- 1Department of Pharmacy, Guangxi Academy of Medical Sciences and the People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Guilin Medical University, Guilin, China
Background: The Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) criteria were officially introduced in 2018 with the aim of establishing a standardized global framework for the diagnosis of malnutrition. Synthesizing expert consensus from multiple international organizations, the GLIM criteria proposed a two-step diagnostic model integrating both phenotypic and etiologic components. Although GLIM-related research has expanded rapidly in recent years, a comprehensive bibliometric evaluation remains absent.
Methods: Relevant literature published between 2018 and 2024 was retrieved from the Scopus database. Only English-language original research articles and reviews were included. A total of 729 eligible publications were analyzed using VOSviewer (v1.6.10), CiteSpace (v5.8.R3), and the online platform Bioinformatics. The analysis covered various dimensions, including countries, institutions, authors, journals, keywords, and highly cited references.
Results: The volume of GLIM-related publications has shown a steady upward trajectory, peaking in 2024. China emerged as the most prolific country, followed by Spain and Japan. The top contributing institutions included Uppsala University, Capital Medical University, and Beijing Shijitan Hospital. Among the most productive authors were Cederholm T, Shi H, and Correia MITD. Clinical Nutrition and Nutrients were identified as the core journals in this field. Keyword analysis revealed that “malnutrition,” “diagnosis,” “sarcopenia,” “cancer,” and “nutritional risk” were pre-dominant themes, while “systematic review,” “protein blood level,” and “gastric cancer” represented emerging areas of interest.
Conclusion: This study represents the first comprehensive bibliometric analysis of research related to the GLIM criteria. It identifies key contributors, collaboration networks, and thematic evolutions in the field, highlighting a transition from the development of diagnostic frameworks to clinical application and individualized nutritional assessment. These findings provide a valuable reference for guiding future research directions in GLIM-related domains.
1 Introduction
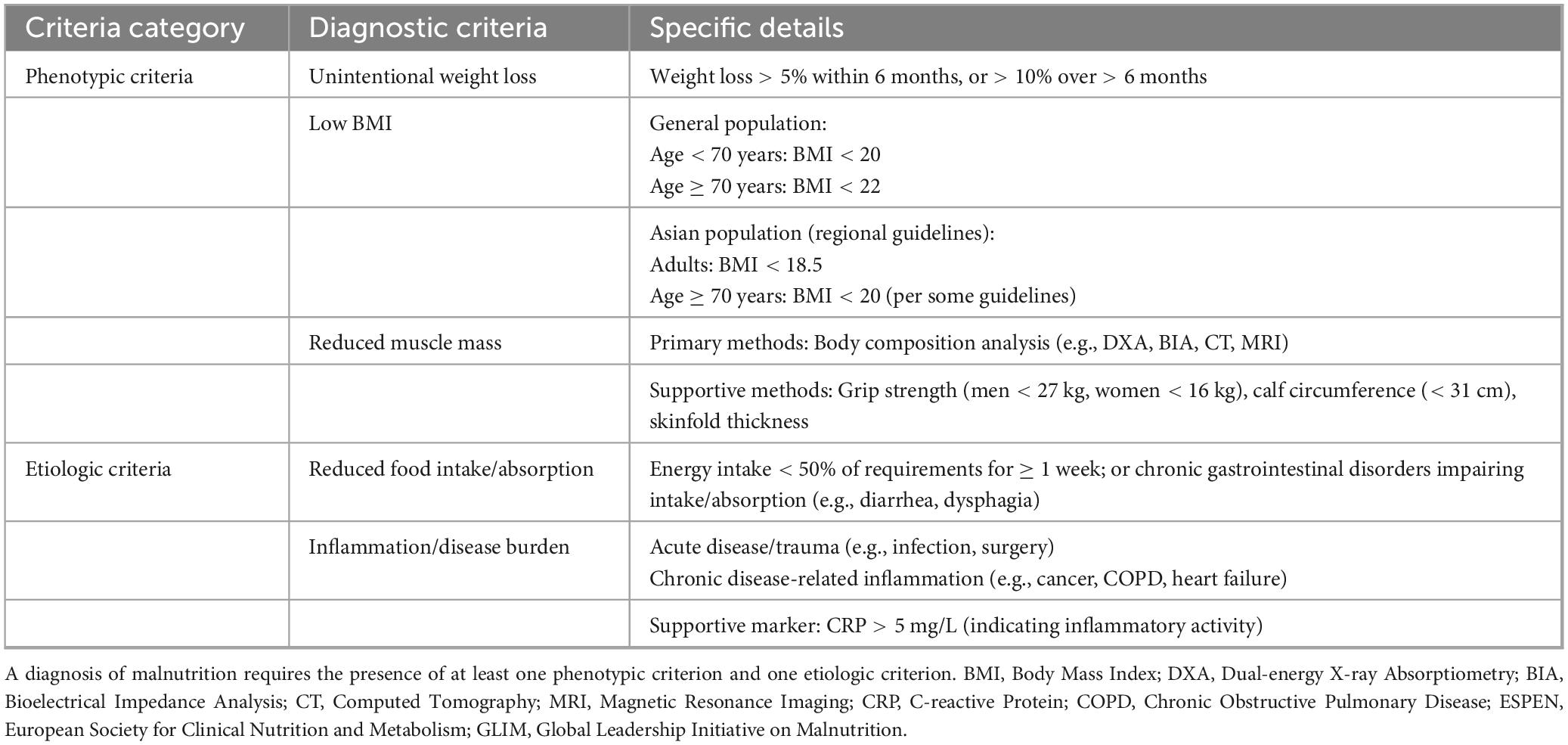
Malnutrition remains a significant global health concern, adversely affecting patient outcomes and straining healthcare systems through increased risk of complications, prolonged hospital stays, higher readmission rates, elevated mortality, and greater medical expenditures (1–4). Current diagnostic approaches face challenges in standardization, as conventional indicators—such as dietary intake, weight changes, and serum albumin levels—have inherent limitations that preclude their use as standalone diagnostic criteria (5–7). To address these limitations, various international nutritional societies have proposed different diagnostic frameworks. In 2012, the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) and the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (AND) jointly introduced a two-step diagnostic algorithm incorporating both etiologic and phenotypic components. In contrast, the 2015 consensus by the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) emphasized body mass index (BMI) as a core parameter (5, 8). These discrepancies underscore the pressing need for a globally unified diagnostic standard for malnutrition. In 2018, the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) proposed a standardized diagnostic framework that combines phenotypic criteria (involuntary weight loss, low BMI, and reduced muscle mass) with etiologic criteria (reduced food intake/assimilation and inflammation/disease burden) (9). A diagnosis of malnutrition under the GLIM criteria requires the presence of at least one phenotypic and one etiologic criterion. This framework offers a practical and universally applicable diagnostic model adaptable to various populations and clinical contexts, thereby advancing the global standardization of malnutrition assessment. The specific diagnostic components of the GLIM framework are summarized in Table 1.
Bibliometrics is a methodological approach that quantitatively and qualitatively analyzes scientific literature to assess publication output and research trends within a given field (10, 11). It enables the extraction and synthesis of information on authors, keywords, journals, countries, institutions, and references (11). Widely used bibliometric tools such as CiteSpace (12), VOSviewer (13), the R package bibliometrix (14), and HistCite (11) facilitate visualization and interpretation of analytical data, and have been extensively applied in medical disciplines, including oncology (15, 16), orthopedics (17), thoracic surgery (18), and rheumatology (19). As a globally endorsed framework, the GLIM criteria have played a pivotal role in establishing standardized diagnostic protocols and guiding clinical nutrition interventions. In recent years, the number of publications related to GLIM has steadily increased; however, systematic evaluations and methodological syntheses remain relatively scarce. Therefore, conducting a comprehensive bibliometric analysis is both timely and necessary. This study aims to systematically analyze the literature on GLIM from 2018 to 2024, with the objectives of identifying influential contributors, mapping the evolution of research priorities, and highlighting future directions for the development and refinement of GLIM standards.
2 Methods
2.1 Data sources and search strategy
All relevant publications were retrieved from the Scopus database, which offers a comprehensive and standardized export format widely used in academic research. To minimize potential bias caused by continuous database updates, the search was conducted on a single day (February 17, 2025). The search strategy was as follows:
[TITLE-ABS-KEY(global AND leadership AND initiative AND on AND malnutrition) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(glim)].
The search was restricted to English-language original research articles and reviews published between 2018 and 2024. A total of 729 eligible records were initially identified. The detailed screening process is illustrated in Figure 1.
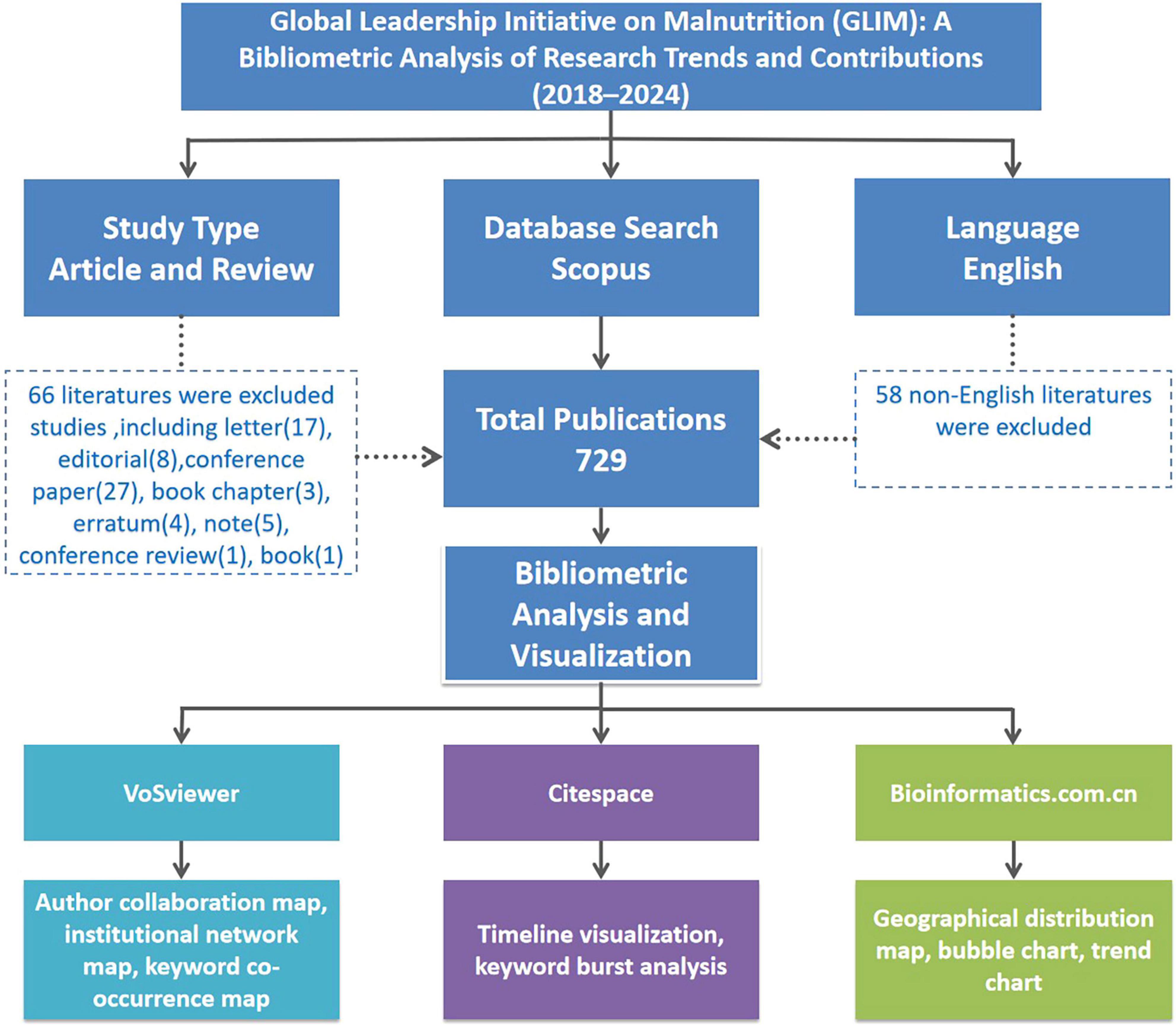
Figure 1. Flowchart illustrating the literature selection process and bibliometric analysis framework for GLIM-related research from 2018 to 2024. A total of 729 English-language articles and reviews were identified from Scopus. Non-English publications and other non-eligible document types were excluded. Bibliometric visualization was conducted using VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and the Bioinformatics online platform.
