- 1Department of Physical Education, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, Henan, China
- 2Zhengzhou Tourism College, Zhengzhou, China
- 3Department of Physical Education, Xi’an University of Finance and Economics, Xi’an, China
- 4Department of Military Theory, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, China
Purpose: To investigate the effects of different doses of taurine on endurance exercise performance and physiological parameters under hot and humid conditions.
Methods: This study adopted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over design. Sixteen male university students majoring in physical education (age: 20.12 ± 1.12 years; training status: ≥3 endurance sessions/week) received 4 supplement conditions: (1) placebo (maltodextrin), (2) low-dose (1 g taurine), (3) medium-dose (4 g taurine), and (4) high-dose (6 g taurine). Participants performed a graded cycling test (initial 50 W, +50 W every 3 min at 70 rpm) until exhaustion in an environmental chamber (35 °C, 65% RH). Heart rate, core temperature, skin temperature, sweat rate, RPE, and thermal sensation were measured.
Results: Compared to placebo, time to exhaustion was significantly longer in the medium-dose group (p < 0.05), with no significant or trend-level effects in low- or high-dose groups. Blood lactate accumulation and sweating rate were higher in the medium-dose group (p < 0.05). Core temperature (9 min-End) was lower in the medium-dose group during the latter exercise phase (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Under hot and humid conditions, acute 4 g taurine supplementation enhanced time to exhaustion during graded cycling by improving thermoregulatory responses, whereas 1 g and 6 g doses showed no ergogenic effects.
1 Introduction
Exercise performance in hot and humid environments is significantly impaired due to reduced evaporative cooling efficiency (1), leading to accelerated (2) strain and thermoregulatory failure (3, 4). While proper hydration strategies can partially mitigate these effects, targeted nutritional interventions such as taurine supplementation may offer additional protection by addressing underlying physiological stressors (5). Taurine, a conditionally essential amino acid, has demonstrated particular relevance for thermal stress management through three primary mechanisms (6): its antioxidant capacity to scavenge exercise-induced reactive oxygen species (7), osmoregulatory function in maintaining cellular volume and electrolyte balance during dehydration (8), and direct thermoregulatory effects through enhanced sweat gland responsiveness and hypothalamic regulation (9–11). These distinct mechanisms position taurine as a uniquely promising ergogenic aid for humid heat conditions exceeding 60% relative humidity (6, 12).
Current understanding of taurine’s dose-response relationship remains unclear due to conflicting evidence across studies. While low-dose acute supplementation (1 g) showed no performance benefits in cycling time trials (13), chronic high-dose administration (6 g/day) improved maximal oxygen uptake (7) but required prolonged use (14). Animal studies suggest moderate doses (3–4 g) may offer acute thermoregulatory advantages, though human data under controlled environmental stress remain limited (6, 10, 15). This inconsistency likely stems from variations in exercise protocols, environmental conditions, and supplementation regimens, highlighting the need for systematic dose comparisons under standardized heat stress conditions (6).
Emerging evidence specifically suggests taurine’s efficacy in hot environments may differ from its general ergogenic effects. Studies have demonstrated that acute taurine intake can increase sweating rates by 12.7% at 35 °C (16), while chronic supplementation appears to delay critical core temperature thresholds during progressive heat exposure (12). However, existing research has predominantly examined these effects at moderate humidity levels (≤40% RH) (6, 16), leaving a critical gap in understanding taurine’s potential under the more physiologically challenging conditions of high humidity (≥60% RH) where evaporative cooling is substantially impaired.
Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the acute effects of three doses of taurine (1, 4, and 6 g) on endurance cycling performance and thermoregulatory responses under controlled hot and humid conditions (35 °C and 65% relative humidity). We hypothesized that moderate-dose taurine (4 g) would optimally enhance time to exhaustion by improving thermoregulatory efficiency, while lower and higher doses would prove less effective due to insufficient physiological stimulation and potential osmotic stress, respectively (13, 17–19). This investigation provides the first systematic evaluation of taurine’s dose-dependent ergogenic effects under conditions of combined heat and high humidity, offering practical insights for athletic performance in environmentally challenging conditions.
2 Methods
2.1 Research design
This study adopted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over design. Participants reported to the laboratory in 5 visits. Participants familiarized with the experimental equipment and procedures and adjusted the power bike seat and handles position during their 1st visit to the lab.
During the formal experiment (2–5 visits), participants were divided into a placebo group (P), a low-dose group (L), a medium-dose group (M), and a high-dose group (H) according to the random assignment method (GraphPad, https://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/randomize1.cfm).
A seven-day interval between conditions was selected to allow for complete recuperation from the protocols and sufficient time to consume the crossover supplementation. Taurine has a clearance/bioavailability ratio of approximately 21 h, which was deemed an adequate washout period (17, 20). The entire experiment was conducted within a Controlled High-Temperature and High-Humidity Chamber, meticulously regulated by a combination of heating (SAWO, CON4, Finland) and humidifying (BELIN, SC-G060ZS, CHN) equipment, ensuring a precise temperature range of 35 °C ± 1 °C and humidity level of 65% ± 2%, thereby fostering optimal conditions for the experimental proceedings. This study received institutional ethical approval (Capital University of Physical Education and Sports, No. 2020A55) and was performed in conformity with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration.
