- 1Department of Nutrition, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2Department of Medical Record Management and Statistics, Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital and The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China
- 3Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, College of Public Health, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 4The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 5Biotherapy Center and Cancer Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 6Department of Clinical Nutrition, Luoyang New Area People’s Hospital, Luoyang, China
- 7Department of Obstetrics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 8School of Public Health, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 9Zhongyuan Cell and Immunotherapy Laboratory, Henan Academy of Medical Sciences, Zhengzhou, China
Background: Vitamin D insufficiency is associated with an increased risk of preeclampsia. However, the role of T helper cell type 1 (Th1)/Th2 and Th17/regulatory T cell (Treg) balance in this association is unclear.
Methods: We conducted a case–control study to explore the mediating effects of immune balance on the relationship between the plasma vitamin D concentration and preeclampsia. This study included 373 pregnant women recruited between March 2016 and February 2019 (192 cases and 181 controls). The cytokines as well as various T cell subsets were analyzed using ELISA and flow cytometry, respectively. Spearman’s correlation was used to investigate the association between vitamin D and cytokines as well as T cell subsets and mediating analysis was performed to identify the modifying effects of immune balance on this association.
Results: The Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg ratios were negatively associated with the plasma concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 (25(OH)D2). Mediation analysis found that the Th1/Th2 as well as Th17/Treg ratios mediated the effect of 25(OH)D2 on the risk of preeclampsia, the mediating effects accounted for 59.59 and 40.45%, respectively.
Conclusion: Our results provided preliminary evidence for a potential mediating role of the Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balance in the association between plasma 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia. Keeping higher levels of vitamin D, especially 25(OH)D2 might help maintain the immune balance and decrease the risk of preeclampsia.
Introduction
Preeclampsia, defined as the presence of new-onset hypertension and proteinuria or other end-organ damage occurring after 20 weeks of gestation, is a leading complication of pregnancy. Approximately 4–5% pregnant women worldwide are affected by preeclampsia (1–3). Preeclampsia is associated with elevated risks of eclampsia, liver rupture and stroke, as well as cardiovascular disease later in life (4, 5). Preeclampsia is also associated with fetal growth restriction and preterm birth, which increases the risks of cerebral palsy and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in offspring (6–8). Delivery and removal of the placenta is the only definitive cure for preeclampsia (9). Therefore, pregnancy is a critical window through which the future health of both the mother and offspring can be elevated. Prevention of preeclampsia is a highly important clinical goal (6, 10).
Immune imbalances, particularly between the Th1 and Th2 cell subsets as well as the Th17 and Treg cell subsets, have been identified as the main mechanism underlying preeclampsia (11, 12). In our previous study, we identified an inverse association between vitamin D and the risk of preeclampsia (13), consistent with findings from other studies (14–16). Previous studies also found that immune imbalance is independently associated with risk of preeclampsia (17), while, it remains unclear whether vitamin D is related to the immune status in preeclampsia and how vitamin D affects the preeclampsia by regulating immune balance. Thus it is imperative to clarify the mediating effects of immune imbalance between vitamin D and preeclampsia in pregnant women.
To address this knowledge gap, this case–control study focused on the epidemiological links between the plasma vitamin D concentration and immune imbalance in pregnant women and examined the potential mediating role of Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg imbalance in the association between vitamin D and preeclampsia.
Methods
Participants
This case–control study was conducted between March 2016 and February 2019 at a large general hospital in central China. Pregnant women aged ≥18 years with a singleton pregnancy and a gestational age ≥28 weeks were included. Preeclampsia was diagnosed according to China’s Diagnosis and Treatment Guideline of Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy (2015) (18). Details of the inclusion and exclusion criteria are described elsewhere (19). This study included 373 participants (192 cases and 181 controls), and all participants provided written informed consent. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Scientific Research and Clinical Trials at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (Approval No. Scientific Research-2016-LW-34).
Cytokine measurement
Fasting peripheral blood (FPB) was collected from participants into the sterile tubes containing EDTA on the day of delivery, which were centrifuged (4 °C, 800 g, 10 min), the plasma was then collected into tubes and stored at −80 °C. The concentrations of cytokines in plasma samples were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). As described previously, interferon (IFN)-γ was used to define a Th1 response, while IL-4, IL-17A and IL-10 were used to define Th2, Th17, and Treg responses, respectively (20–23). The ELISAs were performed according to the instructions provided by the kit manufacturer. Briefly, the samples and standards were added to a microplate that was precoated with a specific mouse monoclonal antibody and incubated at temperature for 2 h. Then, wash and added to 100 μL diluted detection antibody solution to each well, incubated at temperature for 1 h. Next, wash and added to 100 μL diluted Avidin-HRP solution to each well, incubated at temperature for 30 min. Wash, and then 100 μL freshly mixed substrate solution were added to each well and the plate was incubated in the dark. Subsequently, 100 μL stop solution was added to each well to stop the reaction. Finally, the absorbance at 450 nm was read in each well using a spectrophotometer (Molecular Devices, SpectraMax iD3, United States). All the ELISA kits were purchased from BioLegend (San Diego, CA, United States). Cytokine concentrations were detected in samples from 373 participants in this study.
Flow cytometry
T cell subsets were analyzed by flow cytometry according to the following procedure. First, FPB (the obtained time was on the day of delivery) was collected from participants into the sterile tubes containing EDTA, and then centrifuged (4 °C, 800 g, 10 min) to remove the plasma. Next, sterile normal saline was added to precipitate and mixed, which was added carefully to a sterile centrifuge tube containing lymphocyte separation solution. The mixture was subjected to density gradient centrifugation (4 °C, 800 g, 25 min). The peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected and seeded into 24-well plates at a density of 2 × 106 PBMCs per mL RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine plasma (Lonsera, United States) and 100 IU/mL penicillin/streptomycin. To each well, 1 μL of 1 mg/mL phorbol myristate acetate (Sigma-Aldrich), 50 ng/mL ionomycin (Sigma-Aldrich) and 5 mg/mL brefeldin A solution (BioLegend) were added, and the plate was incubated for 4–6 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2 and then harvested. The cells were resuspended in phosphate-buffered saline containing 0.5% bovine serum albumin and incubated with an Fc receptor blocking regent for 15 min at 4 °C. The single-cell suspensions were then incubated with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies specific for CD3 (fluorochrome: PE-CY7), CD4 (APC-CY7), and CD25 (FITC) for 15 min at 4 °C in the dark. Next, intracellular staining using fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies specific for IL-17A (PE), IL-4 (FITC), and IFN-γ (APC) and nucleoprotein staining to detect FOXP3 (APC) were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, the cells were stained with antibodies against intracellular cytokines after surface antibody staining, fixation, and permeabilization. The Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg subsets were defined as CD3+ CD4+ IFN-γ+, CD3+ CD4+ IL-4+, CD3+ CD4+ IL-17A+ and CD3+ CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ (24–27). All of the flow cytometry antibodies were purchased from BioLegend (San Diego, CA, United States). Flow cytometry was performed using FACS Canto II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, United States). A total of 65 samples (including 34 cases and 31 controls) were detected T cell subsets in this study. The distribution of 65 flow cytometry samples between cases and controls showed in Supplementary Table 1. Flow Jo software was used to analyze the data.
