- 1Department of Endocrinology, Geriatrics Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 2The First Clinical Medical College, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 3Department of Endocrinology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 4Health Management Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, Anhui, China
Background: The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) is a novel composite lipid biomarker associated with metabolic diseases. This study aims to explore the potential relationship between early-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with NAFLD and NHHR.
Methods: A total of 1,158 patients with type 2 diabetes were enrolled and categorized by age at onset into the early-onset type 2 diabetes (EOT2D) group (260 cases, <40 years) and the late-onset type 2 diabetes (LOT2D) group (898 cases, ≥40 years). The EOT2D group was further subdivided into those with NAFLD (136 cases) and those without NAFLD (124 cases). Multivariate logistic regression assessed the association between NHHR and EOT2D, as well as EOT2D combined with NAFLD. Additionally, we employed subgroup analysis, interaction analysis, smoothing curve fitting, and receiver operating characteristic curve analysis to further explore risk factors for EOT2D and EOT2D combined with NAFLD.
Results: This cross-sectional study included 260 EOT2D patients and 898 LOT2D patients. After adjusting for confounding factors, the study found that for every 1-unit increase in NHHR, the risk of EOT2D increased by 22% (OR = 1.22, 95% CI: 1.05–1.42), and the risk of EOT2D with NAFLD increased by 41% (OR = 1.41, 95% CI: 1.01–1.98). The AUC for diagnosing EOT2D with NAFLD using NHHR was 0.658 (95% CI: 0.592–0.724), with an optimal cutoff of 3.105 (sensitivity 77.21%, specificity 50.00%).
Conclusion: Our study suggests that NHHR is a risk factor for EOT2D and EOT2D combined with NAFLD, serving as a reference indicator for screening this high-risk population.
Introduction
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been on the rise globally over the past few decades (1), which may be the cause of lethal events such as stroke, heart failure, kidney disease, and retinopathy (2). In recent years, the incidence of early-onset type 2 diabetes (EOT2D) has been increasing annually, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, and this incidence has risen dramatically (3). Compared with late-onset type 2 diabetes (LOT2D), patients with early-onset type 2 diabetes (EOT2D) exhibit a more rapid decline in β-cell secretory function, faster disease progression, higher risk of complications, and earlier onset of complications (4, 5). Several studies have shown that nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and T2DM are two frequently co-existing pathologic states and that there is a bidirectional relationship between them (6), the prevalence of NAFLD was significantly higher in T2DM patients than in non-T2DM patients (7). Researchers are now proposing metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) as a more instructive medical diagnosis to describe this disease, which emphasizes the causative role of metabolic dysfunction in the development and progression of this highly prevalent disease. MAFLD emphasizes the role of metabolic dysfunction in the development and progression of this highly prevalent disease, and T2DM in combination with NAFLD is a case of MAFLD (8). In addition, NAFLD is more common in patients with EOT2D than LOT2D (9). Relevant studies have shown that the association between T2DM and increased risk of patient death is more pronounced in younger patients with MAFLD (10), and that patients with T2DM combined with NAFLD who ultimately develop nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are also relatively younger (11), and that there is no approved of clearly effective drug therapy.
The strong association between dyslipidemia and T2DM and NAFLD (12, 13). The development of NAFLD is associated with severe abnormalities in hepatic lipid metabolism (14). Insulin resistance (IR) is central to the development of NAFLD and T2DM and the main physiopathological link between the two, triggering an increase in free fatty acids in peripheral adipose tissue and promoting dyslipidemia (15). Lipid disorders are strongly associated with insulin resistance and disorders of glucose metabolism (16, 17). Metabolic dyslipidemia is very common in patients with type 2 diabetes (40%) (18), Hypercholesterolemia and lowered high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) occur more often in patients with diabetes mellitus (19). The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) is a novel indicator of atherogenic lipids that has received much attention in recent years. It provides a more comprehensive assessment of lipid metabolism disorders (20), which is closely related to the correlation and predictive value of cardiovascular diseases, stroke, inflammatory diseases, etc. (21–23). In addition, studies have shown that NHHR is superior to traditional lipid markers in the diagnosis of insulin resistance (IR) and metabolic syndrome (Mts) (12, 24).
Although previous studies have suggested associations between NHHR and both T2DM and NAFLD, the predictive value of NHHR for the high-risk population with EOT2D complicated by NAFLD remains unclear. Given that patients with EOT2D and NAFLD typically exhibit more severe metabolic abnormalities and poorer clinical outcomes, early identification of this group holds significant clinical importance. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the association between NHHR and EOT2D, as well as their co-occurrence with NAFLD, with the goal of providing new evidence-based support for the early identification and intervention of this high-risk population.
Materials and methods
Study population
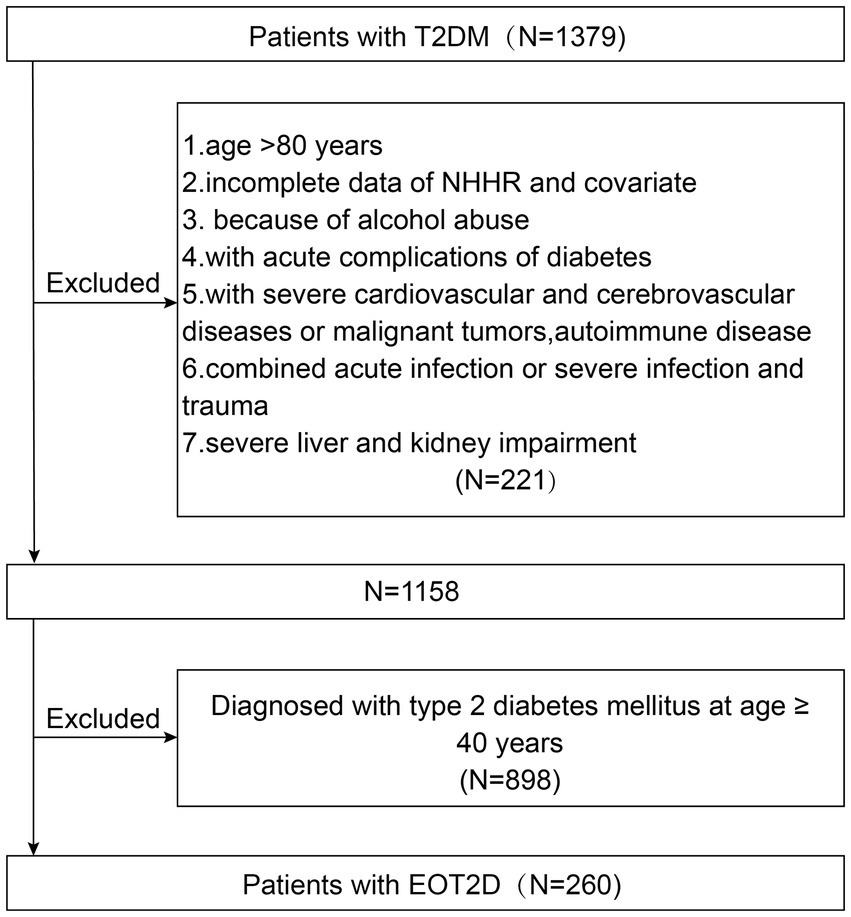
In this study, 1,158 patients with T2DM admitted to the Department of Endocrinology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from April 2023 to April 2025 were retrospectively clinically analyzed. Initially, 1,379 participants with T2DM were selected. The exclusion criteria were (1) age >80 years; (2) with acute complications of diabetes; (3) with severe cardiovascular or cerebrovascular diseases or malignant tumors, autoimmune diseases; (4) with acute or severe infections, trauma; (5) with severe hepatic or renal impairment; (6) with excessive alcohol consumption (defined as an average of >70 g per week for women, or >140 g per week for men) (25); (7) Missing TC or HDL-C data prevented the calculation of NHHR. One thousand one hundred fifty-eight participants were finally included in the study (Figure 1). This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 2025AH-103) and followed the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki (1964).
