- Xiamen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Hyperuricemia (HUA), characterized by elevated serum uric acid levels (>420 μmol/L), is a metabolic disorder linked to gout, cardiovascular diseases, renal disorders, diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers a holistic approach to HUA management, employing dialectical treatments to address underlying pathogenesis, reduce uric acid, mitigate inflammation, and protect organ function. This review synthesizes recent advances in TCM for HUA and its comorbidities, drawing from pharmacological studies of single herbs, compound formulas, and TCM pathogenesis theories. We introduce innovative strategies, including network pharmacology, metabolomics, personalized TCM diagnostics, and nanotechnology, to enhance therapeutic precision and efficacy. By integrating TCM's traditional wisdom—emphasizing balance among vital energies like “qi” (vital energy) and bodily fluids, with modern scientific methodologies, this review highlights potential risks, toxicities, and challenges in TCM application, aiming to improve patient outcomes in HUA and related diseases.
1 Introduction
Hyperuricemia (HUA) is a prevalent metabolic disorder defined by serum uric acid levels exceeding 420 μmol/L in men and 360 μmol/L in women, resulting from dysregulated purine metabolism or impaired uric acid excretion (1, 2). It is a major risk factor for gout, cardiovascular diseases, renal disorders, diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (3). The global prevalence of HUA is rising due to dietary shifts, obesity, and aging populations.
In modern medicine, HUA is managed with uric acid-lowering drugs such as allopurinol and febuxostat, which inhibit xanthine oxidase (XOD), or uricosurics like benzbromarone, which enhance uric acid excretion (4, 5). However, these treatments are associated with side effects, including hepatotoxicity, renal impairment, and gastrointestinal disturbances, and often fail to address comorbidities or prevent gout recurrence (6, 7). Moreover, patient adherence is low due to adverse effects and the chronic nature of the condition (8).
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers a holistic alternative, viewing HUA as a condition of “ben xu biao shi” (deficiency in the root and excess in the manifestation), often linked to deficiencies in the spleen and kidney (organs associated with digestion, fluid metabolism, and vitality in TCM), damp-heat accumulation (a pathogenic factor resembling inflammation and fluid retention), phlegm-turbidity (mucus-like stagnation correlating to metabolic buildup), and blood stasis (impaired circulation akin to vascular dysfunction) (9). TCM employs single herbs and compound formulas to reduce uric acid levels, suppress inflammation, and protect organ function, with potentially fewer adverse effects compared to Western drugs in some studies (10, 11). However, challenges such as herb-drug interactions, variability in herb quality, and rare reports of hepatotoxicity must be considered. This review synthesizes findings from various sources, expands on TCM's therapeutic mechanisms, and introduces innovative approaches such as network pharmacology, metabolomics, personalized diagnostics, and nanotechnology to advance HUA treatment.
Despite these advantages, TCM faces limitations, including inconsistent evidence from clinical trials, potential toxicities from improper use, and the need for stronger backing for safety claims.
2 Methodology
This narrative review synthesizes recent advances in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for the treatment of hyperuricemia (HUA) and its associated diseases, focusing on pathogenesis, mechanisms, therapeutic approaches, and future directions. To ensure transparency and rigor, the review process followed a structured approach adapted from guidelines for narrative reviews, including elements of systematic methodology where applicable (e.g., explicit search strategies and quality appraisal) to minimize bias and improve reliability (12). Literature was selected through systematic searches conducted in major databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Data, and VIP Database. Search terms included “hyperuricemia,” “gout,” “traditional Chinese medicine,” “Chinese herbal medicine,” “uric acid metabolism,” “xanthine oxidase,” and related combinations in both English and Chinese. The search covered publications from January 2000 to June 2025 to ensure inclusion of contemporary studies while building on foundational research. Manual hand-searching of reference lists from key articles and relevant journals (e.g., Journal of Ethnopharmacology, Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine) was also conducted to identify additional sources. Duplicates were removed using reference management software (EndNote X9), with discrepancies resolved through discussion.
Inclusion criteria were: (1) peer-reviewed articles, clinical trials, experimental studies, or reviews addressing TCM's role in HUA pathogenesis, mechanisms, treatments, or innovations; (2) studies demonstrating clear methodologies, such as in vitro/in vivo experiments or randomized controlled trials; and (3) relevance to human health outcomes or molecular mechanisms. Exclusion criteria included: (1) non-peer-reviewed sources (e.g., conference abstracts or gray literature); (2) case reports or small-scale studies with fewer than 10 participants; (3) articles focused solely on Western medicine without TCM integration; and (4) duplicates or irrelevant topics. Initial searches yielded approximately 1,200 articles, which were screened by title and abstract, followed by full-text review. Ultimately, 138 references were selected based on quality, relevance, and contribution to the field, with an emphasis on high-impact journals and evidence-based findings to minimize bias. No formal meta-analysis was performed, as this is a narrative synthesis aimed at providing a comprehensive overview rather than quantitative pooling, given the heterogeneity in study designs (e.g., in vitro vs. clinical) and TCM-specific outcomes.
3 Mechanisms and associated diseases of hyperuricemia (HUA)
3.1 Uric acid metabolism and production
Uric acid is the final product of purine metabolism in humans, primarily synthesized in the liver through the enzymatic activity of xanthine oxidase (XOD). Purine nucleotides, derived from dietary sources or endogenous cellular turnover, are metabolized into hypoxanthine and xanthine, which XOD converts into uric acid. Approximately 70% of uric acid is excreted via the kidneys, with the remaining 30% eliminated through the intestines (13). The kidneys reabsorb about 90% of filtered uric acid, mediated by specific transporters, making renal handling a critical determinant of serum uric acid levels.
3.2 Mechanisms of hyperuricemia
HUA arises from an imbalance between uric acid production and excretion, leading to elevated serum uric acid levels (>6.8 mg/dL) (13). The key mechanisms include:
3.2.1 Overproduction of uric acid
A primary driver of HUA is the overproduction of uric acid, which occurs when XOD activity is upregulated, accelerating the conversion of purine precursors (hypoxanthine and xanthine) into uric acid. Several factors contribute to this process. Genetic mutations or polymorphisms in genes such as phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase (PRPS) enhance uric acid synthesis by altering purine metabolism pathways. High-purine diets, including consumption of red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and certain fish (e.g., sardines, anchovies), increase purine load, thereby elevating uric acid production. Alcohol consumption, particularly beer and spirits, exacerbates this by promoting ATP degradation to purines and enhancing hepatic XOD activity, leading to higher uric acid levels (14). Additionally, high fructose intake, common in sweetened beverages, upregulates purine metabolism via the fructokinase pathway, further contributing to uric acid overproduction (15).
3.2.2 Underexcretion of uric acid
A significant contributing factor to HUA is the dysregulation of uric acid transporters in the proximal tubules of the kidneys. Urate Transporter 1 (URAT1), encoded by the SLC22A12 gene, facilitates uric acid reabsorption, with polymorphisms like rs475688 linked to decreased excretion and increased HUA risk (16). Similarly, Glucose Transporter 9 (GLUT9), encoded by SLC2A9, is a critical regulator of uric acid reabsorption, and its genetic variants are strongly associated with HUA and gout susceptibility (17). Organic Anion Transporters (OAT1 and OAT3), encoded by SLC22A6 and SLC22A8, respectively, mediate uric acid secretion, but dysfunctional variants impair this process, contributing to elevated uric acid levels (18, 19). Additionally, the ATP-Binding Cassette Subfamily G Member 2 (ABCG2) transporter, encoded by the ABCG2 gene, supports uric acid secretion in both kidneys and intestines; the Q141K polymorphism (rs2231142) is a well-established risk factor for HUA and gout (20). Other factors, including renal dysfunction, diuretics (e.g., thiazides, loop diuretics), and lactic acidosis, further inhibit uric acid excretion by competing for transporter activity, exacerbating HUA (21–24). These molecular and physiological disruptions highlight the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors in HUA pathogenesis, necessitating targeted therapeutic strategies to enhance renal uric acid clearance.
3.2.3 Uricase deficiency
Unlike most mammals, humans lack functional uricase, an enzyme that degrades uric acid into the more soluble allantoin. This evolutionary loss results in higher baseline uric acid levels in humans (typically 3.5–7.2 mg/dL) compared to other mammals (e.g., <2 mg/dL in rodents) (25, 26). Uricase deficiency, combined with dietary and genetic factors, predisposes humans to HUA (13).
3.3 Diseases associated with hyperuricemia
Elevated uric acid levels contribute to multiple pathological conditions through crystal-dependent and crystal-independent mechanisms (9). These include:
3.3.1 Gout
Gout results from the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in joints and soft tissues, triggering acute inflammatory responses (27, 28). MSU crystals activate the NLRP3 inflammasome, leading to interleukin-1β (IL-1β) release and neutrophil infiltration, causing gouty arthritis. Risk factors include obesity, hyperlipidemia, and alcohol consumption, which exacerbate HUA and crystal formation (29, 30).
