- 1Department of Clinical Nutrition, Zibo First Hospital, Zibo, China
- 2Department of Dialysis Room, Zibo First Hospital, Zibo, China
Background and aim: Patients on maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) experience various complications, including malnutrition, reduced physical function, and psychological problems. Single-discipline medical approaches prove inadequate in addressing these complex situations. The multidisciplinary management model adopted by the nutritional support team has demonstrated effectiveness in managing such challenges. However, patient compliance remains suboptimal due to limited understanding of treatment regimens, fatigue from prolonged therapy, and insufficient psychological support. Consequently, establishing a patient-centered, transparent, and interactive communication platform is essential to improving treatment adherence through enhanced patient support.
Methods: This prospective randomized controlled trial assigned patients to either an experimental group receiving community-based management or a control group receiving traditional management. Health status was evaluated through laboratory parameters, body composition analysis, anthropometric measurements, and standardized scale assessments.
Results: A total of 28 patients with MHD were enrolled. Four patients died from primary disease (1 in the experimental group and 3 in the control group), leaving 24 who completed the trial. Statistical analysis was conducted on a dataset of 24 patients, including 13 in the experimental group and 11 in the control group. Seven outcomes demonstrated statistically significant differences. In terms of laboratory parameters, the experimental group achieved superior outcomes in serum albumin (12 patients, 92.3% versus 3 patients, 27.3%; p = 0.002), hemoglobin (11 patients, 84.6% versus 4 patients, 36.4%; p = 0.033), and blood phosphorus levels (10 patients, 76.9% versus 2 patients, 18.2%; p = 0.012), compared to control group. Body composition analysis indicated greater improvement in muscle mass (9 patients, 69.2% versus 3 patients, 27.3%; p = 0.038) and more favorable visceral fat distribution (11 patients, 84.6% versus 3 patients, 27.3%; p = 0.011) in the experimental group. Additionally, the experimental group scored higher on the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB; 10 patients, 76.9% versus 3 patients, 27.3%; p = 0.038) and exhibited better treatment compliance (10 patients, 76.9% versus 2 patients, 18.2%; p = 0.012). Notably, compliance mediated the effect of community-based management on SPPB scores (Proportion Mediated = 76.2%; p = 0.038).
Conclusion: Community-based management by the nutrition support team substantially improves patient compliance and enhances clinical outcomes.
Clinical trial registration: chictr.org.cn, identifier ChiCTR2500104523.
Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects over 10% of the global population (1). As the disease progresses, an increasing number of patients require maintenance hemodialysis (MHD), a trend that continues to rise (2). By 2030, over 5.4 million individuals worldwide are projected to undergo renal replacement therapy (3), with more than 80% of patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) dependent on MHD for survival (4, 5). Although MHD sustains life in patients with ESRD, it does not resolve all associated complications. Patients continue to experience malnutrition (6), coronary artery calcification (7), treatment-resistant hypertension (8), frailty (9), impaired physical function (10), and psychological problems (11, 12). The complexity of these conditions limits the effectiveness of single-specialty care in nephrology, highlighting the need for multidisciplinary collaborative management.
The interdisciplinary management model of the nutrition support team (NST) (13) effectively addresses this issue. Established in the 1970s, the NST formed an interdisciplinary team comprising physicians, nurses, nutritionists, and pharmacists (13). Initially, the team aimed to reduce the high rates of central venous catheter-related sepsis and mechanical complications (13). Over time, NST has consistently delivered significant clinical benefits (13). Previously, the NST focused on inpatient care by identifying individuals with nutritional issues, conducting comprehensive nutritional assessments, and delivering safe, effective nutritional interventions (13). Currently, NST provides management for hospitalized patients and extends support to those requiring home-based nutritional therapy (14). Although the NST provides safe and up-to-date nutritional support (15), its impact on clinical outcomes remains poorly understood, with limited supporting evidence (16). Patient compliance remains a critical factor influencing effectiveness (17, 18).
Research highlights a high prevalence of psychological disorders among patients with MHD (11, 12). These conditions substantially reduced both quality of life (19) and self-efficacy (20). According to social cognitive theory, self-efficacy refers to an individual’s confidence in their ability to perform specific behaviors, which is closely linked to treatment compliance (21). Low self-efficacy contributes to poor adherence (20), resulting in biased treatment and uncertain outcomes. For patients with MHD, hemodialysis is only one aspect of treatment; compliance is crucial for achieving effective outcomes.
Community-based management plays a vital role in supporting patient outcomes. Its primary objective is to foster group development by establishing an interactive platform that facilitates patient engagement. Under the guidance of healthcare professionals, patients gain knowledge about their treatment, share personal experiences, ask questions, and collaboratively identify solutions. Regularly structured activities, including health seminars, experience-sharing sessions, and group psychological counseling, encourage proactive self-management. Simultaneously, healthcare providers act as supportive partners, offering essential guidance and assisting patients in addressing specific challenges during therapy, thereby enhancing the overall treatment experience.
