- 1Department of Epidemiology and Health Statistics, School of Public Health, Southeast University, Nanjing, China
- 2Zhongda Hospital Affiliated to Southeast University, Nanjing, China
- 3Department of Integrated Services, Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Nanjing, China
Introduction: Vitamin D is a necessary nutrient that is important for calcium homeostasis and bone health. Dyslipidemia is thought to be a risk factor for the development of atherosclerotic illnesses. Recent research suggests that vitamin D may influence lipid metabolism, specifically the levels of circulating lipids in the blood. However, the relationship between vitamin D and dyslipidemia remains controversial, indicating a need for further research to clarify this association.
Objectives: Data from 780 participants in the “Early Identification, Early Diagnosis Techniques, and Points of Risk for Diabetes in Major Chronic Non-communicable Disease Prevention and Control Studies” were analyzed.
Methods: We employed machine learning with the XGboost algorithm, Least Absolute Shrinkage Selection Operator (LASSO) regression, and univariate logistic regression to screen variables. Subsequently, multiple logistic regression and a generalized additive model (GAM) were utilized to construct models analyzing the association between vitamin D levels and dyslipidemia.
Results: In our study, the XGboost machine learning algorithm explored the relative importance of all included variables, confirming a robust association between vitamin D levels and dyslipidemia. After adjusting for all the important covariates, the results showed that the risk of dyslipidemia in vitamin D insufficiency group and vitamin D deficiency group was 2.11 times and 2.77 times of that in vitamin D sufficiency group, respectively. A smooth curve was constructed based on GAM and a significant negative association was found between 25(OH)D and the risk of dyslipidemia.
Conclusion: There may be a negative association between 25(OH)D and the risk of dyslipidemia. Nonetheless, additional well-designed studies are necessary to substantiate this relationship.
1 Introduction
A 25(OH)D level lower than 20 ng/mL is considered vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D deficiency has become a global public health problem, affecting individuals of all age groups, races and socioeconomic status (1, 2). It is reported that the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is very high in the United States, Canada and Europe (ranging from 24 to 40%) (3). Beyond its detrimental effects on bone health, inadequate vitamin D levels can lead to a range of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, stroke, and diabetes (4, 5). Dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated levels of triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), alongside reduced levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), has been identified as an important risk factor for atherosclerotic diseases such as coronary heart disease, ischemic cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral vascular disease (6, 7). The diagnostic criteria for dyslipidemia are as follows: Satisfy one or more of the following conditions: (1) TC ≥ 6.22 mmol/L; (2) TG ≥ 2.26 mmol/L; (3) HDL-C < 1.04 mmol/L; (4) LDL-C ≥ 4.14 mmol/L (8).
Serum 25(OH)D serves as a sensitive biomarker of vitamin D levels in vivo (9). Previous research has linked serum 25(OH)D concentrations with lipid profiles (10, 11). Notably, a study within a Polish cohort found inverse correlations between vitamin D levels and TC, TG, and LDL-C (10). A substantial connection between atherosclerotic lipid profiles and vitamin D deficiency was identified through the analysis of 25 (OH) D levels and other lipid components in 20,000 patients (12). Although various mechanisms have been proposed to elucidate the influence of vitamin D on lipid levels, these effects remain somewhat unclear (13). Considering the significance of blood vitamin D levels, it follows that raising these levels could have a positive impact on the treatment of related conditions such hyperlipidemia in those who are afflicted. Therefore, the relationship between vitamin D levels and dyslipidemia is need to be further explored. The traditional statistical model (logistic regression) simplifies the interaction of variables through linear assumptions and provides clear effect estimates, but fails to capture the potential nonlinear dynamics between vitamin D levels and dyslipidemia. To address these limitations, machine learning has become a powerful tool for modeling complex nonlinear relationships in epidemiology.
Advancements in computer processing power, memory, and storage capacities have enabled machine learning algorithms to efficiently process large data volumes (14). XGBoost, an effective implementation of the gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) algorithm, has enhanced prediction accuracy, reduced overfitting, and improved algorithm generalization and interpretability, thereby gaining broad acceptance in machine learning and data mining fields (15, 16). We employed a 10-fold cross-validation approach to assess the performance of our data set using the XGBoost model and the LASSO regression algorithm. This involved partitioning the data set into ten folds for cross-validation, with each fold alternately used as a test set while the others served as training sets. The average results from these ten replicates determined the optimal machine learning coefficient. Compared to logistic regression, linear regression better describes the association between two continuous variables while controlling for other confounding factors, but in the case of nonlinear associations, generalized additive model (GAM) is more applicable (17). GAM is a statistical model used to fit data with higher degrees of freedom (18). Before modeling, there is no need to examine the relationship between the response variable and the explanatory variable. Instead, the response variable and each explanatory variable are modeled separately and combined to obtain the GAM. Consequently, this study utilized machine learning with the XGBoost algorithm, LASSO regression, and univariate logistic regression for variable screening. The relationship between vitamin D and dyslipidemia was analyzed using multiple Logistic regression and GAM model.
This study seeks to elucidate the relationship between vitamin D levels and dyslipidemia using a combination of traditional statistical methods and advanced machine learning techniques. By integrating these approaches, we aim to provide a more comprehensive understanding of how vitamin D influences lipid profiles and the potential for its therapeutic modulation in hyperlipidemic conditions. The findings of this study could contribute significantly to the ongoing discussions in nutritional science and clinical practice regarding the management of dyslipidemia and the broader implications of vitamin D deficiency in public health.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population
The study population was derived from the research project titled “Early identification, early diagnosis techniques and cutting Points of Diabetes risk factors for the Prevention and Control of major Chronic Non-communicable Diseases,” which was conducted among residents aged 18 and elder in Yandu District, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province from April to July 2018. The investigation encompassed three main components:
1. Epidemiological survey: this included demographic information (e.g., gender, age, and education level), medical history of chronic diseases (e.g., diabetes and hypertension), and behavioral and lifestyle factors (e.g., diet, sleep, exercise, smoking, and alcohol consumption).
2. Physical examination: trained medical personnel measured height, weight, waist circumference, hip circumference, diastolic blood pressure (DBP), systolic blood pressure (SBP), and other indicators.
3. Biochemical indexes testing: venous blood samples were collected after at least 8 h of fasting. Total cholesterol (TC) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) tests were performed by Nanjing Adicon Bio-Testing Company. Fasting blood glucose (FPG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TG) and other blood biochemical indicators. Serum 25(OH)D level was measured by electrochemiluminescence.
The inclusion criteria were adults 18 years of age and older. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients with missing main study indicators (TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C); (2) Pregnant women or breastfeeding persons; (3) taking lipid-lowering drugs and vitamin D supplements. Based on the above, a total of 780 subjects were included in the study.
2.2 Ethical considerations
All participants understand and consent to the data collection activities. Ethical approval and informed consent signed by participants were obtained prior to data collection.
2.3 Evaluation criterion
Vitamin D levels were separated into three groups based on Holick et al.’s (19) reference value. 25(OH)D ≤ 20 ng/mL was considered deficient, 20 ng/mL < 25(OH)D < 29 ng/mL was considered insufficient, and ≥30 ng/mL was considered sufficient.
