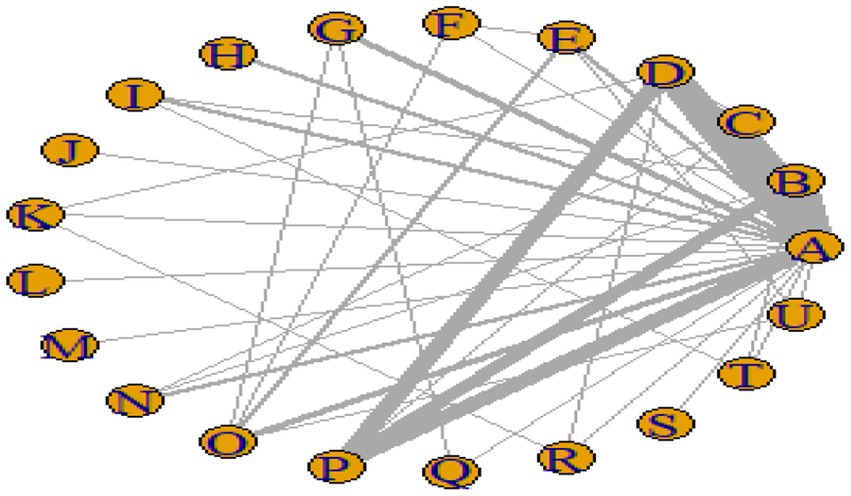
Figures 3–6 illustrate the network relationships of various interventions—including vitamin supplementation, unsaturated fatty acids, trace elements, curcumin, aerobic exercise, resistance training, combined vitamin and exercise interventions, and combinations of vitamins with unsaturated fatty acids plus exercise—on insulin resistance and related metabolic indicators (glucose, insulin, and hemoglobin A1c) in patients with type 2 diabetes. All the network plots were centered on the control group and did not form closed loops. Overall, the comparisons focused primarily on aerobic exercise, resistance training, vitamin D supplementation, and combined vitamin plus exercise interventions relative to the control group outcomes.
Forest plot
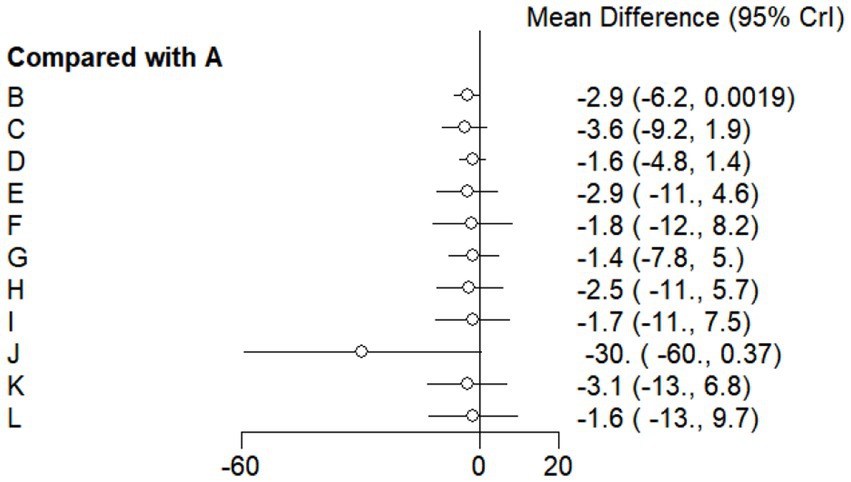
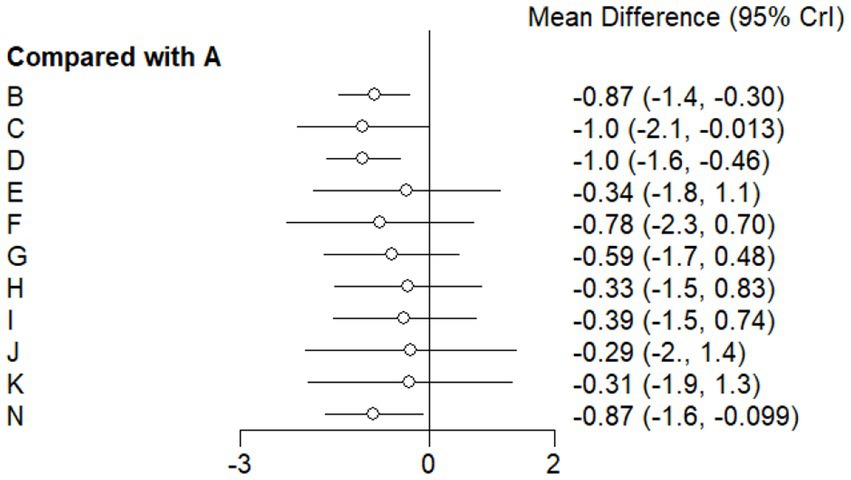
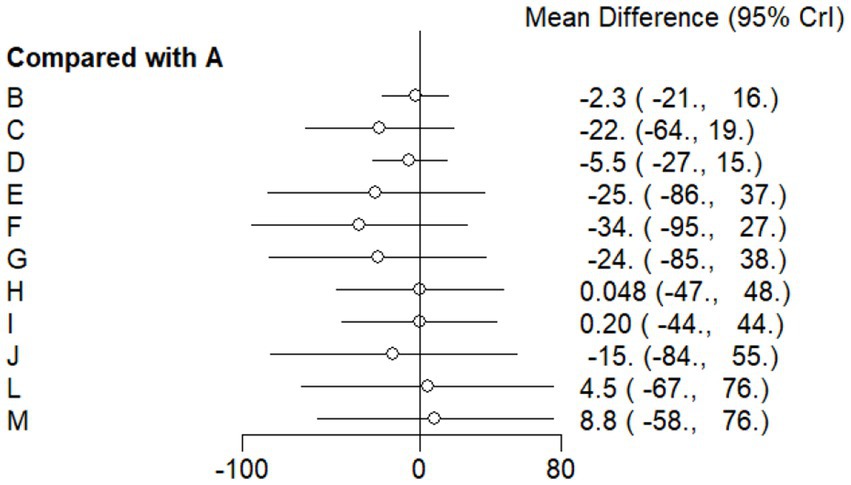
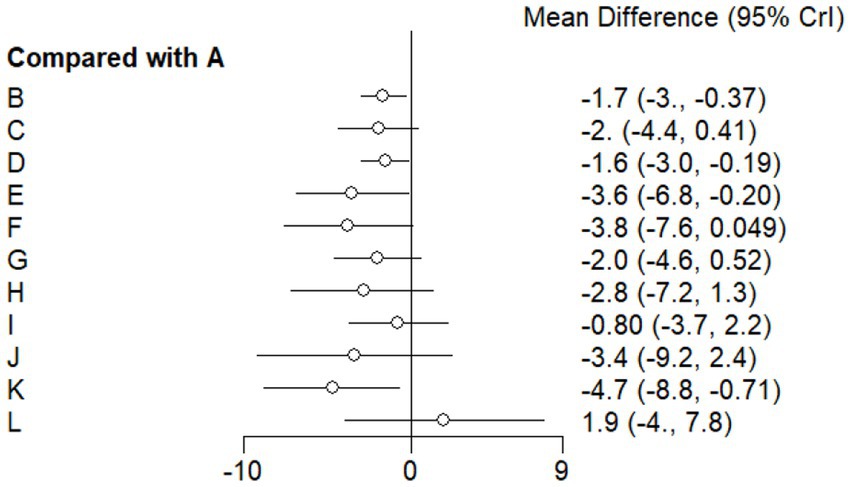
This study included 33 trials on single vitamin supplementation, 21 trials on resistance training, 36 trials on aerobic exercise, and 28 trials on combined interventions, including vitamin plus exercise, combined vitamin supplementation, combined exercise, exercise plus probiotics, and exercise plus unsaturated fatty acids. The results of the network meta-analysis indicated that, compared with the control diet without exercise or corresponding vitamin interventions, probiotics produced the greatest improvement in insulin resistance. Vitamin D significantly improved HbA1c, whereas vitamin C had the most pronounced effects on FBS and insulin levels. The detailed results are presented in Figures 7–10.