2.2 Procedure
Participants took a temperature capsule to measure gastrointestinal temperature 6 h before performing the exhaustion test to ensure that the temperature capsule was not in the stomach and to avoid the temperature capsule being affected by ingested food or beverages. Participants ingested 300 mL of water mixed with supplements 1 h before the start of the test to ensure a homogeneous status. Before warming up, participants put on a heart rate belt and skin temperature buttons. Participants were initially performed in a laboratory environment (25 °C, 30% RH) for a 5 min 100 W steady-state warm-up. Subsequently, the body weight was measured. Then, the participants entered a high-temperature and humidity chamber for an exhaustion test. Heart rate, core temperature, skin temperature, RPE, and thermal sensation were recorded throughout the exhaustion test. Exhaustion time was recorded immediately after the exhaustion test. Then, the body was dried with a towel and the weight was measured again (Figure 1).
2.3 Participants
Sixteen male college students majoring in physical education volunteered to participate in this study (age: 20.12 ± 1.12 years; stature: 1.76 ± 0.06 m; body mass: 72.06 ± 5.99 kg; maximal oxygen uptake (V̇O2max): 46.24 ± 4.07 mL/kg/min). A priori sample sizes were calculated using G*Power (Version No. 3.1.9.7. Franz Faul University Kiel, Germany) (21). The parameters are set as follows: α = 0.05, power = 0.85, effect size = 0.25. Participants voluntarily enrolled in this experiment and were aware of the procedure and requirements and the potential for uncomfortable reactions. The Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire (PAR-Q) was used to identify those at risk for exercise. The experimental protocol, though involving thermal stress, was conducted under controlled conditions with predefined termination criteria to ensure safety. Participants signed an informed consent form and ensured that they had sufficient time to complete the experiment. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) 1. Aged between 18 and 22 years old, with at least 3 physical training sessions per week; (2) Good health, no major illnesses, no injuries or surgeries within the last 6 months; (3) No intake of any ergogenic aid in the last 3 months; and (4) No habit of exercising in high temperature or high humidity environments.
2.4 Supplementation and standardization
Prior research has classified taurine intake doses into three categories: low (0.5–2 g), medium (3–5 g), and high (>5 g) (6). All supplements were prepared in powder form and measured using an analytical balance and subsequently ingested in liquid form, mixed with 300 mL of water. Participants ingested the supplement 1 hour prior to the experiment. 1 h timing was chosen as this accounted for the peak plasma availability of taurine after oral administration. Participants were randomized to the following 4 supplementation groups: placebo (maltodextrin), low-dose (1 g TAU), medium-dose (4 g TAU), and high-dose (6 g TAU), followed by a randomized crossover trial (22). Before the experiment, participants were asked to record their diets. They were then instructed to repeat these diets 24 h before the formal experiment. Throughout the study period, participants were prohibited from consuming any nutritional supplements. Compliance was verified through daily dietary logs, periodic interviews, and random spot checks (with participant consent). Any supplement use would have resulted in immediate exclusion from the study. All subjects entered the laboratory at least 3 h after eating. The same period in 1 day was selected to complete each experiment to minimize the effects of circadian rhythms (8:00 a.m.–10:00 a.m.).
2.5 Measurements
2.5.1 Time to exhaustion
TTE is frequently employed as a measure of endurance performance in a laboratory setting (23). The participants started cycling (LODE 906900, Netherlands) at 50 W and increased 50 W every three (24).
Participants were asked to maintain a pedal cadence of 70 rpm until complete exhaustion. Exhaustion was defined as voluntary withdrawal or a decrease in pedal cadence to below 60 rpm for more than 10 s. The TTE is recorded immediately at the end of the exhaustion test.
2.5.2 Heart rate
Participants wore a polar heart rate belt throughout the session (Polar H10, Finland). The heart rate belt must be in close contact with the skin, paying particular attention to the wearing position at the middle connection between the chest and the abdomen.
2.5.3 Blood lactate
BLa was obtained by testing ear blood with a blood lactate meter (EKF Diagnostics Holdings plc, Cardiff, United Kingdom). BLa was measured before and immediately after the exhaustion test.
2.5.4 Sweat rate
SR was calculated by collecting information on the participant’s body weight before and after the exercise session and using the following formula: Sweat rate = (Δmass + fluid)/exercise time (4, 25).
2.5.5 Core temperature
Core temperature was measured using an ingestible, noninvasive temperature capsule (e-CELSIUS®, BMedical Pty LTb, Australia), which was taken by the subject 6 h before the experiment (26). The temperature capsule was used to measure human gastrointestinal temperature (gastrointestinal temperature), and the sampling frequency of the temperature capsule was set to 30 s. After connecting with an external sensor (e-CELSIUS®, BMedical Pty LTb, Australia), the core temperature data were received and the gastrointestinal temperature was continuously monitored.
2.5.6 Mean skin temperature
Skin temperature was measured using temperature recording buttons (DS1922L, Maxim Integrated, United States), which were attached to the sternal incision, forearm, thigh, and calf to record skin temperatures of the chest (Tchest), forearm (Tarm), thigh (Tthigh), and calf (Tcalf). The whole body MST was calculated using the formula: MST = 0.3 (Tchest + Tarm) + 0.2 (Tthigh + Tcalf) (4).
