- 1Department of Chinese Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 2Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 3Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 4Henan Key Laboratory for Digestive Organ Transplantation, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
Objective: Xianyu capsule (XYC) is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine in the clinical treatment of epilepsy, with significant curative effect and good safety. However, its mechanism of action remains poorly understood. This research employed a multi-omics approach to systematically evaluate the anti-epileptic efficacy of XYC and elucidate its underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Epilepsy rat model was established by lithium-pilocarpine hydrochloride injection. XYC was administered and the effects and mechanism was analyzed with H&E and Nissl staining, TUNEL assay, ELISA assay for inflammatory cytokines, 16S rDNA, non-targeted metabolomics and network pharmacology. The potential target were experimentally validated with RT-qPCR and Western blotting analysis.
Results: XYC administration ameliorated the pathological changes and neurons apoptosis of brain hippocampus CA1 region, with reduced MDA and increased SOD and CAT levels in hippocampus, and decreased inflammation cytokine in serum. 16S rDNA sequencing revealed distinct gut microbial restructuring in XYC-treated epileptic models, characterized by phylum-level alterations in lipid-associated taxa (Tenericutes, Patescibacteria, Epsilonbacteraeota, Proteobacteria) and genus-level modulations (Lactobacillus, Ramboutsia, Staphylococcus). Serum metabolomics identified 149 differentially expressed metabolites positively correlated with XYC’s anti-epileptic effects, predominantly enriched in glycerophospholipid metabolic pathways. Network pharmacology identified AKT1, INS, and IL-6 as pivotal mediators of XYC’s therapeutic effects, which were subsequently validated with Western blotting and ELISA assay.
Conclusion: Our results proved that XYC exerted favorable effect on epilepsy by modulating the gut microbiota and serum lipid metabolic, especially neuroinflammation and glycerophospholipid metabolism by regulating the AKT1, INS and IL-6 expression levels. In addition, targeting neuroinflammatory pathways and modulating glycerophospholipid metabolism may represent a promising therapeutic strategy for epilepsy management.
1 Introduction
As a disabling neurological condition affecting people of all ages, races, and geographical regions, epilepsy manifests in over 65 million patients worldwide, with China accounting for 15.4% of the total burden (10 million cases). The hallmark neuropathological feature involves paroxysmal cerebral network dysregulation caused by pathological neuronal hypersynchrony. With an annual incidence of approximately 650,000 new cases worldwide, this condition demonstrates significant etiological heterogeneity and substantial heritability (1–3). Epilepsy is a disease associated with various etiologies and risk factors, and exhibits high heritability. Clinical studies indicate that, nearly 30–40% epilepsy cases demonstrate resistance to conventional antiepileptic drugs, while 60% of epileptic seizures are idiopathic (4). While current clinical arsenals comprise more than 30 antiseizure drugs, 30–35% of epilepsy patients develop pharmacoresistance, with seizure recurrence rates exceeding 50% despite optimized antiseizure drugs regimens (5). Therefore, it is necessary to further explore the pathogenesis and effective treatment methods of epilepsy.
Accumulating evidence indicates that seizure episodes are closely associated with a cascade of inflammatory cytokine upregulation, which drives neuroinflammatory processes, exacerbates cerebral pathophysiology, and facilitates ictal propagation. Notably, immune responses have been implicated in initiating sustained neuroinflammatory cascades that contribute to the molecular mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis (6, 7). And there is a potential interaction between gut microbiota and neuroinflammation in central nervous system (CNS) disorder diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease (8, 9). The gut microbiota modulates CNS activity via microbial metabolites, neurotransmitters, and immune-inflammatory signaling, while the CNS influences gut microbial composition through neuroendocrine pathways, conversely. This bidirectional communication system is termed the gut-brain axis (10). The bidirectional gut-brain axis communication is significantly mediated by intestinal flora metabolites, with short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and amino acids serving as critical mediators in modulating neuroinflammation and maintaining CNS homeostasis. These microbiota-generated metabolites modulate critical neural mechanisms including blood–brain barrier integrity maintenance, myelin formation, neuronal regeneration, and microglial development. Furthermore, they modulate various aspects of animal behavior, demonstrating the microbiota-brain axis’s critical role in CNS functionality (11–13). The gut-brain axis functions bidirectionally, with the CNS modulating gut physiology through autonomic pathways. Neural control of digestive processes—including secretion of intestinal peptides and mucus—along with CNS-mediated regulation of mucosal immunity, collectively shapes the gut microenvironment. These neurogenic influences create dynamic habitat conditions that directly affect microbial colonization and population dynamics (14, 15). Epileptic patients, particularly pharmacoresistant cases, demonstrate characteristic gut microbial dysbiosis and topographical reorganization relative to healthy controls (16, 17). These dysbiotic patterns may reflect disease-specific microbial signatures associated with seizure pathogenesis.
Recent studies have revealed that both individuals with epilepsy and preclinical animal models exhibit characteristic gut dysbiosis. Liu et al. (18) demonstrated that epilepsy patients exhibit microbiome dysbiosis, while the clinical findings were corroborated in animal models, where metagenomic analysis of epileptic rats showed an elevated Bacteroidota-to-Firmicutes ratio compared to controls (19). Complementing these results, Oliveira et al. (20) reported reduced microbial diversity (lower Chao1 index) in lithium-pilocarpine-induced epileptic rats, along with increased Desulfobacterota and decreased Patescibacteria abundance at the phylum level. The consistent dysbiosis patterns across species suggest intestinal microbiome emerges as a dual-function modulator in epilepsy pathogenesis (17, 21). Notably, fecal microbiota transplantation has demonstrated anti-seizure efficacy in human patients, canines, and rodent models (22, 23), collectively validating the microbiota-brain axis dysregulation hypothesis in epileptogenesis.
Disordered lipid homeostasis constitutes a central etiological factor in epileptogenesis, manifesting specifically through dysregulated metabolism of triglycerides (TGs), cholesterol (CHOL), and fatty acid (FA) (24). Clinical and preclinical studies demonstrate that epilepsy induces lipid metabolic reprogramming through FA-associated signaling pathways in both pediatric patients and rodent models (25, 26). This metabolic disruption manifests as elevated TG accumulation, impaired CHOL homeostasis (inhibited efflux and enhanced influx), and reduced FA β-oxidation. These alterations promote reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, exacerbating neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis (27). Additionally, epilepsy progression involves abnormal metabolism of SLs (crucial for neurodevelopment) and phospholipids (essential membrane components) (28, 29). The ketogenic diet (KD) has emerged as an effective therapeutic strategy for epileptic pharmacoresistant cases. This high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate intervention induces ketone bodies (β-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, and acetone) concomitant with elevated serum CHOL and TG concentrations. The KD demonstrates anticonvulsant efficacy via multimodal mechanisms: stabilizing neuronal hyperexcitability, optimizing mitochondrial energetics, and restructuring enteric microbial ecology (30, 31). These findings position lipid metabolism modulation as a promising therapeutic paradigm for epilepsy management (32).
Xianyu Capsule (XYC), a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formulation, is clinically employed as an antiepileptic therapeutic agent, formulated by modifying and combining two classical TCM prescriptions: Qianzheng San (Symmetry-Restoring Powder) and Tianma Gouteng Yin (Gastrodia-Uncaria Decoction), with phlegm-resolving and consciousness-restoring, sedative and anticonvulsant, wind-extinguishing and spasmolytic effect. XYC containing 16 medicinal compounds (Hedysarum Multijugum Maxim., Codonopsis Radix, Radix Salviae, Radix Bupleuri, Ziziphi Spinosae Semen, Polygala tenuifolia Willd., Rhizom Gastrodiae, Uncariae Ramulus Cumuncis, Curcumae Radix, Arisaema Cum Bile, Angelicae Sinensis Radix, Acoritataninowii Rhizoma, Bombyx Batryticatus, Massa Medicata Fermentata, licorice and Typhonii Rhizoma, and Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.). XYC has been used in the treatment of epilepsy for more than twenty years in clinical settings (SFDA approval number: Z20025728). However, the precise molecular underpinnings remain incompletely elucidated.
In this study, we employed a lithium-pilocarpine hydrochloride induced rat model of epilepsy to evaluate the neuroprotective effects of XYC. A multi-omics approach was implemented, combining untargeted serum metabolomics, gut microbiomics, and network pharmacology analysis to comprehensively assess XYC’s protective mechanisms.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Chemical and reagents
Xianyu Capsule (XYC, Lot #20220401) was obtained from Xi’an Chiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Xi’an, China). Pilocarpine hydrochloride (#HY-B0726) was purchased from MCE (Shanghai, China). Malondialdehyde (MDA, #A003-1) and Superoxide dismutase (SOD, #A001-3) assay kits were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China). TUNEL BrightRed Apoptosis Detection Kit (#A113-02) were obtained from Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). Akt1-Specific Recombinant antibody (#80816-1-RR) and Alpha Tubulin polyclonal antibody (#11224-1-AP) were acquired from Proteintech (Wuhan, China). ELISA assay kit for IL-6 (#E-EL-R0015), TNF-α (#E-EL-R2856), IL-1β (#E-EL-R0012) were obtained from Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China).
2.2 UPLC-MS analysis of XYC
XYC constituents were analyzed with UPLC-Orbitrap-MS as previously described (33). Chromatography on Waters HSS T3 column (100 × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm). High-resolution mass spectrometric data were acquired using Q Exactive HFX Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific) equipped with a heated ESI source and operating in Full-ms/ddMS2 mode.
2.3 Lithium-pilocarpine hydrochloride-induced epileptic rat model
SD rats (180–220 g) were purchased from SLAC Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and housed under specific pathogen-free (SPF) conditions at the laboratory animal center of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, with 22 ± 2°C temperature, 50% humidity, 12 h light/dark cycle, and ad libitum access to food and water. According to clinical application, the dosage of XYC and CBZ is 6.6 g and 1.2 g per person per day, respectively. Based on the body surface area normalization from rodent-to-human equivalent dose conversion, the equivalent dose for rat is 0.70 g/kg and 0.125 g/kg per day. Thirty rats were randomly assigned to five groups (Control, Model, CBZ, XYC 0.35 g/kg and 0.70 g/kg group) using a computer-generated block randomization scheme (block size = 6) to ensure balanced distribution of body weights and baseline metabolic parameters. Randomization was performed by an independent researcher not involved in data collection, and group allocation was concealed until interventions began. After 7 days of adaptive feeding, the rats were administered with CBZ or XYC by gavage for 14 days. The dosage of CBZ was 0.125 g/kg, the high dosage of XYC was 0.70 g/kg, and the low dosage was 0.35 g/kg. On the 15th day, epilepsy was induced as previously described (34, 35). Following an initial intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of lithium chloride (3 mmol/kg), rats received pilocarpine (35.3 mg/kg, i.p.) 20 h post-injection. Seizures manifested 15–35 min post-induction and were quantified over 30 min using the established modified Racine scale (36). The seizures were terminated with 10% chloral hydrate saline solution 1 h after the seizures. The epileptic rats were housed with food and water available ad libitum. After 7 days of continuous intragastric administration, the rats were sacrificed, blood was collected for metabonomic detection. The cecal contents were collected for 16S rDNA sequencing. The hippocampal tissues were collected for the determination of MDA, SOD and pathological observation. Throughout the experiment, investigator blinding and outcome assessor blinding was implemented. Ethical approval (2023-KY-1341) was granted by the Research Ethics Committee at Zhengzhou University First Hospital, with informed consent obtained following NIH guidelines for animal welfare.
2.4 Biochemical analysis
The catalase activity analysis was added here: “Catalase (CAT) activity was quantified by measuring the absorbance at 405 nm of a yellow-colored complex formed between residual H₂O₂ and ammonium molybdate, which reflects the remaining H₂O₂ after catalase-mediated decomposition.”
2.5 ELISA
The serum concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β) were determined via ELISA according to manufacturer protocols. Absorbance measurements at 450 nm were performed on a Varioskan LUX multimode microplate reader.
2.6 Hematoxylin and eosin and Nissl staining
Following intervention, hippocampal specimens were immediately immersion-fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. Gradient ethanol dehydration preceded paraffin embedding. Serial coronal sections (5 μm thickness) were obtained for subsequent histological processing, including hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) and cresyl violet-based Nissl staining (37). Histopathological scoring was performed by two independent pathologists blinded to treatment conditions.
2.7 16S rDNA sequencing
The isolation of total DNA from intestinal microbiota, followed PCR reaction and sequencing were performed as described before (38). RDP classifier1 was used to annotate the representative sequences after clustering, and a threshold of 70% was set against the Silva database (SSU128/16 s bacteria). Using the R language tool to draw the community histogram, we determined the structural composition of different groups of the bacterial community at the phylum and generic levels.