Methods
Research design
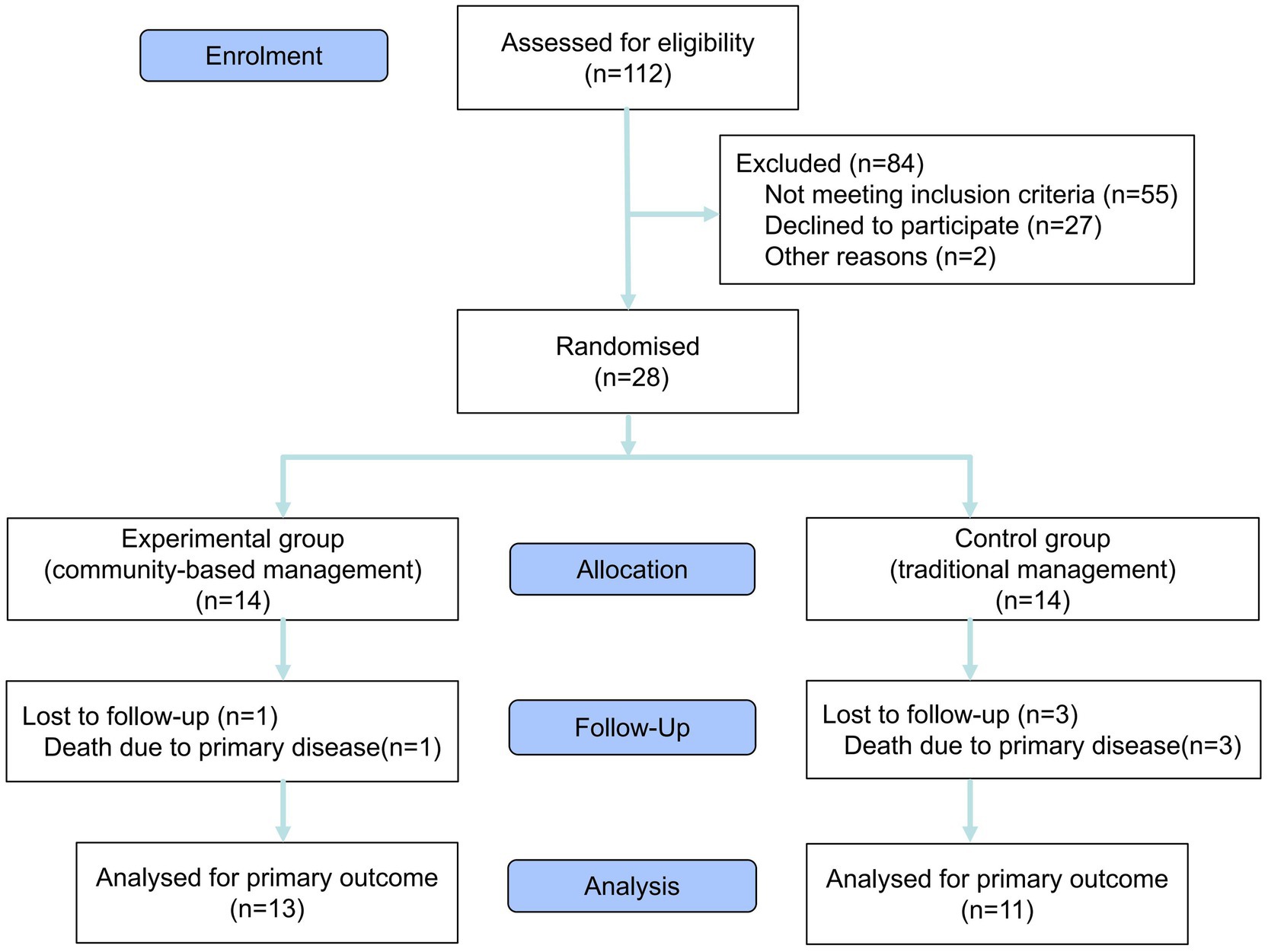
A prospective randomized controlled trial was conducted in January 2025. This was a single-center pilot study, involving 28 patients recruited from the dialysis department at Zibo First Hospital, with the study period lasting from January to June 2025. Before the trial commenced, demographic and laboratory data were collected for all 112 patients in the dialysis unit. Eligible participants were screened using a baseline survey. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) confirmed diagnosis of ESRD; (2) serum albumin (ALB) levels below 38 g/L; (3) absence of malignancy; (4) age ≥ 18 years; (5) provision of informed consent and agreement to comply with all study-related requirements. Patients not meeting these criteria were excluded. Ultimately, 28 patients met eligibility criteria and provided informed consent to participate. Fourteen slips marked with odd numbers and 14 with even numbers were placed in an opaque container. Subsequently, all 28 patients were instructed to randomly draw one slip each from an opaque container. Patients selecting even numbers were assigned to the experimental group, while those drawing odd numbers were allocated to the control group. The experimental cohort adopted a community-based management model. Individualized treatment plans were developed for the 14 participants, incorporating tailored nutritional regimens, structured exercise routines, and prescribed medication schedules. Monthly follow-ups were conducted to adjust treatment protocols as needed. A dedicated WeChat group facilitated communication between researchers and participants, providing weekly online health education, monthly in-person exchange meetings, and twice-monthly group psychological counseling sessions. Themes for all activities were proposed by researchers and communicated to participants 2 days in advance to promote full engagement. Simultaneously, all researchers and participants were notified that they were not allowed to reveal the content of the activities. The control group followed conventional management methods. Individualized treatment plans were also developed for the 14 participants in the control group, comprising nutritional guidance, structured exercise routines, and prescribed medication schedules. Adjustments to treatment plans were made exclusively during monthly follow-ups, with no additional interventions beyond routine care. All 28 participants underwent assessments at both the beginning and end of the trial, including laboratory tests, body composition analysis, anthropometric measurements, and standardized scale evaluation (Figure 1 provides details). This study was conducted as a single-blind trial. To maintain research anonymity and objectivity in data processing, participants’ identities in this study were anonymized through the assignment of randomized numerical identifiers. The experimental data collection was independently executed by a professionally trained medical staff member, ensuring that the entire data acquisition and processing workflow remained confidential from the researchers responsible for statistical analysis.
Definition of traditional management
Traditional management entails the development of individualized nutrition and exercise regimens, the establishment and maintenance of comprehensive health records, and the scheduling of regular consultations. Management is structured around the individual as the primary unit of care.
Definition of community-based management
Community-based management involves designing personalized nutrition and exercise regimens, maintaining comprehensive health records, and scheduling regular consultations. In parallel, a WeChat group was established for patients to receive regular-dialysis-related nutritional education and to monitor lifestyle behaviors through a check-in system encompassing diet, physical activity, medication adherence, and related activities. Regular group psychological counseling sessions were conducted, incorporating activities such as mandala painting (22), psychological games, and peer-sharing discussions. Management is structured around the group as the central unit of care.
Assessment of indicators
ALB, prealbumin, and grip strength
Improvement: Values were higher at the end of the trial compared to baseline.
