- 1Laboratory of Metabolic Manipulation of Herbivorous Animal Nutrition, College of Animal Science and Technology, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 2College of Animal Science and Technology, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 3Department of Animal and Fish Production, Faculty of Agriculture (Al-Shatby), Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
- 4College of Veterinary Medicine, Albutana University, Rufaa, Sudan
- 5State Key Laboratory of Sheep Genetic Improvement and Healthy Production, Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Reclamation Sciences, Shihezi, Xinjiang, China
Investigating Moringa oleifera (M. oleifera)’ is potential as a livestock feed additive, this review explores its nutritional and phytochemical profiles and its mechanistic roles, specifically focusing on its immunomodulatory and antioxidant properties. M. oleifera is a rich source of diverse bioactive compounds, including polyphenols, alkaloids, terpenoids, flavonoids (e.g., quercetin, kaempferol), saponins, and tocopherols. These compounds exert significant immunomodulatory effects by modulating cytokine production and immune cell activity. Notably, Moringa-derived arabinogalactans (water-soluble polysaccharides comprising arabinose and galactose monomers) activate the gut-associated immune system through beneficial modulation of gut microbiota composition, increasing genera such as Muribaculaceae and Lactobacillus. The immunomodulatory activity is mediated via multiple pathways, including the promotion of anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion (e.g., IL-10) and the inhibition of pro-inflammatory enzymes [e.g., cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)]. Furthermore, M. oleifera exhibits potent antioxidant capabilities by enhancing endogenous defenses, neutralizing reactive oxygen species, and mitigating oxidative stress-induced tissue damage. These findings underscore M. oleifera is potential to enhance disease resistance and immune function in animals, advocating for its strategic incorporation into sustainable animal nutrition practices.
Introduction
The entire livestock sector is facing unprecedented threats due to rising global consumption of animal-derived products like meat, milk, and eggs. Looking at the current situation of animal global meat production, there is a 55 percent increase between 2000 and 2022, reaching a total of 361 million tons (1). A key development during this period was the rise of chicken, which accounted for the largest share of this growth and surpassed pork as the most produced meat globally in 2022. Asia, home to nearly 60% of the world’s population, is an unparalleled force in global livestock production and consumption. The sheer demographic weight and ongoing economic growth within the continent position it as the primary driver of global livestock trends (2). China stands as the world’s largest livestock-producing country, a position that grants its internal dynamics significant influence over global markets and trends. Many publications have predicted the changes by 2050 regarding livestock production and consumption. By 2050, the demand for animal products globally is estimated to increase by 60 to 70%, and developing countries will have a bulk of this increase (3). Due to population growth, urbanization, and income growth, livestock, along with their products will change rapidly by 2050. While in animal health, welfare, and food security concerns, biotechnology and nanotechnology will play a key role (4). Poultry meat demand in sub-Saharan Africa is expected to rise by 214% by 2050, and for pork, by 161%, due to the main factor- urbanization, as well as demand for animal-sourced foods (5). China’s livestock industry change has severe global implications, especially large changes and effects expected in the 2050s (6). These changes have created an alarming situation regarding food security. Climate change affects livestock production and emission of greenhouse gases, hence the need to develop appropriate technologies for sustainable production and contribute to the global food supply (7). This growth requires improvement in feed supply technologies to increase productivity efficiently and cost-effectively.
Now the major inputs in livestock feed production are the traditional crops such as maize and soybean meals, which are the energy and source of protein, respectively, in animal feed. Farm animals account for over 30% of global food consumption, primarily relying on grains, with soybeans making up 90% of that total. A minimal amount of these grains is utilized within factory farming operations (8). However, the cultivation of these crops has its economic and environmental consequences. Soybean, for example, is one of the causes of deforestation more particularly in South America, and they also significantly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions (9). Soybean trade impacts the environment and socio-economy of the world, and therefore, there is a need to find ways to increase sustainability in the trade (10). Moreover, competition drawn from feeding humans and animals using these crops continues to complicate food security issues around the world (11, 12). The development of the “maize/soybean system” has taken place and changed the structure of competition and interaction between human and animal consumption of vegetable proteins (12).
Environmental sustainability is another pressing concern. Feed production currently accounts for a significant proportion of global agricultural land use, water consumption, and nitrogen pollution. Food systems are dependent on livestock greenhouse gas emissions, which can only be tackled on a global scale while supporting food security (13). The cultivation of soybean and maize, and exclusive for the feeding of stock rations, has been linked with undesirable effects on lands and water resources, planetary nutrient imbalances (14). These environmental impacts highlight the urgent need to identify and integrate alternative feed resources.
In addition to environmental challenges, economic volatility in feed prices poses significant issues for farmers. Grain prices in particular have trended higher in 2005 and 2006, which has put pressure on livestock feed costs and has also resulted in high volatility shocks (15). High and frequently changing feed costs, as well as high and rapidly changing output prices, are challenges to livestock farmers (16).
To meet the rising demand for livestock and poultry feed, researchers have sought alternatives to its traditional ingredients, which could be novel sources of protein and energy. Following recent years, innovations like the use of agricultural byproducts, insects, microalgae, and drought-resistant plants have increased. Tree leaves, along with traditional crops like camelina and oil seeds, offer promising alternative feed resources that can either replace or complement conventional crops in ruminant diets, leading to improved animal performance in a sustainable manner (17). Moreover, the livestock sector has identified insect-based products as a viable option to support sustainable development within the industry (18). Incorporating tree leaves as a feed ingredient presents a beneficial strategy, as they typically possess higher nutritional value than grasses, making them more appealing to herbivores (19).
A versatile plant, Moringa oleifera (M. oleifera), with a lot of nutrients, can be used as an alternative feed and forage to traditional animal feed and fodder with no negative effects on health, survival, and reproduction (20). M. oleifera holds significant promise for addressing the livestock feeding crisis due to its rich nutrient content, elevated protein biological value, and positive effects on animal nutrition (8). Using M. oleifera leaves in place of sunflower seed cake for goat feed promotes dry matter consumption and improves product breakdown capabilities without losing nitrogen content (21). It contains phenolic and flavonoid compounds that have been associated with enhanced health, improved feed conversion efficiency, and better growth performance in livestock (20, 22). Due to its abundant nutrients, high protein biological value, good feeding effect, and great potential make M. oleifera is suitable mean to deal with the feeding crisis for livestock (8). The phenolics in M. oleifera leaves include a wide variety of kaempferol derivatives, caffeoylquinic acid, and feruloylquinic acid, and are responsible for their antioxidant capacity (23). Antioxidant potential in M. oleifera leaves appears very strong when combined with flavonoids, flavanols, phenolics, and proanthocyanidins elements (24). The direct radical scavenging action and indirect enhancement of cellular antioxidant defenses are expressed by antioxidant compounds in M. oleifera leaves. These substances completely remove free radicals while boosting antioxidant enzyme function, including superoxide dismutase and catalase, to lower oxidative stress levels (23, 25). Besides having antioxidant ability, M. oleifera leaves are rich in protein, minerals, vitamins, and essential amino acids (26). Analyses show M. oleifera leaves contain 28.7% crude protein alongside 7.1% fat, while the protein content exists as insoluble compounds that display poor in vitro digestibility (27). Ruminant farmers can prepare concentrated mixtures at 20% concentration, which improves goat performance while reducing methane releases (28). The introduction is explained graphically in Figure 1. Considering the importance of M. oleifera, in this review, we will give detailed nutritional composition of M. oleifera and the mechanism of action of its bioactive components as immunomodulator. Application of M. oleifera in animal feed is discussed in detail, along with challenges of M. oleifera as animal feed and future directions. This review systematically evaluates M. oleifera nutritional-phytochemical synergy and its translational potential for sustainable livestock production.
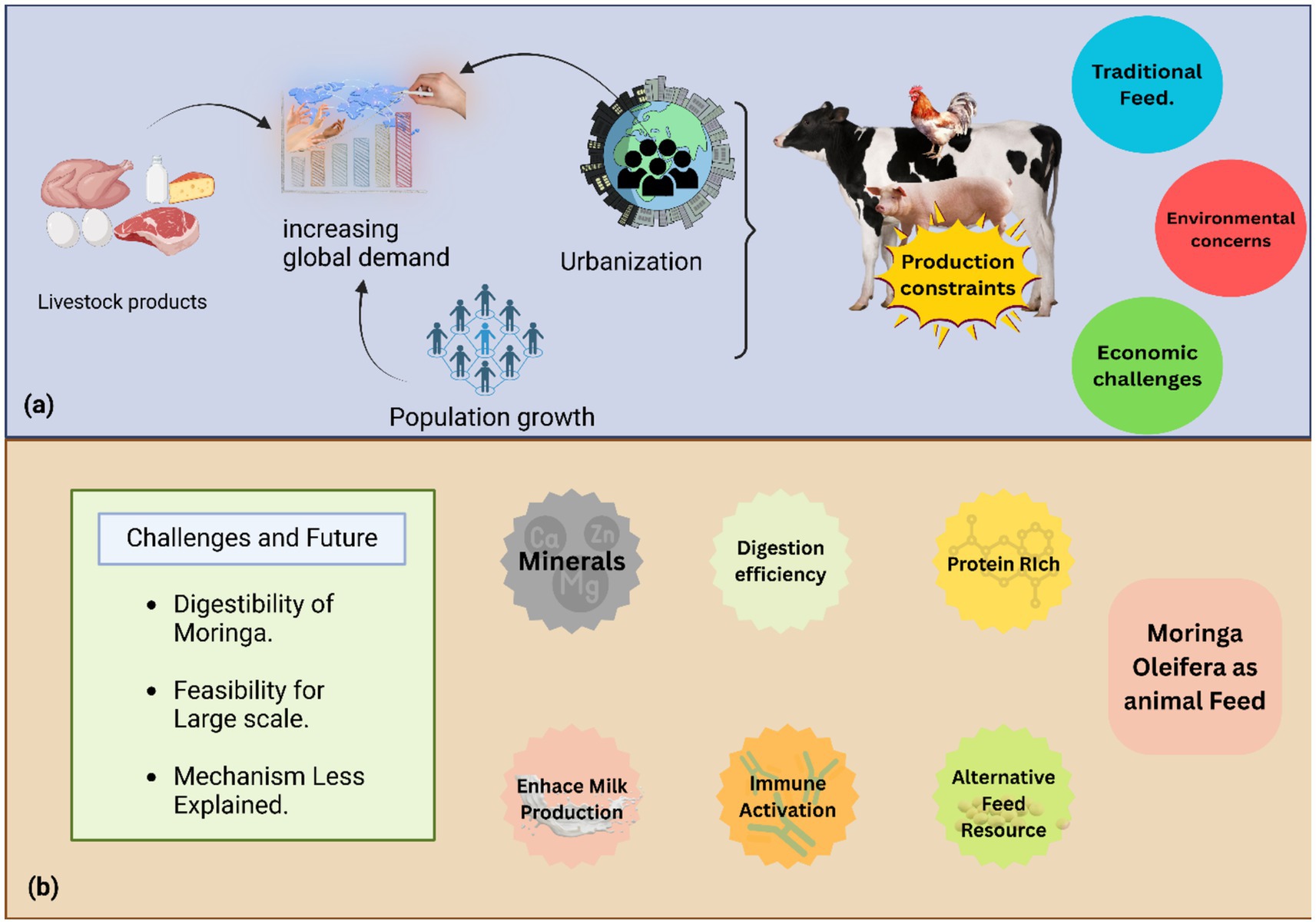
Figure 1. (a) This figure illustrates how increasing global demand for livestock products, driven by population growth and urbanization, creates operational difficulties for the worldwide livestock industry, including production constraints, reliance on traditional feed, environmental concerns from maize and soybean cultivation, and economic risks from variable feed costs. (b) This figure presents M. oleifera as a sustainable and alternative animal feed, highlighting its protein and mineral richness, and its potential to enhance digestion efficiency, activate immune responses, and increase milk production, thereby mitigating environmental damage and market fluctuations. The figure also identifies key research areas for M. oleifera ‘s effective implementation, including its digestibility, large-scale feasibility, and precise mechanisms of action.
Taxonomy, botanical characters, and cultivation
The initial description of M. oleifera was made in 1785 by the French naturalist Jean Baptiste Lamarck. The name “M. oleifera “is thought to originate from the Tamil word “murungai,” which translates to “twisted hand length structure of the young M. oleifera fruit.” In Latin, “oleum” signifies “oil,” while “ferre” means “to bear” (29). M. oleifera from the Moringaceae family represents a widely grown plant species that demonstrates significant medical characteristics as well as valuable nutritional benefits (30). Which has 13 species of different trees and shrubs, having the potential to be used for medicinal and nutritional purposes (31). All species have their native origin (Table 1).
Among these, M. oleifera stands out as the most economically important variety that grows throughout Asia and is spreading across Africa and America (31, 32). It is a widely planted tree because it possesses high nutritional value while offering prospects to fight malnutrition (33).
M. oleifera is considered to have high phytonutrient content, with the ability of drought, is used to deal with malnutrition, and also has nutraceutical properties (34). It is a perennial tree with a height range from 5 to 12 cm (35).