2.8 Ultra high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for untargeted metabolomics in serum
For metabolomics analysis, serum were collected after treatment. The chromatographic conditions in UHPLC system and the QExactive high-resolution system for mass spectrometry systems were conducted as previously described (39, 40).
Briefly, Serum were vortexed with methanol/acetonitrile (1:1, v/v), centrifuged (4°C 14,000 × g for 20 min), and the resultant supernatant lyophilized before reconstitution in acetonitrile/water (1:1, v/v).
UHPLC system (Vanquish, Thermo) with HILIC column were used. Mobile phase: A = 25 mM ammonium acetate/hydroxide, B = acetonitrile. Gradient: 98% B (1.5 min) to 2% B (10.5 min), held 2 min, rapidly restored to 98% B (0.1 min) with 3 min re-equilibration in both ESI modes.
Processed raw MS data (ProteoWizard) using XCMS with centWave (peakwidth = 10–60, m/z = 10 ppm) and grouping parameters (mzwid = 0.025, bw = 5). CAMERA annotated isotopes/adducts. Metabolites were identified via m/z (<10 ppm) and MS/MS matching against an authentic standards database. Normalized data underwent multivariate analysis (Pareto-scaled PCA/OPLS-DA) via ropls. Model robustness was verified by 7-fold cross-validation/permutation tests.
2.9 Network pharmacology analyze
Bioactive constituents of XYC’s constituent herbs were systematically curated from the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP, https://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php) or BATMN-TCM2 using the keywords “Hedysarum Multijugum Maxim.,” “Codonopsis Radix,” “Radix Salviae,” “Radix Bupleuri,” “Ziziphi Spinosae Semen,” “Polygala tenuifolia Willd.,” “Rhizom Gastrodiae,” “Uncariae Ramulus Cumuncis,” “Acoritataninowii Rhizoma,” “Arisaema Cum Bile,” “Angelicae Sinensis Radix,” “Bombyx Batryticatus,” “Massa Medicata Fermentata,” “Curcumae Radix,” “licorice” and “Typhonii Rhizoma.” Then screen the retrieved compounds by ADME parameters (oral bioavailability (OB) ≥ 30%, drug-likeness (DL) ≥ 0.18) (41). Epilepsy-related disease targets were obtained from OMIM,3 DisGeNET,4 and GeneCards databases.5 Then XYC-epilepsy-related target screening and PPI network construction were obtained as previously described (42).
2.10 RT-qPCR
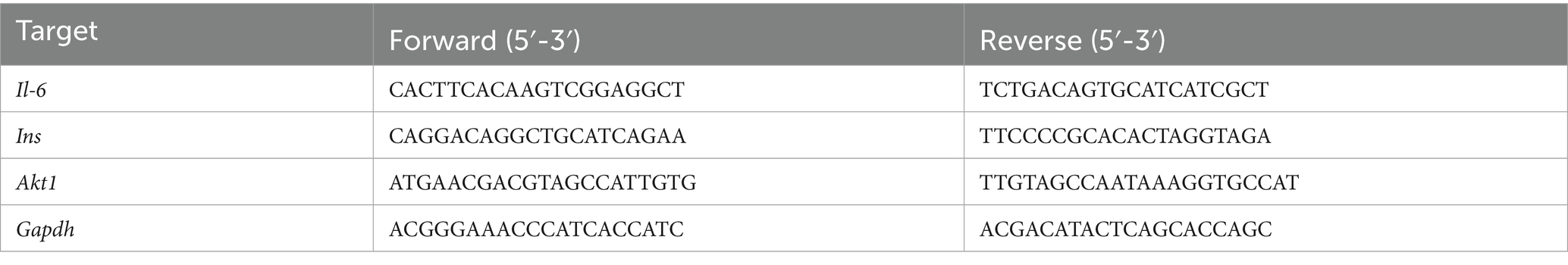
Total RNA from hippocampal tissues were isolated using TRIzol and reversed into cDNA. RT-qPCR was conducted using SYBR qPCR Master Mix (#A57155, Applied Biosystems, MA, United States). Primers sequences were listed in Table 1.
2.11 Western blotting assay
Hippocampal protein was extracted using ice-cold RIPA lysis buffer (#R0010, Solarbio) supplemented with 1% protease/phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (#P1260, Solarbio, Beijing, China), and then separated with SDS-PAGE, and PVDF membranes were used for the incubation of primary antibodies followed by secondary antibodies, and ECL substrate for visualizing the results.
2.12 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted with SPSS Statistics (v19.0, IBM Corp.) using the mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). The significance between three or more groups was determined by one-way ANOVA, with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Chemical components of XYC
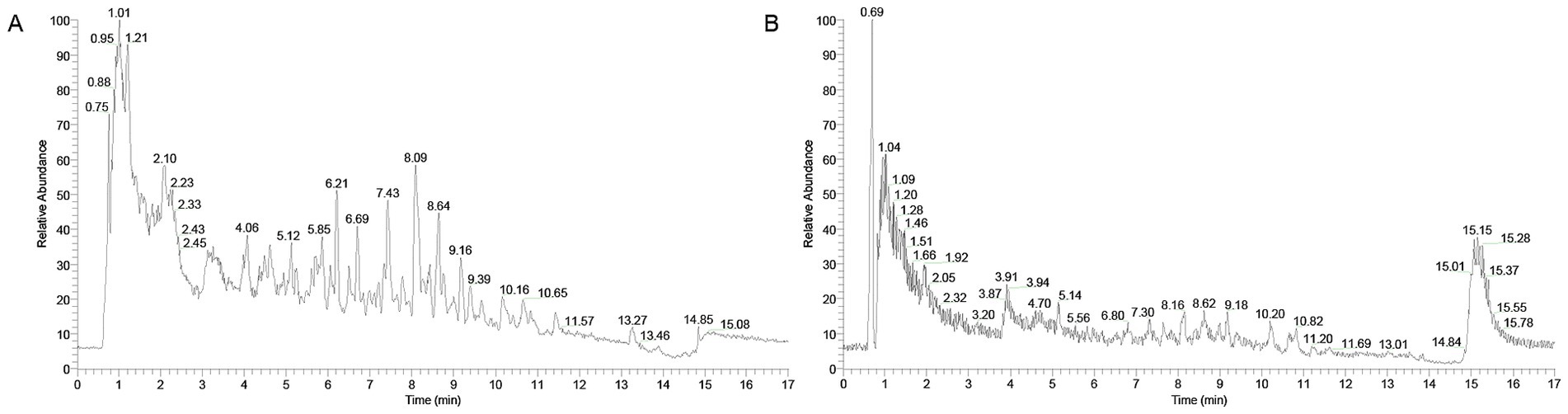
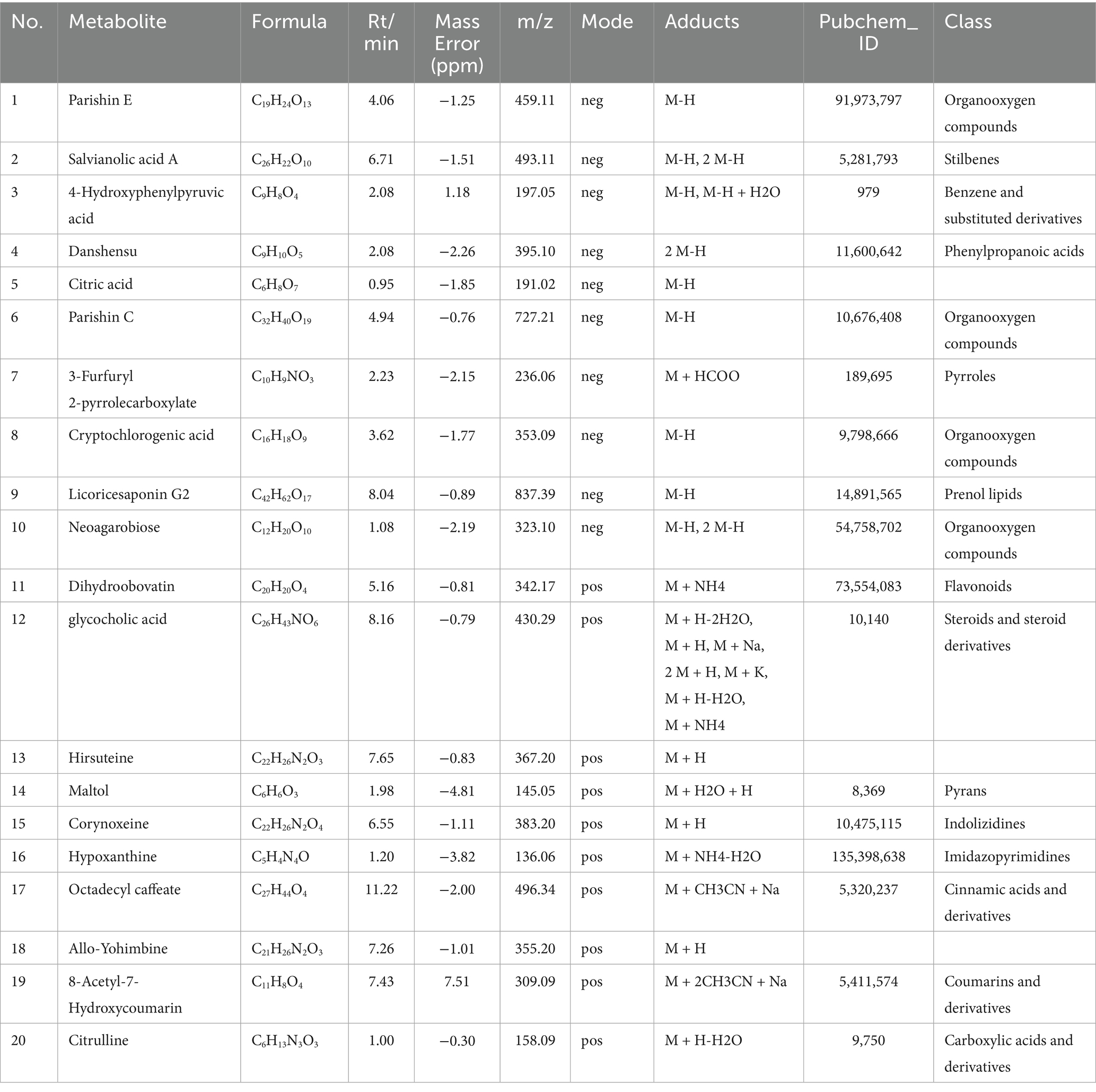
The chemical constituents of XYC were identified by UPLC-MS analysis. Our study revealed that XYC contains abundant constituents, including organic oxygen compounds, phenylpropanoids and polyketides, benzenoids, organoheterocyclic compounds and lipids and lipid-like molecules. A total of 904 compounds were identified, the positive and negative ion flow chromatography were shown in Figure 1 and the top ten anionic and cationic constituents, ranked by peak area, were presented in Table 2.
3.2 XYC treatment alleviated seizure in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rat model
To delineate XYC’s anti-epileptic pharmacodynamics, we established a lithium-pilocarpine rat model of acute epileptogenesis. A schematic overview of the treatment regimen and experimental workflow is presented in Figure 2A. Treatment with CBZ and XYC significantly prolonged the seizure latency and reduced the seizure frequency induced by pilocarpine in rat models of epilepsy (Table 3). H&E staining results found that, the hippocampal CA1 region tissues in the control group exhibited normal cellular morphology with neatly arranged cells, abundant cytoplasm, and large, round nuclei. In contrast, the model group showed a noticeable reduction in cell count, accompanied by a loose and disorganized arrangement. The cytoplasm appeared deeply stained, with evident nuclear dissolution and fragmentation, along with vacuolated manifestations. Both the CBZ and XYC groups demonstrated improved hippocampal cellular characteristics compared to the model group. Specifically, these groups exhibited increased cell density, gradual restoration of normal cellular morphology, and better-organized cellular alignment. Furthermore, the pathological manifestations of nuclear fragmentation and pyknosis were significantly alleviated (Figure 2B).
