- 1Department of Pharmaceutical Botany, Faculty of Pharmacy, Cukurova University, Adana, Türkiye
- 2Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Cukurova University, Adana, Türkiye
- 3Department of Food Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Adana Alparslan Turkes Science and Technology University, Adana, Türkiye
- 4Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Bahçeşehir University, Istanbul, Türkiye
- 5Department of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Cukurova University, Adana, Türkiye
- 6Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Türkiye
- 7Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Dicle University, Diyarbakir, Türkiye
- 8Department of Seafood Processing Technology, Faculty of Fisheries, Cukurova University, Adana, Türkiye
- 9Department of Molecular Food Chemistry and Food Development, Institute of Food and One Health, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz University Hannover, Hannover, Germany
- 10Biotechnology Research and Application Center, Cukurova University, Adana, Türkiye
Background and aims: Thymbra spicata L. has been widely recognized as a food additive due to its therapeutic benefits and low toxicity risk. This study focuses on the chemical constituents of T. spicata essential oil, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties of essential oil (EO)-based nanoemulsions (NEs) and for the first time their effect on the preservation of curd cheese.
Methods: Nanoemulsions containing three different concentrations of EO (1%, 3%, and 5%) were tested for conductivity, droplet size, pH, polydispersity index (PDI), rheological properties, viscosity, and zeta potential. In addition, chemical composition was analyzed using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Moreover, the antimicrobial properties of the EOs and its nanoemulsion forms were evaluated in vitro against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Bacillus subtilis using the agar well diffusion assay. After in vitro studies, the nanoemulsion concentrations of 1%, 3%, and 5% and pure EO were incorporated into curd cheese. Curd cheese treatments were assessed in terms of total yeast and mold, mesophilic aerobic and lactic acid bacteria count, and quality analyses for 28 days.
Results: The results showed that the dispersions with a spherical shape and droplet sizes were smaller than 165 nm for all three concentrations (154.9, 165.0, and 151.3 nm, respectively). All formulations maintained their physical properties even after stability tests. Major components in the essential oil (EO) were identified as γ-terpinene, thymol, carvacrol, and p-cymene. The nanoemulsion delayed the growth of mold and yeast for up to 28 days.
Conclusions: Consequently, these findings indicate that T. spicata EO and derived nanoemulsions could be used as vital sources for developing new and impactful antimicrobial agents for food and different industries.
1 Introduction
Food safety is the main concern of producers, regulators, and consumers. Foodborne pathogens pose a public health risk, and despite current breakthroughs in production procedures, the frequency of foodborne infections is not reducing effectively (1, 2). Essential oils (EOs) have gained widespread commercial use across various industries due to their aromatic, therapeutic, and antimicrobial properties. For instance, lavender EO is frequently incorporated into skincare products such as Aveeno Stress Relief Moisturizing Lotion for its calming effects, while peppermint oil is found in Dr. Bronner's Peppermint Pure-Castile Soap and Burt's Bees Cooling Lip Balm for its refreshing and soothing properties. Tea tree oil, known for its antimicrobial activity, is a key ingredient in The Body Shop Tea Tree Oil line, targeting acne, and skin blemishes. Additionally, eucalyptus oil is used in Vicks VapoRub for its respiratory benefits (3). Growing consumer demand for foods with fewer chemical additives has boosted interest in essential oils (EOs). Rich in terpenoids and phenolic acids, EOs exhibit potent antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant activities (1). These natural, eco-friendly compounds deliver broad-spectrum microbial suppression by allowing the hydroxyl groups on their phenolic rings to interact with and disrupt microbial cell membranes, making them an effective alternative for extending the shelf life of various food products (2).
Currently, the food industry has shown an increasing need for formulations based on natural products to create new food preservatives that can stop the growth of microorganisms, extend the shelf life of food, and preserve food in different storage conditions (4). EOs are natural, volatile compounds extracted from plants. They are widely utilized in numerous sectors, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical industries. In the pharmaceutical sector, EOs are used in medication topical formulations, aromatherapy, and alternative medicine owing to their antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and therapeutic properties (5). EOs on the “Generally Recognized As Safe” (GRAS) list have emerged in recent years as attractive antimicrobial agents with significant potential for use in bioactive food packaging. However, even GRAS-status EOs face limitations regarding their permissible concentrations and the types of foods to which they can be applied due to factors such as potential sensory impacts and regulatory restrictions. Plenty of research has investigated the bioactivity of EO-based nanoemulsions (NEs) to address these challenges and enhance their effectiveness and applicability (5–7). There are some studies of EO-based nanoemulsion on cheese (8, 9). Cai et al. (10) reported that the orange EO-based nanoemulsion with guar gum/chitosan edible films was effective for the preservation of cheese. Faramarzi et al. (11) investigated the inhibitory effect of Urtica dioica EO-based nanoemulsion and placebos on the food pathogen bacteria in pizza cheese. Rossi et al. (12) assessed the antimicrobial activity of Cinnamon EO-based nanoemulsions against Pseudomonas paracarnis in fresh cheese.
Nanoemulsions (NEs) are heterogeneous dispersions of colloidal particles composed of two separate liquid phases (oil and water phases) stabilized by surfactants and cosurfactants. NEs are optically transparent with a mean droplet diameter of <200 nm. This transparency is crucial in their widespread use in developing clear food products and drug delivery systems (13, 14). NEs are prepared using low-energy methods by exploiting the chemical capacity of their components and high-energy methods based on shearing and homogenization under high pressure. Low-energy approaches are preferred for thermosensitive compounds since they impose lower energy demand. Spontaneous emulsification enhances the production of nanometric droplets by increasing the surface area of the oil–water interface, compared with the use of fixed carrier oils for stability due to a significant proportion of medium-chain fatty acids (15). Nanoemulsions are especially useful for EOs due to their ability to enhance stability, protect volatile components from environmental degradation, and improve water dispersibility. Their small droplet size increases surface area, enabling better bioavailability and antimicrobial activity. Additionally, nanoemulsions allow for controlled and sustained release, which prolongs the functional effects of EOs in various applications (5, 13).
Bioactive compounds, such as certain polyphenols, carotenoids, and EOs, which have low solubility in polar solutions such as water, are less soluble in polar solutions, which may limit their dispersion and interaction within aqueous food systems, potentially reducing their effectiveness in preserving food. NE formulations have a small droplet size (O/W system), which enhances the solubility of the components via surfactants and the absorption of the formulation. Many previous studies have used NEs as carrier systems for evaluating the activity of various EOs, such as Foeniculum vulgare, Ocimum, Tribute citrus, cinnamon, and thyme. Thymbra spicata is an aromatic plant that belongs to the Lamiaceae family. Previous studies on EO nanoemulsions have demonstrated that formulating EOs into nano-sized droplets significantly enhances their stability, solubility, and bioavailability, especially in aqueous environments. These studies also highlighted improved antimicrobial and antioxidant properties due to the increased surface area and better dispersion. Inspired by these findings, we aimed to explore whether a similar nanoemulsion formulation could enhance the biological activity of T. spicata EO, which is known for its rich phenolic content and strong bioactivity but suffers from volatility and poor water solubility. The goal was to apply the benefits observed in earlier EO nanoemulsion work to a less-studied but highly promising plant species (16–20).
In Mediterranean countries, it is used as medicine or food, adding flavor to meat dishes, soups, and salads. T. spicata EO comprises many chemical compounds such as thymol, p-cymene, carvacrol, gamma-terpinene, and caryophyllene (21, 22). T. spicata EO is highly valuable in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries owing to its potent aroma and therapeutic properties. It has demonstrated antimicrobial, antioxidant, antifungal, anti-biofilm, cytotoxic activities, and anti-quorum-sensing (23–25).
Gedikoglu and Çikrikci Erünsal (26) reported that T. spicata EO-based NEs revealed an extremely high antibacterial activity against S. epidermidis, B. cereus, E. coli, and Salmonella enteritidis. Previously, T. spicata EOs were evaluated by Gedikoglu (27) for their antimicrobial activity against S. typhimurium and antioxidant activity in pectin-based edible coatings for aerobically packaged, ready-to-eat, sliced Bologna meat products during cold storage. Sengun et al. (28) examined the impact of T. spicata EO and its extract against S. aureus, revealing that the EOs more effectively inhibited the growth of B. subtilis and L. monocytogenes. However, no study has yet evaluated T. spicata EO-based nanoemulsions in preserving curd cheese under real storage conditions.
In this study, the chemical composition of the T. spicata EO was analyzed using GC-MS. Besides, in vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activities and antioxidant properties were tested using the EO-based nanoemulsions. There are a limited number of studies on the use of T. spicata EO-based nanoemulsions in cheese preservation. Therefore, this study focuses on the chemical constituents of T. spicata EO, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of EO-based nanoemulsions, and their effect on the preservation of curd cheese.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant material
Thymbra spicata plant samples used in this study were obtained from the herbal market in Adana, Southern Turkey, in August 2024. The samples were determined by S. Demirci Kayiran.
2.2 Preparation of T. spicata EO
The plant material was allowed to dry in the shade at room temperature. A Clevenger apparatus (ISOLAB) was used to hydrodistillate a 50-g portion of the dried materials with distilled water (250 ml) for 3 h. After three repetitions of the procedure, the resulting EO was stored for later usage at 4°C.
2.3 GC-MS analysis of T. spicata EO
The T. spicata EOs were analyzed using an Agilent MS system (7010B) coupled to an Agilent GC (7890B; Agilent Technologies Inc., CA, USA).
The EOs were analyzed using Gas Chromatography–Flame Ionization Detection/Mass Spectrometry (GC-FID/MS) instrument, following the protocol of Demirci Kayiran et al. (29). GC analyses were performed using a DB-Wax column (60 m × 0.25 I.D., film thickness 0.25 μm; J&W Scientific, CA, USA). The injector and detector temperatures were set to 250°C. Helium, with a flow rate of 1.4 ml/min, was the carrier gas. The split ratio was 20:1, and 1.0 μl was used as the sample size. The initial temperature of the oven was kept at 40°C for a period of 4 min, then elevated up to 250°C in steps of 5°C/min, and could be kept at this temperature for 10 min. The NIS14L software was used to calculate the percentage composition of the EO.
2.4 Construction of pseudo-ternary phase diagrams
The NE formulations were prepared by the pseudo-ternary phase diagram method. The oil phase, surfactant, cosurfactant, and aqueous phase were used while constructing the diagrams, which were oleic acid, Cremophor EL, ethanol, and distilled water, respectively. Combinations of surfactant and cosurfactant (S/CoS or Smix) were investigated with weight ratios of 1:1, 1.5:1, and 2:1. Nine different concentrations were used to achieve the oil-to- Smix ratios of 1:9, 2:8, 3:7, 4:6, 5:5, 6:4, 7:3, 8:2, and 9:1. All the preparations were titrated with distilled water at room temperature with continuous mixing using a mechanical stirrer (HEIDOLPH; 600 rpm). Distilled water was added to the system until it began to cloud, and the volume was recorded. Computer software was utilized to create pseudo-ternary phase diagrams to determine the percentages of oil, Smix, and distilled water during NE formulation (30).
2.5 Preparation of NE formulations by low-energy methods
The formulation that yielded an NE system was chosen based on the phase diagram results. The best NE ratio was determined to be at the center of the NE-forming regions. Selecting the NE ratio from the center of the NE-forming region is a rational approach, as it reflects optimal component balance and promotes thermodynamic stability. This region typically yields homogeneous, clear, and kinetically stable systems with smaller droplet sizes and improved physical stability. The formulation was prepared by titrating an oil and Smix with distilled water at room temperature with mechanical stirring using a low-energy method, similar to the preparation of pseudo-ternary phase diagrams. T. spicata EO was used at various concentrations (1%, 3%, and 5%) by dissolving it in the oil phase. The placebo was achieved by preparing the formulation using the same process as T. spicata EO but without the oil (15, 31).