The criteria for determining dyslipidemia were based on the Chinese Adult Dyslipidemia Prevention and Treatment guidelines for the Chinese population, that is, meeting one or more of the following conditions: (1) TC ≥ 6.2 mmol/L; (2) TG ≥ 2.3 mmol/L; (3) HDL-C < 1.0 mmol/L; (4) LDL-C ≥ 4.1 mmol/L (20).
2.4 Statistical analysis
All analyses were performed using SPSS 26 and R 4.3.2. The Mann–Whitney U test, t-test, and linear regression were employed for the analysis of continuous variables, while the chi-square test was used for categorical variables. Variable selection was performed using LASSO regression, and their significance was assessed through a multivariate logistic regression model. Generalized additive models (GAM) were utilized to better characterize the association between 25(OH)D levels and dyslipidemia, minimizing the risks of overfitting and underfitting. Finally, the XGBoost algorithm was applied to calculate, rank, and output the most relevant and significant changes in dyslipidemia, ensuring the stability and reliability of the conclusions.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of the study population
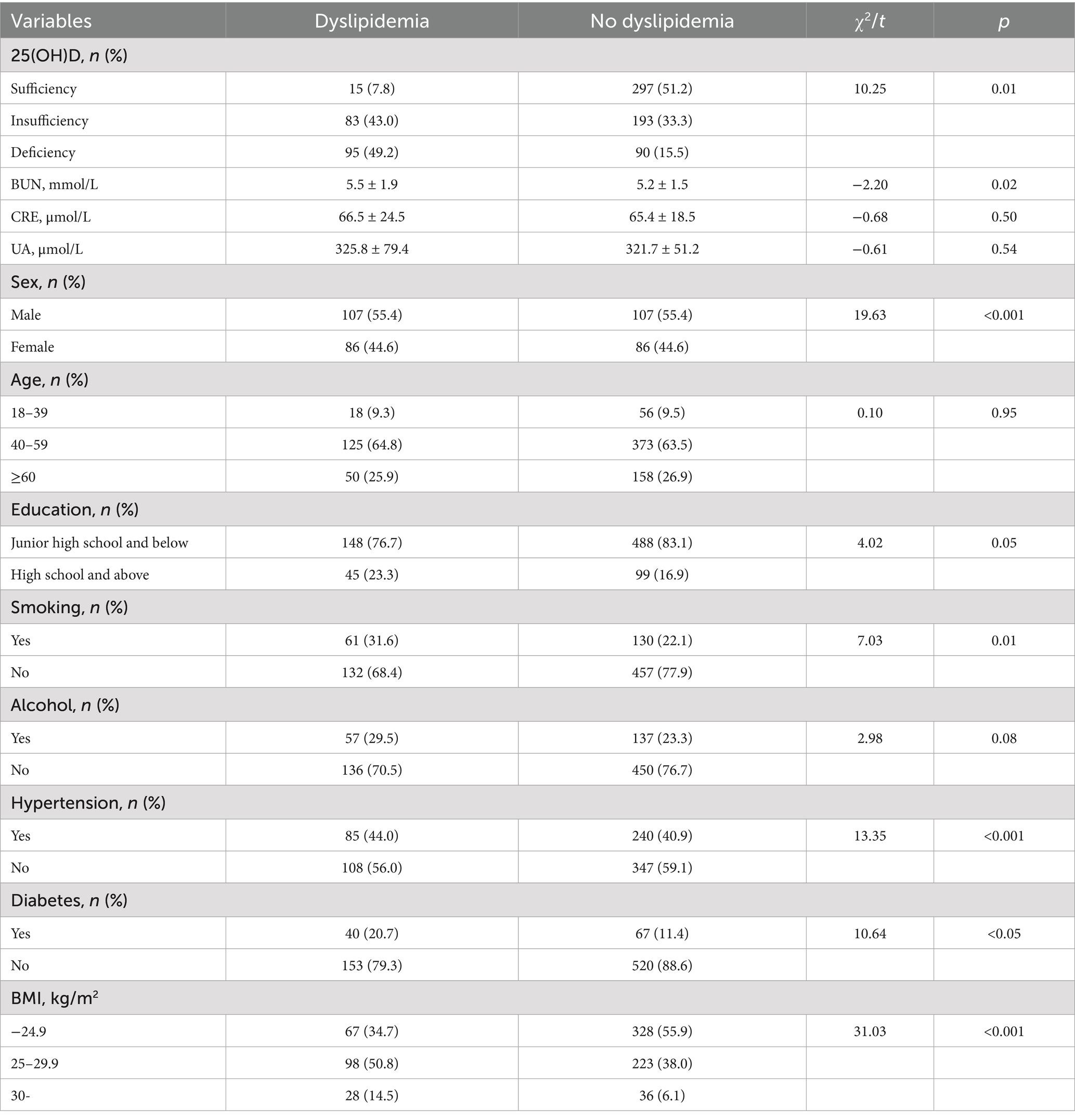
There were 780 participants in the study. Statistically significant differences were found in vitamin D levels, BUN, gender, education level, prevalence of hypertension and diabetes, smoking status, and BMI between people with dyslipidemia and people without dyslipidemia (Table 1).
3.2 Single factor analysis: univariate logistic regression
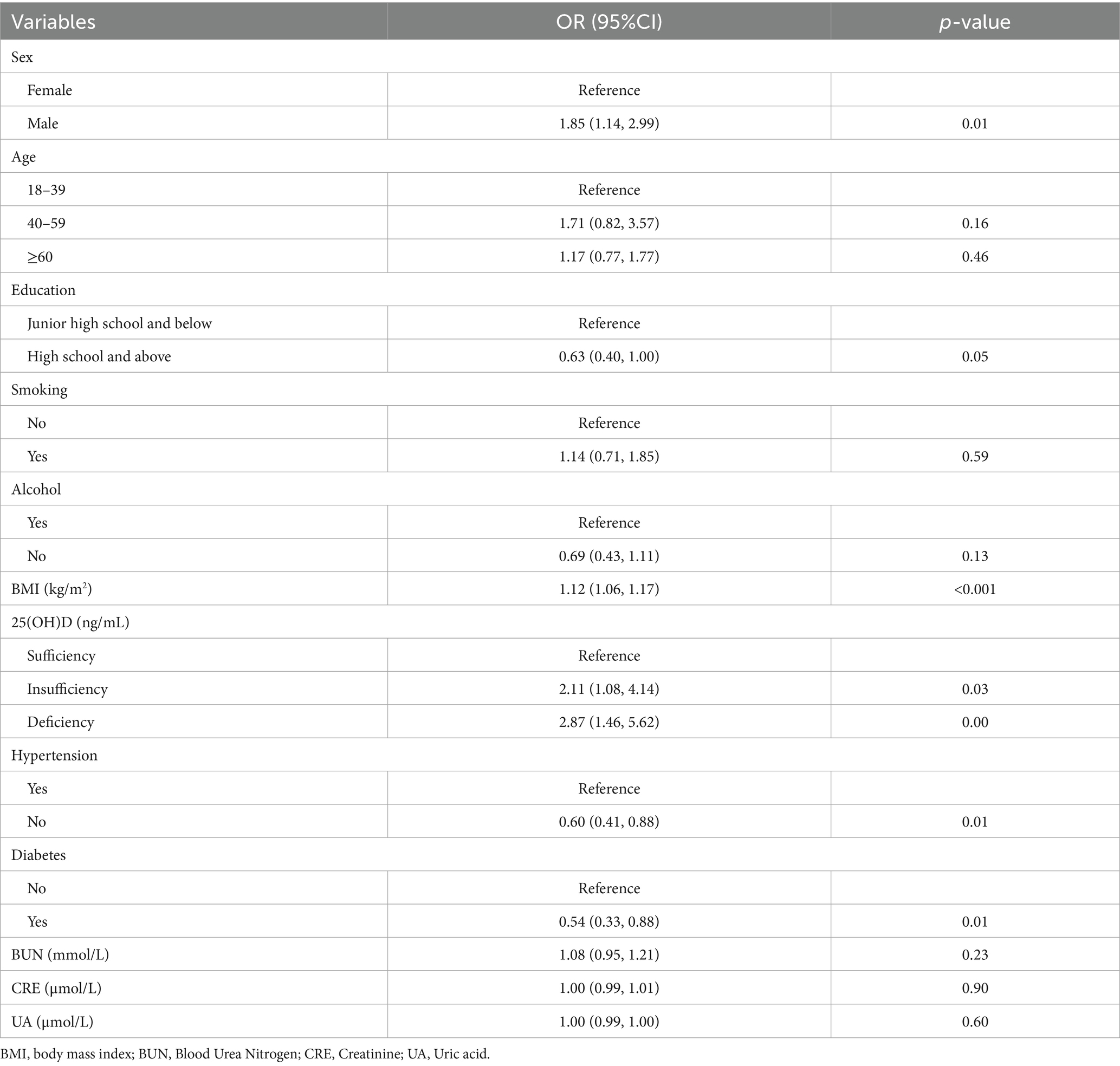
Univariate logistic regression was used to analyze the correlation between dyslipidemia and serum 25(OH)D level, sex, age, education level, smoking, alcohol consumption, BMI, hypertension, and diabetes. There was a positive correlation between BMI levels and dyslipidemia. Men have a greater risk of dyslipidemia than women. High school and above, no hypertension, and no diabetes were negatively correlated with dyslipidemia (Table 2).
