- Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China
Background: Rectal cancer is a highly prevalent malignant tumor, and surgery is one of the main treatment methods. Although preventive ileostomy can reduce postoperative complications, it is also prone to cause malnutrition and other problems.
Objective: To construct and validate an early postoperative home dietary management program for patients with preventive ileostomy for rectal cancer, aiming to improve their nutritional status and mitigate clinical ileostomy complications.
Methods: An evidence-based dietary management program was developed, covering dietary transition, nutrient intake, and fluid management. A non-concurrent controlled study was conducted with 66 patients at the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine. The intervention group received personalized one-on-one dietary guidance (including pre-discharge assessment of dietary habits, individualized meal planning, and weekly WeChat-based follow-up for food diary reviews) in addition to routine health education, while the control group received routine education only.
Results: At 1 month postoperatively, the intervention group showed significantly better outcomes than the control group in serum albumin (41.00 g/L vs. 38.00 g/L, p = 0.010, r = 0.368), lymphocyte count (1.30 × 10?/L vs. 1.10 × 10?/L, p = 0.009, r = 0.374), and PG-SGA scores (9.85 vs. 10.94, p = 0.037, Cohen's d = 0.525). The intervention group had lower incidences of high-output stoma (HOS; 6.06% vs. 18.18%, OR = 0.29, 95% CI = 0.05–1.56, p = 0.258) and peristomal moisture-associated skin damage (PMASD; 18.18% vs. 24.24%, OR = 0.69, 95% CI = 0.21–2.29, p = 0.547), with positive clinical trends despite no statistical significance.
Conclusion: This home dietary management program can effectively improve short-term postoperative nutritional status in patients, and also plays a positive role in reducing the occurrence of HOS and PMASD.
1 Background
Colorectal cancer ranks third in global incidence and second in mortality among malignant tumors. In China, its incidence ranks second and mortality fourth, accounting for 28.2% of global cases (1, 2). Surgical treatment is a main approach for rectal cancer, and with the continuous development of surgical techniques, sphincter-preserving surgery for rectal cancer has been widely adopted. Preventive ileostomy, used in such surgeries, serves to decrease the incidence of postoperative anastomotic dehiscence and attenuate the severity of pelvic sepsis in the event of fistula formation (3). However, ileostomy presents significant challenges. In the absence of the colon's ability to absorb water and electrolytes, a substantial volume of digestive fluids is expelled through the ileostomy. This physiological alteration renders patients vulnerable to high-output stoma (HOS), malnutrition, metabolic imbalances, and immune dysregulation. Studies have found that 23.7% of patients develop HOS after ileostomy (4), while the incidence of malnutrition is as high as 79.09% (5).
To cope with these issues, some ileostomy patients adjust their dietary intake by avoiding certain foods or reducing food intake to reduce stoma output or avoid issues like odor. Additionally, the lack of professional home rehabilitation dietary guidance leads to further problems. For instance, 39.7% of patients with peristomal moisture-associated skin damage (PMASD) within 1 month after surgery still consumed semi-liquid diets (6), which is significantly associated with increased stoma output. This, in turn, leads to insufficient energy intake or nutritional imbalance, thereby increasing malnutrition risk (7). Thus, professional dietary guidance interventions are needed to reduce stoma output, alter stool characteristics, and improve patients' nutritional status.
Although existing guidelines provide dietary management recommendations for ileostomy patients (8, 9), their content is fragmented and lacks systematic dietary advice. This hinders the rapid and effective clinical implementation of dietary management, and patients may even receive inconsistent dietary advice. Therefore, this study aims to construct and evaluate an evidence-based early postoperative home rehabilitation dietary management program for patients with preventive ileostomy after rectal cancer surgery, providing a reference for dietary management interventions.
2 Methods
2.1 Construction of early postoperative dietary management program for patients with preventive ileostomy for rectal cancer
2.1.1 Establishing the research team
The research team consisted of 8 members: 1 head nurse from gastrointestinal oncology surgery responsible for project guidance, 2 specialist physicians responsible for disease diagnosis and treatment, 1 nutritionist responsible for reviewing and modifying the dietary management program, 3 stoma therapists responsible for patient education and follow-up management, and 1 research nurse primarily responsible for overall project coordination, consultation, and data collection. The research team held regular meetings to advance the project with close collaboration.