No improvement: (1) Values lower at the end than at baseline; (2) No change.
Potassium (K), phosphorus (P), calcium (Ca), hemoglobin (HGB), body fat percentage, visceral fat area, and body mass index
Improvement: (1) Values within the normal range; (2) Values abnormal but trending toward normal.
No improvement: Values were abnormal and trending toward deterioration.
References values were as follows: K 3.5–5.3 mmol/L (23), P 0.85–1.51 mmol/L (24), Ca 2.11–2.52 mmol/L (24), HGB 130–175 g/L for males and 115–150 g/L for females (25), body fat percentage < 17.5% for males and < 31.5% for females (26), visceral fat area < 100 cm2 (27), and body mass index 18.5–23.9 kg/m2 (28).
Creatinine and urea nitrogen
Improvement: Levels were lower at the end compared to the baseline.
No improvement: (1) Levels were higher at the end than at baseline; (2) No change.
Muscle mass and arm circumference
Improvement: (1) Levels were higher at the end than at baseline; (2) No change.
No improvement: (1) Levels were lower at the end compared to the baseline.
Body water
Improvement: Results reported within the normal range.
No improvement: Results indicated fluid overload or insufficiency.
Subjective global assessment (SGA)
Improvement: (1) Grade A at the end of the trial: (2) Improvements from Grade C to B.
No improvement: (1) Grade C at the end; (2) Grade A and B at baseline and Grade B at the end.
SGA interpretation: Grade A indicates normal nutritional status; Grade B represents mild to moderate malnutrition; and Grade C reflects severe malnutrition (29).
Sarcopenia risk
Improvement: Sarcopenia five (SARC-F) score < 4 at the end of the trial.
No improvement: Sarcopenia five (SARC-F) score ≥ 4 at the end of the trial.
Evaluation results: according to the SARC-F scale, a score ≥ 4 indicates a risk of sarcopenia (30).
Short physical performance battery (SPPB)
Improvement: Score ≥ 10 at the end of the trial.
No improvement: Score < 10 at the end of the trial.
Interpretation: A score ≥ 10 reflects normal physical performance (31).
Self-rating depression scale (SDS)
Improvement: Score < 40 at the end of the trial.
No improvement: Score ≥ 40 at the end of the trial.
SDS interpretation: A score ≥ 40 suggests the presence of depressive symptoms (32).
Statistical analysis
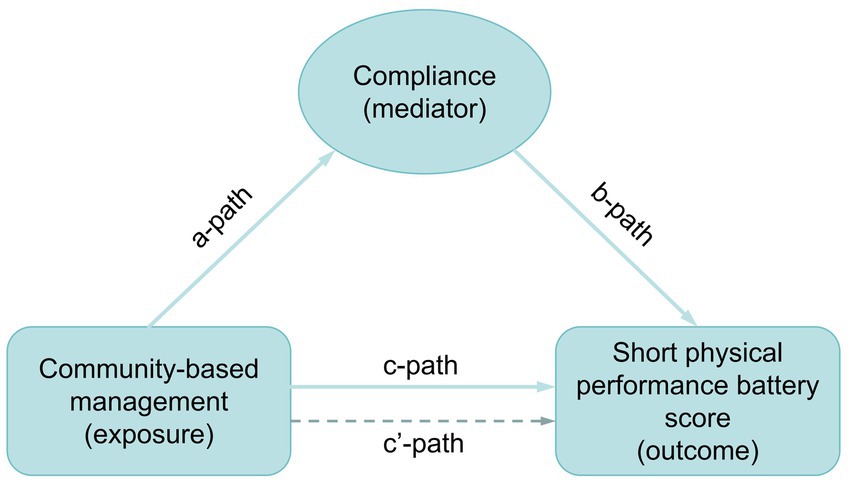
Data from all 24 patients who completed the trial—13 in the experimental group and 11 in the control group—were included in the statistical analysis. Descriptive analysis was conducted by classifying study variables as either continuous or categorical. Dialysis duration, treated as a continuous variable, is presented as mean and standard deviation. The remaining demographic data and clinical variables were treated as categorical and expressed as frequency and percentage. Statistical differences in categorical variables were assessed using two-sided Fisher’s exact probability tests, while differences in continuous variables were evaluated using the Kruskal–Wallis rank sum test. The management model of the NST was further analyzed using a one-sided Fisher’s exact probability test to assess associations across all outcome measures, including ALB, P, HGB, muscle mass, visceral fat area, SPPB score, and compliance. Statistically significant outcomes (ALB, P, HGB, muscle mass, visceral fat area, and SPPB) were reanalyzed in relation to compliance using a one-sided Fisher’s exact probability test. Compliance was examined as a potential mediator in the relationship between the NST management model and SPPB score. The overall effect of the association between management model (exposure) and SPPB score (outcome) was evaluated through pathway c’. Mediation analysis was conducted through three distinct paths: pathway a evaluated the association between management model and compliance; pathway b assessed the relationship between compliance and SPPB score; and pathway c (direct effect) examined the influence of compliance on the relationship between management model and SPPB score (Figure 2). The mediation effect ratio was calculated as (mediation effect/total effect) × 100. The Karson-Holm-Breen (KHB) method was applied to test the significance of the mediation effect. Furthermore, the impact of demographic factors on compliance was examined. Differences in categorical variables were analyzed using Fisher’s exact probability test, while Kendall’s correlation was used for continuous variables.
All statistical analyses were performed using EmpowerStats (version 2.0) and STATA (version 17.0) software, with a statistical significance defined as p < 0.05.