NHHR calculation and assessment of early onset type 2 diabetes and NAFLD and subgroups
NHHR was calculated as non-HDL-C/HDL-C, an exposure variable, and was derived from the participants’ lipid values, with non-HDL-C being the serum TC value minus HDL-C. Lipids were measured by a Roche Cobas 6,000 automatic biochemical analyzer for numerical measurements. The diagnosis of T2DM was based on the diagnostic criteria proposed by the WHO Expert Committee on Diabetes Mellitus in 1999. Year of type 2 diabetes diagnosis age less than 40 years is defined as early onset type 2 diabetes (EOT2D) and 40 years or older is defined as late onset type 2 diabetes (LOT2D) (5). Diagnosis of NAFLD is based on an ultrasound examination of the upper abdomen, which is done using a Myers Nuewa R9 Pro color ultrasound diagnostic machine (abdominal probe, probe frequency 3.5–5.0 MHz), and the diagnosis of fatty liver is confirmed by a combination of two experienced ultrasonographers. The diagnosis of fatty liver by ultrasound is based on at least two of the following three abnormalities: diffuse hepatic echogenic enhancement (“bright”)—liver echogenicity is greater than that of the kidneys or spleen; vascular blurring; and deep attenuation of the ultrasound signal (26). Two groups were categorized according to whether the age of onset of diabetes was less than 40 years, one group of EOT2D patients (260 cases) and one group of LOT2D patients (898 cases). The EOT2D group was further divided into the group with NAFLD (136 cases) and the group without NAFLD (124 cases) based on the results of an ultrasound examination of the upper abdomen. Subgroup analyses categorized individuals by age (≤45, 45–60, >60), sex (male, female), smoking status (yes, no), BMI (<24, ≥24), and history of hypertension (yes, no).
General clinical information and laboratory tests
To investigate the independent relationship between NHHR and the risk of EOT2D comorbid NAFLD, we recorded some basic clinical information such as age, gender, duration of diabetes, history of smoking, history of hypertension, presence or absence of comorbid diabetic kidney disease (DKD), and body mass index (BMI), which was calculated as the square of the body weight (kg) divided by the height (m). Laboratory parameters included fasting insulin (FINS, uIU/mL), fasting C-peptide (FCP, μg/L), fasting glucose (FBG, mmol/L), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c, %), alanine aminotransferase (ALT, U/L), aspartate aminotransferase (AST, U/L), albumin (ALB, g/L), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT, U/L), urea nitrogen (BUN, mmol/L), creatinine (Cr, μmol/L), uric acid (UA, μmol/L), triglycerides (TG, mmol/L), total cholesterol (TC, mmol/L), HDL-C, mmol/L, LDL-C, mmol/L, and blood pressure (BP/mmHg), white blood cell count (WBC, 109/L), neutrophil count (N, 109/L), lymphocyte count (L, 109/L), monocyte count (M, 109/L), platelet count (PLT, 109/L), and urine albumin creatinine ratio (UACR, mg/g). Smoking status was determined based on lifetime smoking of at least 100 cigarettes. History of hypertension was defined as a self-reported physician diagnosis or blood pressure over 140/90 mmHg.
Statistical analysis
Normally distributed continuous variables are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, non-normally distributed data are expressed as median (interquartile spacing), and comparisons between 2 groups were performed using the independent samples t-test or Mann–Whitney U-test, and comparisons between multiple groups were performed using the Kruskal–Wallis H rank-sum test. Categorical variables were expressed as counts and percentages (%), and differences between groups were tested using the chi-square test. Three different logistic regression models were used to analyze the relationship between NHHR and EOT2D and between NHHR and EOT2D combined with NAFLD, and the odds ratios (OR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated and adjusted for a range of covariates for the three models. In addition, trend tests, subgroup analyses, and interaction analyses were performed. Smoothed curves were used to explore the associations between NHHR and EOT2D and EOT2D combined with NAFLD, and the validity of NHHR in assessing the risk of developing EOT2D combined with NAFLD was analyzed using subject work characteristics (ROC) curves. To account for multiple comparisons and determine statistical significance, the Bonferroni correction was applied, setting the adjusted significance threshold at α = 0.01 for subgroup interaction tests (calculated as 0.05 divided by five subgroups). All statistical calculations were performed using R Statistical Software version 4.2.0 in conjunction with Empower software (www.empowerstats.com), and statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
Results
Participants characteristics
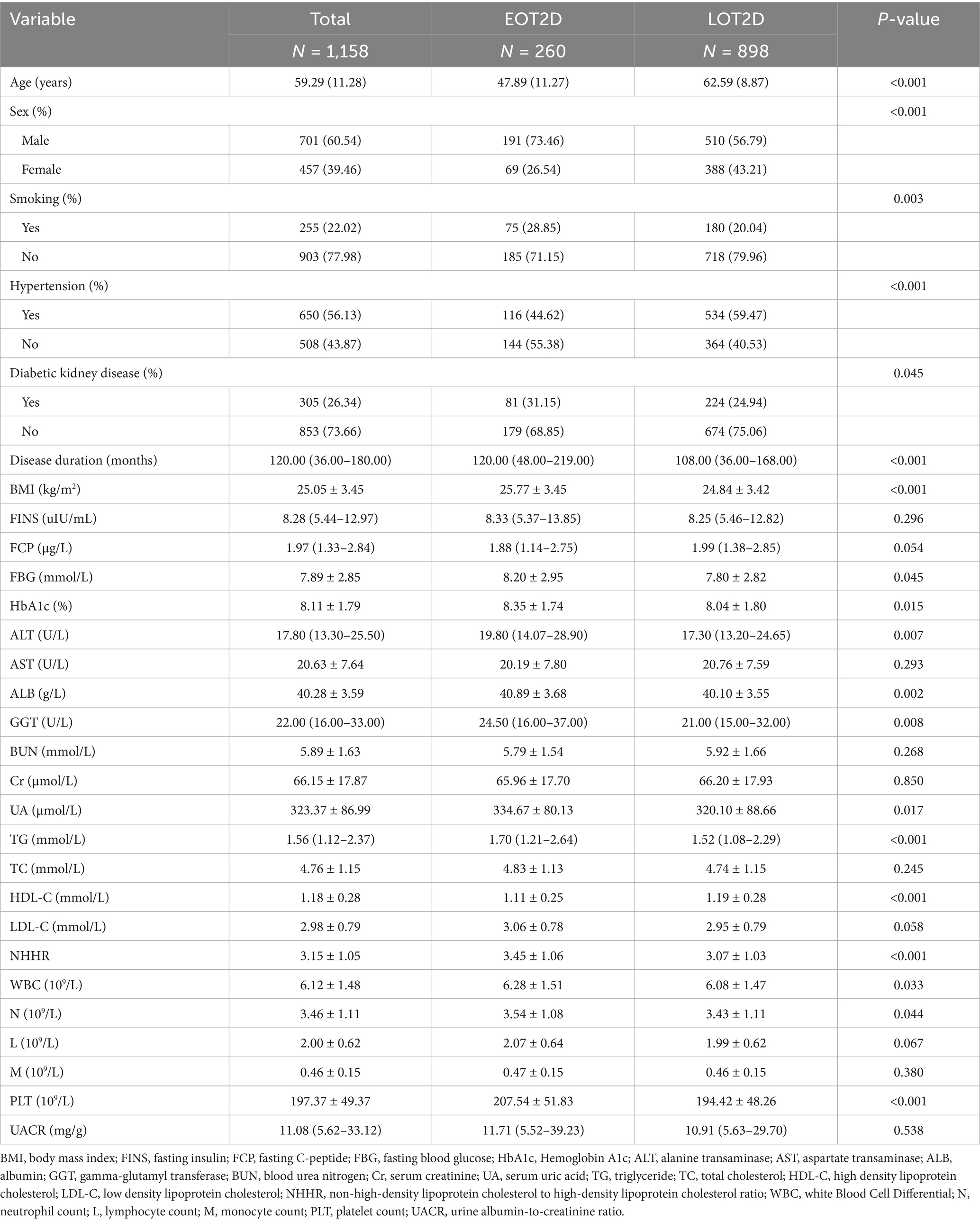
Of the 1,158 participants with T2DM, 260 were in the EOT2D group and 898 in the LOT2D group. 73.46% (191/260) of the EOT2D group and 56.79% (510/898) of the LOT2D group were male. Compared with the patients in the LOT2D group, the duration of diabetes, NHHR, the proportion of smokers, the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy, BMI, FBG, HbA1c, ALT, ALB, GGT, UA, TG, WBC, N, and PLT levels were significantly higher in the EOT2D group (P < 0.05), and HDL-C was lower than in the LOT2D group (P < 0.05) (Table 1). The levels of FINS, AST, BUN, Cr, TC, LDL-C, and UACR were not significantly different between the two groups of participants. Supplementary Table S1 describes the baseline characteristics of the subjects based on NHHR quartiles, and significant differences were observed between NHHR quartiles and baseline characteristics. Individuals in the higher quartile group had a higher prevalence of NAFLD and EOT2D compared with the Q1 group.