M. oleifera thrives in tropical and subtropical regions, especially in areas with average annual rainfall between 1,000 and 2,000 mm and high levels of solar radiation (36). It has various climatic adaptations, including temperate, subtropical, and tropical regions, which makes it suitable for the semi-arid regions as a contributor to nutritional security (37). High vigor and resistance to salinity stress are promoted more effectively when seeds of M. oleifera are pre-soaked for 24 h, making them suitable for planting in areas that are subjected to salinity (38). M. oleifera is a high-yielder in terms of biomass production. The annual biomass yield of M. oleifera is reported as 43 to 115 t/h (39). The leaf production is 1–5 kg per tree annually, which is equal to10,000–50,000 kg/h if plants are cultivated at 1 m × 1 m spacing (40). Due to its distinctive cultivation attributes, M. oleifera is currently grown in India, southern China, and certain regions of Africa (41).
Nutritional and phytochemical profile
M. oleifera is a superior nutritional source because of its extensive nutritional benefits, which make it an important supplement for livestock feed. M. oleifera demonstrates remarkable potential to solve livestock feeding problems through its supply of rich nutrients and excellent protein value, alongside positive nutritional advantages (8). Extensive research analysis has reported that M. oleifera leaves have great amounts of protein, vitamins, and amino acids, along with bioactive components that are beneficial to livestock. It offers valuable nutrient content as animal feed because it contains significant amounts of protein, along with carotenoids and minerals together with vitamins, and phytochemicals (42).
Macronutrients and minerals
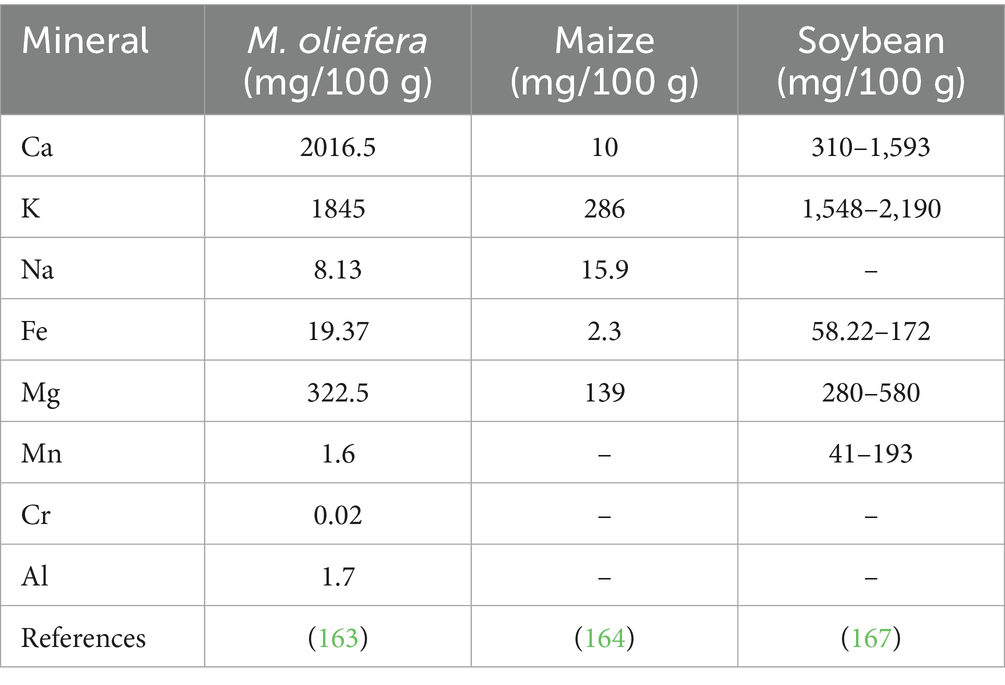
M. oleifera leaves are a rich source of essential macronutrients, providing building blocks for animal growth, development, and productivity. These macronutrients, including protein, lipids, and carbohydrates, significantly influence the overall nutritional value of M. oleifera as a feed resource. The leaves of M. oleifera contains 19.34–28.7%, providing a rich source of essential amino acids required for muscle growth and maintenance (27). Due to its high protein, M. oleifera is comparable with other conventional feed resources like maize in terms of percentage and with soybean, having a comparatively similar profile of amino acids (Table 2). The analysis of dietary fiber becomes essential for understanding plant cell wall nutritional value and its effects on animal digestive and absorption processes (43). M. oleifera leaves contain approximately 8.07% crude fiber, contributing to their overall nutritional profile (44). In general, the feed source with low fiber content is considered good due to better digestibility. Another appealing feature of M. oleifera is its content. In recent studies, the mineral content in the form of ash is reported to be 11.65% in M. oleifera leaves (45), which is significantly higher than soybean meal, which is 5.6–7.2 (46). Analysis of M. oleifera leaves cultivated in Gaborone, Botswana, revealed a variable ash content ranging from 5.6 to 9.1%, with a mean value of 7.34%. This variation underscores the influence of environmental factors and sample origin on the mineral composition of M. oleifera leaves (47). Another experiment testified to an ash content of 6.00% for M. oleifera leaf protein concentrate (48). The mineral composition of M. oleifera leaves exhibits variability, influenced by factors such as edaphic conditions and environmental parameters during cultivation. For instance, research has demonstrated comparable calcium concentrations in M. oleifera leaves (11,153 mg/kg) and roots (12,834 mg/kg), while seed calcium levels (565 mg/kg) were significantly lower. This observation highlights the division and difference accumulation of minerals within different plant tissues (49). There is a considerable amount of lipids in the leaves of M. oleifera, contributing to their nutritional value. On the dry meter basis, analysis of M. oleifera leaves samples have a range of lipid concentration from 1.7 to 10.42%. This variation is likely attributable to different factors, including the specific source of leaf sample, the analytical methods employed for lipid determination, and environmental conditions during cultivation (47). A mean lipid content of 7.8 ± 0.13% is shown by analysis of M. oleifera leaves from Botswana and Gaborone. This value exceeds previously reported values of 2.3, 5.2, and 3.0%, pointing out potential regional changes in M. oleifera lipid composition (50). The lipid fraction of M. oleifera leaves are characterized by the predominance of unsaturated fatty acids, notably palmitic, oleic, and linoleic acids (51). These purchases fulfill essential physiological roles and contribute to the energetic value of the leaves. A monounsaturated fatty acid, Oleic acid, has been implicated in the modulation of inflammatory responses and positive cardiovascular health outcomes (47).
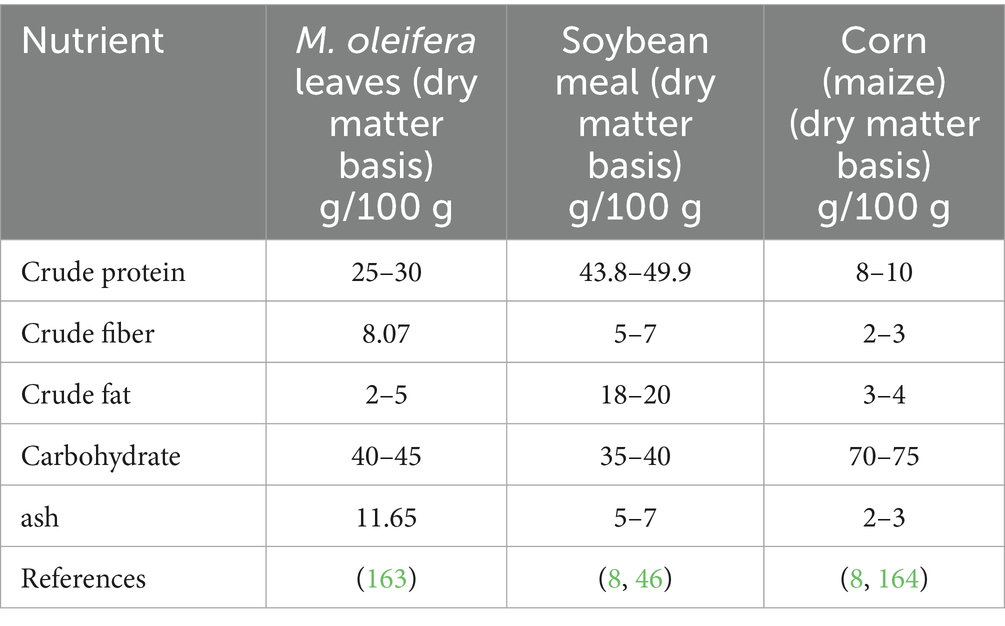
Table 2. Proximate analysis: comparison of M. oleifera leaf powder with soybean meals and maize on a dry matter basis.
Amino acids
Serving as the fundamental building blocks of proteins, amino acids are essential components in animal feed. Although they have a structural role, they also participate in cellular processes, including gene expression, cell signaling, and metabolic regulation. Therefore, that’s sufficient supply of amino acids is necessary for supporting overall well-being, optimal growth, development, reproduction, and lactation of animals (52). The metabolic pathways that are crucial for sporting growth, reproductive, and lactation functions are organized by amino acids, so in that way contributing to enhanced animal health (53). M. oleifera, due to its amino acid profile, is presented as a primary amino acid supplement in animal feed formulations, specifically when integrated with conventional forages (8). Phytochemical analyses have revealed the presence of 16–19 amino acids in M. oleifera, encompassing all ten essential amino acids: threonine, tyrosine, methionine, valine, phenylalanine, isoleucine, leucine, histidine, lysine, and tryptophan (54). M. oleifera exhibits comparatively elevated levels of lysine, leucine, histidine, glutamic acid, valine, isoleucine, alanine, phenylalanine, and arginine relative to other woody plant species (55). Some recent studies have reported M. oleifera is a notable source of essential amino acids, including threonine, valine, methionine, leucine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, histidine, lysine, and arginine (56, 57). Amino acids that cannot be synthesized de novo by animals are classified as essential. Efficient protein synthesis depends on the availability of both essential and non-essential amino acids at the ribosomal site, in proportions commensurate with the animal’s physiological needs. A deficit in any single amino acid can constrain the utilization of other amino acids within the dietary protein. The amino acid that initially restricts the rate of protein synthesis is defined as the first limiting amino acid. The second limiting amino acid, representing the next most deficient amino acid, can also negatively impact growth even when the first limiting amino acid is supplemented (58). For instance, in weaned calves consuming a corn and soybean meal-based diet, methionine has been identified as the first limiting amino acid, with lysine subsequently becoming limiting (59). Researchers have found that Supplementation with synthetic methionine or methionine-rich feed ingredients can improve dietary amino acid balance and consequently enhance animal performance (60, 61). Maintaining an appropriate balance between essential and non-essential amino acids in animal feed formulations is vital for ensuring optimal nutrition. As indicated in Table 3, M. oleifera leaves provide a variety of amino acids, with essential amino acids making up over 50% of the total amino acid content. Although the methionine content in M. oleifera leaves exceeds that of corn meal, it remains about two-thirds of the amount found in soybean meal (Table 3). Sulfur-containing amino acids are crucial for preserving cellular integrity and may also contribute to the detoxification of heavy metals through chelation (62). Dietary supplementation of cystine, a sulfur-containing amino acid, may be necessary in M. oleifera leaf meal formulations to ensure that animal requirements for sulfur-containing amino acids are met.
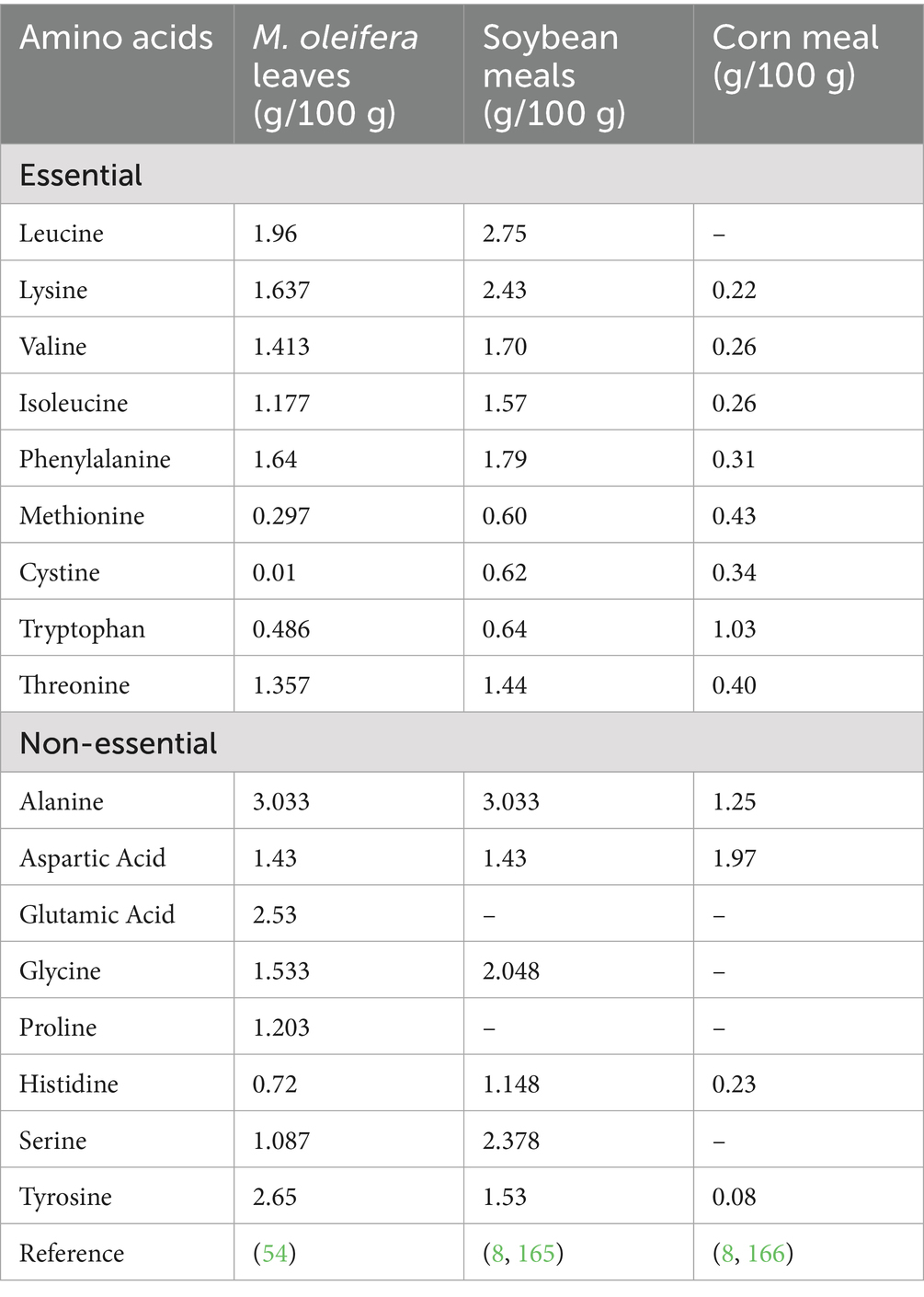
Table 3. Comparison: amino acid profile (g/100 g dry weight) of M. oleifera with conventional feed resources.