3.3.2 Cardiovascular diseases
HUA is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases through multiple molecular mechanisms. In hypertension, HUA induces oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction by reducing nitric oxide bioavailability and activating the renin-angiotensin system, resulting in elevated blood pressure (31, 32). Similarly, HUA promotes coronary heart disease by driving vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and atherosclerotic plaque formation, increasing the risk of myocardial infarction (31, 32). Furthermore, elevated uric acid levels contribute to atrial fibrillation by promoting atrial remodeling and oxidative stress, which precipitate arrhythmic events (33).
3.3.3 Renal disorders
HUA contributes significantly to renal pathology through multiple mechanisms. The deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in renal tubules triggers interstitial nephritis, leading to tubular obstruction and inflammation, which impair kidney function (34). Chronic HUA further exacerbates renal damage by inducing tubulointerstitial fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis, accelerating the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) (35). This relationship is bidirectional, as HUA both causes and results from renal dysfunction, creating a vicious cycle that amplifies kidney injury (21).
3.3.4 Type 2 diabetes
HUA exacerbates insulin resistance by inducing oxidative stress and impairing glucose uptake in peripheral tissues, such as skeletal muscle and adipose tissue (36, 37). These molecular disruptions contribute to metabolic dysfunction, with elevated uric acid levels correlating with higher fasting glucose and HbA1c concentrations, thereby increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes (38–40). By promoting oxidative stress and disrupting insulin signaling pathways, HUA plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of diabetes, highlighting the need for integrated therapeutic strategies to address both uric acid levels and glucose metabolism.
3.3.5 Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
HUA is closely associated with insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), exacerbating its metabolic and hormonal disturbances. Elevated uric acid levels promote oxidative stress and inflammation, which impair insulin signaling and amplify hormonal imbalances, contributing to metabolic dysfunction in PCOS patients (41, 42).
3.3.6 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
HUA promotes hepatic fat accumulation, contributing to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through distinct molecular mechanisms. Uric acid induces mitochondrial oxidative stress, which impairs fatty acid β-oxidation, leading to lipid accumulation in hepatocytes (43, 44). Additionally, uric acid upregulates lipogenic enzymes, such as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1), driving hepatic steatosis and accelerating NAFLD progression (44, 45).
3.4 TCM pathogenesis
In TCM, HUA, though not explicitly named, is classified under conditions such as “li jie” (calendar joint pain, akin to arthralgia or gout-like symptoms), “bi zheng” (arthralgia syndrome, referring to obstructive pain syndromes), or “tong feng” (gout), reflecting its systemic and articular manifestations (46, 47). TCM attributes HUA to internal deficiencies, primarily of the spleen (associated with digestion and fluid transformation) and kidney (linked to filtration and essence storage), and external pathogenic factors, including wind (rapid onset symptoms), cold (constricting pain), dampness (heaviness and swelling), and heat (inflammation and redness) (48, 49). Spleen deficiency impairs water metabolism, while kidney deficiency hinders fluid and uric acid excretion, leading to the accumulation of damp-heat (a combination of fluid retention and inflammation) or phlegm-turbidity (mucus-like stagnation resembling metabolic deposits), which correlates with impaired uric acid clearance observed in modern studies (50). Excessive damp-heat stagnation obstructs “qi” and blood flow, manifesting as joint pain, swelling, and systemic inflammation, akin to gouty arthritis (49). Chronic HUA further promotes phlegm-turbidity and blood stasis, contributing to organ damage and comorbidities such as cardiovascular and renal diseases, mirroring molecular findings of uric acid-induced inflammation and fibrosis (48).
External pathogens, such as wind, cold, or dampness, exacerbate joint symptoms and systemic imbalances by invading the body and disrupting homeostasis (9). TCM categorizes HUA-related diseases into syndromes—such as damp-heat, phlegm-turbidity, or liver-kidney “yin” deficiency—guiding dialectical treatments tailored to individual patterns, which align with personalized medicine approaches (46, 51). This framework highlights TCM's holistic perspective, offering insights that complement molecular understanding of HUA pathogenesis. Recent integrative research using multi-omics techniques has further elucidated these TCM patterns, revealing that spleen deficiency correlates with disrupted purine metabolism and gut dysbiosis, impairing uric acid degradation, while kidney deficiency aligns with transporter dysregulation (e.g., URAT1 inhibition) and chronic kidney disease progression (52). External factors like damp-heat are supported by studies showing TCM extracts promoting UA excretion and repairing oxidative damage through multi-target effects, such as modulating immune-inflammatory responses (53). This convergence validates TCM's role in addressing HUA's root causes, paving the way for personalized therapies. While TCM theories align with modern findings, contradictions exist in clinical outcomes, where some studies show variable efficacy due to individual differences and a lack of standardization (54).
4 TCM monotherapy for hyperuricemia
TCM monotherapies target uric acid production, excretion, and associated symptoms in HUA, offering a safer profile with fewer side effects compared to Western drugs like allopurinol in preliminary studies (55); however, risks such as hepatotoxicity from high doses or contaminated herbs have been reported (56). Table 1 summarizes key TCM herbs, their active compounds, molecular mechanisms, uric acid reduction efficacy, and additional therapeutic effects, highlighting their multi-target approach for HUA management. Besides, these herbs demonstrate dose-dependent efficacy, targeting multiple pathways (XOD inhibition, transporter modulation, anti-inflammation) and offering a safer profile than allopurinol. Emerging 2024–2025 research highlights how these herbs exert multi-target effects, such as inhibiting UA reabsorption and promoting excretion via transporters like URAT1, while alleviating oxidative stress—aligning TCM's “clearing heat and dampness” with anti-inflammatory mechanisms in hyperuricemia models (57, 58).
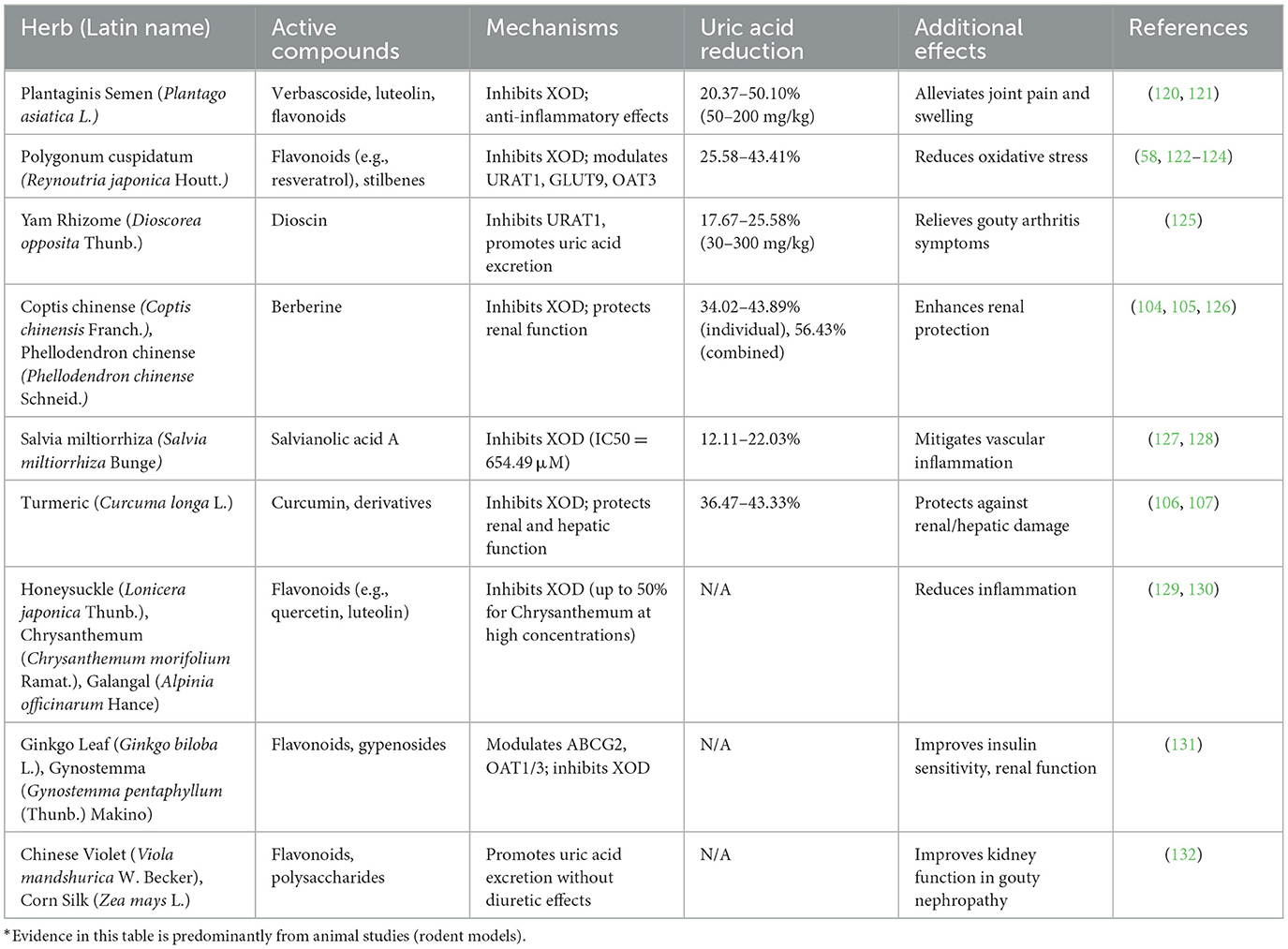
Table 1. Key TCM single herbs for hyperuricemia: active compounds, mechanisms, and therapeutic effects.