2.6 Characterization of NE formulations
2.6.1 Droplet size, distribution, and zeta potential
The droplet size and the droplet size distribution of placebo and EO-based NEs were analyzed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) technique (Horiba SZ100, Japan). In this analysis, a 532-nm laser and scattering angles of 90 and 173° were used by the HORIBA SZ-100 DLS instrument, depending on sample conditions. Average droplet size was measured, and data were presented as average diameter ± standard deviation (SD). The zeta potential was determined by means of disposable flat-fold capillary zeta cells, and the measurements were performed through the system software. Measurements were repeated three times to obtain the mean millivolt ± SD at 25°C (32).
2.6.2 Morphology of NEs
The microscopic image was used to analyze the shape of the microemulsions using a high-resolution inverted microscope (Leica DM IL LED Fluo, Germany). The results were represented in corresponding figures (33).
2.6.3 pH value
The pH value of placebo and EO-based NE formulations was measured at 25 ± 1°C with a digital pH meter (Mettler Toledo FiveGo, Switzerland). The test was achieved in triplicate and displayed as mean ± SD (34).
2.6.4 Conductivity
The electrical conductivity of placebo and EO-based NEs was determined using a conductivity meter (Mettler Toledo FiveEasy Plus). The samples were kept at 25 ± 1°C. The measurements were accomplished in triplicate and pointed out as mean ± SD (35).
2.6.5. Viscosity and rheological properties
A Brookfield cone and plate rheometer were used to measure the shear stress, shear rate, and apparent viscosity of placebo and EO-based NEs in triplicate (Brookfield DV3THACJ0; Brookfield Engineering Labs. Inc., MA, USA) under controlled temperature (25 ± 0.5°C). Rotation speed was adjusted at 10–100 rpm (31).
2.7 Stability of NE formulations
Thermodynamic stability assays were conducted to elucidate the long-term stability of the formulations. The formulations were evaluated by centrifugation and cycles of freeze-thaw and heating-cooling. Each formulation was centrifuged using a centrifuge (5,000 rpm for 30 min, performed in triplicate). In addition, the formulations were subjected to a cycle of heating and cooling and then stored at 4 and 45°C, respectively, for 48 h. This was followed by a cycle of freeze-thaw. The formulations were placed in vials and frozen at −4°C for 12 h and at room temperature for 12 h. Each experiment was performed in triplicate (36, 37).
2.8 Antimicrobial activity analysis of EO and NE formulations
The agar well diffusion assay was applied to determine antimicrobial activities using B. subtilis, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and. E. coli, which were activated by incubation at 37°C for 24 h. After activation, the bacteria were mixed with sterile 0.9% NaCl solution and adjusted to a density of McFarland 0.5 (~108 cfu/ml). This bacterial solution (100 μl) was applied to the Muller–Hinton agar (MHA) medium by spreading method. Then, 7 mm diameter wells were made on the medium, and 100 μl of the extract was added to each well. The concentrations of the extracts ranged from 100 to 0.315 mg/ml. Petri dishes were incubated at 37°C for 24–48 h. Following incubation, the diameters of the inhibition zones around the wells were measured with a caliper. The well diffusion test was performed in two parallel runs for each petri, and the diameter of the inhibition zones was measured at three different points (38).
2.9 Application of the nanoemulsions on the curd cheese
Curd cheese was obtained daily from the Dairy Products Processing Unit of the Food Branch under the Directorate of the Research and Application Farm of the Faculty of Agriculture, Çukurova University. Curd cheese was classified into six groups: control (plain curd cheese), T. spicata EO, nanoemulsions containing 1%, 3%, and 5% T. spicata EO, and placebo. Each group was prepared in 500-g portions. Curd cheese of ~100 g was put into single-use plastic containers and stored for 28 days at 4 ± 1°C in a refrigerator. Antioxidant activity, total phenolic content (TPC), pH, color parameters, and microbiological analysis of these curd cheese samples were determined at 0, 3, 5, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days of storage period. To minimize potential carry-over effects of residual EOs, the EO-containing agar media were allowed to stand under a laminar flow hood for a predetermined period before inoculation. This step was applied to allow the volatile compounds to stabilize before microbial analysis.
2.9.1 Physicochemical analysis of cheese samples during storage
The cheese sample (10 g) was homogenized with 100 ml distilled water for 1 min using a homogenizer. The pH was carried out using a digital pH meter (Mettler-Toledo, Schwerzenbach, Switzerland), according to the method of Polat Yemiş et al. (39). Color measurements were carried out at room temperature to ensure consistency and minimize temperature-related variations using a Minolta Chroma meter (Chroma Meter CM-5; Minolta Camera Co. Ltd., Osaka, Japan), following the method of Cai et al. (10). The values of L*, a*, and b* were done and the whiteness index (WI) was calculated according to the following equation (40).
2.9.2 Antioxidant activity and total phenol compounds
Antioxidant activity and total phenol compounds were accomplished by using the method of Shawir et al. (41). For antioxidant activity (ABTS) and total phenolic content, the samples, weighing 5 g, were placed completely in 10 ml of methanol and then centrifuged at 5,000 rpm for 10 min.
2.9.3 ABTS assay
The ABTS method was done with slight modifications as described by Re et al. (42). The reaction between the diluted sample and 3.9 ml ABTS radical solution (7 mM; mixed with 2.45 mM potassium persulfate and left for 12–16 h) was carried out kinetically by measuring the change in 734 nm absorbance (Cary 60 UV-Vis Spectrophotometer, Agilent Technologies) for 15 min. Antioxidant activities were expressed as μmol Trolox/L from the absorbances of Trolox standards prepared at different concentrations (6.25–200.0 ppm) determined by the same method.
2.9.4 Total phenolic content analysis
Total phenolic content (TPC) analysis was done according to the method of Singleton et al. (43) with minor changes. Before analysis, 0.5 ml of Folin–Ciocalteu solution was added to cheese samples prepared according to the procedure of Shawir et al. (41), and the mixture was left for 3 min. After that, 20% sodium carbonate was added to this mixture and allowed to stand for 60 min at room temperature in the dark room. Absorbance values were read at 765 nm with a UV/VIS spectrophotometer (Cary 60, Agilent Technologies). Using the calibration received from the absorbances of standards (gallic acid) prepared at different concentrations (between 31.25 and 500.0 ppm) by the same method, the TPC values were then calculated. Data were presented as mg/g of gallic acid equivalents.
2.9.5 Microbiological analysis of cheese samples during storage
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB), total aerobic mesophilic bacteria (TAMB), and yeast–mold assays were performed on curd cheese samples. The results were calculated as log cfu/g.
2.9.5.1 Determination of total aerobic mesophilic bacteria counts (TAMB)
TAMB counts in curd cheese samples were determined by inoculation on plate count agar medium using the pour plate method. Following inoculation, colonies that developed after 48–72 h of incubation at 30°C were counted (44, 45).
2.9.5.2 Determination of yeast and mold counts
Yeast and mold counts were determined using the spread plate counting method on Yeast Extract Glucose Chloramphenicol Agar medium. Following inoculation, yeast colonies were counted on the third day, and mold colonies were counted on the fifth day of incubation at 30°C (44).
2.9.5.3 Determination of lactic acid bacteria count
Enumeration of lactic acid bacteria was performed using the pour plate method, administering De Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe Agar (MRS). The sample (10 g) was blended with 10 ml of distilled water, serially diluted, and 1 ml of the appropriate dilution was transferred into sterile petri dishes. Then, molten MRS agar was poured over the sample, gently mixed, and allowed to solidify. The plates were incubated at 30°C for 3 days. After incubation, LAB colonies were counted and expressed as log cfu/g (46). All experiments were carried out in triplicate.
2.10 Statistical analysis
Data analysis of ANOVA Fisher's Least Significant Difference (level of confidence 95%, p < 0.05) was performed using Minitab® 17 software (Minitab Inc., State College, PA, USA). The values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test to compare the physicochemical properties of different nanoemulsion formulations (NE 2:1 Placebo, 1%, 3%, and 5%). A p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The analysis showed no significant differences in pH and conductivity among the formulations (p > 0.05), while droplet size and viscosity exhibited minor but non-significant variations. Notably, the polydispersity index (PDI) of the 1% formulation was significantly higher than that of the placebo (p < 0.05), indicating a broader size distribution at this concentration.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Chemical components of EOs
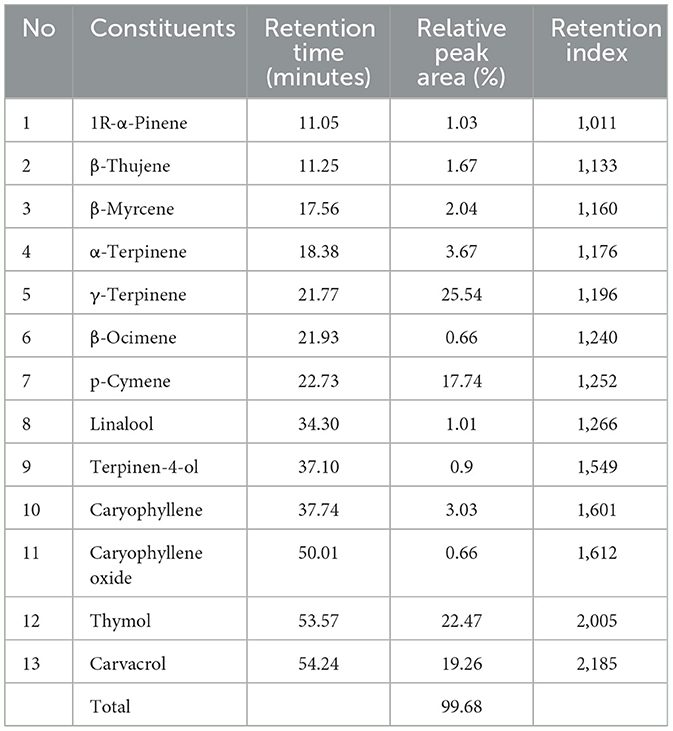
The analysis of T. spicata EO revealed that its chemical composition is dominated by four major compounds, including γ-terpinene (25.54%), thymol (22.47%), carvacrol (19.26%), and p-cymene (17.74%; Table 1). These constituents accounted for ~85% of the total oil content, underscoring their primary role in the biological activities of the oil. The predominance of γ-terpinene was consistent with previous findings on Thymbra and Thymus species (47). As a monoterpene hydrocarbon, γ-terpinene serves as a biosynthetic precursor for oxygenated monoterpenes such as carvacrol and thymol (48). The high levels of thymol and carvacrol in this study aligned with the thymol-carvacrol chemotype widely reported in T. spicata populations (49).
The ratios of thymol and carvacrol vary based on environmental factors such as geographical location, climate, and extraction methods. Studies on T. spicata species collected from various regions of Turkey have revealed variations in the chemical composition of their EOs. In a previous study, the EOs extracted from T. spicata leaves collected from Nizip and Gaziantep using subcritical water extraction were found to be mainly composed of carvacrol (86.2%), thymol (3.67%), and E-3-caren-2-ol (3.08%) (50), whereas the EO obtained through hydrodistillation of T. spicata collected from Diyarbakir was predominantly composed of thymol (55.3%), carvacrol (8.7%), caryophyllene (4.2%), and p-cymene (11.2%) (47). Inan et al. (51) found that the highest proportion (64.53%) of carvacrol was discovered in the EO of T. spicata collected from Kahta, Adiyaman, after flowering, whereas the lowest proportion (53.55%) was observed before the flowering stage. Moreover, thymol was not detected in the EO. Another study determined the EO content of T. spicata var. spicata collected from Aksu, Antalya. The most abundant compounds were carvacrol (63.23%), p-cymene (8.31%), and γ-terpinene (18.94%) (52). Additionally, the composition of the EO obtained by hydrodistillation from T. spicata collected from Eskişehir revealed that the major compounds were carvacrol (56.03%), p-cymene (9.61%), γ-terpinene (6.87%), and trans-caryophyllene (10.41%) (28). Moreover, Nath et al. (53) studied the chemical composition of the EO of T. spicata collected from Kepsut, Balikesir, and the results revealed that the main components of T. spicata EO were carvacrol (52.3%) and p-cymene (21.1%).