2.2 Data collection
The identified records were exported and processed using Microsoft Excel 2016. Extracted bibliographic information included authors, affiliations, countries/regions, journals, number of publications (Np), number of citations (Nc), publication years, H-index, keywords, and references. The data were then used for further bibliometric analysis, and the original dataset has been provided as Supplementary material to support transparency and reproducibility.
2.3 Bibliometric analysis
Bibliometric analysis was performed using VOSviewer (version 1.6.10), CiteSpace (version 5.8.R3), and the online platform.1 Two primary indicators—number of publications (Np) and number of citations (Nc)—were used to assess research performance. Np reflects scientific productivity, while Nc indicates academic influence. Both are standard measures for evaluating the value of scholarly output. The H-index was used to evaluate individual academic contributions and potential future impact. An H-index of h indicates that a researcher has published h papers, each cited at least h times. While initially intended for individual evaluation, the H-index is now also used to measure the scholarly performance of countries, institutions, and journals (20, 21).
The Impact Factor (IF), as reported in the latest Journal Citation Reports (JCR), remains one of the most recognized metrics for evaluating journal quality and influence in the medical field (22). The Global Citation Score (GCS) refers to the total number of citations an article has received worldwide and serves as an important indicator of its contribution to the scientific community (23). To model the temporal trend of research output, a polynomial regression model was fitted to the annual number of publications. In this model, the number of publications per year is represented by f(x), with x denoting the publication year.
VOSviewer (version 1.6.10.0) was used to construct and visualize bibliometric network maps, including co-citation and keyword co-occurrence analyses (24, 25). In the resulting visualizations, node size represents the number of publications, line thickness reflects the strength of relationships, and different colors are used to distinguish clusters or time periods.
CiteSpace (version 5.8.R3) was applied to explore research hotspots and thematic evolution through keyword clustering, timeline views, and burst detection analysis (26). Keyword clustering helps delineate research themes and identify core topics in GLIM-related studies. The timeline view visualizes the temporal evolution of keyword clusters, while burst detection reveals emerging topics that received sudden attention during specific time intervals.
The Bioinformatics online platform2 supports the generation of various graphical modules, such as geographical distribution maps, bubble charts, and trend plots. With a user-friendly graphical interface, it allows researchers without programing experience to produce high-quality, publication-ready figures (exportable in PDF or SVG formats), and is widely used in bibliometrics and bioinformatics research (27).
3 Results
3.1 Overview of GLIM-related publications
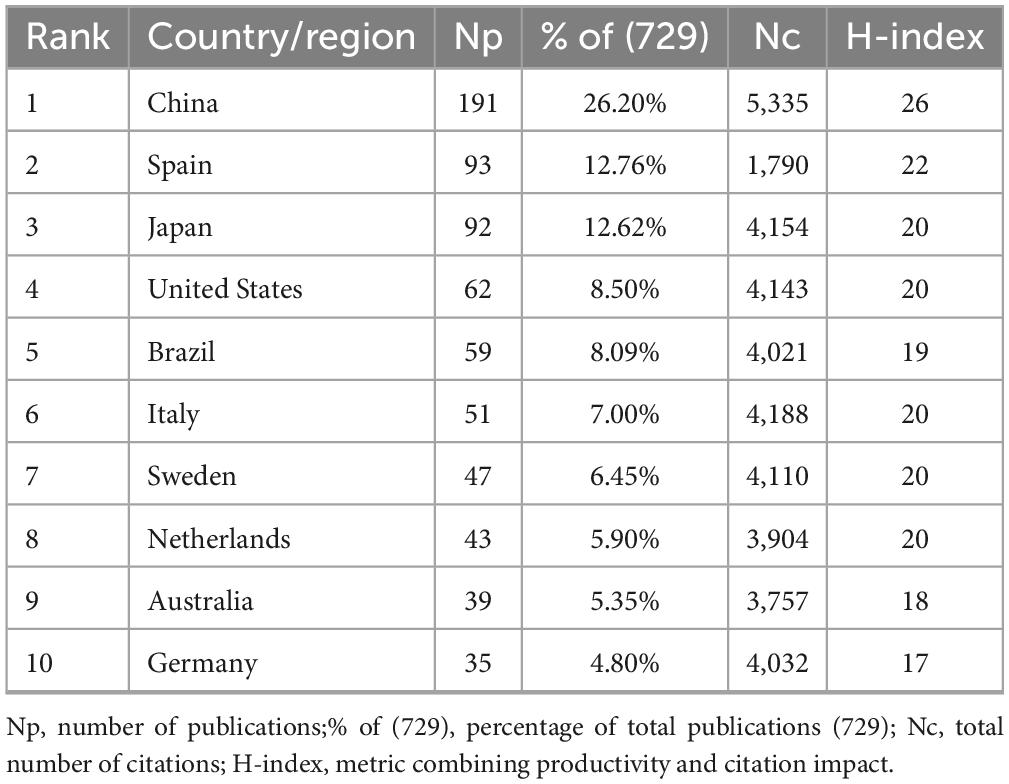
A total of 729 GLIM-related publications were retrieved from the Scopus database between 2018 and 2024, including 683 original research articles and 46 reviews. These publications received a total of 13,146 citations (Nc), with an average of 18.03 citations per article. The collective H-index for all publications was 49. The global distribution of GLIM-related research is shown in Figure 2A. The top five contributing countries—China, Spain, Japan, the United States, and Brazil—accounted for approximately two-thirds of the total output, revealing notable regional disparities in research activity.
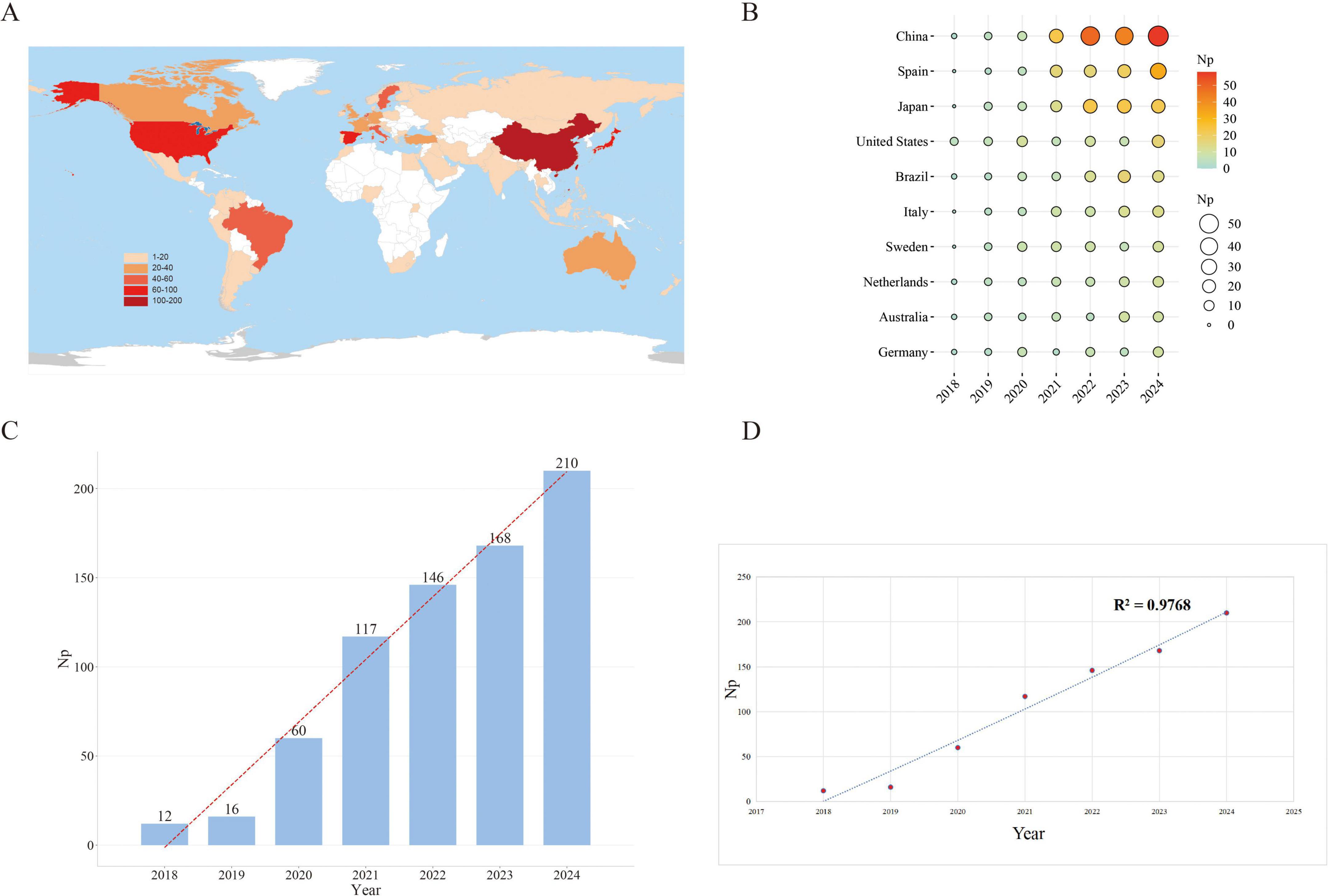
Figure 2. Trends in GLIM-related publication output from 2018 to 2024. (A) Global distribution of GLIM-related publications by country. (B) Annual publication output of the top 10 contributing countries, with circle size and color intensity reflecting publication volume. (C) Yearly number of publications, illustrating a steady increase over time. (D) Polynomial regression curve indicating the overall growth trend, with an R2 of 0.9768. Np, Number of publications.
Among the top 10 countries contributing annually (Figure 2B), China consistently ranked first, publishing 58 papers in 2024 alone, followed by Spain (33) and Japan (22). China’s consistently high output underscores its leading role in this field, as well as the nation’s sustained academic investment and strategic prioritization of GLIM research.
3.2 Annual trend in publication volume
Figure 2C illustrates the yearly number of GLIM-related publications. The volume of publications increased markedly from 12 in 2018 to 210 in 2024, with Np reaching its historical peak in 2024. This growth trajectory indicates that GLIM has gradually emerged as a central topic in global academic research, with research activity exhibiting a trend of exponential growth.
Figure 2D displays the linear regression curve (dashed line) representing the year-by-year change in publication output (R2 = 0.9768). Although minor fluctuations were observed in certain years, the overall trend demonstrates a nearly linear and robust upward trajectory. Notably, since 2020, the annual growth rate has accelerated further, highlighting the accelerating academic interest and cumulative momentum in GLIM-related research.
3.3 National contributions to global publication output
The top 10 countries/regions with the highest academic output were identified (Table 2). China ranked first with 191 publications, accounting for 26.20% of the total (729), followed by Spain (93, 12.76%) and Japan (92, 12.62%). In terms of Nc, China led with 5,335 citations, followed by Italy (4,188), Japan (4,154), and the United States (4,143). China also had the highest H-index (26), followed by Spain (22), Japan (20), and a four-way tie among the United States, Italy, Sweden, and the Netherlands (all at 20). Notably, although Spain ranked second in publication volume (Np = 93), its citation count (1,790) was substantially lower than those of countries with similar Np, such as Japan (4,154) and the United States (4,143)—less than half in both cases. However, Spain’s H-index (22) was second only to China (26) and exceeded that of Japan (20).