Mineral content
Ash content is often regarded as a measure of total mineral content. M. oleifera leaves serve as an important source of essential minerals, such as calcium, iron, potassium, and sodium (63). The levels of these minerals in M. oleifera leaves are generally higher compared to those found in other tree leaf species. Calcium ions are crucial for various cellular functions, including the regulation of cell motility, gene transcription, muscle contraction, and exocytosis (64, 65). M. oleifera leaves exhibit higher calcium content and bio accessibility compared to spinach and sweet potato leaves, suggesting their potential to enhance calcium intake, particularly in tropical and warm temperate regions (66). Notably, iron deficiency is frequently observed in many plant-based foods, except those derived from M. oleifera leaves. M. oleifera leaves provide substantially higher iron levels compared to other plant sources; for example, the iron content of M. oleifera leaves is reportedly 25 times greater than that of spinach (67). While M. oleifera leaves are a source of magnesium, which can positively influence milk yield and composition, for example, Magnesium supplementation in cattle diets has been reported to increase milk fat concentration and yield, with one study noting a 12% increase within 4 days (68). The recommendation to add excess magnesium salt to cattle feed is not universally supported. Although magnesium is essential for various physiological functions, including milk production, excessive intake can have detrimental effects. Cows do possess homeostatic mechanisms to regulate mineral balance, but their capacity to handle excess magnesium is limited. Hypermagnesemia, a condition characterized by elevated magnesium levels in the blood, can result from over-supplementation and lead to serious health problems, including muscle weakness, cardiac arrhythmias, and even death (69). Therefore, determining the appropriate magnesium level in cattle feed should be based on the animal’s growth stage, production status, and dietary context, rather than simply adding excess magnesium (Table 4).
Bioactive compounds and their distribution
M. oleifera, contributing to its recognized medicinal, nutritional, and therapeutic properties, presents a notable abundance of bioactive compounds (70). Bioactive compounds in M. oleifera include polyphenols, flavonoids, carotenoids, terpenoids, alkaloids, glucosinolates, tocopherols, and saponins. These compounds play important roles in enhancing animal health and optimizing livestock productivity (71). M. oleifera tree with its seeds, leaves, and bark packed with health boosting compounds like polyphenols, vitamins, and essential amino acids is considered a nutritional powerhouse (72). For example, glucosinolates and flavonoids play a crucial role as natural immune regulators, helping animals to combat infections and stress (73). Moreover, its saponins and tannins improve metabolic efficiency and nutrient absorption in animals, leading to healthier herds (74).
The leaves of M. oleifera are a rich source of nutrients, loaded with bioactive substances like phytosterols, polyphenols, and essential vitamins that actively reinforce livestock health. Flavonoids, such as kaempferol and quercetin, are among the most important immunomodulatory compounds found in leaves of M. oleifera (75). These compounds have been shown to influence the activity of immune cells and production of cytokines to modulate the cellular immune responses (76). M. oleifera is renowned for its diverse phytochemical composition. This includes a variety of polysaccharides contributing to their reported health benefits (77). Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates made up of monosaccharide units, such as galactose, arabinose, rhamnose, glucose, and xylose (45). Among these, Arabinogalactan is identified as a significant polysaccharide found in M. oleifera leaves (78). These leaves are abundant in essential nutrients, including minerals, protein, and vitamins, as well as a diverse array of bioactive compounds such as saponins, tannins, and flavonoids (79). These elements take part in observed, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects of plants (80, 81). M. oleifera pods are also a rich nutrient source and have bioactive components. They have protein, fiber, and immunoglobulin data, which are important components of immune function. Studies have shown that pods of M. oleifera can boost cell-mediated immunity in broiler chicken (82). Similarly, the seeds of M. oleifera are also a good source of oil and contain bioactive components like tannins and saponins. These cells can modulate immune response and have shown influence on immune cell activity (83). There is an enzyme in M. oleifera seeds called myrosinase, which can catalyze the production of isothiocyanates on plant damage or processing (84). The seeds of M. oleifera have shown anti-cancer activity by preventing cancer cell proliferation (85). They also have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities (86). The detailed bioactive components in different parts of M. oleifera in graphically shown in Figure 2.
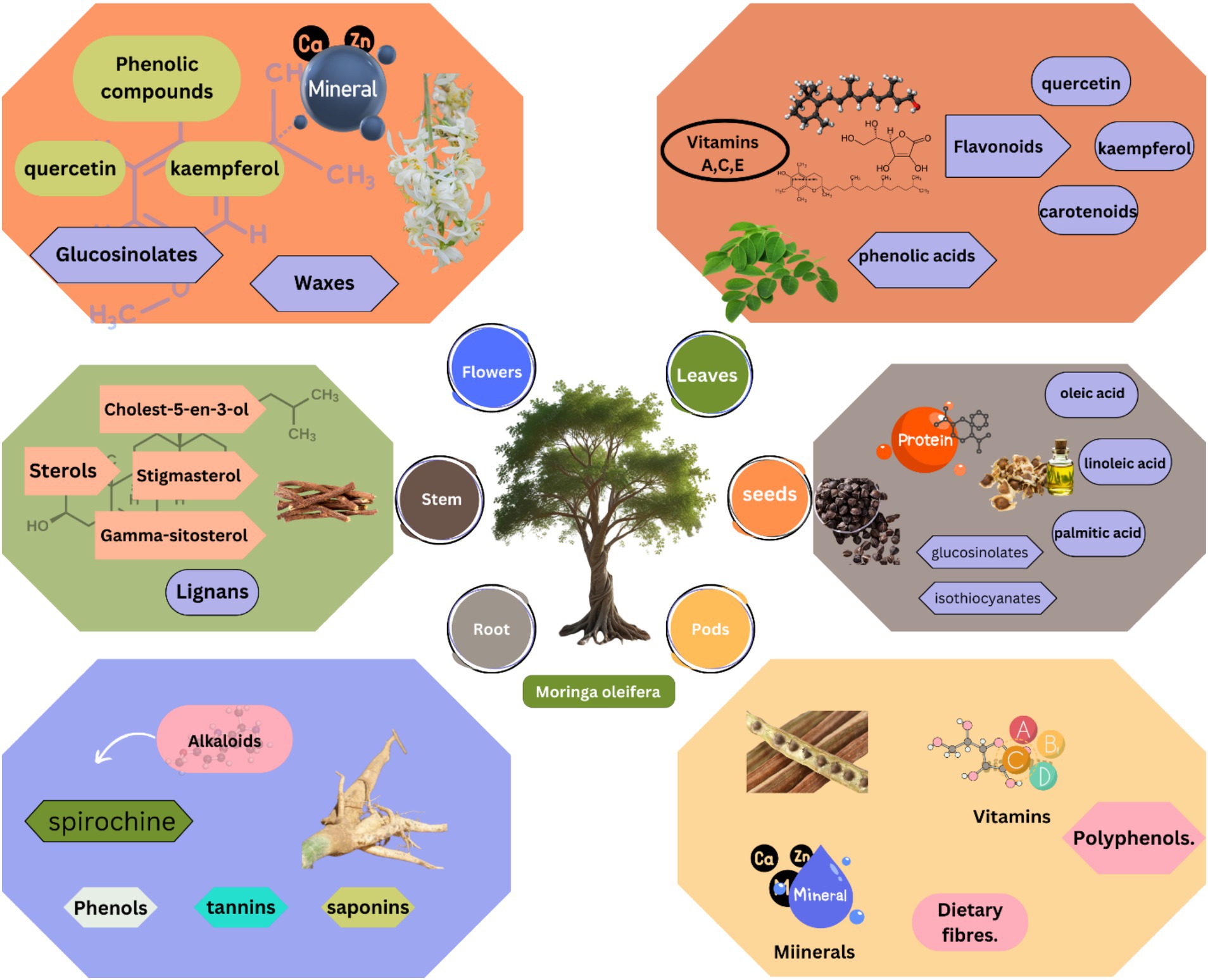
Figure 2. Spatial distribution of bioactive compounds in M. oleifera tissues. Leaves contain highest flavonoid concentrations (quercetin: 4.2 mg/g DW), while seeds are rich in isothiocyanates (4.1 mg/g DW). Pods provide unique combinations of fiber (32% DW) and immunomodulatory phenolics.
Immunomodulatory mechanisms
Gut microbiota modulation
Immunomodulation in livestock involves the targeted manipulation of the immune system to strengthen immune responses, ultimately leading to improved disease resistance and overall health (87). Dietary immunomodulation involves the incorporation of specific nutrients and bioactive compounds into animal feed to optimize immune function (88). For example, probiotics have demonstrated efficacy in improving livestock health by modulating gut microbiota composition and stimulating host immune responses through the secretion of specific factors and competitive exclusion of pathogenic bacteria (89). Likewise, the administration of immunomodulatory feed additives in cattle has been employed to modulate physiological parameters and enhance performance under stressful conditions, such as transportation (90). M. oleifera, commonly known as the “miracle tree,” is recognized for its immunomodulatory effects (91). These properties are attributed to its diverse array of bioactive compounds, including essential amino acids, oleic acid, vitamins, flavonoids, polyphenols, and minerals (92). M. oleifera contains flavonoids, like kaempferol and quercetin, that express significant anti-inflammatory activity (91). The activity of pro-inflammatory enzymes, such as cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase is inhibited by these compounds to reduce the production of inflammatory mediators (93). This mechanism takes part in the reduction of inflammation and modulation of immune response in animals. There are different pathways for immunomodulation in animals, including Gut-associated immune system activation, antioxidant defense, and anti-inflammatory action. Comparison of bioactive compounds and immunomodulatory properties of M. oleifera with conventional feed crops (Supplementary Table S1).
Gut-associated immune system activation
The gut, being the largest immunological organ, plays an important role both in digestion and nutrient absorption (94). The intestine of animals contains a vast and complex population of microorganisms, comprising billions of bacteria (95). These microbes play a critical role in nutrient absorption and digestion, taking part significantly in the body’s immune function and participating in a range of other biochemical and physiological processes (96). The composition of the intestinal microbiota of a healthy animal is predominantly composed of the phyla Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria. Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes are particularly represented by the most abundant phyla, often covering 90% of the total intestinal microbial community (97). Any changes in intestinal flora can induce pathological changes within the intestinal tissue. Moreover, such disruption can contribute to the formation of carcinogenic compounds and chronic inflammation, thereby causing a significant risk to animal health (98).
Polysaccharides present in M. oleifera has been linked with different biological activities, including antioxidant properties, immunomodulatory effects, and potential antimicrobial actions (78). The diverse and significant biological activities of polysaccharides extracted from M. oleifera have been highlighted by recent researchers, leading to their increased prominence. Research teams have isolated and characterized MOP-1 as a newly discovered arabinogalactan that shows efficient in vitro antioxidant effects from M. oleifera leaves (99). Dong et al. (100) extracted MOP-2 from M. oleifera leaves and then examined the in vitro immunomodulatory activity.