The association between NHHR with EOT2D
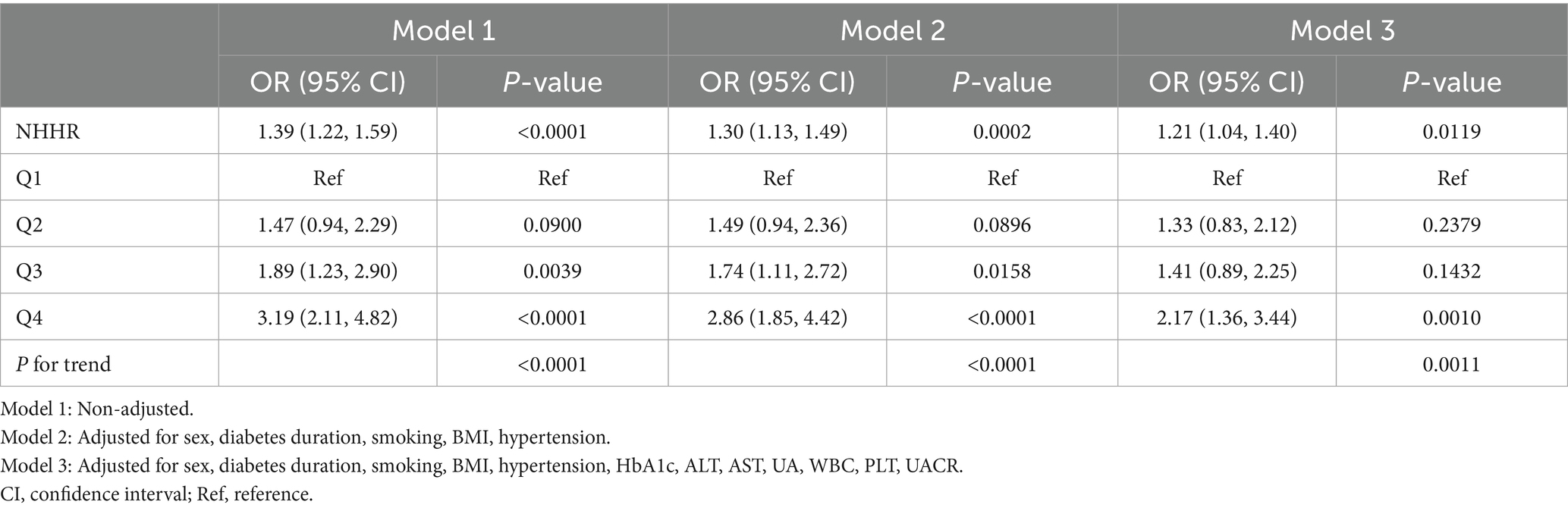
Multifactorial logistic regression modeling confirmed that NHHR was an independent risk factor for EOT2D, and the results of the analysis are presented in Table 2. The results showed that in model 1, which was not adjusted for any covariates, there was a 39% increase in the risk of EOT2D for each 1-unit increase in NHHR (OR = 1.39; 95% CI, 1.22–1.59; P < 0.0001). In model 2, which was adjusted for sex, duration of diabetes, smoking status, BMI, and history of hypertension, the risk increased by 30% (OR = 1.30; 95% CI, 1.13–1.49; P = 0.0002). Model 3 was further adjusted for HbA1c, ALT, AST, UA, WBC, PLT, and UACR, and the risk of EOT2D increased by 21%, suggesting that NHHR was independently associated with EOT2D. Analyzing NHHR as a categorical variable (quartiles), participants in the highest quartile (Q4) had a significantly higher risk of developing EOT2D than those in the lowest quartile (Q1), with a 1.17-fold increase in risk in model 3 (OR = 2.17; 95% CI, 1.36–3.44; P = 0.0010). In addition, trend analysis revealed that the risk of EOT2D increased progressively with increasing NHHR quartiles (P for trend = 0.0011). In addition, smoothed curve fitting showed a linear correlation between NHHR and EOT2D (P = 0.432), with no significant threshold or saturation effects (Figure 2A).
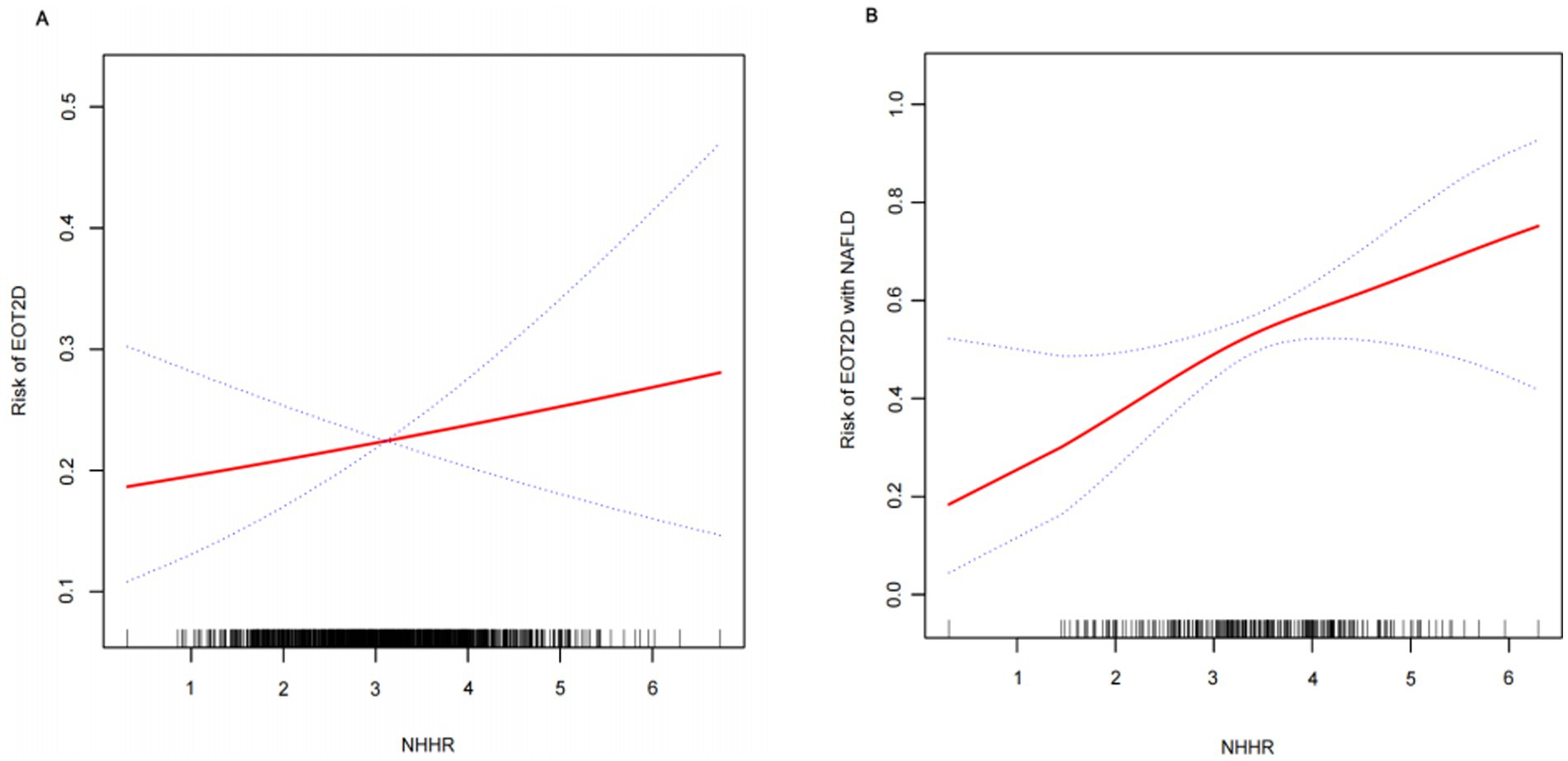
Figure 2. Smooth curve fitting depicting the association between NHHR and EOT2D, as well as EOT2D complicated by NAFLD.