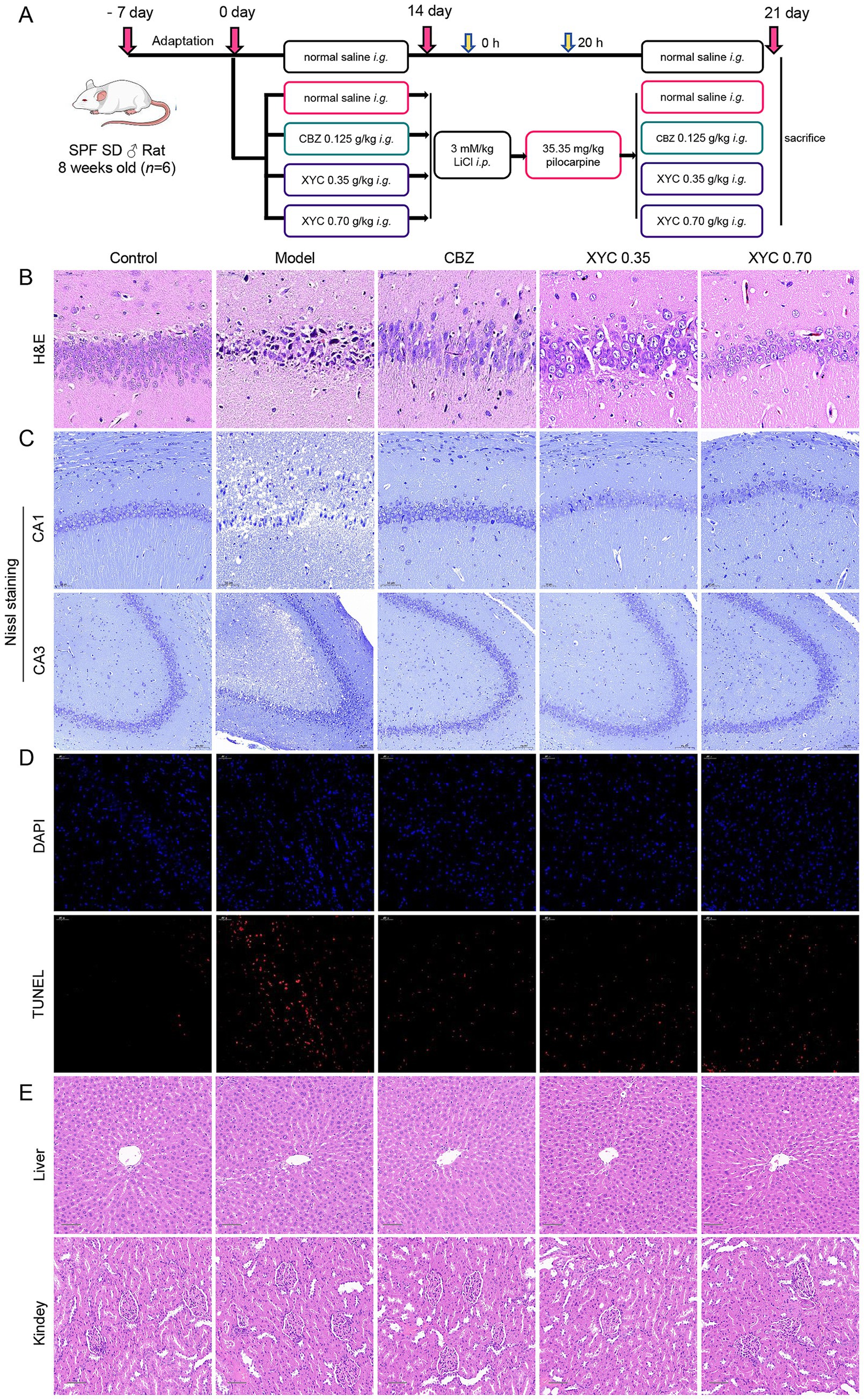
Figure 2. XYC treatment alleviated seizure in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rats. (A) Schematic of the rat epilepsy model construction and XYC administration. (B–D) Hippocampus CA1 region tissues were collected and the histological changes were assessed using H&E and Nissl staining. (B) Representative images of H&E staining (Scale bar = 50 μm). (C) Representative images of Nissl staining (Scale bar = 50 μm in CA1 region, Scale bar = 100 μm in CA3 region). (D) Representative images and quantitative analysis results of TUNEL staining (Scale bar = 50 μm). (E) Pathological changes in the liver and kidney tissues were examined with H&E staining (scale bar = 100 μm).
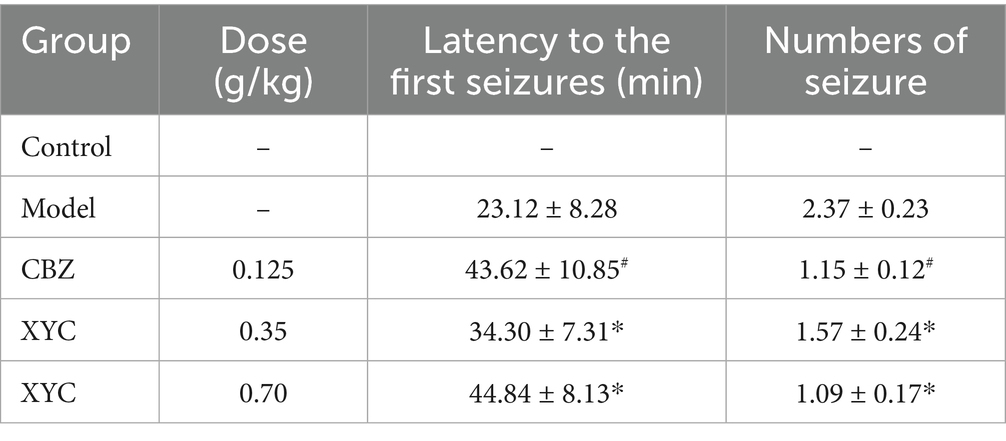
Table 3. Effect of XYC on lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy determined as seizure latency and numbers of seizure.
As shown in Figure 2C, Nissl staining revealed morphological changes of hippocampal CA1 neurons. Neurons in control group showing neatly arranged with intact morphology and clearly discernible Nissl bodies. While, model group exhibited a significant neuronal loss accompanied by disorganized cellular alignment and enlarged intercellular spaces. However, the CBZ and XYC treatment groups exhibited partial preservation of neuronal architecture in the hippocampal CA1 region, though with distinct pathological features. While neurons in these groups maintained relatively intact cellular morphology with preserved structural integrity, mild disorganization in cellular alignment was observed. Notably, Nissl body staining intensity demonstrated moderate attenuation, coupled with discernible enlargement of intercellular spaces. Despite these morphological alterations, the majority of neurons retained detectable viability and functional capacity. Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive cells combined with nuclear counterstaining revealed that both CBZ and XYC treatments significantly reduced apoptosis in CA1 neurons compared to the Model group (Figure 2D). Furthermore, the H&E staining of the liver and kidneys of each group were observed, and found that CBZ and XYC treatment did not changed the tissue morphology and showing no toxicity on liver and kidney (Figure 2E). These consistent findings across multiple staining techniques demonstrate that XYC pretreatment effectively mitigates seizure-induced neuronal injury in the hippocampal CA1 region.
3.3 Effect of XYC on lipid peroxidation and inflammation in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rats
Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress represent pivotal mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis, with their pathophysiological contributions being linked to elevated disease susceptibility (43). Consequently, interventions that targeting these dual pathological processes may provide effective therapeutic strategies for mitigating epileptogenesis. As shown in Figure 3, biochemical analyses revealed that epilepsy induction significantly elevated MDA levels while reducing SOD activity and CAT content in hippocampal tissues, indicating pronounced oxidative stress. Both CBZ and XYC treatments effectively attenuated these pathological changes, demonstrating significant reductions in MDA content and restoration of SOD activity and CAT contents compared to untreated epileptic controls (Figure 3A). Furthermore, ELISA assay found that IL-6, TNF-α and IL-1β pro-inflammation cytokine levels were significantly increased in epileptic rats, while both CBZ and XYC treatments effectively reversed this upward trend (Figure 3B). These findings demonstrate that XYC treatment not only induced anti-oxidant but also anti-inflammatory properties in epilepsy rats.
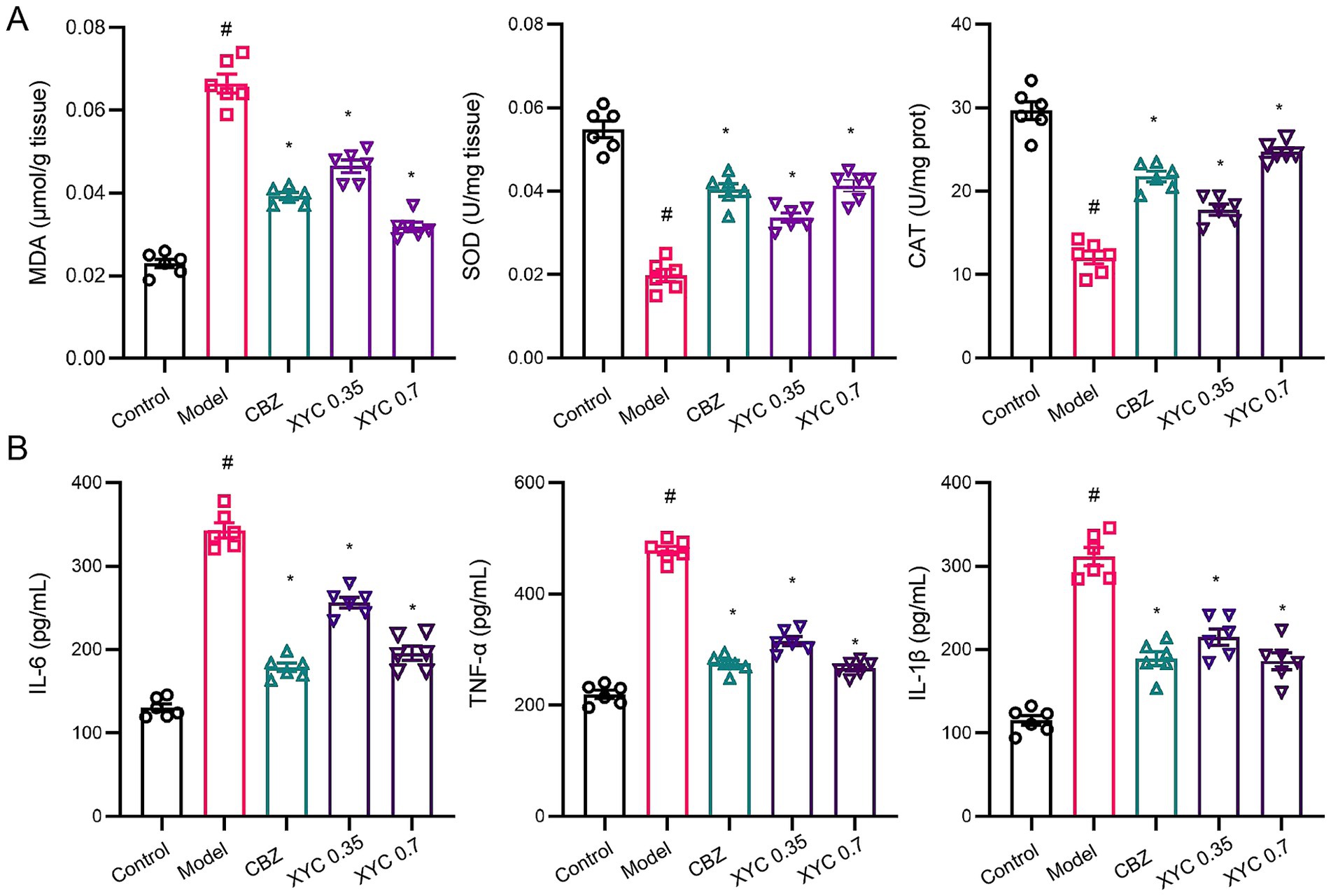
Figure 3. XYC treatment reduced lipid peroxidation and inflammation response in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rats. (A) Effects of CBZ (0.125 g/kg) and XYC (0.35 and 0.70 g/kg) on lipid peroxidation and oxidative/nitrosative stress, specifically MDA, SOD and CAT in the hippocampus tissues. (B) Effect of CBZ and XYC on serum IL-6, TNF-α and IL-1β levels. Data are shown as mean±SEM (n = 6). # p < 0.05 vs. Control group; * p < 0.05 vs. Model group.
3.4 Effect of XYC on gut microbiota profiles in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rats
Emerging research has revealed that sophisticated interactions between gut microbiota and cerebral functions are mediated through an integrated network of cellular signaling mechanisms and neural communication circuits, collectively termed the “bidirectional microbiota-gut-brain axis” (44). Elucidating the microbiota’s dual role in both epileptogenesis processes and anticonvulsant therapeutic interventions could fundamentally advance our understanding of the neurobiological foundations underlying seizure disorders.
To elucidate the impact of XYC on intestinal homeostasis, 16S rDNA were amplified followed by bioinformatic analysis. Alpha diversity analysis (Chao1 index, Shannon index, and Observed OTUs) demonstrated significant microbial community changes following epilepsy induction and XYC treatment. While rank abundance curves and diversity indices showed comparable bacterial composition patterns among Control, Model, and XYC 0.7 groups (Figures 4A–C), quantitative analysis revealed distinct differences. The Model group exhibited significantly reduced species richness (Chao1 index, p < 0.05) compared to controls, consistent with established microbiota depletion in epilepsy (45). XYC treatment effectively restored microbial diversity, significantly increasing both the Chao1 index and Shannon diversity (p < 0.05 versus Model group, Figure 4D). Beta diversity analysis using PLS-DA demonstrated clear separation of gut microbiota communities among the three groups (Figure 4E). Venn diagram analysis at the OTU level identified 2067, 1,591, and 1972 operational taxonomic units in Control, Model, and XYC groups respectively, revealing both shared and group-specific microbial signatures (Figure 4F).