Despite promising results, contradictions in efficacy exist; for instance, some animal studies show inconsistent uric acid reduction due to dosage variability (10). Potential toxicities include renal strain from diuretic herbs like Plantaginis Semen (Plantago asiatica L.) in long-term use (59), and allergic reactions to flavonoids in Polygonum cuspidatum (Reynoutria japonica Houtt.) (60). Challenges include herb standardization, as bioactive compound levels vary by source (61), and limited human trials to confirm safety over Western drugs (62). Future studies should address these to substantiate safety claims.
5 TCM compound formulas for hyperuricemia and related diseases
TCM compound formulas combine multiple herbs to address complex syndromes in HUA, leveraging synergistic effects to target uric acid metabolism, inflammation, and organ protection with fewer side effects than Western drugs. Recent advances demonstrate these formulas' efficacy in rodent HUA models through regulating purine metabolism and immune responses, with integrative studies confirming alignment between TCM dampness resolution and biomedical UA transporter modulation for enhanced safety and precision (58). Table 2 summarizes TCM compound formulas, their constituent herbs, molecular mechanisms, uric acid reduction efficacy, and additional therapeutic effects, highlighting their multi-target approach for managing HUA and its comorbidities. These formulas embody TCM principles like “jun chen zuo shi” (emperor-minister-assistant-courier herb roles) while aligning with biomedical synergy in pathway modulation.
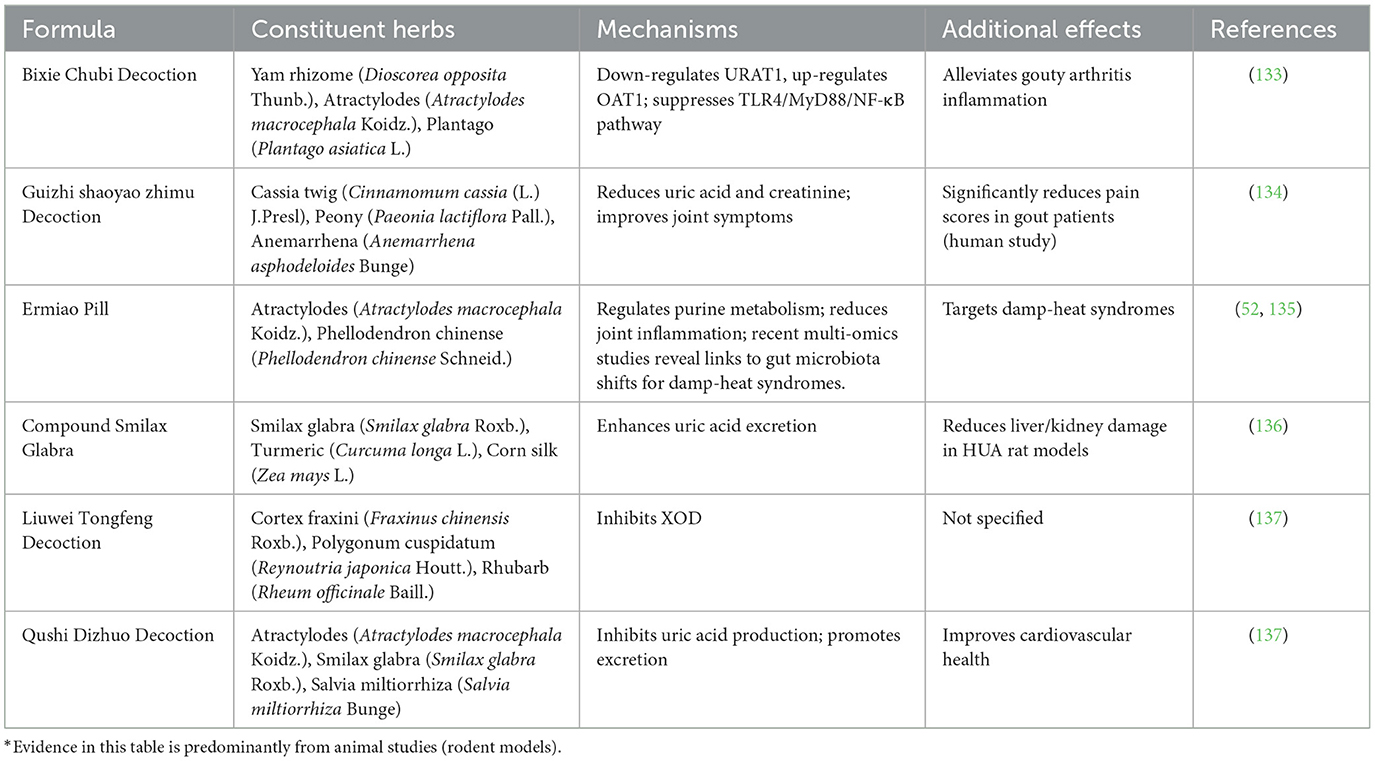
Table 2. TCM compound formulas for hyperuricemia: constituent herbs, mechanisms, and additional therapeutic effects.
While synergistic effects are highlighted, contradictions arise in meta-analyses showing high heterogeneity in trial outcomes, possibly due to poor blinding or small sample sizes (63). Toxicities may include liver enzyme elevation from berberine-rich formulas like Ermiao Pill (Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. and Phellodendron chinense Schneid.) in susceptible patients, and challenges in quality control lead to contamination risks (64). Claims of superior safety require more robust RCTs comparing TCM to allopurinol directly (65).
6 TCM treatment for HUA-related diseases
6.1 Cardiovascular diseases
HUA is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including coronary heart disease, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation, driven by oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and vascular smooth muscle proliferation (66). In TCM, these conditions are attributed to “qi” deficiency (vital energy depletion), blood stasis (circulation impairment), and phlegm-turbidity (metabolic stagnation), which align with molecular disruptions such as inflammation and vascular remodeling (67). TCM offers targeted interventions to address these pathologies holistically (68). Buyang Huanwu Decoction, comprising Astragalus (Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge), Angelica sinensis (Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels), and Ligusticum (Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort.), promotes “qi” and blood circulation (enhancing energy flow and vascular health), reducing uric acid levels, and mitigating cardiovascular risk factors (69). Danhong Injection, combining Salvia miltiorrhiza and Safflower, resolves blood stasis, enhances endothelial function, and reduces uric acid by 20–30%, offering protection against vascular complications (70). Similarly, Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction targets blood stasis and “qi” stagnation, effectively lowering hypertension and uric acid levels in HUA patients with cardiovascular comorbidities (71).
6.2 Gout
Gout, driven by MSU crystal deposition, manifests as acute joint inflammation or chronic tophi, resulting from hyperuricemia-induced crystal formation that triggers NLRP3 inflammasome activation and interleukin-1β release (13). In TCM, gout is classified into distinct syndromes based on its acute and chronic phases, guiding targeted treatments. In the acute phase, characterized by damp-heat or wind-damp-heat syndromes (inflammation with fluid retention or rapid-onset swelling), Qingre Lishi Decoction (containing Plantago asiatica L. and Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.) and Canxiang Decoction reduce uric acid levels and inflammation, effectively alleviating pain and swelling by addressing damp-heat accumulation (72). In the chronic phase, marked by phlegm-turbidity or liver-kidney “yin” deficiency, Wuling Powder (containing Poria and Atractylodes) and Qufeng Huoluo Xiezhuo Decoction promote uric acid excretion, while Gui Shao Dihuang Decoction nourishes “yin” (restoring fluid balance) and reduces tophi formation, mitigating chronic joint damage (73). These TCM interventions target both uric acid metabolism and inflammatory pathways, offering a holistic approach to managing gout's acute and chronic manifestations, complementing molecular insights into MSU-driven pathology (54).
6.3 Renal disorders
In TCM, renal disorders are attributed to spleen-kidney deficiency (impaired digestion and filtration) and damp-turbidity accumulation (fluid and metabolic stagnation), which align with impaired uric acid clearance and inflammation observed in modern studies (74). TCM offers targeted interventions to mitigate these pathologies. Smilax glabra (Smilax glabra Roxb.) and Corn silk (Zea mays L.) promote uric acid excretion and protect renal tubules, reducing proteinuria and creatinine levels to preserve kidney function (75, 76).
Clerodendranthus spicatus (Orthosiphon stamineus Benth.) enhances uric acid clearance and improves glomerular filtration rate, offering therapeutic benefits in gouty nephropathy (77). Zhenwu Decoction (containing Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf, Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz., Paeonia lactiflora Pall., Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC., and Zingiber officinale Roscoe) strengthens spleen and kidney function, reduces dampness (fluid retention), and protects against renal fibrosis, addressing both the root causes and manifestations of HUA-related renal damage (78).