Baseline characteristics of EOT2D patients by NAFLD status
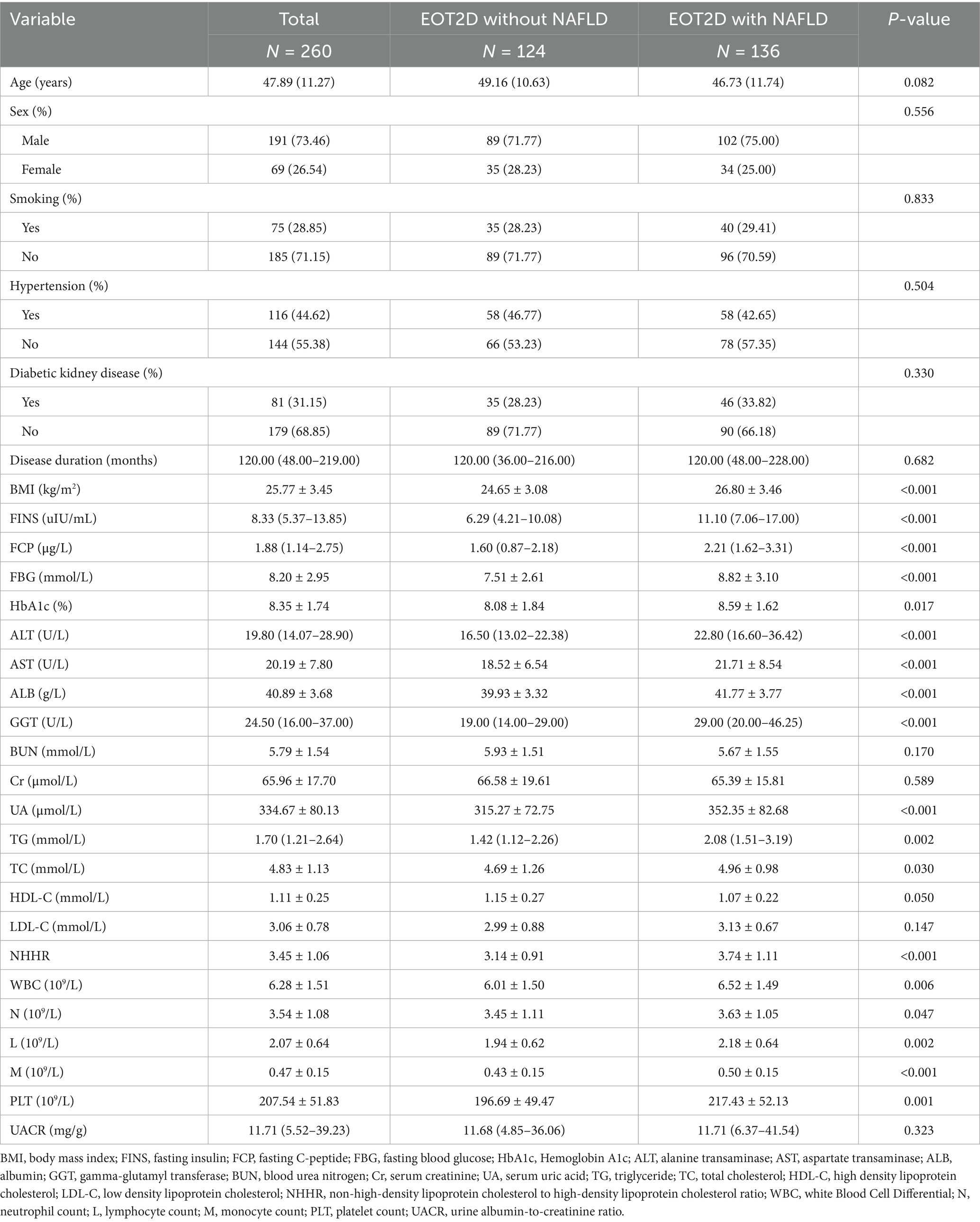
Patients with EOT2D were categorized into two groups according to the presence or absence of comorbid NAFLD and the baseline characteristics of the participants were compared. There were 124 patients in the EOT2D uncomplicated NAFLD group, 71.77% of males and 28.23% of females, who had NHHR values of 3.14 ± 0.91. There were 136 patients in the EOT2D complicated NAFLD group, 75% of males and 25% of females, who had an NHHR value was 3.74 ± 1.11. Compared with the patients in the EOT2D-uncombined NAFLD group, the EOT2D-combined NAFLD group had significantly higher levels of BMI, FINS, FCP, FBG, HbA1c, ALT, AST, ALB, GGT, UA, TG, TC, NHHR, WBC, N, L, M, and PLT (P < 0.05) (see Table 3). Supplementary Table S2 describes the baseline characteristics of EOT2D patients based on NHHR quartiles, and significant differences in NHHR quartiles and baseline characteristics were observed. The prevalence of NAFLD was higher in the higher quartile group of EOT2D patients compared with the Q1 group (see Table 3).
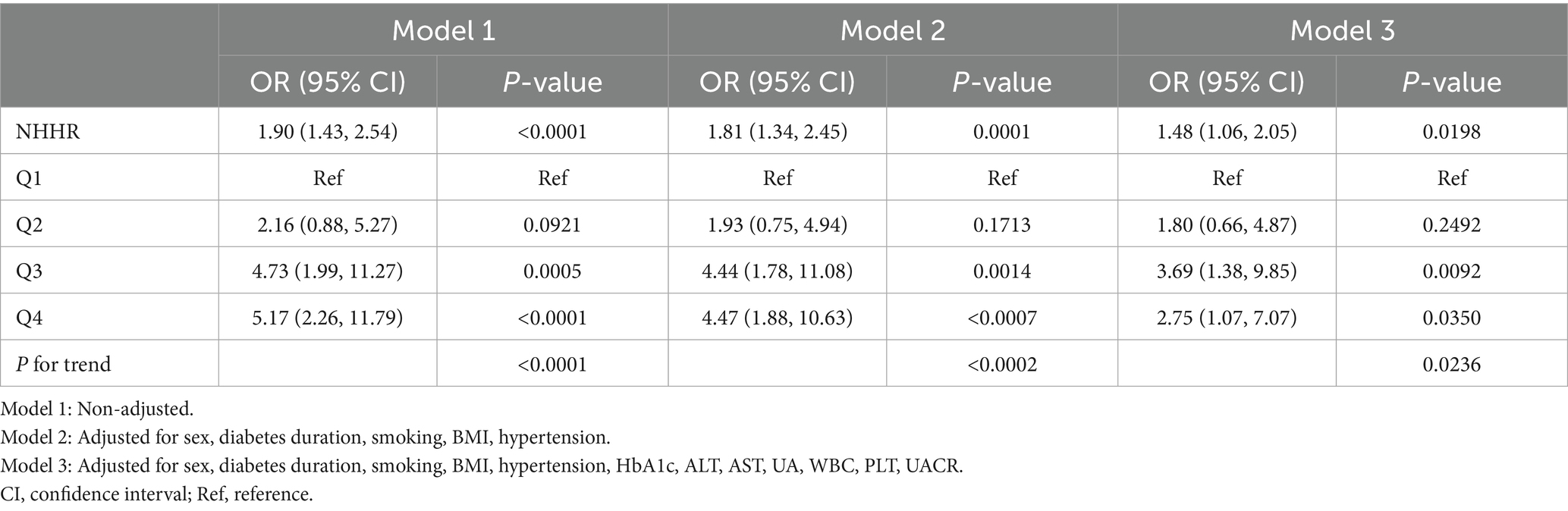
Association between NHHR and EOT2D complicated by NAFLD
Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to investigate the correlation between NHHR and NAFLD combined with EOT2D. Table 4 shows a statistically significant positive correlation between NHHR and NAFLD combined with EOT2D across three models: the unadjusted Model 1 yielded an odds ratio (OR) of 1.90 (95% CI, 1.43–2.54); Model 2, adjusted for sex, diabetes duration, smoking status, BMI, and history of hypertension, yielded an OR of 1.81 (95% CI, 1.34–2.45); and Model 3, further adjusted for HbA1c, ALT, AST, UA, WBC, PLT, and UACR, yielded an OR of 1.48 (95% CI, 1.06–2.05). This positive association remained consistent across all models. To further explore the relationship between NHHR and NAFLD combined with EOT2D, we categorized NHHR into quartiles. In Model 2, higher NHHR levels in the Q3 and Q4 groups were significantly and positively associated with an increased risk of NAFLD combined with EOT2D. In Model 3, compared to the lowest quartile (Q1) of NHHR, the highest quartile (Q4) remained significantly associated with an increased risk of NAFLD combined with EOT2D (OR = 3.69; 95% CI: 1.38–9.85). Trend analysis revealed that the risk of developing NAFLD in EOT2D patients increased significantly with ascending NHHR quartiles (P for trend = 0.0236). Furthermore, smooth curve fitting indicated a linear relationship between NHHR and NAFLD combined with EOT2D (P = 0.131), with no obvious threshold or saturation effect observed (Figure 2B).