3.3 Multivariate analysis: LASSO regression
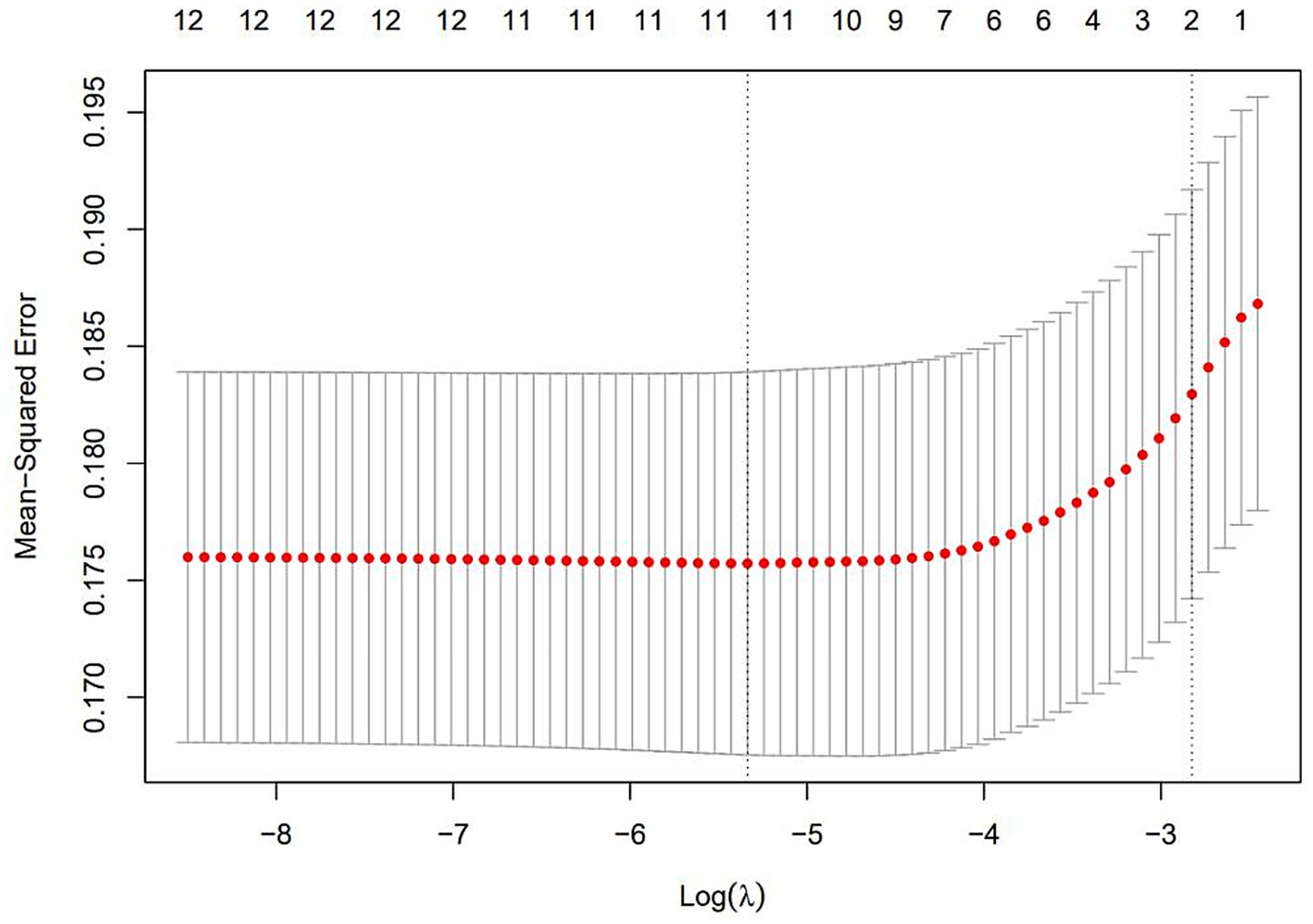
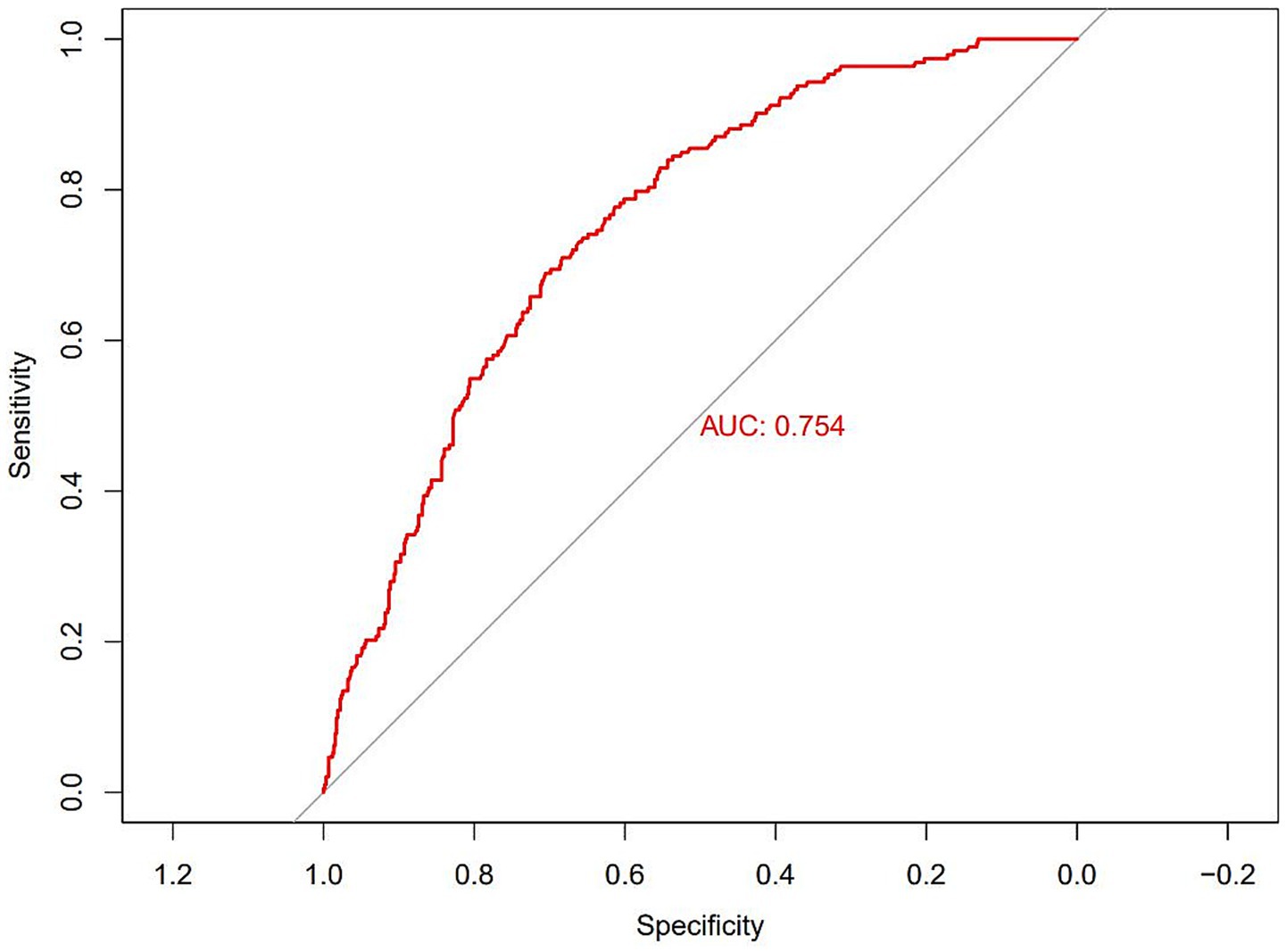
The results of selecting variables using LASSO regression are as follows. In Figure 1, the red dots represent the adjustment parameter (Lambda), and the two dashed lines represent the two special Lambda(log) values selected in the LASSO model using 10x cross-validation. That is, Lambda(log) values [lambda. Min(log)] and larger lambda(log) values are given for the minimum average cross-validation error so that the error is within 1 standard error of the minimum [lambda.1se (log)]. The