6.4 Diabetes
In TCM, this comorbidity is termed “xiaoke tongfeng” (thirsting-wasting with gout-like pain), attributed to damp-heat and phlegm stasis, which align with molecular disruptions in glucose and uric acid metabolism (79). TCM offers targeted interventions to address these overlapping pathologies. Gynostemma [Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino] and Sophora flower (Sophora japonica L.) improve insulin sensitivity and reduce uric acid levels by 15–25%, mitigating metabolic dysfunction (80). Salvia miltiorrhiza (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) and Astragalus [Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge] enhance glucose metabolism and protect pancreatic β-cells, addressing both HUA and diabetes through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects (81). Liuwei Dihuang Pill [containing Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC., Dioscorea opposita Thunb., Cornus officinalis Siebold & Zucc., Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews, Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf, and Alisma plantago-aquatica L.] nourishes the kidney “yin,” improving insulin sensitivity and reducing uric acid, offering a holistic approach to managing this dual pathology (82).
6.5 Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is attributed to kidney deficiency (vitality depletion) and phlegm-damp stagnation (metabolic and fluid buildup), which align with molecular disruptions in insulin signaling and hyperandrogenism (83). TCM offers targeted interventions to address these overlapping pathologies. Cangfu Daotan Decoction, Atractylodes (Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.) and Poria [Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf], resolves phlegm-dampness, reduces uric acid levels, and improves ovulatory function by mitigating metabolic dysfunction (84). Heqi Powder [containing Bupleurum chinense DC., Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, and others] regulates liver “qi” (smoothing emotional and energy flow) and clears dampness, addressing HUA and enhancing fertility in PCOS patients by balancing hormonal and metabolic pathways (85).
6.6 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
In TCM, NAFLD is attributed to phlegm-stasis (metabolic obstruction), reflecting metabolic and inflammatory disruptions (86). TCM employs herbs like Salvia miltiorrhiza (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge), Poria [Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf], and Hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge) to resolve phlegm-stasis, reduce hepatic lipid accumulation, and mitigate inflammation (87). Formulas such as Yinchenhao Decoction (containing Artemisia scoparia Waldst. & Kitam., Gardenia jasminoides J.Ellis, and Rheum officinale Baill.) lower uric acid levels and liver enzymes, improving NAFLD outcomes by targeting both metabolic and inflammatory pathways (88). These TCM interventions offer a holistic approach, complementing molecular insights into HUA-driven NAFLD pathogenesis by addressing uric acid accumulation and hepatic lipid metabolism (89).
7 Innovative approaches in TCM for HUA
7.1 Network pharmacology and metabolomics
Network pharmacology has transformed TCM research by elucidating herb-compound-target interactions, offering a systems-level understanding of therapeutic mechanisms for HUA (90). For instance, studies of Polygonum cuspidatum (Reynoutria japonica Houtt.) and Bixie Chubi Decoction (Dioscorea opposita Thunb., Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz., Plantago asiatica L.) demonstrate multi-target effects on xanthine oxidase (XOD), urate transporter 1 (URAT1), and inflammatory pathways such as TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB, revealing how TCM formulas modulate uric acid metabolism and inflammation—bridging traditional “multi-herb synergy” with biomedical network analysis (91). For a concrete example, in the TCM formula Ermiao Pill, the active compound berberine (derived from Phellodendron chinense) demonstrates strong molecular docking affinity to xanthine oxidase (XOD), with binding energies around −10 kJ/mol, effectively inhibiting uric acid production as validated in vitro and in hyperuricemia models (92). Another instance involves Simiao Powder, where compounds like quercetin target key inflammatory proteins such as IL-1β and TNF, modulating the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway to reduce gout-related inflammation (93). Metabolomics complements this approach by identifying key biomarkers, such as purine, tryptophan, and tyrosine metabolites, which guide the optimization of formulas like Ermiao Pill for enhanced efficacy and specificity (94). Specific biomarkers include L-tyrosine and L-phenylalanine, which are downregulated in HUA patients, indicating disruptions in amino acid metabolism that affect thyroid hormone synthesis and contribute to metabolic disorders like insulin resistance. Additionally, arachidonic acid serves as a biomarker, showing reduced levels linked to heightened inflammation and cardiovascular risks in HUA (95). Looking forward, these approaches hold immense potential to advance TCM for HUA management. They can predict herb-drug interactions to improve safety profiles, mitigating risks of adverse effects when combining TCM with conventional therapies (90). Additionally, network pharmacology can uncover synergistic effects in compound formulas, enabling the design of more effective herb combinations tailored to specific HUA syndromes. Metabolomics-driven insights will further optimize dosages and herb selections by correlating biomarker profiles with TCM syndromes, facilitating personalized treatment strategies. Recent literature on TCM-modern integration highlights network pharmacology's role in drug innovation, predicting synergies for HUA by mapping herb targets to UA pathways, including novel atavistic approaches like mRNA-mediated uricase expression in hepatocytes (52, 96). Future research should integrate these tools with artificial intelligence and clinical trials to validate multi-target mechanisms, refine TCM formulations, and establish standardized protocols for global adoption (97). This convergence of TCM wisdom and cutting-edge omics technologies promises to enhance therapeutic precision, improve patient outcomes, and bridge traditional and modern medicine in addressing HUA and its comorbidities.
Despite promising results, challenges include database inaccuracies and incomplete data on TCM compounds, leading to biased predictions. Limited technological advancements hinder novel target identification, and the complexity of TCM formulas complicates validation in clinical settings (98). Metabolomics faces issues with biomarker specificity in HUA, as metabolic profiles vary by patient factors like diet, potentially causing inconsistent outcomes (99). Future efforts should focus on standardized databases and multi-omics integration to overcome these barriers.
7.2 Personalized TCM diagnostics—enhancing TCM's dialectical approach with genetic and metabolic profiling for hyperuricemia
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) employs a dialectical approach (“bian zheng lun zhi”), customizing treatments to an individual's unique syndrome patterns, such as damp-heat (inflammation with retention) or spleen-kidney deficiency (digestive and filtrative weakness), rather than targeting the disease alone. This holistic, patient-centered method draws on a practitioner's expertise and clinical observation, offering flexibility but sometimes lacking objective precision.
Integrating genetic and metabolic profiling into TCM provides a scientific basis to enhance its personalized approach. For hyperuricemia (HUA), these advanced techniques identify specific genetic variants and metabolic alterations driving the condition. By complementing TCM's syndrome-based framework, this data enables precise, evidence-based interventions, strengthening the efficacy of tailored treatments.
A prime example involves polymorphisms in the URAT1 gene (SLC22A12), a uric acid transporter in the kidneys. Patients with certain URAT1 variants, such as rs475688, exhibit impaired uric acid excretion, exacerbating HUA (16). TCM herbs like Yam rhizome (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) and Plantago (Plantago asiatica L.) are traditionally used for their diuretic and uric acid-lowering effects, aligning with “promoting water metabolism” in TCM (100). Genetic profiling can confirm that these herbs are particularly beneficial for patients with URAT1 polymorphisms by targeting the underlying molecular mechanism, thus refining herb selection and improving outcomes.
Machine learning models, trained on datasets combining TCM syndrome patterns with omics data (genomics, metabolomics), hold transformative potential for HUA treatment:
° Predicting Optimal Herb Combinations: By analyzing a patient's genetic and metabolic profile, machine learning can recommend herb combinations tailored to their specific needs, minimizing trial-and-error and enhancing efficacy.
° Correlating TCM Syndromes with Genetic Markers: These models can identify links between TCM syndromes (e.g., kidney deficiency) and genetic variants (e.g., SLC2A9 or SLC22A12), improving diagnostic precision and aligning traditional classifications with molecular evidence.
° Developing Personalized Treatment Plans: Machine learning can integrate HUA severity, comorbidities (e.g., diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease), and patient-specific data to design treatment plans that optimize dosages, herb selections, and therapeutic strategies.
This fusion of TCM's dialectical approach with cutting-edge science bridges ancient wisdom and modern precision medicine. It offers a data-driven path to more effective, individualized HUA treatments, reducing side effects and improving patient outcomes. The approach also sets a precedent for applying similar integrations to other chronic conditions addressed by TCM. Future advancements in genomics and artificial intelligence could further refine this model, fostering collaborations between TCM practitioners and researchers. Large-scale studies validating these correlations and the development of accessible AI tools for clinical use will be key to realizing its full potential.
Implementation faces ethical issues in genetic testing, such as informed consent and potential discrimination based on HUA risk profiles (101). Data privacy concerns arise from handling sensitive omics data, with risks of breaches in TCM databases lacking robust regulations (102). Limited access to genetic profiling in resource-poor settings exacerbates inequities, and variability in TCM practitioner expertise hinders standardization (103). Addressing these requires ethical guidelines and secure data frameworks.
7.3 Nanotechnology for TCM delivery
TCM utilizes bioactive compounds like curcumin (from Curcuma longa L., or turmeric, used in TCM for “invigorating blood”) and berberine (from Coptis chinensis Franch., known for “clearing heat”) to manage chronic conditions such as HUA (104–107). However, their therapeutic efficacy is often hindered by poor bioavailability due to low water solubility and limited gastrointestinal absorption. Compounds like curcumin are rapidly degraded, while berberine undergoes extensive metabolism, posing challenges for consistent delivery in HUA treatment, where sustained uric acid reduction and inflammation control are critical (108).
