- 1School of Pharmacy, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China
- 2Guangxi Institute for Drug Control, Nanning, China
Background: In recent years, the potential role of probiotics in modulating gut microbiota, enhancing immune function and improving metabolic diseases has become a highly field in biomedical and clinical research. The rapid increase in global probiotic clinical trials necessitates a systematic evaluation of current research status, developmental trends, and collaborative networks in this field.
Purpose: This study employs bibliometric analysis to comprehensively evaluate research progress and hotspots in clinical applications of probiotics.
Method: A systematic search was performed in the Web of Science database to collect articles and reviews regarding the clinical application of probiotics between 2000 and 2025. The retrieved records were analyzed using Microsoft Office Excel, Cite Space and VOS viewers.
Result: During the period from 2000 to 2025, we retrieved a total of 3,674 papers related to the clinical application of probiotics, and the number of papers is showing a continuous growth trend. The research was mainly focused on North America, Western Europe, and East Asia, with the United States leading the way with 714 papers, high impact (H-index 107, total citations 44,833), and top institutions (Harvard Univ). Nutrition and microbiology are the main academic fields. The current research hotspots and development directions focus on the application of probiotics in diseases such as “inflammation”, “obesity”, “insulin resistance”, “depression”, “hyperlipidemia”, and “cancer”.
Conclusion: This study represents the first application of bibliometric methods to systematically visualize and analyze research progress in the field of probiotic clinical applications, identifying key research trends and frontiers. The findings offer valuable insights for researchers at various career stages, particularly those new to the field, enabling them to identify critical developments and serving as a foundational reference for future clinical applications of probiotics.
1 Introduction
In 1907, Russian scientist Elie Metchnikoff first proposed the concept of probiotics. His observations of Bulgarian farmers' longevity associated with long-term consumption of fermented dairy products led him to hypothesize that lactic acid bacteria conferred health benefits. Metchnikoff proposed that these bacteria could inhibit pathogenic intestinal microbiota, potentially extending lifespan. This theory established the scientific foundation for probiotic research. In 1965, Lilly and Stillwell first coined the term “Probiotics”, originally defining them as “microbial-derived substances that stimulate the growth of other probiotics.” Over time, this definition has evolved to its current form: “live probiotics that confer health benefits when administered in adequate amounts”. Advances in molecular biology and microbiological techniques have enabled researchers to elucidate probiotic mechanisms of action, including microbiota modulation, immune function enhancement, and prevention effects (1–3). This scientific progress initiated a new era of probiotic research.
Probiotics are live microorganisms defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the World (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO). Recent advances have led to the conceptualization of “next-generation probiotics (NGP)”, which were defined as living biological therapeutic drugs (4). As functional microorganism with significant potential, NGPs demonstrate broad application prospects across multiple domains including food science, medical therapeutics, and health management. Probiotics are mainly classified into the following categories: Lactobacillus, (such as Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnoses, and Lactobacillus plantarum, etc.), Bifidobacterium, (such as Bifidobacterium infants, Bifidobacterium longum, Bifidobacterium breve, etc.), Yeast, (such as Saccharomyces bouvardia), Other bacterial genera, (such as certain streptococcus (including Streptococcus thermophilus) and Bacillus (including Bacillus coagulase) etc. Probiotics have been extensively applied in clinical practice, demonstrating efficacy in disease prevention, treatment and adjunctive management. They exhibit significant therapeutic value across multiple medical domains, particularly in gastrointestinal disorders, immune-mediated conditions, metabolic diseases, women's health, and mental health (5). Recent years have witnessed exponential growth in publications concerning probiotic clinical applications. As research advances, the mechanisms of probiotics action are being elucidated with increasing comprehensiveness, while personalized therapies and novel probiotic formulations are emerging as key research priorities. This bibliometric analysis delineates the developmental trajectory of probiotic research through visual analytics. Employing a chronological framework, we systematically analyze research hotspots, identify emerging trends, and critically evaluate both major advances and persistent challenges in probiotic clinical applications over the past three decades. Consequently, this review provides valuable insights to guide future probiotic development and facilitate innovation in therapeutic translation.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data source and search strategy
The study retrieved bibliographic data from the Web of Science, spanning publications from 2000 to February 23, 2025. This analysis focused on identifying research hotpots and developmental trends in probiotic research. The core database was used as the basic data for the research. The reason why Web of Science was selected as the primary data source due to its comprehensive coverage of over 12,000 high-impact journals indexed in the Science Citation Index (SCI), Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI), Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI). Compared to alternative databases such as Scopus, Medline and PubMed, Web of Science offers superior bibliometric analysis capabilities, as evidenced by its widespread adoption in visualization studies and established academic authority. The search strategy employed the title field query: [TI = (Probiotic*) AND TI = (“Clinical practice*” OR “clinical using” OR “clinical use” OR “clinical application” OR “clinical study” OR “clinical studies” OR “clinical trial*” OR “clinical usage” OR “clinical utility”)] OR [AB = (Probiotic*) AND AB = (“Clinical practice*” OR “clinical using” OR “clinical use” OR “clinical application” OR “clinical study” OR “clinical studies” OR “clinical trial*” OR “clinical usage” OR “clinical utility”)] OR [AK = (Probiotic*) AND AK = (“Clinical practice*” OR “clinical using” OR “clinical use” OR “clinical application” OR “clinical study” OR “clinical studies” OR “clinical trial*” OR “clinical usage” OR “clinical utility”)] search queries.
2.2 Data processing
(I) Inclusion Criteria.
(1) Literature related to the clinical application of probiotics; (2) Literature published in English; (3) Literature types include origin, art ide and review; (4) The literature information must be complete (including title, country, author, keywords, source, etc.).
(II) Exclusion Criteria.
(1) Duplicate publications (2) Self-cited publications.
2.3 Data normalization
The selected records were exported in plain text format with all special characters removed. Subsequently, duplicate publications were identified and excluded using the Cite Space software.
2.4 Methods and data analysis
This study employed bibliometric methods to analyze research hotpots, advances and frontiers in the field. The bibliometric analysis was conducted using RStudio, VOS viewer, Cite Space and Microsoft Excel with the bib-biomatrix package. Among these tools, VOS viewer and Cite Space have gained widespread recognition in academic circle (6). Specifically, VOS viewer is a bibliometric visualization tool developed by van Eck and Waltman at Leiden University's Center for Science and Technology Studies. In addition, the VOS viewer demonstrates distinct advantages in bibliometric analyses including keyword co-occurrence mapping, cluster identification, and research hotspot visualization (7). Cite Space was proposed by Professor Chen at Drexel University, it is a special bibliometric analysis tool designed for visualizing temporal patterns and emerging trends in scientific literature through citation network analysis and cluster mapping (8, 9). Visual and serialized knowledge maps were used to display the complex relationships among keywords, authors, institutions, countries and other information elements, including interactions, intersections and evolutions. The Cite Space software focuses on expressing relationship strength between various themes through tree diagrams and connecting lines, while VOS viewer software primarily illustrates clustering relationships among structural nodes through distance and density visualization. The advantages of Cite Space and VOS viewer software can complement each other (10). The implementation and development of these two-software tool have significantly advanced research progress and application expansion in the field of information visualization. Accordingly, this study employed VOS viewer to analyze co-occurrence knowledge maps of authors, institutions, and countries in probiotic research, and utilized Cite Space to examine co-citation bursts in the literature.
3 Result
3.1 Literature retrieval and screening results
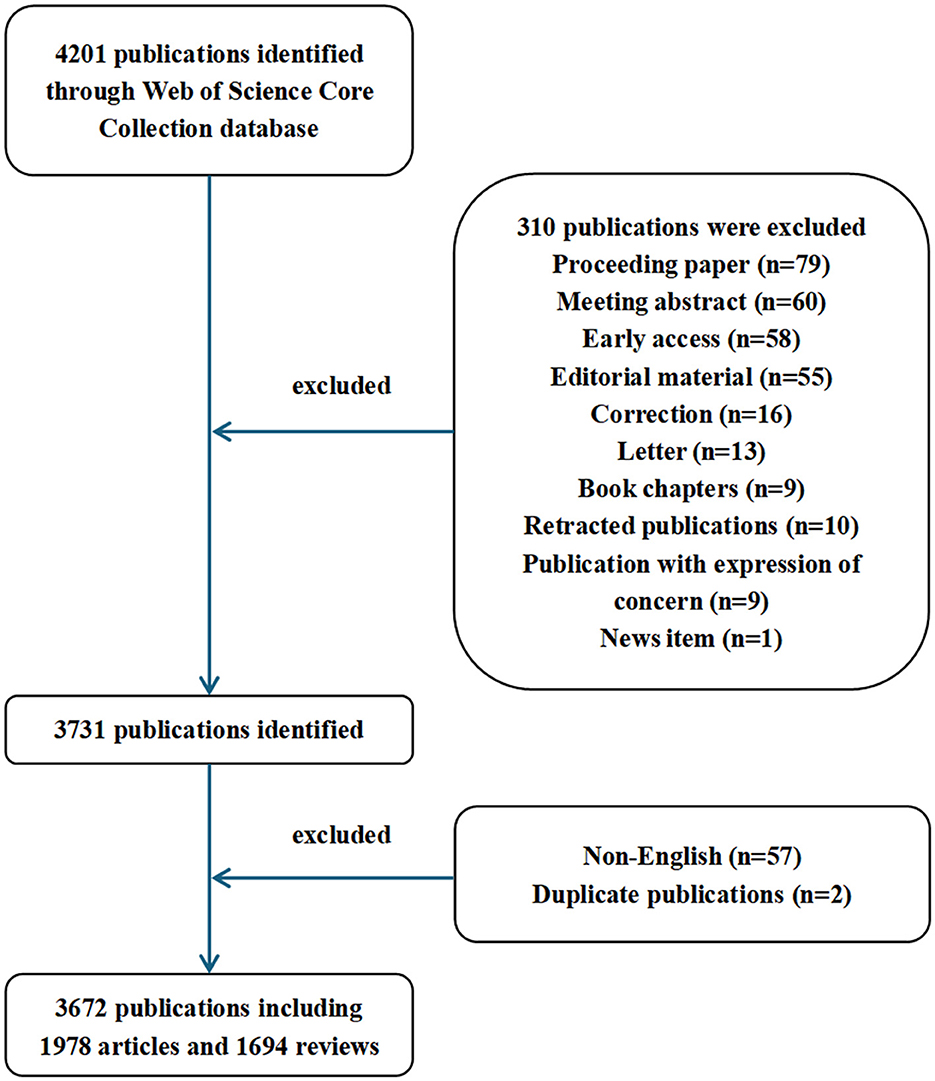
We initially searched 3,674 documents in the WOS database. After applying the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, 3,672 publications were included for analysis. The specific steps are shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Analysis of the annual number of publications and citations
Publication volume within a given timeframe serves as a reliable indicator of research activity and developmental trends in a field. Figure 2A shows the global trends from 2000 to 2025. The analysis reveals a consistent upward trajectory in probiotic clinical application research. Annual publications first surpassed 100 in 2013, demonstrated accelerated growth since 2019, and peaked in 2024 with 476 articles. These findings demonstrate growing research interest in this field, suggesting continued increases in publication output. As of February 2025, the dataset comprised 3,672 publications, which collectively received 155,819 citations (excluding 142,772 self-citations).