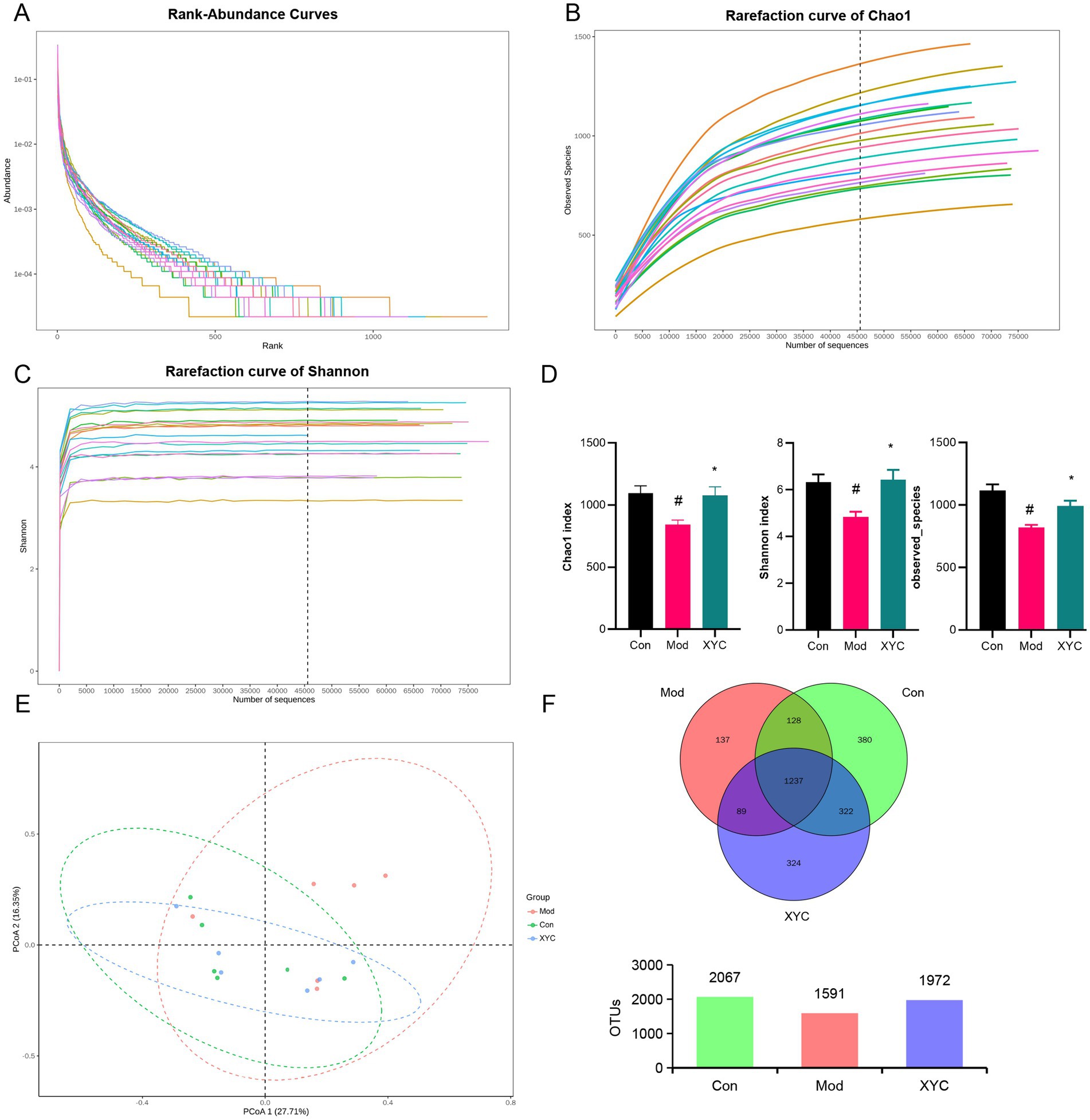
Figure 4. XYC improved the composition of the gut microbiota in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rats. (A) Rank-abundance curves analysis at the OTU classification level. (B) Rarefaction curve of Chao1. (C) Dilution curve analysis: the Shannon index of the sample sequence at the OTU level. (D) Alpha diversity includes the Chao1 index, Shannon indices, and Observed OTUS. (E) PCoA obtained from LEfSe analysis. (F) Venn diagram analysis: counting the number of shared and unique OTUs in each group. Data are shown as mean±SEM (n = 6). # p < 0.05 vs. Control group; * p < 0.05 vs. Model group.
Microbiome profiling demonstrated marked taxonomic restructuring of gut microbial architecture across phylum and genus hierarchies post-epileptogenesis and XYC intervention. At the phylum level, epileptic rats exhibited marked reductions in Tenericutes, Patescibacteria, Epsilonbacteraeota, and Proteobacteria abundance compared to controls (p < 0.05). XYC treatment substantially restored these depleted phyla to near-normal levels (Figures 5A,B). Genus-level analysis demonstrated that XYC effectively counteracted epilepsy-induced dysbiosis, significantly preserving populations of beneficial taxa including Lactobacillus, Ramboutsia, Staphylococcus, and Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group (Figures 5C,D).
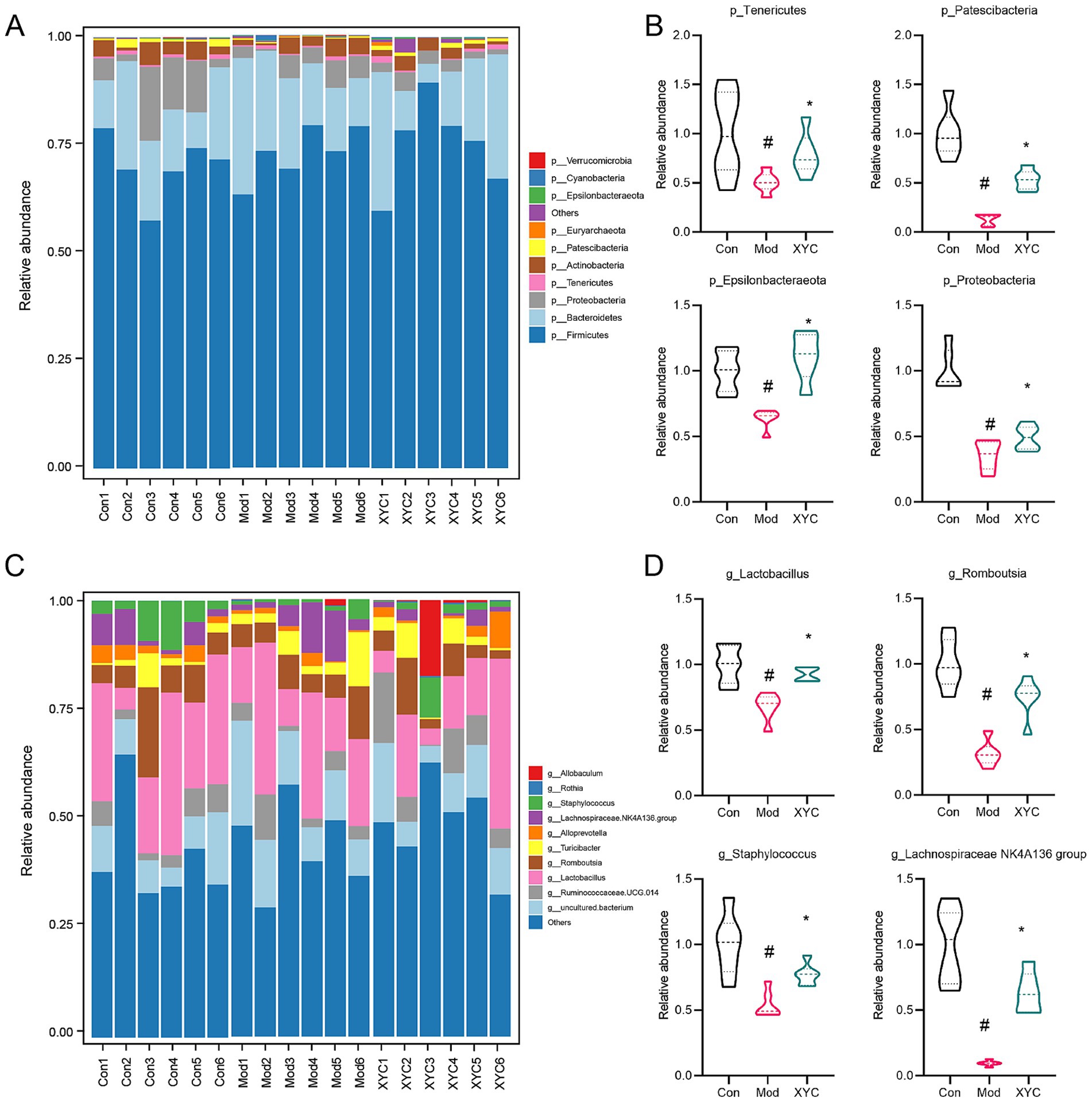
Figure 5. XYC treatment altered the gut microbiota disturbance in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rats. (A,B) Dominant phylum-level microbiota distribution (top 10 taxa) was compared between groups, while genus-specific abundance variations among each group were quantified. (C,D) Dominant genus distributions (top 10 taxa) were compared between groups, while LEfSe analysis identified differential abundance patterns among each group. Data are shown as the mean±SEM (n = 6). # p < 0.05 compared to the Control group; * p < 0.05 compared to the Model group.
Microbial community differences among the three experimental groups were visualized through LEfSe analysis, generating a cladogram that highlights taxonomically distinct features at multiple phylogenetic levels (Figure 6A). Using stringent criteria (LDA score > 2, p < 0.05), we identified group-specific microbial signatures: Staphylococcus, Ruminococcaceae_UCG_008 and Blautia abundance characterized the Control, Model and XYC group, respectively (Figure 6B).
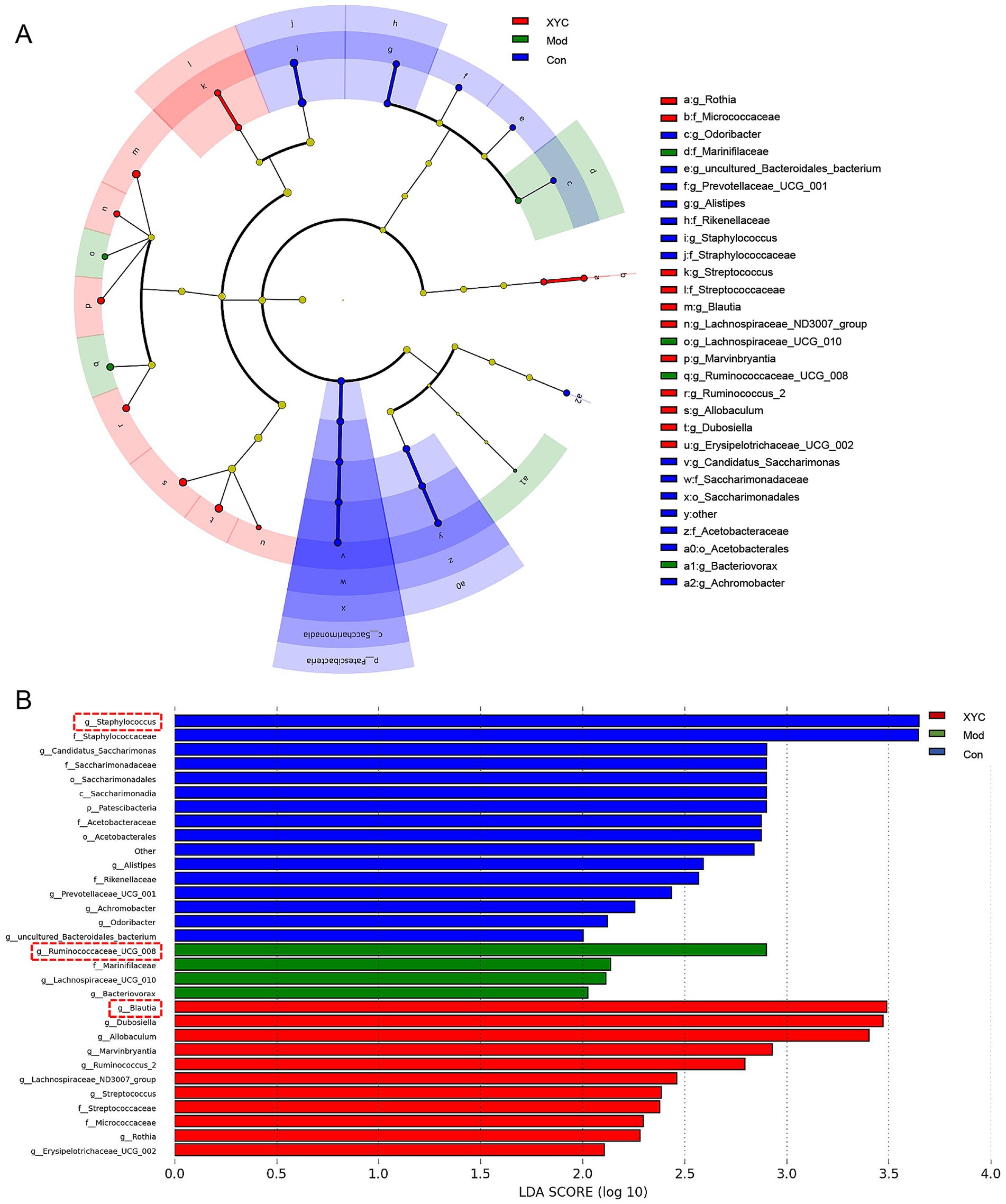
Figure 6. Taxonomic biomarkers identification via LEfSe. (A) Cladogram illustrating phylogenetic distribution of discriminative taxa across three experimental groups, with radiating circles denoting taxonomic hierarchy. Node diameters reflect relative abundance. (B) Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) scores highlight group-specific biomarkers.
