- 1School of Athletic Training, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 2Badminton Technical and Tactical Analysis and Diagnostic Laboratory, National Academy of Badminton, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Objective: A growing body of evidence confirms that nutritional supplementation strategies combined with resistance training can enhance muscle strength and mass in older adults. However, the optimal supplementation approach remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the comparative efficacy of different nutritional interventions combined with resistance training on muscle strength and mass in healthy older adults and determine the optimal strategy.
Methods: A systematic search was performed across three major biomedical databases (PubMed, Web of Science, and EMbase) to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the effects of nutritional supplementation combined with resistance training on muscle strength and mass in healthy older adults. A total of 19 eligible RCTs were included. The search covered literature from database inception to April 2025. Two researchers independently screened studies against predefined eligibility criteria and assessed methodological quality using the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool. Stata 18.0 was used to conduct network meta-analysis.
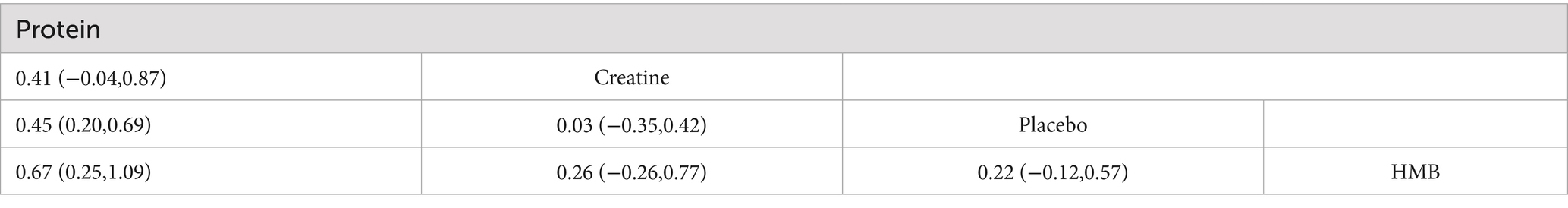
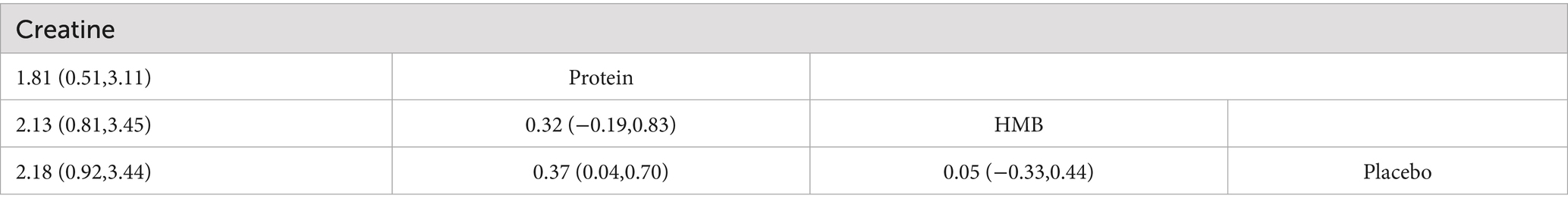
Conclusion: Compared with resistance training alone, protein supplementation combined with resistance training significantly enhanced muscle strength [Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) = 0.45, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.20,0.69; surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) = 98.7%] and muscle mass [Mean Difference (MD) = 0.37, 95%CI: 0.04,0.70],whereas creatine supplementation demonstrated non-significant effects on muscle strength versus training alone (SMD = 0.03, 95% CI: −0.35,0.42) but yielded the most pronounced improvement in muscle mass (MD = 2.18, 95%CI: 0.92,3.44; SUCRA = 99.9%), outperforming both protein and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) interventions, with HMB supplementation critically failing to demonstrate significant benefits for muscle strength (SMD = −0.22, 95%CI: −0.57,0.12) or mass outcomes (MD = 0.05, 95%CI: −0.33,0.44).
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD420251026016.
1 Introduction
With the accelerating pace of global population aging, the World Health Organization predicts that the proportion of individuals aged 65 and older will reach 16% by 2050 (1). This demographic shift has positioned age-related sarcopenia as a major public health challenge. Recent epidemiological data indicate that the prevalence of sarcopenia among community-dwelling older adults aged 60 and above ranges from 10 to 27% worldwide (2). Sarcopenia is associated with increased risks of falls (OR = 3.21), disability (HR = 1.79), and all-cause mortality (RR = 1.58) (3).
The degenerative loss of muscle mass and function, a hallmark of sarcopenia, is closely linked to age-related anabolic resistance (4). Resistance training serves as a critical intervention to mitigate muscle decline. The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) recommends that older adults engage in systematic resistance training ≥2 times per week at 60–80% of 1-repetition maximum (1RM) intensity for 8–12 weeks to significantly enhance muscle strength and lean body mass (5). Beyond exercise interventions, various nutritional supplements have emerged as adjunct strategies to counteract muscle atrophy, including whey protein, creatine, and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB). These supplements act through distinct physiological pathways: whey protein provides essential amino acids (particularly leucine) to activate the mTORC1 pathway, thereby stimulating muscle protein synthesis (6); creatine enhances phosphocreatine reserves to improve type II muscle fiber recruitment (7); and HMB inhibits the ubiquitin-proteasome system to reduce muscle breakdown (8). While these mechanisms suggest potential benefits, their efficacy in practice is often constrained by factors such as insufficient nutritional support and inadequate training stimulus. For instance, when protein intake falls below 0.8 g/kg/day, the efficiency of resistance training-induced protein synthesis may decrease by 42% (9). Furthermore, even with adequate protein supplementation, up to 56% of amino acids may remain underutilized in the absence of mechanical loading (10). Thus, combined interventions integrating nutritional supplementation with resistance training are considered synergistic, particularly in older populations.
Although multiple randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have validated the effectiveness of resistance training combined with various nutritional strategies, existing evidence has limitations. Previous studies predominantly focus on evaluating single-nutrient interventions combined with resistance training, lacking direct or indirect comparisons among multiple nutritional approaches (11). Additionally, age-related metabolic alterations may modify dose–response relationships for nutritional supplements in older adults, warranting further investigation (12).
Network Meta-Analysis (NMA), an advanced evidence synthesis methodology, enables the integration of direct and indirect comparative evidence to rank multiple interventions quantitatively (13). This study is the first to employ NMA to systematically compare the effects of three mainstream nutritional strategies—protein, creatine, and HMB—combined with resistance training on muscle strength and mass in healthy older adults. The findings aim to establish a hierarchy of relative efficacy among these supplements, providing high-level evidence to inform personalized exercise-nutrition prescriptions and offering critical clinical insights for delaying age-related muscle decline.
2 Methods
This study adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, specifically the PRISMA extension for Network Meta-Analysis (PRISMA-NMA) (14). The protocol was prospectively registered in PROSPERO (Registration No. CRD420251026016).