Variables
The information on demographic characteristics were collected using our standardized interview questionnaires. Maternal age, gestational week, parity (multiparous or primiparous), pre-pregnancy BMI, education level (high school or below, university or above) and monthly income (≤4,000 RMB or >4,000 RMB) were included in the adjusted model.
Statistical analysis
For normally distributed data, Student’s t or Wilcoxon test were used to compare continuous parameters between the cases and controls, and chi-squared tests were conducted to compare differences in qualitative variables between cases and controls. Spearman’s correlation was used to analyze the correlations between vitamin D concentrations and immune parameters.
The R package “mediation” (Version 4.5.0) was used to conduct a mediation effect analysis of the potential modifying effect of immune balance on the relationship between the vitamin D concentration and the risk of preeclampsia (Y as outcome: preeclampsia or not, X as exposure: 25(OH)D/25(OH)D2/25(OH)D3, M as mediator: immune parameters). This analysis presented the direct effect of exposure on preeclampsia as well as the indirect effect bypassing the mediator. Other details of the mediation analysis were described previously (28). A two-tailed p-value of <0.05 was regarded as significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software, version 25.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, United States).
Results
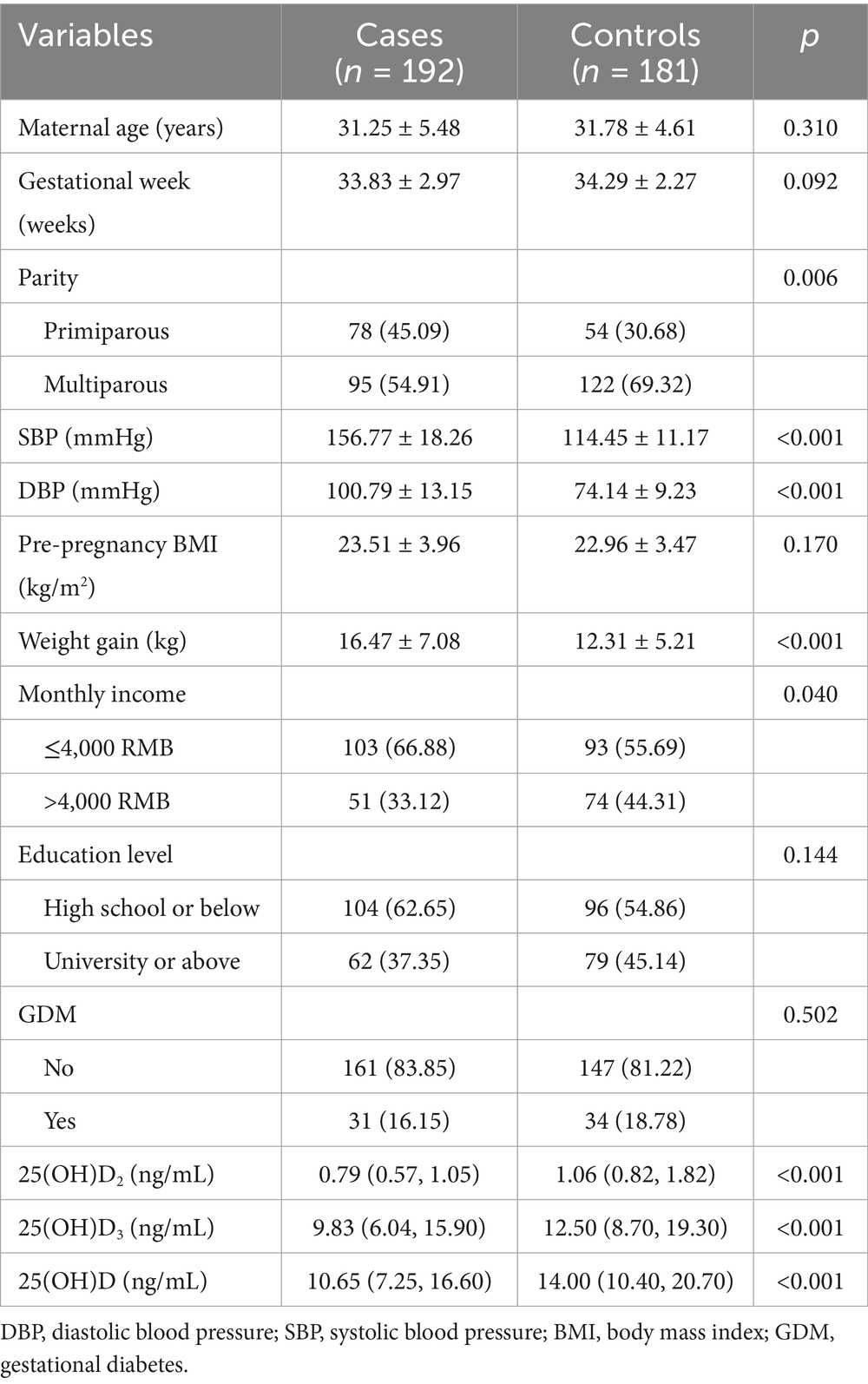
The characteristics of the participants are presented in Table 1. There were no significant differences between the cases and controls in terms of maternal age, gestational week, pre-pregnant BMI or education. However, compared with controls, women with preeclampsia had a higher SBP, DBP, greater weight gain during pregnancy, a higher income level, and significantly lower serum concentrations 25(OH)D2, 25(OH)D3 and 25(OH)D. Additionally, primiparous women were more likely to suffer from preeclampsia than multiparous women.