3.5 XYC altered serum metabolites in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rats
Serum metabolite profiling was conducted using UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS, revealing distinct metabolic patterns among experimental groups. OPLS-DA demonstrated clear separation among groups (R2X = 0.35, R2Y = 0.952, Q2 = 0.512 for negative ion mode, R2X = 0.566, R2Y = 0.993, Q2 = 0.532 for positive ion mode, Figure 7A). Using stringent criteria (VIP > 1, p < 0.05), we identified 970 significantly altered metabolites. Metabolomic profiling showed 157 differentially expressed metabolites between groups (FC ≥ 2 or ≤ 0.5, p < 0.05), with Model specimens exhibiting 73 upregulated versus 84 downregulated species relative to Controls. Notably, XYC treatment modulated 149 metabolites compared to the Model group, including 72 elevated and 77 reduced species (Figure 7B). Hierarchical clustering analysis and fold-change distributions further illustrated these metabolic shifts (Supplementary Figures S1, S2).
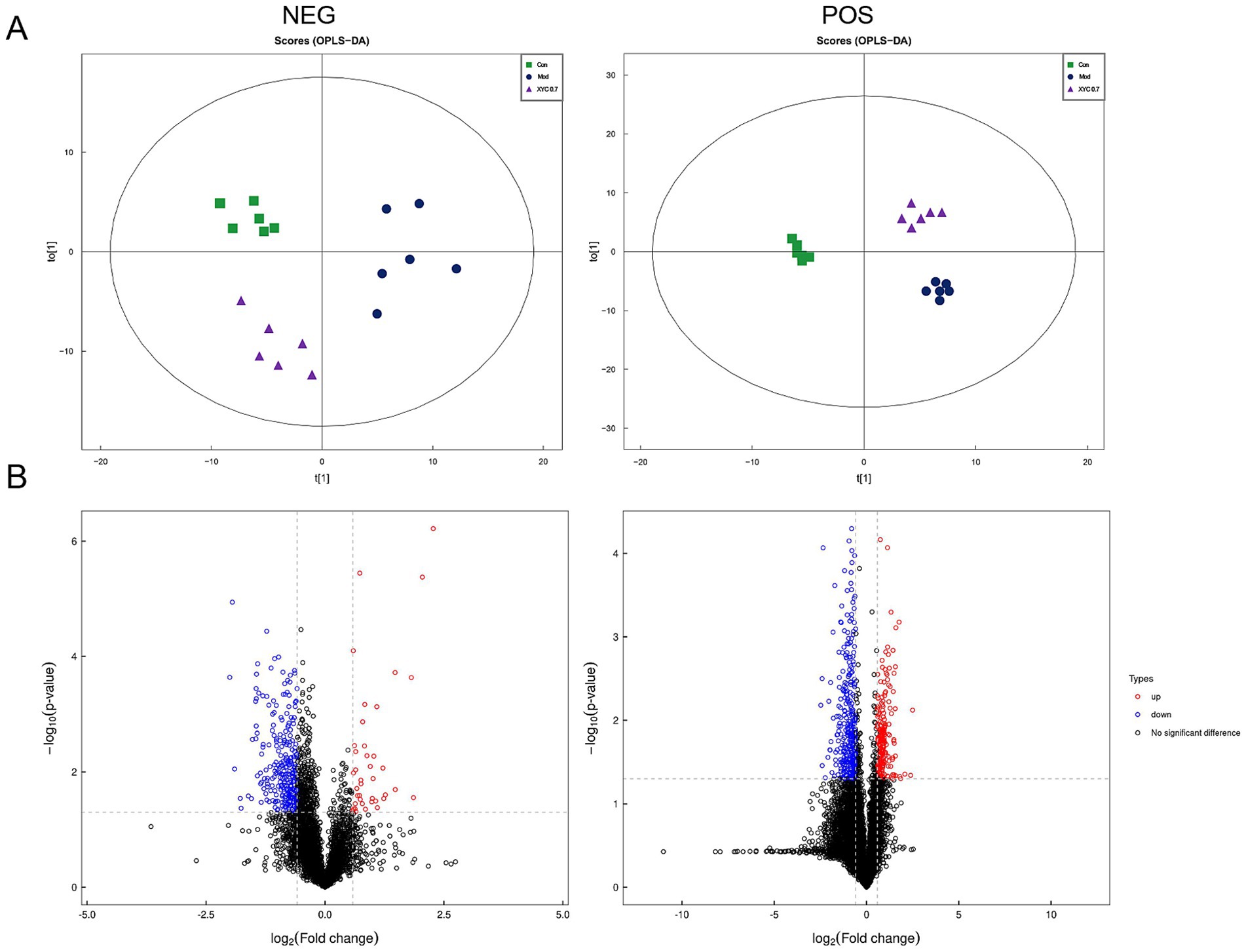
Figure 7. XYC treatment altered the serum metabolites in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rats. (A) OPLS-DA of the negative and positive ion mode. (B) Volcano plot of the differential metabolites.
3.6 Regulation of XYC on the glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway of epilepsy rats
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis demonstrated that XYC treatment significantly modulated multiple metabolic pathways in epileptic rats (Figure 8A). The most affected pathways included glycerophospholipid metabolism, pyrimidine metabolism, ABC transporters, proximal tubule bicarbonate reclamation, choline metabolism, and mineral absorption. The relative content of metabolites in the glycerophospholipids pathway were shown in Supplementary Table S1. Targeted analysis of glycerophospholipid metabolism revealed three significantly elevated metabolites in the Model group compared to controls: glycerophosphate (log2FC = 1.05, p = 0.004), glycerophosphocholine (log2FC = 0.89, p = 0.003), and sn-glycerol-3-phosphoethanolamine (log2FC = 1.01, p = 0.021). XYC treatment effectively normalized these aberrant metabolite levels (p < 0.05 vs. Model group; Figure 8B).
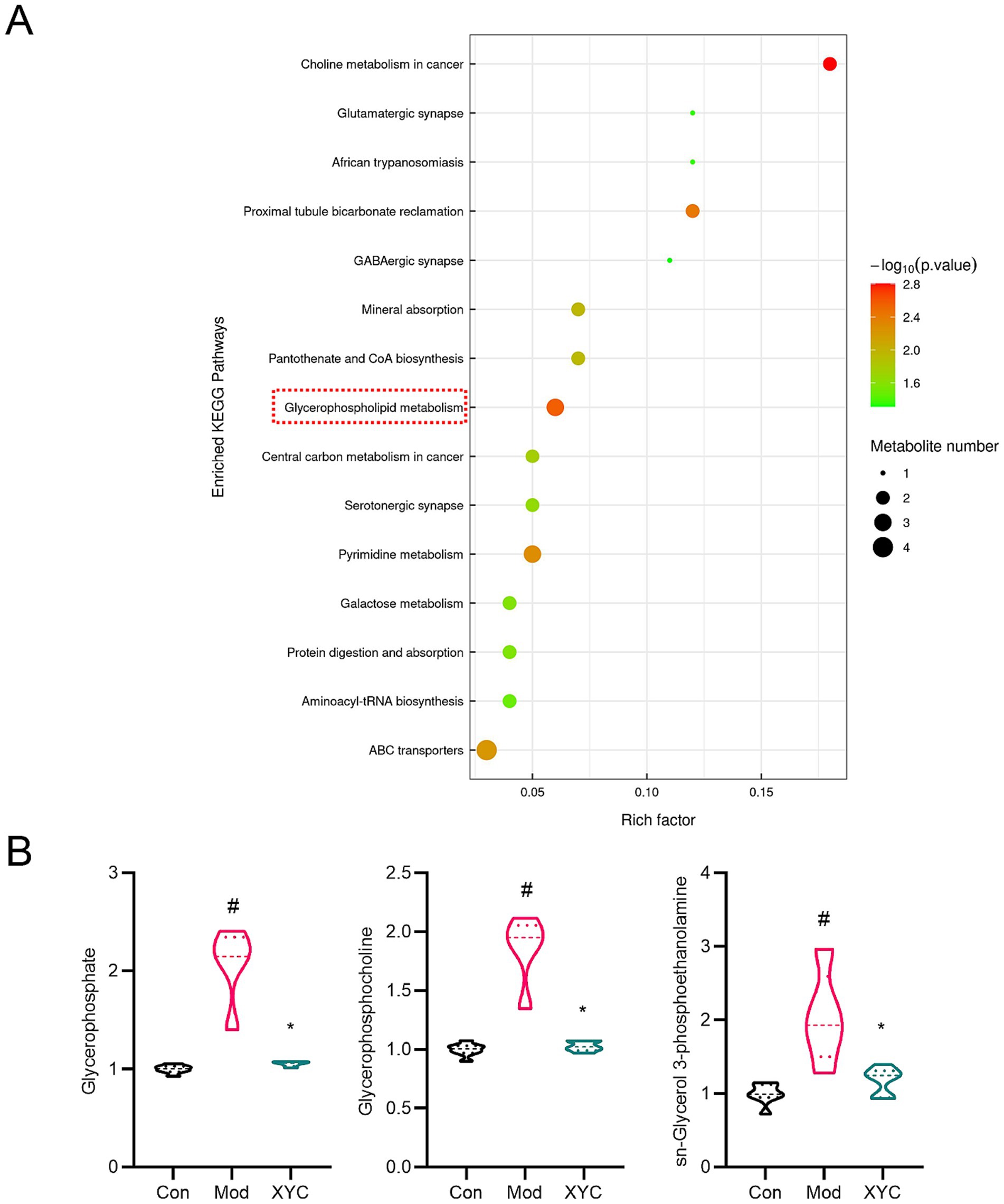
Figure 8. XYC altered the metabolites levels in glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway. (A) KEGG analysis of differential metabolites. (B) Diagram of relative abundance of different metabolites in serum. Data are shown as mean±SEM (n = 6). #p < 0.05 vs. Control group; *p < 0.05 vs. Model group.
3.7 Correlation between gut microbes and metabolites
To investigate potential microbiota-metabolite interactions, spearman correlation analysis was performed to examine associations between the 19 most abundant bacterial genera and 9 differentially expressed metabolites. Figure 9 delineates statistically robust associations between specific microbial taxa and glycerophospholipid metabolites: Candidatus_Saccharimonas exhibited negative correlations with glycerophosphate, glycerophosphocholine and sn-Glycerol 3-phosphoethanolamine; Bacteriovorax showed positive correlations with glycerophosphate and glycerophosphocholine; and Ruminococcaceae_UCG_008 demonstrated a distinct pattern, correlating positively with sn-glycerol 3-phosphoethanolamine.