2.1 Search strategy and inclusion/exclusion criteria
Two researchers independently conducted a systematic search across three major biomedical databases (PubMed, Web of Science, and EMbase) from inception to April 2025. The search strategy utilized the following Boolean terms: (“nutritional supplements” OR “dietary supplements” OR “nutrients”) AND (“resistance training” OR “strength training” OR “resistance exercise” OR “strength exercise”) AND (“elderly” OR “older adults” OR “aged” OR “aging population”) AND (“muscle strength” OR “muscle mass” OR “strength performance” OR “muscle hypertrophy”).
2.1.1 Inclusion criteria
(1) Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with accessible full texts.
(2) Participants: Community-dwelling adults aged ≥60 years (15), free from major chronic diseases, with normal physical/cognitive function and mental health (16).
(3) Interventions: Detailed protocols for nutritional supplementation (type, dose, frequency) and resistance training (intensity, frequency, duration).
(4) Outcomes: At least one validated measure of muscle strength or mass.
2.1.2 Exclusion criteria
(1) Insufficient intervention details.
(2) Incomplete baseline/post-intervention data.
(3) Outcomes unrelated to muscle strength/mass.
2.2 Study screening and data extraction
Search results were imported into EndNote X8 (Clarivate Analytics) for removal of duplicate records. Two reviewers independently screened titles, abstracts, and full texts against eligibility criteria.
Data extraction was performed independently by two reviewers using a standardized template, with discrepancies resolved through consultation with a senior investigator. Extracted data included:
1. Study characteristics: First author, publication year, country.
2. Participant demographics: Sample size, sex distribution, mean age.
3. Intervention details: Nutritional supplement type (e.g., whey protein, creatine), dosage, resistance training protocol (e.g., intensity, frequency), and duration.
4. Outcome metrics: Mean and standard deviation (SD) for muscle strength and mass pre-and post-intervention. Missing data were requested from corresponding authors via email.
2.3 Risk of bias assessment
Two researchers assessed the methodological quality of included studies using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool. The Cochrane tool consists of the following domains: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data reporting, selective reporting, and other biases. Each domain was categorized as low risk, high risk, or unclear risk of bias. The risk of bias assessment was visualized using RevMan 5.1. A study was classified as high risk if it demonstrated high risk of bias in two or more domains, as low risk if five or more domains were rated as low risk, and as moderate risk in all other cases (17).
2.4 Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using Stata 18.0 software. For studies investigating muscle strength outcomes, which involved continuous numerical data with heterogeneous assessment tools and measurement units, the standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) was employed as the effect size metric using random-effects models. In contrast, mean difference (MD) with 95% CI was utilized to pool effect sizes for muscle mass outcomes under fixed-effect models, due to the consistency in measurement units across studies and low heterogeneity confirmed by the global inconsistency test (p = 0.789). Global inconsistency was assessed through the node-splitting approach. This model selection strategy follows the Cochrane Handbook recommendations for addressing clinical heterogeneity in network meta-analyses (18). The significance of efficacy differences in muscle strength and mass was examined using SMD and MD (95% CI), with statistical significance defined as p < 0.05. The efficacy ranking of nutritional interventions was determined by calculating the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA). SUCRA values range from 0 to 100%, where higher values indicate greater probability of superior therapeutic effectiveness. Funnel plots were used to assess publication bias and small study effects in the NMA.
3 Results
3.1 Search results
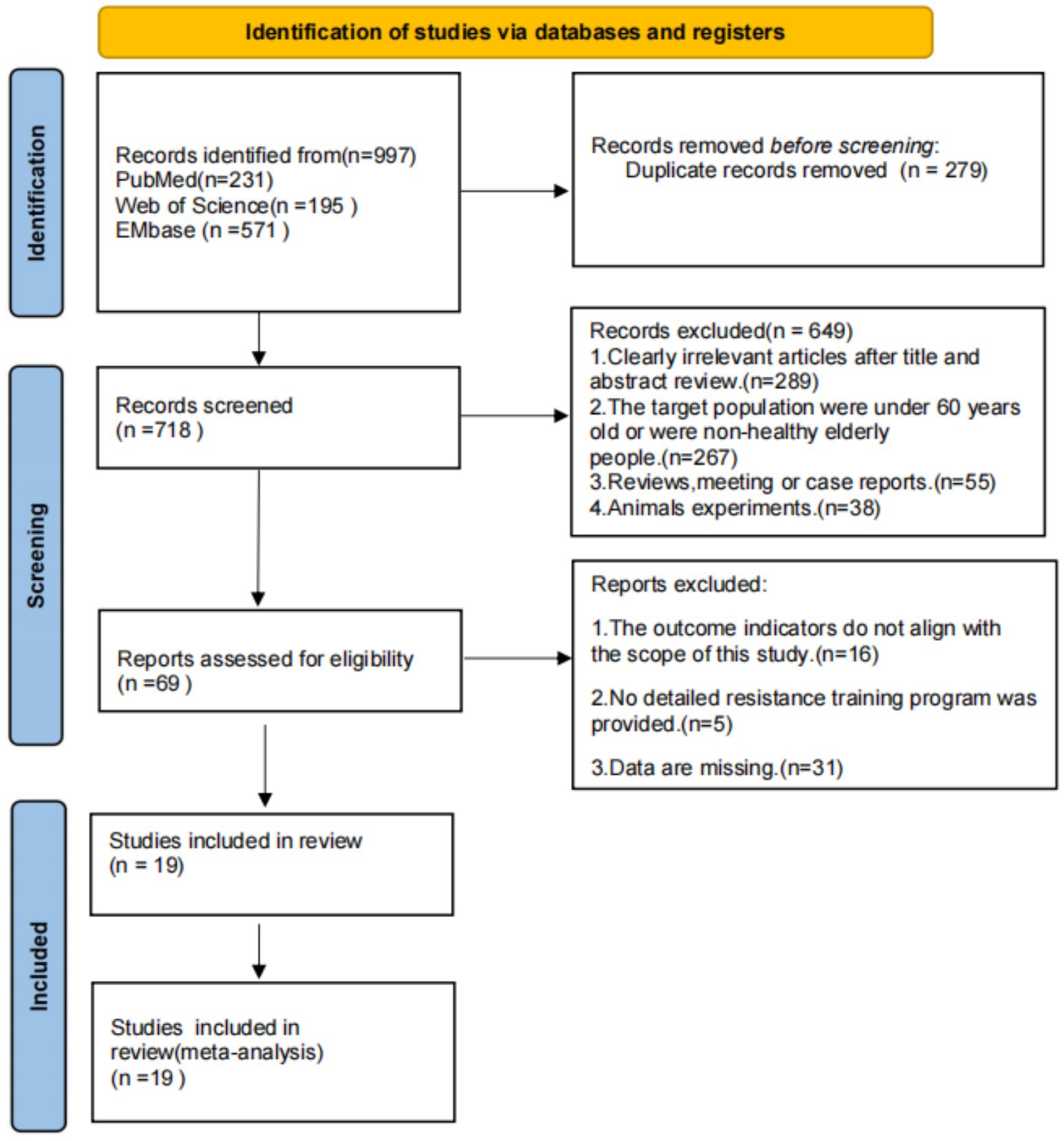
A systematic search across PubMed, Web of Science, and EMbase yielded 997 records. After applying eligibility criteria, 19 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included in the network meta-analysis (NMA). The study selection process, adhering to PRISMA guidelines, is detailed in Figure 1.