2.1.2 Construction of the early postoperative dietary management program
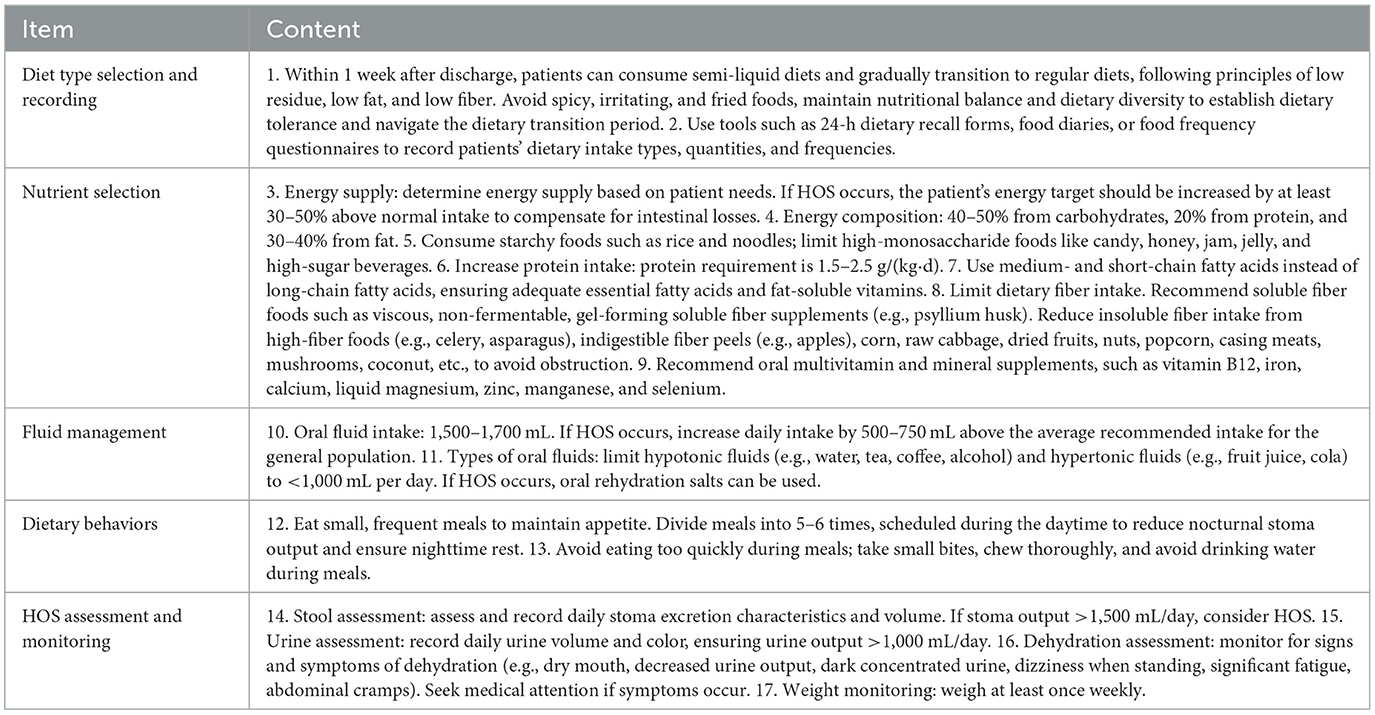
This study summarized evidence on dietary management interventions for patients after preventive ileostomy for rectal cancer through evidence-based methods, extracted relevant content, and formed a preliminary draft of the dietary management program. Ten experts were selected to complete the consultation, resulting in the program. Eight patients were selected for a pilot test. The program was adjusted based on pilot results, ultimately forming the final dietary management program (Table 1).
