- 1Department of General Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China
- 2Hubei Key Laboratory of Digestive System Disease, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China
- 3General Surgery Laboratory, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China
- 4Department of General Surgery, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei Province, China
Objective: This study aimed to explore the prognostic relevance of the lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio (LAR) in cancer patients.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted across PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library for studies published before March 15, 2025. The primary outcomes included pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and recurrence-free survival (RFS). In addition, a retrospective cohort of 71 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors at our institution was analyzed to assess the prognostic impact of baseline LAR on OS and PFS.
Results: Eighteen studies comprising 8,335 patients were incorporated into the meta-analysis. Elevated LAR was consistently associated with poorer outcomes: OS (HR: 2.02, 95% CI: 1.74–2.34, p < 0.001), PFS (HR = 1.35, 95% CI: 1.14–1.61, p < 0.001), and RFS (HR = 1.97, 95% CI: 1.47–2.64, p < 0.001). Subgroup evaluations stratified by LAR thresholds, geographical regions, treatment regimens, and statistical models confirmed the robustness of these associations. In our institutional cohort, patients presenting with pretreatment higher LAR experienced significantly diminished OS (HR = 2.04, 95% CI: 1.19–3.57, p = 0.008) and PFS (HR = 1.89, 95% CI: 1.14–3.13, p = 0.01) compared with those having lower LAR levels.
Conclusion: These findings underscore the prognostic value of pretreatment LAR in cancer patients. Integrating LAR into clinical decision-making may aid clinicians in enhancing risk stratification and personalizing treatment strategies.
1 Introduction
Despite major strides in cancer prevention, early detection, and therapeutic innovation over recent decades, malignancies persist as the second most common cause of mortality globally (1). While survival has markedly improved across numerous tumor types, the overall burden of cancer continues to escalate (2). Current projections indicate that cancer-related deaths, estimated at 10 million in 2022, may climb to 16.3 million by 2040, primarily driven by demographic aging and shifting environmental and lifestyle-related exposures (3). As therapeutic advancements prolong patient survival, the population of individuals living beyond a cancer diagnosis is anticipated to expand considerably (4). However, many of these survivors face long-term complications arising from both the malignancy and its associated treatments (5). As such, the medical community is increasingly focused on identifying robust biomarkers to refine prognostic evaluation. These tools could inform the intensification of care for patients at elevated risk of recurrence and, conversely, support therapeutic de-escalation in those with more favorable disease trajectories, thereby minimizing unnecessary treatment-related toxicity (6–8).
Currently, there is broad consensus that an individual's immune competence and systemic inflammatory milieu are critically linked to therapeutic responsiveness and cancer prognosis (9). Owing to its accessibility and minimally invasive nature, peripheral blood serves as a valuable source for assessing inflammation-related biomarkers that may influence clinical trajectories in oncology patients (10). In light of this, it becomes particularly valuable to identify relevant biochemical indices and evaluate their combined prognostic relevance in determining individualized outcomes (11).
A range of hematological and nutritional indices has been evaluated in the oncology setting, including the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (12), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (11), prognostic nutritional index (8), and the controlling nutritional status score (13). Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a key enzyme in anaerobic glycolysis, has been implicated in tumorigenesis, modulation of the immune milieu, and malignant progression (14). Elevated LDH levels prior to treatment initiation have been consistently linked to unfavorable survival outcomes across malignancies (15). Likewise, serum albumin—reflecting the host's nutritional reserve—has demonstrated prognostic value in oncologic populations (14). Notably, the LDH-to-albumin ratio (LAR), which integrates metabolic inflammation and nutritional depletion, has not yet been comprehensively investigated through evidence-based frameworks in cancer research (16).
Although the LAR has shown promise as a convenient prognostic indicator for cancer patients, variations across existing studies—including differences in study design, participant characteristics, and sample sizes—have limited the generalizability of individual findings. To address this, we conducted a systematic review of the current literature to clarify the relationship between LAR and clinical outcomes in oncology populations.
2 Methods
2.1 Search strategy, inclusion criteria, and exclusion criteria for the meta-analysis
This systematic review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines (17). A thorough literature search was carried out across three major databases—PubMed, Cochrane Library, and EMBASE—to capture all relevant publications available until 15 March 2025. The search strategy employed predefined keywords such as “Lactate Dehydrogenase-to-albumin Ratio” and “Lactic Dehydrogenase-albumin Ratio” to ensure coverage of all relevant topics. A comprehensive overview of the search methodology is available in Supplementary Material 1. In addition, the reference sections of eligible studies were manually examined to identify potentially overlooked articles. To ensure methodological rigor and minimize selection bias, two reviewers (CD and YT) independently conducted the screening process. In case of any dispute, it shall be adjudicated by the senior author (WW).
Eligible studies were selected based on the following inclusion criteria: (1) retrospective or prospective investigations assessing the relationship between LAR and survival outcomes, including progression-free survival (PFS), recurrence-free survival (RFS), and overall survival (OS); (2) classification of participants into high and low LAR groups; (3) provision of hazard ratios (HRs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) comparing these groups; and (4) availability of full-text articles published in English. Studies were excluded if they met any of the following: (1) duplicate records; (2) case series, abstracts, case reports, review articles, editorials, or guidelines. When multiple investigations included shared patient cohorts, preference was given to those reports that demonstrated methodological robustness and provided the most extensive dataset (18).
2.2 Data extraction and quality assessment for the meta-analysis
In the course of extracting data, we methodically collected key study attributes, including authorship, year of publication, study timeframe, study location, cancer classification, therapeutic interventions, cohort size, patient demographics (such as age and sex), and cut-off values for LAR. Multivariate models were the primary source for deriving HRs. When multivariate results were not available, univariate models or Kaplan-Meier estimates were used instead. NOS (Newcastle-Ottawa Scale) is a tool for assessing the risk of bias in non-randomized studies. It is mainly used to evaluate the quality of case-control studies and cohort studies (19). A score of 6 or above indicates high methodological quality.
2.3 Study cohort and data collection for the retrospective study
We also conducted a retrospective study using data from our center to analyze the association of baseline LAR with HCC outcomes. This study received approval from the institutional review board (2020WDRM0203). Given its retrospective design, the requirement for informed consent was waived. We evaluated patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who underwent immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) therapy between 2020 and 2022. Therapeutic regimens consisted of anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 agents. Eligibility required at least one measurable lesion in accordance with RECIST version 1.1 criteria. Individuals were excluded if they had previously received ICIs or lacked a baseline LDH and albumin.
Detailed clinical data were extracted from electronic medical records, including age, sex, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS), hepatitis origin, presence of cirrhosis, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage, Child–Pugh classification, number of tumors, macrovascular invasion status, line of treatment, modified albumin-bilirubin (mALBI) score, alpha-fetoprotein concentration, serum albumin, and LDH levels. The LAR was computed using the formula: LAR = LDH (U/L) ÷ ALB (g/L). Tumor progression was evaluated using RECIST v1.1 guidelines. Follow-up CT scans were routinely scheduled at 1- to 2-month intervals following treatment initiation. PFS was defined as the time span from the first administration of immune checkpoint inhibitors to either radiological progression or death. OS was measured from treatment initiation to death from any cause.