3.2 Characteristics of included studies
The 19 studies in this network meta-analysis involved 997 healthy older adults and evaluated three interventions: 11 studies focused on protein supplementation, 5 on creatine supplementation, and 3 on HMB supplementation. Muscle strength outcomes were reported in 16 studies, while muscle mass outcomes were reported in 18 studies. The basic characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1.
3.3 Risk of bias assessment
As illustrated in Figure 2, the assessment revealed domain-specific limitations frequently observed in sports nutrition RCTs. Specifically, allocation concealment demonstrated unclear risk in 73.7% of studies (14/19), while blinding of participants and personnel showed unclear risk in 68.4% (13/19). This pattern reflects the inherent complexities of blinding procedures and the frequent impracticality of complete blinding in nutritional interventions owing to supplement palatability or administration routes (19, 20). Performance bias was rated high risk in 10.5% of studies (2/19) due to unblinded researchers. Detection bias exhibited unclear risk in 89.5% of studies (17/19) owing to insufficient methodological details regarding muscle mass assessment techniques. None of the RCTs included in this network meta-analysis were classified as high risk (defined as ≥2 high-risk domains), while 31.6% (6/19) achieved low risk and 68.4% (13/19) moderate risk.
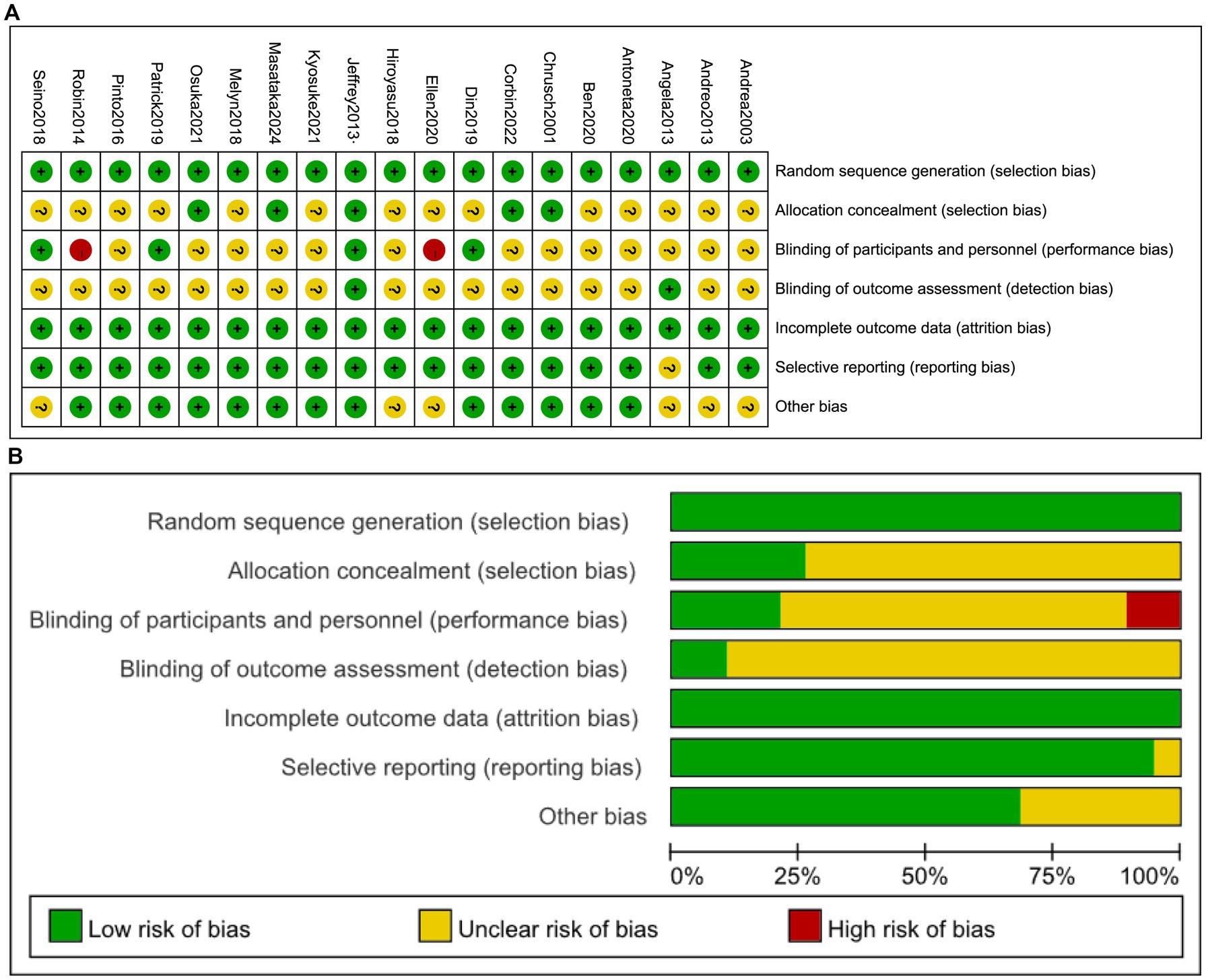
Figure 2. Risk of bias assessment: (A) across all studies; (B) per-item risk distribution within individual studies.
3.4 Network meta-analysis results
3.4.1 Consistency check
Consistency tests for the network meta-analysis revealed no significant inconsistency among the included RCTs. For muscle strength outcomes in older adults (p = 0.2001) and muscle mass outcomes (p = 0.789), both p-values exceeded 0.05, indicating homogeneity across studies.
3.4.2 Network geometry
The network geometry diagrams (Figures 3A,B) illustrate the comparative evidence structure of nutritional interventions for muscle strength and mass outcomes. Each node represents an intervention (placebo, protein, creatine, HMB), with node sizes proportional to the number of participants and line thickness reflecting the number of direct comparisons between interventions. The placebo node serves as the common comparator anchoring the network. For muscle strength outcomes (Figure 3A), protein supplementation demonstrates the most extensive direct evidence connections, while creatine shows predominant centrality in the muscle mass network (Figure 3B).