Gender-stratified analysis
Multivariate logistic regression models confirmed that NHHR is an independent risk factor for EOT2D and EOT2D combined with NAFLD in the male subgroup, with results presented in Supplementary Table S3. Supplementary Table S3(1) indicates that in the male subgroup, each one-unit increase in NHHR is associated with a 32% higher risk of EOT2D in Model 1. In Model 2, the risk increased by 30%; in Model 3, the risk increased by 21%, indicating that NHHR is independently associated with EOT2D in the male subgroup. Supplementary Table S3(2) shows a statistically significant positive correlation between NHHR and EOT2D with NAFLD in all three models within the male subgroup. In contrast, the results in Supplementary Table S4 indicate that this association is not statistically significant in the female subgroup.
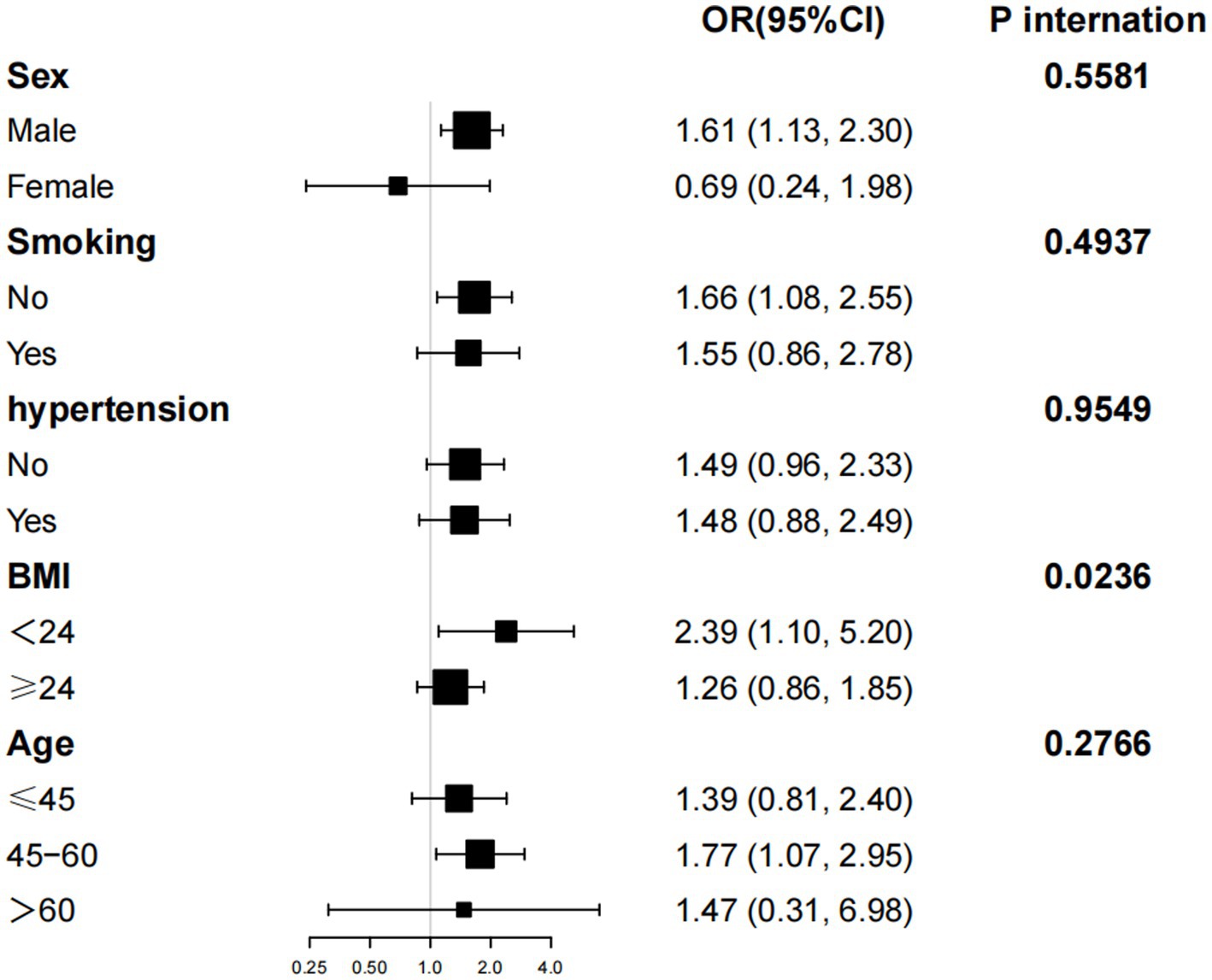
Subgroup analysis
Further subgroup analyses and interaction tests, stratified by age, gender, smoking status, hypertension, and BMI, were conducted to assess the robustness of the association between NHHR levels and the risk of NAFLD combined with EOT2D across different subpopulations. Significant associations were observed among participants with a BMI < 24 kg/m2 (OR: 2.39; 95% CI: 1.10–5.23). Interaction analyses revealed no significant effect modification by gender, age, BMI smoking status, or hypertension on the positive association between NHHR and NAFLD with EOT2D (P-interaction>0.01 for all) (see Figure 3).
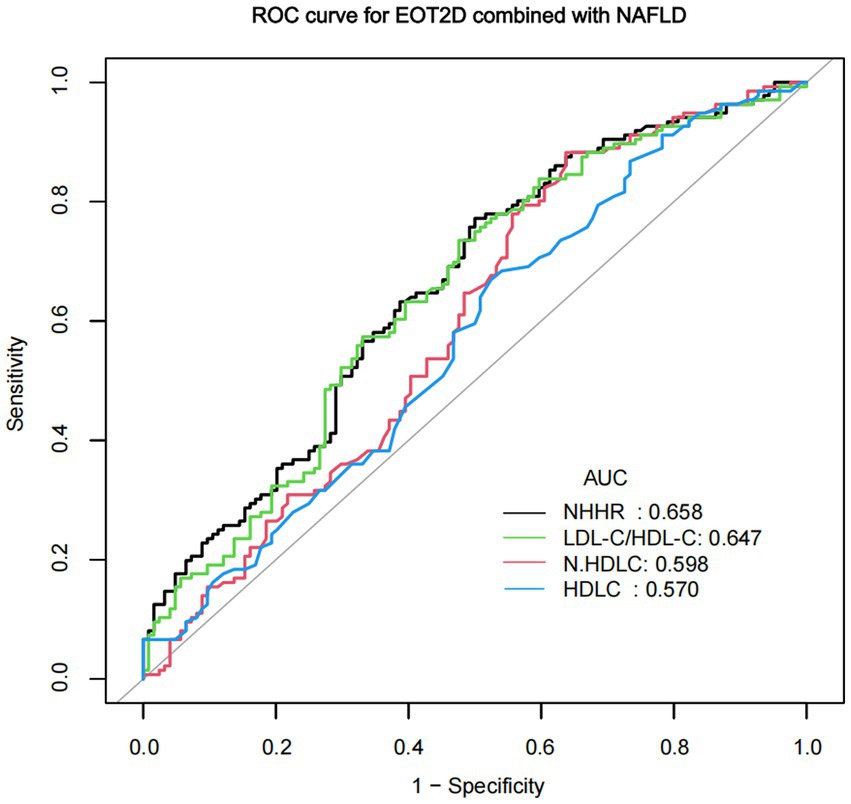
ROC analysis of NHHR for NAFLD comorbid with EOT2D
In previous studies, HDL-C, non-HDL-C, and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio have been identified as valid predictors of T2DM combined with NAFLD (15, 27). EOT2D combined NAFLD is one type of T2DM combined NAFLD. In this study, we compared NHHR with these factors using ROC curve analysis (Figure 4). ROC curve analysis showed that NHHR had a better diagnostic value with an area under the curve (AUC) greater than that of the other three factors, with an AUC value of 0.658 (95% CI 0.5919–0.7243). The AUC remains at a moderate level, indicating its moderate discriminatory ability for EOT2D with NAFLD. By calculating Jorden’s index, the optimal critical value of NHHR was 3.105. The sensitivity of NHHR for diagnosing EOT2D combined with NAFLD was 77.21%, and the specificity was 50.00%.