Consistency test and model convergence diagnosis
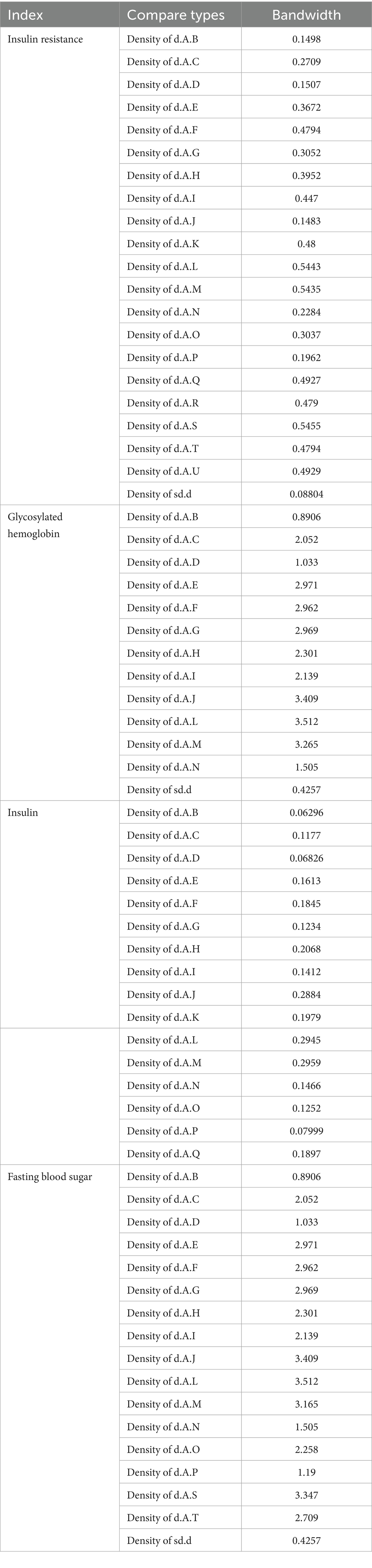
In this study, trace plots were used to assess model convergence, whereas bandwidth indicators from density plots were used to evaluate model stability. Theoretically, as the number of iterations increases sufficiently, a bandwidth approaching zero indicates progressively enhanced model stability. The results revealed that insulin resistance values ranged from 0.08804 to 0.5455, with the highest value observed for d.A.S. (0.5455). HbA1c ranged from 0.4257 to 3.512, with a d.A.L. of 3.512 as the peak value. Insulin values ranged from 0.06296 to 0.2959, peaking at d.A.M. (0.2959), and FBS ranged from 0.4257 to 3.512, also peaking at d.A.L (3.512). Most sd.d values were low, whereas d.A.L represented a core high value across indicators. Overall, HbA1c and FBS exhibited greater density and more complete information (see Table 6).
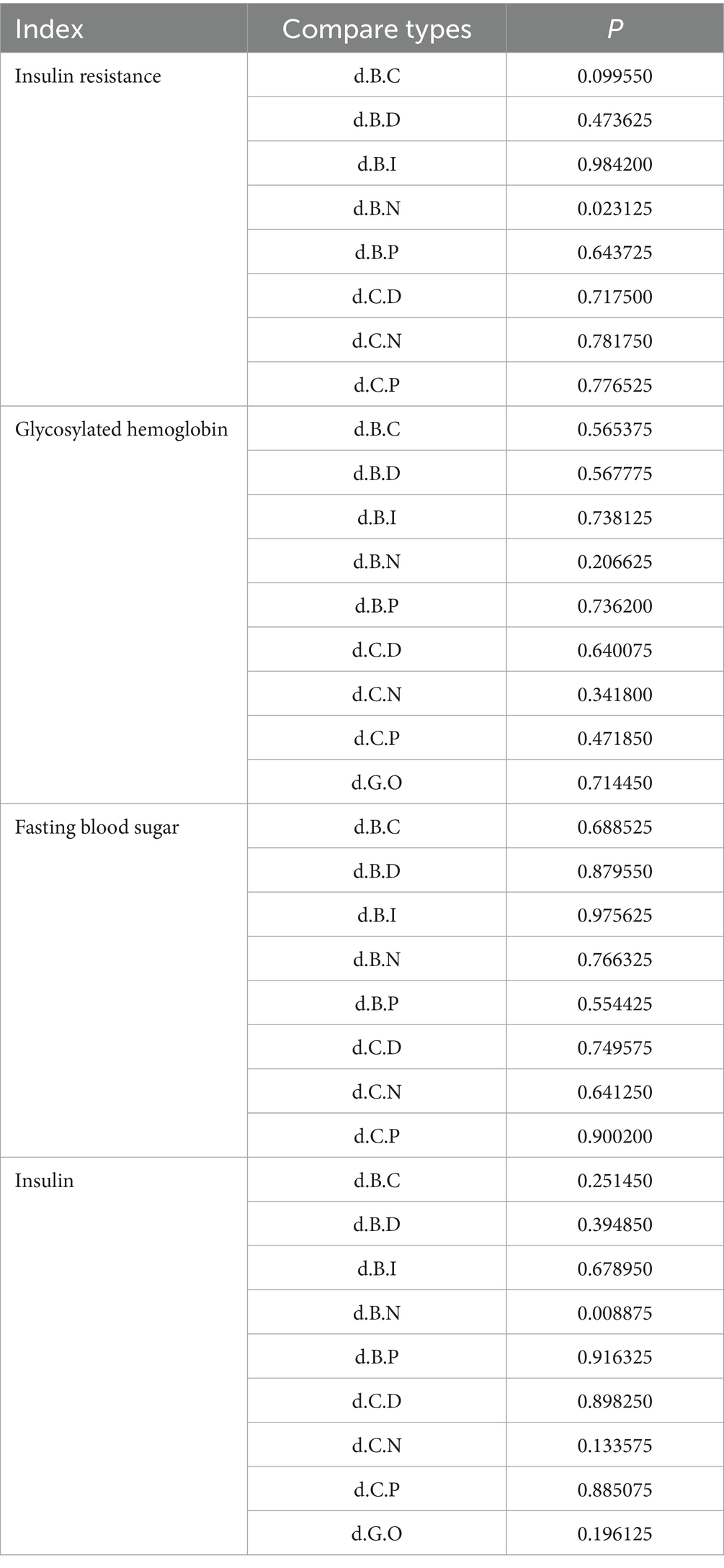
This study employed the node-splitting method to evaluate consistency among interventions for IR, HbA1c, FBS, and FINS outcomes. The analysis indicated that insulin resistance outcomes for interventions B versus N, as well as insulin outcomes for interventions B versus N, demonstrated poor consistency (p < 0.05). All the other outcome measures showed good consistency across the interventions (p > 0.05). The detailed results are presented in Table 7.
Cumulative ranking results
This study ranked the effects of vitamin supplementation, exercise interventions, and combined vitamin plus exercise interventions on IR and related metabolic outcomes (FBS, FINS, and HbA1c) in patients with type 2 diabetes via SUCRA values. The SUCRA values range from 0 to 1, with values approaching 1 indicating maximal efficacy and values near 0 indicating minimal efficacy. The ranking results demonstrated that probiotics produced the greatest improvement in insulin resistance. Combined vitamin plus exercise interventions achieved the most pronounced effect on hemoglobin A1c. Vitamin C supplementation significantly reduced FBS levels. Combined vitamin plus exercise interventions again had the optimal effect on hemoglobin A1c outcomes, whereas fatty acid plus exercise interventions produced the greatest improvement in insulin levels. The detailed results are presented in Table 8 and Appendix 1.