The associations between vitamin D and preeclampsia had been reported in our previous study. In brief, higher concentration of 25(OH)D was associated with a lower risk of preeclampsia, with generally similar results observed for 25(OH)D2 and 25(OH)D3 (13).
The distributions of cytokines in the two groups are showed in Figure 1. Women with preeclampsia had significantly higher concentrations IFN-γ (4.94 versus 3.72 pg/mL, p < 0.001), IL-17A (3.31 versus 2.87 pg/mL, p = 0.016) and IL-4 (1.90 versus 1.74 pg/mL, p = 0.018) than controls, whereas no significant difference in the IL-10 concentration was observed between the groups (5.12 versus 4.47 pg/mL, p > 0.05). Furthermore, there were no statistically significant differences in the ratio of IFN-γ/IL-4 (3.57 versus 3.12, p > 0.05) and IL-17A/IL-10 (0.85 versus 0.75, p > 0.05) between the groups.
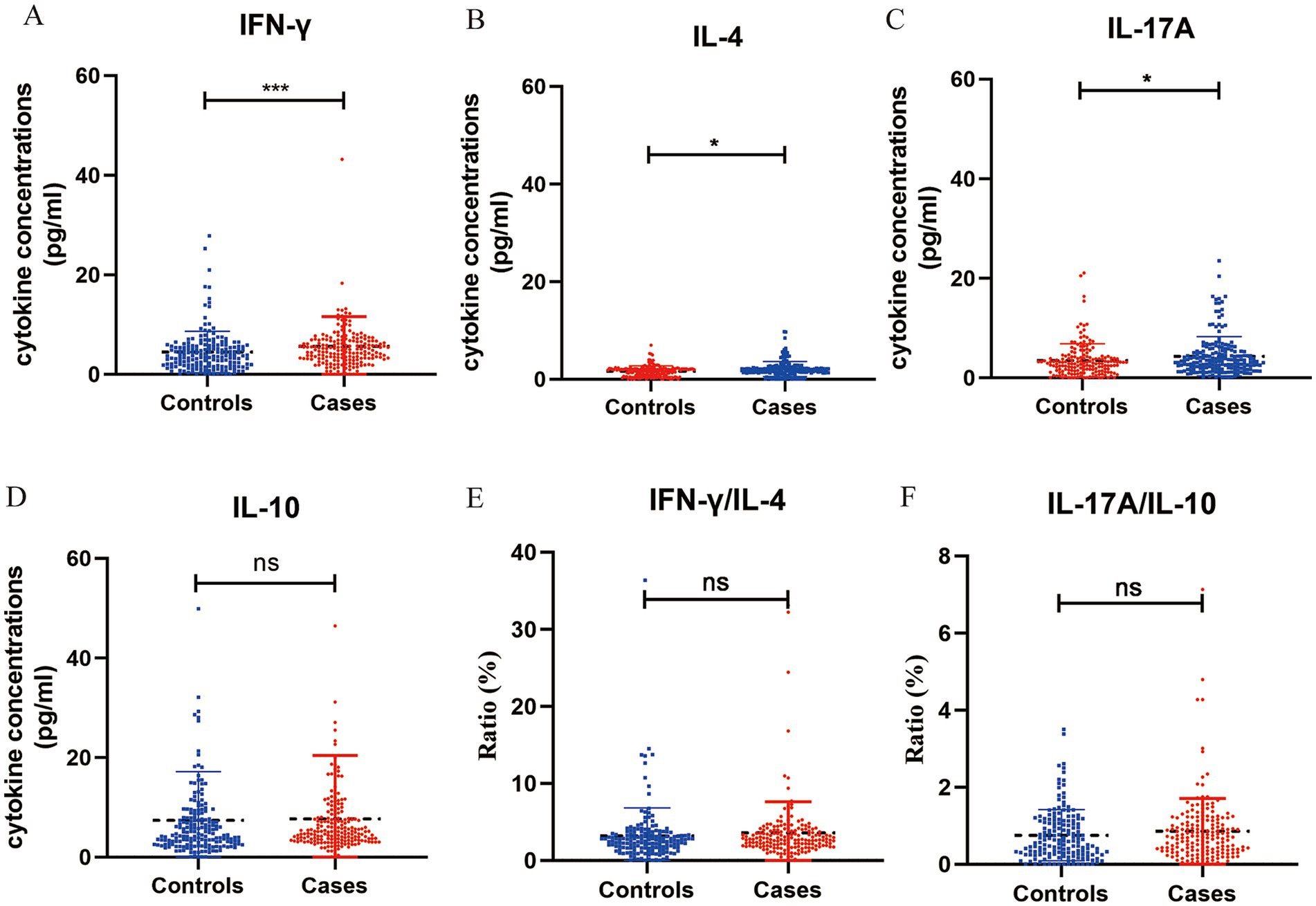
Figure 1. Concentration of cytokines in plasma samples from pregnant women with preeclampsia (n = 192) and without preeclampsia (n = 181). The concentration of interferon (IFN)-γ (A), IL-4 (B), IL-17A (C), IL-10 (D) (pg/mL) were measured in both groups using ELISA, the ratio of IFN-γ/IL-4 (E) and IL-17A/IL-10 (F). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and nsp > 0.05.