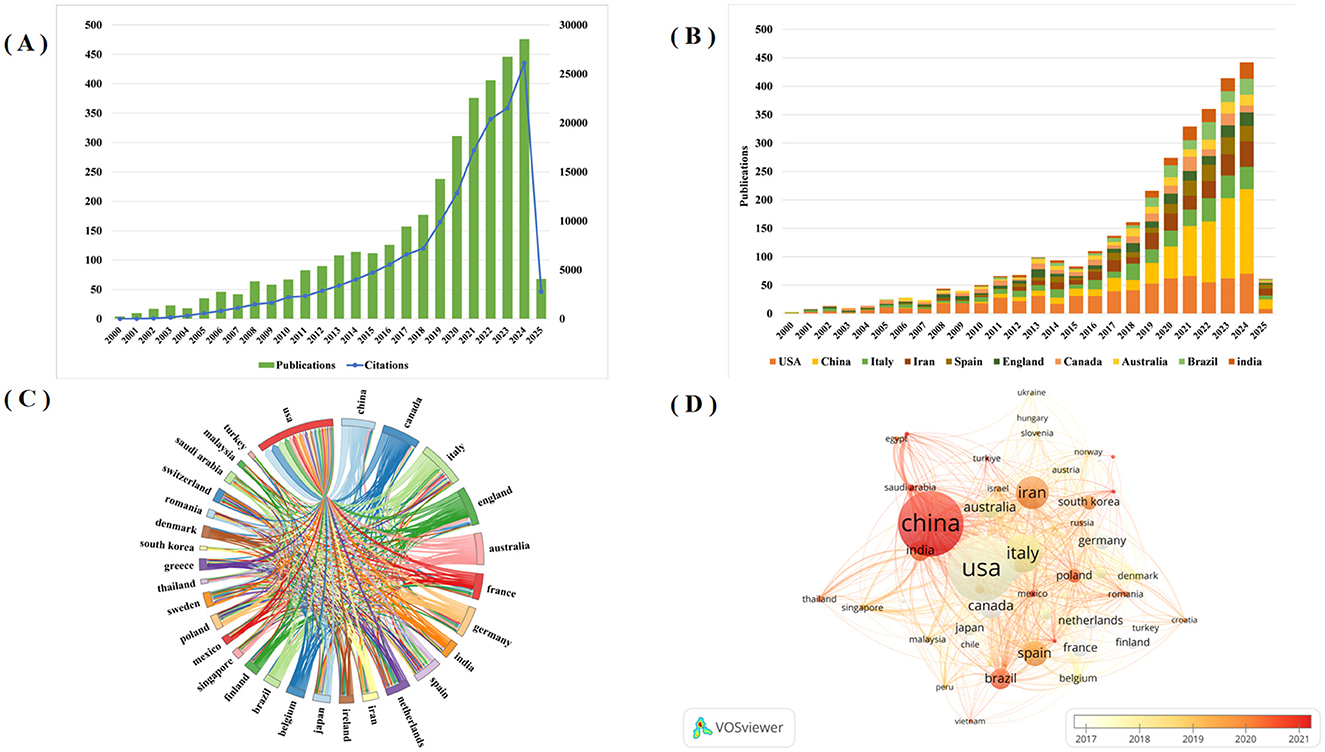
Figure 2. (A) The global trend in the annual number of Probiotics in Clinical Applications publications and citation from 2000 to 2025; (B) The annual number of publications in the top 10 most productive countries; (C) Scientific cooperation between the top 30 countries in terms of the number of publications worldwide; (D) Overlay visualization map of country co-authorship analysis generated by VOS viewer software.
3.3 Analysis of the number of publications and cooperation among countries
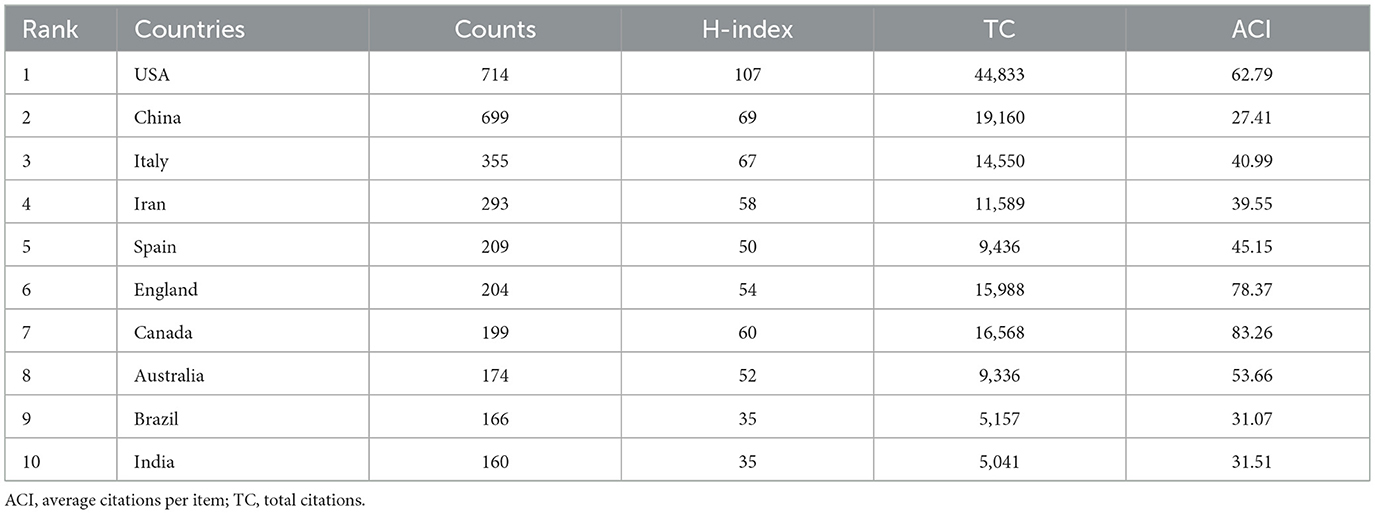
The study identified 99 countries that have contributed publications in this research domain. Table 1 shows the top ten productive countries are ranked by publication volume. The United States leads with the highest publications count (714), H-index (107), and total citations (44,833). China and Italy follow in second and third positions with 699 and 355 publications, respectively. These findings demonstrate particularly strong research engagement in probiotic clinical applications from these three nations. For Average number of citations, Canada ranked first in average citation count (83.26), followed by the United Kingdom (78.37) and the United States (62.79). Furthermore, Figure 2B shows the annual publication growth among the top ten most productive countries. Notably, while the United States maintained research dominance prior to 2021, China's annual publication output has exceeded that of the United States since 2021, demonstrating a rapid growth trajectory.
Figure 2C shows the collaboration networks among the top 30 most productive countries. The United States demonstrated the strongest international collaborations, with China (59), Canada (57), Italy (52), England (36) and Australia (31). In addition, we also used the VOS viewer software to create a temporal co-authorship network among countries, as shown in Figure 2D, where node size corresponds to publication volume and color gradient (white-orange-dark red) indicates the average publication year. This visualization reveals that Canada, France, and the Netherlands were early contributors in this field, while China emerged more recently.
3.4 Analysis of the number of publications and collaborations of key authors
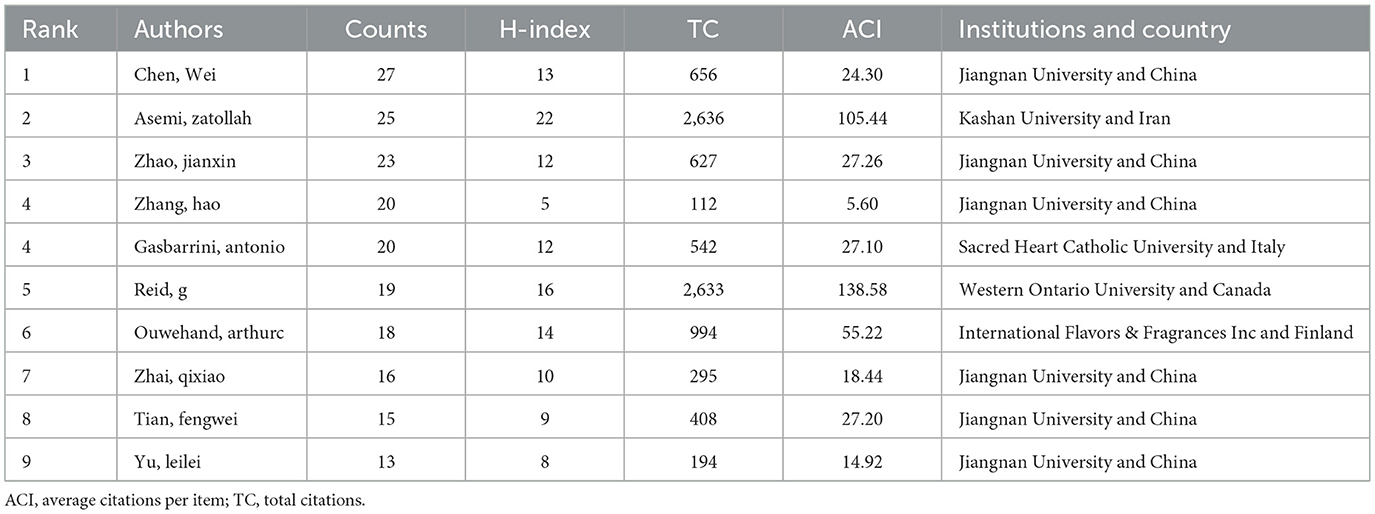
Table 2 shows the top ten authors probiotic clinical application research, ranked by publication output. Chen, Wei ranked first with 27 publications, followed by Asemi Zatollah and Zhao jianxin with 25 and 23 publications. Asemi Zatollah achieved the highest H-index of 22 and total citations of 2,636, while Reid G ranked second with an H-index of 16 and total citations of 2,633. Among these ten authors, six were affiliated with Chinese institutions, with the remaining four representing Iran, Italy, Canada and Finland respectively. Figure 3A shows the author collaboration network. The network graph shows that there are at least 10 published papers with a total of 31 authors. Authors are clustered by node color, enabling intuitive identification of core researchers and collaborative teams. Analysis revealed three core research groups: (1) the red cluster (Ouwehand AC, Lebeer S, et al.), (2) the green cluster (Chen W, et al.), and (3) the blue cluster (Asemi Z, et al.). These groups represent the dominant research teams in this field. Figure 3B shows the time overlap graph of cooperation among authors, revealing that Chinese researchers including Chao Wei, Zhao hao and Zhai qixiao are represent more recent contributors in this field.
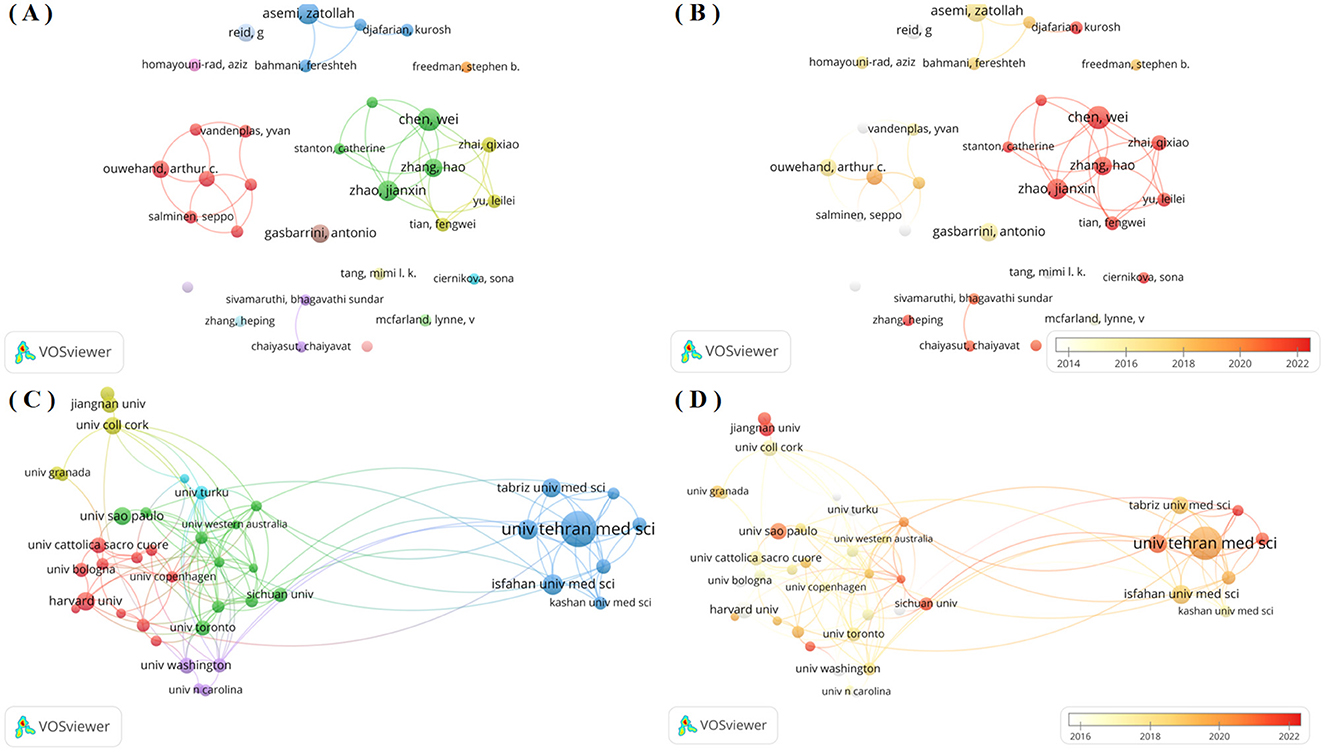
Figure 3. (A) Network visualization map of author co-authorship analysis generated by VOS viewer software; (B) Overlay visualization map of author co-authorship analysis generated by VOS viewer software; (C) Network visualization map of institution co-authorship analysis generated by VOS viewer software; (D) Overlay visualization map of institution co-authorship analysis generated by VOS viewer software;
3.5 Analysis of literature publishing institutions
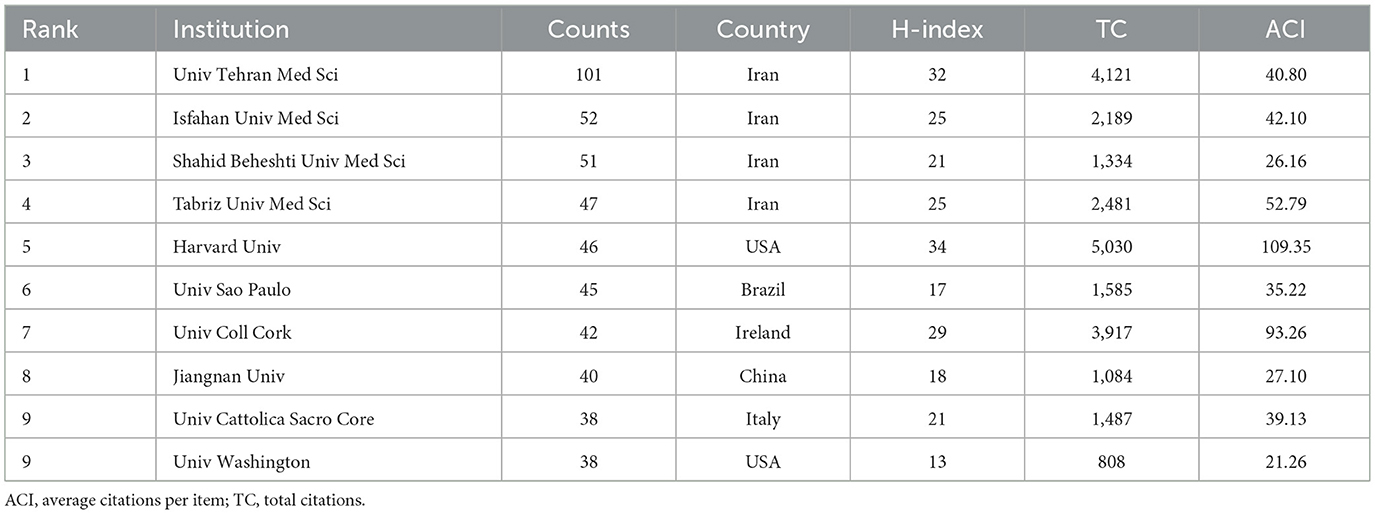
Institutional analysis identified approximately 12,610 research-active institutions in this field. Table 3 shows the top 10 institutions in terms of the number of publications. Among the analyzed institutions, Univ Tehran Med Sci ranks first with 101 publications, significantly surpassing other institutions. Isfahan Univ Med Sci and Shahid Beheshti Univ Med Sci followed with 52 and 51 publications respectively. Notably, Harvard Univ from the United States achieved the highest H-index (34) and total citations (5,030). Institutional collaboration networks reflect both academic influence and research cooperation patterns (11). Accordingly, we employed VOS viewer software to conduct a network graph analysis of the cooperation among research institutions that have published at least 20 papers, as shown in Figure 3C. The network comprises 41 institutions clustered into 6 distinct groups, revealing strong collaborative relationships between Univ Tehran Med Sci, Monash Univ and Univ Melbourne of Melbourne and their partners. However, several institutions including Univ Granada, Jiangnan Univ, exhibited more dispersed nodal connections with limited internal cohesion and variable research output. These patterns suggest comparatively lower publication volumes, reduced academic influence, and less developed collaborative networks among these institutions, indicating an absence of large-scale institutional research partnerships. Additionally, we have also produced a temporal overlap chart of inter-agency cooperation as shown in Figure 3D, which identifies more recent contributors to this field, including Shiraz Univ and Jiangnan Univ (represented by dark red nodes).