Studies indicate that the oils from warmer regions have higher carvacrol content, whereas those from cooler climates are more likely to produce thymol (54). The composition reported in the present study suggests a balanced synthesis of these phenolic compounds, reflecting the influence of local environmental conditions on the EO profile.
From a biological perspective, thymol and carvacrol are well-documented for their potent antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities (55). Their presence at elevated levels suggests significant therapeutic potential of the T. spicata EO. In addition, γ-terpinene and p-cymene exhibit synergistic effects with thymol and carvacrol, enhancing their biological efficacy (56). This synergism may contribute to the enhanced antimicrobial properties commonly associated with T. spicata EO (57).
3.2 Pseudo-ternary phase diagrams and preparation of NE formulations
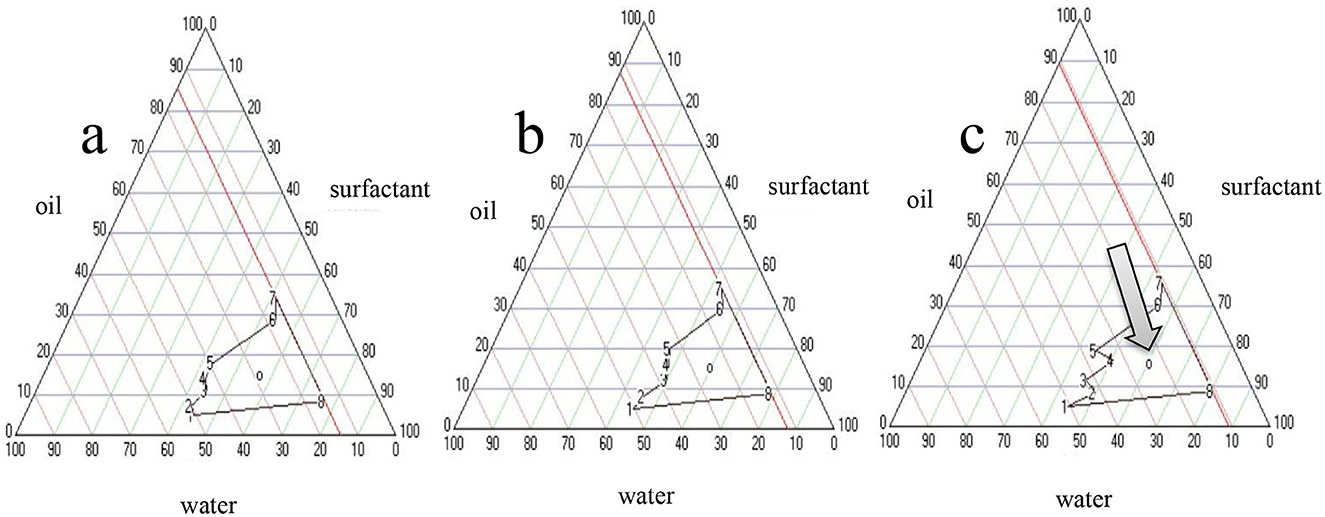
The pseudo-ternary phase diagram method was used to determine the NE formation regions and obtain a clear and stable NE. Thus, a pseudo-ternary phase diagram was used to obtain the best concentration ratios of surfactant, co-surfactant (Smix), and oil. Different concentration ratios ranging from 1:9 to 9:1 of Cremophor EL and ethanol were used as the surfactant-co-surfactant mixtures to prepare Smix. Cremophor EL is well known for its outstanding emulsifying activity in the development of NEs. These surfactants are non-toxic; hence, they create oil-in-water NEs with high stability (58–60). Akhter et al. (61) successfully prepared an NE gel using an extract of Cucumis melo. Ethanol was chosen as the cosurfactant in the formulation since short-chain alcohols are commonly used as cosurfactants to enhance NE formation. The NE regions of the diagrams obtained with three different Smix ratios were determined. The compositions corresponding to the central points of NE regions are shown in Table 2.
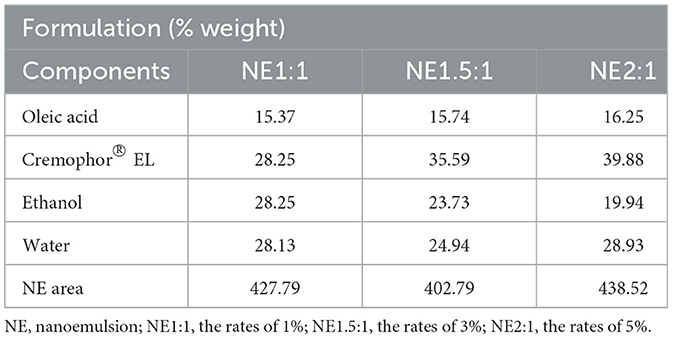
Table 2. Blank nanoemulsion compositional ratios and relative nanoemulsion areas from pseudo-ternary phase diagrams.
The NE formation region in the pseudo-ternary phase diagram is shown in Figure 1. Notably, a distinct order of NE formation region was seen where the ratio of Smix followed the order Smix 2:1 > Smix 1:1 > Smix 1.5:1. The NE formation had a larger region with a Smix ratio of 2:1, indicating that NE formation was optimal at a Smix ratio of 2:1. Therefore, this formulation was chosen for characterization and activity tests.
Turbidity or transparency of NE formulations not only provides a good appearance but also serves as a crucial parameter indicating thermodynamic stability. Transparent, homogeneous, and non-turbid NEs are more stable than conventional emulsions, with higher shelf life (61, 62).
3.3 Characterization of nanoemulsions
The oil phase was prepared by adding T. spicata EO at the rates of 1%, 3%, and 5% (w/w) concentrations. The optimal NEs displayed a yellowish color with translucency against a blue background and carried the distinctive aroma of T. spicata EO. The characteristics of the formulation were evaluated in terms of droplet size and distribution, pH value, zeta potential, viscosity, and rheological properties.
3.3.1 Droplet size, distribution, and zeta potential
One of the most essential properties for stability is droplet size and distribution. The concentration of oil and Smix has a synergy with the droplet size. Besides the small droplet size, the distribution is also important and is quantified using the polydispersity index (PDI) (26, 62). Wei et al. (63) reported that the droplet size of fenpropathrin NE decreased by increasing the concentrations of surfactant and cosurfactant, and the stability of the emulsion also improved. Similar results were found by Salama et al. (64).
The PDI is a parameter that measures the homogeneity of droplets, ranging between 0.0 and 1.0. A low PDI value indicates closely packed droplet size and homogeneity in the distribution of NE formulations. A PDI value ≤ 0.7 corresponds to a monodisperse formulation, suggesting a uniform NE. A PDI value < 0.25 signifies a narrow size distribution in the system. The other values indicate that the formulations are in acceptable ranges (30, 65). The average droplet size and PDI values of optimum formulations are shown in Table 3.
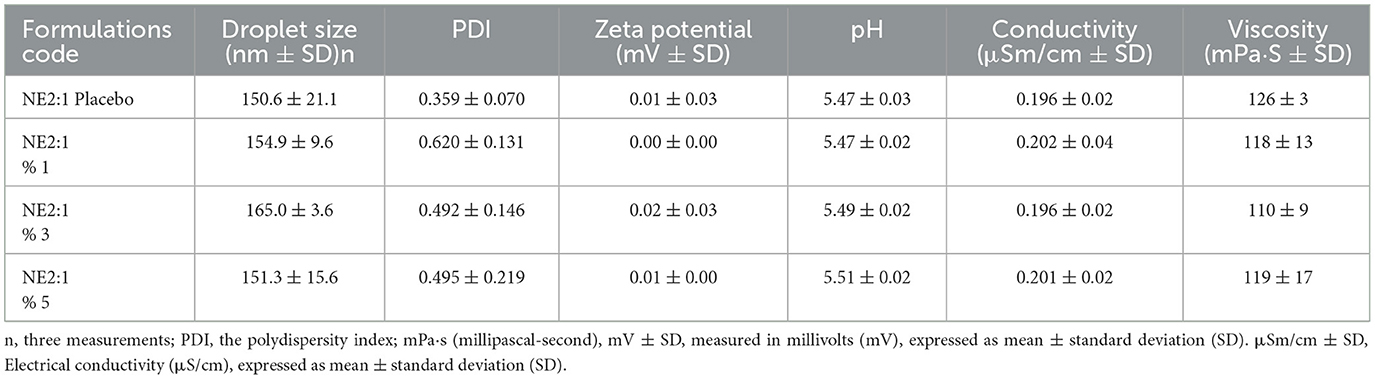
Table 3. Mean droplet size, PDI, zeta potential, pH, conductivity, and viscosity obtained for the characterization of nanoemulsions [mean ± standard deviation (SD), triplicate].
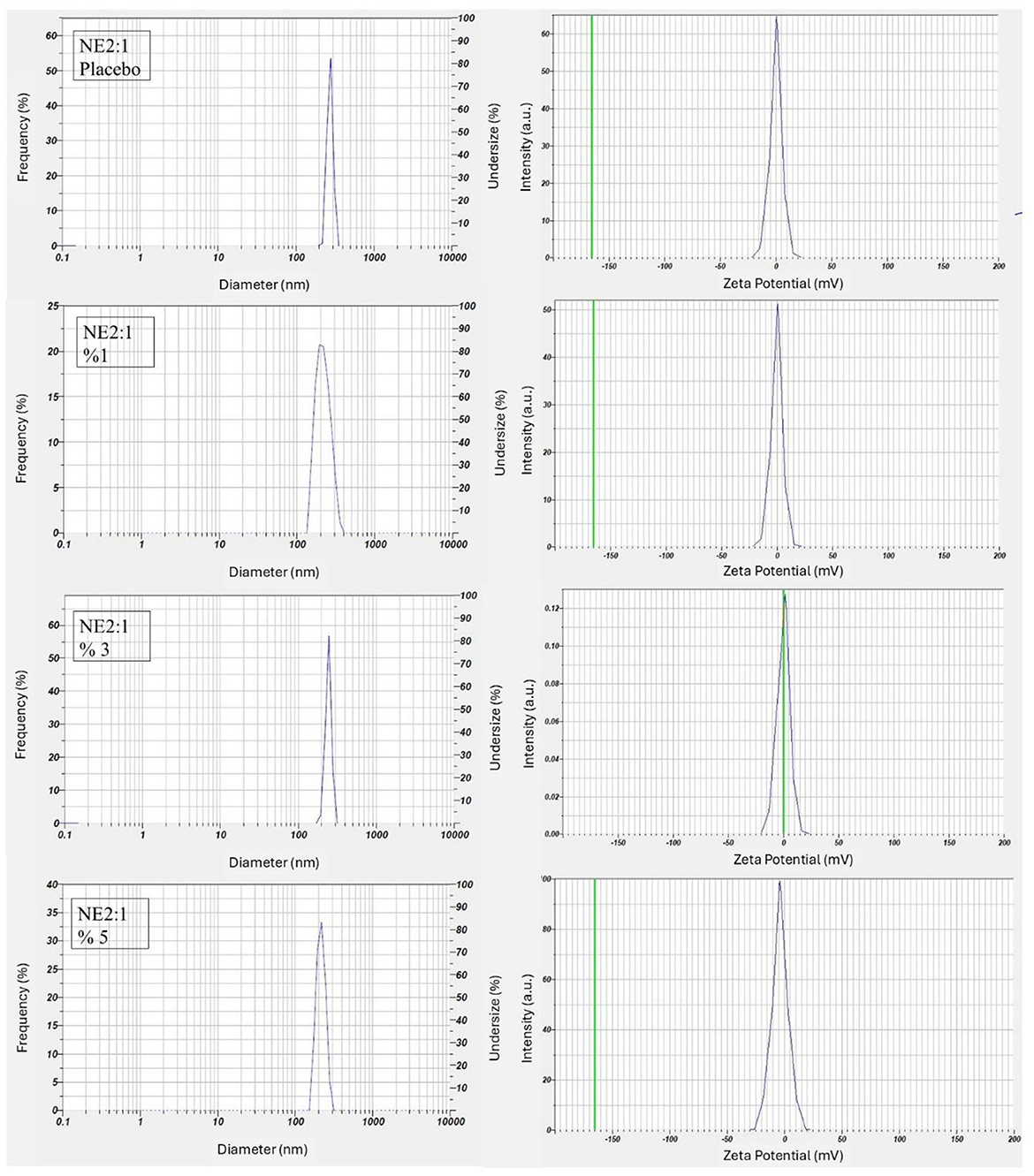
All reported values correspond to the mean ± SD of three measurements. The average droplet size for 1%, 3%, and 5% NEs was 154.9 ± 9.6, 165.0 ± 3.6, and 151.3 ± 15.6 nm, respectively. The droplet size distribution and zeta potential graphs for each formulation are presented in Figure 2. The results of all formulations were within the nanometre range and exhibited the desired characteristics. In a previous study, various formulation combinations were designed using ethyl oleate, Cremophor EL, and Tween 80 to develop an NE containing corosolic acid. The distribution of droplet size and PDI of the prepared NE were characterized using DLS (Malvern Instruments, United Kingdom). The smallest droplet size of 181.3 nm and a PDI of 0.424 were obtained in formulations containing oleic acid (60).