2.5.7 Rating of perceived exertion
RPE was recorded on a 6 to 20-point Borg scale (27). RPE was recorded at baseline, every 3 min after the start of the exhaustion test, and immediately after the end of the exhaustion test. Participants provided verbal ratings, which were immediately documented by the research team.
2.5.8 Thermal sensation
TS was recorded on a 9-point scale where −4 = “very cold,”0 = “neutral,” and 4 = “very hot.” TS was recorded using the same verbal recording method as RPE.
2.6 Statistical analysis
The statistical analyzes were conducted using the SPSS version 27.0 software package (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, United States). The data is presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). The normality test was assessed by Shapiro–Wilk for all the data and the sphericity test was performed on the data by Mauchly test. CT, B[La], HR, TS, and RPE were analyzed using repeated measures of two-way (group x time) ANOVA. TTE and SR were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. The statistical significance level was set at p < 0.05. Effect sizes were interpreted using Cohen’s guidelines for partial η2 (0.01 = small, 0.06 = medium, 0.14 = large).
3 Results
3.1 Time to exhaustion
TTE values for P (mean = 702.38; SD = 83.088), L (mean = 754.81, SD = 125.378), M (mean = 812.38, SD = 90.948) and H (mean = 760.44, SD = 121.962) groups were recorded. The data showed significant differences in TTE between interventions, F(3, 33) = 4.858, MSE = 1442.365; p = 0.046. Follow-up multiple comparisons showed that TTE was significantly higher in the M group than in the P group (p = 0.031) (Figure 2).
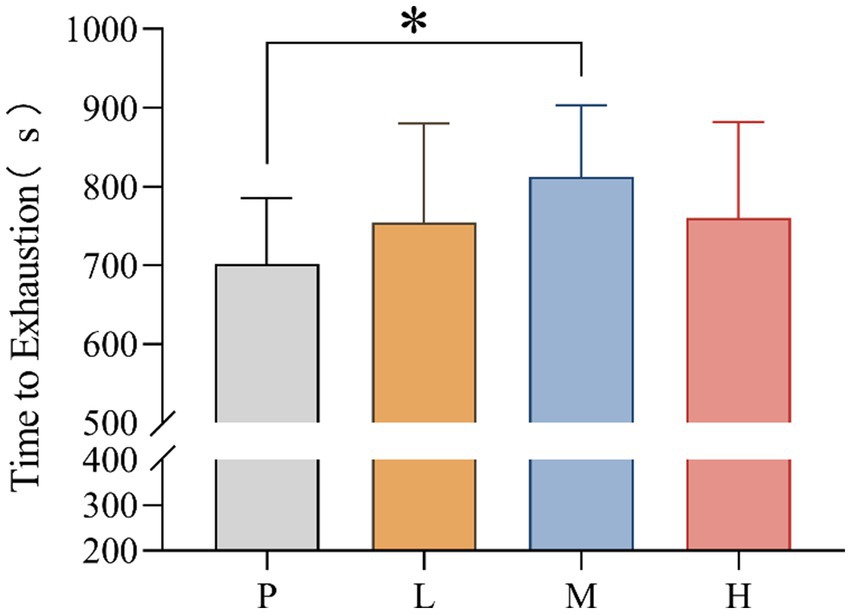
Figure 2. Time to exhaustion (* p < 0.05) after supplementation with different doses of taurine or placebo (n = 16) under hot and humid conditions (35 °C, 65% RH).
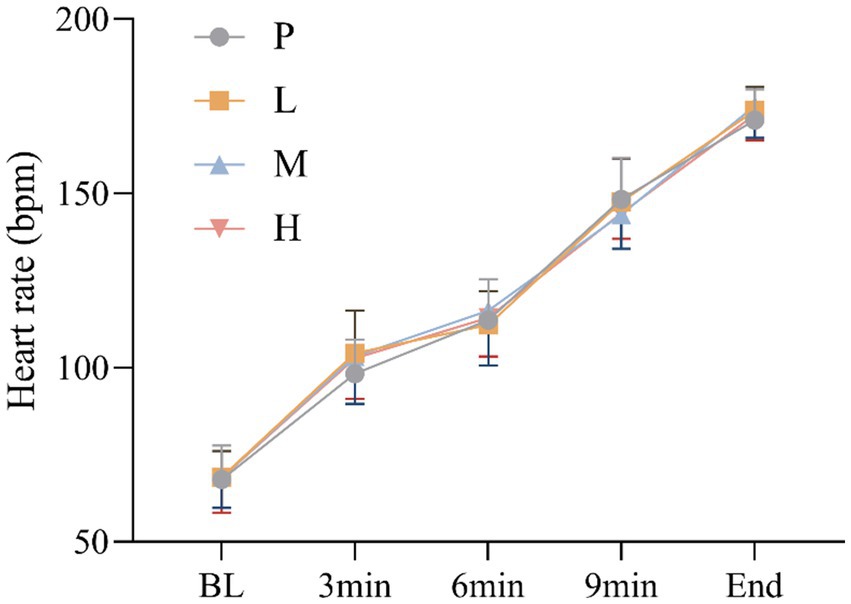
3.2 Heart rate
These results showed no significant main effect of intervention [F(3, 60) = 0.237, p = 0.870, η2partial = 0.012], and a significant main effect of time, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 57) = 1177.885, p < 0.001, η2partial = 0.988], there was no significant intervention × time interaction effect, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 59) = 2.018, p = 0.104, η2partial = 0.120] (Figure 3).