2.2 Application of the dietary management program
2.2.1 Study design and participants
A non-concurrent controlled study was conducted in the general surgery and gastrointestinal oncology surgery wards of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital. Patients undergoing preventive ileostomy for rectal cancer between July 2024 and February 2025 were included. Thirty-three patients from July-November 2024 were assigned to the control group, and thirty-three patients from December 2024-February 2025 were assigned to the intervention group. Inclusion criteria: (a) Diagnosed with rectal cancer, underwent radical tumor resection with preventive ileostomy, expected survival >1 year; (b) Age 18–75 years; (c) Conscious with unimpaired communication. Exclusion criteria: (a) Eating disorders; (b) Severe primary heart, liver, lung, kidney, blood diseases or other serious conditions affecting survival; (c) Participation in other similar clinical trials. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital (2024NL-181-02). Sample size calculation based on comparing means of two groups: n1 = n2 = 2[(μα + μβ)σ/δ]2, with α = 0.05 (two-sided), β = 0.10 (one-sided). From preliminary results, δ = 3.40, σ = 3.82, yielding n1 = n2 ≈27. Considering 20% attrition, the adjusted sample size was 33 per group (total 66).
2.2.2 Intervention methods
2.2.2.1 Control group
Received routine health education. Before discharge, they received home care manuals and were educated by stoma therapists about ileostomy characteristics and dietary points. They were informed about stoma clinics and instructed to follow up regularly. Telephone follow-ups were conducted within 1 week after discharge.
2.2.2.2 Intervention group
In addition to the control group's intervention, they received in-depth communication with stoma therapists and nutritionists 2–3 days before discharge to understand preoperative eating habits and care needs. They received personalized one-on-one dietary guidance tailored to their eating habits and preventive ileostomy