Nanotechnology offers innovative solutions through nanoparticle-based delivery systems, such as liposomes, micelles, and polymeric nanoparticles. These systems encapsulate hydrophobic TCM compounds, protecting them from degradation, enhancing solubility, and improving absorption across biological barriers. By increasing blood concentrations and prolonging therapeutic effects, nanotechnology ensures more effective management of HUA, addressing both uric acid metabolism and inflammation.
For HUA, nanotechnology enables precise targeting of affected tissues, such as the kidneys, where uric acid is excreted, and inflamed joints, where gout-related damage occurs (109). Surface-modified nanoparticles can concentrate in renal tissue, while the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect allows accumulation in joints, reducing local inflammation (110). This targeted approach enhances efficacy and minimizes systemic exposure, improving treatment outcomes.
Nanoparticle types offer distinct advantages for TCM delivery. Liposomes, biocompatible lipid vesicles, carry both water- and fat-soluble compounds, with liposomal curcumin showing improved stability (111). Micelles excel at solubilizing hydrophobic drugs like berberine (112), while polymeric nanoparticles, such as PLGA, provide controlled release, making them versatile for tailored formulations (113). These systems allow lower doses to achieve therapeutic effects, reducing side effects like gastrointestinal irritation and improving patient compliance (114).
A notable example is nano-encapsulated curcumin, which has demonstrated a 10-fold increase in bioavailability in animal models, alongside enhanced anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects (115). These improvements suggest that smaller doses could effectively manage HUA-related inflammation, offering a model for other TCM compounds. However, challenges remain in optimizing formulations for human use and confirming safety and efficacy through clinical trials.
Key challenges include scalability and translation from bench to clinic, with high production costs and regulatory hurdles for TCM-nano hybrids (116). Potential toxicities from nanomaterials (e.g., accumulation in organs) require long-term safety studies, especially for chronic HUA treatment. Variability in TCM extract quality complicates nano-formulation standardization. Future directions involve clinical trials to validate efficacy and safety.
Looking ahead, nanotechnology holds transformative potential to elevate TCM into a precise and potent therapeutic option for HUA and other chronic conditions. Continued research and clinical validation will be key to overcoming current limitations, bridging traditional TCM wisdom with modern delivery innovations to enhance patient outcomes.
7.4 AI-driven TCM optimization for HUA
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing TCM by analyzing vast datasets of syndromes, herb compositions, and clinical outcomes to optimize treatment for HUA. By merging centuries-old TCM wisdom, such as syndrome patterns like “damp-heat,” with modern computational techniques, AI enhances therapeutic precision and efficacy in managing HUA.
AI algorithms, including natural language processing and machine learning, excel at identifying novel herb combinations for HUA. By sifting through extensive TCM literature, historical clinical data, and patient records, these algorithms uncover synergistic herbal interactions that traditional formulas may overlook. For instance, network pharmacology predicts how herbs interact with molecular targets and pathways involved in uric acid metabolism, enabling the design of innovative combinations with improved efficacy and fewer side effects (90, 91, 94, 97, 100).
Personalized medicine is advanced through AI's ability to predict treatment responses based on individual patient profiles. Supervised learning models, trained on datasets encompassing genetic profiles, lifestyle factors, and medical histories, identify patterns and biomarkers linked to successful HUA outcomes. This predictive power allows practitioners to customize herbal prescriptions and treatment plans, enhancing therapeutic effectiveness and patient satisfaction.
The integration of omics data—genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics—with TCM diagnostics represents a groundbreaking leap. AI processes these complex datasets to map traditional TCM syndromes, such as dampness-heat or “qi” deficiency, to specific molecular profiles associated with HUA. This fusion validates TCM's holistic approach with scientific evidence, improves diagnostic precision, and enables biologically informed, personalized treatments, bridging traditional practices with modern biomedical science.
Ethical issues in AI-based personalized medicine include bias in algorithms trained on limited datasets, potentially overlooking diverse populations in HUA treatment (117). Data privacy concerns are prominent, as AI relies on patient genetic and metabolic data, risking breaches without stringent protections like GDPR equivalents for TCM (102). Trust challenges arise from AI's “black box” nature, complicating TCM diagnosis validation, and data scarcity in TCM hinders model accuracy (118). Solutions involve transparent AI models and ethical frameworks.
By transforming TCM into a more precise, evidence-based practice, these AI-driven applications offer new strategies for effectively managing HUA. The synergy of ancient knowledge and cutting-edge technology paves the way for redefined therapeutic approaches, promising improved outcomes for patients with HUA and its comorbidities.
8 Limitations and challenges in TCM application
While Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) shows promise in managing hyperuricemia (HUA), its limitations—such as variability in herb quality, inconsistent clinical evidence, and potential herb-drug interactions—must be addressed for safe and effective integration. Herb quality varies due to factors like geographical origin, harvest timing, processing, and contamination risks (e.g., heavy metals or pesticides), resulting in inconsistent bioactive levels, for example, batch-to-batch fluctuations in resveratrol content in Polygonum cuspidatum can diminish xanthine oxidase (XOD) inhibition and clinical reliability, highlighting the need for enhanced standardization through quality control databases and authentication protocols (12). Clinical trials often suffer from methodological flaws, including small samples, lack of randomization, and poor reporting, as seen in reviews of TCM for gout, where efficacy appeared superior but evidence was weak due to bias; TCM's individualized approach further clashes with standardized RCTs, necessitating pragmatic designs and CONSORT extensions. Herb-drug interactions, such as berberine from Coptis chinensis inhibiting cytochrome P450 enzymes or Polygonum cuspidatum amplifying anticoagulants, raise safety concerns with urate-lowering drugs like allopurinol, demanding pharmacovigilance and monitoring (119). Ultimately, overcoming these hurdles through rigorous research, quality assurance, and interaction studies will bolster TCM's holistic benefits in HUA management.
9 Conclusions and future directions
TCM offers a holistic and effective approach to managing HUA and its comorbidities, with single herbs and compound formulas targeting uric acid metabolism, inflammation, and organ protection. Herbs like Plantaginis Semen (Plantago asiatica L.), Polygonum cuspidatum (Reynoutria japonica Houtt.), and compound formulas like Bixie Chubi Decoction (Dioscorea opposita Thunb., Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz., Plantago asiatica L.) demonstrate significant efficacy, often surpassing Western drugs in safety profiles. Innovations such as network pharmacology, metabolomics, personalized diagnostics, nanotechnology, and AI-driven optimization promise to enhance TCM's therapeutic precision and efficacy, bridging concepts like “qi” and “blood stasis” with biomedical pathways.
Future research should focus on:
• Safety and Toxicity Studies: Investigate potential risks, including herb-induced toxicities and contradictions in efficacy through post-marketing surveillance.
• Balanced Integration: Address challenges like standardization and evidence quality to support safety claims.
• Clinical Trials: Conducting large-scale, randomized controlled trials to validate TCM efficacy and safety across diverse populations.
• Omics Integration: Combining genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics to identify HUA-specific biomarkers and optimize TCM formulations.
• Personalized Medicine: Developing AI-driven tools to tailor TCM treatments based on individual genetic, metabolic, and syndrome profiles.
• Nanotechnology: Exploring nano-delivery systems to improve TCM compound bioavailability and target specificity.
• Global Collaboration: Integrating TCM with Western medicine through international research consortia to standardize protocols and expand clinical applications.