2.4 Statistical methods
Categorical variables were presented as counts alongside corresponding percentages. For comparisons between groups, either Fisher's exact test or the chi-square test was employed, based on test assumptions. Continuous data were described using either the median with interquartile ranges or the mean with standard deviation, as appropriate. Group differences in continuous variables were evaluated using independent samples t-tests. The Cox proportional-hazards model and the Kaplan-Meier method were used to assess survival curves across different groups.
Meta-analysis was conducted using Stata version 18.0, with results visually represented through forest plots. To assess inter-study variability, both Cochran's Q test and I2 index were employed, with heterogeneity deemed significant when the I2 statistic surpassed 25% (20). In cases of marked heterogeneity, analyses were conducted using the DerSimonian–Laird random-effects model; otherwise, a fixed-effects approach based on the Inverse Variance method was adopted. Potential publication bias was examined through both Begg's and Egger's tests (7). The robustness of the results was further confirmed by sensitivity testing, wherein each study was systematically excluded in turn to evaluate its individual impact on pooled estimates (21). Additional subgroup analyses were undertaken, stratifying the data by LAR cutoff levels, Cox model, treatments, and Country. Statistical significance was determined using a two-sided p-value threshold of <0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Search results and study characteristics
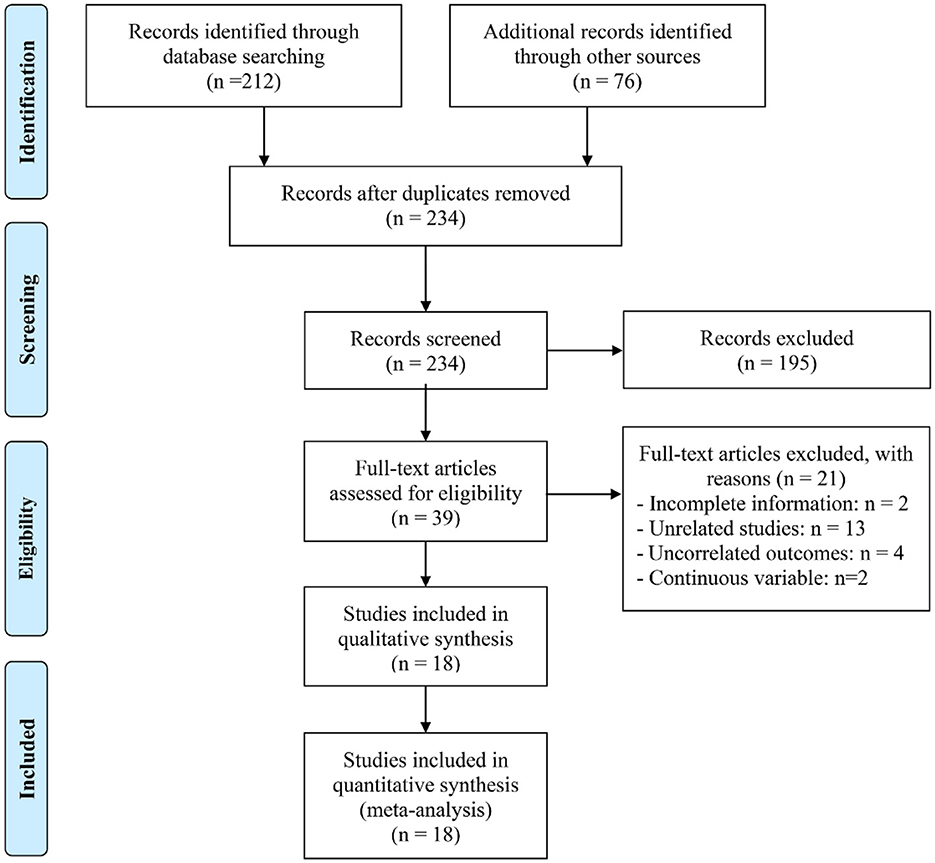
The initial database query, complemented by manual reference list screening, identified 288 records deemed potentially relevant. After eliminating 54 duplicates, 195 entries were removed based on title and abstract evaluation due to failure to meet the inclusion criteria. A detailed review of the remaining 39 full-text papers led to the exclusion of 21 that did not fulfill the prespecified eligibility requirements. Ultimately, 18 article were retained for the final meta-analysis (22–39) (Figure 1).
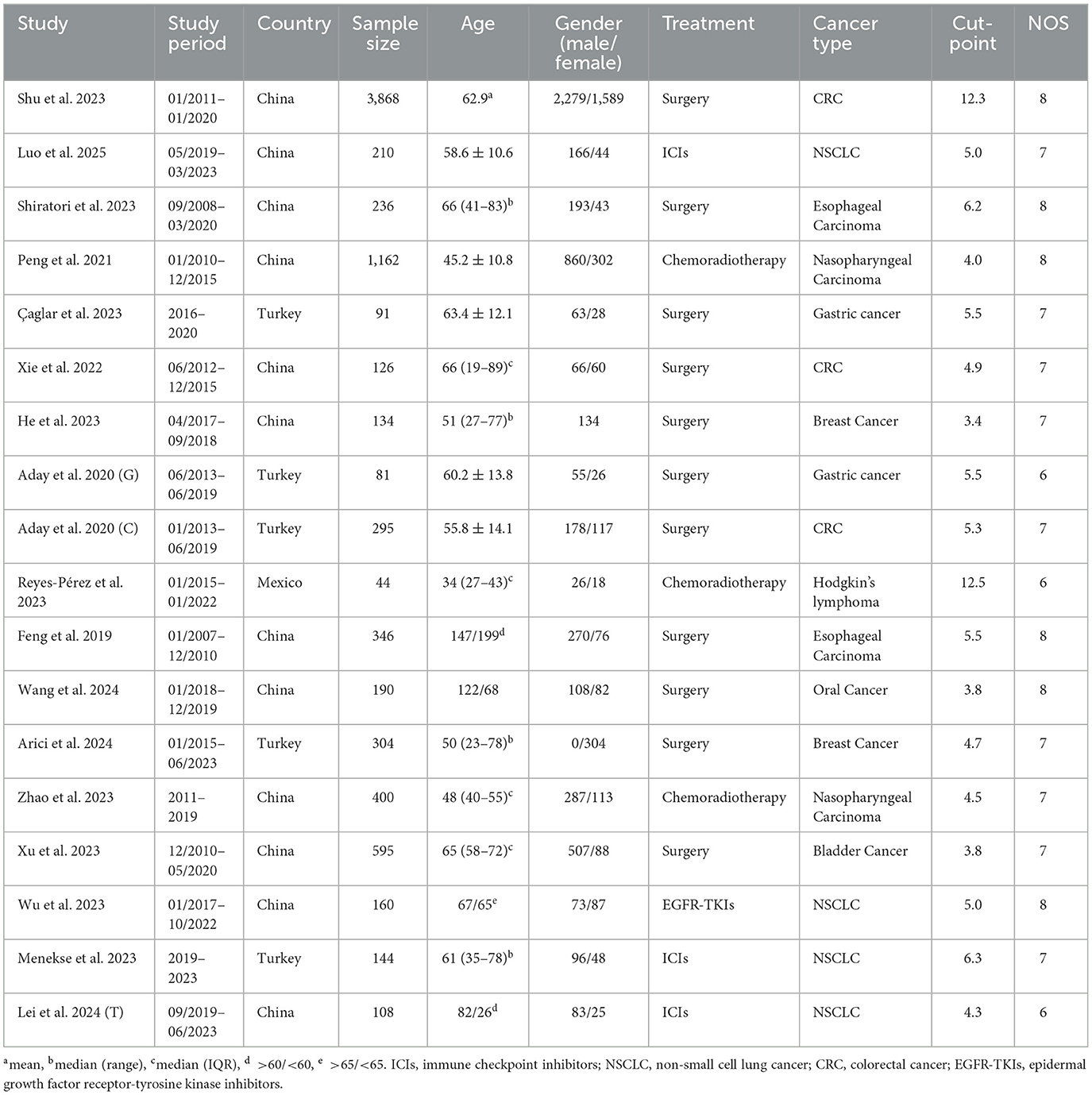
Table 1 provides an overview of the key characteristics of the included studies. In total, 8,335 individuals were enrolled, with sample sizes ranging from 44 to 3,868 per study. Of the 18 studies, 12 were conducted in China, five in Turkey, and one in Mexico. Four studies involved patients with non-small cell lung cancer, three with colorectal cancer, two with esophageal carcinoma, two with gastric cancer, two with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and two with breast cancer. Patients in 11 studies underwent surgery, while those in three studies received chemoradiotherapy, and three others received ICIs. All studies employed a retrospective design. Based on the NOS, quality scores ranged from 6 to 8, indicating a low risk of bias (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S2).