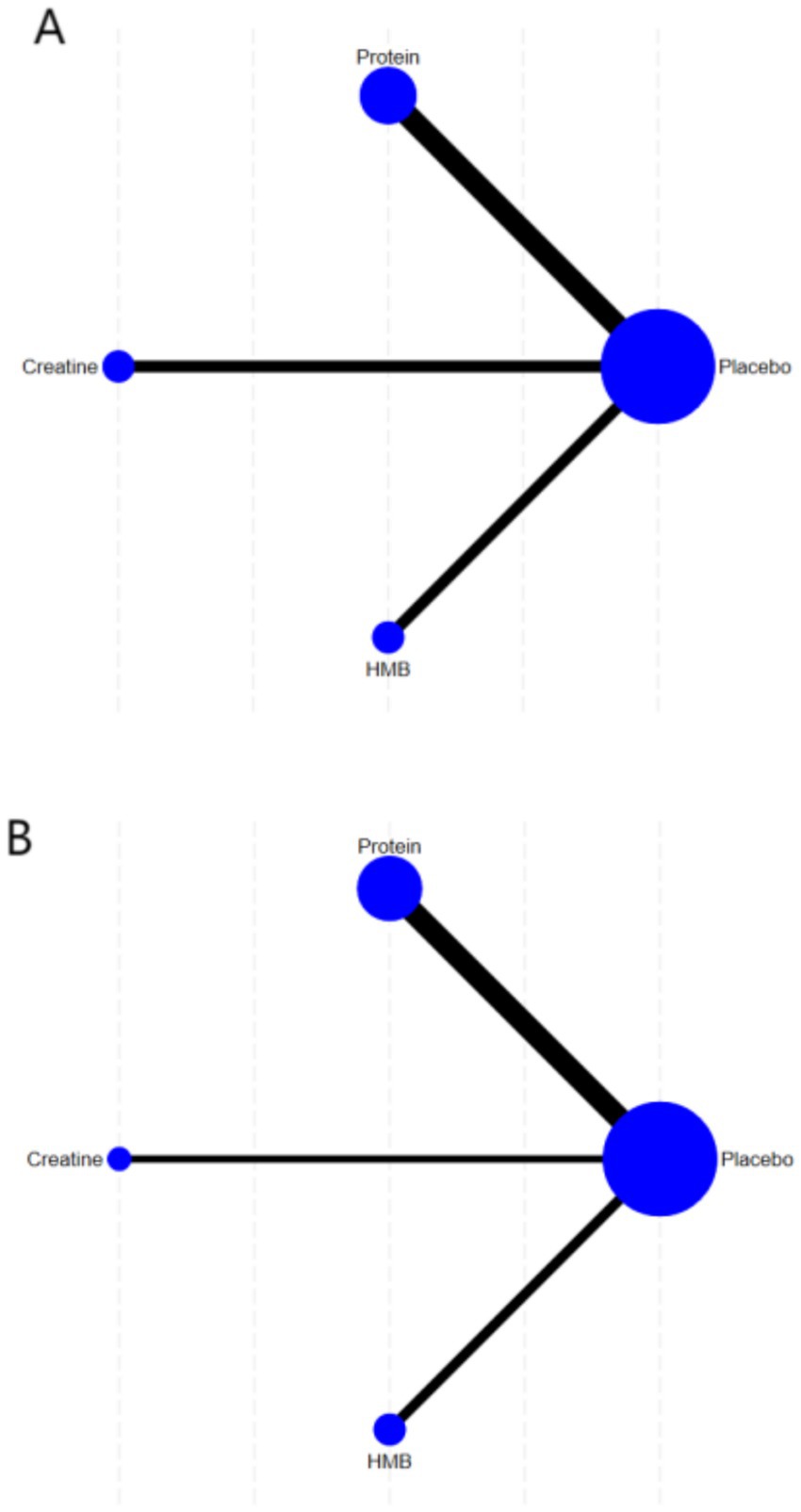
Figure 3. Network geometry of interventions for (A) muscle strength outcomes and (B) muscle mass outcomes.
3.4.3 Ranking probabilities
As shown in Figure 4, based on the Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) values, protein supplementation ranked highest for improving muscle strength in healthy older adults (SUCRA: 98.7%), followed by creatine (SUCRA: 48.9%), placebo (SUCRA: 43.8%), and HMB (SUCRA: 8.7%). For muscle mass, creatine supplementation ranked highest (SUCRA: 99.9%), followed by protein (SUCRA: 62.5%), HMB (SUCRA: 23.9%), and placebo (SUCRA: 13.7%).
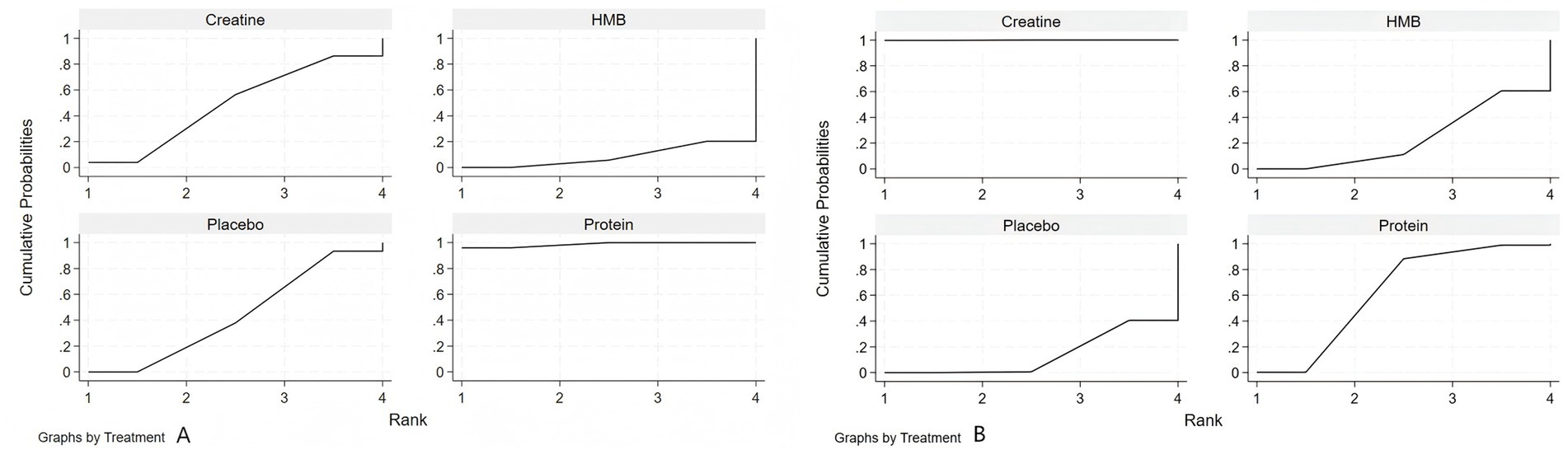
Figure 4. Surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) for nutritional interventions on (A) muscle strength and (B) muscle mass in healthy older adults.
3.4.4 Meta-analysis results
The network meta-analysis (Tables 2, 3) demonstrated that, compared to resistance training alone (SUCRA: 43.8%), protein supplementation significantly improved muscle strength (SMD = 0.45, 95%CI: 0.20 to 0.69; SUCRA: 98.7%). Creatine (MD = 2.18, 95% CI: 0.93 to 3.44; SUCRA: 99.9%) and protein (MD = 0.37, 95% CI: 0.04 to 0.70; SUCRA: 62.5%) significantly enhanced muscle mass.