The stability of NEs under storage is assessed by the zeta potential, which is an important parameter indicating the electrostatic surface charge of globules or particles. A higher absolute zeta potential value (both positive and negative) represents a higher stability. Stable NEs can also be obtained using non-ionic or polymeric surfactants, with zeta potentials as close to zero as possible (66, 67). The zeta potential measurement results showed that the formulations prepared with Cremophor EL, a non-ionic surfactant, did not exhibit any electrical charge (Table 3).
The results demonstrate that varying the concentration of the active ingredient within the NE 2:1 formulation has a limited impact on most physicochemical characteristics. Zeta potential values were close to zero for all samples, which may indicate steric stabilization provided by Cremophor® EL rather than electrostatic repulsion. The stable pH and conductivity across all groups suggest that the internal structure of the nanoemulsions was not significantly altered by increasing active ingredient concentrations. Furthermore, viscosity remained within an acceptable range, indicating good flow properties suitable for topical or transdermal application. Overall, the data suggest that the NE 2:1 system is robust and tolerant to variations in active content within the tested range.
3.3.2 Morphology of NEs
The surface morphology of the microemulsion formulations was investigated using a Leica light microscope (DM750). The sample was analyzed to determine the size of the NEs. The microscope images of the NEs revealed globular-shaped droplets with well-defined outlines. There was no aggregation. The sizes of the nanodroplets were consistent with the measurements obtained from the droplet size assessment, further supporting the accuracy of the size analysis (16).
3.3.3 Value of pH
The pH values ranged from 5.0 to 6.0, as shown in Table 3. All formulations had a neutral pH value and did not exhibit highly acidic or highly basic characteristics.
3.3.4 Conductivity
Conductivity is an important parameter to characterize emulsion type. The outcomes of the optimized formulations are presented in Table 3. The conductivity of w/o emulsions was usually low. This proved that the formulation was o/w type, confirming that the oil phase was indeed the inner phase and dispersed in the aqueous phase as desired (37).
3.3.5 Rheological properties and viscosity
The main factors influencing emulsion viscosity are the colloidal interactions, droplet charge, droplet size, and volume fraction of the dispersed phase (26). The viscosity of the NEs incorporating EO at 1%, 3%, and 5% concentrations was 150, 250, and 350 mPa·s (millipascal-second), respectively, whereas the viscosity of the placebo formulation was 100 mPa·s. An ideal viscous emulsion was obtained compared with that in other studies on NEs (61, 62, 67).
The rheological behavior of the rheograms is shown in Figure 3. The shear rate increased proportionally with shear stress, but viscosity remained constant. This invariability confirmed that the NE behaved as a Newtonian fluid, suggesting a well-organized internal structure in which the components maintained their arrangement and resisted significant changes when subjected to applied stress. The linear increase in shear stress with shear rate, which is a characteristic of Newtonian fluids, confirmed the mechanical stability of the NEs. The steady rise in shear stress without deviation highlighted the robustness and consistency of the formulation under mechanical stress. The formulations were developed in accordance with the fluid nature of NEs, exhibiting low viscosity and aligning with the Newtonian fluid model (67–69).
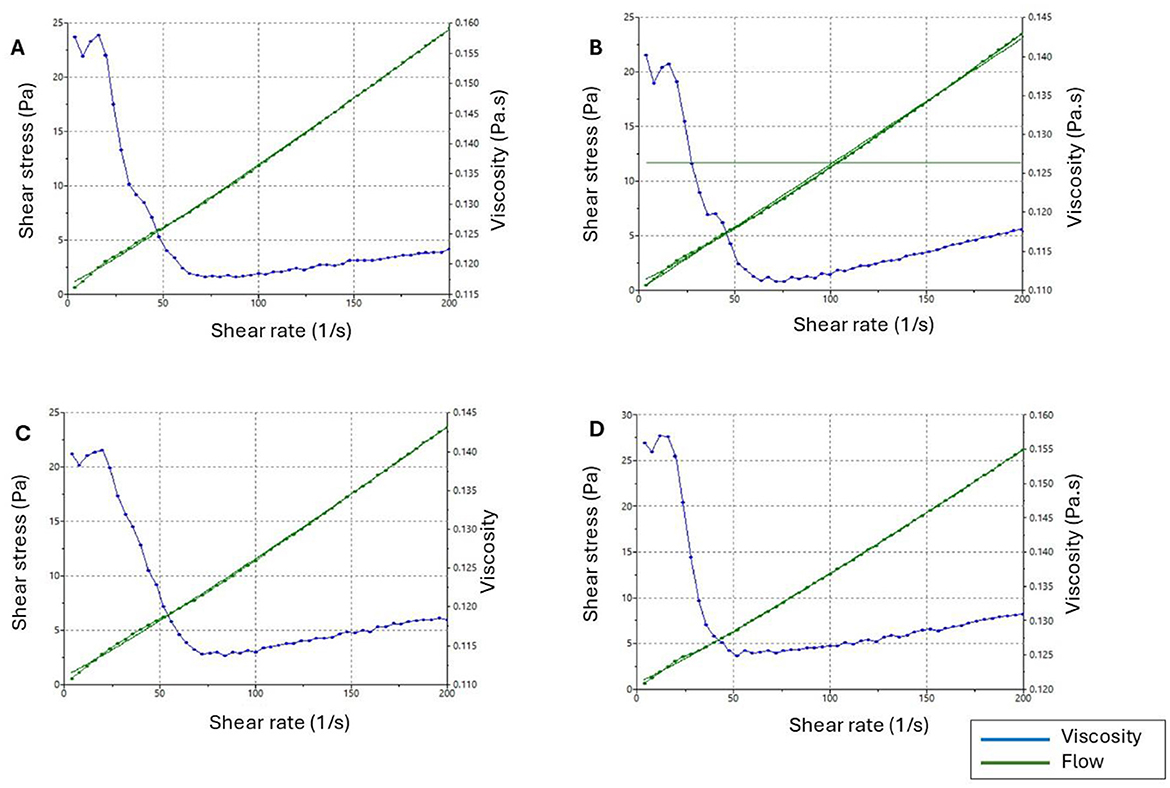
Figure 3. Rheograms showing the correlation between shear rate, viscosity, and shear stress. (A) NE2:1 Placebo, (B) NE2:1 1%, (C) NE2:1 3%, (D) NE2:1 5%).
3.4 Stability of NE formulations
The formulations can change (coalescence, cracking, creaming, precipitation, or phase separation) during long-term storage. Thus, stress tests, such as centrifugation and cycles of heating and cooling and freeze and thaw, were performed to explore the optimum formulations (37). Stable emulsions remained unchanged. The appearance and clarity were measured visually. In this study, the formulations maintained their original features when assessed against a blue background, indicating their long-term stability (61). In a comparable study, this was attributed to the order of the scale (nanometric), offering high kinetic stability, interfacial area, and optical transparency, and to the effect of Brownian motion, opposing gravity and favoring droplet separation (15).
Moreover, the other major benefit of using low-energy methods for preparing NEs is their spontaneous formation at room temperature, which does not need high energy, depending on the surfactant and cosurfactant mixture. It means no energy loss when conducting this reaction into the system, making it a less energy-consuming process. Usage is extremely important since NEs are influenced by both heat and high energy due to their thermodynamic stability. In particular, it must be emphasized that the stabilization of NEs is also ascribed to the adsorption of surfactant and cosurfactant molecules on the droplet surface, leading to repulsions between these structures via steric interactions (15, 70).