characteristics. On discharge day, stoma therapists reviewed the education and provided additional guidance as needed. Patients received a home dietary management manual and joined a stoma patient WeChat group for nutrition and dietary questions. Patients uploaded weekly food diaries and bowel movement records for monitoring.
2.2.3 Outcome measures
Patient demographics and tumor-related indicators (age, gender, Body Mass Index (BMI), education level, tumor stage) were recorded. Outcome measures included primary and secondary endpoints assessed pre-intervention and 1 month post-discharge.
2.2.3.1 Primary outcomes
Nutritional indicators (serum albumin, lymphocyte count, PG-SGA, BMI). Fasting blood samples were collected in the morning and analyzed at the hospital's clinical laboratory to determine serum albumin levels and lymphocyte counts. PG-SGA were assessed by the nutritionist. BMI was calculated using the formula: BMI = Weight (kg)/Height (m)2. The nutritionist measured the patients' height and fasting weight using the Meilen hospital-specific integrated ultrasonic height and weight measuring instrument (Model: MSG003).
2.2.3.2 Secondary outcomes
Incidence of HOS and PMASD within 1 month postoperatively. HOS was defined as stoma output >1,500 mL/24 h.
2.2.4 Statistical analysis
SPSS 25.0 was used. Normally distributed continuous data were expressed as mean±SD and analyzed with independent t-tests; non-normally distributed data were expressed as median (P25, P75) and analyzed with Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were described as counts and percentages, analyzed with χ2 tests, Fisher's exact test, or rank-sum tests. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Comparison of general patient characteristics
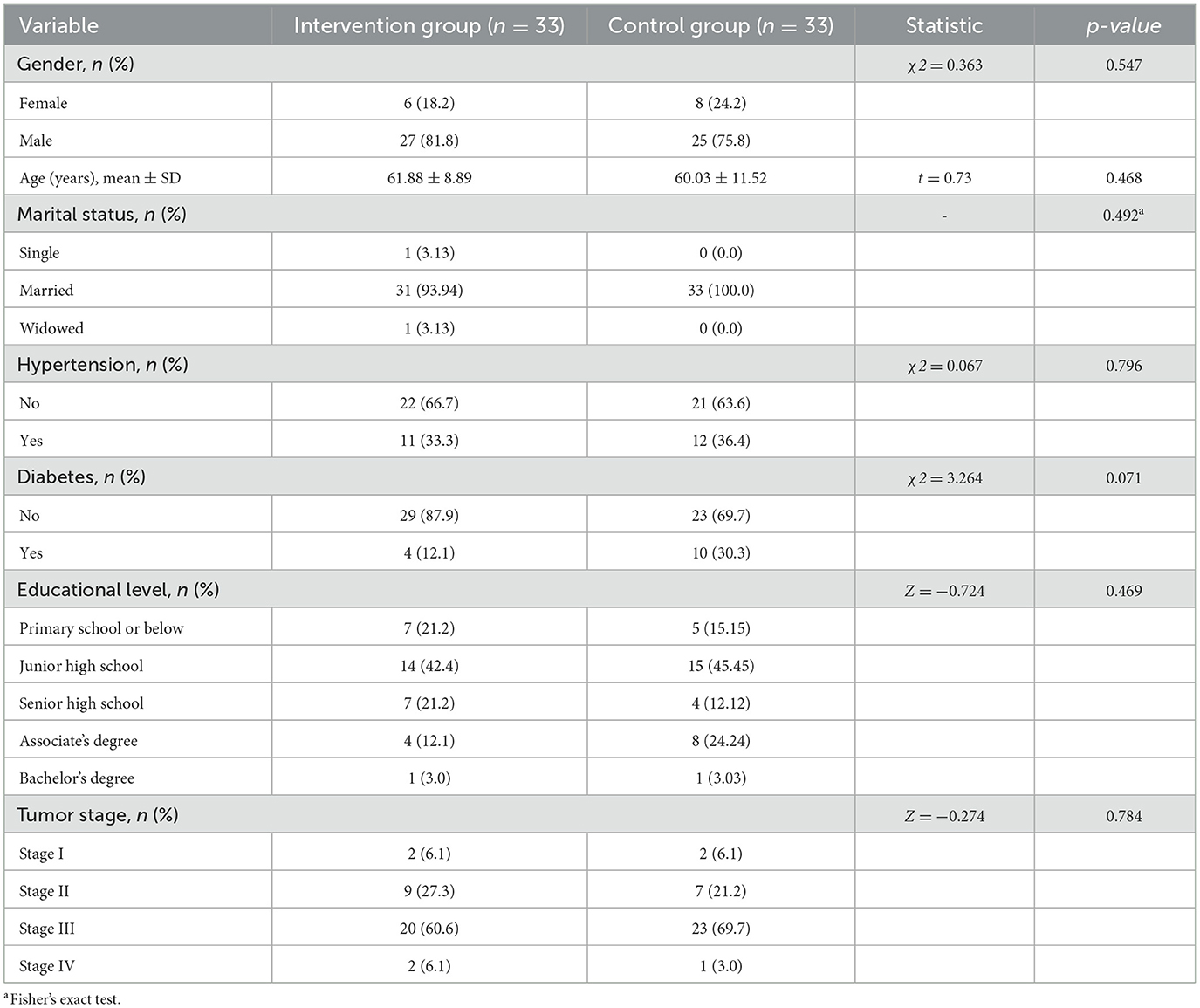
A total of 66 patients were included in this study, all of whom completed the 1-month postoperative follow-up. There were no statistically significant differences in the general characteristics between the two groups (p > 0.05, Table 2).