Pairwise comparisons revealed that protein supplementation was superior to HMB for improving muscle strength (SMD = −0.67, 95% CI: −1.09 to −0.25; SUCRA: 8.7%). Creatine supplementation outperformed both protein (MD = 1.81, 95% CI: 0.51 to 3.11) and HMB (MD = −2.13, 95% CI: −3.45 to −0.81; SUCRA: 23.9%) in increasing muscle mass.
3.4.5 Publication bias
Funnel plots assessing the effects of nutritional interventions on muscle strength and mass in healthy older adults are shown in Figures 5A,B. Both funnel plots exhibited approximate symmetry, suggesting well-distributed studies and a low likelihood of publication bias.
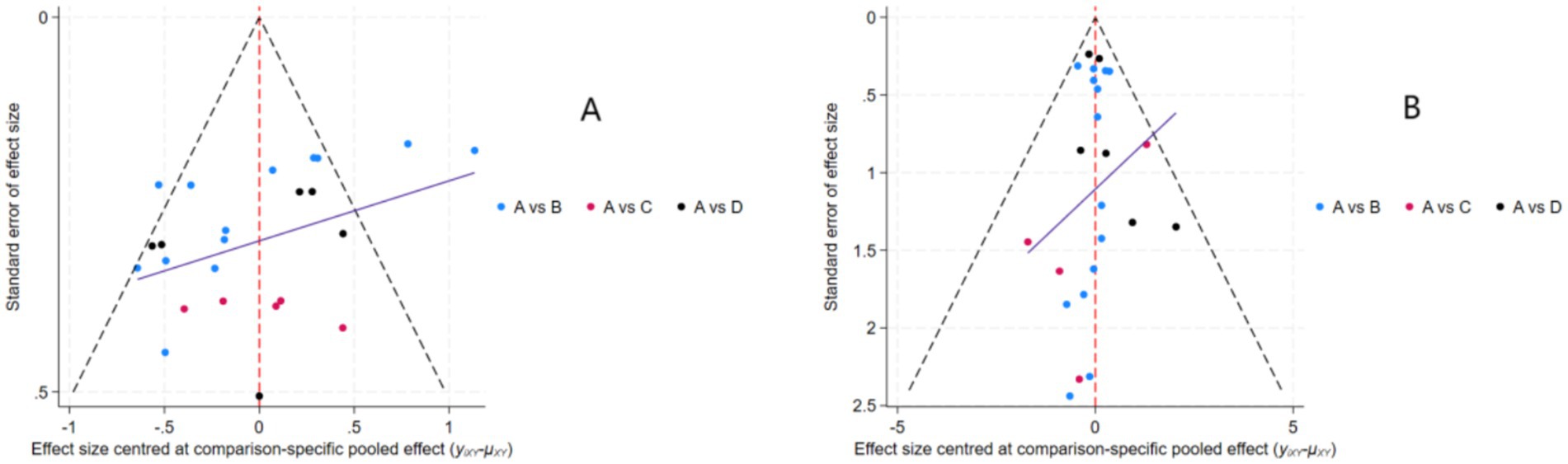
Figure 5. Funnel plots assessing publication bias and small-study effects: (A) muscle strength outcomes; (B) muscle mass outcomes. Intervention nodes: A = Placebo; B = Protein; C = Creatine; D = HMB.
4 Discussion
This study represents the first network meta-analysis (NMA) to compare the efficacy of protein, creatine, and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) supplementation combined with resistance training in improving muscle strength and mass among healthy older adults. The findings demonstrate that protein supplementation significantly enhances both muscle strength (SMD = 0.45, 95%CI: 0.20,0.69) and mass (MD = 0.37, 95%CI: 0.04,0.70), ranked second only to creatine in terms of muscle mass improvement. (MD = 1.81, 95%CI: 0.51,3.11). Creatine supplementation yielded the most pronounced effects on muscle mass (MD = 2.18, 95%CI: 0.92,3.44; SUCRA = 99.9%), surpassing both protein and HMB. In contrast, HMB supplementation demonstrated no statistically significant effects on either muscle strength (SMD = −0.22, 95%CI: −0.57,0.12) or muscle mass outcomes (MD = 0.05, 95%CI: −0.33,0.44).
4.1 Protein supplementation
The superior efficacy of protein supplementation aligns with its critical role in counteracting age-related anabolic resistance, a hallmark of sarcopenia pathogenesis. Older adults require higher-quality protein intake (≥1.2 g/kg/day) to stimulate muscle protein synthesis (MPS) when combined with resistance training (21). The dosage range in this analysis aligns with Morton et al.’s (9) threshold for optimizing muscle adaptation, likely explaining the observed benefits.
For instance, Angela et al. reported a 1.8 kg increase in lean mass following 12 weeks of 40 g/day whey protein supplementation, while Hiroyasu et al. achieved a 1.2 kg gain with 1.2 g/kg/day over 24 weeks. These findings corroborate Liao et al.’s (22) meta-analysis, which synthesized 12 RCTs and concluded that 30–45 g/day of whey protein combined with ≥8 weeks of resistance training increases lean mass by 1.4 kg in older adults. Notably, Robin et al. (41) demonstrated equivalent efficacy using whole-food protein sources (220 g red meat, 6 servings/week) (23), supporting a “food-first” nutritional strategy. However, age-related declines in mastication capacity may limit the practicality of whole-food approaches in this population (24).
4.2 Creatine supplementation
Creatine supplementation combined with resistance training demonstrated a significant improvement in muscle mass (MD = 2.18) in healthy older adults, with an effect size 5.9 times greater than that of protein. Its absolute superiority in SUCRA rankings (99.9%) underscores its efficacy. These findings align with creatine’s unique role in cellular energy metabolism. By increasing phosphocreatine reserves, creatine facilitates rapid ATP regeneration, prolongs high-intensity exercise during resistance training, and amplifies mechanical tension on muscle fibers (25). Although creatine did not show statistically significant effects on muscle strength (SMD = 0.03), its pronounced impact on muscle mass suggests that it promotes structural remodeling via myofibrillar protein accretion rather than neuromuscular adaptation (7), a mechanism well-suited to the anabolic characteristics of aging muscle. Creatine enhances muscle hypertrophy through two synergistic pathways, Direct osmotic effects: Increased intramyocellular creatine concentrations elevate osmotic pressure, stimulating cellular hydration and activating protein synthesis signaling pathways (26).
Indirect mechanical overload: Improved training capacity enhances mechano-growth factor release, further promoting hypertrophy (27).