The immunomodulatory mechanism of M. oleifera leaf polysaccharides has been shown in recent studies. For instance, a study by Mohamed Husien et al. (78) has shown that high doses of M. oleifera polysaccharides promote intestinal health in UC mice by modulating gut microbiome compositions. The mechanism of action of M. oleifera in gut-associated immunomodulation is shown in Figure 3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is an inflammatory conditions that affect the gastrointestinal tract and can cause an increase in Bacteroides as reported previously (101). Treatment with MOLP-H significantly reduces Bacteroidetes abundance (29% decrease, p < 0.05) while increasing Firmicutes (40% rise) in DSS-induced colitis models (101). This observation aligns with a prior study that reported a 40% higher prevalence of Firmicutes compared to Bacteroidetes in mice subjected to a high-fat diet (102). Bacteroidetes and a few Firmicutes species, notably Bacteroides and Lactobacillus, have been implicated in modulating physiological conditions in mice subjected to dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) treatment (103). A decrease in Lactobacillus abundance has been correlated with an increase in ulcerative colitis (UC) induced by DSS. This suggests that Lactobacillus plays a beneficial role in immunomodulation (104). The study demonstrated that treatment with MOLP-H resulted in increased Lactobacillus levels (105). Research studies show that supplementation with M. oleifera leads to elevated Lactobacillus levels when obesity occurs through high-fat diet intake (104). Recent research exploring the interplay between gut microbiota and host immune responses has revealed that members of the Muribaculaceae family, a dominant component of the murine gut microbiota, can modulate host immunity. Natural killer (NK) cell activity is influenced by sucrose, while the nuclear factor-kappa B-alpha (NF-κB) signaling pathways experience impairment because of its presence (106). Treatment with MOLP induces changes in the gut microbiota composition, specifically increasing the abundance of families such as Muribaculaceae (107). These bacterial families have been identified to support greater activity of NK cells. The innate immune system relies on NK cells to perform recognition and elimination of abnormal infected cells (108). The pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter exists as an established cause of different gastric abnormalities. High Helicobacter counts in the body tend to worsen the outcomes of IBD (109). Research using mice established that M. oleifera polysaccharide administration minimized Helicobacter growth levels, while DSS treatment usually increases Helicobacter levels (105, 107).
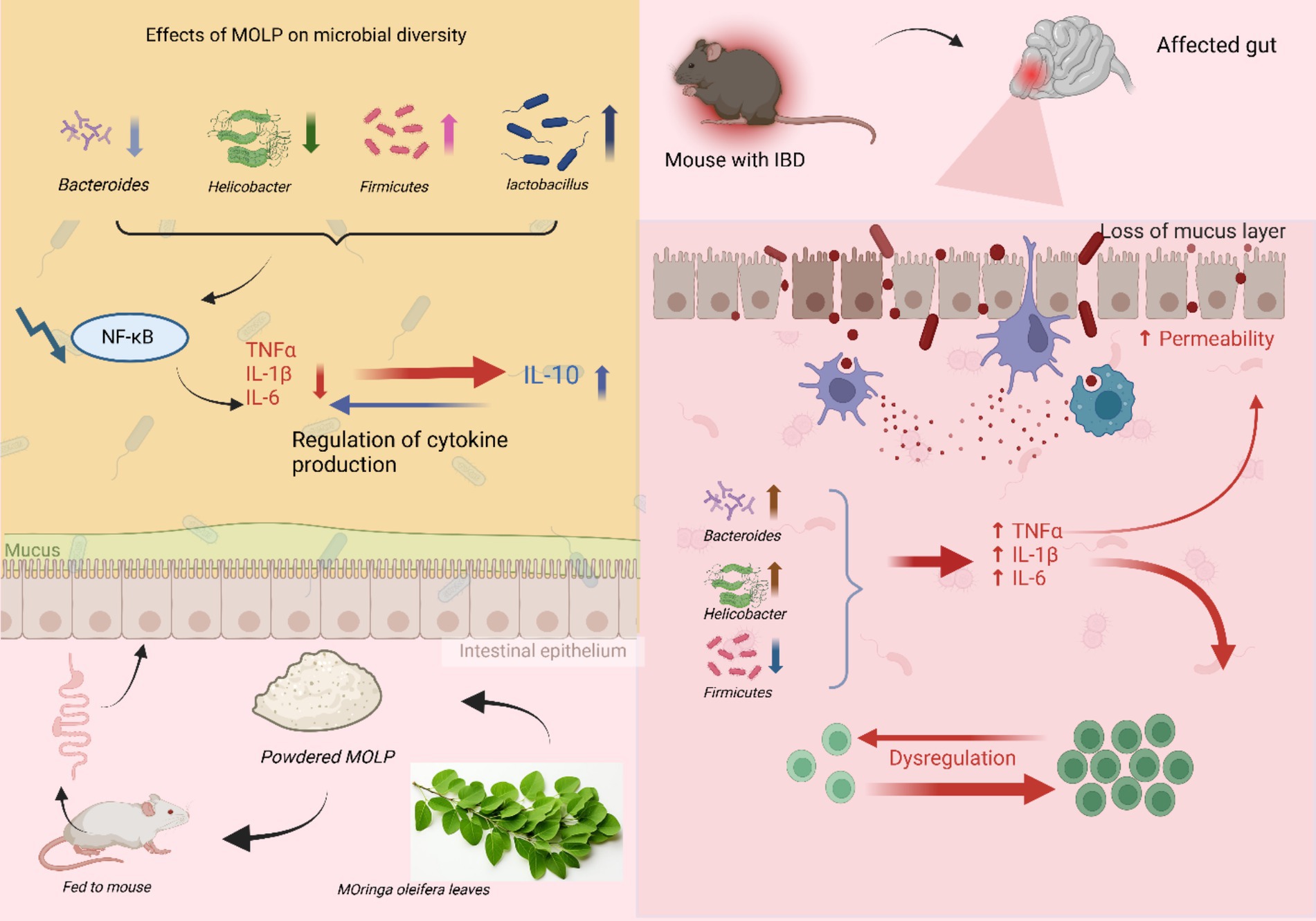
Figure 3. Explain the mechanism by which M. oleifera polysaccharides (MOLP) mitigate inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) involves modulation of gut microbiota composition and subsequent dampening of pro-inflammatory signaling. In IBD, dysbiosis is characterized by an increased abundance of pro-inflammatory bacteria (e.g., Bacteroidetes and Helicobacter) and a reduction in anti-inflammatory taxa (e.g., Firmicutes) contributes to mucosal barrier disruption and increased intestinal permeability. Oral administration of powdered M. oleifera leaves, rich in MOLP, appears to shift the gut microbial profile towards a more favorable composition, evidenced by increased beneficial genera such as Lactobacillus and the phylum Firmicutes. This modulation of the gut microbiota is associated with the downregulation of NF-κB signaling pathway and a consequent regulation of cytokine production, leading to a reduction in intestinal inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory pathways
The natural protective mechanism against stimuli is inflammation (110). The initial inflammatory response leads to acute inflammation, yet chronic inflammation occurs when the response endures for multiple weeks up to several years (111). Inflammation is essential for tissue regeneration and repair, necessitating optimal activation of both the innate and adaptive immune systems to mount an effective response to injury (112). Activated macrophages, key players in the inflammatory response, release a suite of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) (113). These cells also generate reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, such as nitric oxide (NO), synthesized by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), contributing to the oxidative stress environment characteristic of inflammation (114).
Anti-inflammation, a process involving active suppression of pro-inflammatory signaling and restoration of tissue homeostasis, is crucial for limiting immunopathology following pathogen clearance or sterile injury. Chronic inflammation and subsequent tissue damage can be the result of failure to adequately control the inflammation cascade (115). The production of immunomodulatory molecules, like IL-10, and the regulation of specific signaling pathways to suppress the activity of pro-inflammatory responses can resolve the problem of inflammation, culminating in the repair of tissue homeostasis and preservation of immune equilibrium (116). This complex regulatory mechanism is crucial for maintaining physiological health (117). M. oleifera delivers anti-inflammatory benefits through its mix of health-enhancing chemical substances, including isothiocyanates, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. The anti-inflammatory effects of M. oleifera compounds are believed to be mediated through multiple mechanisms (93).
Inhibition of pro-inflammatory enzymes
iNOS is an enzyme expressed in various immune cells, such as macrophages, in response to pro-inflammatory stimuli like lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and cytokines (118). Upon induction, iNOS catalyzes the conversion of L-arginine to NO. In contrast to the constitutive isoforms, endothelial NOS (eNOS) and neuronal NOS (nNOS), iNOS produces substantial quantities of NO over prolonged periods. Excessive NO production, especially in the presence of superoxide, can lead to the formation of peroxynitrite, a highly reactive species capable of damaging proteins, lipids, and DNA, thus contributing to the exacerbation of inflammation and tissue injury (119). The isothiocyanates, flavonoids, and phenolic acids present in M. oleifera can attenuate iNOS expression, thereby modulating NO production. This downregulation is often mediated through the suppression of upstream signaling pathways, particularly the NF-κB pathway (74). These bioactive compounds can stabilize the NF-κB inhibitor, IκB, preventing NF-κB translocation to the nucleus. Consequently, the transcriptional activity of the iNOS gene is diminished, resulting in reduced iNOS protein levels and a subsequent decrease in NO synthesis.
Similarly, Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an inducible enzyme, catalyzes the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins, such as prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (120). These prostaglandins are pivotal inflammatory mediators implicated in the pathogenesis of pain, fever, and edema. In contrast to COX-1, which is constitutively expressed, COX-2 expression is markedly upregulated in response to inflammatory stimuli, positioning it as a key driver of inflammatory processes (121). The bioactive constituents of M. oleifera attenuates COX-2 expression, primarily through suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Inhibition of NF-κB diminishes the transcriptional activity of the COX-2 gene, resulting in decreased COX-2 protein levels and a subsequent reduction in the synthesis of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins (93, 122). Furthermore, certain flavonoids present in M. oleifera may also exert a direct inhibitory effect on COX-2 enzyme activity.
Regulation of cytokine production
Cytokines are a diverse group of signaling molecules that play a crucial role in the complex process of inflammation (123). Following tissue injury or pathogen invasion, immune cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, and T lymphocytes, rapidly synthesize and secrete a variety of cytokines to initiate and regulate the inflammatory cascade (124). Pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, are rapidly released at the site of tissue damage or infection (125). These cytokines initiate a cascade of events, activating resident cells and recruiting additional immune cells, such as neutrophils and monocytes, to the affected area, thereby amplifying and propagating the inflammatory response. It is very important to maintain a delicate equilibrium between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins. This equilibrium is essential for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies aimed at mitigating the detrimental effects of chronic inflammation and sepsis (126).
Administration of M. oleifera bio actives, such as M. oleifera isothiocyanate-1 (MIC-1) or MOLP, have demonstrated a significant decrease in tissue concentration and serum of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, in experimental models of acute inflammation or sepsis such as LPS-induced sepsis in mice (127). Moreover, along with suppression of pro-inflammatory signaling, certain M. oleifera extracts have shown the capacity to enhance the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, in animal models. This increase in IL-10 contributes to counterbalancing the inflammatory cascade and promoting resolution. For example, in a murine model of DSS-induced colitis, administration of MOLP not only reduced colonic levels of TNF-α and IL-1β but also concurrently elevated IL-10 expression, thereby facilitating the resolution of inflammation (78).
Mechanism of action as an antioxidant
Oxidative stress occurs when the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) overwhelms the body’s endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms, leading to an imbalance that favors ROS accumulation and subsequent cellular damage (128). This imbalance can arise from either increased ROS production, decreased antioxidant capacity, or a combination of both (129). During oxidative phosphorylation, the process by which ATP is generated in mitochondria, electrons can escape from the electron transport chain, resulting in the formation of superoxide radicals (O₂−) (130). These superoxide radicals can subsequently be converted into other ROS, including hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) and highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (OḤ). While ROS plays essential physiological roles in cellular signaling and host defense, excessive ROS production overwhelms endogenous antioxidant systems, leading to a state of oxidative stress (131, 132). Activated immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, generate ROS as a crucial component of the innate immune response against invading pathogens. While this ROS production is a physiological process essential for microbial killing, chronic inflammation can result in sustained and excessive ROS generation, which contributes to oxidative damage of host tissues and the progression of various diseases. Excessive production of ROS can lead to significant oxidative damage to critical cellular components, including lipids, proteins, and DNA (133). Such damage can impair cellular function, trigger cell death pathways (apoptosis or necrosis), and contribute to the aging process and the development of a wide range of pathological conditions (134). Oxidative stress can negatively impact immune function, rendering animals more susceptible to infections and disease (135). The mechanism of oxidative damage through phosphorylation is shown in Figure 4. In ruminants, for instance, oxidative stress has been linked to compromised immune responses, particularly during periods of physiological stress, such as the periparturient period or heat stress (136).