two lambda values select variables that are included in the corresponding optimization model. The Lambda minimum (log) is 0.005281067 (−5.243627) (Figure 2). The AUC value of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the prediction model based on variables screened by Lambda values was 0.754 (Figure 3), indicating that LASSO regression can effectively screen out variables strongly associated with dyslipidemias.
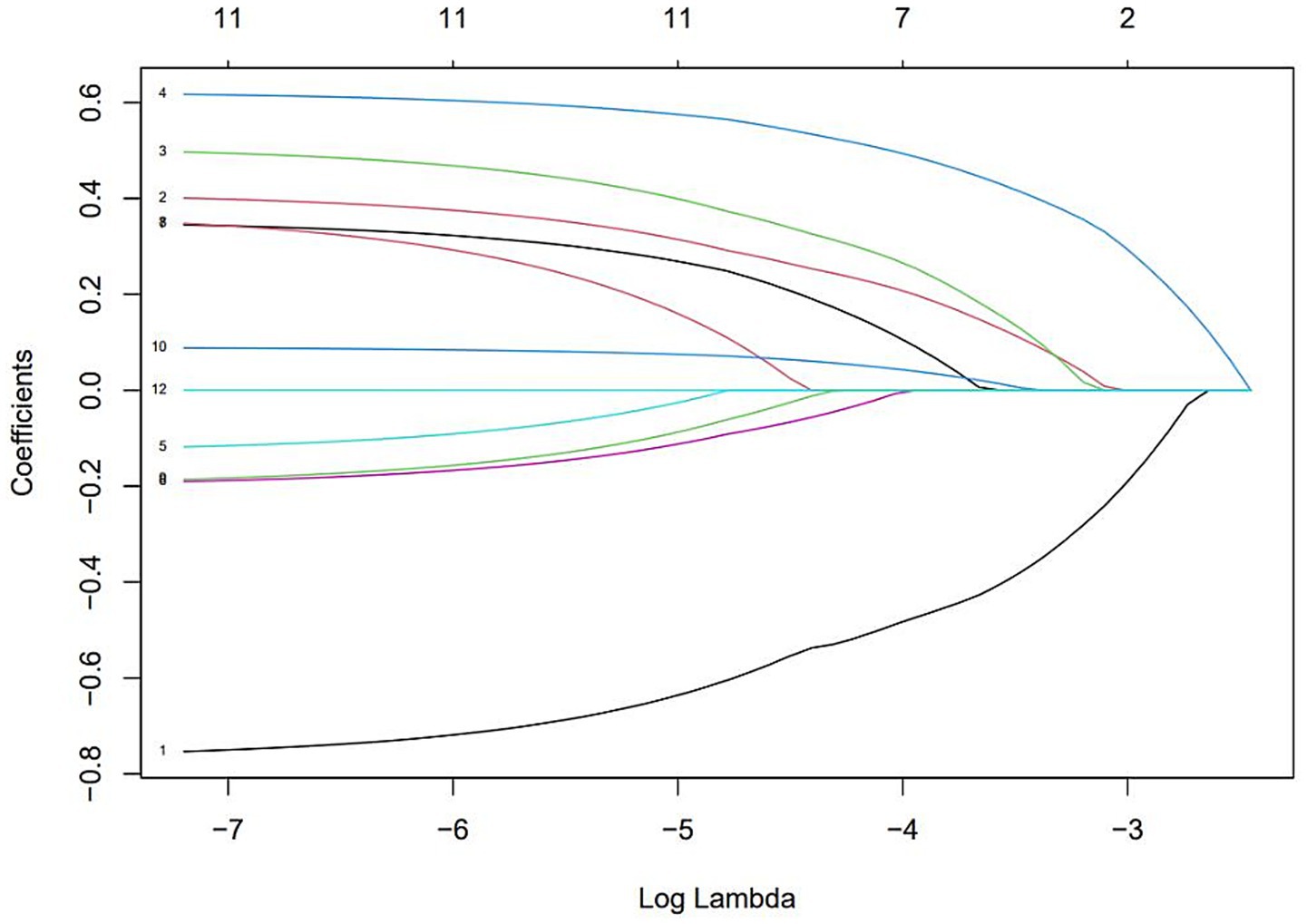
Figure 2. The optimal penalty coefficient [Lambda (log) = 0.005281067 (−5.243627)] in the Lasso regression was identified with the minimum criterion.