By merging TCM's holistic principles with cutting-edge technologies, we can advance the prevention and treatment of HUA and its associated diseases, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Author contributions
ZH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. BL: Validation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Braga F, Pasqualetti S, Ferraro S, Panteghini M. Hyperuricemia as risk factor for coronary heart disease incidence and mortality in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med. (2016) 54:7–15. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2015-0523
2. Cabău G, Crişan TO, Klück V, Popp RA, Joosten LAB. Urate-induced immune programming: consequences for gouty arthritis and hyperuricemia. Immunol Rev. (2020) 294:92–105. doi: 10.1111/imr.12833
3. Strilchuk L, Fogacci F, Cicero AF. Safety and tolerability of available urate-lowering drugs: a critical review. Expert Opin Drug Saf. (2019) 18:261–71. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2019.1594771
4. Khanna D, Khanna PP, Fitzgerald JD, Singh MK, Bae S, Neogi T, et al. (2012) American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout. Part 2: therapy and antiinflammatory prophylaxis of acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. (2012) 64:1447–61. doi: 10.1002/acr.21773
5. Pacher P, Nivorozhkin A, Szabó C. Therapeutic effects of xanthine oxidase inhibitors: renaissance half a century after the discovery of allopurinol. Pharmacol Rev. (2006) 58:87–114. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.1.6
6. Becker MA, Schumacher HR Jr, Wortmann RL, MacDonald PA, Eustace D, Palo WA, et al. Febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. N Engl J Med. (2005) 353:2450–61. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050373
7. Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Comorbidities of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: NHANES 2007-2008. Am J Med. (2012) 125:679–87.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2011.09.033
8. Harrold LR, Andrade SE, Briesacher BA, Raebel MA, Fouayzi H, Yood RA, et al. Adherence with urate-lowering therapies for the treatment of gout. Arthritis Res Ther. (2009) 11:R46. doi: 10.1186/ar2659
9. Du L, Zong Y, Li H, Wang Q, Xie L, Yang B, et al. Hyperuricemia and its related diseases: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:212. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01916-y
10. Li XX, Han M, Wang YY, Liu JP. Chinese herbal medicine for gout: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Clin Rheumatol. (2013) 32:943–59. doi: 10.1007/s10067-013-2274-7
11. Lin J, Chen S, Li S, Lu M, Li Y, Su Y. Efficacy and safety of chinese medicinal herbs for the treatment of hyperuricemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2016) (2016):2146204. doi: 10.1155/2016/2146204
12. Ferrari R. Writing narrative style literature reviews. Med Writ. (2015) 24:230–5. doi: 10.1179/2047480615Z.000000000329
14. Yamamoto T, Moriwaki Y, Takahashi S. Effect of ethanol on metabolism of purine bases (hypoxanthine, xanthine, and uric acid). Clin Chim Acta. (2005) 356:35–57. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2005.01.024
15. Johnson RJ, Nakagawa T, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Shafiu M, Sundaram S, Le M, et al. Sugar, uric acid, and the etiology of diabetes and obesity. Diabetes. (2013) 62:3307–15. doi: 10.2337/db12-1814
16. Enomoto A, Kimura H, Chairoungdua A, Shigeta Y, Jutabha P, Cha SH, et al. Molecular identification of a renal urate anion exchanger that regulates blood urate levels. Nature. (2002) 417:447–52. doi: 10.1038/nature742
17. Vitart V, Rudan I, Hayward C, Gray NK, Floyd J, Palmer CN, et al. SLC2A9 is a newly identified urate transporter influencing serum urate concentration, urate excretion and gout. Nat Genet. (2008) 40:437–42. doi: 10.1038/ng.106
18. Vávra J, Mančíková A, Pavelcová K, Hasíková L, Bohatá J, Stiburková B. Functional characterization of rare variants in OAT1/SLC22A6 and OAT3/SLC22A8 urate transporters identified in a gout and hyperuricemia cohort. Cells. (2022) 11:1063. doi: 10.3390/cells11071063
19. Nian YL, You CG. Susceptibility genes of hyperuricemia and gout. Hereditas. (2022) 159:30. doi: 10.1186/s41065-022-00243-y
20. Matsuo H, Takada T, Ichida K, Nakamura T, Nakayama A, Ikebuchi Y, et al. Common defects of ABCG2, a high-capacity urate exporter, cause gout: a function-based genetic analysis in a Japanese population. Sci Transl Med. (2009) 1:5ra11. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000237
21. Johnson RJ, Bakris GL, Borghi C, Chonchol MB, Feldman D, Lanaspa MA, et al. Hyperuricemia, acute and chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: report of a scientific workshop organized by the National Kidney Foundation. Am J Kidney Dis. (2018) 71:851–65. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.12.009
22. Reyes AJ. The increase in serum uric acid concentration caused by diuretics might be beneficial in heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. (2005) 7:461–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2004.03.020
23. Lipkowitz MS. Regulation of uric acid excretion by the kidney. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2012) 14:179–88. doi: 10.1007/s11926-012-0240-z
24. Maesaka JK, Fishbane S. Regulation of renal urate excretion: a critical review. Am J Kidney Dis. (1998) 32:917–33. doi: 10.1016/S0272-6386(98)70067-8
25. Bentley R, Neuberger A. The mechanism of the action of uricase. Biochem J. (1952) 52:694–9. doi: 10.1042/bj0520694
26. Oda M, Satta Y, Takenaka O, Takahata N. Loss of urate oxidase activity in hominoids and its evolutionary implications. Mol Biol Evol. (2002) 19:640–53. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004123
27. Martinon F, Pétrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature. (2006) 440:237–41. doi: 10.1038/nature04516
28. Busso N, So A. Mechanisms of inflammation in gout. Arthritis Res Ther. (2010) 12:206. doi: 10.1186/ar2952
29. Choi HK, Atkinson K, Karlson EW, Willett W, Curhan G. Purine-rich foods, dairy and protein intake, and the risk of gout in men. N Engl J Med. (2004) 350:1093–103. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa035700
30. Roddy E, Choi HK. Epidemiology of gout. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. (2014) 40:155–75. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2014.01.001
31. Feig DI, Kang DH, Johnson RJ. Uric acid and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med. (2008) 359:1811–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0800885
32. Mazzali M, Hughes J, Kim YG, Jefferson JA, Kang DH, Gordon KL, et al. Elevated uric acid increases blood pressure in the rat by a novel crystal-independent mechanism. Hypertension. (2001) 38:1101–6. doi: 10.1161/hy1101.092839
33. Deng Y, Liu F, Yang X, Xia Y. The key role of uric acid in oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis, apoptosis, and immunity in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:641136. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.641136
35. Kang DH, Nakagawa T, Feng L, Watanabe S, Han L, Mazzali M, et al. A role for uric acid in the progression of renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2002) 13:2888–97. doi: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000034910.58454.FD
36. Nakagawa T, Hu H, Zharikov S, Tuttle KR, Short RA, Glushakova O, et al. A causal role for uric acid in fructose-induced metabolic syndrome. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2006) 290:F625–31. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00140.2005
37. Tassone EJ, Cimellaro A, Perticone M, Hribal ML, Sciacqua A, Andreozzi F, et al. Uric acid impairs insulin signaling by promoting Enpp1 binding to insulin receptor in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Front Endocrinol. (2018) 9:98. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00098
38. Dehghan A, Köttgen A, Yang Q, Hwang SJ, Kao WL, Rivadeneira F, et al. Association of three genetic loci with uric acid concentration and risk of gout: a genome-wide association study. Lancet. (2008) 372:1953–61. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61343-4
39. Bhole V, Choi JW, Kim SW, de Vera M, Choi H. Serum uric acid levels and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a prospective study. Am J Med. (2010) 123:957–61. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2010.03.027
40. Kodama S, Saito K, Yachi Y, Asumi M, Sugawara A, Totsuka K, et al. Association between serum uric acid and development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2009) 32:1737–42. doi: 10.2337/dc09-0288
41. González F, Nair KS, Daniels JK, Basal E, Schimke JM. Hyperandrogenism sensitizes mononuclear cells to promote glucose-induced inflammation in lean reproductive-age women. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 302:E297–306. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00416.2011
42. Mohammadi M. Oxidative stress and polycystic ovary syndrome: a brief review. Int J Prev Med. (2019) 10:86. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_576_17
43. Lanaspa MA, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Choi YJ, Cicerchi C, Kanbay M, Roncal-Jimenez CA, et al. Uric acid induces hepatic steatosis by generation of mitochondrial oxidative stress: potential role in fructose-dependent and -independent fatty liver. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:40732–44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.399899
44. Choi YJ, Shin HS, Choi HS, Park JW, Jo I, Oh ES, et al. Uric acid induces fat accumulation via generation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and SREBP-1c activation in hepatocytes. Lab Invest. (2014) 94:1114–25. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2014.98
45. Yang C, Yang S, Xu W, Zhang J, Fu W, Feng C. Association between the hyperuricemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease risk in a Chinese population: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e0177249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177249
46. Wang, Y.B. and C.Z. Jin, Roles of traditional Chinese medicine extracts in hyperuricemia and gout treatment: mechanisms and clinical applications. World J Gastroenterol. (2024) 30:5076–80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i47.5076
47. Jiang Z, Chen J, You Y, Ji S, Chen L, He Q, et al. The correlation between traditional chinese medicine constitution and hyperuricemia and gout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2023) 2023:5097490. doi: 10.1155/2023/5097490
48. Liang H, Deng P, Ma YF, Wu Y, Ma ZH, Zhang W, et al. Advances in experimental and clinical research of the gouty arthritis treatment with traditional Chinese medicine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:8698232. doi: 10.1155/2021/8698232
49. Yang L, Wang B, Ma L, Fu P. Traditional Chinese herbs and natural products in hyperuricemia-induced chronic kidney disease. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:971032. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.971032
50. Wang X, Wang YG. Progress in treatment of gout using chinese and western medicine. Chin J Integr Med. (2020) 26:8–13. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3058-y
51. Xiao YZ, Ye ZZ, Liang YT, Chen XP, Wang YH, Xu Q, et al. association between chinese herbal medicine therapy and the risk of chronic kidney disease in gout patients. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:661282. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.661282
52. Li K, Xia X, Fu T, Ma Y, Wang Y, Fan M, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of hyperuricemic nephropathy based on multi-omics technique: a review. Medicine. (2024) 103:e40975. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040975
53. Wang T, Li L, Liu L, Tan R, Wu Q, Zhu X, et al. Overview of pharmacodynamical research of traditional Chinese medicine on hyperuricemic nephropathy: from the perspective of dual-regulatory effect on the intestines and kidneys. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1517047. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1517047
54. Chi X, Zhang H, Zhang S, Ma K. Chinese herbal medicine for gout: a review of the clinical evidence and pharmacological mechanisms. Chin Med. (2020) 15:17. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-0297-
55. LiverTox. Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. NationalBethesda, MD: Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (2012).