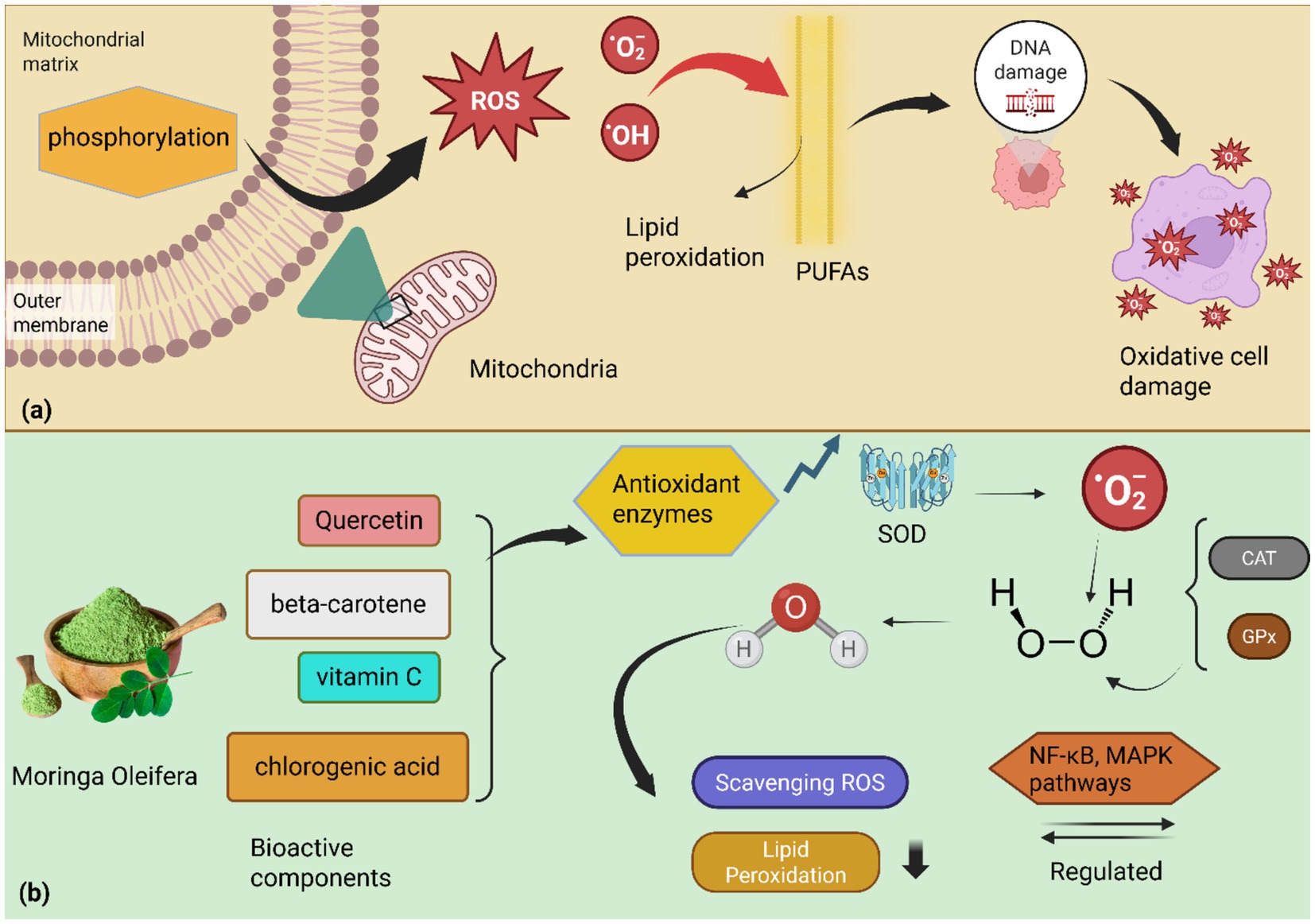
Figure 4. (a) Oxidative stress mechanism: mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation generates superoxide radicals (O2•-) due to electron leakage from the electron transport chain. These radicals further transform into reactive oxygen species (ROS), including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (OH•). When ROS production overwhelms cellular antioxidant defenses, it leads to an imbalance that attacks polyunsaturated fatty acids in cell membranes, initiating lipid peroxidation. Byproducts of lipid peroxidation subsequently cause DNA damage and overall oxidative cell damage. (b) M. oleifera’s antioxidant action: M. oleifera combats oxidative stress through its bioactive components, including quercetin, beta-carotene, vitamin C, and chlorogenic acid, which provide potent antioxidant protection. These antioxidants directly scavenge ROS and neutralize free radicals like superoxide (O2•-). M. oleifera also enhances the activity of key antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx)1, enhancing cellular defense against oxidative damage. By scavenging ROS and boosting antioxidant enzyme activities, M. oleifera reduces lipid damage in membranes. Furthermore, M. oleifera modulates cellular signaling pathways, including NF-κB and MAPK, which regulate inflammatory responses triggered by oxidative stress, thereby ensuring cell health through its rigorous antioxidant properties.
M. oleifera leaves are recognized for their significant antioxidant capacity, a property attributed to their rich composition of bioactive compounds (137, 138). These antioxidants play a critical role in scavenging free radicals and mitigating oxidative stress within biological systems (139). The abundance of bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, and vitamin C, in M. oleifera leaves contributes significantly to their ability to mitigate oxidative damage and inflammation (140). Specific antioxidant constituents, such as quercetin, chlorogenic acid, and beta-carotene, present in M. oleifera contribute significantly to its protective effects against oxidative damage and inflammation (141, 142). M. oleifera has a series of events in its mechanism as an antioxidant, which are shown in Figure 4. These are scavenging free radicals, increasing endogenous antioxidant defenses, reducing lipid peroxidation, and modulating cellular signaling pathways that are related to oxidative stress (79). The 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay is a widely used method to assess the activity of an antioxidant. Antioxidants reacted with that free radical DPPH by donating either an electron or a hydrogen atom (143). After the reaction, DPPH reduces to a non-radical form, α,α-diphenyl-β-picryl hydrazine, that results in loss of its purple color (144). Studies have shown that extracts of M. oleifera have a significant effect in reducing DPPH free radicals (145, 146). The radical scavenging and the antioxidant properties of different extracts of M. oleifera leaves from various agro-climatic regions were examined by Siddhuraju and Becker (147). The results found that the aqueous and aqueous ethanol extracts of freeze-dried leaves of M. oleifera inhibit 89.7–92.0% of peroxidation of linoleic acid and possess scavenging activities on superoxide radicals in the β-carotene-linoleic acid system. M. oleifera enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, in which glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase (CAT), and superoxide dismutase (SOD). This enhancement of these enzymes boosts the immune function against oxidative stress (148).
Free radicals interact with lipids in cell membranes, initiating a chain reaction of lipid peroxidation that can lead to cell damage and contribute to various diseases impacting the immune system (149, 150). Lipid peroxidation is recognized as a well-established biomarker of oxidative stress (151). This process primarily affects polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) such as linoleic acid, linolenic acid, and arachidonic acid, which are essential components of cell membranes (150, 152). The byproducts of this reaction include malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (153). These compounds possess mutagenic, cytotoxic, and neurotoxic properties, allowing them to alter DNA, damage cells, and harm nerve tissues (154).
M. oleifera has proven effective in inhibiting lipid peroxidation by lowering MDA levels. Research indicates that the percentage of lipid peroxidation observed in M. oleifera leaves and stems was 85.88 and 77.63%, respectively (155). In a study involving Swiss albino mice experiencing oxidative stress, pre-treatment with M. oleifera leaf extract successfully restored glutathione (GSH) levels, effectively reducing lipid peroxidation (156, 157). Similarly, a daily administration of M. oleifera extract for 60 days to rats with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatic lipid peroxidation demonstrated a reduction in hepatotoxicity, attributed to phenolic compounds and flavonoids, including β-sitosterol, quercetin, and kaempferol found in the extract (158). In broiler chickens, supplementing M. oleifera leaf meal up to 5% of dry matter intake has shown improvements in fatty acid profiles and a reduction in lipid peroxidation (159). Recent studies on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) have indicated that M. oleifera leaf extracts enhance feed utilization and growth while also improving the innate immune response, evidenced by increased lysosome levels and phagocytic activity (160, 161). A recent study involving crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) found that incorporating 1% of fermented M. oleifera leaves into the diet significantly improved growth performance and antioxidant capacity (162). Overall, due to its rich phenolic content, M. oleifera exhibits strong antioxidant properties.
Future directions
Multiple essential investigations need completion before M. oleifera can achieve its complete potential as an environmentally friendly animal feed source for nutrition and health benefits. Research needs to focus on developing better processing methods that will boost the bioactive compound availability in M. oleifera. Scientific research is necessary to develop drying techniques and fermentation processes with enzymatic treatments, which will make M. oleifera nutrients more accessible after processing. Research needs to progress further to create well-balanced animal feed compositions that effectively integrate M. oleifera into animal dietary plans. There is a need to evaluate M. oleifera connection with dietary elements to discover optimal combinations that maximize nutrient uptake and promote animal development with improved wellness.
The ongoing research must focus on extended investigations to determine how M. oleifera supplementation affects livestock throughout multiple periods. More research about M. oleifera long-term influence on livestock performance must investigate its effects on reproductive outcomes and disease resistance, and animal welfare, regardless of demonstrated short-term enhancements in growth and feed conversion. The inconsistent bioactive component levels in M. oleifera require scientists to investigate the effects of growing conditions, together with the differences observed across cultivars. Extraction of M. oleifera cultivars alongside optimal cultivation methods that maximize beneficial compound concentrations will optimize the effectiveness of M. oleifera as a feed resource.
Research must determine the molecular processes that explain M. oleifera ability to modulate immune functions. The evaluation of M. oleifera bioactive compound-substance interactions with immune pathways and antioxidant systems, and gut microbiota needs comprehensive research to determine its potential as a natural animal feed immunostimulant. Research into M. oleifera biological mechanisms will optimize its value as a health promoter for livestock during times of stress.
Environmental assessment methods and economic modeling practices need to be implemented to determine the complete advantages M. oleifera has over conventional feed crops. Studies using life-cycle assessments need to evaluate the environmental effects of M. oleifera farming in addition to its capacity to minimize greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land degradation relative to maize and soybean as conventional feed crops. The cost-effectiveness assessment of M. oleifera in extended-scale livestock production requires economic studies to determine expense-to-worth ratios and the resulting lower feed costs while enhancing livestock health.
The rising acceptance of M. oleifera as an essential feed ingredient needs proper regulations to guarantee its secure usage within the livestock industry. Research about M. oleifera safety profiles alongside compliance with animal feed regulations will enable its integration into international commercial feeding systems. Driving market demand for sustainable livestock production with M. oleifera will be facilitated by educating consumers about its advantages. The successful adoption of M. oleifera requires research-based partnerships between researchers and both agricultural stakeholders and policymakers who will develop strategies for global livestock adoption.
M. oleifera shows extensive value because it represents a sustainable source of nourishing feed material for agricultural purposes. Research efforts into M. oleifera must advance through optimization of processing techniques, along with formulation research and studies of molecular effects and environmental and economic assessments. The implementation of these tactics ensures M. oleifera significantly contributes to solving current international issues regarding food supply stability and livestock health as well as environmental preservation.
Conclusion
M. oleifera is increasingly recognized as a promising solution for sustainable livestock production due to its rich nutritional content and therapeutic properties. Packed with protein, essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals, it enhances animal growth and overall health. Its immunomodulatory effects help regulate gut immunity and reduce oxidative stress, boosting disease resistance in livestock. Additionally, M. oleifera serves as a viable alternative to traditional feed sources like soybeans and maize, addressing concerns of feed supply, environmental impact, and price stability. Cultivating M. oleifera in arid regions can also contribute to food security in developing countries. While its potential is significant, the effective use of M. oleifera requires further research on diet optimization and its long-term effects on livestock performance. Overall, M. oleifera offers substantial benefits for enhancing livestock nutrition and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. M. oleifera triple-action benefits—nutritional (complete EAA profile), environmental (3.5 × lower carbon footprint than soybean), and therapeutic (40–60% cytokine reduction)—position it as a transformative feed additive. Critical findings include:
1 Optimal inclusion: 15% for ruminants (↑ milk yield 12%), 5% for poultry (↑ weight gain 8%).
2 Processing protocols: Freeze-drying retains 92% flavonoids vs. 67% in sun-drying.
3 Economic viability: 0.18/kgproductioncostvs0.31/kg for soybean meal.
Priority research areas:
• Long-term toxicity (>6 months consumption).
• Breed-specific formulation optimization.
• Policy frameworks for smallholder adoption.
Author contributions
RM: Software, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation, Conceptualization. SE: Writing – review & editing. MZ: Writing – review & editing. ZC: Writing – review & editing. AS: Writing – review & editing. HH: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. MW: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National 14th Five-Year Plan Key Research and Development Program (2024YFD1300204, 2023YFD1301705), high-end foreign experts from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (G2023014066L), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institution (PAPD), P.R. China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1615349/full#supplementary-material
References
2. Yang, C, Li, Q, Wang, X, Cui, A, Chen, J, Liu, H, et al. Human expansion-induced biodiversity crisis over Asia from 2000 to 2020. Research. (2023) 6:14–7. doi: 10.34133/research.0226
3. Makkar, H. Review: feed demand landscape and implications of food-not feed strategy for food security and climate change. Animal. (2017) 12:1744–54. doi: 10.1017/S175173111700324X
4. Yitbarek, MB. Livestock and livestock product trends by 2050. International Journal of Animal Research (IJAR) (2019). 4:30.