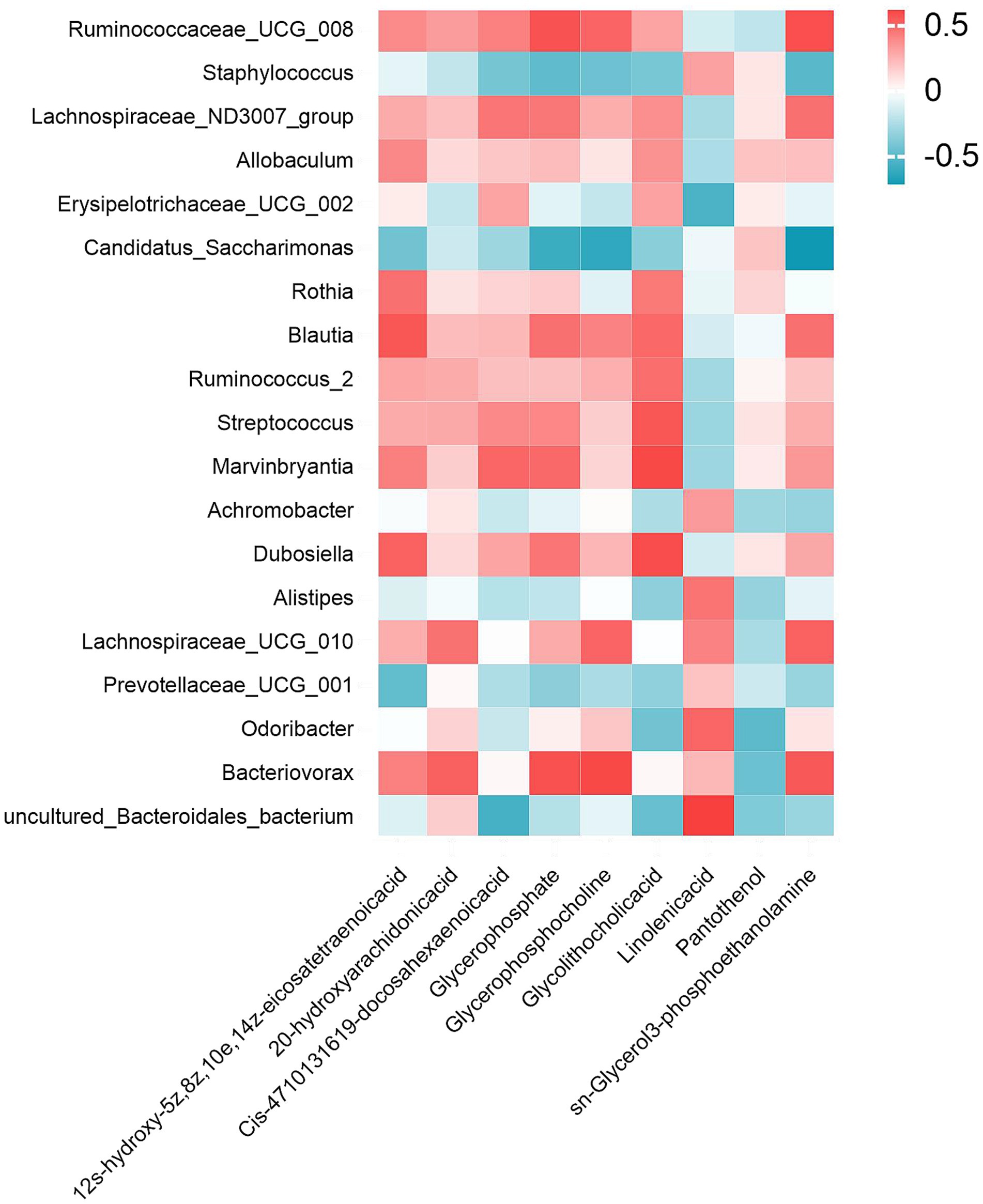
Figure 9. Gut microbiota-metabolite interaction network. Spearman correlation heatmap illustrating significant associations between the top 19 genus-level microbial taxa and 9 XYC modulated dysregulated metabolites. Red/blue hues denote positive/negative correlations.
3.8 Network pharmacology of XYC against epilepsy
Using the TCMSP database, we systematically screened herbal components for the XYC formulation based on pharmacokinetic properties, while excluding compounds lacking biological targets. The analysis identified bioactive constituents from 16 medicinal herbs: Glycyrrhiza uralensis (88 compounds), Salvia miltiorrhiza (46), Astragalus membranaceus (17), Uncaria rhynchophylla (32), Bupleurum chinense (13), Gastrodia elata (14), Polygala tenuifolia (18), Codonopsis pilosula (16), Ziziphus jujuba var. spinosa (7), Acorus tatarinowii (4), along with fewer components from Angelica sinensis (2), Arisaema erubescens (3), Aconitum coreanum (3), Curcuma aromatica (3), Bombyx batryticatus (1), and Massa Medicata Fermentata (2). Target integration and deduplication yielded 773 unique protein targets, representing the potential therapeutic target space of the XYC formulation.
Through comprehensive integration of disease target databases (GeneCards, OMIM, and DisGeNET), we identified 9,615 epilepsy-associated targets, which were subsequently normalized using UniProt identifiers. Comparative analysis revealed 558 overlapping targets between these epilepsy-related genes and the XYC’s potential therapeutic targets (Figure 10A), representing the putative molecular targets through which the formulation may exert its anti-epileptic effects.
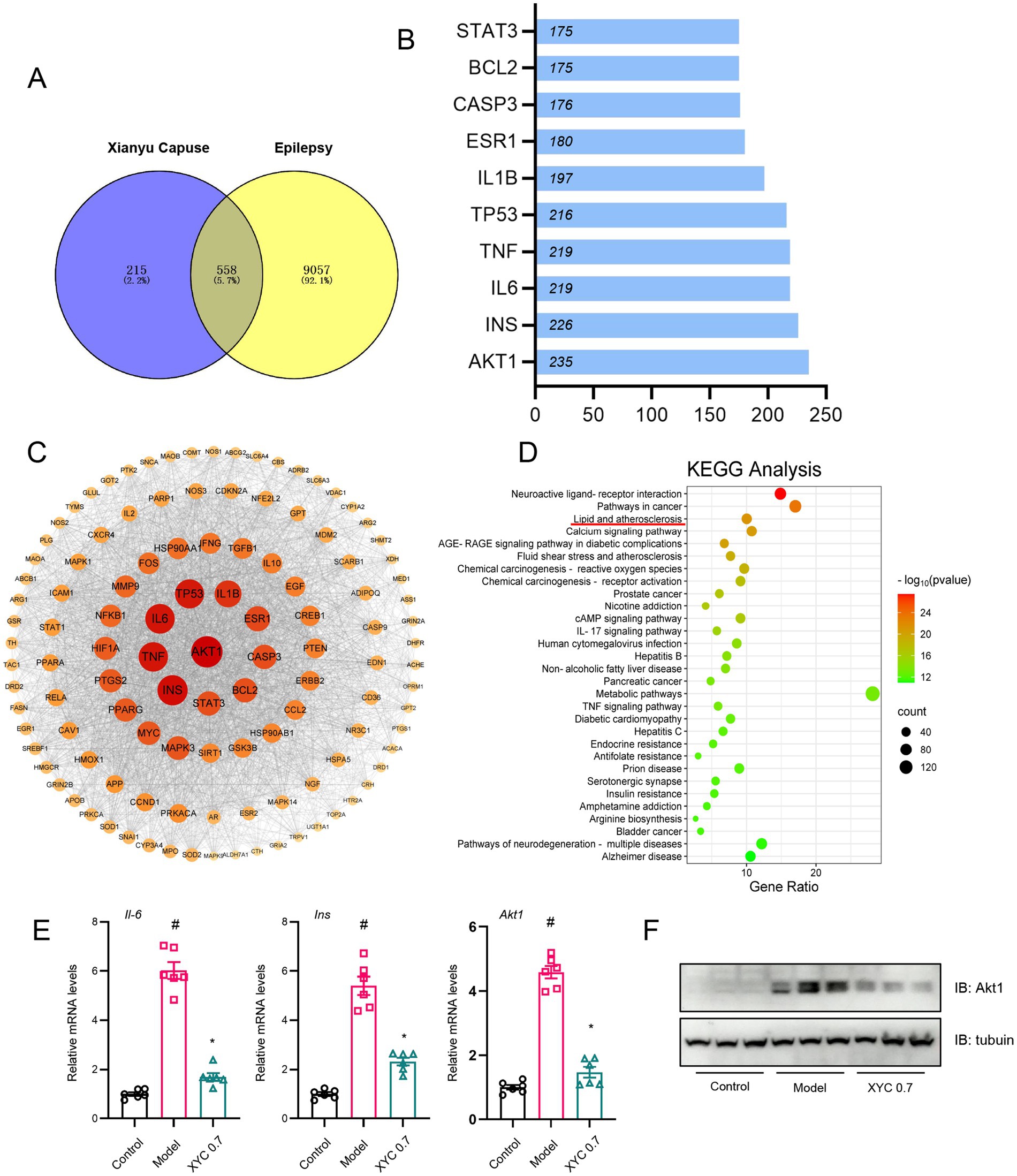
Figure 10. Network pharmacology analysis and validation of XYC. (A) Network pharmacology analysis revealed 558 overlapping nodes between XYC’s bioactive compounds and epileptogenesis-associated pathways, delineating therapeutic target convergence. (B) The PPI network of targets. (C) The ‘Compound-Target-Pathway-Disease’ network delineates polypharmacological interactions among XYC’s phytochemicals, epileptogenesis-associated targets, and dysregulated signaling axes. (D) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of top 30 dysregulated metabolic routes, with lipid metabolism and inflammation showing highest significance. (E) Il-6, Ins and Akt1 mRNA levels were quantified by RT-qPCR. (F) Hippocampal Akt1 protein levels were validated via immunoblotting. Data are shown as the mean±SEM (n = 6). #p < 0.05 compared to the Control group; *p < 0.05 compared to the Model group.
Ingredient-target network (283 active ingredients from XYC and 588 targets in epilepsy) was constructed with Cytoscape (version 3.10.3) (Supplementary Figure S3), and the PPI network was shown in Supplementary Figure S4. Topological analysis the top 10 targets as shown in Figure 10B, and the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed using Cytoscape, with the top 25 hub genes identified by node degree analysis (Figure 10C). KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of these hub genes revealed the top 30 significantly enriched pathways (Figure 10D), among which neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions, pathways in cancer, and lipid metabolism/atherosclerosis were most prominent. Notably, AKT1, INS, and IL-6 emerged as central nodes, which were functionally associated with lipid metabolic and inflammation processes, particularly glycerophospholipid metabolism, suggesting their potential as key therapeutic targets of XYC for epilepsy treatment.
To investigate the targets underlying the anti-epileptic effects of XYC, we performed RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses. RT-qPCR revealed elevated mRNA levels of Il-6, Ins, and Akt1 in the hippocampal tissues of model groups compared to controls. Notably, XYC intervention significantly attenuated these increases (Figure 10E). Consistent with the mRNA findings, immunoblotting showed upregulated AKT1 protein expression in the epileptic models. Importantly, this elevated expression was normalized by XYC treatment (Figure 10F).
These findings suggest that XYC effectively alleviated seizure in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy by preserved neuro-inflammatory and glycerophospholipid metabolism.
4 Discussion
Epilepsy constitutes a persistent neurological condition characterized by unprovoked seizure episodes stemming from dysregulated neuronal hyperexcitability (47). Growing evidence implicates neuroinflammation triggered by brain injury in epileptogenesis. Preclinical and human studies consistently show post-seizure events like gliosis, elevated pro-inflammatory mediators, blood–brain barrier disruption, and activated inflammatory pathways. Disrupted lipid homeostasis also act as a potential contributor to epileptogenesis through multifaceted mechanisms involving neuroinflammation, membrane instability, and metabolic dysfunction (48). The complex metabolic network governing lipids-including TG, cholesterol fractions, and fatty acids—regulates critical neuronal processes ranging from membrane integrity to energy metabolism. Recent studies have identified that particular metabolic derangements, such as impaired fatty acid β-oxidation and aberrant cholesterol metabolism, demonstrate strong epidemiological associations with epilepsy susceptibility (49). This correlation appears particularly pronounced in pediatric populations with inborn disorder of fatty acid metabolism (50). So, understanding these processes identifies potential therapeutic targets and diagnostic/prognostic biomarkers for epilepsy.
TCM has served as a clinically validated therapeutic modality for epilepsy management through multimodal mechanisms, including neurotransmitter modulation, anti-inflammatory action, and neuroprotection (51). However, existing mechanistic research primarily focuses on neurotransmitter systems, immune dysfunction, and glial cell activity. Recently, accumulating evidence implicates gut dysbiosis and lipid metabolic disturbances in epileptogenesis (32, 52). Nevertheless, whether TCM interventions can ameliorate epilepsy by targeting these pathways remains systematically underexplored.