3.6 Analysis of the most influential journals
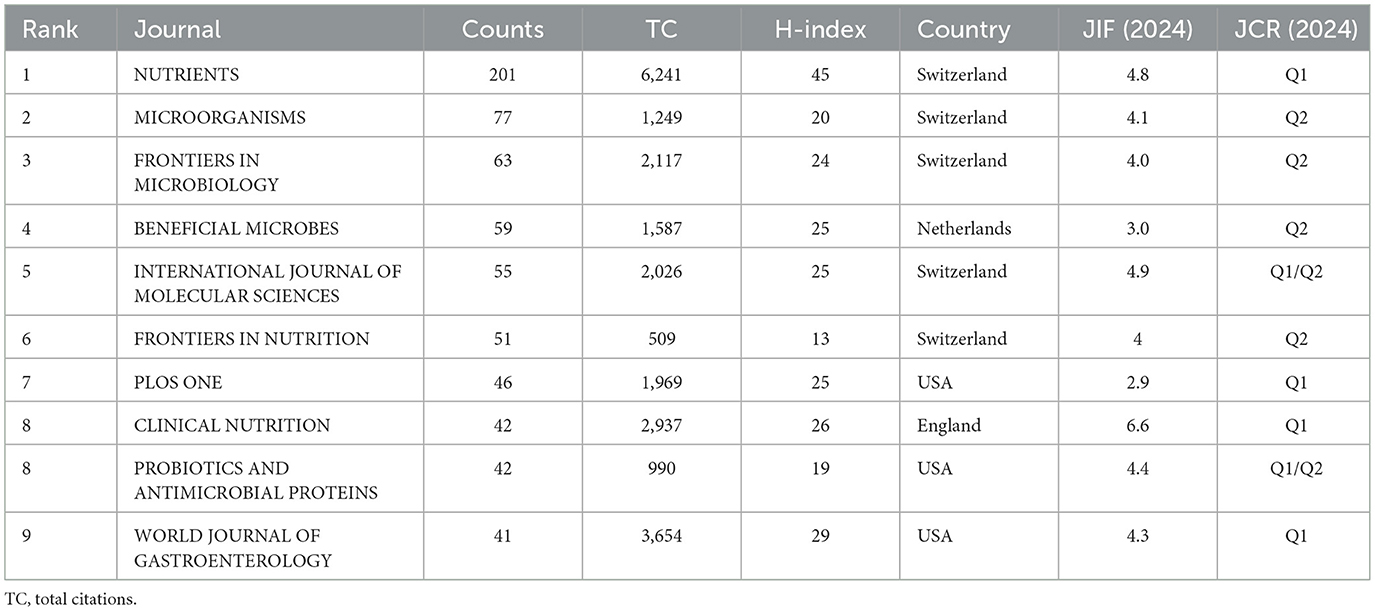
For centuries, peer-reviewed scientific publications have served as a fundamental medium for interdisciplinary scholarly communication. Publication in international journals remains essential for establishing valid scientific discourse and disseminating research findings (12, 13). Analysis of journal source distribution enables researchers to efficiently identify the most suitable publication venues for their work. Our findings indicate that publications on probiotic clinical applications are disseminated across approximately 1,000 distinct journals. Table 4 summarizes the basic information of the top 10 journals with the largest number of publications in this field. Among them, NUTRIENTS (201) produced the most, followed by MICROORGANISMS (77) and FRONTIERS IN MICROBIOLOGY (63). A journal's Journal Impact Factor (JIF) serves as a key parameter for assessing both the journal's academic influence and the citation impact of its published articles, representing a 2-year moving average of citation frequency (14). Among the top 10 academic journals, CLINICAL NUTRITION (6.6) had the highest JIF, followed by INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES (4.9) and NUTRIENTS (4.8), etc. Accordingly, the journal citation reports also divide the journals belonging to the same discipline category in the Web of Science database into four equal parts based on the JIF value. The top 25% are attributed to Q1, the top 25-50% are attributed to Q2, and so on. It can be seen from Table 4 that 4 journals belong to Q1, 4 journals belong to Q2, and 2 journals belong to Q1/Q2. In addition, geographical distribution analysis revealed that five of the ten journals originate from Switzerland, three from the United States, with the remaining two based in the United Kingdom and the Netherlands respectively. Notably, these high-activity journals are located in Western Europe and North America. The absence of East Asian representation, particularly Chinese journals, in this ranking suggests the need for enhanced international journal development in Asian countries to strengthen their academic influence. It is noteworthy that the Chinese government has implemented substantial investments and policy incentives to foster international journal development in recent years (15).
3.7 Analysis of the most relevant topic categories
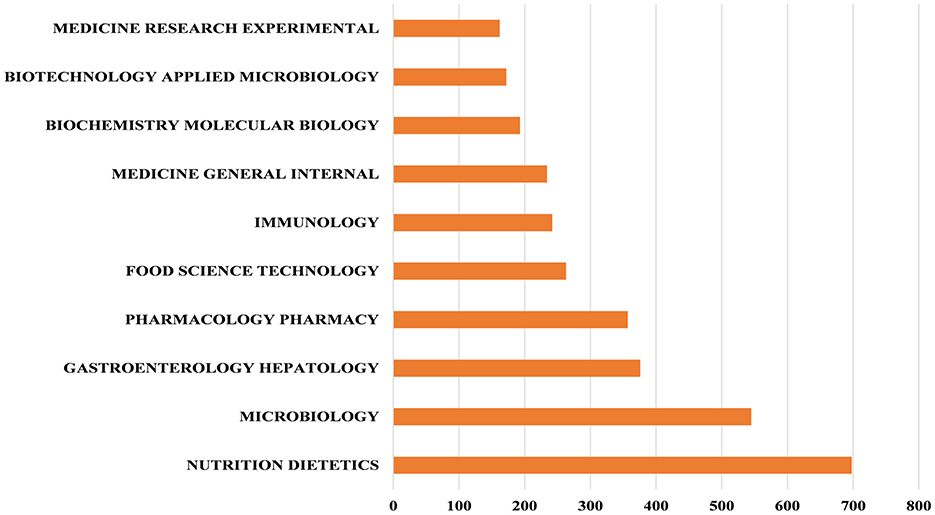
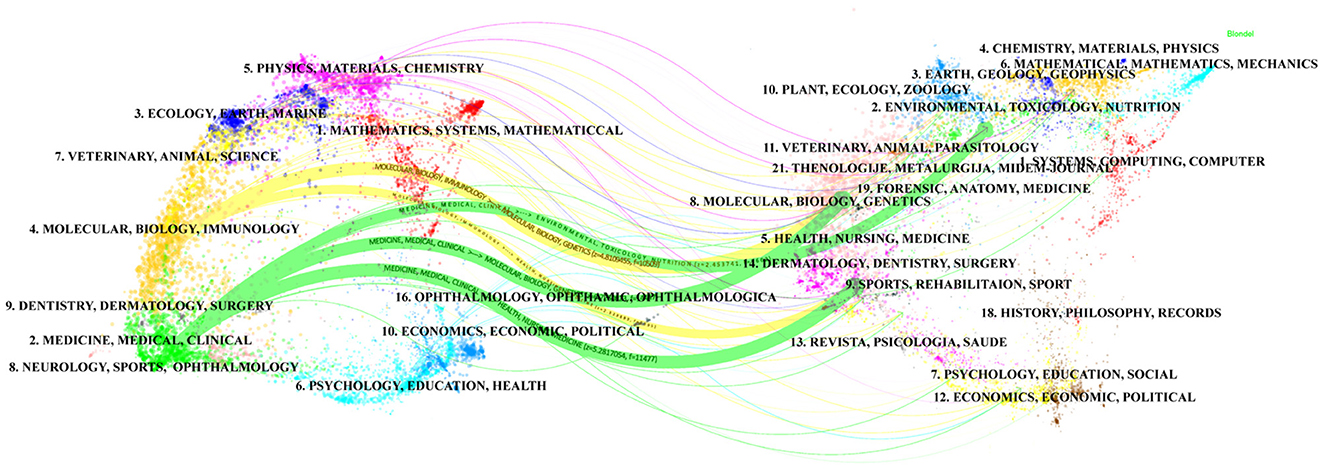
In the Web of Science database, each publication is assigned one or more subject categories for efficient retrieval. Figure 4 shows the top 10 subject categories with the highest number of publications. We found that NUTRITION, DIETETICS, MICROBIOLOGY and GASTROENTEROLOGY HEPATOLOGY are the most prominent and frequently represented subject categories in this research domain. Furthermore, the dual-map overlay visualization delineates the disciplinary distribution of journals publishing probiotic clinical application research, as shown in Figure 5. The dual-map overlay is generated from 10,000 source journals indexed in Web of Science. Using this dataset, citation trajectories were established through the dual-map overlay module. This visualization method clearly demonstrates interdisciplinary knowledge flow and identifies disciplinary research hotpots, with citing journals displayed on the left and cited journals on the right. The colored paths indicate the citation relationships. On the figure, we can see the following five core reference paths. Two orange paths said published in Molecular Biology/Immunology journal literature usually references published in Molecular Biology/Genetics and Health/Nursing/Medicine journal literature. The green path means that most papers published in medical/medical/clinical journals may tend to cite those published in environmental/toxicology/nutrition and molecular/biological/genetic as well as health/nursing/medical journals.