In the studies included in this NMA, Andrea et al. and Chrusch et al. utilized a loading phase (20–25 g/day for 5 days) followed by maintenance dosing (5 g/day), achieving lean mass gains of 2.3–3.1 kg. These results support Candow et al.’s (28) “creatine loading threshold theory” for older adults, which posits that reduced endogenous creatine synthesis (30% lower than in younger adults) necessitates higher doses to achieve creatine pool saturation (29). The average intervention duration of 12 weeks in creatine-supplemented groups aligns with Forbes et al.’s (30) systematic review, which concluded that ≥8 weeks are required for cumulative effects on muscle mass.
4.3 HMB supplementation
HMB, a metabolite of leucine, theoretically functions through dual mechanisms: suppressing muscle catabolism by inhibiting the ubiquitin-proteasome system to reduce muscle breakdown (31), and activating protein synthesis via stimulation of the mTOR pathway (32). This study found that HMB supplementation combined with resistance training failed to significantly improve muscle strength (SMD = −0.22, 95%CI: −0.57, 0.12) or muscle mass (MD = 0.05, 95%CI: −0.33, 0.44) in healthy older adults, with HMB ranking lowest in SUCRA values (strength: 8.7%; muscle mass: 23.9%). These conclusions align closely with both the 2023 ABCD Supplement Classification Framework updated by the Australian Institute of Sport (AIS), which categorizes HMB as Class C evidence (33). Furthermore, a meta-analysis by Javier et al. demonstrated that for adults aged 50 to 80 years, HMB supplementation adjunctive to conventional physical exercise regimens either yielded no statistically significant effects or elicited only marginal improvements in body composition parameters, muscle strength outcomes, or physical performance metrics (34). Therefore, existing evidence does not confirm clinically significant benefits of HMB with resistance training in healthy older populations.
Despite variations in the resistance training protocols (intensity, frequency, duration) and supplement dosages among the included studies, these factors are unlikely to substantially confound the primary conclusions of the present study.
Regarding training frequency, all interventions met or exceeded the minimum threshold (≥2 sessions/week) recommended by the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) for older adults (5). Furthermore, Pina et al. demonstrated that resistance training (RT)-induced muscular adaptations occur in older adults regardless of whether training is performed twice or three times weekly, with both frequencies providing similar adaptations (35). Training intensity could not be quantitatively evaluated due to the lack of precise %1RM data reported in the original studies. However, all trials explicitly employed standardized resistance training, inherently ensuring therapeutic intensity ranges. Concerning intervention duration, the variation in resistance training periods (6–24 weeks) across the included studies had a limited impact on the efficacy assessment. A systematic review by Brittany et al. indicated that in untrained individuals, significant increases in muscle hypertrophy relative to baseline can be expected within the initial weeks following the commencement of training. However, this growth trajectory tends to plateau, and the rate of gain slows, around approximately 12 weeks (36).
A meta-analysis by Ryoichi et al. noted that during resistance training, the incremental benefit of protein supplementation rapidly diminishes when total protein intake exceeds 1.3 g/kg BW/d. This finding suggests that the efficiency of ingested protein conversion into lean body mass (LBM) decreases when sufficient or greater amounts of protein are consumed (37). For the different forms of HMB supplementation, the International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) states that two forms of HMB are currently used: HMB-Ca and HMB-FA. HMB-FA may increase plasma absorption and retention of HMB to a greater extent than HMB-Ca. However, research on HMB-FA is in its early stages, and currently, insufficient evidence exists to definitively support the superiority of either form (38).
In summary, coupled with the present network meta-analysis demonstrating no statistically significant global inconsistency (muscle strength: p = 0.2001; muscle mass: p = 0.789; both > 0.05), these findings collectively indicate that the results of this study are robust.
4.4 Safety
Long-term safety evidence supports the sustained use of creatine and protein supplementation in older adults. A 5-year follow-up study by Gualano et al. (39) demonstrated that creatine supplementation (5 g/day) in healthy older adults did not induce renal dysfunction (ΔeGFR = −1.2 mL/min). However, caution is warranted for ultra-high protein intake (>2.0 g/kg/day), which may accelerate glomerulosclerosis; regular monitoring of urinary nitrogen excretion is recommended (40). For HMB, long-term safety data remain limited, with no systematic evidence from extended monitoring studies. Further research is required to validate its safety profile.
4.5 Limitations
This study has several limitations that warrant careful consideration. First, although 11 randomized controlled trials on protein supplementation were systematically identified and included, variations in protein sources and the limited number of eligible studies precluded subgroup analyses by protein type. This limitation may obscure the dose–response relationships specific to particular protein forms. Second, the evidence base for HMB interventions remains relatively limited. Only three studies with small sample sizes were included, notably the study by Din et al., which involved only 16 participants. This may lead to an underestimation of the potential effects of HMB, particularly when considering age-related differences in HMB absorption efficiency among older adults. Lastly, future investigations should prioritize larger sample sizes and incorporate newer nutritional supplements. This will enable the exploration of synergistic mechanisms between different supplements, thereby providing more refined evidence to support personalized nutrition and exercise regimens.
5 Conclusion
This network meta-analysis demonstrates that protein supplementation combined with resistance training significantly improves both muscle strength and mass in healthy older adults, with comparable efficacy to creatine for strength enhancement. Creatine supplementation exhibited superior efficacy for increasing muscle mass, outperforming both protein and HMB. In contrast, HMB supplementation provided no significant benefits for either outcome. To maximize the synergistic effects of nutrition and resistance training, integrated supplementation strategies prioritizing protein and creatine should be developed, with careful attention to dosage, formulation, and intervention duration. Future studies should clarify response heterogeneity across older subpopulations (e.g., sarcopenic individuals) and establish long-term safety and dose–response relationships to optimize personalized exercise-nutrition regimens.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YM: Writing – original draft. RY: Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – original draft. TC: Writing – original draft. XL: Writing – review & editing. XS: Writing – review & editing. DL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Anonymous. Collaborative sales force automation tools – drivers and challenges. Popul Dev Rev. (2020) 2020:857–8. doi: 10.15444/GMC2020.06.08.02
2. Cruz-Jentoft, AJ, Bahat, G, Bauer, J, Boirie, Y, Bruyère, O, Cederholm, T, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. (2019) 48:16–31. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afy169
3. Beaudart, C, Zaaria, M, Pasleau, F, Reginster, JY, and Bruyere, O. Health outcomes of sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0169548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169548