In this study, 16S rDNA sequencing revealed that XYC treatment significantly increased the relative abundance of four bacterial phyla (Tenericutes, Patescibacteria, Epsilonbacteraeota, and Proteobacteria) in epileptic rats. Intriguingly, Patescibacteria, a phylum found in human adipose tissue, may regulate fatty acid metabolism, proposing a novel gut-lipid-brain axis mechanism for XYC’s antiepileptic action (53, 54). At the genus level, XYC treatment effectively counteracted epilepsy-associated microbial alterations, significantly restoring the abundances of Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group, Lactobacillus, Staphylococcus, and Romboutsia, which were diminished in epileptic rats. Notably, these genera play crucial roles in maintaining gut homeostasis, with Lactobacillus and Romboutsia being particularly recognized for their anti-inflammatory properties and short-chain fatty acid production. Previous clinical studies have identified a significant reduction in Lactobacillus abundance in epileptic patients (55). Lactobacillus species biosynthesize gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter (56). Increased colonic GABA bioavailability demonstrates neurochemical coupling with central GABAergic tone, suggesting microbiota-mediated gut-brain signaling contributes to seizure pathophysiology (57). Lactobacillus species also play critical roles in lipid metabolism and obesity regulation by modulating gut microbiota composition to enhance food digestion and nutrient absorption (58, 59). Suppressing Lactobacillus proliferation attenuates intestinal lipid absorption and inhibits adipose deposition, highlighting its dual role in metabolic and neurological disease (59). Notably, Romboutsia, a SCFA producing genus, was significantly increased in abundance following XYC treatment, with its levels showing a positive correlation with seizure severity scores (46). These data demonstrate that XYC mediates seizure suppression exerts via bidirectional modulation of gut microbial ecology and systemic metabolomic networks, by restoring epilepsy-depleted beneficial genera (e.g., Lactobacillus, Lachnospiraceae NK4A136) while enhancing SCFA-producing taxa (Romboutsia) and reconciling lipid metabolism dysregulation.
The brain exhibits unique metabolic features characterized by high mitochondrial density, enrichment of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), and elevated oxygen consumption, rendering it particularly susceptible to metabolic disturbances. These metabolic peculiarities underlie the growing recognition of metabolite-trait associations in neurological disorders. For instance, altered levels of glycerophosphocholines (GPCs)-key phospholipid metabolites involved in membrane integrity and neurotransmission-are linked to synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease (60). Epileptic seizures are marked by transient surges in neuronal energy demand, necessitating dynamic metabolic adaptations. This cyclical interplay between energy expenditure and compensatory mechanisms underscores the pivotal role of metabolic dysfunction in epilepsy, a disorder primarily characterized by recurrent seizures. Notably, perturbations in glycerophospholipid metabolism have been implicated not only in epilepsy but also in neuropsychiatric disorders. Studies across murine, rodent, and non-human primate models of depression consistently report dysregulated glycerophospholipid profiles (61–63). For instance, D-ribose administration induces depressive-like behaviors in rodents by disrupting gut microbiota homeostasis, thereby altering glycerophospholipid metabolism (64). AnGong NiuHuang Pill ameliorates traumatic brain injury via modulation of glycerophospholipid metabolism (65). These findings position glycerophospholipid pathways as promising targets for metabolic intervention in neurological diseases, but its role in epileptogenesis and disease progression remains unelucidated.
In this study, we discovered that XYC administration significantly attenuated seizure severity and frequency in a rat model of epilepsy. Untargeted serum metabolomics profiling further identified XYC-mediated suppression of key intermediates in the glycerophospholipid metabolic pathway, with pronounced reductions in glycerophosphate, GPC, and sn-glycerol 3-phosphoethanolamine levels. These results indicate that XYC exerts its anti-seizure effects through normalizing hyperactivated glycerophospholipid metabolism, and reestablishing neurochemical homeostasis-potentially via restoring membrane phospholipid balance.
Integrated network pharmacology analysis identified 558 overlapping targets between XYC’s putative therapeutic targets and epilepsy-associated genes. AKT1 (a hub node in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling), INS (insulin, regulating neuronal glucose metabolism), and IL-6 (a pro-inflammatory cytokine) emerged as the top three prioritized targets based on topological centrality, suggesting XYC may exert anti-epileptic effects by synergistically modulating neuroinflammatory cascades, metabolic homeostasis, and survival signaling pathways.
The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, a central regulator of cellular survival and proliferation, is ubiquitously expressed in the central nervous system. In experimental models of epilepsy, activation of this pathway has been shown to modulate neuronal apoptosis and mitigate seizure severity, suggesting its dual role in neuroprotection and seizure suppression (66, 67). And AKT1 directly phosphorylates voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.1, attenuating peak sodium currents (68), a pivotal mechanism regulating GABAergic neuronal excitability and ictogenesis.
Proinflammatory cytokines (PIC), including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, play pivotal roles in neuroinflammation and epileptogenesis by exacerbating neuronal hyperexcitability. Elevated PIC levels are consistently observed during epileptic seizures, with IL-6 demonstrating persistent upregulation across diverse epilepsy subtypes- even during interictal and postictal phases (69). Clinically, heightened serum IL-6 concentrations correlate with disease progression and may serve as a prognostic biomarker for epileptogenesis (70, 71).
Insulin functions as a critical neurotrophic factor, regulating synaptic plasticity, neurogenesis, and metabolic homeostasis within the central nervous system. Mounting evidence implicates cerebral metabolic syndrome—particularly insulin resistance—in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders and acute neurological injuries, including cerebral ischemia and epilepsy (72). And recent evidence suggests pediatric populations with obesity-driven insulin resistance exhibit a increased risk of developing epilepsy compared to metabolically healthy cohorts (73). This bidirectional interplay between metabolism and epilepsy is further exemplified by the metabolic sequelae of antiepileptic drugs: long-term valproate therapy induces hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in both adults and children, concomitant with elevated adiposity and dysregulated adipocytokine profiles (74). Our results indicating that, XYC could alleviate seizures in epileptic rats by affecting the expression of inflammatory cytokines and insulin resistance in central nervous system.
Based on the above findings, we have preliminarily elucidated the role and mechanisms of XYC in ameliorating hepatic lipid metabolism in NAFLD mice. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of translating these results to clinical applications. For instance, although lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy rats models are well-established to simulating human epileptic seizures, their inability to fully recapitulate human pathophysiology, combined with the absence of clinical data, limits the direct clinical translation of our findings. Additionally, to further elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which XYC ameliorates the epileptic state in rats, subsequent studies will employ hippocampus-specific gene knockout models for in-depth investigation.
5 Conclusion
In this study, a multi-omics integrative approach (16S rDNA sequencing, untargeted metabolomics, and network pharmacology) was employed to elucidate the anti-epileptic mechanisms of XYC in a rat model. Metabolomic profiling identified glycerophospholipid metabolism as the predominant pathway modulated by XYC, with significant elevation of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) levels. Gut microbiota analysis revealed that epilepsy-induced dysbiosis was partially reversed by XYC treatment, particularly through enrichment of SCFA producing Lactobacillus and suppression of pro-inflammatory Enterobacteriaceae. Network pharmacology further prioritized three core targets—AKT1, INS, and IL-6 —exhibiting strong binding affinities to XYC’s active compounds. Crucially, these targets functionally converge on glycerophospholipid homeostasis, mechanistically linking lipid remodeling (via AKT1/INS-mediated phospholipid biosynthesis) and neuroinflammation resolution (via IL-6 pathway inhibition) to XYC’s therapeutic efficacy.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
DY: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. SL: Data curation, Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, Writing – original draft. XL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Resources. XZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. DG: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by funding from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81900468 and 81901571), Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (grant nos. 242300421276 and 232300420257), Henan Provincial Medical Science and Technology Research Plan (grant no. LHGJ20220419), and Henan Sunshine Medical and Health Development Foundation (grant no. HKP2023009).
Acknowledgments
We thank to Sanshu Biotechnology for its analysis of intestinal microbiota and metabolomics data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1625533/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1. Kanner, AM, and Bicchi, MM. Antiseizure medications for adults with epilepsy: a review. JAMA. (2022) 327:1269–81. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.3880
2. Ding, D, Zhou, D, Sander, JW, Wang, W, Li, S, and Hong, Z. Epilepsy in China: major progress in the past two decades. Lancet Neurol. (2021) 20:316–26. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00023-5
3. Severino, M, Geraldo, AF, Utz, N, Tortora, D, Pogledic, I, Klonowski, W, et al. Definitions and classification of malformations of cortical development: practical guidelines. Brain. (2020) 143:2874–94. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa174
4. Frauscher, B. Localizing the epileptogenic zone. Curr Opin Neurol. (2020) 33:198–206. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000790
5. Loscher, W, Potschka, H, Sisodiya, SM, and Vezzani, A. Drug resistance in epilepsy: clinical impact, potential mechanisms, and new innovative treatment options. Pharmacol Rev. (2020) 72:606–38. doi: 10.1124/pr.120.019539
6. Hollis, A, and Lukens, JR. Role of inflammasomes and neuroinflammation in epilepsy. Immunol Rev. (2025) 329:e13421. doi: 10.1111/imr.13421
7. Mu, J, Cao, C, Gong, Y, and Hu, G. Relationship between inflammation/immunity and epilepsy: a multi-omics mendelian randomization study integrating GWAS, eQTL, and mQTL data. Epilepsy Behav. (2024) 161:110112. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2024.110112
8. Pellegrini, C, Fornai, M, D'Antongiovanni, V, Antonioli, L, Bernardini, N, and Derkinderen, P. The intestinal barrier in disorders of the central nervous system. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:66–80. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00241-2
9. Doroszkiewicz, J, Groblewska, M, and Mroczko, B. The role of gut microbiota and gut-brain interplay in selected diseases of the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:10028. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810028
10. Agirman, G, Yu, KB, and Hsiao, EY. Signaling inflammation across the gut-brain axis. Science. (2021) 374:1087–92. doi: 10.1126/science.abi6087
11. Muller, PA, Schneeberger, M, Matheis, F, Wang, P, Kerner, Z, Ilanges, A, et al. Microbiota modulate sympathetic neurons via a gut-brain circuit. Nature. (2020) 583:441–6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2474-7
12. Needham, BD, Funabashi, M, Adame, MD, Wang, Z, Boktor, JC, Haney, J, et al. A gut-derived metabolite alters brain activity and anxiety behaviour in mice. Nature. (2022) 602:647–53. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04396-8
13. Mitra, S, Dash, R, Nishan, AA, Habiba, SU, and Moon, IS. Brain modulation by the gut microbiota: from disease to therapy. J Adv Res. (2023) 53:153–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.12.001
14. Papazoglou, I, Lee, JH, Cui, Z, Li, C, Fulgenzi, G, Bahn, YJ, et al. A distinct hypothalamus-to-beta cell circuit modulates insulin secretion. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:285–298.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.12.020
15. Zhuang, M, Zhang, X, and Cai, J. Microbiota-gut-brain axis: interplay between microbiota, barrier function and lymphatic system. Gut Microbes. (2024) 16:2387800. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2387800
16. Dong, L, Zheng, Q, Cheng, Y, Zhou, M, Wang, M, Xu, J, et al. Gut microbial characteristics of adult patients with epilepsy. Front Neurosci. (2022) 16:803538. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.803538
17. Russo, E. The gut microbiota as a biomarker in epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. (2022) 163:105598. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105598
18. Liu, T, Jia, F, Guo, Y, Wang, Q, Zhang, X, Chang, F, et al. Altered intestinal microbiota composition with epilepsy and concomitant diarrhea and potential indicator biomarkers in infants. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:1081591. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1081591
19. Riva, A, Sahin, E, Volpedo, G, Petretto, A, Lavarello, C, Di Sapia, R, et al. Identification of an epilepsy-linked gut microbiota signature in a pediatric rat model of acquired epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. (2024) 194:106469. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106469
20. Oliveira, MET, Paulino, GVB, Dos Santos Junior, ED, da Silva Oliveira, FA, Melo, VMM, Ursulino, JS, et al. Multi-omic analysis of the gut microbiome in rats with lithium-pilocarpine-induced temporal lobe epilepsy. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59:6429–46. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02984-3
21. Iannone, LF, Gomez-Eguilaz, M, and De Caro, C. Gut microbiota manipulation as an epilepsy treatment. Neurobiol Dis. (2022) 174:105897. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105897