3.4 Analysis of affiliations
Affiliation-level analysis was conducted to identify the top 10 institutions in terms of GLIM-related publication output. As shown in Table 3, Capital Medical University (China) had the highest number of publications (Np = 36), followed by Uppsala University (Sweden, Np = 35) and Beijing Shijitan Hospital (China, Np = 33). Citation performance and academic impact were evaluated using total citation count (Nc) and H-index, revealing notable regional variations. Uppsala University ranked first with an Nc of 4,024 and an H-index of 19. Karolinska University Hospital (Sweden) and the Federal University of Minas Gerais (Brazil) followed with Nc values of 3,719 and 3,682, respectively. While six of the top 10 institutions were based in China, including Capital Medical University, Beijing Shijitan Hospital, and the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, these institutions generally showed lower Nc values (e.g., 1,003 and 684, respectively) and H-indices (ranging from 12 to 17). The Carlos III Institute of Health (Spain) had the lowest Nc among the top 10 institutions (299). These metrics collectively reflect institutional differences in research productivity and impact within the GLIM field.
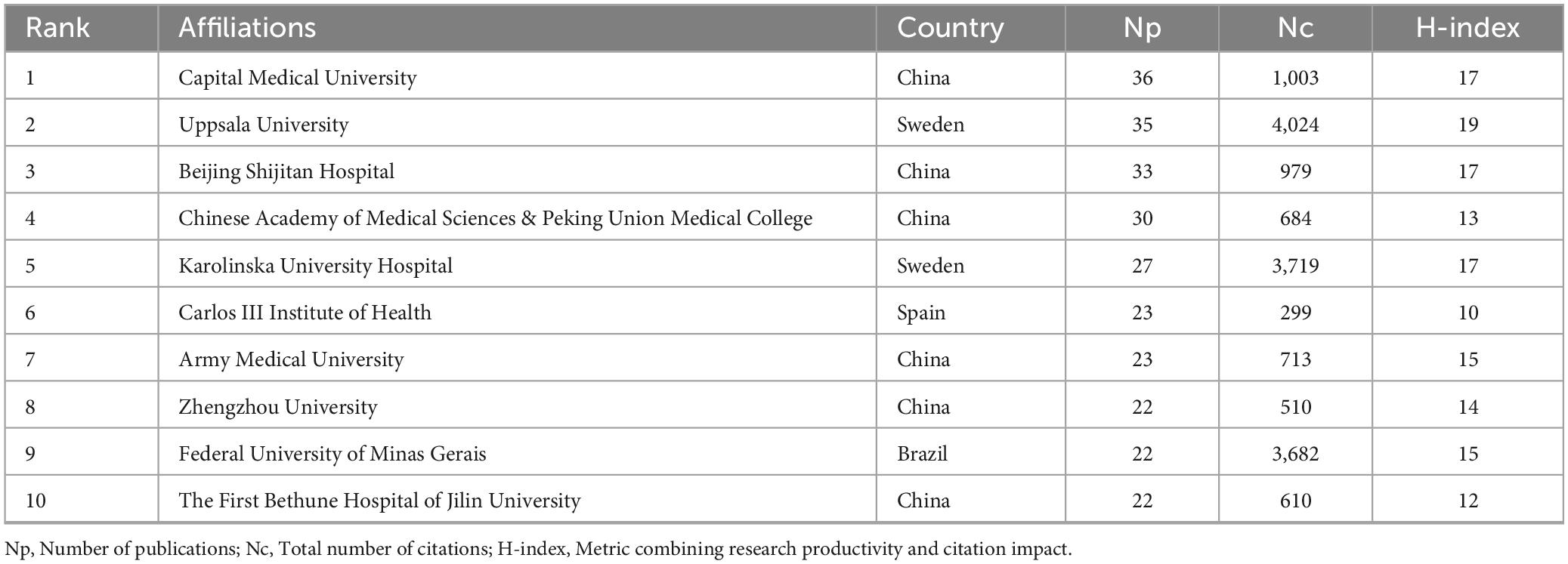
Table 3. Top 10 affiliations in GLIM-related research based on publication output and citation impact (2018–2024).
3.5 Author analysis
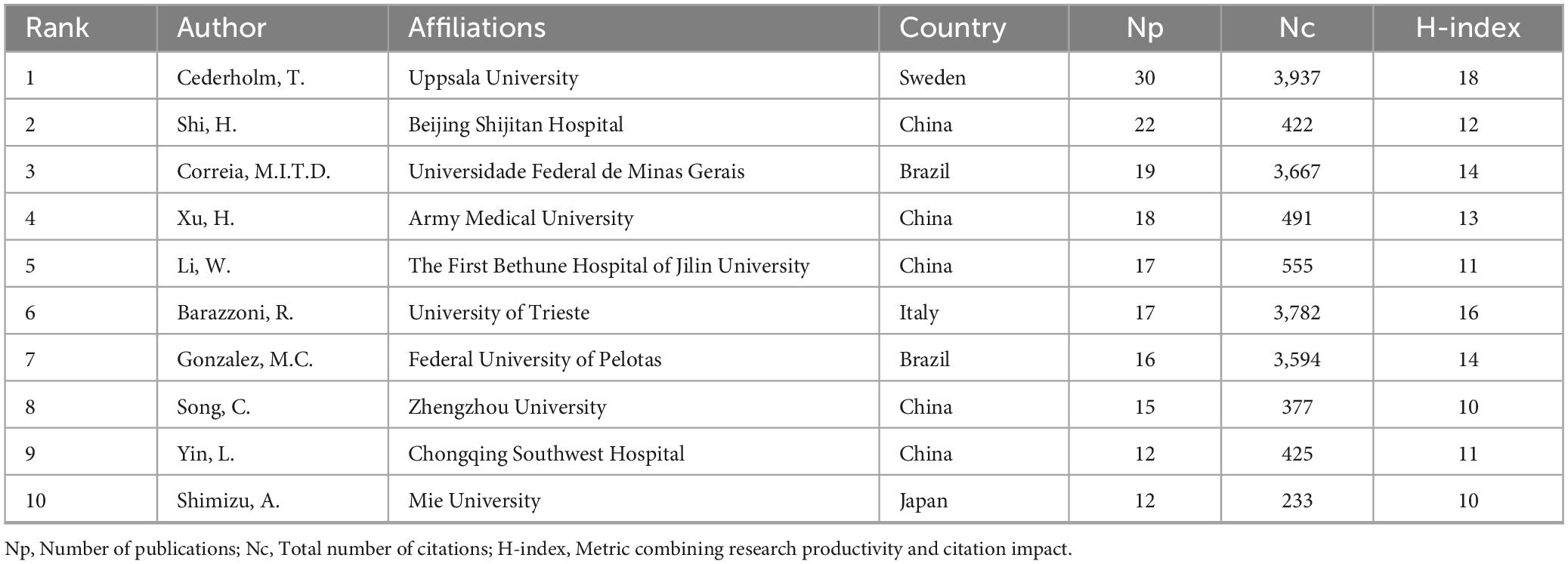
Table 4 lists the top 10 most prolific authors in the field of GLIM research. To further explore their academic influence and collaborative patterns, an author co-citation network was constructed (Figure 3A) to identify highly cited researchers and their interconnections within the field. Collectively, these authors contributed 178 publications, accounting for 24.4% of the total global output in this domain. Among them, Cederholm, T. from Uppsala University (Sweden) ranked first with 30 publications, 3,937 citations (Nc), and an H-index of 18. His work has exerted substantial influence on the development and validation of the GLIM criteria. In addition, Correia, M.I.T.D. from the Federal University of Minas Gerais (Brazil) and Barazzoni, R. from the University of Trieste (Italy) exhibited significant impact in the clinical application of the GLIM framework, with Nc values of 3,667 and 3,782, respectively. From a regional perspective, Chinese scholars were highly productive, occupying five of the top 10 positions. For example, Shi, H. from Beijing Shijitan Hospital (Nc = 422) and Xu, H. from Army Medical University (Nc = 491) made notable contributions to the clinical validation and dissemination of the GLIM criteria in China. However, despite their high publication output, Chinese researchers exhibited relatively lower citation counts. This may be related to certain gaps in theoretical innovation and international academic influence. In contrast, scholars from Europe and the United States demonstrated greater citation impact, indicating higher recognition of their work in both academic and clinical contexts.
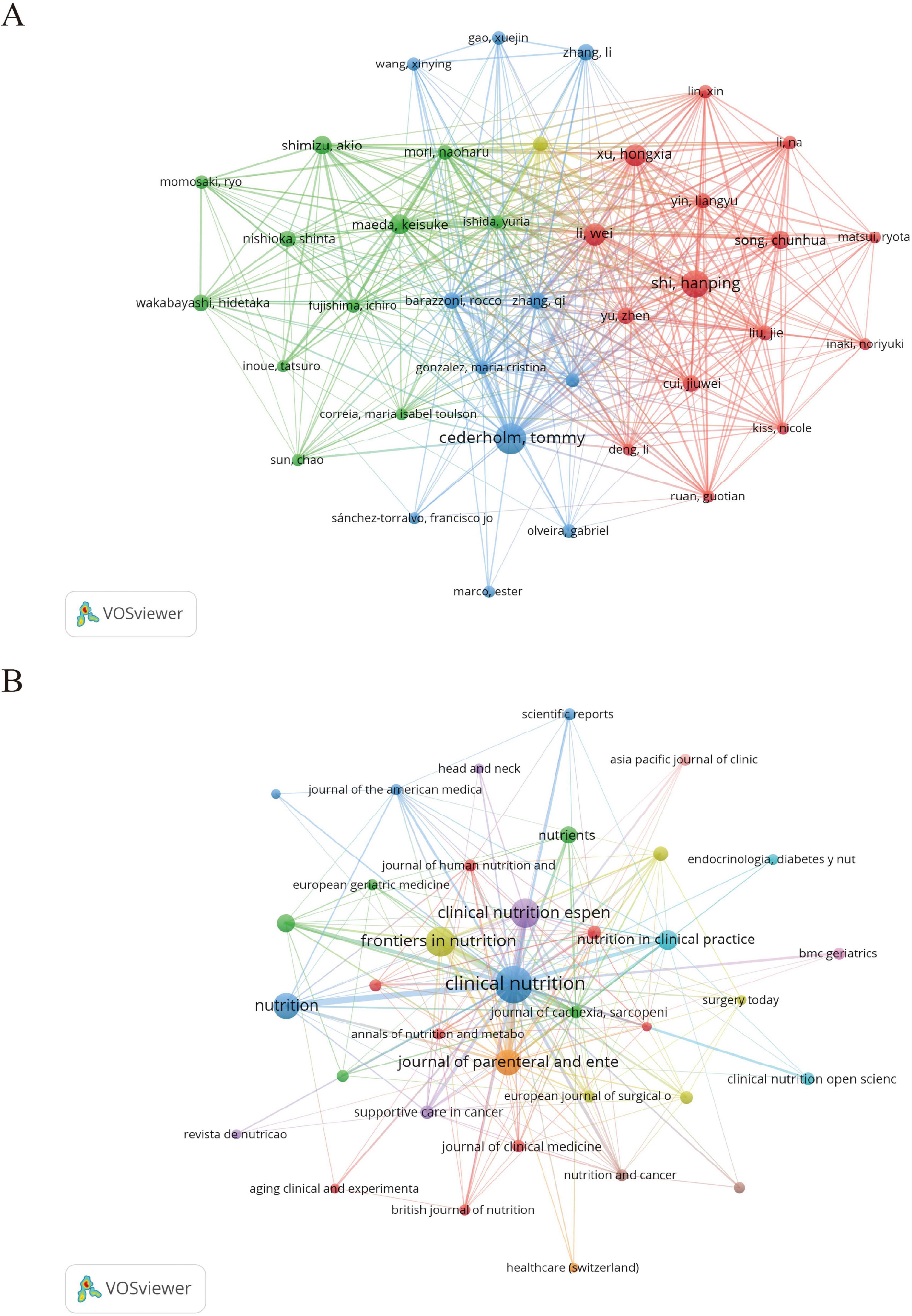
Figure 3. Author and journal co-citation network maps generated by VOSviewer. (A) Author co-citation network based on 729 GLIM-related publications. A minimum citation threshold of 7 was applied, resulting in 38 authors included in the analysis. (B) Journal co-citation network with a minimum citation threshold of 3, including 37 journals. In both maps, node size represents citation frequency, node color indicates cluster grouping, and line thickness reflects the strength of co-citation links.