Results
Characteristics of participants
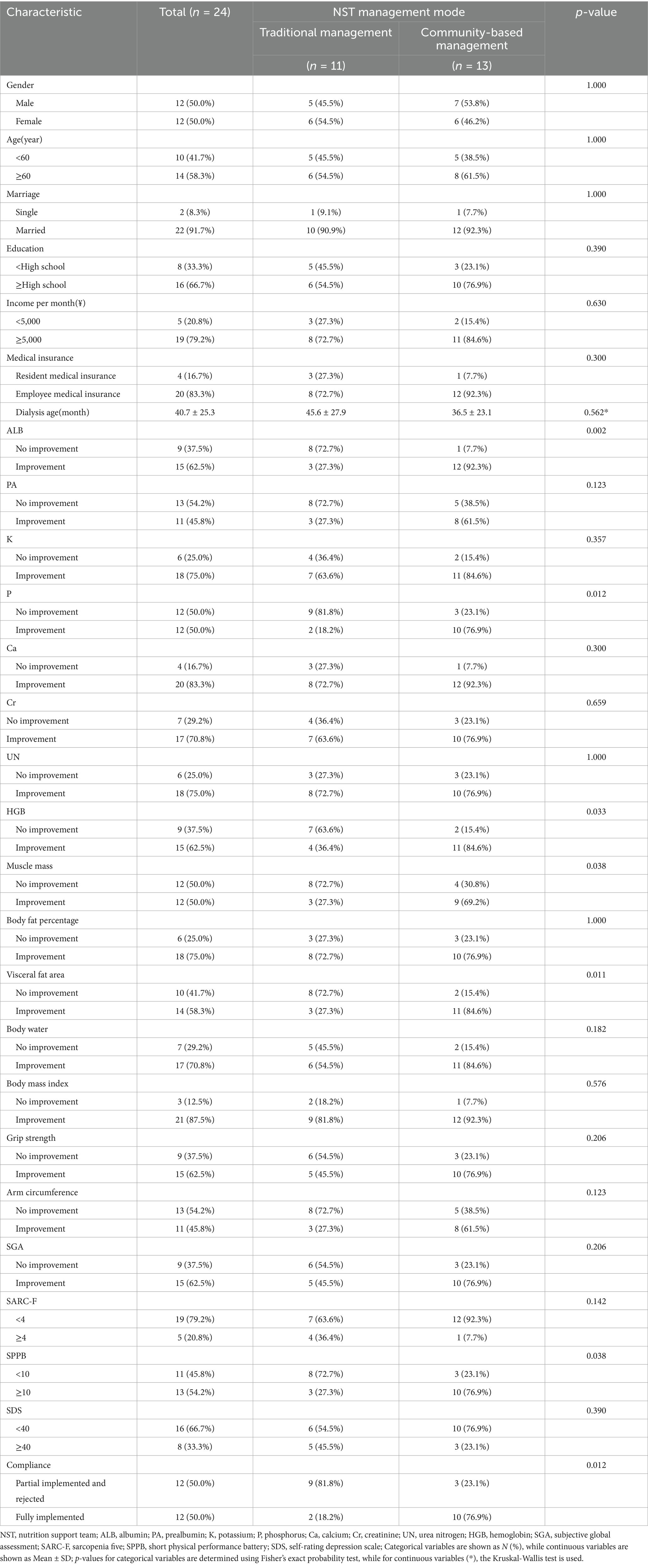
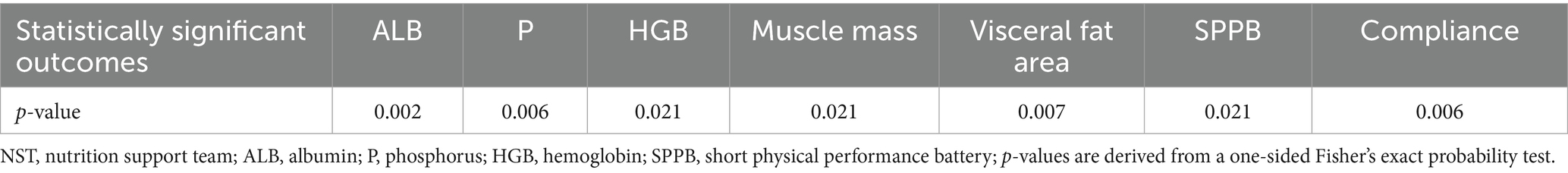
Among 24 participants who completed the trial, 12 (50%) were males and 12 (50%) were females. Ten (41.7%) participants were under 60 years of age, while 14 (58.3%) were aged 60 years or older. Two participants (8.3%) were single, and 22 (91.7%) cohabited with a partner. Sixteen (66.7%) participants attained a high school education or above, whereas eight (33.3%) participants did not complete high school. Regarding monthly income, five (20.8%) participants earned less than ¥5,000, and 19 (79.2%) earned more than ¥5,000. Four (16.7%) participants were enrolled in resident medical insurance, while 20 (83.3%) were covered by employee medical insurance. The mean age since initiation of dialysis was 40.7 ± 25.3 months. Utilizing Fisher’s exact probability test, seven indicators exhibited statistically significant differences (p < 0.05). These included three laboratory parameters: ALB (p = 0.002), P (p = 0.012), and HGB (p = 0.033); two body composition measures: muscle mass (p = 0.038) and visceral fat area (p = 0.011); one functional assessment: the SPPB score (p = 0.038); and compliance (p = 0.012) (Table 1 provides details).
Correlation between NST management model and seven statistically significant outcomes
A one-sided Fisher’s exact probability test indicated improvement across all seven indicators in the community-based management group (Table 2).
Correlation between compliance and six outcomes: ALB, P, HGB, muscle mass, visceral fat area, and SPPB
A one-sided Fisher’s exact probability test identified a significant association between compliance and SPPB scores (p < 0.001), indicating that participants with higher compliance achieved SPPB scores ≥ 10 (Table 3).
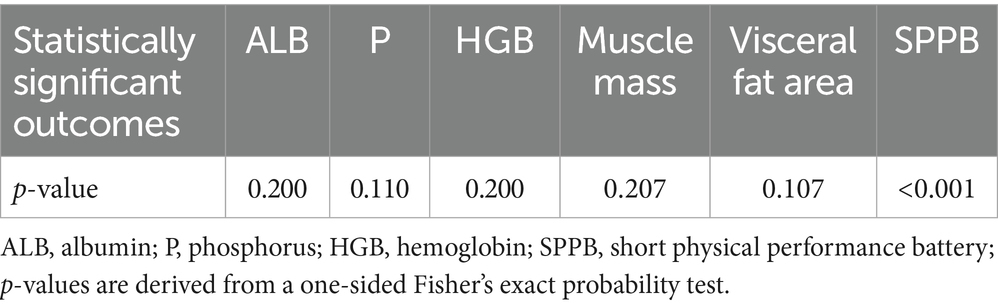
Table 3. Correlation between compliance and six outcomes, including ALB, P, HGB, Muscle mass, Visceral fat area and SPPB.