56. Wei Y, Liu M, Liu J, Li H. Influence factors on the hepatotoxicity of polygoni multiflori radix. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2019) 2019:5482896. doi: 10.1155/2019/5482896
57. Li Y, Lin Z, Jin H, Wei F, Ma S, Zhang B, et al. The uric acid lowering potential of bioactive natural products and extracts derived from traditional Chinese medicines: a review and perspective. J Pharm Anal. (2025) 15:101183. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101183
58. Bai H, Zhang Z, Zhu M, Sun Y, Wang Y, Li B, et al. Research progress of treating hyperuricemia in rats and mice with traditional Chinese medicine. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1428558. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1428558
59. Yang B, Xie Y, Guo M, Rosner MH, Yang H, Ronco C. Nephrotoxicity and Chinese Herbal Medicine. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2018) 13:1605–11. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11571017
60. Ernst E. Adverse effects of herbal drugs in dermatology. Br J Dermatol. (2000) 143:923–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03822.x
61. Busia K. Herbal medicine dosage standardisation. J Herbal Med. (2024) 46:100889. doi: 10.1016/j.hermed.2024.100889
62. Parveen A, Parveen B, Parveen R, Ahmad S. Challenges and guidelines for clinical trial of herbal drugs. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. (2015) 7:329–33. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.168035
63. Yang J, Li G, Xiong D, Chon TY, Bauer BA. The impact of natural product dietary supplements on patients with gout: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med. (2020) 2020:7976130. doi: 10.1155/2020/7976130
64. Ma X, Peng JH, Hu YY. Chinese herbal medicine-induced liver injury. J Clin Transl Hepatol. (2014) 2:170–5. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2014.00009
65. Castrejon I, Toledano E, Rosario MP, Loza E, Pérez-Ruiz F, Carmona L. Safety of allopurinol compared with other urate-lowering drugs in patients with gout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. (2015) 35:1127–37. doi: 10.1007/s00296-014-3189-6
66. Kanellis J, Kang DH. Uric acid as a mediator of endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and vascular disease. Semin Nephrol. (2005) 25:39–42. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2004.09.007
67. Gao D, Wu LY, Jiao YH, Chen WY, Chen Y, Kaptchuk TJ, et al. The effect of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction on in vitro endothelial progenitor cell tube formation. Chin J Integr Med. (2010) 16:50–3. doi: 10.1007/s11655-010-0050-y
68. Hao P, Jiang F, Cheng J, Ma L, Zhang Y, Zhao Y. Traditional Chinese medicine for cardiovascular disease: evidence and potential mechanisms. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 69:2952–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.041
69. Han X, Zhang G, Chen G, Wu Y, Xu T, Xu H, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction promotes angiogenesis in myocardial infarction through suppression of PTEN and activation of the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2022) 287:114929. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114929
70. Kan Z, Yan W, Chen C, Gao H, Song Y. Efficacy and safety of Danhong injection on inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial function in patients with unstable angina pectoris: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1389746. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1389746
71. Zhang S, Chen ZL, Tang YP, Duan JL, Yao KW. Efficacy and safety of Xue-Fu-Zhu-Yu Decoction for patients with coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:9931826. doi: 10.1155/2021/9931826
72. Yu J, Li L, Liu J, Chen Z. Influence of intervention treatment by “heat-clearing and diuresis-promoting” prescription on NALP3, an inflammatory factor in acute gouty arthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2022) 17:162. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03046-z
73. Yang Y, Sha W, Hou K, Xu Y, Tan S, Yin H, et al. Efficacy and safety of wuling powder in the treatment of patients with diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:1720749. doi: 10.1155/2022/1720749
74. Wang Y, Feng Y, Li M, Yang M, Shi G, Xuan Z, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of chronic kidney diseases: theories, applications, and mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:917975. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.917975
75. Wang KJ, Zhao JL. Corn silk (Zea mays L.), a source of natural antioxidants with α-amylase, α-glucosidase, advanced glycation and diabetic nephropathy inhibitory activities. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 110:510–7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.126
76. Chen L, Yin H, Lan Z, Ma S, Zhang C, Yang Z, et al. Anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of Smilax china L. J Ethnopharmacol. (2011) 135:399–405. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.03.033
77. Zhou Z, Xu M, Bian M, Nie A, Sun B, Zhu C. Anti-hyperuricemia effect of Clerodendranthus spicatus: a molecular biology study combined with metabolomics. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:15449. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66454-7
78. Li S, Xiao X, Han L, Wang Y, Luo G. Renoprotective effect of Zhenwu decoction against renal fibrosis by regulation of oxidative damage and energy metabolism disorder. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:14627. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32115-9
79. Liu H, Peng S, Yuan H, He Y, Tang J, Zhang X. Chinese herbal medicine combined with western medicine for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperuricemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1102513. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1102513
80. Huyen VT, Phan DV, Thang P, Hoa NK, Ostenson CG. Gynostemma pentaphyllum tea improves insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients. J Nutr Metab. (2013) 2013:765383. doi: 10.1155/2013/765383
81. Shen Z, Cui T, Liu Y, Wu S, Han C, Li J. Astragalus membranaceus and Salvia miltiorrhiza ameliorate diabetic kidney disease via the “gut-kidney axis”. Phytomedicine. (2023) 121:155129. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155129
82. Lin L, Wang Q, Yi Y, Wang S, Qiu Z. Liuwei Dihuang pills enhance the effect of western medicine in treating diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2016) 2016:1509063. doi: 10.1155/2016/1509063
83. Chen H, Deng C, Meng Z, Meng S. Effects of TCM on polycystic ovary syndrome and its cellular endocrine mechanism. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:956772. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.956772
84. Wu L, Zhang H, Fan M, Yan Y. Efficacy and safety of Cangfu Daotan Decoction in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:4395612. doi: 10.1155/2022/4395612
85. Jung W, Choi H, Kim J, Kim J, Kim W, Nurkolis F, et al. Effects of natural products on polycystic ovary syndrome: from traditional medicine to modern drug discovery. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e20889. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20889
86. Shen T, Wang S, Wang Z, Jia H, Wei Y, Li Y, et al. Association between the traditional Chinese medicine constitution and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in older people: a cross-sectional study. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e24905. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24905
87. Dai X, Feng J, Chen Y, Huang S, Shi X, Liu X, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. Chin Med. (2021) 16:68. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00469-4
88. Lu Y, Xie Y, Yang X, Nie L, Cheng Z, He Y, et al. The use of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a review. Pharmacol Res Modern Chin Med. (2024) 12:100475. doi: 10.1016/j.prmcm.2024.100475
89. Ding X, He X, Tang B, Lan T. Integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine in the prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: future directions and strategies. Chin Med. (2024) 19:21. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00894-1
90. Zhai Y, Liu L, Zhang F, Chen X, Wang H, Zhou J, et al. Network pharmacology: a crucial approach in traditional Chinese medicine research. Chin Med. (2025) 20:8. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-01056-z
91. Guo F, Xing Z, Sun Q. Investigation of the potential key genes and the multitarget mechanisms of Polygonum cuspidatum against Heart failure based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. Dis Markers. (2022) 2022:7784021. doi: 10.1155/2022/7784021
92. Zhang Y, Zhu S, Gu Y, Feng Y, Gao B. Network pharmacology combined with experimental validation to investigate the mechanism of the anti-hyperuricemia action of Portulaca oleracea extract. Nutrients. (2024) 16:3549. doi: 10.3390/nu16203549
93. Qian Y, Yin J, Ni J, Chen X, Shen Y. [Retracted] A network pharmacology method combined with molecular docking verification to explore the therapeutic mechanisms underlying simiao pill herbal medicine against hyperuricemia. Biomed Res Int. (2023) 2023:2507683. doi: 10.1155/2023/2507683
94. Grams ME, Shafi T, Rhee EP. Metabolomics research in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2018) 29:1588–90. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2018030256
95. Qin N, Qin M, Shi W, Kong L, Wang L, Xu G, et al. Investigation of pathogenesis of hyperuricemia based on untargeted and targeted metabolomics. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:13980. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18361-y
96. Zhang M, Hussain A, Hu B, Yang H, Li C, Guo S, et al. Atavistic strategy for the treatment of hyperuricemia via ionizable liposomal mRNA. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:6463. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50752-9
97. Wang Y, Yu Z, Zhang Z, Mu R, Song J, Yang Z, et al. Integrating metabolomics with network pharmacology to reveal the mechanism of Poria cocos in hyperuricemia treatment. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 337(Pt 3):118977. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118977
98. Ren Y. Research progress and challenges of network pharmacology in field of traditional Chinese medicine. Zhongcaoyao. (2020) 2020:4789–97.