5. Erdaw, M. Contribution, prospects and trends of livestock production in sub-Saharan Africa: a review. Int J Agric Sustain. (2023) 21:2247776. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2023.2247776
6. Bai, Z, Wenqi, L, Velthof, G, Wei, Z, Havlík, P, Oenema, O, et al. China’s livestock transition: driving forces, impacts, and consequences. Sci Adv. (2018) 4:eaar8534. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar8534
7. Rojas-Downing, M, Nejadhashemi, A, Harrigan, T, and Woznicki, S. Climate change and livestock: impacts, adaptation, and mitigation. Clim Risk Manag. (2017) 16:145–63. doi: 10.1016/J.CRM.2017.02.001
8. Su, B, and Chen, X. Current status and potential of Moringa oleifera leaf as an alternative protein source for animal feeds. Front Vet Sci. (2020) 7:53. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00053
9. Parrini, S, Aquilani, C, Pugliese, C, Bozzi, R, and Sirtori, F. Soybean replacement by alternative protein sources in pig nutrition and its effect on meat quality. Animals. (2023) 13:494. doi: 10.3390/ani13030494
10. Boerema, A, Peeters, A, Swolfs, S, Vandevenne, F, Jacobs, S, Staes, J, et al. Soybean trade: balancing environmental and socio-economic impacts of an intercontinental market. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0155222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155222
11. Khan, NM, Qadeer, A, Khan, A, Nasir, A, Sikandar, A, Adil, M, et al. Alternative sources of proteins in FARM animal feeding. J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci. (2024) 13:e10605. doi: 10.55251/jmbfs.10605
12. Dronne, Y. Agricultural raw materials for food and feed: the world. INRA Prod Anim. (2018) 31:165–80. doi: 10.20870/PRODUCTIONS-ANIMALES.2018.31.3.2345
13. Uwizeye, A, de, I, Opio, C, Schulte, R, Falcucci, A, Tempio, G, et al. Nitrogen emissions along global livestock supply chains. Nat Food. (2020) 1:437–46. doi: 10.1038/s43016-020-0113-y
14. Wang, J, Liu, Q, Hou, Y, Qin, W, Lesschen, J, Zhang, F, et al. International trade of animal feed: its relationships with livestock density and N and P balances at country level. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst. (2017) 110:197–211. doi: 10.1007/s10705-017-9885-3
15. Tejeda, H, and Goodwin, B. Price volatility, nonlinearity, and asymmetric adjustments in corn, soybean, and cattle markets: implications of ethanol-driven (market) shocks. (2009). Available online at: https://consensus.app/papers/price-volatility-nonlinearity-and-asymmetric-tejeda-goodwin/32015c95e5915fbe8537186d29158186/ (Accessed December 5, 2024).
16. Minh, CLT, Lebailly, P, and Nguyen, T. Cost, return analysis and constraints in livestock production and marketing in Hai Duong, Vietnam. (2013)1194–1199. Available online at: https://consensus.app/papers/cost-return-analysis-and-constraints-in-livestock-minh-lebailly/c68848f9a21c52fba73135ce9a78848b/ (Accessed December 5, 2024).
17. Halmemies-Beauchet-Filleau, A, Rinne, M, Lamminen, M, Mapato, C, Ampapon, T, Wanapat, M, et al. Review: alternative and novel feeds for ruminants: nutritive value, product quality and environmental aspects. Animal. (2018) 12:s295–309. doi: 10.1017/S1751731118002252
18. Gasco, L, Biasato, I, Dabbou, S, Schiavone, A, and Gai, F. Animals fed insect-based diets: state-of-the-art on digestibility, performance and product quality. Animals. (2019) 9:170. doi: 10.3390/ani9040170
19. Bryant, JP, Joly, K, Chapin, FS, DeAngelis, DL, and Kielland, K. Can antibrowsing defense regulate the spread of woody vegetation in arctic tundra? Ecography Cop. (2014) 37:204–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0587.2013.00436.x
20. Rizwan, N, Rizwan, D, and Banday, M. Moringa oleifera: the miracle tree and its potential as non-conventional animal feed: a review. Agric Rev. (2022) 45:369–379. doi: 10.18805/ag.r-2405
21. Sarwatt, S, Kapange, S, and Kakengi, A. Substituting sunflower seed-cake with Moringa oleifera leaves as a supplemental goat feed in Tanzania. Agrofor Syst. (2002) 56:241–7. doi: 10.1023/A:1021396629613
22. Sonkar, N, Singh, N, Santra, A, Mishra, S, Verma, L, and Soni, A. Application of munga (Moringa oleifera) in livestock feed: a review. Int J Chem Stud. (2020) 8:1729–35. doi: 10.22271/chemi.2020.v8.i1y.8513
23. Nouman, W, Anwar, F, Gull, T, Newton, A, Rosa, E, and Domínguez-Perles, R. Profiling of polyphenolics, nutrients and antioxidant potential of germplasm’s leaves from seven cultivars of Moringa oleifera lam. Ind Crop Prod. (2016) 83:166–76. doi: 10.1016/J.INDCROP.2015.12.032
24. Moyo, B, Oyedemi, S, Masika, P, and Muchenje, V. Polyphenolic content and antioxidant properties of Moringa oleifera leaf extracts and enzymatic activity of liver from goats supplemented with Moringa oleifera leaves/sunflower seed cake. Meat Sci. (2012) 91:441–7. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.02.029
25. Tumer, T, Rojas-Silva, P, Poulev, A, Raskin, I, and Waterman, C. Direct and indirect antioxidant activity of polyphenol- and isothiocyanate-enriched fractions from Moringa oleifera. J Agric Food Chem. (2015) 63:1505–13. doi: 10.1021/jf505014n
26. Falowo, A, Mukumbo, F, Idamokoro, E, Lorenzo, J, Afolayan, A, and Muchenje, V. Multi-functional application of Moringa oleifera lam. In nutrition and animal food products: a review. Food Res Int. (2018) 106:317–34. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.12.079
27. Teixeira, E, Carvalho, M, Neves, V, Silva, M, and Arantes-Pereira, L. Chemical characteristics and fractionation of proteins from Moringa oleifera lam. Leaves. Food Chem. (2014) 147:51–4. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.135
28. Leitanthem, VK, Chaudhary, P, Maiti, S, Mohini, M, and Mondal, G. Impact of Moringa oleifera leaves on nutrient utilization, enteric methane emissions, and performance of goat kids. Animals. (2023) 13:1–15. doi: 10.3390/ani13010097
29. Boopathi, NM, and Abubakar, BY. Botanical Descriptions of Moringa spp.,. In: Boopathi, N.M., Raveendran, M., Kole, C. (eds). The Moringa Genome. Compendium of Plant Genomes. Springer, Cham (2021).
30. Tshabalala, T, Ncube, B, Madala, N, Nyakudya, T, Moyo, H, Sibanda, M, et al. Scribbling the cat: A case of the “miracle” plant, Moringa oleifera. Plan Theory. (2019) 8:510. doi: 10.3390/plants8110510
31. Dhiman, J. A review on medicinal uses of Moringa oleifera. J Drug Deliv Ther. (2023) 13:197–201. doi: 10.22270/jddt.v13i11.6042
32. Alshoaibi, A. Seed germination, seedling growth and photosynthetic responses to temperature in the tropical tree Moringa oleifera and its relative desert, Moringa peregrina. Egypt J Bot. (2021) 61:541–51. doi: 10.21608/EJBO.2021.63271.1631
33. Rajalakshmi, R, Rajalakshmi, S, and Parida, A. Evaluation of the genetic diversity and population structure in drumstick (Moringa oleifera L.) using SSR markers. Curr Sci. (2017) 112:1250–6. doi: 10.18520/CS/V112/I06/1250-1256
34. Anzano, A, Ammar, M, Papaianni, M, Grauso, L, Sabbah, M, Capparelli, R, et al. Moringa oleifera lam.: a phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Horticulturae. (2021) 7:409. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7100409
35. Farooq, F, Rai, M, Tiwari, A, Khan, A, and Farooq, S. Medicinal properties of Moringa oleifera: an overview of promising healer. J Med Plants Res. (2012) 6:4368–74. doi: 10.5897/JMPR12.279
36. Dania, SO, Akpansubi, P, and Eghagara, OO. Comparative effects of different fertilizer sources on the growth and nutrient content of Moringa (Moringa oleifera) seedling in a greenhouse trial. Adv Agric. (2014) 2014:726313. doi: 10.1155/2014/726313
37. Mashamaite, CV, Ramatsitsi, MN, and Manyevere, A. Moringa oleifera lam.: a versatile climate-smart plant for nutritional security and therapeutic usage in semi-arid regions. J Agric Food Res. (2024) 16:101217. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101217
38. Santos, A, Silva-Mann, R, Ferreira, R, and Brito, A Water pre-hydration as priming for Moringa oleifera lam. Seeds under salt stress. Trop Subtrop Agroecosyst (2011) 14 201–207. Available online at: https://consensus.app/papers/water-prehydration-as-priming-for-moringa-oleifera-lam-santos-silva-mann/9c085dead6cd57f9bf4a2aec797e6ca6/ (Accessed January 2, 2024).
39. Kholif, A, Morsy, T, Gouda, G, Anele, U, and Galyean, M. Effect of feeding diets with processed Moringa oleifera meal as protein source in lactating Anglo-Nubian goats. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2016) 217:45–55. doi: 10.1016/J.ANIFEEDSCI.2016.04.012
40. Sánchez, NR, Ledin, S, and Ledin, I. Biomass production and chemical composition of Moringa oleifera under different management regimes in Nicaragua. Agrofor Syst. (2006) 66:231–42. doi: 10.1007/s10457-005-8847-y
41. Oduro, I, Ellis, WO, and Owusu, D. Nutritional potential of two leafy vegetables: Moringa oleifera and Ipomoea batatas leaves. Sci Res Essays. (2008) 3:057–60. doi: 10.5897/SRE.9000686
42. El-Hack, M, Alagawany, M, Elrys, A, Desoky, E, Tolba, H, Elnahal, A, et al. Effect of forage Moringa oleifera L. (moringa) on animal health and nutrition and its beneficial applications in soil, plants and water purification. Agriculture. (2018) 8:145. doi: 10.3390/AGRICULTURE8090145
43. Knudsen, K. The nutritional significance of “dietary fibre” analysis. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2001) 90:3–20. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8401(01)00193-6
44. Lesten, ECC, and Emmanuel, CM. Proximate, physical and chemical composition of leaves and seeds of Moringa (Moringa oleifera) from Central Malawi: a potential for increasing animal food supply in the 21st century. Afr J Agric Res. (2018) 13:2872–80. doi: 10.5897/ajar2018.13535
45. Ahmed, M, Marrez, DA, Abdelmoeen, NM, Mahmoud, EA, Abdel-Shakur Ali, M, Decsi, K, et al. Proximate analysis of Moringa oleifera leaves and the antimicrobial activities of successive leaf Ethanolic and aqueous extracts compared with green chemically synthesized ag-NPs and crude aqueous extract against some pathogens. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3529. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043529
46. Kumar, V, Rani, A, and Chauhan, GS. Nutritional value of soybean. In: The soybean: botany, production and uses. (ed.) Guriqbal S. Wallingford UK: CABI (2010). 375–403.