3.8 Analysis of highly cited literature
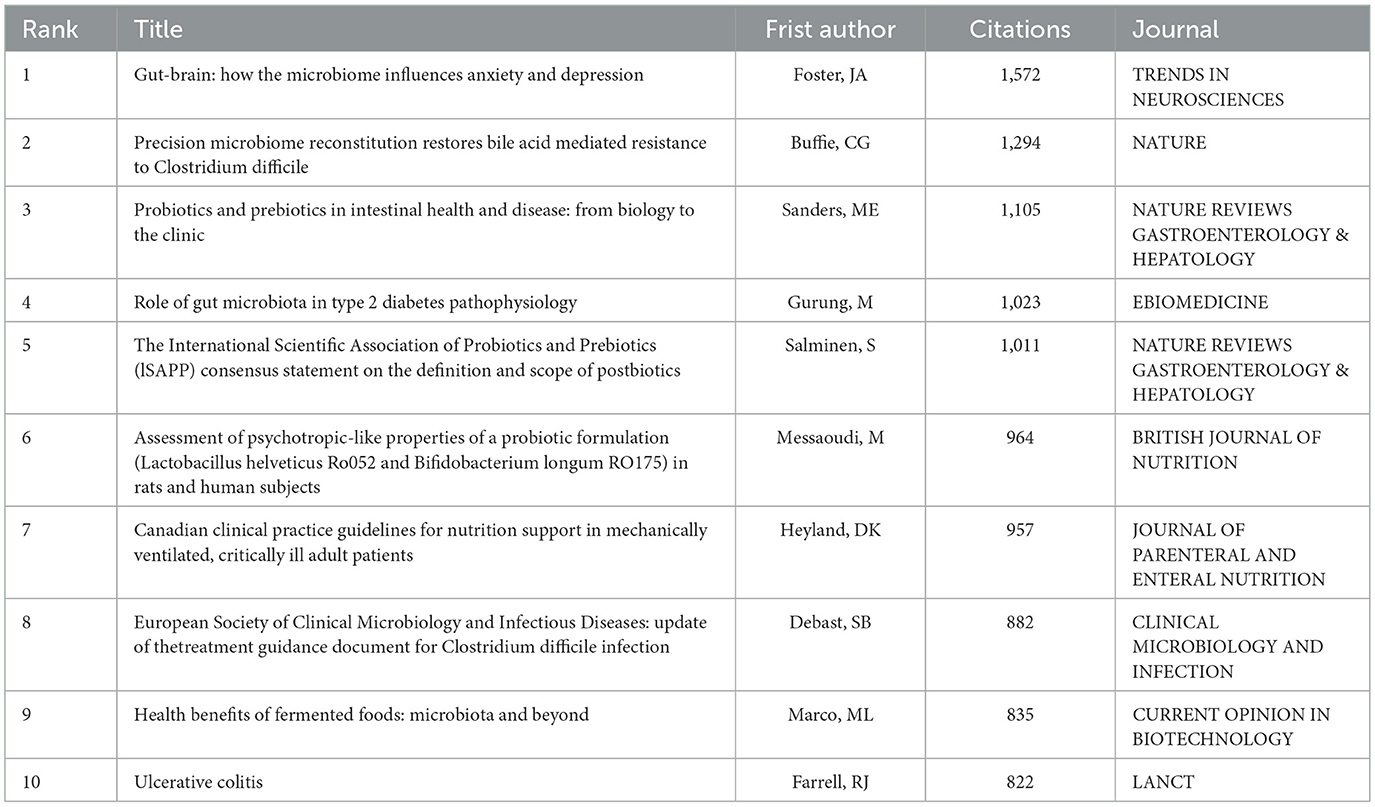
The Web of Science enables multiple classification approaches for scholarly literature, allowing identification of articles that have garnered significant attention within the scientific community. Consequently, citation analysis serves as a principal methodology in bibliometric investigations. While some debate persists regarding the interpretation of citation metrics (16), the academic consensus maintains that citation frequency correlates with a publication's scholarly influence, wherein higher citation counts typically reflect greater academic impact within a given field (17). Table 5 lists the top 10 most frequently cited papers in clinical application research related to probiotics. For each article, we have provided the journal name, citation count, paper title, first author's name and publication year. The journals presented in this table are ranked by publication volume. Specifically, No. 1 is the “Gut-Brain axis:” by Foster, JA, published IN TRENDS IN NEUROSCIENCES the article “how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression” has been cited 1,572 times and is the most frequently cited paper in this field. The research results of this article indicate that the bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract (GI), including symbiotic bacteria, probiotics and pathogenic bacteria, can activate neural pathways and the central nervous system (CNS) signaling system, further demonstrating that the microbiota plays a very important role in normal brain functions. This provides new approaches for understanding ongoing or future animal clinical studies on the microbiota-gut-brain axis in the prevention and treatment of mental illnesses, including anxiety and depression. The second most highly cited paper is “Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile.” published in NATURE by Buffie, CG et al, this article has been cited 1,294 times (18), It is indicated that when antibiotics disrupt the microbiota, the risk of infection increases. However, specific intestinal bacteria (such as Clostridium glitter) enhance their resistance to Clostridium difficile infection through bile acid metabolism, thereby reducing antibiotic-induced diarrhea. The third most frequently cited paper is “The Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics in Gut Health and Diseases: From Biology to Clinical Practice” published by Sanders, ME et al.in NATURE REVIEWS GASTROENTEROLOGY & HEPATOLOGY. In this review, insights into the mechanisms by which probiotics and prebiotics affect health are discussed, and facts and supporting information regarding their clinical application and use are reaffirmed, as well as prospects for the future are presented (19).
3.9 Reference literature explosion application
Research frontiers represent the most promising and potentially research impactful directions in scientific investigation. Kleinberg's burst detection algorithm serves as an effective analytical tool for identifying sudden increases in citation frequency or keyword usage within defined time periods. This method provides an effective way to identify the concepts and track evolving trends in probiotic clinical research. The Burst Detection function in Cite Space identifies keywords demonstrating significant citation surges within defined time periods, with these results serving as valuable indicators for research frontier analysis (20). This study employed Cite Space's burst detection function to extract emerging keywords related to probiotic clinical applications. Figure 6 shows the top 25 references with the strongest citation bursts. In this picture, the blue line represents the time interval, and the red part represents the time period during which the reference outbreak occurred. Among these references, the one with the strongest burst value was written by Gionchetti et al. (21), their research revealed that probiotic preparations could significantly reduce postoperative chronic risk in ulcerative colitis patients following ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. In addition, the second most prominent citation burst was observed for the publication by Kalliomäki et al. (22), which outbreak lasted for 4 years. The article details how oral administration of lactic acid bacteria in children with specific diseases can enhance endogenous TGF-β and IL-10 in the body, Moreover, these anti-inflammatory cytokines play a key role in the prevention and treatment of atopic disease, perhaps even more important than the role of T helper type 1 inducible factor. Notably, while citation bursts have subsided for most references, several persist, suggesting sustained research interest in these topics in recent years.
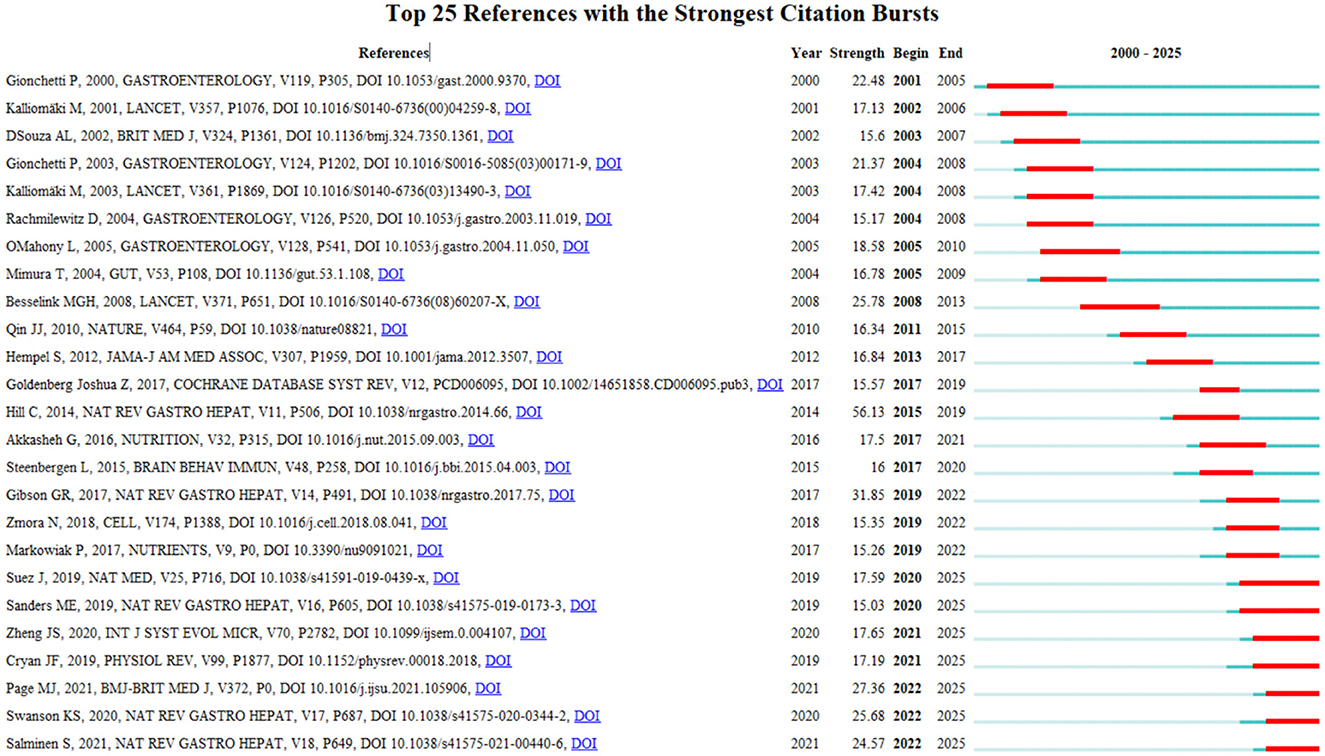
Figure 6. Visualization map of top 25 references with the strongest citation bursts by Cite space software.
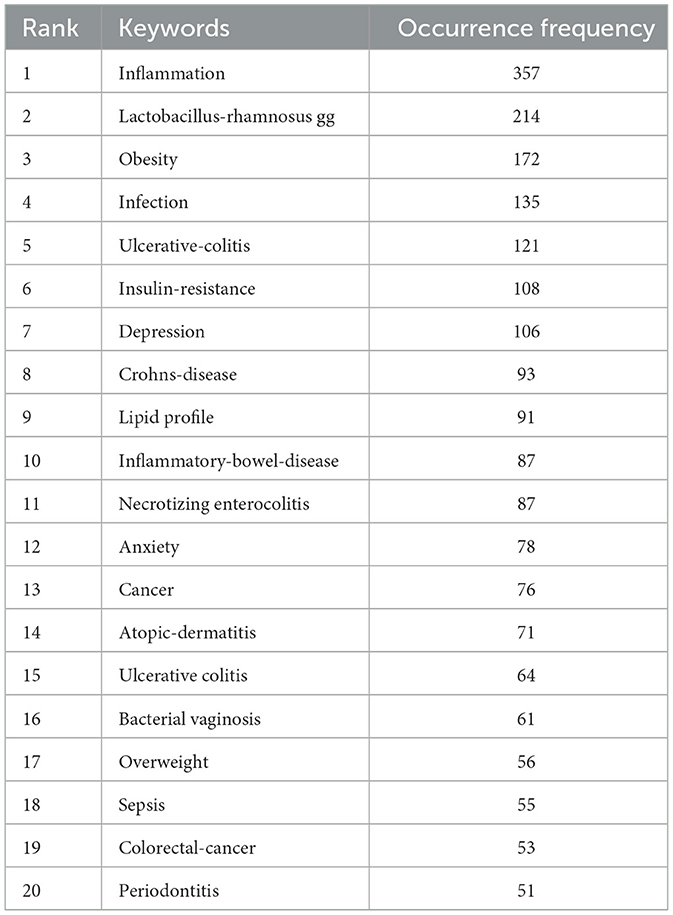
3.10 Key word co-occurrence analysis
Beyond cited references, keywords equally represent the central themes and core concepts of a research topic (23). Keyword co-occurrence analysis represents another established bibliometric method for detecting research hotspots. This approach determines keyword relevance through their joint appearance frequency in publications (13). This study employed VOS viewer software to perform keyword co-occurrence analysis. We established a threshold to a minimum co-occurrence of 50 times, and after merging synonyms and removing meaningless keywords, there are total of 118 keywords as shown in Figures 7A, B. Node size corresponds to keyword occurrence frequency, while inter-node distance inversely reflects relationship strength. Line thickness indicates co-occurrence frequency between terms (13). Figure 7A demonstrates 6 keyword clusters, the largest cluster is the red cluster, with 39 keywords. Furthermore, Figure 7B identifies current research hotspots through deep-red nodes, including “dysbiosis”, “fecal microbiota transplantation” and “gut-brain axis”. Furthermore, we have listed the top 20 keywords related to clinical applications as shown in Table 6.