3.6 Journal analysis
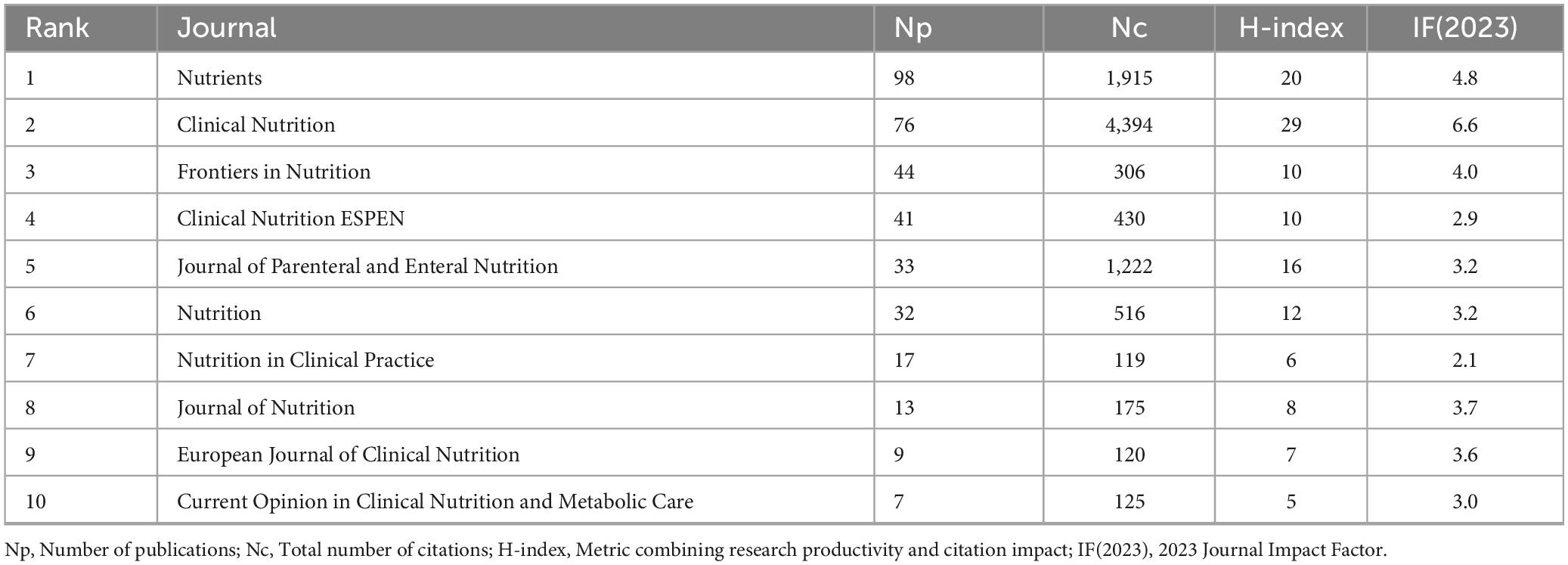
As shown in Table 5, Nutrients ranked first in terms of publication volume on GLIM-related research, with 98 articles published [impact factor (IF) = 4.8]. It was followed by Clinical Nutrition, which published 76 articles (IF = 6.6) and exhibited the highest academic impact in this field, with the greatest number of citations (Nc = 4,394) and the highest H-index (29) among the top 10 journals. Frontiers in Nutrition ranked third, with 44 publications (IF = 4.0).
To further explore core journals and their inter-citation relationships, a journal co-citation network was constructed (Figure 3B). The top 10 journals contributed 370 publications, representing 50.75% of the total output (370/729), underscoring their dominant role in the GLIM research landscape. Notably, among the top 10 journals, only Clinical Nutrition ESPEN (IF = 2.9) and Nutrition in Clinical Practice (IF = 2.1) had impact factors below 3.000.
3.7 Analysis of highly cited articles
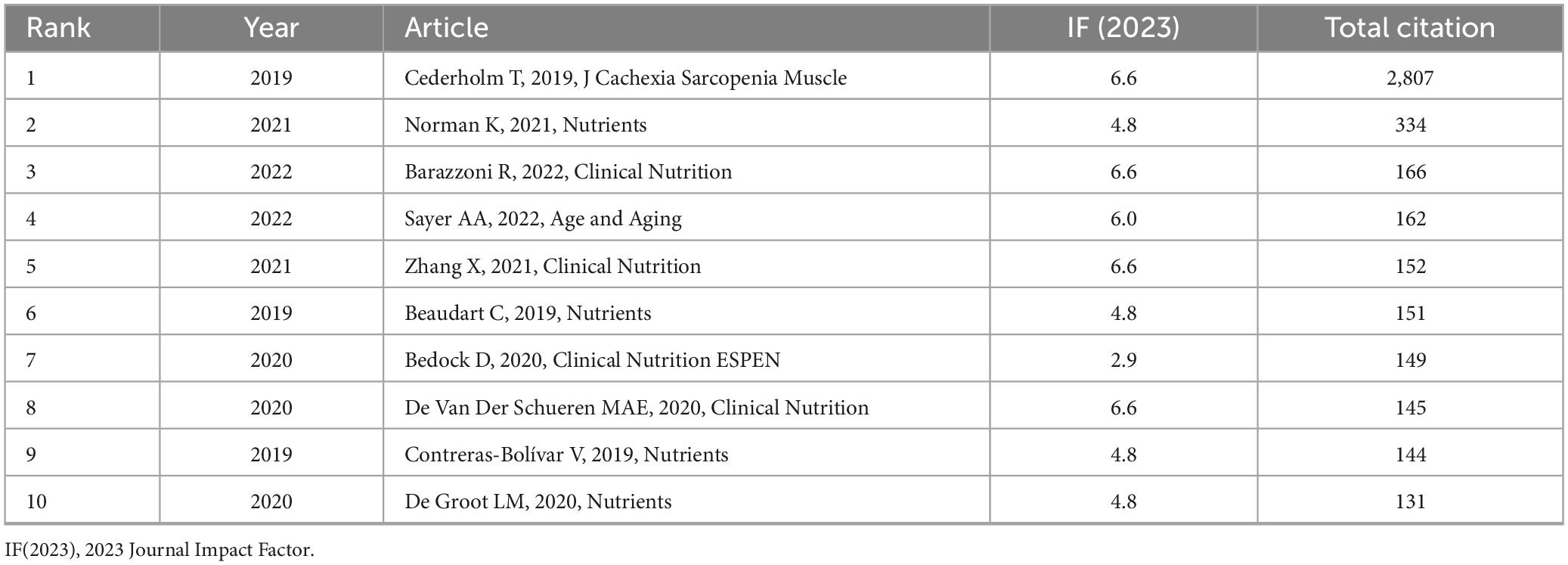
The articles listed in Table 6 are ranked in descending order based on total citation count. The top 10 most cited studies were primarily published between 2019 and 2022. Leading the list by a significant margin is the article titled “GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition – A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community” (9) (IF = 6.6), which has received 2,807 citations. It is followed by “Malnutrition in Older Adults—Recent Advances and Remaining Challenges” (34) (IF = 4.8; 334 citations), and “Guidance for assessment of the muscle mass phenotypic criterion for the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) diagnosis of malnutrition” (35) (IF = 6.6; 166 citations).
3.8 GCS analysis of highly influential publications
Figure 4A presents a bubble chart illustrating the annual GCS of highly cited references in the GLIM research field, offering insight into their academic influence and citation trends over time. Notably, the 2019 GLIM consensus report by Cederholm et al. recorded a peak GCS of 727 in 2024, with a total citation count of 2,927, significantly outpacing other publications. This underscores its pivotal role in the development and validation of the GLIM criteria. Since its publication, the paper has shown a steady increase in citations, reaching its highest impact in 2024, further reflecting its importance in clinical nutrition research. In addition to Cederholm’s work, the 2021 review by Norman K., published in Nutrients, also showed a high GCS in 2024, highlighting the growing attention toward malnutrition in older adults. Other studies—such as Sayer et al. (36) in Age and Aging, Barazzoni et al. (35) in Clinical Nutrition, and Beaudart et al. (37) in Nutrients—have also maintained substantial academic influence in recent years.
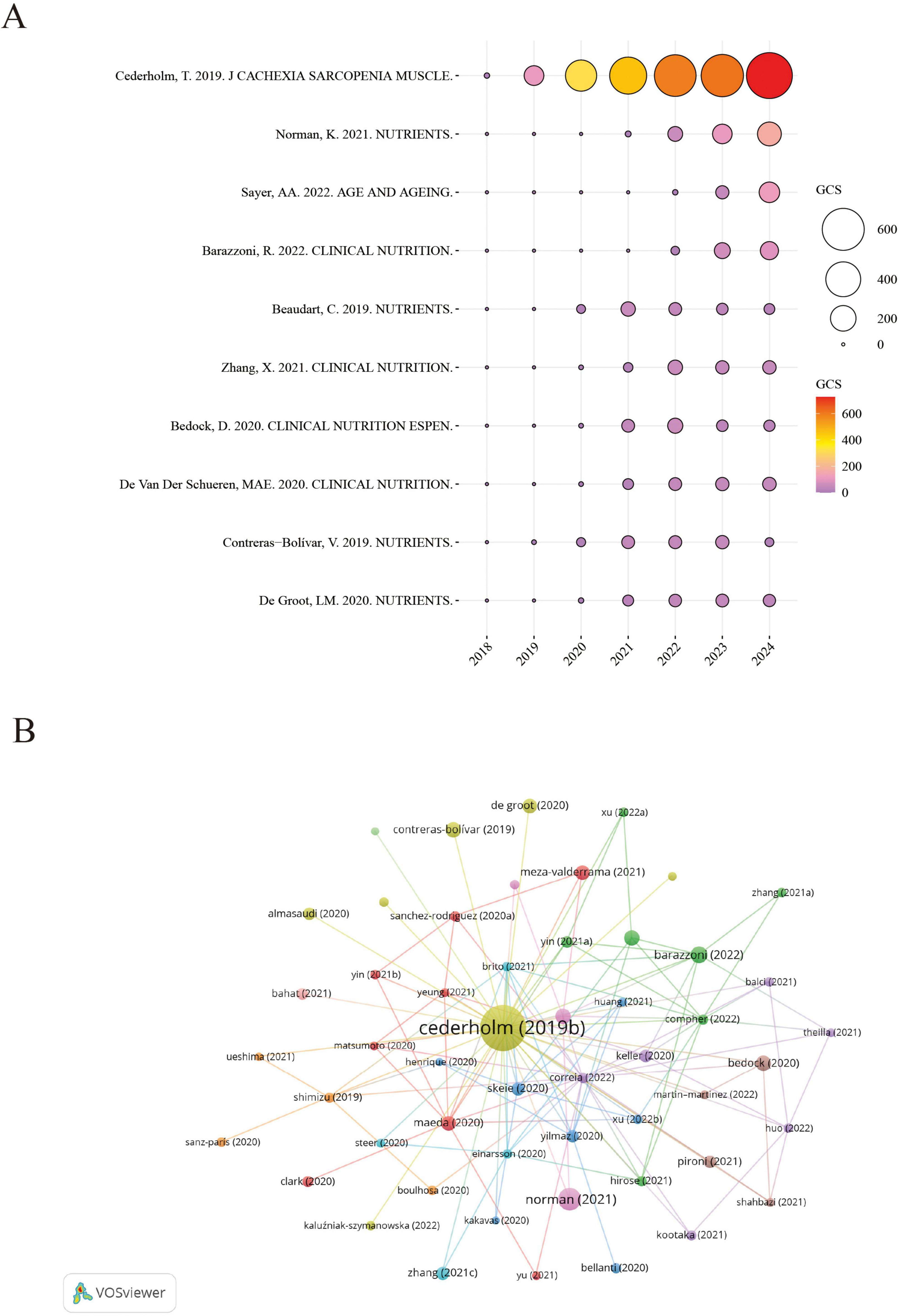
Figure 4. Citation impact and co-citation analysis of highly influential GLIM-related references. (A) Annual GCS of the top-cited references. Bubble size and color reflect GCS values, with larger and redder circles indicating higher global citation impact. (B) Reference co-citation network generated from 729 GLIM-related publications. A minimum co-citation threshold of 40 was applied, resulting in the inclusion of 63 references. Node size represents co-citation frequency, node color indicates cluster grouping, and line thickness reflects co-citation strength. GCS (Global Citation Score): Total citation count extracted from Scopus database.