3.2 Comparison of nutritional indicators
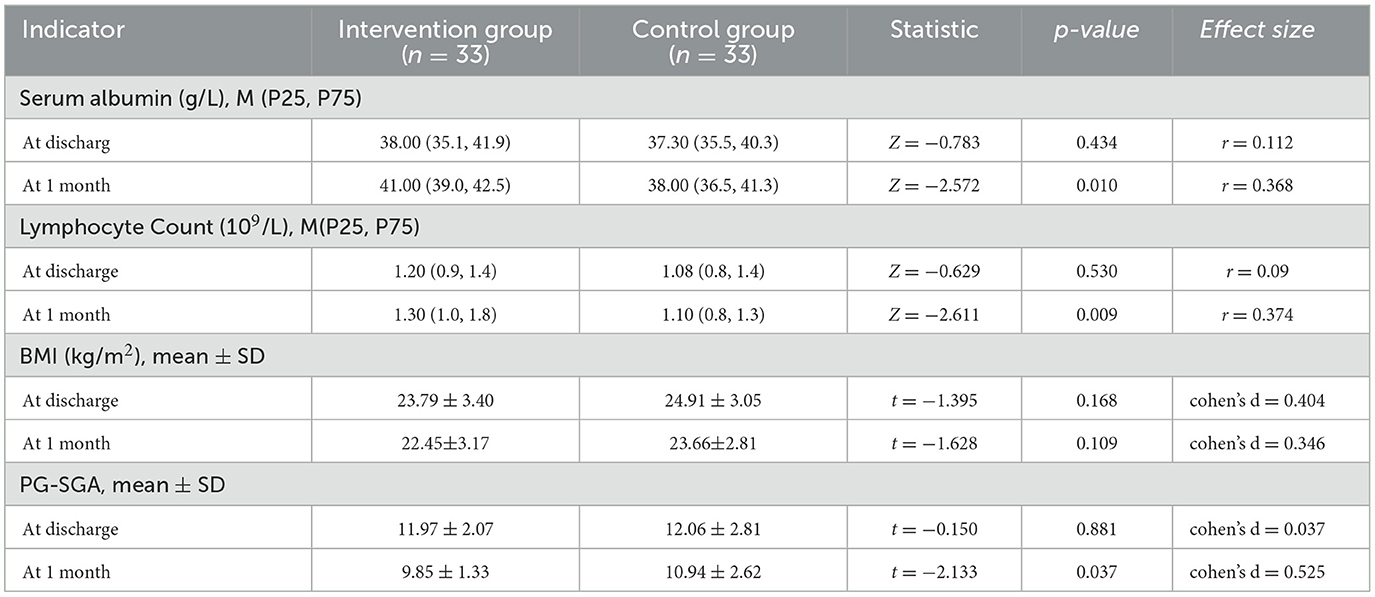
Comparison results of nutritional indicators between the two groups at discharge and 1 month postoperatively are shown in Table 3. There were no significant differences in nutritional indicators between the two groups at baseline. At 1 month postoperatively, significant differences were observed in serum albumin, lymphocyte count, and PG-SGA scores (P < 0.05), but no significant difference was found in BMI changes between the two groups.
3.3 Comparison of complication rates
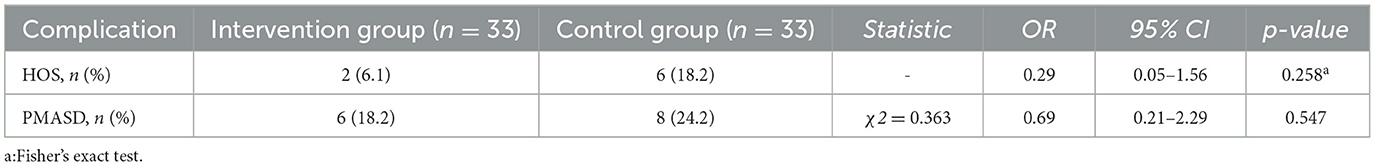
Comparison results of HOS and PMASD incidence rates within 1 month postoperatively between the two groups are shown in Table 4. Two patients in the control group were readmitted due to dehydration caused by HOS. Although the incidence of HOS and PMASD was higher in the control group than in the intervention group, there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups.
4 Discussion
4.1 Scientific rationale and practical value of the home dietary management program
The development of this home dietary management program was grounded in current evidence-based guidelines and clinical best practices. It integrates key aspects such as staged dietary transition, macronutrient and micronutrient optimization, fluid and electrolyte balance, fiber modulation, eating behavior coaching, and stoma output monitoring. This comprehensive and structured approach addresses the complex nutritional needs of ileostomy patients and provides actionable strategies for home implementation.
In clinical settings, patients with ileostomy often report confusion and anxiety regarding dietary choices. Prior surveys indicate that approximately 55% of patients feel overwhelmed by postoperative dietary restrictions and uncertain about appropriate food selection (10). Although guidelines suggest resumption of low-residue semi-liquid diets within the first week and regular diets by the second postoperative week (11), study findings reveal that 16.74% of patients remain on liquid or semi-liquid diets beyond 2 weeks postoperatively, predisposing them to malnutrition (12). This discrepancy highlights a gap between guidelines and patient behaviors, underscoring the need for individualized, behavior-oriented interventions.