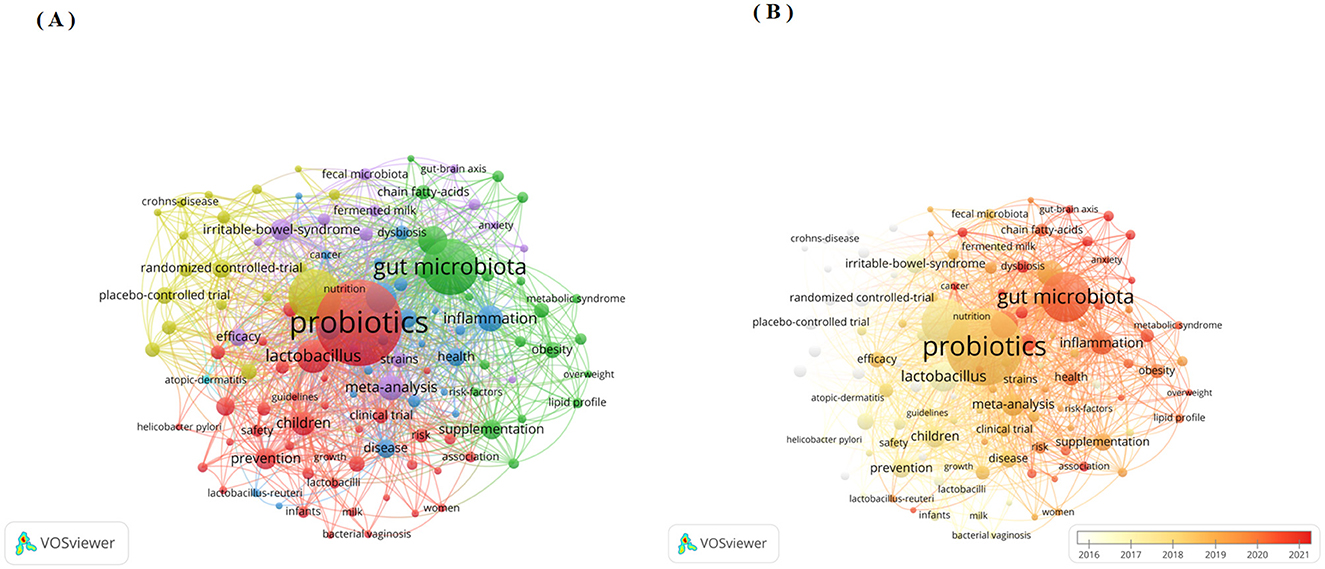
Figure 7. (A) Network visualization map of authors' keywords co-occurrence analysis by VOS viewer software; (B) Overlay visualization map of authors' keywords co-occurrence analysis by VOS viewer software.
4 Discussion
4.1 Basic information
This study employed Cite Space and VOS viewer for quantitative analysis of probiotics clinical applications, systematically summarizing research findings and advancements. Quantitative analysis of journals by publication volume, country, authors, institutions, subject, periodicals and other basic information. Analysis of publication volume reveals 3,604 articles on probiotic clinical applications since 2000, demonstrating a consistent growth trend. Higher citation frequency correlates with greater scientific influence and quality within this research domain. As shown in Figure 2, citation frequency in this field demonstrates a consistent annual increase. Based on the statistical analysis of publication outputs across countries/regions and institutions, key countries/regions and research institutions in probiotic clinical applications, while simultaneously mapping their collaborative networks. The United States, China and Italy are the main countries for researching the clinical applications related to probiotics. Research on the clinical application of probiotics in countries such as the United States, China and Canada is relatively mature. Among the top ten institutions, four are from Iran, two are from the United States, one is from Brazil and one is from Italy. Notably, China represents only one entry. Among the included institutions, Univ Tehran Med Sci ranked first in both publication output and H-index. The results demonstrate close international and interinstitutional collaboration. Such cooperative networks facilitate the elimination of academic barriers and promote advancements in probiotic clinical research. Among the top 10 authors, Chen, Wei (24) who published the most articles, followed by Asemi, zatollah (25) and Zhao, jianxin (23). It indicates that these three authors have made the most outstanding contributions in the field of clinical application research related to probiotics. Professor Asemi zatollah from Kashan University of Iran is the author with the highest H-index, which is a comprehensive quantitative indicator used to evaluate the quantity and level of academic output of researchers (26). Professor Asemi, zatollah demonstrated that probiotic supplementation may significantly improve wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers, clinical symptoms in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome, metabolic indicators in patients with diabetic retinopathy, and clinical characteristics of nervous system metabolism through randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trials (24, 25, 27), Especially, it has a significant effect on the clinical, metabolic and genetic status of Alzheimer's disease (24). The second ranking institution is the Western Ontario University of Canada Reid, g. He believes that Bifidobacterium not merely as an evolutionary feature of the maternal vagina and differentiating microbiota, capable of regulating immune responses to produce short-chain fatty acids, enhancing the intestinal barrier, and becoming a core component for the healthy growth of infants (28), but also can acidify the local environment and prevent the colonization of urological and gynecological pathogens, reducing the risks of bacterial vaginosis, urinary tract infections, cystitis, and chronic kidney disease (29, 30). Third on the list is Ouwehand arthur c from International Flavors and Fragrances Inc of Finland, which found that the saccharide2′-fucosyl lactose2′-FL and Bifidobacterium infantile subspecies (B. infantis), these microorganisms demonstrate potential symbiosis in infant immune system development, significantly influencing immunological maturation (31). The study further elucidates the mechanistic pathway through which the novel prebiotic combination—chitin glucan (CG) with Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM—attenuates visceral nociception and intestinal inflammation, while also delineating probiotic-mediated microbiota modulation as a critical therapeutic strategy (32–34). Notably, he realized the microbiota in mood disorders-im-brain axis from preclinical to the transformation of the clinical research challenges (35). Analysis of literature source distribution facilitates identification of core journals publishing probiotic clinical research and supports researchers in establishing scientific contributions. These findings demonstrate significant interest in probiotic clinical research among high-impact, quality journals. These data will help scholars choose journals for submission. Figure 5 shows Published in Molecular Biology/journal of Immunology and Medicine/Medical/Clinical journals are often published in Molecular Biology/Genetics/Health/Nursing/Medicine journal and Envirnmental/Toxicology/Nutrition/Molecular/Biology/Genetics/Health/Nursing/Medicine journals references. These findings indicate that current research on the clinical applications related to probiotics mainly focuses on basic research and transitional medicine. Most of the top ten references involve applications related to the nervous system, the gastrointestinal tract and metabolism. More and more evidence proves the microbiota not only a bidirectional pathway in the gut-brain axis, enabling the intestinal flora, including symbiotic bacteria, probiotics and pathogenic bacteria, to communicate through direct or indirect signaling pathways (35), activate neural pathways and the central nervous system (CNS) signaling system (36), but also directly interact with immune cells. It plays an important role in maintaining the immune balance of the gastrointestinal tract (37, 38), and plays a critical role in preventing and treating mental disorders, including anxiety, depression, and neurodevelopmental conditions (39–41). Meanwhile, Clostridium glitter, as a bile acid 7α-dehydroxylated intestinal bacterium, can also reduce diarrhea caused by intestinal infections (18). According to the highly explosive cited literature, the intensity and time intervals of the directions that researchers have been interested in in recent years can be referred to. From the 25 most frequently cited literatures, it can be seen that the most frequently cited literatures in recent years mainly involve the clinical applications of probiotics in gastrointestinal diarrhea, colitis, neurological diseases and specific diseases.
4.2 Research hotspots and frontiers
High-frequency keyword analysis reveals research hotpots and frontiers in this field. We employed keyword co-occurrence analysis to delineate the evolutionary trajectory of primary research foci and emerging trends in probiotic clinical applications (42). Cluster analysis of keywords combined with examination of the top 20 strongest citation bursts demonstrates both the broad clinical utility of probiotics and identifies current research hotpots in probiotic clinical applications. The main contents are as follows.
4.2.1 Inflammation
The human body constitutes a complex holobiont, integrating human cells with symbiotic microbial communities. These microbiota colonize multiple anatomical sites, establishing dynamically balanced microecosystems that influence both local tissue homeostasis and systemic inflammatory regulation through various pathways (43), anti-inflammatory probiotics primarily exert systemic immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects through indirect regulation of intestinal microbiota composition and function (44). Probiotic applications in inflammatory conditions have emerged as a predominant research focus in clinical practice over the past decade. Keyword hotspot analysis reveals their therapeutic potential across multiple inflammatory disorders, including diarrheal diseases, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, necrotizing enterocolitis, atopic dermatitis, and periodontitis.
4.2.1.1 Diarrhea
Intestinal dysbiosis, alternatively termed gut microbiota dysregulation, refers to the compositional and functional imbalance of microbial communities within the gastrointestinal tract (45). Current evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis serves as a primary etiological factor in the pathogenesis of numerous disease states (46, 47), Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), one of the most prevalent functional gastrointestinal disorders, is clinically characterized by recurrent abdominal pain associated with altered bowel movement frequency and stool consistency (48). Indeed, both diarrhea and constipation result from: intestinal microbiota dysbiosis, compositional alterations in human gut microbiota, and dysregulation of complex microbiota-host immune system interactions (49). Probiotics, defined as live microorganisms administered as nutritional supplements, demonstrate significant potential in restoring gut homeostasis and ameliorating gastrointestinal symptoms (50, 51). Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated superior clinical efficacy of probiotic interventions compared to placebo controls, with multi-strain formulations outperforming single-strain preparations (52, 53). Radomańska et al. discovered five types of lactic acid bacteria (such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus LR110, Lactobacillus paracasei LPC100, Lactobacillus acidophilus LA120, Lactobacillus casei LC130, and Lactobacillus plantarum LP140) and four types of bifidobacterium (such as Bifidobacterium breve BB010 and Bifidobacterium longum BL020), bifidobacterium bifidum BF030, Bifidobacterium lactis BL040 and Streptococcus thermophilus ST250 can safely and effectively improve the overall symptoms of patients with IBS (54); Ishaque et al. also evaluated the effectiveness of 14 different types of probiotic mixtures (such as Bacillus subtilis, 4 types of Bifidobacteria, 7 types of lactic acid bacteria, Lactococcus lactis and Streptococcus thermophilus) against moderate to severe IBS (55); At the same time, the clinical trial by JanŁukasik et al. further confirmed that multi-strain probiotic formulations significantly prevent antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD), establishing their evidence-based utility in diarrheal prophylaxis (56). In conclusion, probiotics play a significant role in the occurrence and prevention of diarrhea, and this field is one of the hot applications.
4.2.1.2 Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is an intestinal inflammation, which caused by an imbalance between the intestinal microbiota and mucosal immunity (57). Patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) exhibit impaired functional diversity and ecosystem stability of gut microbiota, characterized by reduced Firmicutes abundance alongside increased Bacteroidetes and facultative anaerobes (58). Zhao-Hua Shen et al. performed a meta-analysis of 1,763 clinical cases, demonstrating that probiotic supplementation significantly enhances remission rates in active ulcerative colitis (UC) patients, especially Lactobacillus and Escherichia coli (59). In addition, adding lactic acid bacteria strains to conventional treatment can also reduce the recurrence rate of UC patients (60); Oliva et al. also demonstrated that topical administration of standard-dose Lactobacillus reuteri and Escherichia coli strains significantly reduces rectal mucosal inflammation in pediatric UC cases and promotes sustained clinical remission (61), co-administration of Saccharomyces boulardii with mesalazine therapy significantly alleviates clinical symptoms in patients with mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis (UC) (62, 63). In a word, probiotics demonstrate dual therapeutic benefits for ulcerative colitis patients by both enhancing anti-inflammatory factor secretion and suppressing pathogenic gut bacteria through intestinal barrier and immune system modulation, as well as preventing and repairing pathogen-induced mucosal barrier dysfunction and associated epithelial damage.