47. Masitlha, EP, Seifu, E, and Teketay, D. Nutritional composition and mineral profile of leaves of Moringa oleifera provenances grown in Gaborone, Botswana. Food Prod Process Nutr. (2024) 6:3. doi: 10.1186/s43014-023-00183-8
48. Laura, R. Nutritional and mineral composition of leaves, roots and seeds of Moringa oleifera lam. Tree from Tenerife, Spain. J Soc Trop Plant Res. (2021) 8:1–5. doi: 10.22271/tpr.2021.v8.i1.001
49. Sodamade, A, Bolaji, OS, and Adeboye, OO. Proximate analysis, mineral contents and functional properties of Moringa oleifera leaf protein concentrate. IOSR J Appl Chem. (2013) 4:47–51. doi: 10.9790/5736-0464751
50. Waterman, C, Rojas-Silva, P, Tumer, TB, Kuhn, P, Richard, AJ, Wicks, S, et al. Isothiocyanate-rich Moringa oleifera extract reduces weight gain, insulin resistance, and hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2015) 59:1013–24. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201400679
51. Sánchez- Machado, D, Núñez- Gastélum, J, Reyes- Moreno, C, Ramírez- Wong, B, and López- Cervantes, J. Nutritional quality of edible parts of Moringa oleifera. Food Anal Methods. (2010) 3:175–80. doi: 10.1007/S12161-009-9106-Z
52. Wu, G, Bazer, F, Dai, Z, Li, D, Wang, J, and Wu, Z. Amino acid nutrition in animals: protein synthesis and beyond. Annu Rev Anim Biosci. (2014) 2:387–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev-animal-022513-114113
53. Sefer, M, Petronijevic, RB, Trbovic, D, Ciric, J, Baltic, T, Parunovic, N, et al. Amino acids in animal feed: significance and determination techniques. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. (2021) 854:012082. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/854/1/012082
54. Moyo, B, Masika, PJ, Hugo, A, and Muchenje, V. Nutritional characterization of Moringa (Moringa oleifera lam.) leaves. Afr J Biotechnol. (2011) 10:12925–33. doi: 10.5897/ajb10.1599
55. Kong, C, and Adeola, O. Evaluation of amino acid and energy utilization in feedstuff for swine and poultry diets. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2014) 27:917–25. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2014.r.02
56. Abbas, R, Elsharbasy, F, and Fadlelmula, AA. Nutritional values of Moringa oleifera, total protein, amino acid, vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, total fat and crude fiber, under the semi-arid conditions of Sudan. J Microb Biochem Technol. (2018) 10:56–8. doi: 10.4172/1948-5948.1000396
57. Aderinola, TA, Fagbemi, TN, Enujiugha, VN, Alashi, AM, and Aluko, RE. Amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of Moringa oleifera seed protein isolate and enzymatic hydrolysates. Heliyon. (2018) 4:e00877. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00877
58. Park, BC. Amino acid imbalance-biochemical mechanism and nutritional aspects. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2006) 19:1361–8. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2006.1361
59. Abe, M, Iriki, T, Funaba, M, and Onda, S. Limiting amino acids for a corn and soybean meal diet in weaned calves less than three months of age. J Anim Sci. (1998) 76:628–36. doi: 10.2527/1998.762628x
60. Monte Singer, W, Zhang, B, Rouf Mian, MA, and Huang, H. Soybean amino acids in health, genetics, and evaluation. Soybean Hum Consum Anim Feed. (2020) 19:1361–1368. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.89497
61. Bunchasak, C. Role of dietary methionine in poultry production. J Poult Sci. (2009) 46:169–79. doi: 10.2141/jpsa.46.169
62. Čolović, M, Vasić, V, Djuric, D, and Krstić, D. Sulphur-containing amino acids: protective role against free radicals and heavy metals. Curr Med Chem. (2018) 25:324–35. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170609075434
63. Valdez- Solana, M, Mejía- García, V, Téllez- Valencia, A, García- Arenas, G, Salas- Pacheco, J, Alba- Romero, J, et al. Nutritional content and elemental and phytochemical analyses of Moringa oleifera grown in Mexico. J Chem. (2015) 20:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2015/860381
65. Luan, S, and Wang, C. Calcium signaling mechanisms across kingdoms. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 37:311–40. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-120219-035210
66. Allen, J, Issa, J, and Cai, W. Calcium content, in vitro digestibility, and bioaccessibility in leaves of spinach (Spinacia oleracea), sweet potato (Ipomea batatas), and drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera). F1000Res. (2014) 3:65. doi: 10.12688/F1000RESEARCH.3287.1
67. Rajbhar, Y, Rajbhar, G, Rawat, P, Shukla, S, and Kumar, M. Grow Moringa (Moringa oleifera), the miracle tree on the earth. Hortic Int J. (2018) 2:166–72. doi: 10.15406/hij.2018.02.00047
68. Razzaghi, A, Vakili, A, Khorrami, B, Ghaffari, M, and Rico, D. Effect of dietary supplementation or cessation of magnesium-based alkalizers on milk fat output in dairy cows under milk fat depression conditions. J Dairy Sci. (2022) 105:2275–87. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-20457
69. Pinotti, L, Manoni, M, Ferrari, L, Tretola, M, Cazzola, R, and Givens, I. The contribution of dietary magnesium in farm animals and human nutrition. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1–15. doi: 10.3390/nu13020509
70. Ferreira, PPM, Farias, DF, Oliveira, JTDA, and Carvalho, ADF. Moringa oleifera: bioactive compounds and nutritional potential Moringa oleifera: compostos bioativos e potencialidade nutricional. Rev Nutr. (2008) 21:431–7. doi: 10.1590/S1415-52732008000400007
71. Lata, M, and Mondal, BC. Moringa oleifera leaf meal: a sustainable approach for poultry production: a review. Arch Curr Res Int. (2024) 24:176–85. doi: 10.9734/acri/2024/v24i11959
72. Gopalakrishnan, L, Doriya, K, and Kumar, DS. Moringa oleifera: a review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application. Food Sci Human Wellness. (2016) 5:49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2016.04.001
73. Leone, A, Spada, A, Battezzati, A, Schiraldi, A, Aristil, J, and Bertoli, S. Cultivation, genetic, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Moringa oleifera leaves: an overview. Int J Mol Sci. (2015) 16:12791–835. doi: 10.3390/ijms160612791
74. Kou, X, Li, B, Olayanju, JB, Drake, JM, and Chen, N. Nutraceutical or pharmacological potential of Moringa oleifera lam. Nutrients. (2018) 10:343. doi: 10.3390/nu10030343
75. Poluan, JC, Zubair, MS, Ramadani, AP, and Hayati, F. Narrative review: potential of flavonoids from Moringa (Moringa oleifera lam.) leaves as immunomodulators. Jurnal Farmasi Galenika. (2023) 9:270–83. doi: 10.22487/j24428744.2023.v9.i2.16265
76. Nfambi, J, Bbosa, GS, Sembajwe, LF, Gakunga, J, and Kasolo, JN. Immunomodulatory activity of methanolic leaf extract of Moringa oleifera in Wistar albino rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. (2015) 26:603–11. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2014-0104
77. Li, L, Ma, L, Wen, Y, Xie, J, Yan, L, Ji, A, et al. Crude polysaccharide extracted from Moringa oleifera leaves prevents obesity in association with modulating gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:1–17. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.861588
78. Mohamed Husien, H, Peng, WL, Su, H, Zhou, RG, Tao, Y, Huang, JJ, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharide alleviates experimental colitis by inhibiting inflammation and maintaining intestinal barrier. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:1–14. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1055791
79. Vergara-Jimenez, M, Almatrafi, MM, and Fernandez, ML. Bioactive components in Moringa oleifera leaves protect against chronic disease. Antioxidants. (2017) 6:91. doi: 10.3390/antiox6040091
80. Kusmiyati, K, Rahmawati, E, Waangsir, FWF, and Selasa, P. Alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins and saponins contents in Moringa oleifera leaves. Indones J Glob Health Res. (2022) 4:139–44. doi: 10.37287/ijghr.v4i1.832
81. Goswami, R, Arya, D, Siddiqui, R, Kumar, S, Sarma, O, and Arora, N. The multifaceted benefits and applications of Moringa oleifera: a comprehensive review. Eur J Nutr Food Saf. (2024) 16:1–13. doi: 10.9734/ejnfs/2024/v16i81489
82. Eladia, R, and Ampode, KM. Moringa (Moringa oleifera lam.) pod meal: nutrient analysis and its effect on the growth performance and cell-mediated immunity of broiler chickens. J Anim Health Prod. (2021) 9:170–7. doi: 10.17582/journal.jahp/2021/9.2.170.177
83. Dzuvor, CKO, Pan, S, Amanze, C, Amuzu, P, Asakiya, C, and Kubi, F. Bioactive components from Moringa oleifera seeds: production, functionalities and applications–a critical review. Crit Rev Biotechnol. (2022) 42:271–93. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.1931804
84. Pop, OL, Kerezsi, AD, and Ciont, C. A comprehensive review of Moringa oleifera bioactive compounds—cytotoxicity evaluation and their encapsulation. Food Secur. (2022) 11:1–18. doi: 10.3390/foods11233787
85. Mitsiogianni, M, Koutsidis, G, Mavroudis, N, Trafalis, DT, Botaitis, S, Franco, R, et al. The role of isothiocyanates as cancer anti-melanoma agents. Antioxidants. (2019) 8:1–35. doi: 10.3390/antiox8040106
86. Habtemariam, S. Anti-inflammatory therapeutic mechanisms of Isothiocyanates: insights from Sulforaphane. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:1169. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061169
87. Byrne, KA, Loving, CL, and McGill, JL. Innate immunomodulation in food animals: evidence for trained immunity? Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1099. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01099
88. Bobeck, EA. Nutrition and health: companion animal applications: functional nutrition in livestock and companion animals to modulate the immune response. J Anim Sci. (2020) 98:1–8. doi: 10.1093/JAS/SKAA035
89. Kober, H AKM, Rajoka, MSR, Mehwish, HM, Villena, J, and Kitazawa, H. Immunomodulation potential of probiotics: a novel strategy for improving livestock health, immunity, and productivity. Microorganisms. (2022) 10:388. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020388
90. Batista, LHC, Oliveira, IM, Prados, LF, Araújo, LC, Ferreira, IM, de Abreu, MJI, et al. The strategic use of an immunomodulatory feed additive in supplements for grazing young Nellore bulls transported after weaning: performance, physiological, and stress parameters. Agriculture. (2023) 13:1027. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13051027
91. Pareek, A, Pant, M, Gupta, MM, Kashania, P, Ratan, Y, Jain, V, et al. Moringa oleifera: an updated comprehensive review of its pharmacological activities, Ethnomedicinal, Phytopharmaceutical formulation, clinical, phytochemical, and toxicological aspects. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:2098. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032098
92. Xiao, X, Wang, J, Meng, C, Liang, W, Wang, T, Zhou, B, et al. Moringa oleifera lam and its therapeutic effects in immune disorders. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:1–9. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.566783
93. Chiș, A, Noubissi, PA, Pop, OL, Mureșan, CI, Fokam Tagne, MA, Kamgang, R, et al. Bioactive compounds in Moringa oleifera: mechanisms of action, focus on their anti-inflammatory properties. Plan Theory. (2024) 13:20. doi: 10.3390/plants13010020
94. Pamuru, RR, Sucharitha, K V., and Vadde, R. Immuno-Oncology of Colorectal Cancer. In: Vadde, R., Nagaraju, G.P. (eds) Immunotherapy for Gastrointestinal Malignancies. Diagnostics and Therapeutic Advances in GI Malignancies. Springer, Singapore.
95. Min, L, Chi, Y, and Dong, S. Gut microbiota health closely associates with PCB153-derived risk of host diseases. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2020) 203:111041. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111041
96. Lu, D, Huang, Y, Kong, Y, Tao, T, and Zhu, X. Gut microecology: why our microbes could be key to our health. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 131:110784. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110784
97. Magne, F, Gotteland, M, Gauthier, L, Zazueta, A, Pesoa, S, Navarrete, P, et al. The firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio: A relevant marker of gut dysbiosis in obese patients? Nutrients. (2020) 12:1474. doi: 10.3390/nu12051474
98. Singh, S, Sharma, P, Sarma, DK, Kumawat, M, Tiwari, R, Verma, V, et al. Implication of obesity and gut microbiome dysbiosis in the etiology of colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:1–28. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061913
99. He, T-B, Huang, Y-P, Huang, Y, Wang, X-J, Hu, J-M, and Sheng, J. Structural elucidation and antioxidant activity of an arabinogalactan from the leaves of Moringa oleifera. Int J Biol Macromol. (2018) 112:126–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.110
100. Liu, X, Xu, Q-X, Wang, D-B, Zhao, J, Wu, Y, Liu, Y, et al. Improved methane production from waste activated sludge by combining free ammonia with heat pretreatment: performance, mechanisms and applications. Bioresour Technol. (2018) 268:230–6. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.109
101. Guo, C, Wang, Y, Zhang, S, Zhang, X, Du, Z, Li, M, et al. Crataegus pinnatifida polysaccharide alleviates colitis via modulation of gut microbiota and SCFAs metabolism. Int J Biol Macromol. (2021) 181:357–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.137
102. Do, MH, Lee, H-B, Oh, M-J, Jhun, H, Choi, SY, and Park, H-Y. Polysaccharide fraction from greens of Raphanus sativus alleviates high fat diet-induced obesity. Food Chem. (2021) 343:128395. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128395
103. Miranda, PM, De Palma, G, Serkis, V, Lu, J, Louis-Auguste, MP, McCarville, JL, et al. High salt diet exacerbates colitis in mice by decreasing Lactobacillus levels and butyrate production. Microbiome. (2018) 6:57. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0433-4
104. Elabd, EMY, Morsy, SM, and Elmalt, HA. Investigating of moringa oleifera role on gut microbiota composition and inflammation associated with obesity following high fat diet feeding. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. (2018) 6:1359–64. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.313
105. Husien, HM, Rehman, SU, Duan, Z, and Wang, M. Effect of Moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharide on the composition of intestinal microbiota in mice with dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1–10. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1409026
106. Zeng, X, Cao, Y, Huang, K, Yan, Y, Chen, D, Zhao, Y, et al. Ascorbic acid derivative 2-o-β-d-glucopyranosyl-l-ascorbic acid from the fruit of lycium barbarum modulates microbiota in the small intestine and colon and exerts an immunomodulatory effect on cyclophosphamide-treated BALB/c mice. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:11128–43. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04253
107. Wen, Z, Tian, H, Liang, Y, Guo, Y, Deng, M, Liu, G, et al. Moringa oleifera polysaccharide regulates colonic microbiota and immune repertoire in C57BL/6 mice. Int J Biol Macromol. (2022) 198:135–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.085
108. Cooper, MA, Colonna, M, and Yokoyama, WM. Hidden talents of natural killers: NK cells in innate and adaptive immunity. EMBO Rep. (2009) 10:1103–10. doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.203
109. Bretto, E, Frara, S, Armandi, A, Caviglia, GP, Saracco, GM, Bugianesi, E, et al. Helicobacter pylori in inflammatory bowel diseases: active protagonist or innocent bystander? Antibiotics. (2024) 13:267. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030267
110. Korniluk, A, Koper, O, Kemona, H, and Dymicka-Piekarska, V. From inflammation to cancer. Ir J Med Sci. (2017) 186:57–62. doi: 10.1007/s11845-016-1464-0
111. Sindhu, R, Sood, N, Puri, V, and Arora, S. Various animal models for preclinical testing of anti-inflammatory agents. (2017). Available online at: https://consensus.app/papers/various-animal-models-for-preclinical-testing-of-sindhu-sood/316ec8d26de85b9cb62f360a58a58b98/ (Accessed February 10, 2024).