This program addresses that gap by offering tailored, structured guidance. Through collaborative efforts between stoma therapists and clinical dietitians, the program respects preoperative eating habits while promoting gradual adaptation through weekly follow-ups. The emphasis on patient autonomy and continuous engagement helps establish self-management capabilities. These findings are aligned with previous studies (13), yet this study adds value by operationalizing dietary guidance into a home-based model and confirming its feasibility and acceptability among patients post-ileostomy.
4.2 Program effectively supports early nutritional recovery
Both groups demonstrated significant improvements in serum albumin, total lymphocyte count, and PG-SGA scores 1 month after surgery, with the intervention group showing more pronounced gains. This reinforces the nutritional benefit of structured home dietary interventions. The observed outcomes are consistent with Lin's findings (14), yet our study expands on them by incorporating micronutrient and fiber management into the intervention, which was less emphasized in prior work.
Interestingly, BMI declined slightly in both groups at 1 month, mirroring the findings of Vasilopoulos et al. (15), who attributed weight loss to postoperative catabolism and fluid shifts. Kim et al. (16) reported continued BMI reduction up to 40 days post-surgery, hypothesizing that intestinal adaptation post-ileostomy plays a role. These findings suggest that while short-term nutritional biomarkers may recover with intervention, anthropometric parameters like BMI require longer follow-up and possibly adjusted energy targets.
The high stoma output characteristic of ileostomy leads to nutrient losses—particularly protein, electrolytes, and micronutrients—contributing to protein-energy malnutrition in over half of patients (17). This program addressed this by recommending high-protein intake (1.5–2.5 g/kg/day), with energy intake increased by 30–50% based on individual needs. Compared to earlier studies (18, 19), this study introduced a more nuanced approach by incorporating stoma output monitoring and adjusting macronutrients in real-time, showing favorable trends in immune and nutritional markers.
Moreover, the program's emphasis on refined starches and low-fiber foods for output control was supported by previous research (18, 19). However, unlike Lee's case-specific report (19), our study systematically applied this strategy across a broader cohort, providing stronger evidence for generalizability. Additionally, the inclusion of soluble fiber, known to enhance nutrient retention and absorption (20), added a novel dimension to traditional dietary recommendations for ileostomy patients.
This study also incorporated medium- and short-chain fatty acids (MCFAs/SCFAs) as alternatives to long-chain fats, based on bile acid metabolism disturbances observed in ileostomy patients (21). These changes are not commonly emphasized in existing nutritional protocols. SCFAs' role in promoting mucosal immunity and maintaining barrier integrity further underscores the long-term benefits of this dietary strategy. Deficiencies in micronutrients such as B12, iron, and zinc, which affect up to 31% of patients (22), were proactively addressed through supplementation—highlighting the program's comprehensiveness and preventive orientation.
4.3 Positive trend in preventing complications: toward clinical relevance
While the reduction in high-output stoma (HOS) incidence in the intervention group (6.06% vs. 18.18%) was not statistically significant (p = 0.258), the observed trend suggests a clinically meaningful reduction in risk. Notably, two patients in the control group required rehospitalization due to severe HOS, underscoring the real-world relevance of dietary management in complication prevention. This finding is particularly important as most previous studies have not quantitatively assessed HOS incidence in relation to dietary interventions.
The intervention emphasized behaviorally informed strategies—frequent small meals, thorough chewing, and avoidance of hypotonic fluids—to modulate intestinal transit and stoma output. While earlier studies (18) have identified these factors individually, the present program integrates them into a patient-centered home regimen, allowing for early detection of dehydration through daily monitoring and prompt intervention. Compared to generalized hydration advice, our program adapted the WHO oral rehydration model to suit ileostomy patients, yielding significant improvements in urea and creatinine levels (23). This practical approach offers a replicable template for clinical guidance and extends the application of standardized hydration strategies to surgical patients.