Discussion
Previous studies have identified NHHR as a risk factor for T2DM as well as NAFLD (12, 24). Owing to shared pathogenic mechanisms, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are closely interrelated. The coexistence of these two conditions increases the risk of adverse liver-related outcomes and imposes a heavier burden of extrahepatic complications, making it a significant public health concern. Currently, there is no research investigating the relationship between the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and NAFLD comorbid with EOT2D. The aim of this study was to investigate the correlation between NHHR and EOT2D combined with NAFLD.
The global burden of diabetes is substantial and continues to grow. Early-onset type 2 diabetes (EOT2D), defined by diagnosis before 40 years of age, has witnessed a concerning rise in prevalence over recent decades. This trend parallels the increasing prevalence of obesity within younger populations. EOT2D follows a more aggressive clinical course than later-onset disease, characterized by heightened insulin resistance and accelerated deterioration of beta-cell function. This pathophysiology leads to a more rapid progression of hyperglycemia, consequently conferring a significantly higher risk of diabetes-related complications and premature mortality (28). In addition, the results of a cohort study showed that EOT2D was associated with an increased risk of early-onset overall cancer, as well as a significant association with an elevated risk of diabetes-related cancers and obesity-related cancers (29). Wang et al. (30) showed that in the normal population, the incidence of NAFLD was higher in the lower age group than in other age groups, which reflects the trend of younger NAFLD onset. Alarmingly, people with NAFLD are becoming younger and younger, and young people may experience long-term and early exposure to the diabetic environment. The findings of He et al. (31) found a stronger association between cardiometabolic risk factors and early-onset NAFLD, with early-onset NAFLD also leading to worse outcomes. NAFLD patients under 45 years of age have a significantly higher risk of developing cancer compared to other age groups (32). Epidemiologic data consistently show that patients with T2DM have twice the prevalence of NAFLD (including advanced hepatic fibrosis) and a higher risk of liver-related morbidity (advanced hepatic fibrosis, hepatocellular carcinoma) and mortality than the general population (33). In previous studies, the majority of data on EOT2D have come from children and adolescents (<19 years of age) (34, 35) rather than individuals aged 19–39 years, and adults with early-onset T2DM are severely underrepresented in clinical studies (36). This group of patients has more confidence in their health, which can lead to suboptimal glycemic control and delayed detection of diabetes-related complications and comorbidities. Chen et al. (37) showed that after 1 year of standardized management of T2DM patients, EOT2D patients showed more significant improvements in metabolic markers and greater improvements in FCP, HBA1c, and BMI compared to LOT2D patients. So it is important to pay attention to this specific population as well as to the comprehensive management of their comorbidities and complications.
NHHR is a novel lipid marker newly proposed in recent years, containing all the information related to anti-atherogenic and pro-atherogenic lipid particles, reflecting the balance between lipoproteins and emerging as a potential marker of metabolic disorders (12, 27, 38). There is growing evidence that NHHR can predict various lipid metabolism-related diseases, such as metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance, with a higher diagnostic value than traditional lipid parameters (12, 38, 39). The pathophysiological relationship between T2DM and NAFLD is characterized by insulin resistance, dysregulated hepatic lipid metabolism resulting in steatosis, and hyperinsulinemia-induced metabolic dysfunction. This triad drives a self-perpetuating cycle of glucolipotoxicity, accelerating progression to advanced liver disease and diabetes complications (40). Results of a study suggest that NHHR may be a predictor of screening for NAFLD in the T2DM population (41). Understanding this metric may help identify those who may benefit from early intervention and assist in the next step of clinical decision-making (42).
In this study, 1,158 patients with T2DM were divided into EOT2D and LOT2D groups. Compared with the patients in the LOT2D group, the EOT2D group had a higher proportion of males, a higher BMI, poorer glycemic control, higher NHHR. This is consistent with the findings of Zeitler et al. (28) that patients with EOT2D had higher blood glucose levels and worse overall metabolic profiles at baseline compared to patients with LOT2D. A cross-sectional study in China also showed a higher proportion of men among newly diagnosed EOT2D patients (43). Subsequently, logistic regression modeling confirmed that NHHR is an independent risk factor for EOT2D. We further categorized this group of EOT2D into a combined NAFLD group and an uncomplicated NAFLD group, and NHHR was also significantly higher in the combined NAFLD group than in the uncomplicated NAFLD group. BMI, FINS, FCP, FBG, HbA1c, ALT, AST, ALB, GGT, UA, TG, TC, WBC, N, L, M, and PLT levels were significantly higher in the combined NAFLD group compared with the group without NAFLD. In a study by Cheng et al. (44) it was shown that the MAFLD group exhibited higher levels of biochemical markers such as BMI, SBP, DBP, and TG, and lower levels of HDL-C, which is also in agreement with the results of our study. We compared the basic characteristics of all participants in the four groups grouped by NHHR quartile and showed that participants in the highest NHHR quartile were more likely to be male, younger, had a higher BMI, and were more likely to be smokers and be comorbidly hypertensive, and that participants in this group had higher levels of glucose and HBA1c, and poorer overall metabolic health. Among EOT2D participants, baseline information was analyzed after grouping by NHHR quartiles, which showed higher BMI, increased prevalence of NAFLD, and poorer glycemic and HBA1c control in the higher quartile group. T2DM hyperglycemia leads to alterations in lipid metabolism, including enhanced HDL clearance, reduced apoA-1 transcription, and accelerated HDL glycation (45). Non-HDL-C has become a more reliable predictor of coronary artery disease risk than traditional lipid parameters (46). NHHR, a composite lipid metabolism index that incorporates non-HDL-C, also has better efficacy in predicting T2DM as well as NAFLD (47, 48).
After logistic regression analysis, NHHR proved to be a significant risk factor for EOT2D patients as well as EOT2D patients with combined NAFLD. Gender-stratified analysis revealed that in the male subgroup, the association between NHHR and EOT2D, as well as the composite endpoint of EOT2D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), was significantly stronger. In contrast, this association was not statistically significant in the female subgroup. This may be because gender potentially influences the association between NHHR and metabolic outcomes through multiple pathways, such as estrogen promoting high-density lipoprotein synthesis, and men being more prone to visceral fat accumulation and atherosclerotic lipid profiles (49). Visceral fat storage influences insulin metabolism by releasing free fatty acids into the portal venous circulation. This may diminish the liver’s insulin clearance capacity, leading to insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia (50). The results of the fitted curve analysis showed that NHHR remained a significant risk factor for EOT2D as well as for EOT2D combined with NAFLD after adequate adjustment for confounders. ROC curve analysis showed that NHHR had a greater predictive value for EOT2D combined NAFLD compared to traditional lipid-related metrics such as HDL-C, non-HDL-C, and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, its moderate AUC suggests it may be most useful as part of a composite risk assessment rather than as a standalone diagnostic tool. NHHR calculation is based on routine lipid panel test reports, requires no additional costs, and demonstrates high feasibility in primary care settings and large-scale population screening. In addition, the correlation between NHHR and the risk of NAFLD was more significant in EOT2D participants with a BMI < 24. EOT2D patients with a BMI < 24 may exhibit “hidden obesity” despite having overall body weight within the normal range—characterized by a predominant accumulation of visceral adipose tissue (VAT) (51). VAT reduces the uptake of free fatty acids (FFAs) while increasing their release. When free fatty acid concentrations in the blood become excessively high, these molecules trigger insulin resistance. Additionally, portal vein blood contains high levels of free fatty acids and cytokines secreted by VAT, which are believed to drive the progression of NAFLD (52). Although their BMI falls within the normal range, lean NAFLD patients often present with sarcopenia. Sarcopenia is now recognized as a progressive pathological process associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), metabolic syndrome, liver disease, and cardiovascular disease (53). It should be clarified that the results of this subgroup analysis are currently preliminary findings and require validation through larger prospective cohort studies. Our findings further underscore the critical importance of targeted health education initiatives and early, sustained clinical interventions in improving metabolic outcomes among young populations.