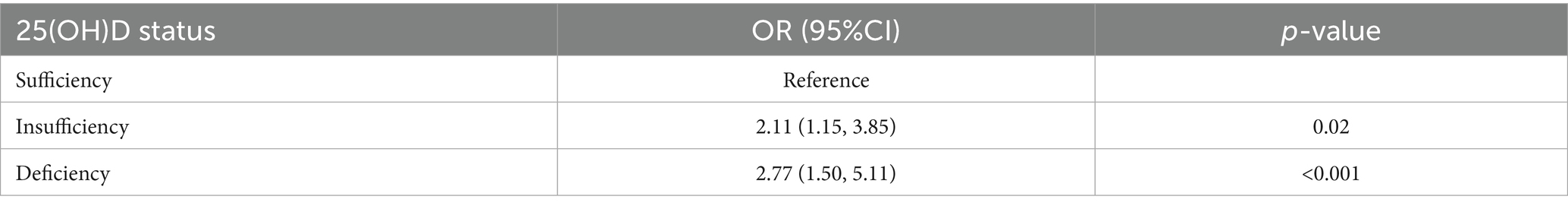
According to the 10-fold cross-verified Lambda min (log), the selected variables are sex, hypertension, diabetes, BMI, age, 25(OH)D, education, alcohol, smoking, BUN, and UA (Supplementary Table 1). The variables screened by LASSO regression were included in multivariate logistic regression. Compared with the vitamin D sufficiency group, the risk of dyslipidemia was 2.11 times higher in the vitamin D insufficiency group and 2.77 times higher in the vitamin D deficiency group (Table 3).
3.4 Generalized additive model
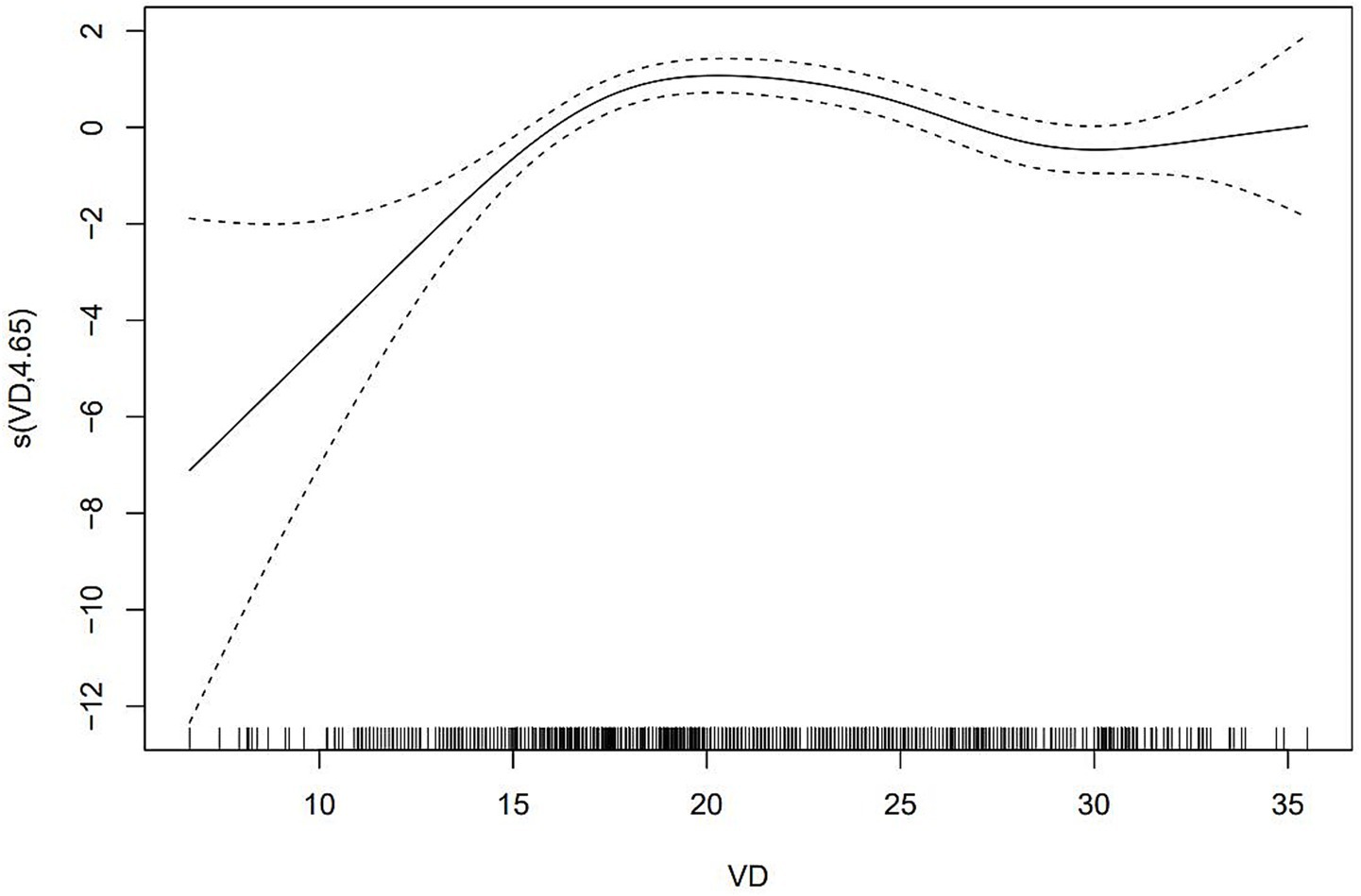
After adjusting for the statistically significant variables of LASSO regression screening in GAM, 25(OH)D levels were found to be significantly negatively associated with the risk of dyslipidemia (Figure 4). The risk of dyslipidemia decreased rapidly as vitamin D levels increased, and the risk of dyslipidemia stabilized when vitamin D levels were above 30 ng/mL.
3.5 Machine learning using the XGBoost algorithm model
We input all the variables into the XGboost machine learning algorithm, which is based on a 10-fold cross-validation approach for dyslipidemia. These variables included sociodemographic data of the participants and all relevant laboratory data. Based on the relative importance of the XGboost algorithm’s additional variables, 25(OH)D, BUN, UA, CRE, BMI, and hypertension are the six most important variables in the dataset (Figure 5).