3.3 Blood lactate
B[La] pre-post difference values for P (mean = 10.006; SD = 2.406), L (mean = 10.130, SD = 2.879), M (mean = 12.275, SD = 1.882) and H (mean = 11.600, SD = 1.892) groups were recorded. The data showed significant differences in B[La] pre-post difference between interventions, F(3, 33) = 3.876, MSE = 5.30; p = 0.014. Follow-up multiple comparisons showed that B[La] pre-post difference was significantly higher in the M group than in the P group (p = 0.043) (Figure 4).
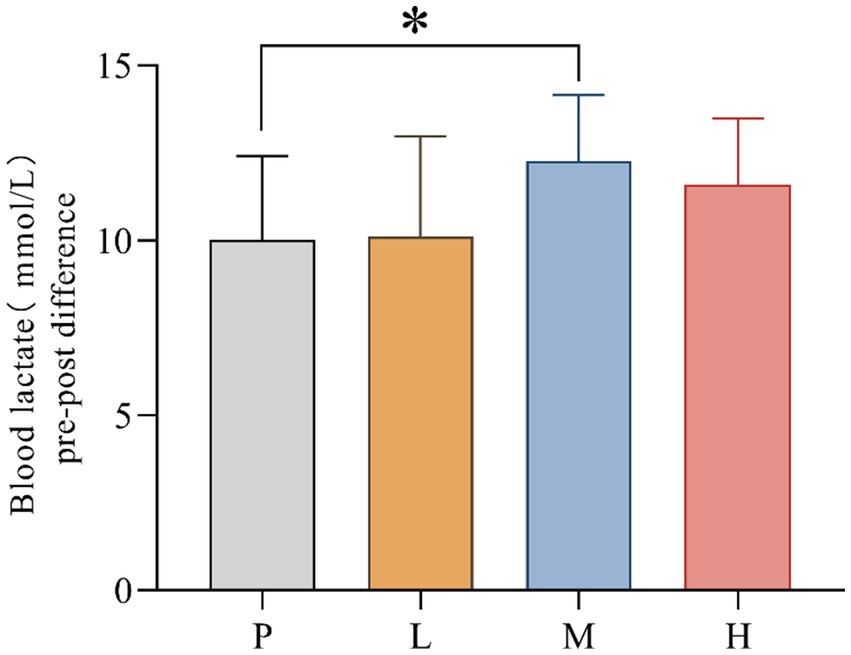
Figure 4. Comparison of blood lactate differences pre- and post-exhaustion testing (* p < 0.05) in 4 groups under hot and humid conditions (35 °C, 65% RH).
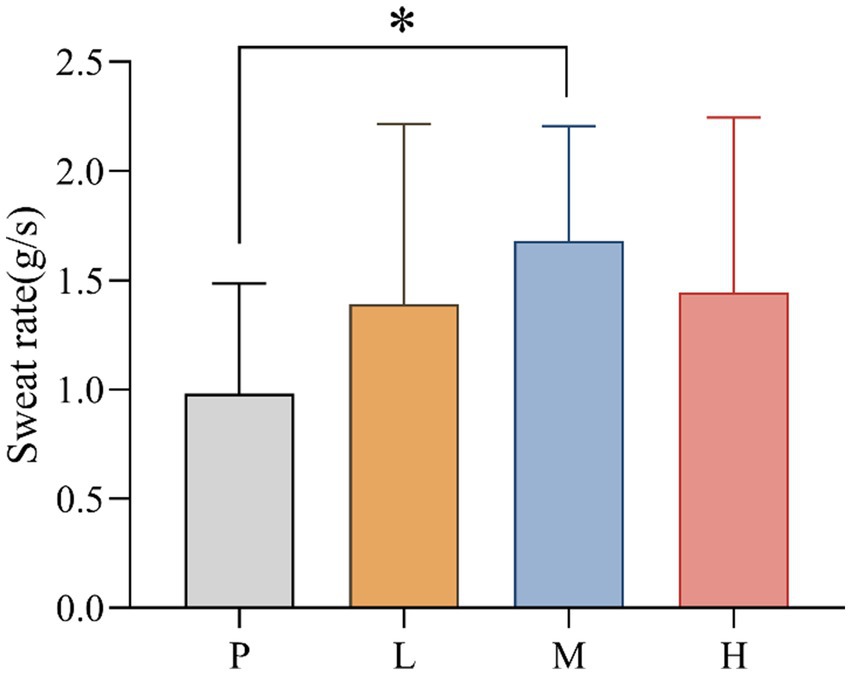
3.4 Sweat rate
SR values for P (mean = 0.981; SD = 0.506), L (mean = 1.388, SD = 0.828), M (mean = 1.681, SD = 0.525) and H (mean = 1.444, SD = 0.802) groups were recorded. The data showed significant differences in SR between interventions, F(3, 33) = 4.858, MSE = 0.465; p = 0.041. Follow-up multiple comparisons showed that SR was significantly higher in the M group than in the P group (p = 0.031) (Figure 5).