Analysis of mediation effects between NST community-based management and SPPB score
Compliance significantly mediated the effect of NST community-based management on the SPPB score, accounting for 76.2% of the total effect (p = 0.038) (Table 4).
Association between compliance and demographic indicators
Fisher’s exact probability test and Kendall correlation identified a significant association between compliance and education level, with participants possessing higher educational attainment demonstrating superior compliance (p = 0.014) (Table 5).
Discussion
In the 21st century, chronic diseases have emerged as the predominant global health concern (33). Approximately 2% of patients with CKD progress to ESRD annually (34, 35). As a principal therapy for ESRD, MHD requires prolonged and frequent sessions and carries substantial complications. Prolonged dialysis exacerbates malnutrition (36), frailty (37), diminished physical function (38, 39), reduced quality of life (19), and psychological problems (11, 12). The prognosis remains poor; despite advancements in dialysis techniques and improvements in care quality, the average life expectancy of patients undergoing dialysis is nearly half that of age-matched individuals in the general population (40). The five-year survival rate after initiating maintenance dialysis was only 40% (41). Notably, MHD adversely influences nutritional status (42), physical capabilities (41), and psychology well-being (11, 12).
Malnutrition is prevalent among dialysis patients (36) and is driven by numerous risk factors, including uremia, dialysis-related complications, inflammation, acidosis, endocrine disorders, nutrient loss during treatment, psychological conditions, reduced physical activity, intestinal dysbiosis, and anorexia (6, 43). In patients with ESRD, malnutrition is associated with diminished quality of life and increased mortality risk (6, 44). Therefore, implementation of preventive and targeted nutritional interventions remains critical for addressing malnutrition. Evidence from existing studies demonstrates that nutrition-focused strategies, particularly those involving dietitian guidance, considerably improve nutritional status and physical function in patients (45–47). However, hyperphosphatemia continues to present clinical challenges (48). In this study, the community-based management group achieved superior control of serum P levels compared to the traditional management group (10 patients, 76.9% versus 2 patients, 18.2%; p = 0.012), highlighting the effectiveness of the community-based management model. The integration of nutritional interventions within this framework contributed to enhanced outcomes. Notably, greater improvements in ALB levels (12 patients, 92.3% versus 3 patients, 27.3%, p = 0.002) and HGB levels (11 patients, 84.6% versus 4 patients, 36.4%, p = 0.033) were observed in the community-based management group compared to the traditional management group, further supporting the clinical benefits of this approach.
Frailty is prevalent among patients undergoing MHD, resulting in increased physical vulnerability and reduced physiological resilience (49). This condition impairs self-care capacity, lowers quality of life, and elevates the risk of adverse events such as falls and fractures (9). Exercise participation can mitigate physical weakness and improve cardiovascular function, functional capacity, and overall quality of life (50). Evidence indicates that appropriately prescribed exercise provides significant clinical benefits for this population (51, 52). Engagement in exercise was associated with alleviation of depressive symptoms (53), improved sleep quality (54), and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease (55). This study’s findings are consistent with previous studies demonstrating greater improvements in body composition and physical function in the community-based management group compared to the traditional management group. Notably, increases in muscle mass were more pronounced in the community-based management group (9 patients, 69.2% versus 3 patients, 27.3%; p = 0.038), and visceral fat levels were more favorable (11 patients, 84.6% versus 3 patients, 27.3%; p = 0.011). Regarding the SPPB score, the community-based management group exhibited superior performance (10 patients, 76.9% versus 3 patients, 27.3%; p = 0.038), supporting the efficacy of the community-based management model. Furthermore, analysis of patient compliance indicated that the improvement observed in the community-based management group (10 group, 76.9% versus 2 patients, 18.2%, p = 0.012) was not solely attributable to the intervention but also served as a significant mediator in the enhancement of SPPB score (Proportion Mediated = 76.2%; p = 0.038).
Psychological disorders are highly prevalent among patients undergoing MHD, with the majority experiencing anxiety, depression, and various forms of psychological distress (11, 12). These symptoms are occasionally atypical and frequently underdiagnosed (56), yet the associated disease burden remains substantial (57). Recent research has identified potential interventions for this issue. Notably, a study on guided meditation reported significant improvements in self-confidence, psychological well-being, and reduced perceived stress among participants (58). A separate investigation on psychoeducation demonstrated that effective psychoeducational strategies significantly improved psychological symptoms and enhanced quality of life in both the short- and medium-term durations (59). However, this study did not provide direct evidence regarding the impact of community-based management models on depressive symptoms, potentially due to limitations imposed by a small sample size. Nevertheless, a rationale persists to suggest that the psychological support component of the community-based management model contributed to improved outcomes, as indicated by the significantly higher compliance rates in the community-based management group (10 patients, 76.9% versus 2 patients, 18.2%, p = 0.012). As previously discussed, compliance serves as an indicator of self-efficacy, which correlates positively with self-confidence (21).
Given the multifaceted nature of diseases and health challenges faced by patients with MHD, the effective application of health management strategies has become a critical focus. Contemporary medical practice in the 21st century is guided by three core principles: patient-centered care, active involvement of patients and their families, and shared decision-making (60). The emphasis in health management has shifted from medical specialist guidance to active patient engagement. In the context of chronic dialysis treatment, patient-reported outcomes should be prioritized over evidence-based clinical indicators (61). Extensive research by prominent scholars and organizations has contributed to advancing self-management among dialysis patients (62–64), yielding significant findings. However, not all studies have yielded favorable outcomes (65). Non-disease-related factors, such as public awareness of dialysis (66), patient-incurred expenses (67), and insurance and reimbursement policies (67), also influence the implementation of health management strategies. For instance, this study found that patients with higher educational attainment exhibited significantly superior compliance (p = 0.014).