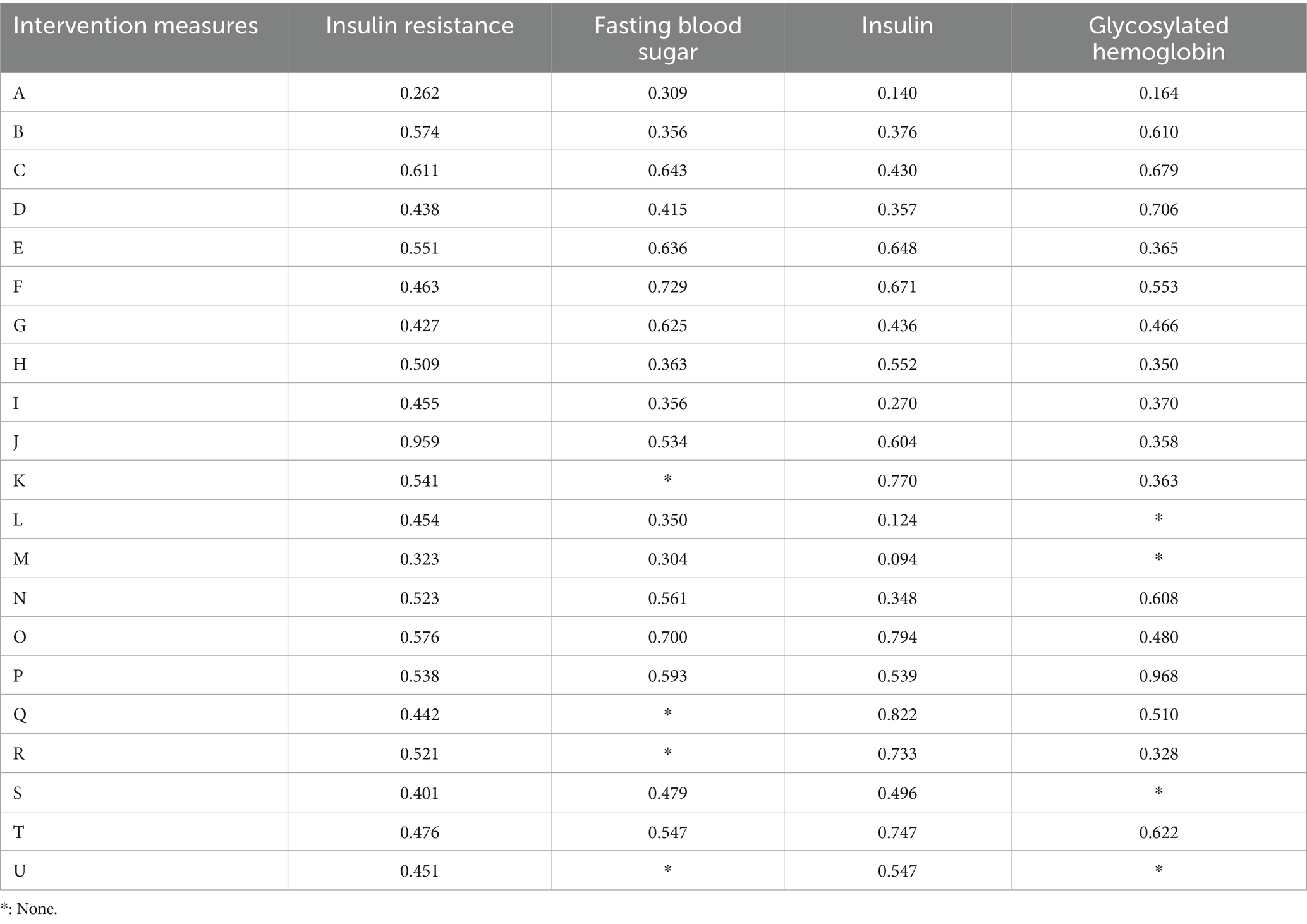
Table 8. Cumulative probability results (SUCRA values) of network meta-analysis on insulin resistance and corresponding indicators under different intervention methods.
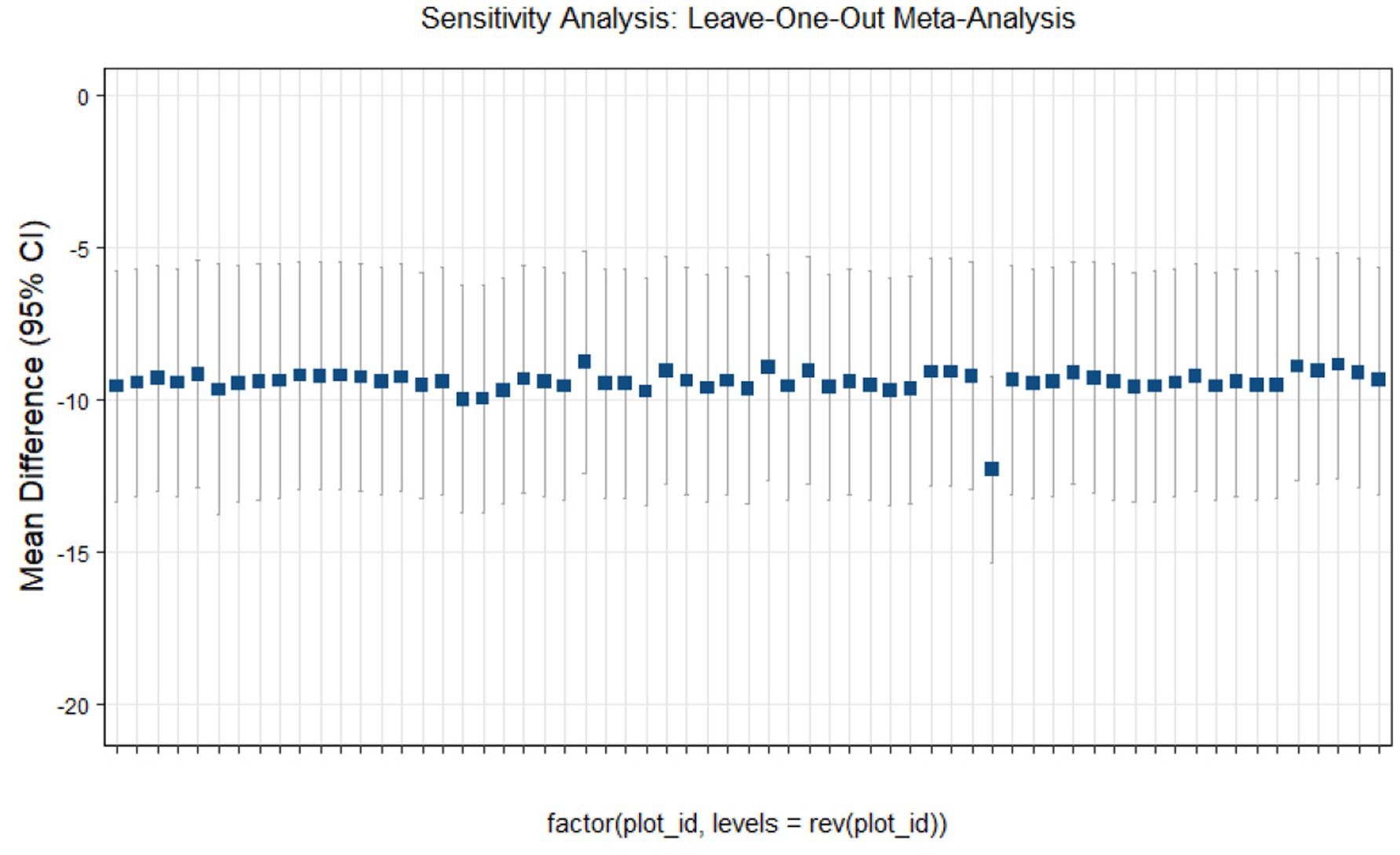
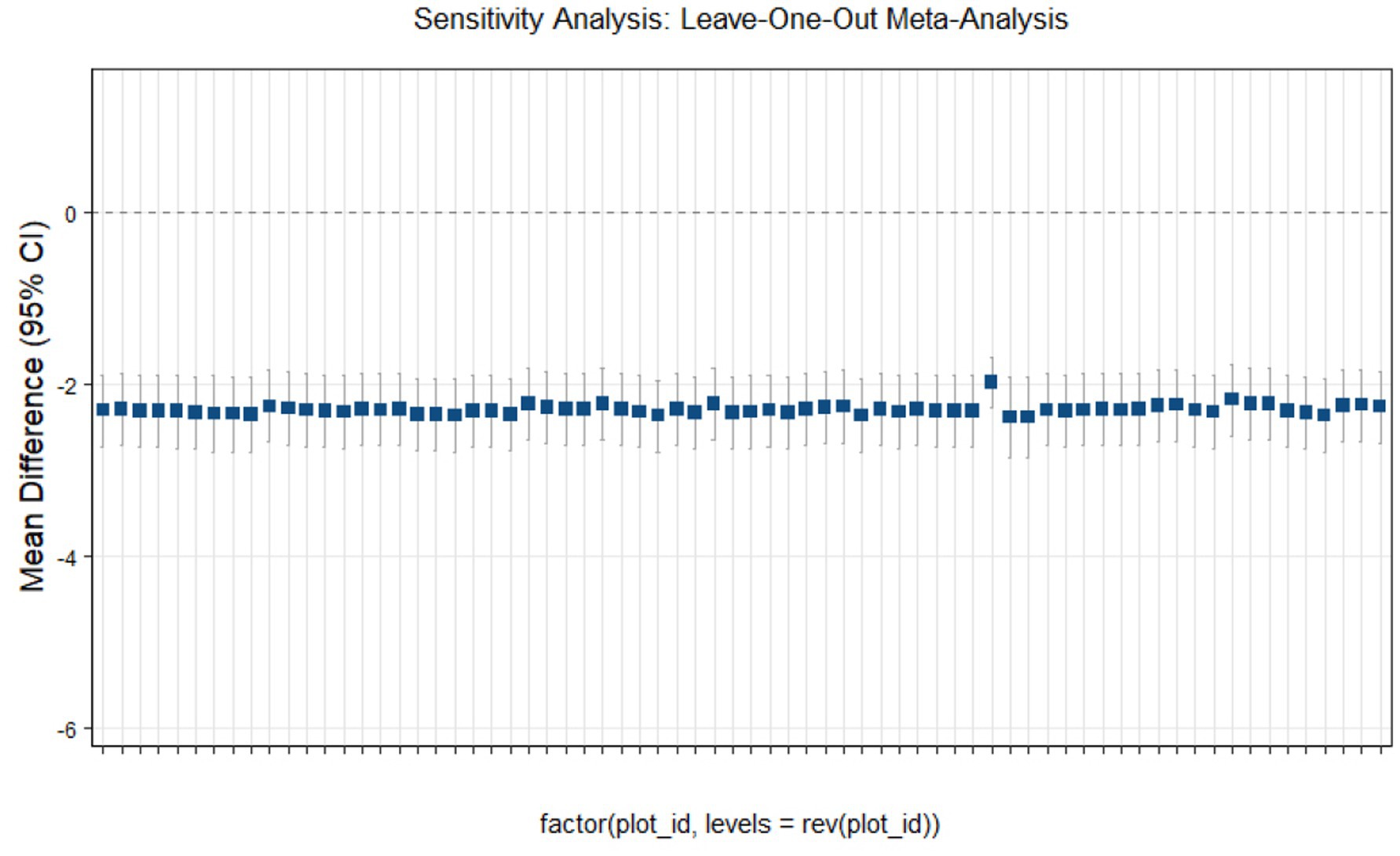
Sensitivity analysis