3.2 Baseline dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and overall survival
In this meta-analysis, a total of 16 eligible studies encompassing 8,253 patients were systematically examined to evaluate the prognostic significance of LAR on OS in cancers. The pooled HR demonstrated that high LAR was significantly correlated with inferior OS outcomes (HR: 2.02, 95% CI: 1.74–2.34, p < 0.001; Figure 2). Heterogeneity across studies was minimal, as evidenced by Cochran's Q and I2 metrics (I2 = 31.2%, p = 0.113), justifying the adoption of a fixed-effect model.
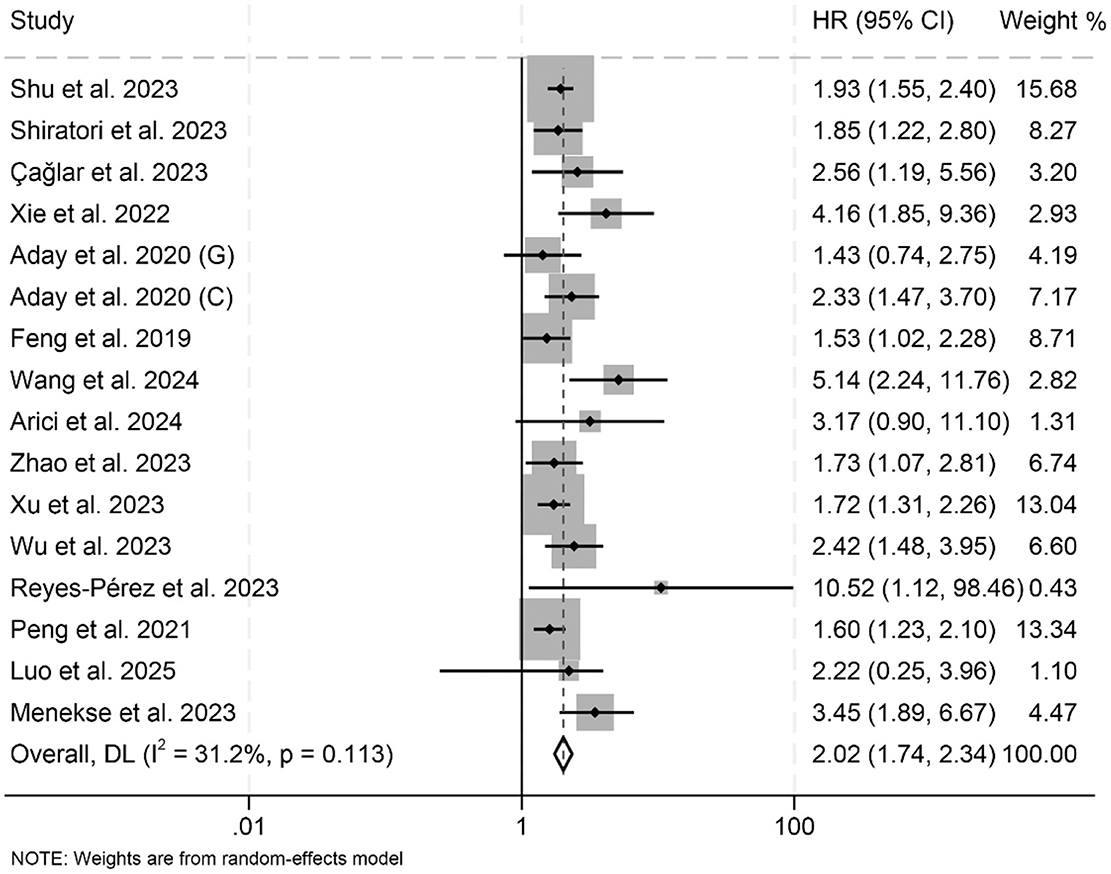
Figure 2. Forest plots depicting the association between the baseline lactate dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and overall survival in cancer patients. HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Subgroup analyses showed that both univariate and multivariate models consistently identified a significant association between elevated LAR and poorer OS (Table 2). This association remained robust across different treatment modalities and cancer types (Table 2). Additionally, variations in LAR cut-off values and differences in geographical location did not affect the strength or direction of the observed relationship between LAR and OS (Table 2).