3.5 Antimicrobial activity analysis of EO and NE formulations
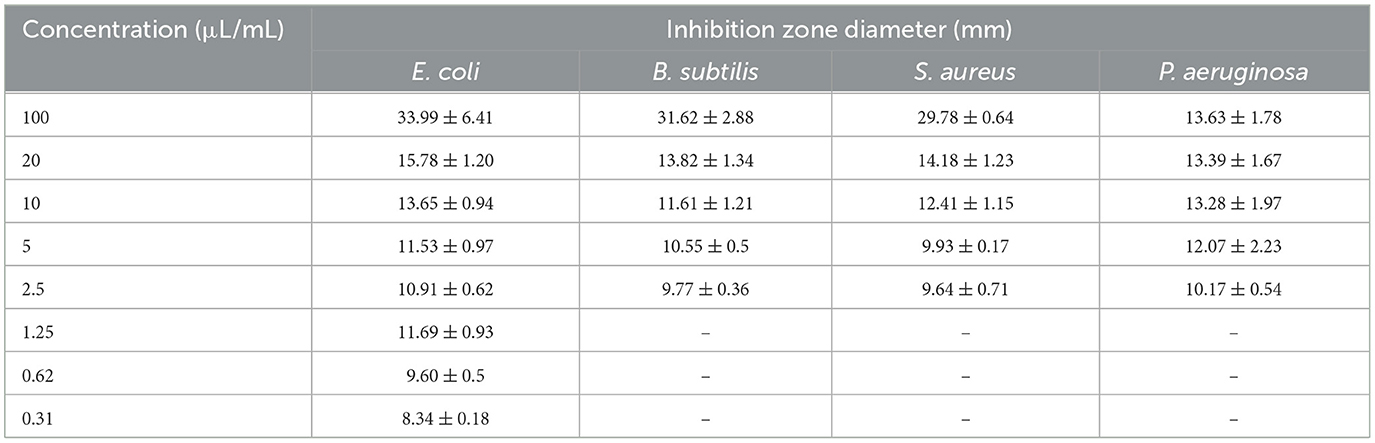
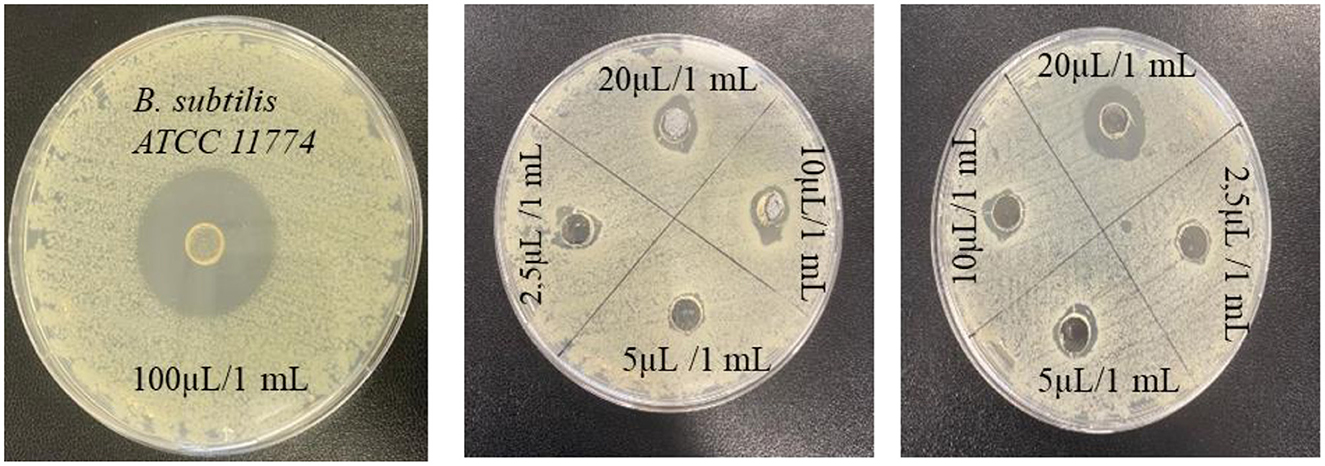
The antimicrobial activity of the EO of T. Spicata was tested against four different bacterial species using the agar well diffusion method (Table 4). On the tested microorganisms, the inhibition zone diameters of the EO varied in the range of 8.02 ± 41.18 mm, and it was found that it exhibited an inhibitory effect on all bacteria. In addition, the T. spicata EO showed high antimicrobial activity at concentrations ranging from even below 2.5 to 100 μl/ml. The highest inhibition zone was observed against B. subtilis at 41.28 mm, while the lowest inhibition effect was detected against P. aeruginosa at 11.22 mm. However, E. coli ATCC 25922 formed an inhibition zone even at 0.3125 μl/ml concentration, while the other test bacteria (B. subtilis ATCC 11774, P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853, and S. aureus ATCC 29213) did not exhibit any antimicrobial activity at concentrations below 2.5 μl/ml. Moreover, 1%, 3%, and 5% T. spicata EO nanoemulsions did not show any antimicrobial activity against S. aureus ATCC 29213, E. coli ATCC 25922, B. subtilis ATCC 11774 and P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 (Figure 4).
Kilic (71) reported that T. spicata EO exhibited antimicrobial activity against B. subtilis, C. albicans, E. coli, E. faecalis, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, S. epidermidis, and S. typhimurium microorganisms. The results of the study revealed that the EO has a high antimicrobial capacity against all tested microorganisms, with the exception of P. aeruginosa. The data obtained from this study support that the content of T. spicata has a broad range of antimicrobial activity, and they are in line with previous findings in the literature. In another study reported by Erturk et al. (72), T. spicata EO and extracts grown in Amasya produced zones of inhibition ranging from 10 to 43 mm against 10 different microorganisms, namely A. niger, B. subtilis, C. albicans, K. pneumoniae, M. luteus, P. vulgaris, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, Streptomyces murinus, and Y. enterocolitica. Besides, in a study conducted by Sengun et al. (28), the antimicrobial activity, total phenolic content, and antioxidant capacity of T. spicata EO were higher than the plant extract. Thus, all test samples demonstrated antimicrobial activity against all bacteria at various levels, and the chemical composition of the EO showed that carvacrol was predominant. Karakaş and Bekler (73) examined T. spicata EO against S. aureus ATCC 25923, E. coli ATCC 25922, and C. albicans ATCC 14053 with the disk diffusion method. A zone of inhibition of 36 ± 1.0 mm in diameter were found as the highest antimicrobial activities of T. spicata EO against C. albicans, a zone of inhibition of 26 ± 1.52 mm in diameter against S. aureus and a zone of inhibition of 28 ± 1.52 mm in diameter against E. coli. According to a study carried out by Kerem et al. (74), the antimicrobial activities of ethanol, hexane, and chloroform extracts of T. spicata were evaluated against E. coli, E. faecalis, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus using the disc-diffusion method. The results showed that the ethanol and chloroform extracts of T. spicata were determined to be the most effective species against both the Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains (74). Barak et al. (25) developed a T. spicata EO using broth microdilution method partially exhibited against S. aureus.
While pure EOs exhibit immediate antimicrobial effects due to their direct interaction with microbial cells, encapsulating them into nanoemulsions can alter their release dynamics. Specifically, the encapsulation may lead to a controlled and sustained release of the active compounds, resulting in a delayed antimicrobial action compared to the rapid effect observed with pure EOs. This phenomenon has been reported in the literature. For instance, Donsì and Ferrari (75) discussed that nanoemulsions could provide a controlled release of EOs, which may prolong their antimicrobial activity over time but could also delay the onset of their effects. Similarly, Noori et al. observed that the antibacterial activity of geraniol nanoemulsions depended on the concentration and release rate of the EO from the emulsion, indicating that the encapsulation could modulate the timing and extent of antimicrobial action. Therefore, the lack of immediate antimicrobial activity in the NE form of the EO in our study could be attributed to the controlled release properties of the nanoemulsion, which may require a longer time to exhibit noticeable antimicrobial effects compared to the pure EO (76).
3.6 Application of the nanoemulsions on the curd cheese
The physicochemical properties of foods are very effective in determining their quality and how long they can be stored without spoiling (41).
3.6.1 Physicochemical parameters of cheese samples during storage
Table 5 demonstrates how the physicochemical characteristics of curd cheese samples changed during 28 days of storage. The pH is one of the most important factors influencing the texture and flavor of cheese, as it affects the solubility of caseins and the activity of enzymes involved in ripening (39). The pH in all cheese samples varied between 6.54 ± 0.04 and 5.42 ± 0.01, indicating that nanoemulsions with T. spicata EO had a significant impact on the pH of curd cheese (p < 0.05). The release of alkaline compounds during proteolysis may explain the slight increase in the pH of the cheese, especially on day 5 (39). Additionally, in a recent study conducted to determine the effect of microencapsulated allspice nanoemulsion on the quality and shelf life of Ras cheese, total acidity increases and pH decreases in cheeses fortified with various concentrations of microcapsules emerging during the ripening period (77). Al-Obaidi (78) showed no significant differences in pH, ash, protein, fat, and moisture between normal cheese and cheese with three different amounts of Curcuma longa (0.1%, 0.2%, and 0.3%) immediately after production. Christaki et al. (79) determined the pH of oregano EO-based nanoemulsion at 4.28 and 6.34 in whey cheese. There were no significant differences in pH and other contents between the control and the trial, respectively, and curcumin nanoemulsion and emulsion-based cheese were also reported by Bagale et al. (80). Cai et al. (10) examined the pH of cheese increased in edible films reinforced with orange EO-based nanoemulsion during storage. The pH of cheese samples packaged with edible films increased slightly from 6.27 ± 0.014 on the first day to 6.465 ± 0.01 on the 12th day, indicating that no spoilage occurred in the cheese after 12 days of storage. The results showed that edible film packaging slowed down the pH changes of cheese, thereby preventing the cheese samples from spoiling. The particle size of nanoemulsions is closely related to WI. Hence, parameters such as droplet size, concentration, and refractive index directly affect the overall optical properties of the emulsion (81). In the study, all nanoemulsions visually exhibited a transparent appearance in cheese. However, WI measurements showed minor differences depending on the concentration of EO used in nanoemulsion (Table 5). In this study, the WI value decreased as the droplet size decreased. This situation reveals that the optical properties of nanoemulsions change depending on the particle size. The optical characteristics of nanoemulsions are an important factor when it comes to food applications (39). In most cases, transparent film-forming solutions are preferred to produce films that almost do not change the color of the food (82). Christaki et al. (79) incorporated nanoemulsions of oregano EO in whey cheese, and they observed that C. citratus or C. reticulata compared to Origanum or Thymus nanoemulsions (44.50 ± 0.17 and 32.94 ± 0.03), which had a significantly lower WI (27.89 ± 0.08 and 26.77 ± 0.49) (79).
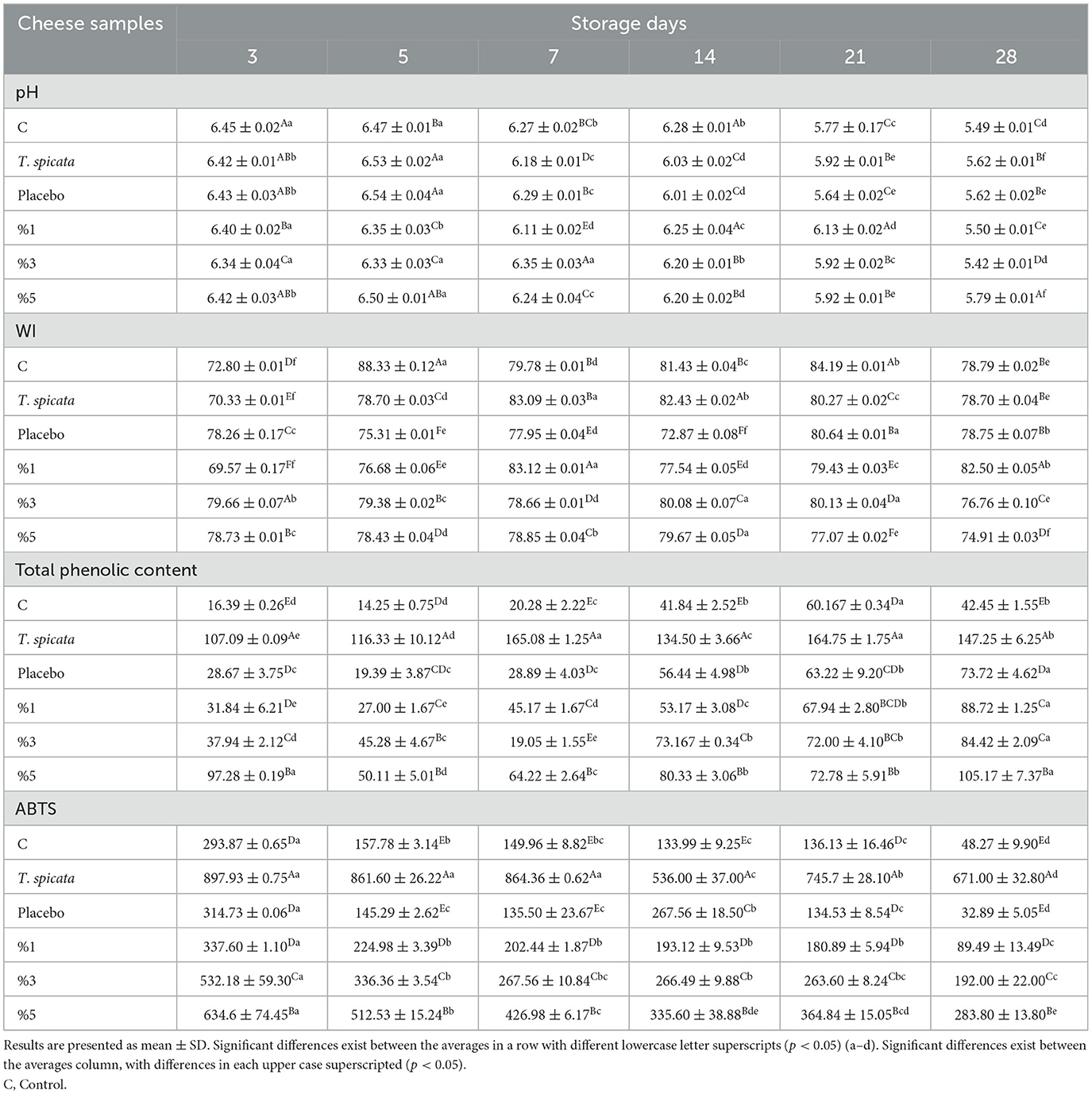
Table 5. Effect of nanoemulsions on physicochemical characteristics of cheese samples during storage.