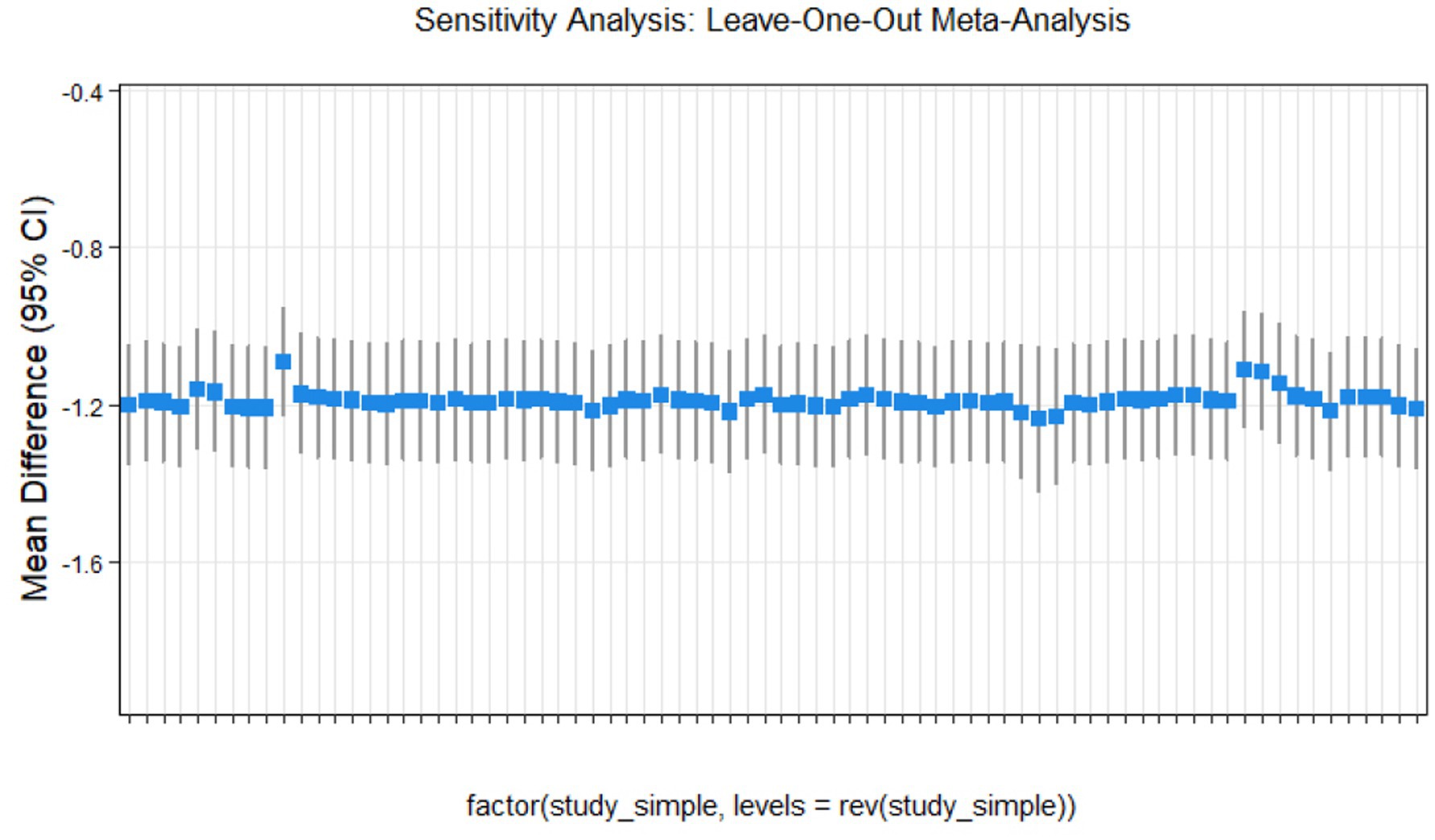
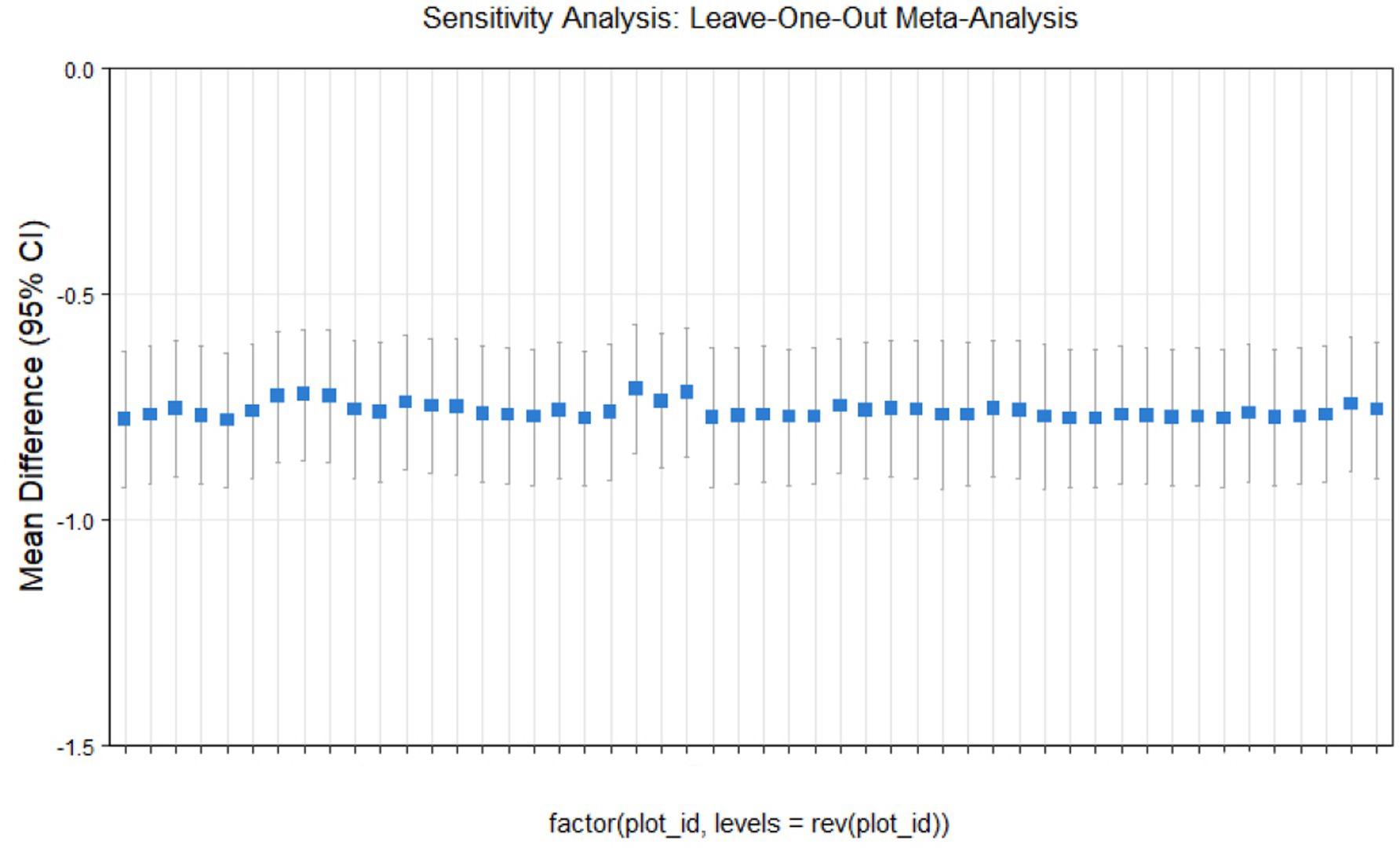
This study conducted sensitivity analyses via R software, as shown in Figures 11–14. The meta-analysis results for IR, HbA1c, FBS, and FINS outcomes remained stable, with no evidence of significant heterogeneity detected.