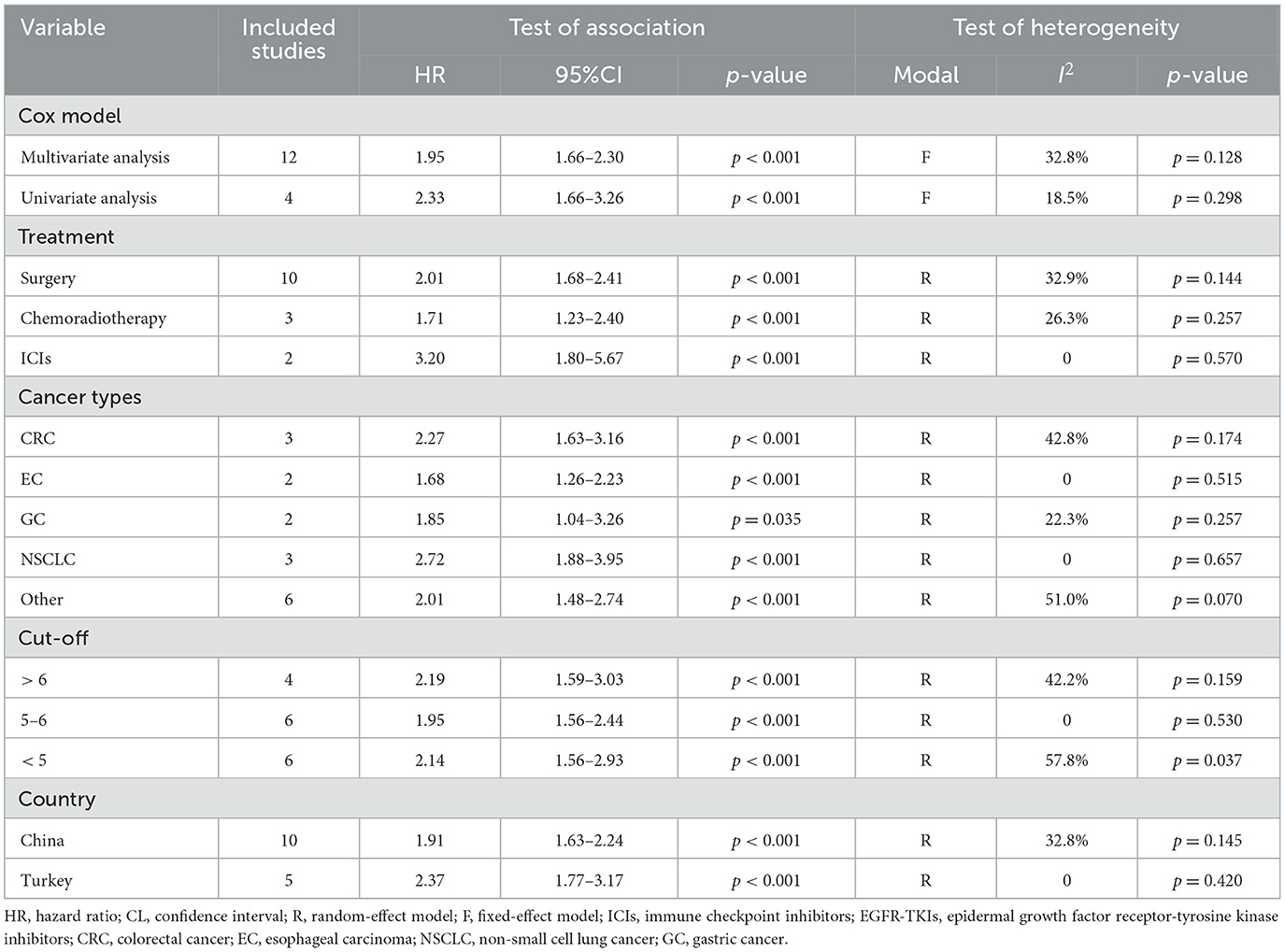
Table 2. Subgroup analysis of the association between serum lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio and overall survival in cancer patients.
A sensitivity analysis, performed by sequentially omitting each study, confirmed that the combined HRs for OS remained stable and reliable (Figure 3A). Additionally, Begg's and Egger's tests detected no significant publication bias for OS (Begg: p = 0.142; Egger: p = 0.212). However, the funnel plot appeared to be asymmetrical (Figure 3B). Therefore, we conducted a trim-and-fill analysis to evaluate the potential impact of publication bias on the results. The analysis revealed that the overall conclusions remained unchanged after adjustment, indicating that potential publication bias did not materially affect our findings.
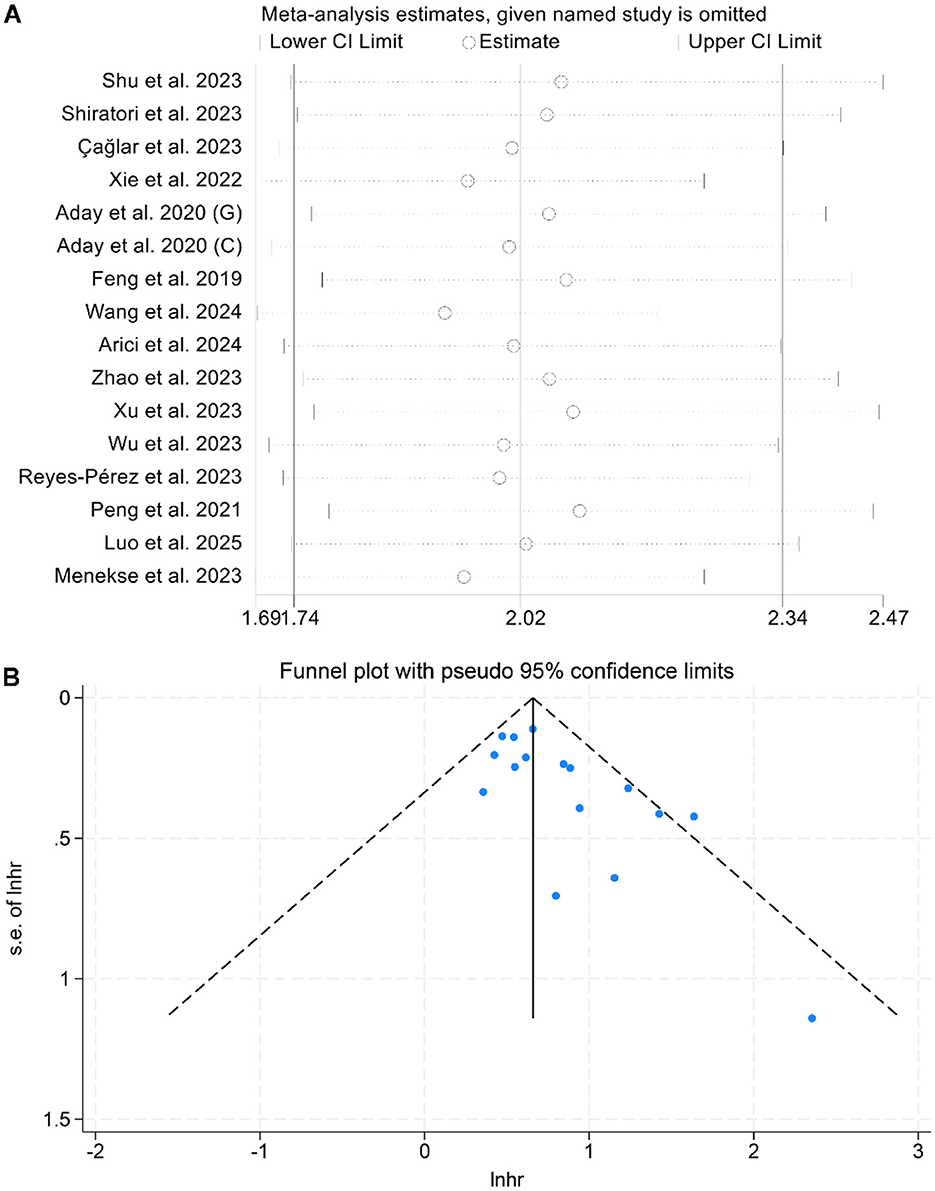
Figure 3. Sensitivity analysis of the association between baseline lactate dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and overall survival in cancer patients (A). Funnel plots of the relationship between lactate dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and overall survival in cancer patients (B). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
3.3 Baseline dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and progression-free survival
A total of five studies, including 1,725 cancer patients, were analyzed to assess the association between LAR and PFS. Three studies reported a significant negative association between elevated LAR and OS, while two found no statistically significant relationship. The meta-analysis demonstrated that higher LAR was significantly associated with poorer PFS (I2 = 0, p = 0.555; HR = 1.35, 95% CI: 1.14–1.61, p < 0.001; Figure 4A). To test the stability of this finding, a sensitivity analysis was conducted by sequentially excluding each study, which confirmed that the pooled HR remained stable (Figure 4B). Additionally, publication bias was evaluated using Begg's and Egger's tests, both of which showed no significant evidence of bias (Begg's test: p = 1.000; Egger's test: p = 0.368).