In conclusion, the burden of disease and health-related challenges among patients with MHD is multifaceted, and as research progresses, increasingly complex issues are anticipated. As an emerging discipline, NST has demonstrated considerable potential in nutritional management and continues to develop (17); however, limited research has specifically explored its application in MHD. The community-based management model utilized in this study prioritizes team-based care and psychological counseling, aligning with the medical philosophies of “patient-centered care” (60).
Conclusion
The community-based management model led by the NST improves patient compliance and delivers greater clinical benefits.
Strengths of this study
This study introduced an innovative community-based management model that designates the patient group as the primary unit of care. It emphasizes team-based collaboration and psychological support while encouraging patients to engage in proactive self-management. This study is grounded in the principle of “patient first, with medical personnel in a supportive role,” aligning with contemporary medical philosophy. It also highlights the concept that “patient behavior is a key determinant of prognosis.”
Limitations of this study
This single-center trial involved a limited sample size, introducing an inherent risk of bias in the findings. Such bias is a common concern in small-sample research. Additional studies with similar designs are needed to consistently validate these findings. Although the nutritional and exercise protocols were designed and supervised by medical professionals, their patient-led implementation may have introduced subjective bias that is difficult to mitigate. Furthermore, while data from deceased patients were excluded from the statistical analysis, fluctuations in the sample sizes of the two groups during the study period may have influenced the results.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Ethics Committee of Zibo First Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from primarily isolated as part of your previous study for which ethical approval was obtained. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
HS: Supervision, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. LF: Writing – original draft, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1652718/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
MHD, maintenance hemodialysis; ALB, albumin; HGB, hemoglobin; SPPB, short physical performance battery; CKD, chronic kidney disease; ESRD, end stage renal disease; NST, nutrition support team; PA, prealbumin; K, potassium; P, phosphorus; Ca, calcium; Cr, creatinine; UN, urea nitrogen; SGA, subjective global assessment; SARC-F, sarcopenia five; SDS, self-rating depression scale; KHB, Karson-Holm-Breen.
References
1. Bello, AK, Levin, A, Tonelli, M, Okpechi, IG, Feehally, J, Harris, D, et al. Assessment of global kidney health care status. JAMA. (2017) 317:1864–81. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.4046
2. Liyanage, T, Ninomiya, T, Jha, V, Neal, B, Patrice, HM, Okpechi, I, et al. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet. (2015) 385:1975–82. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61601-9
3. Jing, C, Jing, X, Yanqing, J, Xiajun, W, Haifen, Z, Bihong, H, et al. Expert consensus on clinical practice of injection safety in hemodialysis. Chin J Nurs. (2022) 57:785–90. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2022.07.003
4. Thiery, A, Severac, F, Hannedouche, T, Couchoud, C, Do, VH, Tiple, A, et al. Survival advantage of planned haemodialysis over peritoneal dialysis: a cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2018) 33:1411–9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy007
5. Thurlow, JS, Joshi, M, Yan, G, Norris, KC, Agodoa, LY, Yuan, CM, et al. Global epidemiology of end-stage kidney disease and disparities in kidney replacement therapy. Am J Nephrol. (2021) 52:98–107. doi: 10.1159/000514550
6. Lodebo, BT, Shah, A, and Kopple, JD. Is it important to prevent and treat protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney disease and chronic Dialysis patients? J Ren Nutr. (2018) 28:369–79. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2018.04.002
7. Isaka, Y, Hamano, T, Fujii, H, Tsujimoto, Y, Koiwa, F, Sakaguchi, Y, et al. Optimal phosphate control related to coronary artery calcification in Dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2021) 32:723–35. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020050598
8. Georgianos, PI, and Agarwal, R. Resistant hypertension in Dialysis: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2024) 35:505–14. doi: 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000315
9. Cheng, M, He, M, Ning, L, Gan, H, Liu, H, Liu, Q, et al. Association between frailty and adverse outcomes in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren Fail. (2024) 46:2367716. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2367716
10. Mapes, DL, Lopes, AA, Satayathum, S, McCullough, KP, Goodkin, DA, Locatelli, F, et al. Health-related quality of life as a predictor of mortality and hospitalization: the Dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study (DOPPS). Kidney Int. (2003) 64:339–49. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00072.x
11. Zhang, Y, Niu, J, Qin, H, Huang, L, Zhang, X, Yu, L, et al. Prevalence and correlates of depression among maintenance hemodialysis patients in Huhhot region, China: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Nephrol. (2022) 22:574–83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2022.07.008
12. Al Naamani, Z, Gormley, K, Noble, H, Santin, O, and Al Maqbali, M. Fatigue, anxiety, depression and sleep quality in patients undergoing haemodialysis. BMC Nephrol. (2021) 22:157. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02349-3
13. Wesley, JR. Nutrition support teams: past, present, and future. Nutr Clin Pract. (1995) 10:219–28. doi: 10.1177/0115426595010006219
14. Bischoff, SC, Austin, P, Boeykens, K, Chourdakis, M, Cuerda, C, Jonkers-Schuitema, C, et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Home enteral nutrition. Clin Nutr. (2022) 41:468–88. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.10.018
15. Nightingale, J. Nutrition support teams: how they work, are set up and maintained. Frontline Gastroenterol. (2010) 1:171–7. doi: 10.1136/fg.2009.000224
16. Mistiaen, P, and Van den Heede, K. Nutrition support teams: a systematic review. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2020) 44:1004–20. doi: 10.1002/jpen.1811
17. Ji, T, Zhang, L, Han, R, Peng, L, Shen, S, Liu, X, et al. Management of malnutrition based on multidisciplinary team decision-making in Chinese older adults (3M study): a prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled study protocol. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:851590. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.851590
18. Cong, MH, Li, SL, Cheng, GW, Liu, JY, Song, CX, Deng, YB, et al. An interdisciplinary nutrition support team improves clinical and hospitalized outcomes of Esophageal Cancer patients with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Chin Med J. (2015) 128:3003–7. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.168963
19. Weisbord, SD, Fried, LF, Arnold, RM, Fine, MJ, Levenson, DJ, Peterson, RA, et al. Prevalence, severity, and importance of physical and emotional symptoms in chronic hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2005) 16:2487–94. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005020157
20. Darvishi, A, Otaghi, M, and Mami, S. The effectiveness of spiritual therapy on spiritual well-being, self-esteem and self-efficacy in patients on Hemodialysis. J Relig Health. (2020) 59:277–88. doi: 10.1007/s10943-018-00750-1
21. Hu, L, St-Jules, DE, Popp, CJ, and Sevick, MA. Determinants and the role of self-efficacy in a sodium-reduction trial in Hemodialysis patients. J Ren Nutr. (2019) 29:328–32. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2018.10.006
22. Khademi, F, Rassouli, M, Rafiei, F, Moayedi, S, Torres, M, Marzban, N, et al. The effect of mandala colouring on anxiety in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Int J Ment Health Nurs. (2021) 30:1437–44. doi: 10.1111/inm.12901
23. Ministry of Health, People’s Republic of China. Reference intervals for common clinical biochemistry tests—part 3:serum potassium, sodium and chloride. Available online at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ewebeditor/uploadfile/2013/01/20130109170954741.pdf (Accessed June 27, 2025).