3.5 Core temperature
These results showed no significant main effect of intervention [F(3, 60) = 1.051, p = 0.377, η2partial = 0.050], and a significant main effect of time, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 57) = 49.150, p < 0.001, η2partial = 0.775], there was significant intervention × time interaction effect, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 59) = 3.689, p = 0.010, η2partial = 0.200]. CT was significantly lower in group M than in group P at 9 min (p = 0.037) and at the end of exhaustion (p = 0.001) (Figure 6).
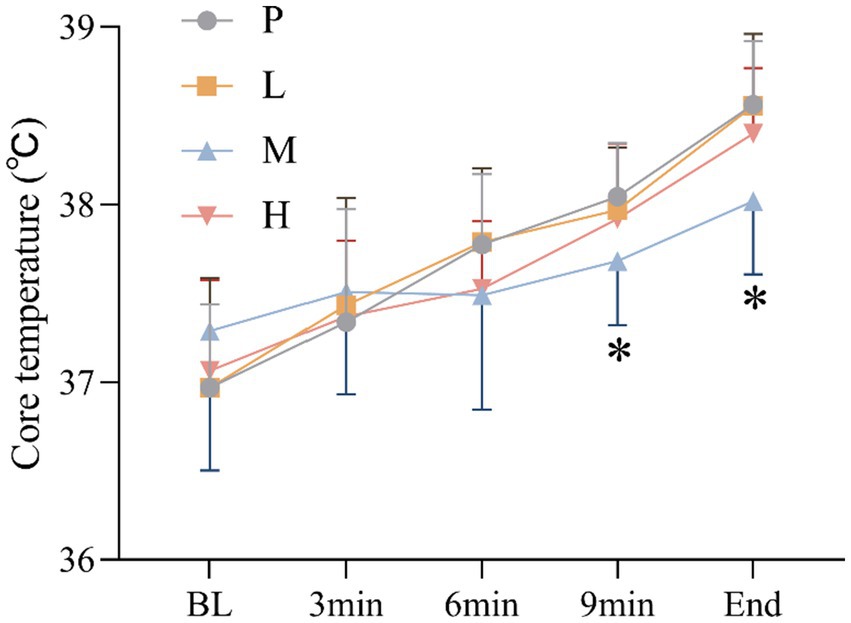
Figure 6. Changes in CT (* p < 0.05) during the exhaustion test under hot and humid conditions (35 °C, 65% RH).
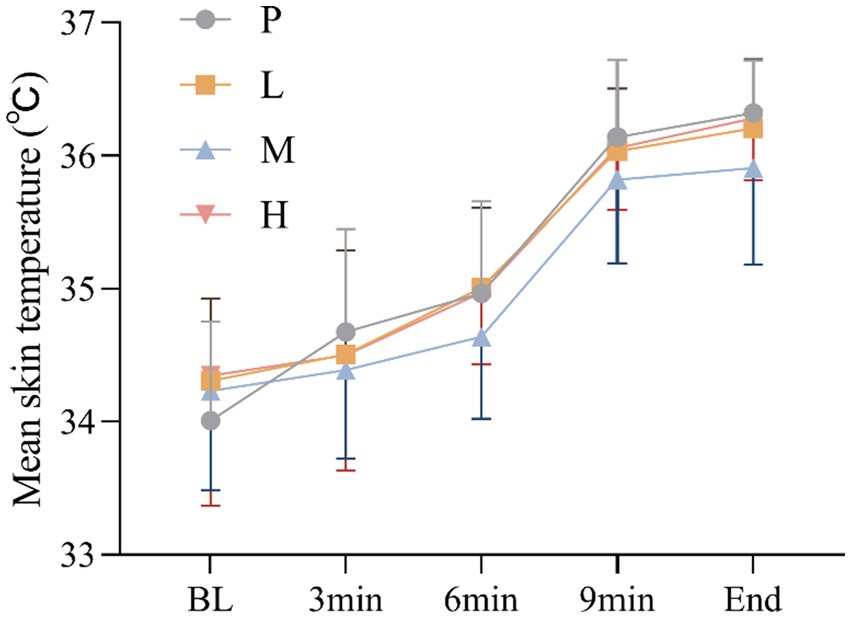
3.6 Mean skin temperature
These results showed no significant main effect of intervention [F(3, 60) = 1.964, p = 0.129, η2partial = 0.089], and a significant main effect of time, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 57) = 94.695, p<0.001, η2partial = 0.869], there was no significant intervention × time interaction effect, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 59) = 1.276, p = 0.290, η2partial = 0.080] (Figure 7).
3.7 Rating of perceived exertion and thermal sensation
For RPE, these results showed no significant main effect of intervention [F(3, 60) = 0.300, p = 0.826, η2partial = 0.015], and a significant main effect of time, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 57) = 366.065, p < 0.001, η2partial = 0.963], there was no significant intervention × time interaction effect, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 59) = 2.093, p = 0.093, η2partial = 0.124].