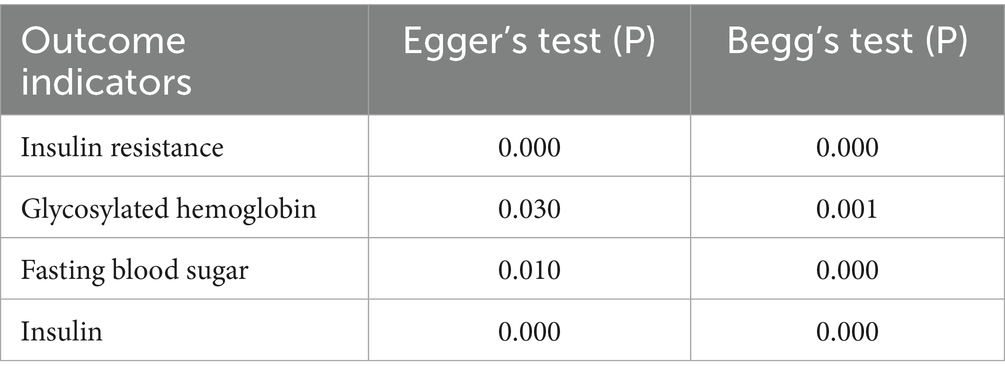
Heterogeneity test
This study used Egger’s and Begg’s tests to assess heterogeneity among the included outcome measures. The results indicated significant heterogeneity for IR, HbA1c, FBS, and FINS outcomes. The detailed results are presented in Table 9.
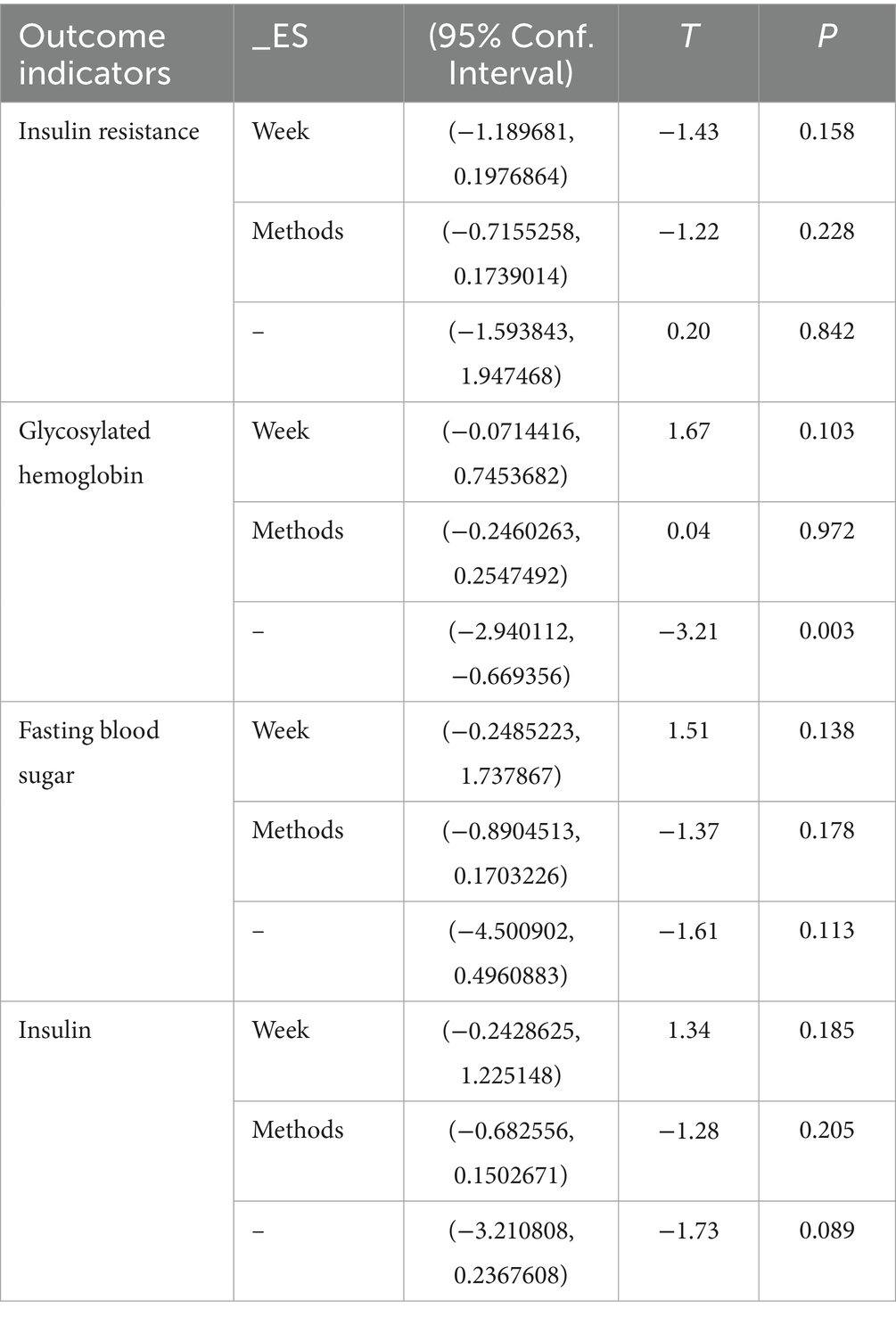
Regression analysis
This study employed Stata software to perform meta-regression analyses to identify sources of heterogeneity among the included studies. We treated the pooled effect sizes as the dependent variable and used intervention duration and frequency as covariates to construct the meta-regression model. The results indicated that combined exercise and vitamin interventions did not reveal significant sources of heterogeneity for IR, FBS, or FINS outcomes (p > 0.05). Similarly, intervention duration and frequency did not account for heterogeneity in hemoglobin A1c outcomes (p > 0.05). However, heterogeneity in HbA1c outcomes was detected (p < 0.05). The detailed results are presented in Table 10.
Evaluation of evidence quality
This study used the GRADE framework to evaluate the quality of the included outcome measures. The assessment indicated that IR, HbA1c, FBS, and FINS outcomes were moderate. The detailed results are presented in Figure 15.
Discussion
This study employed network meta-analysis to evaluate the effects of combined exercise and vitamin interventions on insulin resistance and related metabolic indicators in patients with T2D. The traditional meta-analysis results indicated that intervention periods of both <12 weeks and >12 weeks significantly improved insulin resistance and related indicators. Except for the effects of combined vitamin interventions on HbA1c, single exercise or single vitamin interventions on fasting blood glucose, and combined exercise interventions on FINS levels, all other intervention strategies produced significant improvements in IR and associated metrics. Dose–response subgroup analysis revealed that vitamin supplementation at 4,100–7,500 IU/day combined with exercise at approximately 4 MET, performed three times per week with each session lasting 45–60 min, produced optimal improvements in insulin resistance and related metabolic indicators.