4. Wall, BT, Gorissen, SH, Pennings, B, Koopman, R, Groen, BBL, Verdijk, LB, et al. Aging is accompanied by a blunted muscle protein synthetic response to protein ingestion. PLoS One. (2015) 10:11. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140903
5. Mazzeo, RS, Cavanagh, P, Evans, WJ, Fiatarone, M, Hagberg, J, McAuley, E, et al. Exercise and physical activity for older adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. (1998) 30:992–1008. doi: 10.1097/00005768-199806000-00033
6. Bauer, J, Biolo, G, Cederholm, T, Cesari, M, Cruz-Jentoft, AJ, Morley, JE, et al. Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: a position paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2013) 14:542–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.05.021
7. Candow, DG, Vogt, E, Johannsmeyer, S, Forbes, SC, and Farthing, JP. Strategic creatine supplementation and resistance training in healthy older adults. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab Physiol Appl Nutr Metab. (2015) 40:689–94. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2014-0498
8. Oktaviana, J, Zanker, J, Vogrin, S, and Duque, G. The effect of β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) on sarcopenia and functional frailty in older persons: a systematic review. J Nutr Health Aging. (2019) 23:145–50. doi: 10.1007/s12603-018-1153-y
9. Morton, RW, Murphy, KT, McKellar, SR, Schoenfeld, BJ, Henselmans, M, Helms, E, et al. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression of the effect of protein supplementation on resistance training-induced gains in muscle mass and strength in healthy adults. Br J Sports Med. (2018) 52:376–84. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-097608
10. Churchward-Venne, TA, Burd, NA, and Phillips, SM. Nutritional regulation of muscle protein synthesis with resistance exercise: strategies to enhance anabolism. Nutr Metab. (2012) 9:40. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-40
11. Jansen, JP, and Cope, S. Meta-regression models to address heterogeneity and inconsistency in network meta-analysis of survival outcomes. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2012) 12:152. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-152
12. Landi, F, Calvani, R, Cesari, M, Tosato, M, Martone, AM, Ortolani, E, et al. Sarcopenia: an overview on current definitions, diagnosis and treatment. Curr Protein Pept Sci. (2018) 19:633–8. doi: 10.2174/1389203718666170607113459
13. Salanti, G, Del Giovane, C, Chaimani, A, Caldwell, DM, and Higgins, JPT. Evaluating the quality of evidence from a network meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e99682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099682
14. Hutton, B, Salanti, G, Caldwell, DM, Chaimani, A, Schmid, CH, Cameron, C, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. (2015) 162:777–84. doi: 10.7326/M14-2385
15. Beard, JR, Officer, AM, and Cassels, AK. The world report on ageing and health. Gerontologist. (2016) 56:S163–6. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnw037
16. Bousquet, J, Kuh, D, Bewick, M, Standberg, T, Farrell, J, Pengelly, R, et al. Operational definition of active and healthy ageing (aha): a conceptual framework. J Nutr Health Aging. (2015) 19:955–60. doi: 10.1007/s12603-015-0589-6
17. Wang, M, Chen, H, Yang, F, Xu, X, and Li, J. Effects of digital psychotherapy for depression and anxiety: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2023) 338:569–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.06.057
18. Cumpston, M, Li, T, Page, MJ, Chandler, J, Welch, VA, Higgins, JPT, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 10:ED000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142
19. Martínez-López, E, Pérez-Guerrero, EE, Torres-Carrillo, NM, López-Quintero, A, Betancourt-Núñez, A, and Gutiérrez-Hurtado, IA. Methodological aspects in randomized clinical trials of nutritional interventions. Nutrients. (2022) 14:2365. doi: 10.3390/nu14122365
20. Stadelmaier, J, Roux, I, Petropoulou, M, and Schwingshackl, L. Empirical evidence of study design biases in nutrition randomised controlled trials: a meta-epidemiological study. BMC Med. (2022) 20:330. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02540-9
21. Phillips, SM, Chevalier, S, and Leidy, HJ. Protein “requirements” beyond the RDA: implications for optimizing health. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. (2016) 41:565. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2015-0550
22. Liao, CD, Wu, YT, Tsauo, JY, Chen, PR, Tu, YK, Chen, HC, et al. Effects of protein supplementation combined with exercise training on muscle mass and function in older adults with lower-extremity osteoarthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized trials. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2422. doi: 10.3390/nu12082422
23. Ames, BN. Prolonging healthy aging: Longevity vitamins and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2018) 115:10836–44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1809045115
24. Tieland, M, Borgonjen-Van den Berg, KJ, van Loon, LJ, and de Groot, LC. Dietary protein intake in community-dwelling, frail, and institutionalized elderly people: scope for improvement. Eur J Nutr. (2012) 51:173–9. doi: 10.1007/s00394-011-0203-6
25. Kreider, RB, Kalman, DS, Antonio, J, Ziegenfuss, TN, Wildman, R, Collins, R, et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. (2017) 14:18. doi: 10.1186/s12970-017-0173-z
26. Deldicque, L, Louis, M, Theisen, D, Nielens, H, Dehoux, M, Theisen, J-P, et al. Increased IGF mRNA in human skeletal muscle after creatine supplementation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. (2005) 37:731–6. doi: 10.1249/01.MSS.0000162690.39830.27
27. Burke, DG, Chilibeck, PD, Parise, G, Candow, DG, Mahoney, D, and Tarnopolsky, M. Effect of creatine and weight training on muscle creatine and performance in vegetarians. Med Sci Sports Exerc. (2003) 35:1946–55. doi: 10.1249/01.MSS.0000093614.17517.79
28. Candow, DG, Chilibeck, PD, and Forbes, SC. Creatine supplementation and aging musculoskeletal health. Endocrine. (2014) 45:354–61. doi: 10.1007/s12020-013-0070-4
29. Brosnan, JT, da Silva, RP, and Brosnan, ME. The metabolic burden of creatine synthesis. Amino Acids. (2011) 40:1325–31. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-0853-y
30. Forbes, SC, Candow, DG, Ostojic, SM, Roberts, MD, and Chilibeck, PD. Meta-analysis examining the importance of creatine ingestion strategies on lean tissue mass and strength in older adults. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1912. doi: 10.3390/nu13061912
31. Slater, GJ, and Jenkins, D. Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) supplementation and the promotion of muscle growth and strength. Sports Med. (2000) 30:105–16. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200030020-00004
32. Eley, HL, Russell, ST, Baxter, JH, Mukerji, P, and Tisdale, MJ. Signaling pathways initiated by beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate to attenuate the depression of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle in response to cachectic stimuli. Am J Physiol-Endocrinol Metab. (2007) 293:E923–31. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00314.2007
33. Australian Sports Commission. Supplements. Available online at: https://www.ausport.gov.au/ais/nutrition/supplements (Accessed July 19, 2025)
34. Courel-Ibáñez, J, Vetrovsky, T, Dadova, K, Pallarés, JG, and Steffl, M. Health benefits of β-hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) supplementation in addition to physical exercise in older adults: a systematic review with Meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2082. doi: 10.3390/nu11092082
35. Pina, FLC, Nunes, JP, Nascimento, MA, Ribeiro, AS, Mayhew, JL, and Cyrino, ES. Similar effects of 24 weeks of resistance training performed with different frequencies on muscle strength, muscle mass, and muscle quality in older women. Int J Exerc Sci. (2019) 12:623–35. doi: 10.70252/QSOM3270