Based on the reference co-citation network (Figure 4B), key publications in the GLIM field and their interrelationships were identified. The visualization highlights clusters of frequently co-cited studies, reflecting thematic connections and intellectual structure within the research landscape.
Overall, Figure 4A reveals distinct citation trajectories among highly cited GLIM-related publications, with the 2019 consensus report by Cederholm et al. standing out as the most influential. Meanwhile, several other core papers have continued to attract attention.
3.9 Research hotspot analysis
Beyond the pre-defined search terms, author keyword clustering was conducted on 729 publications using VOSviewer and CiteSpace. As shown in Figure 5A, five major clusters were identified: Cluster 1 (purple) focuses on the standardized GLIM assessment system and nutritional screening tools; Cluster 2 (green) relates to muscle health and rehabilitation interventions; Cluster 3 (red) highlights the nutritional risk characteristics of elderly and chronically ill patients; Cluster 4 (blue) emphasizes nutritional diagnosis and inflammatory biomarkers in older populations; and Cluster 5 (yellow) centers on prognosis and clinical outcomes in cancer patients. High-frequency keywords such as “diagnosis,” “inflammation,” and “survival” suggest that current research is concentrated on the clinical translation of the GLIM framework and the interactions between malnutrition, inflammation, and disease progression.
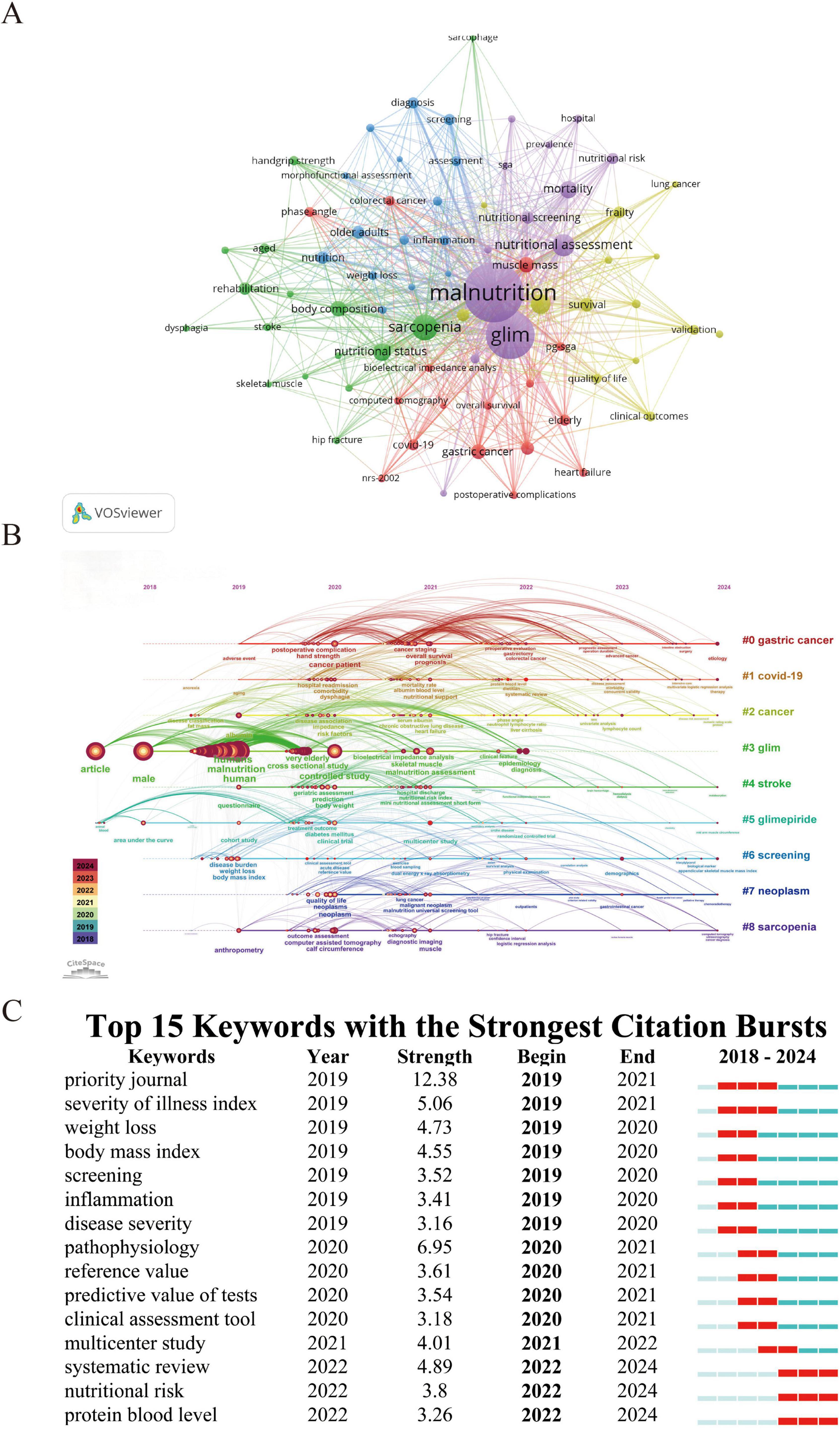
Figure 5. Keyword mapping and research trends related to GLIM. (A) Co-occurrence network of 74 keywords that appeared more than six times, grouped into five clusters and visualized in different colors: Red, yellow, blue, green, and purple. Node size reflects keyword frequency. (B) Timeline view of keyword clustering analysis, showing the temporal distribution and evolution of research themes across the period 2018–2024. (C) Top 15 keywords with the strongest citation bursts. The “Begin” and “End” years indicate the time period during which each keyword had high citation intensity. Light green indicates years before the keyword emerged, dark green indicates periods of low influence, and red indicates years of high citation burst intensity.
As illustrated in Figure 5B, keywords like “malnutrition,” “screening,” “diagnosis,” and “bioelectrical impedance analysis” have remained central themes in GLIM-related research over time. Meanwhile, Figure 5C reveals that in the past 2 y, emerging hotspots include “systematic review,” “nutritional risk,” “protein blood level,” and “multicenter study,” indicating a recent shift toward evidence synthesis, personalized nutritional assessment, and clinical validation within the GLIM research landscape.
4 Discussion
4.1 Global publication trends and regional differences
This study represents the first systematic bibliometric analysis of research related to the GLIM framework. Using data retrieved from the Scopus database, combined with visualization tools such as VOSviewer and CiteSpace, we systematically mapped and analyzed research trends and thematic hotspots in the GLIM literature. A total of 729 publications, including original articles and reviews published between 2018 and 2024, were identified. Although annual publication counts have shown some fluctuations in recent years, the polynomial regression model demonstrated a steadily increasing trend, with a notable surge in research activity observed after 2020. This growth pattern suggests that GLIM has attracted increasing scholarly attention.
As shown in Figure 2A, the global distribution of GLIM-related publications from 2018 to 2024 reveals that China ranked first with 191 articles (26.20%), followed by Spain (93 articles, 12.76%) and Japan (92 articles, 12.62%). However, despite China’s leading position in Np, countries such as Sweden and the United States demonstrated greater influence in terms of Nc and H-index when considering national, institutional, and author-level metrics. For example, Uppsala University in Sweden ranked first among institutions, with an Nc of 4,024 and an H-index of 19, far surpassing Chinese institutions such as Capital Medical University (Nc = 1,003; H-index = 17). At the author level, Cederholm, T., also from Sweden, led with 3,937 citations and an H-index of 18. In contrast, although Chinese scholars occupied five of the top ten positions in terms of Np, their average Nc values were substantially lower. For instance, Shi, H. had 422 citations, significantly fewer than his European and American counterparts. This disparity may reflect differences in research focus: The Swedish team, including Cederholm et al., concentrated on the theoretical development and international consensus of the GLIM framework (e.g., the 2019 consensus report with 2,807 citations), while many Chinese studies emphasized regional clinical data analyses. To enhance global academic influence, Chinese researchers are encouraged to strengthen international collaboration, improve theoretical innovation, and publish in high-impact journals. Although Spain demonstrated a relatively high H-index (22), its Nc (1,790) remained substantially lower than countries with similar Np, suggesting a need to further enhance the quality and impact of its research output.
4.2 Institutional and author-level contributions
Among the top 10 contributing institutions, six are based in China, highlighting the country’s strong academic presence in this field. The institution with the highest publication volume is Capital Medical University (36 publications, 1,003 citations), followed by Uppsala University in Sweden (35 publications, 4,024 citations) and Beijing Shijitan Hospital in China (33 publications, 979 citations). Regarding author contributions, the top three most productive scholars are Cederholm, T. (Sweden; 30 publications, 3,937 citations), Shi, H. (China; 22 publications, 422 citations), and Correia, M.I.T.D. (Brazil; 19 publications, 3,667 citations). These researchers have demonstrated both high productivity and academic influence, underscoring their leadership roles in the field. Greater attention should be paid to their work, as it often reflects the forefront of GLIM research and can guide future investigations. Notably, a highly valuable collaborative network has formed among these core scholars. Collaborative studies between Cederholm and Correia (2019–2020) laid the theoretical foundation for the GLIM criteria. Their 2019 consensus report was the first to systematically propose the diagnostic standards for GLIM, aiming to standardize the definition, assessment process, and diagnostic framework of malnutrition (9). This landmark paper, endorsed by the global clinical nutrition community, provides unified diagnostic criteria applicable across various healthcare settings and serves as a foundation for future clinical research and guideline development. The 2020 follow-up study established operational standards for validating the GLIM criteria. It proposed a hybrid validation strategy combining retrospective cohort analyses and prospective clinical studies and incorporated machine learning techniques to optimize threshold selection, ensuring the diagnostic criteria’s applicability and reliability across populations and clinical scenarios (28). In 2021, a collaboration between Cederholm and Shi promoted the clinical translation of GLIM in oncology nutrition. Three pivotal studies collectively demonstrated the multidimensional utility of GLIM: First, a study in older adult cancer patients (n = 1,192) showed that GLIM-defined malnutrition independently predicted mortality risk (HR = 1.71), and a nomogram integrating clinical variables achieved accurate prognostic stratification (C-index = 0.82) (29). Second, the development of the Scored-GLIM system (n = 3,547) quantified the prognostic weight of core indicators such as involuntary weight loss (HR = 1.82), significantly improving 1-year survival prediction (C-index = 0.62) and demonstrating superior net clinical benefit compared to traditional GLIM assessments (30). Third, a multicenter cohort study involving 3,777 patients confirmed the moderate diagnostic agreement between GLIM and the sPG-SGA (κ = 0.54), with sensitivity and specificity of 70.5 and 88.3%, respectively, supporting GLIM as a valid and efficient alternative to the sPG-SGA (31). These findings provide robust evidence for standardized GLIM application in oncology settings. Further collaboration among Cederholm, Shi, and Correia addressed key methodological challenges in GLIM implementation. A 2022 guideline paper systematically defined muscle mass assessment methods, recommending imaging techniques (e.g., DXA, CT) as the preferred options while also offering anthropometry-based alternatives for resource-limited settings (32). In 2024, a new consensus based on the modified Delphi approach achieved a high level of expert agreement and introduced a composite diagnostic framework that integrates clinical evaluation, laboratory testing, and underlying disease analysis to enhance the global applicability of GLIM criteria (33). These methodological advances have laid a strong foundation for the standardized implementation of GLIM across diverse healthcare settings.