22. Watanangura, A, Meller, S, Farhat, N, Suchodolski, JS, Pilla, R, Khattab, MR, et al. Behavioral comorbidities treatment by fecal microbiota transplantation in canine epilepsy: a pilot study of a novel therapeutic approach. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1385469. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1385469
23. Medel-Matus, JS, Simpson, CA, Ahdoot, AI, Shin, D, Sankar, R, Jacobs, JP, et al. Modification of post-traumatic epilepsy by fecal microbiota transfer. Epilepsy Behav. (2022) 134:108860. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2022.108860
24. Su, Y, Cao, N, Zhang, D, and Wang, M. The effect of ferroptosis-related mitochondrial dysfunction in the development of temporal lobe epilepsy. Ageing Res Rev. (2024) 96:102248. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102248
25. Guo, HL, Wang, WJ, Dong, N, Zhao, YT, Dai, HR, Hu, YH, et al. Integrating metabolomics and lipidomics revealed a decrease in plasma fatty acids but an increase in triglycerides in children with drug-refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia Open. (2023) 8:466–78. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12712
26. Gao, L, Xie, R, Yang, X, Liu, Y, Lin, R, Yao, Z, et al. Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction alleviates pentylenetetrazol-induced epileptic seizures in rats by preventing neuronal cell damage and apoptosis and altering serum and urine metabolic profiles. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 338:119112. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119112
27. Wei, H, Liu, D, Geng, L, Liu, Y, Wang, H, and Yan, F. Application value of serum metabolic markers for cognitive prediction in elderly epilepsy. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2022) 18:2133–40. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S371751
28. Yang, LX, Yao, YY, Yang, JR, Cheng, HL, Zhu, XJ, and Zhang, ZJ. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 regulates blood-brain barrier permeability in epileptic mice. Neural Regen Res. (2023) 18:1763–9. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.360263
29. Mondal, S, Nandy, A, Dande, G, Prabhu, K, Valmiki, RR, Koner, D, et al. Mass spectrometric imaging of anionic phospholipids desorbed from human hippocampal sections: discrimination between temporal and nontemporal lobe epilepsies. ACS Chem Neurosci. (2024) 15:983–93. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00693
30. Barzegar, M, Afghan, M, Tarmahi, V, Behtari, M, Rahimi Khamaneh, S, and Raeisi, S. Ketogenic diet: overview, types, and possible anti-seizure mechanisms. Nutr Neurosci. (2021) 24:307–16. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2019.1627769
31. Yilmaz, U, Edizer, S, Kose, M, Akisin, Z, Guzin, Y, Pekuz, S, et al. The effect of ketogenic diet on serum lipid concentrations in children with medication resistant epilepsy. Seizure. (2021) 91:99–107. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2021.06.008
32. Wang, C, Zhai, J, Zhou, X, and Chen, Y. Lipid metabolism: novel approaches for managing idiopathic epilepsy. Neuropeptides. (2024) 108:102475. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2024.102475
33. Yu, D, Li, J, Wei, Q, Zhu, C, Zhang, X, Li, X, et al. Trichosanthis Pericarpium injection ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via inhibiting the KLF6/ABCC5 pathway in mice. Phytomedicine. (2025) 145:156998. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156998
34. Wang, P, Ma, K, Yang, L, Zhang, G, Ye, M, Wang, S, et al. Predicting signaling pathways regulating demyelination in a rat model of lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy: a proteomics study. Int J Biol Macromol. (2021) 193:1457–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.209
35. Faure, JB, Akimana, G, Carneiro, JE, Cosquer, B, Ferrandon, A, Geiger, K, et al. A comprehensive behavioral evaluation in the lithium-pilocarpine model in rats: effects of carisbamate administration during status epilepticus. Epilepsia. (2013) 54:1203–13. doi: 10.1111/epi.12219
36. Kumar, H, Katyal, J, and Kumar Gupta, Y. Effect of U50488, a selective kappa opioid receptor agonist and levetiracetam against lithium-pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus, spontaneous convulsive seizures and related cognitive impairment. Neurosci Lett. (2023) 815:137477. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2023.137477
37. Li, J, Yu, D, He, C, Yu, Q, Huo, Z, Zhang, Y, et al. KLF6 alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:393. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05872-3
38. Wu, W, Sun, Y, Luo, N, Cheng, C, Jiang, C, Yu, Q, et al. Integrated 16S rRNA gene sequencing and LC-MS analysis revealed the interplay between gut microbiota and plasma metabolites in rats with ischemic stroke. J Mol Neurosci. (2021) 71:2095–106. doi: 10.1007/s12031-021-01828-4
39. Liu, Y, Zhang, H, Lu, W, and Jiang, T. Integrating metabolomics, 16S rRNA sequencing, network pharmacology, and metorigin to explore the mechanism of Cinnamomi cortex in treating chronic atrophic gastritis rats. Phytomedicine. (2023) 121:155084. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155084
40. Sun, J, Chen, X, Wang, Y, Song, Y, Pan, B, Fan, B, et al. Neuroprotective effects of Longxue Tongluo capsule on ischemic stroke rats revealed by LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics approach. Chin Herb Med. (2023) 15:430–8. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.12.010
41. Li, P, Hon, SS, Tsang, MS, Kan, LL, Lai, AY, Chan, BC, et al. Integrating 16S rRNA sequencing, microflora metabolism, and network pharmacology to investigate the mechanism of SBL in alleviating HDM-induced allergic rhinitis. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:8655. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168655
42. Wang, ZY, Li, MZ, Li, WJ, Ouyang, JF, Gou, XJ, and Huang, Y. Mechanism of action of Daqinjiao decoction in treating cerebral small vessel disease explored using network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. Phytomedicine. (2023) 108:154538. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154538
43. Terrone, G, Balosso, S, Pauletti, A, Ravizza, T, and Vezzani, A. Inflammation and reactive oxygen species as disease modifiers in epilepsy. Neuropharmacology. (2020) 167:107742. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107742
44. Yue, Q, Cai, M, Xiao, B, Zhan, Q, and Zeng, C. The microbiota-gut-brain Axis and epilepsy. Cell Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 42:439–53. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01130-2
45. Valassi, E, Manichanh, C, Amodru, V, Fernandez, PG, Gaztambide, S, Yanez, F, et al. Gut microbial dysbiosis in patients with Cushing's disease in long-term remission. Relationship with cardiometabolic risk. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1074757. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1074757
46. Ozcan, E, Lum, GR, and Hsiao, EY. Interactions between the gut microbiome and ketogenic diet in refractory epilepsy. Int Rev Neurobiol. (2022) 167:217–49. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2022.06.002
47. Falco-Walter, J. Epilepsy-definition, classification, pathophysiology, and epidemiology. Semin Neurol. (2020) 40:617–23. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1718719
48. Rho, JM, and Boison, D. The metabolic basis of epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. (2022) 18:333–47. doi: 10.1038/s41582-022-00651-8
49. Rae, CD, Baur, JA, Borges, K, Dienel, G, Diaz-Garcia, CM, Douglass, SR, et al. Brain energy metabolism: a roadmap for future research. J Neurochem. (2024) 168:910–54. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16032
50. Tao, L, Mohammad, MA, Milazzo, G, Moreno-Smith, M, Patel, TD, Zorman, B, et al. MYCN-driven fatty acid uptake is a metabolic vulnerability in neuroblastoma. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:3728. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31331-2
51. Wu, J, Cao, M, Peng, Y, Dong, B, Jiang, Y, Hu, C, et al. Research progress on the treatment of epilepsy with traditional Chinese medicine. Phytomedicine. (2023) 120:155022. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155022
52. Zou, S, Yang, X, and Zhou, L. Gut microbiota in epilepsy: how antibiotics induce dysbiosis and influence seizure susceptibility. Microbiol Res. (2025) 298:128225. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2025.128225
53. Massier, L, Chakaroun, R, Tabei, S, Crane, A, Didt, KD, Fallmann, J, et al. Adipose tissue derived bacteria are associated with inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Gut. (2020) 69:1796–806. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-320118
54. Hagihara, M, Kato, H, Yamashita, M, Shibata, Y, Umemura, T, Mori, T, et al. Lung cancer progression alters lung and gut microbiomes and lipid metabolism. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e23509. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23509
55. He, X, and Zhang, Y. Changes in gut flora in patients with epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1480022. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1480022
56. Barrett, E, Ross, RP, O'Toole, PW, Fitzgerald, GF, and Stanton, C. Gamma-aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J Appl Microbiol. (2012) 113:411–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05344.x
57. Go, J, Kim, JE, Kwak, MH, Koh, EK, Song, SH, Sung, JE, et al. Neuroprotective effects of fermented soybean products (Cheonggukjang) manufactured by mixed culture of Bacillus subtilis MC31 and Lactobacillus sakei 383 on trimethyltin-induced cognitive defects mice. Nutr Neurosci. (2016) 19:247–59. doi: 10.1179/1476830515Y.0000000025
58. Zhong, H, Wang, L, Jia, F, Yan, Y, Xiong, F, Li, Y, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum supplementation on glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus and prediabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2024) 61:377–84. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2024.04.009
59. Zhong, W, Wang, H, Yang, Y, Zhang, Y, Lai, H, Cheng, Y, et al. High-protein diet prevents fat mass increase after dieting by counteracting Lactobacillus-enhanced lipid absorption. Nat Metab. (2022) 4:1713–31. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00687-6
60. Wang, C, Yang, C, Western, D, Ali, M, Wang, Y, Phuah, CL, et al. Genetic architecture of cerebrospinal fluid and brain metabolite levels and the genetic colocalization of metabolites with human traits. Nat Genet. (2024) 56:2685–95. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01973-7
61. Tian, T, Mao, Q, Xie, J, Wang, Y, Shao, WH, Zhong, Q, et al. Multi-omics data reveals the disturbance of glycerophospholipid metabolism caused by disordered gut microbiota in depressed mice. J Adv Res. (2022) 39:135–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.10.002
62. Jiang, W, Chen, J, Gong, L, Liu, F, Zhao, H, and Mu, J. Alteration of Glycerophospholipid metabolism in Hippocampus of post-stroke depression rats. Neurochem Res. (2022) 47:2052–63. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03596-y
63. Zheng, P, Wu, J, Zhang, H, Perry, SW, Yin, B, Tan, X, et al. The gut microbiome modulates gut-brain axis glycerophospholipid metabolism in a region-specific manner in a nonhuman primate model of depression. Mol Psychiatry. (2021) 26:2380–92. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0744-2
64. Xu, K, Ren, Y, Zhao, S, Feng, J, Wu, Q, Gong, X, et al. Oral D-ribose causes depressive-like behavior by altering glycerophospholipid metabolism via the gut-brain axis. Commun Biol. (2024) 7:69. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05759-1
65. Zhang, J, Tian, L, Cao, G, Yin, Z, Wang, S, Zhao, C, et al. AnGong NiuHuang (AGNH) pill attenuated traumatic brain injury through regulating NF-kappaB/Nlrp3 axis and glycerophospholipid metabolism. Phytomedicine. (2024) 132:155798. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155798
66. Wei, H, Duan, G, He, J, Meng, Q, Liu, Y, Chen, W, et al. Geniposide attenuates epilepsy symptoms in a mouse model through the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. (2018) 15:1136–42. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5512
67. Dai, H, Wang, P, Mao, H, Mao, X, Tan, S, and Chen, Z. Dynorphin activation of kappa opioid receptor protects against epilepsy and seizure-induced brain injury via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Cell Cycle. (2019) 18:226–37. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1562286
68. Arribas-Blazquez, M, Piniella, D, Olivos-Ore, LA, Bartolome-Martin, D, Leite, C, Gimenez, C, et al. Regulation of the voltage-dependent sodium channel Na(V)1.1 by AKT1. Neuropharmacology. (2021) 197:108745. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108745
69. Soltani Khaboushan, A, Yazdanpanah, N, and Rezaei, N. Neuroinflammation and Proinflammatory cytokines in Epileptogenesis. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59:1724–43. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02725-6
70. Tao, H, Gong, Y, Yu, Q, Zhou, H, and Liu, Y. Elevated serum matrix Metalloproteinase-9, Interleukin-6, hypersensitive C-reactive protein, and homocysteine levels in patients with epilepsy. J Interf Cytokine Res. (2020) 40:152–8. doi: 10.1089/jir.2019.0137
71. Numis, AL, Foster-Barber, A, Deng, X, Rogers, EE, Barkovich, AJ, Ferriero, DM, et al. Early changes in pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in neonates with encephalopathy are associated with remote epilepsy. Pediatr Res. (2019) 86:616–21. doi: 10.1038/s41390-019-0473-x
72. Kim, B, and Feldman, EL. Insulin resistance in the nervous system. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 23:133–41. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2011.12.004
73. Lee, EB, Warmann, G, Dhir, R, and Ahima, RS. Metabolic dysfunction associated with adiponectin deficiency enhances kainic acid-induced seizure severity. J Neurosci. (2011) 31:14361–6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3171-11.2011
Keywords: Xianyu capsule, epilepsy, neuroinflammation, glycerophospholipid metabolism, gut microbiota
Citation: Yu D, Li S, Li X, Zhang X and Guo D (2025) Xianyu capsule ameliorates neuroinflammatory and glycerophospholipid metabolism in lithium-pilocarpine-induced acute epilepsy. Front. Nutr. 12:1625533. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1625533
Edited by:
Chuanfeng Tang, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaReviewed by:
Sijie Feng, Henan Polytechnic University, ChinaFenglian He, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Li, Li, Zhang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoping Li, enl5eGI2QDE2My5jb20=; Danfeng Guo, eWZ5Z3VvZGZAenp1LmVkdS5jbg==; Xiaodan Zhang, enhkeTIwMTlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Dongsheng Yu
Dongsheng Yu Shuang Li2†
Shuang Li2† Danfeng Guo
Danfeng Guo