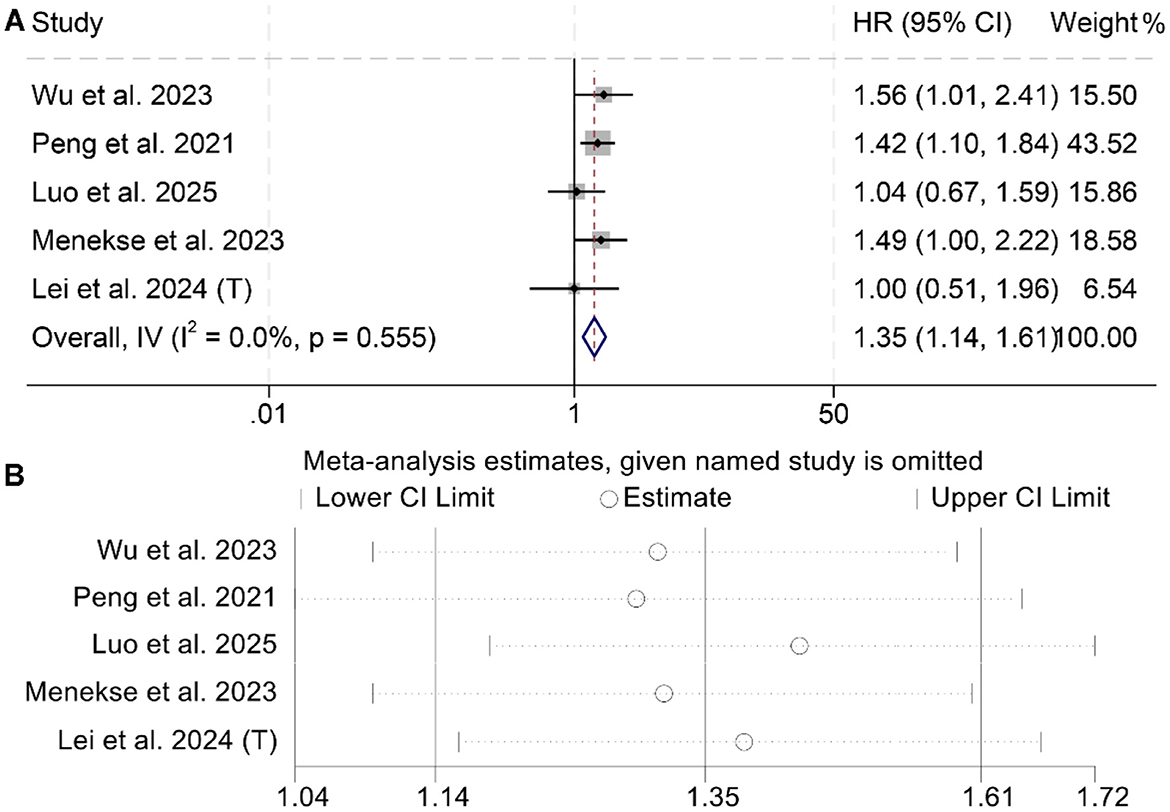
Figure 4. Forest plots depicting the association between the baseline lactate dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and progression-free survival in cancer patients (A). Sensitivity analysis of the association between baseline lactate dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and progression-free survival in cancer patients (B). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
3.4 Baseline dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and recurrence-free survival
The meta-analysis of six studies revealed that individuals with elevated baseline LAR had significantly poorer RFS compared to those with lower levels (HR = 1.97, 95% CI: 1.47–2.64, p < 0.001; Figure 5A). Substantial heterogeneity was observed among the studies (I2 = 54.7%, p = 0.051), warranting the use of a random-effects model. The robustness of the pooled effect estimate was confirmed through sensitivity analyses, which involved sequentially excluding each study and produced consistent results (Figure 5B). Additionally, Begg's and Egger's tests indicated no significant publication bias for RFS (Begg's test: p = 0.103; Egger's test: p = 0.260). Subgroup analysis confirmed that the above conclusion held true in all subgroups (Table 3).
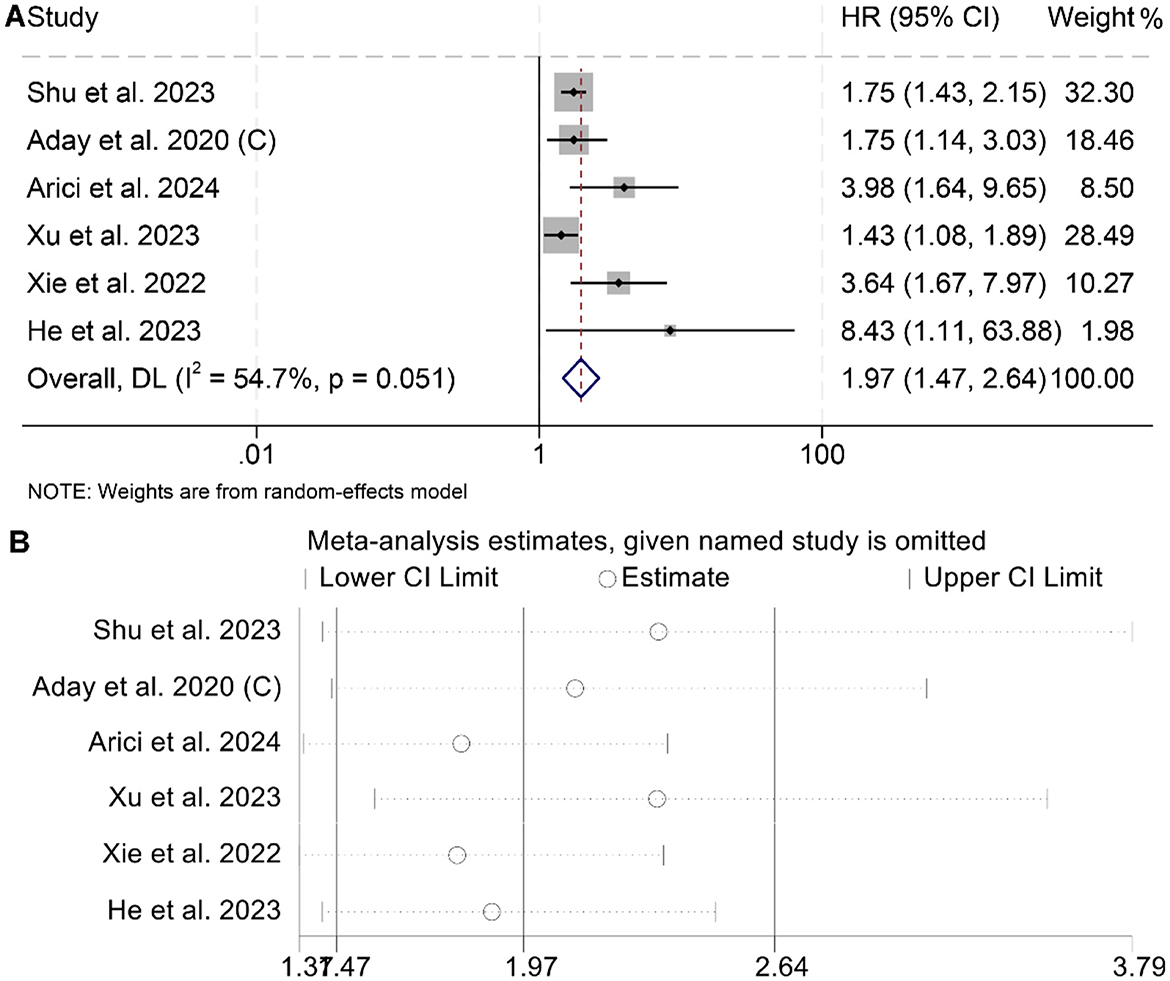
Figure 5. Forest plots depicting the association between the serum lactate dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and recurrence-free survival in cancer patients (A). Sensitivity analysis of the association between lactate dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and recurrence-free survival (B). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
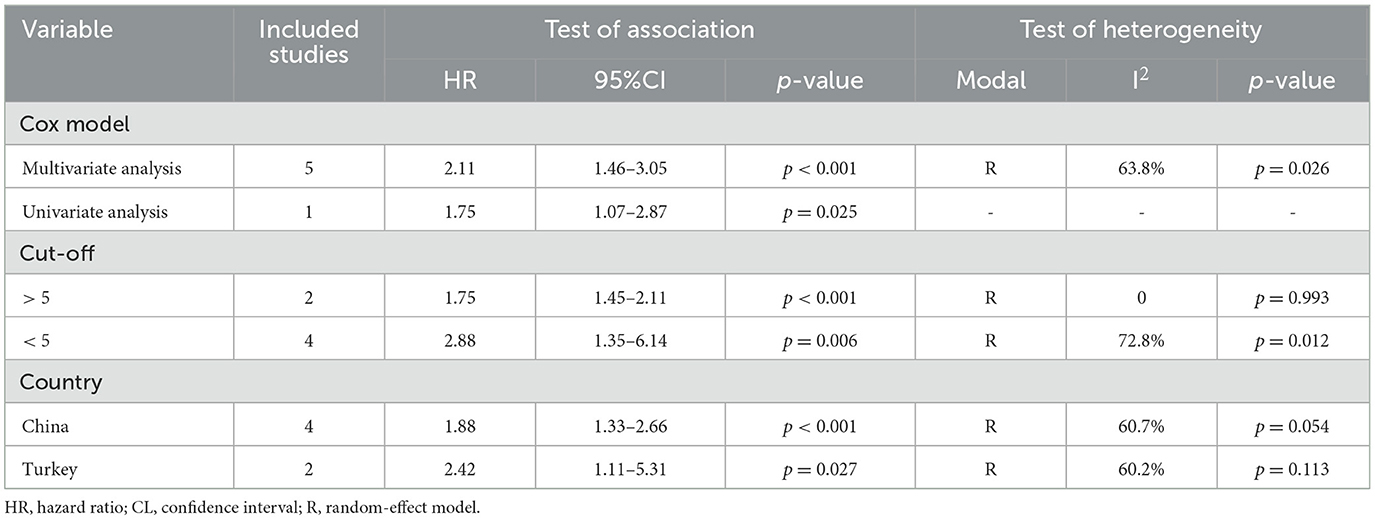
Table 3. Subgroup analysis of the association between serum lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio and recurrence-free survival in cancer patients.
3.5 Baseline dehydrogenase/albumin ratio and prognosis in our cohort