4.3 Journal distribution and dissemination pathways
It is noteworthy that eight of the top 10 most productive journals in GLIM-related research have relatively high impact factors (IFs). Journals such as Nutrients, Clinical Nutrition, Frontiers in Nutrition, and the Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (JPEN) have made significant contributions to the field. This phenomenon may be partly attributed to the relatively high IFs of these journals, which enhance their academic appeal. More importantly, their research scopes are highly aligned with the scientific focus of the GLIM criteria, particularly in areas such as clinical nutrition, metabolic disorders, geriatrics, and dietary interventions. This alignment increases the relevance and visibility of GLIM-related studies within these journals, making them preferred publication venues for researchers in the field. To elaborate, Nutrients is an open-access journal that covers a broad range of topics in nutritional science, including basic and applied nutrition, dietary patterns, metabolic health, and chronic disease prevention. It is dedicated to promoting the role of dietary interventions in disease management. Clinical Nutrition, the official journal of the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN), focuses on the latest advances in clinical nutrition, especially in the areas of malnutrition, metabolic disorders, and nutritional support strategies, and has played a central role in the development and dissemination of the GLIM criteria. Frontiers in Nutrition mainly publishes high-quality research in food science, dietary patterns, nutritional metabolism, and health promotion, emphasizing the integration of basic research and clinical application. JPEN, a leading journal in the field of parenteral and enteral nutrition, concentrates on clinical nutrition therapies, nutrition support techniques, and their application in disease management. It holds substantial influence in the safety and efficacy assessment of nutritional support strategies. Collectively, the strong alignment between these journals’ scopes and the core themes of GLIM research, along with their academic visibility and relatively efficient peer-review process, has contributed to their status as preferred publication venues for GLIM-related studies.
Among the top 10 most cited articles, the study by Cederholm T. recorded the highest GCS in 2024 (727). This landmark publication introduced the GLIM diagnostic framework, which has since become the most cited reference in the field. The study established standardized criteria for the identification, assessment, and stratification of malnutrition across global clinical settings, effectively addressing the long-standing gap in unified nutritional care guidelines (9). Subsequent research has further validated and expanded the application of the GLIM criteria. Norman et al. provided a comprehensive review of malnutrition in older adults, detailing its multifactorial etiology—including age-related physiological changes, comorbidities, and chronic inflammationon of the GLIM criteria. Norman et al. provided a comprehensive revie (34). Barazzoni et al. contributed significant methodological advancements through a consensus guideline, proposing standardized approaches for muscle mass assessment using DXA, CT, and BIA, while offering anthropometric alternatives for low-resource environments (35). Through the Global Leadership Initiative on Sarcopenia (GLIS), Sayer et al. refined the diagnostic model of sarcopenia, highlighting the importance of muscle functione functionGLIS), Sayer et al. reometric alternativeto GLIM-related frameworks (36). Zhang et al. confirmed the clinical utility of the GLIM criteria in elderly cancer patients, demonstrating its value in diagnosing malnutrition and predicting survival outcomes. They also developed a nomogram based on GLIM indicators with strong prognostic performance (29). Beaudart et al., analyzing 4-y data from the SarcoPhAge cohort, revealed a significant association between malnutrition and the incidence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia, underscoring the need for early nutritional intervention (37). In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, Bedock et al. found a malnutrition prevalence of 42.1% among hospitalized patients and identified hypoalbuminemia as a predictor of ICU admission, reinforcing the clinical necessity of nutritional screening (38). De van der Schueren et al. systematically evaluated the feasibility and validation strategies of the GLIM criteria, advocating for consensus-based diagnostic frameworks and recommending the use of large-scale datasets and machine learning to improve reliability and adaptability across populations (28). Contreras-Bolontrerass populations adaparning mmending the use of largealidation strategies 6-month mortality in hospitalized cancer patients, reinforcing the role of functional assessment in malnutrition diagnosis (39). Lastly, De Groot et al. compared the performance of the PG-SGA SF and GLIM criteria in ambulatory cancer care, showing that PG-SGA SF had higher sensitivity and specificity, while GLIM effectively predicted 1-year mortality, although the addition of HGS did not significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy (40).
4.4 Thematic evolution and emerging research frontiers
Keyword clustering analysis reveals that GLIM-related research primarily revolves around five thematic clusters, reflecting the key research focuses and developmental trends in the field. The purple cluster includes keywords such as malnutrition, GLIM, nutritional assessment, mortality, and nutritional screening, emphasizing the application of the GLIM criteria in clinical malnutrition evaluation and screening. The green cluster features sarcopenia, body composition, nutritional status, and rehabilitation, underscoring the relevance of GLIM in sarcopenia research and body composition analysis. The red cluster, represented by terms like PG-SGA, elderly, gastric cancer, COVID-19, and heart failure, reflects the widespread use of GLIM in assessing nutritional risk among older adults and patients with chronic or acute illnesses. The blue cluster centers on nutrition, older adults, diagnosis, inflammation, and screening, highlighting the value of GLIM in geriatric nutrition assessment, inflammation-related studies, epidemiological research, and disease screening. The yellow cluster includes cancer, survival, frailty, validation, clinical outcomes, and quality of life, indicating a growing focus on prognosis, outcome optimization, and frailty assessment in cancer populations. CiteSpaceil timeline analysis further reveals the dynamic evolution of research topics within the GLIM domain. Between 2018 and 2024, keywords such as malnutrition, sarcopenia, and screening appeared consistently across multiple time periods, suggesting that these themes have remained long-standing focal points of GLIM research. Since 2022, however, the research focus has shifted noticeably toward clinical validation and personalized nutritional assessment. Burst keyword analysis shows that from 2019 to 2021, GLIM research primarily focused on weight loss, body mass index (BMI), and screening, highlighting efforts to define malnutrition and establish diagnostic standards. In contrast, between 2022 and 2024, systematic review (burst strength: 4.89) and multicenter study (burst strength: 4.01) emerged as major hotspots, indicating a transition toward evidence synthesis and clinical validation. Moreover, nutritional risk and protein blood level have become newly emerging burst keywords, suggesting that biomarker detection and precision nutritional assessment may be key directions for future research. Looking ahead, GLIM research is expected to continue evolving toward precision nutritional interventions, incorporating biomarker profiling, genomics, and machine learning to enhance individualized diagnosis and nutrition management strategies. In parallel, strengthening multicenter clinical validation will be critical to improving the applicability and reliability of the GLIM criteria across diverse populations.
Based on the keyword timeline and burst analysis, we identified three representative research themesnd burst analysis, we identified a across diverse populations.al validatnered increasing attention and demonstrated a rising trend over the past 2 years. The following sections provide an in-depth discussion of these emerging hotspots to further elucidate the developmental trajectory and potential directions of current research frontiers.
4.4.1 Gastric cancer
Gastric cancer is a globally prevalent malignancy with poor prognosis, and malnutrition is common among patients, with reported prevalence ranging from 19 to 70.6% (41). Malnutrition in this population is closely associated with postoperative complications, reduced survival rates, and impaired quality of life. In recent years, GLIM has gained increasing attention in the nutritional management of gastric cancer due to its standardized diagnostic approach. Clinical studies have shown that severe malnutrition, as defined by GLIM, is an independent risk factor for postoperative complications (Clavien-Dindo grade ≥ II, OR: 1.339lications (Claviendent risk facshown that severe) (42). However, the prognostic implications of moderate malnutrition remain inconsistent, with some studies reporting a significant reduction in OS, while others failed to confirm such associations (43). Several studies conducted in China have highlighted diagnostic discrepancies between GLIM and PG-SGA. PG-SGA is widely regarded as the s widely regarded cted in China have higent. A study by Qin et al. (44) reported malnutrition prevalence rates of 65% using GLIM and 74.2% using PG-SGA, suggesting that GLIM may underestimate the risk of sarcopenia. Similarly, studies by Xu et al. (45) and Zheng et al. (46) reported moderate agreement between the two tools (Cohen’s κ = 0.483–0.548). Zheng et al. (46) further demonstrated that malnutrition prevalence based on GLIM was 68.81%, compared to 76.76% with PG-SGA. Moreover, PG-SGA exhibited superior sensitivity and specificity in identifying malnutrition. Recent research efforts have focused on optimizing the clinical applicability of GLIM in gastric cancer patients. Various studies have validated the consistency between muscle mass assessment tools, such as CT and HGS, in the diagnosis of malnutrition. For example, Huang et al. reported a high agreement between HGS-based GLIM classification and CT-derived SMI, with a Cohen and CT malnutrition. For example, Huang et aHGS as a reliable alternative in resource-limited settings (47). Zhou et al. also confirmed the feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of using HGS for muscle mass assessment within the GLIM framework (48). Additionally, combining VAT evaluation with GLIM has been shown to enhance predictive accuracy. Zhang et al. found that incorporating low VAT improved the AUC from 0.78 to 0.83 in predicting postoperative adverse outcomes and long-term survival, suggesting that VAT assessment adds prognostic value (49). Beyond conventional tools, AI, particularly deep learning models based on CT imaging, has been introduced for early detection of malnutrition. These models, which integrate clinical data such as BMI and lymphocyte counts, demonstrated high accuracy (AUC = 0.857) and offer promising potential for personalized nutritional intervention (50). Despite the clinical potential of GLIM in gastric cancer, several challenges hinder its broader implementation. First, differences in muscle mass thresholds between East Asian and Western populations (e.g., SMI < 40.8 cm2/m2 in East Asian men vs. < 52.4 cm2/m2 in Western men) may lead to diagnostic bias, underscoring the need for population-specific adaptations (41). Second, dynamic postoperative nutritional monitoring (e.g., phase angle and continuous glucose monitoring) has revealed significant associations between nocturnal hypoglycemia (TBR > 20%) and severe malnutrition defined by GLIM. In one study, the incidence of nocturnal hypoglycemia was notably higher in severely malnourished patients compared to those with normal or moderate nutritional status (TBR: 41.1 vs. 30.6%, P = 0.034). However, such biomarkers have not yet been incorporated into the current GLIM framework (51). To further advance the application of GLIM in gastric cancer nutrition management, future studies should move beyond traditional assessment methods by integrating real-time monitoring, multi-source data, and AI technologies. These efforts must also account for population-specific characteristics and practical implementation feasibility, with the ultimate goal of enabling more precise and personalized nutritional interventions.
4.4.2 Protein blood level
Protein blood levels serve as important biomarkers for assessing malnutrition and inflammatory status, and occupy a critical role in the GLIM framework. They are widely used in clinical practice to evaluate nutritional status and predict disease prognosis. Among them, serum albumin and pre-albumin are the most frequently tested indicators. Low levels of these proteins not only suggest malnutrition but are also closely associated with various adverse clinical outcomes. In hospitalized cancer patients, Contreras-Bolncer patients, Contrerasteins not only suggest malnutrition but are also closely asso-defined malnutrition and independently predicted 6-month mortality (OR = 2.72, p = 0.004) (39). Pre-albumin, as a more sensitive marker of short-term nutritional changes, has been shown to correlate with decreased muscle mass and functional decline. In patients with systemic sclerosis, low pre-albumin levels were often accompanied by reduced handgrip strength and fat-free mass, highlighting its potential utility in muscle function assessment (52).
However, in inflammatory states, reliance on serum proteins—especially albumin and prealbumin—for nutritional assessment is problematic. As negative acute-phase reactants, their hepatic synthesis is downregulated and capillary permeability increases under systemic inflammation, leading to reduced serum levels that do not reflect actual nutritional status (7). Although they often correlate with adverse clinical outcomes, such associations mainly indicate disease severity and inflammatory burden rather than true nutritional reserves. Accordingly, GLIM no longer includes serum proteins as diagnostic criteria due to their limited specificity and sensitivity (53). Supporting this concern, a recent study found that nearly 23% of patients identified as malnourished still had normal pre-operative albumin concentrations (54).