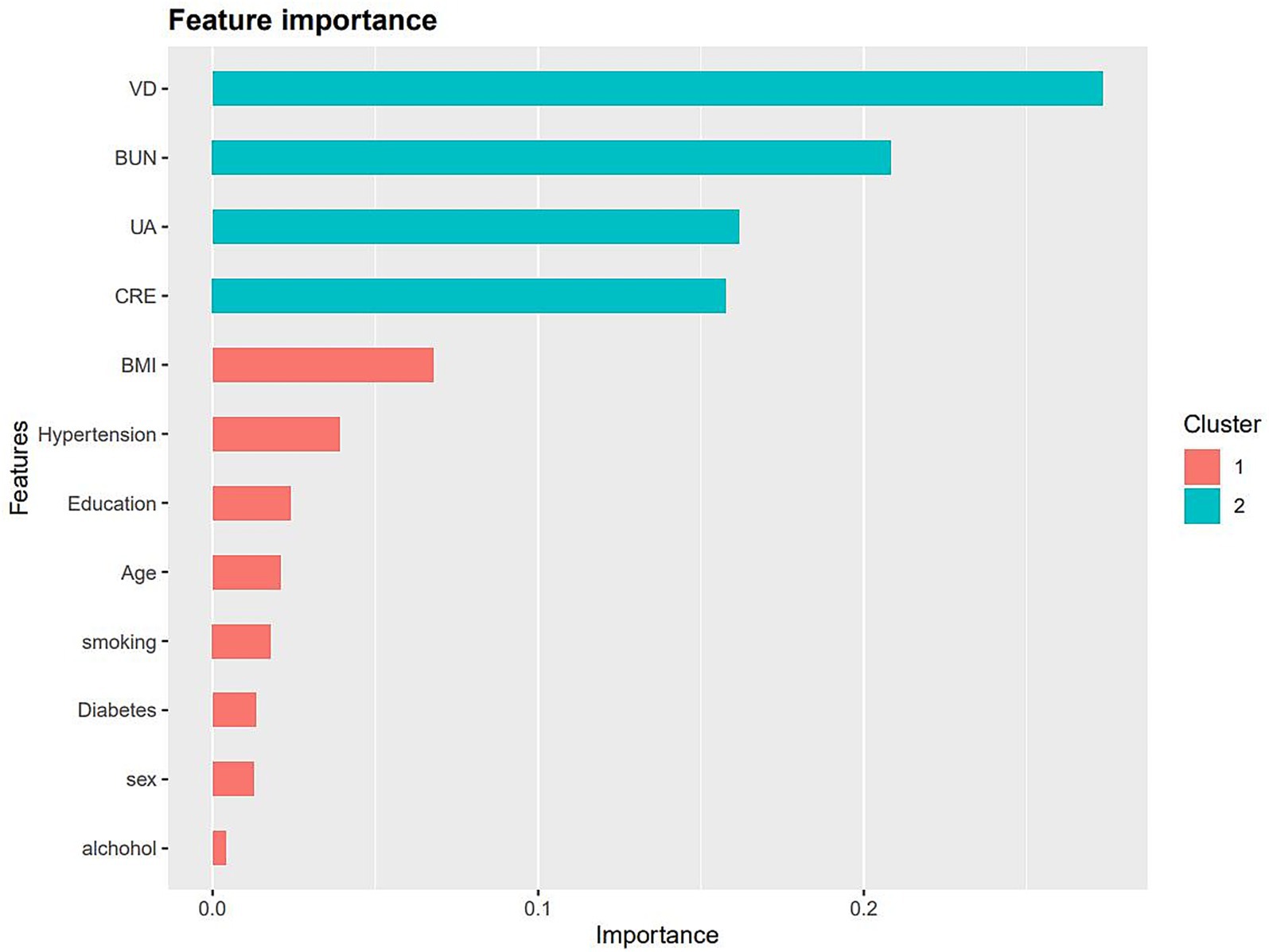
Figure 5. The relative importance of the selected variables using XGBoost and the corresponding variable importance score. The x-axis indicates the importance score, which is the relative number of a variable that is used to distribute the data, y-axis indicates the selected variable.
4 Discussion
Dyslipidemia and vitamin D deficiency are two significant global health challenges, each contributing to a wide array of diseases and increased mortality. Dyslipidemia, particularly elevated plasma LDL-C levels, is a well-established risk factor for CVD (21). Recent studies indicates that dyslipidemia is significantly associated with an increased risk of mortality from various conditions, including diabetes, malignancies, systemic autoimmune diseases, and kidney disease (22–25). Epidemiological evidence further confirms that dyslipidemia is both a recognized and modifiable risk factor for CVD, emphasizing the importance of effective lipid management to prevent cardiovascular events and reduce the global burden of cardiovascular disease (26).
Similarly, vitamin D deficiency represents a pervasive health issue that affects populations worldwide and is linked to numerous diseases, including cardiovascular disease (27, 28). Extensive evidence supports the association between lower vitamin D levels and an increased risk of conditions such as osteoporosis, chronic kidney disease, autoimmune diseases, neurological disorders, and specific types of cancer (29–32). Furthermore, consistent findings reveal a strong relationship between reduced vitamin D levels and increased risk of death. Like dyslipidemia, serum vitamin D levels significantly influence the development and progression of CVD and diabetes. Adequate levels of vitamin D have been shown to protect the cardiovascular system and help prevent diseases such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, and stroke (4). In conclusion, addressing these two critical health challenges can significantly improve population health and reduce the burden of chronic diseases.
In this study, vitamin D was identified as a significant protective factor against dyslipidemia based on the relative importance of variables analyzed using the XGBoost algorithm. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses confirmed that vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency significantly increased the risk of dyslipidemia. The generalized additive model (GAM) further demonstrated a nonlinear association between vitamin D levels and dyslipidemia risk, with a rapid decline in risk as vitamin D levels increased. This trend stabilized when serum vitamin D levels exceeded 30 ng/mL. These findings align with previous studies, such as that of Ying Wang et al., which reported an increased risk of dyslipidemia associated with vitamin D deficiency (11). Similarly, a cross-sectional study of 3,788 Chinese adults found that 25(OH)D levels were negatively correlated with triglycerides (β = −0.077, p < 0.05) and LDL cholesterol (β = −0.245, p < 0.05) (33). Globally, more than 50% of the population has vitamin D levels below 30 ng/mL, affecting over 1 billion children and adults (1). Given the potential adverse effects of vitamin D deficiency on lipid metabolism and cardiovascular health, our findings highlight the importance of prioritizing vitamin D screening in high-risk populations with serum levels below 30 ng/mL. BMI showed a positive correlation with dyslipidemia risk, consistent with findings from other prospective cohort studies. These studies demonstrated that increased BMI and obesity significantly contribute to dyslipidemia risk (34–36). Additionally, men displayed a higher risk of dyslipidemia, potentially due to smoking-related factors. Nicotine and other harmful substances in tobacco smoke raise free fatty acid levels in the blood, promoting hepatic triglyceride synthesis and reducing lipoprotein lipase activity. This leads to elevated triglyceride levels and reduced HDL-C production (37–39).
The mechanisms underlying the effect of vitamin D on lipid levels remain unclear, although several hypotheses have been proposed. First, vitamin D may inhibit hepatic triglyceride synthesis and secretion by enhancing intestinal calcium absorption (40). Vitamin D may also regulate calcium metabolism and increase intestinal calcium absorption, thereby reducing fatty acid absorption (11). Second, elevated serum calcium levels can enhance fecal fat excretion and bile acid secretion, leading to reduced cholesterol levels (41, 42). Third, high levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH) may lead to elevated TG, while 25(OH)D can inhibit serum PTH secretion (43, 44). Specifically, adequate vitamin D will increase the calcium level within fat cells, enhance the activity of fatty acid synthase, inhibit fat breakdown, and increase the storage of lipids within fat cells (45). Moreover, vitamin D can inhibit the migration and phagocytic activity of macrophages, thereby reducing the deposition of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (46). Therefore, vitamin D can affect TG concentration by regulating parathyroid hormone levels. Additionally, vitamin D deficiency has been linked to insulin resistance and impaired beta-cell activity, both of which disrupt lipoprotein metabolism, resulting in elevated triglycerides and reduced HDL-C levels (47, 48). Finally, vitamin D may regulate genes involved in cholesterol synthesis and clearance, such as CYP7A1 and ABCA1, and also regulate the inflammatory pathways that play a crucial role in lipid metabolism (49).