3.6.2 Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content analysis
TPC and the antioxidant activity of curd cheese fortified with T. spicata EO nanoemulsion during the stored period were given in Table 5. In this study, the antioxidant capacity (15.47 ± 1.05), which was very low on the first day in the control sample, increased on the third day and started to decrease on the following storage days (p < 0.005). T. spicata pure oil has the highest antioxidant activity starting from the third day (Table 5). However, an increasing trend was obtained in antioxidant activity of 1%−5% EO-added nanoemulsion (p < 0.005). The results obtained from this study are in agreement with the literature. The study conducted on the antioxidant activities of Kareish cheese that was supplemented with curcumin nanoemulsions at 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 mg/g showed the highest antioxidant activity in the nanoemulsion at 2.0 mg/g. Shawir et al. reported that the antioxidant activity of kareish cheese was between 19.23 and 42.31% and the antioxidant effects of kareish cheese applied with curcumin nanoemulsions at 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 mg/g were 33.40%, 37.80%, and 42.31%, respectively (41).
Although all antioxidant activities decreased over time during storage, significant activity was detected in T. spicata oil and 1%, 3%, and 5% nanoemulsions on the 28th day of storage than the control cheese sample. In addition, the change in antioxidant capacity results was correlated with the total phenolic content of nanoemulsions (Table 5). Moreover, in a study, El-Sayed et al. (83) aimed to increase the phenolic compound and antioxidant content in Ras cheese by the addition of microencapsules containing nanoemulsions of allspice fruit extracts. The results revealed that the control cheese had lower TPC content (6.26 mg/100 g) and antioxidant activity (9.89%) than the supplemented cheese samples. TPC and antioxidant activity increased significantly (p < 0.05) with increasing microcapsule concentrations in Ras cheese. The total antioxidant activity, total phenolic content, and radical scavenging activity of T. spicata were analyzed by Bener (84). All models calculated for the three responses that are total phenolic, antioxidant, and radical scavenging activities were noteworthy (p < 0.0001) and showed that there was a significant relationship between the response and the independent parameters (84). The antioxidant capacity of T. spicata EO-based nanoemulsions on cheese has not been studied, but it has been studied on cheese with nanoemulsions containing EO from different plant species. Pérez-Soto et al. incorporated phenolic compounds and the antioxidant capacity of microemulsions from Opuntia oligacantha to fresh cheese, and they observed that phenolic compounds decreased during storage. As observed with ABTS, the microemulsion maintained a higher antioxidant acitivity with DPPH from day 0 (19.50 ± 0.43mg AAE/g). This behavior was observed up to 45 days (85). Shabani et al. (86) investigated the antioxidant activities of Urtica dioica EO-based nanoemulsions on L. monocytogenes and E. coli and reported that the values of DPPH were identified in EO-based nanoemulsions as 33.7 ± 12.2. Faramarzi et al. investigated a similar study with Shabani et al. (86) and applied it to the same bacteria, and the effect of Urtica dioica EO and nanoemulsions was identified in the nanoemulsions as 31.25 ± 1.50 % (11).
3.6.3 Microbiological analysis of cheese samples during storage
Microbiological analyses of curd cheeses were performed on each storage day. Total mesophilic aerobic bacteria (TMAB) counts, lactic acid bacteria (LAB), and yeast counts of curd cheeses during storage were given in Figures 5a–c, respectively. TMAB counts were found between 7.58 and 8.18 log cfu/g in curd cheese with pure oil added, 6.97 and 8.29 log cfu/g in control curd cheese sample, 7.64 and 8.04 log cfu/g in placebo added curd cheese, and 7.52 and 8.17, 7.55 and 8.05, and 7.68 and 8.01 log cfu/g in curd cheese sample containing 1%, 3%, and 5% T. spicata EO nanoemulsion, respectively. The total number of aerobic mesophilic bacteria in the curd cheese to which different EOs (1%, 3%, and 5%) containing nanoemulsions were added before storage decreased slightly. LAB counts were found between 2.80 and 5.41 log cfu/g in curd cheese with pure oil added, 2.21 and 5.41 log cfu/g in control curd cheese sample, 3.02 and 5.42 log cfu/g in placebo added curd cheese, and 2.84 and 4.85, 2.91 and 5.26, and 2.81 and 5.05 log cfu/g with 1%, 3%, and 5% T. spicata EO nanoemulsion, respectively. Yeast counts were found between 4.17 and 7.54 log cfu/g in pure oil-added curd cheese, 3.82 and 7.49 log cfu/g in control curd cheese sample, 4.35 and 7.72 log cfu/g in placebo-added curd cheese, and 4.13 and 7.70, 4.13 and 7.54, and 3.59 and 7.44 log cfu/g in 1%, 3%, and 5% T. spicata EO nanoemulsions, respectively. It was observed that the number of yeasts increased as the storage was prolonged. No mold growth was observed in the curd cheese sample. El-Sayed et al. reported the preservation effect of cumin EO nanoemulsion as a brined solution on the microbiological properties of white soft cheese during 60 days of storage time (77). The total mesophilic bacterial counts and lactic acid bacteria counts of white soft cheese treatments gradually reduced significantly in the presence of cumin EO nanoemulsion. However, it is observed that this decrease was more noticeable after a 30-day storage period. The reason for the small change in this study could be related to the shorter period of storage time for cheese samples. Elsherif and Al Shrief studied the effectivity of Szygium aromaticum and Cuminum cyminum EOs and its nanoemulsions against foodborne pathogens after inoculation in manufactured cheese at different concentrations. Complete reduction of L. monocytogenes was observed after 2 weeks of treatment with carvacrol nanoemulsions at 0.78 and 1.56% (2).
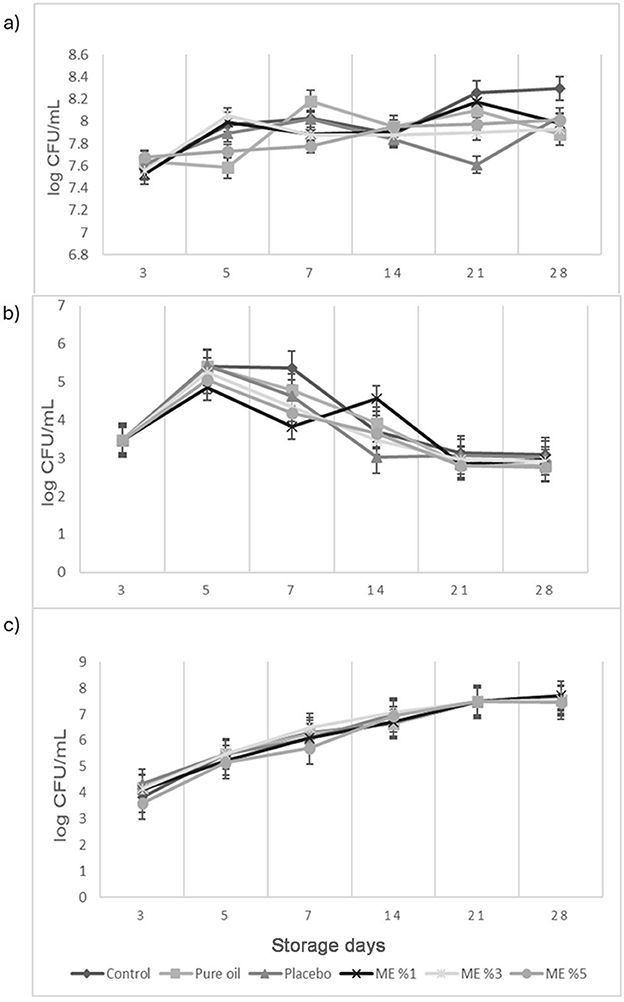
Figure 5. (a) Total mesophilic aerobic bacteria; (b) Lactic acid bacteria; (c) Yeast counts of cheeses during storage.
Gadallah et al. showed antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of Rosmarinus officinalis EO-based nanoemulsions as a natural alternative to Karish cheese. The results demonstrated a complete reduction of A. flavus, B. cereus, and L. monocytogenes, on days 5, 7, and 10, respectively, and a 96.93% reduction of P. aeruginosa at the end of the storage time. In the viability study of Karish cheese, C. albicans, A. flavus, and P. aeruginosa were completely reduced on days 10, 10, and 15 of storage, respectively (4).
Abd El Gwad et al. developed Thymus vulgaris and Syzygium aromaticum EOs-based nanoemulsions to improve the quality of soft cheese. The results showed that different concentrations of T. vulgaris nanoemulsion (0.03%, 0.06%, and 0.1%), as well as S. aromaticum nanoemulsions (0.06%, 0.1%, and 0.25%), were used to preserve the cheese. During a cold storage period of 50 days, the microbiological analysis and sensory evaluation of different cheeses were evaluated. The results showed that the droplet size of the prepared NEs was 94.85 and 68.67 nm for T.vulgaris and S. aromaticum nanoemulsions, respectively (3). Kamal et al. investigated the inhibitory effect of thyme oil against C. sakazakii in Tallaga cheese. Furthermore, thyme oil also inhibited the growth of Salmonella and mesophilic aerobic bacteria in other food products, maintained until the end of storage at 4°C (87). Shawir et al. showed that increasing the concentration of Curcumin nanoemulsions (1.0, 1.5, and 2 mg/ml) can be used in the preservation of Kareish cheese to enhance antimicrobial protection (41).
4 Conclusion
T. spicata EOs showed antimicrobial activity against all bacteria tested (Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus). The strong antibacterial properties of T. spicata EO may be due to its thymol and carvacrol components. Despite its low stability, the nanoemulsion demonstrated a strong antioxidant activity on the cheese. Of particular importance, the antibacterial activity of the EO decreased against tested bacterial strains when it was converted to a nanoemulsion. The nanoemulsion concentrations of 1%, 3%, and 5%, as well as pure EO were incorporated into curd cheese; the nanoemulsion delayed mold and yeast growth up to 28 days.
The chemical profile identified in this study suggested that T. spicata EO could serve as a natural preservative or antimicrobial agent in the pharmaceutical and food sectors. The high content of bioactive monoterpenes supports the potential use of T. spicata EO in therapeutic formulations targeting microbial infections and oxidative stress.