Several studies have explored multidimensional models that integrate protein biomarkers with other nutritional and inflammatory indicators to improve clinical utility. Olpe et al. reported that while albumin alone had modest prognostic value (AUC = 0.62), combining it with muscle mass and function parameters in a multidimensional model improved prediction accuracy (AUC = 0.71) (55). The integration of serum proteins with inflammatory markers also shows significant clinical promise. Pourhassan et al. suggested that C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥ 3.0 mg/dL could serve as a risk threshold for inflammation-associated malnutrition, strongly linked to recent reductions in food intake (OR = 1.61) (56). Shi et al. further demonstrated a positive correlation between serum GDF15 and CRP (r = 0.318, p < 0.001). When elevated GDF15 was combined with low albumin (< 36.15 g/L), the model’s predictive accuracy for malnutrition significantly improved (AUC = 0.935), outperforming single indicators (57). In prognostic evaluation, protein biomarkers also play a pivotal role. Liu et al. developed a nomogram based on GLIM to predict postoperative complications and confirmed that low albumin was an independent risk factor following cardiac surgery (OR = 1.66, AUC = 0.72) (58). In lung cancer patients, Yin et al. found that combining low albumin (< 35 g/L) with decreased muscle mass effectively distinguished prognostic subgroups, with a median survival gap of up to 9 months (P < 0.001), supporting its use in personalized nutrition-prognosis models (59).
In conclusion, protein blood levels not only aid in diagnosing malnutrition within the GLIM framework but also serve as valuable tools for assessing inflammation, prognosis, and response to nutritional interventions. Future research should aim to standardize measurement methods and explore the combined use of emerging biomarkers such as GDF15, thereby enhancing the precision and clinical utility of GLIM.
4.4.3 Nutritional risk
In the diagnostic process outlined by GLIM, the first and most important step is to screen patients for nutritional risk. This step helps identify people who may need further evaluation to confirm if they are malnourished. However, in real clinical settings, the tools used for screening are quite varied, and their accuracy can differ depending on the population. This makes it hard to apply the GLIM process in a consistent and standardized way. A review by Correia et al. showed that only 57% of studies actually followed GLIMhowed that onlytwo-step approachctually follirst, then diagnosis—suggesting that many real-world applications still fall short (60). Similarly, research by MacDonell et al. found that in a diverse elderly population in New Zealand, the SCREEN-II tool predicted 5-year death rates better than the GLIM criteria for Māori individuals. This highlights the need to tailor screening tools to specific ethnic groups and local populations (61). Once the importance and challenges of identifying nutritional risk became clear, researchers started paying more attention to which screening tools work best in different situations. For example, in a large study, Tan et al. found that using GLIM together with the MNA-SF tool gave the most accurate predictions of infection and wound problems after abdominal cancer surgery (62). However, Kutnik et al. noted that although about 20% of elective surgery patients were found to be at nutritional risk, very few of them actually received any nutritional treatment, pointing to a gap between identifying risk and taking action (63). To make screening more accurate and practical, some studies have looked at objective physical indicators. For instance, Fu et al. found that measuring calf circumference is a useful and easy way to estimate muscle loss in Asian patients with gastric cancer (64). Another study by Muñoz-Redondo et al. showed that patients with a phase angle (PhA) of ≤ 4.85 had a much higher chance of being malnourished (odds ratio = 3.53), suggesting that PhA could be a helpful clinical tool for identifying those at risk (65). In addition to being a first step in diagnosis, nutritional risk screening is now also used to help plan treatment strategies. In a follow-up analysis of the EFFORT trial, Kaegi-Braun et al. found that hospitalized patients who were both GLIM-positive and at nutritional risk showed clear improvement when they received personalized nutrition support (odds ratio = 0.69). However, patients who were not at risk didnwedseem to benefit, showing that risk screening can help doctors decide who is most likely to benefit from treatment (66). To make screening even more efficient, researchers have started using artificial intelligence (AI). Wu et al. created machine learning models for patients with colorectal cancer, which could accurately detect GLIM-defined malnutrition even without knowing the patient’s weight loss. Their random forest model had a strong predictive performance (AUC = 0.83), and they also developed an online prediction tool. This shows that AI can help improve how we identify patients at risk, even when clinical data is incomplete, making the GLIM process more useful and accurate in real-world settings (67).
Overall, the emergence of gastric cancer, protein blood biomarkers, and nutritional risk as leading research hotspots underscores a critical transition in GLIM-related studiescfrom establishing diagnostic criteria toward optimizing their clinical applicability and predictive utility. Despite significant progress, challenges remain in achieving diagnostic consistency across populations, integrating objective biomarkers into routine practice, and tailoring nutritional assessment tools to diverse clinical contexts. Future research should prioritize refining GLIM-based models through multicenter validation, biomarker standardization, and deeper investigation into the mechanistic links between malnutrition and disease progression. Such efforts will not only enhance the diagnostic precision of the GLIM framework but also support its broader adoption in global nutritional care systems.
4.5 Strengths and limitations of the study
This study has several notable strengths. First, it represents the first systematic bibliometric analysis of GLIM-related research, addressing a gap in the quantitative assessment of this field. The findings provide comprehensive and visualized insights for researchers interested in the evolution of malnutrition diagnostic standards. Second, we employed three mainstream bibliometric toolslVOSviewer, CiteSpace, and the Bioinformatics online platform. VOSviewer and CiteSpace are well-established tools in medical bibliometric research and greatly enhance the scientific rigor and objectivity of our analysis. Third, compared with traditional narrative reviews, bibliometric analysis allows for a more systematic and traceable exploration of research hotspots and frontier trends in GLIM research, while also identifying key authors, institutions, and highly influential publications. However, this study also has some limitations. First, all data were extracted solely from the Scopus database, and studies from other databases may have been missed. Second, only English-language publications were included, which may underestimate the contribution of non-English research.
5 Conclusion
This study conducted a systematic bibliometric analysis of research on the GLIM criteria from 2018 to 2024. The findings show that since the introduction of the GLIM standard, related research has developed rapidly, with the number of publications increasing steadily and accelerating notably after 2020—reflecting growing academic interest in this field. China and Sweden emerged as leading contributors, with China taking the lead in publication volume, while Sweden demonstrated strong performance in highly cited papers and research impact. Despite the overall research activity, international institutional collaboration remains an area for improvement. Clinical Nutrition and Nutrients were identified as the most influential journals in this domain, leading in both publication output and academic dissemination. In addition, this study used keyword co-occurrence and burst analysis to uncover research hotspots and their evolution, offering valuable insights and directions for future investigations in the GLIM field.
Data availability statement
The dataset analyzed in this study was retrieved from the Scopus database (https://www.scopus.com/) using institutional access. Due to licensing restrictions, the raw dataset cannot be made publicly available in its entirety. However, the original bibliographic data file (in.csv format) used for VOSviewer and CiteSpace analysis has been provided as Supplementary material. Additional information is available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Author contributions
QX: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis. QL: Visualization, Data curation, Validation, Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis. YY: Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Data curation, Validation. YH: Writing – review and editing, Data curation, Methodology, Validation. ST: Formal Analysis, Software, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. XL: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. XC: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2023JJA141291), the Guangxi Pharmaceutical Society (No. GXYXH-202205), and the Wu Jieping Medical Foundation (No. 320.6750.2024-25-8).
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all authors and study participants for their support in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1613395/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1. Felder S, Lechtenboehmer C, Bally M, Fehr R, Deiss M, Faessler L, et al. Association of nutritional risk and adverse medical outcomes across different medical inpatient populations. Nutrition. (2015) 31:1385–93. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.06.007
2. Goates S, Du K, Braunschweig C, Arensberg M. Economic burden of disease-associated malnutrition at the state level. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0161833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161833
3. Lanctin D, Merced-Nieves F, Mallett RM, Arensberg MB, Guenter P, Sulo S, et al. Prevalence and economic burden of malnutrition diagnosis among patients presenting to United States emergency departments. Acad Emerg Med. (2021) 28:325–35. doi: 10.1111/acem.13887
4. Norman K, Pichard C, Lochs H, Pirlich M. Prognostic impact of disease-related malnutrition. Clin Nutr. (2008) 27:5–15. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2007.10.007
5. White JV, Guenter P, Jensen G, Malone A, Schofield M Academy Malnutrition Work Group, et al. Consensus statement: Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: Characteristics recommended for the identification and documentation of adult malnutrition (undernutrition). J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2012) 36:275–83. doi: 10.1177/0148607112440285
6. Jensen G, Hsiao P, Wheeler D. Adult nutrition assessment tutorial. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2012) 36:267–74. doi: 10.1177/0148607112440284
7. Evans DC, Corkins MR, Malone A, Miller S, Mogensen KM, Guenter P, et al. The use of visceral proteins as nutrition markers: An ASPEN position paper. Nutr Clin Pract. (2021) 36:22–8. doi: 10.1002/ncp.10588
8. Cederholm T, Bosaeus I, Barazzoni R, Bauer J, Van Gossum A, Klek S, et al. Diagnostic criteria for malnutrition – An ESPEN consensus statement. Clin Nutr. (2015) 34:335–40. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2015.03.001
9. Cederholm T, Jensen G, Correia M, Gonzalez M, Fukushima R, Higashiguchi T, et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition – A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin Nutr. (2019) 38:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.002
10. Wang B, Xing D, Zhu Y, Dong S, Zhao B. The state of exosomes research: A global visualized analysis. BioMed Res Int. (2019) 2019:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2019/1495130
11. Lu C, Liu M, Shang W, Yuan Y, Li M, Deng X, et al. Knowledge mapping of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (Danggui) research: A scientometric study. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:294. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00294
12. Synnestvedt MB, Chen C, Holmes JH. CiteSpace II: visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. (2005) 2005:724–8.