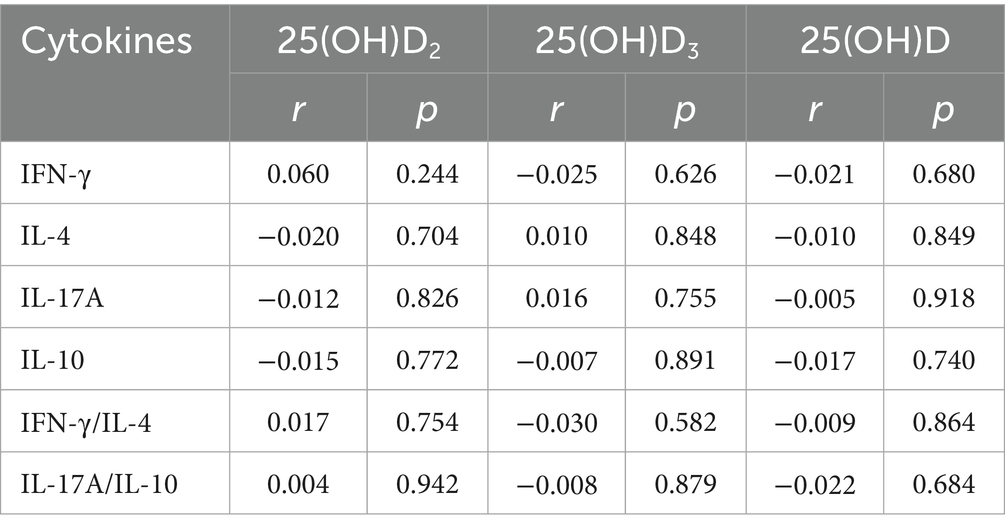
Table 2 showed the correlations between vitamin D and cytokines, while no significant associations were found. Supplementary Table 2 presented the correlations between cytokines and preeclampsia, and IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-17A were significant correlated with preeclampsia. Moreover, mediating analysis suggested that cytokines did not mediate the relationship between vitamin D and preeclampsia. Detailed results were presented in Supplementary Tables 3–5.
The T cell populations in the two groups were presented in Figure 2. Women with preeclampsia had higher percentages of Th1 (17.22% versus 10.21%, p = 0.006) and Th17 cells (3.15% versus 1.69%, p = 0.004), and lower percentages of Th2 (4.16% versus 6.54%, p = 0.008) and Treg cells (33.39% versus 51.05%, p = 0.001) than controls. Additionally, the Th1/Th2 (3.83 versus 1.55, p < 0.001) and Th17/Treg ratios (0.11 versus 0.04, p < 0.001) were significantly elevated in women with preeclampsia.
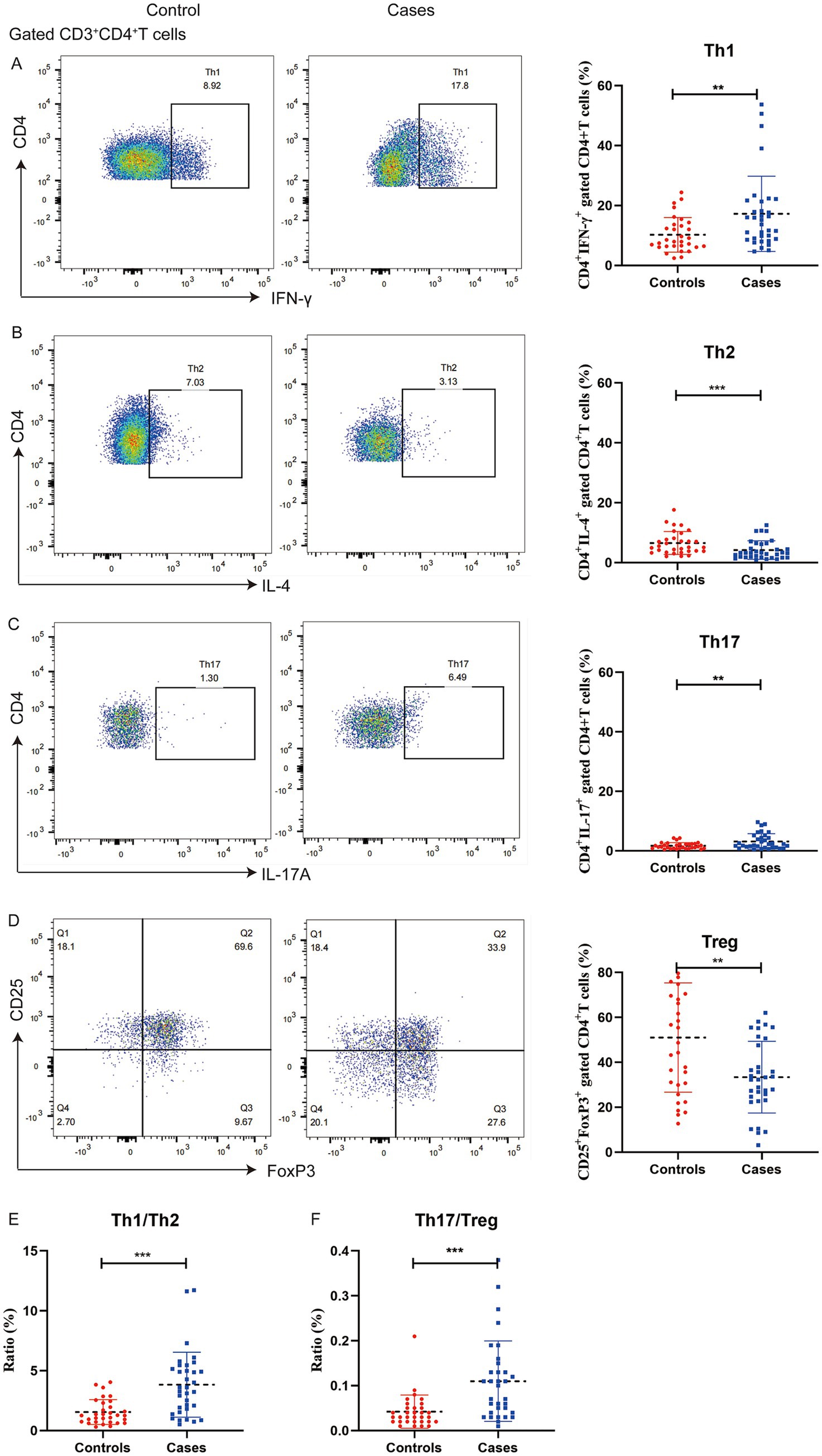
Figure 2. Distribution of T cell subsets in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from pregnant women with preeclampsia (n = 34) and without preeclampsia (n = 31). The percentages of IFN-γ+ of CD4+ T cells (A), IL-4+ of CD4+ T cells (B), IL-17A+ of CD4+ T cells (C), and CD25+ FOXP3+ of CD4+ T cells (D) were determined using flow cytometry, the ratio of Th1/Th2 (E) and Th17/Treg (F). **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.