112. Cooke, J. Inflammation and its role in regeneration and repair. Circ Res. (2019) 124:1166–8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314669
113. Rajan, TS, Giacoppo, S, Iori, R, De Nicola, GR, Grassi, G, Pollastro, F, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of a combination of cannabidiol and moringin in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Fitoterapia. (2016) 112:104–15. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.05.008
114. Marrocco, A, and Ortiz, LA. Role of metabolic reprogramming in pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion from LPS or silica-activated macrophages. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1–13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.936167
115. Bordon, Y. Inflammasome blockade keeps the thymus young. Nat Rev Immunol. (2012) 12:154. doi: 10.1038/nri3188
116. Iyer, SS, and Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit Rev Immunol. (2012) 32:23–63. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v32.i1.30
117. Fioranelli, M, Roccia, MG, Flavin, D, and Cota, L. Regulation of inflammatory reaction in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:1–13. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105277
118. Saini, R, and Singh, S. Inducible nitric oxide synthase: an asset to neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. (2018) 105:49–61. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4RU0418-161R
119. Packer, M, Porteous, C, and Murphy, M. Superoxide production by mitochondria in the presence of nitric oxide forms peroxynitrite. IUBMB Life. (1996) 40:527–34. doi: 10.1080/15216549600201103
120. Frejborg, E, Salo, T, and Salem, A. Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in head and neck tumorigenesis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:9246. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239246
121. Simmons, DL, Botting, RM, and Hla, T. Cyclooxygenase isozymes: the biology of prostaglandin synthesis and inhibition. Pharmacol Rev. (2004) 56:387–437. doi: 10.1124/pr.56.3.3
122. Luetragoon, T, Sranujit, RP, Noysang, C, Thongsri, Y, Potup, P, Suphrom, N, et al. Bioactive compounds in moringa oleifera lam. Leaves inhibit the pro-inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-induced human monocyte-derived macrophages. Molecules. (2020) 25:1–16. doi: 10.3390/molecules25010191
123. Leonard, WJ, and Lin, JX. Cytokine receptor signaling pathways. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2000) 105:877–88. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.106899
124. Chang, D, Dela Cruz, C, and Sharma, L. Beneficial and detrimental effects of cytokines during influenza and COVID-19. Viruses. (2024) 16:308. doi: 10.3390/v16020308
125. Megha, K, Joseph, X, Akhil, V, and Mohanan, P. Cascade of immune mechanism and consequences of inflammatory disorders. Phytomedicine. (2021) 91:153712. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153712
126. Wautier, J, and Wautier, M. Pro- and anti-inflammatory prostaglandins and cytokines in humans: A Mini review. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:24. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119647
127. Sailaja, BS, Aita, R, Maledatu, S, Ribnicky, D, Verzi, MP, and Raskin, I. Moringa isothiocyanate-1 regulates Nrf2 and NF-κB pathway in response to LPS-driven sepsis and inflammation. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0248691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248691
128. Jomova, K, Raptova, R, Alomar, SY, Alwasel, SH, Nepovimova, E, Kuca, K, et al. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging. Arch Toxicol. (2023) 97:2499–574. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03562-9
129. Afzal, S, Abdul Manap, AS, Attiq, A, Albokhadaim, I, Kandeel, M, and Alhojaily, SM. From imbalance to impairment: the central role of reactive oxygen species in oxidative stress-induced disorders and therapeutic exploration. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1–22. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1269581
130. Brand, M. Mitochondrial generation of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide as the source of mitochondrial redox signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. (2016) 100:14–31. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.04.001
131. Jain, A, and Shakkarpude, J. Oxidative stress: a biomarker for animal health and production: a review. Indian J Anim Res. (2024) 58:1–12. doi: 10.18805/IJAR.B-5300
132. Zhang, L, Wang, X, Cueto, R, Effi, C, Zhang, Y, Tan, H, et al. Biochemical basis and metabolic interplay of redox regulation. Redox Biol. (2019) 26:101284. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101284
133. Andrés Juan, C, Pérez, M, de la Lastra, J, Plou, FJ, Pérez-Lebeña, E, and Reinbothe, S. Molecular sciences the chemistry of reactive oxygen species (ROS) revisited: outlining their role in biological macromolecules (DNA, lipids and proteins) and induced pathologies. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:4642. doi: 10.3390/ijms
134. Redza-Dutordoir, M, and Averill-Bates, DA. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Cell Res. (2016) 1863:2977–92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.09.012
135. Adamo, SA. The effects of stress hormones on immune function may be vital for the adaptive reconfiguration of the immune system during fight-or-flight behavior. Integr Comp Biol. (2014) 54:419–26. doi: 10.1093/icb/icu005
136. Khan, MZ, Huang, B, Kou, X, Chen, Y, Liang, H, Ullah, Q, et al. Enhancing bovine immune, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory responses with vitamins, rumen-protected amino acids, and trace minerals to prevent periparturient mastitis. Front Immunol. (2024) 14:1290044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1290044
137. Younis, N, Khan, MI, Zahoor, T, and Faisal, MN. Phytochemical and antioxidant screening of Moringa oleifera for its utilization in the management of hepatic injury. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:1–11. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1078896
138. Singh, VK. A review of Moringa oleifera as animal fodder: nutritive value and health aspects. Int J Vet Sci Anim Husb. (2024) 9:81–4.
139. Olvera-Aguirre, G, Mendoza-Taco, MM, Moo-Huchin, VM, Lee-Rangel, HA, Roque-Jiménez, JA, Gómez-Vázquez, A, et al. Effect of extraction type on bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera lam. Leaves. Agriculture. (2022) 12:1–9. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12091462
140. Shalaby, EA, Shanab, SMM, El-Raheem, WMA, and Hanafy, EA. Biological activities and antioxidant potential of different biosynthesized nanoparticles of Moringa oleifera. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:18400–14. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23164-2
141. Paikra, BK, Dhongade, HKJ, and Gidwani, B. Phytochemistry and pharmacology of Moringa oleifera lam. J Pharmacopuncture. (2017) 20:194–200. doi: 10.3831/kpi.2017.20.022
142. Modisaojang-Mojanaga, MM, Ogbuewu, IP, Oguttu, JW, and Mbajiorgu, CA. Moringa leaf meal improves haemato-biochemical and production indices in broiler chickens: a review. Comp Clin Path. (2019) 28:621–32. doi: 10.1007/s00580-019-02900-7
143. Baliyan, S, Mukherjee, R, Priyadarshini, A, Vibhuti, A, Gupta, A, Pandey, RP, et al. Determination of antioxidants by DPPH radical scavenging activity and quantitative phytochemical analysis of Ficus religiosa. Molecules. (2022) 27:1326. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041326
144. Gulcin, İ, and Alwasel, SH. DPPH radical scavenging assay. Processes. (2023) 11:2248. doi: 10.3390/pr11082248
145. Sreelatha, S, and Padma, PR. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of Moringa oleifera leaves in two stages of maturity. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. (2009) 64:303–11. doi: 10.1007/s11130-009-0141-0
146. Ojha, PS, Tripathi, V, and Dwivedi, P. Antioxidant capacity and radical scavenging activities of Moringa oleifera. Acta Sci Agric. (2024) 8:35–7.
147. Siddhuraju, P, and Becker, K. Antioxidant properties of various solvent extracts of total phenolic constituents from three different agroclimatic origins of drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera lam.) leaves. J Agric Food Chem. (2003) 51:2144–55. doi: 10.1021/jf020444+
148. Duranti, G, Maldini, M, Crognale, D, Horner, K, Dimauro, I, Sabatini, S, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf extract upregulates nrf2/ho-1 expression and ameliorates redox status in c2c12 skeletal muscle cells. Molecules. (2021) 26:26. doi: 10.3390/molecules26165041
149. Gaschler, M, and Stockwell, B. Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 482:419–25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.086
150. Mortensen, MS, Ruiz, J, and Watts, JL. Polyunsaturated fatty acids drive lipid peroxidation during Ferroptosis. Cells. (2023) 12:804. doi: 10.3390/cells12050804
151. Wood, LG, Gibson, PG, and Garg, ML. Biomarkers of lipid peroxidation, airway inflammation and asthma. Eur Respir J. (2003) 21:177–86. doi: 10.1183/09031936.03.00017003a
153. Larsson, K, Harrysson, H, Havenaar, R, Alminger, M, and Undeland, I. Formation of malondialdehyde (MDA), 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (HHE) and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) in fish and fish oil during dynamic gastrointestinal in vitro digestion. Food Funct. (2016) 7:1176–87. doi: 10.1039/c5fo01401h
154. Papastergiadis, A, Fatouh, A, Jacxsens, L, Lachat, C, Shrestha, K, Daelman, J, et al. Exposure assessment of malondialdehyde, 4-Hydroxy-2-(E)-Nonenal and 4-Hydroxy-2-(E)-Hexenal through specific foods available in Belgium. Food Chem Toxicol. (2014) 73:51–8. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.06.030
155. Fitri, A, Toharmat, T, Astuti, DA, and Tamura, H. The potential use of secondary metabolites in moringa oleifera as an antioxidant source. Media Peternak. (2015) 38:169–75. doi: 10.5398/medpet.2015.38.3.169
156. Sinha, M, Das, DK, Bhattacharjee, S, Majumdar, S, and Dey, S. Leaf extract of moringa oleifera prevents ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress in mice. J Med Food. (2011) 14:1167–72. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2010.1506
157. Sinha, M, Das, DK, Datta, S, Ghosh, S, and Dey, S. Amelioration of ionizing radiation induced lipid peroxidation in mouse liver by Moringa oleifera lam. Leaf extract. Indian J Exp Biol. (2012) 50:209–15.
158. Singh, D, Arya, PV, Aggarwal, VP, and Gupta, RS. Evaluation of antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of Moringa oleifera lam. Leaves in carbon tetrachloride-intoxicated rats. Antioxidants. (2014) 3:569–91. doi: 10.3390/antiox3030569
159. Nkukwana, T, Muchenje, V, Masika, PJ, Dzama, K, and Descalzo, A. Fatty acid composition and oxidative stability of breast meat from broiler chickens supplemented with Moringa oleifera leaf meal over a period of refrigeration. Food Chem. (2014) 142:255–61. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.07.059
160. Kamble, MT, Gallardo, W, Salin, KR, Pumpuang, S, Chavan, BR, Bhujel, RC, et al. Effect of Moringa oleifera leaf extract on the growth performance, hematology, innate immunity, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus agalactiae biotype 2. Animals. (2024) 14:953. doi: 10.3390/ani14060953
161. El-Kassas, S, Aljahdali, N, Abdo, SE, Alaryani, FS, Moustafa, EM, Mohamed, R, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf powder dietary inclusion differentially modulates the antioxidant, inflammatory, and histopathological responses of Normal and Aeromonas hydrophila-infected mono-sex Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:918933. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.918933
162. Li, Z, Luo, W, Zhou, Q, Sun, C, Zheng, X, Liu, B, et al. Investigation of the fermentation process of Moringa oleifera leaves and its effects on the growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal microbiome of Procambarus clarkii. Antioxidants. (2024) 13:1355. doi: 10.3390/antiox13111355
163. Peñalver, R, Martínez-zamora, L, Lorenzo, JM, Ros, G, and Nieto, G. Nutritional and antioxidant properties of Moringa oleifera leaves in functional foods. Food Secur. (2022) 11:1–13. doi: 10.3390/foods11081107
164. Sanodiya, P, Prasad, K, Neel, B, and Mishra, K Maize nutritional quality and value addition: a brief overview. Maize Journal (2024) 11:75–82.
165. A, W III, and B, J. Soybean meal quality and analytical techniques. In: Soybean and nutrition. Intech Open. (2011)
166. Li, J, Zhang, S, Gu, X, Xie, J, Zhu, X, Wang, Y, et al. Effects of alfalfa levels on carcass traits, meat quality, fatty acid composition, amino acid profile, and gut microflora composition of Heigai pigs. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:975455. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.975455
Keywords: Moringa oleifera, nutritional profile, immunomodulatory mechanism, animal, feed additive
Citation: Mohai Ud Din R, Eman S, Zafar MH, Chong Z, Saleh AA, Husien HM and Wang M (2025) Moringa oleifera as a multifunctional feed additive: synergistic nutritional and immunomodulatory mechanisms in livestock production. Front. Nutr. 12:1615349. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1615349
Edited by:
Xiaolong Ji, Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, ChinaReviewed by:
Hirdayesh Anuragi, Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), IndiaXuefeng Guo, Tarim University, China
Jing Zhang, Academy of National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration, China
Copyright © 2025 Mohai Ud Din, Eman, Zafar, Chong, Saleh, Husien and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hosameldeen Mohamed Husien, MDA4NkA0M3l6dS5lZHUuY24=; Mengzhi Wang, bWVuZ3poaXdhbmd5ekAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Raza Mohai Ud Din
Raza Mohai Ud Din Salwa Eman1†
Salwa Eman1† Muhammad Hammad Zafar
Muhammad Hammad Zafar Ahmed A. Saleh
Ahmed A. Saleh Hosameldeen Mohamed Husien
Hosameldeen Mohamed Husien Mengzhi Wang
Mengzhi Wang