4.2.1.3 Atopic dermatitis
The skin is an important interface that constantly interacts with and perceives environmental stimuli, having evolutionarily adapted to maintain homeostatic equilibrium with its resident microbial communities comprising the cutaneous microbiome. With the development of sequencing technology, many studies have revealed the correlation between gut microbiota composition and human diseases, including allergic asthma and specific dermatitis (64, 65). The “gut-skin” axis has been scientifically established and is now recognized as a novel therapeutic target for both prevention and treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) (66). The surface of the skin has a wide microenvironment with distinct physicochemical properties, necessitating selective colonization by microbiome species adapted to their specific anatomical niches (67). Current research demonstrates show that in areas rich in sebum, there are abundant lipid-dependent Clostridium and the fungus Malassezia, while in moist skin areas, more Staphylococcus and Corynebacterium are colonized (68). The lesion skin area of AD shows excessive growth of Staphylococcus aureus and expresses higher levels of virulence factors (69, 70). Notably, infants exhibiting reduced gut microbiota diversity demonstrate significantly higher susceptibility to AD compared to healthy controls, as evidenced by a cross-sectional study of 1,440 infant subjects (71); Enomoto et al. emphasized that perinatal supplement two types of bifidobacterium (Bifidobacterium breve and Bifidobacterium longum) before and after childbirth can reduce the risk of eczema and AD in infants (72); The meta-analysis conducted by Tan-Lim et al. indicates that the best probiotic formulations Mix8 (Lactobacillus parabases, Bifidobacterium longum) and Mix3 (Lactobacillus rhamnoses, Bifidobacterium animalic) exhibit the greatest efficacy in reducing AD risk (73). Probiotic supplements alter the intestinal environment, including regulating the composition of intestinal microbiota, preventing pathogen colonization, influencing bacterial metabolism, and restoring immune balance. These changes have all been proven to reduce inflammation in AD and improve clinical manifestations.
4.2.1.4 Periodontitis
Periodontitis pathogenesis is primarily mediated by host immune responses that drive periodontal tissue destruction, with bacterial infection serving as the fundamental trigger for this immunopathologic cascade (74). Periodontal disease etiology primarily involves pathogenic bacterial colonization, commensal microbiota depletion, and host susceptibility. Patients with severe periodontitis may ingest 108-1010 Porphyromonas gingivalis cells daily, a keystone periodontal pathogen (75). The therapeutic application of beneficial bacteria has emerged a novel approach for periodontal disease prevention and treatment. The therapeutic application of beneficial bacteria has emerged as a novel approach for periodontal disease prevention and treatment. The probiotic strains most frequently employed in periodontitis management include lactic acid bacteria, Bifidobacterium, and yeast. As highlighted in the review by Matsubara et al., oral probiotics demonstrate clinical utility as adjunctive therapy to scaling and root planning in periodontitis cases (76). Kuru et al. demonstrated that gingivitis patients pretreated with Bifidobacterium lactis exhibited significantly reduced IL-1β levels and elevated IL-10 concentrations in gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) compared to untreated controls (77); In vitro have further demonstrated the inhibitory effects of Bifidobacterium strains on periodontal pathogens, including Porphyromonas gingivalis (78). Oliveira et al. pointed that Bifidobacterium lactis can reduce the number of periodontal pathogenic bacteria on biofilms (79). While periodontitis exhibits multifactorial etiology, microbial dysbiosis persists as the primary pathogenic driver. Consequently, probiotics and their bioactive metabolites maintain demonstrable efficacy in promoting periodontal homeostasis.
4.2.1.5 Bacterial vaginitis
Probiotics may help prevent female reproductive disorders by sustaining microbiome equilibrium. The vaginal microbiota balance is essential for optimal host-microbe interactions that maintain vaginal health (80), demonstrating therapeutic potential against bacterial vaginosis (BV), vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), sexually transmitted infections (STIs), trichomoniasis, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, Chlamydia trachomatis infection, HIV susceptibility reduction, and genital herpes infection. BV represents the predominant cause of abnormal vaginal discharge in women aged 15–44 years, pathologically characterized by marked lactobacilli depletion accompanied by 100–1,000 fold proliferation of facultative and obligate anaerobes including Gardnerella, Prevotella, Atopobium, Mobiluncus, Bifidobacterium, Sneathia, Leptotrichia and BV-associated bacteria (81). Bastani confirmed Lactobacillus as a non-chemotherapy approach for restoring and maintaining normal urogenital flora, and indicated that probiotics, especially Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus fermentum, administered in units for 2 months can maximize the normalization of vaginal flora, help cure existing infections and prevent the recurrence of BV (82); Ling et al. demonstrated that long-term probiotic administration demonstrates superior efficacy to conventional metronidazole therapy for bacterial vaginosis (BV). Their findings indicate probiotics stabilize the vaginal microbiome by reinforcing ecological homeostasis through suppression of pathogenic bacterial proliferation (83). Furthermore, current evidence indicates that although while oral probiotics reduce recurrent BV recurrence rates, intravaginal administration may provide more rapid therapeutic resolution (84, 85).
4.2.2 Obesity
Obesity is defined as an abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may be harmful to health (86). In recent years, it has been believed that changes in the bacterial strains residing in the human intestinal tract are pathogenic factors for obesity (87). Modifying the gut microbiota of obese individuals to enhance beneficial microorganisms or probiotics has been demonstrated as a therapeutic strategy against obesity and its associated disorders (88). More specifically, owing to their high pathogenicity barrier and antibiotic resistance, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria have been shown to reduce weight and fat accumulation to varying degrees (89). Cuffaro et al. pointed out that the abundance of specific bacterial species—including Akkermansia muciniphila, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Eubacterium hallii, Anaerobutyricum hallii, Anaerobutyricum soehngenii, Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides coprocola, Parabacteroides distasonis, Parabacteroides goldsteinii, Hafnia alvei, Odoribacter laneus, and Christensenella minuta is significantly decreased in obese individuals and patients with obesity-related metabolic disorders. This microbial depletion may contribute to impaired beneficial regulation of obesity. These metabolically active commensal microbes could serve as key players in obesity prevention and treatment strategies (90). Concurrently, certain probiotic-derived components and metabolites—including cell-free extracts, extracellular polysaccharides, and short-chain fatty acids—exert inhibitory effects on metabolic syndrome through modulation of multiple signaling pathways (91). Therefore, probiotic administration represents the most direct and effective clinical approach for managing obesity and obesity-related metabolic disorders, as it can selectively enrich beneficial microbial populations and ameliorate the gut microecological imbalance characteristic of obesity.
4.2.3 Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is characterized by either diminished pancreatic insulin secretion or impaired insulin sensitivity in target tissues, ultimately leading to elevated blood glucose levels (92). Numerous studies have shown a significant association between alterations in gut microbiota composition and diabetes pathogenesis (112). Notably, dysbiosis characterized by an altered Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio correlates with enhanced intestinal permeability. The translocation of microbial metabolites across the compromised intestinal barrier can initiate downstream inflammatory cascades typical of diabetes. Importantly, specific bacterial taxa have been shown to confer protective effects through attenuation of pro-inflammatory mediators and preservation of intestinal barrier integrity, thereby mitigating diabetes risk. For example, Lactobacillus fermentans, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus casei, Rhodobacter, Achaemenophilus mucinophila and Bacteroides fragilis (93). Asemi et al. have demonstrated that multi-species probiotic supplements (a mixture of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium) can reduce fasting blood glucose (FBG) levels in patients with insulin resistance (94); Tao et al. summarized 15 randomized controlled trials involving 902 individuals. The meta-analysis results further indicated that probiotic supplementation significantly reduces glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, fasting blood glucose (FBG), and insulin resistance in patients with impaired insulin sensitivity.” (95). Consequently, gut microbiota modulation through probiotic intervention may exert beneficial effects on diabetes control and its associated complications.
4.2.4 Depression
It is well-established that the brain modulates gut function and shapes the gut microbial composition via autonomic nervous system regulation of intestinal transport, motility, secretion, and permeability (96). The gut microbiota, especially Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, has been proven to influence mental health via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Gut microbiota dysbiosis may be linked to mental disorders, including anxiety and depression. Currently, the treatment of depression is still mainly based on drug therapy. However, depression treatment remains primarily drug-based. However, orally administered pharmaceuticals substantially alter the gut microbiota. Studies indicate that clinically used antidepressants exhibit antibacterial properties, particularly against Gram-positive bacteria. Compared to drug-free controls, duloxetine increased the abundance of Mycobacterium rectum by more than 100 times (97). Evidence indicates that specific lactic acid bacteria strains (including Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus paracasei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus brevis) generate anti-inflammatory butyrates during metabolic processes. Elevated abundance of these strains may provide adjunctive benefits to antidepressant therapy by potentiating therapeutic effects (98). Wallace et al. administered Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium longum supplements to 10 patients with major depressive disorder (MDD). Their results demonstrated that daily probiotic supplementation significantly alleviated anxiety symptoms (99). Consequently, probiotic-based interventions have emerged as a novel therapeutic approach for depression management.
4.2.5 High blood lipid
Bile acids (BAs) are regarded as the key regulators of intestinal microbiota composition and function. Hepatic lipid metabolic efficiency determines the quantity of bile acids (BAs) entering the intestinal lumen, thereby influencing gut microbiota homeostasis (100), this dual regulatory mechanism inhibits bacterial overgrowth and preserves intestinal microbiota equilibrium, thereby mitigating intestinal barrier dysfunction (101). The clinical trial by Guerrero-Bonmatty et al. revealed that a triple-strain combination of Lactobacillus plantarum significantly reduced serum cholesterol levels in patients (102); Furthermore, a clinical trial by Park et al. involving 70 healthy adults showed that daily supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum Q180 significantly improved postprandial lipid parameters indicators, including low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and total cholesterol (TC), through gut microbiota modulation (103). These studies demonstrate that probiotics can modulate serum lipid profiles (TC, TG, HDL-C, and LDL-C) by enhancing probiotic colonization and regulating associated metabolites. Consequently, the involvement and mechanistic role of gut microbiota in hyperlipidemia pathogenesis have become increasingly evident. Microbiota-targeted therapeutic strategies for hyperlipidemia management and prevention represent a promising research frontier.
4.2.6 Cancer
Through the gut-organ axis, the intestinal microbiota exerts both direct and indirect effects on immune responses and host physiology, thereby transforming cancer immunology (104). Specific cellular components of probiotic lactic acid bacteria may exert potential immunomodulatory effects, including regulation of cell-mediated immune responses, activation of the reticuloendothelial system, potentiation of cytokine signaling pathways, and modulation of interleukin and tumor necrosis factor production (105). Thirabunyanon et al. demonstrated that the viable probiotic strains of Enterococcus faecium and Lactobacillus fermentum in fermented milk effectively induced anti-proliferation effects in colon cancer cells in vitro (106); Toi et al. demonstrated in their study that regular intake of Lactobacillus casei probiotics combined with soy isoflavones significantly lowers breast cancer risk (107); Zhang et al. reported that Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus casei produce bioactive compounds capable of inhibiting MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation (108). We observed that certain inhibitory compounds produced by probiotics exhibit beneficial effects against tumor cells. Escamilla et al. demonstrated that cell-free supernatants containing secreted bioactive macromolecules from Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG inhibited metastasis of human colon carcinoma cells (HCT-116) in vitro (109). Moreover, the probiotic Acetobacter syzygii exhibits prophylactic efficacy against oral cavity carcinoma, particularly squamous cell carcinoma. This demonstrates the beneficial role of probiotics in preventing oral diseases. Secretions from these strains demonstrate cytotoxic effects against oral cancer cell lines through apoptosis induction (110). In summary, as a valuable dietary supplement, probiotics contribute to reducing the risk of multiple cancer types while supporting the safety of conventional cancer treatments including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgical procedures. The combination of probiotics with prebiotics demonstrates enhanced efficacy in both cancer prevention and treatment compared to probiotic use alone. Moreover, successful cancer prevention and treatment outcomes depend on specific probiotic strains, whether bacterial or fungal, along with appropriate dosage regimens and treatment duration.
5 Limitation
This study has several limitations. (1) To ensure high-quality bibliometric analysis, the investigation was restricted to English-language articles indexed in the Web of Science database. While Web of Science represents the most authoritative database for scientific publications across numerous research fields, this approach inevitably excluded studies published in non-SCI journals or other databases, introducing potential selection bias. Additionally, some high-quality publications might have been overlooked due to recent publication dates or low citation frequencies. Consequently, this bibliometric approach cannot fully substitute comprehensive systematic review methods. (2) The Cite Space and VOS viewer software packages present certain limitations. These analytical tools lack the capability to automatically consolidate keywords or subject terms with similar semantic meanings. Consequently, researchers must manually analyze and merge such terms, a process that may introduce potential inaccuracies in the research outcomes. (3) In identifying research hotspots and developmental trends, this study analyzed keyword frequency, centrality, and temporal distribution. While this approach is data-driven through literature keywords, it nevertheless retains an inherent degree of methodological subjectivity. (4) Bibliometrics analysis cannot evaluate the quality of individual studies as citation metrics are time-sensitive, More recent articles may receive fewer citations compared to earlier works primarily due to their publication date (111), These restrictions may have a slight impact on the overall results, but they do not affect the final results. Overall, our research provides a basis for understanding the research topics, hotspots and development trends of clinical applications related to probiotics.