Compared with previous studies, this research has several advantages. First, it is based on a real-world population study, providing practical relevance. Second, it utilizes robust statistical techniques such as the XGBoost algorithm and LASSO regression for variable screening and validation. The XGBoost model is an algorithm based on decision tree integration and gradient boosting, which solves the problem of class imbalance through sample weighting and class weighting mechanisms and has powerful functions for handling high-dimensional features and capturing nonlinear relationships. Additionally, the use of the GAM model to analyze serum vitamin D levels as a continuous variable provided insights into the nonlinear relationship between vitamin D levels and dyslipidemia, avoiding overfitting and underfitting. GAM extends the traditional regression model, allowing predictor variables to flexibly influence the results, using a data-driven curve fitting approach instead of assuming a fixed logarithmic linear form. Despite these strengths, the study has limitations. First, in the data collection process, factors that may affect vitamin D levels, such as daily diet, sun exposure duration, and sunscreen use, were not taken into account. These factors may interfere with the research results and affect the accuracy of the conclusions. In addition, since the study population is based on Chinese data, the general applicability of these results in other countries and regions requires further research. Due to its cross-sectional study nature, it is impossible to determine the causal relationship. Future prospective cohort studies are needed to confirm these findings. Nonetheless, this study provides valuable insights into the relationship between vitamin D status and dyslipidemia. Further research, including cohort and experimental studies, is necessary to explore the causal mechanisms linking vitamin D levels to dyslipidemia.
5 Conclusion
Dyslipidemia is an important risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, so effective control of lipid levels is crucial for preventing cardiovascular events and reducing the associated medical burden. In this study, based on the XGBoost algorithm, vitamin D was identified as an important protective factor for preventing dyslipidemia. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis confirmed that insufficient and deficient vitamin D levels significantly increase the risk of dyslipidemia. The GAM model further indicated that there is a non-linear association between vitamin D levels and the risk of dyslipidemia, that is, individuals with insufficient or deficient vitamin D levels seem to have a higher risk of dyslipidemia than those with adequate vitamin D levels. When the serum vitamin D level is below 30 ng/mL, targeted screening for high-risk populations may help prevent dyslipidemia and its adverse cardiovascular consequences. These findings emphasize the importance of incorporating vitamin D status into the lipid dyslipidemia prevention strategy, and also indicate the need for more research, including cohort studies and experimental studies, to verify and deepen our understanding of this association.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because due to the nature of this research, participants of this study did not agree for their data to be shared publicly, so supporting data is not available. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to MTA2MDU4MTg3OUBxcS5jb20=.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhongda Hospital affiliated to Southeast University and the Ethics Committee of Jiangsu Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YTX: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. ZC: Writing – review & editing. LYX: Writing – review & editing. ZXY: Writing – review & editing. HJY: Writing – review & editing. GHJ: Writing – review & editing. WB: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1618610/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Cui, A, Zhang, T, Xiao, P, Fan, Z, Wang, H, and Zhuang, Y. Global and regional prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in population-based studies from 2000 to 2022: a pooled analysis of 7.9 million participants. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1070808. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1070808
2. Gu, P, Pu, B, Chen, B, Zheng, X, Zeng, Z, and Luo, W. Effects of vitamin D deficiency on blood lipids and bone metabolism: a large cross-sectional study. J Orthop Surg Res. (2023) 18:20. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03491-w
3. Amrein, K, Scherkl, M, Hoffmann, M, Neuwersch-Sommeregger, S, Köstenberger, M, Tmava Berisha, A, et al. Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2020) 74:1498–513. doi: 10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
4. Sofianopoulou, E, Kaptoge, SK, Afzal, S, Jiang, T, Gill, D, Gundersen, TE, et al. Estimating dose-response relationships for vitamin D with coronary heart disease, stroke, and all-cause mortality: observational and Mendelian randomisation analyses. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2024) 12:e2–e11. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(23)00287-5
5. Wimalawansa, SJ. Associations of vitamin D with insulin resistance, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2018) 175:177–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.09.017
6. Stone, NJ, Robinson, JG, Lichtenstein, AH, Bairey Merz, CN, Blum, CB, Eckel, RH, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2014) 63:2889–934. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.002
7. Radkhah, N, Zarezadeh, M, Jamilian, P, and Ostadrahimi, A. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on lipid profiles: an umbrella review of meta-analyses. Adv Nutr. (2023) 14:1479–98. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.08.012
8. Zhu, J, Gao, R, Zhao, H, Lu, G, Zhao, D, and Li, J. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in Chinese adults (revised edition 2016). Chin Circ J. (2016) 31:937–53.
9. Hariri, Z, Kord-Varkaneh, H, Alyahya, N, Prabahar, K, Găman, MA, and Abu-Zaid, A. Higher dietary vitamin D intake influences the lipid profile and hs-CRP concentrations: cross-sectional assessment based on the national health and nutrition examination survey. Life (Basel). (2023) 13:581. doi: 10.3390/life13020581
10. Dziedzic, EA, Przychodzeń, S, and Dąbrowski, M. The effects of vitamin D on severity of coronary artery atherosclerosis and lipid profile of cardiac patients. Arch Med Sci. (2016) 12:1199–206. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2016.60640
11. Wang, Y, Si, S, Liu, J, Wang, Z, Jia, H, Feng, K, et al. The associations of serum lipids with vitamin D status. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0165157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165157
12. Lupton, JR, Faridi, KF, Martin, SS, Sharma, S, Kulkarni, K, Jones, SR, et al. Deficient serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with an atherogenic lipid profile: the very large database of lipids (VLDL-3) study. J Clin Lipidol. (2016) 10:72–81.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2015.09.006
13. Surdu, AM, Pînzariu, O, Ciobanu, DM, Negru, AG, Căinap, SS, Lazea, C, et al. Vitamin D and its role in the lipid metabolism and the development of atherosclerosis. Biomedicine. (2021) 9:172. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9020172
14. Deo, RC. Machine learning in medicine. Circulation. (2015) 132:1920–30. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.001593
15. Lundberg, SM, Erion, G, Chen, H, DeGrave, A, Prutkin, JM, Nair, B, et al. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nat Mach Intell. (2020) 2:56–67. doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0138-9
16. Jiang, YQ, Cao, SE, Cao, S, Chen, JN, Wang, GY, Shi, WQ, et al. Preoperative identification of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by XGBoost and deep learning. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2021) 147:821–33. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03366-9
17. Ikawa, F, Ichihara, N, Uno, M, Shiokawa, Y, Toyoda, K, Minematsu, K, et al. Visualisation of the non-linear correlation between age and poor outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2021) 92:1173–80. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2020-325306
18. Xiao, D, Wu, K, Tan, X, Le, J, Li, H, Yan, Y, et al. Modeling and predicting hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome trends based on meteorological factors in Hu County, China. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0123166. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123166
19. Holick, MF, Binkley, NC, Bischoff-Ferrari, HA, Gordon, CM, Hanley, DA, Heaney, RP, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2011) 96:1911–30. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0385
20. Wang, Z, Liu, J, Li, J, Wu, N, Lu, G, Chen, Z, et al. Chinese guidelines for lipid management (2023). Chin Circ J. (2023) 38:237–71.