Regarding peristomal moisture-associated skin damage (PMASD), while no statistically significant differences were found (18.18% vs. 24.24%, p = 0.547), the lower incidence in the intervention group supports the potential of nutritional and behavioral measures in reducing skin complications. As highlighted by Indrebø et al. (24), PMASD is multifactorial, influenced by stoma care practices, nutrition, comorbidities, and skin integrity. Our findings suggest that integrating dietary management into a comprehensive stoma care protocol may contribute to better skin outcomes, though further research is needed to confirm these associations.
5 Limitations
This study used a non-concurrent controlled design, which may be subject to time bias or uncontrollable confounding factors. The lack of statistically significant differences in complication rates between groups is mainly attributed to the small sample size and low statistical power. Additionally, the follow-up period was only 1 month postoperatively, insufficient to evaluate the program's long-term effects and potential impact on ultimate tumor prognosis. Future studies should expand sample sizes and extend follow-up periods.
6 Conclusion
This study constructed and clinically validated an evidence-based, systematic, individualized, and multidisciplinary early postoperative home dietary management program addressing the common malnutrition risks in patients with preventive ileostomy. Preliminary application demonstrates that the program effectively improves short-term postoperative nutritional status (serum albumin, lymphocyte count, PG-SGA scores) and reduces HOS incidence. A positive trend was also observed in reducing peristomal moisture-associated skin damage (PMASD) incidence, though these differences did not reach statistical significance due to sample size and study design limitations. Future research with larger samples, more rigorous designs, and longer follow-up periods is needed to further validate the program's long-term effects, complication prevention efficacy, and impact on patient quality of life.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
JZ: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. YS: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. JL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. SW: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. WS: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. MS: Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by [the Nightingale Scientific Research Project of Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine; Grant number (Y23025)].
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the medical workers and patients involved in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Zhou J, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, Wang S, Chen R, et al. Colorectal cancer burden and trends: comparison between China and major burden countries in the world. Chin J Cancer Res. (2021) 33:1–10. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2021.01.01
3. Ostomy Ostomy Professional Committee Chinese Society of Coloproctology Chinese Medical Doctor Association Chinese Chinese Society of Colorectal Surgery Chinese Chinese Society of Surgery Chinese Medical Association Colorectal Tumor Professional Committee Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Chinese expert consensus on protective ostomy for mid-low rectal cancer (version 2022). Chin J Gastrointest Surg. (2022) 25:471–8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441530-20220421-00169
4. Bai D, Li L, Shen Z, Huang T, Wang Q, Wang Y, et al. Risk factors for developing high-output ileostomy in CRC patients: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. (2021) 21:300. doi: 10.1186/s12893-021-01288-y
5. Du XX, Zou QY, Huo MK, Li J, Jin Y. Correlation between nutritional status and psychosocial adaptation in colorectal cancer patients with ileostomy. J Nurs Adm. (2019) 19:845–8.
6. Liu YG, Wu Y, Cao Q, Qiu Q, Lv GF, Bu LW, et al. The predictive value of diet in peristomal moisture associated skin damage. Chin J Clin Med Res. (2021) 28:485–91.
7. England C, Mitchell A, Atkinson C. Diet after ileostomy study: an observational study describing dietary intake and stoma-related symptoms in people with an ileostomy. J Hum Nutr Diet. (2023) 36:1600–12. doi: 10.1111/jhn.13168
8. Wound Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society. Clinical Guideline: Management of the Adult Patient with a Fecal or Urinary Ostomy (2018). Available online at: https://guidelines.wocn.org/home (Accessed May 30, 2025).
9. Registered Nurses' Association of Ontario. Supporting adults who anticipate or live with an ostomy (2019). Available online at: https://rnao.ca/bpg/guidelines/ostomy (Accessed May 30, 2025).