Network meta-analysis further demonstrated that probiotic supplementation most effectively improved insulin resistance in T2D patients; combined exercise and vitamin interventions had the greatest effect on HbA1c; vitamin C supplementation most significantly improved FBS and insulin levels; and combined fatty acid and exercise interventions had the strongest effect on FINS levels. Specifically, interventions with periods >12 weeks or <12 weeks, exercise performed three times per week, and single-session durations of 45–60 min at ~4 MET, combined with weekly vitamin supplementation of 5,000 IU achieved the most pronounced effects on IR and related outcomes. These findings provide evidence-based guidance for designing exercise plus vitamin intervention programs for T2D patients.
The results highlight the importance of specific intervention doses and intensities. Exercise at ≤4 MET significantly improved insulin resistance and insulin levels (p < 0.01) and significantly modulated HbA1c (p < 0.01) and FBS (p < 0.05). Vitamin supplementation at 4,100–7,500 IU/day significantly affected all measured outcomes except HbA1c. Furthermore, combining exercise with vitamin and nutrient supplementation produced even greater improvements in IR and related indicators. Exercise not only reduces body weight but also enhances glycemic control, decreases body fat, and improves insulin responsiveness. Vitamins reduce oxidative stress by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), thereby improving insulin signaling pathways.
Insulin serves as a central regulator of metabolic homeostasis, and dysregulation of insulin secretion and action is closely linked to modern sedentary lifestyles, overnutrition, and metabolic syndrome, which are key contributors to T2D development. When pancreatic β-cells fail to compensate for IR, hyperglycemia occurs, promoting T2D progression. This process involves β-cell oxidative stress, inflammation, and disrupted redox signaling, which are often triggered by chronic nutrient overload leading to lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity (6). Vitamin D (VitD) exerts multiple metabolic regulatory effects via its nuclear receptor: it protects mitochondrial function by upregulating components of the respiratory chain, thereby reducing oxidative stress-mediated vascular complications; for example, 2,000 IU/day VitD supplementation for 3 months reduces DNA oxidative damage (7, 8). VitD also regulates β-cell Ca2+ flux as a chemical messenger, influencing insulin secretion by modulating extracellular Ca2+ concentration and membrane Ca2+ transport. VitD deficiency impairs β-cell secretory function, while supplementation (2,000–7,500 IU/day) restores intracellular Ca2+ levels and enhances insulin secretion (9). VitD deficiency also elevates parathyroid hormone (PTH) and induces mild pancreatic inflammation, both of which are related to IR (10). Supplementation increases anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and decreases the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12, and IFN-γ, thereby improving immune homeostasis and IR (11).
Clinical studies support these mechanisms. Twelve weeks of progressive endurance cycling (2–3 sessions/week, 1 h/session at 65–80% maximum heart rate) combined with 1,000 IU/day VitD3 did not improve HOMA-IR but significantly reduced FBS (11.9% change, effect size 0.65, p < 0.05) (12). Higher-dose interventions (50,000 IU of VitD weekly for 8 weeks) normalized serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels (p < 0.001) and significantly reduced FBS (p = 0.04), FINS (p = 0.02), and HOMA-IR (p = 0.007) (13). Another multi-arm study also demonstrated that 8 weeks of aerobic exercise (30 min, 50–75% heart rate reserve, 3 times per week) combined with 25 min of resistance training, along with daily supplementation of 4,000 IU of vitamin D₃, significantly reduced HOMA-IR [F = 24.07; p < 0.001], FINS levels [F = 17.97; p < 0.001], and FBS [F = 11.28; p < 0.001] compared to the placebo group. However, the combination of vitamin D₃ and exercise resulted in the highest percentage reductions (−20.73, −10.68%, −11.54%, respectively) (14). Furthermore, daily supplementation of 600 mg of calcium with 60 min of aerobic and resistance exercise also significantly reduced FBS, FINS, IR levels, and pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 (p < 0.005) compared to either exercise alone, vitamin D intervention, or the placebo group. The combination group had higher levels of 25(OH)D and fasting C-peptide than the vitamin D group, exercise group, and placebo group, and lower HbA1c levels than the other groups (p < 0.05). Additionally, the combination group exhibited lower levels of TNF-α and IL-6 compared to the vitamin D, exercise, and placebo groups, with statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) (15).
Exercise improves glucose uptake and metabolism through multiple pathways, including enhancing insulin sensitivity, promoting cellular glucose transport, and reducing fat accumulation, making it a critical intervention for T2D management (16). The regulation of blood glucose and fatty acid levels depends on energy utilization patterns: short-duration, high-intensity exercise relies primarily on glycogen, whereas long-duration, low-intensity exercise depends on fatty acid metabolism. Exercise intensity modulates glucose utilization via the dynamic balance between FINS and counterregulatory hormones such as glucagon, epinephrine, and cortisol (17, 18).
Clinical evidence shows that 12 weeks of low- to moderate-intensity running (40 min/session) significantly improved HOMA-IR (F(1,144) = 89.29, p < 0.001), fasting insulin (F(1,144) = 129.10, p < 0.001), FINS (F(1,144) = 12.193, p < 0.001), postprandial glucose (F(1,144) = 53.015, p < 0.001), and HbA1c (F(1,144) = 80.050, p < 0.001) (19). Twelve weeks of combined moderate-intensity walking (30 min) or high-intensity interval training (28 min) performed three times weekly also significantly improved fasting glucose, HbA1c, insulin, and HOMA-IR (20). Aerobic exercise performed three times per week for 25 weeks, totaling 75 min, or combined aerobic and resistance training, significantly reduced fasting blood glucose, improved glycemic control, and lowered plasma insulin and insulin resistance. However, the combined exercise group showed better outcomes in fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, insulin resistance index, peak exercise load, lean body mass, and overall quality of life scores compared to the aerobic-only group (p < 0.05) (21).
However, exercise effects vary. Ten weeks of resistance or endurance training (3 sessions/week, 40 min/session) significantly reduced insulin resistance but did not significantly improve FINS levels (p > 0.05) (21). Mechanistically, exercise enhances insulin-mediated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, with resistance training resulting in particularly pronounced improvements, thereby reducing overall insulin dependence. A multiarm trial confirmed that 12 weeks of aerobic, resistance, or combined exercise (3 sessions/week, ~5.5 MET) reduced fasting glucose, but improvements in HOMA-IR were significant only in the aerobic and combined exercise groups (22).
Beyond metabolic regulation, exercise confers systemic benefits: it enhances cardiac function, lowers blood pressure, improves lipid profiles (reducing LDL-C and increasing HDL-C), and mitigates disease risk. Exercise also alleviates psychological stress, indirectly lowering glucose levels and reducing diabetes complications (18, 23). Studies have shown that exercise can improve HbA1c baseline levels by 10–20%, significantly optimizing T2D and insulin resistance status (24). This study also revealed marked improvements in HbA1c, which were further enhanced when vitamin supplementation was combined with vitamin C, suggesting a synergistic effect that warrants further investigation.
Limitations and implications
This study represents the first effort to apply network meta-analysis and dose–response analysis to evaluate the effects of combined exercise and vitamin interventions on insulin resistance and related metabolic indicators in patients with type 2 diabetes (t2d). However, several limitations should be noted: 1. Limited standardization of outcomes: the included studies used inconsistent measurement units for key outcomes such as blood glucose (mg/dl vs. mmol/l), which may increase heterogeneity and reduce the precision of effect size estimates. 2. Subgroup analysis constraints: The analysis did not fully account for covariates such as sex, disease duration, or comorbidities (e.g., obesity, cardiovascular disease), limiting the ability to detect differential intervention effects across specific populations. 3. Intervention heterogeneity: differences in exercise modality (aerobic, resistance, or combined), intensity control, and vitamin supplementation (e.g., d3 vs. d2, timing of administration) may obscure the specificity of optimal intervention protocols. 4. Limited strength of evidence: direct comparison studies for some interventions, such as specific vitamin–plus–exercise combinations, are scarce. Network meta-analysis relies on indirect evidence to infer effects, which may reduce the robustness of conclusions. 5. Short follow-up periods: Most included trials had intervention durations ≤24 weeks, limiting the ability to assess long-term (≥1 year) effects on insulin resistance and diabetes-related complications.