24. Ministry of Health, People’s Republic of China. Reference intervals for common clinical biochemistry tests—part 6:serum calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron. Available online at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ewebeditor/uploadfile/2015/05/20150504152426630.pdf (Accessed June 27, 2025).
25. Ministry of Health, People’s Republic of China. Reference intervals for blood cell analysis. Available online at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ewebeditor/uploadfile/2013/01/20130109171100186.pdf (Accessed June 27, 2025).
26. Lobman, TG, Houtkooper, L, and Going, SB. Body fat measurement Goes high-tech: not all are created equal. ACSMs Health Fit J. (1997) 1:30–5.
27. Carvalho, JB, de Andrade, GKP, do Nascimento, LA, Golin, N, Rodrigues, A, Suiter, E, et al. Visceral fat area measured by electrical bioimpedance as an aggravating factor of COVID-19: a study on body composition. BMC Infect Dis. (2023) 23:826. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08833-5
28. Zhou, BF. Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain related diseases in Chinese adults--study on optimal cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese adults. Biomed Environ Sci. (2002) 15:83–96.
29. Detsky, AS, McLaughlin, JR, Baker, JP, Johnston, N, Whittaker, S, Mendelson, RA, et al. What is subjective global assessment of nutritional status? JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (1987) 11:8–13. doi: 10.1177/014860718701100108
30. Chen, LK, Woo, J, Assantachai, P, Auyeung, TW, Chou, MY, Iijima, K, et al. Asian working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2020) 21:300–307.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012
31. Izquierdo, M, Casas-Herrero, A, Zambom-Ferraresi, F, Martínez-Velilla, N, Alonso-Bouzón, C, and Rodriguez-Mañas, L. Multicomponent physical exercise program Vivifrail. A practical guide for prescribing a multicomponent physical training program to prevent weakness and falls in people over 70. (2017). Available online at: http://vivifrail.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/VIVIFRAIL-ENG-Interactivo.pdf (Accessed June 27, 2025).
32. Biggs, JT, Wylie, LT, and Ziegler, VE. Validity of the Zung self-rating depression scale. Br J Psychiatry. (1978) 132:381–5. doi: 10.1192/bjp.132.4.381
33. Budreviciute, A, Damiati, S, Sabir, DK, Onder, K, Schuller-Goetzburg, P, Plakys, G, et al. Management and prevention strategies for non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and their risk factors. Front Public Health. (2020) 8:574111. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.574111
34. Haileamlak, A. Chronic kidney disease is on the rise. Ethiop J Health Sci. (2018) 28:681–2. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v28i6.1
35. Zhang, L, Zhao, MH, Zuo, L, Wang, Y, Yu, F, Zhang, H, et al. China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET) 2015 annual data report. Kidney Int Suppl. (2019) 9:e1–e81. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2018.11.001
36. Carrero, JJ, Thomas, F, Nagy, K, Arogundade, F, Avesani, CM, Chan, M, et al. Global prevalence of protein-energy wasting in kidney disease: a Meta-analysis of contemporary observational studies from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. J Ren Nutr. (2018) 28:380–92. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2018.08.006
37. Wei, Q, Zhaohua, Z, Zihan, Y, Xingying, X, and Hong, X. Construction of risk prediction model for patients with maintenance hemodialysis with frailty and pre-frailty. Nurs Res. (2024) 38:233–9. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2024.02.007
38. Evangelidis, N, Tong, A, Manns, B, Hemmelgarn, B, Wheeler, DC, Tugwell, P, et al. Developing a set of core outcomes for trials in hemodialysis: an international Delphi survey. Am J Kidney Dis. (2017) 70:464–75. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.11.029
39. Jegatheesan, DK, Modderman, R, Krishnasamy, R, Tong, A, Coombes, JS, Viecelli, AK, et al. A systematic review of scope and consistency of outcome measures for physical fitness in chronic kidney disease trials. Kidney Int Rep. (2021) 6:1280–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.02.010
40. Nakai, S, Wada, A, Wakai, K, Abe, M, and Nitta, K. Calculation of expected remaining lifetime of dialysis patients in Japan. Ren Replace Ther. (2020) 6:58. doi: 10.1186/s41100-020-00301-z
41. Flythe, JE, and Watnick, S. Dialysis for chronic kidney failure: a review. JAMA. (2024) 332:1559–73. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.16338
42. Fang, W, Fuxu, W, and Hongwei, Z. Progress of clinical research on protein energy consumption in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Chin Blood Purif. (2019) 18:127–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4091.2019.02.013
43. Sabatino, A, Regolisti, G, Karupaiah, T, Sahathevan, S, Sadu Singh, BK, Khor, BH, et al. Protein-energy wasting and nutritional supplementation in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Clin Nutr. (2017) 36:663–71. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.06.007
44. Ikizler, TA, and Hakim, RM. Nutrition in end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. (1996) 50:343–57. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.323
45. St-Jules, DE, Rozga, MR, Handu, D, and Carrero, JJ. Effect of phosphate-specific diet therapy on phosphate levels in adults undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2020) 16:107–20. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09360620
46. Molfino, A, Chiappini, MG, Laviano, A, Ammann, T, Bollea, MR, Alegiani, F, et al. Effect of intensive nutritional counseling and support on clinical outcomes of hemodialysis patients. Nutrition. (2012) 28:1012–5. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2012.01.008
47. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Nutrition Services for Medicare Beneficiaries. The role of nutrition in maintaining health in the nation's elderly: Evaluating coverage of nutrition Services for the Medicare Population. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US) (2000).