10. Mitchell A, England C, Atkinson C. Provision of dietary advice for people with an ileostomy: a survey in the UK and Ireland. Colorectal Dis. (2020) 22:2222–31. doi: 10.1111/codi.15268
11. Weimann A, Braga M, Carli F, Higashiguchi T, Hübner M, Klek S, et al. ESPEN practical guideline: clinical nutrition in surgery. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:4745–61. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.03.031
12. Li RH, Zhen L, Zhu ML, Ye XM, Qin F, Zhang XX, et al. Nutritional status and influencing factors in patients undergoing preventive ileostomy. Chin J Nurs. (2025) 60:396–403.
13. Fernández-Gálvez A, Rivera S, Durán Ventura MDC, de la Osa RMR. Nutritional and educational intervention to recover a healthy eating pattern reducing clinical ileostomy-related complications. Nutrients. (2022) 14:3431. doi: 10.3390/nu14163431
14. Lin HY, Chen J, Liu YJ, Lin MJ, Liao XQ, Peng, SL. Nutrition education for patients with rectal cancer undergoing prophylactic ileostomy. J Nurs Sci. (2022) 37:10–4.
15. Vasilopoulos G, Makrigianni P, Polikandrioti M, Tsiampouris I, Karayiannis D, Margari N, et al. Pre- and post-operative nutrition assessment in patients with colon cancer undergoing ileostomy. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:6124. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176124
16. Kim MS, Kim HK, Kim DY, Ju JK. The influence of nutritional assessment on the outcome of ostomy takedown. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. (2012) 28:145–51. doi: 10.3393/jksc.2012.28.3.145
17. Santamaría MM, Villafranca JJA, Abilés J, Ruiz FR, Navarro PU, Goitia BT. Impact of a nutrition consultation on the rate of high output stoma-related readmission: an ambispective cohort study. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:16620. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96136-7
18. Mitchell A, England C, Perry R, Lander T, Shingler E, Searle A, et al. Dietary management for people with an ileostomy: a scoping review. JBI Evid Synth. (2021) 19:2188–306. doi: 10.11124/JBIES-20-00377
19. Lee YJ, Kweon M, Park M. Nutritional management of a patient with a high-output stoma after extensive small bowel resection to treat crohn's disease. Clin Nutr Res. (2019) 8:247–53. doi: 10.7762/cnr.2019.8.3.247
20. Ho CY, Majid HA, Jamhuri N, Ahmad AF, Selvarajoo TA. Lower ileostomy output among patients with postoperative colorectal cancer after being supplemented with partially hydrolyzed guar gum: outcome of a pilot study. Nutrition. (2022) 103–4:111758. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2022.111758
21. Nissinen MJ, Gylling H, Järvinen HJ, Miettinen TA. Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis, conventional ileostomy and ileorectal anastomosis modify cholesterol metabolism. Dig Dis Sci. (2004) 49:1444–53. doi: 10.1023/B:DDAS.0000042244.56689.72
22. Schiergens TS, Hoffmann V, Schobel TN, Englert GH, Kreis ME, Thasler WE, et al. Long-term quality of life of patients with permanent end ileostomy: results of a nationwide cross-sectional survey. Dis Colon Rectum. (2017) 60:51–60. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000000732
23. Migdanis A, Koukoulis G, Mamaloudis I, Baloyiannis I, Migdanis I, Kanaki M, et al. Administration of an oral hydration solution prevents electrolyte and fluid disturbances and reduces readmissions in patients with a diverting ileostomy after colorectal surgery: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Dis Colon Rectum. (2018) 61:840–6. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000001082
Keywords: ileostomy, rectal cancer, dietary management, malnutrition, high-output stoma
Citation: Zhu J, Shen Y, Li J, Wang S, Shang W and Sun M (2025) Construction and application of home dietary management program for postoperative patients with preventive ileostomy for rectal cancer. Front. Nutr. 12:1639987. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1639987
Received: 05 June 2025; Accepted: 25 August 2025;
Published: 12 September 2025.
Edited by:
Marilia Seelaender, University of São Paulo, BrazilReviewed by:
Maha Gasmi, University of Manouba, TunisiaHuma Naqeeb, Women University Mardan, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Shen, Li, Wang, Shang and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juyun Li, bGlqdXl1bmZseUAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Jianhua Zhu†
Jianhua Zhu† Juyun Li
Juyun Li