Given the lack of existing studies on the relationship between LAR and prognosis in HCC patients, we analyzed data from our center to further contribute to the current understanding of LAR as a prognostic marker in cancer.
The demographic and clinical characteristics of the 71 HCC patients in our cohort are summarized in Supplementary Table 1. The median age was 62.4 years, ranging from 40.2 to 82.6 years. The majority of participants were male (59.15%, n = 42). In terms of functional status, 63.38% (n = 45) had an ECOG PS of 0, while 36.62% (n = 26) had a score of 1. Chronic viral hepatitis was present in 76.06% (n = 54) of patients, and hepatic cirrhosis was diagnosed in 63.38% (n = 45). According to the BCLC staging system, 7.04% (n = 5) were classified as early stage, 42.25% (n = 30) as intermediate stage, and 50.71% (n = 36) as advanced stage.
We divided the cohort into two groups based on the cutoff value for the median pretreatment LAR. Survival curves revealed significantly shorter OS (HR: 2.04, 95% CI: 1.19–3.57, p = 0.008, Figure 6A) and PFS (HR: 1.89, 95% CI: 1.14–3.13, p = 0.01; Figure 6B) in HCC patients with high LAR compared to those with low LAR.
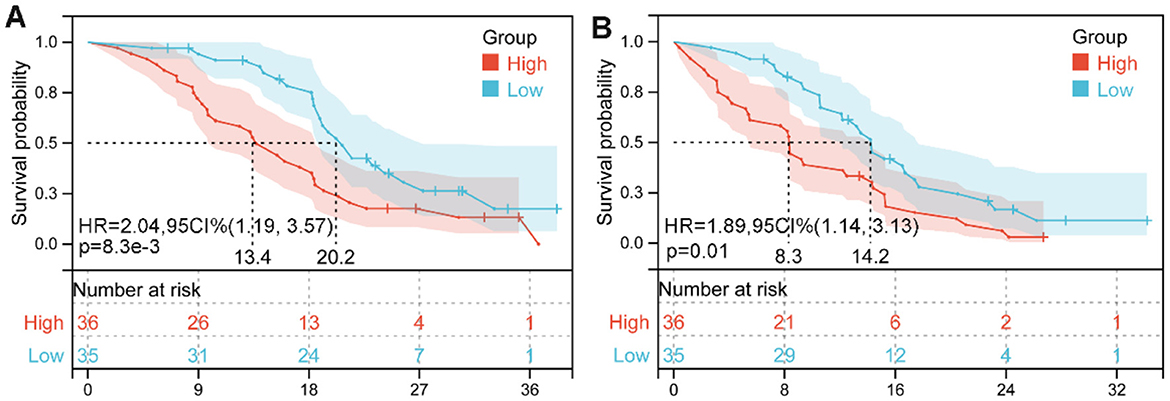
Figure 6. Kaplan–Meier survival estimates for overall survival (A) and progression-free survival (B) are presented, stratified by baseline lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio (LAR) levels in our cohorts. HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
4 Discussion
The LAR is a low-cost and easily obtainable biomarker derived from routine laboratory parameters. In the present analysis, elevated LAR levels were significantly associated with poorer survival outcomes in individuals with malignancies. Furthermore, subgroup analyses consistently supported the prognostic significance of LAR across various stratifications, including Cox regression models, treatment modalities, geographic regions, and LAR cut-off values.