This hospital-based cross-sectional study ensured cohort consistency and demographic stability. The NHHR measurement demonstrates significant clinical utility due to its cost-effectiveness and accessibility, facilitating early identification of NAFLD risk in EOT2D patients—crucial for guiding targeted interventions. Previous studies have primarily focused on the association between NHHR and populations with T2DM or NAFLD (12, 20, 24), while analyses targeting the EOT2D with NAFLD subgroup have not yet been reported. This is the first study to investigate the association value of NHHR in a specific subgroup of EOT2D patients with NAFLD comorbidity.
Several limitations warrant acknowledgment: the diagnosis of NAFLD relies on ultrasound examination, which can only assess the degree of hepatic steatosis and cannot distinguish between nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis; this study did not adjust for the use of medications such as lipid-lowering or hypoglycemic agents, thereby potentially introducing bias to the outcomes. Future studies should incorporate detailed medication use data to further validate; Furthermore, due to the cross-sectional nature of this study, we cannot establish a causal relationship between NHHR and EOT2D or EOT2D combined with NAFLD, and the directionality of the association remains uncertain. We will address these through expanded cohorts and prospective studies. These findings hold particular relevance for China, where delayed EOT2D diagnosis affects >50% of diabetes patients due to untimely care access.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our study suggests that NHHR is an important risk factor for EOT2D patients, especially for EOT2D patients with comorbid NAFLD. Therefore, it is particularly important for us to promptly identify young-onset T2DM patients with comorbid NAFLD in our future clinical work.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
NW: Writing – original draft. YN: Writing – review & editing. RH: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. ML: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HH: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JL: Writing – review & editing. JZ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82274468), the Scientific Research Program of Higher Education Institutions in Anhui Province (2023AH040103) and 2024 Young Backbone Teachers Overseas Study Visit Research Funding Project (JWFX2024014).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1662125/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Niño-de-Guzmán, E, Bracchiglione, J, Vásquez-Mejía, A, de Graaf, G, Rocha Calderón, C, and Alonso-Coello, P. How do patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus value the importance of outcomes? An overview of reviews. Value Health. (2023) 26:1782–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2023.07.003
2. Uniyal, P, Panwar, S, Bhatt, A, Marianesan, AB, Kumar, R, Singh, TG, et al. An update on current type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2dm) druggable targets and drugs targeting them. Mol Divers. (2025) 31:1–27. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11149-y
3. Jiang, Y, and Lai, X. Clinical features of early-onset type 2 diabetes and its association with triglyceride glucose-body mass index: a cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1356942. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1356942
4. Magliano, DJ, Sacre, JW, Harding, JL, Gregg, EW, Zimmet, PZ, and Shaw, JE. Young-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus—implications for morbidity and mortality. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2020) 16:321–31. doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-0334-z
5. Strati, M, Moustaki, M, Psaltopoulou, T, Vryonidou, A, and Paschou, SA. Early onset type 2 diabetes mellitus: an update. Endocrine. (2024) 85:965–78. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-03772-w
6. Yu, Y, Yu, Y, Wang, Y, Chen, Y, Wang, N, Wang, B, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: an observational and Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1156381. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1156381
7. Fujii, H, and Kawada, N. The role of insulin resistance and diabetes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:3863. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113863
8. Boccatonda, A, Andreetto, L, D’Ardes, D, Cocco, G, Rossi, I, Vicari, S, et al. From Nafld to Mafld: definition, pathophysiological basis and cardiovascular implications. Biomedicine. (2023) 11:883. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030883
9. Bjornstad, P, Chao, LC, Cree-Green, M, Dart, AB, King, M, Looker, HC, et al. Youth-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus: an urgent challenge. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2022) 19:168–84. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00645-1
10. Zhu, Y, Liu, C, Xu, X, Ma, X, Liu, J, Zhang, Z, et al. Association of diabetes mellitus with all-cause and cause-specific mortality among patients with metabolic-dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a longitudinal cohort study. J Pers Med. (2023) 13:554. doi: 10.3390/jpm13030554
11. Younossi, ZM, Golabi, P, de Avila, L, Paik, JM, Srishord, M, Fukui, N, et al. The global epidemiology of Nafld and Nash in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Hepatol. (2019) 71:793–801. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021
12. Tan, M-Y, Weng, L, Yang, Z-H, Zhu, S-X, Wu, S, and Su, J-H. The association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with type 2 diabetes mellitus: recent findings from Nhanes 2007–2018. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:151. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02143-8
13. Vitulo, M, Gnodi, E, Rosini, G, Meneveri, R, Giovannoni, R, and Barisani, D. Current therapeutical approaches targeting lipid metabolism in Nafld. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:12748. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612748
14. Pei, K, Gui, T, Kan, D, Feng, H, Jin, Y, Yang, Y, et al. An overview of lipid metabolism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:4020249. doi: 10.1155/2020/4020249
15. Zhu, Z, Yang, N, Fu, H, Yuan, G, Chen, Y, Du, T, et al. Associations of lipid parameters with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetic patients according to obesity status and metabolic goal achievement. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:1002099. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1002099
16. Kim, SW, Jee, JH, Kim, HJ, Jin, SM, Suh, S, Bae, JC, et al. Non-Hdl-cholesterol/Hdl-cholesterol is a better predictor of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance than apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A1. Int J Cardiol. (2013) 168:2678–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.03.027
17. Sheng, G, Liu, D, Kuang, M, Zhong, Y, Zhang, S, and Zou, Y. Utility of non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in evaluating incident diabetes risk. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2022) 15:1677–86. doi: 10.2147/dmso.S355980
18. Kaze, AD, Santhanam, P, Musani, SK, Ahima, R, and Echouffo-Tcheugui, JB. Metabolic Dyslipidemia and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus: findings from the look ahead study. J Am Heart Assoc. (2021) 10:e016947. doi: 10.1161/jaha.120.016947
19. Kane, JP, Pullinger, CR, Goldfine, ID, and Malloy, MJ. Dyslipidemia and diabetes mellitus: role of lipoprotein species and interrelated pathways of lipid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Pharmacol. (2021) 61:21–7. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2021.08.013
20. Lu, S, Kuang, M, Yue, J, Hu, C, Sheng, G, and Zou, Y. Utility of traditional and non-traditional lipid indicators in the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Japanese population. Lipids Health Dis. (2022) 21:95. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01712-z
21. Ma, HX, Chen, HQ, and Wang, PC. Association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (Nhhr) and stroke among adults in the USA: a cross-sectional Nhanes study. Biomed Environ Sci. (2025) 38:37–46. doi: 10.3967/bes2025.001
22. Tian, RN, Zhang, SX, Zhang, N, Shi, Y, Guo, HQ, Wang, C, et al. J-shaped association between non-HDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratios and gout in US adults with gout. J Multidiscip Healthc. (2025) 18:933–46. doi: 10.2147/jmdh.S508765
23. Wang, B, Li, L, Tang, Y, Lin, T, Wu, J, Wang, G, et al. Changes in non-high-density lipoprotein to high-density lipoprotein ratio (Nhhr) and cardiovascular disease: insights from Charls. Lipids Health Dis. (2025) 24:112. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02536-3
24. Huang, X, Li, J, Zhang, L, Zhang, C, and Li, C. The association between the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in us adults: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:24847. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76002-y
25. Fang, JX, Han, Y, Meng, J, Zou, HM, Hu, X, Han, YX, et al. Relationship between non-alcoholic fatty liver and progressive fibrosis and serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Endocr Disord. (2024) 24:108. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01640-2