13. Yeung A, Tzvetkov N, Balacheva A, Georgieva M, Gan R, Jozwik A, et al. Lignans: Quantitative analysis of the research literature. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:37. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00037
14. Li C, Ojeda-Thies C, Renz N, Margaryan D, Perka C, Trampuz A. The global state of clinical research and trends in periprosthetic joint infection: A bibliometric analysis. Int J Infect Dis. (2020) 96:696–709. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.014
15. Shi S, Gao Y, Liu M, Bu Y, Wu J, Tian J, et al. Top 100 most-cited articles on exosomes in the field of cancer: A bibliometric analysis and evidence mapping. Clin Exp Med. (2021) 21:181–94. doi: 10.1007/s10238-020-00624-5
16. Teles R, Yano R, Villarinho N, Yamagata A, Jaeger R, Meybohm P, et al. Advances in breast cancer management and extracellular vesicle research, a bibliometric analysis. Curr Oncol. (2021) 28:4504–20. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28060382
17. Wu H, Cheng K, Tong L, Wang Y, Yang W, Sun Z. Knowledge structure and emerging trends on osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A bibliometric and visualized study. J Orthop Surg Res. (2022) 17:194. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03068-7
18. Oo S, Fan K, Khare Y, Fan K, Chan J, Lam C, et al. Top 100 cited manuscripts in aortic valve replacement: A bibliometric analysis. J Cardiac Surg. (2020) 35:2943–9. doi: 10.1111/jocs.14941
19. Wu H, Cheng K, Guo Q, Yang W, Tong L, Wang Y, et al. Mapping knowledge structure and themes trends of osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis: A bibliometric analysis. Front Med. (2021) 8:787228. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.787228
20. Wang S, Zhou H, Zheng L, Zhu W, Zhu L, Feng D, et al. Global trends in research of macrophages associated with acute lung injury over past 10 years: A bibliometric analysis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:669539. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.669539
21. Noruzi A, Gholampour B, Gholampour S, Jafari S, Farshid R, Stanek A, et al. Current and future perspectives on the COVID-19 vaccine: A scientometric review. JCM. (2022) 11:750. doi: 10.3390/jcm11030750
22. Roldan-Valadez E, Salazar-Ruiz S, Ibarra-Contreras R, Rios C. Current concepts on bibliometrics: A brief review about impact factor, Eigenfactor score, CiteScore, SCImago journal rank, source-normalised impact per Paper, H-index, and alternative metrics. Ir J Med Sci. (2019) 188:939–51. doi: 10.1007/s11845-018-1936-5
23. Khazaneha M, Osareh F, Shafiee K. Trend linking of multiple system atrophy: A scientometric study. EMIDDT. (2021) 21:700–10. doi: 10.2174/1871530320666200607194810
24. Van Eck N, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. (2010) 84:523–38. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
25. Liu T, Yang L, Mao H, Ma F, Wang Y, Zhan Y. Knowledge domain and emerging trends in podocyte injury research from 1994 to 2021: A bibliometric and visualized analysis. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:772386. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.772386
26. Deng P, Shi H, Pan X, Liang H, Wang S, Wu J, et al. Worldwide research trends on diabetic foot ulcers (2004–2020): Suggestions for researchers. J Diabetes Res. (2022) 2022:1–14. doi: 10.1155/2022/7991031
27. Tang D, Chen M, Huang X, Zhang G, Zeng L, Zhang G, et al. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0294236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294236
28. De Van Der Schueren MAE, Keller H, Cederholm T, Barazzoni R, Compher C, Correia MITD, et al. Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM): Guidance on validation of the operational criteria for the diagnosis of protein-energy malnutrition in adults. Clin Nutr. (2020) 39:2872–80. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.12.022
29. Zhang X, Tang M, Zhang Q, Zhang K, Guo Z, Xu H, et al. The GLIM criteria as an effective tool for nutrition assessment and survival prediction in older adult cancer patients. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:1224–32. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.08.004
30. Zhang Q, Zhang K, Zhang X, Tang M, Song C, Cong M, et al. Scored-GLIM as an effective tool to assess nutrition status and predict survival in patients with cancer. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:4225–33. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.01.033
31. Zhang K, Tang M, Fu Z, Zhang Q, Zhang X, Guo Z, et al. Global leadership initiative on malnutrition criteria as a nutrition assessment tool for patients with cancer. Nutrition. (2021) 91–92:111379. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111379
32. Compher C, Cederholm T, Correia M, Gonzalez M, Higashiguch T, Shi H, et al. Guidance for assessment of the muscle mass phenotypic criterion for the global leadership initiative on malnutrition diagnosis of malnutrition. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2022) 46:1232–42. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2366
33. Jensen G, Cederholm T, Ballesteros-Pomar MD, Blaauw R, Correia MITD, Cuerda C, et al. Guidance for assessment of the inflammation etiologic criterion for the GLIM diagnosis of malnutrition: A modified Delphi approach. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2024) 48:145–54. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2590
34. Norman K, Haß U, Pirlich M. Malnutrition in older adults—Recent advances and remaining challenges. Nutrients. (2021) 13:2764. doi: 10.3390/nu13082764
35. Barazzoni R, Jensen G, Correia M, Gonzalez M, Higashiguchi T, Shi H, et al. Guidance for assessment of the muscle mass phenotypic criterion for the Global leadership initiative on malnutrition (GLIM) diagnosis of malnutrition. Clin Nutr. (2022) 41:1425–33. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2022.02.001
36. Sayer A, Cruz-Jentoft A. Sarcopenia definition, diagnosis and treatment: Consensus is growing. Age Ageing. (2022) 51:afac220. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afac220
37. Beaudart C, Sanchez-Rodriguez D, Locquet M, Reginster J, Lengelé L, Bruyère O. Malnutrition as a strong predictor of the onset of sarcopenia. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2883. doi: 10.3390/nu11122883
38. Bedock D, Bel Lassen P, Mathian A, Moreau P, Couffignal J, Ciangura C, et al. Prevalence and severity of malnutrition in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2020) 40:214–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.09.018
39. Contreras-Bolívar V, Sánchez-Torralvo F, Ruiz-Vico M, González-Almendros I, Barrios M, Padín S, et al. Criteria using hand grip strength adequately predict six-month mortality in cancer inpatients. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2043. doi: 10.3390/nu11092043
40. De Groot L, Lee G, Ackerie A, Van Der Meij B. Malnutrition screening and assessment in the cancer care ambulatory setting: mortality predictability and validity of the patient-generated subjective global assessment short form (PG-SGA SF) and the GLIM criteria. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2287. doi: 10.3390/nu12082287
41. Wang J, Liu B, Chen J. Validity of the Global leadership initiative on malnutrition criteria in East Asian patients with gastric cancer: A comprehensive narrative review. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1462487. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1462487
42. Li Q, Zhang X, Tang M, Song M, Zhang Q, Zhang K, et al. Different muscle mass indices of the Global leadership initiative on malnutrition in diagnosing malnutrition and predicting survival of patients with gastric cancer. Nutrition. (2021) 89:111286. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111286
43. Matsui R, Inaki N, Tsuji T. Impact of GLIM defined malnutrition on long term prognosis in patients with gastric cancer after gastrectomy. Anticancer Res. (2022) 42:4611–8. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.15965
44. Qin L, Tian Q, Zhu W, Wu B. The validity of the GLIM criteria for malnutrition in hospitalized patients with gastric cancer. Nutr Cancer. (2021) 73:2732–9. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2020.1856894
45. Xu L, Shi M, Huang Z, Zhang W, Zhang H, Shen X, et al. Impact of malnutrition diagnosed using Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria on clinical outcomes of patients with gastric cancer. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2022) 46:385–94. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2127
46. Zheng X, Ruan X, Wang X, Zhang X, Zang Z, Wang Y, et al. Bayesian diagnostic test evaluation and true prevalence estimation of malnutrition in gastric cancer patients. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2024) 59:436–43. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.12.019
47. Huang D, Yu D, Wang W, Song H, Luo X, Wu G, et al. Global leadership initiative in malnutrition (GLIM) criteria using hand-grip strength adequately predicts postoperative complications and long-term survival in patients underwent radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2022) 76:1323–31. doi: 10.1038/s41430-022-01109-2
48. Zhou L, Yu D, Ma B, Shen Z, Zou H, Zhang X, et al. Feasibility of substituting handgrip strength for muscle mass as a constituent standard in the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition for diagnosing malnutrition in patients with gastrointestinal cancers. Nutrition. (2021) 84:111044. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.111044
49. Zhang Y, Jiang L, Su P, Yu T, Ma Z, Kang W, et al. Visceral adipose tissue assessment enhances the prognostic value of GLIM criteria in patients with gastric cancer undergoing radical gastrectomy after neoadjuvant treatment. Nutrients. (2022) 14:5047. doi: 10.3390/nu14235047
50. Huang W, Wang C, Wang Y, Yu Z, Wang S, Yang J, et al. Predicting malnutrition in gastric cancer patients using computed tomography(CT) deep learning features and clinical data. Clin Nutr. (2024) 43:881–91. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.02.005
51. Nishibeppu K, Kubota T, Yubakami M, Ohashi T, Kiuchi J, Shimizu H, et al. Impact of hypoglycemia after gastrectomy on global leader initiative on malnutrition-defined malnutrition: A retrospective study. Surg Today. (2024) 54:743–50. doi: 10.1007/s00595-024-02799-w
52. Wojteczek A, Dardzińska J, Małgorzewicz S, Gruszecka A, Zdrojewski Z. Prevalence of malnutrition in systemic sclerosis patients assessed by different diagnostic tools. Clin Rheumatol. (2020) 39:227–32. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04810-z
53. Zhou C, Ling K, Fang J, Ye M, Liu M, Chen J, et al. Prognostic value of postoperative decrease of albumin (ΔAlb) in combination with GLIM-defined malnutrition for the prediction of postoperative outcomes in rectal cancer patients with normal preoperative albumin levels. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1542581. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1542581
54. Przekop Z, Milewska M, Szostak-Węgierek D, Panczyk M, Sobocki J. GLIM-Defined malnutrition in patients with head and neck cancer during the qualification visit for home enteral nutrition. Nutrients. (2022) 14:502. doi: 10.3390/nu14030502
55. Olpe T, Wunderle C, Bargetzi L, Tribolet P, Laviano A, Stanga Z, et al. Muscle matters: Prognostic implications of malnutrition and muscle health parameters in patients with cancer. A secondary analysis of a randomised trial. Clin Nutr. (2024) 43:2255–62. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.07.020
56. Pourhassan M, Cederholm T, Trampisch U, Volkert D, Wirth R. Inflammation as a diagnostic criterion in the GLIM definition of malnutrition—what CRP-threshold relates to reduced food intake in older patients with acute disease? Eur J Clin Nutr. (2022) 76:397–400. doi: 10.1038/s41430-021-00977-4
57. Shi G, Yue L, Tang Z, Wang Y, Hu X, Tong Y. Serum growth differentiation factor 15 as a biomarker for malnutrition in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1404063. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1404063
58. Liu Z, Shen Z, Zang W, Zhou J, Yu Z, Zhang P, et al. Development and validation of global leadership initiative on malnutrition for prognostic prediction in patients who underwent cardiac surgery. Nutrients. (2022) 14:2409. doi: 10.3390/nu14122409
59. Yin L, Lin X, Li N, Zhang M, He X, Liu J, et al. Evaluation of the global leadership initiative on malnutrition criteria using different muscle mass indices for diagnosing malnutrition and predicting survival in lung cancer patients. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2021) 45:607–17. doi: 10.1002/jpen.1873
60. Correia M, Tappenden K, Malone A, Prado C, Evans D, Sauer A, et al. Utilization and validation of the Global leadership initiative on malnutrition (GLIM): A scoping review. Clin Nutr. (2022) 41:687–97. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2022.01.018
61. MacDonell S, Moyes S, Teh R, Dyall L, Kerse N, Wham C. Is the utility of the GLIM criteria used to diagnose malnutrition suitable for bicultural populations? findings from life and living in advanced age cohort study in New Zealand (LiLACS NZ). J Nutr Health Aging. (2023) 27:67–74. doi: 10.1007/s12603-022-1874-9
62. Tan S, Wang J, Zhou F, Tang M, Xu J, Zhang Y, et al. Validation of GLIM malnutrition criteria in cancer patients undergoing major abdominal surgery: A large-scale prospective study. Clin Nutr. (2022) 41:599–609. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2022.01.010
63. Kutnik P, Wichowska O, Sysiak-Sławecka J, Szczukocka M, Rypulak E, Piwowarczyk P, et al. Malnutrition risk in elective surgery patients and effectiveness of preoperative nutritional interventions at a pre-anaesthetic clinic: A 4-year apart, single-centre, observational study. Ait. (2023) 55:179–85. doi: 10.5114/ait.2023.130632
64. Fu L, Xu X, Zhang Y, Jin J, Zhu S, Shi H, et al. Agreements between GLIM using left calf circumference as criterion for reduced muscle mass and PG-SGA, and GLIM using ASMI for the diagnosis of malnutrition in gastric cancer patients. Nutr Hosp. (2024) 41:824–34. doi: 10.20960/nh.05024
65. Muñoz-Redondo E, Morgado-Pérez A, Pérez-Sáez M, Faura A, Sánchez-Rodríguez D, Tejero-Sánchez M, et al. Low phase angle values are associated with malnutrition according to the global leadership initiative on malnutrition criteria in kidney transplant candidates: preliminary assessment of diagnostic accuracy in the FRAILMar study. Nutrients. (2023) 15:1084. doi: 10.3390/nu15051084
66. Kaegi-Braun N, Boesiger F, Tribolet P, Gomes F, Kutz A, Hoess C, et al. Validation of modified GLIM criteria to predict adverse clinical outcome and response to nutritional treatment: A secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr. (2022) 41:795–804. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2022.02.009
Keywords: GLIM criteria, malnutrition, bibliometric analysis, sarcopenia, nutritional assessment, clinical application
Citation: Xu Q, Li Q, Yao Y, He Y, Tan S, Liu X and Chen X (2025) Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition: a bibliometric analysis of research trends and contributions (2018–2024). Front. Nutr. 12:1613395. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1613395
Received: 17 April 2025; Accepted: 14 June 2025;
Published: 08 July 2025.
Edited by:
Maryanne Zilli Canedo Silva, São Paulo State University, BrazilReviewed by:
Salvatore Vaccaro, IRCCS Local Health Authority of Reggio Emilia, ItalyAna Cláudia Thomaz, University of Tuiuti do Paraná, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Li, Yao, He, Tan, Liu and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoxia Liu, cDI0MTI1NzRAbXB1LmVkdS5tbw==; Xiaoyu Chen, Y3h5dGd6eUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Qimeng Xu1,2†
Qimeng Xu1,2† Yucheng Yao
Yucheng Yao Ying He
Ying He Xiaoxia Liu
Xiaoxia Liu Xiaoyu Chen
Xiaoyu Chen