For TS, these results showed no significant main effect of intervention [F(3, 60) = 1.867, p = 0.145, η2partial = 0.085], and a significant main effect of time, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 57) = 151.966, p < 0.001, η2partial = 0.914], there was no significant intervention × time interaction effect, Greenhouse–Geisser adjusted [F(4, 59) = 1.631, p = 0.178, η2partial = 0.100] (Figure 8).
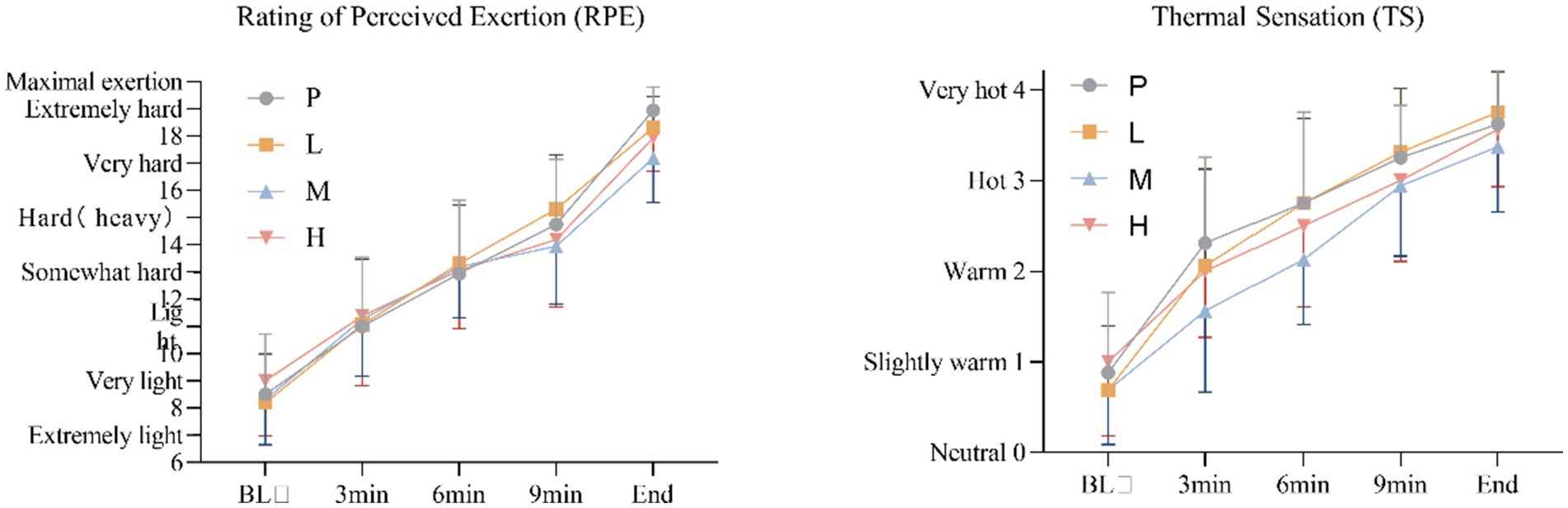
Figure 8. Changes in RPE and TS during the exhaustion test under hot and humid conditions (35 °C, 65% RH).
4 Discussion
The present study investigated the dose-response effects of acute taurine supplementation on endurance cycling performance under hot and humid conditions (35 °C, 65% RH). Our findings demonstrate that moderate-dose taurine (4 g) significantly improved time to exhaustion by 12.4% compared to placebo, while low (1 g) and high (6 g) doses showed no ergogenic benefits. These results suggest a U-shaped dose-response relationship, with 4 g emerging as the optimal dose for performance enhancement in these environmental conditions.
The performance benefits observed with 4 g taurine appear mediated through improved thermoregulation. Specifically, we found that this dose reduced core temperature during the latter stages of exercise while increasing the sweat rate. These findings align with previous work showing taurine’s ability to enhance evaporative cooling through sweat gland modulation (16) and hypothalamic thermoregulation (28). The higher sweat rate may reflect taurine’s role in upregulating aquaporin-5 expression in eccrine sweat glands (6, 29), though future studies should directly measure this mechanism. Importantly, the humid conditions in our study (65% RH) likely amplified the thermoregulatory challenge, making these improvements particularly meaningful for athletic performance.
The lack of benefit from the 6 g dose warrants careful consideration. Several factors may explain this finding: First, high-dose taurine may induce osmotic diuresis that counteracts its thermoregulatory benefits (30). Second, intestinal taurine transporters may become saturated above 4 g, limiting bioavailability (31). Third, the combination of high dose and extreme humidity may have overwhelmed the body’s cooling capacity (14). While our data cannot definitively distinguish these possibilities, they highlight the importance of dose optimization for hot/humid conditions.
Metabolically, the 4 g group showed greater blood lactate accumulation post-exercise compared to placebo. This likely reflects their prolonged exercise duration rather than impaired clearance, as taurine typically reduces lactate accumulation in thermoneutral conditions (12, 16). The humidity-induced metabolic shift toward anaerobic glycolysis may explain this discrepancy (4, 10, 11), suggesting environmental conditions significantly modify taurine’s metabolic effects.