6 Conclusion
At the dawn of the twentieth century, probiotics emerged as a distinct scientific concept. Over subsequent decades, probiotic-related publications increased exponentially. However, existing studies failed to provide a comprehensive overview encompassing literature distribution, research themes, and field frontiers, thereby limiting further advancement in this research domain. Building upon this foundation, the present study employs bibliometric visualization techniques utilizing VOS viewer and Cite Space software to analyze 3,674 probiotic-related clinical research articles indexed in the Web of Science core database. Through systematic keyword and core author selection, this investigation conducts a comprehensive, in-depth evaluation of publication patterns across temporal, geographic, institutional, authorial, and journal-specific dimensions, while innovatively assessing research themes within this field. Hot spots, collaborative networks and emerging trends collectively provide a macroscopic perspective on the current status and developmental trajectory of probiotic applications in medical research. This study reveals that scholarly attention in this field initially emerged in 2002. Our study offers foundational insights into current research within this field while identifying potential collaborators for researchers. The primary research foci currently center on probiotic applications in inflammatory conditions (including diarrhea, ulcerative colitis, dermatitis, periodontitis, and bacterial vaginosis), metabolic disorders (obesity, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia), mental health (depression), and oncology. Moreover, there has been a progressive increase in other clinical studies investigating probiotic applications. However, cooperation network among authors, institutions and countries within this research domain remain relatively fragmented, with only small clusters primarily concentrated in scientifically advanced developed and developing countries. These findings enable the academic community to identify emerging research directions and facilitate future clinical applications of probiotics, potentially serving as valuable references for subsequent investigations.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
YL: Writing – original draft. YY: Writing – original draft. ZZ: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. YG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Drug Safety Research Project 2024 of Guangxi Drug Administration (No. 039).
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all the authors for their support of the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rohr MW, Narasimhulu CA, Rudeski-Rohr TA, Parthasarathy S. Negative effects of a high-fat diet on intestinal permeability: a review. Adv Nutr. (2020) 11:77–91. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmz061
2. Zeyda M, Stulnig TM. Adipose tissue macrophages. Immunol Lett. (2007) 112:61–7. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.07.003
3. Kanneganti TD, Dixit VD. Immunological complications of obesity. Nat Immunol. (2012) 13:707–12. doi: 10.1038/ni.2343
4. O'toole P. W, Marchesi J. R, Hill C. (2017). Next-generation probiotics: the spectrum from probiotics to live biotherapeutics. Nat Microbiol. 2, 17057. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.57
5. Khatun MT, Hoque F, Hoque NS, Hossain MS, Alam MA, Afrin S, et al. Emerging role of probiotics in advancement of combating physical abnormalities and diseases: a systematic perspective analysis. Asian J Biochem Genet Mol Biol. (2024) 16:1–23. doi: 10.9734/ajbgmb/2024/v16i8397
6. Zhu E, Qi Q, Sha M. Identify the effects of urbanization on carbon emissions (EUCE): a global scientometric visualization analysis from 1992 to 2018. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2021) 28:31358–69. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-12858-1
7. Van Eck NJ, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. (2010) 84:523–38. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
8. Chen C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2004) 101:5303–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307513100
9. Chen C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol. (2005) 57:359–77. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317
10. Cheng P, Tang H, Dong Y, Liu K, Jiang P, Liu Y, et al. Knowledge mapping of research on land use change and food security: a visual analysis using CiteSpace and VOSviewer. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:13065. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182413065
11. Waqas A, Teoh SH, Lapao LV, Messina LA, Correia JC. Harnessing telemedicine for the provision of health care: bibliometric and scientometric analysis. J Med Internet Res. (2020) 22:e18835. doi: 10.2196/18835
12. Zhao Y, Zhang X, Song Z, Wei D, Wang H, Chen W, et al. Bibliometric analysis of ATAC-Seq and its use in cancer biology via nucleic acid detection. Front Med. (2020) 7:584728. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.584728
13. Wu H, Li Y, Tong L, Wang Y, Sun Z. Worldwide research tendency and hotspots on hip fracture: a 20-year bibliometric analysis. Arch Osteoporos. (2021) 16:73. doi: 10.1007/s11657-021-00929-2
14. Garfield E. The history and meaning of the journal impact factor. JAMA. (2006) 295:90–3. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.1.90
15. Cyranoski D. China splashes millions on hundreds of home-grown journals. Nature. (2019) 576:346–7. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-03770-3
16. Fuster V. Impact factor: a curious and capricious metric. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 70:1530–1. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.08.002
17. Gao Q, Zhang C, Wang J, Wei Q, Wei Q, Miyamoto A, et al. The top 100 highly cited articles on osteoporosis from 1990 to 2019: a bibliometric and visualized analysis. Arch Osteoporos. (2020) 15:144. doi: 10.1007/s11657-020-0705-z
18. Buffie CG, Bucci V, Stein RR, Mckenney PT, Ling L, Gobourne A, et al. Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile. Nature. (2015) 517:205–8. doi: 10.1038/nature13828
19. Sanders ME, Merenstein DJ, Reid G, Gibson GR, Rastall RA. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: from biology to the clinic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 16:605–16. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0173-3
20. Ye N, Kueh T-B, Hou L, Liu Y, Yu H. A bibliometric analysis of corporate social responsibility in sustainable development. J Clean Prod. (2020) 272:122679. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122679
21. Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Venturi A, Brigidi P, Matteuzzi D, Bazzocchi G, et al. Oral bacteriotherapy as maintenance treatment in patients with chronic pouchitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology. (2000) 119:305–9. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.9370
22. Kalliomaki M, Salminen S, Arvilommi H, Kero P, Koskinen P, Isolauri E, et al. Probiotics in primary prevention of atopic disease: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. (2001) 357:1076–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04259-8
23. Zhang X, Lai H, Zhang F, Wang Y, Zhang L, Yang N, et al. Visualization and Analysis in the Field of Pan-Cancer Studies and Its Application in Breast Cancer Treatment. Front Med. (2021) 8:635035. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.635035
24. Tabrizi R, Ostadmohammadi V, Akbari M, Lankarani KB, Vakili S, Peymani P, et al. The effects of probiotic supplementation on clinical symptom, weight loss, glycemic control, lipid and hormonal profiles, biomarkers of inflammation, and oxidative stress in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. (2022) 14:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s12602-019-09559-0
25. Farajipour H, Matin HR, Asemi Z, Sadr S, Tajabadi-Ebrahimi M, Sharifi N, et al. The effects of probiotics supplements on metabolic indices and clinical signs in patients with diabetic retinopathy, a randomized double blind clinical trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord. (2024) 23:1133–40. doi: 10.1007/s40200-024-01399-2
26. Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2005) 102:16569–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507655102
27. Tamtaji OR, Milajerdi A, Reiner Z, Asemi Z, Dadgostar E, Heidari-Soureshjani R, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis: the effects of probiotic supplementation on metabolic profile in patients with neurological disorders. Complement Ther Med. (2020) 53:102507. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102507
28. Stuivenberg GA, Burton JP, Bron PA, Reid G. Why are bifidobacteria important for infants? Microorganisms. (2022) 10:278. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020278
29. Al KF, Parris J, Engelbrecht K, Reid G, Burton JP. Interconnected microbiomes-insights and innovations in female urogenital health. FEBS J. (2025) 292:1378–96. doi: 10.1111/febs.17235
30. Stuivenberg GA, Chmiel JA, Akouris PP, White J, Wilcox H, Seney S, et al. Supplementing yogurt with probiotic bifidobacteria to counter chronic kidney disease. Fermentation. (2023) 9:391. doi: 10.3390/fermentation9040391
31. Daniels VC, Monaco MH, Hirvonen J, Ouwehand AC, Jensen HM, Mukerjea R, et al. Interactions between the human milk oligosaccharide2′-fucosyllactose and Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis in influencing systemic immune development and function in piglets. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1444594. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1444594
32. Capirchio L, Rousseaux C, Dubuquoy C, Ouwehand AC, Maquet V, Modica S, et al. A synbiotic combining chitin-glucan and Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM induces a colonic molecular signature soothing intestinal pain and inflammation in an animal model of IBS. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:10732. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910732
33. Jensen BAH, Heyndrickx M, Jonkers D, Mackie A, Millet S, Naghibi M, et al. Small intestine vs. colon ecology and physiology: Why it matters in probiotic administration. Cell Rep Med. (2023) 4:101190. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101190
34. Anglenius H, Makivuokko H, Ahonen I, Forssten SD, Wacklin P, Matto J, et al. In vitro screen of lactobacilli strains for gastrointestinal and vaginal benefits. Microorganisms. (2023) 11:329. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020329
35. Forssten SD, Ouwehand AC, Griffin SM, Patterson E. One giant leap from mouse to man: the microbiota-gut-brain axis in mood disorders and translational challenges moving towards human clinical trials. Nutrients. (2022) 14:568. doi: 10.3390/nu14030568
36. Foster JA, Mcvey Neufeld KA. Gut-brain axis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. (2013) 36:305–12. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2013.01.005
37. Wilkins T, Sequoia J. Probiotics for gastrointestinal conditions: a summary of the evidence. Am Fam Physician. (2017) 96:170–8.
38. Sebastian Domingo JJ. Review of the role of probiotics in gastrointestinal diseases in adults. Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 40:417–29. doi: 10.1016/j.gastre.2016.12.001
39. Burokas A, Moloney RD, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Microbiota regulation of the Mammalian gut-brain axis. Adv Appl Microbiol. (2015) 91:1–62. doi: 10.1016/bs.aambs.2015.02.001
40. Rieder R, Wisniewski PJ, Alderman BL, Campbell SC. Microbes and mental health: a review. Brain Behav Immun. (2017) 66:9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.01.016
41. Bruce-Keller AJ, Salbaum JM, Berthoud HR. Harnessing gut microbes for mental health: getting from here to there. Biol Psychiatry. (2018) 83:214–23. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.08.014
42. Guo S, Wang L, Xie Y, Luo X, Zhang S, Xiong L, et al. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of stem cells therapy for spinal cord injury based on web of science and CiteSpace in the last 20 years. World Neurosurg. (2019) 132:e246–58. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.08.191
43. Algieri F, Garrido-Mesa J, Vezza T, Rodriguez-Sojo MJ, Rodriguez-Cabezas ME, Olivares M, et al. Intestinal anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics in DNBS-colitis via modulation of gut microbiota and microRNAs. Eur J Nutr. (2021) 60:2537–51. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02441-8
44. Cristofori F, Dargenio VN, Dargenio C, Miniello VL, Barone M, Francavilla R, et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: a door to the body. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:578386. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.578386
45. Weiss GA, Hennet T. Mechanisms and consequences of intestinal dysbiosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2017) 74:2959–77. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2509-x
46. Bhattarai Y, Muniz Pedrogo DA, Kashyap PC. Irritable bowel syndrome: a gut microbiota-related disorder? Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2017) 312:G52–62. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00338.2016
47. Mari A, Abu Baker F, Mahamid M, Sbeit W, Khoury T. The evolving role of gut microbiota in the management of irritable bowel syndrome: an overview of the current knowledge. J Clin Med. (2020) 9. doi: 10.3390/jcm9030685
48. Ford AC, Lacy BE, Talley NJ. Irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med. (2017) 376:2566–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1607547
49. Zheng D, Liwinski T, Elinav E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. (2020) 30:492–506. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0332-7
50. Kechagia M, Basoulis D, Konstantopoulou S, Dimitriadi D, Gyftopoulou K, Skarmoutsou N, et al. Health benefits of probiotics: a review. ISRN Nutr. (2013) 2013:481651. doi: 10.5402/2013/481651
51. Abid MB, Koh CJ. Probiotics in health and disease: fooling Mother Nature? Infection. (2019) 47:911–7. doi: 10.1007/s15010-019-01351-0
52. Liang D, Longgui N, Guoqiang X. Efficacy of different probiotic protocols in irritable bowel syndrome: a network meta-analysis. Medicine. (2019) 98:e16068. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016068
53. Niu HL, Xiao JY. The efficacy and safety of probiotics in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: Evidence based on 35 randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. (2020) 75:116–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.01.142
54. Skrzydlo-Radomanska B, Prozorow-Krol B, Cichoz-Lach H, Majsiak E, Bierla JB, Kanarek E, et al. The effectiveness and safety of multi-strain probiotic preparation in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized controlled study. Nutrients. (2021) 13:756. doi: 10.3390/nu13030756
55. Ishaque SM, Khosruzzaman SM, Ahmed DS, Sah MP. A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial of a multi-strain probiotic formulation (Bio-Kult(R)) in the management of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol. (2018) 18:71. doi: 10.1186/s12876-018-0788-9
56. Lukasik J, Dierikx T, Besseling-Van Der Vaart I, De Meij T, Szajewska H, Multispecies Probiotic AAD Study Group. Multispecies probiotic for the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. (2022) 176:860–6. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.1973
57. Ahmed J, Reddy BS, Molbak L, Leser TD, Macfie J. Impact of probiotics on colonic microflora in patients with colitis: a prospective double blind randomised crossover study. Int J Surg. (2013) 11:1131–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2013.08.019
58. Hansen J, Gulati A, Sartor RB. The role of mucosal immunity and host genetics in defining intestinal commensal bacteria. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. (2010) 26:564–71. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e32833f1195
59. Sarowska J, Choroszy-Krol I, Regulska-Ilow B, Frej-Madrzak M, Jama-Kmiecik A. The therapeutic effect of probiotic bacteria on gastrointestinal diseases. Adv Clin Exp Med. (2013) 22:759–66.