48. Ikizler, TA, Burrowes, JD, Byham-Gray, LD, Campbell, KL, Carrero, JJ, Chan, W, et al. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for nutrition in CKD: 2020 update. Am J Kidney Dis. (2020) 76:S1–S107. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.05.006
49. Chen, X, Mao, G, and Leng, SX. Frailty syndrome: an overview. Clin Interv Aging. (2014) 9:433–41. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S45300
50. Huang, M, Lv, A, Wang, J, Xu, N, Ma, G, Zhai, Z, et al. Exercise training and outcomes in Hemodialysis patients: systematic review and Meta-analysis. Am J Nephrol. (2019) 50:240–54. doi: 10.1159/000502447
51. Hu, H, Wu, C, Kwok, JYY, Ho, MH, Chau, PH, Lok, KYW, et al. Effects of different exercises on physical function, dialysis adequacy, and health-related quality of life in maintenance hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Am J Nephrol. (2023) 54:379–90. doi: 10.1159/000532109
52. Cheema, B, Abas, H, Smith, B, O'Sullivan, A, Chan, M, Patwardhan, A, et al. Progressive exercise for anabolism in kidney disease (PEAK): a randomized, controlled trial of resistance training during hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2007) 18:1594–601. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006121329
53. Liu, H, Zheng, F, Yao, W, Zhu, J, Du, X, Shi, H, et al. The impact of aerobic exercise on health-related quality of life among patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Medicine (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e35990. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035990
54. Correa, HL, Moura, SRG, Neves, RVP, Tzanno-Martins, C, Souza, MK, Haro, AS, et al. Resistance training improves sleep quality, redox balance and inflammatory profile in maintenance hemodialysis patients: a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:11708. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68602-1
55. Bronas, UG. Exercise training and reduction of cardiovascular disease risk factors in patients with chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. (2009) 16:449–58. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2009.07.005
56. Cohen, SD, Cukor, D, and Kimmel, PL. Anxiety in patients treated with Hemodialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2016) 11:2250–5. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02590316
57. Al-Jabi, SW, Sous, A, Jorf, F, Taqatqa, M, Allan, M, Sawalha, L, et al. Depression in patients treated with haemodialysis: a cross-sectional study. Lancet. (2018) 391:S41. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30407-0
58. Vaishnav, BS, Hirapara, JJ, and Shah, MK. Study of effect of guided meditation on quality of life in patients of end stage renal disease (ESRD) on maintenance hemodialysis - a randomised controlled trial. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2022) 22:238. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03717-8
59. Zhang, L, Zou, L, and Zhou, L. Effectiveness of psychoeducational interventions on psychological distress and health-related quality of life among patients with maintenance hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren Fail. (2024) 46:2331613. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2331613
60. Barry, MJ, and Edgman-Levitan, S. Shared decision making--pinnacle of patient-centered care. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:780–1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1109283
61. Nissenson, AR. Improving outcomes for ESRD patients: shifting the quality paradigm. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2014) 9:430–4. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05980613
62. Xia, F, and Wang, G. Influence of teach-back strategy on hemodialysis related knowledge level, self-efficacy and self-management in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:4010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54044-6
63. Dawson, J, Campbell, KL, Craig, JC, Tong, A, Teixeira-Pinto, A, Brown, MA, et al. A text messaging intervention for dietary Behaviors for people receiving maintenance Hemodialysis: a feasibility study of KIDNEYTEXT. Am J Kidney Dis. (2021) 78:85–95.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.11.015
64. Valente, A, Jesus, J, Breda, J, Dinis, A, Correia, A, Godinho, J, et al. Dietary advice in Hemodialysis patients: impact of a telehealth approach during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Ren Nutr. (2022) 32:319–25. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2021.04.002
65. Rozga, M, Burrowes, JD, Byham-Gray, LD, and Handu, D. Effects of sodium-specific medical nutrition therapy from a registered dietitian nutritionist in individuals with chronic kidney disease: an evidence analysis Center systematic review and meta-analysis. J Acad Nutr Diet. (2022) 122:445–460.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2021.03.016
66. Schneider, ST, Klug, A, and Andrade, JM. Phosphorus knowledge and dietary intake of phosphorus of US adults undergoing Dialysis. Nutrients. (2024) 16:2034. doi: 10.3390/nu16132034
Keywords: nutrition support team, community-based management, maintenance hemodialysis, compliance, mediation effect
Citation: Shi H and Fan L (2025) The success of community-based management in improving maintenance hemodialysis outcomes: a pilot study. Front. Nutr. 12:1652718. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1652718
Edited by:
Jeanette Mary Andrade, University of Florida, United StatesReviewed by:
Mahathir Mahathir, Andalas University, IndonesiaMarouane Ouirdani, Hassan Premier University, Morocco
Copyright © 2025 Shi and Fan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Fan, MzY3NTkyOTc4N0BxcS5jb20=
 Hui Shi
Hui Shi Lei Fan
Lei Fan