While we observed trends toward improved thermal sensation with 4 g taurine, subjective measures (RPE, TS) did not reach statistical significance. This may reflect the high interindividual variability in perceptual responses to heat stress (17, 18, 32), suggesting future studies should employ larger samples to detect potential psychological benefits.
Several limitations should be acknowledged. First, the lack of plasma taurine measurements prevents definitive conclusions about absorption and kinetics. Second, our graded exercise protocol differs from real-world endurance events, potentially limiting generalizability. Third, the homogeneous sample (young male athletes) necessitates caution when extrapolating to other populations. Future research should investigate weight-adjusted dosing (e.g., 50 mg/kg), include female and masters athletes, and examine prolonged exercise scenarios.
In conclusion, this study establishes that 4 g represents the optimal acute taurine dose for improving endurance performance in hot/humid conditions, primarily through enhanced thermoregulation. The U-shaped dose-response relationship underscores the importance of avoiding both insufficient and excessive dosing. These findings provide practical guidance for athletes and coaches while highlighting the need for further research on individualization strategies and long-term supplementation protocols.
5 Conclusion
Under hot and humid conditions, acute oral administration of a moderate 4 g taurine dose effectively enhances endurance exercise performance by improving thermoregulatory responses. This finding highlights the practical potential of taurine supplementation as a strategy to mitigate heat-related performance decrements. Future studies should explore dose-response relationships, utilizing plasma taurine levels to optimize dosing strategies for athletic and occupational populations exposed to extreme environments.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
This study received institutional ethical approval (Capital University of Physical Education and Sports, No. 2020A55). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
XL: Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LH: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. LW: Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Maughan, R, and Shirreffs, S. Exercise in the heat: challenges and opportunities. J Sports Sci. (2004) 22:917–27. doi: 10.1080/02640410400005909
2. Rowell, LB. Human cardiovascular adjustments to exercise and thermal stress. Physiol Rev. (1974) 54:75–159. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.1.75
3. Périard, JD, Racinais, S, and Sawka, MN. Adaptations and mechanisms of human heat acclimation: applications for competitive athletes and sports: adaptations and mechanisms of heat acclimation. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2015) 25:20–38. doi: 10.1111/sms.12408
4. Maughan, RJ, Otani, H, and Watson, P. Influence of relative humidity on prolonged exercise capacity in a warm environment. Eur J Appl Physiol. (2012) 112:2313–21. doi: 10.1007/s00421-011-2206-7
5. Tan, PMS, and Lee, JKW. The role of fluid temperature and form on endurance performance in the heat. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2015) 25:39–51. doi: 10.1111/sms.12366
6. Kurtz, JA, VanDusseldorp, TA, Doyle, JA, and Otis, JS. Taurine in sports and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. (2021) 18:39. doi: 10.1186/s12970-021-00438-0
7. Liu, Z, Qi, B, Zhang, M, Izumi, I, Kagamimori, S, Sokejima, S, et al. Role of taurine supplementation to prevent exercise-induced oxidative stress in healthy young men. Amino Acids. (2004) 26:203–7. doi: 10.1007/s00726-003-0002-3
8. Cuisinier, C, Michotte de Welle, J, Verbeeck, R, Poortmans, J, Ward, R, Sturbois, X, et al. Role of taurine in osmoregulation during endurance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. (2002) 87:489–95. doi: 10.1007/s00421-002-0679-0
9. Simmonds, R, Cole, J, Tallent, J, Jeffries, O, Theis, N, and Waldron, M. Physiological and thermoregulatory effects of oral taurine supplementation on exercise tolerance during forced convective cooling. Eur J Sport Sci. (2022) 22:209–17. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2020.1858175
10. Win, RK, and Pycock, CJ. Role of taurine as a possible transmitter in the thermoregulatory pathways of the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2011) 31:466–70. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13555.x
11. Bouchama, A, Yusuf, A, Al-Sedairy, S, and El-Yazigi, A. Alteration of taurine homeostasis in acute heatstroke. Crit Care Med. (1993) 21:551–4. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199304000-00016
12. Peel, JS, McNarry, MA, Heffernan, SM, Nevola, VR, Kilduff, LP, Coates, K, et al. The effect of 8-day oral taurine supplementation on thermoregulation during low-intensity exercise at fixed heat production in hot conditions of incremental humidity. Eur J Appl Physiol. (2024) 124:2561–76. doi: 10.1007/s00421-024-05478-3
13. Ward, R, Bridge, CA, McNaughton, LR, and Sparks, SA. The effect of acute taurine ingestion on 4-km time trial performance in trained cyclists. Amino Acids. (2016) 48:2581–7. doi: 10.1007/s00726-016-2282-4
14. Milioni, F, Malta, EDS, Rocha, LGSDA, Mesquita, CAA, de Freitas, EC, and Zagatto, AM. Acute administration of high doses of taurine does not substantially improve high-intensity running performance and the effect on maximal accumulated oxygen deficit is unclear. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. (2016) 41:498–503. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2015-0435