99. Gu C, Hu X, Shan B, Wu X, Chen J. Targeted and non-targeted metabolomics uncovering the effects of Er-Miao-Wan formula on rats with hyperuricemia. J Pharm Biomed Anal. (2023) 226:115246. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115246
100. Tang R, Peng X, Wang Y, Zhou X, Liu H. Network pharmacology-based investigation of the mechanism of action of plantaginis herba in hyperuricemia treatment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:5595384. doi: 10.1155/2021/5595384
101. Dalbeth N, Stamp LK, Merriman TR. The genetics of gout: towards personalised medicine? BMC Med. (2017) 15:108. doi: 10.1186/s12916-017-0878-5
102. Lu L, Lu T, Tian C, Zhang X. AI: bridging ancient wisdom and modern innovation in traditional Chinese medicine. JMIR Med Inform. (2024) 12:e58491. doi: 10.2196/58491
103. Zhang W-Z. Hyperuricemia: current state and prospects. [Preprint]. (2024). doi: 10.20944/preprints202406.1458.v1
104. Chen Q, Li D, Wu F, He X, Zhou Y, Sun C, et al. Berberine regulates the metabolism of uric acid and modulates intestinal flora in hyperuricemia rats model. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. (2023) 26:2057–66. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666221124093228
105. Xu L, Lin G, Yu Q, Li Q, Mai L, Cheng J, et al. Anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of dihydroberberine in potassium oxonate- and hypoxanthine-induced hyperuricemic mice. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:645879. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.645879
106. Chen Y, Li C, Duan S, Yuan X, Liang J, Hou S. Curcumin attenuates potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and kidney inflammation in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 118:109195. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109195
107. Ao GZ, Zhou MZ, Li YY, Li SN, Wang HN, Wan QW, et al. Discovery of novel curcumin derivatives targeting xanthine oxidase and urate transporter 1 as anti-hyperuricemic agents. Bioorg Med Chem. (2017) 25:166–74. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.10.022
108. Yang KY, Lin LC, Tseng TY, Wang SC, Tsai TH. Oral bioavailability of curcumin in rat and the herbal analysis from Curcuma longa by LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. (2007) 853:183–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.03.010
109. Qi CW, Nordin UUM, Karusan NR, Nordin N, Mahmood S, Khalid R, et al. Gout management using nanocarrier systems: a review. ACS Applied Nano Materials. (2024) 7:9816–46. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c06079
110. Wang R, Liu T, Li X, Lu E, Chen Y, Luo K, et al. Biomimetic integrated nanozyme for flare and recurrence of gouty arthritis. Asian J Pharm Sci. (2024) 19:100913. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2024.100913
111. Feng T, Wei Y, Lee RJ, Zhao L. Liposomal curcumin and its application in cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. (2017) 12:6027–44. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S132434
112. Wang T, Wang N, Song H, Xi X, Wang J, Hao A, et al. Preparation of an anhydrous reverse micelle delivery system to enhance oral bioavailability and anti-diabetic efficacy of berberine. Eur J Pharm Sci. (2011) 44:127–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2011.06.015
113. Makadia HK, Siegel SJ. Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers. (2011) 3:1377–97. doi: 10.3390/polym3031377
114. Feng S, Zhao L, Zhang Z, Bhakta G, Win KY, Dong Y, et al. Chemotherapeutic engineering: vitamin E TPGS-emulsified nanoparticles of biodegradable polymers realized sustainable paclitaxel chemotherapy for 168 h in vivo. Chem Eng Sci. (2007) 62:6641–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2007.08.006
115. Yavarpour-Bali H, Ghasemi-Kasman M, Pirzadeh M. Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles: a novel therapeutic strategy in treatment of central nervous system disorders. Int J Nanomed. (2019) 14:4449–60. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S208332
116. đordević S, Gonzalez MM, Conejos-Sánchez I, Carreira B, Pozzi S, Acúrcio RC, et al. Current hurdles to the translation of nanomedicines from bench to the clinic. Drug Deliv Transl Res. (2022) 12:500–25. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-01024-2
117. Li W, Ge X, Liu S, Xu L, Zhai X, Yu L. Opportunities and challenges of traditional Chinese medicine doctors in the era of artificial intelligence. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1336175. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1336175
118. Gangwal A, Ansari A, Ahmad I, Azad AK, Wan Sulaiman WMA. Current strategies to address data scarcity in artificial intelligence-based drug discovery: a comprehensive review. Comput Biol Med. (2024) 179:108734. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108734
119. Bathaei P, Imenshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H. Effects of Berberis vulgaris, and its active constituent berberine on cytochrome P450: a review. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol. (2025) 398:179–202. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03326-x
120. Liu T, Wang L, Ji L, Mu L, Wang K, Xu G, et al. Plantaginis semen ameliorates hyperuricemia induced by potassium oxonate. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:8548. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158548
121. Zhao J, Fu Y, Qiu H. Effect and mechanism of Plantaginis Semen polysaccharides on intestinal microecology in rats with hyperuricemia. Front Microbiol. (2025) 16:1555734. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1555734
122. Guo H, Hu S, Ran H, Dong H, Wang X, Zhao H. Screening and characterization of potential anti-gout components from Polygonum cuspidatum by integration off-line two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with affinity ultrafiltration and on-line HPLC-ABTS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. (2024) 243:116103. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116103
123. Zhou H, Yang J, Yuan X, Song X, Zhang X, Cao T, et al. Hyperuricemia research progress in model construction and traditional Chinese medicine interventions. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1294755. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1294755
124. Hu Q, Ji J, Xu D, Ye Y, Sun J, Sheng L, et al. Isolation and characterization of uric acid-lowering functional components from Polygonum cuspidatum. Food Biosci. (2023) 53:102314. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.102314
125. Chen GL, Zhu LR, Na S, Li L. [Effect of total saponin of Dioscorea on chronic hyperuricemia and expression of URAT1 in rats]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2013) 38:2348–53.
126. Fan Z, Wei X, Zhu X, Yang K, Tian L, Wang X, et al. Unveiling the therapeutic potential of berberine: its therapeutic role and molecular mechanisms in kidney diseases. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1549462. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1549462
127. Kim JK, Kim WJ, Hyun JM, Lee JS, Kwon JG, Seo C, et al. Salvia plebeia extract inhibits xanthine oxidase activity in vitro and reduces serum uric acid in an animal model of hyperuricemia. Planta Med. (2017) 83:1335–41. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-111012
128. Zhang HF, Wang YL, Gao C, Gu YT, Huang J, Wang JH, et al. Salvianolic acid A attenuates kidney injury and inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2018) 39:1855–64. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0026-6
129. Huang Y, Tao M, Li R, Liang F, Xu T, Zhong Q, et al. Identification of key phenolic compounds for alleviating gouty inflammation in edible chrysanthemums based on spectrum-effect relationship analyses. Food Chem X. (2023) 20:100897. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100897
130. Cho BO, Shin JY, Kang HJ, Park JH, Hao S, Wang F, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of Chrysanthemum zawadskii, peppermint, Glycyrrhiza glabra herbal mixture in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Mol Med Rep. (2021) 24:532. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12171
131. Pang M, Fang Y, Chen S, Zhu X, Shan C, Su J, et al. Gypenosides inhibits xanthine oxidoreductase and ameliorates urate excretion in hyperuricemic rats induced by high cholesterol and high fat food (lipid emulsion). Med Sci Monit. (2017) 23:1129–40. doi: 10.12659/MSM.903217
132. Yuan L, Bao Z, Ma T, Lin S. Hypouricemia effects of corn silk flavonoids in a mouse model of potassium oxonated-induced hyperuricemia. J Food Biochem. (2021) 45:e13856. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13856
133. Liu P, Ma G, Wang Y, Wang L, Li P. Therapeutic effects of traditional Chinese medicine on gouty nephropathy: based on NF-κB signalingpathways. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 158:114199. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114199
134. Li T, Zeng H, Zeng Y, Zhang X, Ren Y, Gao Y, et al. Characterization of the bioactive compounds with efficacy against gout in Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS combined with network pharmacological analysis. Arab J Chem. (2021) 14:103185. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103185
135. Shan B, Chen T, Huang B, Liu Y, Chen J. Untargeted metabolomics reveal the therapeutic effects of Ermiao wan categorized formulas on rats with hyperuricemia. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 281:114545. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114545
136. Wang S, Fang Y, Yu X, Guo L, Zhang X, Xia D. The flavonoid-rich fraction from rhizomes of Smilax glabra Roxb. ameliorates renal oxidative stress and inflammation in uric acid nephropathy rats through promoting uric acid excretion. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 111:162–8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.050
Keywords: hyperuricemia, Traditional Chinese Medicine, gout, cardiovascular diseases, renal disorders, personalized medicine, network pharmacology, nanotechnology
Citation: Huang Z, Li B and Bi M-h (2025) Advances in Traditional Chinese Medicine for the treatment of hyperuricemia and associated diseases: pathogenesis, mechanisms, and future directions. Front. Nutr. 12:1663096. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1663096
Received: 10 July 2025; Accepted: 20 August 2025;
Published: 11 September 2025.
Edited by:
Omar Guzmán Quevedo, Higher Technological Institute of Tacambaro, MexicoCopyright © 2025 Huang, Li and Bi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ming-hui Bi, eG16eXkyMDI1MDAxQGZqdGNtLmVkdS5jbg==
 Zhuo Huang
Zhuo Huang Ming-hui Bi
Ming-hui Bi