36. Counts, BR, Buckner, SL, Mouser, JG, Dankel, SJ, Jessee, MB, Mattocks, KT, et al. Muscle growth: to infinity and beyond? Muscle Nerve. (2017) 56:1022–30. doi: 10.1002/mus.25696
37. Tagawa, R, Watanabe, D, Ito, K, Ueda, K, Nakayama, K, Sanbongi, C, et al. Dose-response relationship between protein intake and muscle mass increase: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev. (2020) 79:66–75. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuaa104
38. Rathmacher, JA, Pitchford, LM, Stout, JR, Townsend, JR, Jäger, R, Kreider, RB, et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB). J Int Soc Sports Nutr. (2025) 22:2434734. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2024.2434734
39. Gualano, B, Roschel, H, Lancha, AH, Brightbill, CE, and Rawson, ES. International society of sports nutrition position stand: β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB). Amino Acids. (2012) 43:519–29. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-1132-7
40. Cribb, PJ, Williams, AD, Carey, MF, and Hayes, A. In sickness and in health: the widespread application of creatine supplementation. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. (2006) 16:494–509. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.16.5.494
41. Daly, RM, O’Connell, SL, Mundell, NL, Grimes, CA, Dunstan, DW, and Nowson, CA. Protein-enriched diet, with the use of lean red meat, combined with progressive resistance training enhances lean tissue mass and muscle strength and reduces circulating IL-6 concentrations in elderly women: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. (2014) 99:899–910. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.113.064154
42. Pinto, CL, Botelho, PB, Carneiro, JA, and Mota, JF. Impact of creatine supplementation in combination with resistance training on lean mass in the elderly. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2016) 7:413–21. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12094
43. Granic, A, Hurst, C, Dismore, L, Stevenson, E, Sayer, AA, and Aspray, T. Feasibility and acceptability of a milk and resistance exercise intervention to improve muscle function in community-dwelling older adults (MIlkMAN): Pilot study. PLOS ONE. (2020) 15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235952
44. Chalé, A, Cloutier, GJ, Hau, C, Phillips, EM, Dallal, GE, and Fielding, RA. Efficacy of whey protein supplementation on resistance exercise-induced changes in lean mass, muscle strength, and physical function in mobility-limited older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2013) 68:682–90. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gls221
45. Nakayama, K, Saito, Y, Sanbongi, C, Murata, K, and Urashima, T. Effects of low-dose milk protein supplementation following low-to-moderate intensity exercise training on muscle mass in healthy older adults: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Nutr. (2021) 60:917–28. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02302-4
46. Seino, S, Sumi, K, Narita, M, et al. Effects of Low-Dose Dairy Protein Plus Micronutrient Supplementation during Resistance Exercise on Muscle Mass and Physical Performance in Older Adults: A Randomized. Controlled Trial. J Nutr Health Aging. (2018) 22:59–67. doi: 10.1007/s12603-017-0904-5
47. Bernat, P, Candow, DG, Gryzb, K, Butchart, S, Schoenfeld, BJ, and Bruno, P. Effects of high-velocity resistance training and creatine supplementation in untrained healthy aging males. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab Physiol Appl Nutr Metab. (2019) 44:1246–53. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2019-0066
48. Kirk, B, Mooney, K, Cousins, R, et al. Effects of exercise and whey protein on muscle mass, fat mass, myoelectrical muscle fatigue and health-related quality of life in older adults: a secondary analysis of the Liverpool Hope University-Sarcopenia Ageing Trial (LHU-SAT). Eur J Appl Physiol. (2020) 120:493–503. doi: 10.1007/s00421-019-04293-5
49. Galbreath, M, Campbell, B, LaBounty, P, et al. Effects of Adherence to a Higher Protein Diet on Weight Loss, Markers of Health, and Functional Capacity in Older Women Participating in a Resistance-Based Exercise Program. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1070. doi: 10.3390/nu10081070
50. van Dongen, EJI, Haveman-Nies, A, Doets, EL, Dorhout, BG, and de Groot, LCPGM. Effectiveness of a Diet and Resistance Exercise Intervention on Muscle Health in Older Adults: ProMuscle in Practice. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2020) 21:1065–1072.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.11.026
51. Mori, H, and Tokuda, Y. Effect of whey protein supplementation after resistance exercise on the muscle mass and physical function of healthy older women: A randomized controlled trial. Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2018) 18:1398–404. doi: 10.1111/ggi.13499
52. Uchida, M, Park, J, Fujie, S, et al. Effect of resistance training and chicken meat on muscle strength and mass and the gut microbiome of older women: A randomized controlled trial. Physiol Rep. (2024) 12:e16100. doi: 10.14814/phy2.16100
53. Brose, A, Parise, G, and Tarnopolsky, MA. Creatine supplementation enhances isometric strength and body composition improvements following strength exercise training in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2003) 58:11–9. doi: 10.1093/gerona/58.1.b11
54. Osuka, Y, Fujita, S, Kitano, N, et al. Effects of Aerobic and Resistance Training Combined with Fortified Milk on Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength, and Physical Performance in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Nutr Health Aging. (2017) 21:1349–57. doi: 10.1007/s12603-016-0864-1
55. Stout, JR, Smith-Ryan, AE, Fukuda, DH, et al. Effect of calcium β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (CaHMB) with and without resistance training in men and women 65+yrs: A randomized, double-blind pilot trial. Exp Gerontol. (2013) 48:1303–10. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.08.007
56. Din, USU, Brook, MS, Selby, A, et al. A double-blind placebo controlled trial into the impacts of HMB supplementation and exercise on free-living muscle protein synthesis, muscle mass and function, in older adults. Clin Nutr. (2019) 38:2071–8. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.09.025
57. Aguiar, AF, Januário, RSB, Junior, RP, et al. Long-term creatine supplementation improves muscular performance during resistance training in older women. Eur J Appl Physiol. (2013) 113:987–96. doi: 10.1007/s00421-012-2514-6
58. Griffen, C, Duncan, M, Hattersley, J, Weickert, MO, Dallaway, A, and Renshaw, D. Effects of resistance exercise and whey protein supplementation on skeletal muscle strength, mass, physical function, and hormonal and inflammatory biomarkers in healthy active older men: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Exp Gerontol. (2022) 158:111651. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2021.111651
Keywords: nutritional intervention, resistance training, muscle strength, muscle mass, healthy older adults
Citation: Ma Y, Yan R, Li Y, Chen T, Liu X, Sun X and Li D (2025) The impact of nutritional intervention and resistance training on muscle strength and mass in healthy older adults—a comparative analysis. Front. Nutr. 12:1640858. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1640858
Edited by:
Paulina Mazur-Kurach, Akademia Wychowania Fizycznego im. Bronisława Czecha w Krakowie, PolandReviewed by:
Zixian Song, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaŁukasz Tota, Akademia Wychowania Fizycznego im. Bronisława Czecha w Krakowie, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Yan, Li, Li, Sun, Chen and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xingyu Liu, NTEwOThAZ3pzcG9ydC5lZHUuY24=; Tao Chen, MTEwMDRAZ3pzcG9ydC5lZHUuY24=
 Yongye Ma
Yongye Ma Ruixiang Yan
Ruixiang Yan Yueming Li1
Yueming Li1 Duanying Li
Duanying Li