60. Cain AM, Karpa KD. Clinical utility of probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Altern Ther Health Med. (2011) 17:72–9.
61. Oliva S, Di Nardo G, Ferrari F, Mallardo S, Rossi P, Patrizi S, et al. Randomised clinical trial: the effectiveness of Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 rectal enema in children with active distal ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2012) 35:327–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04939.x
62. Schultz M. Clinical use of E. coli Nissle 1917 in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2008) 14:1012–8. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20377
63. Kruis W, Fric P, Pokrotnieks J, Lukas M, Fixa B, Kascak M, et al. Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut. (2004) 53:1617–23. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.037747
64. Stefanovic N, Flohr C, Irvine AD. The exposome in atopic dermatitis. Allergy. (2020) 75:63–74. doi: 10.1111/all.13946
65. Salem I, Ramser A, Isham N, Ghannoum MA. The gut microbiome as a major regulator of the gut-skin axis. Front Microbiol. (2018) 9:1459. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01459
66. O'neill CA, Monteleone G, Mclaughlin JT, Paus R. The gut-skin axis in health and disease: a paradigm with therapeutic implications. Bioessays. (2016) 38:1167–76. doi: 10.1002/bies.201600008
67. Oh J, Byrd AL, Park M, Program NCS, Kong HH, Segre JA, et al. Temporal Stability of the Human Skin Microbiome. Cell. (2016) 165:854–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.008
68. Oh J, Byrd AL, Deming C, Conlan S, Program NCS, Kong HH, et al. Biogeography and individuality shape function in the human skin metagenome. Nature. (2014) 514:59–64. doi: 10.1038/nature13786
69. Byrd AL, Deming C, Cassidy SKB, Harrison OJ, Ng WI, Conlan S, et al. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis strain diversity underlying pediatric atopic dermatitis. Sci Transl Med. (2017) 9:aal4651. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal4651
70. Leyden JJ, Marples RR, Kligman AM. Staphylococcus aureus in the lesions of atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. (1974) 90:525–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1974.tb06447.x
71. Hevia A, Milani C, Lopez P, Donado CD, Cuervo A, Gonzalez S, et al. Allergic patients with long-term asthma display low levels of Bifidobacterium adolescentis. PLoS ONE. (2016) 11:e0147809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147809
72. Enomoto T, Sowa M, Nishimori K, Shimazu S, Yoshida A, Yamada K, et al. Effects of bifidobacterial supplementation to pregnant women and infants in the prevention of allergy development in infants and on fecal microbiota. Allergol Int. (2014) 63:575–85. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.13-OA-0683
73. Tan-Lim CSC, Esteban-Ipac NAR, Recto MST, Castor MAR, Casis-Hao RJ, Nano ALM, et al. Comparative effectiveness of probiotic strains on the prevention of pediatric atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. (2021) 32:1255–70. doi: 10.1111/pai.13514
74. Sanz M, Quirynen M, European Workshop In Periodontology Group A. Advances in the aetiology of periodontitis. Group A consensus report of the 5th European Workshop in Periodontology. J Clin Periodontol. (2005) 32:54–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00827.x
75. Olsen I, Yamazaki K. Can oral bacteria affect the microbiome of the gut? J Oral Microbiol. (2019) 11:1586422. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2019.1586422
76. Matsubara VH, Bandara HM, Ishikawa KH, Mayer MP, Samaranayake LP. The role of probiotic bacteria in managing periodontal disease: a systematic review. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. (2016) 14:643–55. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2016.1194198
77. Kuru BE, Laleman I, Yalnizoglu T, Kuru L, Teughels W. The influence of a Bifidobacterium animalis probiotic on gingival health: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. (2017) 88:1115–23. doi: 10.1902/jop.2017.170213
78. Jasberg H, Soderling E, Endo A, Beighton D, Haukioja A. Bifidobacteria inhibit the growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis but not of Streptococcus mutans in an in vitro biofilm model. Eur J Oral Sci. (2016) 124:251–8. doi: 10.1111/eos.12266
79. Oliveira LF, Salvador SL, Silva PH, Furlaneto FA, Figueiredo L, Casarin R, et al. Benefits of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis probiotic in experimental periodontitis. J Periodontol. (2017) 88:197–208. doi: 10.1902/jop.2016.160217
80. Tama RT, Hossain MS, Rahaman MA, Alam MA, Rahman M-M, Parvin A, et al. Harnessing the power of natural products against bacterial urinary tract infections: a perspective review for cultivating solutions. Health Sci Rev. (2024) 13:100199. doi: 10.1016/j.hsr.2024.100199
81. Muzny CA, Taylor CM, Swords WE, Tamhane A, Chattopadhyay D, Cerca N, et al. An updated conceptual model on the pathogenesis of bacterial vaginosis. J Infect Dis. (2019) 220:1399–405. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz342
82. Reid G, Younes JA, Van Der Mei HC, Gloor GB, Knight R, Busscher HJ, et al. Microbiota restoration: natural and supplemented recovery of human microbial communities. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2011) 9:27–38. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2473
83. Ling Z, Liu X, Chen W, Luo Y, Yuan L, Xia Y, et al. The restoration of the vaginal microbiota after treatment for bacterial vaginosis with metronidazole or probiotics. Microb Ecol. (2013) 65:773–80. doi: 10.1007/s00248-012-0154-3
84. Tester R, Al-Ghazzewi FH. Intrinsic and extrinsic carbohydrates in the vagina: a short review on vaginal glycogen. Int J Biol Macromol. (2018) 112:203–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.166
85. Reznichenko H, Henyk N, Maliuk V, Khyzhnyak T, Tynna Y, Filipiuk I, et al. Oral intake of lactobacilli can be helpful in symptomatic bacterial vaginosis: a randomized clinical study. J Low Genit Tract Dis. (2020) 24:284–9. doi: 10.1097/LGT.0000000000000518
86. Bray GA, Ryan DH. Clinical evaluation of the overweight patient. Endocrine. (2000) 13:167–86. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:13:2:167
87. Castaner O, Goday A, Park YM, Lee SH, Magkos F, Shiow STE, et al. The gut microbiome profile in obesity: a systematic review. Int J Endocrinol. (2018) 2018:4095789. doi: 10.1155/2018/4095789
88. Li HY, Zhou DD, Gan RY, Huang SY, Zhao CN, Shang A, et al. Effects and mechanisms of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics on metabolic diseases targeting gut microbiota: a narrative review. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3211. doi: 10.3390/nu13093211
89. Luoto R, Kalliomaki M, Laitinen K, Isolauri E. The impact of perinatal probiotic intervention on the development of overweight and obesity: follow-up study from birth to 10 years. Int J Obes (Lond). (2010) 34:1531–7. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2010.50
90. Cuffaro B, Assohoun ALW, Boutillier D, Peucelle V, Desramaut J, Boudebbouze S, et al. Identification of new potential biotherapeutics from human gut microbiota-derived bacteria. Microorganisms. (2021) 9:565. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030565
91. Chen YC, Huang SD, Tu JH, Yu JS, Nurlatifah AO, Chiu WC, et al. Exopolysaccharides of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens modulate glycemic level in mice and promote glucose uptake of cells through the activation of Akt. Int J Biol Macromol. (2020) 146:202–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.217
92. Defronzo RA. Current issues in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Overview of newer agents: where treatment is going. Am J Med. (2010) 123:S38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.12.008
93. Lee CB, Chae SU, Jo SJ, Jerng UM, Bae SK. The relationship between the gut microbiome and metformin as a key for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:3566. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073566
94. Asemi Z, Zare Z, Shakeri H, Sabihi SS, Esmaillzadeh A. Effect of multispecies probiotic supplements on metabolic profiles, hs-CRP, and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann Nutr Metab. (2013) 63:1–9. doi: 10.1159/000349922
95. Li C, Li X, Han H, Cui H, Peng M, Wang G, et al. Effect of probiotics on metabolic profiles in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Medicine. (2016) 95:e4088. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004088
96. Furness JB. The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2012) 9:286–94. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.32
97. Vich Vila A, Collij V, Sanna S, Sinha T, Imhann F, Bourgonje AR, et al. Impact of commonly used drugs on the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:362. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14177-z
98. Klunemann M, Andrejev S, Blasche S, Mateus A, Phapale P, Devendran S, et al. Bioaccumulation of therapeutic drugs by human gut bacteria. Nature. (2021) 597:533–8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03891-8
99. Wallace CJK, Milev RV. The efficacy, safety, and tolerability of probiotics on depression: clinical results from an open-label pilot study. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 12:618279. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.618279
100. Zhu L, Baker RD, Zhu R, Baker SS. Bile acids and the gut microbiome as potential targets for NAFLD treatment. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2018) 67:3–5. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002010
101. Parseus A, Sommer N, Sommer F, Caesar R, Molinaro A, Stahlman M, et al. Microbiota-induced obesity requires farnesoid X receptor. Gut. (2017) 66:429–37. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310283
102. Guerrero-Bonmatty R, Gil-Fernandez G, Rodriguez-Velasco FJ, Espadaler-Mazo J. A combination of Lactoplantibacillus plantarum strains CECT7527, CECT7528, and CECT7529 plus monacolin K reduces blood cholesterol: results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1206. doi: 10.3390/nu13041206
103. Park YE, Kim MS, Shim KW, Kim YI, Chu J, Kim BK, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Q180 on postprandial lipid levels and intestinal environment: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel trial. Nutrients. (2020) 12:255. doi: 10.3390/nu12010255
104. Derosa L, Routy B, Desilets A, Daillere R, Terrisse S, Kroemer G, et al. Microbiota-centered interventions: the next breakthrough in immuno-oncology? Cancer Discov. (2021) 11:2396–412. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0236
105. Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. (2013) 49:1374–403. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.12.027
106. Thirabunyanon M, Boonprasom P, Niamsup P. Probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented dairy milks on antiproliferation of colon cancer cells. Biotechnol Lett. (2009) 31:571–6. doi: 10.1007/s10529-008-9902-3
107. Toi M, Hirota S, Tomotaki A, Sato N, Hozumi Y, Anan K, et al. Probiotic beverage with soy isoflavone consumption for breast cancer prevention: a case-control study. Curr Nutr Food Sci. (2013) 9:194–200. doi: 10.2174/15734013113099990001
108. Zhang G, Zhang J, Wang X, Yang W, Sun Z, Kumar CN, et al. Apoptosis of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell (CAL-27) induced by Lactobacillus sp. A-2 metabolites. J Appl Oral Sci. (2014) 22:282–6. doi: 10.1590/1678-775720130645
109. Escamilla J, Lane MA, Maitin V. Cell-free supernatants from probiotic Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG decrease colon cancer cell invasion in vitro. Nutr Cancer. (2012) 64:871–8. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2012.700758
110. Aghazadeh Z, Pouralibaba F, Yari Khosroushahi A. The prophylactic effect of Acetobacter syzygii probiotic species against squamous cell carcinoma. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. (2017) 11:208–14. doi: 10.15171/joddd.2017.037
111. Nichols JJ, Jones LW, Morgan PB, Efron N. Bibliometric analysis of the meibomian gland literature. Ocul Surf. (2021) 20:212–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2021.03.004
112. Mohseni S, Bayani M, Bahmani F, Tajabadi-Ebrahimi M, Bayani MA, Jafari P, et al. The beneficial effects of probiotic administration on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2018) 34:e2970. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2970
Keywords: probiotics, clinical application, bibliometrics, visual analysis, Cite Space, VOS viewer
Citation: Li Y, Yao Y, Zhang Z and Gan Y (2025) Research status and development trends of probiotics in clinical applications. Front. Nutr. 12:1650883. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1650883
Received: 23 June 2025; Accepted: 25 August 2025;
Published: 09 September 2025.
Edited by:
Hengyi Xu, Nanchang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Emre Batuhan Kenger, Istanbul Bilgi University, TürkiyeRahima Tanbin Tama, Islamic University, Bangladesh
Copyright © 2025 Li, Yao, Zhang and Gan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zan Zhang, MjU3MTY5OTBAcXEuY29t; Yongqi Gan, amFja3lnYW5fNDEzQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yang Li
Yang Li Yucheng Yao
Yucheng Yao Zan Zhang2*
Zan Zhang2*