Future studies should explore the seasonal variability in the EO composition and its effect on biological activities. Additionally, comparative analyses with EOs from different ecological zones may provide further insight into the impact of environmental factors on the chemical profile of T. spicata.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
SK: Writing – original draft. UB: Writing – original draft. EA: Writing – original draft. PK: Writing – original draft. NC: Writing – original draft. TC: Writing – review & editing. DO: Writing – review & editing. EO: Writing – original draft. GB: Writing – review & editing. MB: Writing – original draft. YO: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. TE: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FO: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The publication of this article was funded by the Open Access Fund of Leibniz University Hannover.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Mukurumbira AR, Shellie RA, Keast R, Palombo EA, Jadhav SR. Encapsulation of essential oils and their application in antimicrobial active packaging. Food Control. (2022) 136:108883. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.108883
2. El Sherif WM, Shrief LMTA. Effects of three essential oils and their nano-emulsions on Listeria monocytogenes and Shigella flexneri in Egyptian Talaga cheese. Int J Food Microbiol. (2021) 355:109334. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109334
3. Abd El Gwad A, Mohammed SA, El-Sayed SM, Abdel-Hakim EH. The role of thyme and clove essential oils nanoemulsions in quality improvement of soft cheese. Suez Canal Vet Med J. (2024) 29:437–47. doi: 10.21608/scvmj.2024.395228
4. Gadallah AH, Hafez RS, Fahim KM, Ahmed LI. Application of rosemary oil nano-emulsion as antimicrobial and antioxidant natural alternative in pasteurized cream and Karish cheese. Int J Food Microbiol. (2024) 422:110823. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2024.110823
5. Kumar A, Kanwar R, Mehta SK. Nanoemulsion as an effective delivery vehicle for essential oils: properties, formulation methods, destabilizing mechanisms and applications in agri-food sector. Next Nanotechnol. (2025) 7:100096. doi: 10.1016/j.nxnano.2024.100096
6. Sharma R, Nath PC, Das P, Rustagi S, Sharma M, Sridhar N, et al. Essential oil-nanoemulsion based edible coating: innovative sustainable preservation method for fresh/fresh-cut fruits and vegetables. Food Chem. (2024) 460:140545. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.140545
7. Hanan E, Dar AH, Shams R, Goksen G. New insights into essential oil nano emulsions loaded natural biopolymers recent development, formulation, characterization and packaging applications: a comprehensive review. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 280:135751. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135751
8. Sassi G, Shankar S, Jaiswal L, Salmieri S, Karboune S, Lacroix M. Nanoemulsion based spray-dried formulation of essential oils, whey protein isolate, and maltodextrin: an approach for antifungal preservation of grated mozzarella cheese. Int Dairy J. (2024) 154:105919. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2024.105919
9. Cruz GA, Ferreira EN, Cunha FET, Muniz CR, Nascimento HOD, Nascimento RFD. Carvalho JD. Nanoemulsion of kefiran and coriander (Coriandrum sativum L) essential oil: chemical and technological aspects. J Braz Chem Soc. (2024) 36:e20240187. doi: 10.21577/0103-5053.20240187
10. Cai R, Jia L, Yang R, Tao H, Cui H, Lin L, et al. Fabrication of guar gum/chitosan edible films reinforced with orange essential oil nanoemulsion for cheese preservation. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 285:138285. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138285
11. Faramarzi H, Fazeli F, Shariatifar N, Ghorbani-HasanSaraei A. Shahidi SA. Investigating the inhibitory effect of nettle (Urtica dioica L) essential oil and Pickering nanoemulsion on some pathogenic bacteria inoculated into pizza cheese. Int J Food Microbiol. (2025) 430:111060. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2025.111060
12. Rossi LE, Júlio AA, Vanetti MCD, de Alencar ER, de Oliveira JM, Dutra JP, Machado SG. Cinnamon essential oil and nanoemulsions for inhibiting Pseudomonas paracarnis and pigment production in fresh cheese. Food Bioprocess Technol. (2025) 18:5479–96. doi: 10.1007/s11947-025-03784-y
13. Jacob S, Kather FS, Boddu SH, Shah J, Nair AB. Innovations in nanoemulsion technology: enhancing drug delivery for oral, parenteral, and ophthalmic applications. Pharmaceutics. (2024) 16:1333. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101333
14. Kishore A, Jain A, Asthana N, Milan R, Lakshmi SM, Gupta M, et al. Selection criteria for oils, surfactants, and co-surfactants in ocular nanoemulsion formulation: a mini review. Curr Pharm Des. (2025) 31:1259–69. doi: 10.2174/0113816128350573241202105210
15. Kotwiski FO, São Paulo Í, Carneiro PIS, de Melo Barbosa R, Viseras C, Rangel AL, et al. Development of a nanoemulsion containing Lippia origanoides essential oil with antifungal activity by low energy method: from extraction to formulation. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. (2024) 102:106392. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2024.106392
16. Çiçek S, Korkmaz YB, Tüzün B, Işik S, Yilmaz MT, Özogul F, et al. study on insecticidal activity of the fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) essential oil and its nanoemulsion against stored product pests and molecular docking evaluation. Ind Crops Prod. (2024) 222:119859. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.119859
17. Kaur M, Tandon R, Kalia A, Mahajan BVC, Kairam N. ROS-mediated antifungal activity of Ocimum essential oil-loaded nanoemulsions against postharvest fungal pathogens of Kinnow. Food Biosci. (2024) 57:103429. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.103429
18. Li G, Zhou Q, Liu S, Qian C, Han J, Zhou T, et al. Effect of tribute citrus essential oil nanoemulsion-loaded gelatin on the gel behavior and gelation surface morphologies. Food Biosci. (2023) 51:102322. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.102322
19. Hou K, Xu Y, Cen K, Gao C, Feng X, Tang X. Nanoemulsion of cinnamon essential oil co-emulsified with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and Tween-80: antibacterial activity, stability and slow release performance. Food Biosci. (2021) 43:101232. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101232
20. Ozogul Y, Boga EK, Akyol I, Durmus M, Ucar Y, Regenstein JM, et al. Antimicrobial activity of thyme essential oil nanoemulsions on spoilage bacteria of fish and food-borne pathogens. Food Biosci. (2020) 36:100635. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100635
21. Solgi M, Bagnazari M, Mohammadi M., Azizi A. Thymbra spicata extract and arbuscular mycorrhizae improved the morphophysiological traits, biochemical properties, and essential oil content and composition of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L) under salinity stress. BMC Plant Biol. (2025) 25:220. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06221-6
22. Tayoub G, Mohamad F, Haider N. Chemical and molecular characterization of three plant species from Lamiaceae that grow in Syria: chemical and molecular characterization of medicinal plants. Biol Sci-PJSIR. (2024) 67:15–23.
23. Özbey C, Aydemir I, Çetindag E, Özkan O. Investigation of the cytotoxic effects of Thymbra spicata polysaccharides on MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation and migration in vitro conditions. (preprint). (2025). doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4093817/v1
24. Cengiz M, Baytar O, Sahin Ö, Kutlu HM, Ayhanci A, Vejselova Sezer C, et al. Biogenic synthesized bare and boron-doped copper oxide nanoparticles from Thymbra spicata ssp. spicata: in silico and in vitro studies. J Cluster Sci. (2024) 35:265–84. doi: 10.1007/s10876-023-02481-0
25. Barak TH, Eryilmaz M, Karaca B, Servi H, Kara Ertekin S, Dinc M, et al. Antimicrobial, anti-biofilm, anti-quorum sensing and cytotoxic activities of Thymbra spicata L. subsp spicata essential oils. Antibiotics. (2025) 14:181. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14020181
26. Gedikoglu A, Çikrikci Erünsal S. Characterization of a Thymbra spicata essential oil–pectin nanoemulsion, and antimicrobial activity against foodborne pathogenic bacteria. J Food Meas Charact. (2023) 17:3195–206. doi: 10.1007/s11694-023-01855-2
27. Gedikoglu A. The effect of Thymus vulgaris and Thymbra spicata essential oils and/or extracts in pectin edible coating on the preservation of sliced bolognas. Meat Sci. (2022) 184:108697. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2021.108697
28. Sengun IY, Yucel E, Ozturk B, Kilic G. Chemical compositions, total phenolic contents, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the extract and essential oil of Thymbra spicata L. growing wild in Turkey. J Food Meas Charact. (2021) 15:386–93. doi: 10.1007/s11694-020-00639-2
29. Demirci Kayiran S, Eroglu Ozkan E, Mataraci Kara E, Yilmaz MA, Zengin G, Boga M. Comprehensive analysis of an uninvestigated wild edible medicinal garlic species from Turkey: Allium macrochaetum Boiss. & Hausskn. J Food Biochem. (2019) 43:e12928. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12928
30. Güven UM, Kayiran SD, Aygül A, Nenni M, Kirici S. Design of microemulsion formulations loaded Scutellaria salviifolia Benth, Sideritis libanotica Labill. subsp. linearis (Bentham) Bornm, and Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. extracts from Turkey and in vitro evaluation of their biological activities. Turk J Bot. (2021) 45:789–99. doi: 10.3906/bot-2108-50
31. Çaglar ES, Okur ME, Kolbaşi B, Sahin M, Özhan Y, Sipahi H, Okur NÜ. A synergistic microemulsion approach with cetyl myristoleate and hyaluronic acid for enhanced osteoarthritis therapy: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. (2025) 106:106694. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2025.106694
32. Solak B, Soyer P, Tilki EK, Öztürk AA. Evaluation of antimicrobial properties and antioxidant activity of rosmarinic acid-loaded Resomer RG 502 H-based nanoparticles against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress: a detailed formulation, characterization and efficacy determination study. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. (2025) 106:106721. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2025.106721
33. Demirci Kayiran S, Bolgen UMG, Cevikelli T, Kizilyildirim S, Yildir B, Ferahoglu E, et al. Chemical composition and antibacterial properties of microemulsion and microemulgel formulations containing Lavandula angustifolia Mill. essential oils. Ind Crops Prod. (2025) 226:120654. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2025.120654
34. Çevikelli T, Güven UM, Öztürk AA. Metronidazole loaded novel microemulsion formulation for topical delivery and characterization with validated new UPLC method. Fabad J Pharm Sci. (2024) 49:111–28. doi: 10.55262/fabadeczacilik.1359138
35. Manyala DL, Varade D. Formation and characterization of microemulsion with novel anionic sodium N-lauroylsarcosinate for personal care. J Mol Liq. (2021) 343:117657. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117657
36. Rajora A, Kohli K, Nagpal K. Formulation of itraconazole loaded clove oil based nanoemulsion using pseudoternary phase diagram for improved thermodynamic stability. Indian J Pure Appl Phys. (2024) 62:124–32. doi: 10.56042/ijpap.v62i2.7698
37. Verma K, Chandane-Tak M, Gaikwad SY, Mukherjee A, Kumar S. Optimizing rosemary oil nanoemulsion loaded with nelfinavir and epigallocatechin gallate: a Design Expert® endorsed approach for enhanced neuroAIDS management. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 280:135885. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135885
38. Kobya O, Çaglak E. Kara B. Olive leaves (Olea europaea L) collected from Balikesir-Ayvalik and Trabzon-Çarşibaşi: comparison of antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of extracts obtained by drying by different methods. J Anatol Environ Anim Sci. (2019) 4:257–62. doi: 10.35229/jaes.584408
39. Polat Yemiş G, Sezer E, Siçramaz H. Inhibitory effect of sodium alginate nanoemulsion coating containing myrtle essential oil (Myrtus communis L) on Listeria monocytogenes in Kasar cheese. Molecules. (2022) 27:7298. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217298
40. Artiga-Artigas M, Acevedo-Fani A, Martín-Belloso O. Improving the shelf life of low-fat cut cheese using nanoemulsion-based edible coatings containing oregano essential oil and mandarin fiber. Food Control. (2017) 76:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.01.001
41. Shawir SM, Lotfy TM, Kamel RM, Khater AE, Younes NM. Potential application of curcumin nanoemulsions to preserve properties of refrigerated cheese. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. (2024) 59:103243. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2024.103243
42. Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med. (1999) 26:1231–7. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
43. Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventos RM. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. (1999) 299:152–79. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(99)99017-1
46. Sanders ER. Aseptic laboratory techniques: plating methods. J Vis Exp. (2012) 63:e3064. doi: 10.3791/3064-v
47. Gedikoglu A, Sökmen M, Çivit A. Evaluation of Thymus vulgaris and Thymbra spicata essential oils and plant extracts for chemical composition, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. Food Sci Nutr. (2019) 7:1542–51. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1007
48. Başer KHC, Buchbauer G, editors. Handbook of Essential Oils: Science, Technology, and Applications, 3rd edn. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press (2020). doi: 10.1201/9781351246460
49. Rustaiee A, Sefidkon F, Tabatabaei SMF, Omidbaigi R, Mirahmadi SF. Chemical polymorphism of essential oils from five populations of Thymus daenensis Celak. subsp daenensis endemic to Iran. J Essent Oil Res. (2011) 23:6–11. doi: 10.1080/10412905.2011.9700450
50. Özel MZ, Gögüş F, Lewis AC. Subcritical water extraction of essential oils from Thymbra spicata. Food Chem. (2003) 82:381–6. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00558-7
51. Inan M, Kirpik M, Kaya DA, Kirici S. Effect of harvest time on essential oil composition of Thymbra spicata L. growing in the flora of Adiyaman. Adv Environ Biol. (2011) 5:356–8.