15. Frosini, M, Sesti, C, Saponara, S, Ricci, L, Valoti, M, Palmi, M, et al. A specific taurine recognition site in the rabbit brain is responsible for taurine effects on thermoregulation. Br J Pharmacol. (2003) 139:487–94. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705274
16. Page, LK, Jeffries, O, and Waldron, M. Acute taurine supplementation enhances thermoregulation and endurance cycling performance in the heat. Eur J Sport Sci. (2019) 19:1101–9. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2019.1578417
17. Buzdağlı, Y, Eyipınar, C, Öget, F, Şıktar, E, Forbes, S, and Tekin, A. Taurine supplementation enhances anaerobic power in elite speed skaters: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Biol Sport. (2022) 40:741–51. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2023.119990
18. Warnock, R, Jeffries, O, Patterson, S, and Waldron, M. The effects of caffeine, taurine, or caffeine-taurine coingestion on repeat-sprint cycling performance and physiological responses. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. (2017) 12:1341–7. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2016-0570
19. Batitucci, G, Terrazas, SIBM, Nóbrega, MP, Carvalho, FGD, Papoti, M, Marchini, JS, et al. Effects of taurine supplementation in elite swimmers performance. Mot Rev Educ Física. (2018) 24:e1018137. doi: 10.1590/s1980-6574201800010011
20. Lim, ZX, Singh, A, Leow, ZZX, Arthur, PG, and Fournier, PA. The effect of acute taurine ingestion on human maximal voluntary muscle contraction. Med Sci Sports Exerc. (2018) 50:344–52. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001432
21. Faul, F, Erdfelder, E, Buchner, A, and Lang, AG. Statistical power analyses using G*power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods. (2009) 41:1149–60. doi: 10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149
22. Waldron, M, Patterson, SD, Tallent, J, and Jeffries, O. The effects of an Oral taurine dose and supplementation period on endurance exercise performance in humans: a Meta-analysis. Sports Med. (2018) 48:1247–53. doi: 10.1007/s40279-018-0896-2
23. Coakley, SL, and Passfield, L. Cycling performance is superior for time-to-exhaustion versus time-trial in endurance laboratory tests. J Sports Sci. (2018) 36:1228–34. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2017.1368691
24. Fan, Y, Zhang, B, Wang, Y, and Wu, H. Different humidity environments do not affect the subsequent exercise ability of college football players after aerobic high-intensity interval training. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:16205. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66757-9
25. Yamaguchi, K, Kasai, N, Hayashi, N, Yatsutani, H, Girard, O, and Goto, K. Acute performance and physiological responses to repeated-sprint exercise in a combined hot and hypoxic environment. Physiol Rep. (2020) 8:e14466. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14466
26. Wendt, D, Van Loon, LJC, and Van Marken Lichtenbelt, WD. Thermoregulation during exercise in the heat: strategies for maintaining health and performance. Sports Med. (2007) 37:669–82. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200737080-00002
27. Ritchie, C. Rating of perceived exertion (RPE). J Physiother. (2012) 58:62. doi: 10.1016/S1836-9553(12)70078-4
28. Peel, JS, McNarry, MA, Heffernan, SM, Nevola, VR, Kilduff, LP, and Waldron, M. The effect of dietary supplements on endurance exercise performance and core temperature in hot environments: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Sports Med. (2021) 51:2351–71. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01500-2
29. Smith, CJ, and Johnson, JM. Responses to hyperthermia. Optimizing heat dissipation by convection and evaporation: neural control of skin blood flow and sweating in humans. Auton Neurosci. (2016) 196:25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2016.01.002
30. Schaffer, S, and Kim, HW. Effects and mechanisms of taurine as a therapeutic agent. Biomol Ther. (2018) 26:225–41. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2017.251
31. Han, X, Patters, AB, Jones, DP, Zelikovic, I, and Chesney, RW. The taurine transporter: mechanisms of regulation. Acta Physiol. (2006) 187:61–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2006.01573.x
Keywords: taurine, endurance cycling performance, hot and humid condition, dosage, thermoregulatory responses
Citation: Li X, Huo L, Wang L and Zhang W (2025) Dose-response relationship of taurine on endurance cycling performance under hot and humid conditions. Front. Nutr. 12:1632131. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1632131
Edited by:
Ana Maria Teixeira, University of Coimbra, PortugalReviewed by:
Reinout Van Schuylenbergh, KU Leuven, BelgiumLucie Lipková, Masaryk University, Czechia
Copyright © 2025 Li, Huo, Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenjuan Zhang, emhhbmd3ZW5qdWFuOTAxMTAxQDE2My5jb20=
 Xinlei Li1
Xinlei Li1 Wenjuan Zhang
Wenjuan Zhang![Diagram showing an experimental procedure for an exhaustion test. CT capsules are taken six hours before. A 60-minute period includes a five-minute 100W steady-state warm-up on a cycle, followed by blood lactate (B[La]) measurement. The exhaustion test occurs at 35°C ± 1°C and 65% ± 2% humidity. Measurements include time to exhaustion (TTE), heart rate (HR), core temperature (CT), mean skin temperature (MST), rating of perceived exertion (RPE), and thermal sensation (TS).](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1632131/fnut-12-1632131-HTML/image_m/fnut-12-1632131-g001.jpg)