LDH is a metabolic enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of lactate and pyruvate within the cellular cytoplasm. In malignant cells, LDH plays a particularly critical role due to their preferential reliance on glycolysis for energy production—a metabolic shift known as the “Warburg effect” (40, 41). Instead of depending on mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, these cells primarily generate ATP through aerobic glycolysis, during which LDH facilitates lactate accumulation (42). This metabolic reprogramming leads to elevated lactate concentrations, resulting in acidification of the tumor microenvironment and promoting both cancer cell survival and invasiveness (43). Beyond its metabolic function, LDH also contributes to maintaining pH balance within the tumor niche, thereby supporting tumor growth and metastatic potential (44, 45). Numerous studies have shown that elevated circulating LDH levels are significantly associated with poor prognosis in various malignancies, including melanoma, prostate cancer, and renal cell carcinoma (46). These findings highlight the central role of LDH in the pathophysiology of solid tumors.
Albumin serves as an essential plasma protein involved in multiple physiological processes, particularly in maintaining oncotic pressure and facilitating the transport of vital substances such as hormones, fatty acids, and trace elements—functions that collectively uphold nutritional balance in the human body (47, 48). Beyond its nutritional role, albumin has emerged as a valuable prognostic marker in oncology (49). A diminished serum albumin concentration, termed hypoalbuminemia, has been consistently linked to adverse outcomes in a range of malignancies, highlighting its relevance in tumor biology (50). Within the immune milieu, albumin contributes both energy and nutrients to immune cells, thereby modulating their functional performance. Moreover, its antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effects, and role in mediating cytokine distribution and lymphocyte responsiveness further underscore its immunological significance (51). An in-depth understanding of albumin's diverse biological functions may offer new perspectives for optimizing therapeutic strategies and clinical decision-making in cancer care.
By incorporating both LDH, a surrogate marker of tumor metabolic activity, and albumin, which reflects systemic nutritional status, the LAR provides a comprehensive snapshot of the patient's physiological and oncological state. This integrated parameter may offer superior prognostic value compared to LDH or albumin when considered individually. Accumulating evidence supports LAR as an emerging prognostic biomarker across a wide range of malignancies. Our findings highlight the clinical relevance of incorporating LAR into standard pretreatment assessments, potentially enhancing therapeutic planning and patient stratification.
The findings of this meta-analysis underscore the potential utility of the lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio (LAR) as a simple, cost-effective, and readily available prognostic biomarker across various cancers. Clinically, LAR may assist physicians in risk stratification, treatment planning, and follow-up scheduling by identifying patients with a poorer prognosis who may benefit from more aggressive or tailored therapeutic approaches. From a public health perspective, the use of routinely measured laboratory parameters to predict cancer outcomes could be particularly valuable in low-resource settings where access to advanced molecular testing is limited.
Nonetheless, this meta-analysis is subject to several limitations. Primarily, the reliance on retrospective cohort studies may compromise the robustness of the pooled estimates. Additionally, as the majority of the data originate from cohorts based in China and Turkey, the extrapolation of these results to other ethnic or geographic populations warrants caution. Furthermore, inconsistency in LAR threshold definitions among the included studies introduces an additional layer of heterogeneity. Although LAR shows promise as a prognostic biomarker, its advantages over established factors such as tumor stage and pathological subtype remain unclear, limiting its immediate clinical applicability. Finally, all the included studies seemed to be single-arm cohorts and lacked comparison groups, which greatly limited causal inference. To address these concerns, future investigations should aim to validate these findings through well-designed, prospective, multinational trials, thereby strengthening the generalizability of LAR's prognostic utility in cancers.
5 Conclusion
These findings underscore the prognostic value of pretreatment LAR in cancer patients. Integrating LAR into clinical decision-making may aid clinicians in enhancing risk stratification and personalizing treatment strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The Ethics Committee/Institutional Review Board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin because this was a retrospective cohort study and did not require patients to provide any human specimens.
Author contributions
DC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources. Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. TY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JF: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. WW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 82303512).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1610487/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
2. Hudock NL, Mani K, Khunsriraksakul C, Walter V, Nekhlyudov L, Wang M, et al. Future trends in incidence and long-term survival of metastatic cancer in the United States. Commun Med. (2023) 3:76. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00304-x
3. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
4. Bluethmann SM, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH. Anticipating the “silver tsunami”: prevalence trajectories and comorbidity burden among older cancer survivors in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2016) 25:1029–36. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-0133
6. Rizzo A, Ricci AD. Biomarkers for breast cancer immunotherapy: PD-L1, TILs, and beyond. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2022) 31:549–55. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2022.2008354
7. Zhang L, Li X, Wang K, Wu M, Liu W, Wang W. Prognostic impact of body composition in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with immunotherapy. Ann Med. (2024) 56:2395062. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2395062
8. Zhang L, Ma W, Qiu Z, Kuang T, Wang K, Hu B, et al. Prognostic nutritional index as a prognostic biomarker for gastrointestinal cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1219929. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1219929
9. Elinav E, Nowarski R, Thaiss CA, Hu B, Jin C, Flavell RA. Inflammation-induced cancer: crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat Rev Cancer. (2013) 13:759–71. doi: 10.1038/nrc3611
10. Liu X, Meng QH, Ye Y, Hildebrandt MA, Gu J, Wu X. Prognostic significance of pretreatment serum levels of albumin, LDH and total bilirubin in patients with non-metastatic breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. (2015) 36:243–8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu247
11. Zhang L, Feng J, Kuang T, Chai D, Qiu Z, Deng W, et al. Blood biomarkers predict outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a pooled analysis of 44 retrospective sudies. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 118:110019. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110019
12. Gao Q, Quan M, Zhang L, Ran Y, Zhong J, Wang B. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic indicator in thyroid cancer. Cancer Control. (2024) 31:10732748241309048. doi: 10.1177/10732748241309048
13. Zhang J, Li M, Zhang L, Kuang T, Yu J, Wang W. Prognostic value of controlling nutritional status on clinical and survival outcomes in cancer patients treated with immunotherapy. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:17715. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45096-1
14. Doherty JR, Cleveland JL. Targeting lactate metabolism for cancer therapeutics. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123:3685–92. doi: 10.1172/JCI69741
15. Zhang J, Yao YH, Li BG, Yang Q, Zhang PY, Wang HT. Prognostic value of pretreatment serum lactate dehydrogenase level in patients with solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:9800. doi: 10.1038/srep09800
16. Li J, Cheng Y, Liu G, Ji Z. The association of pretreatment serum albumin with outcomes in bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. (2018) 11:3449–59. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S162066
17. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
18. Zhang L, Kuang T, Chai D, Deng W, Wang P, Wang W. The use of antibiotics during immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment is associated with lower survival in advanced esophagogastric cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 119:110200. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110200
19. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the newcastle-ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