52. Kirkan B, Sarikürkçü C, Amarowicz R. Composition, and antioxidant and enzyme-inhibition activities, of essential oils from Satureja thymbra and Thymbra spicata var. spicata Flavour. Fragr J. (2019) 34:362–70. doi: 10.1002/ffj.3522
53. Nath EÖ, Gündogan GI, Kartal M. Chemical components of Thymbra spicata subsp. spicata L essential oil and its in vitro physiological effects on human origin cell lines. Rec Nat Prod. (2023) 17:647. doi: 10.25135/rnp.387.23.01.2671
54. Novak J, Lukas B, Franz C. Temperature influences thymol and carvacrol differentially in Origanum spp. (Lamiaceae). J Essent Oil Res. (2010) 22:412–5. doi: 10.1080/10412905.2010.9700359
55. Nabavi SF, Marchese A, Izadi M, Curti V, Daglia M, Nabavi SM. Plants belonging to the genus Thymus as antibacterial agents: from farm to pharmacy. Food Chem. (2015) 173:339–47. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.042
56. Zarai Z, Kadri A, Ben Chobba I, Ben Mansour R, Bekir A, Mejdoub H, et al. The in-vitro evaluation of antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic properties of Marrubium vulgare L. essential oil grown in Tunisia. Lipids Health Dis. (2011) 10:161. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-161
57. Miladi H, Zmantar T, Kouidhi B, Al Qurashi YMA, Bakhrouf A, Chaabouni Y, et al. Synergistic effect of eugenol, carvacrol, thymol, p-cymene and γ-terpinene on inhibition of drug resistance and biofilm formation of oral bacteria. Microb Pathog. (2017) 112:156–63. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.09.057
58. Janik-Zabrotowicz E, Arczewska M, Zubik M, Terpilowski K, Skrzypek TH, Swietlicka I, et al. Cremophor EL nano-emulsion monomerizes chlorophyll a in water medium. Biomolecules. (2019) 9:881. doi: 10.3390/biom9120881
59. Callender SP, Wettig SD. Phase behavior of non-ionic surfactant-medium chain triglyceride-water microemulsion systems. J Surfactants Deterg. (2021) 24:603–29. doi: 10.1002/jsde.12510
60. Li H, Tan X, Qin L, Gatasheh MK, Zhang L, Lin W, Qi J. Preparation, process optimisation, stability and bacteriostatic assessment of composite nanoemulsion containing corosolic acid. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e38283. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38283
61. Akhter A, Shirazi JH, Hussain MD, Kazi M. Development and evaluation of nanoemulsion gel loaded with bioactive extract of Cucumis melo var. agrestis: a novel approach for enhanced skin permeability and antifungal activity. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e35069. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35069
62. Gurumukhi VC, Sonawane VP, Tapadiya GG, Bari SB, Surana SJ, Chalikwar SS. Quality-by-design based fabrication of febuxostat-loaded nanoemulsion: statistical optimization, characterizations, permeability, and bioavailability studies. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e15404. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15404
63. Wei N, Hou C, Liu Z, Liang Q, Lv Z, Meng X, et al. Preparation of fenpropathrin nanoemulsions for eco-friendly management of Helicoverpa armigera: improved insecticidal activity and biocompatibility. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. (2023) 656:130442. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130442
64. Salama A, Soliman GM, Elsherbiny N, Safwat MA. Chitosan-coated nanoemulsion for the direct nose-to-brain delivery of sildenafil: development and in vivo evaluation in a brain oxidative stress and inflammation model. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. (2024) 98:105842. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105842
65. Ozogul Y, Karsli GT, Yazgan H, Kuley E, Oztop HM, Ozogul F, Esatbeyoglu T. Enhanced pathogen control through thymol and carvacrol nanoemulsions: a microfluidization approach. Food Bioprocess Technol. (2025) 18:5377–87. doi: 10.1007/s11947-025-03759-z
66. Mehrandish S, Mirzaeei S. Design of novel nanoemulsion formulations for topical ocular delivery of itraconazole: development, characterization and in vitro bioassay. Adv Pharm Bull. (2021) 12:93. doi: 10.34172/apb.2022.009
67. Koch P, Dhua S, Mishra P. Critical review on Citrus essential oil extracted from processing waste-based nanoemulsion: preparation, characterization, and emerging food application. J Essent Oil Res. (2024) 36:407–25. doi: 10.1080/10412905.2024.2397700
68. Oliveira TS, Costa AMM, Cabral LMC, Freitas-Silva O, Tonon RV. Physical and biological properties of alginate-based cinnamon essential oil nanoemulsions: study of two different production strategies. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 275:133627. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133627
69. Tartari APS, Jacumazo J, Lorenzett AKP, Freitas RAD, Mainardes RM. Development and characterization of silibinin-loaded nanoemulsions: a promising mucoadhesive platform for enhanced mucosal drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. (2025) 17:192. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020192
70. Shabaaz Begum JP, Sahu P, Vinode R, Patel A, Alomary MN, Begum MY, et al. Antimicrobial nanoemulsion: a futuristic approach in antibacterial drug delivery system. J Saudi Chem Soc. (2024) 28:101896. doi: 10.1016/j.jscs.2024.101896
71. Kilic T. Analysis of essential oil composition of Thymbra spicata var. spicata: antifungal, antibacterial and antimycobacterial activities. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. (2006) 61:324–8. doi: 10.1515/znc-2006-5-604
72. Erturk O, Tanrikulu GI, Yavuz C, Can Z, Ebru H. Chemical compositions, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the essential oil and extracts of Lamiaceae family (Ocimum basilicum and Thymbra spicata) from Turkey. Int J Sec Metab. (2017) 4:340–8. doi: 10.21448/ijsm.373828
73. Karakaş Ö, Bekler FM. Essential oil compositions and antimicrobial activities of Thymbra spicata L. var spicata L, Lavandula x intermedia Emeric ex Loisel, Satureja macrantha CA Meyer and Rosmarinus officinalis L. Braz Arch Biol Technol. (2022) 65:e22210297. doi: 10.1590/1678-4324-2022210297
74. Kerem S, Koşar N, Tekin F, Güreser AS, Özbek Ö. Investigation of antimicrobial activities and molecular characterization of the species belong to Origanum, Thymus and Thymbra genera by ISSR. Mol Biol Rep. (2023) 50:289–98. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07923-y
75. Donsì F, Ferrari G. Essential oil nanoemulsions as antimicrobial agents in food. J Biotechn. (2016) 233:106–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.07.005
76. Noori S, Zare D, Jafari SM. Preparation and characterization of geraniol nanoemulsions and its antibacterial activity against Listeria monocytogenes. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:1080300. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1080300
77. El-Sayed SM, Kholif AM, El-Sayed HS, Youssef AM. Augmenting the quality and shelf life of Ras cheese by adding microencapsulated allspice berry extract nanoemulsion. Food Bioprocess Technol. (2025) 18:588–604. doi: 10.1007/s11947-024-03473-2
78. Al-Obaidi LFH. Effect of adding different concentrations of turmeric powder on the chemical composition, oxidative stability and microbiology of the soft cheese. Plant Arch. (2019) 19:317–21.
79. Christaki S, Moschakis T, Hatzikamari M, Mourtzinos I. Nanoemulsions of oregano essential oil and green extracts: characterization and application in whey cheese. Food Control. (2022) 141:109190. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109190
80. Bagale U, Kadi A, Abotaleb M, Potoroko I, Sonawane SH. Prospect of bioactive curcumin nanoemulsion as effective agency to improve milk based soft cheese by using ultrasound encapsulation approach. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:2663. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032663
81. Salvia-Trujillo L, Rojas-Graü MA, Soliva-Fortuny R, Martín-Belloso O. Effect of processing parameters on physicochemical characteristics of microfluidized lemongrass essential oil-alginate nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll. (2013) 30:401–7. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.07.004
82. Acevedo-Fani A, Salvia-Trujillo L, Rojas-Graü MA, Martín-Belloso O. Edible films from essential-oil-loaded nanoemulsions: physicochemical characterization and antimicrobial properties. Food Hydrocoll. (2015) 47:168–77. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.01.032
83. El-Sayed HS, El-Sayed SM. A modern trend to preserve white soft cheese using nano-emulsified solutions containing cumin essential oil. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag. (2021) 16:100499. doi: 10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100499
84. Bener M. Modeling and optimizing microwave-assisted extraction of antioxidants from Thymbra spicata L. and characterization of their phenolic constituents. Food Sci Biotechnol. (2019) 28:1733–45. doi: 10.1007/s10068-019-00687-5
85. Pérez-Soto E, Cenobio-Galindo ADJ, Espino-Manzano SO, Franco-Fernández MJ, Ludeña-Urquizo FE, Jiménez-Alvarado R, et al. The addition of microencapsulated or nanoemulsified bioactive compounds influences the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of a fresh cheese. Molecules. (2021) 26:2170. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082170
86. Shabani M, Ghorbani-HasanSaraei A, Shariatifar N, Savadkoohi F, Shahidi SA. Effect of Urtica dioica L. essential oil (forms of free and nanoliposome) on some inoculated pathogens (Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes) in minced camel meat. Food Chem X. (2023) 20:101050. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.101050
Keywords: Thymbra spicata, essential oil, nanoemulsion, antimicrobial activity, food preservation, curd cheese, antioxidant properties
Citation: Kayiran SD, Bolgen UMG, Akgül E, Kadiroglu P, Cengiz N, Cevikelli T, Onan D, Ozkan EE, Bozdogan G, Boga M, Ozogul Y, Esatbeyoglu T and Ozogul F (2025) Chemical composition, characterization, and antimicrobial properties of Thymbra spicata essential oil-based nanoemulsions and its application on curd cheese. Front. Nutr. 12:1615832. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1615832
Received: 21 April 2025; Accepted: 30 May 2025;
Published: 18 June 2025.
Edited by:
Miguel Angel Prieto Lage, University of Vigo, SpainReviewed by:
Pauline Donn, University of Yaounde I, CameroonSepidar Seyyedimansour, Islamic Azad University of Tabriz, Iran
Paula Barciela, University of Vigo, Spain
Copyright © 2025 Kayiran, Bolgen, Akgül, Kadiroglu, Cengiz, Cevikelli, Onan, Ozkan, Bozdogan, Boga, Ozogul, Esatbeyoglu and Ozogul. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tuba Esatbeyoglu, ZXNhdGJleW9nbHVAZm9oLnVuaS1oYW5ub3Zlci5kZQ==; Serpil Demirci Kayiran, c2RlbWlyY2lAY3UuZWR1LnRy
 Serpil Demirci Kayiran
Serpil Demirci Kayiran Umay Merve Guven Bolgen2
Umay Merve Guven Bolgen2 Pinar Kadiroglu
Pinar Kadiroglu Nurten Cengiz
Nurten Cengiz Mehmet Boga
Mehmet Boga Yesim Ozogul
Yesim Ozogul Tuba Esatbeyoglu
Tuba Esatbeyoglu Fatih Ozogul
Fatih Ozogul