21. Bozkurt, B, Aguilar, D, Deswal, A, Dunbar, SB, Francis, GS, Horwich, T, et al. Contributory risk and Management of Comorbidities of hypertension, obesity, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and metabolic syndrome in chronic heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2016) 134:e535–78. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000450
22. Fan, D, Li, L, Li, Z, Zhang, Y, Ma, X, Wu, L, et al. Effect of hyperlipidemia on the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. (2018) 17:102. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0676-x
23. Chen, X, Zhou, M, Yan, H, Chen, J, Wang, Y, and Mo, X. Association of serum total 25-hydroxy-vitamin D concentration and risk of all-cause, cardiovascular and malignancies-specific mortality in patients with hyperlipidemia in the United States. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:971720. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.971720
24. Yu, HH, Chen, PC, Yang, YH, Wang, LC, Lee, JH, Lin, YT, et al. Statin reduces mortality and morbidity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with hyperlipidemia: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Atherosclerosis. (2015) 243:11–8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.08.030
25. Feng, X, Zhan, X, Wen, Y, Peng, F, Wang, X, Wang, N, et al. Hyperlipidemia and mortality in patients on peritoneal dialysis. BMC Nephrol. (2022) 23:342. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02970-w
26. Brunham, LR, Lonn, E, and Mehta, SR. Dyslipidemia and the current state of cardiovascular disease: epidemiology, risk factors, and effect of lipid lowering. Can J Cardiol. (2024) 40:S4–s12. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2024.04.017
27. Skaaby, T. The relationship of vitamin D status to risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality. Dan Med J. (2015) 62:B5008
28. Mozos, I, and Marginean, O. Links between vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular diseases. Biomed Res Int. (2015) 2015:109275. doi: 10.1155/2015/109275
29. Yuan, C, Wang, J, Zhang, W, Yi, H, Shu, B, Li, C, et al. Effects of obesity with reduced 25(OH)D levels on bone health in elderly Chinese people: a nationwide cross-sectional study. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1162175. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1162175
30. Duan, S, Lu, F, Wu, B, Zhang, C, Nie, G, Sun, L, et al. Association of Serum 25 (OH) vitamin D with chronic kidney disease progression in type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:929598. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.929598
31. Pelajo, CF, Lopez-Benitez, JM, and Miller, LC. Vitamin D and autoimmune rheumatologic disorders. Autoimmun Rev. (2010) 9:507–10. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.02.011
32. Navale, SS, Mulugeta, A, Zhou, A, Llewellyn, DJ, and Hyppönen, E. Vitamin D and brain health: an observational and Mendelian randomization study. Am J Clin Nutr. (2022) 116:531–40. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac107
33. Jiang, X, Peng, M, Chen, S, Wu, S, and Zhang, W. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with dyslipidemia: a cross-sectional study in 3788 subjects. Curr Med Res Opin. (2019) 35:1059–63. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2018.1552849
34. Rangel-Baltazar, E, Cuevas-Nasu, L, Shamah-Levy, T, Rodríguez-Ramírez, S, Méndez-Gómez-Humarán, I, and Rivera, JA. Association between high waist-to-height ratio and cardiovascular risk among adults sampled by the 2016 half-way National Health and nutrition survey in Mexico (ENSANUT MC 2016). Nutrients. (2019) 11:1402. doi: 10.3390/nu11061402
35. Liu, J, Tse, LA, Liu, Z, Rangarajan, S, Hu, B, Yin, L, et al. Predictive values of anthropometric measurements for Cardiometabolic risk factors and cardiovascular diseases among 44 048 Chinese. J Am Heart Assoc. (2019) 8:e010870. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010870
36. Cao, L, Zhou, J, Chen, Y, Wu, Y, Wang, Y, Liu, T, et al. Effects of body mass index, waist circumference, waist-to-height ratio and their changes on risks of dyslipidemia among Chinese adults: the Guizhou population health cohort study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 19:341. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010341
37. Liu, X, Wu, W, Mao, Z, Huo, W, Tu, R, Qian, X, et al. Prevalence and influencing factors of overweight and obesity in a Chinese rural population: the Henan rural cohort study. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:13101. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31336-2
38. Chen, H, Zhang, X, Feng, Q, and Zeng, Y. The effects of "diet-smoking-gender" three-way interactions on cognitive impairment among Chinese older adults. Nutrients. (2022) 14:2144. doi: 10.3390/nu14102144
39. Li, ZR, Ruan, HF, Shen, LP, Zhang, XP, and Wan, LH. Gender difference in the association between stroke knowledge and health behavior before the onset of stroke among Chinese hypertensive patients. J Neurosci Nurs. (2021) 53:160–5. doi: 10.1097/JNN.0000000000000599
40. Cho, HJ, Kang, HC, Choi, SA, Ju, YC, Lee, HS, and Park, HJ. The possible role of Ca2+ on the activation of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in rat hepatocytes. Biol Pharm Bull. (2005) 28:1418–23. doi: 10.1248/bpb.28.1418
41. Christensen, R, Lorenzen, JK, Svith, CR, Bartels, EM, Melanson, EL, Saris, WH, et al. Effect of calcium from dairy and dietary supplements on faecal fat excretion: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. (2009) 10:475–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00599.x
42. Jiang, W, Miyamoto, T, Kakizawa, T, Nishio, SI, Oiwa, A, Takeda, T, et al. Inhibition of LXRalpha signaling by vitamin D receptor: possible role of VDR in bile acid synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2006) 351:176–84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.027
43. Song, SJ, Si, S, Liu, J, Chen, X, Zhou, L, Jia, G, et al. Vitamin D status in Chinese pregnant women and their newborns in Beijing and their relationships to birth size. Public Health Nutr. (2013) 16:687–92. doi: 10.1017/S1368980012003084
44. Zemel, MB, Shi, H, Greer, B, Dirienzo, D, and Zemel, PC. Regulation of adiposity by dietary calcium. FASEB J. (2000) 14:1132–8. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.14.9.1132
45. Riek, AE, Oh, J, and Bernal-Mizrachi, C. Vitamin D regulates macrophage cholesterol metabolism in diabetes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2010) 121:430–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.03.018
46. Ruiz-Ojeda, FJ, Anguita-Ruiz, A, Leis, R, and Aguilera, CM. Genetic factors and molecular mechanisms of vitamin D and obesity relationship. Ann Nutr Metab. (2018) 73:89–99. doi: 10.1159/000490669
47. Chen, Y, Chen, YQ, and Zhang, Q. Association between vitamin D and insulin resistance in adults with latent tuberculosis infection: results from the National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES) 2011-2012. J Infect Public Health. (2022) 15:930–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.07.007
48. Sharafi, SM, Yazdi, M, Goodarzi-Khoigani, M, and Kelishadi, R. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and homeostatic model of insulin resistance levels in healthy pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Iran J Med Sci. (2023) 48:4–12. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2021.90586.2166
Keywords: dyslipidemia, 25(OH)D, XGBoost, GAM, machine learning
Citation: Tianxiu Y, Chen Z, Yuxiang L, Xiaoyue Z, Jingyao H, Haijian G and Bei W (2025) Exploring the association between vitamin D levels and dyslipidemia risk: insights from machine learning and generalized additive models. Front. Nutr. 12:1618610. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1618610
Edited by:
Amani Kallel, Ministry of Public Health, TunisiaReviewed by:
Runnan Grace Li, University of Kentucky, United StatesDi Zhu, Chi Forest (Beijing) Food Technology Group Co., Ltd., China
Copyright © 2025 Tianxiu, Chen, Yuxiang, Xiaoyue, Jingyao, Haijian and Bei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wang Bei, d2FuZ2JlaWx4YkAxNjMuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
 Yin Tianxiu
Yin Tianxiu Zhang Chen2†
Zhang Chen2† Guo Haijian
Guo Haijian Wang Bei
Wang Bei