26. Fan, JG, and Farrell, GC. Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China. J Hepatol. (2009) 50:204–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.10.010
27. Yang, D, Dai, H, Wang, Y, Zhang, J, Wei, M, Shan, M, et al. Association between the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and metabolic dysfunction-associated Steatotic liver disease. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1557751. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1557751
28. Zeitler, P, Galindo, RJ, Davies, MJ, Bergman, BK, Thieu, VT, Nicolay, C, et al. Early-onset type 2 diabetes and Tirzepatide treatment: a post hoc analysis from the surpass clinical trial program. Diabetes Care. (2024) 47:1056–64. doi: 10.2337/dc23-2356
29. Zhang, Y, Song, M, Cao, Y, Eliassen, AH, Wolpin, BM, Stampfer, MJ, et al. Incident early- and later-onset type 2 diabetes and risk of early- and later-onset Cancer: prospective cohort study. Diabetes Care. (2023) 46:120–9. doi: 10.2337/dc22-1575
30. Wang, J, Du, J, Wang, M, Jin, M, Tang, Z, and Mao, Y. Global, regional, and National Burden of Nafld in youths and young adults aged 15-39 years, 1990-2021, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2035: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2021. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1509232. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1509232
31. He, L, Zheng, W, Liao, Y, Kong, W, and Zeng, T. Individuals with cardiometabolic risk factors are at higher risk for early-onset Nafld. J Hepatol. (2024) 81:e99–e101. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.04.027
32. Liu, C, Liu, T, Zhang, Q, Jia, P, Song, M, Zhang, Q, et al. New-onset age of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cancer risk. JAMA Netw Open. (2023) 6:e2335511. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35511
33. Cernea, S, and Raz, I. Nafld in type 2 diabetes mellitus: still many challenging questions. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2021) 37:e3386. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3386
34. Kim, B, Jin, HY, Yoon, JS, Noh, ES, and Hwang, IT. Triglyceride glucose index is associated with ultrasonographic fatty liver Indicator in children and adolescents with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. (2024) 16:306–13. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2024.2024-2-5
35. Li, J, Ha, A, Rui, F, Zou, B, Yang, H, Xue, Q, et al. Meta-analysis: global prevalence, trend and forecasting of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents, 2000-2021. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 56:396–406. doi: 10.1111/apt.17096
36. Sargeant, JA, Brady, EM, Zaccardi, F, Tippins, F, Webb, DR, Aroda, VR, et al. Adults with early-onset type 2 diabetes (aged 18-39 years) are severely underrepresented in diabetes clinical research trials. Diabetologia. (2020) 63:1516–20. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05174-9
37. Chen, M, Feng, P, Liang, Y, Ye, X, Wang, Y, Liu, Q, et al. The relationship between age at diabetes onset and clinical outcomes in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a real-world two-center study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2024) 17:4069–78. doi: 10.2147/dmso.S485967
38. Li, J, Kou, C, Chai, Y, Li, Y, Liu, X, Zhang, L, et al. The relationship between the ratio of non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (Nhhr) and both Masld and advanced liver fibrosis: evidence from Nhanes 2017-2020. Front Nutr. (2025) 11:1508106. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1508106
39. Lin, L, Xie, Y, Lin, Z, Lin, C, and Yang, Y. Machine learning for predicting metabolic-associated fatty liver disease including Nhhr: a cross-sectional Nhanes study. PLoS One. (2025) 20:e0319851. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319851
40. Lin, J, Li, H, and Wan, Q. A cross-sectional study of the correlation between the atherogenic index of plasma and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2022) 15:2227–34. doi: 10.2147/dmso.S375300
41. Ma, XM, Guo, YM, Jiang, SY, Li, KX, Zheng, YF, Guo, XG, et al. Potential predictive role of non-Hdl to Hdl cholesterol ratio (Nhhr) in Masld: focus on obese and type 2 diabetic populations. BMC Gastroenterol. (2025) 25:79. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03659-8
42. Suvitaival, T, Bondia-Pons, I, Yetukuri, L, Pöhö, P, Nolan, JJ, Hyötyläinen, T, et al. Lipidome as a predictive tool in progression to type 2 diabetes in Finnish men. Metab Clin Exp. (2018) 78:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.08.014
43. Zou, X, Zhou, X, Ji, L, Yang, W, Lu, J, Weng, J, et al. The characteristics of newly diagnosed adult early-onset diabetes: a population-based cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:46534. doi: 10.1038/srep46534
44. Cheng, Z, Hu, C, Zhang, Y, Zhou, J, Shi, J, Sun, L, et al. The different predictive effects of multiple body fat indexes on metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2024) 17:3875–90. doi: 10.2147/dmso.S469859
45. Drew, BG, Rye, KA, Duffy, SJ, Barter, P, and Kingwell, BA. The emerging role of Hdl in glucose metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2012) 8:237–45. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.235
46. Aggarwal, DJ, Kathariya, MG, and Verma, DPK. Ldl-C, non-Hdl-C and apo-B for cardiovascular risk assessment: looking for the ideal marker. Indian Heart J. (2021) 73:544–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2021.07.013
47. Yang, Y, Li, S, An, Z, and Li, S. The correlation between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (Nhhr) with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an analysis of the population-based Nhanes (2017-2018). Front Med. (2024) 11:1477820. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1477820
48. Yu, B, Li, M, Yu, Z, Zheng, T, Feng, X, Gao, A, et al. The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (Nhhr) as a predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in us adults with diabetes or prediabetes: Nhanes 1999-2018. BMC Med. (2024) 22:317. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03536-3
49. Palmisano, BT, Zhu, L, Eckel, RH, and Stafford, JM. Sex differences in lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Mol Metab. (2018) 15:45–55. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.05.008
50. Huang, H, Zheng, X, Wen, X, Zhong, J, Zhou, Y, and Xu, L. Visceral fat correlates with insulin secretion and sensitivity independent of BMI and subcutaneous fat in Chinese with type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1144834. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1144834
51. Dhokte, S, and Czaja, K. Visceral adipose tissue: the hidden culprit for type 2 diabetes. Nutrients. (2024) 16:1015. doi: 10.3390/nu16071015
52. Kim, HK, Bae, SJ, Lee, MJ, Kim, EH, Park, H, Kim, HS, et al. Association of Visceral fat Obesity, sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease without obesity. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2023) 29:987–1001. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2023.0035
53. Chen, M, Cao, Y, Ji, G, and Zhang, L. Lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and sarcopenia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1217249. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1217249
Glossary
NHHR - non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio
BMI - body mass index
FINS - fasting insulin
FCP - fasting C-peptide
FBG - fasting blood glucose
HbA1c - Hemoglobin A1c
ALT - alanine transaminase
AST - aspartate transaminase
ALB - albumin
GGT - gamma-glutamyl transferase
BUN - blood urea nitrogen
Cr - serum creatinine
UA - serum uric acid
TG - triglyceride
TC - total cholesterol
HDL-C - high density lipoprotein cholesterol
LDL-C - low density lipoprotein cholesterol
WBC - white Blood Cell Differential
N - neutrophil count
L - lymphocyte count
M - monocyte count
PLT - platelet count
UACR - urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio
ROC - receiver operating characteristic
AUC - areas under the curve
MASLD - metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
T2DM - type 2 diabetes mellitus
EOT2D - early onset type 2 diabetes
LOT2D - late onset type 2 diabetes
Keywords: NHHR, early onset, type 2 diabetes mellitus, NAFLD, cross-sectional study
Citation: Wu N, Ni Y, Huang R, Wang J, Li M, Hu H, Zhang Y, Li J and Zhang J (2025) The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is associated with early onset type 2 diabetes with NAFLD: a cross-sectional study in China. Front. Nutr. 12:1662125. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1662125
Edited by:
Domenico Sergi, University of Ferrara, ItalyReviewed by:
Hengyi Xu, The University of Texas at Austin, United StatesShinsuke Hidese, Teikyo University, Japan
Rashu Barua, New York University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Ni, Huang, Wang, Li, Hu, Zhang, Li and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juyi Li, ZWVsbGp5QDE2My5jb20=; Jinjun Zhang, emhhbmdqaW5qdW4xMTAzQDE2My5jb20=
†ORCID: Juyi Li, https://orcid.org/0009-0000-6555-8847
Jinjun Zhang, https://orcid.org/0009-0000-5064-7599
 Nini Wu
Nini Wu Yingqun Ni
Yingqun Ni Rilong Huang4
Rilong Huang4