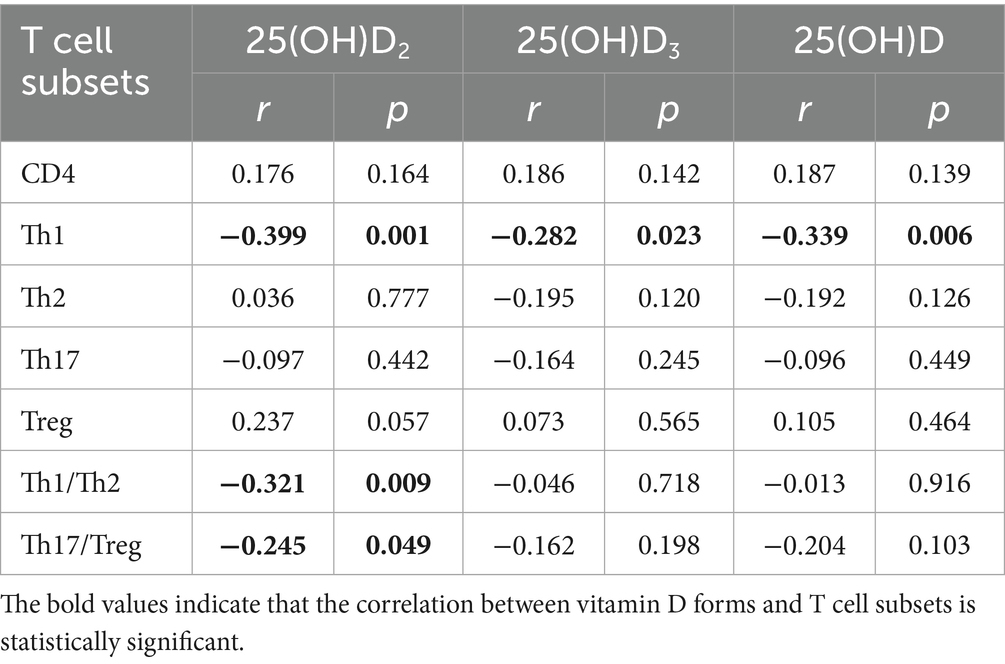
The correlations of the vitamin D concentration with T cell subsets and the immune balance status are presented in Table 3. The vitamin D concentration was associated with Th1 cells, with correlation coefficients of r = −0.399 (p = 0.001), r = −0.282 (p = 0.023), and r = −0.339 (p = 0.006) between Th1 and 25(OH)D2, 25(OH)D3 as well as 25(OH)D, respectively. In the correlation analysis between vitamin D and immune balance of T cell subsets, only 25(OH)D2 was found to be associated with Th1/Th2 as well as Th17/Treg, the correlation coefficients for the associations 25(OH)D2 with the Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg ratios were r = −0.321 (p = 0.009), and r = −0.245 (p = 0.049), respectively. The correlations between T cell subsets and preeclampsia were showed in Supplementary Table 6.
Figure 3 and Supplementary Tables 7–9 illustrated the model for the mediating effects of T cell subsets, Th1/Th2 as well as Th17/Treg ratios on the relationship between 25(OH)D2/25(OH)D2/25(OH)D and preeclampsia. The Th1/Th2 partly mediated the relationship between 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia, with the significant direct effect of 25(OH)D2 on preeclampsia (βdirect: −0.084, 95% CI: −0.332, −0.010) and significant indirect effect (βindirect: −0.124, 95%CI: −0.181, −0.050). The Th1/Th2 weakened the correlation between 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia, and the respective mediation effect proportion was 59.59%, indicating that lower 25(OH)D2 could result in an imbalance between Th1 and Th2 and further increased the risk of preeclampsia. The similar mediation effects of Treg and Th17/Treg on 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia were also found.
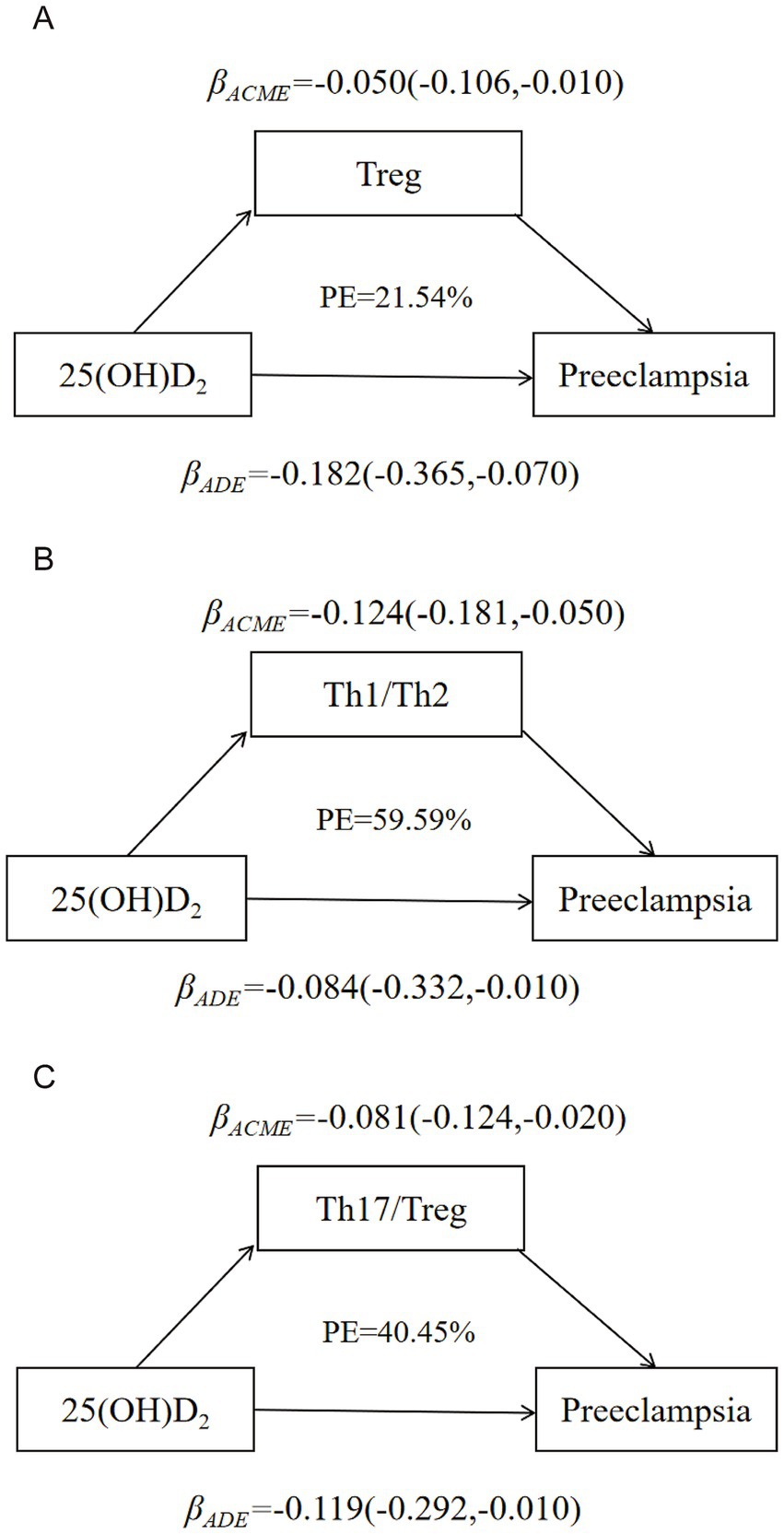
Figure 3. Model of the mediation effects of immune balance on the correlation between 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia. (A) The mediating effect of Treg on the correlation between 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia. (B) The mediating effect of Th1/Th2 balance on the correlation between 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia. (C) The mediating effect of Th17/Treg balance on the correlation between 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia. Maternal age, gestational week, parity (multiparous or primiparous), pre-pregnancy BMI, education level (high school or below, university or above) and monthly income (≤4,000 RMB or >4,000 RMB).