Implications for future research: 1. To increase study design rigor, future large-scale, multidimensional RCTs should standardize outcome measurement and reporting, objectively monitor exercise intensity, evaluate vitamin bioavailability, and clearly document intervention details to minimize methodological heterogeneity. 2. Refined subgroup analyses: future studies should stratify t2d patients by sex, age, disease duration, and comorbidities to explore differential responses and support the development of individualized intervention strategies. 3. Precision intervention exploration: RCTs should investigate varying vitamin doses (e.g., 2000 iu vs. 4,100–7,500 iu), exercise intensities (4 met vs. higher), and combined intervention modes, using dose–response models to identify optimal thresholds. 4. Mechanistic investigation: Integrating molecular biology techniques, such as measuring inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress markers, and gut microbiota composition, can clarify the biological mechanisms underlying exercise- and vitamin-mediated improvements in insulin resistance, including mitochondrial function regulation and the Ca2+ signaling pathway. 5. Long-term effect evaluation: Cohort studies with ≥1 year follow-up should examine sustained the impacts on diabetes and related complications, while evaluating adherence to interventions to provide comprehensive evidence for clinical practice. 6. Integrated multimodal interventions: Future research should explore combined strategies involving exercise, vitamins, dietary modifications, and psychological interventions, evaluating their synergistic effects on metabolic syndrome management and enhancing overall t2d prevention and control.
Conclusion
Combined vitamin interventions produced the greatest improvements in FINS levels in patients with type 2 diabetes; vitamin C supplementation most effectively reduced FBS; Probiotic intervention has the best effect on IR robiotic intervention has the best effect on insulin resistance and intervention and combined vitamin-plus-exercise interventions achieved the optimal effect on HbA1c. Moreover, vitamin supplementation at 4,100–7,500 iu/day, exercise at approximately 4 met, and exercise three times per week for 45–60 min per session produced maximal improvements in insulin resistance and related metabolic indicators. Given the limitations of this study, high-quality experimental research is still needed to further validate these findings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
FD: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Software, Data curation. YJ: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HK: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. YF: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study has received financial support from the key project of the “2024 Higher Education Scientific Research Planning Project” — “Construction and Implementation of Safety First Aid Education in College Physical Education Courses under the Healthy China Strategy” (Project No. 24BJ0305), funded by the Chinese Society of Higher Education. This support provides directional guidance at the macro level for college physical education research and ensures the smooth progress of the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1608634/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Zhang, B. Effect of exercise on insulin resistance in obese type 2 diabetes patients. Rev Bras Med Esporte. (2022) 28:59–61. doi: 10.1590/1517-86922022v28n1p59-61
2. Chen, HJ, Wang, M, Zou, DM, Liang, GY, and Yang, SY. Effects of vitamin family members on insulin resistance and diabetes complications. World J Diabetes. (2024) 15:568–71. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.568
3. Lee, SH, Park, SY, and Choi, CS. Insulin resistance: from mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Diabetes Metab J. (2022) 46:15–37. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0280
4. Tambuwal, UM, Ahmad, SA, Hayatu, U, Sadiq, MA, Kolawale, JA, Bello, SK, et al. Exploring the effect of exercise versus metformin on insulin resistance amongst Nigerians with pre-diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Niger Postgrad Med J. (2024) 31:274–9. doi: 10.4103/npmj.npmj_148_24
5. Rajabi-Naeeni, M, Dolatian, M, Qorbani, M, and Vaezi, AA. The effect of omega-3 and vitamin D co-supplementation on glycemic control and lipid profiles in reproductive-aged women with pre-diabetes and hypovitaminosis D: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2020) 12:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13098-020-00549-9
6. Ježek, P, Jabůrek, M, and Plecitá-Hlavatá, L. Contribution of oxidative stress and impaired biogenesis of pancreatic β-cells to type 2 diabetes. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2019) 31:722–51. doi: 10.1089/ars.2018.7656
7. Salum, E, Kals, J, Kampus, P, Salum, T, Zilmer, K, Aunapuu, M, et al. Vitamin D reduces deposition of advanced glycation end-products in the aortic wall and systemic oxidative stress in diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2013) 100:243–9. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.03.008
8. Wenclewska, S, Szymczak-Pajor, I, Drzewoski, J, Bunk, M, and Śliwińska, A. Vitamin D supplementation reduces both oxidative DNA damage and insulin resistance in the elderly with metabolic disorders. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:2891. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122891
9. Dos Santos, GJ, Ferreira, SM, Ortis, F, Rezende, LF, Li, C, Naji, A, et al. Metabolic memory of ß-cells controls insulin secretion and is mediated by CaMKII. Mol Metab. (2014) 3:484–9. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.03.011
10. Reis, JP, von Mühlen, D, Kritz-Silverstein, D, Wingard, DL, and Barrett-Connor, E. Vitamin D, parathyroid hormone levels, and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in community-dwelling older adults. Diabetes Care. (2007) 30:1549–55. doi: 10.2337/dc06-2438
11. He, LP, Li, CP, Liu, CW, and Gu, W. The regulatory effect of vitamin D on pancreatic beta cell secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Chem. (2025) 35:2890–8. doi: 10.2174/0109298673270429240805050928
12. Sun, X, Yan, T, Li, Z, Zhou, S, Peng, W, Cui, W, et al. Effects of endurance exercise and vitamin D supplementation on insulin resistance and plasma Lipidome in middle-aged adults with type 2 diabetes. Nutrients. (2023) 15:3027. doi: 10.3390/nu15133027
13. Baziar, N, Jafarian, K, Shadman, Z, Qorbani, M, Khoshniat Nikoo, M, and Abd Mishani, M. Effect of therapeutic dose of vitamin D on serum adiponectin and glycemia in vitamin D-insufficient or deficient type 2 diabetic patients. Iran Red Crescent Med J. (2014) 16:e21458. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.21458
14. Rostamian Mashhadi, M, Bijeh, N, Rashidlamir, A, and Raoof, AA. Vitamin D3 supplementation could improve the effect of exercise training on type 2 diabetes-induced metabolic disorders via BDNF/irisin axis in elderly women. Sport Sci Health. (2024) 20:1281–90. doi: 10.1007/s11332-024-01204-w
15. Yang, SG, Lin, H, and Yang, H. Effect of vitamin D combined with aerobic exercise on insulin resistance in elderly type 2 diabetic patients with vitamin D deficiency. Chin J Geriatr. (2020) 40:1893–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2020.09.015
16. Sigal, RJ, Kenny, GP, Wasserman, DH, Castaneda-Sceppa, C, and White, RD. Physical activity/exercise and type 2 diabetes: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. (2006) 29:1433–8. doi: 10.2337/dc06-9910
17. Stokie, JR, Abbott, G, Howlett, KF, Hamilton, DL, and Shaw, CS. Intramuscular lipid utilization during exercise: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. J Appl Physiol. (2023) 134:581–92. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00637.2021
18. Coyle, EF. Substrate utilization during exercise in active people. Am J Clin Nutr. (1995) 61:968S–79S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/61.4.968S
19. Amaravadi, SK, Maiya, GA, Vaishali, K, and Shastry, BA. Effectiveness of structured exercise program on insulin resistance and quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus–a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. (2024) 19:e0302831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302831
20. Martins, FM, de Paula Souza, A, Nunes, PRP, Michelin, MA, Murta, EFC, Resende, EAMR, et al. High-intensity body weight training is comparable to combined training in changes in muscle mass, physical performance, inflammatory markers and metabolic health in postmenopausal women at high risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Exp Gerontol. (2018) 107:108–15. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2018.02.016
21. Mogharnasi, M, TajiTabas, A, Tashakorizadeh, M, and Nayebifar, SH. The effects of resistance and endurance training on levels of nesfatin-1, HSP70, insulin resistance and body composition in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sci Sports. (2019) 34:e15–23. doi: 10.1016/j.scispo.2018.04.010
22. AminiLari, Z, Fararouei, M, Amanat, S, Sinaei, E, Dianatinasab, S, AminiLari, M, et al. The effect of 12 weeks aerobic, resistance, and combined exercises on omentin-1 levels and insulin resistance among type 2 diabetic middle-aged women. Diabetes Metab J. (2017) 41:205–12. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.205