20. Ma W, Shi Q, Zhang L, Qiu Z, Kuang T, Zhao K, et al. Impact of baseline body composition on prognostic outcomes in urological malignancies treated with immunotherapy: a pooled analysis of 10 retrospective studies. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:830. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12579-x
21. Zhang L, Wang K, Liu R, Kuang T, Chen C, Yao F, et al. Body composition as a prognostic factor in cholangiocarcinoma: a meta-analysis. Nutr J. (2024) 23:145. doi: 10.1186/s12937-024-01037-w
22. Arici MO, Kivrak Salim D, Kocer M, Alparslan AS, Karakas BR, Ozturk B. Predictive and prognostic value of inflammatory and nutritional indexes in patients with breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Medicina. (2024) 60:1849. doi: 10.3390/medicina60111849
23. He J, Tong L, Wu P, Wu Y, Shi W, Chen L. Prognostic significance of preoperative lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio in breast cancer: a retrospective study. Int J Gen Med. (2023) 16:507–14. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S396871
24. Lei W, Wang W, Qin S, Yao W. Predictive value of inflammation and nutritional index in immunotherapy for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer and model construction. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:17511. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66813-4
25. Luo M, Wei H, Qiu M, Su C, Ning R, Zhou S. Prognostic value of the lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with the first-line PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors combined with chemotherapy. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1473962. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1473962
26. Menekse S, Kut E, Almuradova E. Elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio is a useful poor prognostic predictor of nivolumab in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2023) 27:86–94. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202310_34076
27. Peng RR, Liang ZG, Chen KH, Li L, Qu S, Zhu XD. Nomogram based on lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio (LAR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) for predicting survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Inflamm Res. (2021) 14:4019–33. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S322475
28. Reyes-Pérez EN, Flores-Cuevas LM, Martínez-Mier G, Chávez-Güitrón LE, Martínez-Jiménez MC, Audelo-Guzmán M, et al. Predictive value of the lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio (LAR) in classical hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Blood. (2023) 8. doi: 10.21037/aob-23-24
29. Wang X, Ji X. Effect of preoperative serum lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio on the survival of oral cancer: a retrospective study. J Inflamm Res. (2024) 17:5129–38. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S472041
30. Wu Y, Du B, Lv C, Ji X, Lai J. LAPS score for individualized treatment of advanced EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer receiving EGFR-TKIs with or without bevacizumab. Ann Med. (2023) 55:2257227. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2257227
31. Xu H, Lin T, Ai J, Zhang J, Zhang S, Li Y, et al. Utilizing the lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio for survival prediction in patients with bladder cancer after radical cystectomy. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:1733–44. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S384338
32. Zhao R, Liang Z, Chen K, Zhu X. Nomogram based on hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet score to predict overall survival in patients with T3-4N0-1 nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:1995–2006. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S411194
33. ADAY U, Böyük A, Akkoç H. The prognostic significance of serum lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio in colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res. (2020) 99:161–70. doi: 10.4174/astr.2020.99.3.161
34. Aday U, Tatli F, Akpulat FV, Inan M, Kafadar MT, Bilge H, et al. Prognostic significance of pretreatment serum lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio in gastric cancer. Wspolczesna Onkologia. (2020) 24:145–9. doi: 10.5114/wo.2020.100219
35. Çaglar R. The relationship of different preoperative inflammatory markers with the prognosis of gastric carcinoma. Asian J Surg. (2023) 46:360–5. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2022.04.075
36. Feng JF, Wang L, Yang X, Jiang YH. Prognostic value of lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio (LAR) in patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. (2019) 11:7243–51. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S208320
37. Shiratori F, Suzuki T, Yajima S, Oshima Y, Nanami T, Funahashi K, et al. Is high score of preoperative lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio predicting poor survivals in esophageal carcinoma patients?. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2023) 29:215–22. doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.23-00004
38. Shu X-P, Xiang Y-C, Liu F, Cheng Y, Zhang W, Peng D. Effect of serum lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio (LAR) on the short-term outcomes and long-term prognosis of colorectal cancer after radical surgery. BMC Cancer. (2023) 23:915. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11446-5
39. Xie Z, Zhou H, Wang L, Wu Y. The significance of the preoperative lactate dehydrogenase/albumin ratio in the prognosis of colon cancer: a retrospective study. PeerJ. (2022) 10:e13091. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13091
40. Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A. Warburg effect, lactate dehydrogenase, and radio/chemo-therapy efficacy. Int J Radiat Biol. (2019) 95:408–26. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2018.1490041
41. Li Z, Li J, Bai X, Huang X, Wang Q. Tumor microenvironment as a complex milieu driving cancer progression: a mini review. Clin Transl Oncol. (2024) 27:1943–52. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03697-w
42. Sharma D, Singh M, Rani R. Role of LDH in tumor glycolysis: regulation of LDHA by small molecules for cancer therapeutics. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 87:184–95. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.11.007
43. Hayes C, Donohoe CL, Davern M, Donlon NE. The oncogenic and clinical implications of lactate induced immunosuppression in the tumour microenvironment. Cancer Lett. (2021) 500:75–86. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.021
44. Ding J, Karp J E, Emadi A. Elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) can be a marker of immune suppression in cancer: interplay between hematologic and solid neoplastic clones and their microenvironments. Cancer Biomark. (2017) 19:353–63. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160336
45. Li Z, Liu Y, Huang X, Wang Q, Fu R, Wen X, et al. F. Nucleatum enhances oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation via E-cadherin/β-Catenin pathway. BMC Oral Health. (2024) 24:518. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04252-3
46. Wulaningsih W, Holmberg L, Garmo H, Malmstrom H, Lambe M, Hammar N, et al. Serum lactate dehydrogenase and survival following cancer diagnosis. Br J Cancer. (2015) 113:1389–96. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.361
47. Gupta D, Lis CG. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: a systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr J. (2010) 9:69. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-9-69
48. Ye B, Wang Q, Zhu X, Zeng L, Luo H, Xiong Y, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies a novel proliferation cell type affecting clinical outcome of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1236435. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1236435
49. Chen N, Yu Y, Shen W, Xu X, Fan Y. Nutritional status as prognostic factor of advanced oesophageal cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Clin Nutr. (2024) 43:142–53. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.11.030
50. Miura K, Hamanaka K, Koizumi T, Kitaguchi Y, Terada Y, Nakamura D, et al. Clinical significance of preoperative serum albumin level for prognosis in surgically resected patients with non-small cell lung cancer: comparative study of normal lung, emphysema, and pulmonary fibrosis. Lung Cancer. (2017) 111:88–95. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.07.003
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer, lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio, prognosis, hepatocellular carcinoma
Citation: Chai D, Yang T, Zhang L, Hui Y, Feng J and Wang W (2025) Prognostic value of the lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio in cancer patients. Front. Nutr. 12:1610487. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1610487
Received: 15 April 2025; Accepted: 12 June 2025;
Published: 07 July 2025.
Edited by:
Lilia Bardoscia, Healthcare Company Tuscany Nord Ovest, ItalyReviewed by:
Diana Chiru, University Hospital of Basel, SwitzerlandXiaoli Ji, The Affiliated Huaian No.1 People's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Chai, Yang, Zhang, Hui, Feng and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weixing Wang, d2FuZ3d4QHdodS5lZHUuY24=; Jiarui Feng, ZmpyXzYzOTFfY25Ac2luYS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Dongqi Chai1,2,3†
Dongqi Chai1,2,3† Lilong Zhang
Lilong Zhang Yuanjian Hui
Yuanjian Hui Weixing Wang
Weixing Wang