Discussion
This case–control study found that women with preeclampsia had larger populations of Th1 and Th17 cells and lower levels of Th2 and Treg cells than the controls. Furthermore, Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg ratios were negatively associated with the 25(OH)D2 concentration. The relationship between 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia was weakened by the mediating effects of the Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg ratio, a lower level of 25(OH)D2 may result in the imbalance between Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg, thus increasing the risk of preeclampsia.
We previously found that a lower vitamin D concentration was associated with a higher risk of preeclampsia (OR: 0.26, 95% CI: 0.11, 0.60) (13). While, the mechanisms between vitamin D and preeclampsia still further exploration. Immune balance, particularly with respect to the Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balances, is considered an important immune mechanism underlying preeclampsia (12, 29). In a normal pregnancy, Th2 and Treg cells suppress the proliferation and activity of Th1 and Th17 cells to promote maternal-fetal tolerance and support a healthy pregnancy (30–33). However, in preeclampsia, the populations of Th1 and Th17 cells increase significantly, which disrupt maternal-fetal tolerance. These dominant of Th1 and Th17 cells further suppress the populations and functions of Th2 and Treg cells, exacerbating the immune imbalance of T cell subsets and contributing to the development of preeclampsia (29). Vitamin D plays a crucial role in modulating the immune system to promote a more tolerogenic immune environment by promoting Treg function and modulating T helper cell differentiation (17, 34, 35) and thus regulates the Th17/Treg and Th1/Th2 balance in women with infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss (36–38). While vitamin D deficiency can result in dominance of Th1 and Th17, as well as inhibition of the development and functions of Th2 and Treg cells, resulting in an imbalance between Th1 and Th2 as well as Th17 and Treg (39–41). Such imbalance contributes to immune system dysfunction and can lead to conditions such as hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia. While, the mediating effects of Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg ratios on vitamin D and preeclampsia were still unclear. In our study, we also observed that Th17/Treg and Th1/Th2 imbalances in women with preeclampsia. However, the concentration of cytokine in these two groups was not entirely consistent with those in previous studies or our flow cytometry results (40). This discrepancy may be attributable to various factors that influence cytokine levels, such as the gestational age, diet, and other environmental variables (40, 42).
Vitamin D exerts its biological effects by binding to vitamin D receptors on immune cells to promote Treg differentiation, enhance Th2 activity, and reduce Th17 and Th1 responses (43). It also has been shown to suppress the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, and IL-6, in experimental models (34, 44, 45). The results of the current study suggest that 25(OH)D2 plays a key role in regulating the balance between Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balances and thereby influence the development of preeclampsia, as far as we know, this is the first study to explore the mediating effect of immune imbalance between 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia. This effect may be due to the higher affinity of vitamin D receptors expressed by immune cells for 25(OH)D2 (46). This finding might help explain our findings that Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balances mediated the association between 25(OH)D2, but not 25(OH)D3, and preeclampsia.
Strengths and limitations
The major strength of this study is that it is the first study to assess the mediating effect of Th1/Th2 as well as Th17/Treg imbalance on the relationship between vitamin D and preeclampsia in pregnant women. The results indicate that 25(OH)D2 is negatively associated with the Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg immune balance, such that 25(OH)D2 deficiency increases the risk of preeclampsia by promoting Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg immune imbalance. Second, we explored the mediating effects of Th1/Th2 as well as Th17/Treg immune imbalance on different forms of vitamin D and preeclampsia in this study. The results offer insights regarding the use of different forms of vitamin D to regulate immune balance in pregnant women and providing clues for regarding vitamin D2 or vitamin D3 supplementation to maintain immune balance and prevent preeclampsia.
However, some limitations of this study warrant further exploration. First, due to the case–control study design of our study, our findings just provide a supportive evidence instead of a direct causal evidence to support the mediating effect of Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balance on association between 25(OH)D2 and preeclampsia. Second, T cell subsets are more accurate and objective measure of immune status, while given its high cost and operational complexity, flow cytometry is unsuitable for large-scale studies, the relatively small sample size of T cell subsets from pregnant women may introduce potential residual confounding, highlighting the need for further replication in larger prospective studies to validate the findings obtained from this study.
Conclusion
In summary, this study found inverse correlations between 25(OH)D2 and the Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg ratios. Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg imbalances were also found to mediate the relationship between the 25(OH)D2 concentration and risk of preeclampsia. Future prospective cohort studies and well-designed randomized controlled trials with larger sample of pregnant women are needed to further explore the mechanisms linking various forms of vitamin D, immune status and the risk of preeclampsia.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found in Figshare: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/Immune_imbalance_mediates_the_relationship_between_plasma_vitamin_D_concentration_and_preeclampsia_in_Chinese_pregnant_women_A_case-control_study/30464585.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Scientific Research and Clinical Trials at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (Approval No. Scientific Research-2016-LW-34). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(s)’ legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
HC: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Conceptualization, Investigation, Software. YB: Methodology, Writing – original draft. YC: Data curation, Writing – original draft. JL: Writing – review & editing. JN: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DD: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. WD: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. WF: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing. YL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81602852) and the Chinese Nutrition Society (CNS-HPNK2023-43).