23. Piras, A, and Raffi, M. A narrative literature review on the role of exercise training in managing type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Healthcare. (2023) 11:2947. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11222947
24. Gracia-Sánchez, A, López-Pineda, A, Chicharro-Luna, E, and Gil-Guillén, VF. A Delphi study protocol to identify recommendations on physical activity and exercise in patients with diabetes and risk of foot ulcerations. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:10988. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182010988
25. Meng, Q, Chen, W, Zhang, M, and Gao, M. Effects of aerobic and resistance exercise combined on patients with type 2 diabetes. Chin J Rehabil Theory Pract. (2018) 24:1465–70. doi: 10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1006-9771.2018.12.011
26. Imanparast, F, Javaheri, J, Kamankesh, F, Rafiei, F, Salehi, A, Mollaaliakbari, Z, et al. The effects of chromium and vitamin D3 co-supplementation on insulin resistance and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in type 2 diabetes: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. (2020) 45:471–7. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2019-0113
27. Abd El-Aal, A, Abd El-Ghffar, EA, Ghali, AA, El-Aal, AA, El-Ghffar, EAA, Zughbur, MR, et al. The effect of vitamin C and/or E supplementation on type 2 diabetic adult males under metformin treatment: a single-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev. (2018) 12:483–9. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.03.013
28. Aguayo-Ruiz, JI, García-Cobián, TA, Pascoe-González, S, Sánchez-Enríquez, S, Llamas-Covarrubias, IM, García-Iglesias, T, et al. Effect of supplementation with vitamins D3 and K2 on undercarboxylated osteocalcin and insulin serum levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2020) 12:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13098-020-00580-w
29. Raygan, F, Ostadmohammadi, V, Bahmani, F, and Asemi, Z. The effects of vitamin D and probiotic co-supplementation on mental health parameters and metabolic status in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary heart disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2018) 84:50–5. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.02.007
30. Darmian, MA, Hoseini, R, Amiri, E, and Golshani, S. How combined and separate aerobic training and turmeric supplementation alter lipid profile and glycemic status? A clinical trial in middle-aged females with type 2 diabetes and hyperlipidemia. Int Cardiovasc Res J. (2021) 15:120–27. doi: 10.15412/icrj2021v15n3p120-127
31. de Oliveira, AM, Rondó, PHC, Luzia, LA, D’Abronzo, FH, and Illison, VK. The effects of lipoic acid and α-tocopherol supplementation on the lipid profile and insulin sensitivity of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2011) 92:253–60. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.02.010
32. Hua, L, Lei, M, Xue, S, Li, X, Li, S, and Xie, Q. Effect of fish oil supplementation combined with high-intensity interval training in newly diagnosed non-obese type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2020) 66:146–51. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.19-64
33. Yavari, A, Najafipoor, F, Aliasgarzadeh, A, Niafar, M, and Mobasseri, M. Effect of aerobic exercise, resistance training or combined training on glycaemic control and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Biol Sport. (2012) 29:135–43. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.3934
34. Ali, AM, Abbassi, MM, Sabry, NA, Fawzi, M, and Mousa, S. The effect of vitamin K4 supplementation on insulin resistance in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur J Nutr. (2023) 62:3241–9. doi: 10.1007/s00394-023-03215-8
35. Shabkhiz, F, Khalafi, M, Rosenkranz, S, Karimi, P, and Moghadami, K. Resistance training attenuates circulating FGF-21 and myostatin and improves insulin resistance in elderly men with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Eur J Sport Sci. (2021) 21:636–45. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2020.1762755
36. Shakil-ur-Rehman, S, Karimi, H, and Gillani, SA. Effects of supervised structured aerobic exercise training program on fasting blood glucose level, plasma insulin level, glycemic control, and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pak J Med Sci. (2017) 33:576–80. doi: 10.12669/pjms.333.12023
37. Farrokhian, A, Bahmani, F, Taghizadeh, M, Mirhashemi, SM, Aarabi, MH, Raygan, F, et al. Selenium supplementation affects insulin resistance and serum hs-CRP in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary heart disease. Horm Metab Res. (2016) 48:263–8. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1569276
38. Chiti, H. The effects of 12-weeks combined exercises on cost, dosage of insulin, and glycemic indices in type 2 diabetic patients. J Adv Med Biomed Res. (2024) 32:191–201. doi: 10.61186/jambr.32.152.191
39. Terauchi, Y, Takada, T, and Yoshida, S. A randomized controlled trial of a structured program combining aerobic and resistance exercise for adults with type 2 diabetes in Japan. Diabetol Int. (2022) 13:75–84. doi: 10.1007/s13340-021-00506-5
40. Jeon, YK, Kim, SS, Kim, JH, Kim, HJ, Kim, HJ, Park, JJ, et al. Combined aerobic and resistance exercise training reduces circulating apolipoprotein J levels and improves insulin resistance in postmenopausal diabetic women. Diabetes Metab J. (2020) 44:103–12. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0160
41. Hodaei, H, Adibian, M, Nikpayam, O, Hedayati, M, and Sohrab, G. The effect of curcumin supplementation on anthropometric indices, insulin resistance and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2019) 11:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0437-7
42. Khalili, L, Alipour, B, Jafar-Abadi, MA, Asghari Jafar-Abadi, M, Faraji, I, Hassanalilou, T, et al. The effects of Lactobacillus casei on glycemic response, serum sirtuin1 and fetuin-a levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Iran Biomed J. (2019) 23:68–77. doi: 10.29252/ibj.23.1.68
43. Crochemore, ICC, Souza, AF, de Souza, ACF, and Rosado, EL. ω −3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation does not influence body composition, insulin resistance, and lipemia in women with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Nutr Clin Pract. (2012) 27:553–60. doi: 10.1177/0884533612444535
44. Li, FX. Research on the clinical efficacy of Baduanjin combined with resistance exercise in patients with type 2 diabetes Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2020).
45. Salarinia, M, Azizi, M, Tahmasebi, W, and Khalvandi, H. Effect of eight weeks of vitamin D supplementation and water-based exercise on cardiometabolic profile in women with type 2 diabetes. Sci Sports. (2023) 38:283–92. doi: 10.1016/j.scispo.2022.04.008
46. Dadrass, A, Mohamadzadeh Salamat, K, Hamidi, K, and Azizbeigi, K. Anti-inflammatory effects of vitamin D and resistance training in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus and vitamin D deficiency: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord. (2019) 18:323–31. doi: 10.1007/s40200-019-00416-z
47. Hoseini, R, Rahim, HA, and Ahmed, JK. Concurrent alteration in inflammatory biomarker gene expression and oxidative stress: how aerobic training and vitamin D improve T2DM. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2022) 22:165. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03645-7
48. El Hajj, C, Walrand, S, Helou, M, and Yammine, K. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on inflammatory markers in non-obese Lebanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2033. doi: 10.3390/nu12072033
49. Zhou, WP, Li, LF, and Zhang, WH. Clinical study on the combined Chinese medicinal exercise and conventional nursing intervention in type 2 diabetes. New Chin Med. (2020) 52:188–90. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2020.08.057
50. El-Khodary, NM, Dabees, H, and Werida, RH. Folic acid effect on homocysteine, sortilin levels and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Nutr Diabetes. (2022) 12:33. doi: 10.1038/s41387-022-00210-6
51. Rezagholizadeh, F, Keshavarz, SA, Djalali, M, Rad, EY, Alizadeh, S, and Javanbakht, MH. Vitamin D3 supplementation improves serum SFRP5 and Wnt5a levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. (2019) 89:341–50. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831/a000598
52. Safarpour, P, Daneshi-Maskooni, M, Vafa, M, Nourbakhsh, M, Janani, L, Maddah, M, et al. Vitamin D supplementation improves SIRT1, Irisin, and glucose indices in overweight or obese type 2 diabetic patients: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. BMC Fam Pract. (2020) 21:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12875-020-1096-3
Keywords: type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, vitamin intervention, exercise intervention, network meta-analysis
Citation: Deng F, Ji Y, Kong H, Fu Y, Zhang H and Zhang J (2025) Network meta-analysis of the effects of combined exercise and vitamin intervention on insulin resistance and related indicators in patients with type 2 diabetes. Front. Nutr. 12:1608634. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1608634
Edited by:
Donny Michael Camera, Swinburne University of Technology, AustraliaReviewed by:
Xiangjin Gao, Tongji University, ChinaYue Xianfeng, The Center for the Inheritance and Development of Central Plains Sports Culture, China
Copyright © 2025 Deng, Ji, Kong, Fu, Zhang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fangquan Deng, Mjk1MjE4ODgwMUBxcS5jb20=
 Fangquan Deng
Fangquan Deng Yin Ji2
Yin Ji2