Acknowledgments
All of the authors would like to thank the participants who taken part in our study. The authors also acknowledge the staffs for their assistance in collecting questionnaire and handling samples.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1665593/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Phipps, EA, Thadhani, R, Benzing, T, and Karumanchi, SA. Pre-eclampsia: pathogenesis, novel diagnostics and therapies. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2019) 15:275–89. doi: 10.1038/s41581-019-0119-6
2. Abalos, E, Cuesta, C, Grosso, AL, Chou, D, and Say, L. Global and regional estimates of preeclampsia and eclampsia: a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (2013) 170:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.05.005
3. American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists. Hypertension in pregnancy. Report of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Task Force on hypertension in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. (2013):1122–31. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000437382.03963.88
4. Souza, JP, Gulmezoglu, AM, Vogel, J, Carroli, G, Lumbiganon, P, Qureshi, Z, et al. Moving beyond essential interventions for reduction of maternal mortality (the WHO multicountry survey on maternal and newborn health): a cross-sectional study. Lancet. (2013) 381:1747–55. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60686-8
5. Epstein, FH. Late vascular effects of toxemia of pregnancy. N Engl J Med. (1964) 271:391–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196408202710803
6. Mol, BWJ, Roberts, CT, Thangaratinam, S, Magee, LA, de Groot, CJM, and Hofmeyr, GJ. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. (2016) 387:999–1011. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00070-7
7. Strand, KM, Heimstad, R, Iversen, AC, Austgulen, R, Lydersen, S, Andersen, GL, et al. Mediators of the association between pre-eclampsia and cerebral palsy: population based cohort study. BMJ. (2013) 347:f4089. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f4089
8. Hansen, AR, Barnes, CM, Folkman, J, and McElrath, TF. Maternal preeclampsia predicts the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. (2010) 156:532–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.10.018
9. Everett, TR, Wilkinson, IB, and Lees, CC. Drug development in preeclampsia: a ‘no go’ area? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2012) 25:50–2. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2011.557791
10. Meggyes, M, Miko, E, Lajko, A, Csiszar, B, Sandor, B, Matrai, P, et al. Involvement of the PD-1/PD-L1 co-inhibitory pathway in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory stage of early-onset preeclampsia. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:583. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030583
11. Jianjun, Z, Yali, H, Zhiqun, W, Mingming, Z, and Xia, Z. Imbalance of T-cell transcription factors contributes to the Th1 type immunity predominant in pre-eclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol. (2010) 63:38–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2009.00763.x
12. Ding, H, Dai, Y, Lei, Y, Wang, Z, Liu, D, Li, R, et al. Upregulation of CD81 in trophoblasts induces an imbalance of Treg/Th17 cells by promoting IL-6 expression in preeclampsia. Cell Mol Immunol. (2019) 16:302–12. doi: 10.1038/s41423-018-0186-9
13. Huang, XM, Liu, YH, Zhang, H, Cao, Y, Dou, WF, Duan, DD, et al. Dietary and serum vitamin D and preeclampsia risk in Chinese pregnant women: a matched case–control study. Br J Nutr. (2021) 128:84–92. doi: 10.1017/S0007114521002956
14. Mirzakhani, H, Litonjua, AA, McElrath, TF, O’Connor, G, Lee-Parritz, A, Iverson, R, et al. Early pregnancy vitamin D status and risk of preeclampsia. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:4702–15. doi: 10.1172/JCI89031
15. van der Pligt, P, Willcox, J, Szymlek-Gay, EA, Murray, E, Worsley, A, and Daly, RM. Associations of maternal vitamin D deficiency with pregnancy and neonatal complications in developing countries: a systematic review. Nutrients. (2018) 10:640. doi: 10.3390/nu10050640
16. Achkar, M, Dodds, L, Giguere, Y, Forest, JC, Armson, BA, Woolcott, C, et al. Vitamin D status in early pregnancy and risk of preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2015) 212:511.e1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2014.11.009
17. Zheng, S, Dong, S, Shen, H, Xu, P, and Shu, C. Role of vitamin D in the pathogenesis of early-onset preeclampsia: a narrative review. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1598691. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1598691
18. Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy Subgroup, Chinese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Chinese Medical Association. Diagnosis and treatment guideline of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy (2015). Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. (2015) 50:721–8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2015.10.001
19. Cao, Y, Liu, Y, Zhao, X, Duan, D, Dou, W, Fu, W, et al. Adherence to a dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH)-style diet in relation to preeclampsia: a case–control study. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:9078. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65912-2
20. Zeng, G, Zhang, G, and Chen, X. Th1 cytokines, true functional signatures for protective immunity against TB? Cell Mol Immunol. (2018) 15:206–15. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.113
21. Nakayama, T, Hirahara, K, Onodera, A, Endo, Y, Hosokawa, H, Shinoda, K, et al. Th2 cells in health and disease. Annu Rev Immunol. (2017) 35:53–84. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-051116-052350
22. Neurath, MF, Finotto, S, and Glimcher, LH. The role of Th1/Th2 polarization in mucosal immunity. Nat Med. (2002) 8:567–73. doi: 10.1038/nm0602-567
23. Field, CS, Baixauli, F, Kyle, RL, Puleston, DJ, Cameron, AM, Sanin, DE, et al. Mitochondrial integrity regulated by lipid metabolism is a cell-intrinsic checkpoint for Treg suppressive function. Cell Metab. (2020) 31:422–37 e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.021
24. Summers, SA, Steinmetz, OM, Li, M, Kausman, JY, Semple, T, Edgtton, KL, et al. Th1 and Th17 cells induce proliferative glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 20:2518–24. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009030337
25. Ghoreschi, K, Thomas, P, Breit, S, Dugas, M, Mailhammer, R, van Eden, W, et al. Interleukin-4 therapy of psoriasis induces Th2 responses and improves human autoimmune disease. Nat Med. (2003) 9:40–6. doi: 10.1038/nm804
26. Barbi, J, Pardoll, D, and Pan, F. Treg functional stability and its responsiveness to the microenvironment. Immunol Rev. (2014) 259:115–39. doi: 10.1111/imr.12172
27. Zhang, Y, Liu, Z, Tian, M, Hu, X, Wang, L, Ji, J, et al. The altered PD-1/PD-L1 pathway delivers the ‘one-two punch’ effects to promote the Treg/Th17 imbalance in pre-eclampsia. Cell Mol Immunol. (2018) 15:710–23. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.70
28. Wang, S, Li, M, Lin, H, Wang, G, Xu, Y, Zhao, X, et al. Amino acids, microbiota-related metabolites, and the risk of incident diabetes among normoglycemic Chinese adults: findings from the 4C study. Cell Rep Med. (2022) 3:100727. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100727
29. Darmochwal-Kolarz, D, Kludka-Sternik, M, Tabarkiewicz, J, Kolarz, B, Rolinski, J, Leszczynska-Gorzelak, B, et al. The predominance of Th17 lymphocytes and decreased number and function of Treg cells in preeclampsia. J Reprod Immunol. (2012) 93:75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2012.01.006
30. Lin, H, Mosmann, TR, Guilbert, L, Tuntipopipat, S, and Wegmann, TG. Synthesis of T helper 2-type cytokines at the maternal-fetal interface. J Immunol. (1993) 151:4562–73.
31. Wang, W, Sung, N, Gilman-Sachs, A, and Kwak-Kim, J. T helper (Th) cell profiles in pregnancy and recurrent pregnancy losses: Th1/Th2/Th9/Th17/Th22/Tfh cells. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:2025. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02025
32. Robertson, SA, Care, AS, and Moldenhauer, LM. Regulatory T cells in embryo implantation and the immune response to pregnancy. J Clin Invest. (2018) 128:4224–35. doi: 10.1172/JCI122182
33. Robertson, SA, Green, ES, Care, AS, Moldenhauer, LM, Prins, JR, Hull, ML, et al. Therapeutic potential of regulatory T cells in preeclampsia-opportunities and challenges. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:478. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00478
34. Sassi, F, Tamone, C, and D’Amelio, P. Vitamin D: nutrient, hormone, and immunomodulator. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1656. doi: 10.3390/nu10111656
35. Prietl, B, Treiber, G, Pieber, TR, and Amrein, K. Vitamin D and immune function. Nutrients. (2013) 5:2502–21. doi: 10.3390/nu5072502
36. Ikemoto, Y, Kuroda, K, Nakagawa, K, Ochiai, A, Ozaki, R, Murakami, K, et al. Vitamin D regulates maternal T-helper cytokine production in infertile women. Nutrients. (2018) 10:902. doi: 10.3390/nu10070902
37. Rafiee, M, Gharagozloo, M, Ghahiri, A, Mehrabian, F, Maracy, MR, Kouhpayeh, S, et al. Altered Th17/Treg ratio in recurrent miscarriage after treatment with paternal lymphocytes and vitamin D3: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Iran J Immunol. (2015) 12:252–62.
38. Ji, J, Zhai, H, Zhou, H, Song, S, Mor, G, and Liao, A. The role and mechanism of vitamin D-mediated regulation of Treg/Th17 balance in recurrent pregnancy loss. Am J Reprod Immunol. (2019) 81:e13112. doi: 10.1111/aji.13112
39. Granger, JP. Inflammatory cytokines, vascular function, and hypertension. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. (2004) 286:R989–90. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00157.2004
40. Aggarwal, R, Jain, AK, Mittal, P, Kohli, M, Jawanjal, P, and Rath, G. Association of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in preeclampsia. J Clin Lab Anal. (2019) 33:e22834. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22834
41. Jokhi, PP, King, A, and Loke, YW. Cytokine production and cytokine receptor expression by cells of the human first trimester placental-uterine interface. Cytokine. (1997) 9:126–37. doi: 10.1006/cyto.1996.0146
42. Rodriguez-Santana, Y, Ochoa, JJ, Lara-Villoslada, F, Kajarabille, N, Saavedra-Santana, P, Hurtado, JA, et al. Cytokine distribution in mothers and breastfed children after omega-3 LCPUFAs supplementation during the last trimester of pregnancy and the lactation period: a randomized, controlled trial. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. (2017) 126:32–8. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2017.09.006
43. Yang, CY, Leung, PS, Adamopoulos, IE, and Gershwin, ME. The implication of vitamin D and autoimmunity: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2013) 45:217–26. doi: 10.1007/s12016-013-8361-3
44. Carvalho, JTG, Schneider, M, Cuppari, L, Grabulosa, CC, D, TA, Qr, BM, et al. Cholecalciferol decreases inflammation and improves vitamin D regulatory enzymes in lymphocytes in the uremic environment: a randomized controlled pilot trial. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0179540. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179540
45. Xie, Z, Chen, J, Zheng, C, Wu, J, Cheng, Y, Zhu, S, et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 -induced dendritic cells suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by increasing proportions of the regulatory lymphocytes and reducing T helper type 1 and type 17 cells. Immunology. (2017) 152:414–24. doi: 10.1111/imm.12776
Keywords: vitamin D, preeclampsia, immune imbalance, mediation effect, Chinese
Citation: Chen H, Bo Y, Cao Y, Liu J, Nie J, Duan D, Dou W, Zhao X, Fu W, Zhang Y and Liu Y (2025) Immune imbalance mediates the relationship between plasma vitamin D concentration and preeclampsia in Chinese pregnant women: a case–control study. Front. Nutr. 12:1665593. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1665593
Edited by:
Margarida Castell, University of Barcelona, SpainReviewed by:
Zainab Alimoradi, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, IranHasan Abd Ali Khudhair, Southern Technical University (STU), Iraq
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Bo, Cao, Liu, Nie, Duan, Dou, Zhao, Fu, Zhang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Zhang, eWl6aGFuZ0B6enUuZWR1LmNu; Yanhua Liu, bGl1eWFuaHVhMTAxNUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Huanan Chen
Huanan Chen Yacong Bo
Yacong Bo Yuan Cao
Yuan Cao Jinyan Liu
Jinyan Liu Jiaqi Nie3
Jiaqi Nie3 Yi Zhang
Yi Zhang Yanhua Liu
Yanhua Liu